- Games, topic printables & more
- The 4 main speech types
- Example speeches
- Commemorative
- Declamation
- Demonstration
- Informative
- Introduction
- Student Council
- Speech topics
- Poems to read aloud
- How to write a speech
- Using props/visual aids
- Acute anxiety help
- Breathing exercises
- Letting go - free e-course
- Using self-hypnosis
- Delivery overview
- 4 modes of delivery
- How to make cue cards
- How to read a speech
- 9 vocal aspects
- Vocal variety
- Diction/articulation
- Pronunciation
- Speaking rate
- How to use pauses
- Eye contact
- Body language
- Voice image
- Voice health
- Public speaking activities and games
- About me/contact
- Writing a persuasive speech
- Persuasive speech outline

Persuasive speech outline example
-an outline using Monroe's 5 step Motivated Sequence
By: Susan Dugdale
This persuasive speech outline example uses Monroe's Motivated Sequence (MMS) - a 5 step structural pattern for organizing material focusing on, as its name suggests, motivational appeals.
The sequence forms the basis of many of the successful political, public awareness or advertising campaigns you see and hear around you on a daily basis.
For example: campaigns to raise awareness of health issues: The Heart Truth, NDAFW - National Drugs and Alcohol Facts Week, or STOMP Out Bullying. *
Why is the framework so popular? Because it faithfully follows the psychology of persuasion. In a nutshell, it works. Exceedingly well.
Use the quick links to get around this very long page efficiently. Each of the five steps is fully explained and illustrated in an example speech outline. There's a printable MMS speech outline document for your own use too!
Page quick links
- Step overview
- Step 1 - Attention
- Step 2 - Need
- Step 3 - Satisfaction
- Step 4 - Visualization
- Step 5 - Action
- Download blank outline template
More persuasive speech resources

About Monroe's Motivated Sequence

The pattern, or steps, of the sequence mirror those identified as being the normal thinking processes that occur whenever a person is confronted by a problem.
Because the steps are perceived as reasonable and logical using them prepares and motivates an audience to respond positively to the speaker's message.
The sequence is named after Dr Alan H Monroe who, after graduating from Northwestern University in 1924, joined the staff at Purdue University (USA) as an Instructor in English. Two years later he became Instructor in Public Speaking and was subsequently promoted to Assistant Professor and head of the speech section of the English department. He retired from the role in 1963.
Overview of Monroe's 5 step motivation sequence
In developing your persuasive speech outline you will follow these 5 steps:
- Attention Grab the audience's attention
- Need Establish there is a problem (need) demanding their attention
- Satisfaction Outline a solution to the problem
- Visualization Show the audience how they will benefit from your solution
- Action Provide the impetus and means to act
Monroe's five steps in more detail
Now let's examine those steps more closely.
To make the process easier to follow I've prepared a simple example speech illustrating each step and the transitions between them. That's the text in the green boxes.
As you read start thinking about your audience and your topic. Jot any ideas down for later use.
About this sample speech - topic, purpose and audience
The subject is fear of public speaking.
The specific purpose of the speech is to persuade and encourage people in the audience to take a course to overcome their fear of public speaking.
The central idea of the speech is that the ability to speak in public opens doors to many opportunities.
The audience is drawn from the local community. They range in age from late teens to forties plus.
The 5 steps of Monroe's motivation sequence
Getting attention - step 1.

This step is your introductory "listen up" call. To make it effective it needs to grab the audience. It could be any of the following:
- a startling statement
- a rhetorical question
- a quotation
- a funny story
- a dramatic story
- a photograph or other visual aid
Put yourself in the position of your audience when deciding how to hook and hold their attention. Why should they listen to you? How does what you have to say benefit them? Is it relevant to them? How?
Step one - attention
Do you know the real costs of public speaking fear?
The price is high.
Research reveals that a person with public speaking fear is 10% less likely to graduate from college, is likely to receive 10% less in wages and is 15% less likely to take on management or leadership positions.
Who pays? You. Me. Us. Anybody who allows fear to govern their decision making. We pay by sacrificing our potential selves, putting our dreams away and settling for less.
Establishing credibility
As well as getting their attention you also need to establish your credibility or right to talk on the subject. Your audience needs to know that they can believe what you're telling them. If they feel they can trust your expertise and experience they will be much more likely to follow your lead.
Credibility statement
That’s a question I asked myself a long time ago. As a teacher with many years of experience I saw far too many students who would do anything they could to avoid public speaking. To answer it I researched.
Then I used those answers to devise public speaking programs that were effective and fun.
Transition - the link from step 1 to step 2
Can you imagine the positive impact feeling OK about speaking up would have? On individuals? On families? On our community?
E stablish the need - step 2

This step develops the need for change. Now that you have your audience's attention you will clearly show them what the problem is and the extent of it.
To be effective use:
- examples to illustrate how it impacts on them - their happiness, future, health, family, neighborhood...
- statistics - facts, figures, graphs, diagrams... Remember to cite your sources and remember too that some are more credible than others. You need recognized sources to give your speech the credibility you want.
- expert witness testimony - the more authoritative, the better
Your goal at the conclusion of this step is to have your audience eager to hear your solution. They agree with you that there is a problem and want the answer.
Step two – Need
A. According to frequently cited statistics 75% of people suffer from some degree of glossophobia - fear of speaking in public. Source: Hamilton, C. (2008) [2005]. Communicating for Results, a Guide for Business and the Professions (eighth edition)
- At the extreme upper end of this very large group are the people who would literally run a mile rather than speak. For example, they will not apply for promotions if the new position means giving presentations. They will not give a speech at a special family occasion - a wedding, birthday or funeral. Public speaking makes them ill, literally. There maybe quite a few of you here, so you’ll know exactly what I mean.
- At the other end of the scale are the people who have one or two butterflies fluttering around – enough to make them register they’re a little nervous about speaking but it’s nothing to worry about. There’s likely not so many of you here. If you have come along, it’s probably to support someone who needs it! Thank you.
- The majority of us are somewhere in the middle where it’s neither all fine nor all bad. Some days are OK. We manage. And some days it’s definitely not OK. We just hang in there by the skin of our chattering teeth.
B. Bad public speaking experiences often lead to more of the same. History repeats.
- We focus on the criticism we received and interpret it as a criticism of ourselves. Our speech is bad therefore I am bad. This makes a shaky platform to build public speaking skills and confidence on.
- When given a presentation to prepare we procrastinate because we don’t feel confident or competent. That means we don’t put the work in which in turn leads to another bad experience. It becomes a vicious circle.
- When we feel ashamed about ourselves we often close off. We don’t ask for help and it becomes easier to expect less of ourselves and our lives.
- Here's those stats again. According to Franklin Schneier, MD, s omeone with public speaking fear is likely to receive 10% less in wages, be 10% more likely to drop out of college and be 15% less likely to apply for leadership or management roles.
C. Begins in youth.
- “The fear of public speaking is more common in younger patients as compared to older ones and may be more prevalent in females as compared to males,” says Jeffrey R. Strawn, MD, FAACAP, associate professor of psychiatry and pediatrics and director of the Anxiety Disorders Research Program in the Department of Psychiatry & Behavioral Neuroscience at the University of Cincinnati.
- More than 75% of people experience their first symptoms of Social Anxiety Disorder which often includes fear of public speaking during their childhood or early teenage years - American Psychiatric Association. (2014). Understanding Mental Disorders
- Let’s conduct a quick informal survey to test that– raise your hand if any anxiety you feel about public speaking began when you were young.
Transition - the link between step 2 and step 3
However there is a way to break this pattern of anxiety. It can be stopped, and everyone who wants to can learn to speak in public confidently.
S atisfy the need - step 3

Now you outline your answer or solution and show the audience how it will work.
To do this well:
- outline your solution succinctly
- demonstrate how it meets the problem
- use examples to show how effective it is
- support with facts, figures, graphs, diagrams, statistics, testimony...
- if there is known opposition to your solution, acknowledge and counteract showing how your plan overturns it
The ideal outcome of this step is the audience nodding and saying to themselves: " Yes. This is possible, practical and sensible." Your answer satisfies them. It gives them "satisfaction".
Step three - Satisfaction
A. Come along to an introductory course
- It's free, led by experienced teachers and especially designed for people with a history of being nervous about speaking in public.
- Once a week for 4 weeks you'll have 2 hours of practical public speaking training and practice.
- You'll learn tips and tricks to manage your anxiety, to give varying types of presentations, to effectively structure a speech, and to confidently deliver a speech.
B. When people overcome fear of public speaking there are so many things they can do:
- Complete their college education and go on to further study if they wanted to
- Apply for the positions they know would give them greater work satisfaction
- Speak up when they need to about issues concerning themselves, their family and their community
- Inspire others to follow their example
C. Exchanging public speaking fear for confidence will help people to:
- Communicate more effectively
- Listen more carefully to others
- Understand the power of the spoken word and what it can achieve
Transition - the link between step 3 and step 4
Can you imagine the positive impact that would have on people’s lives? Maybe yours?
S ee the future - step 4

In this step the audience "experiences" the solution. They see (feel, hear, taste...) what will happen if they do as you are suggesting contrasted against what will happen if they don't do as you are suggesting.
This step relies on your use of vivid imagery to portray the outcome of their action, or inaction. They see and feel the pleasure, or pain, in their imagination. To bring it home to your audience the pictures you provide, the stories you tell, need to be relevant and believable.
What you want folk thinking as you conclude this step is: "I can see that this would be good for me."
Step four - Visualization
A. Imagine what society would be like if everyone took full advantage of the educational opportunities that best fitted their interests and abilities. How would that feel?
- There would be much less personal dissatisfaction and social unrest caused by people working in positions that do not pay very well or extend their skills and well being. That would be much more healthy: physically, emotionally and mentally, for everybody. You could ask for a raise! Apply for that job you always wanted! Give a presentation! Toast your bride!
- It would generate a ripple effect. People who speak up confidently and competently encourage others to do likewise. People would feel empowered – free to become the best of themselves - shoulders back, head up, standing tall, looking the world straight in the eye!
B. What disadvantages could there possibly be?
- Perhaps it could uncomfortable for those who have got used to assuming the right to talk for others without consultation. Is that really a bad thing?
- Perhaps it could lead to robust conversations where there are differing opinions over issues? Again, is that a bad thing? It could be an opportunity to polish debating skills.
- There are no real disadvantages! Overcoming public speaking fear is good for everyone. A win-win.
Transition - the link from step 4 to step 5
Let’s do more than imagine speaking in public freely and competently. Let’s take the steps towards making it happen.
T ake action - step 5

In this last step you present your call to action.
The call to action can be embedded in any combination of the following:
- a challenge or appeal
- a personal statement of intent
To be effective the action step must be readily doable and executed as soon as possible. Make it as easy as you can for your audience. If you want them to sign up for something, have the forms available. If you wish them to lodge a personal protest in writing to your local government have stock letters and envelopes ready. In other words do the leg work for them!
Action steps that are delayed even for 48 hours are less likely to be acted on. We're human - life goes on. Other things intervene and the initial urgency is lost.
Step five – Action
A. (Summary) Apparently 3/4 of us – 75%, are nervous about public speaking – often the result of a bad experience when were young. That has a direct impact on our adult lives. If we allow it to continue it is likely we will be paid less, fall out of college without graduating and settle for less-challenging jobs. In short – live a lesser life. However it doesn’t have to be like that. We could choose to change. We could become our bigger and best selves.
B. (Call to Immediate Action)
We could, in the famous words of Susan Jeffers, "Feel the fear and do it anyway!"
I’ve got enrollment forms here for that free introductory public speaking course. That’s four two hour sessions over the next four weeks using tried, tested and proven methods of teaching with experienced instructors. You’ll learn how to prepare and deliver speeches. And you'll swap fear for confidence and competence while having fun!
C. (Memorable Close) Who knows what magic may happen once you speak up!
There are 15 places available. Make one of them yours.
Sources/references
- Rosemary Black. (2018, June 4) Glossophobia (Fear of Public Speaking): Are You Glossophobic? Retrieved from https://www.psycom.net/glossophobia-fear-of-public-speaking
- Franklin Schneier. (2005) Social Anxiety Disorder. Retrieved from: http://www.columbia.edu/itc/hs/medical/psychmed2/3_2005/Schneier-SocialAnxietyDisorderBW.pdf
- Author and date of publication unknown. Social Anxiety Disorder. Retrieved from: http://www.mentalhealthamerica.net/conditions/social-anxiety-disorder
- Doug Staneart. (2018, March). Podcast 29 - How to Scare the Gooey Out of a Nervous Public Speaker. Retrieved from: https://www.fearlesspresentations.com/how-to-scare-the-gooey-out-of-a-new-public-speaker/
F itting the standard speech format
If you are wondering how these 5 steps of Monroe's Motivated Sequence fit into the standard 3 part speech format , they go like this:
- Step 1 ( Attention ) forms the Introduction.
- Steps 2, 3 and 4 ( Need, Satisfaction and Visualization ) form the Body.
- Step 5 ( Action ) is the Conclusion.
Download a persuasive speech outline template
And now download printable blank ready-to-complete Monroe's Motivated Sequence persuasive speech outline template . You'll find the entire 5 step process laid out clearly, ready for you to fill in the gaps.
A sample persuasive speech

Want to read a persuasive speech example ?
This example speech ("After they're gone") follows the sequence outlined on this page.
Before you click through to it you should know the topic is somber; the impact of suicide on family and friends. I wrote it to persuade those in need to seek and accept help and to raise awareness of the issues around suicide.
Persuasive speech topics

Maybe you haven't found the persuasive speech topic you want yet? Check these pages:
- 100 great persuasive speech ideas
- 50 good persuasive speech topics
- 205 fun persuasive speech topics
- 309 'easy' persuasive speech topics
- 310 persuasive speech topics for college
- 108 feminist persuasive speech topics
Communication coach Alex Lyon explains
If you'd like more on Monroe's Motivated Sequence here's a great video with excellent examples from communication coach Alex Lyons.
And lastly, here's the links to those campaigns I mentioned at the top of the page: The Heart Truth , National Drug and Alcohol Facts Week (NDAFW) and STOMP Out Bullying .
speaking out loud
Subscribe for FREE weekly alerts about what's new For more see speaking out loud

Top 10 popular pages
- Welcome speech
- Demonstration speech topics
- Impromptu speech topic cards
- Thank you quotes
- Impromptu public speaking topics
- Farewell speeches
- Phrases for welcome speeches
- Student council speeches
- Free sample eulogies
From fear to fun in 28 ways
A complete one stop resource to scuttle fear in the best of all possible ways - with laughter.

Useful pages
- Search this site
- About me & Contact
- Blogging Aloud
- Free e-course
- Privacy policy
©Copyright 2006-24 www.write-out-loud.com
Designed and built by Clickstream Designs

Improve your practice.
Enhance your soft skills with a range of award-winning courses.
Persuasive Speech Outline, with Examples
March 17, 2021 - Gini Beqiri
A persuasive speech is a speech that is given with the intention of convincing the audience to believe or do something. This could be virtually anything – voting, organ donation, recycling, and so on.
A successful persuasive speech effectively convinces the audience to your point of view, providing you come across as trustworthy and knowledgeable about the topic you’re discussing.
So, how do you start convincing a group of strangers to share your opinion? And how do you connect with them enough to earn their trust?
Topics for your persuasive speech
We’ve made a list of persuasive speech topics you could use next time you’re asked to give one. The topics are thought-provoking and things which many people have an opinion on.
When using any of our persuasive speech ideas, make sure you have a solid knowledge about the topic you’re speaking about – and make sure you discuss counter arguments too.
Here are a few ideas to get you started:
- All school children should wear a uniform
- Facebook is making people more socially anxious
- It should be illegal to drive over the age of 80
- Lying isn’t always wrong
- The case for organ donation
Read our full list of 75 persuasive speech topics and ideas .

Preparation: Consider your audience
As with any speech, preparation is crucial. Before you put pen to paper, think about what you want to achieve with your speech. This will help organise your thoughts as you realistically can only cover 2-4 main points before your audience get bored .
It’s also useful to think about who your audience are at this point. If they are unlikely to know much about your topic then you’ll need to factor in context of your topic when planning the structure and length of your speech. You should also consider their:
- Cultural or religious backgrounds
- Shared concerns, attitudes and problems
- Shared interests, beliefs and hopes
- Baseline attitude – are they hostile, neutral, or open to change?
The factors above will all determine the approach you take to writing your speech. For example, if your topic is about childhood obesity, you could begin with a story about your own children or a shared concern every parent has. This would suit an audience who are more likely to be parents than young professionals who have only just left college.
Remember the 3 main approaches to persuade others
There are three main approaches used to persuade others:
The ethos approach appeals to the audience’s ethics and morals, such as what is the ‘right thing’ to do for humanity, saving the environment, etc.
Pathos persuasion is when you appeal to the audience’s emotions, such as when you tell a story that makes them the main character in a difficult situation.
The logos approach to giving a persuasive speech is when you appeal to the audience’s logic – ie. your speech is essentially more driven by facts and logic. The benefit of this technique is that your point of view becomes virtually indisputable because you make the audience feel that only your view is the logical one.
- Ethos, Pathos, Logos: 3 Pillars of Public Speaking and Persuasion
Ideas for your persuasive speech outline
1. structure of your persuasive speech.
The opening and closing of speech are the most important. Consider these carefully when thinking about your persuasive speech outline. A strong opening ensures you have the audience’s attention from the start and gives them a positive first impression of you.
You’ll want to start with a strong opening such as an attention grabbing statement, statistic of fact. These are usually dramatic or shocking, such as:
Sadly, in the next 18 minutes when I do our chat, four Americans that are alive will be dead from the food that they eat – Jamie Oliver
Another good way of starting a persuasive speech is to include your audience in the picture you’re trying to paint. By making them part of the story, you’re embedding an emotional connection between them and your speech.
You could do this in a more toned-down way by talking about something you know that your audience has in common with you. It’s also helpful at this point to include your credentials in a persuasive speech to gain your audience’s trust.

