

What Is Creative Writing? (Ultimate Guide + 20 Examples)
Creative writing begins with a blank page and the courage to fill it with the stories only you can tell.
I face this intimidating blank page daily–and I have for the better part of 20+ years.
In this guide, you’ll learn all the ins and outs of creative writing with tons of examples.
What Is Creative Writing (Long Description)?
Creative Writing is the art of using words to express ideas and emotions in imaginative ways. It encompasses various forms including novels, poetry, and plays, focusing on narrative craft, character development, and the use of literary tropes.

Table of Contents
Let’s expand on that definition a bit.
Creative writing is an art form that transcends traditional literature boundaries.
It includes professional, journalistic, academic, and technical writing. This type of writing emphasizes narrative craft, character development, and literary tropes. It also explores poetry and poetics traditions.
In essence, creative writing lets you express ideas and emotions uniquely and imaginatively.
It’s about the freedom to invent worlds, characters, and stories. These creations evoke a spectrum of emotions in readers.
Creative writing covers fiction, poetry, and everything in between.
It allows writers to express inner thoughts and feelings. Often, it reflects human experiences through a fabricated lens.
Types of Creative Writing
There are many types of creative writing that we need to explain.
Some of the most common types:
- Short stories
- Screenplays
- Flash fiction
- Creative Nonfiction
Short Stories (The Brief Escape)
Short stories are like narrative treasures.
They are compact but impactful, telling a full story within a limited word count. These tales often focus on a single character or a crucial moment.
Short stories are known for their brevity.
They deliver emotion and insight in a concise yet powerful package. This format is ideal for exploring diverse genres, themes, and characters. It leaves a lasting impression on readers.
Example: Emma discovers an old photo of her smiling grandmother. It’s a rarity. Through flashbacks, Emma learns about her grandmother’s wartime love story. She comes to understand her grandmother’s resilience and the value of joy.
Novels (The Long Journey)
Novels are extensive explorations of character, plot, and setting.
They span thousands of words, giving writers the space to create entire worlds. Novels can weave complex stories across various themes and timelines.
The length of a novel allows for deep narrative and character development.
Readers get an immersive experience.
Example: Across the Divide tells of two siblings separated in childhood. They grow up in different cultures. Their reunion highlights the strength of family bonds, despite distance and differences.
Poetry (The Soul’s Language)
Poetry expresses ideas and emotions through rhythm, sound, and word beauty.
It distills emotions and thoughts into verses. Poetry often uses metaphors, similes, and figurative language to reach the reader’s heart and mind.
Poetry ranges from structured forms, like sonnets, to free verse.
The latter breaks away from traditional formats for more expressive thought.
Example: Whispers of Dawn is a poem collection capturing morning’s quiet moments. “First Light” personifies dawn as a painter. It brings colors of hope and renewal to the world.
Plays (The Dramatic Dialogue)
Plays are meant for performance. They bring characters and conflicts to life through dialogue and action.
This format uniquely explores human relationships and societal issues.
Playwrights face the challenge of conveying setting, emotion, and plot through dialogue and directions.
Example: Echoes of Tomorrow is set in a dystopian future. Memories can be bought and sold. It follows siblings on a quest to retrieve their stolen memories. They learn the cost of living in a world where the past has a price.
Screenplays (Cinema’s Blueprint)
Screenplays outline narratives for films and TV shows.
They require an understanding of visual storytelling, pacing, and dialogue. Screenplays must fit film production constraints.
Example: The Last Light is a screenplay for a sci-fi film. Humanity’s survivors on a dying Earth seek a new planet. The story focuses on spacecraft Argo’s crew as they face mission challenges and internal dynamics.
Memoirs (The Personal Journey)
Memoirs provide insight into an author’s life, focusing on personal experiences and emotional journeys.
They differ from autobiographies by concentrating on specific themes or events.
Memoirs invite readers into the author’s world.
They share lessons learned and hardships overcome.
Example: Under the Mango Tree is a memoir by Maria Gomez. It shares her childhood memories in rural Colombia. The mango tree in their yard symbolizes home, growth, and nostalgia. Maria reflects on her journey to a new life in America.
Flash Fiction (The Quick Twist)
Flash fiction tells stories in under 1,000 words.
It’s about crafting compelling narratives concisely. Each word in flash fiction must count, often leading to a twist.
This format captures life’s vivid moments, delivering quick, impactful insights.
Example: The Last Message features an astronaut’s final Earth message as her spacecraft drifts away. In 500 words, it explores isolation, hope, and the desire to connect against all odds.
Creative Nonfiction (The Factual Tale)
Creative nonfiction combines factual accuracy with creative storytelling.
This genre covers real events, people, and places with a twist. It uses descriptive language and narrative arcs to make true stories engaging.
Creative nonfiction includes biographies, essays, and travelogues.
Example: Echoes of Everest follows the author’s Mount Everest climb. It mixes factual details with personal reflections and the history of past climbers. The narrative captures the climb’s beauty and challenges, offering an immersive experience.
Fantasy (The World Beyond)
Fantasy transports readers to magical and mythical worlds.
It explores themes like good vs. evil and heroism in unreal settings. Fantasy requires careful world-building to create believable yet fantastic realms.
Example: The Crystal of Azmar tells of a young girl destined to save her world from darkness. She learns she’s the last sorceress in a forgotten lineage. Her journey involves mastering powers, forming alliances, and uncovering ancient kingdom myths.
Science Fiction (The Future Imagined)
Science fiction delves into futuristic and scientific themes.
It questions the impact of advancements on society and individuals.
Science fiction ranges from speculative to hard sci-fi, focusing on plausible futures.
Example: When the Stars Whisper is set in a future where humanity communicates with distant galaxies. It centers on a scientist who finds an alien message. This discovery prompts a deep look at humanity’s universe role and interstellar communication.
Watch this great video that explores the question, “What is creative writing?” and “How to get started?”:
What Are the 5 Cs of Creative Writing?
The 5 Cs of creative writing are fundamental pillars.
They guide writers to produce compelling and impactful work. These principles—Clarity, Coherence, Conciseness, Creativity, and Consistency—help craft stories that engage and entertain.
They also resonate deeply with readers. Let’s explore each of these critical components.
Clarity makes your writing understandable and accessible.
It involves choosing the right words and constructing clear sentences. Your narrative should be easy to follow.
In creative writing, clarity means conveying complex ideas in a digestible and enjoyable way.
Coherence ensures your writing flows logically.
It’s crucial for maintaining the reader’s interest. Characters should develop believably, and plots should progress logically. This makes the narrative feel cohesive.
Conciseness
Conciseness is about expressing ideas succinctly.
It’s being economical with words and avoiding redundancy. This principle helps maintain pace and tension, engaging readers throughout the story.
Creativity is the heart of creative writing.
It allows writers to invent new worlds and create memorable characters. Creativity involves originality and imagination. It’s seeing the world in unique ways and sharing that vision.
Consistency
Consistency maintains a uniform tone, style, and voice.
It means being faithful to the world you’ve created. Characters should act true to their development. This builds trust with readers, making your story immersive and believable.
Is Creative Writing Easy?
Creative writing is both rewarding and challenging.
Crafting stories from your imagination involves more than just words on a page. It requires discipline and a deep understanding of language and narrative structure.
Exploring complex characters and themes is also key.
Refining and revising your work is crucial for developing your voice.
The ease of creative writing varies. Some find the freedom of expression liberating.
Others struggle with writer’s block or plot development challenges. However, practice and feedback make creative writing more fulfilling.
What Does a Creative Writer Do?
A creative writer weaves narratives that entertain, enlighten, and inspire.
Writers explore both the world they create and the emotions they wish to evoke. Their tasks are diverse, involving more than just writing.
Creative writers develop ideas, research, and plan their stories.
They create characters and outline plots with attention to detail. Drafting and revising their work is a significant part of their process. They strive for the 5 Cs of compelling writing.
Writers engage with the literary community, seeking feedback and participating in workshops.
They may navigate the publishing world with agents and editors.
Creative writers are storytellers, craftsmen, and artists. They bring narratives to life, enriching our lives and expanding our imaginations.
How to Get Started With Creative Writing?
Embarking on a creative writing journey can feel like standing at the edge of a vast and mysterious forest.
The path is not always clear, but the adventure is calling.
Here’s how to take your first steps into the world of creative writing:
- Find a time of day when your mind is most alert and creative.
- Create a comfortable writing space free from distractions.
- Use prompts to spark your imagination. They can be as simple as a word, a phrase, or an image.
- Try writing for 15-20 minutes on a prompt without editing yourself. Let the ideas flow freely.
- Reading is fuel for your writing. Explore various genres and styles.
- Pay attention to how your favorite authors construct their sentences, develop characters, and build their worlds.
- Don’t pressure yourself to write a novel right away. Begin with short stories or poems.
- Small projects can help you hone your skills and boost your confidence.
- Look for writing groups in your area or online. These communities offer support, feedback, and motivation.
- Participating in workshops or classes can also provide valuable insights into your writing.
- Understand that your first draft is just the beginning. Revising your work is where the real magic happens.
- Be open to feedback and willing to rework your pieces.
- Carry a notebook or digital recorder to jot down ideas, observations, and snippets of conversations.
- These notes can be gold mines for future writing projects.
Final Thoughts: What Is Creative Writing?
Creative writing is an invitation to explore the unknown, to give voice to the silenced, and to celebrate the human spirit in all its forms.
Check out these creative writing tools (that I highly recommend):
| Recommended Tools | Learn More |
|---|---|
| Jasper AI | |
| Show Not Tell GPT | |
| Dragon Professional Speech Dictation and Voice Recognition | |
| Surface Laptop | |
| Bluehost | |
| Sqribble (eBook maker) |
Read This Next:
- What Is a Prompt in Writing? (Ultimate Guide + 200 Examples)
- What Is A Personal Account In Writing? (47 Examples)
- How To Write A Fantasy Short Story (Ultimate Guide + Examples)
- How To Write A Fantasy Romance Novel [21 Tips + Examples)

What is Creative Writing? A Key Piece of the Writer’s Toolbox
Not all writing is the same and there’s a type of writing that has the ability to transport, teach, and inspire others like no other.
Creative writing stands out due to its unique approach and focus on imagination. Here’s how to get started and grow as you explore the broad and beautiful world of creative writing!
What is Creative Writing?
Creative writing is a form of writing that extends beyond the bounds of regular professional, journalistic, academic, or technical forms of literature. It is characterized by its emphasis on narrative craft, character development, and the use of literary tropes or poetic techniques to express ideas in an original and imaginative way.
Creative writing can take on various forms such as:
- short stories
- screenplays
It’s a way for writers to express their thoughts, feelings, and ideas in a creative, often symbolic, way . It’s about using the power of words to transport readers into a world created by the writer.
5 Key Characteristics of Creative Writing
Creative writing is marked by several defining characteristics, each working to create a distinct form of expression:
1. Imagination and Creativity: Creative writing is all about harnessing your creativity and imagination to create an engaging and compelling piece of work. It allows writers to explore different scenarios, characters, and worlds that may not exist in reality.
2. Emotional Engagement: Creative writing often evokes strong emotions in the reader. It aims to make the reader feel something — whether it’s happiness, sorrow, excitement, or fear.
3. Originality: Creative writing values originality. It’s about presenting familiar things in new ways or exploring ideas that are less conventional.
4. Use of Literary Devices: Creative writing frequently employs literary devices such as metaphors, similes, personification, and others to enrich the text and convey meanings in a more subtle, layered manner.
5. Focus on Aesthetics: The beauty of language and the way words flow together is important in creative writing. The aim is to create a piece that’s not just interesting to read, but also beautiful to hear when read aloud.
Remember, creative writing is not just about producing a work of art. It’s also a means of self-expression and a way to share your perspective with the world. Whether you’re considering it as a hobby or contemplating a career in it, understanding the nature and characteristics of creative writing can help you hone your skills and create more engaging pieces .
For more insights into creative writing, check out our articles on creative writing jobs and what you can do with a creative writing degree and is a degree in creative writing worth it .
Styles of Creative Writing
To fully understand creative writing , you must be aware of the various styles involved. Creative writing explores a multitude of genres, each with its own unique characteristics and techniques.
Poetry is a form of creative writing that uses expressive language to evoke emotions and ideas. Poets often employ rhythm, rhyme, and other poetic devices to create pieces that are deeply personal and impactful. Poems can vary greatly in length, style, and subject matter, making this a versatile and dynamic form of creative writing.
Short Stories
Short stories are another common style of creative writing. These are brief narratives that typically revolve around a single event or idea. Despite their length, short stories can provide a powerful punch, using precise language and tight narrative structures to convey a complete story in a limited space.
Novels represent a longer form of narrative creative writing. They usually involve complex plots, multiple characters, and various themes. Writing a novel requires a significant investment of time and effort; however, the result can be a rich and immersive reading experience.
Screenplays
Screenplays are written works intended for the screen, be it television, film, or online platforms. They require a specific format, incorporating dialogue and visual descriptions to guide the production process. Screenwriters must also consider the practical aspects of filmmaking, making this an intricate and specialized form of creative writing.
If you’re interested in this style, understanding creative writing jobs and what you can do with a creative writing degree can provide useful insights.
Writing for the theater is another specialized form of creative writing. Plays, like screenplays, combine dialogue and action, but they also require an understanding of the unique dynamics of the theatrical stage. Playwrights must think about the live audience and the physical space of the theater when crafting their works.
Each of these styles offers unique opportunities for creativity and expression. Whether you’re drawn to the concise power of poetry, the detailed storytelling of novels, or the visual language of screenplays and plays, there’s a form of creative writing that will suit your artistic voice. The key is to explore, experiment, and find the style that resonates with you.
For those looking to spark their creativity, our article on creative writing prompts offers a wealth of ideas to get you started.
Importance of Creative Writing
Understanding what is creative writing involves recognizing its value and significance. Engaging in creative writing can provide numerous benefits – let’s take a closer look.
Developing Creativity and Imagination
Creative writing serves as a fertile ground for nurturing creativity and imagination. It encourages you to think outside the box, explore different perspectives, and create unique and original content. This leads to improved problem-solving skills and a broader worldview , both of which can be beneficial in various aspects of life.
Through creative writing, one can build entire worlds, create characters, and weave complex narratives, all of which are products of a creative mind and vivid imagination. This can be especially beneficial for those seeking creative writing jobs and what you can do with a creative writing degree .
Enhancing Communication Skills
Creative writing can also play a crucial role in honing communication skills. It demands clarity, precision, and a strong command of language. This helps to improve your vocabulary, grammar, and syntax, making it easier to express thoughts and ideas effectively .
Moreover, creative writing encourages empathy as you often need to portray a variety of characters from different backgrounds and perspectives. This leads to a better understanding of people and improved interpersonal communication skills.
Exploring Emotions and Ideas
One of the most profound aspects of creative writing is its ability to provide a safe space for exploring emotions and ideas. It serves as an outlet for thoughts and feelings , allowing you to express yourself in ways that might not be possible in everyday conversation.
Writing can be therapeutic, helping you process complex emotions, navigate difficult life events, and gain insight into your own experiences and perceptions. It can also be a means of self-discovery , helping you to understand yourself and the world around you better.
So, whether you’re a seasoned writer or just starting out, the benefits of creative writing are vast and varied. For those interested in developing their creative writing skills, check out our articles on creative writing prompts and how to teach creative writing . If you’re considering a career in this field, you might find our article on is a degree in creative writing worth it helpful.
4 Steps to Start Creative Writing
Creative writing can seem daunting to beginners, but with the right approach, anyone can start their journey into this creative field. Here are some steps to help you start creative writing .
1. Finding Inspiration
The first step in creative writing is finding inspiration . Inspiration can come from anywhere and anything. Observe the world around you, listen to conversations, explore different cultures, and delve into various topics of interest.
Reading widely can also be a significant source of inspiration. Read different types of books, articles, and blogs. Discover what resonates with you and sparks your imagination.
For structured creative prompts, visit our list of creative writing prompts to get your creative juices flowing.
Editor’s Note : When something excites or interests you, stop and take note – it could be the inspiration for your next creative writing piece.
2. Planning Your Piece
Once you have an idea, the next step is to plan your piece . Start by outlining:
- the main points
Remember, this can serve as a roadmap to guide your writing process. A plan doesn’t have to be rigid. It’s a flexible guideline that can be adjusted as you delve deeper into your writing. The primary purpose is to provide direction and prevent writer’s block.
3. Writing Your First Draft
After planning your piece, you can start writing your first draft . This is where you give life to your ideas and breathe life into your characters.
Don’t worry about making it perfect in the first go. The first draft is about getting your ideas down on paper . You can always refine and polish your work later. And if you don’t have a great place to write that first draft, consider a journal for writing .
4. Editing and Revising Your Work
The final step in the creative writing process is editing and revising your work . This is where you fine-tune your piece, correct grammatical errors, and improve sentence structure and flow.
Editing is also an opportunity to enhance your storytelling . You can add more descriptive details, develop your characters further, and make sure your plot is engaging and coherent.
Remember, writing is a craft that improves with practice . Don’t be discouraged if your first few pieces don’t meet your expectations. Keep writing, keep learning, and most importantly, enjoy the creative process.
For more insights on creative writing, check out our articles on how to teach creative writing or creative writing activities for kids.
Tips to Improve Creative Writing Skills
Understanding what is creative writing is the first step. But how can one improve their creative writing skills? Here are some tips that can help.
Read Widely
Reading is a vital part of becoming a better writer. By immersing oneself in a variety of genres, styles, and authors, one can gain a richer understanding of language and storytelling techniques . Different authors have unique voices and methods of telling stories, which can serve as inspiration for your own work. So, read widely and frequently!
Practice Regularly
Like any skill, creative writing improves with practice. Consistently writing — whether it be daily, weekly, or monthly — helps develop your writing style and voice . Using creative writing prompts can be a fun way to stimulate your imagination and get the words flowing.
Attend Writing Workshops and Courses
Formal education such as workshops and courses can offer structured learning and expert guidance. These can provide invaluable insights into the world of creative writing, from understanding plot development to character creation. If you’re wondering is a degree in creative writing worth it, these classes can also give you a taste of what studying creative writing at a higher level might look like .
Joining Writing Groups and Communities
Being part of a writing community can provide motivation, constructive feedback, and a sense of camaraderie. These groups often hold regular meetings where members share their work and give each other feedback. Plus, it’s a great way to connect with others who share your passion for writing.
Seeking Feedback on Your Work
Feedback is a crucial part of improving as a writer. It offers a fresh perspective on your work, highlighting areas of strength and opportunities for improvement. Whether it’s from a writing group, a mentor, or even friends and family, constructive criticism can help refine your writing .
Start Creative Writing Today!
Remember, becoming a proficient writer takes time and patience. So, don’t be discouraged by initial challenges. Keep writing, keep learning, and most importantly, keep enjoying the process. Who knows, your passion for creative writing might even lead to creative writing jobs and what you can do with a creative writing degree .
Happy writing!
Brooks Manley

Creative Primer is a resource on all things journaling, creativity, and productivity. We’ll help you produce better ideas, get more done, and live a more effective life.
My name is Brooks. I do a ton of journaling, like to think I’m a creative (jury’s out), and spend a lot of time thinking about productivity. I hope these resources and product recommendations serve you well. Reach out if you ever want to chat or let me know about a journal I need to check out!
Here’s my favorite journal for 2024:

Gratitude Journal Prompts Mindfulness Journal Prompts Journal Prompts for Anxiety Reflective Journal Prompts Healing Journal Prompts Cognitive Behavioral Therapy Journal Prompts Mental Health Journal Prompts ASMR Journal Prompts Manifestation Journal Prompts Self-Care Journal Prompts Morning Journal Prompts Evening Journal Prompts Self-Improvement Journal Prompts Creative Writing Journal Prompts Dream Journal Prompts Relationship Journal Prompts "What If" Journal Prompts New Year Journal Prompts Shadow Work Journal Prompts Journal Prompts for Overcoming Fear Journal Prompts for Dealing with Loss Journal Prompts for Discerning and Decision Making Travel Journal Prompts Fun Journal Prompts
Inspiring Ink: Expert Tips on How to Teach Creative Writing
You may also like, a guide to shadow work journaling.
Is Working from Home or from the Office More Productive?
Planner review: at-a-glance monthly planner, leave a reply cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Productivity
- Favorite Journals

Writing Nestling

What Is Creative Writing? (Definition & 11 Best Steps)
Creative writing is the celestial dance of words, an art form that transcends the ordinary to forge literary constellations that illuminate the human experience.
At its core, creative writing is a cosmic exploration of imagination, a journey into the uncharted realms where storytelling becomes a vehicle for self-expression, creativity, and connection.
It encompasses a diverse array of genres, from the poetic landscapes of verse to the intricate narratives of fiction and the introspective reflections of creative nonfiction.
Creative writing is both an ancient practice, rooted in the oral traditions of storytelling, and a contemporary force, shaped by the dynamic currents of literary movements and the digital age.
In this cosmic voyage of words, writers become cosmic architects, crafting worlds, characters, and emotions that resonate across the galaxies of human thought and emotion.
This exploration delves into the historical evolution, elements, genres, and the transformative process of creative writing, inviting both novice stargazers and seasoned explorers to embark on a literary odyssey through the cosmos of human imagination.
Table of Contents
What Is Creative Writing?
Creative writing is the process of expressing thoughts, ideas, and emotions through the artful use of language. Here’s a step-by-step breakdown:
Idea Generation
Start by brainstorming and generating ideas. This could be inspired by personal experiences, observations, or purely imaginative concepts.
Organize your thoughts and structure your writing. This might involve outlining the plot for a story, creating characters, or planning the flow of a poem.
Choosing a Form or Genre
Decide on the type of creative writing you want to pursue – whether it’s fiction, non-fiction, poetry, drama, or any other form.
Setting the Tone and Style
Define the tone and style of your writing. This could range from formal to informal, humorous to serious, depending on the intended effect.
Creating Characters or Themes
Develop characters, themes, or central ideas that will drive your narrative and engage your audience.
Begin writing your first draft. Allow yourself the freedom to explore ideas without worrying too much about perfection at this stage.
Review and revise your work. This involves refining your language, improving clarity, and ensuring your writing effectively communicates your intended message or story.
Pay attention to grammar, spelling, and punctuation. Edit your work to eliminate errors and enhance overall readability.
Seek feedback from peers, writing groups, or mentors. Constructive criticism can help you identify areas for improvement and refine your work.
Make final adjustments based on feedback and your own revisions. Polish your creative writing until you are satisfied with the result.
Publishing or Sharing
Decide whether you want to share your work publicly. This could involve submitting it to literary magazines, self-publishing, or simply sharing it with friends and family.
Creative writing is a dynamic and iterative process, allowing for continuous refinement and exploration of ideas.

