
More Like this
What is the difference between a business plan and a strategic plan.
It is not uncommon that the terms ‘strategic plan’ and ‘business plan’ get confused in the business world. While a strategic plan is a type of business plan, there are several important distinctions between the two types that are worth noting. Before beginning your strategic planning process or strategy implementation, look at the article below to learn the key difference between a business vs strategic plan and how each are important to your organization.
Definition of a business plan vs. a strategic plan
A strategic plan is essential for already established organizations looking for a way to manage and implement their strategic direction and future growth. Strategic planning is future-focused and serves as a roadmap to outline where the organization is going over the next 3-5 years (or more) and the steps it will take to get there.
Get the Free Guide for Setting OKRs that Work (with 100 examples!)
A strategic plan serves 6 functions for an organization that is striving to reach the next level of their growth:.
- Defines the purpose of the organization.
- Builds on an organization’s competitive advantages.
- Communicates the strategy to the staff.
- Prioritizes the financial needs of the organization.
- Directs the team to move from plan to action.
- Creates long-term sustainability and growth impact
Alternatively, a business plan is used by new businesses or organizations trying to get off the ground. The fundamentals of a business plan focus on setting the foundation for the business or organization. While it looks towards the future, the focus is set more on the immediate future (>1 year). Some of the functions of a business plan may overlap with a strategic plan. However, the focus and intentions diverge in a few key areas.
A business plan for new businesses, projects, or organizations serves these 5 functions:
- Simplifies or explains the objectives and goals of your organization.
- Coordinates human resource management and determines operational requirements.
- Secures funding for your organization.
- Evaluates potential business prospects.
- Creates a framework for conceptualizing ideas.
In other words, a strategic plan is utilized to direct the momentum and growth of an established company or organization. In contrast, a business plan is meant to set the foundation of a newly (or not quite) developed company by setting up its operational teams, strategizing ways to enter a new market, and obtaining funding.
A strategic plan focuses on long-term growth and the organization’s impact on the market and its customers. Meanwhile, a business plan must focus more on the short-term, day-to-day operational functions. Often, new businesses don’t have the capacity or resources to create a strategic plan, though developing a business plan with strategy elements is never a bad idea.
Business and strategic plans ultimately differ in several key areas–timeframe, target audience, focus, resource allocation, nature, and scalability.
While both a strategic and business plan is forward-facing and focused on future success, a business plan is focused on the more immediate future. A business plan normally looks ahead no further than one year. A business plan is set up to measure success within a 3- to 12-month timeframe and determines what steps a business owner needs to take now to succeed.
A strategic plan generally covers the organizational plan over 3 to 5+ years. It is set with future expansion and development in mind and sets up roadmaps for how the organization will reach its desired future state.
Pro Tip: While a vision statement could benefit a business plan, it is essential to a strategic plan.
Target Audience
A strategic plan is for established companies, businesses, organizations, and owners serious about growing their organizations. A strategic plan communicates the organization’s direction to the staff and stakeholders. The strategic plan is communicated to the essential change makers in the organization who will have a hand in making the progress happen.
A business plan could be for new businesses and entrepreneurs who are start-ups. The target audience for the business plan could also be stakeholders, partners, or investors. However, a business plan generally presents the entrepreneur’s ideas to a bank. It is meant to get the necessary people onboard to obtain the funding needed for the project.
A strategic plan provides focus, direction, and action to move the organization from where they are now to where they want to go. A strategic plan may consist of several months of studies, analyses, and other processes to gauge an organization’s current state. The strategy officers may conduct an internal and external analysis, determine competitive advantages, and create a strategy roadmap. They may take the time to redefine their mission, vision, and values statements.
Alternatively, a business plan provides a structure for ideas to define the business initially. It maps out the more tactical beginning stages of the plan.
Pro Tip: A mission statement is useful for business and strategic plans as it helps further define the enterprise’s value and purpose. If an organization never set its mission statement at the beginning stages of its business plan, it can create one for its strategic plan.
A strategic plan is critical to prioritizing resources (time, money, and people) to grow the revenue and increase the return on investment. The strategic plan may start with reallocating current financial resources already being utilized more strategically.
A business plan will focus on the resources the business still needs to obtain, such as vendors, investors, staff, and funding. A business plan is critical if new companies seek funding from banks or investors. It will add accountability and transparency for the organization and tell the funding channels how they plan to grow their business operations and ROI in the first year of the business.
The scalability of a business plan vs. strategic plan
Another way to grasp the difference is by understanding the difference in ‘scale’ between strategic and business plans. Larger organizations with multiple business units and a wide variety of products frequently start their annual planning process with a corporate-driven strategic plan. It is often followed by departmental and marketing plans that work from the Strategic Plan.
Smaller and start-up companies typically use only a business plan to develop all aspects of operations of the business on paper, obtain funding and then start the business.
Why understanding the differences between a business plan vs a strategic plan matters
It is important to know the key differences between the two terms, despite often being used interchangeably. But here’s a simple final explanation:
A business plan explains how a new business will get off the ground. A strategic plan answers where an established organization is going in the future and how they intend to reach that future state.
A strategic plan also focuses on building a sustainable competitive advantage and is futuristic. A business plan is used to assess the viability of a business opportunity and is more tactical.
10 Comments
I agree with your analysis about small companies, but they should do a strategic plan. Just check out how many of the INC 500 companies have an active strategic planning process and they started small. Its about 78%,
Strategic management is a key role of any organization even if belong to small business. it help in growth and also to steam line your values. im agree with kristin.
I agree with what you said, without strategic planning no organization can survive whether it is big or small. Without a clear strategic plan, it is like walking in the darkness.. Best Regards..
Vision, Mission in Business Plan VS Strategic Plan ?
you made a good analysis on strategic plan and Business plan the difference is quite clear now. But on the other hand, it seems that strategic plan and strategic management are similar which I think not correct. Please can you tell us the difference between these two?. Thanks
Thank you. I get points to work on it
super answer Thanking you
Hi. I went through all the discussions, comments and replies. Thanks! I got a very preliminary idea about functions and necessity of Strategic Planning in Business. But currently I am looking for a brief nice, flowery, juicy definition of “Business Strategic Planning” as a whole, which will give anyone a fun and interesting way to understand. Can anyone help me out please? Awaiting replies…… 🙂
that was easy to understand,
Developing a strategic plan either big or small company or organization mostly can’t achieve its goal. A strategic plan or formulation is the first stage of the strategic management plan, therefore, we should be encouraged to develop a strategic management plan. We can develop the best strategic plan but without a clear plan of implementation and evaluation, it will be difficult to achieve goals.
Comments Cancel
Join 60,000 other leaders engaged in transforming their organizations., subscribe to get the latest agile strategy best practices, free guides, case studies, and videos in your inbox every week..

Leading strategy? Join our FREE community.
Become a member of the chief strategy officer collaborative..
Free monthly sessions and exclusive content.
Do you want to 2x your impact.
The magazine of Glion Institute of Higher Education
- Strategic planning vs business planning: how they’re both key to success

Any thriving hospitality business needs thorough planning to make sure it succeeds. If you’ve heard the terms business planning and strategic planning, you might think they’re interchangeable, but they’re actually two distinct things companies need at different times for continued success.
The biggest difference is that business plans are mostly used when you are starting to build a business so you can quickly and smoothly create your vision. Strategic planning is what existing companies use to grow and improve their businesses.
If you’re looking for a career in hospitality management, it’s important to know the difference between the two and how to use them to best effect. In this article, we’ll go over what strategic planning and business planning are and how they are important to running a successful hospitality business.
We’ll also look at how you can learn to harness different planning methods and get the skills needed to develop your career.
Business planning
A business plan is one of the first things a fledgling business will draft. Alternatively, it can be used to set business goals when launching a new product or service.
The business plan will usually look at short-term details and focus on how things should run for around a year or less. This will include looking at concepts such as:
- What the business idea is
- Short-term goals
- Who your customers are
- What your customers need
- What investment or financing you will need to start your business
- How you make revenue
- What profitability to expect
- How you can appeal to potential shareholders
- What the short-term operational needs of the business are
- What the company’s values are
- What the budget is for different parts of the business
This means market analysis and research are vital when you are making a business plan.
What are the objectives of business planning?
The primary objective of a business plan is to have all the main details of your business worked out before you start. This will give you a roadmap to use when you launch your business or when you start offering a different product or service.
For example, if you wanted to become an event planner and open your own event planning business, your plan might include how to get funds to rent an office and pay staff.
Strategic planning

A strategic plan is where you set out the company’s goals and define the steps you will need to take to reach those goals.
A strategic plan would include:
- What current capabilities the company has
- Making measurable goals
- A full strategy for business growth
- How the company’s values, mission and vision tie in with the services and products the company intends to offer
- Who in the organization will handle certain roles
- What the timeline is for reaching certain goals
- A SWOT analysis, looking at the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats in the company
- Examining the external environment for factors that will affect your company using a PEST (political, economic, social and technological) analysis
A strategic plan can be a long-term blueprint. You might find you use basically the same strategic plan for several years.
What is the objective and strategy of planning?
The aim of a strategic plan is to provide a tool that allows you to improve your business, grow the company, streamline processes or make other changes for the health of your business. Strategy implementation and meeting strategic objectives should generally lead to growth.
What is the difference between business planning and strategic planning?
There are a few major differences between strategic planning and business planning, which are outlined below.
Scope and time frame
A strategic plan is usually long-term, typically covering at least two to five years. By contrast, a business plan usually covers a year or less, since this is roughly how long it usually takes for a business to become established.
A business plan focuses on starting a business in its early stages. A strategic plan is used to guide the company through later stages. Put simply, the business plan is about direction and vision, while the strategic plan focuses on operations and specific tactics for business growth.
Stakeholders
A strategic plan will be presented to stakeholders and employees to make sure everyone knows what is going on in the company. This will help reassure everyone with a stake or role in the business.
By comparison, a business plan will often be shown to investors or lenders to help show the business idea is worth funding.
Flexibility and adaptability
A strategic plan typically has more flexibility. This is because it is meant to be in place for a longer period of time and the company should already be established. There is more leeway for refining strategy evolution, while your business plan should remain stable.
Similarities between business planning and strategic planning
Both of these activities will require some of the same analytical components, such as market analysis, financial projections and setting objectives you can track. Of course, both also require you to be highly organized and focused to ensure your business model or strategy development is appropriate for your business.
When to use strategic planning vs business planning

As we’ve already mentioned, you’ll generally use a business plan when you’re setting up a business or moving in a new direction. This will dictate much of the day-to-day running of a business. You would use strategic planning when you want to work on growth and drive innovation.
Can a business plan be used for strategic planning?
No, a business plan and a strategic plan are two different concepts with specific goals. While a business plan outlines short or mid-term goals and steps to achieve them, a strategic plan focuses on a company’s mid to long-term mission and how to accomplish this.
If you want to prepare for success, you need to make sure you are using the right type of plan.
Integrating strategic planning and business planning
While the two plans are different, you may end up using them together to ensure optimal success. As with any type of management role, such as hotel management , strategic and business plan management requires effective communication between different departments.
This includes different strategy managers as well as strategic and operational teams. You also need to make sure that, when you are using either plan, you find the right balance between flexibility and strict adherence to the plan. With strategic planning, this means constant strategy evaluation to assess your tactics and success.
Can strategic planning and business planning be used simultaneously?
In many hospitality careers , you’ll want to juggle growth and new directions, so you could end up using both planning types. However, it’s most common for the two to be distinct. This is because you’ll generally be using a business plan only when you are starting a new venture.
What are the career prospects in strategic and business planning?
There are plenty of options for what you can do if you have skills in strategic planning and business planning. Almost every management role will require these planning skills, including how to write strategic planning documents and measure success.
If you want to work in the hospitality sector, you could look into hotel planning and other careers with a business management degree . These will enable you to grow and nurture a business, but there is also a lot of scope to start your own business. Great planning skills can give you a real competitive advantage.
World-class degrees for making your mark in business
If you want the skills and insider knowledge to guide a business from inception to expansion, our courses provide expert teaching and real-world experience.

What skills do I need for a career in planning?
If you want to work in planning and management, you should work on various skills, such as:
- Decision-making
- Analytical skills
- Risk assessment knowledge
- Market analysis and forecasting
- Team management
- Communication, both written and verbal
- Organization
What qualifications can help with a career in strategic planning or business planning?
If you want to work in hotel planning and management, the most common route is to get a hospitality degree from a well-respected hospitality school in Switzerland . This will help you get the skills and knowledge you need to properly plan businesses as well as handle the execution of these plans.
Business degrees also teach you many transferable skills, such as good communication with your strategy team or data analysis, that you can use in almost any role in hospitality. They can also reduce the need to work your way up through the hospitality industry.
How can hospitality school help with planning careers?
Attending hospitality school can help you learn skills dedicated to hospitality as well as more general management, business and planning skills. This includes everything from how to handle a team to specifics such as hotel revenue management strategies .
If you find a hospitality school offering professional hospitality internships , you’ll also get experience in managing hotels and hospitality venues, helping you leap ahead in your career.
Hospitality degrees to kickstart your career
Our international business course combines leading industry expertise with essential internships to provide an exceptional foundation for a thriving career in the hospitality industry.

Both strategic and business planning are vital to build and grow a business. While business planning focuses on setting up the business and handling investment, vision and overall goals, strategic planning concentrates on growing the business and processing operational efficiency and resource allocation on a longer-term basis.
If you want to learn how to develop a hotel business plan or manage a hospitality venue, one of the best ways to get started is to study for a hospitality degree. This will give you hands-on experience of the strategic planning process or business management as well as the skills you need to succeed.
Photo credits Main image: Westend61/Westend61via Getty Images