Obama would spend hours with his team working on the opening and closing statements of his speech.
2. Stating your argument
You should pick between 2 and 4 themes to discuss during your speech so that you have enough time to explain your viewpoint and convince your audience to the same way of thinking.
It’s important that each of your points transitions seamlessly into the next one so that your speech has a logical flow. Work on your connecting sentences between each of your themes so that your speech is easy to listen to.
Your argument should be backed up by objective research and not purely your subjective opinion. Use examples, analogies, and stories so that the audience can relate more easily to your topic, and therefore are more likely to be persuaded to your point of view.
3. Addressing counter-arguments
Any balanced theory or thought addresses and disputes counter-arguments made against it. By addressing these, you’ll strengthen your persuasive speech by refuting your audience’s objections and you’ll show that you are knowledgeable to other thoughts on the topic.
When describing an opposing point of view, don’t explain it in a bias way – explain it in the same way someone who holds that view would describe it. That way, you won’t irritate members of your audience who disagree with you and you’ll show that you’ve reached your point of view through reasoned judgement. Simply identify any counter-argument and pose explanations against them.
- Complete Guide to Debating
4. Closing your speech
Your closing line of your speech is your last chance to convince your audience about what you’re saying. It’s also most likely to be the sentence they remember most about your entire speech so make sure it’s a good one!
The most effective persuasive speeches end with a call to action . For example, if you’ve been speaking about organ donation, your call to action might be asking the audience to register as donors.
Practice answering AI questions on your speech and get feedback on your performance .
If audience members ask you questions, make sure you listen carefully and respectfully to the full question. Don’t interject in the middle of a question or become defensive.
You should show that you have carefully considered their viewpoint and refute it in an objective way (if you have opposing opinions). Ensure you remain patient, friendly and polite at all times.
Example 1: Persuasive speech outline
This example is from the Kentucky Community and Technical College.
Specific purpose
To persuade my audience to start walking in order to improve their health.
Central idea
Regular walking can improve both your mental and physical health.
Introduction
Let’s be honest, we lead an easy life: automatic dishwashers, riding lawnmowers, T.V. remote controls, automatic garage door openers, power screwdrivers, bread machines, electric pencil sharpeners, etc., etc. etc. We live in a time-saving, energy-saving, convenient society. It’s a wonderful life. Or is it?
Continue reading
Example 2: Persuasive speech
Tips for delivering your persuasive speech
- Practice, practice, and practice some more . Record yourself speaking and listen for any nervous habits you have such as a nervous laugh, excessive use of filler words, or speaking too quickly.
- Show confident body language . Stand with your legs hip width apart with your shoulders centrally aligned. Ground your feet to the floor and place your hands beside your body so that hand gestures come freely. Your audience won’t be convinced about your argument if you don’t sound confident in it. Find out more about confident body language here .
- Don’t memorise your speech word-for-word or read off a script. If you memorise your persuasive speech, you’ll sound less authentic and panic if you lose your place. Similarly, if you read off a script you won’t sound genuine and you won’t be able to connect with the audience by making eye contact . In turn, you’ll come across as less trustworthy and knowledgeable. You could simply remember your key points instead, or learn your opening and closing sentences.
- Remember to use facial expressions when storytelling – they make you more relatable. By sharing a personal story you’ll more likely be speaking your truth which will help you build a connection with the audience too. Facial expressions help bring your story to life and transport the audience into your situation.
- Keep your speech as concise as possible . When practicing the delivery, see if you can edit it to have the same meaning but in a more succinct way. This will keep the audience engaged.
The best persuasive speech ideas are those that spark a level of controversy. However, a public speech is not the time to express an opinion that is considered outside the norm. If in doubt, play it safe and stick to topics that divide opinions about 50-50.
Bear in mind who your audience are and plan your persuasive speech outline accordingly, with researched evidence to support your argument. It’s important to consider counter-arguments to show that you are knowledgeable about the topic as a whole and not bias towards your own line of thought.
How To Write A Persuasive Speech: 7 Steps
Table of contents
- 1 Guidance on Selecting an Effective and Relevant Topic
- 2 Strategies for Connecting With Different Types of Audiences
- 3 Developing Your Thesis Statement
- 4.1 Writing the Introduction
- 4.2 Body of Your Speech
- 4.3 Concluding Effectively
- 5 Techniques for Creating a Coherent Flow of Ideas
- 6 Importance of Transitions Between Points
- 7 Importance of Tone and Style Adjustments Based on the Audience
- 8 Prepare for Rebuttals
- 9 Use Simple Statistics
- 10 Practicing Your Speech
- 11 Additional Resources to Master Your Speech
- 12 Master the Art of Persuasion With PapersOwl
Are you about to perform a persuasive speech and have no idea how to do it? No need to worry; PapersOwl is here to guide you through this journey!
What is persuasive speaking? Persuasive speaking is a form of communication where the speaker aims to influence or convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or belief or take specific actions. The goal is to sway the listeners’ opinions, attitudes, or behaviors by presenting compelling arguments and supporting evidence while appealing to their emotions.
Today, we prepared a guide to help you write a persuasive speech and succeed in your performance, which will surprise your audience. We will:
- Understand how to connect with your audience.
- Give you persuasive speech tips.
- Provide you with the best structure for a persuasive speech outline.
- Prepare yourself for rebuttals!
- Talk about the importance of flow in your speech.
- Discover additional resources for continuous improvement.
Let’s begin this journey together!
Guidance on Selecting an Effective and Relevant Topic
The most important thing in convincing speeches is the topic. Indeed, you must understand the purpose of your speech to succeed. Before preparing for your performance, you should understand what you want to discuss! To do that, you can:
- Choose a compelling speech topic relevant to your audience’s interests and concerns.
- Find common interests or problems to form a genuine relationship.
- Remember that a persuasive speech format should be adapted to your audience’s needs and ideals. Make your content relevant and appealing.
And if you are struggling on this step, PapersOwl is already here to help you! Opt to choose persuasive speech topics and find the one that feels perfect for you.
Strategies for Connecting With Different Types of Audiences
A successful persuasive speech connects you with your audience. To do that, you should really know how to connect yourself to people.
Thus, the speaker connects with and persuades the audience by using emotions such as sympathy or fear. Therefore, you can successfully connect with different types of audiences through different emotions. You can do it by showing that you have something in common with the audience. For example, demonstrate that you have a comparable history or an emotional connection. Additionally, include personal stories or even make a part of a speech about yourself to allow your audience to relate to your story.
Developing Your Thesis Statement
When you give a persuasive speech, there should be a thesis statement demonstrating that your goal is to enlighten the audience rather than convince them.
A thesis statement in persuasive speaking serves as the central argument or main point, guiding the entire presentation. A successful thesis anchors your speech and briefly expresses your position on the subject, giving a road map for both you and your audience.
For instance, in pushing for renewable energy, a thesis may be: “Transitioning to renewable sources is imperative for a sustainable future, mitigating environmental impact and fostering energy independence.” This statement summarizes the argument and foreshadows the supporting points.
Overview of speech structure (introduction, body, conclusion)
The key elements of a persuasive speech are:
- introduction (hook, thesis, preview);
- body (main points with supporting details and transitions);
- conclusion (summary, restated thesis, closing statement).
Let’s look closer at how to structure them to write a good persuasive speech.
Writing the Introduction
The introduction to persuasive speech is crucial. The very beginning of your discourse determines your whole performance, drawing in your audience and creating a foundation for trust and engagement. Remember, it’s your opportunity to make a memorable first impression, ensuring your listeners are intrigued and receptive to your message.
Start off a persuasive speech with an enticing quotation, image, video, or engaging tale; it can entice people to listen. As we mentioned before, you may connect your speech to the audience and what they are interested in. Establish credibility by showcasing your expertise or connecting with shared values. Ultimately, ensure your thesis is clear and outline which specific purpose statement is most important in your persuasive speech.
Body of Your Speech
After choosing the topic and writing an intro, it’s time to concentrate on one of the most critical parts of a persuasive speech: the body.
The main body of your speech should provide the audience with several convincing reasons to support your viewpoint. In this part of your speech, create engaging primary points by offering strong supporting evidence — use statistics, illustrations, or expert quotations to strengthen each argument. Also, don’t forget to include storytelling for an emotional connection with your audience. If you follow this combination, it will for sure make a speech persuasive!
Concluding Effectively
After succeeding in writing the main points, it is time to end a persuasive speech! Indeed, a call to action in persuasive speech is vital, so we recommend you end your performance with it. After listening to your argument and proof, you want the audience to make a move. Restate your purpose statement, summarize the topic, and reinforce your points by restating the logical evidence you’ve provided.
Techniques for Creating a Coherent Flow of Ideas
Your ideas should flow smoothly and naturally connect to strengthen the persuasive speech structure . You can do this by employing transitional words and organizing your thoughts methodically, ensuring that each point flows effortlessly into the next.
Importance of Transitions Between Points
No one can underestimate the importance of transition. They are important persuasive speech elements. Thus, each idea must flow smoothly into the following one with linking phrases so your speech has a logical flow. Effective transitions signal shifts, aiding audience comprehension and improving the overall structure of the speech.
Importance of Tone and Style Adjustments Based on the Audience
To be persuasive in a speech, don’t forget to analyze your audience in advance, if possible. Customizing your approach to specific listeners encourages their engagement. A thorough awareness of your target audience’s tastes, expectations, and cultural subtleties ensures that your message connects, making it more approachable and appealing to the people you seek to reach.
Prepare for Rebuttals
Still, be aware that there may be different people in the audience. The main point of persuasive speaking is to convince people of your ideas. Be prepared for rebuttals and that they might attack you. Extensively research opposing points of view to prove yours. You may manage any objections with elegance by being prepared and polite, reaffirming the strength of your argument.
Use Simple Statistics
We’ve already discussed that different techniques may reach different audiences. You could also incorporate simple data to lend credibility to your persuasive talk. Balance emotional appeal with plain numerical statistics to create a captivating blend that will appeal to a wide audience.
Practicing Your Speech
We all have heard Benjamin Franklin’s famous quote, “Practice makes perfect.” Even though he said it hundreds of years ago, it still works for everything, including persuasive public speaking! Consequently, you can improve your text with these pieces of advice:
- Go through and edit your persuasive speech sample.
- Practice your speech with body language and voice variation to find the perfect way to perform it.
- Reduce anxiety by practicing in front of a mirror or telling it to someone ready to provide you with valuable feedback.
- Embrace pauses for emphasis, and work on regulating your pace.
It will help you to know your content well, increase confidence, and promote a polished delivery, resulting in a dynamic and engaging speech to persuade your audience.
Additional Resources to Master Your Speech
PapersOwl wants you to ace your speech! We recommend using additional sources to help master your persuasive speech presentation!
- For inspiration, study any example of persuasive speech from a famous speaker, such as Martin Luther King Jr.’s “I Have a Dream” or Steve Jobs’ Stanford commencement address. Analyzing these speeches can provide valuable insights into effective communication techniques.
- Explore Coursera’s course “Speaking to Persuade: Motivating Audiences With Solid Arguments and Moving Language” by the University of Washington.
- Go through different persuasive speech examples for students around the internet, for instance, “Talk Like TED” by Carmine Gallo.
Make your persuasive speech successful by continuously learning and drawing inspiration from accomplished speakers!
Master the Art of Persuasion With PapersOwl
In conclusion, speaking to persuade is an art that helps convince with words . You can craft it by following our tips: include a well-structured persuasive speech introduction, a compelling body, and memorable conclusion. To ace your speech, practice it in advance, be ready for rebuttals, and confidently state your message. The secret lies in blending both for a nuanced and compelling communication style, ensuring your message resonates with diverse audiences in various contexts.
Nevertheless, writing a persuasive speech that can hold your audience’s attention might be difficult. You do not need to step on this path alone. You may quickly construct a persuasive speech that is both successful and well-organized by working with PapersOwl.com . We’ll be there for you every step, from developing a convincing argument to confidently giving the speech. Just send us a message, “ write a speech for me ,” and enjoy the results!
Readers also enjoyed

WHY WAIT? PLACE AN ORDER RIGHT NOW!
Just fill out the form, press the button, and have no worries!
We use cookies to give you the best experience possible. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy.
My Speech Class
Public Speaking Tips & Speech Topics
How to Write an Outline for a Persuasive Speech, with Examples

Jim Peterson has over 20 years experience on speech writing. He wrote over 300 free speech topic ideas and how-to guides for any kind of public speaking and speech writing assignments at My Speech Class.

Persuasive speeches are one of the three most used speeches in our daily lives. Persuasive speech is used when presenters decide to convince their presentation or ideas to their listeners. A compelling speech aims to persuade the listener to believe in a particular point of view. One of the most iconic examples is Martin Luther King’s ‘I had a dream’ speech on the 28th of August 1963.
In this article:
What is Persuasive Speech?
Here are some steps to follow:, persuasive speech outline, final thoughts.

Persuasive speech is a written and delivered essay to convince people of the speaker’s viewpoint or ideas. Persuasive speaking is the type of speaking people engage in the most. This type of speech has a broad spectrum, from arguing about politics to talking about what to have for dinner. Persuasive speaking is highly connected to the audience, as in a sense, the speaker has to meet the audience halfway.
Persuasive Speech Preparation
Persuasive speech preparation doesn’t have to be difficult, as long as you select your topic wisely and prepare thoroughly.
1. Select a Topic and Angle
Come up with a controversial topic that will spark a heated debate, regardless of your position. This could be about anything. Choose a topic that you are passionate about. Select a particular angle to focus on to ensure that your topic isn’t too broad. Research the topic thoroughly, focussing on key facts, arguments for and against your angle, and background.
2. Define Your Persuasive Goal
Once you have chosen your topic, it’s time to decide what your goal is to persuade the audience. Are you trying to persuade them in favor of a certain position or issue? Are you hoping that they change their behavior or an opinion due to your speech? Do you want them to decide to purchase something or donate money to a cause? Knowing your goal will help you make wise decisions about approaching writing and presenting your speech.
3. Analyze the Audience
Understanding your audience’s perspective is critical anytime that you are writing a speech. This is even more important when it comes to a persuasive speech because not only are you wanting to get the audience to listen to you, but you are also hoping for them to take a particular action in response to your speech. First, consider who is in the audience. Consider how the audience members are likely to perceive the topic you are speaking on to better relate to them on the subject. Grasp the obstacles audience members face or have regarding the topic so you can build appropriate persuasive arguments to overcome these obstacles.
Can We Write Your Speech?
Get your audience blown away with help from a professional speechwriter. Free proofreading and copy-editing included.
4. Build an Effective Persuasive Argument
Once you have a clear goal, you are knowledgeable about the topic and, have insights regarding your audience, you will be ready to build an effective persuasive argument to deliver in the form of a persuasive speech.
Start by deciding what persuasive techniques are likely to help you persuade your audience. Would an emotional and psychological appeal to your audience help persuade them? Is there a good way to sway the audience with logic and reason? Is it possible that a bandwagon appeal might be effective?
5. Outline Your Speech
Once you know which persuasive strategies are most likely to be effective, your next step is to create a keyword outline to organize your main points and structure your persuasive speech for maximum impact on the audience.
Start strong, letting your audience know what your topic is, why it matters and, what you hope to achieve at the end of your speech. List your main points, thoroughly covering each point, being sure to build the argument for your position and overcome opposing perspectives. Conclude your speech by appealing to your audience to act in a way that will prove that you persuaded them successfully. Motivation is a big part of persuasion.
6. Deliver a Winning Speech
Select appropriate visual aids to share with your audiences, such as graphs, photos, or illustrations. Practice until you can deliver your speech confidently. Maintain eye contact, project your voice and, avoid using filler words or any form of vocal interference. Let your passion for the subject shine through. Your enthusiasm may be what sways the audience.

