

How to Format Your Research Paper
- APA 7 Paper Format
Writing Your Paper: MLA
Mla style papers.
- Chicago Paper Format
- Hanging Indents
- Ask a Librarian
MLA Resources
- Ask the MLA Search a list of Frequently Asked Questions about the MLA style. If you donʻt see the answer youʻre looking for, ask the MLA yourself!
- Purdue OWL: MLA Style Guide This Purdue OWL citation guide will help you in citing your sources in the MLA (Modern Language Association) Style commonly used to cite sources within the area of language arts. You can find written and video instructions with examples on how to format your citations. Click on the title above to see more...
Always consult your assignment guidelines for course-specific formatting.
Things to know before you begin:
- Font: An easily readable typeface (Times New Roman, Calibri, Arial, etc...) that is maintained throughout the paper.
- Font Size: 11-13 point
- Margins: 1 inch
- Paragraphs: All paragraphs should be indented.
- Spacing: All of the text in your paper should be double-spaced.
Typical MLA style papers have two sections:
- Works Cited
See the tabs below for a breakdown of how each portion should be formatted.
- Paper Templates
- Sample Papers
Below you will find templates for MLA Style papers. Click the link to make a copy of the file.
- Google Docs : To make a copy of this template you must first sign in to your Google account. After you’re signed in, click file and then click “make a copy.”
- Microsoft Word : To make a copy of this template, simply download the file.
- MLA Style Paper Template - Word Make a copy of this Word Doc and change the pre-filled information to your own.
Below you will find an example of an accurately formatted MLA Style paper.
- Sample Paper MLA: 3D Printing (.pdf) Click here to see a sample of an accurately formatted MLA style paper.
- Sample Paper MLA: 3D Printing Click here to see a sample of an accurately formatted MLA style paper.

- Your paper should have your name, your instructor's name, the class name, and the due date in the top left corner of the page. It should be double spaced and use the same font type and size as the rest of your paper.
- The title of your paper should be centered on the first line after your heading. It should be in Title Case and use the same font type and size as the rest of your paper.
- Place your last name and page numbers in the header in the same font type and size as the rest of your paper. Be sure to use the header function, do not type this into the body of your paper.

- Center the words "Works Cited" on the first line of a new page. If you only have a single reference, use "Work Cited" instead.
- Your citations should be alphabetical.
- All entries should be double-spaced with no extra lines between them.
- Be sure to use a hanging indent for any citations that require more than one line.
Need help formatting your MLA style citations using the 8th edition of the Modern Language Association Handbook ? Click the image or link below to go to the citation guide.

- MLA Style Citations
Need help learning what hanging indents are and how to create them using Google Docs or Microsoft Word?

- Hanging Indents This page gives a brief description of what they are, where to find information on when and how to properly use them, and also video tutorials on how to create them.
- << Previous: APA 7 Paper Format
- Next: Chicago Paper Format >>
- Last Updated: Mar 29, 2024 2:49 PM
- URL: https://necc.mass.libguides.com/formatting
To cite this LibGuide use the following templates:
APA : Northern Essex Community College Library. (Date updated). Title of page . Title of LibGuide. URL
MLA : Northern Essex Community College Library. "Title of Page." Title of LibGuide, Date updated, URL.

MLA Style Guide, 8th & 9th Editions: Formatting Your MLA Paper
- Works Cited entries: What to Include
- Title of source
- Title of container
- Contributors
- Publication date
- Supplemental Elements
- Book with Personal Author(s)
- Book with Organization as Author
- Book with Editor(s)
- Parts of Books
- Government Publication
- Journal Article
- Magazine Article
- Multivolume Works
- Newspaper Article
- Other Formats
- Websites, Social Media, and Email
- About In-text Citations
- In-text Examples
- How to Paraphrase and Quote
- Citing Poetry
- Formatting Your MLA Paper
- Formatting Your Works Cited List
- MLA Annotated Bibliography
- MLA 9th Edition Quick Guide
- Submit Your Paper for MLA Style Review
MLA recommends using 12-point Times New Roman font or another readable typeface (e.g. serif ).
Line Spacing & Margins
Use double-spacing throughout the entire paper.
Leave 1 inch margins on the top, bottom, and each side.
Indent the first line of each paragraph half an inch from the left margin.
Quotes longer than 4 lines should be written as a block of text a half an inch from the left margin.
Heading and Title
An MLA research paper does not need a title page, but your instructor may require one. If no instructions are given, follow the MLA guidelines below:
Type the following one inch from the top of the first page, flush with the left margin (double spacing throughout).
Your Instructor's Name
Course Number or Name
Center the title on the next line. Follow the rules for capitalization. Do not italicize, underline, or bold the title. An exception is when your title includes a title. Example: The Attitude toward Violence in A Clockwork Orange
Indent the next line and begin typing your text.
Include your last name and page numbers in the upper right-hand corner of every page. The page numbers will be one-half inch from the top and flush with the right margin. If your instructor prefers no page number on the first page, begin numbering from 2 on the second page.
Sample Papers from MLA
There are sample papers available in the MLA Style Center. Check them out to see the correct formatting.
Styling Headings and Subheadings
According to the MLA Style Center website, writers should avoid using headings in shorter papers. If you are writing a longer research paper, you may want to include headings and subheadings to help organize the sections of your paper. Advice from the MLA Style Center :
"Levels
The paper or chapter title is the first level of heading, and it must be the most prominent.
Headings should be styled in descending order of prominence. After the first level, the other headings are subheadings—that is, they are subordinate. Font styling and size are used to signal prominence. In general, a boldface, larger font indicates prominence; a smaller font, italics, and lack of bold can be used to signal subordination. For readability, don’t go overboard: avoid using all capital letters for headings (in some cases, small capitals may be acceptable):
Heading Level 1
Heading Level 2
Heading Level 3
Note that word-processing software often has built-in heading styles.
Consistency
Consistency in the styling of headings and subheadings is key to signaling to readers the structure of a research project. That is, each level 1 heading should appear in the same style and size, as should each level 2 heading, and so on. Generally, avoid numbers and letters to designate heads unless you are working in a discipline where doing so is conventional. Note that a heading labeled “1” requires a subsequent heading labeled “2,” and a heading labeled “a” requires a subsequent heading labeled “b.”
In a project that is not professionally designed and published, headings should be flush with the left margin, to avoid confusion with block quotations. (The exception is the paper or chapter title, which is centered in MLA style.)
For readability, it is helpful to include a line space above and below a heading, as shown in this post.
No internal heading level should have only one instance. For example, if you have one level 1 heading, you need to have a second level 1 heading. (The exceptions are the paper or chapter title and the headings for notes and the list of works cited.) You should also generally have text under each heading.
Capitalization
Capitalize headings like the titles of works, as explained in section 1.2 of the MLA Handbook.
The shorter, the better."
Modern Language Association. "How Do I Style Headings and Subheadings in a Research Paper?" MLA Style Center., 13 December 2018, style.mla.org/styling-headings-and-subheadings .
MLA Style Paper Template
- MLA 9th Edition Paper Template This template was created and saved as a Word template for Microsoft Word 2016. The process for saving and using the template is the same for the instructions given above for 2013.
You can save a personal template in Microsoft Word (IRSC students, download Office for free, see a librarian if you need help). Above is a template you can use every time you need to set-up a research paper using MLA style format. Simply open the template and type your own information every time you need to write an MLA style paper. Microsoft Word will allow you to save personal templates. Once you have the template opened in Word
Click "Save as"
Give the file a name
Under "Save as type", select Word Template

Then when you open Word, you will be able to choose a template rather than a blank document. You might have to select Personal to find your template.

Sample MLA Paper

How to Use the MLA Style Template
Formatting Group Project Papers
For a research paper written collaboratively by several students, such as for a group project, create a title page instead of listing all authors in the header on page 1 of the essay. On the title page, list each student's full name, placing one name on each double-spaced line. After the final student name, enter the professor's name. After the professor's name, give the course name. The last line of the heading will be the date in 5 August 2021 format. Press Enter a few times to move down the page then give the paper title, centered.

- << Previous: Citing Poetry
- Next: Formatting Your Works Cited List >>
- Last Updated: Jan 23, 2024 11:37 AM
- URL: https://irsc.libguides.com/mla