BUSINESS OF LUXURY

Hospitality internships

LISTENING TO LEADERS
LIVING WELL

HOSPITALITY UNCOVERED

WELCOME TO GLION.
This site uses cookies. Some are used for statistical purposes and others are set up by third party services. By clicking ‘Accept all’, you accept the use of cookies
Privacy Overview
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
What Is a Business Plan?
Understanding business plans, how to write a business plan, common elements of a business plan, how often should a business plan be updated, the bottom line, business plan: what it is, what's included, and how to write one.
Adam Hayes, Ph.D., CFA, is a financial writer with 15+ years Wall Street experience as a derivatives trader. Besides his extensive derivative trading expertise, Adam is an expert in economics and behavioral finance. Adam received his master's in economics from The New School for Social Research and his Ph.D. from the University of Wisconsin-Madison in sociology. He is a CFA charterholder as well as holding FINRA Series 7, 55 & 63 licenses. He currently researches and teaches economic sociology and the social studies of finance at the Hebrew University in Jerusalem.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/adam_hayes-5bfc262a46e0fb005118b414.jpg)
- How to Start a Business: A Comprehensive Guide and Essential Steps
- How to Do Market Research, Types, and Example
- Marketing Strategy: What It Is, How It Works, How To Create One
- Marketing in Business: Strategies and Types Explained
- What Is a Marketing Plan? Types and How to Write One
- Business Development: Definition, Strategies, Steps & Skills
- Business Plan: What It Is, What's Included, and How to Write One CURRENT ARTICLE
- Small Business Development Center (SBDC): Meaning, Types, Impact
- How to Write a Business Plan for a Loan
- Business Startup Costs: It’s in the Details
- Startup Capital Definition, Types, and Risks
- Bootstrapping Definition, Strategies, and Pros/Cons
- Crowdfunding: What It Is, How It Works, and Popular Websites
- Starting a Business with No Money: How to Begin
- A Comprehensive Guide to Establishing Business Credit
- Equity Financing: What It Is, How It Works, Pros and Cons
- Best Startup Business Loans
- Sole Proprietorship: What It Is, Pros & Cons, and Differences From an LLC
- Partnership: Definition, How It Works, Taxation, and Types
- What is an LLC? Limited Liability Company Structure and Benefits Defined
- Corporation: What It Is and How to Form One
- Starting a Small Business: Your Complete How-to Guide
- Starting an Online Business: A Step-by-Step Guide
- How to Start Your Own Bookkeeping Business: Essential Tips
- How to Start a Successful Dropshipping Business: A Comprehensive Guide
A business plan is a document that details a company's goals and how it intends to achieve them. Business plans can be of benefit to both startups and well-established companies. For startups, a business plan can be essential for winning over potential lenders and investors. Established businesses can find one useful for staying on track and not losing sight of their goals. This article explains what an effective business plan needs to include and how to write one.
Key Takeaways
- A business plan is a document describing a company's business activities and how it plans to achieve its goals.
- Startup companies use business plans to get off the ground and attract outside investors.
- For established companies, a business plan can help keep the executive team focused on and working toward the company's short- and long-term objectives.
- There is no single format that a business plan must follow, but there are certain key elements that most companies will want to include.
Investopedia / Ryan Oakley
Any new business should have a business plan in place prior to beginning operations. In fact, banks and venture capital firms often want to see a business plan before they'll consider making a loan or providing capital to new businesses.
Even if a business isn't looking to raise additional money, a business plan can help it focus on its goals. A 2017 Harvard Business Review article reported that, "Entrepreneurs who write formal plans are 16% more likely to achieve viability than the otherwise identical nonplanning entrepreneurs."
Ideally, a business plan should be reviewed and updated periodically to reflect any goals that have been achieved or that may have changed. An established business that has decided to move in a new direction might create an entirely new business plan for itself.
There are numerous benefits to creating (and sticking to) a well-conceived business plan. These include being able to think through ideas before investing too much money in them and highlighting any potential obstacles to success. A company might also share its business plan with trusted outsiders to get their objective feedback. In addition, a business plan can help keep a company's executive team on the same page about strategic action items and priorities.
Business plans, even among competitors in the same industry, are rarely identical. However, they often have some of the same basic elements, as we describe below.
While it's a good idea to provide as much detail as necessary, it's also important that a business plan be concise enough to hold a reader's attention to the end.
While there are any number of templates that you can use to write a business plan, it's best to try to avoid producing a generic-looking one. Let your plan reflect the unique personality of your business.
Many business plans use some combination of the sections below, with varying levels of detail, depending on the company.
The length of a business plan can vary greatly from business to business. Regardless, it's best to fit the basic information into a 15- to 25-page document. Other crucial elements that take up a lot of space—such as applications for patents—can be referenced in the main document and attached as appendices.
These are some of the most common elements in many business plans:
- Executive summary: This section introduces the company and includes its mission statement along with relevant information about the company's leadership, employees, operations, and locations.
- Products and services: Here, the company should describe the products and services it offers or plans to introduce. That might include details on pricing, product lifespan, and unique benefits to the consumer. Other factors that could go into this section include production and manufacturing processes, any relevant patents the company may have, as well as proprietary technology . Information about research and development (R&D) can also be included here.
- Market analysis: A company needs to have a good handle on the current state of its industry and the existing competition. This section should explain where the company fits in, what types of customers it plans to target, and how easy or difficult it may be to take market share from incumbents.
- Marketing strategy: This section can describe how the company plans to attract and keep customers, including any anticipated advertising and marketing campaigns. It should also describe the distribution channel or channels it will use to get its products or services to consumers.
- Financial plans and projections: Established businesses can include financial statements, balance sheets, and other relevant financial information. New businesses can provide financial targets and estimates for the first few years. Your plan might also include any funding requests you're making.
The best business plans aren't generic ones created from easily accessed templates. A company should aim to entice readers with a plan that demonstrates its uniqueness and potential for success.
2 Types of Business Plans
Business plans can take many forms, but they are sometimes divided into two basic categories: traditional and lean startup. According to the U.S. Small Business Administration (SBA) , the traditional business plan is the more common of the two.
- Traditional business plans : These plans tend to be much longer than lean startup plans and contain considerably more detail. As a result they require more work on the part of the business, but they can also be more persuasive (and reassuring) to potential investors.
- Lean startup business plans : These use an abbreviated structure that highlights key elements. These business plans are short—as short as one page—and provide only the most basic detail. If a company wants to use this kind of plan, it should be prepared to provide more detail if an investor or a lender requests it.
Why Do Business Plans Fail?
A business plan is not a surefire recipe for success. The plan may have been unrealistic in its assumptions and projections to begin with. Markets and the overall economy might change in ways that couldn't have been foreseen. A competitor might introduce a revolutionary new product or service. All of this calls for building some flexibility into your plan, so you can pivot to a new course if needed.
How frequently a business plan needs to be revised will depend on the nature of the business. A well-established business might want to review its plan once a year and make changes if necessary. A new or fast-growing business in a fiercely competitive market might want to revise it more often, such as quarterly.
What Does a Lean Startup Business Plan Include?
The lean startup business plan is an option when a company prefers to give a quick explanation of its business. For example, a brand-new company may feel that it doesn't have a lot of information to provide yet.
Sections can include: a value proposition ; the company's major activities and advantages; resources such as staff, intellectual property, and capital; a list of partnerships; customer segments; and revenue sources.
A business plan can be useful to companies of all kinds. But as a company grows and the world around it changes, so too should its business plan. So don't think of your business plan as carved in granite but as a living document designed to evolve with your business.
Harvard Business Review. " Research: Writing a Business Plan Makes Your Startup More Likely to Succeed ."
U.S. Small Business Administration. " Write Your Business Plan ."
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/GettyImages-1456193345-2cc8ef3d583f42d8a80c8e631c0b0556.jpg)
- Terms of Service
- Editorial Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Your Privacy Choices
- Business Essentials
- Leadership & Management
- Credential of Leadership, Impact, and Management in Business (CLIMB)
- Entrepreneurship & Innovation
- Digital Transformation
- Finance & Accounting
- Business in Society
- For Organizations
- Support Portal
- Media Coverage
- Founding Donors
- Leadership Team

- Harvard Business School →
- HBS Online →
- Business Insights →
Business Insights
Harvard Business School Online's Business Insights Blog provides the career insights you need to achieve your goals and gain confidence in your business skills.
- Career Development
- Communication
- Decision-Making
- Earning Your MBA
- Negotiation
- News & Events
- Productivity
- Staff Spotlight
- Student Profiles
- Work-Life Balance
- AI Essentials for Business
- Alternative Investments
- Business Analytics
- Business Strategy
- Business and Climate Change
- Design Thinking and Innovation
- Digital Marketing Strategy
- Disruptive Strategy
- Economics for Managers
- Entrepreneurship Essentials
- Financial Accounting
- Global Business
- Launching Tech Ventures
- Leadership Principles
- Leadership, Ethics, and Corporate Accountability
- Leading Change and Organizational Renewal
- Leading with Finance
- Management Essentials
- Negotiation Mastery
- Organizational Leadership
- Power and Influence for Positive Impact
- Strategy Execution
- Sustainable Business Strategy
- Sustainable Investing
- Winning with Digital Platforms
What Is Business Strategy & Why Is It Important?

- 20 Oct 2022
Every business leader wants their organization to succeed. Turning a profit and satisfying stakeholders are worthy objectives but aren’t feasible without an effective business strategy.
To attain success, leaders must hone their skills and set clear business goals by crafting a strategy that creates value for the firm, customers, suppliers, and employees. Here's an overview of business strategy and why it's essential to your company’s success.
Access your free e-book today.
What’s a Business Strategy?
Business strategy is the strategic initiatives a company pursues to create value for the organization and its stakeholders and gain a competitive advantage in the market. This strategy is crucial to a company's success and is needed before any goods or services are produced or delivered.
According to Harvard Business School Online's Business Strategy course, an effective strategy is built around three key questions:
- How can my business create value for customers?
- How can my business create value for employees?
- How can my business create value by collaborating with suppliers?
Many promising business initiatives don’t come to fruition because the company failed to build its strategy around value creation. Creativity is important in business , but a company won't last without prioritizing value.
The Importance of Business Strategy
A business strategy is foundational to a company's success. It helps leaders set organizational goals and gives companies a competitive edge. It determines various business factors, including:
- Price: How to price goods and services based on customer satisfaction and cost of raw materials
- Suppliers: Whether to source materials sustainably and from which suppliers
- Employee recruitment: How to attract and maintain talent
- Resource allocation: How to allocate resources effectively
Without a clear business strategy, a company can't create value and is unlikely to succeed.
Creating Value
To craft a successful business strategy, it's necessary to obtain a thorough understanding of value creation. In the online course Business Strategy , Harvard Business School Professor Felix Oberholzer-Gee explains that, at its core, value represents a difference. For example, the difference between a customer's willingness to pay for a good or service and its price represents the value the business has created for the customer. This difference can be visualized with a tool known as the value stick.
The value stick has four components, representing the value a strategy can bring different stakeholders.

- Willingness to pay (WTP) : The maximum amount a customer is willing to pay for a company's goods or services
- Price : The actual price of the goods or services
- Cost : The cost of the raw materials required to produce the goods or services
- Willingness to sell (WTS) : The lowest amount suppliers are willing to receive for raw materials, or the minimum employees are willing to earn for their work
The difference between each component represents the value created for each stakeholder. A business strategy seeks to widen these gaps, increasing the value created by the firm’s endeavors.
Increasing Customer Delight
The difference between a customer's WTP and the price is known as customer delight . An effective business strategy creates value for customers by raising their WTP or decreasing the price of the company’s goods or services. The larger the difference between the two, the more value is created for customers.
A company might focus on increasing WTP with its marketing strategy. Effective market research can help a company set its pricing strategy by determining target customers' WTP and finding ways to increase it. For example, a business might differentiate itself and increase customer loyalty by incorporating sustainability into its business strategy. By aligning its values with its target audiences', an organization can effectively raise consumers' WTP.
Increasing Firm Margin
The value created for the firm is the difference between the price of an item and its cost to produce. This difference is known as the firm’s margin and represents the strategy's financial success. One metric used to quantify this margin is return on invested capital (ROIC) . This metric compares a business's operating income with the capital necessary to generate it. The formula for ROIC is:
Return on Invested Capital = Net Operating Cost After Tax (NOCAT) / Invested Capital (IC)
ROIC tells investors how successful a company is at turning its investments into profit. By raising WTP, a company can risk increasing prices, thereby increasing firm margin. Business leaders can also increase this metric by decreasing their costs. For example, sustainability initiatives—in addition to raising WTP—can lower production costs by using fewer or more sustainable resources. By focusing on the triple bottom line , a firm can simultaneously increase customer delight and margin.
Increasing Supplier Surplus & Employee Satisfaction
By decreasing suppliers' WTS, or increasing costs, a company can create value for suppliers—or supplier surplus . Since increasing costs isn't sustainable, an effective business strategy seeks to create value for suppliers by decreasing WTS. How a company accomplishes this varies. For example, a brick-and-mortar company might partner with vendors to showcase its products in exchange for a discount. Suppliers may also be willing to offer a discount in exchange for a long-term contract.
In addition to supplier WTS, companies are also responsible for creating value for another key stakeholder: its employees. The difference between employee compensation and the minimum they're willing to receive is employee satisfaction . There are several ways companies can increase this difference, including:
- Increasing compensation: While most companies hesitate to raise salaries, some have found success in doing so. For example, Dan Price, CEO of Gravity Payments, increased his company's minimum wage to $80,000 per year and enjoyed substantial growth and publicity as a result.
- Increasing benefits: Companies can also decrease WTS by making working conditions more desirable to prospective employees. Some offer remote or hybrid working opportunities to give employees more flexibility. Several have also started offering four-day work weeks , often experiencing increased productivity as a result.
There are several ways to increase supplier surplus and employee satisfaction without hurting the company's bottom line. Unfortunately, most managers only devote seven percent of their time to developing employees and engaging stakeholders. Yet, a successful strategy creates value for every stakeholder—both internal and external.

Strategy Implementation
Crafting a business strategy is just the first step in the process. Implementation takes a strategy from formulation to execution . Successful implementation includes the following steps :
- Establish clear goals and key performance indicators (KPIs)
- Set expectations and ensure employees are aware of their roles and responsibilities
- Delegate work and allocate resources effectively
- Put the plan into action and continuously monitor its progress
- Adjust your plan as necessary
- Ensure your team has what they need to succeed and agrees on the desired outcome
- Evaluate the results of the plan
Throughout the process, it's important to remember to adjust your plan throughout its execution but to avoid second-guessing your decisions. Striking this balance is challenging, but crucial to a business strategy's success.

Learn More About Creating a Successful Business Strategy
Business strategy constantly evolves with changing consumer expectations and market conditions. For this reason, business leaders should continuously educate themselves on creating and executing an effective strategy.
One of the best ways to stay up-to-date on best practices is to take an online course, such as HBS Online's Business Strategy program. The course will provide guidance on creating a value-driven strategy for your business.
Do you want to learn how to craft an effective business strategy and create value for your company's stakeholders? Explore our online course Business Strategy , or other strategy courses , to develop your strategic planning skills. To determine which strategy course is right for you, download our free flowchart .

About the Author

- What Is TAB
- Advisory Boards
- Business Coaching
- StratPro Leadership Transformation Program
- Strategic Leadership Tools
- Our Members
- Case Studies
- White Papers
- Business Diagnostic

The Alternative Board Blog
The difference between a strategic plan and a business plan.

Every business needs a strategic plan. Every business needs a business plan. It’s knowing precisely what each plan entails and when that plan can be of most use that makes the difference between these two essential documents.
Let’s start by defining the purpose behind each type of plan. This can help both budding entrepreneurs and veteran CEOs avoid the mistake of pursuing the wrong kind of plan at the wrong time in the growth cycle of their companies.
The Strategic Plan
As we have noted before, a strategic plan “is a written document that points the way forward for your business.” The focus of a strategic plan can include (but isn’t limited to):
- Expanding business operations
- Reaching into new market segments
- Solving organizational problems
- Potential restructuring a business
By staying focused on your original purpose, goals, and objectives, strategic planning reintroduces you to “the big picture.” It’s the basis for business owners to achieve their vision, which they communicate to stakeholders in a strategic business plan and program.
A strategic plan serves as a roadmap for determining what will likely lie ahead for your business in the next 3-5 years, while also including a series of actions or activities that can turn strategy into operational reality.
Want additional insight? Read 4 Step Guide to Strategic Planning now to learn more

The Business Plan
Generally speaking, a business plan is needed when a company is in its earliest phase of growth. This plan offers a description of how your business will operate, its objectives for growth and financial success, and how it aims to get there. Essentially, it articulates the why behind a business. Key elements include:
- Executive summary and mission statement
- Projected staffing and equipment needs
- Short- and long-term marketing strategy
- Financial statement, including anticipated startup expenses and capitalization
- Outline of management structure and operational processes
A business plan “is a broader, more preliminary document that sets your course when your company may still be nothing more than a twinkle in your eye,” notes BDC of Canada. This plan “not only accurately summarizes what your business is all about, but why it’s a viable proposition.”
Strategic Business Planning
Strategic planning is the systematic process for developing an organization’s direction. This includes pinpointing objectives and actions required to achieve that future vision, and metrics to measure success.
A business plan, as described by the Center for Simplified Strategic Planning, Inc., aims to define “the initial goals and objectives of the company, its structure and processes, products and services, financial resources [and] all of the basics that go into forming a company ” and getting it up and running.
TAB offers its members a different kind of approach— strategic business planning . It’s the basis for business owners to achieve their vision, which they will then communicate to stakeholders in a strategic business plan and program.
Action steps embodied in a strategic business plan include:
- Understanding your business. Assess where your business is today. Review core business information and revisit your vision, mission statement, and core values.
- Analyzing your strengths, weaknesses, and threats. Conduct a SWOT analysis to evaluate where your business is operating at peak efficiency and where organizational weaknesses (and threats from competitors) might stunt future growth.
- Defining objectives and set goals. Drill down into specific objectives that will help you achieve your vision—everything from developing new marketing strategies and launching a new product to re-allocating key financial resources.
- Putting the plan in action . Take action steps to translate the plan from paper to reality. Break tasks down into small steps, assign a responsible party to be accountable for each task, and establish a schedule for reviewing your overall plan on a regular basis.
As we enter into a new year, strategic business planning is more urgently needed than ever before. Want to learn more? Register for our free TAB white paper, “4 Step Guide to Strategic Planning.”

Read our 19 Reasons You Need a Business Owner Advisory Board

Written by The Alternative Board
Related posts, unlearning conformity: how to overhaul old business paradigms, top 3 strategic musts for the coming year, 5 “must-have” elements of a strategic plan, what does the future of remote work look like, tips on future-proofing your business, what can predictive analytics do for your business, subscribe to our blog.
- Sales and marketing (140)
- Strategic Planning (135)
- Business operations (128)
- People management (69)
- Time Management (52)
- tabboards (39)
- Technology (38)
- Customer Service (37)
- Entrepreneurship (35)
- company culture (25)
- Business Coaching and Peer Boards (24)
- Money management (24)
- Work life balance (22)
- employee retention (22)
- businessleadership (20)
- Family business (17)
- leadership (15)
- business strategy (12)
- human resources (12)
- employment (11)
- employee engagement (10)
- communication (9)
- productivity (7)
- adaptability (6)
- businesscoaching (6)
- cybersecurity (6)
- professional development (6)
- salesstrategy (6)
- strategic planning (6)
- strategy (6)
- businessethics (5)
- innovation (5)
- leadership styles (5)
- marketing (5)
- peeradvisoryboards (5)
- remote teams (5)
- branding (4)
- hiring practices (4)
- socialmedia (4)
- supplychain (4)
- Mentorship (3)
- business vision (3)
- collaboration (3)
- culture (3)
- employeedevelopment (3)
- environment (3)
- future proof (3)
- newnormal (3)
- remote work (3)
- sustainability (3)
- work from home (3)
- worklifebalance (3)
- workplacewellness (3)
- Planning (2)
- ecofriendly (2)
- globalization (2)
- recession management (2)
- salescycle (2)
- salesprocess (2)
- #contentisking (1)
- #customerloyalty (1)
- accountability partners (1)
- artificial intelligence (1)
- blindspots (1)
- building trust (1)
- business owner (1)
- businesstrends (1)
- customer appreciation (1)
- customerengagement (1)
- data analysis (1)
- digitalpersona (1)
- financials (1)
- globaleconomy (1)
- greenmarketing (1)
- greenwashing (1)
- onlinepresence (1)
- post-covid (1)
- risk management (1)
- riskassessment (1)
- social media (1)
- talent optimization (1)
- transparency (1)

Do you want additional insight?
Download our 19 Reasons Why You Need a Business Advisory Board Now!

TAB helps forward-thinking business owners grow their businesses, increase profitability and improve their lives by leveraging local business advisory boards, private business coaching and proprietary strategic services.
Quick Links
- Find a Local Board
- My TAB Login
keep in touch
- Privacy Policy
- Terms & Conditions
Our content is reader-supported. Things you buy through links on our site may earn us a commission
Join our newsletter
Never miss out on well-researched articles in your field of interest with our weekly newsletter.
- Project Management
- Starting a business
Get the latest Business News
Business plans vs. strategic plans.

