
What (Exactly) Is A Research Proposal?
A simple explainer with examples + free template.
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) | Reviewed By: Dr Eunice Rautenbach | June 2020 (Updated April 2023)
Whether you’re nearing the end of your degree and your dissertation is on the horizon, or you’re planning to apply for a PhD program, chances are you’ll need to craft a convincing research proposal . If you’re on this page, you’re probably unsure exactly what the research proposal is all about. Well, you’ve come to the right place.
Overview: Research Proposal Basics
- What a research proposal is
- What a research proposal needs to cover
- How to structure your research proposal
- Example /sample proposals
- Proposal writing FAQs
- Key takeaways & additional resources
What is a research proposal?
Simply put, a research proposal is a structured, formal document that explains what you plan to research (your research topic), why it’s worth researching (your justification), and how you plan to investigate it (your methodology).
The purpose of the research proposal (its job, so to speak) is to convince your research supervisor, committee or university that your research is suitable (for the requirements of the degree program) and manageable (given the time and resource constraints you will face).
The most important word here is “ convince ” – in other words, your research proposal needs to sell your research idea (to whoever is going to approve it). If it doesn’t convince them (of its suitability and manageability), you’ll need to revise and resubmit . This will cost you valuable time, which will either delay the start of your research or eat into its time allowance (which is bad news).

What goes into a research proposal?
A good dissertation or thesis proposal needs to cover the “ what “, “ why ” and” how ” of the proposed study. Let’s look at each of these attributes in a little more detail:
Your proposal needs to clearly articulate your research topic . This needs to be specific and unambiguous . Your research topic should make it clear exactly what you plan to research and in what context. Here’s an example of a well-articulated research topic:
An investigation into the factors which impact female Generation Y consumer’s likelihood to promote a specific makeup brand to their peers: a British context
As you can see, this topic is extremely clear. From this one line we can see exactly:
- What’s being investigated – factors that make people promote or advocate for a brand of a specific makeup brand
- Who it involves – female Gen-Y consumers
- In what context – the United Kingdom
So, make sure that your research proposal provides a detailed explanation of your research topic . If possible, also briefly outline your research aims and objectives , and perhaps even your research questions (although in some cases you’ll only develop these at a later stage). Needless to say, don’t start writing your proposal until you have a clear topic in mind , or you’ll end up waffling and your research proposal will suffer as a result of this.
Need a helping hand?
As we touched on earlier, it’s not good enough to simply propose a research topic – you need to justify why your topic is original . In other words, what makes it unique ? What gap in the current literature does it fill? If it’s simply a rehash of the existing research, it’s probably not going to get approval – it needs to be fresh.
But, originality alone is not enough. Once you’ve ticked that box, you also need to justify why your proposed topic is important . In other words, what value will it add to the world if you achieve your research aims?
As an example, let’s look at the sample research topic we mentioned earlier (factors impacting brand advocacy). In this case, if the research could uncover relevant factors, these findings would be very useful to marketers in the cosmetics industry, and would, therefore, have commercial value . That is a clear justification for the research.
So, when you’re crafting your research proposal, remember that it’s not enough for a topic to simply be unique. It needs to be useful and value-creating – and you need to convey that value in your proposal. If you’re struggling to find a research topic that makes the cut, watch our video covering how to find a research topic .

It’s all good and well to have a great topic that’s original and valuable, but you’re not going to convince anyone to approve it without discussing the practicalities – in other words:
- How will you actually undertake your research (i.e., your methodology)?
- Is your research methodology appropriate given your research aims?
- Is your approach manageable given your constraints (time, money, etc.)?
While it’s generally not expected that you’ll have a fully fleshed-out methodology at the proposal stage, you’ll likely still need to provide a high-level overview of your research methodology . Here are some important questions you’ll need to address in your research proposal:
- Will you take a qualitative , quantitative or mixed -method approach?
- What sampling strategy will you adopt?
- How will you collect your data (e.g., interviews, surveys, etc)?
- How will you analyse your data (e.g., descriptive and inferential statistics , content analysis, discourse analysis, etc, .)?
- What potential limitations will your methodology carry?
So, be sure to give some thought to the practicalities of your research and have at least a basic methodological plan before you start writing up your proposal. If this all sounds rather intimidating, the video below provides a good introduction to research methodology and the key choices you’ll need to make.
How To Structure A Research Proposal
Now that we’ve covered the key points that need to be addressed in a proposal, you may be wondering, “ But how is a research proposal structured? “.
While the exact structure and format required for a research proposal differs from university to university, there are four “essential ingredients” that commonly make up the structure of a research proposal:
- A rich introduction and background to the proposed research
- An initial literature review covering the existing research
- An overview of the proposed research methodology
- A discussion regarding the practicalities (project plans, timelines, etc.)
In the video below, we unpack each of these four sections, step by step.
Research Proposal Examples/Samples
In the video below, we provide a detailed walkthrough of two successful research proposals (Master’s and PhD-level), as well as our popular free proposal template.
Proposal Writing FAQs
How long should a research proposal be.
This varies tremendously, depending on the university, the field of study (e.g., social sciences vs natural sciences), and the level of the degree (e.g. undergraduate, Masters or PhD) – so it’s always best to check with your university what their specific requirements are before you start planning your proposal.
As a rough guide, a formal research proposal at Masters-level often ranges between 2000-3000 words, while a PhD-level proposal can be far more detailed, ranging from 5000-8000 words. In some cases, a rough outline of the topic is all that’s needed, while in other cases, universities expect a very detailed proposal that essentially forms the first three chapters of the dissertation or thesis.
The takeaway – be sure to check with your institution before you start writing.
How do I choose a topic for my research proposal?
Finding a good research topic is a process that involves multiple steps. We cover the topic ideation process in this video post.
How do I write a literature review for my proposal?
While you typically won’t need a comprehensive literature review at the proposal stage, you still need to demonstrate that you’re familiar with the key literature and are able to synthesise it. We explain the literature review process here.
How do I create a timeline and budget for my proposal?
We explain how to craft a project plan/timeline and budget in Research Proposal Bootcamp .
Which referencing format should I use in my research proposal?
The expectations and requirements regarding formatting and referencing vary from institution to institution. Therefore, you’ll need to check this information with your university.
What common proposal writing mistakes do I need to look out for?
We’ve create a video post about some of the most common mistakes students make when writing a proposal – you can access that here . If you’re short on time, here’s a quick summary:
- The research topic is too broad (or just poorly articulated).
- The research aims, objectives and questions don’t align.
- The research topic is not well justified.
- The study has a weak theoretical foundation.
- The research design is not well articulated well enough.
- Poor writing and sloppy presentation.
- Poor project planning and risk management.
- Not following the university’s specific criteria.
Key Takeaways & Additional Resources
As you write up your research proposal, remember the all-important core purpose: to convince . Your research proposal needs to sell your study in terms of suitability and viability. So, focus on crafting a convincing narrative to ensure a strong proposal.
At the same time, pay close attention to your university’s requirements. While we’ve covered the essentials here, every institution has its own set of expectations and it’s essential that you follow these to maximise your chances of approval.
By the way, we’ve got plenty more resources to help you fast-track your research proposal. Here are some of our most popular resources to get you started:
- Proposal Writing 101 : A Introductory Webinar
- Research Proposal Bootcamp : The Ultimate Online Course
- Template : A basic template to help you craft your proposal
If you’re looking for 1-on-1 support with your research proposal, be sure to check out our private coaching service , where we hold your hand through the proposal development process (and the entire research journey), step by step.

Psst… there’s more!
This post is an extract from our bestselling short course, Research Proposal Bootcamp . If you want to work smart, you don't want to miss this .
You Might Also Like:

51 Comments
I truly enjoyed this video, as it was eye-opening to what I have to do in the preparation of preparing a Research proposal.
I would be interested in getting some coaching.
I real appreciate on your elaboration on how to develop research proposal,the video explains each steps clearly.
Thank you for the video. It really assisted me and my niece. I am a PhD candidate and she is an undergraduate student. It is at times, very difficult to guide a family member but with this video, my job is done.
In view of the above, I welcome more coaching.
Wonderful guidelines, thanks
This is very helpful. Would love to continue even as I prepare for starting my masters next year.
Thanks for the work done, the text was helpful to me
Bundle of thanks to you for the research proposal guide it was really good and useful if it is possible please send me the sample of research proposal
You’re most welcome. We don’t have any research proposals that we can share (the students own the intellectual property), but you might find our research proposal template useful: https://gradcoach.com/research-proposal-template/
Cheruiyot Moses Kipyegon
Thanks alot. It was an eye opener that came timely enough before my imminent proposal defense. Thanks, again
thank you very much your lesson is very interested may God be with you
I am an undergraduate student (First Degree) preparing to write my project,this video and explanation had shed more light to me thanks for your efforts keep it up.
Very useful. I am grateful.
this is a very a good guidance on research proposal, for sure i have learnt something
Wonderful guidelines for writing a research proposal, I am a student of m.phil( education), this guideline is suitable for me. Thanks
You’re welcome 🙂
Thank you, this was so helpful.
A really great and insightful video. It opened my eyes as to how to write a research paper. I would like to receive more guidance for writing my research paper from your esteemed faculty.
Thank you, great insights
Thank you, great insights, thank you so much, feeling edified
Wow thank you, great insights, thanks a lot
Thank you. This is a great insight. I am a student preparing for a PhD program. I am requested to write my Research Proposal as part of what I am required to submit before my unconditional admission. I am grateful having listened to this video which will go a long way in helping me to actually choose a topic of interest and not just any topic as well as to narrow down the topic and be specific about it. I indeed need more of this especially as am trying to choose a topic suitable for a DBA am about embarking on. Thank you once more. The video is indeed helpful.
Have learnt a lot just at the right time. Thank you so much.
thank you very much ,because have learn a lot things concerning research proposal and be blessed u for your time that you providing to help us
Hi. For my MSc medical education research, please evaluate this topic for me: Training Needs Assessment of Faculty in Medical Training Institutions in Kericho and Bomet Counties
I have really learnt a lot based on research proposal and it’s formulation
Thank you. I learn much from the proposal since it is applied
Your effort is much appreciated – you have good articulation.
You have good articulation.
I do applaud your simplified method of explaining the subject matter, which indeed has broaden my understanding of the subject matter. Definitely this would enable me writing a sellable research proposal.
This really helping
Great! I liked your tutoring on how to find a research topic and how to write a research proposal. Precise and concise. Thank you very much. Will certainly share this with my students. Research made simple indeed.
Thank you very much. I an now assist my students effectively.
Thank you very much. I can now assist my students effectively.
I need any research proposal
Thank you for these videos. I will need chapter by chapter assistance in writing my MSc dissertation
Very helpfull
the videos are very good and straight forward
thanks so much for this wonderful presentations, i really enjoyed it to the fullest wish to learn more from you
Thank you very much. I learned a lot from your lecture.
I really enjoy the in-depth knowledge on research proposal you have given. me. You have indeed broaden my understanding and skills. Thank you
interesting session this has equipped me with knowledge as i head for exams in an hour’s time, am sure i get A++
This article was most informative and easy to understand. I now have a good idea of how to write my research proposal.
Thank you very much.
Wow, this literature is very resourceful and interesting to read. I enjoyed it and I intend reading it every now then.
Thank you for the clarity
Thank you. Very helpful.
Thank you very much for this essential piece. I need 1o1 coaching, unfortunately, your service is not available in my country. Anyways, a very important eye-opener. I really enjoyed it. A thumb up to Gradcoach
What is JAM? Please explain.
Thank you so much for these videos. They are extremely helpful! God bless!
very very wonderful…
thank you for the video but i need a written example
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Assignments
- Annotated Bibliography
- Analyzing a Scholarly Journal Article
- Group Presentations
- Dealing with Nervousness
- Using Visual Aids
- Grading Someone Else's Paper
- Types of Structured Group Activities
- Group Project Survival Skills
- Leading a Class Discussion
- Multiple Book Review Essay
- Reviewing Collected Works
- Writing a Case Analysis Paper
- Writing a Case Study
- About Informed Consent
- Writing Field Notes
- Writing a Policy Memo
- Writing a Reflective Paper
- Writing a Research Proposal
- Generative AI and Writing
- Acknowledgments
The goal of a research proposal is twofold: to present and justify the need to study a research problem and to present the practical ways in which the proposed study should be conducted. The design elements and procedures for conducting research are governed by standards of the predominant discipline in which the problem resides, therefore, the guidelines for research proposals are more exacting and less formal than a general project proposal. Research proposals contain extensive literature reviews. They must provide persuasive evidence that a need exists for the proposed study. In addition to providing a rationale, a proposal describes detailed methodology for conducting the research consistent with requirements of the professional or academic field and a statement on anticipated outcomes and benefits derived from the study's completion.
Krathwohl, David R. How to Prepare a Dissertation Proposal: Suggestions for Students in Education and the Social and Behavioral Sciences . Syracuse, NY: Syracuse University Press, 2005.
How to Approach Writing a Research Proposal
Your professor may assign the task of writing a research proposal for the following reasons:
- Develop your skills in thinking about and designing a comprehensive research study;
- Learn how to conduct a comprehensive review of the literature to determine that the research problem has not been adequately addressed or has been answered ineffectively and, in so doing, become better at locating pertinent scholarship related to your topic;
- Improve your general research and writing skills;
- Practice identifying the logical steps that must be taken to accomplish one's research goals;
- Critically review, examine, and consider the use of different methods for gathering and analyzing data related to the research problem; and,
- Nurture a sense of inquisitiveness within yourself and to help see yourself as an active participant in the process of conducting scholarly research.
A proposal should contain all the key elements involved in designing a completed research study, with sufficient information that allows readers to assess the validity and usefulness of your proposed study. The only elements missing from a research proposal are the findings of the study and your analysis of those findings. Finally, an effective proposal is judged on the quality of your writing and, therefore, it is important that your proposal is coherent, clear, and compelling.
Regardless of the research problem you are investigating and the methodology you choose, all research proposals must address the following questions:
- What do you plan to accomplish? Be clear and succinct in defining the research problem and what it is you are proposing to investigate.
- Why do you want to do the research? In addition to detailing your research design, you also must conduct a thorough review of the literature and provide convincing evidence that it is a topic worthy of in-depth study. A successful research proposal must answer the "So What?" question.
- How are you going to conduct the research? Be sure that what you propose is doable. If you're having difficulty formulating a research problem to propose investigating, go here for strategies in developing a problem to study.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Failure to be concise . A research proposal must be focused and not be "all over the map" or diverge into unrelated tangents without a clear sense of purpose.
- Failure to cite landmark works in your literature review . Proposals should be grounded in foundational research that lays a foundation for understanding the development and scope of the the topic and its relevance.
- Failure to delimit the contextual scope of your research [e.g., time, place, people, etc.]. As with any research paper, your proposed study must inform the reader how and in what ways the study will frame the problem.
- Failure to develop a coherent and persuasive argument for the proposed research . This is critical. In many workplace settings, the research proposal is a formal document intended to argue for why a study should be funded.
- Sloppy or imprecise writing, or poor grammar . Although a research proposal does not represent a completed research study, there is still an expectation that it is well-written and follows the style and rules of good academic writing.
- Too much detail on minor issues, but not enough detail on major issues . Your proposal should focus on only a few key research questions in order to support the argument that the research needs to be conducted. Minor issues, even if valid, can be mentioned but they should not dominate the overall narrative.
Procter, Margaret. The Academic Proposal. The Lab Report. University College Writing Centre. University of Toronto; Sanford, Keith. Information for Students: Writing a Research Proposal. Baylor University; Wong, Paul T. P. How to Write a Research Proposal. International Network on Personal Meaning. Trinity Western University; Writing Academic Proposals: Conferences, Articles, and Books. The Writing Lab and The OWL. Purdue University; Writing a Research Proposal. University Library. University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign.
Structure and Writing Style
Beginning the Proposal Process
As with writing most college-level academic papers, research proposals are generally organized the same way throughout most social science disciplines. The text of proposals generally vary in length between ten and thirty-five pages, followed by the list of references. However, before you begin, read the assignment carefully and, if anything seems unclear, ask your professor whether there are any specific requirements for organizing and writing the proposal.
A good place to begin is to ask yourself a series of questions:
- What do I want to study?
- Why is the topic important?
- How is it significant within the subject areas covered in my class?
- What problems will it help solve?
- How does it build upon [and hopefully go beyond] research already conducted on the topic?
- What exactly should I plan to do, and can I get it done in the time available?
In general, a compelling research proposal should document your knowledge of the topic and demonstrate your enthusiasm for conducting the study. Approach it with the intention of leaving your readers feeling like, "Wow, that's an exciting idea and I can’t wait to see how it turns out!"
Most proposals should include the following sections:
I. Introduction
In the real world of higher education, a research proposal is most often written by scholars seeking grant funding for a research project or it's the first step in getting approval to write a doctoral dissertation. Even if this is just a course assignment, treat your introduction as the initial pitch of an idea based on a thorough examination of the significance of a research problem. After reading the introduction, your readers should not only have an understanding of what you want to do, but they should also be able to gain a sense of your passion for the topic and to be excited about the study's possible outcomes. Note that most proposals do not include an abstract [summary] before the introduction.
Think about your introduction as a narrative written in two to four paragraphs that succinctly answers the following four questions :
- What is the central research problem?
- What is the topic of study related to that research problem?
- What methods should be used to analyze the research problem?
- Answer the "So What?" question by explaining why this is important research, what is its significance, and why should someone reading the proposal care about the outcomes of the proposed study?
II. Background and Significance
This is where you explain the scope and context of your proposal and describe in detail why it's important. It can be melded into your introduction or you can create a separate section to help with the organization and narrative flow of your proposal. Approach writing this section with the thought that you can’t assume your readers will know as much about the research problem as you do. Note that this section is not an essay going over everything you have learned about the topic; instead, you must choose what is most relevant in explaining the aims of your research.
To that end, while there are no prescribed rules for establishing the significance of your proposed study, you should attempt to address some or all of the following:
- State the research problem and give a more detailed explanation about the purpose of the study than what you stated in the introduction. This is particularly important if the problem is complex or multifaceted .
- Present the rationale of your proposed study and clearly indicate why it is worth doing; be sure to answer the "So What? question [i.e., why should anyone care?].
- Describe the major issues or problems examined by your research. This can be in the form of questions to be addressed. Be sure to note how your proposed study builds on previous assumptions about the research problem.
- Explain the methods you plan to use for conducting your research. Clearly identify the key sources you intend to use and explain how they will contribute to your analysis of the topic.
- Describe the boundaries of your proposed research in order to provide a clear focus. Where appropriate, state not only what you plan to study, but what aspects of the research problem will be excluded from the study.
- If necessary, provide definitions of key concepts, theories, or terms.
III. Literature Review
Connected to the background and significance of your study is a section of your proposal devoted to a more deliberate review and synthesis of prior studies related to the research problem under investigation . The purpose here is to place your project within the larger whole of what is currently being explored, while at the same time, demonstrating to your readers that your work is original and innovative. Think about what questions other researchers have asked, what methodological approaches they have used, and what is your understanding of their findings and, when stated, their recommendations. Also pay attention to any suggestions for further research.
Since a literature review is information dense, it is crucial that this section is intelligently structured to enable a reader to grasp the key arguments underpinning your proposed study in relation to the arguments put forth by other researchers. A good strategy is to break the literature into "conceptual categories" [themes] rather than systematically or chronologically describing groups of materials one at a time. Note that conceptual categories generally reveal themselves after you have read most of the pertinent literature on your topic so adding new categories is an on-going process of discovery as you review more studies. How do you know you've covered the key conceptual categories underlying the research literature? Generally, you can have confidence that all of the significant conceptual categories have been identified if you start to see repetition in the conclusions or recommendations that are being made.
NOTE: Do not shy away from challenging the conclusions made in prior research as a basis for supporting the need for your proposal. Assess what you believe is missing and state how previous research has failed to adequately examine the issue that your study addresses. Highlighting the problematic conclusions strengthens your proposal. For more information on writing literature reviews, GO HERE .
To help frame your proposal's review of prior research, consider the "five C’s" of writing a literature review:
- Cite , so as to keep the primary focus on the literature pertinent to your research problem.
- Compare the various arguments, theories, methodologies, and findings expressed in the literature: what do the authors agree on? Who applies similar approaches to analyzing the research problem?
- Contrast the various arguments, themes, methodologies, approaches, and controversies expressed in the literature: describe what are the major areas of disagreement, controversy, or debate among scholars?
- Critique the literature: Which arguments are more persuasive, and why? Which approaches, findings, and methodologies seem most reliable, valid, or appropriate, and why? Pay attention to the verbs you use to describe what an author says/does [e.g., asserts, demonstrates, argues, etc.].
- Connect the literature to your own area of research and investigation: how does your own work draw upon, depart from, synthesize, or add a new perspective to what has been said in the literature?
IV. Research Design and Methods
This section must be well-written and logically organized because you are not actually doing the research, yet, your reader must have confidence that you have a plan worth pursuing . The reader will never have a study outcome from which to evaluate whether your methodological choices were the correct ones. Thus, the objective here is to convince the reader that your overall research design and proposed methods of analysis will correctly address the problem and that the methods will provide the means to effectively interpret the potential results. Your design and methods should be unmistakably tied to the specific aims of your study.
Describe the overall research design by building upon and drawing examples from your review of the literature. Consider not only methods that other researchers have used, but methods of data gathering that have not been used but perhaps could be. Be specific about the methodological approaches you plan to undertake to obtain information, the techniques you would use to analyze the data, and the tests of external validity to which you commit yourself [i.e., the trustworthiness by which you can generalize from your study to other people, places, events, and/or periods of time].
When describing the methods you will use, be sure to cover the following:
- Specify the research process you will undertake and the way you will interpret the results obtained in relation to the research problem. Don't just describe what you intend to achieve from applying the methods you choose, but state how you will spend your time while applying these methods [e.g., coding text from interviews to find statements about the need to change school curriculum; running a regression to determine if there is a relationship between campaign advertising on social media sites and election outcomes in Europe ].
- Keep in mind that the methodology is not just a list of tasks; it is a deliberate argument as to why techniques for gathering information add up to the best way to investigate the research problem. This is an important point because the mere listing of tasks to be performed does not demonstrate that, collectively, they effectively address the research problem. Be sure you clearly explain this.
- Anticipate and acknowledge any potential barriers and pitfalls in carrying out your research design and explain how you plan to address them. No method applied to research in the social and behavioral sciences is perfect, so you need to describe where you believe challenges may exist in obtaining data or accessing information. It's always better to acknowledge this than to have it brought up by your professor!
V. Preliminary Suppositions and Implications
Just because you don't have to actually conduct the study and analyze the results, doesn't mean you can skip talking about the analytical process and potential implications . The purpose of this section is to argue how and in what ways you believe your research will refine, revise, or extend existing knowledge in the subject area under investigation. Depending on the aims and objectives of your study, describe how the anticipated results will impact future scholarly research, theory, practice, forms of interventions, or policy making. Note that such discussions may have either substantive [a potential new policy], theoretical [a potential new understanding], or methodological [a potential new way of analyzing] significance. When thinking about the potential implications of your study, ask the following questions:
- What might the results mean in regards to challenging the theoretical framework and underlying assumptions that support the study?
- What suggestions for subsequent research could arise from the potential outcomes of the study?
- What will the results mean to practitioners in the natural settings of their workplace, organization, or community?
- Will the results influence programs, methods, and/or forms of intervention?
- How might the results contribute to the solution of social, economic, or other types of problems?
- Will the results influence policy decisions?
- In what way do individuals or groups benefit should your study be pursued?
- What will be improved or changed as a result of the proposed research?
- How will the results of the study be implemented and what innovations or transformative insights could emerge from the process of implementation?
NOTE: This section should not delve into idle speculation, opinion, or be formulated on the basis of unclear evidence . The purpose is to reflect upon gaps or understudied areas of the current literature and describe how your proposed research contributes to a new understanding of the research problem should the study be implemented as designed.
ANOTHER NOTE : This section is also where you describe any potential limitations to your proposed study. While it is impossible to highlight all potential limitations because the study has yet to be conducted, you still must tell the reader where and in what form impediments may arise and how you plan to address them.
VI. Conclusion
The conclusion reiterates the importance or significance of your proposal and provides a brief summary of the entire study . This section should be only one or two paragraphs long, emphasizing why the research problem is worth investigating, why your research study is unique, and how it should advance existing knowledge.
Someone reading this section should come away with an understanding of:
- Why the study should be done;
- The specific purpose of the study and the research questions it attempts to answer;
- The decision for why the research design and methods used where chosen over other options;
- The potential implications emerging from your proposed study of the research problem; and
- A sense of how your study fits within the broader scholarship about the research problem.
VII. Citations
As with any scholarly research paper, you must cite the sources you used . In a standard research proposal, this section can take two forms, so consult with your professor about which one is preferred.
- References -- a list of only the sources you actually used in creating your proposal.
- Bibliography -- a list of everything you used in creating your proposal, along with additional citations to any key sources relevant to understanding the research problem.
In either case, this section should testify to the fact that you did enough preparatory work to ensure the project will complement and not just duplicate the efforts of other researchers. It demonstrates to the reader that you have a thorough understanding of prior research on the topic.
Most proposal formats have you start a new page and use the heading "References" or "Bibliography" centered at the top of the page. Cited works should always use a standard format that follows the writing style advised by the discipline of your course [e.g., education=APA; history=Chicago] or that is preferred by your professor. This section normally does not count towards the total page length of your research proposal.
Develop a Research Proposal: Writing the Proposal. Office of Library Information Services. Baltimore County Public Schools; Heath, M. Teresa Pereira and Caroline Tynan. “Crafting a Research Proposal.” The Marketing Review 10 (Summer 2010): 147-168; Jones, Mark. “Writing a Research Proposal.” In MasterClass in Geography Education: Transforming Teaching and Learning . Graham Butt, editor. (New York: Bloomsbury Academic, 2015), pp. 113-127; Juni, Muhamad Hanafiah. “Writing a Research Proposal.” International Journal of Public Health and Clinical Sciences 1 (September/October 2014): 229-240; Krathwohl, David R. How to Prepare a Dissertation Proposal: Suggestions for Students in Education and the Social and Behavioral Sciences . Syracuse, NY: Syracuse University Press, 2005; Procter, Margaret. The Academic Proposal. The Lab Report. University College Writing Centre. University of Toronto; Punch, Keith and Wayne McGowan. "Developing and Writing a Research Proposal." In From Postgraduate to Social Scientist: A Guide to Key Skills . Nigel Gilbert, ed. (Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2006), 59-81; Wong, Paul T. P. How to Write a Research Proposal. International Network on Personal Meaning. Trinity Western University; Writing Academic Proposals: Conferences , Articles, and Books. The Writing Lab and The OWL. Purdue University; Writing a Research Proposal. University Library. University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign.
- << Previous: Writing a Reflective Paper
- Next: Generative AI and Writing >>
- Last Updated: May 31, 2024 1:46 PM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide/assignments
Reference management. Clean and simple.
How to write a research proposal