Topic: What topic are you trying to persuade your audience on?
Specific Purpose:
Central idea:
- Attention grabber – This is potentially the most crucial line. If the audience doesn’t like the opening line, they might be less inclined to listen to the rest of your speech.
- Thesis – This statement is used to inform the audience of the speaker’s mindset and try to get the audience to see the issue their way.
- Qualifications – Tell the audience why you are qualified to speak about the topic to persuade them.
After the introductory portion of the speech is over, the speaker starts presenting reasons to the audience to provide support for the statement. After each reason, the speaker will list examples to provide a factual argument to sway listeners’ opinions.
- Example 1 – Support for the reason given above.
- Example 2 – Support for the reason given above.
The most important part of a persuasive speech is the conclusion, second to the introduction and thesis statement. This is where the speaker must sum up and tie all of their arguments into an organized and solid point.
- Summary: Briefly remind the listeners why they should agree with your position.
- Memorable ending/ Audience challenge: End your speech with a powerful closing thought or recommend a course of action.
- Thank the audience for listening.
Persuasive Speech Outline Examples

Topic: Walking frequently can improve both your mental and physical health.
Specific Purpose: To persuade the audience to start walking to improve their health.
Central idea: Regular walking can improve your mental and physical health.
Life has become all about convenience and ease lately. We have dishwashers, so we don’t have to wash dishes by hand with electric scooters, so we don’t have to paddle while riding. I mean, isn’t it ridiculous?
Today’s luxuries have been welcomed by the masses. They have also been accused of turning us into passive, lethargic sloths. As a reformed sloth, I know how easy it can be to slip into the convenience of things and not want to move off the couch. I want to persuade you to start walking.
Americans lead a passive lifestyle at the expense of their own health.
- This means that we spend approximately 40% of our leisure time in front of the TV.
- Ironically, it is also reported that Americans don’t like many of the shows that they watch.
- Today’s studies indicate that people were experiencing higher bouts of depression than in the 18th and 19th centuries, when work and life were considered problematic.
- The article reports that 12.6% of Americans suffer from anxiety, and 9.5% suffer from severe depression.
- Present the opposition’s claim and refute an argument.
- Nutritionist Phyllis Hall stated that we tend to eat foods high in fat, which produces high levels of cholesterol in our blood, which leads to plaque build-up in our arteries.
- While modifying our diet can help us decrease our risk for heart disease, studies have indicated that people who don’t exercise are at an even greater risk.
In closing, I urge you to start walking more. Walking is a simple, easy activity. Park further away from stores and walk. Walk instead of driving to your nearest convenience store. Take 20 minutes and enjoy a walk around your neighborhood. Hide the TV remote, move off the couch and, walk. Do it for your heart.
Thank you for listening!
Topic: Less screen time can improve your sleep.
Specific Purpose: To persuade the audience to stop using their screens two hours before bed.
Central idea: Ceasing electronics before bed will help you achieve better sleep.
Who doesn’t love to sleep? I don’t think I have ever met anyone who doesn’t like getting a good night’s sleep. Sleep is essential for our bodies to rest and repair themselves.
I love sleeping and, there is no way that I would be able to miss out on a good night’s sleep.
As someone who has had trouble sleeping due to taking my phone into bed with me and laying in bed while entertaining myself on my phone till I fall asleep, I can say that it’s not the healthiest habit, and we should do whatever we can to change it.
- Our natural blue light source is the sun.
- Bluelight is designed to keep us awake.
- Bluelight makes our brain waves more active.
- We find it harder to sleep when our brain waves are more active.
- Having a good night’s rest will improve your mood.
- Being fully rested will increase your productivity.
Using electronics before bed will stimulate your brainwaves and make it more difficult for you to sleep. Bluelight tricks our brains into a false sense of daytime and, in turn, makes it more difficult for us to sleep. So, put down those screens if you love your sleep!
Thank the audience for listening
A persuasive speech is used to convince the audience of the speaker standing on a certain subject. To have a successful persuasive speech, doing the proper planning and executing your speech with confidence will help persuade the audience of your standing on the topic you chose. Persuasive speeches are used every day in the world around us, from planning what’s for dinner to arguing about politics. It is one of the most widely used forms of speech and, with proper planning and execution, you can sway any audience.
How to Write the Most Informative Essay
How to Craft a Masterful Outline of Speech
Leave a Comment
I accept the Privacy Policy
Reach out to us for sponsorship opportunities
Vivamus integer non suscipit taciti mus etiam at primis tempor sagittis euismod libero facilisi.
© 2024 My Speech Class
How to Write and Structure a Persuasive Speech
- Homework Tips
- Learning Styles & Skills
- Study Methods
- Time Management
- Private School
- College Admissions
- College Life
- Graduate School
- Business School
- Distance Learning
- M.Ed., Education Administration, University of Georgia
- B.A., History, Armstrong State University
The purpose of a persuasive speech is to convince your audience to agree with an idea or opinion that you present. First, you'll need to choose a side on a controversial topic, then you will write a speech to explain your position, and convince the audience to agree with you.
You can produce an effective persuasive speech if you structure your argument as a solution to a problem. Your first job as a speaker is to convince your audience that a particular problem is important to them, and then you must convince them that you have the solution to make things better.
Note: You don't have to address a real problem. Any need can work as the problem. For example, you could consider the lack of a pet, the need to wash one's hands, or the need to pick a particular sport to play as the "problem."
As an example, let's imagine that you have chosen "Getting Up Early" as your persuasion topic. Your goal will be to persuade classmates to get themselves out of bed an hour earlier every morning. In this instance, the problem could be summed up as "morning chaos."
A standard speech format has an introduction with a great hook statement, three main points, and a summary. Your persuasive speech will be a tailored version of this format.
Before you write the text of your speech, you should sketch an outline that includes your hook statement and three main points.
Writing the Text
The introduction of your speech must be compelling because your audience will make up their minds within a few minutes whether or not they are interested in your topic.
Before you write the full body you should come up with a greeting. Your greeting can be as simple as "Good morning everyone. My name is Frank."
After your greeting, you will offer a hook to capture attention. A hook sentence for the "morning chaos" speech could be a question:
- How many times have you been late for school?
- Does your day begin with shouts and arguments?
- Have you ever missed the bus?
Or your hook could be a statistic or surprising statement:
- More than 50 percent of high school students skip breakfast because they just don't have time to eat.
- Tardy kids drop out of school more often than punctual kids.
Once you have the attention of your audience, follow through to define the topic/problem and introduce your solution. Here's an example of what you might have so far:
Good afternoon, class. Some of you know me, but some of you may not. My name is Frank Godfrey, and I have a question for you. Does your day begin with shouts and arguments? Do you go to school in a bad mood because you've been yelled at, or because you argued with your parent? The chaos you experience in the morning can bring you down and affect your performance at school.
Add the solution:
You can improve your mood and your school performance by adding more time to your morning schedule. You can accomplish this by setting your alarm clock to go off one hour earlier.
Your next task will be to write the body, which will contain the three main points you've come up with to argue your position. Each point will be followed by supporting evidence or anecdotes, and each body paragraph will need to end with a transition statement that leads to the next segment. Here is a sample of three main statements:
- Bad moods caused by morning chaos will affect your workday performance.
- If you skip breakfast to buy time, you're making a harmful health decision.
- (Ending on a cheerful note) You'll enjoy a boost to your self-esteem when you reduce the morning chaos.
After you write three body paragraphs with strong transition statements that make your speech flow, you are ready to work on your summary.
Your summary will re-emphasize your argument and restate your points in slightly different language. This can be a little tricky. You don't want to sound repetitive but will need to repeat what you have said. Find a way to reword the same main points.
Finally, you must make sure to write a clear final sentence or passage to keep yourself from stammering at the end or fading off in an awkward moment. A few examples of graceful exits:
- We all like to sleep. It's hard to get up some mornings, but rest assured that the reward is well worth the effort.
- If you follow these guidelines and make the effort to get up a little bit earlier every day, you'll reap rewards in your home life and on your report card.
Tips for Writing Your Speech
- Don't be confrontational in your argument. You don't need to put down the other side; just convince your audience that your position is correct by using positive assertions.
- Use simple statistics. Don't overwhelm your audience with confusing numbers.
- Don't complicate your speech by going outside the standard "three points" format. While it might seem simplistic, it is a tried and true method for presenting to an audience who is listening as opposed to reading.
- How to Write a Persuasive Essay
- 5 Tips on How to Write a Speech Essay
- Tips on How to Write an Argumentative Essay
- Writing an Opinion Essay
- How To Write an Essay
- 5 Steps to Writing a Position Paper
- How to Structure an Essay
- Ethos, Logos, Pathos for Persuasion
- What Is Expository Writing?
- Audience Analysis in Speech and Composition
- Definition and Examples of Analysis in Composition
- 100 Persuasive Speech Topics for Students
- What an Essay Is and How to Write One
- How to Write a Good Thesis Statement
- 100 Persuasive Essay Topics
- How to Write a Graduation Speech as Valedictorian
ATLANTA, MAY 23-24 PUBLIC SPEAKING CLASS IS ALMOST FULL! RESERVE YOUR SPOT NOW

- Public Speaking Classes
- Corporate Presentation Training
- Online Public Speaking Course
- Northeast Region
- Midwest Region
- Southeast Region
- Central Region
- Western Region
- Presentation Skills
- 101 Public Speaking Tips
- Fear of Public Speaking
Persuasive Speech: How to Write an Effective Persuasive Speech

Most often, it actually causes the other person to want to play “Devil’s advocate” and argue with you. In this article, we are going to show you a simple way to win people to your way of thinking without raising resentment. If you use this technique, your audience will actually WANT to agree with you! The process starts with putting yourself in the shoes of your listener and looking at things from their point of view.
Background About How to Write a Persuasive Speech. Facts Aren’t Very Persuasive.

Most people think that a single fact is good, additional facts are better, and too many facts are just right. So, the more facts you can use to prove your point, the better chance you have of convincing the other person that you are right. The HUGE error in this logic, though, is that if you prove that you are right, you are also proving that the other person is wrong. People don’t like it when someone proves that they are wrong. So, we prove our point, the other person is likely to feel resentment. When resentment builds, it leads to anger. Once anger enters the equation, logic goes right out the window.
In addition, when people use a “fact” or “Statistic” to prove a point, the audience has a natural reaction to take a contrary side of the argument. For instance, if I started a statement with, “I can prove to you beyond a doubt that…” before I even finish the statement, there is a good chance that you are already trying to think of a single instance where the statement is NOT true. This is a natural response. As a result, the thing that we need to realize about being persuasive is that the best way to persuade another person is to make the person want to agree with us. We do this by showing the audience how they can get what they want if they do what we want.
You may also like How to Design and Deliver a Memorable Speech .
A Simple 3-Step Process to Create a Persuasive Presentation

The process below is a good way to do both.
Step One: Start Your Persuasive Speech with an Example or Story
When you write an effective persuasive speech, stories are vital. Stories and examples have a powerful way to capture an audience’s attention and set them at ease. They get the audience interested in the presentation. Stories also help your audience see the concepts you are trying to explain in a visual way and make an emotional connection. The more details that you put into your story, the more vivid the images being created in the minds of your audience members.
This concept isn’t mystical or anything. It is science. When we communicate effectively with another person, the purpose is to help the listener picture a concept in his/her mind that is similar to the concept in the speaker’s mind. The old adage is that a “picture is worth 1000 words.” Well, an example or a story is a series of moving pictures. So, a well-told story is worth thousands of words (facts).
By the way, there are a few additional benefits of telling a story. Stories help you reduce nervousness, make better eye contact, and make for a strong opening. For additional details, see Storytelling in Speeches .
I’ll give you an example.
Factual Argument: Seatbelts Save Lives

- 53% of all motor vehicle fatalities from last years were people who weren’t wearing seatbelts.
- People not wearing seatbelts are 30 times more likely to be ejected from the vehicle.
- In a single year, crash deaths and injuries cost us over $70 billion dollars.
These are actual statistics. However, when you read each bullet point, you are likely to be a little skeptical. For instance, when you see the 53% statistic, you might have had the same reaction that I did. You might be thinking something like, “Isn’t that right at half? Doesn’t that mean that the other half WERE wearing seatbelts?” When you see the “30 times more likely” statistic, you might be thinking, “That sounds a little exaggerated. What are the actual numbers?” Looking at the last statistic, we’d likely want to know exactly how the reporter came to that conclusion.
As you can see, if you are a believer that seatbelts save lives, you will likely take the numbers at face value. If you don’t like seatbelts, you will likely nitpick the finer points of each statistic. The facts will not likely persuade you.
Example Argument: Seatbelts Save Lives

When I came to, I tried to open my door. The accident sealed it shut. The windshield was gone. So I took my seatbelt off and scrambled out the hole. The driver of the truck was a bloody mess. His leg was pinned under the steering wheel.
The firefighters came a few minutes later, and it took them over 30 minutes to cut the metal from around his body to free him.
A Sheriff’s Deputy saw a cut on my face and asked if I had been in the accident. I pointed to my truck. His eyes became like saucers. “You were in that vehicle?”
I nodded. He rushed me to an ambulance. I had actually ruptured my colon, and I had to have surgery. I was down for a month or so, but I survived. In fact, I survived with very few long-term challenges from the accident.
The guy who hit me wasn’t so lucky. He wasn’t wearing a seatbelt. The initial impact of the accident was his head on the steering wheel and then the windshield. He had to have a number of facial surgeries. The only reason he remained in the truck was his pinned leg. For me, the accident was a temporary trauma. For him, it was a life-long tragedy.
The Emotional Difference is the Key
As you can see, there are major differences between the two techniques. The story gives lots of memorable details along with an emotion that captures the audience. If you read both examples, let me ask you a couple of questions. Without looking back up higher on the page, how long did it take the firefighters to cut the other driver from the car? How many CDs did I have? There is a good chance that these two pieces of data came to you really quickly. You likely remembered this data, even though, the data wasn’t exactly important to the story.
However, if I asked you how much money was lost last year as a result of traffic accidents, you might struggle to remember that statistic. The CDs and the firefighters were a part of a compelling story that made you pay attention. The money lost to accidents was just a statistic thrown at you to try to prove that a point was true.
The main benefit of using a story, though, is that when we give statistics (without a story to back them up,) the audience becomes argumentative. However, when we tell a story, the audience can’t argue with us. The audience can’t come to me after I told that story and say, “It didn’t take 30 minutes to cut the guy out of the car. He didn’t have to have a bunch of reconstructive surgeries. The Deputy didn’t say those things to you! The audience can’t argue with the details of the story, because they weren’t there.
Step 2: After the Story, Now, Give Your Advice
When most people write a persuasive presentation, they start with their opinion. Again, this makes the listener want to play Devil’s advocate. By starting with the example, we give the listener a simple way to agree with us. They can agree that the story that we told was true. So, now, finish the story with your point or your opinion. “So, in my opinion, if you wear a seatbelt, you’re more likely to avoid serious injury in a severe crash.”
By the way, this technique is not new. It has been around for thousands of years. Aesop was a Greek slave over 500 years before Christ. His stories were passed down verbally for hundreds of years before anyone ever wrote them down in a collection. Today, when you read an Aesop fable, you will get 30 seconds to two minutes of the story first. Then, at the conclusion, almost as a post-script, you will get the advice. Most often, this advice comes in the form of, “The moral of the story is…” You want to do the same in your persuasive presentations. Spend most of the time on the details of the story. Then, spend just a few seconds in the end with your morale.