- Cite: Why? When?
- Book or E-book
- Article or Class Handout
- Web Sources
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) Tools
- In-Text Citation
Format Your Paper
- MLA Format Template Document
- MLA Annotated Bibliography Example
Order of Sections
- Introduction/Thesis
- Body (includes tables, figures, and illustrations)
- Works Cited (starts on new page)
Paper Size, Margins, & Page Numbers
- Use letter-sized (8.5 x 11 inch) paper.
- 1-inch margins at the top, bottom, and both sides.
- Indent first line of each paragraph 1/2 inch from left margin.
- In the upper right-hand corner of the margin, insert page numbers and add your last name (ex. Smith 1).
Text Format
- Use easy-to-read font so that regular and italicized text is easy to distinguish (ex. Times New Roman, Arial, Calibri).
- Use a standard size (ex. Times New Roman 12, Arial 11, Calibri 11 or 12).
- Left-align text and start paragraphs with a half-inch indent. Do not justify text.
- Turn off automatic hyphenation.
- Double-space everything.
- Leave one space after concluding punctuation marks, not two.
Heading & Title
- At the top left of the page, type your name, instructor's name, course number, and date.
- Include any information your instructor requires.
- Center title. Do not italicize, underline, or bold. No quotation marks, all caps, or periods.
- Capitalize the first word, principle words, and each part of a hyphenated word. Do not capitalize articles (a, an, the), prepositions, conjunctions, and to-infinitives.
Tables, Figures, & Illustrations
- Put them close to the related text and align them on the left.
- Above tables: capitalize the title of the table like other titles and number it (ex. Table 1).
- Below the table: give the source of the table and any notes with lower-case letters. Double-space it and use dividing lines.
- Below a figure or illustration: label it as "Figure" or "Fig." and number it (ex. Figure 1).
Quotations (p. 75-76, 81*)
- Short quotations (less than four lines) or those without special emphasis are included in the text with quotation marks
- Longer quotations (four lines or more) or those with special emphasis are indented 1/2 inch from left margin and double-spaced with no quotation marks.
- Use an ellipsis with spaces ( . . . ) when omitting sections from a quote. When the ellipsis is at the end of a sentence, use four periods ( . . . . ).
- For poetry, use slashes (/) to show line breaks and double slashes (//) for stanza breaks and keep all punctuation as it appears in the poem.
- Cite your quotes using in-text citation.
Works Cited List (p. 102*)
Begin your Works Cited list on a separate page and put the entries in alphabetical order. Double-space and give entries a hanging indent (i.e the first line is on the left margin and the following lines are indented a half inch from the left).
Annotated Bibliography
Double-space the entire bibliography. give each entry a hanging indent. in the following annotation, indent the entire paragraph a half inch from the left margin and give the first line of each paragraph a half inch indent..
Check with your professor for the length of the annotation and which elements you should evaluate.
*Page numbers refer to the MLA Handbook for Writers of Research Papers, available in the UW-Whitewater libraries in print .
- << Previous: In-Text Citation
- Last Updated: Feb 26, 2024 2:24 PM
- URL: https://libguides.uww.edu/mla
Jerz's Literacy Weblog (est. 1999)
Mla format papers: step-by-step tips for formatting research essays in mla style.
Jerz > Writing > Academic [ Argument | Title | Thesis | Blueprint | Pro/Con | Quoting | MLA Format ]
(View a Google Doc template for an MLA Style paper .)
0.1) If you’ve been asked to submit a paper in MLA style, your instructor is asking you to format the page and present the content in a specific way. Just as football referees dress a certain way, and Japanese chefs cook a certain way, writers in certain disciplines follow a certain set of conventions. This document will show you how to format an essay in MLA style.
0.2) If, instead of questions about putting the final formatting touches on your essay, you have questions about what to write, see instead my handouts on writing a short research paper , coming up with a good thesis statement , and using quotations in the body of your paper .

- Document Settings (1 inch margins; double spaced; 12-point)
- Page Header (name and page number, upper right of every page)
- Title Block (assignment info and an informative title)
- Citations (no comma between the author and page number; commas and periods go outside of inline quotes)
- Works Cited List (lots of tricky details! sort alphabetically by author, not by the order the quotes appear in your paper)
For the most complete information, check your campus library or writing center for the MLA Handbook for Writers of Research Papers , 8th ed.

MLA Style Format (First Page)

How to format the Works Cited page of an MLA style paper.

1. Document Settings
Your word processor comes with default settings (margin, line height, paragraph spacing, and typeface) that will likely need adjustment. For MLA style, you need:
1.1 Adjusting Document Settings in MS-Word (Windows)
My copy of Microsoft Word for Windows defaults to
- 1-inch margins all around
- 1.15 line height
- 10pt spacing between paragraphs
- Calibri 11-point typeface.
Changing to MLA Style (Windows)
- The default margins in my test run were fine, but if you need to change them: Page Layout -> Margins -> Normal (1-inch all around)
- The default line height is too low. Change it to 2.0. Home -> Line Spacing -> 2.0. (You could try fudging it to 1.9 or 2.1 to meet a page count, but any more than that and your instructor may notice.)
- The MS-Word default adds extra space after paragraphs.(MLA Style instead requires you to signal paragraph breaks by indenting the first line.) CTRL-A (select all your text) Home -> Line Spacing -> Remove Space After Paragraph
- Change the typeface to Times New Roman 12-point. Home -> Font Face Selector (change to Times New Roman) Home -> Font Size Selector (change to 12)
1.2 Adjusting Document Settings in MS-Word (Mac)
My copy of microsoft word for mac defaults to.
- 1.25 inch left and right margins, 1 inch top and bottom
- 1.0 line height
- no extra spacing after paragraphs
- Cambria 12-point typeface
Changing to MLA style (Mac)
- In my test run, the left and right margins are too big. To change them: Layout -> Margins -> Normal (1-inch all around)
- The default line height is too low. Change it to 2.0. Home -> Line Spacing -> 2.0
- My Mac copy of MS-Word does not add extra spaces after paragraphs. If yours does: Home -> Line Spacing -> Line Spacing Options… (a new window will pop up) Don’t add space between paragraphs of the same style (check this box) -> OK
- The 12-point Cambria will probably be fine, but to change the typeface: Home -> Font Face Selector (change to Times New Roman) Home -> Font Size Selector (change to 12)
2. Page Header
In the top right of every page, use your word processor’s “Page Header” function add an automatic page number and your surname.
2.1 Adding the Page Header in MS-Word (Windows)
- Insert -> Page Number -> Top of Page -> (choose the right-justified “Plain Number” option)
- The cursor will jump automatically to the right place for you to t ype your surname .
- Click anywhere in the body of the paper to exit the header area.
2.2 Adding the Page Header in MS-Word (Mac)
- Insert (in the top menu) -> Page Numbers… -> (Set “Position” to “Top of Page (header)” and “Alignment” to “Right”)
- Click just to the left of the new page number, and type your surname .
- On my test document, my name was too far over to the left; grab the triangular tab adjuster just above your name, and drag it a notch to the right .
3. Title Block
In the upper left corner, type your name, your instructor’s name, the course number and section, and today’s date. Centered on the next line, type an informative title that actually informs the reader of your main point (not just “English Paper” or “A Comparison between Hamlet and Macbeth”).

- Like all the other text in an MLA style paper, the title block is double-spaced .
- The title is in the same font as the rest of the paper — it is not boldface, or enlarged.
- There is no extra space above or below the title.
- A truly informative title will include the general topic, and your precise opinion on that topic. (So, if you pan to compare Hamlet and Macbeth, your title should state the unique point you want to make about Hamlet and Macbeth. Reuse part of your thesis statement.)
4. Citations
This handout presumes you already know why you should cite your sources (to establish your authority, to introduce persuasive evidence, to avoid plagiarism , etc.).
To fully cite a source requires two stages. The first happens in the body of your paper (the “in-text citation”) and the second happens on a separate page at the end of your paper (see “Works Cited List,” below.)
4.1 Citing a Block Quote (more than three lines)

- Long quotes can start to look like filler. Only use a block quote if you have a very good reason to include the whole passage. (You can usually make your point with a shorter quote.)
- Place the parenthetical citation (the author’s name and the page number) after the period . (This is different from inline quotes, below.)
- There is no comma between the author’s name and the page number.
- If the quotation runs across more than one page: (Wordsworth-Fuller 20-21) or (Wordsworth-Fuller 420-21).
- Skip wordy introductions such as, “In his informative guide The Amazing Writing Book , published by Elizabeth Mount College in 2010, the noted composition expert Maxwell Wordsworth-Fuller describes the importance of citations in MLA style papers.” Cutting the filler leaves more room to develop your own original ideas. (See “ Integrating Quotations .”)
4.2 Citing an Inline Quotation
When the passage you want to quote is less than three lines long, use inline style. Here we have two brief passages, taken from the same page of the same source, so we can handle both with a single parenthetical citation.

- The parenthetical citation appears outside the quoted material.
- The period that ends the sentence comes after the close parenthesis . (This is different from block quotes, above.)
- In this example, we have changed the first word a little, lowercasing it in order to fit it into our own sentence. To let the reader know what we changed, we put [] around it.
- Again, note the absence of a full sentence that explains who Wordsworth-Fuller is and where the quote comes from. All that info will be in the Works Cited list, so we leave it out of the body of the paper.
4.3 Citing a Paraphrase
Let’s imagine we want to reference Wordsworth-Fuller’s general idea about citation as a way to establish credibility, but we don’t need to include any of the technical details. We can save space, and make it much easier on our reader, if we paraphrase:

- Use paraphrasing for variety, or to make a passing reference without taking up much space.
- If we use an author’s idea, rephrased in our own words, we must still cite the idea.
Tips for avoiding common errors in MLA citations.
5. Works Cited List
A research paper isn’t a research paper unless you end with full bibliographical details on every source you cited. This part can be tedious and tricky; leave yourself plenty of time to do it.

How to format the “Works Cited” list of an MLA style paper.
- MS-Word Wind: Insert -> Page Break -> New Page.
- MS-Word Mac: Document Elements -> Break -> Page.
- Title your new page: Works Cited MLA style calls for no extra spaces above or below the page title; no special formatting.
5.1. How to Create an Individual Works Cited Entry
Exactly what goes into each item in your bibliography depends on what kind of item it is. The general format is as follows:
Author. Title of Source. Container, contributors, version, volume and issue, publisher, date, location.
Exactly how that basic format gets turned into a Works Cited entry depends on the source.
Here’s the basic format for any book:

- Gibaldi, Joseph, and George Spelvin.
- Gibaldi, Joseph, Alan Smithee, and George Spelvin.
- GIbaldi, Joseph et al.
- The italicized phrase “ et al. ” is an abbreviation for the Latin “et alia,” meaning “and others.”
- The “ al. ” is short for a longer word, so we mark the abbreviation with a period.
- The “ et” is not an abbreviation, so it doesn’t get a period.
- Place periods after the author’s name, after the title of the book, and at the end of the entry.
- The title of the book is italicized .
- The publisher is the name of the organization responsible for publishing the book. In this example it’s the Modern Language Association. It might instead be Project Gutenberg, the US Department of Agriculture, or the World Health Organization,
Basic Format for Any Academic Article
Author. “Title of Article in Quotation Marks.” Title of Journal in Italics, volume #, issue #, YEAR, pp. [pages of article]. Italicized Name of Database.