What is a research proposal?
What is the purpose of a research proposal , how long should a research proposal be, what should be included in a research proposal, 1. the title page, 2. introduction, 3. literature review, 4. research design, 5. implications, 6. reference list, frequently asked questions about writing a research proposal, related articles.
If you’re in higher education, the term “research proposal” is something you’re likely to be familiar with. But what is it, exactly? You’ll normally come across the need to prepare a research proposal when you’re looking to secure Ph.D. funding.
When you’re trying to find someone to fund your Ph.D. research, a research proposal is essentially your “pitch.”
A research proposal is a concise and coherent summary of your proposed research.
You’ll need to set out the issues that are central to the topic area and how you intend to address them with your research. To do this, you’ll need to give the following:
- an outline of the general area of study within which your research falls
- an overview of how much is currently known about the topic
- a literature review that covers the recent scholarly debate or conversation around the topic
➡️ What is a literature review? Learn more in our guide.
Essentially, you are trying to persuade your institution that you and your project are worth investing their time and money into.
It is the opportunity for you to demonstrate that you have the aptitude for this level of research by showing that you can articulate complex ideas:
It also helps you to find the right supervisor to oversee your research. When you’re writing your research proposal, you should always have this in the back of your mind.
This is the document that potential supervisors will use in determining the legitimacy of your research and, consequently, whether they will invest in you or not. It is therefore incredibly important that you spend some time on getting it right.
Tip: While there may not always be length requirements for research proposals, you should strive to cover everything you need to in a concise way.
If your research proposal is for a bachelor’s or master’s degree, it may only be a few pages long. For a Ph.D., a proposal could be a pretty long document that spans a few dozen pages.
➡️ Research proposals are similar to grant proposals. Learn how to write a grant proposal in our guide.
When you’re writing your proposal, keep in mind its purpose and why you’re writing it. It, therefore, needs to clearly explain the relevance of your research and its context with other discussions on the topic. You need to then explain what approach you will take and why it is feasible.
Generally, your structure should look something like this:
- Introduction
- Literature Review
- Research Design
- Implications
If you follow this structure, you’ll have a comprehensive and coherent proposal that looks and feels professional, without missing out on anything important. We’ll take a deep dive into each of these areas one by one next.
The title page might vary slightly per your area of study but, as a general point, your title page should contain the following:
- The proposed title of your project
- Your supervisor’s name
- The name of your institution and your particular department
Tip: Keep in mind any departmental or institutional guidelines for a research proposal title page. Also, your supervisor may ask for specific details to be added to the page.
The introduction is crucial to your research proposal as it is your first opportunity to hook the reader in. A good introduction section will introduce your project and its relevance to the field of study.
You’ll want to use this space to demonstrate that you have carefully thought about how to present your project as interesting, original, and important research. A good place to start is by introducing the context of your research problem.
Think about answering these questions:
- What is it you want to research and why?
- How does this research relate to the respective field?
- How much is already known about this area?
- Who might find this research interesting?
- What are the key questions you aim to answer with your research?
- What will the findings of this project add to the topic area?
Your introduction aims to set yourself off on a great footing and illustrate to the reader that you are an expert in your field and that your project has a solid foundation in existing knowledge and theory.
The literature review section answers the question who else is talking about your proposed research topic.
You want to demonstrate that your research will contribute to conversations around the topic and that it will sit happily amongst experts in the field.
➡️ Read more about how to write a literature review .
There are lots of ways you can find relevant information for your literature review, including:
- Research relevant academic sources such as books and journals to find similar conversations around the topic.
- Read through abstracts and bibliographies of your academic sources to look for relevance and further additional resources without delving too deep into articles that are possibly not relevant to you.
- Watch out for heavily-cited works . This should help you to identify authoritative work that you need to read and document.
- Look for any research gaps , trends and patterns, common themes, debates, and contradictions.
- Consider any seminal studies on the topic area as it is likely anticipated that you will address these in your research proposal.
This is where you get down to the real meat of your research proposal. It should be a discussion about the overall approach you plan on taking, and the practical steps you’ll follow in answering the research questions you’ve posed.
So what should you discuss here? Some of the key things you will need to discuss at this point are:
- What form will your research take? Is it qualitative/quantitative/mixed? Will your research be primary or secondary?
- What sources will you use? Who or what will you be studying as part of your research.
- Document your research method. How are you practically going to carry out your research? What tools will you need? What procedures will you use?
- Any practicality issues you foresee. Do you think there will be any obstacles to your anticipated timescale? What resources will you require in carrying out your research?
Your research design should also discuss the potential implications of your research. For example, are you looking to confirm an existing theory or develop a new one?
If you intend to create a basis for further research, you should describe this here.
It is important to explain fully what you want the outcome of your research to look like and what you want to achieve by it. This will help those reading your research proposal to decide if it’s something the field needs and wants, and ultimately whether they will support you with it.
When you reach the end of your research proposal, you’ll have to compile a list of references for everything you’ve cited above. Ideally, you should keep track of everything from the beginning. Otherwise, this could be a mammoth and pretty laborious task to do.
Consider using a reference manager like Paperpile to format and organize your citations. Paperpile allows you to organize and save your citations for later use and cite them in thousands of citation styles directly in Google Docs, Microsoft Word, or LaTeX.
Your project may also require you to have a timeline, depending on the budget you are requesting. If you need one, you should include it here and explain both the timeline and the budget you need, documenting what should be done at each stage of the research and how much of the budget this will use.
This is the final step, but not one to be missed. You should make sure that you edit and proofread your document so that you can be sure there are no mistakes.
A good idea is to have another person proofread the document for you so that you get a fresh pair of eyes on it. You can even have a professional proofreader do this for you.
This is an important document and you don’t want spelling or grammatical mistakes to get in the way of you and your reader.
➡️ Working on a research proposal for a thesis? Take a look at our guide on how to come up with a topic for your thesis .
A research proposal is a concise and coherent summary of your proposed research. Generally, your research proposal will have a title page, introduction, literature review section, a section about research design and explaining the implications of your research, and a reference list.
A good research proposal is concise and coherent. It has a clear purpose, clearly explains the relevance of your research and its context with other discussions on the topic. A good research proposal explains what approach you will take and why it is feasible.
You need a research proposal to persuade your institution that you and your project are worth investing their time and money into. It is your opportunity to demonstrate your aptitude for this level or research by showing that you can articulate complex ideas clearly, concisely, and critically.
A research proposal is essentially your "pitch" when you're trying to find someone to fund your PhD. It is a clear and concise summary of your proposed research. It gives an outline of the general area of study within which your research falls, it elaborates how much is currently known about the topic, and it highlights any recent debate or conversation around the topic by other academics.
The general answer is: as long as it needs to be to cover everything. The length of your research proposal depends on the requirements from the institution that you are applying to. Make sure to carefully read all the instructions given, and if this specific information is not provided, you can always ask.

We use essential cookies to make Venngage work. By clicking “Accept All Cookies”, you agree to the storing of cookies on your device to enhance site navigation, analyze site usage, and assist in our marketing efforts.
Manage Cookies
Cookies and similar technologies collect certain information about how you’re using our website. Some of them are essential, and without them you wouldn’t be able to use Venngage. But others are optional, and you get to choose whether we use them or not.
Strictly Necessary Cookies
These cookies are always on, as they’re essential for making Venngage work, and making it safe. Without these cookies, services you’ve asked for can’t be provided.
Show cookie providers
- Google Login
Functionality Cookies
These cookies help us provide enhanced functionality and personalisation, and remember your settings. They may be set by us or by third party providers.
Performance Cookies
These cookies help us analyze how many people are using Venngage, where they come from and how they're using it. If you opt out of these cookies, we can’t get feedback to make Venngage better for you and all our users.
- Google Analytics
Targeting Cookies
These cookies are set by our advertising partners to track your activity and show you relevant Venngage ads on other sites as you browse the internet.
- Google Tag Manager
- Infographics
- Daily Infographics
- Popular Templates
- Accessibility
- Graphic Design
- Graphs and Charts
- Data Visualization
- Human Resources
- Beginner Guides
Blog Business How to Write a Research Proposal: A Step-by-Step
How to Write a Research Proposal: A Step-by-Step
Written by: Danesh Ramuthi Nov 29, 2023

A research proposal is a structured outline for a planned study on a specific topic. It serves as a roadmap, guiding researchers through the process of converting their research idea into a feasible project.
The aim of a research proposal is multifold: it articulates the research problem, establishes a theoretical framework, outlines the research methodology and highlights the potential significance of the study. Importantly, it’s a critical tool for scholars seeking grant funding or approval for their research projects.
Crafting a good research proposal requires not only understanding your research topic and methodological approaches but also the ability to present your ideas clearly and persuasively. Explore Venngage’s Proposal Maker and Research Proposals Templates to begin your journey in writing a compelling research proposal.
What to include in a research proposal?
In a research proposal, include a clear statement of your research question or problem, along with an explanation of its significance. This should be followed by a literature review that situates your proposed study within the context of existing research.
Your proposal should also outline the research methodology, detailing how you plan to conduct your study, including data collection and analysis methods.
Additionally, include a theoretical framework that guides your research approach, a timeline or research schedule, and a budget if applicable. It’s important to also address the anticipated outcomes and potential implications of your study. A well-structured research proposal will clearly communicate your research objectives, methods and significance to the readers.

How to format a research proposal?
Formatting a research proposal involves adhering to a structured outline to ensure clarity and coherence. While specific requirements may vary, a standard research proposal typically includes the following elements:
- Title Page: Must include the title of your research proposal, your name and affiliations. The title should be concise and descriptive of your proposed research.
- Abstract: A brief summary of your proposal, usually not exceeding 250 words. It should highlight the research question, methodology and the potential impact of the study.
- Introduction: Introduces your research question or problem, explains its significance, and states the objectives of your study.
- Literature review: Here, you contextualize your research within existing scholarship, demonstrating your knowledge of the field and how your research will contribute to it.
- Methodology: Outline your research methods, including how you will collect and analyze data. This section should be detailed enough to show the feasibility and thoughtfulness of your approach.
- Timeline: Provide an estimated schedule for your research, breaking down the process into stages with a realistic timeline for each.
- Budget (if applicable): If your research requires funding, include a detailed budget outlining expected cost.
- References/Bibliography: List all sources referenced in your proposal in a consistent citation style.