What sets a business plan apart is its singular focus on market and operational feasibility. In contrast, a strategic plan clarifies the long term direction of the organization; most business plans look at a shorter period of time, typically 2-3 years, and drills down thoroughly how the work will get done and dollars will be earned.
Business plans typically take more resources, both internal and often external (in the form of consulting assistance) to develop the kinds of operational and financial analysis necessary to fully test the feasibility of business venture or an organization as a whole.
It gets down to specifics about who the customers will be, what they will pay (with research backing that up), what marketing will be needed to reach them, who the competition will be, and how the finances will work out, in detail.
The feasibility part of the business plans means that it’s entirely possible that the idea you seek to develop is not feasible, at least not with your current set of assumptions.
While strategic plans in theory have that escape clause also, rarely is it used. Finally, a credible business plan has to include who (the skilled managers) who will carry it out. It’s not a business plan if it doesn’t include the people who will implement it.
The above is a graphic from our colleagues at Social Impact Architects laying out some of these differences for the social sector.
- Copyright © 2014 Rolfe Larson Associates
- Social Impact App , find social enterprises nearby and online
- Venture Forth! endorsed by Paul Newman of Newman’s Own
Rolfe Larson

Resources for Starting a Business
Legal Structures of Organizations Legal Forms and Traditional Structures of Organizations Market Research — Inbound Marketing Planning Your Research Market Research Find and Feed the Feeling Strategizing Understanding Strategy and Strategic Thinking Competitor Analysis Porter’s Five Competitive Forces (Part I) Porter’s Five Competitive Forces (Part 2) Competitive Intelligence Product Planning Product Management E-Commerce Sales and …

Ultimate Business Planning Guide with Updated Resources
Complete Business Planning Guide with Extensive Resources Copyright Carter McNamara, MBA, PhD. NOTE: Your business plan should be highly customized to your current organizational situation. Thus, using a generic business plan template could completely misrepresent the needed focus of your business plan. (This step-by-step manual is a complement to the topic How to Start Your …

Learn Strategic Thinking from Napoleon
Biographers of Napoleon Bonaparte talk about his ability to size up a situation with a single coup d’oeil,(pronounced koo-DOY), meaning “a stroke of the eye” or “glance.” Napoleon was so knowledgeable about his strategic situation—the landscape, the enemy, available technology, similar situations from the past—that he could understand and respond quickly to ever- changing circumstances. …

Strategic Planning Facilitator: Guiding the Planning Process
Strategic Planning: The Crucial Role of a Facilitator The goal of strategic planning should be to produce a Plan that is 1) relevant, realistic, and flexible; 2) with a very high likelihood of being implemented; 3) in order to achieve the purpose of the planning, e.g., a purpose to evolve to the next stage of …

Mistakes Made by Strategic Planning Facilitators
Here’s a list of the biggest mistakes that I have seen made by strategic planning facilitators over the years: 1. Not getting sufficiently trained on how to do facilitating, e.g., planning the meeting, goals, ground rules, which techniques to cultivate complete participation, doing interventions, managing conflict 2. Not learning a variety of strategic planning models, …

Strategic Thinking in the Age of LinkedIn
LinkedIn founder and triple billionaire Reid Hoffman has two endearing mannerisms that reveal the way he sees–and reasons with–the strategic environment. First, he peppers his statements with the word so. Almost a verbal tic that would grate on a speaking coach like the overuse of the dreaded uh … but he uses it more like …
Avoid the Silicon Valley Syndrome!
Guest blog from my colleague, Adam Brock, Director of Social Enterprise at Joining Vision and Action (formerly JVA Consulting): How can a well-meaning startup avoid “Silicon Valley Syndrome” and actually use a social startup to create real value for society? Every era has an industry that epitomizes its values. At the turn of the 20th …

Develop Your Strategic Intuition
The best decision-makers in chaotic “fog of war” conditions seem able to call on intuition – knowing what to do without knowing why or how they know.

Free Online Program to Learn Strategic Planning Facilitation

Moneyball: The Role of the Chief Strategy Officer
Paul DePodesta – role of the Chief Strategy Officer for the Cleveland BrownsPaul DePodesta was recently named the Chief Strategy Officer by the Cleveland Browns of the National Football League. This is significant because, as any fan of Moneyball knows, Mr. DePodesta has spent his career in the sport of baseball, not football. This matters …

50 Tips and Tools for Effective Strategic Thinking Skills
To engage in strategic thought, you must think and reflect on the big picture—on the diverse players and forces in your competitive environment. Anticipate the future. Use your right brain for intuition and wisdom, and your left for planning. As Isaac Newton said, “Truth is the offspring of silence and meditation.” Here are 50 tips …

To Learn Strategy, Know History
When you are faced with the most important and strategic decision of your life, where can you go for wisdom? Can you find insight in a book of history? Facing a world in crisis, John F. Kennedy did just that. Generally, we learn skills by trying something, failing, and trying again until we get it …

Execution Trumps Strategy
The results are in – Execution trumps strategy. Your business plan may have great strategies, but it will be a great failure if executed poorly. So just hire the right people, right? Turns out the answer is not what you think. At least according to a recent Harvard Business Review Article. Five Myths About Effective …

Is Balance Possible?
Now here’s a frank perspective: Balance doesn’t work. So don’t even try. Accept the fact that the only way to really make something happen is to go “full out” at it, with everything you have.

B Corp As A Competitive Edge?
Last week, I attended a celebration for B corps in Colorado. These are for-profit companies certified by a nonprofit called B Lab for achieving social and environmental goals along with business ones. What I noticed differently from other discussions among B Corps in the past, was a stronger focus not only on this vibrant community …
Privacy Overview

Business Plan Development
Masterplans experts will help you create business plans for investor funding, bank/SBA lending and strategic direction
Investor Materials
A professionally designed pitch deck, lean plan, and cash burn overview will assist you in securing Pre-Seed and Seed Round funding
Immigration Business Plans
A USCIS-compliant business plan serves as the foundation for your E-2, L-1A, EB-5 or E-2 visa application
Customized consulting tailored to your startup's unique challenges and goals
Our team-based approach supports your project with personal communication and technical expertise.
Pricing that is competitive and scalable for early-stage business services regardless of industry or stage.
Client testimonials from just a few of the 18,000+ entrepreneurs we've worked with over the last 20 years
Free tools, research, and templates to help with business plans & pitch decks
Understanding The Distinction Between a Business Plan & Business Planning
In the dynamic world of entrepreneurship, our choice of words matters. Our vocabulary can often become a veritable alphabet soup of jargon, acronyms, and those buzzwords (I'm looking at you, "disrupt").
And let's not get started on business cliches – "circle back," "synergy," “deep-dive,” etc.
Yet sometimes, it's worth pausing to consider the words we casually sprinkle around in our business conversations. In a previous article, we explored the differences between strategic and tactical business planning , two related but distinct approaches to guiding a business. Now, we're going to delve into another pair of terms that often get used interchangeably but have unique implications: "business plan" (the noun) and "business planning" (the verb).
The business plan, a noun, is a tactical document. It's typically created for a specific purpose, such as securing a Small Business Administration (SBA) loan . Think of it as a road map – it outlines the route and the destination (in this case, the coveted bank loan). But once you've reached your tactical goal (in this case, getting the loan), it often gets shoved in the glove compartment, forgotten as part of the organization's action plan until the next road trip (i.e., additional funding ).
Business planning is not a static concept, but rather a dynamic verb. It's an ongoing process that necessitates continual adjustments. It's about creating a holistic, interconnected value-creating strategic plan that benefits all stakeholders. This includes attracting top-tier employees, ensuring a return on lending or investment, and making a positive impact on the community, whether online or in real life.
That being said, the customer remains at the heart of this process. Without customers, there are no sales, no revenue, and no value. Everything else is contingent on this key element.
If we were to compare the business plan to a map, then business planning would be the journey. It's a continuous process of making strategic decisions, adapting to new paths, and steering the business towards its goals. Sometimes, it even involves redefining objectives midway.
So, let's do a "deep-dive" (I couldn't resist) into these two terms, examining their application in the real world. Along the way, we'll uncover some tools that can aid us in the ever-evolving process of strategic business planning and the more finite task of crafting a winning business plan.
The Business Plan is a Document
Alright, let's take a closer look at a phrase we've all tossed around: the business plan. Imagine it as the detailed blueprint of your organization's goals, strategies, and tactics. It's like the North Star for your entrepreneurial ship, shedding light on the key questions: what, why, how, and when (speaking of questions, here are some FAQs about the business plan ).
Writing a solid business plan isn't easy , especially if you're just dipping your toes into the world of business planning. But don’t worry; we'll get to that (eventually).
So, let's break it down. What does a business plan document consist of, exactly?
- Executive Summary: Just as it sounds, this is a quick overview of the nitty-gritty that's in the rest of your business plan. It's the introduction to your organization, highlighting your mission statement and serving up the essential details like ownership, location, and structure.
- Company Overview: This is where you will detail your products and/or services, their pricing, and the operational plan. If you're opening a restaurant, this section is where you present your menu, and it's also where you talk about your ingredient sourcing, the type of service you'll provide, and the ambiance you're aiming for.
- Market Analysis Summary: This section demands a comprehensive analysis of your industry, target market, competitors, and your unique selling proposition. Without access to top-notch (and often not free) research tools, it can be challenging to find current industry data. Check out our guide on the best market research tools to get started.
- Strategy and Implementation Summary: Here, you'll lay out your short-term and long-term objectives along with the strategies you'll implement to attract and retain customers. This is where you’ll talk about all the different marketing and sales strategies you'll use to charm your future customers.
- Management Summary: This is your chance to spotlight your company's key personnel. Detail the profiles of your key leaders, their roles, and why they're perfect for it. Don't shy away from acknowledging talent gaps that need to be filled, and do share how you plan to fill them!
- Pro Forma Financials: This is where you get down to the dollars and cents with a detailed five-year revenue forecast along with crucial financial statements like the balance sheet and the profit & loss statement.
A business plan is an essential instrument, not just for securing funding, but also for communicating long-term goals and objectives to key stakeholders. But, while a business plan is essential for many circumstances, it's important to understand its scope and limitations. It's a tactical tool, an important one, but it's not the be-all and end-all of business strategy. Which brings us to our next point of discussion: business planning.
Business Planning is a Process
If we view the business plan as a blueprint, then business planning is the architect. But let's be clear: we're not building just any old house here. We're building the Winchester Mystery House of business. Just as the infamous Winchester House was constantly under construction , with new rooms being added and old ones revamped, so too is your business in a state of perpetual evolution. It's a dynamic, ongoing process, not a one-and-done event.
In the realm of business planning, we're always adding 'rooms' and 'corridors' – new products, services, and market strategies – to our 'house'. And just as Sarah Winchester reputedly consulted spirits in her Séance Room to guide her construction decisions, we consult our customers, market data, and strategic insights to guide our strategy. We're in a constant state of assessing, evolving, executing, and improving.
Business planning touches all corners of your venture. It includes areas such as product development, market research, and strategic management. It's not about predicting the future with absolute certainty – we’re planners, not fortune tellers. It's about setting a course and making calculated decisions, preparing to pivot when circumstances demand it (think global pandemics).
Business planning is not a 'set it and forget it' endeavor. It's akin to being your company's personal fitness coach, nudging it to continually strive for better. Much like physical fitness, if you stop the maintenance, you risk losing your hard-earned progress.
Business Planning Case Study: Solo Stove
Now that summer is here, my Solo Stove stands as a tangible testament to effective business planning.
For those unfamiliar, Solo Stove started with a simple yet innovative product – a smoke-limiting outdoor fire pit that garnered over $1.1 million on Kickstarter in 2016, far exceeding its original objective. Since then, it has expanded its portfolio with products tailored to outdoor enthusiasts. From flame screens and fire tools to color-changing flame additives, each product is designed to fit seamlessly into modern outdoor spaces, exuding a rugged elegance that resonates with their target audience.
This strategic product development, a cornerstone of business planning, has allowed Solo Stove to evolve from a product to a lifestyle brand. By continually listening to their customers, probing their desires and needs, and innovating to meet those needs, they've built a brand that extends beyond the products they sell.
Their strategy also includes a primary "Direct To Consumer" (DTC) revenue model, executed via their e-commerce website. This model, while challenging due to increased customer acquisition costs, offers significant benefits, including higher margins since revenue isn’t split with a retailer or distributor, and direct interaction with the customer.
Through its primary business model, Solo Stove has amassed an email database of over 3.4 million customers . This competitive advantage allows for ongoing evaluation of customer needs, driving product innovation and improvement, and enabling effective marketing that strengthens their mission. The success of this approach is evident in the company's growth: from 2018 to 2020, Solo Stove’s revenue grew from $16 million to $130 million , a 185% CAGR.
While 85% of their revenue comes from online DTC channels, Solo Stove has also enhanced their strategic objectives by partnering with select retailers that align with their reputation, demographic, and commitment to showcasing Solo Brands’ product portfolio and providing superior customer service.
Solo Stove's success underscores how comprehensive business planning fosters regular assessment, constant evolution, and continual improvement. It's more than setting goals – it's about ceaselessly uncovering ways to deliver value to your customers and grow your business.
However, even successful businesses like Solo Stove can explore additional strategic initiatives for growth and diversification, aligning with their strategic direction and operational planning. For instance, a subscription model could provide regular deliveries of products or a service warranty, creating a consistent revenue stream and increasing customer loyalty. Alternatively, a B2B model could involve partnerships with adventure tourism operators, who could purchase Solo Stove products in bulk.
These complementary business models, when integrated into the operational plan, could support the primary DTC model by driving customer acquisition, providing ongoing revenue streams and expanding the customer base. This strategic direction ensures that Solo Stove continues to thrive in a competitive market.
The Interplay between the Business Plan (Noun) and Business Planning (Verb)
In the realm of business strategy, there's an intriguing chicken-and-egg conundrum: which comes first, the business plan or business planning? The answer is both straightforward and complex: they're two sides of the same coin, each indispensable in its own right and yet inextricably linked.
The process of business planning informs and modifies the business plan, just as the business plan provides a strategic foundation for the planning process. This interplay embodies the concept of Model-Based Planning™, where the business model serves as a guide, yet remains flexible to the insights and adaptations borne out of proactive business planning.
Let's revisit the Solo Stove story to elucidate this concept. Their business model, primarily direct-to-consumer, laid the groundwork for their strategy. Yet, it was through continuous business planning – the assessment of customer feedback, market trends, and sales performance – that they were able to refine their model, expand their product portfolio, and enhance their growth objectives. Their business plan wasn't a static document but a living entity, evolving through the insights gleaned from ongoing business planning.
So, how can you harness the power of both the tactical business plan and strategic business planning in your organization? Here are a few guiding principles:
- Embrace Model-Based Planning™: Start with a robust business model that outlines your strategic plan. But remember, this isn't set in stone—it's a guiding framework that will evolve over time as you gain insights from your strategic planning process.
- Make business planning a routine: Regularly review and update your business plan based on your findings from market research, customer feedback, and internal assessments. Use it as a living document that grows and adapts with your business.
- Foster open communication: Keep all stakeholders informed about updates to your business plan and the insights that informed these changes. This promotes alignment and ensures everyone is working towards the same goals.
- Be agile and adaptable: A key part of business planning is being ready to pivot when necessary . Whether it's a global pandemic or a shift in consumer preferences, your ability to respond swiftly and strategically to changing circumstances is crucial for long-term success.
Fanning the Flames: From Planning to Plan
The sparks truly ignite when you understand the symbiotic relationship between tactical business plans, strategic business planning, and the achievement of strategic goals. Crafting a tactical business plan (the noun) requires initial planning (the verb), but then you need to embark on continuous strategic planning (the verb) to review, refine, and realign your strategic business plan (the noun). It's a rhythm of planning, execution, review, and adjustment, all guided by key performance indicators.
Business planning, therefore, isn't a one-off event, but rather an active, ongoing process. A business plan needs constant nurturing and adjustment to stay relevant and guide your organization's path to success. This understanding frames your business plan not as a static document, but as a living, breathing entity, evolving with each step your business takes and each shift in the business landscape. It's a strategic roadmap, continually updated to reflect your organization's objectives and the ever-changing business environment.

How to Write a Management Summary for Your Business Plan
Entrepreneurs are often celebrated for their uncanny ability to understand others – their customers, the market, and the ever-evolving global...

Understanding Venture Debt vs Venture Capital
Despite growth in sectors like artificial intelligence, venture capital funding has seen better days. After peaking at $347.5 billion in 2021, there...

Going Beyond Writing: The Multifaceted Role of Business Plan Consultants
Most people think of a professional business plan company primarily as a "business plan writer." However, here at Masterplans, we choose to approach...