Let’s break that example down.
The author Margaret Kantz wrote the article “Helping Students Use Textual Sources Persuasively.” That article doesn’t exist on its own floating in space; it was published by a journal called College English, in the 52nd year of publication, in the first issue of its 52nd volume, in the year 1990, the article started on page 74 and ran through page 91. The student found this article while searching the database Academic Search Elite .
Every academic article has a specific title, and is published in a journal with a different title. (Online citation generators often get this wrong, and will often repeat the same title twice.)
What is this “volume 52, number 1”?
If College English were a TV series, then “volume” would be which season, and “number” would be the episode number. The title of the article would be the equivalent of a scene within that episode.
The title of the database, Academic Search Elite , is like the title of the streaming service you’d need to sign into. If you were talking about your favorite TV show and you told me it was on Netflix, or Disney+, I could find it. But if you told me “It’s on my MacBook” or “It’s on my Samsung phone,” that wouldn’t help me to find it.
Basic Format for Any Web Page

In the above example, reporter Camila Domonoske filed a news story called “Students Have ‘Dismaying’ Inability To Tell Fake News From Real, Study Finds,” that aired on a news program called The Two-Way , which is published by National Public Radio, and the story aired Nov 23, 2016.
In MLS Style, the full URL is optional. Really long URLs with long strings of numbers in them are often generated for specific users, so someone else who visits that same URL will often get an error message.
You might shorten the URL to “npr.org,” because it would be a simple matter to use a search engine to find the actual story.
Other Citation Examples
What if your source doesn’t fit any of my examples?
You might be trying to cite something that doesn’t fit the above pattern, like a social media post, a video game, a work of art, an email from a relative, a billboard, or something else. It’s just not practical for me to try to include an example of every single thing it’s possible to cite.
The MLA citation format is designed to be flexible, so that it works for forms of media that haven’t been invented yet.
See Purdue OWL’s handouts for how to create a bibliography entry for a book , an article in a periodical (such as a journal or newspaper), or an electronic source (such as an email, web page or a YouTube clip). See also this list of other common sources (such as a personal interview or a movie).
5.2. How to Organize Your Works Cited list
Sort the entries alphabetically by the author ‘s last name.
- If the author is an organization (such as a government agency or non-profit foundation), alphabetize according to the name of the organization .
- If you are citing a painting, or a composer, then obviously “author” has to be interpreted a little loosely.
- Unless your instructor ask you to organize your Works Cited list differently, everything should be alphabetized together, in a single list. MLA does not require that you separate works of different kinds, or that you cite works in the order that they appeared in your paper, or that you write annotations to go along with each item.
- Use double-spaced line height. (in my copy of Word, I select the text and choose Format -> Paragraph -> Line spacing -> Double -> OK.)
- Use hanging indent paragraph format. (In my copy of word, I select the text then choose Format -> Paragraph -> Indentation -> Special -> Hanging Indent.)
29 May 2011 — new document posted, replacing outdated handout written in 1999. 06 Jun 2011 — expanded section on organizing the Works Cited list, since several readers asked for clarification. 07 Jun 2011 — reorganized for emphasis 19 Apr 2012 — added numbers to more subheads 24 Mar 2014 — added details on Works Cited paragraph formatting. 02 Oct 2016 — updated with MLA 8th Edition details. 30 Nov 2016 — added annotated Works Cited sample image. 07 Sep 2020 — updated section 5.1
570 thoughts on “ MLA Format Papers: Step-by-step Tips for Formatting Research Essays in MLA Style ”
The information was very helpful
Pingback: Academic Argument: an evidence-based defense of a non-obvious position on a complex issue. | Jerz's Literacy Weblog (est. 1999)
Thanks for sharing such an informative post with us.
fantastic information
Thanks for info!
hello i am nate sedmack i am here to kill all the furries for what they did to gavin born
I’m learning more writing a paper
it was very informational and helped me a lot
Pingback: Flipped Classes: Omit Housekeeping Mechanics from Recorded Lectures to Lengthen Their Shelf-life | Jerz's Literacy Weblog
Curious how you would Cite this webpage? haha…
awesome reminders
what about if when your using a quote and there is no name just anonomus
Honestly, I’d say find another way to make your point. An anonymous saying like “A stitch in time saves nine” won’t help you demonstrate your ability to write the kind of scholarly paper that MLA is designed for. Certainly investigate the quote to find out whether it maybe comes from Shakespeare or some other source that you can quote. I might identify the example I used as “English proverb,” but since I won’t be marking your paper, you really should check with your instructor.
This article..thing is the only reason I am passing my online college class. Especially the citation builder. Thank you!
I would Like You To Give Simple Instructions Not Complicated Ones , and Include also how much Papers Should be worked on.
Khalid, if there is any particular detail you are confused about, please let me know what question you have and perhaps I can help. There is no specific answer to how much a paper should be worked on. It depends on what grade you want to earn, how much time you have, whether your instructor is willing to meet with you before the due date, whether your instructor will give you the chance to revise your work, and many other factors.
hahahah xD me too same
How do I cite a photo that I found online?
Is it a historical photograph or a photograph published in a book that someone scanned and posted on line, is it a photograph of something like a sculpture? Is your paper focused on the work of the photographer, the makeup artist who prepared the model, the digital image enhancer who altered the image, the model? There is no single correct way to cite a photograph, because there are many different reasons to cite a photograph. Your instructor would be able to give you more specific advice. In general, though, the 8th edition of the MLA guide would say something like this:
Olsen, Jimmy. “Superman Rescues Boy Scouts from Lava Pit.” Photograph. The Daily Planet . July 22, 1956.
If you found the picture on a blog or a Flickr gallery, adjust the citation accordingly. If you found the image as the result of a Google search for something, you might very well end up finding a page that re-uses someone else’s picture without appropriately giving credit. There are many variables. Talk to your instructor, who will be the one grading your work, and will therefore be the right person to advise you on what to do.
is the text or what you wrote supposed to be centered in the page or to the left margin
Left margin.
Pingback: New Graphic for MLA Style Paper Handout | Jerz's Literacy Weblog
cool it was helpful
Pingback: Business Question of the day! Thursday, March 10, 2016 | thebuzinessbreakdown
I think you should include online resource citation instructions
Click on “Citing” at the top of the page. One of the options on the other end of that link is how to cite a web page.
Pingback: How To Put Double Space On Microsoft Works – Information
which writing style (MLA, APA) have more importance for students of social sciences, media sciences and business?
It depends on the instructor or editor who’s calling the shots. http://subjectguides.library.american.edu/c.php?g=175008&p=1154150
Very informative. It helped introduce my tired old mind to the MLA format. So, I can better help coach and prepare my wife for her English course. Thank you very much.
Pingback: For Future Reference: MLA Formatting | wr115fisette
Pingback: For Future Reference: MLA Formatting | wr115mhcc
I’m using a book title and author as my paper heading. How is that formatted?
I would tell my own students that a book title and the name of an author is not a good paper title, and I would ask them to write a title that catches the reader’s attention, identifies the topic, and identifies what position the paper is going to take on the topic. But if you are not my student, then I’m not the person who will be evaluating your paper. MLA style puts the book title in italics. Other than that, I really don’t have any advice for you.
Thank you very much for this useful information. As a freshman in highschool, my biology teacher asked for me to write an essay in mLA format about evolution. I had no clue what mLA format was,so I searched it up and it brought me here. In middle school I never wrote an essay in this format before,but I feel very confident to type my first mLA essay and I’m excited to do so! (Right after I finish my draft >.<) thank you very much! (⌒▽⌒)✌
This wasn’t helpful at all
Shavez, what were you looking for? This page is about formatting a paper you have already written. The first section includes links to pages about how to write essays.
u a real nigga dennis
really dude my collies and I would prefer that you didn’t use any profane language due to younger children that may be reading this
thank u i got an A 97 percent
this was very helpful i got an A 95 percent
hi my name is Jessie i have to writ a 2 pages Essay about MLA can someone help me
Dennis, what lends itself to science in the APA system? And what lends itself to the Humanities with the MLA? TIA.
As compared to MLA papers, APA papers tend to be shorter, and divided up into sections. Authors who use APA style tend to publish more frequently, because their knowledge goes out of date more quickly; so the date is prominent in APA citations, and page numbers are rare.
By contrast, people who use MLA style tend to write longer essays that aren’t divided up into standard sections like “procedure” and “conclusions.” Humanities scholarship generally doesn’t go out of date quickly. Instead of conducting experiments, humanists read and write a lot of longer essays and books, re-interpreting and quoting passages from them. MLA style makes the page numbers prominent, so that other scholars can easily find and re-read those same passages for themselves, and further the work of scholarship as it is conducted in the humanities.
Thanks for the reply. What do you mean by ” MLA style tend to write longer essays that aren’t divided up into standard sections like “procedure” and “conclusions.”? Are we not suppose to use conclusions in MLA format? In my English class, we use MLA with conclusions, but what do you mean by “procedure” and “conclusions”? I understand each instructor is different but is it right to use conclusions in an MLA paper…or am I getting confused?
Typically papers written in MLA style DO have a conclusion, but it would not be set off in a separate section under the subheading “Conclusion.” MLA papers tend NOT to follow a standard, particular structure. Papers written in the sciences DO have a fairly rigid set of sections, with separate subheadings. But it’s best for you to talk to your teacher about the specifics of any asisgnment.
Ok, thanks. I just wanted to ask and clarify it. Also, doesn’t the word “humanist” means something else entirely? The Humanist term today implies ‘human’ and is often used for atheists, for example… or am I wrong?
I used the term “humanist” to mean “a person who studies the culture of humans,” without intending the more specific meaning you mention. At my school, the humanities division includes theologians.
seems easy enough
We get asked often about what “format” the college application essay should be in. Although not generally… http://t.co/v1TTNxtE4e
Pingback: Academic paper style guide research | Screenin' Culture
When using MLA format, do you list the book title, the title of the article or both?
For guidance on citing individual sources, see the link in item 4, above. This page is about formatting the paper once you’ve already written it.