Step 3: End with the Benefit to the Audience

So, the moral of the story is to wear your seatbelt. If you do that, you will avoid being cut out of your car and endless reconstructive surgeries .
Now, instead of leaving your audience wanting to argue with you, they are more likely to be thinking, “Man, I don’t want to be cut out of my car or have a bunch of facial surgeries.”
The process is very simple. However, it is also very powerful.
How to Write a Successful Persuasive Speech Using the “Breadcrumb” Approach
Once you understand the concept above, you can create very powerful persuasive speeches by linking a series of these persuasive stories together. I call this the breadcrumb strategy. Basically, you use each story as a way to move the audience closer to the ultimate conclusion that you want them to draw. Each story gains a little more agreement.
So, first, just give a simple story about an easy to agree with concept. You will gain agreement fairly easily and begin to also create an emotional appeal. Next, use an additional story to gain additional agreement. If you use this process three to five times, you are more likely to get the audience to agree with your final conclusion. If this is a formal presentation, just make your main points into the persuasive statements and use stories to reinforce the points.
Here are a few persuasive speech examples using this approach.
An Example of a Persuasive Public Speaking Using Breadcrumbs
Marijuana Legalization is Causing Huge Problems in Our Biggest Cities Homelessness is Out of Control in First States to Legalize Marijuana Last year, my family and I took a mini-vacation to Colorado Springs. I had spent a summer in Colorado when I was in college, so I wanted my family to experience the great time that I had had there as a youth. We were only there for four days, but we noticed something dramatic had happened. There were homeless people everywhere. Keep in mind, this wasn’t Denver, this was Colorado City. The picturesque landscape was clouded by ripped sleeping bags on street corners, and trash spread everywhere. We were downtown, and my wife and daughter wanted to do some shopping. My son and I found a comic book store across the street to browse in. As we came out, we almost bumped into a dirty man in torn close. He smiled at us, walked a few feet away from the door, and lit up a joint. He sat on the corner smoking it. As my son and I walked the 1/4 mile back to the store where we left my wife and daughter, we stepped over and walked around over a dozen homeless people camped out right in the middle of the town. This was not the Colorado that I remembered. From what I’ve heard, it has gotten even worse in the last year. So, if you don’t want to dramatically increase your homelessness population, don’t make marijuana legal in your state. DUI Instances and Traffic Accidents Have Increased in Marijuana States I was at the airport waiting for a flight last week, and the guy next to me offered me his newspaper. I haven’t read a newspaper in years, but he seemed so nice that I accepted. It was a copy of the USA Today, and it was open to an article about the rise in unintended consequences from legalizing marijuana. Safety officials and police in Colorado, Nevada, Washington, and Oregon, the first four state to legalize recreational marijuana, have reported a 6% increase in traffic accidents in the last few years. Although the increase (6%) doesn’t seem very dramatic, it was notable because the rate of accidents had been decreasing in each of the states for decades prior to the law change. Assuming that only one of the two parties involved in these new accidents was under the influence, that means that people who aren’t smoking marijuana are being negatively affected by the legalization. So, if you don’t want to increase your chances of being involved in a DUI incident, don’t legalize marijuana. (Notice how I just used an article as my evidence, but to make it more memorable, I told the story about how I came across the article. It is also easier to deliver this type of data because you are just relating what you remember about the data, not trying to be an expert on the data itself.) Marijuana is Still Largely Unregulated Just before my dad went into hospice care, he was in a lot of pain. He would take a prescription painkiller before bed to sleep. One night, my mom called frantically. Dad was in a catatonic state and wasn’t responsive. I rushed over. The hospital found that Dad had an unusually high amount of painkillers in his bloodstream. His regular doctor had been on vacation, and the fill-in doctor had prescribed a much higher dosage of the painkiller by accident. His original prescription was 2.5 mg, and the new prescription was 10 mg. Since dad was in a lot of pain most nights, he almost always took two tablets. He was also on dialysis, so his kidneys weren’t filtering out the excess narcotic each day. He had actually taken 20 MG (instead of 5 MG) on Friday night and another 20 mg on Saturday. Ordinarily, he would have had, at max, 15 mg of the narcotic in his system. Because of the mistake, though, he had 60 MGs. My point is that the narcotics that my dad was prescribed were highly regulated medicines under a doctor’s care, and a mistake was still made that almost killed him. With marijuana, there is really no way of knowing how much narcotic is in each dosage. So, mistakes like this are much more likely. So, in conclusion, legalizing marijuana can increase homelessness, increase the number of impaired drivers, and cause accidental overdoses.
If you use this breadcrumb approach, you are more likely to get at least some agreement. Even if the person disagrees with your conclusion, they are still likely to at least see your side. So, the person may say something like, I still disagree with you, but I totally see your point. That is still a step in the right direction.
For Real-World Practice in How to Design Persuasive Presentations Join Us for a Class
Our instructors are experts at helping presenters design persuasive speeches. We offer the Fearless Presentations ® classes in cities all over the world about every three to four months. In addition to helping you reduce nervousness, your instructor will also show you secrets to creating a great speech. For details about any of the classes, go to our Presentation Skills Class web page.
For additional details, see Persuasive Speech Outline Example .

Podcasts , presentation skills
View More Posts By Category: Free Public Speaking Tips | leadership tips | Online Courses | Past Fearless Presentations ® Classes | Podcasts | presentation skills | Uncategorized

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
11.2 Persuasive Speaking
Learning objectives.
- Explain how claims, evidence, and warrants function to create an argument.
- Identify strategies for choosing a persuasive speech topic.
- Identify strategies for adapting a persuasive speech based on an audience’s orientation to the proposition.
- Distinguish among propositions of fact, value, and policy.
- Choose an organizational pattern that is fitting for a persuasive speech topic.
We produce and receive persuasive messages daily, but we don’t often stop to think about how we make the arguments we do or the quality of the arguments that we receive. In this section, we’ll learn the components of an argument, how to choose a good persuasive speech topic, and how to adapt and organize a persuasive message.
Foundation of Persuasion
Persuasive speaking seeks to influence the beliefs, attitudes, values, or behaviors of audience members. In order to persuade, a speaker has to construct arguments that appeal to audience members. Arguments form around three components: claim, evidence, and warrant. The claim is the statement that will be supported by evidence. Your thesis statement is the overarching claim for your speech, but you will make other claims within the speech to support the larger thesis. Evidence , also called grounds, supports the claim. The main points of your persuasive speech and the supporting material you include serve as evidence. For example, a speaker may make the following claim: “There should be a national law against texting while driving.” The speaker could then support the claim by providing the following evidence: “Research from the US Department of Transportation has found that texting while driving creates a crash risk that is twenty-three times worse than driving while not distracted.” The warrant is the underlying justification that connects the claim and the evidence. One warrant for the claim and evidence cited in this example is that the US Department of Transportation is an institution that funds research conducted by credible experts. An additional and more implicit warrant is that people shouldn’t do things they know are unsafe.
Figure 11.2 Components of an Argument
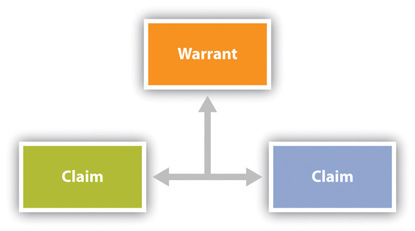
The quality of your evidence often impacts the strength of your warrant, and some warrants are stronger than others. A speaker could also provide evidence to support their claim advocating for a national ban on texting and driving by saying, “I have personally seen people almost wreck while trying to text.” While this type of evidence can also be persuasive, it provides a different type and strength of warrant since it is based on personal experience. In general, the anecdotal evidence from personal experience would be given a weaker warrant than the evidence from the national research report. The same process works in our legal system when a judge evaluates the connection between a claim and evidence. If someone steals my car, I could say to the police, “I’m pretty sure Mario did it because when I said hi to him on campus the other day, he didn’t say hi back, which proves he’s mad at me.” A judge faced with that evidence is unlikely to issue a warrant for Mario’s arrest. Fingerprint evidence from the steering wheel that has been matched with a suspect is much more likely to warrant arrest.
As you put together a persuasive argument, you act as the judge. You can evaluate arguments that you come across in your research by analyzing the connection (the warrant) between the claim and the evidence. If the warrant is strong, you may want to highlight that argument in your speech. You may also be able to point out a weak warrant in an argument that goes against your position, which you could then include in your speech. Every argument starts by putting together a claim and evidence, but arguments grow to include many interrelated units.
Choosing a Persuasive Speech Topic
As with any speech, topic selection is important and is influenced by many factors. Good persuasive speech topics are current, controversial, and have important implications for society. If your topic is currently being discussed on television, in newspapers, in the lounges in your dorm, or around your family’s dinner table, then it’s a current topic. A persuasive speech aimed at getting audience members to wear seat belts in cars wouldn’t have much current relevance, given that statistics consistently show that most people wear seat belts. Giving the same speech would have been much more timely in the 1970s when there was a huge movement to increase seat-belt use.
Many topics that are current are also controversial, which is what gets them attention by the media and citizens. Current and controversial topics will be more engaging for your audience. A persuasive speech to encourage audience members to donate blood or recycle wouldn’t be very controversial, since the benefits of both practices are widely agreed on. However, arguing that the restrictions on blood donation by men who have had sexual relations with men be lifted would be controversial. I must caution here that controversial is not the same as inflammatory. An inflammatory topic is one that evokes strong reactions from an audience for the sake of provoking a reaction. Being provocative for no good reason or choosing a topic that is extremist will damage your credibility and prevent you from achieving your speech goals.
You should also choose a topic that is important to you and to society as a whole. As we have already discussed in this book, our voices are powerful, as it is through communication that we participate and make change in society. Therefore we should take seriously opportunities to use our voices to speak publicly. Choosing a speech topic that has implications for society is probably a better application of your public speaking skills than choosing to persuade the audience that Lebron James is the best basketball player in the world or that Superman is a better hero than Spiderman. Although those topics may be very important to you, they don’t carry the same social weight as many other topics you could choose to discuss. Remember that speakers have ethical obligations to the audience and should take the opportunity to speak seriously.
You will also want to choose a topic that connects to your own interests and passions. If you are an education major, it might make more sense to do a persuasive speech about funding for public education than the death penalty. If there are hot-button issues for you that make you get fired up and veins bulge out in your neck, then it may be a good idea to avoid those when speaking in an academic or professional context.

Choose a persuasive speech topic that you’re passionate about but still able to approach and deliver in an ethical manner.
Michael Vadon – Nigel Farage – CC BY-SA 2.0.
Choosing such topics may interfere with your ability to deliver a speech in a competent and ethical manner. You want to care about your topic, but you also want to be able to approach it in a way that’s going to make people want to listen to you. Most people tune out speakers they perceive to be too ideologically entrenched and write them off as extremists or zealots.
You also want to ensure that your topic is actually persuasive. Draft your thesis statement as an “I believe” statement so your stance on an issue is clear. Also, think of your main points as reasons to support your thesis. Students end up with speeches that aren’t very persuasive in nature if they don’t think of their main points as reasons. Identifying arguments that counter your thesis is also a good exercise to help ensure your topic is persuasive. If you can clearly and easily identify a competing thesis statement and supporting reasons, then your topic and approach are arguable.
Review of Tips for Choosing a Persuasive Speech Topic
- Not current. People should use seat belts.
- Current. People should not text while driving.
- Not controversial. People should recycle.
- Controversial. Recycling should be mandatory by law.
- Not as impactful. Superman is the best superhero.
- Impactful. Colleges and universities should adopt zero-tolerance bullying policies.
- Unclear thesis. Homeschooling is common in the United States.
- Clear, argumentative thesis with stance. Homeschooling does not provide the same benefits of traditional education and should be strictly monitored and limited.
Adapting Persuasive Messages
Competent speakers should consider their audience throughout the speech-making process. Given that persuasive messages seek to directly influence the audience in some way, audience adaptation becomes even more important. If possible, poll your audience to find out their orientation toward your thesis. I read my students’ thesis statements aloud and have the class indicate whether they agree with, disagree with, or are neutral in regards to the proposition. It is unlikely that you will have a homogenous audience, meaning that there will probably be some who agree, some who disagree, and some who are neutral. So you may employ all of the following strategies, in varying degrees, in your persuasive speech.
When you have audience members who already agree with your proposition, you should focus on intensifying their agreement. You can also assume that they have foundational background knowledge of the topic, which means you can take the time to inform them about lesser-known aspects of a topic or cause to further reinforce their agreement. Rather than move these audience members from disagreement to agreement, you can focus on moving them from agreement to action. Remember, calls to action should be as specific as possible to help you capitalize on audience members’ motivation in the moment so they are more likely to follow through on the action.
There are two main reasons audience members may be neutral in regards to your topic: (1) they are uninformed about the topic or (2) they do not think the topic affects them. In this case, you should focus on instilling a concern for the topic. Uninformed audiences may need background information before they can decide if they agree or disagree with your proposition. If the issue is familiar but audience members are neutral because they don’t see how the topic affects them, focus on getting the audience’s attention and demonstrating relevance. Remember that concrete and proxemic supporting materials will help an audience find relevance in a topic. Students who pick narrow or unfamiliar topics will have to work harder to persuade their audience, but neutral audiences often provide the most chance of achieving your speech goal since even a small change may move them into agreement.
When audience members disagree with your proposition, you should focus on changing their minds. To effectively persuade, you must be seen as a credible speaker. When an audience is hostile to your proposition, establishing credibility is even more important, as audience members may be quick to discount or discredit someone who doesn’t appear prepared or doesn’t present well-researched and supported information. Don’t give an audience a chance to write you off before you even get to share your best evidence. When facing a disagreeable audience, the goal should also be small change. You may not be able to switch someone’s position completely, but influencing him or her is still a success. Aside from establishing your credibility, you should also establish common ground with an audience.

Build common ground with disagreeable audiences and acknowledge areas of disagreement.
Chris-Havard Berge – Shaking Hands – CC BY-NC 2.0.
Acknowledging areas of disagreement and logically refuting counterarguments in your speech is also a way to approach persuading an audience in disagreement, as it shows that you are open-minded enough to engage with other perspectives.
Determining Your Proposition
The proposition of your speech is the overall direction of the content and how that relates to the speech goal. A persuasive speech will fall primarily into one of three categories: propositions of fact, value, or policy. A speech may have elements of any of the three propositions, but you can usually determine the overall proposition of a speech from the specific purpose and thesis statements.
Propositions of fact focus on beliefs and try to establish that something “is or isn’t.” Propositions of value focus on persuading audience members that something is “good or bad,” “right or wrong,” or “desirable or undesirable.” Propositions of policy advocate that something “should or shouldn’t” be done. Since most persuasive speech topics can be approached as propositions of fact, value, or policy, it is a good idea to start thinking about what kind of proposition you want to make, as it will influence how you go about your research and writing. As you can see in the following example using the topic of global warming, the type of proposition changes the types of supporting materials you would need:
- Proposition of fact. Global warming is caused by increased greenhouse gases related to human activity.
- Proposition of value. America’s disproportionately large amount of pollution relative to other countries is wrong .
- Proposition of policy. There should be stricter emission restrictions on individual cars.
To support propositions of fact, you would want to present a logical argument based on objective facts that can then be used to build persuasive arguments. Propositions of value may require you to appeal more to your audience’s emotions and cite expert and lay testimony. Persuasive speeches about policy usually require you to research existing and previous laws or procedures and determine if any relevant legislation or propositions are currently being considered.
“Getting Critical”
Persuasion and Masculinity
The traditional view of rhetoric that started in ancient Greece and still informs much of our views on persuasion today has been critiqued for containing Western and masculine biases. Traditional persuasion has been linked to Western and masculine values of domination, competition, and change, which have been critiqued as coercive and violent (Gearhart, 1979).
Communication scholars proposed an alternative to traditional persuasive rhetoric in the form of invitational rhetoric. Invitational rhetoric differs from a traditional view of persuasive rhetoric that “attempts to win over an opponent, or to advocate the correctness of a single position in a very complex issue” (Bone et al., 2008). Instead, invitational rhetoric proposes a model of reaching consensus through dialogue. The goal is to create a climate in which growth and change can occur but isn’t required for one person to “win” an argument over another. Each person in a communication situation is acknowledged to have a standpoint that is valid but can still be influenced through the offering of alternative perspectives and the invitation to engage with and discuss these standpoints (Ryan & Natalle, 2001). Safety, value, and freedom are three important parts of invitational rhetoric. Safety involves a feeling of security in which audience members and speakers feel like their ideas and contributions will not be denigrated. Value refers to the notion that each person in a communication encounter is worthy of recognition and that people are willing to step outside their own perspectives to better understand others. Last, freedom is present in communication when communicators do not limit the thinking or decisions of others, allowing all participants to speak up (Bone et al., 2008).
Invitational rhetoric doesn’t claim that all persuasive rhetoric is violent. Instead, it acknowledges that some persuasion is violent and that the connection between persuasion and violence is worth exploring. Invitational rhetoric has the potential to contribute to the civility of communication in our society. When we are civil, we are capable of engaging with and appreciating different perspectives while still understanding our own. People aren’t attacked or reviled because their views diverge from ours. Rather than reducing the world to “us against them, black or white, and right or wrong,” invitational rhetoric encourages us to acknowledge human perspectives in all their complexity (Bone et al., 2008).
- What is your reaction to the claim that persuasion includes Western and masculine biases?
- What are some strengths and weaknesses of the proposed alternatives to traditional persuasion?
- In what situations might an invitational approach to persuasion be useful? In what situations might you want to rely on traditional models of persuasion?
Organizing a Persuasive Speech
We have already discussed several patterns for organizing your speech, but some organization strategies are specific to persuasive speaking. Some persuasive speech topics lend themselves to a topical organization pattern, which breaks the larger topic up into logical divisions. Earlier, in Chapter 9 “Preparing a Speech” , we discussed recency and primacy, and in this chapter we discussed adapting a persuasive speech based on the audience’s orientation toward the proposition. These concepts can be connected when organizing a persuasive speech topically. Primacy means putting your strongest information first and is based on the idea that audience members put more weight on what they hear first. This strategy can be especially useful when addressing an audience that disagrees with your proposition, as you can try to win them over early. Recency means putting your strongest information last to leave a powerful impression. This can be useful when you are building to a climax in your speech, specifically if you include a call to action.