- Certifications
- Associate Business Strategy Professional
- Senior Business Strategy Professional
- Examination
- Partnership
- For Academic Affiliation
- For Training Companies
- For Corporates
- Help Center
- Associate Business Strategy Professional (ABSP™)
- Senior Business Strategy Professional (SBSP™)
- Certification Process
- TSI Certification Examination
- Get your Institution TSI Affiliated
- Become a Corporate Education Partner
- Become a Strategy Educator
- Frequently Asked Questions
What is Business Strategy? Definition, Importance, Levels, and Examples

Business strategy is the battle plan for a better future. - Patrick Dixon
Scaling up a business without a clear strategy is like captaining a ship without a rudder. The success of any business depends on the strategy that one follows. The business strategy establishes the needs of the business. Business strategy plays an important role for businesses of all sizes and entrepreneurs. It sets the direction of the organization and helps to create goals to aim towards.
What is Business Strategy?
Business strategy is defined as the course of action or set of decisions that support entrepreneurs in achieving certain business goals. It is a master plan that outlines the direction the organization intends to make, the actions it will undertake, and the resources it will give to attain certain competitive benefits and drive sustainable growth. It involves a combination of decisions, actions, and resource allocation that positions an organization in its industry or market.
Why is a Business Strategy important?
Business Strategy plays a crucial role in guiding a firm’s growth, competitiveness, and success. It offers a roadmap for decision-making, resource providing, and adaptation to transforming circumstances, ensuring that the firm stays agile, focused, and well-prepared to achieve its goals successfully. It is carefully planned and flexibly designed with the purpose of:
- Achieving effectiveness
- Perceiving and utilizing opportunities
- Mobilizing resources
- Securing an advantageous position
- Meeting the challenges and threats
- Directing efforts, behavior and
- Gaining command over the situation
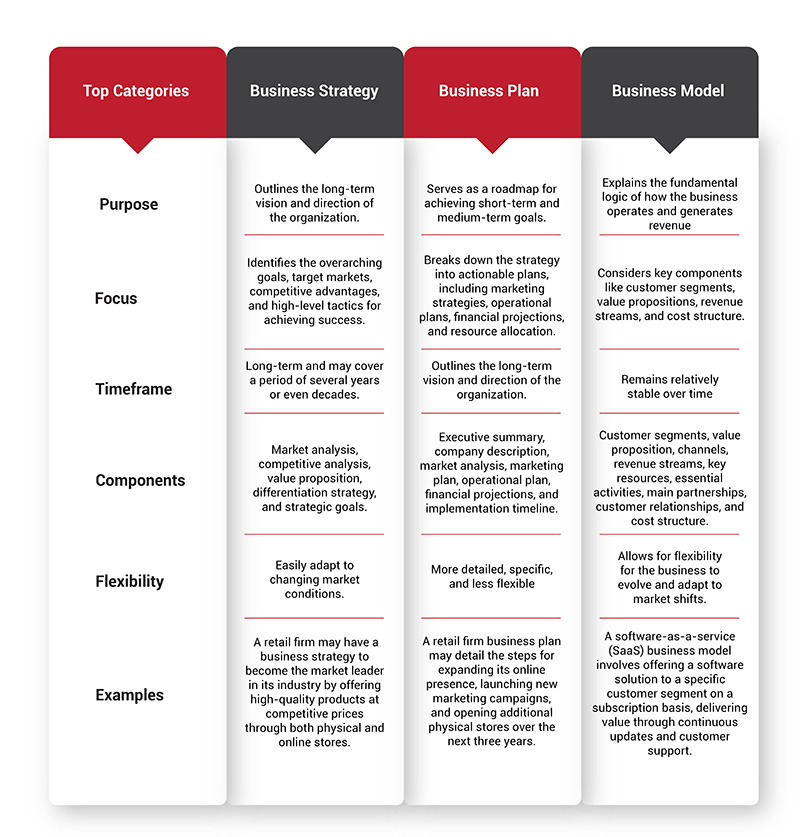
What is the Difference between Business Strategy & Business Plan & Business Model
Business Strategy, Business Plan, and Business Model are three distinct elements that offer various purposes in the world of business. They are vital for the success and sustainability of a business, and they are interconnected, with slight changes which are often confused by several aspiring business strategists , especially during their interviews. Here's a breakdown of the important differences between these:
Levels of Business Strategy
Effective strategic management consists of coordination and alignment across various levels of strategy to achieve the organization's long-term goals and competitive advantage. Business strategy can be categorized into different levels depending on its scope, focus, and the organizational hierarchy at which it functions.
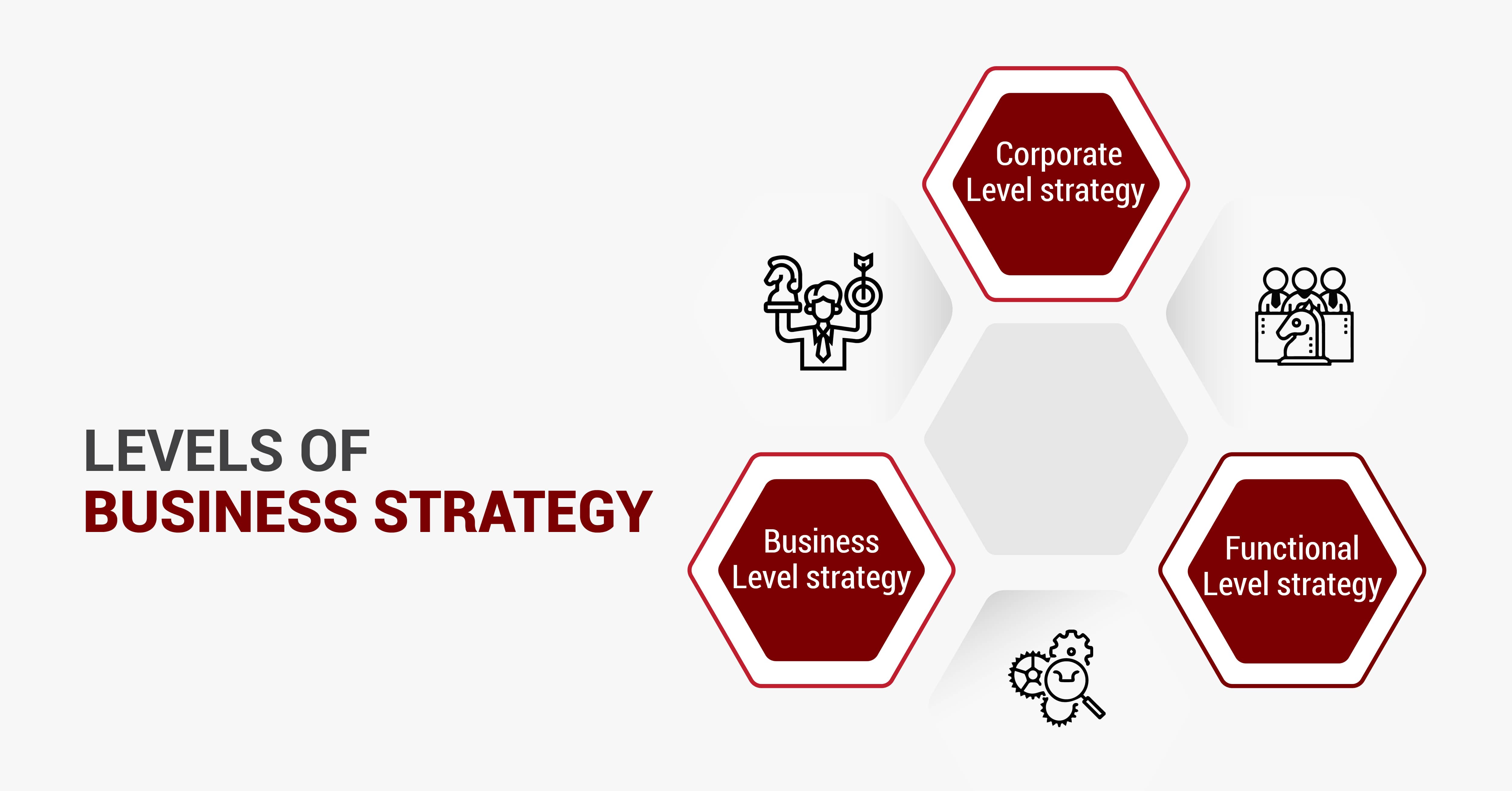
The three primary levels of business strategy are:
- Corporate level strategy Corporate level strategy is a long-range, action-oriented, integrated, and comprehensive plan, which is formulated by the top management of a company. It is very helpful to ascertain business lines, expansion, growth, takeovers and mergers, diversification , integration, and the latest fields for investment.
- Business level strategy The strategies that relate to a specific business are known as business-level strategies. It is developed by the general managers, who convert mission and vision into concrete, clear, and result-driven strategies. It acts like a blueprint for the total business.
- Functional level strategy Developed by the first-line managers or supervisors, the functional level strategy involves decision-making at the operational level concerning functional areas such as marketing, production, human resources, research and development, finance, and so on.
How to Implement a Successful Business Strategy?
A business strategist feels that it is tough to ideate any plan in a few hours. It requires a step-by-step procedure to be associated with completing a SWOT analysis . Here are the top steps that can be considered to build the best business strategies and execute them with precision:
- Understand the targets One of the clearest challenges for growth is poor targeting. Clear target markets offer an organization the ability to create an integrated sales and marketing approach, where marketing enables sales productivity. Sales and marketing business plan gets executed more efficiently if the targets are fixed in a proper way.
- Outline the tactics A successful business strategy is made up of several various tactics, including both online and offline options. The goals, target audience, and industry factor into this decision. For instance, if the target audience is young, focusing on social media is more beneficial as this is primarily where this group consumes content. If the industry is product-based (for instance, jewelry designing), then using a more visual platform would better showcase the products. To be most effective, one must choose which methods are right for the business. Once the selection of tactics is done, list them in the plan and determine how they’ll help to reach the goals.
- Think long term In the scope of constant change, planning the horizons is usually shorter than it can be. However, only thinking quarter to quarter is a trap that may rob organizations of their ability to see around the bend. Best-in-class organizations create processes designed for a series of financial and non-financial metrics to treat strategy as an annual cycle rather than a one-time, static event.
- Create a timeline Time is precious mainly when it is about the business. Based on the goals and objectives one can set for the business. Creating a timeline that will define what tasks can be completed and when they can be completed. It is highly advisable to allocate extra time for unexpected events that may delay some of the goals.
- Focus on growth A thriving organization is a growing organization. It is only through growth that the firms can afford to invest in aspects such as technology, the best staff, and the latest tools. The business strategy should identify the segments where an organization will grow and in what proportion.
- Have a budget plan Creating a budget for the business strategy can inform the efforts by determining what can be done and cannot be. Choosing the most cost-effective options for the business ensures the success of the overall business strategy. This doesn’t have to limit the options. Paid advertising on social media and search engines gives access to manage budgets well.
- Make fact-based decisions Several executives often complain about a lack of fruitful data, but they consistently find information that is useful in the formation of business strategy. The business has a set of values that guides it. Making fact-based decisions will outline the values and ensure that the people who interact with the business are aware of them. It will also ease the message that reflects on the brand honestly so it can actively demonstrate the values outlined in the mission statement through the interactions with clients.
- Invest in pre-work Always allocate time to do proper pre-work so that one can be up to date. It is better to conduct proper end-to-end research and prepare relevant information in advance of the business strategy meetings. The goals and needs will change over time. Ideally, it is important to revisit the business plan every annum to make adjustments as needed. Follow industry news and trends that can add to the existing strategy.
- Execute well and measure results Measuring the effectiveness of the business strategy will inform the current plan and future efforts. Always be sure to track and measure the business so these measurements are effective. Set up a corporate calendar to enhance the productive meetings, and also to form a performance management cycle. One should write the marketing plan with this growth in mind so they can measure it. The execution of strategic planning needs discipline, and it must be taken care of by the senior executives to promote processes that keep the team focused.
Examples of Business Strategy
Hubspot developed and executed a perfect business strategy where it created a market that didn’t even exist – inbound marketing. It created an online resource guide explaining the limitations of interruption marketing and informing about the advantages of inbound marketing. The organizations even offered free courses to help the target audience understand its offering better.
Apple Inc. differentiated its Smartphone operating system iOS by making it simple as compared to Android. This differentiated it and built its followership. The organization has been following a similar business strategy for its other products as well.
Wrapping up
Establishing the business strategy keeps the business goals organized and focused, saving valuable time and money. With the increase in the competition, the demand for business strategy is becoming apparent and there is a tremendous increase in the types of business strategies used by the businesses.

Recent Posts

How Data Analytics Can Revolutionize Your Business - A Strategist's Guide
Download this Strategist's Guide to empower yourself with resourceful insights:
- Roadblocks to Data Usage
- Advantages that Data Analytics offer for businesses
- Elements of a Data Analytics Strategy
- Top reasons why businesses must adopt a Data Analytics Strategy
- Case studies, Scenarios, and more

CredBadge™ is a proprietary, secure, digital badging platform that provides for seamless authentication and verification of credentials across digital media worldwide.
CredBadge™ powered credentials ensure that professionals can showcase and verify their qualifications and credentials across all digital platforms, and at any time, across the planet.


Verify A Credential
Please enter the License Number/Unique Credential Code of the certificant. Results will be displayed if the person holds an active credential from TSI.
Stay Informed!
Keep yourself informed on the latest updates and information about business strategy by subscribing to our newsletter.
Start Your Journey with The Strategy Institute by Creating Your myTSI Account Today.
- Manage your professional profile conveniently.
- Manage your credentials anytime.
- Share your experiences and ideas with The Strategy Institute.
Account Login
- Remember Password
- Forgot Password?
Forgot Password
- Product overview
- All features
- App integrations
CAPABILITIES
- project icon Project management
- Project views
- Custom fields
- Status updates
- goal icon Goals and reporting
- Reporting dashboards
- workflow icon Workflows and automation
- portfolio icon Resource management
- Time tracking
- my-task icon Admin and security
- Admin console
- asana-intelligence icon Asana Intelligence
- list icon Personal
- premium icon Starter
- briefcase icon Advanced
- Goal management
- Organizational planning
- Campaign management
- Creative production
- Content calendars
- Marketing strategic planning
- Resource planning
- Project intake
- Product launches
- Employee onboarding
- View all uses arrow-right icon
- Project plans
- Team goals & objectives
- Team continuity
- Meeting agenda
- View all templates arrow-right icon
- Work management resources Discover best practices, watch webinars, get insights
- What's new Learn about the latest and greatest from Asana
- Customer stories See how the world's best organizations drive work innovation with Asana
- Help Center Get lots of tips, tricks, and advice to get the most from Asana
- Asana Academy Sign up for interactive courses and webinars to learn Asana
- Developers Learn more about building apps on the Asana platform
- Community programs Connect with and learn from Asana customers around the world
- Events Find out about upcoming events near you
- Partners Learn more about our partner programs
- Support Need help? Contact the Asana support team
- Asana for nonprofits Get more information on our nonprofit discount program, and apply.
Featured Reads

- Business strategy |
- What is strategic planning? A 5-step gu ...
What is strategic planning? A 5-step guide