I wrote a paper and it looks just like your example. I followed everything to the “t” and my professor says that my header is indented and my paragraphs are double indented and the page numbers are in wrong format. What can I do?
Winston, I suggest you talk to your professor. I have been teaching from thiis handout for years, and when a student makes a formatting error on a rough draft, I just ask them to fix it for the revision. But your instructor is the one who designed the assignment and who evaluates your submissions, so he or she is the person to approach with questions.
I agree. .let me ask you this. Are your headers indented?
The screenshot was taken from a page that I created following the instructions for using MS-Word with a MacBook Pro. I followed the instructions that are on the page. But surely your instructor gave you guidelines, in a handout or an assigned textbook, which is why I encourage you to have this conversation with your instructor. Whether your instructor does or does not agree with the information on this page really doesn’t matter, since your instructor created the assignment and evaluates it according to his or her own criteria. I suggest you let your your teacher know you are confused about what you did wrong, and ask for an opportunity to make minor formatting changes to a paper that, we hope, met all the major criteria.
How do you add footnotes to an MLA style paper?
Most word processors will have an Insert -> Footnote or Insert -> Note (footnote or endnote) option. Most short college papers don’t need footnotes. (They aren’t for documenting sources — use an in-text citation and a Works Cited list instead.) I suggest you talk to your instructor about whether you really do need to use a footnote.
RT @DennisJerz: MLA Format Papers: Step-by-step Instructions for Writing Research Essays #mlastyle http://t.co/B6pGb3Pkeh
Thank you so much!! I love the Bib builder!!
I’m glad to hear you found it helpful!
Dear Dr. Jerz,
I am writing to request permission to link your webpage, “MLA Format Papers: Step-by-step Instructions for Writing Research Essays” to our website.
Marie Walcroft Librarian Lansdale School of Business
I am glad you found this page helpful. Yes, you are welcome to include a link and a brief extract.
Can you put what information is supposed to be in each paragraph???
Emma, I’m afraid I don’t understand the question. I feel like you’ve asked me what emotions are supposed to be in each verse of a song, or what colors are supposed to be in a painting. The many different kinds of songs or paintings are all created for different reasons; likewise, paragraphs are assigned, written, and read for a whole range of different reasons, so there’s no answer that covers all possible cases.
that was beautiful
I really find this useful (especially fudging the line spacing to 2.1). Good job!
Im in middle school and I have to do this. I have never heard of MLA Format and this helped ALOT. Thanks so much! Hopefully I get a good grade on this paper!
“@pretti_slimm: @Thyler_Jonzy http://t.co/QIf00vlgws try this site looks helpful”I just found a sample paper on Google
Pingback: MLA Format Papers: Step-by-step Instructions for Writing Research Essays - My Blog
Pingback: Freshman English Composition Resources
Is the Table of Contents double spaced – MLA?
i think you should add an explanation about page header. that was what i was looking for
See item 2 from the table of contents: http://jerz.setonhill.edu/writing/academic1/mla-style-papers/#page-header
when you say page numbers (Wordworth-Fuller 20), are you referring to the page number within the MLA document or the page number the text appears on within the authors works?
In this case, your paper would be referring to something you found on page 20 of the text by Wordsworth-Fuller.
With your delicate information about to write MLA format essay in right way will lead me to successful college year.
Thank you for useful information about how to write MLA format essay. Before my college year I didn’t know there were many different forms of essay. When my professor asked me to write MLA format I had no idea how to write it, but with your delicate information I think I will survive my college year. Thank you again.
I’m glad to know you found this page helpful. Most instructors will be happy to help if you stop by during their office hours, and if your prof is too busy for that most universities will have a writing center where you can get help at any stage of any assignment involving writing.
Thank you for valuable information. Before my college year in America I didn’t know what MLA Format was, but with this delicate information I will survive my college year.
Pingback: How to Write a Successful Research Paper with MLA | Critical Approaches to the American Renaissance
That means the quote is from page 20 of the book or article written by Wordsworth-Fuller.
Very good information, I really needed this incite on research paper formats. It has such thorough details and that make it so much easier to understand.
How do you in text cite a website? I didnt really see much about that.
I think you should add an explanation about page numbers. That was what I was looking for, but I couldn’t find the significant area.
Section 2 explains how to put page numbers in the header, and section 4 discusses page numbers in citations.
read it… it’s there.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
In-Text Citations: An Overview
In-text citations are brief, unobtrusive references that direct readers to the works-cited-list entries for the sources you consulted and, where relevant, to the location in the source being cited.
An in-text citation begins with the shortest piece of information that directs your reader to the entry in the works-cited list. Thus, it begins with what ever comes first in the entry: the author’s name or the title (or description) of the work. The citation can appear in your prose or in parentheses.
Citation in prose Naomi Baron broke new ground on the subject. Parenthetical citation At least one researcher has broken new ground on the subject (Baron). Work cited Baron, Naomi S. “Redefining Reading: The Impact of Digital Communication Media.” PMLA , vol. 128, no. 1, Jan. 2013, pp. 193–200.
When relevant, an in-text citation also has a second component: if a specific part of a work is quoted or paraphrased and the work includes a page number, line number, time stamp, or other way to point readers to the place in the work where the information can be found, that location marker must be included in parentheses.
Parenthetical citation According to Naomi Baron, reading is “just half of literacy. The other half is writing” (194).
The author or title can also appear alongside the page number or other location marker in parentheses.
Parenthetical citation Reading is “just half of literacy. The other half is writing” (Baron 194).
All in-text references should be concise. Avoid, for instance, providing the author’s name or title of a work in both your prose and parentheses.
Citation (incorrect) According to Naomi Baron, reading is “just half of literacy. The other half is writing” (Baron 194). Citation (correct) According to Naomi Baron, reading is “just half of literacy. The other half is writing” (194).
For more on what to include in an in-text citation and how to style it, see sections 6.3–6.30 of the ninth edition of the MLA Handbook ).
55 Comments
Brandi unruh 10 april 2021 at 11:04 am.
Hello! I am a high school English teacher trying to answer a question that came up during our research unit. I can’t seem to find a definitive answer online. When using a shortened title in an in-text citation, does an ellipsis need to be included? For example, if the title was “The Problem of Poverty in America: A Historical and Cultural Analysis”, would the in-text citation be (“The Problem of Poverty in America...”) or (“The Problem of Poverty in America”)? Thank you for your time and expertise!
Your e-mail address will not be published
Laura Kiernan 12 April 2021 AT 11:04 AM
No, an ellipsis would not be used in an in-text citation. We provide extensive guidance on shortening titles in 6.10 of the new ninth edition of the MLA Handbook .
angel 10 May 2021 AT 02:05 PM
hii How to write an in text citation of an entry from encyclopedia which has an editor but no separate authors for each entry ?
William Feeler 11 May 2021 AT 01:05 PM
I see no mention of paragraph numbers for unpaginated prose or sections/lines for drama. are these practices gone?
Laura Kiernan 18 May 2021 AT 01:05 PM
This post provides a general overview of our approach to in-text citations. The complete guidelines appear in sections 6.1–6.30 of the ninth edition of the MLA Handbook .
Vonceil Park 11 May 2021 AT 01:05 PM
Dear MLA Staff, A professor at my College demands students to provide paragraph number in the in-text citation for online articles that have no page number nor paragraph number. Do we just count the paragraph number and put them in the parenthesis, for example: (para. 3)?
Laura Kiernan 18 May 2021 AT 12:05 PM
Thank you for your question. Your approach to modifying our style in accordance with your professor's instructions works, but we would suggest confirming that styling with your professor.
Arathi Babu 17 May 2021 AT 08:05 AM
How to write an in text citation of an unsigned entry from a reference work?
Laura Kiernan 08 June 2021 AT 11:06 AM
If the entry was in a print work, the in-text citation would include the entry’s title or a shortened version of the entry’s title and the page number of the quotation. If the entry was in a reference work without page numbers, the in-text citation should just contain the title or shortened title of the entry.
Sethu 17 May 2021 AT 02:05 PM
For example: Can I give an in-text citation like the following: Shakespeare, in his work Hamlet, quotes: "To be or not to be" (7).
For citing commonly studied verse works, see 6.22 in the ninth edition of the MLA Handbook .
Trinity Klein 21 May 2021 AT 11:05 AM
Can you please help with proper in-text citation placement for an embedded quotation? Does the citation come immediately after the quotation or at the very end of the sentence? For example, is this correct: He asks her to take him home “in the voice of a child afraid of the dark” which comes as a shock to Scout because he has so long held a bold and rebellious reputation (372). Or should the (372) come immediately after ...dark"...? Thank you!
For more information about the placement of a parenthetical citations, see 6.43 in the ninth edition of the MLA Handbook .
Karima 30 May 2021 AT 05:05 PM
Dear MLA staff, 1) In case i am quoting from multiple sources by the same author, am i required to introduce again the source i am quoting from in the beginning of my sentence? (Quotes are used in multiple paragraphs)
For guidance on citing multiple sources by the same author, see 6.8 in the ninth edition of the MLA Handbook .
Yves 23 June 2021 AT 06:06 PM
Hello, is there a specific rule about how to format a range of page numbers in the parenthetical citation? For example, could (Eden 44-45) be written as (Eden 44-5), or is only one example correct?
Laura Kiernan 24 September 2021 AT 02:09 PM
For information about styling number ranges, see section 2.139 of the ninth edition of the MLA Handbook .
Faliravo 11 August 2021 AT 05:08 AM
Good morning MLA team, My professor insists that I include the year of publication for in-text citations. Is it going to be okay if I insert the year between the author and the page number?
Thank you very much for your consideration.
Laura Kiernan 24 September 2021 AT 01:09 PM
Your approach to modifying our style in accordance with your professor’s instructions works, but we would suggest confirming that styling with your professor.
Pauline 14 September 2021 AT 11:09 PM
How do I cite an entire work. For example, if I want to say Toni Morrison's the "Bluest Eye" has been used as a textbook for many English literature classes, I suppose I shouldn't put any page number in the parenthetical citation. But I can't find any MLA references on this.
See section 4.14 of the ninth edition of the MLA Handbook .
myron glassenberg 04 February 2022 AT 01:02 PM
if source is the whole book, how do I cite in text and in works cited pages. e.g. freud (no page number) Freud , ( 1892) The Pleasure Principle.