Putting your strongest argument last can help motivate an audience to action.
Celestine Chua – The Change – CC BY 2.0.
The problem-solution pattern is an organizational pattern that advocates for a particular approach to solve a problem. You would provide evidence to show that a problem exists and then propose a solution with additional evidence or reasoning to justify the course of action. One main point addressing the problem and one main point addressing the solution may be sufficient, but you are not limited to two. You could add a main point between the problem and solution that outlines other solutions that have failed. You can also combine the problem-solution pattern with the cause-effect pattern or expand the speech to fit with Monroe’s Motivated Sequence.
As was mentioned in Chapter 9 “Preparing a Speech” , the cause-effect pattern can be used for informative speaking when the relationship between the cause and effect is not contested. The pattern is more fitting for persuasive speeches when the relationship between the cause and effect is controversial or unclear. There are several ways to use causes and effects to structure a speech. You could have a two-point speech that argues from cause to effect or from effect to cause. You could also have more than one cause that lead to the same effect or a single cause that leads to multiple effects. The following are some examples of thesis statements that correspond to various organizational patterns. As you can see, the same general topic area, prison overcrowding, is used for each example. This illustrates the importance of considering your organizational options early in the speech-making process, since the pattern you choose will influence your researching and writing.
Persuasive Speech Thesis Statements by Organizational Pattern
- Problem-solution. Prison overcrowding is a serious problem that we can solve by finding alternative rehabilitation for nonviolent offenders.
- Problem–failed solution–proposed solution. Prison overcrowding is a serious problem that shouldn’t be solved by building more prisons; instead, we should support alternative rehabilitation for nonviolent offenders.
- Cause-effect. Prisons are overcrowded with nonviolent offenders, which leads to lesser sentences for violent criminals.
- Cause-cause-effect. State budgets are being slashed and prisons are overcrowded with nonviolent offenders, which leads to lesser sentences for violent criminals.
- Cause-effect-effect. Prisons are overcrowded with nonviolent offenders, which leads to increased behavioral problems among inmates and lesser sentences for violent criminals.
- Cause-effect-solution. Prisons are overcrowded with nonviolent offenders, which leads to lesser sentences for violent criminals; therefore we need to find alternative rehabilitation for nonviolent offenders.
Monroe’s Motivated Sequence is an organizational pattern designed for persuasive speaking that appeals to audience members’ needs and motivates them to action. If your persuasive speaking goals include a call to action, you may want to consider this organizational pattern. We already learned about the five steps of Monroe’s Motivated Sequence in Chapter 9 “Preparing a Speech” , but we will review them here with an example:
- Hook the audience by making the topic relevant to them.
- Imagine living a full life, retiring, and slipping into your golden years. As you get older you become more dependent on others and move into an assisted-living facility. Although you think life will be easier, things get worse as you experience abuse and mistreatment from the staff. You report the abuse to a nurse and wait, but nothing happens and the abuse continues. Elder abuse is a common occurrence, and unlike child abuse, there are no laws in our state that mandate complaints of elder abuse be reported or investigated.
- Cite evidence to support the fact that the issue needs to be addressed.
- According to the American Psychological Association, one to two million elderly US Americans have been abused by their caretakers. In our state, those in the medical, psychiatric, and social work field are required to report suspicion of child abuse but are not mandated to report suspicions of elder abuse.
- Offer a solution and persuade the audience that it is feasible and well thought out.
- There should be a federal law mandating that suspicion of elder abuse be reported and that all claims of elder abuse be investigated.
- Take the audience beyond your solution and help them visualize the positive results of implementing it or the negative consequences of not.
- Elderly people should not have to live in fear during their golden years. A mandatory reporting law for elderly abuse will help ensure that the voices of our elderly loved ones will be heard.
- Call your audience to action by giving them concrete steps to follow to engage in a particular action or to change a thought or behavior.
- I urge you to take action in two ways. First, raise awareness about this issue by talking to your own friends and family. Second, contact your representatives at the state and national level to let them know that elder abuse should be taken seriously and given the same level of importance as other forms of abuse. I brought cards with the contact information for our state and national representatives for this area. Please take one at the end of my speech. A short e-mail or phone call can help end the silence surrounding elder abuse.
Key Takeaways
- Arguments are formed by making claims that are supported by evidence. The underlying justification that connects the claim and evidence is the warrant. Arguments can have strong or weak warrants, which will make them more or less persuasive.
- Good persuasive speech topics are current, controversial (but not inflammatory), and important to the speaker and society.
- When audience members agree with the proposal, focus on intensifying their agreement and moving them to action.
- When audience members are neutral in regards to the proposition, provide background information to better inform them about the issue and present information that demonstrates the relevance of the topic to the audience.
- When audience members disagree with the proposal, focus on establishing your credibility, build common ground with the audience, and incorporate counterarguments and refute them.
- Propositions of fact focus on establishing that something “is or isn’t” or is “true or false.”
- Propositions of value focus on persuading an audience that something is “good or bad,” “right or wrong,” or “desirable or undesirable.”
- Propositions of policy advocate that something “should or shouldn’t” be done.
- Persuasive speeches can be organized using the following patterns: problem-solution, cause-effect, cause-effect-solution, or Monroe’s Motivated Sequence.
- Getting integrated: Give an example of persuasive messages that you might need to create in each of the following contexts: academic, professional, personal, and civic. Then do the same thing for persuasive messages you may receive.
- To help ensure that your persuasive speech topic is persuasive and not informative, identify the claims, evidence, and warrants you may use in your argument. In addition, write a thesis statement that refutes your topic idea and identify evidence and warrants that could support that counterargument.
- Determine if your speech is primarily a proposition of fact, value, or policy. How can you tell? Identify an organizational pattern that you think will work well for your speech topic, draft one sentence for each of your main points, and arrange them according to the pattern you chose.
Bone, J. E., Cindy L. Griffin, and T. M. Linda Scholz, “Beyond Traditional Conceptualizations of Rhetoric: Invitational Rhetoric and a Move toward Civility,” Western Journal of Communication 72 (2008): 436.
Gearhart, S. M., “The Womanization of Rhetoric,” Women’s Studies International Quarterly 2 (1979): 195–201.
Ryan, K. J., and Elizabeth J. Natalle, “Fusing Horizons: Standpoint Hermenutics and Invitational Rhetoric,” Rhetoric Society Quarterly 31 (2001): 69–90.
Communication in the Real World Copyright © 2016 by University of Minnesota is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.

How it works
For Business
Join Mind Tools
Article • 8 min read
Monroe's Motivated Sequence
Perfecting the call to act.
By the Mind Tools Content Team

Is persuasion a gift? Are some people born with the ability to speak well and "sell" their ideas successfully?
It sure seems that way when you're wowed by a motivational speaker, or galvanized into action by a thought-provoking presentation.
In your role, do you ever need to motivate, inspire, or persuade others? Whether you're a senior executive giving a presentation to the Board, a manager giving a morale-boosting speech to your team, or a production manager giving a presentation on safety standards, at some point, you'll probably have to move people to action.
While there are certainly those who seem to inspire and deliver memorable speeches effortlessly, the rest of us can learn how to give effective presentations, too. In this article, we'll look at the key factors you need to put together a clear and engaging call to action using a five-step process known as Monroe's Motivated Sequence.
Monroe's Motivated Sequence: The Five Steps
Alan H. Monroe, a Purdue University professor, used the psychology of persuasion to develop an outline for making speeches that will deliver results, and wrote about it in his book Monroe's Principles of Speech . It's now known as Monroe's Motivated Sequence.
This is a well-used and time-proven method to organize presentations for maximum impact. You can use it for a variety of situations to create and arrange the components of any message. The steps are explained below:
Step One: Get Attention
Get the attention of your audience. Use storytelling , humor, a shocking statistic, or a rhetorical question – anything that will get the audience to sit up and take notice.
This step doesn't replace your introduction – it's part of your introduction. In your opening, you should also establish your credibility (see The Rhetorical Triangle for tips), state your purpose, and let the audience know what to expect. Delivering Great Presentations provides a strong foundation for building the steps in Monroe's Motivated Sequence.
Lets use the example of a half-day seminar on safety in the workplace. Your attention step might be as follows.
Step Two: Establish the Need
Convince your audience there's a problem. This set of statements must help the audience realize that what's happening right now isn't good enough – and needs to change.
- Use statistics to back up your statements.
- Talk about the consequences of maintaining the status quo and not making changes.
- Show your audience how the problem directly affects them.
Remember, you're not at the "I have a solution" stage yet. Here, you want to make the audience uncomfortable and restless, and ready to do the "something" that you recommend.
Step Three: Satisfy the Need
Introduce your solution. How will you solve the problem that your audience is now ready to address? This is the main part of your presentation. It will vary significantly, depending on your purpose. In this section:
- Discuss the facts.
- Elaborate and give details to make sure the audience understands your position and solution.
- Clearly state what you want the audience to do or believe.
- Summarize your information from time to time as you speak.
- Use examples, testimonials, and statistics to prove the effectiveness of your solution.
- Prepare counterarguments to anticipated objections.
Step Four: Visualize the Future
Describe what the situation will look like if the audience does nothing. The more realistic and detailed the vision, the better it will create the desire to do what you recommend. Your goal is to motivate the audience to agree with you and adopt similar behaviors, attitudes, and beliefs. Help them see what the results could be if they act the way you want them to. Make sure your vision is believable and realistic.
You can use three methods to help the audience share your vision:
- Positive method – Describe what the situation will look like if your ideas are adopted. Emphasize the positive aspects.
- Negative method – Describe what the situation will look like if your ideas are rejected. Focus on the dangers and difficulties caused by not acting.
- Contrast method – Develop the negative picture first, and then reveal what could happen if your ideas are accepted.
Step Five: Action/Actualization
Your final job is to leave your audience with specific things that they can do to solve the problem. You want them to take action now.
Don't overwhelm them with too much information or too many expectations, and be sure to give them options to increase their sense of ownership of the solution. This can be as simple as inviting them to have some refreshments as you walk around and answer questions. For very complex problems, the action step might be getting together again to review plans.
For some of us, persuasive arguments and motivational speaking come naturally. The rest of us may try to avoid speeches and presentations, fearing that our message won't be well received.
But Monroe's Motivated Sequence can help you to improve the quality of your message, and create a call of action that has real impact.
The model includes five key steps:
- Get attention.
- Establish the need.
- Satisfy the need.
- Visualize the future.
- Action/Actualization.
It's a straightforward formula for success that's been used time and again. Try it for your next presentation, and you'll no doubt be impressed with the results!
Monroe, A. (1951). ' Monroe's Principles of Speech (Revised Brief Edition) ,' Scott, Foreman and Company.
You've accessed 1 of your 2 free resources.
Get unlimited access
Discover more content
Motivating your team, how to motivate yourself.
Get Yourself Moving and Beat Procrastination
Add comment
Comments (1)
Nathanial Glockania
Ay bruh facts ima use this to convince the bank to gimme some money on the down low, thanks for the advice lil bro

Get 30% off your first year of Mind Tools
Great teams begin with empowered leaders. Our tools and resources offer the support to let you flourish into leadership. Join today!
Sign-up to our newsletter
Subscribing to the Mind Tools newsletter will keep you up-to-date with our latest updates and newest resources.
Subscribe now
Business Skills
Personal Development
Leadership and Management
Member Extras
Most Popular
Latest Updates

Tips for Dealing with Customers Effectively

Pain Points Podcast - Procrastination
Mind Tools Store
About Mind Tools Content
Discover something new today
Pain points podcast - starting a new job.
How to Hit the Ground Running!
Ten Dos and Don'ts of Career Conversations
How to talk to team members about their career aspirations.
How Emotionally Intelligent Are You?
Boosting Your People Skills
Self-Assessment
What's Your Leadership Style?
Learn About the Strengths and Weaknesses of the Way You Like to Lead
Recommended for you
A Checklist for Making Better Decisions
Business Operations and Process Management
Strategy Tools
Customer Service
Business Ethics and Values
Handling Information and Data
Project Management
Knowledge Management
Self-Development and Goal Setting
Time Management
Presentation Skills
Learning Skills
Career Skills
Communication Skills
Negotiation, Persuasion and Influence
Working With Others
Difficult Conversations
Creativity Tools
Self-Management
Work-Life Balance
Stress Management and Wellbeing
Coaching and Mentoring
Change Management
Team Management
Managing Conflict
Delegation and Empowerment
Performance Management
Leadership Skills
Developing Your Team
Talent Management
Problem Solving
Decision Making
Member Podcast

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

16.5.1: Monroe's Motivated Sequence extended
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 107435

- Lisa Coleman, Thomas King, & William Turner
- Southwest Tennessee Community College
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
Learning Objective
- Examine thoroughly the steps utilized in Monroe’s motivated sequence.
Monroe’s Motivated Sequence
The purpose of Monroe’s motivated sequence is to help speakers plan main points, supporting materials, and motivational appeals to form a useful organizational pattern for persuasive speeches that will lead to an immediate action rather than passive agreement.
Monroe’s Motivated Sequence lists the basic steps of Monroe’s motivated sequence and the subsequent reaction a speaker desires from his or her audience.
The first step in Monroe’s motivated sequence is the attention step, in which a speaker attempts to get the audience’s attention. To gain an audience’s attention, we recommend that you think through three specific parts of the attention step. First, you need to have a strong attention-getting device. Second, you need to make sure you introduce your topic clearly. If your audience doesn’t know what your topic is quickly, they are more likely to stop listening. Third, you need to explain to your audience why they should care about your topic. Next, you will want to establish your credibility with the topic to the audience. And finally, you will want to preview what you will discuss in the speech to guide your audience.
In the need step of Monroe’s motivated sequence, the speaker establishes that there is a specific need or problem. In Monroe’s conceptualization of need, he talks about four specific parts of the need: statement, illustration, ramification, and pointing. First, a speaker needs to give a clear and concise statement of the problem. This part of a speech should be crystal clear for an audience. Second, the speaker needs to provide one or more examples to illustrate the need. The illustration is an attempt to make the problem concrete for the audience. Next, a speaker needs to provide some kind of evidence (e.g., statistics, examples, testimony) that shows the ramifications or consequences of the problem. Lastly, a speaker needs to point to the audience and show exactly how the problem relates to them personally.
Satisfaction
In the third step of Monroe’s motivated sequence, the satisfaction step, the speaker sets out to satisfy the need or solve the problem. Within this step, Monroe (1935) proposed a five-step plan for satisfying a need:
Explanation
Theoretical demonstration
Reference to practical experience
Meeting objections
First, you need to clearly state the attitude, value, belief, or action you want your audience to accept. The purpose of this statement is to clearly tell your audience what your ultimate goal is. Second, you want to make sure that you clearly explain to your audience why they should accept the attitude, value, belief, or action you proposed. Just telling your audience they should do something isn’t strong enough to actually get them to change. Instead, you really need to provide a solid argument for why they should accept your proposed solution. Third, you need to show how the solution you have proposed meets the need or problem. Monroe calls this link between your solution and the need for a theoretical demonstration because you cannot prove that your solution will work. Instead, you theorize based on research and good judgment that your solution will meet the need or solve the problem. Fourth, to help with this theoretical demonstration, you need to reference practical experience, which should include examples demonstrating that your proposal has worked elsewhere. Research, statistics, and expert testimony are all great ways of referencing practical experience. Lastly, Monroe recommends that a speaker responds to possible objections. As a persuasive speaker, one of your jobs is to think through your speech and see what counterarguments could be made against your speech and then rebut those arguments within your speech. When you offer rebuttals for arguments against your speech, it shows your audience that you’ve done your homework and educated yourself about multiple sides of the issue.
Visualization
The next step of Monroe’s motivated sequence is the visualization step, in which you ask the audience to visualize a future where the need has been met or the problem solved. In essence, the visualization stage is where a speaker can show the audience why accepting a specific attitude, value, belief, or behavior can positively affect the future. When helping people to picture the future, the more concrete your visualization is, the easier it will be for your audience to see the possible future and be persuaded by it. You also need to make sure that you clearly show how accepting your solution will directly benefit your audience.
According to Monroe, visualization can be conducted in one of three ways: positive, negative, or contrast. The positive method of visualization is where a speaker shows how adopting a proposal leads to a better future (e.g., recycle, and we’ll have a cleaner and safer planet). Conversely, the negative method of visualization is where a speaker shows how not adopting the proposal will lead to a worse future (e.g., don’t recycle, and our world will become polluted and uninhabitable). Monroe also acknowledged that visualization can include a combination of both positive and negative visualization. In essence, you show your audience both possible outcomes and have them decide which one they would rather have.
The final step in Monroe’s motivated sequence is the action step, in which a speaker asks an audience to approve the speaker’s proposal. For understanding purposes, we break the action into two distinct parts: audience action and approval. Audience action refers to direct physical behaviors a speaker wants from an audience (e.g., flossing their teeth twice a day, signing a petition, wearing seat belts). Approval, on the other hand, involves an audience’s consent or agreement with a speaker’s proposed attitude, value, or belief.
When preparing an action step, it is important to make sure that the action, whether audience action or approval, is realistic for your audience. Asking your peers in a college classroom to donate one thousand dollars to charity isn’t realistic. Asking your peers to donate one dollar is considerably more realistic. In a persuasive speech based on Monroe’s motivated sequence, the action step will end with the speech’s concluding device. As discussed elsewhere in this text, you need to make sure that you conclude in a vivid way so that the speech ends on a high point and the audience has a sense of energy as well as a sense of closure.
Now that we’ve walked through Monroe’s motivated sequence, let’s look at how you could use Monroe’s motivated sequence to outline a persuasive speech: Specific Purpose: To persuade my classroom peers that the United States should have stronger laws governing the use of for-profit medical experiments.
Main Points:
Attention: Want to make nine thousand dollars for just three weeks of work lying around and not doing much? Then be a human guinea pig. Admittedly, you’ll have to have a tube down your throat most of those three weeks, but you’ll earn three thousand dollars a week.
Need: Every day many uneducated and lower socioeconomic-status citizens are preyed on by medical and pharmaceutical companies for use in for-profit medical and drug experiments. Do you want one of your family members to fall prey to this evil scheme?
Satisfaction: The United States should have stronger laws governing the use of for-profit medical experiments to ensure that uneducated and lower-socioeconomic-status citizens are protected.
Visualization: If we enact tougher experiment oversight, we can ensure that medical and pharmaceutical research is conducted in a way that adheres to basic values of American decency. If we do not enact tougher experiment oversight, we could find ourselves in a world where the lines between research subject, guinea pig, and patient become increasingly blurred.
Action: In order to prevent the atrocities associated with for-profit medical and pharmaceutical experiments, please sign this petition asking the US Department of Health and Human Services to pass stricter regulations on this preying industry that is out of control.
This example shows how you can take a basic speech topic and use Monroe’s motivated sequence to clearly and easily outline your speech efficiently and effectively. We've included a simple checklist to help you make sure you hit all the important components of Monroe’s motivated sequence.
Key Takeaway
- Alan H. Monroe’s (1935) motivated sequence is a commonly used speech format that is used by many people to effectively organize persuasive messages. The pattern consists of five basic stages: attention, need, satisfaction, visualization, and action. In the first stage, a speaker gets an audience’s attention. In the second stage, the speaker shows an audience that a need exists. In the third stage, the speaker shows how his or her persuasive proposal could satisfy the need. The fourth stage shows how the future could be if the persuasive proposal is or is not adopted. Lastly, the speaker urges the audience to take some kind of action to help enact the speaker’s persuasive proposal.
Create a speech using Monroe’s motivated sequence to persuade people to recycle.
Create a speech using the problem-cause-solution method for a problem you see on your college or university campus.
Create a comparative advantages speech comparing two brands of toothpaste.
Persuasive Speaking
Organizing persuasive messages.
Once you have selected your topic, know who your audience is, and have settled on an end goal for your persuasive speech, you can begin drafting your speech. Outlines are organized according to the particular speech, and the following organizational patterns are used routinely for persuasive speeches.
Monroe’s Motivated Sequence
Monroe’s Motivated Sequence is an organizational pattern that attempts to convince the audience to respond to a need that is delineated in the speech. [1] Five separate steps characterize the Motivated Sequence organization style:
1. The attention step should get the audience’s attention as well as describe your goals and preview the speech.
2. The need step should provide a description of the problem as well as the consequences that may result if the problem goes unresolved. In this step, the speaker should also alert audience members to their role in mitigating the issue.
3. The satisfaction step is used to outline your solutions to the problems you have previously outlined as well as deal with any objections that may arise.
4. In the visualization step , audience members are asked to visualize what will happen if your solutions are implemented and what will happen if they do not come to fruition. Visualizations should be rich with detail.
5. The action appeal step should be used to make a direct appeal for action. In this step, you should describe precisely how the audience should react to your speech and how they should carry out these actions. As the final step, you should also offer a concluding comment. See Figure 16.1 to see this method of arrangement illustrated.
Direct Method Pattern