How to write a research proposal in 11 steps?
Writing a research proposal template in structured steps ensures a comprehensive and coherent presentation of your research project. Let’s look at the explanation for each of the steps here:
Step 1: Title and Abstract Step 2: Introduction Step 3: Research objectives Step 4: Literature review Step 5: Methodology Step 6: Timeline Step 7: Resources Step 8: Ethical considerations Step 9: Expected outcomes and significance Step 10: References Step 11: Appendices
Step 1: title and abstract.
Select a concise, descriptive title and write an abstract summarizing your research question, objectives, methodology and expected outcomes. The abstract should include your research question, the objectives you aim to achieve, the methodology you plan to employ and the anticipated outcomes.
Step 2: Introduction
In this section, introduce the topic of your research, emphasizing its significance and relevance to the field. Articulate the research problem or question in clear terms and provide background context, which should include an overview of previous research in the field.
Step 3: Research objectives
Here, you’ll need to outline specific, clear and achievable objectives that align with your research problem. These objectives should be well-defined, focused and measurable, serving as the guiding pillars for your study. They help in establishing what you intend to accomplish through your research and provide a clear direction for your investigation.
Step 4: Literature review
In this part, conduct a thorough review of existing literature related to your research topic. This involves a detailed summary of key findings and major contributions from previous research. Identify existing gaps in the literature and articulate how your research aims to fill these gaps. The literature review not only shows your grasp of the subject matter but also how your research will contribute new insights or perspectives to the field.
Step 5: Methodology
Describe the design of your research and the methodologies you will employ. This should include detailed information on data collection methods, instruments to be used and analysis techniques. Justify the appropriateness of these methods for your research.
Step 6: Timeline
Construct a detailed timeline that maps out the major milestones and activities of your research project. Break the entire research process into smaller, manageable tasks and assign realistic time frames to each. This timeline should cover everything from the initial research phase to the final submission, including periods for data collection, analysis and report writing.
It helps in ensuring your project stays on track and demonstrates to reviewers that you have a well-thought-out plan for completing your research efficiently.
Step 7: Resources
Identify all the resources that will be required for your research, such as specific databases, laboratory equipment, software or funding. Provide details on how these resources will be accessed or acquired.
If your research requires funding, explain how it will be utilized effectively to support various aspects of the project.
Step 8: Ethical considerations
Address any ethical issues that may arise during your research. This is particularly important for research involving human subjects. Describe the measures you will take to ensure ethical standards are maintained, such as obtaining informed consent, ensuring participant privacy, and adhering to data protection regulations.
Here, in this section you should reassure reviewers that you are committed to conducting your research responsibly and ethically.
Step 9: Expected outcomes and significance
Articulate the expected outcomes or results of your research. Explain the potential impact and significance of these outcomes, whether in advancing academic knowledge, influencing policy or addressing specific societal or practical issues.
Step 10: References
Compile a comprehensive list of all the references cited in your proposal. Adhere to a consistent citation style (like APA or MLA) throughout your document. The reference section not only gives credit to the original authors of your sourced information but also strengthens the credibility of your proposal.
Step 11: Appendices
Include additional supporting materials that are pertinent to your research proposal. This can be survey questionnaires, interview guides, detailed data analysis plans or any supplementary information that supports the main text.
Appendices provide further depth to your proposal, showcasing the thoroughness of your preparation.

Research proposal FAQs
1. how long should a research proposal be.
The length of a research proposal can vary depending on the requirements of the academic institution, funding body or specific guidelines provided. Generally, research proposals range from 500 to 1500 words or about one to a few pages long. It’s important to provide enough detail to clearly convey your research idea, objectives and methodology, while being concise. Always check
2. Why is the research plan pivotal to a research project?
The research plan is pivotal to a research project because it acts as a blueprint, guiding every phase of the study. It outlines the objectives, methodology, timeline and expected outcomes, providing a structured approach and ensuring that the research is systematically conducted.
A well-crafted plan helps in identifying potential challenges, allocating resources efficiently and maintaining focus on the research goals. It is also essential for communicating the project’s feasibility and importance to stakeholders, such as funding bodies or academic supervisors.

Mastering how to write a research proposal is an essential skill for any scholar, whether in social and behavioral sciences, academic writing or any field requiring scholarly research. From this article, you have learned key components, from the literature review to the research design, helping you develop a persuasive and well-structured proposal.
Remember, a good research proposal not only highlights your proposed research and methodology but also demonstrates its relevance and potential impact.
For additional support, consider utilizing Venngage’s Proposal Maker and Research Proposals Templates , valuable tools in crafting a compelling proposal that stands out.
Whether it’s for grant funding, a research paper or a dissertation proposal, these resources can assist in transforming your research idea into a successful submission.
Discover popular designs

Infographic maker

Brochure maker

White paper online

Newsletter creator

Flyer maker

Timeline maker

Letterhead maker

Mind map maker

Ebook maker

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Chapter 14: The Research Proposal
14.3 Components of a Research Proposal
Krathwohl (2005) suggests and describes a variety of components to include in a research proposal. The following sections – Introductions, Background and significance, Literature Review; Research design and methods, Preliminary suppositions and implications; and Conclusion present these components in a suggested template for you to follow in the preparation of your research proposal.
Introduction
The introduction sets the tone for what follows in your research proposal – treat it as the initial pitch of your idea. After reading the introduction your reader should:
- understand what it is you want to do;
- have a sense of your passion for the topic; and
- be excited about the study’s possible outcomes.
As you begin writing your research proposal, it is helpful to think of the introduction as a narrative of what it is you want to do, written in one to three paragraphs. Within those one to three paragraphs, it is important to briefly answer the following questions:
- What is the central research problem?
- How is the topic of your research proposal related to the problem?
- What methods will you utilize to analyze the research problem?
- Why is it important to undertake this research? What is the significance of your proposed research? Why are the outcomes of your proposed research important? Whom are they important?
Note : You may be asked by your instructor to include an abstract with your research proposal. In such cases, an abstract should provide an overview of what it is you plan to study, your main research question, a brief explanation of your methods to answer the research question, and your expected findings. All of this information must be carefully crafted in 150 to 250 words. A word of advice is to save the writing of your abstract until the very end of your research proposal preparation. If you are asked to provide an abstract, you should include 5 to 7 key words that are of most relevance to your study. List these in order of relevance.
Background and significance
The purpose of this section is to explain the context of your proposal and to describe, in detail, why it is important to undertake this research. Assume that the person or people who will read your research proposal know nothing or very little about the research problem. While you do not need to include all knowledge you have learned about your topic in this section, it is important to ensure that you include the most relevant material that will help to explain the goals of your research.
While there are no hard and fast rules, you should attempt to address some or all of the following key points:
- State the research problem and provide a more thorough explanation about the purpose of the study than what you stated in the introduction.
- Present the rationale for the proposed research study. Clearly indicate why this research is worth doing. Answer the “so what?” question.
- Describe the major issues or problems to be addressed by your research. Do not forget to explain how and in what ways your proposed research builds upon previous related research.
- Explain how you plan to go about conducting your research.
- Clearly identify the key or most relevant sources of research you intend to use and explain how they will contribute to your analysis of the topic.
- Set the boundaries of your proposed research, in order to provide a clear focus. Where appropriate, state not only what you will study, but what will be excluded from your study.
- Provide clear definitions of key concepts and terms. Since key concepts and terms often have numerous definitions, make sure you state which definition you will be utilizing in your research.
Literature review
This key component of the research proposal is the most time-consuming aspect in the preparation of your research proposal. As described in Chapter 5 , the literature review provides the background to your study and demonstrates the significance of the proposed research. Specifically, it is a review and synthesis of prior research that is related to the problem you are setting forth to investigate. Essentially, your goal in the literature review is to place your research study within the larger whole of what has been studied in the past, while demonstrating to your reader that your work is original, innovative, and adds to the larger whole.
As the literature review is information dense, it is essential that this section be intelligently structured to enable your reader to grasp the key arguments underpinning your study. However, this can be easier to state and harder to do, simply due to the fact there is usually a plethora of related research to sift through. Consequently, a good strategy for writing the literature review is to break the literature into conceptual categories or themes, rather than attempting to describe various groups of literature you reviewed. Chapter 5 describes a variety of methods to help you organize the themes.
Here are some suggestions on how to approach the writing of your literature review:
- Think about what questions other researchers have asked, what methods they used, what they found, and what they recommended based upon their findings.
- Do not be afraid to challenge previous related research findings and/or conclusions.
- Assess what you believe to be missing from previous research and explain how your research fills in this gap and/or extends previous research.
It is important to note that a significant challenge related to undertaking a literature review is knowing when to stop. As such, it is important to know when you have uncovered the key conceptual categories underlying your research topic. Generally, when you start to see repetition in the conclusions or recommendations, you can have confidence that you have covered all of the significant conceptual categories in your literature review. However, it is also important to acknowledge that researchers often find themselves returning to the literature as they collect and analyze their data. For example, an unexpected finding may develop as you collect and/or analyze the data; in this case, it is important to take the time to step back and review the literature again, to ensure that no other researchers have found a similar finding. This may include looking to research outside your field.
This situation occurred with one of this textbook’s authors’ research related to community resilience. During the interviews, the researchers heard many participants discuss individual resilience factors and how they believed these individual factors helped make the community more resilient, overall. Sheppard and Williams (2016) had not discovered these individual factors in their original literature review on community and environmental resilience. However, when they returned to the literature to search for individual resilience factors, they discovered a small body of literature in the child and youth psychology field. Consequently, Sheppard and Williams had to go back and add a new section to their literature review on individual resilience factors. Interestingly, their research appeared to be the first research to link individual resilience factors with community resilience factors.
Research design and methods
The objective of this section of the research proposal is to convince the reader that your overall research design and methods of analysis will enable you to solve the research problem you have identified and also enable you to accurately and effectively interpret the results of your research. Consequently, it is critical that the research design and methods section is well-written, clear, and logically organized. This demonstrates to your reader that you know what you are going to do and how you are going to do it. Overall, you want to leave your reader feeling confident that you have what it takes to get this research study completed in a timely fashion.
Essentially, this section of the research proposal should be clearly tied to the specific objectives of your study; however, it is also important to draw upon and include examples from the literature review that relate to your design and intended methods. In other words, you must clearly demonstrate how your study utilizes and builds upon past studies, as it relates to the research design and intended methods. For example, what methods have been used by other researchers in similar studies?
While it is important to consider the methods that other researchers have employed, it is equally, if not more, important to consider what methods have not been but could be employed. Remember, the methods section is not simply a list of tasks to be undertaken. It is also an argument as to why and how the tasks you have outlined will help you investigate the research problem and answer your research question(s).
Tips for writing the research design and methods section:
Specify the methodological approaches you intend to employ to obtain information and the techniques you will use to analyze the data.
Specify the research operations you will undertake and the way you will interpret the results of those operations in relation to the research problem.
Go beyond stating what you hope to achieve through the methods you have chosen. State how you will actually implement the methods (i.e., coding interview text, running regression analysis, etc.).
Anticipate and acknowledge any potential barriers you may encounter when undertaking your research, and describe how you will address these barriers.
Explain where you believe you will find challenges related to data collection, including access to participants and information.
Preliminary suppositions and implications
The purpose of this section is to argue how you anticipate that your research will refine, revise, or extend existing knowledge in the area of your study. Depending upon the aims and objectives of your study, you should also discuss how your anticipated findings may impact future research. For example, is it possible that your research may lead to a new policy, theoretical understanding, or method for analyzing data? How might your study influence future studies? What might your study mean for future practitioners working in the field? Who or what might benefit from your study? How might your study contribute to social, economic or environmental issues? While it is important to think about and discuss possibilities such as these, it is equally important to be realistic in stating your anticipated findings. In other words, you do not want to delve into idle speculation. Rather, the purpose here is to reflect upon gaps in the current body of literature and to describe how you anticipate your research will begin to fill in some or all of those gaps.
The conclusion reiterates the importance and significance of your research proposal, and provides a brief summary of the entire proposed study. Essentially, this section should only be one or two paragraphs in length. Here is a potential outline for your conclusion:
Discuss why the study should be done. Specifically discuss how you expect your study will advance existing knowledge and how your study is unique.
Explain the specific purpose of the study and the research questions that the study will answer.
Explain why the research design and methods chosen for this study are appropriate, and why other designs and methods were not chosen.
State the potential implications you expect to emerge from your proposed study,
Provide a sense of how your study fits within the broader scholarship currently in existence, related to the research problem.
Citations and references
As with any scholarly research paper, you must cite the sources you used in composing your research proposal. In a research proposal, this can take two forms: a reference list or a bibliography. A reference list lists the literature you referenced in the body of your research proposal. All references in the reference list must appear in the body of the research proposal. Remember, it is not acceptable to say “as cited in …” As a researcher you must always go to the original source and check it for yourself. Many errors are made in referencing, even by top researchers, and so it is important not to perpetuate an error made by someone else. While this can be time consuming, it is the proper way to undertake a literature review.
In contrast, a bibliography , is a list of everything you used or cited in your research proposal, with additional citations to any key sources relevant to understanding the research problem. In other words, sources cited in your bibliography may not necessarily appear in the body of your research proposal. Make sure you check with your instructor to see which of the two you are expected to produce.
Overall, your list of citations should be a testament to the fact that you have done a sufficient level of preliminary research to ensure that your project will complement, but not duplicate, previous research efforts. For social sciences, the reference list or bibliography should be prepared in American Psychological Association (APA) referencing format. Usually, the reference list (or bibliography) is not included in the word count of the research proposal. Again, make sure you check with your instructor to confirm.
Research Methods for the Social Sciences: An Introduction Copyright © 2020 by Valerie Sheppard is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book

- Research Process
Writing a Scientific Research Project Proposal
- 5 minute read
- 104.7K views
Table of Contents
The importance of a well-written research proposal cannot be underestimated. Your research really is only as good as your proposal. A poorly written, or poorly conceived research proposal will doom even an otherwise worthy project. On the other hand, a well-written, high-quality proposal will increase your chances for success.
In this article, we’ll outline the basics of writing an effective scientific research proposal, including the differences between research proposals, grants and cover letters. We’ll also touch on common mistakes made when submitting research proposals, as well as a simple example or template that you can follow.
What is a scientific research proposal?
The main purpose of a scientific research proposal is to convince your audience that your project is worthwhile, and that you have the expertise and wherewithal to complete it. The elements of an effective research proposal mirror those of the research process itself, which we’ll outline below. Essentially, the research proposal should include enough information for the reader to determine if your proposed study is worth pursuing.
It is not an uncommon misunderstanding to think that a research proposal and a cover letter are the same things. However, they are different. The main difference between a research proposal vs cover letter content is distinct. Whereas the research proposal summarizes the proposal for future research, the cover letter connects you to the research, and how you are the right person to complete the proposed research.
There is also sometimes confusion around a research proposal vs grant application. Whereas a research proposal is a statement of intent, related to answering a research question, a grant application is a specific request for funding to complete the research proposed. Of course, there are elements of overlap between the two documents; it’s the purpose of the document that defines one or the other.
Scientific Research Proposal Format
Although there is no one way to write a scientific research proposal, there are specific guidelines. A lot depends on which journal you’re submitting your research proposal to, so you may need to follow their scientific research proposal template.
In general, however, there are fairly universal sections to every scientific research proposal. These include:
- Title: Make sure the title of your proposal is descriptive and concise. Make it catch and informative at the same time, avoiding dry phrases like, “An investigation…” Your title should pique the interest of the reader.
- Abstract: This is a brief (300-500 words) summary that includes the research question, your rationale for the study, and any applicable hypothesis. You should also include a brief description of your methodology, including procedures, samples, instruments, etc.
- Introduction: The opening paragraph of your research proposal is, perhaps, the most important. Here you want to introduce the research problem in a creative way, and demonstrate your understanding of the need for the research. You want the reader to think that your proposed research is current, important and relevant.
- Background: Include a brief history of the topic and link it to a contemporary context to show its relevance for today. Identify key researchers and institutions also looking at the problem
- Literature Review: This is the section that may take the longest amount of time to assemble. Here you want to synthesize prior research, and place your proposed research into the larger picture of what’s been studied in the past. You want to show your reader that your work is original, and adds to the current knowledge.
- Research Design and Methodology: This section should be very clearly and logically written and organized. You are letting your reader know that you know what you are going to do, and how. The reader should feel confident that you have the skills and knowledge needed to get the project done.
- Preliminary Implications: Here you’ll be outlining how you anticipate your research will extend current knowledge in your field. You might also want to discuss how your findings will impact future research needs.
- Conclusion: This section reinforces the significance and importance of your proposed research, and summarizes the entire proposal.
- References/Citations: Of course, you need to include a full and accurate list of any and all sources you used to write your research proposal.
Common Mistakes in Writing a Scientific Research Project Proposal
Remember, the best research proposal can be rejected if it’s not well written or is ill-conceived. The most common mistakes made include:
- Not providing the proper context for your research question or the problem
- Failing to reference landmark/key studies
- Losing focus of the research question or problem
- Not accurately presenting contributions by other researchers and institutions
- Incompletely developing a persuasive argument for the research that is being proposed
- Misplaced attention on minor points and/or not enough detail on major issues
- Sloppy, low-quality writing without effective logic and flow
- Incorrect or lapses in references and citations, and/or references not in proper format
- The proposal is too long – or too short
Scientific Research Proposal Example
There are countless examples that you can find for successful research proposals. In addition, you can also find examples of unsuccessful research proposals. Search for successful research proposals in your field, and even for your target journal, to get a good idea on what specifically your audience may be looking for.
While there’s no one example that will show you everything you need to know, looking at a few will give you a good idea of what you need to include in your own research proposal. Talk, also, to colleagues in your field, especially if you are a student or a new researcher. We can often learn from the mistakes of others. The more prepared and knowledgeable you are prior to writing your research proposal, the more likely you are to succeed.
Language Editing Services
One of the top reasons scientific research proposals are rejected is due to poor logic and flow. Check out our Language Editing Services to ensure a great proposal , that’s clear and concise, and properly referenced. Check our video for more information, and get started today.

- Manuscript Review
Research Fraud: Falsification and Fabrication in Research Data

Research Team Structure
You may also like.

Descriptive Research Design and Its Myriad Uses

Five Common Mistakes to Avoid When Writing a Biomedical Research Paper

Making Technical Writing in Environmental Engineering Accessible

To Err is Not Human: The Dangers of AI-assisted Academic Writing

When Data Speak, Listen: Importance of Data Collection and Analysis Methods

Choosing the Right Research Methodology: A Guide for Researchers

Why is data validation important in research?

Writing a good review article
Input your search keywords and press Enter.
- 301 Academic Skills Centre
- Study skills online
How to write a research proposal
Advice and guidance on writing a proposal for a student research project.

