ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Service quality and customer satisfaction in the post pandemic world: a study of saudi auto care industry.

- 1 College of Business Administration, Prince Mohammad Bin Fahd University, Khobar, Saudi Arabia
- 2 Department of Management Sciences, University of Baluchistan, Quetta, Pakistan
The aim of this research is to examine the impact of service quality on customer satisfaction in the post pandemic world in auto care industry. The car care vendor in the study made effective use of social media to provide responsive updates to the customers in the post pandemic world; such use of social media provides bases for service quality and customer satisfaction. The study examined the relationship between service quality and customer satisfaction using the SERVQUAL framework. According to the findings, empathy, reliability, assurance, responsiveness, and tangibles have a significant positive relationship with customer satisfaction. Our findings suggest that it is critical for workshops to recognize the service quality factors that contribute to customer satisfaction. Findings also suggest that empathy, assurance, reliability, responsiveness, and tangibles contribute to customer satisfaction. Auto repair industry must regularly provide personal attention, greet customers in a friendly manner, deliver cars after services, notify customers when additional repairs are required, and take the time to clarify problems to customers. Furthermore, workshops must screen and hire courteous staff who can clearly communicate the services required to customers both in-person and online and effectively communicate the risks associated with repairs. Service quality seems to be aided by prompt services.

Introduction
The previous studies on the effect of pandemic have focused on the behavior related to preventative measures to protect the health of the customers; however, less attention has been paid to the influence of pandemic on customer outcomes. To fill this gap, the SERVQUAL framework was employed to examine the changes in customers’ social media behaviors that have occurred since the pandemic was declared ( Mason et al., 2021 ). In the post pandemic world, the parameters for customer satisfaction have changed considerably ( Monmousseau et al., 2020 ; Srivastava and Kumar, 2021 ; Wu et al., 2021 ). Pandemic has made personal interaction more challenging ( Brown, 2020 ). To be less vulnerable to becoming severely ill with the virus, customers prefer touchless digital mediums of communications. For example, Mason et al. (2021) concluded that pandemic has altered customers’ needs, shopping and purchasing behaviors, and post purchase satisfaction levels. Keeping in view the public healthcare concerns, the governmental pandemic mitigation policies also promotes touchless mediums for shopping; therefore, the role of social media as a communication tool stands to increase at a time when social distancing is a common practice; social media provides avenues for buyers to interact with sellers without physical contact. Thus, the use of social media gains critical importance, especially after the pandemic ( Mason et al., 2021 ), and the businesses may find new opportunities to gain competitive advantage through their use of effective social media strategies.
The car care industry uses traditional means of customer communications. The company in this study made use of social media in improving their service quality through effective and safe communication with their customers. The use of social media to provide updates to customers played a significant role in improving service quality and satisfaction ( Ramanathan et al., 2017 ). The company in the study used Snapchat to provide updates on the work, thus minimizing the customers’ need to physically visit the car care facility. This use of social media gave a significant boost to the responsiveness aspect of the service quality.
Service quality and customer satisfaction are important aspects of business since a company’s growth is largely dependent on how well it maintains its customers through service and how well they keep their customers satisfied ( Edward and Sahadev, 2011 ). According to Chang et al. (2017) ; customer satisfaction is expected to result from good service efficiency, which will improve customer engagement and interrelationship. González et al. (2007) asserted that customer satisfaction is linked to high service quality, which makes businesses more competitive in the marketplace. This study uses the SERVQUAL framework to define service quality. This framework uses five dimensions to account for service quality, namely, tangibles, reliability, responsiveness, assurance, and empathy. Identifying issues in service and customer satisfaction can lead to high service quality. Furthermore, service quality can be characterized by analyzing the variations between planned and perceived service. Service quality and customer satisfaction have a positive relationship.
Recognizing and meeting customer expectations through high levels of service quality help distinguish the company’s services from those of its rivals ( Dominic et al., 2010 ). Social media plays a critical role in shaping these service quality-related variables. Specifically, in the context coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), where customers hesitated to visit auto workshops physically, the importance of online platforms such as auto workshops’ social media pages on Instagram and Facebook has increased, where customers try to get information and book appointment. For example, responsiveness is not only physical responsiveness but also digital means of communication. The car care company in this study uses social media as mode of communication with their customers due to physical interaction restriction caused by the pandemic.
Service quality becomes a critical element of success in car care industry because customer contact is one of the most important business processes ( Lambert, 2010 ). Saudi Arabia is one of the Middle East’s largest new vehicle sales and auto part markets. Saudi Arabia’s car repair industry has grown to be a significant market for automakers from all over the world. As a result, the aim of this research was to see how service quality affects customer satisfaction in the Saudi auto repair industry.
This aim of this research was to answer the following research questions:
(i) What is the contribution of individual dimensions of SERVQUAL on customer perceived service quality of car care industry in Saudi Arabia?
(ii) What is the impact of perceived service quality on customer satisfaction in car care industry in Saudi Arabia?
Literature Review
The concept of service has been defined since the 1980s by Churchill and Surprenant (1982) together with Asubonteng et al. (1996) , who popularized the customer satisfaction theory through measuring the firm’s actual service delivery in conformity with the expectations of customers, as defined by the attainment of perceived quality, and that is meeting the customers’ wants and needs beyond their aspirations. With this premise, Armstrong et al. (1997) later expanded the concept of service into the five dimensions of service quality that comprised tangibles, reliability, responsiveness, assurance, and empathy.
Extant literature on service delivery focuses on the traditional emphasis on the contact between the customer and service provider ( Mechinda and Patterson, 2011 ; Han et al., 2021 ). Doucet (2004) explained that the quality in these traditional settings depends on the design of the location and the behavior of the service provider. More recently, the proliferation of the internet has led to the emergence of the online service centers. In these cases, communication both in-person and online plays a critical role in the quality of service rendered. It follows that service quality in hybrid settings depends on quality of communications on social media as well as the behavioral interactions between the customer and the service provider ( Doucet, 2004 ; Palese and Usai, 2018 ). These factors require subjective assessments by the concerned parties, which means that different persons will have varied assessments of the quality of service received.
SERVQUAL Dimensions
Service quality has been described with the help of five quality dimensions, namely, tangibles, reliability, responsiveness, assurance, and empathy. Definitions relating to these variables have been modified by different authors. The relationship between various dimensions of service quality differs based on particular services.
The tangible aspects of a service have a significant influence on perception of service quality. These comprise the external aspects of a service that influence external customer satisfaction. The key aspects of tangibility include price, ranking relative to competitors, marketing communication and actualization, and word-of-mouth effects ( Ismagilova et al., 2019 ), which enhance the perception of service quality of customers ( Santos, 2002 ). These aspects extend beyond SERVQUAL’s definition of quality within the car care industry settings. Thus, we proposed the following hypothesis:
Hypotheses 1a: Tangibles are positively related with perceived service quality.
Reliability
Reliability is attributed to accountability and quality. There are a bunch of precursors that likewise aid basic methodology for shaping clients’ perspectives toward administration quality and reliability in the car care industry in Saudi ( Korda and Snoj, 2010 ; Omar et al., 2015 ). A portion of these predecessors is identified with car repair benefits and includes the convenient accessibility of assets, specialist’s expertise level and productive issue determination, correspondence quality, client care quality, an exhibition of information, client esteem, proficiency of staff, representatives’ capacity to tune in to client inquiries and respond emphatically to their necessities and protests, security, workers’ dependability, more limited holding up time and quickness, actual prompts, cost of administration, accessibility of issue recuperation frameworks, responsibility, guarantees, for example, mistake-free administrations, generally association’s picture and workers’ politeness, and responsiveness. Despite the innovative changes happening in the car care industry and the instructive degree of car administrations suppliers in Saudi Arabia, car care suppliers in the territory are taught about the need to continually refresh their insight into the advancements in the area of vehicle workshops and the components of administration. Thus, we argued that reliability is important to enhance the perception of service quality of customers.
Hypotheses 1b: Reliability is positively linked with perceived service quality.
Responsiveness
Responsiveness refers to the institution’s ability to provide fast and good quality service in the period. It requires minimizing the waiting duration for all interactions between the customer and the service provider ( Nambisan et al., 2016 ). Nambisan et al. (2016) explained that responsiveness is crucial for enhancing the customers’ perception of service quality. Rather, the institution should provide a fast and professional response as to the failure and recommend alternative actions to address the customer’s needs ( Lee et al., 2000 ). In this light, Nambisan summarizes responsiveness to mean four key actions, i.e., giving individual attention to customers, providing prompt service, active willingness to help guests, and employee availability when required. These aspects help companies to enhance the customers’ perception of service quality. Therefore, we proposed the following hypothesis:
Hypotheses 1c: Responsiveness is positively linked with perceived service quality.
Assurance refers to the skills and competencies used in delivering services to the customers. Wu et al. (2015) explains that employee skills and competencies help to inspire trust and confidence in the customer, which in turn stirs feelings of safety and comfort in the process of service delivery. Customers are more likely to make return visits if they feel confident of the employees’ ability to discharge their tasks. Elmadağ et al. (2008) lists the factors that inspire empathy as competence, politeness, positive attitude, and effective communication as the most important factors in assuring customers. Besides, other factors include operational security of the premises as well as the proven quality of the service provided to the customers. Thus, the assurance has significant contribution in the perception of service quality.
