- Our Mission

Preparing Social Studies Students to Think Critically in the Modern World
Vetting primary resources isn’t easy—but doing it well is crucial for fostering engagement and deeper learning in a rapidly changing world.

In an era when students must sort through increasingly complex social and political issues, absorbing news and information from an evolving digital landscape, social studies should be meaningful and engaging—a means for preparing students for the modern world, writes Paul Franz for EdSurge . Yet much of our social studies curricula emphasizes content knowledge over the development of foundational, critical thinking skills such as understanding the context in which primary sources were created, and determining the credibility of resources.
“The consequence of this approach, coupled with a preference by many schools for multiple-choice assessments, turns out students who are disillusioned with social studies—and creates an environment where “accumulating knowledge and memorizing information is emphasized because that’s what counts on standardized tests,” writes Franz.
In his book Why Learn History (When It’s Already on Your Phone) , author Sam Wineburg, a professor at Stanford’s Graduate School of Education, examines how historians approach resources and argues that this is how teachers should be rigorously vetting—and teaching students to vet—social studies materials for the classroom.
Wineburg first describes how an AP US History student analyzes a New York Times article from 1892 about the creation of Discovery Day, later renamed Columbus Day. The student criticizes the article for celebrating Columbus as a noble hero when, in fact, he “captured and tortured Indians.” However, when real-life historians examine the same article, Wineburg notes that their approach is “wildly different.”
“When historians encounter this resource, their first move is to source it and put it in context, not to engage with the content,” writes Franz. “This article, to them, isn’t really about Columbus at all. It’s about President Harrison, who was responsible for the proclamation, and the immigration politics of the 1890s.”
The skills demonstrated by the historians are the same skills that should form the core of effective social studies education, according to Franz:
- Assessing the point of view of an author and source
- Placing arguments in context
- Validating the veracity of a claim
It is critical that teachers model this process for students: “Vetting social studies resources is important not just because we want to ensure students are learning from accurate, verifiable materials. It’s important also because the ability to ask questions about sources, bias, and context are at the heart of social studies education and are essential skills for thriving in the modern world.”
Much like historians, professional fact-checkers verify digital resources by using lateral reading. As opposed to vertical reading, where a reader might stay within a single website to evaluate a factual claim, fact-checkers scan a resource briefly, then open up new browser tabs to read more widely about the original site and verify its credibility via outside sources. This process mirrors how historians vet primary sources.
Teachers may also, of course, choose to rely on vetted social studies resources and lessons published by reputable sources—Franz recommends Newsela, Newseum, The National Archives, and the Stanford History Education Group.
Encouraging students to seek out knowledge and ideas, and then to deeply explore the reliability of their sources by considering their context, perspective, and accuracy should be the core skill of any rigorous social studies curriculum.