Purpose of a Research Proposal
A research proposal should describe what you will investigate, why it is important to the discipline and how you will conduct your research.
Simply put, it is your plan for the research you intend to conduct. All research proposals are designed to persuade someone about how and why your intended project is worthwhile.
In your proposal you will need to explain and defend your choices. Always think about the exact reasons why you are making specific choices and why they are the best options available to you and your project.
Your research proposal aims should be centred on:
- Relevance - You want to convince the reader how and why your research is relevant and significant to your field and how it is original. This is typically done in parts of the introduction and the literature review.
- Context - You should demonstrate that you are familiar with the field, you understand the current state of research on the topic and your ideas have a strong academic basis (i.e., not simply based on your instincts or personal views). This will be the focus of your introduction and literature review.
- Approach - You need to make a case for your methodology, showing that you have carefully thought about the data, tools and procedures you will need to conduct the research. You need to explicitly defend all of your choices. This will be presented in the research design section.
- Feasibility - You need to demonstrate clearly that your project is both reasonable and feasible within the practical constraints of the course, timescales, institution or funding. You need to make sure you have the time and access to resources to complete the project in a reasonable period.
301 Recommends:
Our Research Writing workshop will look at some of the main writing challenges associated with writing a large-scale research project and look at strategies to manage your writing on a day-to-day basis. It will identify ways to plan, organise and map out the structure of your writing to allow you to develop an effective writing schedule and make continuous progress on your dissertation project.
Proposal format
The format of a research proposal varies between fields and levels of study but most proposals should contain at least these elements: introduction, literature review, research design and reference list.
Generally, research proposals can range from 500-1500 words or one to a few pages long. Typically, proposals for larger projects such as a PhD dissertation or funding requests, are longer and much more detailed.
Remember, the goal of your research proposal is to outline clearly and concisely exactly what your research will entail and accomplish, how it will do so and why it is important. If you are writing to a strictly enforced word count, a research proposal can be a great test of your ability to express yourself concisely!
Introduction
The first part of your proposal is the initial pitch for your project, so make sure it succinctly explains what you want to do and why. In other words, this is where you answer the reader’s “so what?” It should typically include: introducing the topic , outlining your problem statement and research question(s) and giving background and context. Some important questions to shape your introduction include:
- Who has an interest in the topic (e.g. scientists, practitioners, policymakers, particular members of society)?
- How much is already known about the problem and why is it important?
- What is missing from current knowledge and why?
- What new insights will your research contribute?
- Why is this research worth doing?
If your proposal is very long, you might include separate sections with more detailed information on the background and context, problem statement, aims and objectives, and importance of the research.
Literature Review
It’s important to show that you’re familiar with the most important research on your topic. A strong literature review convinces the reader that your project has a solid foundation in existing knowledge or theory (i.e. how it relates to established research in the field).
Your literature review will also show that you’re not simply repeating what other people have already done or said. This is also where you explain why your research is necessary. You might want to consider some of the following prompts:
- Comparing and contrasting: what are the main theories, methods, debates and controversies?
- Being critical: what are the strengths and weaknesses of different approaches?
- Showing how your research fits in: how will you build on, challenge or synthesise the work of others?
- Filling a gap in the existing body of research: why is your idea innovative?
Research design and methods
Following the literature review, it is a good idea to restate your main objectives, bringing the focus back to your own project. The research design/ methodology section should describe the overall approach and practical steps you will take to answer your research questions. You also need to demonstrate the feasibility of the project keeping in mind time and other constraints.
You should definitely include:
- Qualitative vs quantitative research? Combination?
- Will you collect original data or work with primary/secondary sources?
- Is your research design descriptive, correlational or experimental? Something completely different?
- If you are undertaking your own study, when and where will you collect the data? How will you select subjects or sources? Ethics review? Exactly what or who will you study?
- What tools and procedures will you use (e.g. systematic reviews, surveys, interviews, observation, experiments, bibliographic data) to collect your data?
- What tools/methods will you use to analyse your data?
- Why are these the best methods to answer your research question(s)? This is where you should justify your choices.
- How much time will you need to collect the data?
- How will you gain access to participants and sources?
- Do you foresee any potential obstacles and if so, how will you address them?
Make sure you are not simply compiling a list of methods. Instead, aim to make an argument for why this is the most appropriate, valid and reliable way to approach answering your question. Remember you should always be defending your choices!
Implications and Contributions to Knowledge
To ensure you finish your proposal on a strong note, it is a good idea to explore and/or emphasise the potential implications of the research. This means: what do you intend to contribute to existing knowledge on the topic?
Although you cannot know the results of your research until you have actually done the work, you should be going into the project with a clear idea of how your work will contribute to your field. This section might even be considered the most critical to your research proposal’s argument because it expresses exactly why your research is necessary.
You should consider covering at least some of the following topics:
- Ways in which your work can challenge existing theories and assumptions in your field.
- How your work will create the foundation for future research and theory.
- The practical value your findings will provide to practitioners, educators and other academics in your field.
- The problems or issues your work can potentially help to resolve.
- Policies that could be impacted by your findings.
- How your findings can be implemented in academia or other settings and how this will improve or otherwise transform these settings.
This part is not about stating the specific results that you expect to obtain but rather, this is the section where you explicitly state how your findings will be valuable.
This section is where you want to wrap it all up in a nice pretty bow. It is just like the concluding paragraph that you would structure and craft for a typical essay. You should briefly summarise your research proposal and reinforce your research purpose.
Reference List or Bibliography
Your research proposal MUST include proper citations for every source you have used and full references. Please consult your departmental referencing styles to ensure you are citing and referencing in an appropriate way.
Common mistakes to avoid
Try and avoid these common pitfalls when you are writing your research proposal:
- Being too wordy: Remember formal does not mean flowery or pretentious. In fact, you should really aim to keep your writing as concise and accessible as possible. The more economically you can express your goals and ideas, the better.
- Failing to cite relevant information/sources: You are adding to the existing body of knowledge on the subject you are covering. Therefore, your research proposal should reference the main research pieces in your field (while referencing them correctly!) and connect your proposal to these works in some way. This does not mean just communicating the relevance of your work, it should explicitly demonstrate your familiarity with the field.
- Focusing too much on minor issues: Your research is most likely important for so many great reasons. However, they do not all need to be listed in your research proposal. Generally, including too many questions and issues in your research proposal can serve as a red flag and detract from your main purpose(s). This will in turn weaken your proposal. Only involve the main/key issues you plan to address.
- Failing to make a strong argument for your research: This is the simplest way to undermine your proposal. Your proposal is a piece of persuasive and critical writing . This means that, although you are presenting your proposal in an academic and hopefully objective manner, the goal is to get the reader to say ‘yes’ to your work.
- Not polishing your writing : If your proposal has spelling or grammatical errors, an inconsistent or inappropriate tone or even just awkward phrasing it can undermine your credibility. Check out some of these resources to help guide you in the right direction: Manchester Academic Phrasebank , Proofreading Guide , Essay Checklist and Grammar Guide . Remember to double and triple check your work.
Links and Resources
You might also need to include a schedule and/or a budget depending on your requirements. Some tools to help include:
- Manchester University Academic Phrasebank
- Leeds Beckett Assignment Calculator
- Calendarpedia
Related information
Dissertation planning
Writing a literature review
Research methods

The Summer Skills Spark: 5 weeks to ignite your research skills
Are you working on a dissertation or research project this summer?
The Summer Skills Spark offers workshops to support you through every step of the process. You'll have opportunities to plan your projects, develop your research skills, explore dissemination techniques, and consider a future career in research.
Collaboration between 301 Academic Skills Centre, the University Library, Digital Learning, and the Careers and Employability Service.
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- v.23(2); 2008 Apr

How to prepare a Research Proposal
Health research, medical education and clinical practice form the three pillars of modern day medical practice. As one authority rightly put it: ‘Health research is not a luxury, but an essential need that no nation can afford to ignore’. Health research can and should be pursued by a broad range of people. Even if they do not conduct research themselves, they need to grasp the principles of the scientific method to understand the value and limitations of science and to be able to assess and evaluate results of research before applying them. This review paper aims to highlight the essential concepts to the students and beginning researchers and sensitize and motivate the readers to access the vast literature available on research methodologies.
Most students and beginning researchers do not fully understand what a research proposal means, nor do they understand its importance. 1 A research proposal is a detailed description of a proposed study designed to investigate a given problem. 2
A research proposal is intended to convince others that you have a worthwhile research project and that you have the competence and the work-plan to complete it. Broadly the research proposal must address the following questions regardless of your research area and the methodology you choose: What you plan to accomplish, why do you want to do it and how are you going to do it. 1 The aim of this article is to highlight the essential concepts and not to provide extensive details about this topic.
The elements of a research proposal are highlighted below:
1. Title: It should be concise and descriptive. It must be informative and catchy. An effective title not only prick’s the readers interest, but also predisposes him/her favorably towards the proposal. Often titles are stated in terms of a functional relationship, because such titles clearly indicate the independent and dependent variables. 1 The title may need to be revised after completion of writing of the protocol to reflect more closely the sense of the study. 3
2. Abstract: It is a brief summary of approximately 300 words. It should include the main research question, the rationale for the study, the hypothesis (if any) and the method. Descriptions of the method may include the design, procedures, the sample and any instruments that will be used. 1 It should stand on its own, and not refer the reader to points in the project description. 3
3. Introduction: The introduction provides the readers with the background information. Its purpose is to establish a framework for the research, so that readers can understand how it relates to other research. 4 It should answer the question of why the research needs to be done and what will be its relevance. It puts the proposal in context. 3
The introduction typically begins with a statement of the research problem in precise and clear terms. 1
The importance of the statement of the research problem 5 : The statement of the problem is the essential basis for the construction of a research proposal (research objectives, hypotheses, methodology, work plan and budget etc). It is an integral part of selecting a research topic. It will guide and put into sharper focus the research design being considered for solving the problem. It allows the investigator to describe the problem systematically, to reflect on its importance, its priority in the country and region and to point out why the proposed research on the problem should be undertaken. It also facilitates peer review of the research proposal by the funding agencies.
Then it is necessary to provide the context and set the stage for the research question in such a way as to show its necessity and importance. 1 This step is necessary for the investigators to familiarize themselves with existing knowledge about the research problem and to find out whether or not others have investigated the same or similar problems. This step is accomplished by a thorough and critical review of the literature and by personal communication with experts. 5 It helps further understanding of the problem proposed for research and may lead to refining the statement of the problem, to identify the study variables and conceptualize their relationships, and in formulation and selection of a research hypothesis. 5 It ensures that you are not "re-inventing the wheel" and demonstrates your understanding of the research problem. It gives due credit to those who have laid the groundwork for your proposed research. 1 In a proposal, the literature review is generally brief and to the point. The literature selected should be pertinent and relevant. 6
Against this background, you then present the rationale of the proposed study and clearly indicate why it is worth doing.
4. Objectives: Research objectives are the goals to be achieved by conducting the research. 5 They may be stated as ‘general’ and ‘specific’.
The general objective of the research is what is to be accomplished by the research project, for example, to determine whether or not a new vaccine should be incorporated in a public health program.
The specific objectives relate to the specific research questions the investigator wants to answer through the proposed study and may be presented as primary and secondary objectives, for example, primary: To determine the degree of protection that is attributable to the new vaccine in a study population by comparing the vaccinated and unvaccinated groups. 5 Secondary: To study the cost-effectiveness of this programme.
Young investigators are advised to resist the temptation to put too many objectives or over-ambitious objectives that cannot be adequately achieved by the implementation of the protocol. 3
5. Variables: During the planning stage, it is necessary to identify the key variables of the study and their method of measurement and unit of measurement must be clearly indicated. Four types of variables are important in research 5 :
a. Independent variables: variables that are manipulated or treated in a study in order to see what effect differences in them will have on those variables proposed as being dependent on them. The different synonyms for the term ‘independent variable’ which are used in literature are: cause, input, predisposing factor, risk factor, determinant, antecedent, characteristic and attribute.
b. Dependent variables: variables in which changes are results of the level or amount of the independent variable or variables.
Synonyms: effect, outcome, consequence, result, condition, disease.
c. Confounding or intervening variables: variables that should be studied because they may influence or ‘mix’ the effect of the independent variables. For instance, in a study of the effect of measles (independent variable) on child mortality (dependent variable), the nutritional status of the child may play an intervening (confounding) role.
d. Background variables: variables that are so often of relevance in investigations of groups or populations that they should be considered for possible inclusion in the study. For example sex, age, ethnic origin, education, marital status, social status etc.
The objective of research is usually to determine the effect of changes in one or more independent variables on one or more dependent variables. For example, a study may ask "Will alcohol intake (independent variable) have an effect on development of gastric ulcer (dependent variable)?"
Certain variables may not be easy to identify. The characteristics that define these variables must be clearly identified for the purpose of the study.
6. Questions and/ or hypotheses: If you as a researcher know enough to make prediction concerning what you are studying, then the hypothesis may be formulated. A hypothesis can be defined as a tentative prediction or explanation of the relationship between two or more variables. In other words, the hypothesis translates the problem statement into a precise, unambiguous prediction of expected outcomes. Hypotheses are not meant to be haphazard guesses, but should reflect the depth of knowledge, imagination and experience of the investigator. 5 In the process of formulating the hypotheses, all variables relevant to the study must be identified. For example: "Health education involving active participation by mothers will produce more positive changes in child feeding than health education based on lectures". Here the independent variable is types of health education and the dependent variable is changes in child feeding.
A research question poses a relationship between two or more variables but phrases the relationship as a question; a hypothesis represents a declarative statement of the relations between two or more variables. 7
For exploratory or phenomenological research, you may not have any hypothesis (please do not confuse the hypothesis with the statistical null hypothesis). 1 Questions are relevant to normative or census type research (How many of them are there? Is there a relationship between them?). Deciding whether to use questions or hypotheses depends on factors such as the purpose of the study, the nature of the design and methodology, and the audience of the research (at times even the outlook and preference of the committee members, particularly the Chair). 6
7. Methodology: The method section is very important because it tells your research Committee how you plan to tackle your research problem. The guiding principle for writing the Methods section is that it should contain sufficient information for the reader to determine whether the methodology is sound. Some even argue that a good proposal should contain sufficient details for another qualified researcher to implement the study. 1 Indicate the methodological steps you will take to answer every question or to test every hypothesis illustrated in the Questions/hypotheses section. 6 It is vital that you consult a biostatistician during the planning stage of your study, 8 to resolve the methodological issues before submitting the proposal.
This section should include:
Research design: The selection of the research strategy is the core of research design and is probably the single most important decision the investigator has to make. The choice of the strategy, whether descriptive, analytical, experimental, operational or a combination of these depend on a number of considerations, 5 but this choice must be explained in relation to the study objectives. 3
Research subjects or participants: Depending on the type of your study, the following questions should be answered 3 , 5
- - What are the criteria for inclusion or selection?
- - What are the criteria for exclusion?
- - What is the sampling procedure you will use so as to ensure representativeness and reliability of the sample and to minimize sampling errors? The key reason for being concerned with sampling is the issue of validity-both internal and external of the study results. 9
- - Will there be use of controls in your study? Controls or comparison groups are used in scientific research in order to increase the validity of the conclusions. Control groups are necessary in all analytical epidemiological studies, in experimental studies of drug trials, in research on effects of intervention programmes and disease control measures and in many other investigations. Some descriptive studies (studies of existing data, surveys) may not require control groups.
- - What are the criteria for discontinuation?
Sample size: The proposal should provide information and justification (basis on which the sample size is calculated) about sample size in the methodology section. 3 A larger sample size than needed to test the research hypothesis increases the cost and duration of the study and will be unethical if it exposes human subjects to any potential unnecessary risk without additional benefit. A smaller sample size than needed can also be unethical as it exposes human subjects to risk with no benefit to scientific knowledge. Calculation of sample size has been made easy by computer software programmes, but the principles underlying the estimation should be well understood.
Interventions: If an intervention is introduced, a description must be given of the drugs or devices (proprietary names, manufacturer, chemical composition, dose, frequency of administration) if they are already commercially available. If they are in phases of experimentation or are already commercially available but used for other indications, information must be provided on available pre-clinical investigations in animals and/or results of studies already conducted in humans (in such cases, approval of the drug regulatory agency in the country is needed before the study). 3
Ethical issues 3 : Ethical considerations apply to all types of health research. Before the proposal is submitted to the Ethics Committee for approval, two important documents mentioned below (where appropriate) must be appended to the proposal. In additions, there is another vital issue of Conflict of Interest, wherein the researchers should furnish a statement regarding the same.
The Informed consent form (informed decision-making): A consent form, where appropriate, must be developed and attached to the proposal. It should be written in the prospective subjects’ mother tongue and in simple language which can be easily understood by the subject. The use of medical terminology should be avoided as far as possible. Special care is needed when subjects are illiterate. It should explain why the study is being done and why the subject has been asked to participate. It should describe, in sequence, what will happen in the course of the study, giving enough detail for the subject to gain a clear idea of what to expect. It should clarify whether or not the study procedures offer any benefits to the subject or to others, and explain the nature, likelihood and treatment of anticipated discomfort or adverse effects, including psychological and social risks, if any. Where relevant, a comparison with risks posed by standard drugs or treatment must be included. If the risks are unknown or a comparative risk cannot be given it should be so stated. It should indicate that the subject has the right to withdraw from the study at any time without, in any way, affecting his/her further medical care. It should assure the participant of confidentiality of the findings.
Ethics checklist: The proposal must describe the measures that will be undertaken to ensure that the proposed research is carried out in accordance with the World Medical Association Declaration of Helsinki on Ethical Principles for Medical research involving Human Subjects. 10 It must answer the following questions:
- • Is the research design adequate to provide answers to the research question? It is unethical to expose subjects to research that will have no value.
- • Is the method of selection of research subjects justified? The use of vulnerable subjects as research participants needs special justification. Vulnerable subjects include those in prison, minors and persons with mental disability. In international research it is important to mention that the population in which the study is conducted will benefit from any potential outcome of the research and the research is not being conducted solely for the benefit of some other population. Justification is needed for any inducement, financial or otherwise, for the participants to be enrolled in the study.
- • Are the interventions justified, in terms of risk/benefit ratio? Risks are not limited to physical harm. Psychological and social risks must also be considered.
- • For observations made, have measures been taken to ensure confidentiality?
Research setting 5 : The research setting includes all the pertinent facets of the study, such as the population to be studied (sampling frame), the place and time of study.
Study instruments 3 , 5 : Instruments are the tools by which the data are collected. For validated questionnaires/interview schedules, reference to published work should be given and the instrument appended to the proposal. For new a questionnaire which is being designed specifically for your study the details about preparing, precoding and pretesting of questionnaire should be furnished and the document appended to the proposal. Descriptions of other methods of observations like medical examination, laboratory tests and screening procedures is necessary- for established procedures, reference of published work cited but for new or modified procedure, an adequate description is necessary with justification for the same.
Collection of data: A short description of the protocol of data collection. For example, in a study on blood pressure measurement: time of participant arrival, rest for 5p. 10 minutes, which apparatus (standard calibrated) to be used, in which room to take measurement, measurement in sitting or lying down position, how many measurements, measurement in which arm first (whether this is going to be randomized), details of cuff and its placement, who will take the measurement. This minimizes the possibility of confusion, delays and errors.
Data analysis: The description should include the design of the analysis form, plans for processing and coding the data and the choice of the statistical method to be applied to each data. What will be the procedures for accounting for missing, unused or spurious data?
Monitoring, supervision and quality control: Detailed statement about the all logistical issues to satisfy the requirements of Good Clinical Practices (GCP), protocol procedures, responsibilities of each member of the research team, training of study investigators, steps taken to assure quality control (laboratory procedures, equipment calibration etc)
Gantt chart: A Gantt chart is an overview of tasks/proposed activities and a time frame for the same. You put weeks, days or months at one side, and the tasks at the other. You draw fat lines to indicate the period the task will be performed to give a timeline for your research study (take help of tutorial on youtube). 11
Significance of the study: Indicate how your research will refine, revise or extend existing knowledge in the area under investigation. How will it benefit the concerned stakeholders? What could be the larger implications of your research study?
Dissemination of the study results: How do you propose to share the findings of your study with professional peers, practitioners, participants and the funding agency?
Budget: A proposal budget with item wise/activity wise breakdown and justification for the same. Indicate how will the study be financed.
References: The proposal should end with relevant references on the subject. For web based search include the date of access for the cited website, for example: add the sentence "accessed on June 10, 2008".
Appendixes: Include the appropriate appendixes in the proposal. For example: Interview protocols, sample of informed consent forms, cover letters sent to appropriate stakeholders, official letters for permission to conduct research. Regarding original scales or questionnaires, if the instrument is copyrighted then permission in writing to reproduce the instrument from the copyright holder or proof of purchase of the instrument must be submitted.
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Research process
- How to Write a Research Proposal | Examples & Templates
How to Write a Research Proposal | Examples & Templates
Published on 30 October 2022 by Shona McCombes and Tegan George. Revised on 13 June 2023.
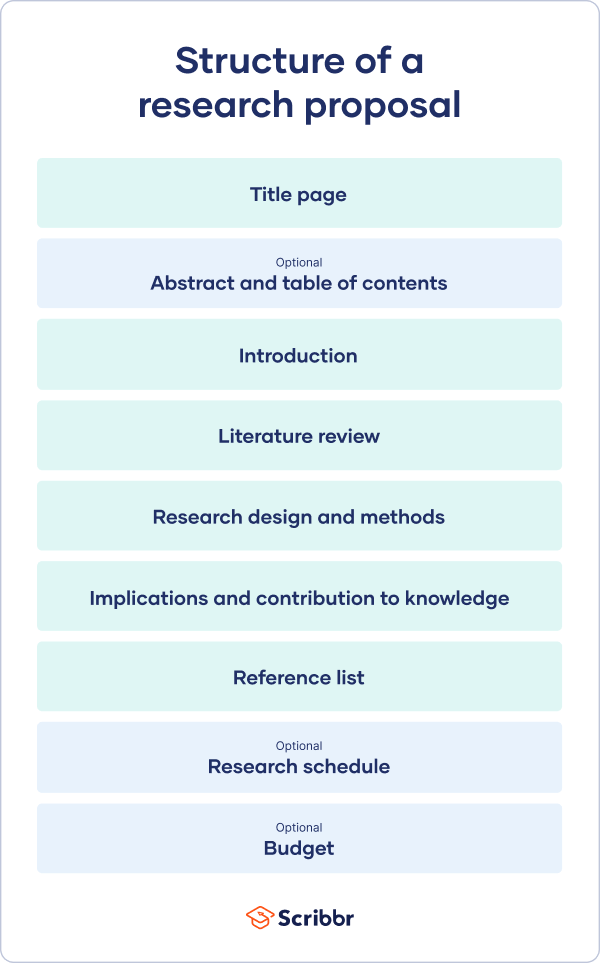
A research proposal describes what you will investigate, why it’s important, and how you will conduct your research.
The format of a research proposal varies between fields, but most proposals will contain at least these elements:
Introduction
Literature review.
- Research design