Hypotheses 1d: Assurance is positively related with perceived service quality.
Empathy refers to the quality of individualized attention given to the customers. The service providers go an extra mile to make the customer feel special and valued during the interaction ( Bahadur et al., 2018 ). Murray et al. (2019) explains that empathy requires visualizing the needs of the customer by assuming their position. Murray et al. (2019) lists the qualities that foster empathy as including courtesy and friendliness of staff, understanding the specific needs of the client, giving the client special attention, and taking time to explain the practices and procedure to be undertaken in the service delivery process. Therefore, we proposed the following hypothesis:
Hypotheses 1e: Empathy is positively related with perceived service quality.
Perceived Service Quality and Customer Satisfaction
Customer satisfaction refers to the level of fulfillment expressed by the customer after the service delivery process. This is a subjective assessment of the service based on the five dimensions of service quality. Customer satisfaction is important due to its direct impact on customer retention ( Hansemark and Albinsson, 2004 ; Cao et al., 2018 ; Zhou et al., 2019 ), level of spending ( Fornell et al., 2010 ), and long-term competitiveness of the organization ( Suchánek and Králová, 2019 ). Susskind et al. (2003) describes that service quality has a direct impact on customer satisfaction. For this reason, this research considers that five dimensions of service quality are the important antecedents of customer satisfaction.
Service quality refers to the ability of the service to address the needs of the customers ( Atef, 2011 ). Customers have their own perception of quality before interacting with the organization. The expectancy-confirmation paradigm holds that customers compare their perception with the actual experience to determine their level of satisfaction from the interaction ( Teas, 1993 ). These assessments are based on the five independent factors that influence quality. Consequently, this research considers service quality as an independent variable.
This study attempts to quantify perceived service quality though SERVQUAL dimensions. We proposed that customers place a high premium on service quality as a critical determinant of satisfaction. Moreover, it is argued that satisfaction prompts joy and reliability among customers in Saudi Arabia. These discoveries infer that the perception of service quality is significantly related to satisfaction, and quality insight can be applied across different cultures with negligible contrasts in the result. Car care industry in Saudi Arabia has grave quality problems. To rectify this situation, it is essential to apply quality systems as tools for development. The SERVQUAL is one of these system options. It is used to gauge the service quality using five dimensions that have been time-tested since 1982. Thus, the significance of SERVQUAL in car care industry in Saudi Arabia cannot be overemphasized. The study further suggests that the SERVRQUAL dimension increases the perceived service quality, which in turn increases customer satisfaction. Thus, we proposed the following hypothesis:
Hypothesis 2: The perceived service quality of car care customers is positively linked with their satisfaction.
Methods and Procedures
In this study, we employed a cross-sectional research design. Using a paper-pencil survey, data were collected form auto care workshops situated in the Eastern Province of Saudi Arabia. According to the study by Newsted et al. (1998) , the survey method is valuable for assessing opinions and trends by collecting quantitative data. We adapted survey instruments from previous studies. The final survey was presented to a focus group of two Ph.D. marketing scholars who specialized in survey design marketing research. The survey was modified keeping in view the recommendations suggested by focus group members. We contacted the customers who used social media to check the updates and book the appointment for their vehicle’s service and maintenance. We abstained 130 surveys, 13 of which were excluded due to missing information. Therefore, the final sample encompassed 117 (26 female and 91 male) participants across multiple age groups: 10 aged less than 25 years, 46 aged between 26 and 30 years, 28 aged between 31 and 35 years, 21 aged between 36 and 40 years, and 12 aged older than 40 years (for details, refer to Table 1 ). Similarly, the averaged participants were graduates with more than 3 years of auto care service experience.
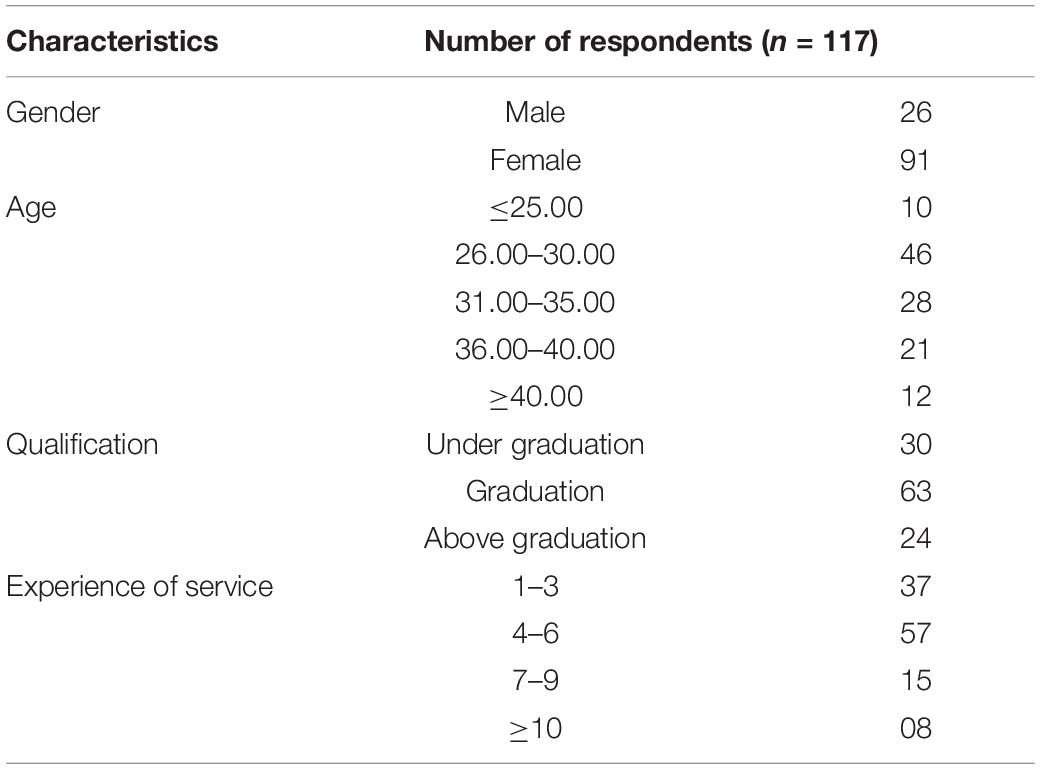
Table 1. Demographic information.
We measured service quality dimensions using 20 indicators. Customer satisfaction of the restaurant customers was assessed using 4-item scale (for detail, refer to Table 2 ). In this research, the 5-point Likert scale from 1 = strongly disagree to 5 = strongly agree was used.

Table 2. Constructs and items included in the questionnaire.
Control Variables
Following the previous research, customer’s gender and age were controlled to examine the influence of service quality dimensions on customer satisfaction.
Data Analysis and Results
For data analysis and hypotheses testing, we employed the structural equation modeling (SEM) based on the partial least squares (PLS) in Smart-PLS. Smart-PLS 3 is a powerful tool, which is used for the confirmatory factor analysis (CFA) and SEM ( Nachtigall et al., 2003 ). Research suggests that CFA is the best approach to examine the reliability and validity of the constructs. We employed SEM for hypotheses testing because it is a multivariate data analysis technique, which is commonly used in the social sciences ( González et al., 2008 ).
Common Method Bias
To ensure that common method bias (CMB) is not a serious concern for our results, we employed procedural and statistical and procedural remedies. During data collection, each survey in the research contained a covering letter explaining the purpose of the study and guaranteed the full anonymity of the participants. Moreover, it was mentioned in the cover letter that there was no right and wrong questions, and respondents’ answers would neither be related to their personalities nor disclosed to anyone. According to Podsakoff et al. (2003) , the confidentiality of the responses can assist to minimize the possibility of CMB. Furthermore, CMB was verified through the Harman’s single-factor test ( Podsakoff et al., 2003 ). All items in this research framework were categorized into six factors, among which the first factor explained 19.01% of the variance. Thus, our results showed that CMB was not an issue in our research. Moreover, using both tolerance value and the variance inflation factors (VIFs), we assessed the level of multicollinearity among the independent variables. Our results indicate that the tolerance values for all dimensions of service quality were above the recommended threshold point of 0.10 ( Cohen et al., 2003 ), and VIF scores were between 1.4 and 1.8, which suggested the absence of multicollinearity; thus, it is not a serious issue for this study.
Measurement Model
We performed CFA to analyze the reliability and validity of the constructs. The measurement model was assessed by examining the content, convergent, and discriminant validities. To assess the content validity, we reviewed the relevant literature and pilot test the survey. We used item loadings, Cronbach’s alpha, composite reliability (CR), and the average variance extracted (AVE) ( Fornell and Larcker, 1981b ) to assess the convergent validity. The findings of CFA illustrate that all item loadings are greater than 0.70. The acceptable threshold levels for all values were met, as the value of Cronbach’s alpha and CR was greater than 0.70 for all constructs ( Fornell and Larcker, 1981b ), and the AVE for all variables was above 0.50 ( Tabachnick and Fidell, 2007 ; see Table 3 ). Thus, these findings show acceptable convergent validity.