“Roman Rackwitz Presentation” by Romrack. CC-BY-SA .
If your goal is to convince your audience to adopt a particular idea, you might prefer the direct method pattern as a way of organizing your speech. This pattern consists of a claim and a list of reasons to support it. Every piece of support in the speech directly supports the central claim you wish to make. As Jaffe points out, “It’s a good pattern to use when listeners are apathetic or neutral, either mildly favoring or mildly opposing your claim.” [2] The outline for a speech on vegetarianism in Figure 16.2 provides three reasons that vegetarianism provides useful health benefits for people struggling with obesity.
History creates comprehensibility primarily by arranging facts meaningfully and only in a very limited sense by establishing strict causal connections. – Johan Huizinga
Causal Pattern
Similar to a problem-solution speech, which was covered in Chapter 8, a causal speech describes a general cause and a specific effect. In other words, a causal pattern first addresses some cause and then shares what effects resulted. A causal speech can be particularly effective when the speaker wants to convince their audience of the relationship between two things. With sound causal reasoning, a speech of this sort can be used to convince the audience of something they were previously opposed to believing.
As the example in Figure 16.3 illustrates, the basic components of the causal speech are the cause and the effect. Such an organizational style is useful when a speaker needs to share the results of a new program, discuss how one act led to another, or discuss the positive/negative outcomes of taking some action. Through this pattern, the speaker can convince audiences to adopt a new belief about a particular phenomenon.
Refutation Pattern

“Jeanette Chong-Aruldoss” by Terence Lee. CC-BY .
Sometimes an occasion will arise when your audience is already opposed to your argument. In this case, a refutation pattern can be engaged to persuade audience members that your side of the argument is better or more accurate. In a refutation speech, the speaker must anticipate the audience’s opposition, then bring attention to the tensions between the two sides, and finally refute them using evidential support. Refutation patterns are frequently seen in debates, where speakers are fundamentally opposed to one another’s arguments. Refutation generally happens through a set of four steps: (1) signaling the argument to which you are responding, (2) stating your own argument, (3) providing justification or evidence for your side of the argument, and (4) summarizing your response. An advocate of reusing as opposed to recycling might present the argument in Figure 16.4 to respond to someone who believes recycling is the best way to individually work on environmental stewardship. As this example illustrates, a refutation speech should clearly delineate where the audience is perceived to stand on an issue, why their view is in disagreement with the speaker’s, and why the audience should adopt the speaker’s position. Moreover, the speaker should be sure to highlight the importance of the debate, which will clue the audience into why they should spend their time listening to a speaker who clearly disagrees with them. An example of this pattern can be found on the next page in Figure 16.4.
Neither irony nor sarcasm is argument. – Samuel Butler
- Monroe, A. H. (1949). Principles and types of speech . Glenview, IL: Scott, Foresman and Company. ↵
- Jaffe, C. (2004). Public speaking: Concepts and skills for a diverse society (4th ed.). Belmont, CA: Wadsworth. ↵
- Chapter 16 Organizing Persuasive Messages. Authored by : Sarah Stone Watt, Ph.D. and Joshua Trey Barnett. Provided by : Pepperdine University, Malibu, CA and Indiana University, Bloomington, IN. Located at : http://publicspeakingproject.org/psvirtualtext.html . Project : The Public Speaking Project. License : CC BY-NC-ND: Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives
- Roman Rackwitz Presentation. Authored by : Romrack. Located at : http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Roman_Rackwitz_Presentation.jpg . License : CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- Jeanette Chong-Aruldoss at a Reform Party rally, Speakers' Corner, Singapore - 20110115. Authored by : Terence Lee. Provided by : NewNation.sg. Located at : http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Jeanette_Chong-Aruldoss_at_a_Reform_Party_rally,_Speakers%27_Corner,_Singapore_-_20110115.jpg . License : CC BY: Attribution
A Comprehensive Guide to Writing a Persuasive Speech
Hrideep barot.
- Speech Writing

The term Persuasion means the efforts to change the attitudes or opinions of others through various means.
It is present everywhere: election campaigns, salesmen trying to sell goods by giving offers, public health campaigns to quit smoking or to wear masks in the public spaces, or even at the workplace; when an employee tries to persuade others to agree to their point in a meeting.
How do they manage to convince us so subtly? You guessed it right! They engage in what is called Persuasive Speech.
Persuasive Speech is a category of speech that attempts to influence the listener’s beliefs, attitudes, thoughts, and ultimately, behavior.
They are used in all contexts and situations . It can be informal , a teenager attempting to convince his or her parents for a sleepover at a friend’s house.
It can also be formal , President or Prime Minister urging the citizens to abide by the new norms.
But not to confuse these with informative speeches! These also aim to inform the audience about a particular topic or event, but they lack any attempt at persuasion.
The most typical setting where this kind of speech is practiced is in schools and colleges.
An effective speech combines both the features of an informative and persuasive speech for a better takeaway from an audience’s point of view.
However, writing and giving a persuasive speech are different in the sense that you as a speaker have limited time to call people to action.
Also, according to the context or situation, you may not be able to meet your audience several times, unlike TV ads, which the audience sees repeatedly and hence believes the credibility of the product.
So, how to write and deliver an effective persuasive speech?
How to start a persuasive speech? What are the steps of writing a persuasive speech? What are some of the tricks and tips of persuasion?
Read along till the end to explore the different dimensions and avenues of the science of giving a persuasive speech.
THINGS TO KEEP IN MIND BEFORE WRITING A PERSUASIVE SPEECH
1. get your topic right, passion and genuine interest in your topic.
It is very important that you as a speaker are interested in the chosen topic and in the subsequent arguments you are about to put forward. If you are not interested in what you are saying, then how will the audience feel the same?
Passion towards the topic is one of the key requirements for a successful speech as your audience will see how passionate and concerned you are towards the issue and will infer you as a genuine and credible person.
The audience too will get in the mood and connect to you on an emotional level, empathizing with you; as a result of which will understand your point of view and are likely to agree to your argument.
Consider this example: your friend is overflowing with joy- is happy, smiling, and bubbling with enthusiasm.
Before even asking the reason behind being so happy, you “catch the mood”; i.e., you notice that your mood has been boosted as a result of seeing your friend happy.
Why does it happen so? The reason is that we are influenced by other people’s moods and emotions.
It also means that our mood affects people around us, which is the reason why speaking with emotions and passion is used by many successful public speakers.
Another reason is that other’s emotions give an insight into how one should feel and react. We interpret other’s reactions as a source of information about how we should feel.
So, if someone shows a lot of anxiety or excitement while speaking, we conclude that the issue is very important and we should do something about it, and end up feeling similar reactions.
Meaningful and thought-provoking
Choose a topic that is meaningful to you and your audience. It should be thought-provoking and leave the audience thinking about the points put forward in your speech.
Topics that are personally or nationally relevant and are in the talks at the moment are good subjects to start with.
If you choose a controversial topic like “should euthanasia be legalized?”, or” is our nation democratic?”, it will leave a dramatic impact on your audience.
However, be considerate in choosing a sensitive topic, since it can leave a negative impression on your listeners. But if worded in a neutral and unbiased manner, it can work wonders.
Also, refrain from choosing sensitive topics like the reality of religion, sexuality, etc.
2. Research your topic thoroughly

Research on persuasion conducted by Hovland, Janis, and Kelley states that credible communicators are more persuasive than those who are seen as lacking expertise.
Even if you are not an expert in the field of your topic, mentioning information that is backed by research or stating an expert’s opinion on the issue will make you appear as a knowledgeable and credible person.
How to go about researching? Many people think that just googling about a topic and inferring 2-3 articles will be enough. But this is not so.
For writing and giving an effective speech, thorough research is crucial for you as a speaker to be prepared and confident.
Try to find as many relevant points as possible, even if it is against your viewpoint. If you can explain why the opposite viewpoint is not correct, it will give the audience both sides to an argument and will make decision-making easier.
Also, give credit to the source of your points during your speech, by mentioning the original site, author, or expert, so the audience will know that these are reliable points and not just your opinion, and will be more ready to believe them since they come from an authority.
Other sources for obtaining data for research are libraries and bookstores, magazines, newspapers, google scholar, research journals, etc.
Analyze your audience
Know who comprises your audience so that you can alter your speech to meet their requirements.
Demographics like age group, gender ratio, the language with which they are comfortable, their knowledge about the topic, the region and community to which they belong; are all important factors to be considered before writing your speech.
Ask yourself these questions before sitting down to write:
Is the topic of argument significant to them? Why is it significant? Would it make sense to them? Is it even relevant to them?
In the end, the speech is about the audience and not you. Hence, make efforts to know your audience.
This can be done by surveying your audience way before the day of giving your speech. Short polls and registration forms are an effective way to know your audience.
They ensure confidentiality and maintain anonymity, eliminating social desirability bias on part of the audience, and will likely receive honest answers.
OUTLINE OF A PERSUASIVE SPEECH
Most speeches follow the pattern of Introduction, Body and Conclusion.
However, persuasive speeches have a slightly different pathway.
INTRODUCTION
BODY OR SUPPORTING STATEMENTS( ATLEAST 3 ARGUMENTS)
CONCLUSION OR A CALL TO ACTION
1. INTRODUCTION
Grab attention of your audience.