Reference list
While the sections may vary, the overall objective is always the same. A research proposal serves as a blueprint and guide for your research plan, helping you get organised and feel confident in the path forward you choose to take.
Table of contents
Research proposal purpose, research proposal examples, research design and methods, contribution to knowledge, research schedule, frequently asked questions.
Academics often have to write research proposals to get funding for their projects. As a student, you might have to write a research proposal as part of a grad school application , or prior to starting your thesis or dissertation .
In addition to helping you figure out what your research can look like, a proposal can also serve to demonstrate why your project is worth pursuing to a funder, educational institution, or supervisor.
Research proposal length
The length of a research proposal can vary quite a bit. A bachelor’s or master’s thesis proposal can be just a few pages, while proposals for PhD dissertations or research funding are usually much longer and more detailed. Your supervisor can help you determine the best length for your work.
One trick to get started is to think of your proposal’s structure as a shorter version of your thesis or dissertation , only without the results , conclusion and discussion sections.
Download our research proposal template
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
Writing a research proposal can be quite challenging, but a good starting point could be to look at some examples. We’ve included a few for you below.
- Example research proposal #1: ‘A Conceptual Framework for Scheduling Constraint Management’
- Example research proposal #2: ‘ Medical Students as Mediators of Change in Tobacco Use’
Like your dissertation or thesis, the proposal will usually have a title page that includes:
- The proposed title of your project
- Your supervisor’s name
- Your institution and department
The first part of your proposal is the initial pitch for your project. Make sure it succinctly explains what you want to do and why.
Your introduction should:
- Introduce your topic
- Give necessary background and context
- Outline your problem statement and research questions
To guide your introduction , include information about:
- Who could have an interest in the topic (e.g., scientists, policymakers)
- How much is already known about the topic
- What is missing from this current knowledge
- What new insights your research will contribute
- Why you believe this research is worth doing
As you get started, it’s important to demonstrate that you’re familiar with the most important research on your topic. A strong literature review shows your reader that your project has a solid foundation in existing knowledge or theory. It also shows that you’re not simply repeating what other people have already done or said, but rather using existing research as a jumping-off point for your own.
In this section, share exactly how your project will contribute to ongoing conversations in the field by:
- Comparing and contrasting the main theories, methods, and debates
- Examining the strengths and weaknesses of different approaches
- Explaining how will you build on, challenge, or synthesise prior scholarship
Following the literature review, restate your main objectives . This brings the focus back to your own project. Next, your research design or methodology section will describe your overall approach, and the practical steps you will take to answer your research questions.
To finish your proposal on a strong note, explore the potential implications of your research for your field. Emphasise again what you aim to contribute and why it matters.
For example, your results might have implications for:
- Improving best practices
- Informing policymaking decisions
- Strengthening a theory or model
- Challenging popular or scientific beliefs
- Creating a basis for future research
Last but not least, your research proposal must include correct citations for every source you have used, compiled in a reference list . To create citations quickly and easily, you can use our free APA citation generator .
Some institutions or funders require a detailed timeline of the project, asking you to forecast what you will do at each stage and how long it may take. While not always required, be sure to check the requirements of your project.
Here’s an example schedule to help you get started. You can also download a template at the button below.
Download our research schedule template
If you are applying for research funding, chances are you will have to include a detailed budget. This shows your estimates of how much each part of your project will cost.
Make sure to check what type of costs the funding body will agree to cover. For each item, include:
- Cost : exactly how much money do you need?
- Justification : why is this cost necessary to complete the research?
- Source : how did you calculate the amount?
To determine your budget, think about:
- Travel costs : do you need to go somewhere to collect your data? How will you get there, and how much time will you need? What will you do there (e.g., interviews, archival research)?
- Materials : do you need access to any tools or technologies?
- Help : do you need to hire any research assistants for the project? What will they do, and how much will you pay them?
Once you’ve decided on your research objectives , you need to explain them in your paper, at the end of your problem statement.
Keep your research objectives clear and concise, and use appropriate verbs to accurately convey the work that you will carry out for each one.
I will compare …
A research aim is a broad statement indicating the general purpose of your research project. It should appear in your introduction at the end of your problem statement , before your research objectives.
Research objectives are more specific than your research aim. They indicate the specific ways you’ll address the overarching aim.
A PhD, which is short for philosophiae doctor (doctor of philosophy in Latin), is the highest university degree that can be obtained. In a PhD, students spend 3–5 years writing a dissertation , which aims to make a significant, original contribution to current knowledge.
A PhD is intended to prepare students for a career as a researcher, whether that be in academia, the public sector, or the private sector.
A master’s is a 1- or 2-year graduate degree that can prepare you for a variety of careers.
All master’s involve graduate-level coursework. Some are research-intensive and intend to prepare students for further study in a PhD; these usually require their students to write a master’s thesis . Others focus on professional training for a specific career.
Critical thinking refers to the ability to evaluate information and to be aware of biases or assumptions, including your own.
Like information literacy , it involves evaluating arguments, identifying and solving problems in an objective and systematic way, and clearly communicating your ideas.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
McCombes, S. & George, T. (2023, June 13). How to Write a Research Proposal | Examples & Templates. Scribbr. Retrieved 31 May 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/the-research-process/research-proposal-explained/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, what is a research methodology | steps & tips, what is a literature review | guide, template, & examples, how to write a results section | tips & examples.
- Affiliate Program

- UNITED STATES
- 台灣 (TAIWAN)
- TÜRKIYE (TURKEY)
- Academic Editing Services
- - Research Paper
- - Journal Manuscript
- - Dissertation
- - College & University Assignments
- Admissions Editing Services
- - Application Essay
- - Personal Statement
- - Recommendation Letter
- - Cover Letter
- - CV/Resume
- Business Editing Services
- - Business Documents
- - Report & Brochure
- - Website & Blog
- Writer Editing Services
- - Script & Screenplay
- Our Editors
- Client Reviews
- Editing & Proofreading Prices
- Wordvice Points
- Partner Discount
- Plagiarism Checker
- APA Citation Generator
- MLA Citation Generator
- Chicago Citation Generator
- Vancouver Citation Generator
- - APA Style
- - MLA Style
- - Chicago Style
- - Vancouver Style
- Writing & Editing Guide
- Academic Resources
- Admissions Resources
What are the Sections of a Research Proposal?
Research proposals that are written by graduate students or academic researchers typically follow a similar format consisting of headings and sections that explain the purpose of the research, specify the scope and scale of the study, and argue for its importance in contributing to the scientific literature. Knowing how to write a research proposal checklist is crucial to getting your dissertation or thesis project accepted.
Although the research proposal sections may vary depending on whether it is a grant, doctoral dissertation , conference paper, or professional project, there are certainly some sections in common. This article will cover sections you will often see in research proposals, explain their purpose, and provide a sample research proposal template.
What are the sections of a research proposal?
Let’s take a look at each section of a research proposal:
- Overall purpose
- Background literature
- Research question
- Definitions of terms and nomenclature
- Research methodology
- Problems and limitations
- Required resources and budget
- Ethical considerations
- Proposed timetable
What is the purpose of each research proposal section?
The research proposal sections and headings above resemble a fully edited and published academic journal article, which you probably can recognize if you are a new PhD or master’s graduate student who is just starting out reading peer-reviewed academic journal articles.
However, the purpose of each heading in a research proposal is quite different from that of a final article.
Purpose : To explain briefly, in a few words, what the research will be about.
What you should do: Give your research proposal a concise and accurate title. Include the name of your faculty mentor (and his/her academic department).
Note : Title pages for research proposals are generally standardized or specified and provide or summarize basic administrative information, such as the university or research institution. Titles should be concise and brief enough to inform the reader of the purpose and nature of the research.
Related Article: How to choose the best title for your research manuscript
Purpose: To provide an overview of the study, which you will expand on in detail in later sections of the research proposal.
What you should do: Provide a brief overview of your project. Include the goals of your research proposal and clearly specify the research questions you want to address. Explain the hypotheses you want to test.
Note : A good summary should emphasize the problems the applicant intends to solve, identify the solution to the problems, and specify the objectives and design of the research. It should also describe the applicant’s qualifications and budget requirements.
Check out a webinar on how to write an effective research introduction
Overall purpose.
Purpose: To state the overall goal of the work in a clear, concise manner.
What you should do : Summarize your problem for someone who is scientifically knowledgeable but potentially uninformed regarding your specific research topic.
Note : The aim or purpose of a research proposal should be results-oriented as opposed to process-oriented. For example, the result of a research study may be “To determine the enzyme involved in X” while the process is “to perform a protein electrophoresis study on mice expressing Y gene.” There should be at least three objectives per proposal.
Background Literature Review
Purpose : To demonstrate the relationship between the goals of the proposed study and what has already been established in the relevant field of study.
What you should do : Selectively and critically analyze the literature. Explain other researchers’ work so that your professor or project manager has a clear understanding of how you will address past research and progress the literature.
Note : One of the most effective ways to support your research’s purpose and importance is to address gaps in the literature, controversies in your research field, and current trends in research. This will put into context how your dissertation or study will contribute to general scientific knowledge. Learn how to write a literature review before writing this section.
Research Question or Hypothesis
Purpose : To state precisely what the study will investigate or falsify.
What you should do : Clearly distinguish the dependent and independent variables and be certain the reader understands them. Make sure you use your terms consistently. Whenever possible, use the same nomenclature.
Note : A research question presents the relationship between two or more variables in the form of a question, whereas a hypothesis is a declarative statement of the relationship between two or more variables. Knowing where to put the research question in a science paper is also crucial to writing a strong Introduction section.
Definition of Terms
Purpose : To define the meanings of the key terms used in the research.
What you should do: Align your term and nomenclature usage throughout your entire research proposal. Clearly define abbreviations and make sure they are understandable to scientists from other disciplines.
Note : Different scientific fields of study often use different terms for the same thing. Further, there are language consistency issues that should be considered. In organic chemistry, there are international standards for naming compounds, but common names are still regularly used, e.g., acetic acid versus ethanoic acid.
Research Methodology
Purpose: To break down the steps of your research proposal.
What you should do: Explain how you will achieve your research goals specified earlier using terms that a general reader can understand. Explain your approach, design, and methods.
Note : Your research proposal should explain the broad scope of your research to other researchers in your field. This section represents the most important part of a research proposal and is therefore the primary concern of reviewers. Knowing how to explain research methodology for reproducibility is important to explaining your methodology to dissertation or thesis advisors and committees.
Problems and Limitations
Purpose: To demonstrate awareness of any study limitations, potential problems, and barriers to answering the research question, and how to deal with them
What you should do: Thoroughly head off any criticisms before they can torpedo your research proposal. Explain that any limitations or potential conflicts will only delay your research or alter/narrow its scope; they will not fundamentally degrade the importance of your research.
Note : Any research proposal or scientific study will have limitations in its scope and execution. Sometimes it may be a key procedure that is problematic or a material you cannot readily obtain. Discussing limitations is key to demonstrating you are an adept and experienced researcher worth approving.
Related Article: How to present study limitations and alternatives
Required resources and budget.
Purpose: To list what resources your research may require and what costs and timelines may affect your completion.
What you should do: Think as a businessperson. Breakdown what resources are available at your institution or university as well as the required resources you still need. These can be materials, machinery, lab equipment, and computers. Resources can also be human: expertise to perform a procedure and other kinds of collaboration.
Note : This section underscores why your funding institution or academic committee should fund your university, laboratory team, or yourself for this particular research.
Ethical Considerations
Purpose: To state how participants will be advised of
the overall nature and purpose of the study and how informed consent will
be obtained.
What you should do: Consult with your academic institution, PhD advisor, and laboratory colleagues. Do not gloss over this part since it has legal consequences.
Note : Often, these types of legal disclaimers are well established and readily available in template format from your research institution or university. Just obtain the proper clearance and permission and have the legal authority at your institution check it over.
Read about how conflicts of interest should be disclosed in research proposals
Proposed timeline.
Purpose: To give a projected timeline for planning, completing, verifying, and reporting your research.
What you should do: Approach this part with a project management style. In an organized fashion, set out a specific timeline for how long each part of your research will take. Identify bottlenecks and specify them.
Note: Savvy time management is something that comes with lots of research experience. Ask your professor or colleagues if you have questions about how long certain procedures will take.
Purpose: To provide detailed bibliographic and reference citations.
What you should do: Use an online citation machine ( APA citation machine , MLA citation machine , Chicago citation machine , Vancouver citation machine ) that can instantly organize your references in any format. Make sure you do this as you go, not saving it for the last when you have lost track.
Note: The bibliographic format used varies according to the research discipline. Consistency is the main consideration; whichever style is chosen should be followed carefully throughout the entire paper.
Related Article: How many references to include in a research proposal?
Purpose : To include any extra materials or information.
What you should do: Add letters of endorsement or collaboration and reprints of relevant articles if they are not available electronically. In addition to the above, you may want to include data tables, surveys, questionnaires, data collection procedures, clinical protocols, and informed consent documents.
Notes : Many writers tend to attach supporting documents to support their research proposal. But remember, more is not always better. Be sure to only include information that strengthens your case, not simply make it longer.
Note : Savvy time management is something that comes with lots of research experience. Ask your professor or colleagues if you have questions about how long certain procedures will take.
The Bottom Line
Whether your research is academic (PhD or master’s graduate student) or professional (competing for government or private funding), how you organize your research proposal sections is one of the first things evaluators will notice. Many academic reviewers will simply scan and check for key section headings. If any headings are missing or strangely written, they may instantly give the reviewer a bad impression of your proposal.
One tip before submitting or even writing your research proposal is to search for the best journal to publish your research in and follow the guidelines in the Guide for Authors section, as well as read as many articles from that journal as possible to gain an understanding of the appropriate style and formatting.
Preparing Your Research Proposal for Publication
So make sure to use some of our resources, such as our FREE APA citation generator and research proposal checklist , or contact us to ask about professional proofreading services , including academic editing and manuscript editing for academic documents.
And check our guide on the editing process to learn more about how language editing for manuscripts can enhance your writing and increase your chances of publication.
Recommended pages
- Undergraduate open days
- Postgraduate open days
- Accommodation
- Information for teachers
- Maps and directions
- Sport and fitness
What to include in a research proposal
You should check with each department to find out whether they provide a specific template for submission.
The word count for research proposals is typically 1,000-1,500 words for Arts programmes and around 2,500 words for Birmingham Law School programmes. Each subject area or department will have slightly different requirements for your research proposal, such as word length and the volume of literature review required. It is a good idea to contact the department before you apply.
Typically, your research proposal should include the following information:
2. Research overview
3. research context.
A well-written introduction is an efficient way of getting your reader’s attention early on. This is your opportunity to answer the questions you considered when preparing your proposal: why is your research important? How does it fit into the existing strengths of the department? How will it add something new to the existing body of literature?
It is unlikely that you will be able to review all relevant literature at this stage, so you should explain the broad contextual background against which you will conduct your research. You should include a brief overview of the general area of study within which your proposed research falls, summarising the current state of knowledge and recent debates on the topic. This will allow you to demonstrate a familiarity with key texts in the relevant field as well as the ability to communicate clearly and concisely.
4. Research questions
The proposal should set out the central aims and key questions that will guide your research. Many research proposals are too broad, so make sure that your project is sufficiently narrow and feasible (i.e. something that is likely to be completed within the normal time frame for a PhD programme).
You might find it helpful to prioritise one or two main questions, from which you can then derive a number of secondary research questions. The proposal should also explain your intended approach to answering the questions: will your approach be empirical, doctrinal or theoretical, etc.?
5. Research methods
How will you achieve your research objectives? The proposal should present your research methodology, using specific examples to explain how you are going to conduct your research (e.g. techniques, sample size, target populations, equipment, data analysis, etc.).
Your methods may include visiting particular libraries or archives, field work or interviews. If your proposed research is library-based, you should explain where your key resources are located. If you plan to conduct field work or collect empirical data, you should provide details about this (e.g. if you plan interviews, who will you interview? How many interviews will you conduct? Will there be problems of access?). This section should also explain how you are going to analyse your research findings.
A discussion of the timescale for completing your research would also beneficial. You should provide a realistic time plan for completing your research degree study, showing a realistic appreciation of the need to plan your research and how long it is likely to take. It is important that you are not over-optimistic with time frames.
6. Significance of research
The proposal should demonstrate the originality of your intended research. You should therefore explain why your research is important (for example, by explaining how your research builds on and adds to the current state of knowledge in the field or by setting out reasons why it is timely to research your proposed topic) and providing details of any immediate applications, including further research that might be done to build on your findings.
Please refer to our top tips page for further details about originality.
7. References
Read our top tips for writing a research proposal
How To Write A Research Proposal
Link Copied
Share on Facebook
Share on Twitter
Share on LinkedIn