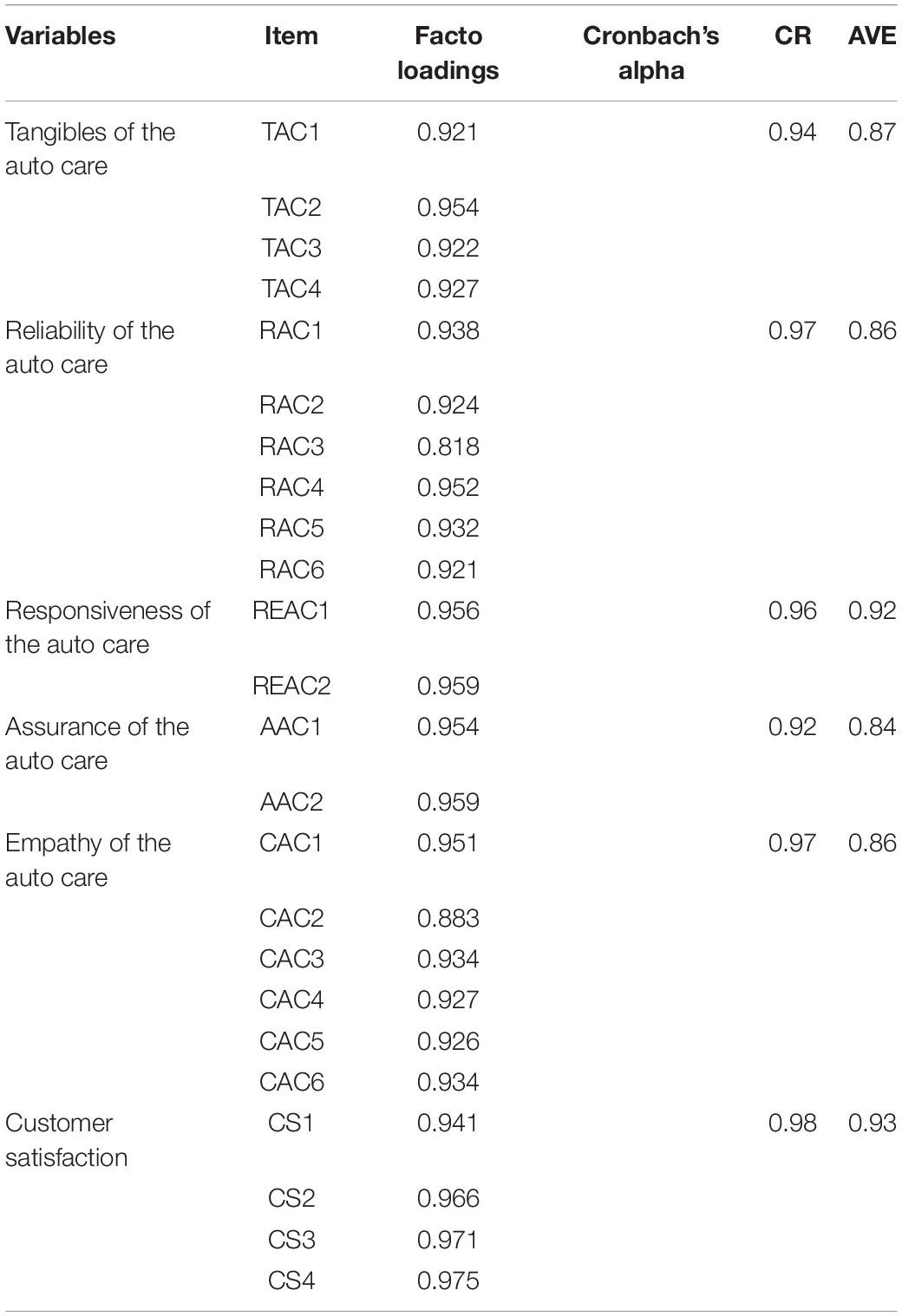
Table 3. Item loadings, Cronbach’s alpha, composite reliability, and average variance extracted.
To analyze the discriminant validity, we evaluated the discriminant validity by matching the association between correlation among variables and the square root of the AVE of the variables ( Fornell and Larcker, 1981a ). The results demonstrate that the square roots of AVE are above the correlation among constructs, hence showing a satisfactory discriminant validity, therefore, indicating an acceptable discriminant validity. Moreover, descriptive statistics and correlations are provided in Table 4 .
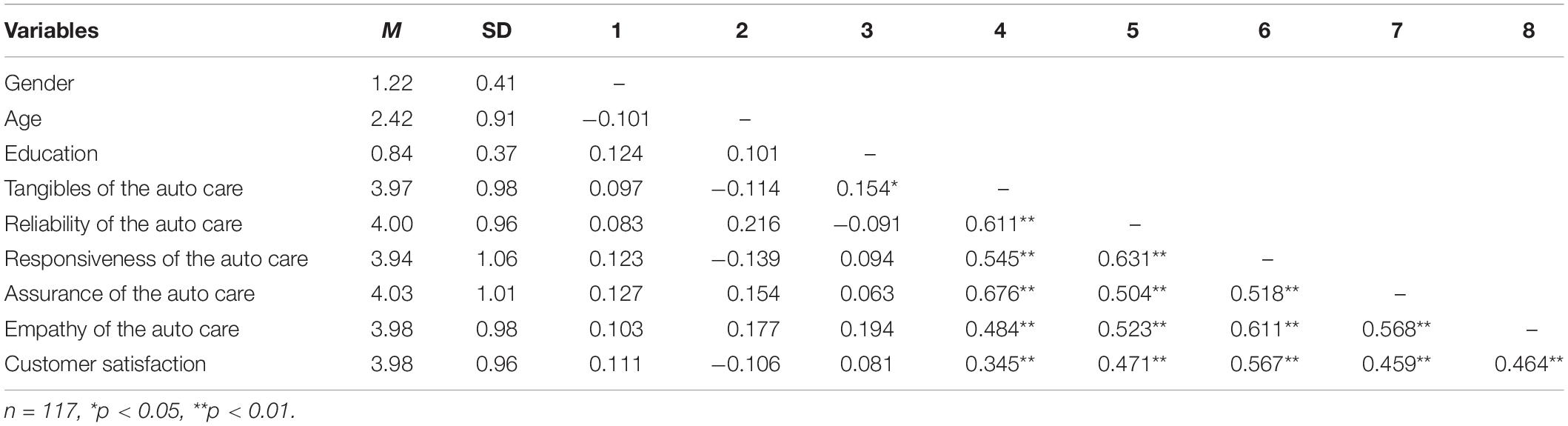
Table 4. Descriptive statistics and correlations.
Structural Model and Hypotheses Testing
After establishing the acceptable reliability and validity in the measurement model, we examined the relationship among variables and analyzed the hypotheses based on the examination of standardized paths. The path significance of proposed relations were calculated using the SEM through the bootstrap resampling technique ( Henseler et al., 2009 ), with 2,000 iterations of resampling. The proposed research framework contains five dimensions of service quality (i.e., tangibles of the auto care, reliability of the auto care, responsiveness of the auto care, assurance of the auto care, and empathy of the auto care) and customer satisfaction of auto care. The results show that five dimensions of service quality are significantly related to customer’s perception of service quality of auto care; thus, hypotheses 1a, 1b, 1c, 1d, and 1e were supported. Figure 1 shows that the service quality of auto care is a significant determinant of customer satisfaction of auto care industry (β = 0.85, p < 0.001), supporting hypothesis 2. The result in Figure 1 also shows that 73.8% of the variation exists in customer satisfaction of auto care.
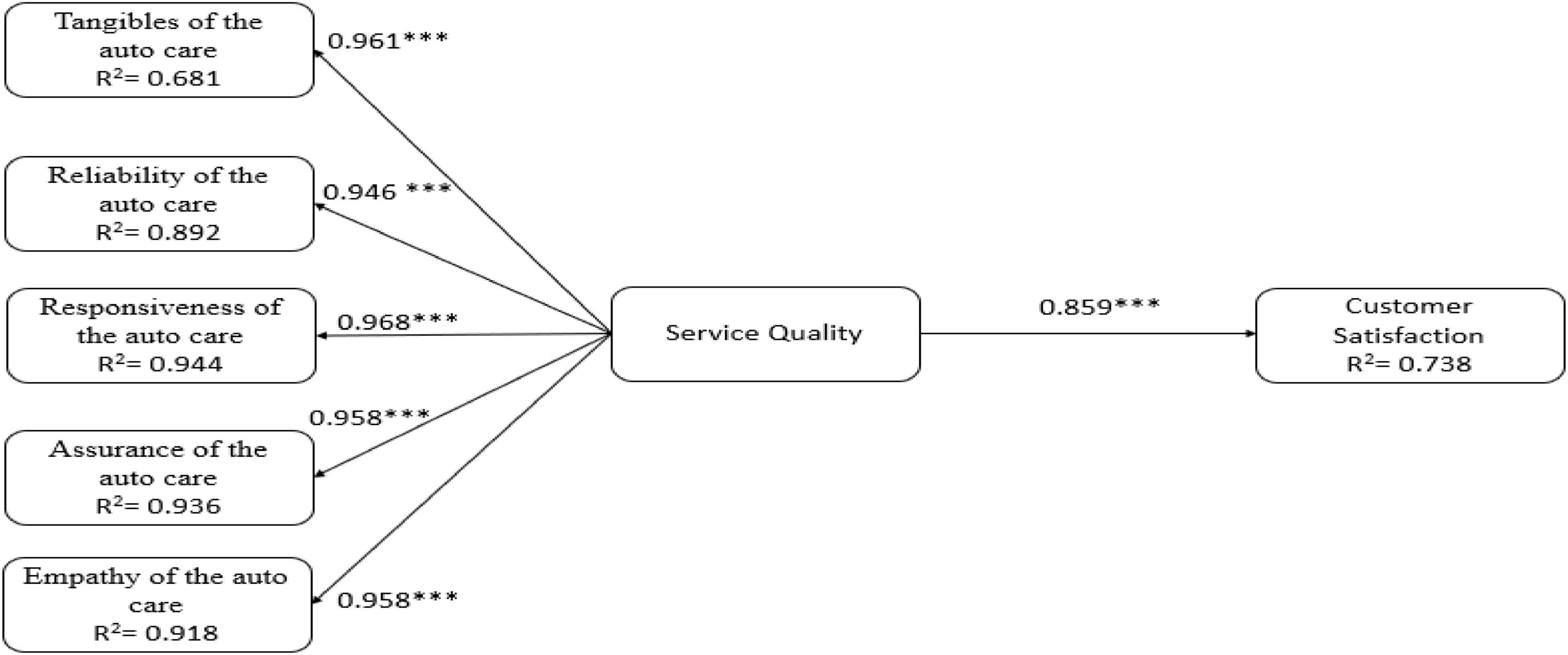
Figure 1. Results of the research model tests. *** p < 0.001.