Rita Rozzi 20 September 2023 AT 07:09 PM
There is no section 4.14 in the ninth edition. Do you have any updated information? Thank you.
Laura Kiernan 21 September 2023 AT 03:09 PM
Section 4.14, which is titled "Passing Mentions," can be found in chapter 4 of the ninth edition of the handbook.
Lauren McFall 13 October 2021 AT 02:10 PM
Students often refer to the same source consecutively across more than one sentence. I'm having a hard time finding information about the preferred approach according to the MLA. As a parallel, APA makes a specific recommendation - "cite the source in the first sentence in which it is relevant and do not repeat the citation in subsequent sentences as long as the source remains clear and unchanged" https://apastyle.apa.org/style-grammar-guidelines/citations/appropriate-citation
Laura Kiernan 20 October 2021 AT 04:10 PM
See 6.45 of the ninth edition of the MLA Handbook .
Ruth Schafer 01 December 2022 AT 07:12 PM
6.45 out of the MLA Handbook's ninth edition does not provide an example of how to cite a multi-sentence paraphrase when using an unpaginated source. Can you give an example of how to cite a multi-sentence paraphrase where the source does not have published page numbering?
Should I introduce the source in my prose and then again at the end of the multi-sentence paraphrase in parentheses when I have finished citing the paraphrase? Example: John Smith from Smith Architecture explains that crawl space foundations are...blah blah blah. These foundations are most commonly used in midwestern constructions where the frost line is...blah, blah, blah. Keep writing the paraphrase and then at the end of the final sentence instead of a page citation write the author's last name (Smith). This way if you switch to a different source, at least the reader knows that you have finished with the Smith source and have moved on to your own commentary or another source's information. Usually, I'd use a page citation at the end of the paraphrase, but when dealing with a source that does not have page numbering, I'm unsure what to do.
Lizzie 18 October 2021 AT 10:10 PM
If I only use textual evidence from the novel I'm examining, do I need to include the authors name with each in text citation? There are no other works cited, so it seems redundant/clutter-y to me
Kayden 29 October 2021 AT 05:10 PM
If I'm trying to cite multiple paragraphs from the same source would it be correct to say (par. 3 and 13) or should it be (par. 3, 13) and is it different if they are next to each other too like (par. 6-7) or (par. 6 and 7).
Laura Kiernan 04 November 2021 AT 11:11 AM
See sections 6.18–6.20 of the ninth edition of the MLA Handbook .
Rachel 17 November 2021 AT 01:11 PM
When citing from an online source without pagination, if you include the author's name in the introduction to the quote, do you need to include anything in parentheses like the article title?
Laura Kiernan 22 November 2021 AT 12:11 PM
See section 6.26 of the ninth edition of the MLA Handbook .
July 25 November 2021 AT 05:11 PM
When quoting an online source (e.g. a website), do I have to indicate the fact that it's an online source in the in-text-citations as in (Name [online]) or is the author's name enough?
Thank you in advance for your answer.
Laura Kiernan 29 November 2021 AT 10:11 AM
According to MLA style, an in-text citation for an online work should not note that the work is online.
Pinkie 19 March 2022 AT 08:03 PM
If I'm writing a response paper, and I need to summarize the whole article to introduce it, then should I use in-text citation?
Laura Kiernan 25 March 2022 AT 01:03 PM
For guidance on paraphrasing, see sections 4.5–4.8 of the ninth edition of the MLA Handbook .
Kay 09 April 2022 AT 06:04 PM
Hi, am I supposed to include the DOI when one is available in the citation? If I cite the print version of a journal article that has a DOI, still include the DOI in the citation? Thank you!
Laura Kiernan 11 April 2022 AT 11:04 AM
Thank you for your questions. For guidance on including a DOI in your works-cited-list entry, see sections 5.84 and 5.93 in the ninth edition of the MLA Handbook .
Mike 16 April 2022 AT 05:04 PM
Website in-text Citation...
When I'm writing an in-text citation for a website, I'm seeing all manner of different things to include. Do I need to add the author name and year of publishing for the article?\ Do I just need the website name? I'm not really understanding what I need to add or obtain for such a citation within the text I'm writing.
I'm writing a book on my life, and I'm quoting a particular webpage to show one particular angle of an argument I'm making, and, of course, it's not common knowledge, so I want to make sure that I follow all the rules for this kind of thing, so I don't get in trouble with the author(s) of the sources I have quoted from...
Laura Kiernan 18 April 2022 AT 02:04 PM
Thank you for your questions about MLA style. For guidance on in-text citations for web pages, see section 6.26 of the ninth edition of the MLA Handbook .
Cynthia 21 May 2022 AT 10:05 PM
When you're doing an In-text citations do you put the quotations over the chapter title and then quotations over what you get from the text or do you italicize the title?
Laura Kiernan 25 May 2022 AT 03:05 PM
Thank you for your question. For guidance on how to style chapter titles, see 2.109 of the ninth edition of the MLA Handbook .
Napatsi 15 August 2022 AT 07:08 PM
I'm trying to find how to put in the in-text citation for a UN declaration article but can only find the "Resolutions of International Governing Bodies" on page 446 of the 9th edition but not how to out it in without an author.
Kim 27 September 2022 AT 12:09 PM
I'm quoting a passage from an unpublished manuscript, and it is not the only work I'm citing by the author, but the only one without a year. So using "Smith 1995, 82" is not possible. What would an in-text citation for this case look like?
Jen 17 November 2022 AT 08:11 PM
How do I cite a news cast for in-text citation like ABC News?
Samantha 04 December 2022 AT 05:12 PM
Hi, For MLA format, should a quote where you need to de-capitalize the first letter be written as "you want" or "(y)ou want". Thanks!
Laura Kiernan 07 December 2022 AT 01:12 PM
Thank you for your question. For guidance on how to indicate that you have lowercased the first letter of a quotation, see 6.56 of the ninth edition of the MLA Handbook .
Maria Albeti 07 February 2023 AT 01:02 PM
Stewart, David W. Focus groups. In: Frey, B.B. (ed.) The SAGE Encyclopedia of Educational Research, Measurement, and Evaluation, vol. 2, pp. 687–692. Thousand Oaks: Sage Publications 2018 In this case, how is the correct form to write, because the article is IN the the book?
Eros Karadzhov 15 February 2023 AT 02:02 PM
If we have a sentence that is a statement, but at the end we quote a question, which punctuation mark do we keep, the question mark or the period; maybe both? Example: (1) The author ends his poem with the following question on purpose: "Or does it explode?" (Hughes 11). (2) The author ends his poem with the following question on purpose: "Or does it explode" (Hughes 11)?
Which would be correct, or maybe both are wrong?
Thank you in advance!
Laura Kiernan 16 February 2023 AT 03:02 PM
Thank you for your question. For guidance on quotations ending in a question mark, see section 6.53 of the ninth edition of the MLA Handbook .
Anonymous 08 March 2023 AT 05:03 PM
What about online articles with no known author or multiple authors? What should the in-text citation look like?
Maria 25 March 2023 AT 04:03 PM
Please settle a dispute with my colleagues. I encourage composition students to avoid listing the title of journal articles within the essay unless it is especially relevant because it clutters their arguments. I came to this conclusion from my interpretation of this statement from MLA: "All in-text references should be concise. Avoid, for instance, providing the author’s name or title of a work in both your prose and parentheses." Could someone please provide an answer or further clarification?
Erika Suffern 30 March 2023 AT 04:03 PM
You are right to identify a principle of concision in our guidelines. That said, it is not wrong to mention a title in prose, but it should be done, as you note, when relevant–not as a de rigeur practice or for “filler.” As Eric Hayot notes in The Elements of Academic Style: Writing for the Humanities (Columbia UP, 2014), “giving the title” in prose “suggests fuller forthcoming treatment” (159). Another reason for including the title in prose might be to call attention to something about it. Many writers who do mention a title in prose fear having an incomplete citation and are tempted also to include the title in a parenthetical reference, which is unnecessary.
Jay 29 April 2023 AT 12:04 AM
How do I in-text cite a direct quote from the introduction of an ebook with no page numbers? Would I write (Author "Introduction") or just write (Author)?
Kiara 11 February 2024 AT 03:02 PM
Hello! I am a university student who is currently creating works cited entries and in-text citations for a reflection essay. How do I properly cite professor and peer comments?
Join the Conversation
We invite you to comment on this post and exchange ideas with other site visitors. Comments are moderated and subject to terms of service.
If you have a question for the MLA's editors, submit it to Ask the MLA!
Home / Guides / Citation Guides / MLA Format / Creating an MLA Bibliography
Creating an MLA Bibliography
If you write a research paper in MLA format, then you will need to include a Works Cited page according to the current 9th edition of the Modern Language Association (MLA) guidelines. Along with citing your sources within the body of your paper, you also need to include full citations of all sources at the end of your paper. The references in a bibliography are formatted in the same way as they would be in a Works Cited page. However, a bibliography refers to all works that you have consulted in your research, even if you did not use their information directly in your paper.
When you use the correct MLA bibliography format, it shows the reader what sources you consulted, makes finding your sources easier for the reader, and gives credibility to your work as a researcher and writer. This MLA sample paper will show you how the bibliography is incorporated into the rest of your paper. We also have a guide on APA reference pages , if you are following APA style in your paper.
Works cited or bibliography?
You may be wondering, what is a bibliography, and how is it different from a Works Cited page? The difference between the two is that while a bibliography refers to any source you consulted to write your research paper, a Works Cited page only includes full citations of the sources you quoted or paraphrased within your paper.
Typically, when someone says, “MLA bibliography” they really mean a Works Cited page, since the MLA format usually uses a Works Cited page instead of a bibliography.
A bibliography in MLA format may also refer to a Works Consulted page. If you used other sources that you did not directly quote or paraphrase within the paper, you will need to create a Works Consulted/Additional Resources page. A Works Consulted page starts on a separate page and follows the Works Cited page. It follows the same formatting guidelines as a Works Cited page, but you will use Works Consulted (or Additional Resources) as the title.
If you’re unsure of what to include in your citations list (works cited, works consulted, or both), ask your instructor. For the rest of this article, we will refer to this page as the MLA bibliography.
MLA bibliography formatting guidelines
These are the formatting rules you need to follow to create your bibliography according to MLA’s current edition guidelines. Your first page(s) will be your Works Cited page(s) and include the references that you directly refer to in your paper. Usually, this is all that is needed. If your instructor wants you to also include the works you consulted but did not include in your paper (more like a bibliography), then add Works Consulted or Additional Resources page for these sources.
- Your MLA Works Cited (and Works Consulted or Additional Resources pages) should begin on a separate page or pages at the end of your essay.
- Your essay should have a header on every page that includes your last name and the page number.
- The last name/page number header should be on the top right of each page with a ½ inch margin from the top of the page.
- One-inch margins.
- Title the page Works Cited (no italicization or quotation marks) unless otherwise instructed. Center the title. The top should look like this:

- Only center the Works Cited title; all citations should be left-justified.
- Double-space citations.
- Do not add an additional space between citations.
- After the first line, use a hanging indent of ½ inch on all additional lines of a citation. The hanging indent should look like this:

- Typically, this is the author’s last name, but sometimes it could be the title of the source if the author’s name is not available.

If you have a Works Consulted or Additional Resources page after your Works Cited page, format it in the same way, but with the title of Works Consulted or Additional Resources instead of Works Cited. Alternatively, your instructor may require a bibliography. If this is the case, all your sources, whether they are cited in your paper are not, are listed on the same page.
MLA citation guidelines
These are the rules you need to follow to create citations for an MLA bibliography. This section contains information on how to correctly use author names, punctuation, capitalization, fonts, page numbers, DOIs, and URLS in the citations on your MLA bibliography.
Author names
After the title Works Cited, the last name of the author of a source should be the first thing to appear on your page.
List the author’s last name followed by a comma, then the first name followed by the middle name or middle initial if applicable, without a comma separating the first and middle names. Add a period after the name.
Rowling, J.K.
Smith, Alexander McCall.
- Do not include titles such as Dr., Mrs., etc. or professional qualifications such as PhD, M.S., etc. with author names.
- Include suffixes such as Jr. or III after the author’s first name. Separate the first name and the suffix by a comma unless the suffix is a numeral. For example, to cite an author named John Smith, Jr., you would type Smith, John, Jr.
Sources with two authors
For a source with two authors, list the author names in your citation in the order they appear on the source, not alphabetically.
Type the last name of the first author listed on the source followed by a comma, then the first author’s first name followed by a comma. Then type the word “and” then list the second author’s first name and last name in the standard order. Follow the second name with a period.
Include middle names or initials and suffixes when applicable according to the guidelines for one author as listed above.
1st Author’s Last Name, First Name, and 2nd Author’s First Name Last Name.
Lutz, Lisa, and David Hayward.
Clark, Mary Higgins, and Alafair Burke.
Sources with three or more authors
For a source with three or more authors, only type the last and first name of the first author listed in the source, followed by a comma and the phrase et al., which is Latin for “and others.” Be sure to always place a period after the al in et al. but never after the et.
1st Author’s Last Name, First Name, et al.
Charaipotra, Sona, et al.
Williams, Beatriz, et al. All the Ways We Said Goodbye . HarperLuxe, 2020.
Organizations and corporations as authors
For sources with organizations or corporations listed as the author, type the name of the corporation in place of an author’s name. If the organization begins with an article like a, an, or the, it should be excluded in the Works Cited entry.
Modern Language Association of America. MLA Handbook . 2016.
*Note: If the organization is listed as both the author and the publisher, begin the citation with the title and include the organization’s name within the publisher field instead.
For a source with no author listed, simply omit the author’s name and begin the citation with the title of the source. Use the first letter of the title when considering alphabetical order in your MLA bibliography.
Capitalization
Use MLA title case when citing titles of sources.
- Nouns, pronouns, verbs, adverbs, adjectives, and subordinating conjunctions should be capitalized.
- Articles, prepositions, and coordinating conjunctions should not be capitalized.
Font formatting
- Italicize the titles of larger works such as magazines and books. Also, italicize database and website names.
- Instead of italicization, use quotation marks around titles of shorter works such as poems, short stories, and articles.
- End all bibliography citations with a period.
Page numbers
Include page numbers in your full citations whenever possible. This helps the reader find the information you cited more quickly than if you just cited the entire source and lends more credibility to your argument. If you cite different pages from the same source within your paper, you should cite the entire source on your MLA bibliography instead of listing all of the page numbers you used.
When including page numbers in a citation, use the abbreviation p. to cite one page and the abbreviation pp. to cite multiple pages with a hyphen between the page numbers.
p. 25 or pp. 16-37
When citing page numbers in MLA, omit the first set of repeated digits.
pp. 365-69, not pp. 365-369
DOIs and URLs
A Digital Object Identifier (DOI) is used to locate and identify an online source. While URLs may change or web pages might be edited or updated, a DOI is permanent and therefore more useful in a source citation.
- Use a DOI (digital object identifier) whenever possible. Otherwise use a permalink or URL.
- DOIs should be formatted with “https://doi.org/” before the DOI number.
- Do not include “http://” or “https://” in your URLs.
- As either one will be the last part of your citation, place a period after the DOI or URL. (Note that this period is not part of the DOI or URL.)
Butarbutar, R, et al. “Analyzing of Puzzle Local Culture-Based in Teaching English for Young Learners.” IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science , vol. 343, 2019, https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/343/1/012208.
Accessed dates
Since the previous 8th edition of the MLA Handbook was published, you do NOT need to list an accessed date for a stable source (e.g., online newspaper article, journal article, photograph, etc.). However, including an access date is good to include when a source does not have a publishing date, and some instructors will request that accessed dates be included for all sources.
If you do include an access date, here’s how to format it:
- Place it at the end of the citation without “http://” or “https://”.
- Write “Accessed” first, followed by the date accessed.
- The date accessed should be formatted as Day Month (abbreviated) Year.
Butarbutar, R, et al. “IOPscience.” IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science , IOP Publishing, 1 Oct. 2019, iopscience.iop.org/article/10.1088/1755-1315/343/1/012208/meta. Accessed 8 Oct. 2020.
Note: If you choose to list an accessed date after a DOI, the accessed date part of the citation will follow the period after the DOI and will end with a period at the end of the citation
Butarbutar, R, et al. “Analyzing of Puzzle Local Culture-Based in Teaching English for Young Learners.” IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science , vol. 343, 2019, https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/343/1/012208. Accessed 8 Oct. 2020.
MLA 8 th edition vs MLA 9 th edition
The 9 th edition of the MLA handbook re-introduces guidelines regarding paper formatting (which were not present in the 8 th edition). The guidance in the 9 th addition is consistent with the guidance in previous editions and expands on the formatting of tables, figures/illustrations, and lists. The 9 th edition also offers new guidance in areas like annotated bibliographies, inclusive language, and footnotes/endnotes.
Many of the differences between the 8 th edition and 9 th edition have to do with the formatting of the core elements in reference list entries. Some of the main changes include:
Written by Grace Turney , freelance writer and artist. Grace is a former librarian and has a Master’s degree in Library Science and Information Technology.
MLA Formatting Guide
MLA Formatting
Annotated Bibliography
Bibliography
- Block Quotes
- et al Usage
- In-text Citations
- Paraphrasing
- Page Numbers
- Sample Paper
- Works Cited
- MLA 8 Updates
- MLA 9 Updates
- View MLA Guide
Citation Examples
- Book Chapter
- Journal Article
- Magazine Article
- Newspaper Article
- Website (no author)
- View all MLA Examples
How useful was this post?
Click on a star to rate it!
We are sorry that this post was not useful for you!
Let us improve this post!
Tell us how we can improve this post?
An MLA bibliography is similar to the Works Cited list that you include at the end of your paper. The only difference between a Works Cited list and a bibliography is that for the former, you need to include the entries for only the sources you cited in the text, whereas for the latter you can also include the sources you consulted to write your paper but didn’t directly cite in your writing. MLA generally prefers Works Cited lists to bibliographies.
If your instructor advises you to create an MLA bibliography, follow the same guidelines you would follow for creating an MLA Works Cited list.
The bibliography list appears at the end of the paper, after any endnotes if they are present.
All margins (top, bottom, left, and right) should be set at 1 inch.
Write the running head in the top right of the page at 0.5 inch from the top. Use the running head “Surname Page #.”
The font should be clear enough to read. Use Times New Roman font of size 12 points.
Entries should be double-spaced. If any entry runs over more than a line, indent the subsequent lines of the entry 0.5 inch from the left margin.
Bibliographic entries are arranged alphabetically according to the first item in each entry.
Title your bibliography as “Bibliography.”
Braidotti, Rosi. The Posthuman . Polity, 2013.
Brisini, Travis. “Phytomorphizing Performance: Plant Performance in an Expanded Field.” Text and Performance Quarterly , vol. 39, 2019, pp. 1–2.
Riccio, Thomas. “Reimagining Yup’ik and Inupiat Performance.” Northwest Theatre Review , vol. 12, no. 1, 1999, pp. 1–30.
General rules for creating an annotated bibliography
The annotation is given after the source entry and is generally about 100-150 words in length. The annotation should be indented 1 inch from the left margin to distinguish it from the hanging indent within the citation entry.
The annotation, in general, should be written as short phrases. However, you may use full sentences as well.
The annotation for each source is usually no longer than one paragraph. However, if multiple paragraphs are included, indent the second and subsequent paragraphs without any extra line space between them.
The annotation provides basic information about the source, but does not include details about the source, quotes from the author, etc. The information can be descriptive (by generally describing what the source covers) or evaluative (by evaluating the source’s usefulness to the argument in your paper).
Example annotated bibliography
The below is an example of an annotated bibliography:
Morritt, Robert D. Beringia: Archaic Migrations into North America . Cambridge Scholars Pub, 2011.
The author studies the migration of cultures from Asia to North America. The connection between the North American Athabaskan language family and Siberia is presented, together with comparisons and examinations of the implications of linguistics from anthropological, archaeological, and folklore perspectives. This book explores the origins of the earliest people in the Americas, including Siberian, Dene, and Navajo Creation myths; linguistic comparisons between Siberian Ket Navajo and Western Apache; and comparisons between indigenous groups that appear to share the same origin.
MLA Citation Examples
Writing Tools
Citation Generators
Other Citation Styles
Plagiarism Checker
Upload a paper to check for plagiarism against billions of sources and get advanced writing suggestions for clarity and style.
Get Started
How Much Research Is Being Written by Large Language Models?
New studies show a marked spike in LLM usage in academia, especially in computer science. What does this mean for researchers and reviewers?