Historical Evolution of Creative Writing
Embarking on a literary time-travel, the historical evolution of creative writing unfolds like an intricately woven tapestry, blending the whispers of ancient oral traditions with the bold strokes of individual expression that emerged during the Renaissance.
Picture storytellers captivating audiences with folk tales around ancient campfires, only to witness the metamorphosis into written words that took place during humanity’s transition from the spoken to the written word.
As the winds of change blew through literary landscapes, the Renaissance breathed life into personal narratives, and Romanticism embraced the turbulent storms of emotion.
Modernism then shattered conventional boundaries, paving the way for experimental forms that mirrored the tumultuous twentieth century.
Today, creative writing stands at the intersection of tradition and innovation, a dynamic force shaped by the echoes of the past and the untamed creativity of the present.
Origins in oral traditions
The origins of creative writing can be traced back to the rich tapestry of human storytelling woven through the fabric of oral traditions.
In the dim glow of ancient campfires, our ancestors spun tales that danced between reality and imagination, passing down knowledge, wisdom, and cultural identity from one generation to the next.
These oral narratives, often rooted in folklore and myths, were the heartbeat of communities, connecting individuals through shared stories.
From the captivating epics of Homer to the enchanting fairy tales whispered in the corners of the world, the oral tradition laid the foundation for the written word, embodying the essence of human creativity, imagination, and the innate desire to communicate through the power of narrative.
Development through literary movements
The historical journey of creative writing unfolds through the dynamic currents of literary movements, each a vibrant chapter in the evolution of human expression.
The Renaissance, a cultural rebirth, marked a pivotal shift as writers embraced the power of individual expression and departed from medieval constraints.
Romanticism followed, a tempest of emotion that stormed the structured landscapes of literature, championing nature, passion, and the sublime.
Modernism emerged as a bold departure from traditional forms, ushering in experimental narratives and fragmented perspectives that mirrored the complexities of the 20th century.
Today’s creative writing landscape, shaped by these movements, is a kaleidoscope of diverse voices and styles, a testament to the enduring influence of literary evolution on the human experience.
Elements of Creative Writing
Dive into the alchemy of creative writing, where the elements of storytelling blend and dance like cosmic particles in a celestial ballet.
Picture the plot and structure as the architectural skeleton, a blueprint for worlds yet to be born. Characters, like sentient constellations, come to life, breathing the very essence of authenticity into the narrative cosmos.
Amidst the vast expanse of setting and atmosphere, landscapes materialize like dreams, painting scenes that are both vivid and haunting.
Style and voice emerge as the enchanting melodies, each writer composing a unique symphony that resonates in the reader’s soul.
In this literary crucible, the elements fuse, giving birth to tales that are not just written but are crafted, where words become spells, and the act of creation is nothing short of magical.
Genres in Creative Writing
Step into the kaleidoscope of creative expression, where genres in creative writing are the vibrant hues that paint the literary canvas with boundless imagination.
Fiction, a realm where novel universes unfurl with every turn of the page, beckons explorers to traverse landscapes of intrigue and emotion.
Poetry, the language of the soul, weaves verses that resonate in the heart’s chambers, from the traditional sonnets to the avant-garde free forms that defy gravity.
Creative nonfiction becomes a literary mirror, reflecting the kaleidoscope of reality through memoirs and essays, blurring the lines between experience and artistry.
These genres are not mere labels; they are portals into worlds where storytelling transcends boundaries, and writers become architects of realms that captivate the mind, stir the emotions, and linger in the echoes of the reader’s imagination.
Fiction, the enchanting realm where the alchemy of words transforms imagination into reality, beckons readers into worlds unknown.
It is the literary tapestry where storytellers weave tales that dance on the precipice between reality and fantasy. Novels, the architects of this fantastical landscape, sculpt characters with palpable depth, crafting intricate plotlines that unfold like secrets waiting to be revealed.
From the classic works of timeless masters to the contemporary symphonies of emerging voices, fiction transcends time and space, inviting readers to escape the ordinary and venture into the extraordinary.
In this boundless expanse, emotions become tangible, and the echoes of imaginary footsteps resonate long after the last page is turned. Fiction is not merely a genre; it is a passport to alternate realities, a magic carpet that carries readers to places uncharted and emotions unexplored.
Poetry, the language of the heart and the echo of the soul, is an art form that transcends the boundaries of ordinary expression.
In the symphony of words, poets become maestros, conducting emotions and experiences into verses that sing with rhythm and grace.
From the structured elegance of traditional forms to the unbridled freedom of free verse, poetry captures the ineffable and distills it into the purest essence.
Every line is a brushstroke painting vivid imagery, and each stanza is a melody that resonates in the chambers of the reader’s spirit. Poets wield words like alchemists, transforming mundane moments into profound revelations.
In the delicate dance between language and emotion, poetry stands as a testament to the human capacity to turn the ordinary into the extraordinary, inviting readers to immerse themselves in the beauty of finely crafted language and the endless possibilities of the poetic imagination.
Creative Nonfiction
Creative nonfiction, a captivating blend of factual precision and artistic expression, serves as a literary bridge between the realms of truth and imagination.
In this genre, writers embark on a compelling journey of storytelling that mines the depths of reality to craft narratives as rich and engaging as any fiction.
From memoirs that illuminate the intricacies of personal experiences to thought-provoking essays that dissect the tapestry of the human condition, creative nonfiction is a mosaic of authenticity painted with the brushstrokes of literary finesse.
The genre encourages writers to artfully blur the lines between fact and narrative, weaving a tapestry that captures the essence of life in all its complexities.
It is a genre where truth is not merely recounted but elevated to the status of art, inviting readers to explore the profound and the ordinary with fresh eyes and a heightened appreciation for the power of storytelling.

The Creative Writing Process
Embark on the enigmatic odyssey of the creative writing process, where inspiration is a clandestine muse that whispers in the stillness of creativity.
The inception, a cosmic spark, ignites the imagination, unleashing a torrent of ideas that cascade like shooting stars across the writer’s mind. The drafting phase is a dance with chaos, a raw manifestation of thoughts and emotions onto the blank canvas of the page.
Yet, the revision process emerges as the phoenix rising from the literary ashes, where words transform and refine, revealing the alchemical magic of refining ideas into a harmonious narrative.
Seeking feedback becomes a cosmic conversation, where the writer navigates the cosmos of criticism to unveil hidden constellations in their work.
The creative writing process is not a linear trajectory but a celestial dance , where writers traverse the nebulae of creativity, forging galaxies of prose and poetry that linger in the reader’s universe long after the final punctuation mark.
Idea generation, the pulsating heartbeat of the creative process, invites writers into the boundless cosmos of imagination.
It is an ethereal dance with inspiration, where sparks of creativity ignite the mind like constellations in the night sky. Whether drawn from personal experiences, fleeting observations, or the whispers of dreams, ideas are the raw stardust that writers mold into narrative galaxies.
The process is as unpredictable as a meteor shower, with writers navigating the celestial expanse to capture elusive fragments of brilliance.
From the quiet corners of introspection to the cacophony of the world, the art of idea generation transforms the mundane into the extraordinary, inviting writers to embark on a cosmic odyssey where every fleeting notion has the potential to blossom into a literary supernova.
Drafting and Revising
Drafting and revising, the twin constellations of the writing process, encapsulate the transformative journey of turning nebulous ideas into polished prose.
In the initial act of drafting, writers plunge into the creative abyss, weaving words into a tapestry of raw emotions and vivid imagery.
It is an untamed exploration, where the exhilarating rush of creation takes precedence over perfection. Yet, the true alchemy occurs in the refining crucible of revision. Like a sculptor chiseling away excess stone to reveal a masterpiece, writers meticulously carve and reshape their narratives.
It is a dance with words, a delicate balancing act of preserving the authenticity of the initial draft while enhancing clarity, coherence, and resonance.
Revision is not merely correction; it is the conscious evolution of a narrative, where every nuanced change breathes new life into the prose.
The tandem of drafting and revising, akin to the ebb and flow of cosmic forces, is the dynamic heartbeat that propels a piece of writing from its embryonic stages to the polished brilliance that captivates the reader’s soul.
Publishing and Sharing
Publishing and sharing mark the culmination of a writer’s odyssey, where the crafted words are prepared to venture beyond the solitary realm of creation.
It is a moment of revelation, where the manuscript, once a private universe, prepares to meet the wider cosmos of readership.
The publishing process, be it through traditional avenues or the burgeoning world of self-publishing, involves the meticulous preparation of the work for public consumption.
The act of sharing becomes a cosmic ripple, as the writer’s voice resonates across the literary landscape, forging connections with readers who may find solace, inspiration, or sheer enjoyment in the words.
It is a dance of vulnerability and courage, as writers release their creations into the literary cosmos, hoping their narrative constellations will find a home in the hearts and minds of others.
The symbiotic relationship between writer and reader transforms the act of publishing into a shared cosmic experience, where words transcend the individual and become part of a collective literary universe.
Challenges and Rewards of Creative Writing
Navigating the cosmos of creative writing reveals a celestial dance of challenges and rewards, where each word penned is a step into the cosmic unknown.
The challenges emerge like elusive comets, from the gravitational pull of writer’s block threatening to derail creativity, to the constant cosmic quest for a harmonious balance between originality and marketability.
Yet, these challenges are the cosmic forge that tempers the writer’s mettle, honing resilience and creativity in the crucible of adversity.
The rewards, akin to dazzling supernovae, illuminate the journey. The cathartic joy of crafting a sentence that resonates, the cosmic connections formed with readers who find solace or delight in the prose – these are the celestial jewels that make the struggles worthwhile.
In the vast expanse of creative writing, challenges and rewards orbit each other like binary stars, their gravitational pull shaping the unique trajectory of every writer’s cosmic odyssey.
Overcoming writer’s block
Writer’s block, that elusive shadow cast over the creative landscape, can feel like navigating a cosmic void where inspiration is but a distant star.
It is the gravitational force that stymies the flow of words and leaves the writer stranded in a sea of blank pages. Yet, overcoming writer’s block is an act of cosmic resilience.
Writers embark on a journey through the nebulae of creativity, employing various strategies to break free from the entangled cosmic web.
Whether it’s the cosmic power of free writing to unravel mental knots or the meteoric inspiration found in changing the writing environment, overcoming writer’s block becomes a transformative process.
It is the writer’s spacecraft pushing through the cosmic fog, a testament to the indomitable spirit that seeks to create even in the face of cosmic resistance.
In this dance with the muse, writers rediscover the cosmic symphony of their imagination and emerge from the creative void with newfound brilliance.
Balancing originality and marketability
In the cosmic dance of creative writing, striking the delicate balance between originality and marketability is akin to navigating the gravitational forces of two celestial bodies.
Originality, the pulsating core of creativity, propels writers into uncharted literary realms, forging unique constellations of thought and expression.
Yet, the cosmic reality of marketability orbits nearby, where commercial considerations seek gravitational stability.
It’s an intricate interplay; too much originality may risk veering into the obscure, while an excessive focus on marketability might compromise the authenticity of the creative vision.
Writers become cosmic architects, constructing narratives that not only resonate with their individual voice but also align with the gravitational pull of audience preferences.
Balancing these cosmic forces is a perpetual challenge, requiring writers to dance on the edge of innovation while staying tethered to the gravitational pull of a wider readership.
In this cosmic balancing act, writers discover the celestial equilibrium where originality and marketability harmonize, creating literary galaxies that captivate both the cosmos of creativity and the earthly realms of audience engagement.
Impact of Creative Writing on Society
Creative writing is the cosmic echo of the human soul, resonating through the annals of time and leaving an indelible imprint on the fabric of society.
It serves as a literary constellation, illuminating the collective consciousness with narratives that mirror, challenge, and redefine societal values.
From ancient epics that shaped cultural identities to contemporary works that spark revolutions of thought, creative writing is a cosmic force that fosters empathy, dismantles prejudices, and holds a mirror to the complexities of the human experience.
It is the catalyst for societal metamorphosis, a cosmic dance that encourages dialogue, fuels revolutions, and shapes the very contours of cultural evolution.
In the vast cosmos of creative expression, the impact of writing is not merely confined to the pages; it permeates the collective psyche, becoming a celestial force that guides, questions, and ultimately shapes the destiny of societies on this cosmic voyage through time.
Educational and Professional Opportunities in Creative Writing
Embarking on the cosmic odyssey of creative writing isn’t just a journey into the realms of imagination; it’s a launchpad to educational and professional constellations that illuminate diverse career trajectories.
Creative writing programs become celestial academies, nurturing literary supernovae through workshops, mentorship, and the exploration of narrative galaxies.
The academic pursuit of the craft transforms writers into cosmic architects, honing not only their creativity but also the analytical skills essential for dissecting the intricacies of language.
Beyond the academic cosmos, the professional opportunities in creative writing are as vast as the universe itself.
Writers may navigate the celestial waters of journalism, become starry-eyed screenwriters crafting cinematic adventures, or soar as literary explorers, publishing novels that leave an indelible mark on the literary cosmos.
In the intersection of education and profession, creative writing unfolds as a cosmic tapestry where words aren’t just written but become portals to boundless opportunities in the vast expanse of the literary universe.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) about What Is Creative Writing?
What exactly is creative writing, and how does it differ from other forms of writing.
Creative writing is the vibrant, expressive art of using words to craft narratives that go beyond mere conveyance of information. It stands apart by prioritizing imagination, self-expression, and often blurs the lines between reality and fiction.
How does the historical evolution of creative writing influence contemporary practices?
The historical journey of creative writing, from ancient oral traditions to the digital age, has shaped the very DNA of the craft. It influences contemporary practices by offering a rich tapestry of literary movements, styles, and themes that writers can draw inspiration from or subvert.
Can anyone become a creative writer, or is it a skill reserved for a select few?
Absolutely anyone can become a creative writer! While innate talent can be an asset, the essence of creative writing lies in practice, exploration, and the willingness to cultivate one’s unique voice and perspective.
What are the key elements that make up creative writing, and how do they contribute to the overall narrative?
The elements of creative writing, such as plot, characterization, setting, style, and voice, are the building blocks that construct the literary cosmos. They contribute by creating immersive worlds, memorable characters, and distinctive narratives that resonate with readers.
How can one overcome writer’s block, a common challenge in creative writing?
Overcoming writer’s block is like navigating through a cosmic fog. Strategies include engaging in free writing, changing the writing environment, seeking inspiration from different mediums, or simply taking a cosmic break to recharge creative energies.
Is creative writing limited to novels and poetry, or are there other genres to explore?
Creative writing spans a diverse universe of genres. While novels and poetry are prominent, there’s also creative nonfiction, flash fiction, screenplays, and more. The cosmos of creative writing is vast and welcomes exploration.
How does one balance the fine line between originality and marketability in creative writing?
Balancing originality and marketability requires navigating a cosmic dance. It involves maintaining authenticity while considering the audience’s preferences, creating a celestial equilibrium where the writer’s unique voice resonates within a broader readership.
What educational and professional opportunities are available in the field of creative writing?
The educational galaxy offers creative writing programs and degrees, nurturing writers with both theoretical knowledge and practical skills. Professionally, opportunities range from traditional publishing avenues to scriptwriting, journalism, and the expansive realm of digital content creation.
In conclusion, creative writing is a cosmic odyssey, an ever-expanding universe of imagination, expression, and connection.
From its ancient roots in oral traditions to the dynamic currents of contemporary literary movements, creative writing has evolved into a diverse and influential art form.
It is a transformative process that involves the careful balance of elements, the exploration of various genres, and the persistent journey through the challenges and rewards of crafting narratives.
Creative writing is not confined to the realms of novels and poetry; it encompasses a vast cosmos of possibilities, from memoirs to screenplays, flash fiction to creative nonfiction.
As writers embark on this celestial exploration, they become architects of worlds, sculptors of characters, and composers of narratives that resonate across the collective human experience.
The educational and professional opportunities within this realm further amplify its significance, turning creative writing into both a personal pursuit and a communal force shaping the literary landscape.
In the grand celestial tapestry of human expression, creative writing emerges as a luminous constellation, inviting writers and readers alike to traverse the cosmic expanse of imagination and storytelling.
Related Posts:
- What Is A Personal Account In Writing? ( Examples)
- What Is Medium Used For? Ultimate Guide For Beginners
- How To Describe A Spaceship In A Story (10 Best Tips)
- What Is A Universal Statement In Writing? (Explained)
- What Does Freeform Mean In Fanfiction?
- Body Swap Writing (9 Best Tips & Ultimate Guide)
Similar Posts

What Is A Cold Open In Writing? (10 Best Tips & Types)
In the realm of storytelling, the term “cold open” is a literary enigma, a narrative device that serves as a captivating entry point into the heart of a tale. Unlike traditional beginnings that unfold with gradual exposition, a cold open thrusts readers directly into the midst of the narrative’s action, dialogue, or mystery from the…

How to Come up With Interesting Story Ideas (10 Best Steps)
In the vast realm of storytelling, the quest for compelling narratives begins with the spark of an idea. Yet, for many writers, summoning that elusive muse can be a daunting endeavor. How does one conjure the threads of imagination into a tapestry of gripping tales? The art of generating interesting story ideas is a captivating…

How To Become An Alpha Reader (12 Best Ways)
Embarking on the journey of becoming an Alpha Reader is akin to stepping into the hallowed halls of literary craftsmanship, where the written word transforms into a collaborative symphony of creativity. An Alpha Reader is not merely a passive consumer of narratives but a discerning guide, navigating the labyrinth of manuscripts with a keen eye…

How To Write A Job Posting Ad (11 Effective Ways And Examples)
Embarking on the art of crafting a compelling job posting ad is akin to sculpting an enticing doorway into your organization’s world. This endeavor requires finesse, precision, and an understanding of the intricate dance between words and aspirations. In this guide, we delve into the nuances of not just penning a vacancy but curating a…

Talking About The Weather In English (11 Steps You Need To Know)
Talking about the weather in English may seem like a simple and mundane endeavor, yet it’s a conversation topic that transcends linguistic borders and cultural boundaries. It’s an art form, an everyday ritual, and a universal connector. Weather talk is the small talk that opens doors to more profound discussions, the social glue that bonds…

Can Content Writing Make You Rich? 12 Best Ways
In the ever-evolving landscape of the digital age, the question resonates with aspiring wordsmiths and seasoned content creators alike: Can content writing make you rich? Beyond the mere arrangement of words, content creation has emerged as a dynamic force in the vast galaxy of online communication. This inquiry is not just about financial aspirations; it…
TRY OUR FREE APP
Write your book in Reedsy Studio. Try the beloved writing app for free today.
Craft your masterpiece in Reedsy Studio
Plan, write, edit, and format your book in our free app made for authors.

Guides • Perfecting your Craft
Last updated on Dec 23, 2022
Creative Writing: 8 Fun Ways to Get Started
Creative writing is a written art form that uses the imagination to tell stories and compose essays, poetry, screenplays, novels, lyrics, and more. It can be defined in opposition to the dry and factual types of writing found in academic, technical, or journalistic texts.
Characterized by its ability to evoke emotion and engage readers, creative writing can tackle themes and ideas that one might struggle to discuss in cold, factual terms.
If you’re interested in the world of creative writing, we have eight fantastic exercises and activities to get you started.

1. Use writing prompts every week

Coming up with ideas for short stories can be challenging, which is why we created a directory of 1700+ creative writing prompts covering a wide range of genres and topics. Writing prompts are flexible in nature, they are meant to inspire you without being too constrictive. Overall, they are a great way to keep your creative muscles limber.

If you’re struggling for motivation, how does a hard deadline and a little prize money sound? Prompts-based writing contests are a fantastic way to dive into creative writing: the combination of due dates, friendly rivalries, prize money, and the potential to have your work published is often just what’s needed to propel you over the finish line.
We run a weekly writing contest over on Reedsy Prompts, where hundreds of writers from all around the world challenge themselves weekly to write a short story between 1,000 and 3,000 words for a chance to win the $250 prize. Furthermore, the community is very active in providing constructive feedback, support, and accountability to each other 一 something that will make your efforts even more worthwhile.
Take a peek at our directory of writing contests which features some of the most prestigious open writing competitions in the world.
2. Start journaling your days

Another easy way to get started with creative writing is to keep a journal. We’re not talking about an hour-by-hour account of your day, but journaling as a way to express yourself without filters and find your ‘voice in writing’. If you’re unsure what to journal about, think of any daily experiences that have had an impact on you, such as…
Special moments . Did you lock yourself out of your house? Or did you catch a beautiful sunset on your way back from groceries? Capture those moments, and how you felt about them.
People . Did you have an unusual exchange with a stranger at the bar? Or did you reconnect with someone you haven’t seen in years? Share your thoughts about it.
World events . Is there something happening in the world right now that is triggering you? That’s understandable. You can reflect on it (and let some steam off) while journaling.
Memories . Did you go down memory lane after a glass of wine? Great, honor those memories by trying to recollect them in detail on paper so that they will always stay vivid in your mind.
Life decisions . Are you having an existential crisis about what to do with your life? Write down your thought process, and the pros and cons of the possible decisions in front of you. You’ll be surprised to discover that, not only is it a great creative writing exercise, but it can also actually help you sort your life out!
If you struggle to write consistently, sign up for our How to Write a Novel course to finish a novel in just 3 months.

NEW REEDSY COURSE
How to Write a Novel
Enroll in our course and become an author in three months.
3. Create an anonymous social media account

Like anonymous blogging, an incognito Twitter account sidesteps the pressure that comes with attaching your name to your work. Anonymously putting tiny stories out into the ether gives you the freedom to create without worrying about the consequences — which is great, so long as you don’t use it as an opportunity to troll people or spread conspiracy theories.
You could use the anonymous account in different ways. For example, you could…
- Tweet from unique points of view (e.g. a dog observing human behavior );
- Create a parody account of real or fictional people (e.g. an English poet from the Middle Ages );
- Challenge yourself to write tiny flash fiction stories that fit into Twitter threads.
Just remember, you’re not doing this to fool anyone into thinking that your account is real: be a good citizen and mark yourself a fiction account in your bio.
But if you’re not really a social media kinda person, you may enjoy our next tip, which is a bit more on the analog side.

GET ACCOUNTABILITY
Meet writing coaches on Reedsy
Industry insiders can help you hone your craft, finish your draft, and get published.
4. Find an old photo and tell its story

Find a random old photo — maybe on the web, maybe from a photo album in a yard sale — and see what catches your attention. Look closely at it and try to imagine the story behind it. What was happening? Who are the people in it and how are they really feeling? Do they share a relationship, and of what kind? What are their goals and dreams?
In other words, bring the photo to life with your imagination. Don't be afraid to take artistic license with your story, as the goal is to be creative and have fun while writing.
How do you know it’s creative writing?

5. Create a character from a random name

Just as our universe started from a few simple elements, you can create a character from a few basic information, like their name, culture, and gender. Reedsy’s handy character name generator can help you with that, offering random names based on archetypes, Medieval roots, fantasy traits and more. A few examples? A Celtic heroine named Fíona O'Keefe, a hero’s sidekick named Aderine, or a Korean track star named Park Kang-Dae.
Once you've chosen their name, begin to develop their personality. Set a timer for 5–10 minutes and write anything that comes to mind about them. It could be a page from their FBI dossier, a childhood diary entry, or simply a scene about them boiling an egg.
Just ‘go with the flow’ and don’t stop writing until your time is up. Repeat the process a few times to further hone the personality. If you like what you end up with, you can always go deeper later with our character profile template .
If a stream-of-consciousness exercise is not your thing, you can try to imagine your character in a specific situation and write down how’d they respond to it. For example, what if they were betrayed by a friend? Or if they were elected in power? To help you imagine situations to put your character in, we made a free template that you can download below.

FREE RESOURCE
Reedsy’s Character Questionnaire
40 questions to help you develop memorable characters.
6. Construct a character by people-watching

People watching is “the action of spending time idly observing people in a public place.” In a non-creepy way, ideally. Sit on a bench on a public square or on a road-side table at your favorite café, and start observing the people around you. Pay attention to any interesting quirks or behaviors, and write it down. Then put on your detective’s hat and try to figure out what that tells you about them.
For example, the man at the table next to you at the restaurant is reading the newspaper. His jacket and hat are neatly arranged next to him. The pages make a whipping sound as he briskly turns them, and he grimaces every time he reads a new article. Try to imagine what he’s reading, and why he’s reacting the way he is. Then, try to build a character with the information you have. It’s a fun creative exercise that will also, hopefully, help you better empathize with strangers.
7. “Map” something you feel strongly about into a new context

Placing your feelings into new contexts can be a powerful creative writing exercise. The idea is to start from something you feel strongly about, and frame it into a completely different context.
For example, suppose your heart is torn apart after you divorce your life-long partner: instead of journaling or crafting an entire novel about it, you could tell a story about a legendary trapeze duo whose partnership has come to an end. If you’re struggling with politicking and petty power dynamics at the office: what if you “mapped” your feelings onto an ant who resents being part of a colony? Directing your frustration at a queen ant can be a fun and cathartic writing experience (that won’t get you in trouble if your co-workers end up reading your story).
8. Capture the moment with a haiku

Haikus are poems from the Japanese tradition that aim to capture, in a few words, daily moments of insight (usually inspired by nature). In a nutshell, it’s about becoming mindful of your surroundings, and notice if you can see something in a new or deeper way 一 then use contrasting imagery to express whatever you noticed.
Here’s an example:
Bright orange bicycle
Speeding through the autumn leaves
A burst of color waves
It may sound a bit complicated, but it shouldn’t be 一 at least not for the purpose of this exercise. Learn the basics of haiku-writing , then challenge yourself to write one per day for a week or month. At the end, you’ll be able to look back at your collection of poems and 一 in the worst case scenario 一 revisit small but significant moments that you would have otherwise forgot about.
Creative writing can be any writing you put your heart and soul into. It could be made for the purpose of expressing your feelings, exploring an idea, or simply entertaining your readers. As you can see there’s many paths to get involved with it, and hundreds of exercises you can use as a starting point. In the next post, we’ll look more in detail at some creative writing examples from some fellow authors.
Join a community of over 1 million authors
Reedsy is more than just a blog. Become a member today to discover how we can help you publish a beautiful book.
Bring your stories to life
Our free writing app lets you set writing goals and track your progress, so you can finally write that book!

1 million authors trust the professionals on Reedsy. Come meet them.
Enter your email or get started with a social account:

What is Creative Writing? (Definition + Tips for Getting Started)
by Ivy Shelden
on Sep 18, 2023
So, you want to know what is creative writing, huh?
You’re not alone.
Whether you’re an aspiring novelist, a high school student, or just someone looking to enhance your creative writing skills, this post is your golden ticket.
But what exactly does it entail?
Is it just stringing words together, or is there more to it?
Spoiler alert: It’s a craft that takes time and skill, but don’t worry, we have some tips and actionable strategies to help you get started.
From exploring different genres to mastering narrative art, you’re about to unlock a universe of possibilities.
Ready to become a creative writer?
Let’s begin!