The main purpose of this research was to assess the relationship between service quality and customer satisfaction in the post pandemic world in Saudi Arabia. This study was designed to examine how satisfaction of auto care customers is influenced by service quality, especially, when pandemic was declared, and due to health concerns, the customers were reluctant to visit workshops physically ( Mason et al., 2021 ). It appears that after the pandemic, customers were increasingly using online platforms for purchasing goods and services. This study reveals how customers of auto repair in Saudi perceive service quality and see how applicable SERVQUAL model across with five dimensions, including tangibles, responsiveness, reliability, assurance, and empathy measure service quality. The findings of this research show that five dimensions of SERVQUAL are positively related to the service quality perception of auto care customers in Saudi Arabia. Moreover, service quality perceptions are positively linked with customer satisfaction. These results indicate that auto care customers view service quality as an important antecedent of their satisfaction. The findings indicate that the customers perceive the service quality as a basic service expectation and will not bear the extra cost for this criterion. In this research, the positive connection between service quality and customer satisfaction is also consistent with previous studies (e.g., González et al., 2007 ; Gallarza-Granizo et al., 2020 ; Cai et al., 2021 ). Thus, service quality plays a key role in satisfying customers. These findings suggest that service organizations, like auto repair industry in Saudi Arabia could enhance satisfaction of their customers through improving service quality. Because of pandemic, people are reluctant to visit auto care workshops, and they try to book appointment through social media; so, by improving the quality of management of their social media pages, the workshops can provide accurate information for monitoring, maintaining, and improving service quality ( Sofyani et al., 2020 ). More specifically, social media, which allows individuals to interact remotely, appears to be gaining significant importance as a tool for identifying customers’ products and service needs. Increasingly, customers are also increasingly engaging with retailers through social media to search and shop for product and services options, evaluate the alternatives, and make purchases.
Furthermore, the research on the customer service quality can be held essential since it acts as a means for the promotion of the competitiveness of an organization. Precisely, the knowledge about the customers’ view concerning service quality can be used by organizations as a tool to improve their customer services. For example, knowledge of the required customer service would help in the facilitation of training programs oriented toward the enlightenment of the overall employees on the practices to improve and offer high-quality customer services. Besides, information concerning customer services would be essential in decision-making process concerning the marketing campaigns of the firm, hence generating competitive advantage of the organization in the marketplace. Findings show that customers demand more from auto repair, so the company must work hard to increase all service quality dimensions to improve customer satisfaction. Thus, organizations ought to venture in customer services initiatives to harness high-quality services.
Managerial Implications
The findings of this research indicate a strong association between SERVQUAL dimensions and perceived service quality. Perception of higher service quality leads to higher level of customer satisfaction among Saudi car care customers. In particular, the results indicate high scores for reliability, empathy, tangibles, and responsiveness. These are clear indications that the immense budgetary allocation has enabled these institutions to develop capacity. Nevertheless, the lack of a strong human resource base remains a key challenge in the car care industry. The effective use of social media plays a critical role in the responsiveness dimension of service quality. Companies need to develop their digital and social media marketing strategies in the post pandemic world to better satisfy their customers.
Saudi Arabia requires a large and well-trained human resource base. This requires intensive investment in training and development. Most of these workers have a limited contract, which reduced their focus on long-term dedication. Consequently, the government should provide longer-term contracts for workers in this critical sector. The contracts should include training on tailored courses to serve the identified needs in effective communication with the customers using digital media. We suggested that the auto car care workshops should provide training to their workers, particularly, on service technicians to enhance their skills that will help to deliver fast and reliable service to their auto customers.
Moreover, the auto car care workshops also provide customer care- or customer handling-related training especially for the service marketing personnel who handles customer directly for them to better understand the customer needs and expectations. This can be done at least once a year. This will help auto care workshops to improve their service quality.
Limitation and Future Research Direction
This research is not without limitations. First, the findings of this study are based on data collected from a single source and at a single point of time, which might be subjected to CMB ( Podsakoff et al., 2003 ). Future research can collect data from different points of time to validate the findings of this research. Second, this research was carried out with data obtained from Saudi auto car care customers; the findings of this research might be different because the research framework was retested in a different cultural context. Therefore, more research is needed to improve the understanding of the principles of service quality and customer satisfaction, as well as how they are evaluated, since these concepts are critical for service organizations’ sustainability and development. A greater sample size should be used in a similar study so that the findings could be applied to a larger population. Research on the effect of inadequate customer service on customer satisfaction, the impact of customer retention strategies on customer satisfaction levels, and the impact of regulatory policies on customer satisfaction is also recommended. Third, because most of the participants participated in this research are men, future studies should obtain data from female participants and provide more insights into the difference between male and female customers’ satisfaction levels. Moreover, due to limitation of time, the sample was collected from the eastern province. Consequently, further research should include a larger and more representative sample of the Saudi population. Because of the non-probability sampling approach used in this research, the results obtained cannot be generalized to a wide range of similar auto repair services situations, even though the methodology used in this study could be extended to these similar situations. Since the sample size considered is not that large, expectations could vary significantly. When compared with the significance of conducting this form of analysis, the limitations mentioned above are minor. Such research should be conducted on a regular basis to track service quality and customer satisfaction levels and, as a result, make appropriate changes to correct any vulnerability that may exist.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Ethics Statement
Ethical review and approval was not required for the study on human participants in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. Written informed consent for participation was not required for this study in accordance with the national legislation and the institutional requirements. The patients/participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Author Contributions
SZ helped in designing the study. ZH helped in designing and writing the manuscript. MAA helped in data collection and analysis and writing the manuscript. SUR repositioned and fine-tuned the manuscript, wrote the introduction, and provided feedback on the manuscript.
This study was received funding from University Research Fund.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s Note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Armstrong, R. W., Mok, C., Go, F. M., and Chan, A. (1997). The importance of cross-cultural expectations in the measurement of service quality perceptions in the hotel industry. Int. J. Hospital. Manag. 16, 181–190. doi: 10.1016/S0278-4319(97)00004-2
CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Asubonteng, P., McCleary, K. J., and Swan, J. E. (1996). Servqual revisited: a critical review of service quality. J. Serv. Market. 10, 62–81. doi: 10.1108/08876049610148602
Atef, T. M. (2011). Assessing the ability of the Egyptian hospitality industry to serve special needs customers. Manag. Leisure 16, 231–242. doi: 10.1080/13606719.2011.583410
Bahadur, W., Aziz, S., and Zulfiqar, S. (2018). Effect of employee empathy on customer satisfaction and loyalty during employee–customer interactions: The mediating role of customer affective commitment and perceived service quality. Cog. Bus. Manag. 5:1491780. doi: 10.1080/23311975.2018.1491780
Brown, G. T. (2020). Schooling beyond COVID-19: an unevenly distributed future. Front. Edu. 8:82. doi: 10.3389/feduc.2020.00082
Cai, G., Hong, Y., Xu, L., Gao, W., Wang, K., and Chi, X. (2021). An evaluation of green ryokans through a tourism accommodation survey and customer-satisfaction-related CASBEE–IPA after COVID-19 Pandemic. Sustainability 13:145. doi: 10.3390/su13010145
Cao, Y., Ajjan, H., and Hong, P. (2018). Post-purchase shipping and customer service experiences in online shopping and their impact on customer satisfaction: an empirical study with comparison. Asia Pacif. J. Market. Logist. 30:71. doi: 10.1108/APJML-04-2017-0071
Chang, M., Jang, H.-B., Li, Y.-M., and Kim, D. (2017). The relationship between the efficiency, service quality and customer satisfaction for state-owned commercial banks in China. Sustainability 9:2163. doi: 10.3390/su9122163
Churchill, G. A. Jr., and Surprenant, C. (1982). An investigation into the determinants of customer satisfaction. J. Mark. Res. 19, 491–504.