In March of this year, a tweet about an academic paper went viral for all the wrong reasons. The introduction section of the paper, published in Elsevier’s Surfaces and Interfaces , began with this line: Certainly, here is a possible introduction for your topic.
Look familiar?
It should, if you are a user of ChatGPT and have applied its talents for the purpose of content generation. LLMs are being increasingly used to assist with writing tasks, but examples like this in academia are largely anecdotal and had not been quantified before now.
“While this is an egregious example,” says James Zou , associate professor of biomedical data science and, by courtesy, of computer science and of electrical engineering at Stanford, “in many cases, it’s less obvious, and that’s why we need to develop more granular and robust statistical methods to estimate the frequency and magnitude of LLM usage. At this particular moment, people want to know what content around us is written by AI. This is especially important in the context of research, for the papers we author and read and the reviews we get on our papers. That’s why we wanted to study how much of those have been written with the help of AI.”
In two papers looking at LLM use in scientific publishings, Zou and his team* found that 17.5% of computer science papers and 16.9% of peer review text had at least some content drafted by AI. The paper on LLM usage in peer reviews will be presented at the International Conference on Machine Learning.
Read Mapping the Increasing Use of LLMs in Scientific Papers and Monitoring AI-Modified Content at Scale: A Case Study on the Impact of ChatGPT on AI Conference Peer Reviews
Here Zou discusses the findings and implications of this work, which was supported through a Stanford HAI Hoffman Yee Research Grant .
How did you determine whether AI wrote sections of a paper or a review?
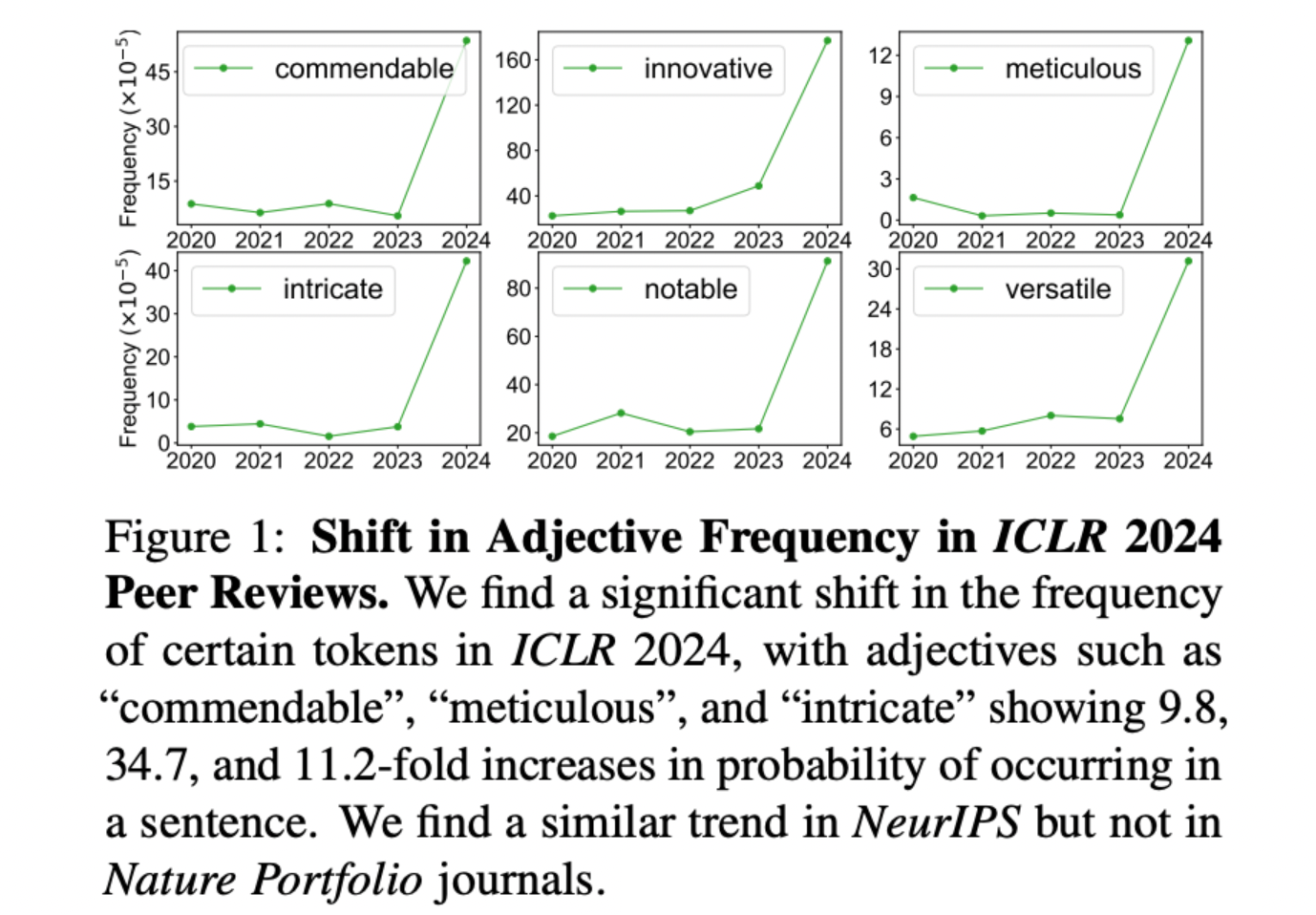
We first saw that there are these specific worlds – like commendable, innovative, meticulous, pivotal, intricate, realm, and showcasing – whose frequency in reviews sharply spiked, coinciding with the release of ChatGPT. Additionally, we know that these words are much more likely to be used by LLMs than by humans. The reason we know this is that we actually did an experiment where we took many papers, used LLMs to write reviews of them, and compared those reviews to reviews written by human reviewers on the same papers. Then we quantified which words are more likely to be used by LLMs vs. humans, and those are exactly the words listed. The fact that they are more likely to be used by an LLM and that they have also seen a sharp spike coinciding with the release of LLMs is strong evidence.
Some journals permit the use of LLMs in academic writing, as long as it’s noted, while others, including Science and the ICML conference, prohibit it. How are the ethics perceived in academia?
This is an important and timely topic because the policies of various journals are changing very quickly. For example, Science said in the beginning that they would not allow authors to use language models in their submissions, but they later changed their policy and said that people could use language models, but authors have to explicitly note where the language model is being used. All the journals are struggling with how to define this and what’s the right way going forward.
You observed an increase in usage of LLMs in academic writing, particularly in computer science papers (up to 17.5%). Math and Nature family papers, meanwhile, used AI text about 6.3% of the time. What do you think accounts for the discrepancy between these disciplines?
Artificial intelligence and computer science disciplines have seen an explosion in the number of papers submitted to conferences like ICLR and NeurIPS. And I think that’s really caused a strong burden, in many ways, to reviewers and to authors. So now it’s increasingly difficult to find qualified reviewers who have time to review all these papers. And some authors may feel more competition that they need to keep up and keep writing more and faster.
You analyzed close to a million papers on arXiv, bioRxiv, and Nature from January 2020 to February 2024. Do any of these journals include humanities papers or anything in the social sciences?
We mostly wanted to focus more on CS and engineering and biomedical areas and interdisciplinary areas, like Nature family journals, which also publish some social science papers. Availability mattered in this case. So, it’s relatively easy for us to get data from arXiv, bioRxiv, and Nature . A lot of AI conferences also make reviews publicly available. That’s not the case for humanities journals.
Did any results surprise you?
A few months after ChatGPT’s launch, we started to see a rapid, linear increase in the usage pattern in academic writing. This tells us how quickly these LLM technologies diffuse into the community and become adopted by researchers. The most surprising finding is the magnitude and speed of the increase in language model usage. Nearly a fifth of papers and peer review text use LLM modification. We also found that peer reviews submitted closer to the deadline and those less likely to engage with author rebuttal were more likely to use LLMs.
This suggests a couple of things. Perhaps some of these reviewers are not as engaged with reviewing these papers, and that’s why they are offloading some of the work to AI to help. This could be problematic if reviewers are not fully involved. As one of the pillars of the scientific process, it is still necessary to have human experts providing objective and rigorous evaluations. If this is being diluted, that’s not great for the scientific community.
What do your findings mean for the broader research community?
LLMs are transforming how we do research. It’s clear from our work that many papers we read are written with the help of LLMs. There needs to be more transparency, and people should state explicitly how LLMs are used and if they are used substantially. I don’t think it’s always a bad thing for people to use LLMs. In many areas, this can be very useful. For someone who is not a native English speaker, having the model polish their writing can be helpful. There are constructive ways for people to use LLMs in the research process; for example, in earlier stages of their draft. You could get useful feedback from a LLM in real time instead of waiting weeks or months to get external feedback.
But I think it’s still very important for the human researchers to be accountable for everything that is submitted and presented. They should be able to say, “Yes, I will stand behind the statements that are written in this paper.”
*Collaborators include: Weixin Liang , Yaohui Zhang , Zhengxuan Wu , Haley Lepp , Wenlong Ji , Xuandong Zhao , Hancheng Cao , Sheng Liu , Siyu He , Zhi Huang , Diyi Yang , Christopher Potts , Christopher D. Manning , Zachary Izzo , Yaohui Zhang , Lingjiao Chen , Haotian Ye , and Daniel A. McFarland .
Stanford HAI’s mission is to advance AI research, education, policy and practice to improve the human condition. Learn more .
More News Topics
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
MLA Sample Works Cited Page