Strategic planning is a process through which business leaders map out their vision for their organization’s growth and how they’re going to get there. In this article, we'll guide you through the strategic planning process, including why it's important, the benefits and best practices, and five steps to get you from beginning to end.
Strategic planning is a process through which business leaders map out their vision for their organization’s growth and how they’re going to get there. The strategic planning process informs your organization’s decisions, growth, and goals.
Strategic planning helps you clearly define your company’s long-term objectives—and maps how your short-term goals and work will help you achieve them. This, in turn, gives you a clear sense of where your organization is going and allows you to ensure your teams are working on projects that make the most impact. Think of it this way—if your goals and objectives are your destination on a map, your strategic plan is your navigation system.
In this article, we walk you through the 5-step strategic planning process and show you how to get started developing your own strategic plan.
How to build an organizational strategy
Get our free ebook and learn how to bridge the gap between mission, strategic goals, and work at your organization.
What is strategic planning?
Strategic planning is a business process that helps you define and share the direction your company will take in the next three to five years. During the strategic planning process, stakeholders review and define the organization’s mission and goals, conduct competitive assessments, and identify company goals and objectives. The product of the planning cycle is a strategic plan, which is shared throughout the company.
What is a strategic plan?
![business plan and business strategy difference [inline illustration] Strategic plan elements (infographic)](https://assets.asana.biz/transform/7d1f14e4-b008-4ea6-9579-5af6236ce367/inline-business-strategy-strategic-planning-1-2x?io=transform:fill,width:2560&format=webp)
A strategic plan is the end result of the strategic planning process. At its most basic, it’s a tool used to define your organization’s goals and what actions you’ll take to achieve them.
Typically, your strategic plan should include:
Your company’s mission statement
Your organizational goals, including your long-term goals and short-term, yearly objectives
Any plan of action, tactics, or approaches you plan to take to meet those goals
What are the benefits of strategic planning?
Strategic planning can help with goal setting and decision-making by allowing you to map out how your company will move toward your organization’s vision and mission statements in the next three to five years. Let’s circle back to our map metaphor. If you think of your company trajectory as a line on a map, a strategic plan can help you better quantify how you’ll get from point A (where you are now) to point B (where you want to be in a few years).
When you create and share a clear strategic plan with your team, you can:
Build a strong organizational culture by clearly defining and aligning on your organization’s mission, vision, and goals.
Align everyone around a shared purpose and ensure all departments and teams are working toward a common objective.
Proactively set objectives to help you get where you want to go and achieve desired outcomes.
Promote a long-term vision for your company rather than focusing primarily on short-term gains.
Ensure resources are allocated around the most high-impact priorities.
Define long-term goals and set shorter-term goals to support them.
Assess your current situation and identify any opportunities—or threats—allowing your organization to mitigate potential risks.
Create a proactive business culture that enables your organization to respond more swiftly to emerging market changes and opportunities.
What are the 5 steps in strategic planning?
The strategic planning process involves a structured methodology that guides the organization from vision to implementation. The strategic planning process starts with assembling a small, dedicated team of key strategic planners—typically five to 10 members—who will form the strategic planning, or management, committee. This team is responsible for gathering crucial information, guiding the development of the plan, and overseeing strategy execution.
Once you’ve established your management committee, you can get to work on the planning process.
Step 1: Assess your current business strategy and business environment
Before you can define where you’re going, you first need to define where you are. Understanding the external environment, including market trends and competitive landscape, is crucial in the initial assessment phase of strategic planning.
To do this, your management committee should collect a variety of information from additional stakeholders, like employees and customers. In particular, plan to gather:
Relevant industry and market data to inform any market opportunities, as well as any potential upcoming threats in the near future.
Customer insights to understand what your customers want from your company—like product improvements or additional services.
Employee feedback that needs to be addressed—whether about the product, business practices, or the day-to-day company culture.
Consider different types of strategic planning tools and analytical techniques to gather this information, such as:
A balanced scorecard to help you evaluate four major elements of a business: learning and growth, business processes, customer satisfaction, and financial performance.
A SWOT analysis to help you assess both current and future potential for the business (you’ll return to this analysis periodically during the strategic planning process).
To fill out each letter in the SWOT acronym, your management committee will answer a series of questions:
What does your organization currently do well?
What separates you from your competitors?
What are your most valuable internal resources?
What tangible assets do you have?
What is your biggest strength?
Weaknesses:
What does your organization do poorly?
What do you currently lack (whether that’s a product, resource, or process)?
What do your competitors do better than you?
What, if any, limitations are holding your organization back?
What processes or products need improvement?
Opportunities:
What opportunities does your organization have?
How can you leverage your unique company strengths?
Are there any trends that you can take advantage of?
How can you capitalize on marketing or press opportunities?
Is there an emerging need for your product or service?
What emerging competitors should you keep an eye on?
Are there any weaknesses that expose your organization to risk?
Have you or could you experience negative press that could reduce market share?
Is there a chance of changing customer attitudes towards your company?
Step 2: Identify your company’s goals and objectives
To begin strategy development, take into account your current position, which is where you are now. Then, draw inspiration from your vision, mission, and current position to identify and define your goals—these are your final destination.
To develop your strategy, you’re essentially pulling out your compass and asking, “Where are we going next?” “What’s the ideal future state of this company?” This can help you figure out which path you need to take to get there.
During this phase of the planning process, take inspiration from important company documents, such as:
Your mission statement, to understand how you can continue moving towards your organization’s core purpose.
Your vision statement, to clarify how your strategic plan fits into your long-term vision.
Your company values, to guide you towards what matters most towards your company.
Your competitive advantages, to understand what unique benefit you offer to the market.
Your long-term goals, to track where you want to be in five or 10 years.
Your financial forecast and projection, to understand where you expect your financials to be in the next three years, what your expected cash flow is, and what new opportunities you will likely be able to invest in.
Step 3: Develop your strategic plan and determine performance metrics
Now that you understand where you are and where you want to go, it’s time to put pen to paper. Take your current business position and strategy into account, as well as your organization’s goals and objectives, and build out a strategic plan for the next three to five years. Keep in mind that even though you’re creating a long-term plan, parts of your plan should be created or revisited as the quarters and years go on.
As you build your strategic plan, you should define:
Company priorities for the next three to five years, based on your SWOT analysis and strategy.
Yearly objectives for the first year. You don’t need to define your objectives for every year of the strategic plan. As the years go on, create new yearly objectives that connect back to your overall strategic goals .
Related key results and KPIs. Some of these should be set by the management committee, and some should be set by specific teams that are closer to the work. Make sure your key results and KPIs are measurable and actionable. These KPIs will help you track progress and ensure you’re moving in the right direction.
Budget for the next year or few years. This should be based on your financial forecast as well as your direction. Do you need to spend aggressively to develop your product? Build your team? Make a dent with marketing? Clarify your most important initiatives and how you’ll budget for those.
A high-level project roadmap . A project roadmap is a tool in project management that helps you visualize the timeline of a complex initiative, but you can also create a very high-level project roadmap for your strategic plan. Outline what you expect to be working on in certain quarters or years to make the plan more actionable and understandable.
Step 4: Implement and share your plan
Now it’s time to put your plan into action. Strategy implementation involves clear communication across your entire organization to make sure everyone knows their responsibilities and how to measure the plan’s success.
Make sure your team (especially senior leadership) has access to the strategic plan, so they can understand how their work contributes to company priorities and the overall strategy map. We recommend sharing your plan in the same tool you use to manage and track work, so you can more easily connect high-level objectives to daily work. If you don’t already, consider using a work management platform .
A few tips to make sure your plan will be executed without a hitch:
Communicate clearly to your entire organization throughout the implementation process, to ensure all team members understand the strategic plan and how to implement it effectively.
Define what “success” looks like by mapping your strategic plan to key performance indicators.
Ensure that the actions outlined in the strategic plan are integrated into the daily operations of the organization, so that every team member's daily activities are aligned with the broader strategic objectives.
Utilize tools and software—like a work management platform—that can aid in implementing and tracking the progress of your plan.
Regularly monitor and share the progress of the strategic plan with the entire organization, to keep everyone informed and reinforce the importance of the plan.
Establish regular check-ins to monitor the progress of your strategic plan and make adjustments as needed.
Step 5: Revise and restructure as needed
Once you’ve created and implemented your new strategic framework, the final step of the planning process is to monitor and manage your plan.
Remember, your strategic plan isn’t set in stone. You’ll need to revisit and update the plan if your company changes directions or makes new investments. As new market opportunities and threats come up, you’ll likely want to tweak your strategic plan. Make sure to review your plan regularly—meaning quarterly and annually—to ensure it’s still aligned with your organization’s vision and goals.
Keep in mind that your plan won’t last forever, even if you do update it frequently. A successful strategic plan evolves with your company’s long-term goals. When you’ve achieved most of your strategic goals, or if your strategy has evolved significantly since you first made your plan, it might be time to create a new one.
Build a smarter strategic plan with a work management platform
To turn your company strategy into a plan—and ultimately, impact—make sure you’re proactively connecting company objectives to daily work. When you can clarify this connection, you’re giving your team members the context they need to get their best work done.
A work management platform plays a pivotal role in this process. It acts as a central hub for your strategic plan, ensuring that every task and project is directly tied to your broader company goals. This alignment is crucial for visibility and coordination, allowing team members to see how their individual efforts contribute to the company’s success.
By leveraging such a platform, you not only streamline workflow and enhance team productivity but also align every action with your strategic objectives—allowing teams to drive greater impact and helping your company move toward goals more effectively.
Strategic planning FAQs
Still have questions about strategic planning? We have answers.
Why do I need a strategic plan?
A strategic plan is one of many tools you can use to plan and hit your goals. It helps map out strategic objectives and growth metrics that will help your company be successful.
When should I create a strategic plan?
You should aim to create a strategic plan every three to five years, depending on your organization’s growth speed.
Since the point of a strategic plan is to map out your long-term goals and how you’ll get there, you should create a strategic plan when you’ve met most or all of them. You should also create a strategic plan any time you’re going to make a large pivot in your organization’s mission or enter new markets.
What is a strategic planning template?
A strategic planning template is a tool organizations can use to map out their strategic plan and track progress. Typically, a strategic planning template houses all the components needed to build out a strategic plan, including your company’s vision and mission statements, information from any competitive analyses or SWOT assessments, and relevant KPIs.
What’s the difference between a strategic plan vs. business plan?
A business plan can help you document your strategy as you’re getting started so every team member is on the same page about your core business priorities and goals. This tool can help you document and share your strategy with key investors or stakeholders as you get your business up and running.
You should create a business plan when you’re:
Just starting your business
Significantly restructuring your business
If your business is already established, you should create a strategic plan instead of a business plan. Even if you’re working at a relatively young company, your strategic plan can build on your business plan to help you move in the right direction. During the strategic planning process, you’ll draw from a lot of the fundamental business elements you built early on to establish your strategy for the next three to five years.
What’s the difference between a strategic plan vs. mission and vision statements?
Your strategic plan, mission statement, and vision statements are all closely connected. In fact, during the strategic planning process, you will take inspiration from your mission and vision statements in order to build out your strategic plan.
Simply put:
A mission statement summarizes your company’s purpose.
A vision statement broadly explains how you’ll reach your company’s purpose.
A strategic plan pulls in inspiration from your mission and vision statements and outlines what actions you’re going to take to move in the right direction.
For example, if your company produces pet safety equipment, here’s how your mission statement, vision statement, and strategic plan might shake out:
Mission statement: “To ensure the safety of the world’s animals.”
Vision statement: “To create pet safety and tracking products that are effortless to use.”
Your strategic plan would outline the steps you’re going to take in the next few years to bring your company closer to your mission and vision. For example, you develop a new pet tracking smart collar or improve the microchipping experience for pet owners.
What’s the difference between a strategic plan vs. company objectives?
Company objectives are broad goals. You should set these on a yearly or quarterly basis (if your organization moves quickly). These objectives give your team a clear sense of what you intend to accomplish for a set period of time.
Your strategic plan is more forward-thinking than your company goals, and it should cover more than one year of work. Think of it this way: your company objectives will move the needle towards your overall strategy—but your strategic plan should be bigger than company objectives because it spans multiple years.
What’s the difference between a strategic plan vs. a business case?
A business case is a document to help you pitch a significant investment or initiative for your company. When you create a business case, you’re outlining why this investment is a good idea, and how this large-scale project will positively impact the business.
You might end up building business cases for things on your strategic plan’s roadmap—but your strategic plan should be bigger than that. This tool should encompass multiple years of your roadmap, across your entire company—not just one initiative.
What’s the difference between a strategic plan vs. a project plan?
A strategic plan is a company-wide, multi-year plan of what you want to accomplish in the next three to five years and how you plan to accomplish that. A project plan, on the other hand, outlines how you’re going to accomplish a specific project. This project could be one of many initiatives that contribute to a specific company objective which, in turn, is one of many objectives that contribute to your strategic plan.
What’s the difference between strategic management vs. strategic planning?
A strategic plan is a tool to define where your organization wants to go and what actions you need to take to achieve those goals. Strategic planning is the process of creating a plan in order to hit your strategic objectives.
Strategic management includes the strategic planning process, but also goes beyond it. In addition to planning how you will achieve your big-picture goals, strategic management also helps you organize your resources and figure out the best action plans for success.
Related resources
What is management by objectives (MBO)?

Write better AI prompts: A 4-sentence framework

How to find alignment on AI

What is content marketing? A complete guide

- Strategic Planning →
What is the Difference Between a Business Plan and a Strategic Plan?

Strategic Planning Expert
By M. Dana Baldwin, Senior Consultant
We often get questions asking what the difference is between a Business Plan and a Strategic Plan. The first difference is there is a significant difference in intent. A Strategic Plan is focused on improving a company’s performance, exploiting opportunities and building market share. A Business Plan is most often used at the beginning of a company’s existence to define the initial goals and objectives of the company, its structure and processes, products and services, financial resources, staffing/talent needs and all of the basics which go into forming a company and getting it functioning.
Elements of this plan usually include:
1. What products and services the company will offer to the marketplace.
2. What types of customers the company will target
3. What skills and capabilities the company will need to compete effectively and where the company will obtain those skills and capabilities
4. Determining trends in the marketplace, and the characteristics of the market segments the company will initially pursue
5. Developing how you will sell into the market segments you are intending to pursue. What demographics will you target? What are their buying behaviors? How will competition likely react to your company entering these markets?
6. What will your costs be in each of the parts of the company? How will you fund them during the start up phase? What are your first and second year projections for revenues and expenses? How will you make a profit?
Usually a business plan is an overall guide to setting up your business, although some will use it as a more detailed one year plan based on the Strategic Plan. Often there is considerable overlap between the two plans inasmuch as they will often cover similar ground. Generally, however, we envision a business plan as the blueprint for setting up your company and getting it started, and a strategic plan as the ongoing game plan to continually improve market share, volume and profitability.
The intent of a strategic plan is to develop a much more targeted vision of where you want to take your business in the future and how you will accomplish your strategies, goals and objectives, once the business is established and ongoing. Strategic planning is the 30,000 foot view of where we take the company. In your strategic planning, your focus turns more toward looking at the current situation, analyzing what your strengths and weaknesses are, determining how best to build on your strengths and avoid being trapped by your weaknesses.
You will look for your strategic competency, which we define as a sustainable competitive advantage built on the skills, processes and knowledge contained within your company.
By building on your strategic competency, making it better and even more effective as a sustainable competitive advantage, you will improve the opportunities to excel as a company, gaining market share and profitability.
All of the elements of strategic planning, starting with your current situation, working through the analyses of your company, your markets, competition, opportunities and finding out where you may have gaps between your current performance and where you should be in the future, lead to the development of logical, attainable (yet ambitious) strategies which will head you toward winning a higher market share and better profits.
M. Dana Baldwin is a Senior Consultant with Center for Simplified Strategic Planning, Inc. and can be reached at [email protected] .
© Copyright 2009 by Center for Simplified Strategic Planning, Inc., Ann Arbor, MI — Reprint permission granted with full attribution
Never Miss Another Post...
Join our update list today!
Example: Yes, I would like to receive emails from Center for Simplified Strategic Planning. (You can unsubscribe anytime)
- Competitive Strategy
- Making predictions
- Other Strategy
- Scenario planning
- Strategic Planning
- Strategic Planning during the COVID-19 pandemic
- Strategic Thinking
- Strategy Implementation
- Succession Planning
- Uncategorized
Recent Posts
- Does your culture help your bottom line?
- What people get wrong in strategic planning – part 3: data sources and estimates
- What people get wrong in strategic planning, part 2 – buy-in
- What people get wrong in strategic planning – Information
- Making your strategic planning practical – how much time should I spend?
Discover more from Center for Simplified Strategic Planning
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Type your email…
Continue reading
Business Plan vs Business Model Canvas Explained

6 min. read
Updated May 10, 2024
It might be stating the obvious, but planning and preparation are keys to success in business.
After all, entrepreneurs put in hard work to develop their product, understand the market they plan to serve, assess their competitive landscape and funding needs, and much more.
Successful business owners also take time to document their strategies for guiding the growth of their companies. They use these strategies to take advantage of new opportunities and pivot away from threats.
Two common frameworks for documenting strategies – the business model canvas and the business plan – are also among the easiest to get confused.
Though they can complement each other, a business model canvas and a business plan are different in ways worth understanding for any entrepreneur who’s refining their business concept and strategy.
Let’s start by digging deeper into what a business model canvas is.
- What is a business model canvas?
You may have heard the term “business model” before. Every company has one.
Your business model is just a description of how your business will generate revenue. In other words, it’s a snapshot of the ways your business will be profitable.
Writing a business plan is one way of explaining a company’s business model. The business model canvas takes a different approach.
A business model canvas is a one-page template that explains your business model and provides an overview of your:
- Relationships with key partners
- Financial structure
- And more…
While the business model is a statement of fact, the business model canvas is a strategic process—a method for either documenting or determining your business model.
It’s meant to be quickly and easily updated as a business better understands what it needs to be successful over time. This makes it especially useful for startups and newer businesses that are still trying to determine their business model.
You can think of a business model canvas as a condensed, summarized, and simplified version of a business plan. It’s a great way to quickly document an idea and get started on the planning process.
The business plan is a way to expand on the ideas from the canvas and flesh out more details on strategy and implementation.

Brought to you by
Create a professional business plan
Using ai and step-by-step instructions.
Secure funding
Validate ideas
Build a strategy
Components of a Business Model Canvas
The simplest way to think about your business model canvas is to map it out visually. A business model canvas covers nine key areas:
- Value proposition : A company’s unique offering in the market and why it will be successful.
- Key activities: The actions that a company takes to achieve its value proposition.
- Customer segments : The types of people or businesses that are likely to want a company’s products or services.
- Channels : How a company reaches customers through marketing and distribution efforts.
- Customer relationships: How a company interacts with customers and maintains important relationships.
- Revenue streams: The ways in which a company makes money.
- Key resources: The assets such as property, equipment and staffing that a company needs to perform its key activities.
- Key partners: The relationships with suppliers, vendors, customers and other stakeholders a company must maintain in order to be successful.
- Cost structure: The major drivers of company expenses that will need to be tracked and managed.
[Want an even simpler alternative? Try downloading our free one-page plan template and start building your plan in less than 30 minutes.]
To get a better sense of how a business model canvas documents business strategy, consider a company like Netflix. The streaming company’s business model is based on generating subscription revenue through its content library and exclusive content.
If Netflix executives were to create a business model canvas, it would map out how the company leverages key resources, partnerships, and activities to achieve its value proposition and drive profitability. The business model is the destination.
The great thing about a business model canvas is that you can quickly document business ideas and see how a business might work at a high level. As you do more research, you’ll quickly refine your canvas until you have a business idea you think will work.
From there, you expand into a full business plan.
- What is a business plan?
If a business model canvas captures what a company looks like when it’s operating successfully, then a business plan is a more detailed version along with a company’s blueprint for getting there.
Think of your business plan as a process of laying out your goals and your strategies for achieving them.
The business plan is more detailed, and changes over time. It examines each aspect of your business, from operations to marketing and financials.
The plan often includes forward-looking forecasts of a company’s projected financial performance. These are always educated guesses. But these forecasts can also be used as a management tool for any growing business.
Comparing actual results to the forecast can be a valuable reality check, telling a business if they’re on track to meet their goals or if they need to adjust their plan.
A business plan is also a must for companies hoping to receive a bank loan , SBA loan , or other form of outside investment . Anyone putting up funds to help you grow will want to see you’ve done your homework.
So a business plan is how you not only prepare yourself, but also show your audience that you’re prepared.
Components of a business plan
While there are several different types of business plans meant for different uses, well-written plans will cover these common areas:
- Executive summary : A brief (1-2 pages) overview of your business.
- Products and services : Detailed descriptions of what you’re selling and how it fills a need in the market.
- Market analysis : Assessing the size of your market, and information about your customers such as demographics (age, income level) and psychographics (interests, values).
- Competitive analysis : Documenting existing businesses and solutions your target customers are finding in the market.
- Marketing and sales plan : Your strategies for positioning your product or service in the market, and developing a customer base.
- Operations plan : Describing how you will run the business from day to day, including how you will manage inventory, equipment, and staff.
- Organization and management team: Detailing the legal structure of the business, as well as key members, their backgrounds and qualifications.
- Financial Plans : Business financials that measure a company’s performance and health, including profit & loss statements, cash flow statements and balance sheets. Effective financial plans also include forward-looking sales forecasts and expense budgets.
How a business plan and business model canvas inform business strategy
Avoid the trap of using the two terms interchangeably. As we’ve shown, the two have different focuses and purposes.
The business model canvas (or our one-page plan template ) is a great starting point for mapping out your initial strategy. Both are easy to iterate on as you test ideas and determine what’s feasible.
Once you have a clearer sense of your idea, you can expand the canvas or one-page plan into a business plan that digs into details like your operations plan, marketing strategy, and financial forecast.
When you understand how – and when – to use each, you can speed up the entire planning process. That’s because the business model canvas lays out the foundation of your venture’s feasibility and potential, while the business plan provides a roadmap for getting there.
The work of business planning is about connecting the dots between the potential and the process.
Tim Berry is the founder and chairman of Palo Alto Software , a co-founder of Borland International, and a recognized expert in business planning. He has an MBA from Stanford and degrees with honors from the University of Oregon and the University of Notre Dame. Today, Tim dedicates most of his time to blogging, teaching and evangelizing for business planning.