What is Creative Writing? (& What it Isn’t )
At its heart, creative writing is all about storytelling and expression. It’s where imagination meets ink, and the human experience takes center stage.
Through writing fiction, poetry, drama, and even creative non-fiction, writers have the freedom to explore and express thoughts, feelings, and experiences that are uniquely their own.
In creative writing, the sky’s the limit — you could dive into the psyche of a Martian, sketch a dystopian future, or chronicle the life of a pebble.
The main objective?
To engage, to provoke thought, to entertain, and to evoke an emotional response in the reader.
Contrast this with technical writing or academic writing .
These forms of writing have a different purpose and follow a different set of rules.
For example, consider technical writing .
It’s used in fields like engineering or computer science to explain complex systems or processes in clear, straightforward language.
Think user manuals, reports, or scientific articles. They’re about precision, consistency, and clarity rather than evoking emotions or telling stories.
Similarly, academic writing — the kind you’ll find in textbooks or scholarly articles — is typically analytical or persuasive, aiming to build a sound argument based on evidence and reasoning.
Academic writing sticks to strict structures and formats, with the primary goal of informing or persuading rather than entertaining.
If academic and technical writing is about precision, evidence, and clear communication, then creative writing is about exploration, expression, and emotional resonance.
Exploring the Wide World of Creative Writing (Types & Genres)

So what are the different types of creative writing? Well, there are a lot — after all, human creativity is boundless.
But here are the most common genres …
Fiction is all about imagining and crafting narratives that aren’t necessarily rooted in reality.
Consider fiction writing in the form of a short story, novella, or novel.
From the fantastical realms in Tolkien’s “The Lord of the Rings” to the dystopian future of Orwell’s “1984”, fiction lets you construct alternate realities or tweak the real one just a bit to explore the ‘what ifs’.
Poetry is the art of condensing emotions and ideas into the fewest possible words, while still stirring deep feelings in readers.
Whether it’s a Shakespearean sonnet or a free verse poem like Whitman’s “Leaves of Grass”, poetry uses rhythm, rhyme, and imagery to create a visceral experience.
Poetry can be a wonderful way to explore complex emotions, ideas, or to just play with language.
Non-fiction
Creative non-fiction is about spinning engaging tales from the fabric of real life.
Examples of creative non-fiction are Frank McCourt’s “Angela’s Ashes” or thought-provoking essays like Virginia Woolf’s “A Room of One’s Own”.
Non-fiction allows writers to explore the truth with a creative twist.
It’s all about turning the lens of your unique perspective on the real world and sharing your insights in an engaging, artistic way.
Drama/Playwriting
Ever been moved by a performance on stage?
Playwriting is the craft of creating stories meant to be performed.
From the tragic elegance of Shakespeare’s “Hamlet” to the modern powerhouse of Lin-Manuel Miranda’s “Hamilton”, playwriting combines dialogue, action, and stage direction to bring stories to life in a very physical and immediate way.
Screenwriting
This is the art of writing scripts for film or television.
As a screenwriter, you’re responsible for creating the blueprint for visual storytelling.
Picture the mind-bending twists of “Inception” or the heartwarming tale of “Finding Nemo”.
Screenwriting involves crafting dialogue and visual directions that help bring the director’s vision to life.
Songwriting
From Bob Dylan to Taylor Swift, songwriting is a form of creative writing many of us engage with every day.
Songs can tell stories, express emotions, or capture a moment in time, all set to a melody that often enhances the meaning and impact of the words.
Flash Fiction
This is a writing style of fictional literature characterized by its extremely short length.
Flash fiction stories are usually under 1000 words, and they challenge the writer to tell a compelling story with a clear narrative in a very confined space.
Every genre of creative writing offers its unique challenges and rewards, and each one can help you grow and evolve as a writer.
So go ahead, dip your toes into these different pools and see which one feels right for you.
14 Creative Writing Tips to Unleash Your Inner Writer

Ready to let your creativity off the leash? Here are some tips to get you started on your creative writing journey.
1. Carve Out Dedicated Writing Time
A daily writing habit can help keep your creative writing skill sharp and your creative juices flowing.
Even if it’s just a few minutes each day, consistency is key.
This dedicated time can also act as a mental space where you allow yourself to create and explore ideas without the interruptions of everyday life.
2. Embrace Freewriting
Freewriting is like stretching before a workout — it warms up your creative muscles and helps you limber up.
It’s about letting your thoughts flow freely, without judgement or restraint, and can lead to unexpected insights and story seeds.
You may find that this practice also helps to reduce writing anxiety by shifting focus away from perfection and towards the process of creation.
3. Experiment with Different Genres
Trying out various genres of creative writing not only helps you discover your strengths and preferences, but also enhances your versatility as a writer.
It can also lead to unexpected discoveries.
Maybe you’ve always thought of yourself as a novelist, but find that you have a knack for poetry.
Keeping an open mind and being willing to experiment can lead you to exciting new creative territories.
4. Master the Art of Observation
Great writers are great observers.
Paying close attention to the world around provides a rich source of inspiration for your writing.
Write down interesting conversations, striking scenery, or even unusual smells.
These small details can lend authenticity and vibrancy to your stories.
So, whether you’re on a crowded subway or strolling through a quiet forest, keep your senses alert and your notebook handy!
5. Practice Descriptive Writing
Creative writing is as much about showing as it is about telling.
Practicing descriptive writing brings your characters, settings, and scenes to life.
Try to engage all the reader’s senses — sight, sound, smell, taste, and touch.
This helps to create an immersive experience for your reader and make your writing more memorable.
6. Experiment with Writing Prompts
Writing prompts are a fantastic way to jumpstart your creativity, especially when you’re feeling stuck.
They can take the form of a phrase, an image, or even a situation.
Try writing a short piece based on a prompt and see where it takes you – it could lead you to a story idea you would never have thought of on your own.
7. Study Story Structure

Understanding the structure of a story — setup, confrontation, and resolution — is essential for crafting compelling narratives.
Each part serves a specific function and propels the story forward.
Read up on different narrative structures and consider how they could apply to your own writing.
This foundational knowledge will serve you well no matter what genre you’re working in.
8. Create Complex Characters
Characters are the heart of any story.
To create characters that feel real to your readers, they need to be fully fleshed out with their own desires, flaws, and contradictions.
Invest time in character development, imagining your characters’ backgrounds, motivations, and fears.
Remember, the most engaging characters are often the ones that readers can empathize with, even if they’re flawed.
9. Read Widely
The more you read, the more you’ll understand about different writing styles , narrative structures, and character development strategies .
But don’t just stick to your favorite genres.
Read widely — across different genres, cultures, and time periods. It will help broaden your perspectives, spark fresh ideas, and enrich your own writing.
10. Start a Writing Journal

A writing journal can serve as a treasure chest for ideas, sketches, character descriptions, or just musings about the world.
Over time, these entries can become a gold mine of inspiration for future writing projects.
It’s also a great tool for tracking your writing progress and reflecting on your journey as a writer.
11. Seek Feedback and Support
Writing doesn’t always have to be a solitary pursuit.
By engaging with writing communities, you can benefit from others’ experiences, receive constructive criticism, and also learn by critiquing others’ work.
This shared camaraderie can be a significant source of motivation and growth.
12. Set Achievable Goals
Setting tangible, achievable goals are like stepping stones on your writing journey.
These could range from small, daily targets like writing a certain number of words, to larger aspirations such as completing a manuscript or getting published.
Celebrating these milestones, no matter how small, will boost your confidence and drive to keep going.
13. Edit and Revise
Your first draft is just the beginning.
Revisiting your work, reworking sections, and fine-tuning language are all part of the writing process.
This is your chance to sharpen your narrative, enhance your characters, and ensure that your story is as compelling as possible.
Remember, every great writer is also a great editor.
14. Embrace Failure and Persevere
Every writer, from Stephen King to J.K. Rowling has faced rejection and failure.
Writing can be a journey of highs and lows, but every stumble is an opportunity to learn and grow.
The most successful writers are those who persevere, who pick themselves up after rejections and setbacks, and who stay committed to refining their craft.
Every word, every sentence, and every story you write is a step forward on your creative journey.
Follow the Ultimate Creative Writing Commandment

There’s one tip that is absolutely crucial to your creative writing journey…
The tip: Start writing .
Like, today.
Know that your writing doesn’t have to be perfect — but it does need to exist.
Remember, there’s no right or wrong way to be creative. Your voice is uniquely yours, and the world needs to hear it.
So go ahead, let your imagination run wild, and let your creative work entertain and inspire.
Happy writing!
Ivy Shelden
GET PAID TO WRITE
Make 2-5k per month, even if you're a beginner . we're seeking writers of any skill level ..
Written by Ivy Shelden
Leave a comment cancel reply, latest from the blog.

How to Use AI to Breathe Life into Modern Storytelling in 2024

Tim Stoddart – What to Do When You’re a Beginner and Feel like a Nobody [PODCAST]

10 Super Simple Social Media Optimization Hacks for 2024

With over 300k subscribers and 4 million readers, Smart Blogger is one of the world's largest websites dedicated to writing and blogging.
Best of the Blog
© 2012-2024 Smart Blogger — Boost Blog Traffic, Inc.
Terms | Privacy Policy | Refund Policy | Affiliate Disclosure

- Onsite training
3,000,000+ delegates
15,000+ clients
1,000+ locations
- KnowledgePass
- Log a ticket
01344203999 Available 24/7
What is Creative Writing?
Discover What Is Creative Writing as we unravel the art of self-expression through words. In this blog, learn the meaning and techniques of creative writing, igniting your imagination and honing your storytelling skills. Unlock the world of literary creativity and learn how to craft compelling narratives that captivate readers.

Exclusive 40% OFF
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
Share this Resource
- Report Writing Course
- Effective Communication Skills
- Speed Writing Course
- E-mail Etiquette Training
- Interpersonal Skills Training Course

Creative Writing is a form of art that allows people to express their thoughts, ideas, and emotions through the written word. It is a mode of self-expression that combines imagination with linguistic skills to create compelling narratives, poems, and other forms of literature. A Statista survey found that 76,300 Authors, Writers and Translators work in the United Kingdom alone in 2023. This shows Creative Writing is a demanding career worldwide.To know more about it, read this blog, to learn What is Creative Writing, how to write captivating narratives, and discover the essence of expressive writing.
Table of Contents
1) Understanding What is Creative Writing
2) Key elements of Creative Writing
3) Types of Creative Writing
4) Importance of Creative Writing
5) The Creative Writing process
6) Tips for effective Content Writing
7) Conclusion
Understanding What is Creative Writing
Creative Writing is the art of crafting original content that elicits readers' emotions, thoughts, and imagination. Unlike Academic or Technical Writing, Creative Writing allows for more personal expression and imaginative exploration. It encompasses various forms such as fiction, poetry, non-fiction, and drama, all of which share the common thread of artistic storytelling.

Key elements of Creative Writing
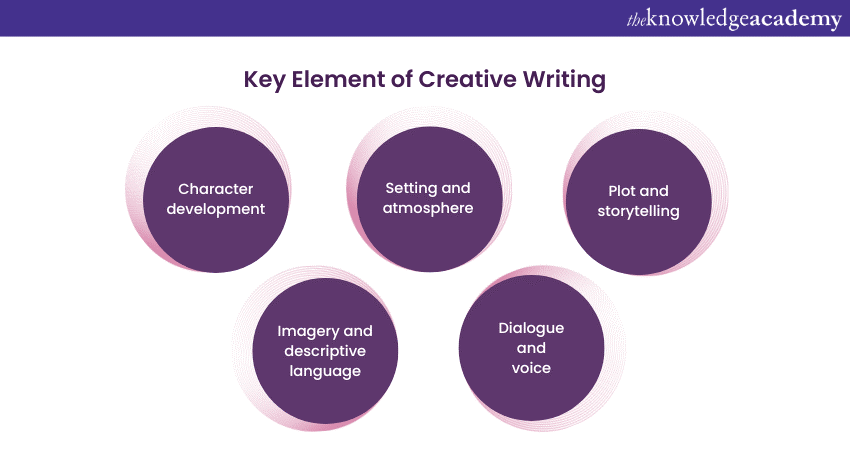
2) Character development: Compelling characters are the heart of any great story. Through careful development, characters become relatable, complex, and capable of driving the plot forward.
3) Setting and atmosphere: The setting and atmosphere create the backdrop for the story. By skilfully crafting these elements, Writers can enhance the overall mood and tone, allowing readers to feel like they're living within the story's world.
4) Plot and storytelling: A well-crafted story keeps readers engaged and invested in the narrative's progression. This includes introducing conflicts, building tension, and crafting satisfying resolutions .
5) Dialogue and voice: Dialogue adds authenticity to characters and provides insight into their personalities. A distinctive narrative voice also contributes to the story's uniqueness and captivates readers.
Types of Creative Writing
Creative Writing encompasses various genres and forms, each offering a unique platform for expressing creativity, storytelling, and emotion. As you delve into the world of Creative Writing, it's essential to explore the various types and discover which resonates with you the most. Here are some of the prominent types of Creative Writing:
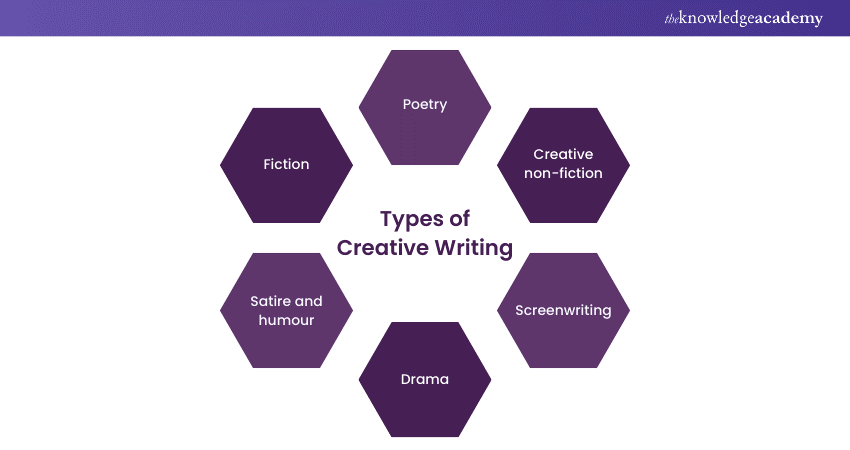
1) Fiction
Fiction is perhaps the most well-known type of Creative Writing. It involves inventing characters, settings, and plotlines from scratch. Writers have the freedom to create entire worlds and realities, whether they're set in the past, present, future, or even in alternate dimensions.
Novels, short stories, novellas, and flash fiction are all forms of fiction that engage readers through compelling characters, intriguing conflicts, and imaginative settings. From fantasy realms to gritty crime dramas, fiction transports readers to new and exciting places.
2) Poetry
Poetry is the art of condensing language to evoke emotions, provoke thoughts, and communicate complex ideas using rhythm, rhyme, and vivid imagery. Poems' conciseness requires Writers to choose their words carefully, often crafting multiple layers of meaning within a few lines.
Poetry can take various forms, including sonnets, haikus, free verse, and slam poetry. Each form carries its own rules and conventions, allowing Poets to experiment with structure and sound to create impactful compositions. Moreover, poetry delves into the depth of emotions, exploring themes ranging from love and nature to social issues and personal reflections.
3) Creative non-fiction
Non-fiction writing draws from real-life experiences, observations, and research to convey information, insights, and personal perspectives. This form includes genres such as essays, memoirs, biographies, autobiographies, and journalistic pieces.
Non-fiction Writers blend storytelling with factual accuracy, presenting their ideas in a compelling and informative manner. Personal essays offer a glimpse into the writer's thoughts and experiences. At the same time, memoirs and autobiographies share personal journeys and reflections, connecting readers with the author's life story.
4) Drama and playwriting
Playwriting is the creation of scripts for theatrical performances. The challenge lies in crafting engaging dialogue and constructing scenes that captivate both the audience and the performers.
Dramatic Writing requires an understanding of pacing, character motivations, and the visual aspects of storytelling. While Theatrical Writing requires a keen sense of the following:
a) Character dynamics: Building relationships between characters and exploring their motivations and conflicts.
b) Stage directions: Providing clear instructions for actors, directors, and stage designers to bring the play to life.
c) Dramatic structure: Crafting acts and scenes that build tension and engage the audience.
5) Satire and humour
Satire and humour utilise wit, sarcasm, and clever wordplay to critique and mock societal norms, institutions, and human behaviour. This form of Creative Writing often challenges readers to view the world from a different perspective.
Moreover, it encourages them to question established conventions. Satirical works, whether in literature, essays, or satirical news articles, aim to entertain while also prompting reflection on serious topics.
Master Copywriting skills with our Copywriting Course – join today and become an expert Copywriter!
Importance of Creative Writing
Creative Writing holds a profound significance beyond its role as a literary pursuit. It bridges imagination and reality, fostering personal growth, communication skills, and cultural preservation. Here's a closer look at why Creative Writing is of paramount importance:
1) Personal expression and catharsis
Creative Writing is a sanctuary for self-expression. Individuals can voice their innermost thoughts, emotions, and experiences through poetry, stories, and essays. This act of sharing vulnerabilities and joy brings about a cathartic release, offering a therapeutic outlet for emotional expression. Moreover, it cultivates a deeper understanding of oneself, promoting self-awareness and self-acceptance.
2) Cultivation of communication skills
The art of Creative Writing cultivates effective Communication Skills that transcend the written word. Writers learn to convey ideas, concepts, and feelings coherently and captivatingly.
This proficiency extends to verbal communication, enabling Writers to articulate their thoughts with clarity and eloquence. As a result, it enriches interpersonal relationships and professional endeavours.
3) Nurturing empathy and perspective
Writers develop a heightened sense of empathy as they craft diverse characters and explore multifaceted narratives. Immersing oneself in the shoes of different characters fosters understanding and tolerance for various viewpoints and backgrounds. Readers, in turn, experience this empathy, gaining insight into the complexities of human nature and the diverse tapestry of human experience.
4) Exploration of social issues
Writers wield the power to effect change through their words. They can shed light on societal issues, challenge norms, and provoke critical conversations. By addressing topics such as social justice, equality, and environmental concerns, Creative Writing becomes a catalyst for positive transformation and advocacy.
5) Connection and impact
Creative Writing builds bridges between individuals by establishing connections on emotional and intellectual levels. Stories resonate across cultures, transcending geographical and temporal boundaries. The impact of a well-crafted story can be enduring, leaving a mark on readers' hearts and minds.
Unlock your creative potential with our Creative Writing Training - register now!
The Creative Writing process
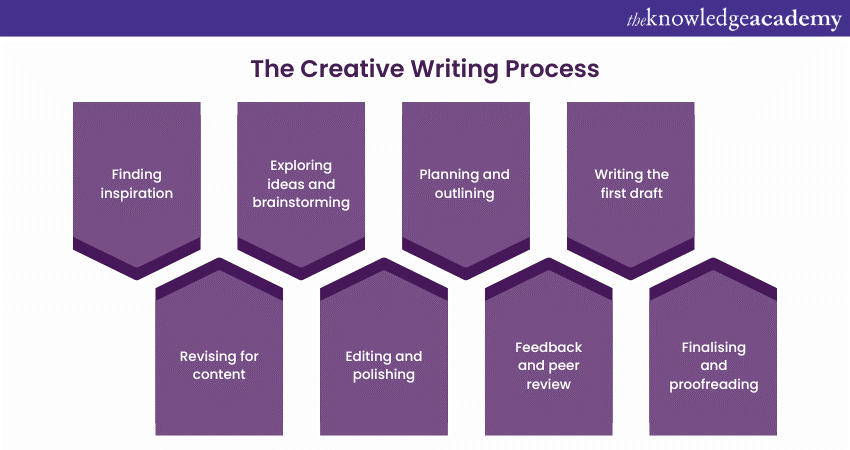
Creating a compelling piece of Creative Writing is a journey that involves a series of steps, each contributing to the evolution of your story. Whether you're crafting a short story, a novel, or a poem, here's a breakdown of the Creative Writing process in eight essential steps:
1) Finding inspiration
The process begins with a moment of inspiration—a fleeting thought, an intriguing image, or a powerful emotion. Inspiration can strike anywhere—nature, experiences, dreams, or simple observation.
Keep a journal or digital note-taking app to capture these sparks of inspiration as they occur. Explore your interests, passions, and emotions to identify themes and ideas that resonate with you.
2) Exploring ideas and brainstorming
Once you've identified an inspiring concept, delve deeper. Brainstorm ideas related to characters, settings, conflicts, and themes. Jot down all possibilities, allowing your imagination to roam freely. This stage is about generating a wealth of creative options that will serve as building blocks for your story.
3) Planning and outlining
Organise your thoughts by creating an outline. Outline your story's major plot points, character arcs, and pivotal moments. This outline acts as a roadmap, guiding you through the narrative's progression while providing flexibility for creative surprises.
4) Writing the first draft
Once you are done with your outline, start writing your first draft. Don't worry about perfection—focus on getting your ideas onto paper. Let your creativity flow and allow your characters to surprise you. The goal is to have a complete manuscript, even if it's messy and imperfect.
5) Revising for content
Once the first draft is complete, take a step back before revisiting your work. During this stage, focus on revising for content. Analyse the structure of your plot, the development of your characters, and the coherence of your themes. Make necessary changes, add details, and refine dialogue. Ensure that your story's foundation is solid before moving on.
6) Editing and polishing
Edit your Manuscript for grammar, punctuation, sentence structure, and style. Pay attention to clarity and consistency. Also, focus on enhancing the flow of your writing and creating a polished narrative that engages readers.
7) Feedback and peer review
Share your revised work with others—friends, writing groups, or beta readers—to gather feedback. Constructive criticism can highlight blind spots and offer perspectives you might have missed. Use this feedback to refine your work further.
8) Finalising and proofreading
Incorporate the feedback you've received and make final revisions. Proofread meticulously for any remaining errors. Ensure that your work is formatted correctly and adheres to any submission guidelines if you plan to publish or share it.
Tips for effective Creative Writing
Here are some of the useful tips you should consider incorporating in your process of writing :
1) Show, don't tell: Instead of directly stating emotions or details, "showing" involves using actions, thoughts, and dialogue to convey information. This technique allows readers to draw their own conclusions and become more immersed in the story.
2) Use of metaphors and similes: Metaphors and similes offer creative ways to describe complex concepts by comparing them to something familiar. These literary devices add depth and creativity to your writing.
3) Building suspense and tension: By strategically withholding information and creating unanswered questions, Writers can build suspense and keep readers eagerly turning pages.
4) Crafting memorable beginnings and endings: A strong opening captures readers' attention, while a satisfying conclusion leaves a lasting impact. These elements bookend your story and influence readers' overall impression.
5) Experimenting with point of view: The choice of point of view (first person, third person, etc.) shapes how readers experience the story. Experimenting with different perspectives can lead to unique narrative opportunities.
Conclusion
We hope this blog gave you a clear idea of What is Creative Writing, along with its process and useful tips. The Creative Writing process is not linear; you might find yourself revisiting earlier steps as your story evolves. Embrace the journey, allowing your writing to develop and transform through each phase.
Enhance your Academic Writing prowess with our comprehensive Academic Writing Masterclass . - sign up now!
Frequently Asked Questions
a) Literary Agent
b) Screenwriter
c) Video Game Story Writer
d) Copywriter
e) Website Editor
f) Creative Director
There are several resources or recommended readings which can help you to hone your Creative Writing skills. Here we have discussed some of such resources:
a) “On Writing: A Memoir of the Craft" by Stephen King
b) "Bird by Bird: Some Instructions on Writing and Life" by Anne Lamott
c) "Writing Down the Bones: Freeing the Writer Within" by Natalie Goldberg
d) Joining book clubs
e) Reading a variety of authors and genre
f) Practicing writing regular prompts and exercises.
The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide. Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 17 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs , videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA .
The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass , a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.
The Knowledge Academy offers various Personal Development courses , including Organisational skills training, Emotional Intelligence Training, and Report Writing Course. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into Journalism . Our Business Skills blogs covers a range of topics related to Sports Journalism, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Creative Writing skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have you covered.
Upcoming Business Skills Resources Batches & Dates
Fri 14th Jun 2024
Fri 30th Aug 2024
Fri 11th Oct 2024
Fri 13th Dec 2024
Get A Quote
WHO WILL BE FUNDING THE COURSE?
My employer
By submitting your details you agree to be contacted in order to respond to your enquiry
- Business Analysis
- Lean Six Sigma Certification
Share this course
Our biggest spring sale.