How it works
For Business
Join Mind Tools
Article • 8 min read
Critical Thinking
Developing the right mindset and skills.
By the Mind Tools Content Team
We make hundreds of decisions every day and, whether we realize it or not, we're all critical thinkers.
We use critical thinking each time we weigh up our options, prioritize our responsibilities, or think about the likely effects of our actions. It's a crucial skill that helps us to cut out misinformation and make wise decisions. The trouble is, we're not always very good at it!
In this article, we'll explore the key skills that you need to develop your critical thinking skills, and how to adopt a critical thinking mindset, so that you can make well-informed decisions.
What Is Critical Thinking?
Critical thinking is the discipline of rigorously and skillfully using information, experience, observation, and reasoning to guide your decisions, actions, and beliefs. You'll need to actively question every step of your thinking process to do it well.
Collecting, analyzing and evaluating information is an important skill in life, and a highly valued asset in the workplace. People who score highly in critical thinking assessments are also rated by their managers as having good problem-solving skills, creativity, strong decision-making skills, and good overall performance. [1]
Key Critical Thinking Skills
Critical thinkers possess a set of key characteristics which help them to question information and their own thinking. Focus on the following areas to develop your critical thinking skills:
Being willing and able to explore alternative approaches and experimental ideas is crucial. Can you think through "what if" scenarios, create plausible options, and test out your theories? If not, you'll tend to write off ideas and options too soon, so you may miss the best answer to your situation.
To nurture your curiosity, stay up to date with facts and trends. You'll overlook important information if you allow yourself to become "blinkered," so always be open to new information.
But don't stop there! Look for opposing views or evidence to challenge your information, and seek clarification when things are unclear. This will help you to reassess your beliefs and make a well-informed decision later. Read our article, Opening Closed Minds , for more ways to stay receptive.
Logical Thinking
You must be skilled at reasoning and extending logic to come up with plausible options or outcomes.
It's also important to emphasize logic over emotion. Emotion can be motivating but it can also lead you to take hasty and unwise action, so control your emotions and be cautious in your judgments. Know when a conclusion is "fact" and when it is not. "Could-be-true" conclusions are based on assumptions and must be tested further. Read our article, Logical Fallacies , for help with this.
Use creative problem solving to balance cold logic. By thinking outside of the box you can identify new possible outcomes by using pieces of information that you already have.
Self-Awareness
Many of the decisions we make in life are subtly informed by our values and beliefs. These influences are called cognitive biases and it can be difficult to identify them in ourselves because they're often subconscious.
Practicing self-awareness will allow you to reflect on the beliefs you have and the choices you make. You'll then be better equipped to challenge your own thinking and make improved, unbiased decisions.
One particularly useful tool for critical thinking is the Ladder of Inference . It allows you to test and validate your thinking process, rather than jumping to poorly supported conclusions.
Developing a Critical Thinking Mindset
Combine the above skills with the right mindset so that you can make better decisions and adopt more effective courses of action. You can develop your critical thinking mindset by following this process:
Gather Information
First, collect data, opinions and facts on the issue that you need to solve. Draw on what you already know, and turn to new sources of information to help inform your understanding. Consider what gaps there are in your knowledge and seek to fill them. And look for information that challenges your assumptions and beliefs.
Be sure to verify the authority and authenticity of your sources. Not everything you read is true! Use this checklist to ensure that your information is valid:
- Are your information sources trustworthy ? (For example, well-respected authors, trusted colleagues or peers, recognized industry publications, websites, blogs, etc.)
- Is the information you have gathered up to date ?
- Has the information received any direct criticism ?
- Does the information have any errors or inaccuracies ?
- Is there any evidence to support or corroborate the information you have gathered?
- Is the information you have gathered subjective or biased in any way? (For example, is it based on opinion, rather than fact? Is any of the information you have gathered designed to promote a particular service or organization?)
If any information appears to be irrelevant or invalid, don't include it in your decision making. But don't omit information just because you disagree with it, or your final decision will be flawed and bias.
Now observe the information you have gathered, and interpret it. What are the key findings and main takeaways? What does the evidence point to? Start to build one or two possible arguments based on what you have found.
You'll need to look for the details within the mass of information, so use your powers of observation to identify any patterns or similarities. You can then analyze and extend these trends to make sensible predictions about the future.
To help you to sift through the multiple ideas and theories, it can be useful to group and order items according to their characteristics. From here, you can compare and contrast the different items. And once you've determined how similar or different things are from one another, Paired Comparison Analysis can help you to analyze them.
The final step involves challenging the information and rationalizing its arguments.
Apply the laws of reason (induction, deduction, analogy) to judge an argument and determine its merits. To do this, it's essential that you can determine the significance and validity of an argument to put it in the correct perspective. Take a look at our article, Rational Thinking , for more information about how to do this.
Once you have considered all of the arguments and options rationally, you can finally make an informed decision.
Afterward, take time to reflect on what you have learned and what you found challenging. Step back from the detail of your decision or problem, and look at the bigger picture. Record what you've learned from your observations and experience.
Critical thinking involves rigorously and skilfully using information, experience, observation, and reasoning to guide your decisions, actions and beliefs. It's a useful skill in the workplace and in life.
You'll need to be curious and creative to explore alternative possibilities, but rational to apply logic, and self-aware to identify when your beliefs could affect your decisions or actions.
You can demonstrate a high level of critical thinking by validating your information, analyzing its meaning, and finally evaluating the argument.
Critical Thinking Infographic
See Critical Thinking represented in our infographic: An Elementary Guide to Critical Thinking .