Table of Contents
- How both inform your strategy
Related Articles

10 Min. Read
Use This Simple Business Plan Outline to Organize Your Plan

When Should You Write a Business Plan?

5 Min. Read
Business Plan Vs Strategic Plan Vs Operational Plan—Differences Explained

14 Reasons Why You Need a Business Plan
The Bplans Newsletter
The Bplans Weekly
Subscribe now for weekly advice and free downloadable resources to help start and grow your business.
We care about your privacy. See our privacy policy .

The quickest way to turn a business idea into a business plan
Fill-in-the-blanks and automatic financials make it easy.
No thanks, I prefer writing 40-page documents.

Discover the world’s #1 plan building software
More From Forbes
Two analyses that are key to strategic planning in business.
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter
- Share to Linkedin
José Luís González Rodriguez is a Partner of ActionCOACH Spain.
In my previous article , I noted that strategic planning continues to be an essential tool for the success and survival of companies. The ability to anticipate, adapt and direct resources toward specific goals is crucial in a competitive environment where changes are exponentially rapid.
In that article, I highlighted the numerous advantages of strategic planning supported by information from a survey involving 576 entrepreneurs and executives from various industries. We concluded that many companies see the need for a strategic plan, although in most cases, this plan isn't actioned out. Today, I want to present key tools for actually implementing strategic planning.
Strategic planning is a continuous process that allows organizations to establish long-term goals, identify their vision and mission, and analyze both internal and external environments. This approach encompasses the formulation of strategies, the implementation of actions and constant evaluation and adaptation.
To conduct effective planning, it can be wise to involve external advisors who can provide fresh perspectives and innovative proposals that respond to market changes. These strategic sessions, ideally held in a relaxed environment away from daily pressures, enable the executive team to develop a more realistic plan aligned with the company's needs. And it prevents the process from being improvised.
iOS 17.5.1: Apple Fixes Frustrating iPhone Photos Glitch
Trump prosecutor fani willis easily wins her democratic primary while judge in georgia case reelected, google chrome under attack do this one thing now.
Strategic planning improves decision-making by providing a solid framework that facilitates the evaluation of options and the making of well-informed choices aligned with corporate objectives. Defining and clearly communicating goals and objectives enhances team alignment, fostering collaboration and ensuring a unified approach toward common goals.
Additionally, flexibility in planning is essential in a volatile business environment because it allows the company to quickly adapt to new challenges and maintain its competitiveness and innovation.
Conduct A SWOT Analysis
The first basic tool that should be incorporated into your strategic planning process is the SWOT analysis. SWOT is an acronym for strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats, and it's an indispensable tool.
This comprehensive analysis is divided into four key components, each of which provides a unique perspective on your company's position.
- Strengths: These are the internal advantages and assets that your company possesses. They may include highly skilled human resources, cutting-edge technology, a strong financial base or a recognized brand. Identifying your company's strengths helps maximize your competitive advantage.
- Weaknesses: Weaknesses are internal limitations or deficiencies that may hinder business performance. They may include poor management, lack of staff training or inefficient processes. Identifying weaknesses allows your company to work on ways to improve and become more efficient.
- Opportunities: Opportunities are positive external factors that your company can leverage. They may arise from market changes, technological advances, changes in regulation or emerging trends. Recognizing and capitalizing on opportunities is essential for growth and expansion.
- Threats: Threats are negative external factors that can affect your company. They may include aggressive competitors, unfavorable economic changes or unexpected events like pandemics. Identifying threats allows your company to take proactive steps to mitigate risks.
Conduct An Environmental Analysis
The second tool or activity key to strategic planning is to conduct an environmental analysis.
The business environment is dynamic and ever-changing. Factors such as global economic conditions, disruptive technological advances, changes in government regulations and changing consumer preferences can have a significant impact on your company. An environmental analysis is a key method for better anticipating challenges and capitalizing on opportunities, which are crucial for survival and growth.
AI tools can be helpful here, as they can synthesize information into a comprehensive presentation that you can continuously update with new content.
Here are some examples of factors to consider:
Market Competition: Who are your direct and indirect competitors, and what are their strategies and market share? Identifying their strengths and weaknesses can even help develop effective, competitive strategies.
Economic And Technological Trends: Staying in touch with current and future economic and technological trends is vital for remaining relevant in the market. This might include adopting emerging technologies or adapting to changes in consumer demand.
Human Resources And Internal Capabilities: Take stock of your current workforce and readily available skill sets in your company. Identifying areas for improvement and training needs can enhance internal efficiency and productivity.
Legal And Regulatory Factors: Staying informed of changes in laws and regulations affecting the industry is essential for compliance and avoiding potential sanctions or legal issues.
Being armed with information is crucial for leading a company. In my next article for this series, we'll take a look at new tools that can allow us to look to the future with less uncertainty and more flexibility in the face of possible change.
Forbes Coaches Council is an invitation-only community for leading business and career coaches. Do I qualify?

- Editorial Standards
- Reprints & Permissions
- Team Alignment Map
- Team Charter
- Templates for Managers
- What is Project Baseline
- Work Log Templates
- Workback Schedule
- Workload Management
- Work Breakdown Structures
- Agile Team Structure
- Avoding Scope Creep
- Cross-Functional Flowcharts
- Precision VS Accuracy
- Scrum-Spike
- User Story Guide
- Creating Project Charters
- Guide to Team Communication
- How to Prioritize Tasks
- Mastering RAID Logs
- Overcoming Analysis Paralysis
- Understanding RACI Model
- Critical Success Factors
- Deadline Management
- Eisenhower Matrix Guide
- Guide to Multi Project Management
- Procure-to-Pay Best Practices
- Procurement Management Plan Template to Boost Project Success
- Project Execution and Change Management
- Project Plan and Schedule Templates
- Resource Planning Templates for Smooth Project Execution
- Risk Management and Quality Management Plan Templates
- Risk Management in Software Engineering
- Stage Gate Process
- Stakeholder Management Planning
- Understanding the S-Curve
- Visualizing Your To-Do List
- 30-60-90 Day Plan
- Work Plan Template
- Weekly Planner Template
- Task Analysis Examples
- Cross-Functional Flowcharts for Planning
- Inventory Management Tecniques
- Inventory Templates
- Six Sigma DMAIC Method
- Visual Process Improvement
- Value Stream Mapping
- Creating a Workflow
- Fibonacci Scale Template
- Supply Chain Diagram
- Kaizen Method
- Procurement Process Flow Chart
- Guide to State Diagrams
- UML Activity Diagrams
- Class Diagrams & their Relationships
- Visualize flowcharts for software
- Wire-Frame Benefits
- Applications of UML
- Selecting UML Diagrams
- Create Sequence Diagrams Online
- Activity Diagram Tool
- Archimate Tool
- Class Diagram Tool
- Graphic Organizers
- Social Work Assessment Tools
- Using KWL Charts to Boost Learning
- Editable Timeline Templates
- Kinship Diagram Guide
- Power of Visual Documentation
- Graphic Organizers for Teachers & Students
- Visual Documentation Techniques
- Visual Tool for Visual Documentation
- Conducting a Thematic Analysis
- Visualizing a Dichotomous Key
- 5 W's Chart
- Circular Flow Diagram Maker
- Cladogram Maker
- Comic Strip Maker
- Course Design Template
- AI Buyer Persona
- AI Data Visualization
- AI Diagrams
- AI Project Management
- AI SWOT Analysis
- Best AI Templates
- Brainstorming AI
- Pros & Cons of AI
- AI for Business Strategy
- Using AI for Business Plan
- AI for HR Teams
- BPMN Symbols
- BPMN vs UML
- Business Process Analysis
- Business Process Modeling
- Capacity Planning Guide
- Case Management Process
- How to Avoid Bottlenecks in Processes
- Innovation Management Process
- Project vs Process
- Solve Customer Problems
- Spaghetti Diagram
- Startup Templates
- Streamline Purchase Order Process
- What is BPMN
- Approval Process
- Employee Exit Process
- Iterative Process
- Process Documentation
- Process Improvement Ideas
- Risk Assessment Process
- Tiger Teams
- Work Instruction Templates
- Workflow Vs. Process
- Process Mapping
- Business Process Reengineering
- Meddic Sales Process
- SIPOC Diagram
- What is Business Process Management
- Process Mapping Software
- Business Analysis Tool
- Business Capability Map
- Decision Making Tools and Techniques
- Operating Model Canvas
- Mobile App Planning
- Product Development Guide
- Product Roadmap
- Timeline Diagrams
- Visualize User Flow
- Sequence Diagrams
- Flowchart Maker
- Online Class Diagram Tool
- Organizational Chart Maker
- Mind Map Maker
- Retro Software
- Agile Project Charter
- Critical Path Software
- Brainstorming Guide
- Brainstorming Tools
- Visual Tools for Brainstorming
- Brainstorming Content Ideas
- Brainstorming in Business
- Brainstorming Questions
- Brainstorming Rules
- Brainstorming Techniques
- Brainstorming Workshop
- Design Thinking and Brainstorming
- Divergent vs Convergent Thinking
- Group Brainstorming Strategies
- Group Creativity
- How to Make Virtual Brainstorming Fun and Effective
- Ideation Techniques
- Improving Brainstorming
- Marketing Brainstorming
- Rapid Brainstorming
- Reverse Brainstorming Challenges
- Reverse vs. Traditional Brainstorming
- What Comes After Brainstorming
- Flowchart Guide
- Spider Diagram Guide
- 5 Whys Template
- Assumption Grid Template
- Brainstorming Templates
- Brainwriting Template
- Innovation Techniques
- 50 Business Diagrams
- Business Model Canvas
- Change Control Process
- Change Management Process
- Macro Environmental Analysis
- NOISE Analysis
- Profit & Loss Templates
- Scenario Planning
- What are Tree Diagrams
- Winning Brand Strategy
- Work Management Systems
- Balanced Scorecard
- Developing Action Plans
- Guide to setting OKRS
- How to Write a Memo
- Improve Productivity & Efficiency
- Mastering Task Analysis
- Mastering Task Batching
- Monthly Budget Templates
- Program Planning
- Top Down Vs. Bottom Up
- Weekly Schedule Templates
- Kaizen Principles
- Opportunity Mapping
- Strategic-Goals
- Strategy Mapping
- T Chart Guide
- Business Continuity Plan
- Developing Your MVP
- Incident Management
- Needs Assessment Process
- Product Development From Ideation to Launch
- Value-Proposition-Canvas
- Visualizing Competitive Landscape
- Communication Plan
- Graphic Organizer Creator
- Fault Tree Software
- Bowman's Strategy Clock Template
- Decision Matrix Template
- Communities of Practice
- Goal Setting for 2024
- Meeting Templates
- Meetings Participation
- Microsoft Teams Brainstorming
- Retrospective Guide
- Skip Level Meetings
- Visual Documentation Guide
- Visual Note Taking
- Weekly Meetings
- Affinity Diagrams
- Business Plan Presentation
- Post-Mortem Meetings
- Team Building Activities
- WBS Templates
- Online Whiteboard Tool
- Communications Plan Template
- Idea Board Online
- Meeting Minutes Template
- Genograms in Social Work Practice
- Conceptual Framework
- How to Conduct a Genogram Interview
- How to Make a Genogram
- Genogram Questions
- Genograms in Client Counseling
- Understanding Ecomaps
- Visual Research Data Analysis Methods
- House of Quality Template
- Customer Problem Statement Template
- Competitive Analysis Template
- Creating Operations Manual
- Knowledge Base
- Folder Structure Diagram
- Online Checklist Maker
- Lean Canvas Template
- Instructional Design Examples
- Genogram Maker
- Work From Home Guide
- Strategic Planning
- Employee Engagement Action Plan
- Huddle Board
- One-on-One Meeting Template
- Story Map Graphic Organizers
- Introduction to Your Workspace
- Managing Workspaces and Folders
- Adding Text
- Collaborative Content Management
- Creating and Editing Tables
- Adding Notes
- Introduction to Diagramming
- Using Shapes
- Using Freehand Tool
- Adding Images to the Canvas
- Accessing the Contextual Toolbar
- Using Connectors
- Working with Tables
- Working with Templates
- Working with Frames
- Using Notes
- Access Controls
- Exporting a Workspace
- Real-Time Collaboration
- Notifications
- Meet Creately VIZ
- Unleashing the Power of Collaborative Brainstorming
- Uncovering the potential of Retros for all teams
- Collaborative Apps in Microsoft Teams
- Hiring a Great Fit for Your Team
- Project Management Made Easy
- Cross-Corporate Information Radiators
- Creately 4.0 - Product Walkthrough
- What's New
Implementing Stakeholder Theory for Business Succes
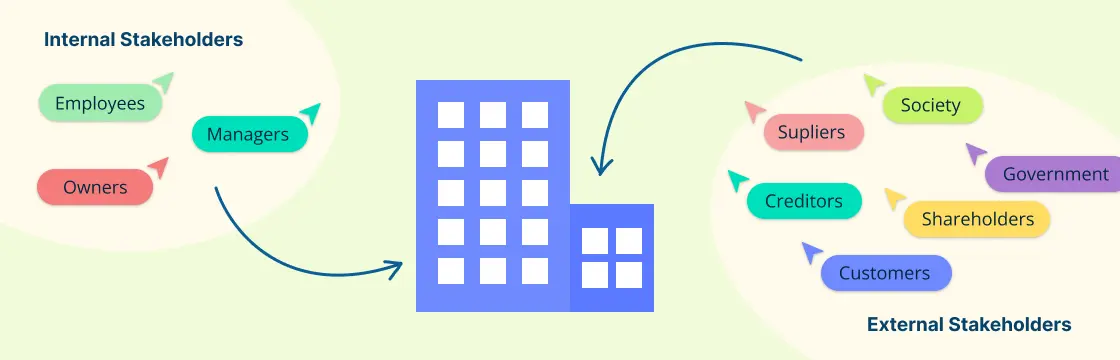
It can take a lot of work for a business to decide on what it should care about most. With so many things to consider, businesses need a framework to identify their most important values. In this article, we’re going to break down what stakeholder theory is, why it matters for projects, and what it means for making decisions in your business.
What is Stakeholder Theory?
The stakeholder theory is a systematic approch suggests that organizations should consider the interests and impacts of all stakeholders, not just shareholders, in their decision-making processes. This approach emphasizes ethical, strategic, and operational dimensions, advocating for a balance that benefits everyone involved, from employees and suppliers to customers and the broader community. Stakeholder Management Plan Templates provides a practical tool to visualize and implement these principles effectively.
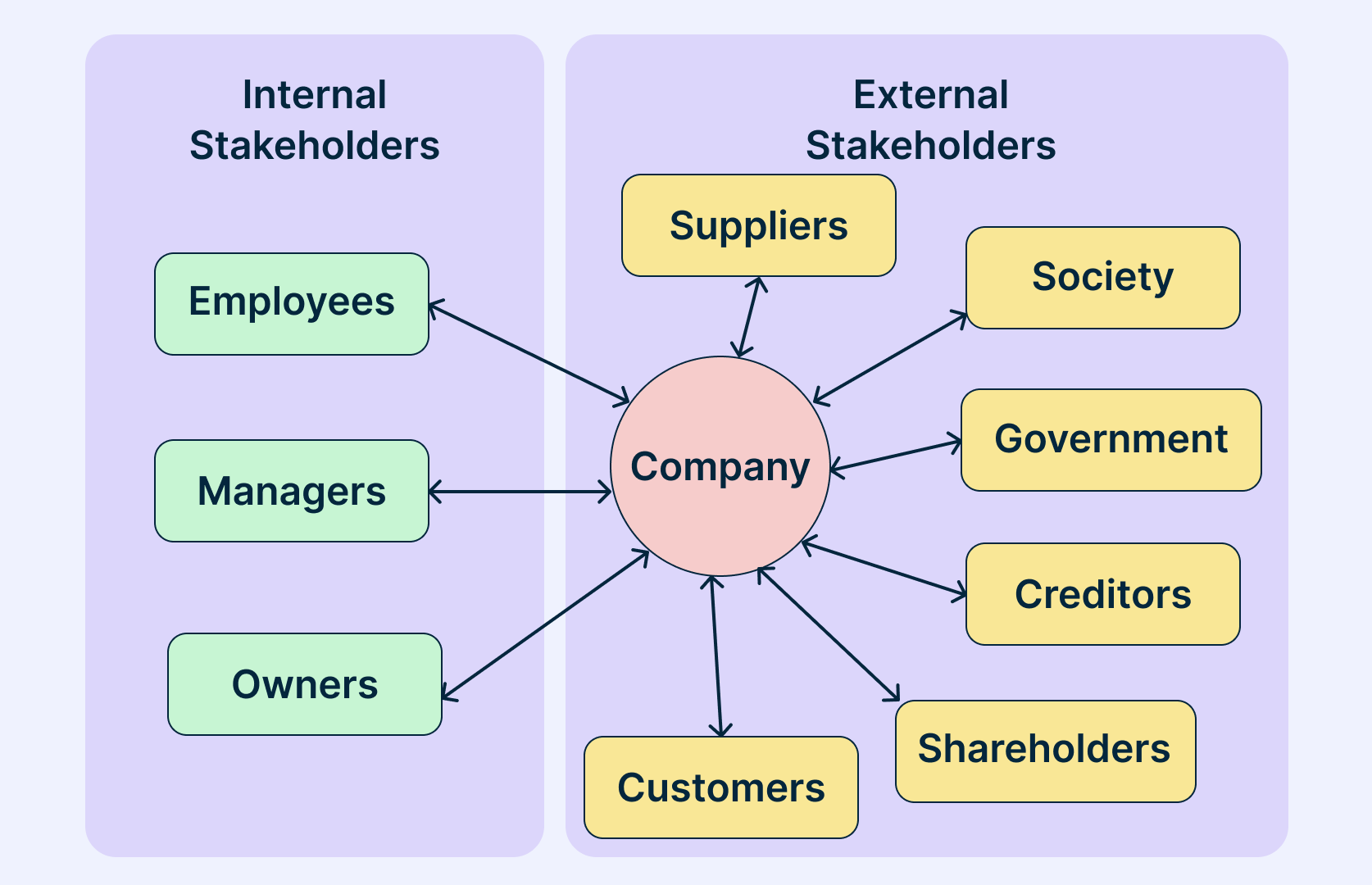
Ethical Dimension
The ethical dimension of stakeholder theory is grounded in the belief that businesses have a responsibility to act in the best interests of all their stakeholders, not just their owners or shareholders. This includes making decisions that are fair and just, ensuring that the rights of all stakeholders are respected, and addressing any adverse impacts that business operations may have on these groups. For instance, a company might implement fair labor practices, ensure equitable treatment of all employees, and actively engage in corporate social responsibility initiatives that benefit society at large.
Strategic Dimension
Strategically, considering the interests of all stakeholders can lead to long-term success for an organization. By fostering positive relationships with various stakeholders, companies can enhance their reputation, build customer loyalty, and attract and retain talented employees. Moreover, engaging with stakeholders can provide valuable insights and feedback that can drive innovation and improve business processes. For example, a company might collaborate with suppliers to develop more sustainable sourcing practices, which not only helps the environment but also meets the growing consumer demand for ethical products.
Operational Dimension
On an operational level, incorporating stakeholder interests into decision-making processes means that organizations must develop systems and practices that ensure ongoing stakeholder engagement and feedback. This can involve regular communication with stakeholders, transparency in business operations, and the establishment of mechanisms for addressing stakeholder concerns. For example, a company might set up a stakeholder advisory panel or conduct regular surveys to gauge stakeholder satisfaction and identify areas for improvement.
Implementing Stakeholder Theory with Management Plans
Stakeholder Management Plan Templates provide a practical tool to visualize and implement these principles effectively. These templates help organizations systematically identify their stakeholders, understand their needs and expectations, and develop strategies to address them. By using these templates, companies can create detailed plans that outline specific actions, assign responsibilities, and set timelines for stakeholder engagement activities. This structured approach ensures that stakeholder considerations are integrated into the fabric of the organization’s operations, leading to more inclusive and sustainable business practices.
In summary, the stakeholder theory advocates for a holistic approach to business management that considers the interests of all parties affected by an organization’s actions. By embracing ethical principles, strategic foresight, and operational efficiency, businesses can create value not only for their shareholders but for all stakeholders, contributing to a more sustainable and equitable business environmen
Historical Background of Stakeholder Theory and Key Figures
The roots of the stakeholder theory trace back to the mid-20th century, but it was R. Edward Freeman’s seminal work in 1984 that fully articulated its importance and framed it within the context of business strategy. Freeman’s insights have encouraged a shift from a purely profit-focused shareholder model to a more inclusive stakeholder approach. This evolution reflects a growing recognition of the interconnectedness of business success with societal well-being.
Understanding the stakeholder theory is crucial for businesses aiming to achieve sustainable success by harmonizing the needs of diverse groups and fostering an environment of cooperation and mutual benefit.
Stakeholder vs. Shareholder Theory: Understanding the Differences
When discussing the stakeholder theory , it’s crucial to contrast it with shareholder theory, as both play significant roles in shaping business strategies. While the stakeholder theory advocates for considering the interests of all parties affected by business operations, shareholder theory focuses primarily on maximizing shareholder wealth. This fundamental difference influences not only the ethical landscape of a company but also its decision-making processes.
- Basic Tenets of Shareholder Theory: This theory posits that the primary responsibility of a company is to maximize profits for its shareholders. The rationale is that by focusing on profit maximization, businesses will operate efficiently, benefiting the economy as a whole.
- Broader Value Creation in Stakeholder Theory: In contrast, the stakeholder theory emphasizes a broader spectrum of value creation. It argues that businesses should account for the impact of their decisions on all stakeholders, including employees, customers, suppliers, and the community, thereby promoting ethical business practices and sustainability.
The implications of these theories extend deeply into corporate governance and business ethics. Companies adhering to the stakeholder theory often experience enhanced corporate reputation and trust, as they prioritize ethical considerations and stakeholder welfare over mere profit maximization. This approach not only aligns with modern ethical standards but also supports long-term business success.
For a deeper understanding of how these theories play out in real-world scenarios, consider exploring resources like A Quick Guide to Effective Stakeholder Mapping and Stakeholder Analysis Examples
The Origins of Stakeholder Theory
Edward Freeman’s seminal work has been pivotal in shaping the stakeholder theory, emphasizing that successful businesses must consider the interests of all stakeholders, not just shareholders. As we navigate the complexities of the 21st century, Freeman’s ideas have evolved to address contemporary business challenges and ethics, making the stakeholder theory more relevant than ever.
Freeman’s Contributions: Freeman’s advocacy for a stakeholder-centric approach in business strategy has encouraged organizations to broaden their perspective beyond profit maximization. His framework suggests that creating value for all stakeholders - including employees, customers, suppliers, and the community - leads to a more sustainable and ethical business model.
- Updates to the theory emphasize transparency and the integration of stakeholder interests into core business strategies.
- Freeman’s work encourages a dialogue about corporate responsibility and ethical business practices, aligning closely with modern concerns about sustainability and social impact.
Modern Applications and Critiques: In recent years, the application of stakeholder theory has expanded into areas like corporate social responsibility (CSR) and environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria. Businesses are increasingly held accountable by a broader audience, making stakeholder theory a critical component of strategic planning.
- Critics argue that balancing diverse stakeholder interests can be challenging and may lead to conflicts in decision-making. However, the benefits of a stakeholder-inclusive approach often outweigh these challenges.
- The theory’s adaptability to modern business environments showcases its enduring relevance and the need for continuous evolution to meet new business landscapes.
Key Benefits of Implementing Stakeholder Theory in Business
Embracing the stakeholder theory can transform an organization’s approach to business, yielding substantial benefits across various dimensions. Here’s how implementing this theory can enhance your business operations and ethical standing:
- Enhanced Corporate Reputation: By considering the interests of all stakeholders, companies can build stronger trust and credibility. This improved reputation can lead to better market positioning and increased loyalty among customers and partners.
- Improved Decision-Making: Involving diverse stakeholders in the decision-making process ensures a variety of perspectives are considered, leading to more balanced and comprehensive decisions using tools like Decision-Making Tools
- Ready to use
- Fully customizable template
- Get Started in seconds