Google Scholar
Cohen, J., Cohen, J., Cohen, P., West, S. G. A., Leona, S., Patricia Cohen, S. G. W., et al. (2003). Applied multiple regression/correlation analysis for the behavioral sciences. New York, NY: Psychology Press.
Dominic, P., Goh, K. N., Wong, D., and Chen, Y. Y. (2010). The importance of service quality for competitive advantage–with special reference to industrial product. Int. J. Bus. Inform. Syst. 6, 378–397. doi: 10.1504/IJBIS.2010.035051
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Doucet, L. (2004). Service provider hostility and service quality. Acad. Manag. J. 47, 761–771. doi: 10.5465/20159617
Edward, M., and Sahadev, S. (2011). Role of switching costs in the service quality, perceived value, customer satisfaction and customer retention linkage. Asia Pacif. J. Market. Logist. 23, 327–345. doi: 10.1108/13555851111143240
Elmadağ, A. B., Ellinger, A. E., and Franke, G. R. (2008). Antecedents and consequences of frontline service employee commitment to service quality. J. Market. Theory Pract. 16, 95–110. doi: 10.2753/MTP1069-6679160201
Fornell, C., Johnson, M. D., Anderson, E. W., Cha, J., and Bryant, B. E. (1996). The American customer satisfaction index: nature, purpose, and findings. J. Market. 60, 7–18. doi: 10.1177/002224299606000403
Fornell, C., and Larcker, D. F. (1981a). Evaluating structural equation models with unobservable variables and measurement error. J. Market. Res. 1987, 39–50. doi: 10.1177/002224378101800104
Fornell, C., and Larcker, D. F. (1981b). Structural equation models with unobservable variables and measurement error: Algebra and statistics. J. Market. Res. 1987, 382–388. doi: 10.1177/002224378101800313
Fornell, C., Rust, R. T., and Dekimpe, M. G. (2010). The effect of customer satisfaction on consumer spending growth. J. Market. Res. 47, 28–35. doi: 10.1509/jmkr.47.1.28
Gallarza-Granizo, M. G., Ruiz-Molina, M.-E., and Schlosser, C. (2020). Customer value in quick-service restaurants: a cross-cultural study. Int. J. Hospital. Manag. 85:102351. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhm.2019.102351
González, J., De Boeck, P., and Tuerlinckx, F. (2008). A double-structure structural equation model for three-mode data. Psychol. Methods 13:337. doi: 10.1037/a0013269
González, M. E. A., Comesaña, L. R., and Brea, J. A. F. (2007). Assessing tourist behavioral intentions through perceived service quality and customer satisfaction. J. Bus. Res. 60, 153–160. doi: 10.1016/j.jbusres.2006.10.014
Han, J., Zuo, Y., Law, R., Chen, S., and Zhang, M. (2021). Service Quality in Tourism Public Health: Trust, Satisfaction, and Loyalty. Front. Psychol. 12:279. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2021.731279
Hansemark, O. C., and Albinsson, M. (2004). Customer satisfaction and retention: the experiences of individual employees. Manag. Serv. Qual. Int. J . 14, 40–57. doi: 10.1108/09604520410513668
Henseler, J., Ringle, C. M., and Sinkovics, R. R. (2009). The use of partial least squares path modeling in international marketing New challenges to international marketing. Bingley: Emerald Group Publishing Limited, 277–319. doi: 10.1108/S1474-7979(2009)0000020014
Ismagilova, E., Slade, E. L., Rana, N. P., and Dwivedi, Y. K. (2019). The effect of electronic word of mouth communications on intention to buy: A meta-analysis. Inform. Syst. Front. 2019, 1–24.
Korda, A. P., and Snoj, B. (2010). Development, validity and reliability of perceived service quality in retail banking and its relationship with perceived value and customer satisfaction. Manag. Glob. Trans. 8:187.
Lambert, D. M. (2010). Customer relationship management as a business process. J. Bus. Indus. Market. 25, 4–17. doi: 10.1108/08858621011009119
Lee, H., Lee, Y., and Yoo, D. (2000). The determinants of perceived service quality and its relationship with satisfaction. J. Serv. Market. 14, 217–231. doi: 10.1108/08876040010327220
Mason, A. N., Narcum, J., and Mason, K. (2021). Social media marketing gains importance after Covid-19. Cog. Bus. Manag. 8:797. doi: 10.1080/23311975.2020.1870797
Mechinda, P., and Patterson, P. G. (2011). The impact of service climate and service provider personality on employees’ customer-oriented behavior in a high-contact setting. J. Serv. Market. 25, 101–113. doi: 10.1108/08876041111119822
Monmousseau, P., Marzuoli, A., Feron, E., and Delahaye, D. (2020). Impact of Covid-19 on passengers and airlines from passenger measurements: Managing customer satisfaction while putting the US Air Transportation System to sleep. Transp. Res. Interdiscipl. Persp. 7:179. doi: 10.1016/j.trip.2020.100179
Murray, J., Elms, J., and Curran, M. (2019). Examining empathy and responsiveness in a high-service context. Int. J. Retail Distrib. Manag. 2019:16. doi: 10.1108/IJRDM-01-2019-0016
Nachtigall, C., Kroehne, U., Funke, F., and Steyer, R. (2003). Pros and cons of structural equation modeling. Methods Psychol. Res. Online 8, 1–22.
Nambisan, P., Gustafson, D. H., Hawkins, R., and Pingree, S. (2016). Social support and responsiveness in online patient communities: impact on service quality perceptions. Health Expect. 19, 87–97. doi: 10.1111/hex.12332
Newsted, P. R., Huff, S. L., and Munro, M. C. (1998). Survey instruments in information systems. Mis. Quart. 22:553. doi: 10.2307/249555
Omar, H. F. H., Saadan, K. B., and Seman, K. B. (2015). Determining the influence of the reliability of service quality on customer satisfaction: The case of Libyan E-commerce customers. Int. J. Learn. Dev. 5, 86–89. doi: 10.5296/ijld.v5i1.6649
Palese, B., and Usai, A. (2018). The relative importance of service quality dimensions in E-commerce experiences. Int. J. Inform. Manag. 40, 132–140. doi: 10.1016/j.ijinfomgt.2018.02.001
Podsakoff, P. M., MacKenzie, S. B., Lee, J., and Podsakoff, N. P. (2003). Common method biases in behavioral research: A critical review of the literature and rec-ommended remedies. J. Appl. Psychol. 88, 879–903. doi: 10.1037/0021-9010.88.5.879
Parasuraman, A., Zeithaml, V. A., and Berry, L. (1988). SERVQUAL: a multiple-item scale for measuring consumer perceptions of service quality. J. Retail. 64, 12–40.
Ramanathan, U., Subramanian, N., and Parrott, G. (2017). Role of social media in retail network operations and marketing to enhance customer satisfaction. Int. J. Operat. Prod. Manag. 37:153. doi: 10.1108/IJOPM-03-2015-0153
Santos, J. (2002). From intangibility to tangibility on service quality perceptions: a comparison study between consumers and service providers in four service industries. Manag. Serv. Qual. Int. J. 12, 292–302. doi: 10.1108/09604520210442083
Srivastava, A., and Kumar, V. (2021). Hotel attributes and overall customer satisfaction: What did COVID-19 change? Tour. Manag. Persp. 40:100867. doi: 10.1016/j.tmp.2021.100867
Sofyani, H., Riyadh, H. A., and Fahlevi, H. (2020). Improving service quality, accountability and transparency of local government: the intervening role of information technology governance. Cogent Bus. Manage. 7:1735690. doi: 10.1080/23311975.2020.1735690
Suchánek, P., and Králová, M. (2019). Customer satisfaction, loyalty, knowledge and competitiveness in the food industry. Eco. Res. Ekonomska istraživanja 32, 1237–1255. doi: 10.1080/1331677X.2019.1627893
Susskind, A. M., Kacmar, K. M., and Borchgrevink, C. P. (2003). Customer service providers’ attitudes relating to customer service and customer satisfaction in the customer-server exchange. J. Appl. Psychol. 88:179. doi: 10.1037/0021-9010.88.1.179
Tabachnick, B., and Fidell, L. (2007). Multivariate analysis of variance and covariance. Multivar. Stat. 3, 402–407.
Teas, R. K. (1993). Consumer expectations and the measurement of perceived service quality. J. Prof. Serv. Market. 8, 33–54. doi: 10.1080/15332969.1993.9985048
Wu, G., Liang, L., and Gursoy, D. (2021). Effects of the new COVID-19 normal on customer satisfaction: can facemasks level off the playing field between average-looking and attractive-looking employees? Int. J. Hospit. Manag. 97:102996. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhm.2021.102996
Wu, Y.-C., Tsai, C.-S., Hsiung, H.-W., and Chen, K.-Y. (2015). Linkage between frontline employee service competence scale and customer perceptions of service quality. J. Serv. Market. 29, 224–234. doi: 10.1108/JSM-02-2014-0058
Zhou, R., Wang, X., Shi, Y., Zhang, R., Zhang, L., and Guo, H. (2019). Measuring e-service quality and its importance to customer satisfaction and loyalty: an empirical study in a telecom setting. Elect. Comm. Res. 19, 477–499. doi: 10.1007/s10660-018-9301-3
Keywords : auto care, customer satisfaction, service quality, Saudi Arabia, pandemic (COVID-19)
Citation: Zygiaris S, Hameed Z, Ayidh Alsubaie M and Ur Rehman S (2022) Service Quality and Customer Satisfaction in the Post Pandemic World: A Study of Saudi Auto Care Industry. Front. Psychol. 13:842141. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2022.842141
Received: 23 December 2021; Accepted: 07 February 2022; Published: 11 March 2022.