We cannot process your enquiry without contacting you, please tick to confirm your consent to us for contacting you about your enquiry.
By submitting your details you agree to be contacted in order to respond to your enquiry.
We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on 01344203999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Or select from our popular topics
- ITIL® Certification
- Scrum Certification
- Change Management Certification
- Business Analysis Courses
- Microsoft Azure Certification
- Microsoft Excel Courses
- Microsoft Project
- Explore more courses
Press esc to close
Fill out your contact details below and our training experts will be in touch.
Fill out your contact details below
Thank you for your enquiry!
One of our training experts will be in touch shortly to go over your training requirements.
Back to Course Information
Fill out your contact details below so we can get in touch with you regarding your training requirements.
* WHO WILL BE FUNDING THE COURSE?
Preferred Contact Method
No preference
Back to course information
Fill out your training details below
Fill out your training details below so we have a better idea of what your training requirements are.
HOW MANY DELEGATES NEED TRAINING?
HOW DO YOU WANT THE COURSE DELIVERED?
Online Instructor-led
Online Self-paced
WHEN WOULD YOU LIKE TO TAKE THIS COURSE?
Next 2 - 4 months
WHAT IS YOUR REASON FOR ENQUIRING?
Looking for some information
Looking for a discount
I want to book but have questions
One of our training experts will be in touch shortly to go overy your training requirements.
Your privacy & cookies!
Like many websites we use cookies. We care about your data and experience, so to give you the best possible experience using our site, we store a very limited amount of your data. Continuing to use this site or clicking “Accept & close” means that you agree to our use of cookies. Learn more about our privacy policy and cookie policy cookie policy .
We use cookies that are essential for our site to work. Please visit our cookie policy for more information. To accept all cookies click 'Accept & close'.
Last places remaining for June 30th start. Don’t miss out. Enrol now to avoid disappointment
- What Is Creative Writing? The ULTIMATE Guide!

At Oxford Royale Academy, we offer a range of summer school programmes that have become extremely popular amongst students of all ages. The subject of creative writing continues to intrigue many academics as it can help to develop a range of skills that will benefit you throughout your career and life.
Nevertheless, that initial question is one that continues to linger and be asked time and time again: what is creative writing? More specifically, what does it mean or encompass? How does creative writing differ from other styles of writing?
During our Oxford Summer School programme , we will provide you with in-depth an immersive educational experience on campus in the colleges of the best university in the world. However, in this guide, we want to provide a detailed analysis of everything to do with creative writing, helping you understand more about what it is and why it could benefit you to become a creative writer.
The best place to start is with a definition.
What is creative writing?
The dictionary definition of creative writing is that it is original writing that expresses ideas and thoughts in an imaginative way. [1] Some academics will also define it as the art of making things up, but both of these definitions are too simplistic in the grand scheme of things.
It’s challenging to settle on a concrete definition as creative writing can relate to so many different things and formats. Naturally, as the name suggests, it is all built around the idea of being creative or imaginative. It’s to do with using your brain and your own thoughts to create writing that goes outside the realms of what’s expected. This type of writing tends to be more unique as it comes from a personal place. Each individual has their own level of creativity, combined with their own thoughts and views on different things. Therefore, you can conjure up your own text and stories that could be completely different from others.
Understanding creative writing can be challenging when viewed on its own. Consequently, the best way to truly understand this medium is by exploring the other main forms of writing. From here, we can compare and contrast them with the art of creative writing, making it easier to find a definition or separate this form of writing from others.
What are the main forms of writing?
In modern society, we can identify five main types of writing styles [1] that will be used throughout daily life and a plethora of careers:
- Narrative Writing
- Descriptive Writing
- Persuasive Writing
- Expository Writing
- Creative Writing
Narrative writing refers to storytelling in its most basic form. Traditionally, this involves telling a story about a character and walking the readers through the journey they go on. It can be a long novel or a short story that’s only a few hundred words long. There are no rules on length, and it can be completely true or a work of fiction.
A fundamental aspect of narrative writing that makes it different from other forms is that it should includes the key elements of storytelling. As per UX Planet, there are seven core elements of a good story or narrative [2] : the plot, characters, theme, dialogue, melody, decor and spectacle. Narrative writing will include all of these elements to take the ready on a journey that starts at the beginning, has a middle point, but always comes to a conclusion. This style of writing is typically used when writing stories, presenting anecdotes about your life, creating presentations or speeches and for some academic essays.
Descriptive writing, on the other hand, is more focused on the details. When this type of writing is used, it’s focused on capturing the reader’s attention and making them feel like they are part of the story. You want them to live and feel every element of a scene, so they can close their eyes and be whisked away to whatever place or setting you describe.
In many ways, descriptive writing is writing as an art form. Good writers can be given a blank canvas, using their words to paint a picture for the audience. There’s a firm focus on the five senses all humans have; sight, smell, touch, sound and taste. Descriptive writing touches on all of these senses to tell the reader everything they need to know and imagine about a particular scene.
This is also a style of writing that makes good use of both similes and metaphors. A simile is used to describe something as something else, while a metaphor is used to show that something is something else. There’s a subtle difference between the two, but they both aid descriptive writing immensely. According to many writing experts, similes and metaphors allow an author to emphasise, exaggerate, and add interest to a story to create a more vivid picture for the reader [3] .
Looking at persuasive writing and we have a form of writing that’s all about making yourself heard. You have an opinion that you want to get across to the reader, convincing them of it. The key is to persuade others to think differently, often helping them broaden their mind or see things from another point of view. This is often confused with something called opinionative writing, which is all about providing your opinions. While the two seem similar, the key difference is that persuasive writing is built around the idea of submitting evidence and backing your thoughts up. It’s not as simple as stating your opinion for other to read; no, you want to persuade them that your thoughts are worth listening to and perhaps worth acting on.
This style of writing is commonly used journalistically in news articles and other pieces designed to shine a light on certain issues or opinions. It is also typically backed up with statistical evidence to give more weight to your opinions and can be a very technical form of writing that’s not overly emotional.
Expository writing is more focused on teaching readers new things. If we look at its name, we can take the word exposure from it. According to Merriam-Webster [4] , one of the many definitions of exposure is to reveal something to others or present them with something they otherwise didn’t know. In terms of writing, it can refer to the act of revealing new information to others or exposing them to new ideas.
Effectively, expository writing focuses on the goal of leaving the reader with new knowledge of a certain topic or subject. Again, it is predominately seen in journalistic formats, such as explainer articles or ‘how-to’ blogs. Furthermore, you also come across it in academic textbooks or business writing.
This brings us back to the centre of attention for this guide: what is creative writing?
Interestingly, creative writing is often seen as the style of writing that combines many of these forms together in one go. Narrative writing can be seen as creative writing as you are coming up with a story to keep readers engaged, telling a tale for them to enjoy or learn from. Descriptive writing is very much a key part of creative writing as you are using your imagination and creative skills to come up with detailed descriptions that transport the reader out of their home and into a different place.
Creative writing can even use persuasive writing styles in some formats. Many writers will combine persuasive writing with a narrative structure to come up with a creative way of telling a story to educate readers and provide new opinions for them to view or be convinced of. Expository writing can also be involved here, using creativity and your imagination to answer questions or provide advice to the reader.
Essentially, creative writing can combine other writing types to create a unique and new way of telling a story or producing content. At the same time, it can include absolutely none of the other forms at all. The whole purpose of creative writing is to think outside the box and stray from traditional structures and norms. Fundamentally, we can say there are no real rules when it comes to creative writing, which is what makes it different from the other writing styles discussed above.
What is the purpose of creative writing?
Another way to understand and explore the idea of creative writing is to look at its purpose. What is the aim of most creative works of writing? What do they hope to provide the reader with?
We can look at the words of Bryanna Licciardi, an experienced creative writing tutor, to understand the purpose of creative writing. She writes that the primary purpose is to entertain and share human experiences, like love or loss. Writers attempt to reveal the truth with regard to humanity through poetics and storytelling. [5] She also goes on to add that the first step of creative writing is to use one’s imagination.
When students sign up to our creative writing courses, we will teach them how to write with this purpose. Your goal is to create stories or writing for readers that entertain them while also providing information that can have an impact on their lives. It’s about influencing readers through creative storytelling that calls upon your imagination and uses the thoughts inside your head. The deeper you dive into the art of creative writing, the more complex it can be. This is largely because it can be expressed in so many different formats. When you think of creative writing, your instinct takes you to stories and novels. Indeed, these are both key forms of creative writing that we see all the time. However, there are many other forms of creative writing that are expressed throughout the world.
What are the different forms of creative writing?
Looking back at the original and simple definition of creative writing, it relates to original writing in a creative and imaginative way. Consequently, this can span across so many genres and types of writing that differ greatly from one another. This section will explore and analyse the different types of creative writing, displaying just how diverse this writing style can be – while also showcasing just what you’re capable of when you learn how to be a creative writer.
The majority of students will first come across creative writing in the form of essays . The point of an essay is to present a coherent argument in response to a stimulus or question. [6] In essence, you are persuading the reader that your answer to the question is correct. Thus, creative writing is required to get your point across as coherently as possible, while also using great descriptive writing skills to paint the right message for the reader.
Moreover, essays can include personal essays – such as writing a cover letter for work or a university application. Here, great creativity is needed to almost write a story about yourself that captivates the reader and takes them on a journey with you. Excellent imagination and persuasive writing skills can help you tell your story and persuade those reading that you are the right person for the job or university place.
Arguably, this is the most common way in which creative writing is expressed. Fictional work includes novels, novellas, short stories – and anything else that is made up. The very definition of fiction by the Cambridge Dictionary states that it is the type of book or story that is written about imaginary characters and events not based on real people and facts. [7] As such, it means that your imagination is called upon to create something out of nothing. It is a quintessential test of your creative writing skills, meaning you need to come up with characters, settings, plots, descriptions and so much more.
Fictional creative writing in itself takes on many different forms and can be completely different depending on the writer. That is the real beauty of creative writing; you can have entirely different stories and characters from two different writers. Just look at the vast collection of fictional work around you today; it’s the perfect way to see just how versatile creative writing can be depending on the writer.
Similarly, scripts can be a type of creative writing that appeals to many. Technically, a script can be considered a work of fiction. Nevertheless, it depends on the script in question. Scripts for fictional television shows, plays or movies are obviously works of fiction. You, the writer, has come up with the characters and story of the show/play/movie, bringing it all to life through the script. But, scripts can also be non-fictional. Creating a play or movie that adapts real-life events will mean you need to write a script based on something that genuinely happened.
Here, it’s a perfect test of creative writing skills as you take a real event and use your creative talents to make it more interesting. The plot and narrative may already be there for you, so it’s a case of using your descriptive writing skills to really sell it to others and keep readers – or viewers – on the edge of their seats.
A speech is definitely a work of creative writing. The aim of a speech can vary depending on what type of speech it is. A politician delivering a speech in the House of Commons will want to get a point across to persuade others in the room. They’ll need to use creative writing to captivate their audience and have them hanging on their every word. A recent example of a great speech was the one by Sir David Attenborough at the recent COP26 global climate summit. [8] Listening to the speech is a brilliant way of understanding how creative writing can help get points across. His speech went viral around the world because of how electrifying and enthralling it is. The use of many descriptive and persuasive words had people hanging onto everything he said. He really created a picture and an image for people to see, convincing them that the time is now to work on stopping and reversing climate change.
From this speech to a completely different one, you can see creative writing at play for speeches at weddings and other jovial events. Here, the purpose is more to entertain guests and make them laugh. At the same time, someone giving a wedding speech will hope to create a lovely story for the guests to enjoy, displaying the true love that the married couple share for one another. Regardless of what type of speech an individual is giving, creative writing skills are required for it to be good and captivating.
Poetry & Songs
The final example of creative writing is twofold; poetry and songs. Both of these formats are similar to one another, relying on creativity to deliver a combination of things. Poetry can take so many forms and styles, but it aims to inspire readers and get them thinking. Poems often have hidden meanings behind them, and it takes a great deal of imagination and creativity to come up with these meanings while also creating a powerful poem. Some argue that poetry is the most creative of all creative writing forms.
Songwriting is similar in that you use creativity to come up with lyrics that can have powerful meanings while also conjuring up a story for people. The best songwriters will use lyrics that stay in people’s minds and get them thinking about the meaning behind the song. If you lack imagination and creativity, you will never be a good songwriter.
In truth, there are so many other types and examples of creative writing that you can explore. The ones listed above are the most common and powerful, and they all do a great job of demonstrating how diverse creative writing can be. If you can hone your skills in creative writing, it opens up many opportunities for you in life. Primarily, creative writing focuses on fictional pieces of work, but as you can see, non-fiction also requires a good deal of creativity.
What’s needed to make a piece of creative writing?
Our in-depth analysis of creative writing has led to a point where you’re aware of this style of writing and its purpose, along with some examples of it in the real world. The next question to delve into is what do you need to do to make a piece of creative writing. To phrase this another way; how do you write something that comes under the creative heading rather than another form of writing?
There is an element of difficulty in answering this question as creative writing has so many different types and genres. Consequently, there isn’t a set recipe for the perfect piece of creative writing, and that’s what makes this format so enjoyable and unique. Nevertheless, we can discover some crucial elements or principles that will help make a piece of writing as creative and imaginative as possible:
A target audience
All creative works will begin by defining a target audience. There are many ways to define a target audience, with some writers suggesting that you think about who is most likely to read your work. However, this can still be challenging as you’re unsure of the correct demographic to target. Writer’s Digest makes a good point of defining your target audience by considering your main motivation for writing in the first place. [9] It’s a case of considering what made you want to start writing – whether it’s a blog post, novel, song, poem, speech, etc. Figuring out your motivation behind it will help you zero in on your target audience.
Defining your audience is vital for creative writing as it helps you know exactly what to write and how to write it. All of your work should appeal to this audience and be written in a way that they can engage with. As a simple example, authors that write children’s stories will adapt their writing to appeal to the younger audience. Their stories include lots of descriptions and words that children understand, rather than being full of long words and overly academic writing.
Establishing the audience lets the writer know which direction to take things in. As a result, this can aid with things like character choices, plot, storylines, settings, and much more.
A story of sorts
Furthermore, great works of creative writing will always include a story of sorts. This is obvious for works such as novels, short stories, scripts, etc. However, even for things like poems, songs or speeches, a story helps make it creative. It gives the audience something to follow, helping them make sense of the work. Even if you’re giving a speech, setting a story can help you create a scene in people’s minds that makes them connect to what you’re saying. It’s a very effective way of persuading others and presenting different views for people to consider.
Moreover, consider the definition of a story/narrative arc. One definition describes it as a term that describes a story’s full progression. It visually evokes the idea that every story has a relatively calm beginning, a middle where tension, character conflict and narrative momentum builds to a peak and an end where the conflict is resolved. [10]
Simplifying this, we can say that all works of creative writing need a general beginning, middle and end. It’s a way of bringing some sort of structure to your writing so you know where you are going, rather than filling it with fluff or waffle.
A good imagination
Imagination is a buzzword that we’ve used plenty of times throughout this deep dive into creative writing. Every creative writing course you go on will spend a lot of time focusing on the idea of using your imagination. The human brain is a marvellously powerful thing that holds the key to creative freedom and expressing yourself in new and unique ways. If you want to make something creative, you need to tap into your imagination.
People use their imagination in different ways; some will be able to conjure up ideas for stories or worlds that exist beyond our own. Others will use theirs to think of ways of describing things in a more creative and imaginative way. Ultimately, a good imagination is what sets your work apart from others within your genre. This doesn’t mean you need to come up with the most fantastical novel of all time to have something classified as creative writing. No, using your imagination and creativity can extend to something as simple as your writing style.
Ultimately, it’s more about using your imagination to find your own personal flair and creative style. You will then be able to write unique pieces that stand out from the others and keep audiences engaged.
How can creative writing skills benefit you?
When most individuals or students consider creative writing, they imagine a world where they are writing stories for a living. There’s a common misconception that creative writing skills are only beneficial for people pursuing careers in scriptwriting, storytelling, etc. Realistically, enhancing ones creative writing skills can open up many windows of opportunity throughout your education and career.
- Improve essay writing – Naturally, creative writing forms a core part of essays and other written assignments in school and university. Improving your skills in this department can help a student get better at writing powerful essays and achieving top marks. In turn, this can impact your career by helping you get better grades to access better jobs in the future.
- Become a journalist – Journalists depend on creative writing to make stories that capture audiences and have people hanging on their every word. You need high levels of creativity to turn a news story into something people are keen to read or watch.
- Start a blog – In modern times, blogging is a useful tool that can help people find profitable and successful careers. The whole purpose of a blog is to provide your opinions to the masses while also entertaining, informing and educating. Again, having a firm grasp of creative writing skills will aid you in building your blog audience.
- Write marketing content – From advert scripts to content on websites, marketing is fuelled by creative writing. The best marketers will have creative writing skills to draw an audience in and convince them to buy products. If you can learn to get people hanging on your every word, you can make it in this industry.
These points all demonstrate the different ways in which creative writing can impact your life and alter your career. In terms of general career skills, this is one that you simply cannot go without.
How to improve your creative writing
One final part of this analysis of creative writing is to look at how students can improve. It begins by reading as much as you can and taking in lots of different content. Read books, poems, scripts, articles, blogs – anything you can find. Listen to music and pay attention to the words people use and the structure of their writing. It can help you pick up on things like metaphors, similes, and how to use your imagination. Of course, writing is the key to improving; the more you write, the more creative you can get as you will start unlocking the powers of your brain.
Conclusion: What is creative writing
In conclusion, creative writing uses a mixture of different types of writing to create stories that stray from traditional structures and norms. It revolves around the idea of using your imagination to find a writing style that suits you and gets your points across to an audience, keeping them engaged in everything you say. From novels to speeches, there are many forms of creative writing that can help you in numerous career paths throughout your life.
[1] SkillShare: The 5 Types of Writing Styles with Examples
[2] Elements of Good Story Telling – UX Planet
[3] Simile vs Metaphor: What’s the Difference? – ProWritingAid
[4] Definition of Exposure by Merriam-Webster
[5] The Higher Purpose of Creative Writing | by Terveen Gill
[6] Essay purpose – Western Sydney University
[7] FICTION | meaning in the Cambridge English Dictionary
[8] ‘Not fear, but hope’ – Attenborough speech in full – BBC News
[9] Writer’s Digest: Who Is Your Target Reader?
[10] What is a Narrative Arc? • A Guide to Storytelling Structure

Elements of Creative Writing
J.D. Schraffenberger, University of Northern Iowa
Rachel Morgan, University of Northern Iowa
Grant Tracey, University of Northern Iowa
Copyright Year: 2023
ISBN 13: 9780915996179
Publisher: University of Northern Iowa
Language: English
Formats Available
Conditions of use.
Learn more about reviews.
Reviewed by Robert Moreira, Lecturer III, University of Texas Rio Grande Valley on 3/21/24
Unlike Starkey's CREATIVE WRITING: FOUR GENRES IN BRIEF, this textbook does not include a section on drama. read more
Comprehensiveness rating: 4 see less
Unlike Starkey's CREATIVE WRITING: FOUR GENRES IN BRIEF, this textbook does not include a section on drama.
Content Accuracy rating: 5
As far as I can tell, content is accurate, error free and unbiased.
Relevance/Longevity rating: 5
The book is relevant and up-to-date.
Clarity rating: 5
The text is clear and easy to understand.
Consistency rating: 5
I would agree that the text is consistent in terms of terminology and framework.
Modularity rating: 5
Text is modular, yes, but I would like to see the addition of a section on dramatic writing.
Organization/Structure/Flow rating: 5
Topics are presented in logical, clear fashion.
Interface rating: 5
Navigation is good.
Grammatical Errors rating: 5
No grammatical issues that I could see.
Cultural Relevance rating: 3
I'd like to see more diverse creative writing examples.
As I stated above, textbook is good except that it does not include a section on dramatic writing.
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Chapter One: One Great Way to Write a Short Story
- Chapter Two: Plotting
- Chapter Three: Counterpointed Plotting
- Chapter Four: Show and Tell
- Chapter Five: Characterization and Method Writing
- Chapter Six: Character and Dialouge
- Chapter Seven: Setting, Stillness, and Voice
- Chapter Eight: Point of View
- Chapter Nine: Learning the Unwritten Rules
- Chapter One: A Poetry State of Mind
- Chapter Two: The Architecture of a Poem
- Chapter Three: Sound
- Chapter Four: Inspiration and Risk
- Chapter Five: Endings and Beginnings
- Chapter Six: Figurative Language
- Chapter Seven: Forms, Forms, Forms
- Chapter Eight: Go to the Image
- Chapter Nine: The Difficult Simplicity of Short Poems and Killing Darlings
Creative Nonfiction
- Chapter One: Creative Nonfiction and the Essay
- Chapter Two: Truth and Memory, Truth in Memory
- Chapter Three: Research and History
- Chapter Four: Writing Environments
- Chapter Five: Notes on Style
- Chapter Seven: Imagery and the Senses
- Chapter Eight: Writing the Body
- Chapter Nine: Forms
Back Matter
- Contributors
- North American Review Staff
Ancillary Material
- University of Northern Iowa
About the Book
This free and open access textbook introduces new writers to some basic elements of the craft of creative writing in the genres of fiction, poetry, and creative nonfiction. The authors—Rachel Morgan, Jeremy Schraffenberger, and Grant Tracey—are editors of the North American Review, the oldest and one of the most well-regarded literary magazines in the United States. They’ve selected nearly all of the readings and examples (more than 60) from writing that has appeared in NAR pages over the years. Because they had a hand in publishing these pieces originally, their perspective as editors permeates this book. As such, they hope that even seasoned writers might gain insight into the aesthetics of the magazine as they analyze and discuss some reasons this work is so remarkable—and therefore teachable. This project was supported by NAR staff and funded via the UNI Textbook Equity Mini-Grant Program.
About the Contributors
J.D. Schraffenberger is a professor of English at the University of Northern Iowa. He is the author of two books of poems, Saint Joe's Passion and The Waxen Poor , and co-author with Martín Espada and Lauren Schmidt of The Necessary Poetics of Atheism . His other work has appeared in Best of Brevity , Best Creative Nonfiction , Notre Dame Review , Poetry East , Prairie Schooner , and elsewhere.
Rachel Morgan is an instructor of English at the University of Northern Iowa. She is the author of the chapbook Honey & Blood , Blood & Honey . Her work is included in the anthology Fracture: Essays, Poems, and Stories on Fracking in American and has appeared in the Journal of American Medical Association , Boulevard , Prairie Schooner , and elsewhere.
Grant Tracey author of three novels in the Hayden Fuller Mysteries ; the chapbook Winsome featuring cab driver Eddie Sands; and the story collection Final Stanzas , is fiction editor of the North American Review and an English professor at the University of Northern Iowa, where he teaches film, modern drama, and creative writing. Nominated four times for a Pushcart Prize, he has published nearly fifty short stories and three previous collections. He has acted in over forty community theater productions and has published critical work on Samuel Fuller and James Cagney. He lives in Cedar Falls, Iowa.
Contribute to this Page
Creative Writing | Definition, Techniques & Examples
Austin Valenzuela earned his bachelor's degree in psychology from Grand Canyon University and has written about psychology for over four years. He is a writer of science-fiction and fantasy. His published novel Unholy: A Gothic Fantasy and short story in the anthology Beneath the Twin Suns are available everywhere. He is a member of the Florida Writers Association and National Society of Collegiate Scholars.
Bryanna has received both her BA in English and MFA in Creative Writing. She has been a writing tutor for over six years.
Amy has taught and tutored college-level English; she has a master's degree from Colorado State University in rhetoric and composition.
Table of Contents
What is creative writing, examples of creative writing, lesson summary, creative writing: writing prompts.
The below writing prompts allow students to flex their creative writing muscles by experimenting with different types of creative writing genres and reflecting on their finished product and writing process.
Prompt 1: Poetry
Write a poem about a common, everyday object like a pencil, a spoon, a t-shirt, or a water bottle. Think about how to create striking imagery and emotion in your work—you may take time to brainstorm possible words you can use to create a visually and emotionally engaging work. In addition, your poem should include at least two metaphors or similes. After writing your poem, which should be at least ten lines long, answer the questions that follow.
- Reflect on your writing process. How did you prepare to write your poem? Did you think about the major theme(s) you wanted your poem to address before you started writing?
- Explore the techniques you used in your poem: how did you create setting? How did you establish point-of-view? How did you appeal to your audience's emotions?