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
Note: We have chosen to include the date of access for the online sources below. The latest MLA guidelines specify that this is optional, but strongly recommended for sources whose date of publication is unavailable.
Note also: The citation for An Inconvenient Truth below assumes the film has been cited by its title in the text. If it had been cited by the name of its director, the citation would need to begin with Guggenheim's surname. MLA guidelines specify that both styles are acceptable (see, e.g., this "Ask the MLA" page ).
Works Cited
Dean, Cornelia. "Executive on a Mission: Saving the Planet." The New York Times , 22 May 2007, www.nytimes.com/2007/05/22/science/earth/22ander.html?_r=0. Accessed 29 May 2019.
Ebert, Roger. Review of An Inconvenient Truth , directed by Davis Guggenheim. Ebert Digital LLC , 1 June 2006, www.rogerebert.com/reviews/an-inconvenient-truth-2006. Accessed 15 June 2019.
Gowdy, John. "Avoiding Self-Organized Extinction: Toward a Co-Evolutionary Economics of Sustainability." International Journal of Sustainable Development and World Ecology, vol. 14, no. 1, 2007, pp. 27-36.
Harris, Rob, and Andrew C. Revkin. “Clinton on Climate Change.” The New York Times , 17 May 2007, www.nytimes.com/video/world/americas/1194817109438/clinton-on-climate-change.html. Accessed 29 July 2016.
An Inconvenient Truth . Directed by Davis Guggenheim, Paramount, 2006.
Leroux, Marcel. Global Warming: Myth or Reality?: The Erring Ways of Climatology . Springer, 2005.
Milken, Michael, et al. "On Global Warming and Financial Imbalances." New Perspectives Quarterly , vol. 23, no. 4, 2006, p. 63.
Nordhaus, William D. "After Kyoto: Alternative Mechanisms to Control Global Warming." American Economic Review , vol. 96, no. 2, 2006, pp. 31-34.
---. "Global Warming Economics." Science, vol. 294, no. 5545, 9 Nov. 2001, pp. 1283-84, DOI: 10.1126/science.1065007.
Regas, Diane. “Three Key Energy Policies That Can Help Us Turn the Corner on Climate.” Environmental Defense Fund , 1 June 2016, www.edf.org/blog/2016/06/01/3-key-energy-policies-can-help-us-turn-corner-climate. Accessed 19 July 2016.
Revkin, Andrew C. “Clinton on Climate Change.” The New York Times , 17 May 2007, www.nytimes.com/video/world/americas/1194817109438/clinton-on-climate-change.html. Accessed 29 July 2016.
Shulte, Bret. "Putting a Price on Pollution." US News & World Report , vol. 142, no. 17, 14 May 2007, p. 37. Ebsco, Access no: 24984616.
Uzawa, Hirofumi. Economic Theory and Global Warming . Cambridge UP, 2003.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Text Formatting. Heading and Title. Running Head with Page Numbers. Placement of the List of Works Cited. Tables and Illustrations. Paper and Printing. Corrections and Insertions on Printouts. Binding a Printed Paper. Electronic Submission.
Formatting a Research Paper. The following formatting rules can be found in the MLA Style Center. Format your paper with 1 inch margins on all sides. Select an easily readable font (e.g. 12 point, Times New Roman) Double-space the entire paper. This should include text and the list of works cited.
Cite your MLA source. Start by applying these MLA format guidelines to your document: Use an easily readable font like 12 pt Times New Roman. Set 1 inch page margins. Use double line spacing. Include a ½" indent for new paragraphs. Include a four-line MLA heading on the first page. Center the paper's title.
Type your paper on a computer and print it out on standard, white 8.5 x 11-inch paper. Double-space the text of your paper and use a legible font (e.g. Times New Roman). Whatever font you choose, MLA recommends that the regular and italics type styles contrast enough that they are each distinct from one another.
MLA (Modern Language Association) style is most commonly used to write papers and cite sources within the liberal arts and humanities. This resource, updated to reflect the MLA Handbook (9th ed.), offers examples for the general format of MLA research papers, in-text citations, endnotes/footnotes, and the Works Cited page.
MLA Works Cited Page: Basic Format; MLA Works Cited Page: Books; MLA Works Cited Page: Periodicals; MLA Works Cited: Electronic Sources (Web Publications) MLA Works Cited: Other Common Sources; MLA Additional Resources; MLA Abbreviations; MLA Sample Works Cited Page; MLA Sample Paper; MLA Tables, Figures, and Examples; MLA PowerPoint Presentation
Your paper should have your name, your instructor's name, the class name, and the due date in the top left corner of the page. It should be double spaced and use the same font type and size as the rest of your paper. The title of your paper should be centered on the first line after your heading.
Capitalize headings like the titles of works, as explained in section 1.2 of the MLA Handbook. Length. The shorter, the better." Work Cited. ... Above is a template you can use every time you need to set-up a research paper using MLA style format. Simply open the template and type your own information every time you need to write an MLA style ...
Above tables: capitalize the title of the table like other titles and number it (ex. Table 1). Below the table: give the source of the table and any notes with lower-case letters. ... *Page numbers refer to the MLA Handbook for Writers of Research Papers, available in the UW-Whitewater libraries in print. << Previous: In-Text Citation; Last ...
Like all the other text in an MLA style paper, the title block is double-spaced.; The title is in the same font as the rest of the paper — it is not boldface, or enlarged.; There is no extra space above or below the title.; A truly informative title will include the general topic, and your precise opinion on that topic. (So, if you pan to compare Hamlet and Macbeth, your title should state ...
MLA Paper Format General Guidelines. In general, the MLA style formatting guidelines are flexible. That's why so many teachers and students like to use this writing style for their middle school, high school, and college research papers. However, while MLA is flexible, it still has a few formatting rules students need to adhere to. The ...
Most research papers use a standard MLA format heading, like the one seen above. If your instructor requires you to create a standalone title page, ask him or her for specifications. MLA does not have specific instructions for developing an MLA title page. We recommend you use an MLA header for your project.
MLA 8 MLA 9 Only include sources cited in the body of the paper in the Works Cited Page. Include sources that helped you in the research process but were not cited in the body of your paper. RULE #4: CONTAINER RULES. The research paper must include at the title of the container for digital sources.
Like the rest of an MLA format paper, the Works Cited should be left-aligned and double-spaced with 1-inch margins. You can use our free MLA Citation Generator to create and manage your Works Cited list. Choose your source type and enter the URL, DOI or title to get started. Generate accurate MLA citations with Scribbr
Revised on March 5, 2024. The first page of your MLA format paper starts with a four-line left-aligned header containing: Your full name. Your instructor's name. The course name and number. The date of submission. After the header, the title of the paper is centred on a new line, in title case. The header and title do not take any special ...
In-Text Citations: An Overview. In-text citations are brief, unobtrusive references that direct readers to the works-cited-list entries for the sources you consulted and, where relevant, to the location in the source being cited. An in-text citation begins with the shortest piece of information that directs your reader to the entry in the ...
MLA 8 th edition vs MLA 9 th edition. The 9 th edition of the MLA handbook re-introduces guidelines regarding paper formatting (which were not present in the 8 th edition). The guidance in the 9 th addition is consistent with the guidance in previous editions and expands on the formatting of tables, figures/illustrations, and lists. The 9 th edition also offers new guidance in areas like ...
MLA (Modern Language Association) style is most commonly used to write papers and cite sources within the liberal arts and humanities. This resource, updated to reflect the MLA Handbook (9th ed.), offers examples for the general format of MLA research papers, in-text citations, endnotes/footnotes, and the Works Cited page.
To create an MLA format title page, list the following on separate lines, left-aligned at the top of the page: Then leave a few blank lines and list the title of the paper, centered and in title case, halfway down the page. All text should be double-spaced and in the same font as the rest of the paper. Note: If you're using a title page ...
If you refer to a journal article that appeared on pages 225 through 250, list the page numbers on your Works Cited page as pp. 225-50 (Note: MLA style dictates that you should omit the first sets of repeated digits. In our example, the digit in the hundreds place is repeated between 2 25 and 2 50, so you omit the 2 from 250 in the citation: pp ...
That's why we wanted to study how much of those have been written with the help of AI.". In two papers looking at LLM use in scientific publishings, Zou and his team* found that 17.5% of computer science papers and 16.9% of peer review text had at least some content drafted by AI. The paper on LLM usage in peer reviews will be presented at ...
MLA Style Annotated Bibliography | Format & Examples. Published on July 13, 2021 by Jack Caulfield.Revised on March 5, 2024. An annotated bibliography is a special assignment that lists sources in a way similar to the MLA Works Cited list, but providing an annotation for each source giving extra information.. You might be assigned an annotated bibliography as part of the research process for a ...
Cambridge UP, 2003. MLA (Modern Language Association) style is most commonly used to write papers and cite sources within the liberal arts and humanities. This resource, updated to reflect the MLA Handbook (9th ed.), offers examples for the general format of MLA research papers, in-text citations, endnotes/footnotes, and the Works Cited page.