Reviewed by:
Copyright © 2022 Zygiaris, Hameed, Ayidh Alsubaie and Ur Rehman. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY) . The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Zahid Hameed, [email protected]
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

THE EFFECT OF SERVICE QUALITY ON CUSTOMER SATISFACTION: THE CASE OF ETHIOPIAN ELECTRIC UTILITY AROUND ADDIS ABABA
Related Papers
tsegay G BERHE
Roman kiros
Veroniki Enriquez
Dejene Deriba
The purpose of this quantitative descriptive research study was to assess the level of service quality and to identify the most important service quality dimensions that influence overall customer satisfaction. Five dimensions of the SERVPERF scale namely; tangibles, reliability, responsiveness, assurance and empathy were used to measure the perceptions of customers of Ethio Telecom. The research was conducted using data collected through a survey of enterprise customers in Addis Ababa. 220 questionnaires were sent to the sample of the study and 170 usable questionnaires were obtained with a response rate of 77%. The findings revealed that three of the service quality dimensions: reliability (t-value= 4.06 p <.001) empathy (t-value= 3 p<.005) and tangibles (t-value= 2.129 p<.005) influence the dependant variable overall customer satisfaction. The findings also indicated that overall service quality was found to be influenced by four of the five service quality dimensions namely, reliability (tvalue= 4.684 p <.001), empathy (t-value= 3.05 p<.005), responsiveness (t-value= 2.187 p<.005) and tangibles (t-value= 2.0 p<.005). Reliability, empathy and tangibles were found to be predictors across both overall service quality and customer satisfaction. The study recommends Ethio Telecom to concentrate on these dimensions to achieve.
legese lemma
Cherinet Alemgena
The primary purpose of this research is Assessing the Role of Service Quality on Customer Satisfaction in Ethio Telecom at South Region: Case Hawassa City. To achieve this objective both primarily and secondary data were collected. The questionnaires were distributed to 380 fixed line telephone customers in Hawassa city. As a way of trying to measure service quality, researcher was developed a methodology known as SERVQUAL a perceived service quality questionnaire survey methodology. SERVQUAL examines five dimensions of service quality: Reliability, Responsiveness, Assurance, Empathy, and Tangibility. The collected data were analyzed and interpreted by Statistical Package for the Social Sciences in version 20. From the results obtained, the consumers perceive service quality as poor in all dimensions, indicating their expectations was higher than their perceptions for fixed line telephone service at ethio telecom. In this regard, consumers were not satisfied with any dimension of service quality. All dimensions were showing a negative gap score. Ethio telecom need to make improvements in all dimensions in order to close gap and that could lead to increased customer satisfaction. Thus the paper, enlighten the Company to get insight about its services quality and level of customers’ satisfaction. Ethio teleocm need to improve its service quality provisions and helps customers to get quality fixed line services from ethio it by amending the problem which was recommended in this thesis. Keywords-: Service Quality, Customer Satisfaction, SERVQUAL, fixed line telephone, Ethio telecom
David Arumainayagam
Abstract The primary purpose of this research is assessing the Role of Service Quality on Customer Satisfaction in Ethio Telecom at South Region: Case Hawassa Cit. To achieve this objective both primarily and secondary data were collected. The questionnaires were distributed to 380 fixed line telephone customers in Hawassa city. As a way of trying to measure service quality, researcher was developed a methodology known as SERVQUAL a perceived service quality questionnaire survey methodology. SERVQUAL examines five dimensions of service quality: Reliability, Responsiveness, Assurance, Empathy, and Tangibility. The collected data were analyzed and interpreted by Statistical Package for the Social Sciences in version 20. From the results obtained, the consumers perceive service quality as poor in all dimensions, indicating their expectations was higher than their perceptions for fixed line telephone service at ethio telecom. In this regard, consumers were not satisfied with any dimension of service quality. All dimensions were showing a negative gap score. Ethio telecom need to make improvements in all dimensions in order to close gap and that could lead to increased customer satisfaction. Thus the paper, enlighten the Company to get insight about its services quality and level of customers’ satisfaction. Ethio teleocm need to improve its service quality provisions and helps customers to get quality fixed line services from ethio it by amending the problem which was recommended in this thesis. Keywords-: Service Quality, Customer Satisfaction, SERVQUAL, fixed line telephone, Ethio telecom
Addisalem Tadesse
The liberalization of the economic system in Ethiopia enabled the emergence of private insurance companies and had created competitive environment in the insurance industries. The motives of this study was examiningthe effects of service quality on customer satisfaction in four selected insurance companies of Hosanna town, SNNPR. This research was carried out through cross-sectional survey design and mainly based on data collected through questionnaires. The correlation and multiple regressions were used to analyse collected data. The result of individual companies and total Gap analyses indicates that the mean score of customers' expectations exceeded perceptions in all five dimensions while, findings suggest that selected insurance companies need to improve all the dimensions of service quality.Therefore,regression analyses responsiveness had relatively strong significant and direct effect on customer satisfaction with beta value of .376 and followed by reliability with beta value of .327, tangibility with beta value of .187, empathy with beta value of .149, and assurance with beta value of .113 respectively.Based on the research results, it is recommended for the selected insurance companies to improve their Service.
RELATED PAPERS
Journal ijmr.net.in(UGC Approved)
Muhaba Nuredin
biniyam kebede
Amtataw Yohannes
Eagle eye ጌታ-ሁን ተስፋዬ
Research Paper
James M Chilembwe
Emmanuel Baffour-Awuah
Theuns Pelser
willy mkumbo
peter mwaura
PUBLIC BUS STUDY ON ASSESSMENT OF SHEGER BUS SERVICE AND OPERATION
Natnael Gizaw
Samrawit Mulu
FATAWU ALHASSAN
Linh Nguyễn
International Res Jour Managt Socio Human
carlo enriqz
Quach Minh Chau
Dawit Daniel
Journal of Business and Social Review in Emerging Economies
Chan Tak Jie , Mei Ling Goh
Eshetie Berhan
karthi keyan
International Journal of Academics & Research, IJARKE Journals
Euro Asia International Journals
Sadman Sakib
bello yekini
Puspa Malla
Lat Vonglattana
Isaac Kwesi Nooni , Samuel Koranteng Fianko
Ameen Olorunnimbe
Patrick Sweet
Anim Patrick
Disaster Mugondi
RELATED TOPICS
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024
Success in your inbox
Get monthly insights handpicked by our editorial team. Act on it.

Connect with customers
LiveChat is a complete customer service platform that delights your customers and fuels your sales.
Trusted by 36,000+ companies

LiveChat helps you delight your customers and fuels your sales.
Showing top 0 results 0 results found, how to measure customer service and improve your customers’ experience.
- Post on Twitter
- Share on Facebook
- Post on LinkedIn
- Post on Reddit
- copy-button#copy track#send" data-controller="track" data-track-category="Success" data-track-action="Share" data-track-label="Copy link" > Copy link to clipboard Link copied to clipboard https://www.livechat.com/success/how-to-measure-customer-service/
Every time your business gains a new customer, there are two possible outcomes. Either you deliver on your promises, satisfying them and creating a repeat or loyal customer. Or you leave them disappointed and likely face negative publicity when they leave a poor review.
According to a Zendesk survey, 52% of customers will switch brands after a single negative customer service interaction.
First impressions are so important when it comes to retaining customers, so you must pay attention to your company’s customer service quality. The only way to do this is to measure customer service and gather the information you need to provide a positive customer experience (CX).
In this article, we will look at what it takes to measure customer service and how you can use customer service data to improve your overall CX.


Why you should track customer service
Customers are notoriously fickle. And with tons of competition in nearly every niche, there’s always an alternative, another option for every product or service available—customers are more than happy to make the most of their choices.
While pricing and quality of goods and services are important concerns, CX plays an equally, if not more important, role in determining consumers’ purchasing decisions. According to a PwC customer satisfaction survey, 73% of customers consider CX a deciding factor in choosing which company to buy from.
Tracking customer service is essential to view the big picture of how your target market perceives your brand. Along with this broad perspective, taking a closer look at the finer details of your customer service operations is also valuable.
Here are three ways measuring customer service improves your overall CX and contributes to your business’ success:
- Understand your customers’ needs Paying close attention to the kind of requests your customer service teams get will form a clearer picture of what your customers want. Whether it's positive or negative feedback, the points raised are valuable to understanding their needs and expectations from your company.
- Identify pain points for customers There are many ways to improve CX, all of which involve identifying the problems as a first step. The nature of the customer support tickets your customer service team receives will highlight the most persistent pain points in your business model. For example, if the problems with your CX are delayed delivery, inferior packaging, or anything else, you can tell by measuring your company’s customer service actions.