Prompt 2: Short Story
In at least 750 words, write a short story about an unlikely friendship. Before writing your short story, consider tracing a plot diagram that sketches out the story's exposition, rising action, climax, falling action, and resolution. After writing your story, answer the questions that follow.
- What is the basic plot of your story? (Consider: exposition, rising action, climax, falling action, and resolution)
- How did you develop the characters in your story?
- How did you use dialogue in your story? (If you didn't use any dialogue, describe what effect this choice has on your audience.)
- What literary devices did you include in your story and what is their overall effect? (e.g. metaphor, personification, alliteration, etc.)
- What is the overall theme of your story? How do you communicate this theme to your audience?
What are the 8 elements of creative writing?
The eight elements of creative writing that are used in short stories and novels are character development, setting, plot, conflict, theme, point of view, tone, and style. Some of these elements are also often used in poems and works of creative nonfiction such as memoir and personal essay.
What is creative writing and its purpose?
Creating writing is a means of using written language to tell an interesting or enjoyable story that will engage, inspire, excite, or surprise a reader, evoking emotions and provoking thought. Its purpose is to artfully educate, entertain, or inform in a meaningful way that the reader will find enjoyable.
What are the 4 forms of creative writing?
The four forms of creative writing are fiction, creative nonfiction, poetry, and scriptwriting which is sometimes called screenwriting or play writing. Creative nonfiction can take several forms such as memoir and personal essay.
What is an example of creative writing?
One example of creative writing is fiction writing. Fiction includes traditional novels, short stories, and graphic novels. By definition, fiction is a story that is not true, although it can be realistic and include real places and facts.
The invention of the written word, sometime around 3200 B.C., launched creative writing with the recording of stories like The Odyssey and tales of Norse gods. Over time, the stories morphed and the skill of storytellers improved as well. Today, over three-fourths of the population can read and write. Oral storytellers have been using elements like voice and personality to entertain and convey human experience. But what is creative writing ? Although the craft has taken many forms from the poem to the novel, the core purpose of conveying human experience remains. Indeed, many of our oldest stories still inspire modern-day storytellers such as Christopher Tolkien and his famous Lord of the Rings trilogy.
The dictionary defines creative writing as writing that displays imagination or invention. Creative, artistic writing uses words to convey emotion or feeling. One must use imaginary scenarios invented by themselves. Rather than being limited to academic or technical subjects, which shun first-person voice and emotion, creative writing uses elements such as character development, plot, and the lyricism of words to share the author's emotion with the reader. Academic writing is different in its essential purpose because it does not allow the author to share emotion. Good creative writing does this best, as we will see in later examples.
Types of Creative Writing
There is an infinite number of ways to convey human experience using words. This is the fun of the craft. Here are some of the most common types of creative writing and their general form:
- Autobiography/Memoir - Narrative writing based on the author's memories.
- Flash Fiction - Offers character and plot in extreme brevity, with a word count of six to one thousand words.
- Novel - Long work of narrative fiction, typically with a word count of eighty-thousand to one-hundred-thousand words.
- Novella - Narrative prose of shorter length, with a word count of ten-thousand to forty-thousand words.
- Play - Work of drama consisting of mostly dialogue intended for theatrical performance.
- Poetry - Uses aesthetic and often rhythmic qualities of language to convey meaning. Poems may not follow a narrative structure.
- Screenplay - Written work by screenwriters intended for film, television, or a video game.
- Short Story - Prose fiction typically read in one sitting, between five thousand to ten thousand words.
Elements of Creative Writing
The purpose of creative writing elements is to aid in the conveyance of aesthetic or symbolic meaning. Different types of creative writing use different elements. However, these elements are used universally within their form and are all critical components of good creative writing. The most helpful elements to learn and perfect are as follows:
- Action - Movements that characters undertake in the story.
- Character - Used to progress the plot and establish inner or outer conflict.
- Conflict - Challenges, suspense, and uncertainty for whether the goal will be achieved.
- Dialogue - A verbal exchange between characters.
- Pacing - The speed at which a story is told.
- Plot - The sequence of a story's events.
- Scene - Dramatic sections in a story within a specific time and place.
- Setting - Time and location in the narrative.
- Suspense - The anticipation of an outcome or plot.
- Theme - Central topic or message of a narrative.
- Tone - The narrator's attitude toward the subject matter.
- Voice - The manner of expression.
Creative Writing Techniques
Unlike elements, creative writing techniques are not universal. They are going to be unique to each author and story. The combination of different techniques will yield different results. Some techniques work better for specific stories and styles of creative writing than others.
- Considering the Audience - When the author appeals to the expectations and emotions of the readership.
- Genre - Determined by technique, tone, content, and sometimes length. Mainly used for marketing purposes.
- Metaphor - Figure of speech meant to address an abstract concept.
- Narration/Point of View - Who is telling the story: first-person (I chased after the dog), second-person (You chased after the dog), third-person (He/she chased after the dog).
- Rhyme - Used to appeal to senses and unify stanzas.
- Structure - Common methods of building stories that specifically address adventure, suspense, and resolution.
- Style - Unique choice of words, tone, and grammar used to affect readers.
To unlock this lesson you must be a Study.com Member. Create your account

An error occurred trying to load this video.
Try refreshing the page, or contact customer support.
You must c C reate an account to continue watching
Register to view this lesson.
As a member, you'll also get unlimited access to over 88,000 lessons in math, English, science, history, and more. Plus, get practice tests, quizzes, and personalized coaching to help you succeed.
Get unlimited access to over 88,000 lessons.
Already registered? Log in here for access
Resources created by teachers for teachers.
I would definitely recommend Study.com to my colleagues. It’s like a teacher waved a magic wand and did the work for me. I feel like it’s a lifeline.
You're on a roll. Keep up the good work!
Just checking in. are you still watching.
- 0:02 Creative Writing
- 1:50 Examples
- 4:03 Lesson Summary
The best creative writing examples use the elements and techniques mentioned above to entertain and at the same time convey a meaningful, timeless message to the reader. Some writers choose to lean on the side of creative writing that is more eloquent and harder to read. In contrast, others prefer to have the meaning of their prose easy to understand. This is typically the difference between poetry and longer-form fiction. Below are some creative writing examples that show the different elements and techniques we've covered at use.
- Fire and Ice:
"Some say the world will end in fire,
Some say in ice.
From what I've tasted of desire
I hold with those who favor fire.
But if it had to perish twice,
I think I know enough of hate
To say that for destruction ice
Is also great
And would suffice."
This poem by Robert Frost effectively uses rhyme, metaphor, and juxtaposition to evoke emotion in the reader. In keeping with the creative writing tradition, this poem by Robert Frost was inspired by an earlier work by Dante Alighieri titled Inferno . The use of rhyme unites key stanzas such as lines one, three, and four, which elaborate upon the meaning of the world ending in fire. This poem is brief and calls for a reread almost immediately, inviting the reader to analyze the text deeply and draw out meaning. The ultimate message commonly interpreted from this poem by Frost is that, although the two elements of fire and ice appear entirely different, their potential destructive force is much the same. At the same time, Frost establishes a metaphor between these natural forces and human emotions of desire and hate.
- Excerpt from The Catcher in the Rye:
"There were never many girls at all at the football games. Only seniors were allowed to bring girls with them. It was a terrible school, no matter how you looked at it. I like to be somewhere at least where you can see a few girls around once in a while, even if they're only scratching their arms or blowing their noses or even just giggling or something."
This novel excerpt for J.D. Salinger's most celebrated novel is a great display of character voice used within setting and context to progress the plot and establish a theme. The novel is about a young boy who is kicked out of his private school because he does not get good grades and the following journey home to his parents' house. Holden hates this school and is probably glad to go home, no matter what. In this section at the beginning of the story, we are getting to know the main character Holden, and in this passage, we learn a lot about his outlook on the world. We know that Holden, like many teenage boys, is more interested in the girls than anything, which might be a reason why he got kicked out of the school in the first place. Moreover, the nonchalant tone of Holden's storytelling and his use of average and repeated words makes the reader feel like they know Holden in an intimate way, making them more invested with his actions and journey back to his parents' home.
While it often has beautiful and awe-inspiring elements, creative writing is best defined as using words to convey emotion to the reader through imagination and invention. Creative writing can include facts about the world but must use them in a made-up fashion to create a unique message. The primary four forms of creative writing are fiction, non-fiction, poetry, and screenwriting. Writers will use a mixture of creative elements and techniques to tell a story or evoke feelings in the reader. The main elements used include:
- Character development
- Point of View
The best creative writers combine all or most of these elements with a story that resonates with audiences of the present and future. When an author uses these elements and techniques effectively and speaks the truth from their heart, the message conveyed is timeless.
Video Transcript
Defining creative writing.
You might have heard it called different things. Traditionally referred to as literature, creative writing is an art of sorts - the art of making things up. It's writing done in a way that is not academic or technical but still attracts an audience. Though the definition is rather loose, creative writing can for the most part be considered any writing that is original and self-expressive. A news article, for example, cannot be considered creative writing because its main goal is to present facts and not to express the feelings of the writer. While a news article can be entertaining, its main purpose is to present the facts.
The purpose of creative writing is to both entertain and share human experience, like love or loss. Writers attempt to get at a truth about humanity through poetics and storytelling. If you'd like to try your hand at creative writing, just keep in mind that whether you are trying to express a feeling or a thought, the first step is to use your imagination.
Types of creative writing include:
- Movie and television scripts
- Fiction (novels, novellas, and short stories)
- Personal essays
As you can see, some nonfiction types of writing can also be considered creative writing. Memoirs and personal essays, for example, can be written creatively to inform your readers about your life in an expressive way. Because these types are written in first person, it's easier for them to be creative.
Techniques used in creative writing include:
- Plot development
- Vivid setting
- Underlying theme
- Point of view
- Metaphors and similes
- Figures of speech
- Imaginative language
- Emotional appeal
- Heavy description
Poetry and Songs
A poem or a song tends to be more elusive, or mysterious, because it has limited space. Because of its spatial limitations, however, it can make leaps in subject and time, and it doesn't have to rely on narrative structure. In poetry and songs, literary devices, like similes and metaphors, can be used to take the readers to surprising places. A good example of this is the opening of the poem 'A Life' by Sylvia Plath:
'Touch it: it won't shrink like an eyeball,
This egg-shaped bailiwick, clear as a tear.
Here's yesterday, last year ---
Palm-spear and lily distinct as flora in the vast
Windless threadwork of a tapestry.'
Note how shocking the comparison is, how it immediately captures the reader's attention. The goal of this poem's image is to build from this idea of life as an eyeball and makes the reader really try to visualize it.
Fiction and Plays
A novel or a play, on the other hand, has plenty of time to unfold. Therefore, fiction usually contains plot and character development. As a creative writer, you want your story to captivate readers. You also want to create a relationship between the readers and the characters. This requires both physical and emotional details so that readers will empathize with the action and whatever pain or pleasure the characters undergo. To use as an example, read the following excerpt from the novel Great Expectations by Charles Dickens:
'There either is or is not, that's the way things are. The colour of the day. The way it felt to be a child. The saltwater on your sunburnt legs. Sometimes the water is yellow, sometimes it's red. But what colour it may be in memory, depends on the day. I'm not going to tell you the story the way it happened. I'm going to tell it the way I remember it.'
The character's voice in this quote is really captivating. It sounds honest and thoughtful and also a little haunting. The foreshadowing of what truly happened will want to make a reader continue forward, and the character being developed is one that readers will want to learn more about.
Creative writing is the art of using words to make things up. However, a good creative writer makes things up that people will want to read. To do this, you have to use your imagination and try to capture an emotion or a human truth, like love or loss. This does not include academic or technical writing because these types of writing cannot include made-up material nor are their purposes to express the writer's feelings.
Creative writing's goal is to captivate an audience and create an emotional or thoughtful appeal, although the type of writing will determine how it will do so. Some types of creative writing, like poems and songs, have limited space, and therefore tend to be more mysterious and less narrative. Types like novels and plays have room to explore character and plot development. Anyone can write creatively; all it takes is imagination and having something to say!
Learning Outcomes
Once you are finished, you should be able to:
- Recall the purpose of creative writing
- List some of the common techniques used in creative writing
- Describe some types of creative writing
Unlock Your Education
See for yourself why 30 million people use study.com, become a study.com member and start learning now..
Already a member? Log In
Recommended Lessons and Courses for You
Related lessons, related courses, recommended lessons for you.

Creative Writing | Definition, Techniques & Examples Related Study Materials
- Related Topics
Browse by Courses
- ILTS Social Science - Psychology (248) Prep
- FTCE Earth/Space Science 6-12 (008) Prep
- FTCE School Counseling PK-12 (018) Prep
- ILTS Social Science - Sociology and Anthropology (249) Prep
- SAT Subject Test World History: Practice and Study Guide
- NYSTCE Music (165) Prep
- Praxis Earth and Space Sciences: Content Knowledge (5571) Prep
- Praxis Psychology (5391) Prep
- LSAT Test: Online Prep & Review
- TExES Music EC-12 (177) Prep
- Writing Review for Teachers: Study Guide & Help
- Reading Review for Teachers: Study Guide & Help
- CBEST Test Prep: Practice & Study Guide
- GRE Test: Practice & Study Guide
- Praxis Core Academic Skills for Educators: Reading (5713) Prep
Browse by Lessons
- How to Write a Creative Story: Lesson for Kids
- What is Creative Writing? - Lesson for Kids
- Personification in The Highwayman
- Olaudah Equiano | Biography, Facts & Works
- Paul Laurence Dunbar Biography, Poems & Influence
- Democratic Vistas by Walt Whitman: Summary & Theme
- Hunter S. Thompson | Books, Biography & Timeline
- Jan Karon's Biography & Book Series
- Karen Cushman: Biography & Books
- The Autobiography of Alice B. Toklas by Gertrude Stein
- The Chosen by Chaim Potok | Summary, Themes & Analysis
- The Feminine Mystique by Betty Friedan | Summary & Criticism
- Harrison Bergeron Vocabulary
- Daniel Ellsberg: Biography & Book
- The Heidi Chronicles | Monologues, Characters & Analysis
Create an account to start this course today Used by over 30 million students worldwide Create an account
Explore our library of over 88,000 lessons
- Foreign Language
- Social Science
- See All College Courses
- Common Core
- High School
- See All High School Courses
- College & Career Guidance Courses
- College Placement Exams
- Entrance Exams
- General Test Prep
- K-8 Courses
- Skills Courses
- Teacher Certification Exams
- See All Other Courses
- Create a Goal
- Create custom courses
- Get your questions answered

What is Creative Writing?

Written by Scott Wilson

Creative writing is any kind of writing that employs creative literary or poetic techniques in the service of either fiction or non-fiction writing. It involves original composition and expressiveness of the individual author.
Ask ten creative writing professors what creative writing is, and you’ll get eleven different answers. Turn to the dictionary and the definition invokes invention and incorporation of imagination. But what are the limits of imagination? Where does invention begin?
Every sentence in every work ever written began as an act of creation in the mind of the writer.
Creative writing may be most easily defined by what it is not…
- Technical writing
- Professional or business writing
- Scholarly or academic writing
Creative writing is the entire body of the writer’s craft that falls outside the boundaries of the ordinary.
Yet you will find many entries in the canon of those fields that might also be considered creative writing. No one would consign Truman Capote’s groundbreaking In Cold Blood to the sterile cells of mere journalism. But that haunting novel is unquestionably also an important work of investigative reporting.
So, what is creative writing, if a non-fiction novel of a horrific quadruple murder falls into the same scope as a classic of American literature like To Kill a Mockingbird ?
It has to do with style and art. Creative writing goes to the heart of the individual expressiveness of the writer. It breaks the boundaries of the typical. That’s an exercise of artistic skill that can happen in any topic, toward almost any goal. And it’s the heart of what it is to be a writer, no matter what you write about.
Defining creative writing isn’t easy. Rooms full of the best authorities routinely disagree. But what is creative writing , isn’t the most interesting question to ask here. Instead, we would be best served by asking another:
Why Is Creative Writing Important?

Storytellers were plying their craft thousands of years before the written word was invented. The creative spark doesn’t belong to words. It may not even depend on language. It draws instead on a deep part of what it is to be human. Invention, imagination, the urge to create… these are all deep and vital parts of the human experience.
Creative writing is important because it is evocative.
That well of creativity flows forth in many arts and forms of expression. But in creative writing it has found a medium where it can be both preserved and shared. It’s a method of human connection that has no expiration date, no geographical or even cultural limit.
Writers touch the souls of their contemporaries first. But like Shakespeare, Wordsworth, and Lady Murasaki, their reach may also span generations.
Creative Writing Fuels Communication in All Forms of Writing
Although fiction is the first refuge of creative writing, that expressiveness serves the purposes of just about any kind of author.
The goals of most other forms of writing are focused on various kinds of literal communication. A journalist seeks to convey the facts and the context of important news stories. Technical writers need to communicate the details of operating programs and machinery, clearly describing all kinds of minute details with zero ambiguity. Business communications are created with a view toward clarity and concision—helping readers get the main points of the piece quickly and without confusion.
Creative writing can also help to serve these purposes.
Creative writing taps into a different level of communication. While it may, and often does, aspire to other goals like offering clarity and detail, it also goes toward developing emotional connection. The reader will take away more than mere words from a piece of creative writing.
Creative Writing is Important For Making Other Kinds of Writing Compelling
Just as importantly, creative writing entertains. In a story about the importance of algorithmic and high-frequency trading, all kinds of technical details must be absorbed to make sense of the issues. Both technological and economic concepts have to be introduced. In a comprehensive article about the subject, readers from outside the field could be expected to nod off about two pages in.
But put the story in the hands of Michael Lewis, and you get Flash Boys , a New York Times Best Seller.
It’s not important that Flash Boys did well because it was entertaining, however. It’s important because the market trends and activities it described have real impacts on many of the readers. Retirement funds, college savings, family investments… all are affected by the story Flash Boys tells. Today, millions of readers who would never otherwise have understood how their investments were being handled can make an informed assessment… thanks to creative writing.
How To Separate Creative Writing From Less Creative Forms of Writing

In general, it’s safe to say that a piece of writing is creative when it makes use of literary devices such as:
- Narrative development
- Imagination and invention
In Cold Blood passes this test due to Capote’s use of characterization, plot development, and world-building. It’s considered today to be a pioneering example of the non-fiction novel, a paragon of the creative writing world.
The original crime reports, local newspaper articles, and subsequent court documents detail the same events with the same participants. Yet they are not works of creative writing. The incident is described in dry, straightforward, technical language. The timeline is linear and offered without consideration of pace or drama.
Both Capote and the authors of those other articles and documents set out to inform. But Capote’s goal was also to captivate.
New Journalism Tells the Story of How Creative Writing Has an Important Role in Non-Fiction

Books like Wolfe’s The Right Stuff mixed truth and dramatization, documentation and invention, to tell larger stories about serious events. In dramatizing those stories, New Journalism writers also drew more readers and achieved broader awareness of the stories.
At the same time, long-form New Journalism pieces, deeply researched and documented, were able to report stories in depth in a way that traditional journalism often did not. By invoking plot, characterization, and narrative structures, the New Journalists could keep readers involved in long and complex issues ranging from crime to politics to culture.
New Journalism is important in defining what is creative writing because it is clearly an example of both creative and journalistic writing. It demonstrates the ways that creative writing can serve other forms of writing and other kinds of writers.
Of course, it’s also possible to come at the divide from the other shore. Categories of writing that are clearly creative in nature include:
- Novels and novellas
- Flash fiction and short stories
- Plays and film scripts
These works incorporate elements of storytelling that may not always be present in other forms of writing. A newspaper article will often have a setting, action, and characters; creative writing will offer plot, pacing, and drama in describing the same story.
What is Creative Writing Coursework Like in College Degree Programs?

All university students are exposed to basic coursework in English language and communication skills. These all go to the elementary aspects of writing—the ability to construct a sentence, a paragraph, a paper. They teach grammatical rules and other elements that make a work readable to any reader of the English language.
Even the general education requirements in college programs touch on creative writing, however. Students may be assigned to write essays that explore creative styles and imagination. They’ll be assigned to read novels and stories that are time-tested examples of the finest kinds of creative writing. And they’ll be asked to explore their impressions and feelings, and to exercise their imaginations and analyze the intent of the author.
Creative writing programs go beyond the basics to touch the imagination of the writer.
Creative writing exists just on the other side of those general English and literature courses. Students in creative writing classes will be asked to take the extra step of creating their own stories using the techniques they have learned.
In fact, they may be encouraged to break the same rules that were so laboriously learned in their regular English writing classes. Creative writing works to allow writers to tap into their own imagination and emotion to forge a deeper connection with readers.
Student Workshops Offer an Interactive Way of Learning What Creative Writing Is All About
Creative writing degrees will go much further into developing a sense of what creative writing is. they continue to include many reading assignments. but instructors also introduce concepts such as:.
Genre is the method used to categorize written works. Creative writing programs explore the tropes and expectations that exist for different genres and deconstruct them for better understanding.
Story structure and form
The structure and form of a novel and a short story are very different. Creative writing programs explore different formats and how they impact creative storytelling.
Plot is not a universal feature of creative writing, but a good plot can make or break a creative work. Classes look at the features and composition of plot, and also teach plotting.
Voice, tone, and creative expression all come out of the narration of a piece of creative writing. Creative writing courses explore both the textbook forms of narrative and show how to use it to serve plot and story.
Style and rhythm
One clear feature of creative writing in all genres is that it rests on a sense of rhythm and of styling that other types of writing ignore. Many courses found in creative writing degree programs explore the ways in which writing style serves story and hooks the reader.
In addition to formal classes, students will better learn why creative writing is important and the purposes it serves through workshops. These informal gatherings are designed to foster discussion, to present examples of different types of writing, and to critique and hone individual creative writing skills .
Through that process, creative writing degrees help students better identify what creative writing is and how to use it effectively.
Creativity is Important No Matter What Your Career Goals in Writing May Be

Creative writing training allows writers in any genre to develop more complete, more meaningful, and more memorable ways to get a point across. Using the skills and techniques learned in creative writing courses can inject humor, gravity, and other sensations into any piece of writing. And those very techniques can improve concision and clarity.
Figuring out what creative writing is and what it is not, is the first thing you should leave behind in a writing career. The dry definitions of the dictionary or droning English professors are the last place you should look.
Creative writing is the process of engaging your imagination and talent to serve the purpose of whatever piece of writing you are working on. And that’s why creative writing is important.
A Look Into Creative Writing | Oxford Summer Courses
Exploring the magic of creative writing with oxford summer courses.
Subscribe to our newsletter to receive helpful tips, tutorials, and thought-provoking articles that can inform and inspire your professional development. Sign up here .
Defining Creative Writing
Creative writing , as taught at Oxford Summer Courses, is the process of crafting original and imaginative works of literature, poetry, prose, or scripts. It transcends conventional writing, encouraging individuals to explore language, structure, and narrative. Whether it's a heartfelt poem, a captivating short story, or a thought-provoking novel, creative writing allows us to communicate our unique perspectives and experiences with the world.
The Magic of Imagination
Creative Writing is a catalyst that sparks our creativity and empowers us to breathe life into our ideas on the page. With Oxford Summer Courses, aspiring writers aged 16-24 can embark on an extraordinary journey of creative expression and growth. Immerse yourself in the captivating realms of Oxford and Cambridge as you explore our inspiring creative writing programs. Teleport readers to distant lands, realms of fantasy and creation, introduce them to captivating characters, and craft new worlds through the transformative art of storytelling. Discover more about our creative writing course here . Unleash your imagination and unlock the writer within.
What Are the Different Types of Creative Writing?
Creative Writing comes in many forms, encompassing a range of genres and styles. There are lots of different types of Creative Writing, which can be categorised as fiction or non-fiction. Some of the most popular being:
- Biographies
- Fiction: novels, novellas, short stories, etc.
- Poetry and Spoken word
- Playwriting/Scriptwriting
- Personal essays
At Oxford Summer Courses, students have the opportunity to delve into these various types of Creative Writing during the Summer School.
The Benefits of Creative Writing with Oxford Summer Courses
Engaging in Creative Writing with Oxford Summer Courses offers numerous benefits beyond self-expression. By joining our dedicated Creative Writing summer school programme, you would:
- Foster self-discovery and gain a deeper understanding of your thoughts, emotions, and personal experiences.
- Improve your communication skills, honing your ability to express yourself effectively and engage readers through refined language and storytelling abilities.
- Enhance empathy by exploring diverse perspectives and stepping into the shoes of different characters, broadening your understanding of the world around you.
- Gain new skills for further education or work, expanding your repertoire of writing techniques and abilities to enhance your academic or professional pursuits.
- Nurture your creativity, encouraging you to think outside the box, embrace unconventional ideas, and challenge the status quo, fostering a life-long mindset of innovation and originality.
Embracing the Journey
To embark on a journey of creative writing, embrace curiosity, take risks, and surrender to the flow of imagination. Write regularly, read widely, embrace feedback from tutors and peers at Oxford Summer Courses. Begin to experiment with styles and genres, and stay persistent in your course of action. The path of creative writing requires dedication, practice, and an open mind. Join us as we provide tips to help you start your creative writing journey and unleash your full creative potential under the guidance of industry professionals.
Creative Writing is a remarkable voyage that invites us to unleash our imagination, share our stories, and inspire others. It offers countless personal and professional benefits, nurturing self-expression, empathy, and creativity. So, grab a pen, open your mind, and embark on this enchanting journey of creative writing with Oxford Summer Courses. Let your words paint a vivid tapestry that captivates hearts and minds under the guidance of experienced tutors from Oxford and Cambridge. Join us as we explore the magic of creative writing and discover the transformative power it holds within through the renowned Oxford Summer Courses summer school.
Ready to study Creative Writing? Apply now to Oxford Summer Courses and join a community of motivated learners from around the world. Apply here .
Share this article
Discover the enchantment of creative writing with Oxford Summer Courses. Unleash your imagination, explore different genres, and enhance your communication skills. Nurture self-expression, empathy, and creativity while gaining valuable writing techniques.
Get Our Newsletter
Oxford Summer Courses LTD
18 Beaumont Street, Oxford, OX1 2NA, United Kingdom
+44 01865 818403