Imagine this: you're sitting in your cluttered dorm room, surrounded by piles of books and stacks of notes. It's the middle of the night, and you're desperately trying to piece together your thoughts for that looming research proposal deadline. The pressure is on – you know this research proposal could be the ticket to kickstarting your academic career or securing that much-needed funding for your groundbreaking research idea. But how to write a research proposal? Don't worry, you're not alone. Making a research proposal can seem daunting, but fear not – with the right approach, it's entirely achievable. In this blog, we'll take you through each step of writing a research proposal, from understanding the basics to putting together a winning research proposal that grabs attention and gets results.
What is a research proposal used for, and why is it important?
A research proposal is important because it helps determine if there is enough expertise to support your research area. It is a key part of evaluating your application, showing that your project is feasible and fits within the institution's strengths. However, the proposal is just the beginning. Your ideas will likely change as you delve deeper into your research, but it provides a clear starting point. This initial plan helps both you and the institution understand the potential direction and significance of your research, laying solid foundations for your future.
What Things to keep in mind while writing a research proposal?
Academics often need to write research proposals to get funding for their projects. As a student, you might need to write one when applying to grad school or before starting your thesis or dissertation. A proposal helps you shape your research plans and shows why your project is valuable to funders, educational institutions, or supervisors.
- Relevance: Show your reader why your project is interesting, unique, and important.
- Context: Show that you are comfortable and knowledgeable in your field. Make it clear that you understand the current research on your topic.
- Approach: Explain why you chose your methodology. Show that you've thought carefully about the data, tools, and steps needed to do your research.
- Achievability: Make sure your project can be done within the time frame of your program or funding deadline.
- Tone: When you write research proposals or any academic work, keep it formal and objective. Remember, being clear and to the point is important. Keep your writing concise; being formal doesn't mean using fancy language.
How long should my research proposal be?
Usually, research proposals for bachelor’s and master’s theses are just a few pages. But for bigger projects like Ph.D. dissertations or asking for funding, they can be longer and more detailed. The main aim of a research proposal is to explain what your research will do clearly. So, while the length of the proposal matters less, what’s really important is that you cover all the necessary information in it.
Sections of a research proposal
Research proposals usually have a simple layout. To meet the goals we talked about earlier, here’s how to write a research proposal:
If your proposal is really long, you might want to add a summary and a list of what's inside to help your reader find their way around. Just like your dissertation or thesis, your proposal should have a title page with the following
- The title of your project
- Your supervisor’s name
- Your school and department
Introduction section of research proposal
The beginning of your proposal is like the first pitch for your project. Make it clear and brief, explaining what you want to do and why.
In your introduction:
- Introduce your topic
- Provide background and context
- Explain the problem you're addressing and your research questions
To help you with your introduction, include:
- Who might care about your topic (like scientists or policymakers)
- What's already known about it
- What's still unknown
- How your research will add new information
- Why do you think this research matters
Literature review
As you begin, it's important to show that you know about the key research on your topic. A good literature review tells your reader that your project is based on solid existing knowledge. It also shows that you're not just repeating what others have said but adding something new.
In this part, explain how your project fits into the ongoing discussion in the field by:
- Comparing different theories, methods, and debates
- Looking at the strengths and weaknesses of different ideas
- Saying how you'll use past research in your own work - whether you'll build on it, challenge it, or bring it together with new ideas
If you're not sure where to start, check out our guide on writing a literature review.
Background significance
Your background section sets the stage for your research. Here, you explain why your topic matters and what questions you're trying to answer. It's like showing the backstory of your project, giving readers a clear picture of why it's worth their attention. In your research proposal, it's crucial to cover:
- Background and why your research is important
- Your field of study
- A brief look at existing research
- The main arguments and changes happening in your area
Research design, methods, and schedule
After looking at existing research, it's time to talk about your plans in this methodology section of a research proposal. One key thing to remember when learning how to write a research proposal is to include details about your research methods, like how you'll collect data and analyse it. Here's what your materials and methods in research proposal should cover:
- What kind of research you'll be doing - qualitative or quantitative, and whether you're gathering new data or using existing data.
- Whether your research is experimental, looking at connections, or describing things.
- Details about your data - if you're in social sciences, who you're studying and how you'll pick them.
- The tools you'll use to gather data - like experiments, surveys, or observations, and why they're right for your research.
When figuring out how to write a research proposal, start by clearly stating your research question and explaining why it's important and don't forget to include:
- Your timeline for the research.
- How much money do you need?
- Any problems you might face and how you'll deal with them.
Suppositions and Implications
Even though you won't know your research results until you do the work, you should have a clear idea of how your project will help and contribute to your field. Knowing how to write a research proposal also involves explaining the potential impact of your study. This part of your research proposal is extremely crucial because it explains why your research is necessary.
In this section on how to write a research proposal, make sure you cover the following:
- How your work might challenge current ideas, theories and assumptions in your field.
- Why your research is a good starting point for future studies.
- How your findings could be useful for professionals, teachers, and other researchers.
- The problems your research could potentially help solve.
- Any rules or guidelines that could change because of what you find.
- How your research could be used in schools or other places, and how that'll make things better.
Basically, in this section of a research proposal, you're not saying exactly what you'll find. Instead, you're explaining why whatever you discover will be important.
When applying for research funding, it's likely you'll need to provide a thorough budget. This demonstrates your projected costs for different aspects of your project. Be sure to review the funding body's guidelines to see what expenses they're willing to fund. For each item in your budget, include:
- Cost : How much money do you need?
- Why : Why do you need this money for your research?
- Source : How did you figure out this amount?
When you're making your budget, think about:
- Travel : Do you need to go somewhere to get your data? How will you get there, and how long will it take? What will you do there?
- Materials : Do you need any special tools or tech?
- Help : Do you need to hire someone to help with your research? What will they do, and how much will you pay them?
In this section of a research proposal, you tie everything together. Your conclusion section, much like the conclusion paragraph of an essay, gives a quick rundown of your research proposal and strengthens the purpose you've laid out. It reminds the reader of the main points and emphasises why your research matters. It's your final chance to leave a lasting impression and make a case for the importance of your work.
Bibliography
Writing a bibliography is essential alongside your literature review. In this part of your research proposal structure, unlike the review, where you explain why you chose your sources and sometimes even question them. The bibliography just lists your sources and who wrote them.
Citing depends on the style guide, like MLA , APA , or Chicago . Each has its own rules, even for unusual sources like websites or speeches. If you don't need a full bibliography, a references list with just the sources you cited is enough. If unsure, ask your supervisor. Be sure to include:
- A list of references to important articles and texts you talked about in your research proposal.
- Choose sources that fit well with your proposed research.
Editing and proofreading a research proposal
When writing a research proposal, use the same six-step process you apply to all your writing tasks. Once you've drafted it, give it some time to cool off before proofreading. This helps you spot errors and gaps more effectively, ensuring a polished final version. Taking breaks between writing and revising enhances the quality of your work.
Common mistakes to avoid when writing a research proposal
When you’re writing a research proposal, avoid these common pitfalls:
Being too wordy
Remember, being formal doesn't mean using fancy words. In fact, it's best to keep your writing short and direct. The clearer and more concise you are about your purpose and goals, the stronger your proposal will be.
Failing to cite relevant sources
When you do research, you contribute to what we already know about your topic. Your proposal should mention important past research in your field and explain how your work relates to it. This shows not just why your work matters but also that you know your stuff. Referencing landmark studies gives your proposal credibility and strengthens your argument.
Focusing too much on minor issues
Your research likely has many important reasons behind it, but you don't need to list them all in your proposal. Including too many details can distract from your main goal, making your proposal weaker. Focus on the big, key issues you'll address. Save the smaller details for your actual research paper. Keeping your proposal focused strengthens your argument and makes it more effective.
Failing to make a strong argument for your research
Overloading your proposal with too many minor issues can weaken it significantly, as this approach is more subjective than others. Essentially, a research proposal is a form of persuasive writing. While it's presented objectively, the aim is to convince the reader to support your work. This applies universally whether your audience is your supervisor, department head, admissions board, funding provider, or journal editor. Keeping your proposal focused enhances its persuasiveness.
Polish your writing into a stellar proposal
When you're seeking approval for research, especially when funding is involved, your proposal needs to be perfect. Spelling mistakes, grammar errors, or awkward wording can hurt your credibility. Even if you've edited carefully, it's essential to double-check. Your research deserves the strongest proposal possible to make the best impression and secure the support it needs.
If you're unsure how to write a research proposal, don't worry! There are plenty of resources and examples available to guide you through the process. We hope this blog helped you answer your question of “how to write a research proposal”. Practice is key when learning how to write a research proposal, so don't be afraid to ask for feedback and revise your proposal until it's clear and compelling.
Frequently Asked Questions
How to write an abstract for a research proposal, what is the research proposal format , how to write a proposal for a research paper, how to write a dissertation proposal, how to write a phd proposal.
Your ideal student home & a flight ticket awaits
Follow us on :

Related Posts

The Best Canadian Universities For Computer Science in 2024

10 Best Engineering Universities in Australia in 2024
.jpg)
Explore Top Yale University Scholarships In 2024

Planning to Study Abroad ?

Your ideal student accommodation is a few steps away! Please fill in your details below so we can find you a new home!
We have got your response

amber © 2024. All rights reserved.
4.8/5 on Trustpilot
Rated as "Excellent" • 4800+ Reviews by students
Rated as "Excellent" • 4800+ Reviews by Students
Frequent Searches
Academic Programs
Academic Calendar
Search Directory
Find contact details for people, departments and facilities information.
$50.00 USD application fee (grad only)
Official high school or college transcript from all previous schools
Test Scores (may be optional) AP or IB results
3 letters of recommendation (grad only)
Apply by 3/1 for Fall start
Apply by 12/1 for Spring start
10 Tips on Creating a Research Program and Proposal Writing
Office of sponsored programs and research.
Start small and early. As a new faculty member-reach out to mentors (on campus and off) and inquire what might be a great first proposal to write. Given that grant funding today is more difficult to obtain than ever before, starting early in your career and capitalizing on the advantages of your "early-career" status is key. Reach out to the Office of Sponsored Programs and Research for a listening session and find grant programs specifically aimed at new faculty members. These grant programs typically do not require significant preliminary data. Instead, funding decisions rely most heavily on your promise and potential as a candidate — your training to date, your mentors, and your topic’s importance.

Early on in your career, it’s critical to envision your ultimate large grant. Drawing a Venn diagram of your research program could help communicate your research expertise to collaborators. Typically a major grant would include five aims. Once you’ve envisioned your big grant and its five aims, your next steps become clear: create component projects of that larger project by writing small grants designed to support one or more of your five specific aims. Small grants will show that each of your aims is feasible. This approach is critical as grant-review panels often see a large grant as the culmination of a growing body of work progressing from modest seed grants to larger and larger awards.
A key factor in developing a vision of your ultimate large grant will be the advice of your mentor(s). If you do not have a mentor in your department ask the chair to assign you one. It is also usually considered acceptable to seek out your own mentor. Indeed, many early-career academics assemble a mentorship team, in which each member provides guidance on different career facets (i.e., a teaching mentor, a research mentor, a work-life mentor). Consider approaching people on other campuses as well as at Coppin.
Look at who and what got funded before. Grant agencies typically list previous award recipients online. This list is critical as it shows the agency’s potential interest in supporting your area of research. Some agencies post abstracts online of both active and prior awards. They can give you a critical sense of what has been successful. Looking at the number of specific aims and the range of acceptable sample sizes will provide you with key insights as to what has appealed to your target agency in the past.
Funding agencies may post a list of prior and current grant reviewers and their affiliations online. Review the list and ask yourself if their expertise overlaps with the aims and methodology of your study. Reach out to program directors with a potential idea many months in advance of the deadline—ask for their feedback.
Spend half of your time on the abstract and aims. Writers of successful grant applications typically report that they spent 50 percent of their time on writing and revising their abstract and aims. When you finally start drafting your proposal, the specific aims should be the first thing you write — well before the background or methods sections.
Send a one-page sketch of your project abstract and aims to your mentor and co-investigators early in the grant-writing process with the goal of kicking off an iterative process of review and revision.
Why is this page so critical? Because of the nature of the peer-review process. Typically, only three or four academics are assigned as primary and secondary reviewers of your grant. The majority of review-panel members will only have read your proposal’s abstract. Therefore, it must not only provide a clear snapshot of the entire study, but also convey what is novel about your application.
Demonstrate your strengths and capabilities to do the research. These skills are a critical factor for reviewers. How do you demonstrate you can feasibly conduct the work?
- First, if possible, collaborate on the grant with senior investigators who have conducted similar projects. A senior scholar’s involvement will be a key factor supporting your potential for success, particularly if you are early in your career.
- Co-investigators should not appear in name only. Show established working relationships with them either via co-authored publications, co-presentations, and/or via an established mentoring relationship (e.g., as part of a training grant). Of course, much of this information will appear in the bio sketches in your proposal, but you cannot rely upon reviewers to connect the dots. Make it easy for reviewers by clearly noting these prior collaborations in your "preliminary studies" section.
- Finally, present evidence that you have conducted smaller-scale feasibility studies. That reassures reviewers that you, as a principal investigator, will be able to conduct your proposed aims and, ideally, translate that work into publications.
Take a focused methodological plan directly tied to your specific aims will be the most impressive to reviewers. For example, include methods in the proposal that relate directly to each of your study’s aims and don’t include additional methods that do not correspond to any aims.
You can never have too many figures or tables. They make it easy for a reviewer to quickly grasp your proposal, as compared with dense text. In addition, the act of creating them will help you to cross check your specific aims and study methods. Figures and tables can save space — reducing the amount of text necessary — which is critical to meeting the page limitations of most grant submissions. This tip is relevant for every section of your grant application: Figures can be used to show how your specific aims interrelate, to depict study designs, and to demonstrate your anticipated results.
Seek external reviews prior to submission. The same person cannot write a grant and review it for clarity. You will miss errors, simply by virtue of your familiarity with the material. So ask colleagues to read the application. Even a generalist can read your grant proposal with the following questions in mind: Are the goals clearly stated? Does the grant extend prior work in the field? What is the impact of your potential findings?