You've accessed 1 of your 2 free resources.
Get unlimited access
Discover more content
How can i improve my memory.
Four Techniques That Can Help
What Is Leadership?
How to Lead Your Team Skilfully
Add comment
Comments (1)
priyanka ghogare

Gain essential management and leadership skills
Busy schedule? No problem. Learn anytime, anywhere.
Subscribe to unlimited access to meticulously researched, evidence-based resources.
Join today and take advantage of our 30% offer, available until May 31st .
Sign-up to our newsletter
Subscribing to the Mind Tools newsletter will keep you up-to-date with our latest updates and newest resources.
Subscribe now
Business Skills
Personal Development
Leadership and Management
Member Extras
Most Popular
Latest Updates

Winning Body Language

Business Stripped Bare
Mind Tools Store
About Mind Tools Content
Discover something new today
Nine ways to get the best from x (twitter).
Growing Your Business Quickly and Safely on Social Media
Managing Your Emotions at Work
Controlling Your Feelings... Before They Control You
How Emotionally Intelligent Are You?
Boosting Your People Skills
Self-Assessment
What's Your Leadership Style?
Learn About the Strengths and Weaknesses of the Way You Like to Lead
Recommended for you
What is posdcorb.
Running Your Team in the Most Efficient Way
Business Operations and Process Management
Strategy Tools
Customer Service
Business Ethics and Values
Handling Information and Data
Project Management
Knowledge Management
Self-Development and Goal Setting
Time Management
Presentation Skills
Learning Skills
Career Skills
Communication Skills
Negotiation, Persuasion and Influence
Working With Others
Difficult Conversations
Creativity Tools
Self-Management
Work-Life Balance
Stress Management and Wellbeing
Coaching and Mentoring
Change Management
Team Management
Managing Conflict
Delegation and Empowerment
Performance Management
Leadership Skills
Developing Your Team
Talent Management
Problem Solving
Decision Making
Member Podcast

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
Margin Size
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

1.2: Critical Thinking Skills
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 155778

- Jim Marteney
- Los Angeles Valley College via ASCCC Open Educational Resources Initiative (OERI)
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
We are not born with natural critical thinking abilities. Critical thinking is a skill that can be developed. The good news is that we all have the ability to improve our critical thinking skills. We can become more effective decision makers and improve our self- confidence. Below are some of those Critical Thinking Skills that can be developed and enhanced:
Critical thinkers are intellectually curious . This skill implies that the critical thinker is never totally satisfied with what they know. He or she seeks answers to various kinds of questions and problems. The critical thinker is concerned with investigating the causes and seeking explanations of events; asking why, how, who, what, when, and where.
Critical thinkers are open-minded . An open-minded person is one who is confident enough in his/her abilities to accept new and contradictory ideas, which challenge his/her current beliefs. This is opposed to being “tolerant” where the dogmatic person may politely listen to other arguments, but their minds will not be changed.
The open-minded person is one who is not only willing to listen to new ideas, but will alter an already adopted position if the new data dictates. The open-minded person is willing to consider a wide variety of positions and beliefs as possibly being valid. Open-minded people are flexible. They are willing to change their beliefs and methods of inquiry, if they are faced with a more valid argument. Open-minded people show a willingness to admit they may be wrong and that other ideas they did not accept may be correct. Critical thinkers do not just want to prove they are correct; they are open- minded enough to change their mind.
Critical thinkers avoid “Red Herrings.” Critical thinkers follow a line of reasoning consistently to a particular conclusion. They avoid irrelevancies, called “red herrings,” that stray from the issue being argued. When Jim and his wife Suzy argue, and Jim feels he is losing, he looks at Suzy and says, “You argue pretty well for a short person.” He is hoping to draw her off the argument and send her fishing for the “red herring,” her being short. If she takes the bait the original argument fades away. Critical thinkers won’t go after “red herrings.”
Critical thinkers are aware of their own biases . All humans are biased, some more than others. Some know that they have biases, some are not aware of their biases. We all have biases that we are not aware of and the critical thinker strives to learn them, so he or she can be more in charge of their thinking. It may be too much of a challenge to eliminate the different biases we have. Instead a critical thinker needs to be aware of the bias and how it will affect the thinking process. Thinking about thinking is referred to as metacognition. A critical thinker looks at how he or she thinks and makes decisions in order to improve the process.
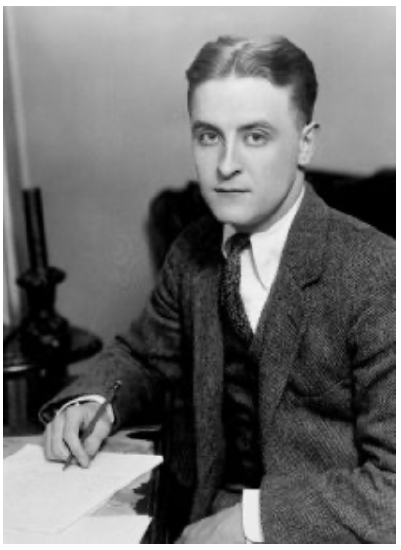
“The test of a first-rate intelligence is the ability to hold two opposed ideas in mind at the same time and still retain the ability to function.”
----F. Scott Fitzgerald 1