Juniors 9-12
Oxford 13-15
Oxford 16-17
Oxford 18-24
Cambridge 13-15
Cambridge 16-17
Advanced Cambridge 18-24
GDPR Notice
Privacy Policy
Terms and Conditions
Sign up to our newsletter
Oxford summer courses is an organisation which contracts with the colleges of the universities of oxford, cambridge and london for the use of facilities, but which has no formal connection with the universities of oxford, cambridge and london., oxford summer courses © 2024, oxford summer courses is a company registered in england and wales with company number 08011543.
Home › Study Tips › Creative Writing Resources For Secondary School Students
What Is Creative Writing? Is It Worth Studying?
- Published October 31, 2022

Table of Contents
As loose as the definition of Creative Writing is, it’s not always easy to understand. Sure, writing a story is Creative Writing. What about poems or personal essays?
Also, how does Creative Writing even help one succeed in university and career life? We empower our Creative Writing summer school students to grasp the power of creative writing and how to use it.
How? By giving them access to personalised tutorials with expert Creative Writing tutors from prestigious universities such as the University of Oxford and Cambridge.
Creative Writing doesn’t have to be confusing or intimidating. In this article, we’ll take you through a simple explanation of what Creative Writing is and why it’s helpful and relevant.
What is Creative Writing?
The simplest description of Creative Writing is what it’s not: it doesn’t revolve around facts like technical writing.
Technical Writing vs Creative Writing
You encounter technical writing in your daily life. You’ll find it in newspapers, journal articles, and textbooks. Do you notice how the presentation of accurate information is necessary in each of these mediums?
Because the goal of technical writing is to explain or relay information as it is .
But in creative writing, such is not the case. The primary goal of Creative Writing is not to present complex information for the sake of educating the audience.
Instead, the goal is to express yourself. Should you want to share information via Creative Writing, the objective becomes persuading your readers to think about it as you do.
Hence, if you contrast Technical Writing and Creative Writing within this context,
- Technical Writing: share information without biases
- Creative Writing: self-expression of how one feels or thinks about said information.
If reducing personal opinion in Technical Writing is virtuous, in creative writing, it is criminal .
Self-Expression in Creative Writing
One must express oneself in Creative Writing to entertain, captivate, or persuade readers. Since Creative Writing involves one’s imagination and self-expression, it’s common for Creative Writers to say that they “poured a part of themselves” into their work.
What are the different ways you can express yourself in Creative Writing?
Types of Creative Writing: 2 Major Types
The two major umbrellas of Creative Writing are Creative Nonfiction and Creative Fiction.
1. Creative Nonfiction
“Nonfiction” means writing based on actual events, persons, and experiences. Some forms of creative nonfiction include:
- Personal Essay – here, the writer shares their personal thoughts, beliefs, or experiences.
- Memoir – captures the writer’s memories and experiences of a life-changing past event.
- Narrative Nonfiction – a factual event written in a story format.
2. Creative Fiction
The bulk of Creative Writing literature is found under the Creative Fiction category, such as:
- Short Story – shorter than a novel, containing only a few scenes and characters.
- Novel – a full-blown plot line with multiple scenes, characters, and subplots.
- Poem – uses specific rhythm and style to express ideas or feelings
- Play – contains dialogue and stage directions for theatre performances.
- Screenplay – script to be used for film production (e.g. movies, video games.)
In short, Creative Fiction involves stories . Do you want more specific examples of Creative Writing? Then, you may want to read this article called “Creative Writing Examples.”
Why Is It Important to Learn Creative Writing?
It’s essential to learn Creative Writing because of the following reasons:
1. Creative Writing is a valuable skill in school and work
As a student, you know well why Creative Writing is important. You submit written work in various situations, such as writing essays for assignments and exams. Or when you have to write a Personal Statement to apply for University.
In these situations, your chances of getting higher grades depend on your ability to write creatively. (Even your chances of getting accepted into a top ranked creative writing university of your dreams!)
What about when you graduate? Do you use Creative Writing in your career? Convincing a recruiter to hire you via cover letters is an example of creative writing.
Once you’re hired, you’ll find that you need to write something up. It depends on your line of work and how often and complex your writing should be.
But mundane tasks such as writing an email response, coming up with a newsletter, or making a PowerPoint presentation involve creative writing.
So when you’ve practised your Creative Writing skills, you’ll find these tasks manageable. Even enjoyable! If you want to study creative writing at university, we put together what a-levels you need for creative writing .
2. Creative Writing enhances several essential skills.
Do you know that writing is thinking? At least that’s what the American Historian and two-time winner of the Pulitzer Prize, David McCullough said.
Many people find Creative Writing challenging because it requires a combination of the following skills:
- Observation
- Critical thinking and analysis
- Reasoning skills
- Communication
Many of these skills make you a valuable employee in many industries. In fact, Forbes reports that:
- Critical Thinking
- and Emotional Intelligence
are three of the Top 10 most in-demand skills for the next decade. That’s why Creative Writing is a valuable endeavour and if you take it at university there are some great creative writing degree career prospects .
3. Creative Writing Is Therapeutic
Do you know that Creative Writing has a significant beneficial effect on your mental and emotional health?
A 2021 study in the Counselling & Psychotherapy Research reports that Creative Writing brought significant health benefits to nine people who worked in creative industries. Writing helped them in their cognitive processing of emotional difficulty.
Result? Improved mood and mental well-being.
A plethora of studies over the decades found the same results. Expressing yourself via creative writing, especially by writing in your daily journal, is beneficial for your mental and emotional health.
4. You may want to work in a Creative Writing-related Career
Creative employment in the UK grows 2x faster than the rest of the economy. In fact, did you know that jobs in the creative industry grew by 30.6% from 2011 to 2018?
Compare that to the average UK growth of 10.1% during the same period, and you can see the potential.
How about in the US? The Bureau of Labor Statistics estimates a 4% increase in employment for authors and writers from 2021 to 2031. Resulting in about 15,200 job openings yearly over the next 10 years.
The median yearly salary? It was at $69,510 as of May 2021.
So if you’re considering a Creative Writing career, now would be a great time to do so!
How To Be A Creative Writer?
You want to be a Creative Writer but don’t know where to start. Don’t worry! The best way to start is to learn from Creative Writing experts .
That’s why we ensure our Creative Writing summer school students have access to 1:1 personalised tutorials with expert Creative Writing tutors.
Our Creative Writing tutors come from world-renowned universities such as the University of Cambridge and Oxford. So you’re in excellent hands!
Here you’ll learn creative writing tips and techniques , such as character creation and plot mapping. But the best part is, you’ll come out of the course having experienced what a Creative Writer is like!
Because by then, you’ll have a Written Portfolio to show for your efforts. Which you presented to your tutor and peers for receiving constructive feedback.
Another surefire way to start becoming a Creative Writer is by practising. Check out this article called “ Creative Writing Exercises .” You’ll begin building a writing routine if you practice these exercises daily.
And trust us, every great writer has a solid writing routine!
Creative Writing is a form of self-expression that allows you to use your imagination and creativity. It can be in the form of personal essays, short stories, or poems. It is often used as an outlet for emotions and experiences. Start with creative writing by reading through creative writing examples to help get you in the mood. Then, just let the words flow daily, and you’re on the road to becoming an excellent Creative Writer!
Related Content
Immerse education: is london the ideal study destination for you.
As a lifelong literature enthusiast, I decided to challenge myself in 2010 by participating in NaNoWriMo (National Novel Writing Month), which tasks participants with writing a 50,000-word draft within a month. Although I’ve only achieved this goal twice since then, the experience has been invaluable. I’ve connected with a wonderful community of writers, both online and in person.
Through my experience, I can confidently say that creative writing is a skill that can be developed and honed, just like any other. While traditionally associated with literature, creative writing is increasingly being recognized as a powerful tool in various forms of writing, from copywriting and storytelling to novels and poetry. It has the ability to captivate readers and elevate the impact of written expression.

If you’re searching for the best online Creative Writing courses and resources, you’ve come to the right place. This Best Courses Guide (BCG) is built from Class Central’s catalog of over 300 Creative Writing courses and selected according to a methodology that you can check below.
Click on the shortcuts for more details:
What is Creative Writing?
Courses overview, why you should trust us, how we made our picks and tested them, here are our top picks.
Click on one to skip to the course details:
| 15 hours | |
| 5-6 hours | |
| 4-5 hours | |
| 12 hours | |
| 1-2 hours | |
| 2 hours | |
| 5-6 hours | |
| 1-2 hours | |
| 1 hour | |
| 18 hours | |
| NA |

Related Guides
- Copywriting
- Content Marketing
- 2D Animation
- Digital Art
Special Picks
- Fashion Design
- Music Theory
- Emotional Intelligence
Trending Guides
- Design Thinking
- Graphic Design
- American Sign Language (ASL)
Creative writing is a genre of writing that seeks to evoke emotions and feelings in its readers. It surpasses the limits of traditional forms of literature and emphasizes narrative craft, character development, and the use of literary tropes and poetic traditions. Creative writing finds application in various forms of writing, including screenplays, plays, novels, poems, and other written works. In this guide, I will delve into some of its most popular facets.
Enhancing resilience and creativity through writing
Research shows that the brains of professional writers work differently from those of novice writers. Moreover, creative writing has been found to boost resilience in students . If you want to enjoy the benefits of writing, it’s important to develop the habit of jotting down your thoughts and words. Doing so can help you overcome writer’s block.
Creative writing is so powerful that it’s used in prisons to give inmates a chance to express themselves in programs like PEN America . “By providing resources, mentorship, and audiences outside the walls, we help these writers to join and enrich the broader literary community.”
Creative writing is a skill that can be learned and practiced like any other. Techniques such as ABDCE structure, 1st or 3rd person point of view, “show don’t tell”, dialogues, and tropes can be easily learned through the online courses in this guide.
- Together, they account for over 1M enrollments
- Skillshare, with 2 courses, is the most featured provider
- The single most popular course has nearly 400k enrollments
- Three courses are entirely free or free-to-audit.
Best Fantasy And Short-Stories Writing Lessons For Beginners (Brandon Sanderson)
Besides being an awesome writer, Sanderson is an instructor with a very unique talent for keeping us engaged. He has also made available a full course in creative writing on YouTube , originally presented at Brigham Young University, which includes the most crucial tools for any beginner or even experienced writers. The course is comprehensive and rich in content, with great sound and video quality.
Each video discusses a specific tool or technique, so you can easily select the theme you want to explore next or watch it all in sequence. It’s up to you. I recommend you take your time, watch one video at a time and experiment with each concept, or even better, find a writing buddy or form a group to practice writing together.
What you’ll learn:
- Plot construction, character development, and engaging storytelling
- Techniques for crafting immersive worlds and believable viewpoints
- Insights into the publishing industry, tailored for emerging writers
- Strategies for writing compelling short stories and leveraging them for larger projects.
“Very informative! I’m a beginner writer looking to study writing for video games, and this class gave me a lot of helpful tools to start understanding how stories work/how to organize my ideas! Will definitely be returning to some of these lectures in the future for guidance 👍” – Paige Webster
| Brigham Young University | |
| Youtube | |
| Brandon Sanderson | |
| Beginner | |
| 15 hours | |
| 1.8M | |
| 5/5 (6 reviews) | |
| None |
Best University-level Creative Writing Course (Wesleyan University)

Creative Writing by Wesleyan University is a specialization for those looking for a way to improve their writing structure, scene and character creations and finding your style. Each course includes writing practice (for paying learners) and insightful interviews. It’s worth your time and effort if you are a disorganized writer like myself.
- Techniques for crafting a bracing story with memorable characters and an interesting setting
- How to employ a fresh descriptive style in your writing
- Skills for analyzing and constructively evaluating peer writing
- The ability to refine your writing, critique writing in general, and draw inspiration from existing literature
- The process of drafting, rewriting, and completing an original story in the genre of your choosing.
It should be noted that the peer-grading system often lacks depth. However, the assignments are well-crafted and can be easily evaluated with minimal effort, providing some insights from other participants in the form of feedback or inspiration from their submissions.
“Great information about plot and scene structure. The information about revision was entirely new to me – thank you! The exercises were good and difficult in a good way that helped me hone my writing.” – Laura B, Coursera learner
| Wesleyan University | |
| Coursera | |
| Brando Skyhorse, Amity Gaige, Amy Bloom and Salvatore Scibona | |
| Beginner | |
| 40 hours | |
| 126K | |
| 4.7 (5K) | |
| Yes, paid |
Best Course to Find Your Voice (Neil Gaiman)
Neil Gaiman is currently one the most prolific writers I know of: he’s written books , comics , movies and even TV shows . Even if you’re not a fan of his style, there is definitely something you can learn from him.
In Neil Gaiman Teaches The Art Of Storytelling you will discover Neil’s philosophy on what drives a story and learn to unlock new stories within yourself.
While MasterClass doesn’t sell single courses, a subscription provides access to their entire library, including other writing courses like Margaret Atwood Teaches Creative Writing , Dan Brown Teaches Writing Thrillers , Malcolm Gladwell Teaches Writing , and James Patterson Teaches Writing . If you are considering the purchase, you should definitely enjoy the rest of their catalog.
By the end of this course, you will be able to:
- Discover and develop your unique writing voice
- Generate and develop original ideas
- Create dynamic, well-rounded characters that come to life on the page.
This course includes a 94-page workbook that includes assignments and supplemental material.
| MasterClass | |
| Neil Gaiman | |
| Beginner | |
| 4-5 hours worth of lectures | |
| Paid Certificate Available |
Best Practical Writing Course With Support (Trace Crawford)

I love it when a passionate teacher like Trace Crawford puts the effort into creating a comprehensive curriculum. COMPLETE Creative Writing – All Genres is a 12-hour course with 145 downloadable resources. In this course, you will learn how to write engaging fiction, poetry, drama, and creative non-fiction, helping you become the successful writer you want to be.
- The four genres of creative writing: fiction, poetry, drama, and creative non-fiction
- How to discover, refine, and share your unique writing voice
- A series of authentic writing assignments designed to target the skills you need to develop
- Writing techniques, literary devices, and specialized skills to enhance your writing
- Opportunities for publishing, podcasts, and how to create a professional creative writing portfolio
- Discover multiple public outlets to share your writing with others as you gain confidence and experience success in your writing ability.
This is a practical creative writing course that includes assignments reviewed by the instructor, though response time may vary.
“The short snippets of theory in combination with the short assignments suits my learning style. I don’t remember the last time I’ve written anything creative, but this course gave me the incentive to set some foundation and its actually quite enjoyable if you stick to it.” – Nikolaos-Stylianos Z., Udemy learner
| Udemy | |
| Trace Crawford | |
| Beginner | |
| 12 hours | |
| 37 quizzes and writing practice | |
| 31K | |
| 4.7 (3.9K) | |
| Available, paid |
Best Course to Overcome Writer’s Block: 10-Day Journaling Challenge (Emily Gould)
I couldn’t resist adding Creative Writing for All: A 10-Day Journaling Challenge to this guide. Emily Gould is a delightful instructor, and her approach to inviting you to participate in the challenge is impossible to decline. It’s the perfect course to overcome writer’s block, which is exactly what she proposes. In this 10-day creative writing challenge, filled with inspiring examples, observation prompts, and clever revision tricks, writers and enthusiasts will be able to express their creativity in a personal and artful way.
This course is the shortest one on the list, and it’s more about the challenge of keeping a journal. If you decide to subscribe to Skillshare, you can also enjoy their entire library of courses. In addition to the other two recommended courses on this list, you can also check out these other Skillshare courses: Writing Suspense: How to Write Stories That Thrill in Any Genre and The Writer’s Toolkit: 6 Steps to a Successful Writing Habit .
| Skillshare | |
| Emily Gould | |
| Beginner | |
| 26 min | |
| 58K | |
| 99% (1K) | |
| Available, paid |
Best Course to Create Fiction From Personal Experience (Shaun Levin)

Shaun’s approach to writing in Short Story Writing: Create Fiction from Personal Experience is an unusual one. It draws from your personal experience to create a compelling fictional story. I can say from experience that this technique will help you write with more depth and authenticity. Every time we bring our own life to the story, it becomes alive, believable and relatable. In a way, all fictional stories are based on the author’s life.
This course will help you with techniques and a series of practical exercises to start writing your scenes from a more philosophical point of view, creating compelling stories. You’ll learn how to delve into your imagination to find everything you’ll need to become a prolific writer, no matter where you are.
By the end of the course, you will have a final project that will receive feedback from Shaun and other learners as well. Actually, if you want to check it out, in the course page on Domestika you can open the submitted projects and read the comments.
Shaun’s other courses: Creative Writing for Beginners: Bringing Your Story to Life .
“A practical course. Shaun Levin talks about theory but also demonstrates his process, which was invaluable. The exercises got my creative juices flowing. Thinking about doing his other course in the future.” – Maya Dicheva
| Domestika | |
| Shaun Levin | |
| Beginner | |
| 2 hours | |
| 30K | |
| 99% (764) | |
| Available, paid |
Best Course to Make Writing Less Stressful with Best Practices (Jennie Nash)
If you struggle to start or get stuck in your writing, Write Your Book: Start Strong and Get It Done can help. With good advice and emotional support, you’ll learn techniques to make writing less stressful. The accompanying workbook guides you to think methodically by asking the right questions to keep you focused on your story and not chasing your own tail.
In this class, you’ll learn how to:
- Design every element of your novel or memoir, including the protagonist, plot, story structure and a project success plan
- Define your narrator’s voice
- Determine where your story begins and where it ends
- Decide what point you’re making about human nature
- Make sure you’re giving your ideal reader exactly what they want
- Gain the confidence you need to push past any doubts and finish your book.
This course is more of a masterclass, so there are no assignments included but it teaches good practices and provides a very useful workbook.
| CreativeLive | |
| Jennie Nash | |
| Beginner | |
| 5-6 hours | |
| 18.8K | |
| 100% (29) | |
| None |
Best Course to Create A Compelling Story (Lisa Cron)

Writing: The Craft of Story is a series of well-produced lectures covering the basic building blocks of a story. Taught by author Lisa Cron, you will learn how to create compelling stories based on the way the brain responds to storytelling. This course emphasizes the importance of capturing the reader’s attention through techniques such as suspense, exploring the protagonist’s inner issues and dreams, specificity, and cause and effect. Upon completion of the quizzes, you will receive a certificate for your LinkedIn profile. Additionally, you can watch all the videos without subscribing to the course.
“Learning the fundamentals of crafting a story was and is a fascinating experience. And yes, I would highly recommend writing to anyone interested in learning how to express the communication of feeling.” – Nicole Gillard, LinkedIn learner.
| LinkedIn Learning | |
| Lisa Cron | |
| Beginner | |
| 1-2 hours worth of material | |
| 100K | |
| 4.7 (649) | |
| Available, paid |
Best Course to Write Personal Essays with Impact (Roxane Gay)
Discover the art of crafting powerful personal essays with best-selling author Roxane Gay in her course, Creative Writing: Crafting Personal Essays with Impact . Through her honest and thoughtful approach, Roxane will help you find your story, craft your truth, and write to make a difference.
This master class offers eight video lessons that are filled with practical guidance, actionable tactics, and example essays to guide you from the first idea to a final, publication-ready work.
You’ll learn how to:
- Find a specific purpose for telling your story
- Connect your work to larger conversations and timely themes
- Conduct crucial research to support your work
- Navigate personal memories to write your truth
- Write and revise your final work, and submit your work for publication.
Additionally, the class provides a downloadable worksheet to support your ongoing creative nonfiction writing practice, as well as links to additional resources.
If you enjoy creative nonfiction writing, you might consider this course that’s also on Skillshare: Creative Nonfiction: Write Truth with Style (Skillshare Original) by Susan Orlean
| Skillshare | |
| Roxane Gay | |
| Beginner | |
| 1 hour | |
| 45K | |
| 100% (1.2K) | |
| Available, paid. |
Best Course to Develop Your Ideas And Research for Characters (The Open University)

Start Writing Fiction explores the writing process, from journaling and idea development to reflection and editing. It features insights from established writers such as Louis de Bernières, Patricia Duncker, Alex Garland, Abdulrazak Gurnah, Tim Pears, Michèle Roberts, and Monique Roffey, who share their approaches to research and turning events into plot. Led by Derek Neale, a novelist and short story writer, this course provides a comprehensive understanding of the writing rituals and techniques used by successful writers.
You’ll get to critique the work of other writers and receive feedback. This course is designed for individuals interested in starting or improving their fiction writing and does not require prior experience in the subject.
You’ll learn:
- Creation of characters in fiction
- Different sources and ways of presenting characters in stories
- Reading as a writer
- Writing practice including creativity, research, observation and editing
- Peer reviewing, workshops and the importance of feedback.
“This course takes learners through many aspects of writing such as developing characters, observing and describing details, finding inspiration, writing and editing. It includes some peer reviews which can be varying in quality. I was lucky enough to have some of my writing reviewed by a reviewer who gave very helpful and positive feedback.” – Pat Bowden
| The Open University | |
| Future Learn | |
| Derek Neale | |
| Beginner | |
| 24 hours | |
| 389,780 learners | |
| 4.7 (923) | |
| Available, paid |
What’s Next
Scribophile is one of the largest online writing communities. You can get feedback on your writing and join writing groups. If you decide to join with a free plan, you need to collect points by reviewing other writers’ work before submitting your own work for review. They also developed some advanced tools for evaluating work and guidelines to make sure you give/receive feedback that is actually meaningful.
NaNoWriMo started out as a month-long challenge where you invite your friends and join other writers in your region, be it online in their forums or in person, to challenge yourself in writing your first draft. Nowadays, they run all-year round writing challenges (but November is still the biggest one in terms of participation). What is cool about it is you actually get to meet people in real life with various writing skills and backgrounds. I was able to make some great friends over the years and even met a few professional writers that decided to join our local group just to support us.
If you have any resources you would like to have added here, leave a comment below.
Class Central , a Tripadvisor for online education, has helped 60 million learners find their next course. We’ve been combing through online education for more than a decade to aggregate a catalog of 200,000 online courses and 200,000 reviews written by our users. And we’re online learners ourselves: combined, the Class Central team has completed over 400 online courses, including online degrees.
Trying to find “the best” can be daunting, even for those of us who live and breathe online courses. Here’s how I approached this task.
First, I combed through Class Central’s Catalog and the internet to find a variety of free and paid open courses, some with certificates. You don’t need to enroll in a university to learn about creative writing.
When choosing courses, I considered the following factors:
- Renowned Institutions : I looked for recognized institutions in creative writing
- Instructor experience : I sought instructors with extensive experience in creative writing and engaging presentation styles
- Popularity : I checked numbers of enrollments and views to find popular courses
- Course content : I examined courses that covered a range of topics and presentation styles, including the basics and more advanced topics. I watched some course videos to sample courses I hadn’t already taken
- Learner reviews : I read learner reviews (when available) to get a sense of the quality of each course, leveraging the Class Central database with its thousands of course ratings and reviews written by our users as well as available course provider reviews.
Then, I defined the scope for these recommendations. A creative writing course can cover various topics, so I chose top courses from a range of sub-fields.
Ultimately, I used a combination of data and my own judgment to make these picks. I’m confident these recommendations will be a reliable way to learn about creative writing.