In fact, it may be preferable for some of your proofreaders not to have expertise in your area at all — given that members of the grant-review panel will not have expertise in every aspect of your proposal.
Use the grant-review criteria as subheadings in your proposal, making it easier for the panelists to fill out their review forms. For example, reviewers typically have to complete a section on "Innovation." A clearly labeled subsection on "Innovation" not only saves the reviewer time, but gives you the opportunity to share your vision with the reviewer on innovative aspects they may not have recognized on their own.
Choose a topic that you find interesting—your expertise and passion will come through in your grant proposal. Having several grants in the pipeline and under review at the same time can help stack the deck in your favor.
Related links
Log in using your username and password
- Search More Search for this keyword Advanced search
- Latest content
- Current issue
- BMJ Journals More You are viewing from: Google Indexer
You are here
- Online First
- Predictors for severe persisting pain in rheumatoid arthritis are associated with pain origin and appraisal of pain
- Article Text
- Article info
- Citation Tools
- Rapid Responses
- Article metrics
- http://orcid.org/0000-0002-1406-3024 Christoph Baerwald 1 ,
- Edgar Stemmler 2 ,
- Sixten Gnüchtel 2 ,
- Katharina Jeromin 2 ,
- Björn Fritz 2 ,
- Michael Bernateck 3 ,
- Daniela Adolf 4 ,
- http://orcid.org/0000-0001-7766-6167 Peter C Taylor 5 ,
- Ralf Baron 6
- 1 Zentrum für Seltene Erkrankungen , University Hospital Leipzig , Leipzig , Germany
- 2 AbbVie Deutschland GmbH & Co KG , Wiesbaden , Germany
- 3 Center for Rheumatology & Pain-Medicine , Hannover , Germany
- 4 StatConsult GmbH , Magdeburg , Germany
- 5 Nuffield Department of Orthopaedics, Rheumatology and Musculoskeletal Sciences , University of Oxford, Botnar Research Centre , Oxford , UK
- 6 Department of Neurology , University Hospital Schleswig Holstein , Kiel , Germany
- Correspondence to Professor Christoph Baerwald, Zentrum für Seltene Erkrankungen, University Hospital Leipzig, Leipzig, Germany; cbaerwald{at}outlook.de
Objectives To determine the proportion of patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) with severe persisting pain and to identify predictive factors despite treatment-controlled disease activity.
Methods This prospective multicentre study included outpatients with RA scheduled for escalation of anti-inflammatory treatment due to active disease and severe pain (Disease Activity Score 28 (DAS28)>3.2 and Visual Analogue Scale (VAS)>50). At week 24, patients were stratified into reference group (DAS28 improvement>1.2 or DAS28≤3.2 and VAS pain score<50), non-responders (DAS28 improvement≤1.2 and DAS28>3.2, regardless of VAS pain score) and persisting pain group (DAS28 improvement>1.2 or DAS28≤3.2 and VAS pain score≥50). The former two subgroups ended the study at week 24. The latter continued until week 48. Demographic data, DAS28-C reactive protein, VAS for pain, painDETECT Questionnaire (PD-Q) to identify neuropathic pain (NeP) and the Pain Catastrophising Scale were assessed and tested for relation to persisting pain.
Results Of 567 patients, 337 (59.4%) were classified as reference group, 102 (18.0%) as non-responders and 128 (22.6%) as patients with persisting pain. 21 (8.8%) responders, 28 (35.0%) non-responders and 27 (26.5%) persisting pain patients tested positive for NeP at week 24. Pain catastrophising (p=0.002) and number of tender joints (p=0.004) were positively associated with persisting pain at week 24. Baseline PD-Q was not related to subsequent persisting pain.
Conclusions Persisting and non-nociceptive pain occur frequently in RA. Besides the potential involvement of NeP, pain catastrophising and a higher number of tender joints coincide with persisting pain.
- Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Outcome Assessment, Health Care
- Risk Factors
Data availability statement
Data are available upon reasonable request. AbbVie is committed to responsible data sharing regarding the clinical trials we sponsor. This includes access to anonymised, individual and trial-level data (analysis data sets), as well as other information (eg, protocols, clinical study reports or analysis plans), as long as the trials are not part of an ongoing or planned regulatory submission. This includes requests for clinical trial data for unlicensed products and indications. These clinical trial data can be requested by any qualified researchers who engage in rigorous, independent, scientific research and will be provided following review and approval of a research proposal, Statistical Analysis Plan (SAP) and execution of a Data Sharing Agreement (DSA). Data requests can be submitted at any time after approval in the USA and Europe and after acceptance of this manuscript for publication. The data will be accessible for 12 months, with possible extensions considered. For more information on the process or to submit a request, visit the following link: https://vivli.org/ourmember/abbvie/ then select ‘Home’.
This is an open access article distributed in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution Non Commercial (CC BY-NC 4.0) license, which permits others to distribute, remix, adapt, build upon this work non-commercially, and license their derivative works on different terms, provided the original work is properly cited, appropriate credit is given, any changes made indicated, and the use is non-commercial. See: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/ .
https://doi.org/10.1136/ard-2023-225414
Statistics from Altmetric.com
Request permissions.
If you wish to reuse any or all of this article please use the link below which will take you to the Copyright Clearance Center’s RightsLink service. You will be able to get a quick price and instant permission to reuse the content in many different ways.
WHAT IS ALREADY KNOWN ON THIS TOPIC
Pain is a cardinal symptom of inflammatory arthritis and represents a critical parameter for evaluating treatment success.
Persisting pain leads to considerable limitations in daily life and occurs in some patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) despite meaningful improvement of inflammatory disease activity.
WHAT THIS STUDY ADDS
Persisting and, in particular, neuropathic pain components are frequent in RA. Neuropathic pain is present more often in non-responders to disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drug treatment and patients with persisting pain despite controlled disease activity.
Pain catastrophising and the number of tender joints are independent predictors of persisting pain in patients with RA.
HOW THIS STUDY MIGHT AFFECT RESEARCH, PRACTICE OR POLICY
As pain in RA represents a multifactorial process, screening for pain catastrophising and the number of tender joints could help to identify patients at risk for chronic pain and support pain phenotyping for suitable treatment. Neuropathic pain and other contributing factors should be adequately identified and treated in patients with persisting pain.
Introduction
Patients diagnosed with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) highlight pain as their most significant problem with the highest need for improvement. 1 2 According to the definition from the International Association for the Study of Pain, pain is an ‘unpleasant sensory and emotional experience associated with actual or potential tissue damage, or described in terms of such damage’. 3 Nociceptive pain in RA usually results from synovitis or structural joint damage due to bone loss induced by osteoclastogenesis, which is caused by pro-inflammatory cytokines such as tumour necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha, interleukin (IL)-1, IL-2 or IL-6. 4 5 It might be augmented by central sensitisation, that is, pain facilitation in the spinal cord. Furthermore, damage to nociceptive nerve endings in the affected joint might induce neuropathic pain (NeP) due to lesions or diseases affecting the somatosensory nervous system either peripherally or centrally. 6 In 2021, the framework for pain phenotyping was refined: besides nociceptive pain caused by inflammation and damage of tissues and NeP resulting from nerve damage, nociplastic pain was introduced as a third category. 7 8 It arises from altered nociception despite no clear evidence of disease or lesion of the somatosensory system, for example, in fibromyalgia. Given that NeP and nociplastic pain potentially involve the central nervous system, it is crucial to acknowledge that reliably distinguishing these non-nociceptive pain phenotypes is a task yet to be mastered. In the literature, the proportion of patients with RA identified to likely have NeP ranges from 5% to 17%; another roughly 20% is reported to possibly have NeP. 9–12 NeP, at the time of the start of this study, not being distinguished from nociplastic pain and pain catastrophising has already been shown to interfere with achieving remission in RA and early RA. 11 13–15 A result which fits well findings for depression and anxiety, which are frequently related to pain and have also been reported to hinder remission achievement. 16 17 Persisting pain as a potential consequence of any pain phenotype mentioned above is usually understood as current and prolonged pain resulting from various causes, including diseases or damage to musculoskeletal structures. Recent findings suggest that 59%–79% of patients with RA have persisting pain. 18 To enrich the knowledge on the occurrence of persisting pain in RA, the aims of the PAIN-CONTROL study were: (a) to determine the proportion of patients with RA having persisting pain and NeP, (b) to compare the clinical and patient-reported outcomes (PROs) of patients with persisting pain to reference patients responding to treatment and non-responders after 24 weeks of disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drug (DMARD) therapy and (c) to identify characteristics that may predict persisting pain.
Patient sample
Patient enrolment started on 8 November 2016 (first patient, first visit) and was completed on 9 July 2021 (last patient, last visit). All participants were outpatients recruited from 50 study centres specialising in rheumatology across Germany. Patients were required to meet the following criteria for enrolment: (a) adult patients (≥18 years of age) with a previously signed informed consent regarding study participation and corresponding procedures, (b) confirmed diagnosis of RA according to the ACR/EULAR 2010 criteria, (c) active disease (Disease Activity Score 28 (DAS28)>3.2) plus swollen joint count (SJC)>3, normal C reactive protein (CRP) or CRP above the normal upper limits, and scheduled for escalation of anti-inflammatory treatment, (d) disease duration (RA)≤8 years, (e) patient-reported pain intensity score of ≥50 on a 0–100 Visual Analogue Scale (VAS) and (f) intellectual capacity to participate in study-related procedures and complete individual questionnaires. Patients with active disease, determined by a distinct inflammatory component and reporting considerable pain (≥50 on a 0–100 VAS), were deemed most suitable for analysing the impact of persisting pain on treatment outcomes following therapy escalation.
Study-related procedures
PAIN-CONTROL was a longitudinal study over 24 and 48 weeks, depending on treatment outcome at week 24, which determined the subgroup classifications as specified below. PAIN-CONTROL is registered in the German Clinical Trial Register (DRKS00010717). Study sites entered data via an electronic case report form with a unique subject ID code on a web-based encrypted platform. Patient questionnaires were transcribed by hand and stored on-site. Plausibility checks on defined limits and variable values were conducted using automated feasibility checks. At baseline, anti-inflammatory treatment initiation or escalation was given, while demographic data (eg, gender, age, disease duration and body mass index) and baseline laboratory values comprising autoantibodies to rheumatoid factor and anti-citrullinated peptide were collected. Clinical assessments included measurement of DAS28 using either C reactive protein (DAS28-CRP) or erythrocyte sedimentation rate (DAS28-ESR). Additionally, the following PROs were completed: the painDETECT Questionnaire (PD-Q) investigating symptoms of NeP, the Rheumatoid Arthritis Impact of Disease Questionnaire (RAID) assessing RA impact on daily life, the Patient Health Questionnaire 9 (PHQ-9) reflecting depressive symptoms, the Health-Assessment Questionnaire Disability-Index (HAQ-DI) measuring physical function, and the Pain Catastrophising Scale (PCS) evaluating the individual appraisal of pain. 19–23 The cut-offs used to evaluate the extent of NeP symptoms were ≤12 points (NeP negative), 13–18 points (inconclusive) and ≥19 points (NeP positive). 20 Clinical assessments and PROs were scheduled at each study visit, that is, baseline and weeks 12, 24 and 48. The anti-inflammatory treatment of study participants was adjustable at the treating physician’s discretion regarding national treatment guidelines for RA. 24 Besides obligatory initiation or escalation of treatment, there were no study-related procedures or limitations regarding anti-rheumatic treatment, including medication to manage inflammatory pain. At week 24, patients were assigned to three subgroups based on their response to treatment (DAS28-ESR or DAS28-CRP) and reported pain level: patients with DAS28 improvement from baseline>1.2 or DAS28≤3.2 and VAS pain score<50 were considered the reference control group. Patients with DAS28 improvement from baseline≤1.2 and DAS28>3.2 were considered non-responders, regardless of the VAS pain score. Patients reporting a VAS pain score ≥50 and either a DAS28 improvement from baseline>1.2 or DAS28≤3.2 were considered the persisting pain group and were followed up to week 48. This classification was supposed to distinguish patients with a primary inflammatory disease component whose pain likely results from inflammation from patients with persisting pain despite reduced disease activity or patients not responding to escalation of treatment. For the reference group and non-responders, the study ended at week 24. Patients with persisting pain continued until week 48 and were recommended at week 24 to seek adjunctive pain treatment based on a shared decision between patient and physician.
Statistical data analysis
Descriptive information from data on interval and ratio levels is presented as arithmetic mean (SD), including CIs for specified outcomes of interest, while results for nominal data are presented using absolute and relative frequencies, n (%). Proportions are presented as relative frequencies only. For patient classification at week 24, treatment response was assessed either by DAS28-CRP or DAS28-ESR. For descriptive statistical analysis and variable selection, only DAS28-CRP values were used. Variable selection for multivariable regression modelling identifying baseline predictors of persisting pain comparing patients of the corresponding subgroup to individuals from the reference group at week 24 was conducted as follows: initial reduction of variables was obtained by factor analysis, selecting the variable with the highest factor loading from factors with eigenvalues >1 obtained by Varimax rotation. Subsequently, study directors (CB, PCT, RB) reviewed the top variables of each factor, whereas they could overrule the results in justifiable cases, for example, when factor loading of a total score was only slightly lower than the score’s item. Second, a stepwise approach in multivariable logistic regression modelling (using a criterion of 15% as the significance level for inclusion and 20% as the significance level for remaining in the model in order to yield a higher power) using bootstrapping (bootstrap sample: B=500) was applied. Variables included in the model in at least 60% of the bootstrapped models were selected for the final regression to identify factors for being assigned to the persisting pain subgroup (in comparison to the reference group). The results were transformed into individual risk scores and included in a nomogram, which, for convenience, can be used to estimate the outcome of an individual patient given baseline values directly. Data processing and analysis were performed using SAS V.9.4 (SAS Institute), and the nomogram was created using R V.4.2.0 (R Foundation, Vienna, Austria). 25 26 The study results are reported according to the Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology guidelines for observational studies. 27
Sample size determination
Given the exploratory nature of this study, the sample size was determined by the requirements for predictive modelling. We assumed patients with persisting pain to be the least common group compared with the reference group and non-responders. According to the literature, regression modelling requires at least 10 times the number of independent variables desired for regression modelling. 28 The maximum planned number was 12 independent variables as potential predictors, meaning that at least 120 patients would have to be classified as having persisting pain at week 24, whereas the maximum number of patients to include in the study was n=700. Therefore, recruitment was stopped after either 120 patients with persisting pain were identified or the total number of patients enrolled exceeded 700.
Patient sample characteristics
Patients with a previous RA diagnosis (n=567) were included in this per-protocol analysis. All patients were scheduled to initiate or escalate anti-inflammatory treatment due to increased disease activity (DAS28>3.2). The proportion of female patients in the total sample was 67.9%. On average, patients had a mean age (SD) of 57.6 (12.9) years and a disease duration of 2.5 (2.6) years. At week 24, given corresponding response to anti-inflammatory treatment, the majority of patients (337, 59.4%) were assigned to the reference group, while 102 (18.0%) patients were classified as non-responders and 128 (22.6%) patients fulfilled the criteria for persisting pain and were followed up to week 48. Patient recruitment was stopped after 120 patients with persisting pain were identified, whereas already included patients were allowed to finish the study, resulting in 128 patients in the respective subgroup (see figure 1 for study design). The baseline characteristics of the three subgroups did not reveal any differences regarding demographic background.
- Download figure
- Open in new tab
- Download powerpoint
PAIN-CONTROL study design. ACR, American College of Rheumatology; CRP, C reactive protein; DAS28, Disease Activity Score 28; ESR, erythrocyte sedimentation rate; EULAR, European Alliance of Associations for Rheumatology; RA, rheumatoid arthritis; SJC, swollen joint count; TJC, tender joint count; VAS, Visual Analogue Scale; VAS-GA, Visual Analogue Scale - Global Assessment of Disease Activity.
However, differences in 95% CIs regarding clinical characteristics and PROs were found between the reference group and patients with persisting pain regarding RAID, HAQ-DI, PCS and the Numerical Rating Scale for global disease activity, with the latter group showing higher baseline scores for these measures ( online supplemental table 1 ). Similar results were obtained for DAS28-CRP and VAS pain, whereas the baseline 95% CI for patients with persisting pain was above the results of both reference patients and non-responders (DAS28-CRP: 95% CI Reference =4.80 to 5.00, 95% CI Non-Responders =4.71 to 5.09, 95% CI Pers.Pain =5.13 to 5.47; VAS pain: 95% CI Reference =66.9 to 69.7, 95% CI Non-Responders =66.5 to 71.5, 95% CI Pers.Pain =71.6 to 76.1). Escalation of RA treatment at baseline was characterised across all subgroups by an increase in conventional synthetic (cs), biological (b) or targeted-synthetic (ts) DMARD prescriptions (ΔcsDMARDs≥16.7%, ΔbDMARDs≥13.3%, ΔtsDMARDs≥2.9%) and glucocorticoids, (Δglucocorticoids≥23.2%). Glucocorticoids and csDMARDs were the most frequently prescribed anti-inflammatory treatment for therapy adjustment at baseline, followed by bDMARDs (see table 1 ). Interestingly, in contrast to increasing prescriptions for DMARDs and glucocorticoids, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and cyclo-oxygenase-2 inhibitors were prescribed less frequently. Non-pharmacological pain management from baseline was used by 26 (7.9%) patients of the reference group, 15 (14.7%) non-responders and 23 (18.5%) patients with persisting pain based on the subgroup classification at week 24. In the 72 patients discontinuing study participation, 38 (52.8%) declined or did not attend follow-up visits without any given reason, 20 (27.8%) wished to withdraw from the study and 7 (9.7%) were unable to attend follow-up visits due to other illnesses or comorbidities ( figure 2 ).
Supplemental material
- View inline
Patient characteristics according to the subgroup classification at week 24
Patient-derived reasons for study discontinuation.
Persisting pain and NeP
At week 24, the proportion of patients having a VAS pain score ≥50 despite a DAS28 improvement was 22.6%. Until week 24, the proportion of patients testing positive for NeP decreased steadily in the reference group (week 0: 28.6%, week 12: 12.7%, week 24: 8.8%) and declined slightly with a rebound between weeks 12 and 24 among non-responders (week 0: 41.0%, week 12: 19.7%, week 24: 35.0%). Patients with persisting pain exhibited a relatively constant proportion of NeP after an initial reduction (week 0: 36.0%, week 12: 21.8%, week 24: 26.5%, week 48: 21.8%) ( figure 3A–C ). Remarkably, in contrast to patients with persisting pain, non-responders had the highest proportion of NeP-positive findings at week 24. However, patients testing positive for NeP were found across all subgroups, and the overall proportion of patients reporting a VAS pain score ≥50 after 24 weeks of (escalated) DMARD treatment was still 69.6%. Furthermore, residual pain (ie, VAS scores ≥20 and <50) was common in all subgroups at the end of the study (reference subgroup: n=188 (55.8%), non-responders: n=26 (25.5%), persisting pain patients: n=42 (36.5%), table 2 ). 87 out of 128 patients with persisting pain at week 24 had valid PD-Q scores at week 48. Of these, 19 patients (21.8%) tested positive for NeP, of which 9 patients (47.4%) still reported persisting pain at week 48. 21 patients (24.2%) tested inconclusive for NeP, and 14 (29.8%) of these still reported persisting pain at week 48. 49 patients classified as having persisting pain at week 24 reported pain alleviation at week 48 and now fulfilled the criteria of the reference group.
Patient-reported outcomes for neuropathic pain, the impact of RA on daily life, depressive symptoms and physical function. HAQ-DI, Health-Assessment Questionnaire Disability-Index; NeP, neuropathic pain; PHQ-9, Patient Health Questionnaire 9; RA, rheumatoid arthritis; RAID, Rheumatoid Arthritis Impact of Disease Questionnaire.
Pain severity on a 0–100 Visual Analogue Scale at week 24 and week 48
DAS28 and symptom-specific PROs
Besides the PROs measuring pain, other outcomes of interest were also considered to provide a more detailed picture of the treatment effects in the specified subgroups. Among these measures, the DAS28, which also determined the subgroup classification, revealed that 192 (57.0%) patients in the reference group and 26 (20.3%) patients with persisting pain had a DAS28<2.6 after 24 weeks of DMARD therapy. By then, another 45 (13.4%) patients in the reference group and 33 (25.8%) persisting pain patients had a DAS28 between 2.6 and 3.2. At week 24, when the reference group and non-responders had reached the end of the study, mean DAS28-CRP values were 2.3 (0.8) (95% CI: 2.2 to 2.4) for the reference group, 4.7 (1.1) (95% CI: 4.5 to 4.9) for non-responders and 3.2 (1.2) (95% CI: 2.9 to 3.5) for patients in the persisting pain subgroup. Thus, as expected, average DAS28-CRP results were lowest for reference patients, followed by patients with persisting pain and non-responders. The same pattern of results was observed for the RAID, PHQ-9, HAQ-DI and PCS, whereas the CIs of the reference group were lowest and did not overlap for all four PROs ( figure 3D–F , online supplemental table 2 ). Notably, less than 25% of non-responders and patients having persisting pain achieved a RAID acceptable symptom state, corresponding to a RAID-score ≤2, whereas 43.8% of patients in the reference group achieved this symptom state. 29 Moreover, 25% of non-responders had a PHQ-9 score ≥10, which is equal to moderate symptoms of depression or worse. 21
Prediction of group classification at week 24 using baseline characteristics
13 baseline variables ( online supplemental table 3 ) and their pairwise interactions were selected for stepwise regression. Overall, 421 patients from the reference and persisting pain subgroups had complete data on the variables to be evaluated and were included in bootstrapped regression modelling. Baseline tender joint count (TJC) (84.0%), pain catastrophising behaviour (81.0%), adjunctive pharmacological pain medication (eg, opioids, antidepressants, anticonvulsants; 73.6%) and DMARDs (68.2%) were included in ≥60% of the bootstrapped models and thus chosen as independent variables for the final regression. Modelling the group affiliation at week 24 (persisting pain subgroup vs reference subgroup) by the previously chosen variables resulted in a significant model fit (Likelihood ratio test: p<0.001) with a reduction of the Akaike information criterion (AIC) from 530.5 (Intercept only) to 512.3 for the model with intercept and covariates. In this final model, the PCS (p=0.002) and the TJC (p=0.004) showed the strongest relation to the group affiliation at week 24 with 95% CI for ORs above 1. In detail, an increase of one point in the PCS score corresponded to a 2.8% higher probability of being assigned to the persisting pain subgroup (95% CI: 1.0% to 4.6%). Similarly, each other tender joint raised the probability of being classified with persisting pain by 4.7% (95% CI: 1.5% to 8.1%). The use of DMARDs up to baseline (p=0.06) and adjunctive pharmacological medication (p=0.135) also fulfilled the previously specified selection criteria and were included in the nomogram ( figure 4 ), although their ORs’ 95% CI included 1, corresponding to a p value >0.05.
Nomogram for persisting pain-related variables identified by stepwise regression and final multivariable regression. bDMARD, biologic disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs; csDMARD, conventional synthetic disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs; PCS, Pain Catastrophising Scale; tsDMARD, targeted synthetic disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs.
To our knowledge, this is the first prospective real-world study in patients presenting with clinically active RA and RA-related pain, which shows that both persisting pain and NeP are common in patients with RA—despite an escalation of DMARD treatment including subsequent standard of care therapy. After 24 weeks of DMARD treatment, 128 of 567 patients (22.6%) still scored ≥50 on the VAS pain despite improving DAS28 by ≥1.2 or attaining low disease activity. Pain of persisting nature despite remission or low disease activity has been reported in previous literature, whereas the choice of the remission criterion may play an essential role. 30 31 A recent study also demonstrated that NeP and comorbidities might hinder patients with RA from achieving Boolean remission. 11 These findings suggest that persisting pain and NeP do not necessarily prevent patients from responding to anti-inflammatory therapy but that these factors may diminish the likelihood of achieving and maintaining remission by impacting the patient global assessment (PtGA). Although patients and therapists differ in their perceptions of relevant treatment outcomes, pain is the strongest predictor for failure to achieve PtGA<1 and, therefore, for not achieving original Boolean remission criteria. 32 33 For this reason, the American College of Rheumatology (ACR) and the European Alliance of Associations for Rheumatology (EULAR) have recently recommended revised Boolean 2.0 criteria for remission in RA by employing a higher threshold for PtGA of 2/10. 34 Our results suggest that persisting pain and NeP represent two different trajectories of RA, with 8.8% of the patients in the reference group scoring positive for NeP at week 24, compared with 35.0% in the non-responder group and 26.5% in the persisting pain group. Thus, NeP seems present irrespective of successful inflammatory suppression or persisting pain. This outcome is likely to reflect the underlying mechanisms of NeP, including damage to the peripheral nociceptors in joints, leading to peripheral sensitisation in combination with secondary central sensitisation related to nerve damage. 6 35 It remains to be investigated whether lesions or diseases affecting the nervous system are more frequent in non-responders and patients with persisting pain than in patients responding to anti-inflammatory treatment. In clinical practice, the symptoms and causes of persisting pain and NeP are not easily distinguishable and, in a worst-case scenario, may remain undetected by standard RA assessments. 36 The independence of NeP and persisting pain was further confirmed in our study using alternative regression analysis, demonstrating that baseline PD-Q was not related to persisting pain at week 24 (data not shown).
Importantly, our results showed that the baseline number of tender joints (TJC28) and pain catastrophising are independently related to the persisting pain classification at week 24. Pain catastrophising, a construct focusing on the individual appraisal of pain perception, is much less commonly assessed in RA routine assessments than the TJC28. Compared with non-catastrophisers, pain catastrophisers have more difficulty controlling and suppressing pain-related thoughts. 37 Pain catastrophising has also been shown to be linked to certain aspects of personality, whereas the discussion about state (situational) or trait (constant) characteristics of pain catastrophising is still ongoing. 38 39 However, recent findings suggest that JAKi may positively affect pain-related outcomes in patients with active RA, including catastrophising thoughts when pain results from extra-synovial mechanisms. 37 40 41 Interestingly, the proportion of pain catastrophisers seems similar across rheumatic diseases, whereas PCS scores ≥4 were reported to be particularly related to PROs focusing on the biological domain. 42 The way patients appraise their health condition – including pain or tender joints—and how they react to feelings resulting from this evaluation process may explain the association of pain and depression in rheumatic diseases. 43–45 According to our findings, non-responders who also had the highest proportion of NeP-positive findings at week 24 seem particularly prone to depressive symptomatology (25% reported moderate symptoms of depression or worse), supporting the pain-depression relation frequently reported. Our results are consistent with previous prospective observational studies reporting similar prevalence rates for depression. 46 47 Importantly, our results also highlight that improving persisting pain after 24 weeks of DMARD treatment is still possible. The use of adjunctive pharmacological therapy, glucocorticoids or NSAIDs may explain this finding only to a minor degree, given that the number of prescriptions for these therapies did not increase between weeks 24 and 48. Thus, it may be hypothesised that late treatment effects of DMARD therapy account for this finding. Concerning potential limitations, 72 patients discontinued their participation in the study. This finding may be attributed to the study conduct overlapping with the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic, resulting in missed or postponed appointments. Moreover, 20 patients withdrew from the study since they no longer wished to complete the study-related questionnaires. However, the total number of patients withdrawing was still acceptable compared with the analysis population (11.7% of 567 patients). Although the sample size was estimated assuming that patients with persisting pain would comprise the smallest subgroup, non-responders were. However, given that only four variables were included in the regression at the final step of the analysis, the ratio of patients to independent variables in the model can be assumed to return valid results. As a limitation of the study design, the extent to which non-responders represent a persistent inflammatory or rather persisting pain phenotype cannot be answered satisfactorily, given that such categories may not be mutually exclusive. This also extends to measuring NeP using the PD-Q which has not been designed to distinguish NeP from nociplastic pain, a novel pain phenotype introduced when this study had started. Thus, although patients with primary fibromyalgia and other interfering comorbidities were not eligible to participate in the study, it is possible that patients testing PD-Q positive had nociplastic pain instead of NeP or a combination of both, for example, in cases of secondary fibromyalgia. Hence, the development of diagnostic tools for reliable and valid pain phenotyping according to the new framework remains a crucial task and requires large longitudinal data samples. Moreover, the generalisability of our findings may be limited by the selection of the DAS28 and VAS pain criteria for response/improvement, whereas directional changes stay the same irrespective of applying the DAS28-ESR in case of DAS28-CRP absence. Thus, it remains debatable whether results would be different if remission criteria (eg, Clinical Disease Activity Index (CDAI), Simplified Disease Activity Index (SDAI), Boolean) had been chosen to define the reference group. With this observational study including real-world data, various therapy combinations could have led to our findings. For the future research schedule, investigating the response of the mentioned pain phenotypes to available (adjunctive) treatments remains of high priority. In the analysis presented, the proportion of patients with persisting pain receiving adjunctive pain treatment between weeks 24 and 48 was too small for statistical analysis. From the findings of our study, it is evident that persisting pain and NeP (as well as potential nociplastic pain) are frequently found in patients with RA undergoing standard-of-care treatment. As a consequence, for clinical practice, if pain-relevant comorbidities have been excluded and patients consistently score on the upper half of a pain VAS, present with a large number of tender joints, or do not respond to DMARD therapy, NeP and nociplastic pain should be considered as explanation to this finding. PROs such as the RAID or the PD-Q may help facilitate patient-physician communication when the response to anti-inflammatory treatment does not extend to patient-reported symptom domains. Thus, these tools may be considered as a starting point for further diagnostic procedures and planning of tailored treatment following underlying pain mechanisms.
Ethics statements
Patient consent for publication.
Not applicable.
Ethics approval
This study involves human participants and was approved by ethics committee of the Medical Faculty of the Christian-Albrechts-University, Kiel, Germany (ID: D497/16). Participants gave informed consent to participate in the study before taking part.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank all participants, study sites and investigators who participated in this clinical trial. CB has served as consultant to AbbVie and has received research funding and speaker fees from AbbVie. ES, SG, KJ and BF are AbbVie employees and may own AbbVie stock or options. MB has served as consultant to AbbVie and has received speaker fees from AbbVie. PCT has served as consultant to AbbVie and has received speaker fees from AbbVie. RB has served as consultant to AbbVie and has received speaker fees from AbbVie. DA is an employee of StatConsult GmbH and led statistical analyses, which was funded by AbbVie. Baseline data of the study were presented at the Annual Congress of the European Alliance of Associations for Rheumatology (EULAR), 1–4 June 2022, Copenhagen, Denmark.
- Cohen M , et al
- McWilliams DF
- Gravallese E
- Nijs J , et al
- Lahousse A ,
- Kapreli E , et al
- ten Klooster PM ,
- Vonkeman HE , et al
- Vargas M , et al
- Salaffi F ,
- Di Carlo M ,
- Carotti M , et al
- Rifbjerg-Madsen S ,
- Christensen AW ,
- Boesen M , et al
- Ten Klooster PM ,
- de Graaf N ,
- Vonkeman HE
- Gerardi MC ,
- Atzeni F , et al
- Yoshida T ,
- Hashimoto M ,
- Horiguchi G , et al
- Michelsen B ,
- Kristianslund EK ,
- Sexton J , et al
- Manning-Bennett AT ,
- Hopkins AM ,
- Sorich MJ , et al
- McWilliams DF ,
- Young A , et al
- Paternotte S ,
- Aanerud GJ , et al
- Freynhagen R ,
- Gockel U , et al
- Kroenke K ,
- Spitzer RL ,
- Williams JB
- Sullivan MJL ,
- Bishop SR ,
- Iking-Konert C , et al
- SAS Institute
- Elm E von ,
- Altman DG ,
- Egger M , et al
- Dougados M ,
- Logeart I , et al
- Lu B , et al
- Yoshida K ,
- Nakano H , et al
- Studenic P ,
- Smolen JS , et al
- Smolen JS ,
- Aletaha D ,
- de Wit M , et al
- Campbell JN ,
- Mathias K ,
- Amarnani A ,
- Pal N , et al
- Carotti M ,
- Farah S , et al
- Sansone RA ,
- Wiederman MW
- Clements KL ,
- Ward LC , et al
- Taylor PC ,
- Fleischmann R , et al
- De Stefano L ,
- Bozzalla Cassione E ,
- Bottazzi F , et al
- Łosińska K ,
- Pripp AH , et al
- Go DJ , et al
- Edwards RR ,
- Cahalan C ,
- Mensing G , et al
- Lerman SF ,
- Haythornthwaite JA
- Englbrecht M ,
- Aringer M , et al
- Behrens F ,
- Burmester G-R ,
- Feuchtenberger M , et al
Supplementary materials
Supplementary data.
This web only file has been produced by the BMJ Publishing Group from an electronic file supplied by the author(s) and has not been edited for content.
- Data supplement 1
- Data supplement 2
- Data supplement 3
Handling editor Josef S Smolen
Contributors CB, ES, DA and RB contributed to the conception and design of the study. SG, KJ and BF contributed to the acquisition of data. CB, ES, MB, DA, PCT and RB contributed to the analysis and interpretation of data. ES serves as the guarantor of the study. All authors contributed to drafting the article or revising it critically for important intellectual content. All authors gave final approval of the version to be submitted.
Funding AbbVie funded this trial and participated in the trial design, research, analysis, data collection, interpretation of data, and the review and approval of the publication. All authors had access to relevant data and participated in the drafting, review and approval of this publication. No honoraria or payments were made for authorship. Statistical analysis support was provided by StatConsult GmbH, which was funded by AbbVie. Medical writing support was provided by Dr Matthias Englbrecht, which was funded by AbbVie.
Competing interests None declared.
Patient and public involvement Patients and/or the public were not involved in the design, or conduct, or reporting, or dissemination plans of this research.
Provenance and peer review Not commissioned; externally peer reviewed.
Supplemental material This content has been supplied by the author(s). It has not been vetted by BMJ Publishing Group Limited (BMJ) and may not have been peer-reviewed. Any opinions or recommendations discussed are solely those of the author(s) and are not endorsed by BMJ. BMJ disclaims all liability and responsibility arising from any reliance placed on the content. Where the content includes any translated material, BMJ does not warrant the accuracy and reliability of the translations (including but not limited to local regulations, clinical guidelines, terminology, drug names and drug dosages), and is not responsible for any error and/or omissions arising from translation and adaptation or otherwise.
Read the full text or download the PDF:

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Research proposal examples. Writing a research proposal can be quite challenging, but a good starting point could be to look at some examples. We've included a few for you below. Example research proposal #1: "A Conceptual Framework for Scheduling Constraint Management" Example research proposal #2: "Medical Students as Mediators of ...
The purpose of the research proposal (its job, so to speak) is to convince your research supervisor, committee or university that your research is suitable (for the requirements of the degree program) and manageable (given the time and resource constraints you will face). The most important word here is "convince" - in other words, your ...
Research Proposal Format. The format of a research proposal may vary depending on the specific requirements of the institution or funding agency. However, the following is a commonly used format for a research proposal: 1. Title Page: Include the title of your research proposal, your name, your affiliation or institution, and the date. 2. Abstract:
Regardless of the research problem you are investigating and the methodology you choose, all research proposals must address the following questions: ... Most proposals should include the following sections: I. Introduction. In the real world of higher education, a research proposal is most often written by scholars seeking grant funding for a ...
1. Title Page: Include the title of your proposal, your name or organization's name, the date, and any other relevant information specified by the guidelines. 2. Executive Summary: Provide a concise overview of your proposal, highlighting the key points and objectives.
A quality example of a research proposal shows one's above-average analytical skills, including the ability to coherently synthesize ideas and integrate lateral and vertical thinking. Communication skills. The proposal also demonstrates your proficiency to communicate your thoughts in concise and precise language.
A research proposal is a concise and coherent summary of your proposed research. You'll need to set out the issues that are central to the topic area and how you intend to address them with your research. To do this, you'll need to give the following: an outline of the general area of study within which your research falls.
Writing a research proposal template in structured steps ensures a comprehensive and coherent presentation of your research project. Let's look at the explanation for each of the steps here: Step 1: Title and Abstract. Step 2: Introduction. Step 3: Research objectives. Step 4: Literature review.
Literature review. This key component of the research proposal is the most time-consuming aspect in the preparation of your research proposal. As described in Chapter 5, the literature review provides the background to your study and demonstrates the significance of the proposed research.Specifically, it is a review and synthesis of prior research that is related to the problem you are setting ...
A dissertation or thesis research proposal may take on a variety of forms depending on the university, but most generally a research proposal will include the following elements: Titles or title pages that give a description of the research. Detailed explanation of the proposed research and its background. Outline of the research project.
Abstract: This is a brief (300-500 words) summary that includes the research question, your rationale for the study, and any applicable hypothesis. You should also include a brief description of your methodology, including procedures, samples, instruments, etc. Introduction: The opening paragraph of your research proposal is, perhaps, the most ...
A research proposal is a formal document expressing the details of a research project, which is usually for science or academic purposes, and it's typically four to seven pages long. Research proposals often include a title page, an abstract, an introduction, background information, research questions, a literature review and a bibliography.
A proposal needs to show how your work fits into what is already known about the topic and what new paradigm will it add to the literature, while specifying the question that the research will answer, establishing its significance, and the implications of the answer. [ 2] The proposal must be capable of convincing the evaluation committee about ...
The format of a research proposal varies between fields and levels of study but most proposals should contain at least these elements: introduction, literature review, research design and reference list. Generally, research proposals can range from 500-1500 words or one to a few pages long. Typically, proposals for larger projects such as a PhD ...
It puts the proposal in context. 3. The introduction typically begins with a statement of the research problem in precise and clear terms. 1. The importance of the statement of the research problem 5: The statement of the problem is the essential basis for the construction of a research proposal (research objectives, hypotheses, methodology ...
Answer: The methods section of a research proposal contains details about how you will conduct your research. It includes your study design - the methodology and methods that you plan to use - as well as your work plan - the activities that you plan to undertake to complete your project. The methods section of a research proposal must contain ...
Research proposal examples. Writing a research proposal can be quite challenging, but a good starting point could be to look at some examples. We've included a few for you below. Example research proposal #1: 'A Conceptual Framework for Scheduling Constraint Management'.
Include the goals of your research proposal and clearly specify the research questions you want to address. Explain the hypotheses you want to test. Note: A good summary should emphasize the problems the applicant intends to solve, identify the solution to the problems, and specify the objectives and design of the research. It ...
A well written introduction will help make a compelling case for your research proposal. To begin with, the introduction must set context for your research by mentioning what is known about the topic and what needs to be explored further. In the introduction, you can highlight how your research will contribute to the existing knowledge in your ...
Typically, your research proposal should include the following information: 1. Title. You should have a clear working title for your research, made up of key words that are relevant to your project. It should give an indication of the intent of your project, directing attention explicitly to the central issue that you will address.
A research proposal is a detailed plan which clearly outlines a suggested (or proposed) research project, ... to include a detailed methodology or research met hods section in the proposal. However, you should provide an outline of how you intend to approach your research problem, the theoretical framework you intend to ...
An effective research proposal should explain the value of your project. The aim, objectives, and techniques of your study should all be explained. ... The scope of your study, its significance to the field, and your methodology should all be included in your research proposal for a research paper. It's your plan for the research you want to do ...
Note that these are merely pointers; a detailed literature search might help you arrive at sharper points for pursuit. Note also that you will need to write a background in your final paper. So, that in the proposal needs to be shorter (crisper). The proposal is more to convey to your professor/supervisor how much you know about research in ...
For example, include methods in the proposal that relate directly to each of your study's aims and don't include additional methods that do not correspond to any aims. Tip #7. You can never have too many figures or tables. They make it easy for a reviewer to quickly grasp your proposal, as compared with dense text.
We've included 12 service proposal templates to help you win over potential customers and close more deals. ... To create a winning proposal, research your clients and outline your service proposal; flesh out the title and table of contents; provide a company overview and write an executive summary.
Objectives To determine the proportion of patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) with severe persisting pain and to identify predictive factors despite treatment-controlled disease activity. Methods This prospective multicentre study included outpatients with RA scheduled for escalation of anti-inflammatory treatment due to active disease and severe pain (Disease Activity Score 28 (DAS28)>3.2 ...
There is no question in my mind that serving on the Tennessee State Board of Education (SBE) is an honor and a privilege. Descriptions we often hear when someone remarks on their experience regardless of what form it may have taken. These words aptly describe how I feel about my own experience over the past ten years. I was reluctant in June 2014, to serve and represent the sixth congressional ...