The first few lines spoken by a speaker are the deciding factor that can make or break a speech.
Hence, if you nail the introduction, half of the task has already been done, and you can rest assured.
No one likes to be silent unless you are an introvert. But the audience expects that the speaker will go on stage and speak. But what if the speaker just goes and remains silent?
Chances are high that the audience will be in anticipation of what you are about to speak and their sole focus will be on you.
This sets the stage.
Use quotes that are relevant and provocative to set the tone of your speech. It will determine the mood of your audience and get them ready to receive information.
An example can be “The only impossible journey is the one you never begin” and then state who gave it, in this case, Tony Robbins, an American author.
Use what-if scenarios
Another way to start your speech is by using what-if scenarios and phrases like “suppose if your home submerges in water one day due to global warming…”.
This will make them the center of attention and at the same time grabbing their attention.
Use personal anecdotes
Same works with personal experiences and stories.
Everyone loves listening to first-hand experiences or a good and interesting story. If you are not a great storyteller, visual images and videos will come to your rescue.
After you have successfully grabbed and hooked your audience, the next and last step of the introduction is introducing your thesis statement.
What is a thesis statement?
It introduces the topic to your audience and is one of the central elements of any persuasive speech.
It is usually brief, not more than 3 sentences, and gives the crux of your speech outline.
How to make a thesis statement?
Firstly, research all possible opinions and views about your topic. See which opinion you connect with, and try to summarize them.
After you do this, you will get a clear idea of what side you are on and this will become your thesis statement.
However, the thesis should answer the question “why” and “how”.
So, for instance, if you choose to speak on the topic of the necessity of higher education, your thesis statement could be something like this:
Although attending university and getting a degree is essential for overall development, not every student must be pushed to join immediately after graduating from school.
And then you can structure your speech containing the reasons why every student should not be rushed into joining a university.
3. BODY OF THE SPEECH
The body contains the actual reasons to support your thesis.
Ideally, the body should contain at least 3 reasons to support your argument.
So, for the above-mentioned thesis, you can support it with possible alternatives, which will become your supporting statements.
The option of a gap year to relax and decide future goals, gaining work experience and then joining the university for financial reasons, or even joining college after 25 or 35 years.
These become your supporting reasons and answers the question “why”.
Each reason has to be resourcefully elaborated, with explaining why you support and why the other or anti-thesis is not practical.
At this point, you have the option of targeting your audience’s ethos, pathos, or logos.
Ethos is the ethical side of the argument. It targets morals and puts forth the right thing or should be.
This technique is highly used in the advertising industry.
Ever wondered why celebrities, experts, and renowned personalities are usually cast as brand ambassadors.?
The reason: they are liked by the masses and exhibit credibility and trust.
Advertisers endorse their products via a celebrity to try to show that the product is reliable and ethical.
The same scenario is seen in persuasive speeches. If the speaker is well-informed and provides information that is backed by research, chances are high that the audience will follow it.
Pathos targets the emotional feelings of the audience.
This is usually done by narrating a tragic or horrifying anecdote and leaves the listener moved by using an emotional appeal to call people to action.
The common emotions targeted by the speaker include the feeling of joy, love, sadness, anger, pity, and loneliness.
All these emotions are best expressed in stories or personal experiences.
Stories give life to your argument, making the audience more involved in the matter and arousing sympathy and empathy.
Visuals and documentaries are other mediums through which a speaker can attract the audience’s emotions.
What was your reaction after watching an emotional documentary? Did you not want to do something about the problem right away?
Emotions have the power to move people to action.
The last technique is using logos, i.e., logic. This includes giving facts and practical aspects of why this is to be done or why such a thing is the most practical.
It is also called the “logical appeal”.
This can be done by giving inductive or deductive reasoning.
Inductive reasoning involves the speaker taking a specific example or case study and then generalizing or drawing conclusions from it.
For instance, a speaker tells a case study of a student who went into depression as the child wasn’t able to cope with back-to-back stress.
This problem will be generalized and concluded that gap year is crucial for any child to cope with and be ready for the challenges in a university.
On the other hand, deductive reasoning involves analyzing general assumptions and theories and then arriving at a logical conclusion.
So, in this case, the speaker can give statistics of the percentage of university students feeling drained due to past exams and how many felt that they needed a break.
This general data will then be personalized to conclude how there is a need for every student to have a leisure break to refresh their mind and avoid having burned out.
Using any of these 3 techniques, coupled with elaborate anecdotes and supporting evidence, at the same time encountering counterarguments will make the body of your speech more effective.
4. CONCLUSION
Make sure to spend some time thinking through your conclusion, as this is the part that your audience will remember the most and is hence, the key takeaway of your entire speech.
Keep it brief, and avoid being too repetitive.
It should provide the audience with a summary of the points put across in the body, at the same time calling people to action or suggesting a possible solution and the next step to be taken.
Remember that this is your last chance to convince, hence make sure to make it impactful.
Include one to two relevant power or motivational quotes, and end by thanking the audience for being patient and listening till the end.
Watch this clip for a better understanding.
TIPS AND TRICKS OF PERSUASION
Start strong.
A general pattern among influential speeches is this: all start with a powerful and impactful example, be it statistics about the issue, using influential and meaning statements and quotes, or asking a rhetorical question at the beginning of their speech.
Why do they do this? It demonstrates credibility and creates a good impression- increasing their chance of persuading the audience.
Hence, start in such a manner that will hook the audience to your speech and people would be curious to know what you are about to say or how will you end it.
Keep your introduction short
Keep your introduction short, and not more than 10-15% of your speech.
If your speech is 2000 words, then your introduction should be a maximum of 200-250 words.
Or if you are presenting for 10 minutes, your introduction should be a maximum of 2 minutes. This will give you time to state your main points and help you manage your time effectively.
Be clear and concise
Use the correct vocabulary to fit in, at the same time making sure to state them clearly, without beating around the bush.
This will make the message efficient and impactful.
Answer the question “why”
Answer the question “why” before giving solutions or “how”.
Tell them why is there a need to change. Then give them all sides of the point.
It is important to state what is wrong and not just what ought to be or what is right, in an unopinionated tone.
Unless and until people don’t know the other side of things, they simply will not change.
Suggest solutions
Once you have stated the problem, you imply or hint at the solution.
Never state solutions, suggest them; leaving the decision up to the audience.
You can hint at solutions: “don’t you think it is a good idea to…?” or “is it wrong to say that…?”, instead of just stating solutions.
Use power phrases
Certain power-phrases come in handy, which can make the audience take action.
Using the power phrase “because” is very impactful in winning and convincing others.
This phrase justifies the action associated with it and gives us an understanding of why is it correct.
For instance, the phrase “can you give me a bite of your food?” does not imply attitude change.
But using “may I have a bite of your food because I haven’t eaten breakfast?” is more impactful and the person will likely end up sharing food if you use this power- phrase, because it is justifying your request.
Another power-phrase is “I understand, but…”.
This involves you agreeing with the opposite side of the argument and then stating your side or your point of view.
This will encourage your audience to think from the other side of the spectrum and are likely to consider your argument put forth in the speech.
Use power words
Use power words like ‘incredible’, ‘fascinating’, ‘unquestionable’, ‘most important’, ‘strongly recommend’ in your speech to provoke your audience into awe.
Watch this video of some of the common but effective words that can be used in a persuasive speech.
Give an emotional appeal
Like mentioned earlier as one of the techniques of persuasion called pathos, targeting emotions like joy, surprise, fear, anticipation, anger, sadness, or disgust gives your speech an emotional appeal, and more feel to your content, rather than just neutrally stating facts and reasons.
Hence, to keep your audience engaged and not get bored, use emotions while speaking.
Make use of the non=verbal elements
Actions speak louder than words, and they create a huge difference if used effectively.
There is so much else to a speech than just words.
Non-verbal elements include everything apart from your words.
Maintaining eye contact, matching your body language with your words for effective transmission of the message including how you express your emotions, making use of the visual signs and symbols via a PPT are all important parts of any speech.
Check your paralanguage i.e., your voice intonation, pitch, speed, effective pauses, stressing on certain words to create an impact.
Doing all of these will make your speech more real and effective, and will persuade your audience into taking action.
Give real-life examples
Speak facts and avoid giving opinions.
However, just mentioning hard statistical facts will take you nowhere, as there is a chance that people may not believe the data, based on the possibility of them recollecting exceptions.
Hence, back up your statistics with real-life examples of situations.
Also, consider using precise numerical data.
For example, using “5487 people die due to road accidents every day”, instead of “approximately 5500 people”.
Have no personal stake
You can lose credibility if the audience feels that you have a personal stake in it.
Suppose that you are speaking for the idea of using reusable plastic products, and you say that you are from a company that sells those goods.
People are likely to perceive your argument as promoting self-interest and will not be ready to change their opinion about reusable plastic products.
Consequently, if you argue against your self-interest, your audience will see you as the most credible.
So, if you say that you are working in a plastics manufacturing company and have a statistical record of the pollution caused by it; and then promote reusable plastic as an alternative to stop pollution and save the environment, people are likely to accept your point of argument.
The you attitude
Shift your focus to the audience, and chances are high that they are likely to relate the issue to themselves and are most likely to change.
Hence, use the “you attitude” i.e., shifting focus to the listener and giving them what they want to hear and then making subtle additions to what you want them to hear.
Make a good first impression
The first impression is indeed the last. This is the reason why image consultancy is such a growing sector.
A good first impression works wonders on the people around you, including the audience, and makes your work of convincing a lot easier.
Avoid appearing shabby, ill-mannered, and refrain from using uncourteous and biased language.
Doing these will reverse the effect you want from the audience and will drive them away from your opinion.
HOW TO MAKE A GOOD FIRST IMPRESSION?
If you are the type who gets nervous easily and have fear of public speaking, practice till you excel in your task.
I used to dread speaking in front of people, and partly still do.
Earlier, unless and until someone called my name to state my opinion or start with the presentation, I didn’t even raise my hand to say that I have an opinion or I am left to present on the topic.
I had to do something about this problem. So, I made a plan.
2 weeks before the presentation, I wrote the script and read it over and over again.
After reading multiple times, I imagined my room to be the classroom and practiced in front of a mirror.
The main thing I was concerned about was keeping my head clear on the day of my presentation. And that’s what happened.
Since my mind was clear and relaxed, and I had practiced my speech over and over again, presenting came more naturally and confidently.
You might ask what is the purpose of impression management?
Impressions are used for Ingratiation i.e., getting others to like us so that they will be more than willing to accept or agree to your point.
If you like someone, you are drawn towards them and are likely to agree on what they agree or say.
TIP- Try to come early to the venue, and dress appropriately to the needs of the occasion. And don’t forget to smile!
PERSUASIVE SPEECH EXAMPLES
1. wendy troxel – why school should start later for teens.
Almost all the important elements of a persuasive speech are found in this TED talk by Wendy Troxel.
Take a closer look at how she starts her introduction in the form of a real-life personal story, and how she makes it relevant to the audience.
Humor is used to hook the audience’s attention and in turn their interest.
She is also likely to be perceived as credible, as she introduces herself as a sleep researcher, and is speaking on the topic of sleep.
Thesis of how early school timings deprive teenagers of their sleep and its effects is introduced subtly.
The speaker supports her statements with facts, answers the question “why” and most importantly, presents both sides of an argument; effects of less to lack of sleep and its consequences and the effects of appropriate and more sleep on teenagers.
The use of non-verbal elements throughout the speech adds value and richness to the speech, making it more engaging.
The use of Pathos as a persuasive technique appeals to the audience’s emotions; at the same time backing the argument with Logos, by giving scientific reasons and research findings to support the argument.
Lastly, the speech is meaningful, relevant, and thought-provoking to the audience, who are mostly parents and teenagers.
2. Crystal Robello- Being an introvert is a good thing
In this example, Crystal Robello starts by giving personal experiences of being an introvert and the prejudices faced.
Notice how even without much statistics the speech is made persuasive by using Ethos as a technique; and how credibility is achieved by mentioning leaders who are introverts.
3. Greta Thunberg- School strike for climate
One of my favorite speeches is the above speech by Greta Thunberg.
She uses all the techniques; pathos, ethos and logos.
Also notice how the speaker speaks with emotions, and uses body and paralanguage efficiently to create a dramatic impact on the audience.
Her genuine interest is clearly reflected in the speech, which makes the audience listen with a level of concern towards the topic, climate change.
To sum up, we looked at the things to keep in mind before writing a speech and also became familiar with the general outline or the structure of a persuasive speech.
We also looked at some of the tips and tricks of persuasion, and lastly, got introduced to 3 amazing persuasive speech examples.
So, now that you know everything about persuasion, rest assured and keep the above-mentioned things in mind before starting your next speech!
Also, check out related posts:
Enroll in our transformative 1:1 Coaching Program
Schedule a call with our expert communication coach to know if this program would be the right fit for you

7 Keys to Emcee Like a Pro: Unlock Your Hosting Potential

8 Ways to Rise Above the Noise to Communicate Better

How to Negotiate: The Art of Getting What You Want

- [email protected]
- +91 98203 57888
Get our latest tips and tricks in your inbox always
Copyright © 2023 Frantically Speaking All rights reserved
Kindly drop your contact details so that we can arrange call back
Select Country Afghanistan Albania Algeria AmericanSamoa Andorra Angola Anguilla Antigua and Barbuda Argentina Armenia Aruba Australia Austria Azerbaijan Bahamas Bahrain Bangladesh Barbados Belarus Belgium Belize Benin Bermuda Bhutan Bosnia and Herzegovina Botswana Brazil British Indian Ocean Territory Bulgaria Burkina Faso Burundi Cambodia Cameroon Canada Cape Verde Cayman Islands Central African Republic Chad Chile China Christmas Island Colombia Comoros Congo Cook Islands Costa Rica Croatia Cuba Cyprus Czech Republic Denmark Djibouti Dominica Dominican Republic Ecuador Egypt El Salvador Equatorial Guinea Eritrea Estonia Ethiopia Faroe Islands Fiji Finland France French Guiana French Polynesia Gabon Gambia Georgia Germany Ghana Gibraltar Greece Greenland Grenada Guadeloupe Guam Guatemala Guinea Guinea-Bissau Guyana Haiti Honduras Hungary Iceland India Indonesia Iraq Ireland Israel Italy Jamaica Japan Jordan Kazakhstan Kenya Kiribati Kuwait Kyrgyzstan Latvia Lebanon Lesotho Liberia Liechtenstein Lithuania Luxembourg Madagascar Malawi Malaysia Maldives Mali Malta Marshall Islands Martinique Mauritania Mauritius Mayotte Mexico Monaco Mongolia Montenegro Montserrat Morocco Myanmar Namibia Nauru Nepal Netherlands Netherlands Antilles New Caledonia New Zealand Nicaragua Niger Nigeria Niue Norfolk Island Northern Mariana Islands Norway Oman Pakistan Palau Panama Papua New Guinea Paraguay Peru Philippines Poland Portugal Puerto Rico Qatar Romania Rwanda Samoa San Marino Saudi Arabia Senegal Serbia Seychelles Sierra Leone Singapore Slovakia Slovenia Solomon Islands South Africa South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands Spain Sri Lanka Sudan Suriname Swaziland Sweden Switzerland Tajikistan Thailand Togo Tokelau Tonga Trinidad and Tobago Tunisia Turkey Turkmenistan Turks and Caicos Islands Tuvalu Uganda Ukraine United Arab Emirates United Kingdom United States Uruguay Uzbekistan Vanuatu Wallis and Futuna Yemen Zambia Zimbabwe land Islands Antarctica Bolivia, Plurinational State of Brunei Darussalam Cocos (Keeling) Islands Congo, The Democratic Republic of the Cote d'Ivoire Falkland Islands (Malvinas) Guernsey Holy See (Vatican City State) Hong Kong Iran, Islamic Republic of Isle of Man Jersey Korea, Democratic People's Republic of Korea, Republic of Lao People's Democratic Republic Libyan Arab Jamahiriya Macao Macedonia, The Former Yugoslav Republic of Micronesia, Federated States of Moldova, Republic of Mozambique Palestinian Territory, Occupied Pitcairn Réunion Russia Saint Barthélemy Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan Da Cunha Saint Kitts and Nevis Saint Lucia Saint Martin Saint Pierre and Miquelon Saint Vincent and the Grenadines Sao Tome and Principe Somalia Svalbard and Jan Mayen Syrian Arab Republic Taiwan, Province of China Tanzania, United Republic of Timor-Leste Venezuela, Bolivarian Republic of Viet Nam Virgin Islands, British Virgin Islands, U.S.

Persuasive Speeches — Types, Topics, and Examples

What is a persuasive speech?
In a persuasive speech, the speaker aims to convince the audience to accept a particular perspective on a person, place, object, idea, etc. The speaker strives to cause the audience to accept the point of view presented in the speech.
The success of a persuasive speech often relies on the speaker’s use of ethos, pathos, and logos.

Ethos is the speaker’s credibility. Audiences are more likely to accept an argument if they find the speaker trustworthy. To establish credibility during a persuasive speech, speakers can do the following:
Use familiar language.
Select examples that connect to the specific audience.
Utilize credible and well-known sources.
Logically structure the speech in an audience-friendly way.
Use appropriate eye contact, volume, pacing, and inflection.
Pathos appeals to the audience’s emotions. Speakers who create an emotional bond with their audience are typically more convincing. Tapping into the audience’s emotions can be accomplished through the following:
Select evidence that can elicit an emotional response.
Use emotionally-charged words. (The city has a problem … vs. The city has a disease …)
Incorporate analogies and metaphors that connect to a specific emotion to draw a parallel between the reference and topic.
Utilize vivid imagery and sensory words, allowing the audience to visualize the information.
Employ an appropriate tone, inflection, and pace to reflect the emotion.
Logos appeals to the audience’s logic by offering supporting evidence. Speakers can improve their logical appeal in the following ways:
Use comprehensive evidence the audience can understand.
Confirm the evidence logically supports the argument’s claims and stems from credible sources.
Ensure that evidence is specific and avoid any vague or questionable information.
Types of persuasive speeches
The three main types of persuasive speeches are factual, value, and policy.

A factual persuasive speech focuses solely on factual information to prove the existence or absence of something through substantial proof. This is the only type of persuasive speech that exclusively uses objective information rather than subjective. As such, the argument does not rely on the speaker’s interpretation of the information. Essentially, a factual persuasive speech includes historical controversy, a question of current existence, or a prediction:
Historical controversy concerns whether an event happened or whether an object actually existed.
Questions of current existence involve the knowledge that something is currently happening.
Predictions incorporate the analysis of patterns to convince the audience that an event will happen again.
A value persuasive speech concerns the morality of a certain topic. Speakers incorporate facts within these speeches; however, the speaker’s interpretation of those facts creates the argument. These speeches are highly subjective, so the argument cannot be proven to be absolutely true or false.
A policy persuasive speech centers around the speaker’s support or rejection of a public policy, rule, or law. Much like a value speech, speakers provide evidence supporting their viewpoint; however, they provide subjective conclusions based on the facts they provide.
How to write a persuasive speech
Incorporate the following steps when writing a persuasive speech:
Step 1 – Identify the type of persuasive speech (factual, value, or policy) that will help accomplish the goal of the presentation.
Step 2 – Select a good persuasive speech topic to accomplish the goal and choose a position .

Step 3 – Locate credible and reliable sources and identify evidence in support of the topic/position. Revisit Step 2 if there is a lack of relevant resources.
Step 4 – Identify the audience and understand their baseline attitude about the topic.
Step 5 – When constructing an introduction , keep the following questions in mind:
What’s the topic of the speech?
What’s the occasion?
Who’s the audience?
What’s the purpose of the speech?
Step 6 – Utilize the evidence within the previously identified sources to construct the body of the speech. Keeping the audience in mind, determine which pieces of evidence can best help develop the argument. Discuss each point in detail, allowing the audience to understand how the facts support the perspective.
Step 7 – Addressing counterarguments can help speakers build their credibility, as it highlights their breadth of knowledge.
Step 8 – Conclude the speech with an overview of the central purpose and how the main ideas identified in the body support the overall argument.

Persuasive speech outline
One of the best ways to prepare a great persuasive speech is by using an outline. When structuring an outline, include an introduction, body, and conclusion:
Introduction
Attention Grabbers
Ask a question that allows the audience to respond in a non-verbal way; ask a rhetorical question that makes the audience think of the topic without requiring a response.
Incorporate a well-known quote that introduces the topic. Using the words of a celebrated individual gives credibility and authority to the information in the speech.
Offer a startling statement or information about the topic, typically done using data or statistics.
Provide a brief anecdote or story that relates to the topic.
Starting a speech with a humorous statement often makes the audience more comfortable with the speaker.
Provide information on how the selected topic may impact the audience .
Include any background information pertinent to the topic that the audience needs to know to understand the speech in its entirety.
Give the thesis statement in connection to the main topic and identify the main ideas that will help accomplish the central purpose.
Identify evidence
Summarize its meaning
Explain how it helps prove the support/main claim
Evidence 3 (Continue as needed)
Support 3 (Continue as needed)
Restate thesis
Review main supports
Concluding statement
Give the audience a call to action to do something specific.
Identify the overall importan ce of the topic and position.
Persuasive speech topics
The following table identifies some common or interesting persuasive speech topics for high school and college students:
Persuasive speech examples
The following list identifies some of history’s most famous persuasive speeches:
John F. Kennedy’s Inaugural Address: “Ask Not What Your Country Can Do for You”
Lyndon B. Johnson: “We Shall Overcome”
Marc Antony: “Friends, Romans, Countrymen…” in William Shakespeare’s Julius Caesar
Ronald Reagan: “Tear Down this Wall”
Sojourner Truth: “Ain’t I a Woman?”
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- Communication Skills
- Public Speaking
- Speechwriting
How to Write an Introduction for a Persuasive Speech
Last Updated: October 2, 2023 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by Gale McCreary and by wikiHow staff writer, Kyle Hall . Gale McCreary is the Founder and Chief Coordinator of SpeechStory, a nonprofit organization focused on improving communication skills in youth. She was previously a Silicon Valley CEO and President of a Toastmasters International chapter. She has been recognized as Santa Barbara Entrepreneurial Woman of the Year and received Congressional recognition for providing a Family-Friendly work environment. She has a BS in Biology from Stanford University. There are 8 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 152,771 times.
A persuasive speech is meant to convince an audience to agree with your point of view or argument relating to a specific topic. While the body of your persuasive speech is where the bulk of your argument will go, it’s important that you don’t overlook the introduction. A good introduction will capture your audience’s attention, which is crucial if you want to persuade them. Fortunately, there are some simple rules you can follow that will make the introduction to your persuasive essay more engaging and memorable.
Organizing Your Introduction

- For example, if your speech is about sleep deprivation in the workplace, you could start with something like “Workplace accidents and mistakes related to sleep deprivation cost companies $31 billion every single year.”
- Or, if your speech is about animal rights, you could open with a quote like “The English philosopher Jeremy Bentham once said, ‘The question is not, Can they reason? Nor, Can they talk? But, Can they suffer?’”
- For a speech about unpaid internships, you could start with a relevant anecdote like “In 2018, Tiffany Green got her dream internship, unpaid, working for a rental company. Unfortunately, a few months later Tiffany returned home from work to find an eviction notice on the door of her apartment, owned by that same rental company, because she was unable to pay her rent.