- Increased Sustainability: The stakeholder theory encourages businesses to go beyond short-term profits and consider long-term impacts on society and the environment, promoting sustainable practices.
- Stronger Community Relations: By actively engaging with local communities and considering their interests, companies can enhance their social license to operate, which is crucial for long-term success.
- Long-term Profitability: While immediate financial gains are important, the stakeholder theory positions organizations for long-term success through stable and positive stakeholder relationships, ultimately impacting the bottom line positively.
Implementing the stakeholder theory not only drives ethical business practices but also aligns with strategic advantages that foster a thriving business environment.r.
Practical Ways to Implement Stakeholder Theory in Your Organization
Implementing the stakeholder theory effectively within an organization requires a strategic and structured approach. Here are some practical steps to ensure that all stakeholders are considered in your business processes, enhancing overall success and sustainability.
Stakeholder Analysis and Mapping
Begin by developing a comprehensive stakeholder analysis. This involves identifying who your stakeholders are, understanding their needs, expectations, and the impact of your business decisions on them. Resources like stakeholder mapping can be instrumental in visualizing these relationships and influences, making it easier to see how different stakeholders are connected and how their interests align with your business objectives.
- Use visual tools to create detailed stakeholder maps.
- Document stakeholder information centrally to ensure it’s easily accessible.
- Analyze stakeholder influence and interest to prioritize engagement efforts.
Engagement and Integration Strategies
Engaging stakeholders through regular communication and feedback loops is crucial. This not only helps in building trust but also in aligning stakeholder interests with the strategic goals of the organization. Incorporate their feedback into your business strategy to ensure that all voices are heard and considered.
- Hold regular meetings and update sessions with stakeholders.
- Use collaborative platforms to facilitate real-time feedback and discussions.
- Integrate stakeholder feedback into project planning and decision-making processes.
Monitoring and adapting strategies based on stakeholder feedback is essential for continuous improvement. By keeping a pulse on stakeholder sentiments and needs, you can make agile adjustments to your strategies, ensuring that your organization remains responsive and relevant in a dynamic business environment.
How Creately Supports In-depth Stakeholder Analysis and Strategy Execution
Implementing the stakeholder theory effectively requires robust tools that facilitate strategic planning and stakeholder management. Creately’s platform offers a suite of visual tools designed to enhance these processes, making it an indispensable resource for businesses aiming to optimize stakeholder engagement.
- Visual Tools for Strategic Planning: Creately’s visual canvas allows teams to create dynamic strategic plans that incorporate stakeholder insights. This visual approach helps in identifying key stakeholders and understanding their influence and needs, which is crucial for successful stakeholder management.
- Benefits of Centralized Stakeholder Information: With Creately, all stakeholder information can be centralized on a single platform. This consolidation improves accessibility and enhances the decision-making process, ensuring that all actions are aligned with stakeholder interests.
By utilizing stakeholder analysis template , teams can leverage ready-to-use frameworks to conduct thorough stakeholder analyses. These templates are designed to streamline the mapping process and provide clear insights into stakeholder relationships and their potential impact on projects.
Moreover, Creately’s platform supports the creation of communicative plans with its advanced diagramming tools. These tools allow for the creation of visual representations that are easy to understand and share across departments, enhancing collaboration and ensuring that all team members are on the same page regarding stakeholder strategies.
Finally, executing projects with a visual command center approach is another standout feature of Creately. This method provides a holistic view of project timelines and stakeholder engagements, facilitating better monitoring and adjustments as projects progress. Teams can also Utilize the stakeholder onion diagram to visualize layers of stakeholder influence and interest, further enhancing strategic execution.
Join over thousands of organizations that use Creately to brainstorm, plan, analyze, and execute their projects successfully.
More Related Articles
- Accountancy
- Business Studies
- Organisational Behaviour
- Human Resource Management
- Entrepreneurship
- Difference between Policies and Strategy
- Difference between Tax Planning and Tax Management
- Difference between Marketing Strategy and Marketing Plan
- Difference between Standing Plans and Single-Use Plans
- Difference between Planning and Forecasting
- Difference between Policies and Rules
- Difference between Leader and Manager
- Difference between Policies and Procedures
- Difference Between State and Strategy Design Pattern in Java
- Differences between ERP and SAP
- Difference between Linux and Plan 9
- Difference between Program and Initiative
- Difference between MRP and ERP
- Difference between MRP and DRP
- Difference between Program and Package
- Difference between ERP and SCM
- Difference between Projects and Operations
- Difference between Program and Project
- Difference between MRP and MRP II
Difference between Planning and Strategy
Both planning and strategy play pivotal roles, though they cater to different aspects of organizational success. Planning is the tactical process of mapping out precise steps to execute short-to-medium-term objectives effectively, focusing on the details of day-to-day operations. In contrast, strategy deals with setting a long-term vision and establishing the overarching direction for an organization, aiming to achieve sustainable competitive advantage.
What is Planning?
Planning is the methodical process of identifying goals and describing how to attain them. It involves setting clear objectives, identifying the resources required, and creating a timeframe for completing tasks effectively. The process usually entails examining current circumstances, anticipating future requirements, and coordinating activities across departments or teams. Effective planning improves productivity and resource usage, allowing firms to react to problems and exploit opportunities.
Planning is essential for both short and medium-term goals, such as project completion, product launches, and quarterly milestones. It promotes concentration, minimizes uncertainty, and improves stakeholder coordination. While planning does not ensure success, it helps reduce risks by giving an organized approach to goal attainment ensuring that everyone understands their roles and the processes required to achieve common goals.
Features of Planning
- Goal-Oriented : The primary feature of planning is its focus on achieving specific goals. It starts with defining clear, achievable objectives and then outlines the necessary steps to reach these goals. This ensures that every action taken is purposeful and directed towards pre-determined outcomes.
- Systematic Process : Planning is not a haphazard activity but a systematic process that follows a logical sequence. It involves analyzing the current situation, forecasting future conditions, setting objectives, and then developing various courses of action. This systematic approach helps in making rational decisions and in organizing resources effectively.
- Flexibility : While plans are generally made for the future, they must also include a degree of flexibility to adapt to the ever-changing business environment . Effective planning anticipates changes and includes provisions for making adjustments as needed, allowing organizations to respond quickly to external or internal shifts.
- Continuity : Planning is a continuous process due to the dynamic nature of business environments. It requires constant monitoring and updating as new information becomes available or as circumstances evolve. This ongoing nature ensures that plans remain relevant and effective over time.
- Resource Allocation : Planning involves the detailed allocation of resources such as time, personnel, and capital. By determining in advance how resources are to be allocated, planning helps prevent wastage and promotes the efficient use of resources to achieve the desired outcomes.
What is Strategy?
Strategy refers to a comprehensive plan or set of actions designed to achieve an organization’s long-term goals and objectives. It involves determining the best path to navigate the competitive landscape, allocate resources effectively, and maximize the organization’s strengths while minimizing its weaknesses.
The strategic process includes identifying opportunities and challenges, spotting new trends, and devising innovative solutions to manage a changing corporate environment. It necessitates balancing risk and reward, prioritizing projects that enhance development, and maintaining the flexibility to respond as circumstances change. While planning focuses on tactical execution, strategy aims to successfully position the business for long-term success. It provides an outline for decision-making across all departments, ensuring that each department works to achieve common long-term goals. Finally, a good strategy allows a firm to differentiate itself and provide distinct value to its customers .
Features of strategy
- Visionary : Strategy is inherently visionary, aiming to set a future direction for the organization. It reflects the aspirations of the organization and defines what it wants to achieve in the long term. This visionary nature helps guide decision-making and aligns the organization with its core values and objectives.
- Comprehensive : A strategy is comprehensive, covering all areas of the organization. It involves making decisions that affect various functions and departments, from marketing and sales to production and human resources . This broad scope ensures that all parts of the organization are working towards the same long-term goals.
- Analytical : Strategy formulation is deeply analytical, involving a thorough analysis of both the internal environment (strengths and weaknesses) and the external environment (opportunities and threats). This SWOT analysis helps in understanding where the organization stands and what it needs to do to improve its position and performance.
- Adaptive : Good strategy is adaptive, designed to be flexible enough to respond to changes in the external environment, such as market trends, economic shifts, and changes in consumer behavior . This adaptability allows the organization to remain relevant and competitive even as conditions change.
- Differentiative : Strategy seeks to provide a unique value proposition to the organization, distinguishing it from competitors. It involves identifying and leveraging the organization’s unique strengths to create a competitive advantage. This differentiation is crucial for establishing a strong market position and attracting customers.
Planning and Strategy – FAQs
Can planning and strategy work independently.
While theoretically possible, planning without strategy can lead to misaligned efforts, and strategy without planning may lack concrete execution. Both are most effective when integrated.
How often should planning and strategy be reviewed or updated?
Planning is generally reviewed regularly, such as monthly or quarterly, while strategy should be revisited annually or in response to significant market or organizational changes.
Who is responsible for creating planning and strategy documents?
Strategy is typically formulated by top management or leaders, while planning is often handled by middle management with input from lower-level teams.
How can an organization ensure effective alignment between planning and strategy?
By clearly communicating the strategic vision across all departments and ensuring that each team’s plans contribute to the strategic objectives, effective alignment can be achieved. Regular reviews also help maintain this alignment.
Please Login to comment...
Similar reads.
- Commerce - Difference Between
Improve your Coding Skills with Practice
What kind of Experience do you want to share?
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
A Model for Expanding Your Business into Foreign Markets
- Joshua Conrad Jackson