Fabio Dantas
Leave a reply.
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .
Browse our catalog
Discover thousands of free online courses from top universities around the world like MIT, Stanford, and Harvard.
Computer Science 13,163 courses
- Artificial Intelligence
- Algorithms and Data Structures
- Internet of Things
- Information Technology
- Computer Networking
- Machine Learning
- Deep Learning
- Cryptography
- Quantum Computing
- Human-Computer Interaction (HCI)
- Distributed Systems
- Blockchain Development
- Operating Systems
- Computer Graphics
- Automata Theory
- Digital Image Processing
- CSS Animation
- Morph Transition
Business 21,411 courses
- Management & Leadership
- Entrepreneurship
- Strategic Management
- Industry Specific
- Business Intelligence
- Human Resources
- Project Management
- Business Software
- Customer Service
- Nonprofit Management
- Operations Management
- Corporate Governance
- Business Plan
- Business Proposal
- Management Consulting
- Business Math
Humanities 8,297 courses
- Grammar & Writing
- Linguistics
- Library Science
- Crisis Management
- Emergency Management
- Language Arts
Data Science 4,785 courses
- Bioinformatics
- Data Mining
- Data Visualization
- Jupyter Notebooks
- Process Mining
- Text Mining
- Topological Data Analysis
Personal Development 5,700 courses
- Communication Skills
- Career Development
- Self Improvement
- Presentation Skills
- Self-Acceptance
- Mental Toughness
- Self-Doubt Management
- Personal Empowerment
- Habit Tracking
Art & Design 20,635 courses
- Digital Media
- Visual Arts
- Design & Creativity
- Art Therapy
- Art Composition
Jump to navigation Skip to content
Search form
- P&W on Facebook
- P&W on Twitter
- P&W on Instagram
Find details about every creative writing competition—including poetry contests, short story competitions, essay contests, awards for novels, grants for translators, and more—that we’ve published in the Grants & Awards section of Poets & Writers Magazine during the past year. We carefully review the practices and policies of each contest before including it in the Writing Contests database, the most trusted resource for legitimate writing contests available anywhere.
Find a home for your poems, stories, essays, and reviews by researching the publications vetted by our editorial staff. In the Literary Magazines database you’ll find editorial policies, submission guidelines, contact information—everything you need to know before submitting your work to the publications that share your vision for your work.
Whether you’re pursuing the publication of your first book or your fifth, use the Small Presses database to research potential publishers, including submission guidelines, tips from the editors, contact information, and more.
Research more than one hundred agents who represent poets, fiction writers, and creative nonfiction writers, plus details about the kinds of books they’re interested in representing, their clients, and the best way to contact them.
Every week a new publishing professional shares advice, anecdotes, insights, and new ways of thinking about writing and the business of books.
Find publishers ready to read your work now with our Open Reading Periods page, a continually updated resource listing all the literary magazines and small presses currently open for submissions.
Since our founding in 1970, Poets & Writers has served as an information clearinghouse of all matters related to writing. While the range of inquiries has been broad, common themes have emerged over time. Our Top Topics for Writers addresses the most popular and pressing issues, including literary agents, copyright, MFA programs, and self-publishing.
Our series of subject-based handbooks (PDF format; $4.99 each) provide information and advice from authors, literary agents, editors, and publishers. Now available: The Poets & Writers Guide to Publicity and Promotion, The Poets & Writers Guide to the Book Deal, The Poets & Writers Guide to Literary Agents, The Poets & Writers Guide to MFA Programs, and The Poets & Writers Guide to Writing Contests.
Find a home for your work by consulting our searchable databases of writing contests, literary magazines, small presses, literary agents, and more.

Poets & Writers lists readings, workshops, and other literary events held in cities across the country. Whether you are an author on book tour or the curator of a reading series, the Literary Events Calendar can help you find your audience.
Get the Word Out is a new publicity incubator for debut fiction writers and poets.
Research newspapers, magazines, websites, and other publications that consistently publish book reviews using the Review Outlets database, which includes information about publishing schedules, submission guidelines, fees, and more.
Well over ten thousand poets and writers maintain listings in this essential resource for writers interested in connecting with their peers, as well as editors, agents, and reading series coordinators looking for authors. Apply today to join the growing community of writers who stay in touch and informed using the Poets & Writers Directory.
Let the world know about your work by posting your events on our literary events calendar, apply to be included in our directory of writers, and more.

Find a writers group to join or create your own with Poets & Writers Groups. Everything you need to connect, communicate, and collaborate with other poets and writers—all in one place.
Find information about more than two hundred full- and low-residency programs in creative writing in our MFA Programs database, which includes details about deadlines, funding, class size, core faculty, and more. Also included is information about more than fifty MA and PhD programs.
Whether you are looking to meet up with fellow writers, agents, and editors, or trying to find the perfect environment to fuel your writing practice, the Conferences & Residencies is the essential resource for information about well over three hundred writing conferences, writers residencies, and literary festivals around the world.
Discover historical sites, independent bookstores, literary archives, writing centers, and writers spaces in cities across the country using the Literary Places database—the best starting point for any literary journey, whether it’s for research or inspiration.
Search for jobs in education, publishing, the arts, and more within our free, frequently updated job listings for writers and poets.
Establish new connections and enjoy the company of your peers using our searchable databases of MFA programs and writers retreats, apply to be included in our directory of writers, and more.

- Register for Classes
Each year the Readings & Workshops program provides support to hundreds of writers participating in literary readings and conducting writing workshops. Learn more about this program, our special events, projects, and supporters, and how to contact us.
The Maureen Egen Writers Exchange Award introduces emerging writers to the New York City literary community, providing them with a network for professional advancement.
Find information about how Poets & Writers provides support to hundreds of writers participating in literary readings and conducting writing workshops.

Bring the literary world to your door—at half the newsstand price. Available in print and digital editions, Poets & Writers Magazine is a must-have for writers who are serious about their craft.
View the contents and read select essays, articles, interviews, and profiles from the current issue of the award-winning Poets & Writers Magazine .
Read essays, articles, interviews, profiles, and other select content from Poets & Writers Magazine as well as Online Exclusives.
View the covers and contents of every issue of Poets & Writers Magazine , from the current edition all the way back to the first black-and-white issue in 1987.
Every day the editors of Poets & Writers Magazine scan the headlines—publishing reports, literary dispatches, academic announcements, and more—for all the news that creative writers need to know.
In our weekly series of craft essays, some of the best and brightest minds in contemporary literature explore their craft in compact form, articulating their thoughts about creative obsessions and curiosities in a working notebook of lessons about the art of writing.
The Time Is Now offers weekly writing prompts in poetry, fiction, and creative nonfiction to help you stay committed to your writing practice throughout the year. Sign up to get The Time Is Now, as well as a weekly book recommendation for guidance and inspiration, delivered to your inbox.
Every week a new author shares books, art, music, writing prompts, films—anything and everything—that has inspired and shaped the creative process.
Listen to original audio recordings of authors featured in Poets & Writers Magazine . Browse the archive of more than 400 author readings.
Ads in Poets & Writers Magazine and on pw.org are the best ways to reach a readership of serious poets and literary prose writers. Our audience trusts our editorial content and looks to it, and to relevant advertising, for information and guidance.
Start, renew, or give a subscription to Poets & Writers Magazine ; change your address; check your account; pay your bill; report a missed issue; contact us.
Peruse paid listings of writing contests, conferences, workshops, editing services, calls for submissions, and more.
Poets & Writers is pleased to provide free subscriptions to Poets & Writers Magazine to award-winning young writers and to high school creative writing teachers for use in their classrooms.
Read select articles from the award-winning magazine and consult the most comprehensive listing of literary grants and awards, deadlines, and prizewinners available in print.

- Subscribe Now
Writing Prompts & Exercises
The time is now.
The Time Is Now offers three new and original writing prompts each week to help you stay committed to your writing practice throughout the year. We also curate a list of essential books on writing —both the newly published and the classics—that we recommend for guidance and inspiration. Whether you’re struggling with writer’s block, looking for a fresh topic, or just starting to write, our archive of writing prompts has what you need. Need a starter pack? Check out our Writing Prompts for Beginners.
Tuesdays: Poetry prompts Wednesdays: Fiction prompts Thursdays: Creative nonfiction prompts
Get immediate access to more than 2,000 writing prompts with the tool below:
Attentiveness
- Printable Version
- Log in to Send
- Log in to Save

Nearly fifty years ago, the writer George Perec spent three days sitting behind a café window in Place Saint-Sulpice in Paris recording everything he saw. In his short book, An Attempt at Exhausting a Place in Paris , his observations of mundane occurrences and objects often considered unnoteworthy—passersby, cars, buses, pigeons, signs, and slogans—are documented. This week situate yourself in one spot, perhaps in your home or workplace, or in a public space like a park, busy crossroad, commercial area, library, or café. Then, jot down the objects and behavior you see, and the snippets of conversation you hear. Write a lyric essay composed of these notes, trying to avoid interpretations or analysis. Taken together, how do your observations create a portrayal of a specific time or place? Pay particular attention to how one observation might lead to another, and to potential rhythms and repetitions.
Power Couple
The 2023 thriller film Fair Play , written and directed by Chloe Domont, follows the lives of a young, newly engaged couple, Luke and Emily, who are colleagues working as analysts in the cutthroat world of high finance in New York. The film focuses on the progression of their relationship, which has been kept hidden from their hedge fund office, and the bitter disintegration of their happiness after a promotion that was initially rumored to go to Luke is unexpectedly bestowed upon Emily, which situates him as a subordinate to his wife within a misogynistic workplace. Write a short story that revolves around an occurrence that catalyzes a shift in the power dynamic between two main characters who have a close relationship. What are the initial responses, and does the transformation happen suddenly or gradually? Are there gender, generational, or other cultural issues that play a role?
Organic Insinuations
“All too often, on a ‘poetry scene,’ people prioritise ‘subject matter,’” says John Burnside in a 2023 interview about his writing process by Jesse Nathan published on McSweeney’s Internet Tendency. “I am sure that, as I am working, environmental concerns insinuate their way into the content of a poem organically, as other concerns will—but I would never start from there.” Inspired by the late Scottish poet, who died at the age of sixty-nine on May 29, write a poem that springs not from a predetermined topic or subject matter, but instead allows you to “trust in the sounds, the rhythms that come out of the day-to-day, the sheer immediacy and truth of the quotidian…and the images that lead, sometimes via fairly roundabout paths, to metaphor.” Later, as you reread and revise, what do you discover is the subject of your poem? What might have organically insinuated itself into your poem?
The maintenance or restoration of native plant and animal species has long been at the heart of many ecological and conservation projects, and has historically been a focus of land and environmental stewardship principles held by native and first peoples all over the world. But what if a beloved plant or animal is considered invasive, like the palm trees of Los Angeles or the cattle of Texas? What are the effects or consequences of centuries of existence with this invasive species in a particular locale? This week reflect on the notion of belonging—what are various places and times when you have felt a strong sense of belonging, and situations when you did not feel you belonged? Consider your own perspectives and responses when you encounter someone or something else that seems invasive or does not belong.
In Stephen King’s 1983 novel, Pet Sematary , a doctor moves into a remote house in Maine with his wife, two young children, and their pet cat, and learns from a neighbor about an ancient burial ground nearby cursed by a malevolent spirit which gave it power to reanimate those buried there. This is put to the test first by the family cat, and then by members of the family who die throughout the course of King’s horror story. While each formerly dead being is returned to the land of the living, they don’t come back quite the same. Write a story in which a creature or person returns from the dead, either in actuality or under circumstances in which their reappearance feels as if they are “back from the dead.” What familiar traits remain the same and what is disconcertingly different? Is their return ultimately for the better or the worse?
“I told a friend about a spill at the grocery store, which—the words ‘conveyor belt’ vanishing midsentence—took place on a ‘supermarket treadmill,’” writes Madeleine Schwartz in a recent essay published by New York Times Magazine about her experience of negotiating with and toggling between the French and English languages after moving from New York to Paris. In the piece, Schwartz notes that as she became more comfortable with living and thinking in French, she noticed a blurring of her linguistic capabilities, including a muddling of her articulative abilities in English. Think about a time or situation when words have failed you, or you’ve drawn a blank as to the mot juste. Write a poem that traces or enacts a loss of language, perhaps using invented words, phrases, and spellings or experimenting with font sizes, line breaks, and spacing.
Edible Memories
Many foods, flavors, and dishes hold a wellspring of emotional associations because they remind us of loved ones, habits and traditions, specific locales, and a different time of our lives when we were different people. Write a series of flash nonfiction pieces this week with each segment focusing on an edible item that evokes particularly resonant memories for you. You might begin by jotting down lists of foods you ate regularly growing up—breakfasts, school lunches, vending machine go-tos, favorite fast-food joints, diners, late night spots, home-cooked specialties—as well as a few momentous meals. Who are the people you associate with each one? Aside from taste and smell, consider the surrounding environment, atmospheric sounds, time of year, and who you were at that point in your life.
Wheels and Nails
While the American proverb “the squeaky wheel gets the grease” may be one you’ve heard time and again, often in reference to the idea that whoever raises or vocalizes a criticism the loudest will be appeased, there is a Japanese saying that translates to “the nail that sticks out gets hammered down,” which points to the positives of conformity in order to maintain a productive and humble society. It can also refer to putting someone who has become too successful back down in their place. Write a story in which your main character diverges from a group of people, and sticks their neck out, so to speak. Perhaps they vocalize a contrary perspective, protest something they feel is unjust, or simply present themselves in an unconventional manner. What are the consequences? Does your story lean toward one proverbial lesson or the other, or does the conclusion demonstrate more ambiguity?
Night at the Museum
If you could spend a night at any museum, which would you choose, and why? The French publisher Editions Stock has a series of books that begins with this premise—each author selects a museum, arrangements are made for an overnight stay, and a book is written about the experience. In Jakuta Alikavazovic’s Like a Sky Inside , translated from the French by Daniel Levin Becker, she spends a night at the Louvre in Paris, where childhood memories of visits with her father are vividly recalled. “From March 7 to 8, 2020, I spent the night in the Louvre, alone. Alone and at the same time anything but,” writes Alikavazovic. Write a poem that imagines a night at a museum of your choosing, anywhere in the world. What memories will you excavate from this imagined, solitary experience?
Chosen Family
Although the origin of the term is unknown and can be defined in many ways, a chosen family is made up of a group of people who choose to embrace, nurture, and support each other despite conventional understandings of biological or marital relationships. Oftentimes a chosen family is formed to take the place of a biological family, however, in some cases, these relationships are formed to expand a family. Write a personal essay about a relationship you have with a chosen family member. How did you first meet? Was there a particular incident that catalyzed what would become an inextricable bond? Has your commitment to each other been tested in ways big or small? Reflect on past memories and experiences you have had with this special person and how your relationship has evolved over the years.
Kingdom of the Planet
In the 1968 science fiction film Planet of the Apes , which is based on French author Pierre Boulle’s 1963 novel and has spawned several sequels and a recent reboot, a crew of astronauts crash-lands on a planet ruled by apes who have developed an advanced and hierarchical civilization, complete with systems of governance, labor, scientific research, and a military force. In this far-off place, humans have been reduced to mute primitive beings who are subjugated and kept captive as workers for the primates. Write a speculative story that takes place in another universe with a premise revolving around a role reversal. What are the rules and governing structures of the society that you invent? You might decide to approach your narrative with a tone of horror, satire, or comedy to emphasize your perspective on stereotypical assumptions and social expectations.
Another Country
“I love these raw moist dawns with / a thousand birds you hear but can’t / quite see in the mist. / My old alien body is a foreigner / struggling to get into another country. / The loon call makes me shiver. / Back at the cabin I see a book / and am not quite sure what that is.” In these eight lines that comprise Jim Harrison’s poem “Another Country,” which appears in his final collection, Dead Man’s Float (Copper Canyon Press, 2016), the late poet moves between observations about a natural outdoor setting and the speaker’s own bodily presence, arriving in the final two lines at a sentiment that expresses a feeling of defamiliarization at the seemingly mundane sight of a book. This week write a poem that explores the concept of being so absorbed in one environment or circumstance that to behold a different scene is like traveling to a strange and unknown realm.
Self-Healing
A recent study in Scientific Reports journal revealed that, for possibly the first time, a nonhuman wild animal was seen using plant medicine to heal an active wound. In a rainforest in Indonesia, a Sumatran orangutan was observed ripping off leaves from a climbing vine plant, chewing them, and applying the plant sap to treat a wound on his face, which then healed after a few days. Write a personal essay on the theme of self-healing. Think about experiences when you’ve witnessed another person perform this task, or particularly resonant memories that pertain to your own past behavior. What are the primary emotions present throughout this process? What instances of self-treatment or self-medication in film, art, or literature created an impression on you?
Campus Story
Take inspiration from the concept of a campus novel—which takes place in and around the campus of a university and often involves the intertwined dynamics of students, professors, and conventions about learning and power—and write a story that engages with a school setting, whether prominently situated in the context of the plot or used for a particular scene. Some recent additions to the campus novel canon include Elif Batuman’s The Idiot (Penguin Press, 2017), Xochitl Gonzalez’s Anita de Monte Laughs Last (Flatiron Books, 2024), Kiley Reid’s Come and Get It (G. P. Putnam’s Sons, 2024), and Brandon Taylor’s Real Life (Riverhead Books, 2020). Will you include a character who is a student, teacher, administrative staff member, custodial worker or caretaker, or possibly an alumni revisiting the past? Consider the multitude of ways the incorporation of an educational environment might permeate the atmosphere of the narrative.
The Last Friend
“The day the last friend / dies / we sit alone. / A visitor / from outer space / tries hard / to summon us. / Someone says / EAT DEATH. / I fish around for answers / but the questions / still won’t come,” writes Jerome Rothenberg, who passed away in April, in his poem “The Last Friend.” Included in his collection of one hundred poems, A Book of Witness: Spells & Gris-Gris (New Directions, 2022), the poem presents a list of statements and observations, many of which refer to death or dying in some personal way, though the connections are enigmatic and the logical progression is oblique. Try your hand at writing a poem that mentions its subject directly, but which also deliberately obfuscates or remains ambiguous in its intentions. How might using the “I” as a witness include the reader into your point of view?
Mind Your Manners
The New York City culture and news website Gothamist recently asked New Yorkers about their thoughts on sidewalk etiquette in the crowded, bustling streets of their beloved city. What are the rules, who has the right-of-way, and who should yield? Respondents focused on always walking to the right of the sidewalk and to “move quickly and never stop.” One thoughtful respondent considered the cultural differences of sidewalks used for recreational strolls versus commuting. But the overall consensus was that among nine-to-fivers, tourists, parents with kids, dogwalkers, bicyclists, and groups, seniors deserve the right-of-way. Write an essay about the unwritten rules or etiquette you have observed in your daily surroundings. How have these common practices adapted to fit the needs of different people? Do they evolve over time as social norms change? Consider some of your own experiences with how public etiquette has helped or hindered harmonious community life.
The term sub rosa means “under the rose” in Latin and refers to something said or done in private. The rose has been associated with secrecy since ancient times, a decorative symbol often carved and painted in places like meeting rooms, banquet halls, and confessionals as reminders of confidentiality. This week write a short story that revolves around a conversation or discussion that occurs sub rosa in an enclosed space. Does a certain detail get leaked out or overheard? How might the secretive nature place a burden on your characters? Consider the ways in which the atmosphere and tone of your story feel distinctive in the time and space of your sub-rosa conversation versus the scenes that take place before or after the talk.
Wisdom in Translation
In the anthology Another Room to Live In: 15 Contemporary Arab Poets (Litmus Press, 2024) edited by Omar Berrada and Sarah Riggs, multinational and multilingual poet-translators challenge foundational narratives and rework mythologies through poetic expression. Yasmine Seale’s poem “Conventional Wisdom (Arabic Saying Translated Twenty Ways)” is composed of translations of an ancient aphorism expressing the inextricable place of poetry within Arab cultural heritage. Each line presents a variation on the truism: “Poetry is the record of the Arabs / The art of poetry is Arabs, collected / Good poetry is a list of Arabs / To speak in verse is to remain in Arab memory / To surpass another poet is the Arab odyssey.” Write a poem inspired by this idea of translating a proverb or maxim—either from another language or from English into English. How might you creatively interpolate different “translations” of the saying by incorporating connotations and riffing on free associations and personal experiences?
In Response
In a recent interview with Aria Aber for the Yale Review , when asked his thoughts on the responsibility of the poet, Jackson Prize–winning poet Fady Joudah says, “I often think that the responsibility of the poet is to strive to become the memory that people may possess in the future about what it means to be human: an ever-changing constant. In poetry, the range of metaphors and topics is limited, predictable, but the styles are innumerable. Think how we read poetry from centuries ago and are no longer bothered by its outdated diction. All that remains of old poetry is the music of what it means to be human.” Write a creative nonfiction piece that presents your personal theory of the responsibility of a writer or an artist. To construct an expansive approach, you might use observations about how different creative disciplines overlap in their goals, or consider what has remained resonant as the arts make their mark throughout various eras.
Earth to You
In honor of Earth Week, write a scene that revolves around a character who experiences an unexpected moment in a natural environment that produces a sensation of wonder, perhaps an unusual encounter with wild flora or fauna. You might contrast the elements of this scene with others in your story in which the character is interacting solely with humans or only attuned to the sounds, rhythms, and sights of city life and densely packed civilization. Is the occurrence mind-bogglingly quick and then reflected upon in hindsight, or does time slow down in the scene? How do you manage or manipulate the pacing and rhythm of your prose to draw attention to the emotional and psychological response of the character?
From Dirt Level
In Sharon Olds’s poem “May 1968,” the speaker recounts the memory of spending the night with other protesting students, who lay down their bodies on a New York City street at a university’s campus gates in order to obstruct the mounted police force that had been called in. While “spine-down on the cobbles,” she observes the city and surrounding scenery—the soaring buildings and the police and horses’ bodies—as she gazes upward, thinking about the state of her pregnant body. Write a poem this week from the vantage point of lying face-up, “from dirt level.” What circumstances bring you into this position? How does this upward point of view transform what you see, and how you feel about your own body?
More, please? Or, no more, please? In The Fast: The History, Science, Philosophy, and Promise of Doing Without (Avid Reader Press, 2024), John Oakes recounts his personal experience conducting a weeklong fast and examines the practice’s history and place within a wide range of religions and philosophies. The book also explores the act of self-deprivation and the potential transformative benefits of subtracting rather than adding to one’s life. “The act of fasting…won’t stop routine, but impedes it for a bit, signifying a shift and a determined unwillingness to follow standard operating procedure,” writes Oakes. Use this idea to consider your personal relationship with consumption—of food, conversation, media, clothes, space—and write a personal essay that reflects on what you might otherwise take for granted.
All in Your Head
In “Table for One,” a short story from Korean author Yun Ko-eun’s new collection of the same name, translated by Lizzie Buehler and published by Columbia University Press in April, a surreal quality seeps into the tale of a lonely office worker who enrolls in a course to make solitary dining easier. Tips from the course include: “Target corner tables rather than those in the middle. Seats at the bar are also good. Hang your coat or bag on the chair facing you and take advantage of tools like a book, earphones, a cell phone, or a newspaper.” The fantastic element of the story lies less in the oddity of the premise than in the narrator’s meticulously recounted neuroses and detailed rendering of processes that become seemingly cyclical. Write a scene that focuses on your character’s minute observations as they attempt to overcome something debilitating. Does the situation lend itself to a quirky or dark sense of humor?
Neither Questions nor Answers
“Where is the homeland / to lay a cradle for the dead / Where is the other shore / for poetry to step across the end point / Where is the peace / that lets the days distribute blue sky...” In Sidetracks , forthcoming in May from New Directions, the Chinese poet Bei Dao begins his book-length poem with a list of twenty-five enigmatic questions that dance around mythological, philosophical, and existential subjects. In Jeffrey Yang’s translation, the speaker’s questions lack the end punctuation of the original text, with question marks omitted. Through these unanswered questions, the poet conjures loss and nostalgia. Loosely following this structure, write a prologue to a poem that poses a series of questions gesturing toward your most pressing uncertainties. While Bei Dao’s lines are mysterious and mystical, allow your poem the tone and allusions that feel instinctive to you.
With Certainty
In a 1789 letter, Benjamin Franklin wrote the phrase, “in this world nothing can be said to be certain, except death and taxes.” Franklin was reflecting on the establishment of the U.S. Constitution, which he said promised to be durable, as well as his own ailing health and mortality. This week write a personal essay that riffs off this proverb, reflecting on your own worldview about what can be certain. You might start off with the prompt: “In this world, nothing can be said to be certain, except death, taxes, and ______.” Tell the story of how you arrived at your own ideas about what you can always count on, whether good or bad. What past experiences, encounters, or memories seem to reinforce your belief?
About Our Writing Prompts
What is a writing prompt and how do you use one? Whether you find yourself in front of a blank page or stuck in a work-in-progress, writing prompts can offer a spark that ignites your creative thinking and can lead to new writing. Prompts offer guidance, fresh ideas, and direction for writers of all levels of experience. First, choose a prompt for the genre in which you’d like to write, then carefully read it and consider what it is asking you to think about. It could be a specific setting, a writing technique, or an element of an imagined character; a specific poem, story, essay, song, book, or film from which you might take inspiration; or a current event or a topical theme. A writing prompt is filled with endless possibilities—and there is no wrong way to use one to generate new writing!
What makes our writing prompts unique? We have an archive of over 2,000 prompts, all original and offered here and in our weekly newsletter . You’ll find a variety of poetry, fiction, and creative nonfiction prompts—some inspired by recent and classic literature and other forms of art, current events, and writing practices, and others that offer guidance for a particular form, including sonnets, erasure poetry, flash fiction, lyric essays, and more. For more than fifty years, Poets & Writers has supported creative writers with trustworthy information and inspiration, and our weekly prompts provide a regular dose of encouragement and motivation.
What are the benefits of using writing prompts? Writing prompts can help you get unstuck if you’re in a rut and the ideas aren’t flowing. But even if you’re not experiencing writer’s block, writing prompts can offer a fresh take or a new approach to a work-in-progress. Writing prompts can also provide the motivation to experiment with a new form, try out a new genre, or learn about other writing techniques. And writing prompts are an invaluable tool for teachers who want to encourage and inspire their writing students.
What is this list of Best Books? Best Books for Writers is a list of essential books for creative writers that we curate to support your writing practice. Every week, we add a book (whether new or a classic) with a synopsis and highlights. Included are books on the writing life, anthologies of craft essays, collections of lectures, practical guides with writing exercises, and more.
Poetry writing prompts Every Tuesday we post a new poetry prompt to guide you in your practice. Get to know the work of contemporary and classic poets, as well as a variety of poetic forms.
Fiction writing prompts Every Wednesday we post a new fiction prompt to spark your imagination. Take inspiration from recently published short stories and novels, and of course, the classics.
Creative nonfiction writing prompts Every Thursday we post a new creative nonfiction prompt to help your exploration of this ever-changing genre. These prompts include information and inspiration for a variety of essays as well as memoirs. Discover new writers and their craft, and fresh ways to generate writing inspired by your life.
Need a starter pack? Check out our Writing Prompts for Beginners .
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Welcome to the Purdue Online Writing Lab

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
The Online Writing Lab at Purdue University houses writing resources and instructional material, and we provide these as a free service of the Writing Lab at Purdue. Students, members of the community, and users worldwide will find information to assist with many writing projects. Teachers and trainers may use this material for in-class and out-of-class instruction.
The Purdue On-Campus Writing Lab and Purdue Online Writing Lab assist clients in their development as writers—no matter what their skill level—with on-campus consultations, online participation, and community engagement. The Purdue Writing Lab serves the Purdue, West Lafayette, campus and coordinates with local literacy initiatives. The Purdue OWL offers global support through online reference materials and services.
A Message From the Assistant Director of Content Development
The Purdue OWL® is committed to supporting students, instructors, and writers by offering a wide range of resources that are developed and revised with them in mind. To do this, the OWL team is always exploring possibilties for a better design, allowing accessibility and user experience to guide our process. As the OWL undergoes some changes, we welcome your feedback and suggestions by email at any time.
Please don't hesitate to contact us via our contact page if you have any questions or comments.
All the best,
Social Media
Facebook twitter.
- Our Mission
Creative Writing in the Early Elementary Grades
A project that incorporates both standard and creative elements of storytelling can help young learners strengthen their literacy skills.