- Improve service delivery You don’t measure customer service just to find out what’s wrong with your business. You also need it to learn what you’re doing well. Customer feedback also contains success stories, which are helpful when figuring out what exactly draws people to your brand. When you learn what attracts your existing customers, you can use those lessons to tweak your offerings, increase customer satisfaction, and draw in new audiences with improved service.
Mapping customer journeys: The starting point for customer service success
To accurately measure customer service, you need to be aware of every touch point between your company and your customers. In other words, you need to be intimately familiar with the customers’ journey.
The customer journey is the sum total of all experiences each person has involving your brand, including the time before and after making a purchase.
By building a map of the customer journey, you gain insight into their needs at every stage. This information can help you streamline customer service operations to help customers have a better experience throughout their journey. A customer journey map is essentially a visual representation of each stage and its impact on the brand’s CX —a critical element in your efforts to increase customer satisfaction and boost loyal customers.
Five stages of every customer journey
Every customer will have a unique journey with your brand. This is where personalization and customer service intersect, but that’s a different topic altogether.
For now, what you should remember is that despite the variables, every customer journey goes through five distinct stages:
- Stage 1 - Awareness: In the first stage, customers become aware of a problem that needs solving or a need of theirs that has to be met. The goal of customer service at this point is to create awareness that there are solutions that your brand can deliver. You should provide potential customers with valuable content to help them learn more about how you can help solve their problems.
- Stage 2—Consideration: As they search for a solution, potential customers should encounter marketing materials that lead them to the solutions your brand provides. At this stage of their journey, customers are likely to explore several competitor brands. The quality of your customer service and brand outreach can be the difference-maker that makes them choose your products or services.
- Stage 3 - Decision: Here’s where things get serious. At this stage, a customer has gathered all the information they need to make a purchasing decision. If your marketing strategy has worked, they will choose your brand, and that’s where your customer service team needs to jump into action. When the customer journey reaches the decision stage, your company needs to make the purchasing process as seamless and simple as possible. Complicating the experience of checking out all the products in their cart will drag down your CX and drive away customers.
- Stage 4 -Retention: In this stage, your customer service team should aim to reduce customer churn rate, or the number of people who stop supporting a business over time. The objective is to turn a one-time buyer into a repeat and loyal customer. Your company needs to provide ongoing, excellent customer service to ensure all customers remain satisfied with their purchases and the brand as a whole.
- Stage 5 - Loyalty: Customer satisfaction increases when they feel valued by the brand. This is why rewarding loyal customers is crucial to customer service. This is the final stage of the customer journey, where they should enjoy the benefits of sticking with your brand through perks like discounts and other exclusive offerings. At this point, your aim should be to provide excellent end-to-end customer service that delights customers and turns them into informal ambassadors for your brand.
The point of breaking up the customer journey into these five stages is to identify and maximize every touch point along the way. By developing strategies to improve the experience at all stages of the journey, you can then focus on customer satisfaction.
Deciding on an approach to measure customer service
How you measure customer service will depend on your business goals. You can opt for a qualitative or quantitative approach or a combination of the two.
If you are focusing more on metrics and key performance indicators (KPIs), then a quantitative approach is better suited to measuring customer service quality. However, a qualitative approach works better if you want to work on attributes that are harder to quantify, like customer sentiment or customer satisfaction.
A quantitative approach to measuring customer service is more structured, as it relies on collecting concrete data connected to CX. Quantitative methods are more concerned with objective data, which is standardized across all customers in their audience.
On the other hand, qualitative data involves more abstract ways of obtaining feedback. The goal of this approach is to capture insights about subjective views held by customers through open-ended survey questions, focus group discussions, or review analysis.
Why you should adopt qualitative methods to measure customer service
You should never overlook qualitative methods when measuring customer service at your company. While quantitative data accurately represent key CX statistics, qualitative methods often go even deeper, giving you a more complete picture of what is happening underneath the surface when it comes to your company’s customer service.
- Qualitative methods capture the voice of the customer.
- You gain more insights into how popular products are perceived by the audience.
With the many advanced tools available to businesses in the digital age, combining a qualitative and quantitative approach is easier than ever. New text analysis tools speed up processing text data from customer feedback, like comments, reviews, and emails. This, paired with the data analytics of modern customer relationship management (CRM) software, gives you a balanced look at the current state of your customer service operations.
KPIs for customer service
While qualitative analysis of customer service data helps establish context and adds nuance to your understanding of CX, no CX transformation can be managed without tracking important KPIs. Several important metrics can be monitored to measure customer service.
If you have chosen quality CRM software, it will have advanced reporting functionality. This will enable you to monitor the metrics you’ve chosen for your customer service transformation. Your list of chosen metrics will depend on your business goals, so it's important to align your KPIs and objectives when deciding which metrics to track. Remember, there are many different metrics relating to the various aspects of customer service. It would be easy to get bogged down by too many details—you should focus only on what’s important.
For example, if retaining existing customers is the top problem for your customer service team, you will want to track metrics like churn rate, average resolution time, and resolution rate. Meanwhile, if the primary issue is related to problems with your product, you will want to track first response time and customer service abandonment rates.
Some other examples of customer service metrics that serve as KPIs include net promoter score (NPS) and customer satisfaction score (CSAT). Take the time to learn how each metric relates to your company’s overall CX, and then prepare your list of KPIs to measure customer service.
Beyond metrics: Holistic approaches to measure customer service
Tracking customer service metrics as KPIs gives you a detailed look at individual aspects of customer service, like issue resolution, customer waiting times, and purchasing experience. However, if you want to evaluate your overall CX from a broader, more holistic perspective, you will need to go beyond traditional metrics.
Instead of monitoring customer service data that is one-dimensional, you need information that paints a comprehensive picture of the entire customer journey.
There are various measurement frameworks you can rely on for this. Let’s look at some of the most common ones you can use.
Customer lifetime value (CLV)
One of the main reasons that customer service teams divide their brand’s customers into different segments is that it helps them focus their energy and resources. Naturally, high-value customers should be given more priority when resolving issues, and CLV is one of the best ways to segment high- and low-value customers.
CLV is such a useful segmenting tool that 25% of marketers in a Gartner survey ranked it among their top five metrics. A simple way to calculate a given customer’s CLV is by multiplying the number of annual purchases by the total profits and by the number of years they have been buying from your company.
Customer effort score (CES)
CES has untapped potential to help you measure your customer service. You should track CES to know precisely how easy it is for your customers to get a hold of your customer service team and find a satisfactory resolution.
A low CES will indicate that your CX is faulty at a fundamental level. Meanwhile, a higher CES is a sign that you have all your bases covered when it comes to customer service and now need to fine-tune certain aspects to improve even further.
To calculate CES, you need to ask customers to rate the difficulty of completing any customer service interaction from 1 to 5. In this rating, 1 means extremely difficult, while 5 means extremely easy. You then calculate the average rating by adding every customer’s response and dividing by the total number of responses. This will give you the CES for any customer service process, and you can yield insights on how to streamline it.
Customer satisfaction index (CSI)
Of all the frameworks to measure customer service, CSI provides the most complete snapshot. By tracking CSI, you can measure aspects of customer service like product satisfaction levels, pricing, and ease of use, among others.
Customers give each aspect an individual rating. You can weigh the ratings according to your own needs, depending on the business goals you want to achieve. Then, all the inputs and different weights are formulated to derive a final index number, the CSI score.
CSI score is a valuable metric to keep in mind because it offers a nuanced consideration of your overall CX. It’s much easier to collect customer insights when there is a convenient metric like CSI letting you know exactly how well your customer service team is performing.
Making sense of customer service data
It doesn’t matter whether you’re trying to track hard metrics or capture subjective customer sentiments; there is no shortage of data for you to collect. How you go about collecting this data is a critical component of your overall customer service strategy. The method you choose will impact several key areas of your business, from targeted marketing campaigns to ongoing customer service operations.
Traditionally, companies would gather customer service insights by directly soliciting feedback from the customers themselves. Those methods have evolved as technology has advanced, but they are just as effective in their new avatars.
Let’s look at some of the time-tested tools for collecting valuable customer service data.
This versatile tool can be used at any stage of a customer journey to measure customer service quality. Conducting surveys among your target audience lets you learn more about your customer base. Because surveys can capture detailed feedback, you can get clearer insights into customers’ pain points and purchasing motivations.
Email newsletters
A great way to get customers to voluntarily share their data with your company is to offer a subscription-based email newsletter. If your newsletter’s content is relevant and interesting to your target audience, they will sign up by themselves and share their name and email address. From there, you can learn more about customers by linking them to surveys within newsletters and asking them to curate the content they receive by indicating their interest in different topics.
Purchase history
Maintaining a record of existing customers’ previous purchases with your company is essential to customer service. On an individual level, it lets you know the personal preferences of any given customer. On a macro level, you gain valuable insights into your best-selling items, average order value (AOV), customer base demographics, and more.
Modern tools to track the quality of your CX
With all the digital tools at your disposal in 2024 and beyond, you can create more advanced strategies for analyzing customer service data by leveraging the following:
Implementing live chat is a basic customer service offering in this digital age. Live chat is gaining popularity with businesses to gather and streamline customer service data. Even customers are growing more familiar with this channel, with a 2022 report finding it second only to email as their preferred mode of communication with brands.