Four strategies leaders should adopt when taking their brand abroad.
It used to be thought that globalization would flatten out cultural differences among countries and regions of the world, making it easier than ever for companies to move into foreign markets. According to a new study by the author and a colleague, however, cultural differences are greater today than they were 40 years ago, which explains why some major corporations have failed in their recent efforts to establish a foothold in new countries. Companies need to adapt, the author argues, and to that end in this article he presents a general model for global leadership in the face of cultural divergence.
Walmart in the 1990s seemed on pace to become a global giant. After rapid growth in the U.S. domestic market throughout the 1980s, the company opened its first international store in Mexico City in 1991, followed by Canada in 1994. By 1998 it had expanded to Germany and South Korea, betting that its “always the low price” approach to business would be enough to outcompete foreign vendors.
- Joshua Conrad Jackson is a Neubauer Family Assistant Professor at the University of Chicago’s Booth School of Business.
Partner Center
Difference Between Fully-Insured vs. Self-Funded Health Plans

Businesses typically choose between fully insured and self-insured (self-funded) plans when evaluating health benefit options. Understanding the difference between self-funded and fully insured plans is crucial for effective health insurance strategy planning.
Overview of Fully-Insured vs Self-Funded Health Plans
What is a fully insured health plan.
In a fully insured plan, the company pays fixed premiums to an insurance carrier, which handles all healthcare claims. The premiums are determined based on employee count, projected healthcare costs, and benefit levels. This model offers predictable costs and minimal management duties, making it attractive to smaller businesses that favor stability and a hands-off approach.
In 2019, 61% of U.S. workers with employer-sponsored health insurance were enrolled in a self-funded plan , indicating a significant shift towards self-insurance among American companies.
Self-Funded vs Fully Insured Insurance
In contrast, self-insured plans involve employers setting aside funds to pay for employee medical claims directly, offering potential cost savings by avoiding insurer profit margins. This model also allows for greater benefits customization to meet specific needs and goals, providing more control over the plan.
Fully Funded vs Self-Funded Insurance
Deciding between fully funded and self-funded insurance hinges on a company’s financial stability, risk tolerance, and administrative capabilities. While fully insured plans are less risky and simpler to manage, self-insured plans can offer significant cost savings and flexibility but come with greater financial variability and management complexity.
More information about small business health insurance plans:
Health insurance for small business
Guide to small business health insurance
What Are Fully-Insured Health Plans?
Fully insured health plans are a traditional model where businesses pay fixed premiums to an insurance provider, assuming all risks and responsibilities for employee healthcare claims. This model is favored by small to medium-sized businesses seeking financial predictability and ease of benefits management. In a fully insured plan, the employer signs a contract with an insurer that agrees to cover all eligible healthcare claims for a set premium. These premiums are calculated monthly based on the number of employees, their risk profiles, and desired coverage levels. Insurers use actuarial data to estimate expected claims and adjust premiums to cover these costs plus a profit margin.
Pros and Cons of Fully-Insured Plans
- Predictability of Costs: Employers can know exactly what they will owe each month, regardless of their employees' actual health care costs. This makes budgeting easier and reduces financial uncertainty.
- Ease of Administration: Because the insurance company handles all claims processing and benefits administration, the employer's administrative burden is significantly reduced.
- Reduced Risk: The insurance company assumes all risks related to health care claims, protecting employers from the financial impact of high or unexpected claims.
- Higher Cost in the Long Term: Premiums include the insurance company's overhead and profit margins, making fully insured plans more expensive over time compared to self-funded plans, where employers might save money in years of lower-than-expected claims.
- Less Flexibility: Employers cannot customize plan options and benefits, as they must choose from the plans the insurance company offers.
- Potential for Premium Increases: Premiums can increase at renewal each year based on overall claim trends within the insured pool, age demographics, and other factors, leading to potential unpredictability in long-term healthcare budgeting.
Understanding Self-Funded Health Plans
As of 2020, 80% of covered workers in larger companies (over 5000 employees) were enrolled in self-funded health plans , demonstrating the scalability and appeal of self-insurance in substantial enterprises.
Self-insured health plans offer an alternative approach where employers assume the financial risk for providing employee health benefits, often favored by larger organizations seeking greater control over plan design and costs.
In this model, rather than paying fixed premiums to an insurance company, employers allocate a pool of funds to cover employee health claims directly. They commonly work with a third-party administrator (TPA) to manage claims processing and benefits administration. This setup allows employers to pay for claims as they occur, potentially yielding significant cost savings when claims are lower than anticipated.
Pros and Cons of Self-Funded Plans
- Cost Savings: If the health claims are lower than expected, the employer can save significant money, as they are not paying a premium that includes margins for an insurance company’s overhead and profit.
- Flexibility and Customization: Employers can design and adjust the plan according to their needs and preferences. This includes choosing which benefits to offer and structuring copays, deductibles, and other plan features.
- Improved Cash Flow: Since premiums are not paid upfront to an insurance company, employers can retain more cash in the business until it is needed to pay claims. This can improve overall cash flow management.
- Financial Risk: The major downside of self-insuring is the potential for high costs from unexpected claims. If claims are higher than anticipated, the employer must cover these costs, which can be financially challenging.
- Administrative Burden: Although third-party administrators can help, employers still face an increased administrative burden in managing the health plan, negotiating with providers, and ensuring compliance with relevant laws and regulations.
- Stop-Loss Insurance Needed: Most self-insured plans purchase stop-loss insurance, which can be a significant expense. This insurance reimburses the employer for claims that exceed a certain dollar threshold to mitigate the risk of very high claims.
While self-funded plans offer greater flexibility and potential cost savings, with average monthly premiums reported at $697 for individuals and $2,004 for families in 2020, they require robust risk management strategies, as evidenced by 79% of private sector establishments with such plans having a stop-loss policy.
Comparing Fully-Insured and Self-Insured Plans
The decision between fully insured and self-insured health plans significantly affects a company's finances, risk management, and benefits design. Understanding the difference between self-funded and fully insured plans is vital to align with a company’s goals.
Cost Implications and Savings Potential
Fully insured plans involve fixed premiums, which may result in higher long-term costs due to the inclusion of the insurer's overhead and profit. Conversely, self-insured plans allow companies to reduce costs by eliminating these overheads, although savings depend on actual claim costs, which can be unpredictable.
Risk Management and Liability
In fully insured plans, the insurer manages all claim risks, offering predictability at the cost of higher premiums. In self-insured plans, the employer bears the claims risk, which might lead to substantial financial exposure but can be mitigated by purchasing stop-loss insurance to cover catastrophic claims.
Flexibility and Customization Options
Self-insured plans offer greater flexibility, allowing employers to customize benefits to meet specific workforce needs, including tailored deductibles and copays. Fully insured plans provide less customization, as employers must select from preset options offered by insurers.
Regulatory and Compliance Considerations
Navigating health insurance regulations is essential for maintaining compliant and effective health plans. Understanding the impact of these regulations on different types of plans helps employers make informed decisions.
ERISA and State Regulations
The Employee Retirement Income Security Act (ERISA) sets federal standards for most private industry health plans, applying to both fully insured and self-insured plans. Fully insured plans must also adhere to state insurance laws, which vary by state and influence claims processing and mandated benefits. Conversely, self-insured plans are generally exempt from state insurance regulations under ERISA, offering greater flexibility but requiring strict compliance with federal standards.
Compliance Requirements for Self-Insured Plans
Self-insured plans must comply with several federal regulations, including specific provisions of the Affordable Care Act (ACA), HIPAA privacy rules, and the Mental Health Parity and Addiction Equity Act. These plans must avoid health-based discrimination, provide adequate coverage, and fulfill reporting and disclosure requirements. Effective management of these requirements typically requires either an adept in-house legal team or a partnership with a knowledgeable third-party administrator (TPA).
Important Considerations For Managing Plans
When choosing between self-funded and fully insured health plans, it's crucial to understand the management responsibilities each entails. Self-funded plans offer the flexibility to design and manage health benefits tailored to specific business and employee needs, but this comes with ensuring efficient operation and compliance. Most self-funded plans utilize a Third-Party Administrator (TPA) to handle administrative tasks like claims processing and regulatory compliance, which reduces the administrative load but may limit customization and control over plan operations.
In contrast, fully insured plans provide less flexibility but increase ease of management as the insurance carrier handles most administrative tasks and assumes risk. This arrangement suits businesses looking for simplicity and less direct involvement in plan management.
It may be worth noting that, in 2020, 39% of firms with multiple locations opted for at least one self-funded plan , compared to 28% of single-location firms. This highlights the administrative considerations and the need for experienced third-party administrators (TPAs) to manage these plans effectively.
Making the Decision: Which Is Right For Your Business?
Choosing between fully insured and self-insured health plans is a critical decision that affects your business's finances, risk management, and employee satisfaction. Understanding the difference between self-funded and fully insured plans is essential for informed decision-making.
Key Factors to Consider:
- Financial Stability and Cash Flow: Self-insured plans may offer cost savings but require a stable cash flow to manage high-cost claims, whereas fully insured plans provide a predictable cost model with fixed premiums, with the insurer bearing the risk of high claims.
- Employee Demographics and Healthcare Needs: Younger, healthier employee groups may see more economic benefits from self-funded plans due to fewer health claims, while a diverse or older workforce may find the risk-sharing and stability of fully insured plans more beneficial.
- Administrative Capacity: Self-insured plans demand significant management for compliance, claims processing, and overall plan administration. Fully insured plans reduce this burden by offloading management to the insurer.
- Risk Tolerance: Fully insured plans offer peace of mind with fixed premiums but may come at a higher cost. Conversely, self-insured plans pose more financial risk due to the potential for unexpectedly high claims.
- Regulatory Considerations: Self-funded plans are predominantly governed by federal laws like ERISA, whereas fully insured plans are subject to state regulations, which can vary and include additional mandates.
Balancing these considerations with each plan type's potential benefits and challenges is crucial. The right choice depends on your company's specific circumstances, including financial health, employee needs, and long-term business strategies. Evaluating these factors will help determine your business's most suitable health insurance option.
Let's talk through your HRA questions

Susanne is a copywriter specializing in the health and wellness industry. Before starting her own business, she spent nearly a decade at a marketing agency doing all of the things – advisor, copywriter, SEO strategist, social media specialist, and project manager. That experience gives her a unique understanding of how the consumer-focused content she writes flows into each marketing piece. Susanne lives in Oklahoma City with her husband and two daughters. She loves being outdoors, exercising and reading.

We’re on a mission to create a consumer-centric healthcare system.
(214) 866-7757
©2024 Take Command. All Rights Reserved.
Take Command Health is not a bank. Banking services are provided by Blue Ridge Bank, N.A, Member FDIC. Deposits are FDIC-insured through Blue Ridge Bank, N.A., Member FDIC. The Take Command Health Visa Debit Card is issued by Blue Ridge Bank, N.A., Member FDIC, pursuant to a license from Visa USA Inc. Your funds are FDIC insured up to $250,000 through Blue Ridge Bank; Member FDIC.
Privacy Policy Terms of Use Licensing Sitemap Secured with SSL

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
A strategic plan answers where an established organization is going in the future and how they intend to reach that future state. A strategic plan also focuses on building a sustainable competitive advantage and is futuristic. A business plan is used to assess the viability of a business opportunity and is more tactical.
The biggest difference between a strategic plan vs. a business plan is its purpose. Existing companies use the strategic plan to grow their business, while entrepreneurs use business plans to start a company. There is also a different timeframe for each plan. Generally, a strategic plan is conducted over several years while a business plan ...
Côté further explains the differences between the two plans: while the business plan lays out how the business is run from day to day, the strategic plan focuses on how you will achieve specific initiatives to develop your business. Every successful business need both a strategic and a business plan. Here's what each one covers.
Strategic plans constitute the basis of operations and responsibilities within the business. These plans lay the paths out for each member of the organization to follow and define the functional outline and the key outcomes for every project and process within the business. A strategic plan goes on to define the operations and their outcomes ...
In contrast, setting strategy should push your organization outside its comfort zone - if you're doing it right. "Plans typically have to do with the resources you're going to spend. Those ...
First, let's look at the difference between a business and a strategic plan. For review: A business plan covers the "who" and "what" of the business. The strategic plan gives us long-term goals and explains "how" the business will get there, providing a long-term view. In broader terms, the business plan tells us who by showing us:
A business plan focuses on starting a business in its early stages. A strategic plan is used to guide the company through later stages. Put simply, the business plan is about direction and vision, while the strategic plan focuses on operations and specific tactics for business growth.
Business Plan: A business plan is a written document that describes in detail how a business, usually a new one, is going to achieve its goals. A business plan lays out a written plan from a ...
A business strategy is foundational to a company's success. It helps leaders set organizational goals and gives companies a competitive edge. It determines various business factors, including: Price: How to price goods and services based on customer satisfaction and cost of raw materials.
A business plan, as described by the Center for Simplified Strategic Planning, Inc., aims to define "the initial goals and objectives of the company, its structure and processes, products and services, financial resources [and] all of the basics that go into forming a company " and getting it up and running. TAB offers its members a ...
A business plan usually lays the foundations of a company's business decisions and strategies at the ownership level. A strategic plan typically establishes the foundations of responsibilities and operations within an existing business. It explains the strategy for each team member to follow and defines the functional outline and significant ...
The Purpose and Goals of the Strategic plan and the Business plan. Strategic plans and business plans are both essential tools for any organization. They provide a clear roadmap for achieving goals and ensuring long-term success. While the two plans are similar in some ways, they serve different purposes and have different goals.
A business plan is more focused than a strategic plan, it should be a detailed report on the operations of the core business activities of the business or nonprofit. These efforts should outline everything from production to sales. It should include detailed information on costs, sales figures, suppliers, customer data, etc.
In contrast, a strategic plan clarifies the long term direction of the organization; most business plans look at a shorter period of time, typically 2-3 years, and drills down thoroughly how the work will get done and dollars will be earned. Business plans typically take more resources, both internal and often external (in the form of ...
The business plan, a noun, is a tactical document. It's typically created for a specific purpose, such as securing a Small Business Administration (SBA) loan. Think of it as a road map - it outlines the route and the destination (in this case, the coveted bank loan). But once you've reached your tactical goal (in this case, getting the loan ...
Corporate level strategy is a long-range, action-oriented, integrated, and comprehensive plan, which is formulated by the top management of a company. It is very helpful to ascertain business lines, expansion, growth, takeovers and mergers, diversification, integration, and the latest fields for investment. Business level strategy.
Step 1: Assess your current business strategy and business environment. Before you can define where you're going, you first need to define where you are. Understanding the external environment, including market trends and competitive landscape, is crucial in the initial assessment phase of strategic planning.
Think of your strategic plan as a layer the sits on top of your business plan - it severs to answer two key questions...
By M. Dana Baldwin, Senior Consultant We often get questions asking what the difference is between a Business Plan and a Strategic Plan. The first difference is there is a significant difference in intent. A Strategic Plan is focused on improving a company's performance, exploiting opportunities and building market share. A Business Plan is most […]
Related: 7 Types of Business Plans Key differences between strategies and plans Though some professionals may use these terms interchangeably, they're both well-suited for certain scenarios depending on the types of goals you've set. Here are some key differences between a strategy and a plan: Short-term and long-term goals
Financial Plans: Business financials that measure a company's performance and health, including profit & loss statements, cash flow statements and balance sheets. Effective financial plans also include forward-looking sales forecasts and expense budgets. How a business plan and business model canvas inform business strategy
A business strategy is a complete contingent plan of action that a business uses to achieve its goals in the market. It lists out the various possible situations a business is likely to find itself in and specifies the set of actions that it should take in each of the situations in order to achieve its goals in the market.
This strategic business plan template spans 7 pages to get you set up with a solid foundation for your business's strategic plan. The layout starts with an executive summary and continues with a company overview, product description, market analysis, and planned strategies. ... Strategic Plan vs. Work Plan: What's the Difference?
The second tool or activity key to strategic planning is to conduct an environmental analysis. The business environment is dynamic and ever-changing. Factors such as global economic conditions ...
Stakeholder Register Template How Creately Supports In-depth Stakeholder Analysis and Strategy Execution. Implementing the stakeholder theory effectively requires robust tools that facilitate strategic planning and stakeholder management. Creately's platform offers a suite of visual tools designed to enhance these processes, making it an indispensable resource for businesses aiming to ...
Planning is less flexible as it focuses on achieving specific targets within set timeframes and resource limits. Strategy is more adaptable and can change in response to external business conditions and internal dynamics. Scope. Planning generally addresses specific projects or operational areas within an organization.
Walmart in the 1990s seemed on pace to become a global giant. After rapid growth in the U.S. domestic market throughout the 1980s, the company opened its first international store in Mexico City ...
While fully insured plans are less risky and simpler to manage, self-insured plans can offer significant cost savings and flexibility but come with greater financial variability and management complexity. More information about small business health insurance plans: Health insurance for small business. Guide to small business health insurance.
GM's existing EV strategy is not, in fact, changing. Barra doubled down on "eliminating tailpipe emissions from light-duty vehicles by 2035" in yesterday's investment call. In fact, the plan for ...
By Paul J. Gough - Reporter, Pittsburgh Business Times. May 22, 2024. MSA Safety's new management team wasted no time in leaving their imprint on the company's direction, announcing Wednesday ...