What can creative writing look, feel, and sound like in a first grade classroom? How can creative writing become a joyful and meaningful learning experience, and how can we educators facilitate the creative process and allow young writers to use their imagination when writing?
Graphic organizers, mind maps, and storyboards are certainly great tools for narrative building and planning, but they do not necessarily scaffold the creative process that story writing requires. In reality, they might even restrict students’ creativity while they “box” ideas in predetermined templates. This year, in my class, going play-based and hands-on has turned out to be a tremendous success.
Examining Elements of Creative Writing in First Grade
For this particular unit, my first grade students were examining literature and storytelling. After they had enjoyed several read-alouds, explored story elements, and studied the story mountain (beginning, rising action, conflict, resolution, and ending) as a team, it was time for them to write their very own stories.
They kicked off by creating their main character and decided on the character’s appearance, personality, likes, and dislikes. They also had the choice to play the main character role in the story. In both cases, while still brainstorming, it was time for action: They drew and decorated their characters with markers and pencils, cut them out, and used a Popsicle stick to make a puppet.
They became even more motivated to continue as they saw their characters come to life. My students spontaneously started interacting with each other and their puppets—creating stories and being imaginative—they went right into storytelling mode. This created the perfect opportunity for me to step back and observe my students’ initiative, creativity, and social and communication skills, not to mention their sense of accomplishment and joy.
Adding Artful Components to the Story
After they had engaged with their characters and interacted with others, it was time for the young writers to further develop their stories and think of a scenario leading to the rising action and resolution. This was the point when loose parts played a crucial role in the storytelling process. Counters, pipe cleaners, bits of paper, pebbles, dice, and buttons became houses, trees, magic wands, you name it. These bits and bobs from around the classroom became a valuable, zero-cost resource.
While students actively arranged and rearranged their chosen loose parts, they wondered about what would happen next in their stories. Unexpectedly, some students chose to collaborate and co-created stories by joining their imagination and characters in one story. In this step of the creative process, the use of loose parts was truly empowering: Before jotting anything down in their notebooks, my students physically, mentally, and verbally constructed their narratives and shared them with their partners.
Turning Ideas Into Words
With the mental representation of their narratives ready, it was all a matter of scribing their ideas. For that, we followed our usual class routines and resources such as word banks, sentence starters, and buddy support. All my students were engaged and confident, and when struggling with ideas, they resorted to loose parts again. As my first grade is a multicultural classroom, some of my students needed language support . However, with all of them hooked on their stories, supporting those who needed help with vocabulary, sentence construction, and spelling was simplified.
I conferred with students individually and in small groups to understand their thinking and offered feedback on paragraphing and some word choice. Instead of using notebooks for their first drafts, they chose to use mini-boards, which motivated them even more and supported them to make quick adjustments to their narratives. Finally, after receiving feedback, they moved on to writing their final drafts and designing their covers in order to turn their stories into books. Each student took their book home to share it with their family after reading it with the class.
Sharing Stories and Making Memorable Learning Experiences
What good is a book if it isn’t read and enjoyed? Buddy reading was the last step of the process but certainly not the least exciting. My students read aloud to each other, commenting on their favorite bits of the story and appreciating the illustrations. The whole project, from getting their characters ready to publishing and reading their books, took around five hours divided into five days.
When reflecting on the writing process, my students said that what they appreciated the most was the making of their puppets and illustrating their stories, highlighting the importance of integrating arts and writing. When asked about what was challenging, they replied that it was creating all the parts of the story mountain. However, they all said that using loose parts was a helpful strategy that they would use again—which they spontaneously have done in subsequent writing engagements. Lastly, when asked how they felt, some of the words they used were “proud,” “good,” and “joyful!”
A recent UNESCO report on the importance of happiness in learning refers to neuroscience research that proves our affective and cognitive domains are interconnected and interdependent. Therefore, emotions do affect learning! Joy is not a trade-off for academic achievement. Creating positive learning experiences makes learning stick.
Very often, students fear and avoid writing as a consequence of previous negative writing experiences. Combining art and a play-based approach to creative writing in first grade can set students on a path to success by building on their confidence, creativity, imagination, and sense of accomplishment. I have witnessed that the integration of art and writing has helped my students discover how writing can be a joyful and memorable experience where they can all be amazing storytellers and writers.
How to Use Em Dashes (—), En Dashes (–) , and Hyphens (-)
What is an em dash.
The em dash (—) can function like a comma, a colon, or parenthesis. Like commas and parentheses, em dashes set off extra information, such as examples, explanatory or descriptive phrases, or supplemental facts. Like a colon, an em dash introduces a clause that explains or expands upon something that precedes it.
The Em Dash Indicates a New Direction
- An em dash can mark an abrupt change or break in the structure of a sentence.
Mabel the Cat was delighted with the assortment of pastries the new bakery featured, but Harry the Dog—he felt otherwise.
- An em dash can indicate interrupted speech or a speaker’s confusion or hesitation.
“Of course you have a point,” Mabel murmured. “That is—I suppose it is concerning.”
The Em Dash as Comma or Parenthesis
- Em dashes are used in place of commas or parentheses to emphasize or draw attention to parenthetical or amplifying material. In this particular task, em dashes occupy a kind of middle ground among the three: when commas do the job, the material is most closely related to what’s around it, and when parentheses do the job, the material is most distantly related to what’s around it; when dashes do the job the material is somewhere in the middle.
And the wide range of its hours of operation—6 a.m. to 6 p.m.—certainly showed concern for customers’ manifold circumstances.
- Dashes set off or introduce defining phrases and lists.
A regular selection of three kinds of croissants—plain, almond, and chocolate—was heartening, both Mabel and Harry agreed.
- An em dash is often used in place of a colon or semicolon to link clauses, especially when the clause that follows the dash explains, summarizes, or expands upon the preceding clause in a somewhat dramatic way.
Harry would never forget the Tuesday that Mabel called him from the bakery, her voice brimming with excitement—the bakery had added cheese Danishes to its selection.
- An em dash or pair of dashes often sets off illustrative or amplifying material introduced by such phrases as for example , namely , and that is , when the break in continuity is greater than that shown by a comma, or when the dash would clarify the sentence structure better than a comma.
The bakery was truly phenomenal. Although they did miss the mark somewhat with the pineapple upside-down cake Mabel ordered—that is, the cake had clearly been baked right-side up.
- An em dash may introduce a summary statement that follows a series of words or phrases.
Chocolate chip, oatmeal raisin, peanut butter, snickerdoodle, both macarons and macaroons—the panoply of cookie varieties was impressive as well.
- A dash often precedes the name of an author or source at the end of a quoted passage—such as an epigraph, extract, or book or film blurb—that is not part of the main text. The attribution may appear immediately after the quotation or on the next line.
“One cannot underestimate the effect a good bakery can have on a person’s well-being.” —Mabel the Cat, The Websterburg Reporter
The Em Dash in the Company of Other Punctuation Marks
- If an em dash appears at a point where a comma could also appear, the comma is omitted.
Within its first year, Mabel and Harry had sampled all of the bakery’s offerings—all 62 items—and had also decided that the exercise was worth repeating.
- When a pair of em dashes sets off material ending with an exclamation point or a question mark, the mark is placed inside the dashes.
Mabel tried, despite her dolefulness—for how could she be otherwise?—to bake her own bread but each loaf that emerged from her oven tasted vaguely of tears.
- Dashes are used inside parentheses, and vice versa, to indicate parenthetical material within parenthetical material. The second dash is omitted if it would immediately precede the closing parenthesis; a closing parenthesis is never omitted.
The bakery’s reputation for scrumptious goods (ambrosial, even—each item was surely fit for gods) spread far and wide.
Em dash vs en dash
- Remembering that the em dash is the length of a capital M, it will surprise no one that the so-called “en dash” is the approximate length of a capital N, –. The en dash is the least loved of all; it’s not easily rendered by the average keyboard user (one has to select it as a special character, whereas the em dash can be conjured with two hyphens), so it’s mostly encountered in typeset material. (A hyphen does its job in other text.) It is most often used between numbers, dates, or other notations to signify “(up) to and including.”
The bakery will be closed August 1–August 31. The bakery is open 6:00 a.m.–6:00 p.m. The exceedingly complex recipe spans pages 128–34. Mabel and Harry lived elsewhere 2007–2019.
Note that one does not need words like from and between in these cases. The phrase “open 6:00 a.m.–6:00 p.m.” can be read as “open between 6:00 a.m. and 6:00 p.m.” or as “open from 6:00 a.m. to/until 6:00 p.m.”
- If you want to be official about things, use the en dash to replace a hyphen in compound adjectives when at least one of the elements is a two-word compound.
the post–Cold War era
The thinking is that using a hyphen here, as in “the post-Cold War era,” risks the suggestion that post attaches only to Cold . It’s unlikely, though, that a reader would truly be confused.
- The en dash replaces the word to between capitalized names, and is used to indicate linkages such as boundaries, treaties, and oppositions.
a Boston–Washington train the pie–cake divide
- A two-em dash, ——, is used to indicate missing letters in a word and, less frequently, to indicate a missing word.
The butter-stained and crumb-embedded note was attributed to a Ms. M—— of Websterburg.
- A three-em dash, ———, indicates that a word has been left out or that an unknown word or figure is to be supplied.
Years later it was revealed that the Websterburg bakers had once had a bakery in ———, a city to the south. But the water quality there was prohibitive to the creating of decent bagels.
While we said above that the em dash, also called the “common dash,” is the most common of the true dashes, hyphens show up more frequently in text. They have a variety of uses.
- Hyphens are used to link elements in compound words .
a baker-owner
- In some words, a hyphen separates a prefix, suffix, or medial element from the rest of the word.
Websterburg’s pre-bakery days a bread-like scone jack-o'-lantern sugar cookies
- As we noted above, a hyphen often does the job of an en dash between numbers and dates, providing the meaning "(up) to and including."
pages 128-34 the years 2007-2019
- A hyphen marks an end-of-line division of a word.
Mabel and Harry don’t like to linger on their memories of Webster- burg’s pre-bakery days.
- A hyphen divides letters or syllables to give the effect of stuttering, sobbing, or halting speech.
"M-m-mabel, the cheese Danish is divine!”
- Hyphens indicate a word spelled out letter by letter.
Let’s not even talk about August, when the bakery is c-l-o-s-e-d.
The em dash is sometimes considered a less formal equivalent of the colon and parenthesis, but in truth it’s used in all kinds of writing, including the most formal—the choice of which mark to use is really a matter of personal preference.
Spacing around an em dash varies. Most newspapers insert a space before and after the dash, and many popular magazines do the same, but most books and journals omit spacing, closing whatever comes before and after the em dash right up next to it. This website prefers the latter, its style requiring the closely held em dash in running text.
Word of the Day
See Definitions and Examples »
Get Word of the Day daily email!
Games & Quizzes

Punctuation
A guide to using semicolons, a guide to deciphering diacritics, on contractions of multiple words, the serial comma explained, the history of 'ampersand', grammar & usage, more words you always have to look up, 'fewer' and 'less', 7 pairs of commonly confused words, what's the difference between 'fascism' and 'socialism', more commonly misspelled words, pilfer: how to play and win, great big list of beautiful and useless words, vol. 4, 9 other words for beautiful, the words of the week - june 7, 8 words for lesser-known musical instruments.
Advanced Paraphrasing Tool
Elevate your writing with our free and ai-powered paraphraser. instantly correct or rephrase your sentences in different tones., paraphrasing tool, please rewrite my sentence, what is paraphrasing.
Paraphrasing is the art of rewriting text into other words. This includes using synonyms, restructuring phrases, and connecting ideas in different ways. A state-of-the-art paraphraser provides automatic and simple-to-use rephrasing of complete sentences.

Why Should I Paraphrase My Sentences?
By paraphrasing existing sentences, you can elevate your writing and achieve different goals as a writer. That’s why rephrasing is helpful in plenty of cases: rewriting citations, strengthening the message of your text, and rewording your ideas while improving style.

How Does Rephrasing Help Me Become a Better Writer?
This feature is highly customizable, meaning you’re in control. Choose from five different categories—general, formal, concise, fluent, or simple—to transform your writing to better suit the context and tone. Paraphrasing helps you by refining and perfecting your masterpieces.
Where Can I Use the Paraphrasing Tool?
Rephrasing is available wherever and whenever! All you need is a LanguageTool account and a stable internet connection to rewrite your sentences in almost all of LanguageTool's extensions. The feature is easily accessible for everyone that aims to improve their writing.
Thunderbird
What exactly does an online paraphraser do.
LanguageTool’s paraphrasing feature does so much more than just rewrite sentences. Not only does it check for stronger, more suitable word choice, but it also corrects your sentence as a whole to ensure high-quality writing. With its intuitive and user-friendly interface, everyone can leverage Artificial Intelligence to achieve the best results possible.

What Other Features Does LanguageTool’s Paraphraser Provide?
The best part of using A.I. to paraphrase your writing is that the suggested sentences come free of spelling, grammar, and punctuation errors. Want to also improve style? Simply go back to the general correction to view stylistic suggestions.

As multilingual as you
Make your text sound professional and avoid embarrassing style, punctuation, and grammar mistakes
It’s an online tool that rewrites texts in a new (stylistically different) way by using alternative wording and a rephrased sentence structure.
This function is recommended for all types of texts, including professional, academic, and creative writing. It’s available for all LanguageTool users, but unlimited paraphrasing is only available in Premium.
A paraphrasing tool can easily enhance your writing by improving the tone and style of your text. Moreover, it helps you avoid having to write direct citations by rewriting copy-and-pasted text.
Premium accounts offer even more useful and powerful features:
Only with Premium
Sentence correction of longer texts
Style guide for customizing individual rules
Team features for companies
More in-depth suggestions, especially for word choice and style
How Can I Effectively Use the Rephrasing Tool?
For basic users, the paraphrasing feature is limited to three times daily. If you need more rephrased sentences, you can upgrade to LanguageTool Premium to get access to unlimited paraphrasing in six languages and several English dialects. Remember: No personal data is stored (ever) and privacy guidelines are strictly followed (always).
Strengthen Your Communication Skills
Try out the best paraphrasing tool for free and discover how LanguageTool can elevate your writing.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Creative Writing is the art of using words to express ideas and emotions in imaginative ways. It encompasses various forms including novels, poetry, and plays, focusing on narrative craft, character development, and the use of literary tropes. (This post may have afilliate links. Please see my full disclosure)
Use of Literary Devices: Creative writing frequently employs literary devices such as metaphors, similes, personification, and others to enrich the text and convey meanings in a more subtle, layered manner. 5. Focus on Aesthetics: The beauty of language and the way words flow together is important in creative writing. The aim is to create a ...
Types of Creative Writing. Examples of creative writing can be found pretty much everywhere. Some forms that you're probably familiar with and already enjoy include: • Fiction (of every genre, from sci-fi to historical dramas to romances) • Film and television scripts. • Songs. • Poetry.
Creative writing is the celestial dance of words, an art form that transcends the ordinary to forge literary constellations that illuminate the human experience. At its core, creative writing is a cosmic exploration of imagination, a journey into the uncharted realms where storytelling becomes a vehicle for self-expression, creativity, and ...
Creative writing is any writing that goes outside the bounds of normal professional, journalistic, academic, or technical forms of literature, typically identified by an emphasis on narrative craft, character development, and the use of literary tropes or with various traditions of poetry and poetics.Due to the looseness of the definition, it is possible for writing such as feature stories to ...
Action: In creative writing, action should occur for a reason—characters' actions should be based on their motivations, their points of view, and their previous choices. A protagonist's actions should always propel them toward their main goal in a way that is related to the plot events at hand. A character's goals affect their character ...
4 Forms of Creative Writing. While there are really no bounds to what creative writing can be, there are four main buckets it falls into. 1. Fiction. Fiction is work that describes imaginary events, places, or people. This can include novels, short stories, or even flash fiction. 2. Creative Nonfiction. Creative nonfiction is about telling true ...
A lot falls under the term 'creative writing': poetry, short fiction, plays, novels, personal essays, and songs, to name just a few. By virtue of the creativity that characterizes it, creative writing is an extremely versatile art. So instead of defining what creative writing is, it may be easier to understand what it does by looking at ...
Creative writing is a written art form that uses the imagination to tell stories and compose essays, poetry, screenplays, novels, lyrics, and more. It can be defined in opposition to the dry and factual types of writing found in academic, technical, or journalistic texts.
Creative writing is as much about showing as it is about telling. Practicing descriptive writing brings your characters, settings, and scenes to life. Try to engage all the reader's senses — sight, sound, smell, taste, and touch. This helps to create an immersive experience for your reader and make your writing more memorable.
Creative Writing is a form of art that allows people to express their thoughts, ideas, and emotions through the written word. It is a mode of self-expression that combines imagination with linguistic skills to create compelling narratives, poems, and other forms of literature. A Statista survey found that 76,300 Authors, Writers and Translators ...
Creative writing can even use persuasive writing styles in some formats. Many writers will combine persuasive writing with a narrative structure to come up with a creative way of telling a story to educate readers and provide new opinions for them to view or be convinced of. Expository writing can also be involved here, using creativity and ...
What is creative writing? The answer can be simple, but breaking it down is far more useful. Learn more and gain some insightful tips for yourself, as well!
This free and open access textbook introduces new writers to some basic elements of the craft of creative writing in the genres of fiction, poetry, and creative nonfiction. The authors—Rachel Morgan, Jeremy Schraffenberger, and Grant Tracey—are editors of the North American Review, the oldest and one of the most well-regarded literary magazines in the United States.
Elements of Creative Writing. The purpose of creative writing elements is to aid in the conveyance of aesthetic or symbolic meaning. Different types of creative writing use different elements.
New Journalism Tells the Story of How Creative Writing Has an Important Role in Non-Fiction. In Cold Blood is seen today as one of the first entries in the field of New Journalism. Capote and his contemporaries, such as Joan Didion, Tom Wolfe, and Hunter S. Thompson broke new ground in the use of traditional creative writing styles and techniques to tell important journalistic stories.
Creative Writing is a catalyst that sparks our creativity and empowers us to breathe life into our ideas on the page. With Oxford Summer Courses, aspiring writers aged 16-24 can embark on an extraordinary journey of creative expression and growth. Immerse yourself in the captivating realms of Oxford and Cambridge as you explore our inspiring ...
Creative Writing is a form of self-expression that allows you to use your imagination and creativity. It can be in the form of personal essays, short stories, or poems. It is often used as an outlet for emotions and experiences. Start with creative writing by reading through creative writing examples to help get you in the mood.
Creative writing is any writing done for creative or artistic purposes. As a result, the rules can be flexible if not outright broken, and there are endless ...
Creative writing also encourages writers to be inventive with their style and use descriptive language to evoke emotion or bring stories alive in readers' minds. Other academic or technical writing types typically involve more research-based information and are usually more objective in their presentation.
Creative writing is an art form that goes beyond traditional writing, allowing individuals to express their thoughts, emotions, and ideas through the power of words. It transcends conventional writing, encouraging individuals to explore language, structure, and narrative. Creative writing is writing meant to evoke emotion in a reader by ...
Creative writing is a genre of writing that seeks to evoke emotions and feelings in its readers. It surpasses the limits of traditional forms of literature and emphasizes narrative craft, character development, and the use of literary tropes and poetic traditions. Creative writing finds application in various forms of writing, including ...
Check out our Writing Prompts for Beginners. Tuesdays: Poetry prompts. Wednesdays: Fiction prompts. Thursdays: Creative nonfiction prompts. Get immediate access to more than 2,000 writing prompts with the tool below: Choose a genre: <Any>. Items/Page: 25.
Mission. The Purdue On-Campus Writing Lab and Purdue Online Writing Lab assist clients in their development as writers—no matter what their skill level—with on-campus consultations, online participation, and community engagement. The Purdue Writing Lab serves the Purdue, West Lafayette, campus and coordinates with local literacy initiatives.
Examining Elements of Creative Writing in First Grade. For this particular unit, my first grade students were examining literature and storytelling. After they had enjoyed several read-alouds, explored story elements, and studied the story mountain (beginning, rising action, conflict, resolution, and ending) as a team, it was time for them to ...
A creative writer strives to tell unique stories in a distinctive voice. Yet with all the fiction writing already out there in the world, it can be hard to feel that your work is legitimately creative compared to the competition. You could be a first-time writer completing in a high school creative writing course, a hobbyist working on your first novel, or a seasoned pro with an MFA who's ...
A two-em dash, ——, is used to indicate missing letters in a word and, less frequently, to indicate a missing word. The butter-stained and crumb-embedded note was attributed to a Ms. M—— of Websterburg. A three-em dash, ———, indicates that a word has been left out or that an unknown word or figure is to be supplied.
Welcome to the NCO Creative Domain - This is a space for creative, insightful, diverse, and unconventional works. An outlet to express yourself in ways different than our traditional, scholarly format. Send us your poetry or short fiction stories. Send us reviews of books, video games, movies, or television shows - send us your inspiration.
Strengthen Your Communication Skills. Try out the best paraphrasing tool for free and discover how LanguageTool can elevate your writing. Enhance your writing with LanguageTool's free AI paraphrasing tool. Discover a smarter way to rewrite and refine your text for improved clarity and uniqueness.
Students and Teachers. Introductory Pricing Terms and Conditions Creative Cloud Introductory Pricing Eligible students 13 and older and teachers can purchase an annual membership to Adobe® Creative Cloud™ for a reduced price of for the first year. At the end of your offer term, your subscription will be automatically billed at the standard subscription rate, currently at (plus applicable ...