Chatbots are a must-have customer service asset because of the following:
- Increase engagement by automatically starting customer conversations based on pre-set triggers.
- Streamline customer communication by integrating various channels, like WhatsApp Business, Messenger, Apple Messages for Business, and more.
- Improve CX by delivering personalized recommendations based on existing customer profiles.
- Assist customer service teams by automating tedious, repetitive tasks.
Grow sales with ChatBot
Optimize your sales process. Leverage customer experience for revenue growth.
Trusted by 2,500+ companies

Apart from the sources of customer data mentioned above, you can also collect customer information by monitoring website traffic and running SEO campaigns. The sheer volume of customer service data available to brands demands a smart hub where it can all be processed. Robust CRM software fulfills that requirement, acting as the heart of your customer service operations. CRM software automatically collects customer information from various sources, integrates with common customer service platforms, and records purchases and sales history.
When you start measuring your customer service, you will need to employ a selection of these tools to get accurate information about the state of your CX. Effective CRM software will have features that allow you to prepare customer service reports and create data visualizations.
Why customer service is a continuous process
Once you’ve begun monitoring your customer service, you better understand how creating a positive CX is a delicate and intricate process. Many factors go into creating CX, and it’s a misconception that it is solely the customer service team’s responsibility. Everything from product design and social media messaging to after-sales service has an impact on CX. The customer journey will have multiple touchpoints connecting to different departments in your company.
This is why fostering a culture of committed customer service at every level of your organization is so important. A clear-cut CX strategy needs to be implemented, and every stakeholder in the company should be brought up to speed. When different departments are all working toward the same goal of customer satisfaction, CX goes through a marked improvement.
To track the gains made by your CX strategy, you will need to measure customer service, which starts the cycle all over again. Creating a culture of constant customer service at your company is the path to continued success and growth.
A new way to measure and improve customer service
If you want to start reaching out to your customers with a tool that can benefit your business, consider including LiveChat in your customer service toolkit.
LiveChat is a complete customer service platform on virtually any channel, whether it be email and messaging services or in-app conversations and website chat links. It contains everything you need to measure your customer service according to your business needs, from customizable chat widgets to detailed customer service reports.
Empower your customer service team to deliver more value to your customers by signing up for LiveChat.
Get a glimpse into the future of business communication with digital natives.

Keep the conversation going
- copy-button#copy track#send" data-controller="track" data-track-category="Success" data-track-action="Share" data-track-label="Copy link" > Copy link Link copied to clipboard https://www.livechat.com/success/how-to-measure-customer-service/
Thanks for your comment!
It will go live straight after moderation. Come back soon!
Something's wrong
We are sorry! Please try again in few moments
Server error
Something went wrong. Please try again in few moments.
LiveChat is a complete customer service platform that delights your customers and fuels your sales
You may also like

0 min watch | May 08 | Kaia Madalinska
How to deal with demanding clients? 4 Types of Difficult Customers

Use These 5 Tips To Boost Your Customer Satisfaction!

5 Easy Ways To Reach Your Customers Online!

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
ABSTRACT. Service quality and customer satisfac tion have been widely recognized as funda mental drivers in. the formation of pu rchase intentions. The concepts ar e important for companies to ...
challenges such as challenges of quality service, customer satisfaction, customer retention, Customer loyalty; Quality service plays a major role in achieving customer satisfaction, and creating brand loyalty in banking sector. 1.1.1.Service Quality Service Quality is a business administration term used to describe achievement in service. It
A Thesis Submitted to Addis Ababa University College of Business and ... Key Words: Service Quality, Customer Satisfaction, Perceived Value, Service Failure, Moderating Variables . The Effect of Service Quality on Customer Satisfaction 2019 1 | P a g e AAU College of Business and Economics ...
Considering the significant relationship between service quality, customer satisfaction, and customer loyalty, more emphasis on improvement will further enhance the customers' favorable feedback. ... [Doctoral thesis]. Purdue University. Google Scholar. Herington C., Weaven S. (2009). E-retailing by banks: E-service quality and its importance ...
So, studying the effect of service quality on customer satisfaction in Ethio telecom is critical given the sector has a huge contribution to the Ethiopian economy and its vast customer base expansion. In the following sections, background to the Ethio telecom and the unit of analysis-enterprise division is discussed.
This thesis analyzes if service quality has any significant impact on brand loyalty, where customer satisfaction is used as an indicator for brand loyalty. Additionally, it tests if the factor of generations, and the generational differences has any impact on how service quality is valued by the consumer in terms of
This Thesis - Open Access is brought to you for free and open access by DSpace @Strathmore University. It has been accepted for ... Service quality and customer satisfaction have increasingly been identified as key factors in the battle for competitive differentiation to gain customer retention and customer loyalty
Extensive research on articles in the niche of business and economics that talk about customer. satisfaction indicates that 2235 studies have got carried out between 1992-2011 (Farooq & Salam, 2018). Amongst these studies, 1088 elaborate on the aspects of customer satisfaction and service.
An extensive review of the literature suggests a lack of bibliometric studies that examine and scientifically map the body of knowledge related to service quality and customer satisfaction. This research aims to examine the trends in service quality and customer satisfaction research, identify the gaps, and propose future research agenda.
This thesis has that the most influential service shown quality dimension on customer satisfaction are responsiveness, empathy and assurance. ... It will be interesting to focus on customer satisfaction and service quality as these constructs have not been explored in the developing countries . 1.3. Motivation and Aim of study
among service quality and customer satisfaction. 2.1 Service Quality Service quality is a complex construct, which has been the focus of a number of studies in the services marketing literature. Two schools of thought dominate this literature: the Nordic school of thought and the North American school of thought.
The thesis has a standard structure comprising five chapters in addition to this introduction. The second chapter offers a critical review of the literature on customer loyalty and ... Numerous studies have linked service quality to high customer satisfaction rates, the likelihood of positive word-of-mouth (WOM) recommendations, repurchase ...
Service quality and customer satisfaction have a positive relationship. Recognizing and meeting customer expectations through high levels of service quality help distinguish the company's services from those of its rivals (Dominic et al., 2010). Social media plays a critical role in shaping these service quality-related variables.
The purpose of the study is to access the customer satisfaction towards service quality of Nepalese commercial banks. This section elaborates on data collection procedure which includes nature and sources of data and also time frame for the study. 3.5.1 Nature and sources of data. This study is based on primary data.
Many empirical and conceptual studies have been done on customer service quality and customer satisfaction. The finding of Mohammad and Alhamadani (2011), indicated that service quality is an important antecedent of customer satisfaction. Parasuraman et al. (1985) "found that service quality is significant predictor of customer satisfaction ...
organization in Malaysia, the quality of customer service government agencies provide. has a tremendous influence on public perceptions of the quality of the public service. Therefore, this study is attempting to answer the following questions: To examine method, frequency and purpose of contact with public sector agencies.
Oliver and Swan (1989) pointed out that customer satisfaction is an evaluative or emotional response to the service a customer perceived and some studies have suggested that favorably perceived service quality leads to improved customer satisfaction (Bolton & Drew, 1991; Boulding, Kalra, Staelin & Zeithaml, 1993; Cronin, Brady & Hult, 2000).
The aim of the thesis was to give quality service and make the customer satisfied. In the food industry there are fewer opportunities for building up ... Service quality and customer satisfaction (adapted from Bateson & Hoffman 1999) GRAPH 2. Nepalese food set Daal-Bhat (adapted from Restaurant Sagarmatha 2009) GRAPH 3. Restaurant Sagarmatha ...
THE EFFECT OF SERVICE QUALITY ON CUSTOMER SATISFACTION: THE CASE OF ETHIOPIAN ELECTRIC UTILITY AROUND ADDIS ABABA A Thesis Submitted to the School of Graduate Studies of Jimma University in Partial Fulfilment of the Requirements for the Award of the Degree of Master of Business Administration (MBA) BY: MEKONNEN TESFAYE G/EYESUS JIMMA UNIVERSITY ...
Service as a component is an integral part of customer satisfaction. Experts have demonstrated that service quality is identified with customer satisfaction. Service quality enhancements and building strong and fruitful relationships with customers is the prime concern for organizations, specifically banks (Khare, 2010).
deliver to their customers must be given great attention because quality service is a key driver of customer satisfaction and organizational sustainability (Shemwell et al. 1998). However, because of the characteristics of service quality, (inseparability, perish ability, and intangibility). Itis always difficult to measure it.
industry, relationship between customer satisfaction and service quality and measurement of service quality. 1.1.1 Service Quality Service quality is a concept that has aroused considerable interest and debate in the research literature because of the difficulties in both defining it and
Murali S., Pugazhendhi S., & Muralidharan C. (2016). Modelling and investigating the relationship of after sales service quality with customer satisfaction, retention and loyalty—a case study of home appliances business. Journal of Retailing and Consumer Services, 30(May), 67-83.
While qualitative analysis of customer service data helps establish context and adds nuance to your understanding of CX, no CX transformation can be managed without tracking important KPIs. Several important metrics can be monitored to measure customer service. If you have chosen quality CRM software, it will have advanced reporting functionality.