- For example, your thesis statement could look something like “Today, I’m going to talk to you about why medical marijuana should be legalized in all 50 states, and I’ll explain why that would improve the lives of average Americans and boost the economy.”

- For example, if you’re a marine biologist who’s writing a persuasive speech about ocean acidification, you could write something like “I’ve studied the effects of ocean acidification on local marine ecosystems for over a decade now, and what I’ve found is staggering.”
- Or, if you’re not an expert on your topic, you could include something like “Earlier this year, renowned marine biologist Ayana Elizabeth Johnson published a decade-long study on the acidification of our oceans, and what she found is deeply concerning.”

- For example, you could sum up your conclusion by writing something like, “To show you that a shorter work week would benefit not only employees but also their employers, first I will touch on the history of the modern average work week. Then, I’ll discuss the mental and physical toll that a long work week can take on a person. Finally, I’ll wrap up by going over fairer, better systems that we as a society could implement.”

- For example, if you time yourself giving your speech (introduction included) and it takes you 5 minutes, your introduction should only take up about 45 seconds of your speech.
- However, if you were giving a speech that’s 20 minutes long, your introduction should be around 3 minutes.
- On average, you’ll want about 150 words for every 1 minute you need to speak for. For example, if your introduction should be 2 minutes, you’d want to write around 300 words.
Tip: If you know how long your speech is going to be before you write it, make the first draft of your introduction the right length so you don’t have to add or delete a lot later.
Polishing Your Writing

- To make your writing more conversational, try to use brief sentences, and avoid including jargon unless you need it to make your point.
- Using contractions, like “I’ll” instead of “I will,” “wouldn’t” instead of “would not,” and “they’re” instead of “they are,” can help make your writing sound more conversational.

Tip: An easy way to make your writing more concise is to start your sentences with the subject. Also, try to limit the number of adverbs and adjectives you use.

- For example, if your audience will be made up of the other students in your college class, including a pop culture reference in your introduction might be an effective way to grab their attention and help them relate to your topic. However, if you’re giving your speech in a more formal setting, a pop culture reference might fall flat.

- For example, you could write something like, “I know a lot of you may strongly disagree with me on this. However, I think if you give me a chance and hear me out, we might end up finding some common ground.”
- Or, you could include a question like “How many of you here tonight have ever come across plastic that's washed up on the beach?” Then, you can have audience members raise their hands.

- You can even record yourself reading your introduction to get a sense of how you'll look delivering the opening of your speech.
Example Introduction for a Persuasive Speech

Community Q&A
You Might Also Like

- ↑ https://open.lib.umn.edu/communication/chapter/11-2-persuasive-speaking/
- ↑ https://2012books.lardbucket.org/books/public-speaking-practice-and-ethics/s12-introductions-matter-how-to-be.html
- ↑ https://www.middlesex.mass.edu/ace/downloads/tipsheets/persvsargu.pdf
- ↑ https://www.speechanddebate.org/wp-content/uploads/Tips-for-Writing-a-Persuasive-Speech.pdf
- ↑ https://open.lib.umn.edu/publicspeaking/chapter/14-1-four-methods-of-delivery/
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/general_writing/academic_writing/essay_writing/argumentative_essays.html
- ↑ https://www.gvsu.edu/speechlab/connecting-with-the-audience-26.htm
- ↑ https://www.gvsu.edu/speechlab/practicing-presentations-33.htm
About This Article

To write an introduction for a persuasive speech, start with a hook that will grab your audience's attention, like a surprising statistic or meaningful quote. Then, introduce your thesis statement, which should explain what you are arguing for and why. From here, you'll need to demonstrate the credibility of your argument if you want your audience to believe what you're saying. Depending on if you are an expert or not, you should either share your personal credentials or reference papers and studies by experts in the field that legitimize your argument. Finally, conclude with a brief preview of the main points you'll cover in your speech, so your audience knows what to expect and can follow along more easily. For more tips from our co-author, including how to polish your introduction, read on! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Did this article help you?

Jun 6, 2021
Noela Ebaneck
Dec 30, 2019
Imani Wilson
May 12, 2019
Mila Del Giudice
Nov 24, 2020

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
wikiHow Tech Help Pro:
Level up your tech skills and stay ahead of the curve

10 Tips for a Persuasive Presentation
Powerful presentation is persuasion. here's how to elevate your impact..
Posted May 11, 2024 | Reviewed by Ray Parker
- Presentations aim to effect change. It's essential to be clear about what change you want to see.
- Powerful presenters embrace and extend empathy to seek first to understand their audience.
- Substance and style both matter to create an audience-informed communication experience.
- Persuasive presentations are relevant, reasoned, real, and resonant.

How many of us realize that giving a presentation or making a speech is all about persuasion , influence, and emotional intelligence ? Impactful presenters understand the power of empathy to understand and engage their audience, the efficiency and kindness of having a clear objective and message, and the importance of substance and style—all as a way to connect in a way that engages and inspires.
Much has been written on the power and behavioral science of persuasion, not least by expert Robert Cialdini. His bestselling book Influence: The Psychology of Persuasion explains seven research-based universal principles of influence .
From my experience as a leadership coach working with thousands of people worldwide, I have compiled a list of ten essentials to elevate our presentation.
1. Maintain an "other" focus. What do you know about your audience and how can you find out more? Ask yourself what kind of a speaker will appeal to your audience, what arguments are likely to resonate with them, and what feelings you want to inspire so the audience will positively respond to your ask. If your audience is predominantly data-driven, you may want to use more evidence-based arguments. If the audience is mixed, a combination of data, authority, and storytelling may be more appropriate. Extend Daniel Goleman’s three types of empathy to gather intelligence , understand your audience, and tailor your intervention to connect more profoundly.
2. Determine a specific objective: Presentations aim to effect change in some way. What change do you want to see in your audience? Every presentation aims to change the audience in some way. For instance, gaining their approval for a certain investment, soliciting their buy-in for a change, or creating a sense of enthusiasm for an idea or initiative. The purpose of a presentation is to bring about change so make sure you are clear on what kind of change you want to bring about.
3. Design a grabber: Our attention spans have shrunk as we have more and more competing demands on our attention . If you want to get someone’s attention you need to grab it at the outset and try and hold on. You can do this in a number of different ways. Throw out a question that demands a response from the audience. Give a surprising fact or statistic, or quote from a well-known figure. Tell a story or an anecdote. A good grabber captures the attention of everyone there, and makes them focus on what you have to say.
4. Crystalize your message and construct your arguments : Your message is the heart of your speech. Craft a brief phrase that clearly defines your proposal in 10-12 words. For example, “This post is about crafting presentations that inspire and engage others to elevate their presentations.” Make it memorable by choosing inspiring words, symbols, catchy expressions, something that will remain in the audience's mind. As Brené Brown says: “Clear is kind,” and a clear message provides a path to develop your ideas.
When you have a clear and concise message, it helps you formulate your arguments. Think of developing your arguments using the rule of three —three compelling arguments to convince but not overwhelm your audience.
5. Prepare a call to action: Remember, we want to change our audience in some way, so we need to make our ask in a clear and concrete manner.
Consider your call to action in terms of what you want your audience to think/feel/do:
- Think—“I want you to think about how you can improve your presentations.”
- Feel—“I want you to feel enthusiastic and motivated so that you can elevate your power to persuade.”
- Do—“I want you to try out some of these tips and tools for yourself.”
6. Craft a memorable closing: Close the speech in an elegant and memorable way. We need people to remember what we've told them, so prepare it well. This is not the time to improvise. Try to connect your closing to your opening grabber, which makes the presentation more memorable. Good preparation means preparing everything to the very end—finish well.

7. Plan your delivery: A dynamic speaker draws listeners in by using vocal variety (tone, intonation, speed, volume, pace, pauses, silence) and body language (posture, gestures, expression, and movement) to highlight important points and hold the audience’s attention. Be intentional: How will you use your voice and your body to emphasize a thought or idea? Think about it: If you increased the time you spent on style or delivery by 20 percent, what would it mean for the impact you make?
8. Think about how you will engage your audience : You want the audience to feel considered throughout. Include pauses so they can process what’s being said; connect with individuals throughout the room and make deliberate eye contact while speaking, especially when delivering key points. Read and respond to the audience by changing how you deliver as you go based on the audience’s nonverbal communication .
9. Rehearse and Practice: Practice is one of the most crucial elements of presenting—and probably the most neglected one. If this is new to you start by reading your presentation in front of a mirror to get comfortable speaking your presentation. Next, video yourself and watch out for nervous or distracting habits to eliminate them and identify any areas where you can improve your delivery. If you are feeling brave, practice in front of an audience and ask for feedback.
10. Prepare your success rituals and mantra: Public speaking and/or stage fright can feel debilitating for some. Have your calm-down ritual prepared and ready to go before you start your presentation. This might be a certain gesture, a power pose, breathwork, or a mantra. Try this tip: Identify three adjectives to describe how you would like to show up during this presentation. This sets an intention and helps focus our cognitive and emotional resources on success.
Powerful presenters embrace and extend empathy to seek first to understand their audience. They use this intelligence to carefully make choices about substance and style to create an audience-informed communication experience that feels relevant, reasoned, real, and resonant and creates a pathway for change.

Palena Neale, Ph.D. , is a women’s leadership coach, lecturer, and founder of unabridged, a boutique leadership development practice.
- Find a Therapist
- Find a Treatment Center
- Find a Psychiatrist
- Find a Support Group
- Find Online Therapy
- International
- New Zealand
- South Africa
- Switzerland
- Asperger's
- Bipolar Disorder
- Chronic Pain
- Eating Disorders
- Passive Aggression
- Personality
- Goal Setting
- Positive Psychology
- Stopping Smoking
- Low Sexual Desire
- Relationships
- Child Development
- Therapy Center NEW
- Diagnosis Dictionary
- Types of Therapy

At any moment, someone’s aggravating behavior or our own bad luck can set us off on an emotional spiral that threatens to derail our entire day. Here’s how we can face our triggers with less reactivity so that we can get on with our lives.
- Emotional Intelligence
- Gaslighting
- Affective Forecasting
- Neuroscience

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
F itting the standard speech format. If you are wondering how these 5 steps of Monroe's Motivated Sequence fit into the standard 3 part speech format, they go like this: Step 1 ( Attention) forms the Introduction. Steps 2, 3 and 4 ( Need, Satisfaction and Visualization) form the Body. Step 5 ( Action) is the Conclusion.
Alan H. Monroe's (1935) motivated sequence is a commonly used speech format that is used by many people to effectively organize persuasive messages. The pattern consists of five basic stages: attention, need, satisfaction, visualization, and action. In the first stage, a speaker gets an audience's attention.
Persuasive Speech Outline, with Examples. A persuasive speech is a speech that is given with the intention of convincing the audience to believe or do something. This could be virtually anything - voting, organ donation, recycling, and so on. A successful persuasive speech effectively convinces the audience to your point of view, providing ...
Choose a compelling speech topic relevant to your audience's interests and concerns. Find common interests or problems to form a genuine relationship. Remember that a persuasive speech format should be adapted to your audience's needs and ideals. Make your content relevant and appealing. And if you are struggling on this step, PapersOwl is ...
Persuasive speaking is the type of speaking people engage in the most. This type of speech has a broad spectrum, from arguing about politics to talking about what to have for dinner. Persuasive speaking is highly connected to the audience, as in a sense, the speaker has to meet the audience halfway. Persuasive Speech Preparation
First, you'll need to choose a side on a controversial topic, then you will write a speech to explain your position, and convince the audience to agree with you. You can produce an effective persuasive speech if you structure your argument as a solution to a problem. Your first job as a speaker is to convince your audience that a particular ...
3. Address the counter-argument. Although it is not strictly necessary, your argument may be stronger if one or more of your supporting points addresses the views of the opposing side. This gives you a chance to address your audience's possible objections and make your argument stronger.
(Need Step) A. Poverty is real and rampant in much of the world. 1. According to a 2018 report of the Secretary General of the United Nations, 9.2% of the world lives on less than $1.90 per day. ... Sample Outline- Persuasive Speech Using Monroe's Motivated Sequence Pattern is shared under a CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 license and was authored, remixed ...
Step 2: After the Story, Now, Give Your Advice. When most people write a persuasive presentation, they start with their opinion. Again, this makes the listener want to play Devil's advocate. By starting with the example, we give the listener a simple way to agree with us.
Persuasive speaking seeks to influence the beliefs, attitudes, values, or behaviors of audience members. In order to persuade, a speaker has to construct arguments that appeal to audience members. Arguments form around three components: claim, evidence, and warrant. The claim is the statement that will be supported by evidence.
Alan H. Monroe, a Purdue University professor, used the psychology of persuasion to develop an outline for making speeches that will deliver results, and wrote about it in his book Monroe's Principles of Speech. It's now known as Monroe's Motivated Sequence. This is a well-used and time-proven method to organize presentations for maximum impact.
Needs. In the need step of Monroe's motivated sequence, the speaker establishes that there is a specific need or problem. Monroe (1935) specified the following four steps as part of the need: Statement: a speaker needs to give a clear and concise statement of the problem. This part of a speech should be crystal clear for the audience.
This is the final step in Monroe's Motivated Sequence. It comes at the very end of your conclusion and will be the last thing your audience hears in your speech. You will want to urge your audience to take action, right now, to fix this problem. By this point of the speech, your audience should be itching to know what they can do to make a ...
Example: "We need to find affordable and sustainable ways to produce clean water." Preview This is the easiest piece of the introduction to write because, at its core, it's the same for every speech. Give the audience a roadmap, or signposts, of the next three big points you'll be discussing. In a persuasive speech, your signposts are
Alan H. Monroe's (1935) motivated sequence is a commonly used speech format that is used by many people to effectively organize persuasive messages. The pattern consists of five basic stages: attention, need, satisfaction, visualization, and action. In the first stage, a speaker gets an audience's attention.
Not sure where to start with writing a persuasive speech? With these six steps, learn how to write a persuasive speech easily and captivate your audience.
Five separate steps characterize the Motivated Sequence organization style: 1. The attention step should get the audience's attention as well as describe your goals and preview the speech. 2. The need step should provide a description of the problem as well as the consequences that may result if the problem goes unresolved.
Persuasive Speech is a category of speech that attempts to influence the listener's beliefs, attitudes, thoughts, and ultimately, behavior. They are used in all contexts and situations. It can be informal, a teenager attempting to convince his or her parents for a sleepover at a friend's house. It can also be formal, President or Prime ...
17.6 Constructing a Persuasive Speech In a sense, constructing your persuasive speech is the culmination of the skills you have learned already. In another sense, you are challenged to think somewhat differently. ... The theoretical demonstration shows or explains how the solution meets the criteria from the Need step or has the necessary features.
Step 2 - Select a good persuasive speech topic to accomplish the goal and choose a position. How to write a persuasive speech. Step 3 - Locate credible and reliable sources and identify evidence in support of the topic/position. Revisit Step 2 if there is a lack of relevant resources. Step 4 - Identify the audience and understand their ...
A persuasive speech is a type of speech where the goal is to convince the audience to accept the speaker's point of view or perform a desired action. The speaker uses words and visuals to guide the audience's thoughts and actions. Persuasive speeches rely on three forms of rhetoric, which are as follows: Ethos: Ethos is the speaker's credibility.
Tip: An easy way to make your writing more concise is to start your sentences with the subject. Also, try to limit the number of adverbs and adjectives you use. 3. Tailor your writing to your audience. Being aware of your audience while you're writing will help you craft a more persuasive message.
Mastering persuasive speech techniques is an invaluable skill in business communications, allowing you to influence others and drive your points home effectively. Persuasive speaking is not just ...
Persuasive presentations are relevant, reasoned, real, and resonant. Source: melnyk58/123rf. How many of us realize that giving a presentation or making a speech is ... you need to grab it at the ...
SAMPLE SPEECH OUTLINE TEMPLATE 1) INTRODUCTION a) "Attention-Getter" Strategy(ies) I want to start today by everybody thinking on the word "INCLUSION". A simple word with different meaning to each of you, but it can bring a lot of emotions for us. Can we go back in time and remember elementary school.