Critical thinkers learn to handle confusion . People will do almost anything to avoid the mental pain that comes with lingering confusion. We bypass it, avoid it, and even try to pass it off to someone else. In this haste to avoid confusion we often make quick decisions based on limited data or overworked stereotypes. The critical thinker allows him or herself to be confused as they work through the argument towards a conclusion.
Critical thinkers are able to control and use their emotions . Notice this does not say, “ Eliminate emotions .” We gather all sorts of valuable data through our emotions, that we can use in the decision-making process. We just have to be careful not to let emotions dominate our critical thinking and argumentation. Nothing will destroy the critical thinking process faster than misplaced or misdirected anger, fear, or frustration.
Critical thinkers are sensitive and empathetic to the needs of others . Critical thinkers need to pay particular attention to the needs of their target audience. The needs, concerns, and desires of your audience may be different than yours. The critical thinker is more effective if he or she can understand those concerns. They may not agree with them, but at least they understand them. The target audience may be the person trying to convince you of their argument or the person you are trying to convince with your argument. Persuasion usually takes place when an advocate is able to meet the needs of his or her target audience. In fact, your needs may be unimportant as it pertains to moving a target audience towards adherence to your point of view.
Critical thinkers can distinguish between a conclusion that might be “true” and one that they would like to be “true.” Notice the use of "truth" with a lower case "t . " This "truth" refers to just what a person believes, not the ultimate correct position that would be indicated by "Truth." A conclusion that might be true, is based on calculating the probability of its outcome, to see if it has a reasonable chance of becoming a reality. The second type, a conclusion that you would like to be true, is based more on your wishing, wanting, and desiring that it become a reality. The first can be put to the tests of critical reasoning, but the second cannot, and, therefore, is of little value in critical thinking. You may believe your child to be a great person, but the evidence might suggest otherwise.
Critical thinkers know when to admit to not knowing something . An essential prerequisite to understanding is humility; to be able to admit when you don’t know an answer to a situation. Although we want to protect our egos by believing we know everything, learning comes from questioning, not from knowing all the answers. When we can admit that we don’t know, we are more likely to ask questions that will enable us to learn. By giving ourselves permission to admit we don’t know everything, we can overcome the fear that our lack of knowledge will be discovered. The energy expended trying to cover up what we don’t know diminishes our ability to learn. If we are always trying to disguise our lack of knowledge of a subject, we will never fully understand what it is we don’t know about it. Feel free to say, "I don't know."
Critical Thinkers are independent Thinkers. They have the confidence to state their opinions and point of view to others who might disagree. They use the skills of critical thinking to support their positions and make their arguments.
Critical thinkers seek a “dialogical” approach to the process of argument. “Dialogical” thinkers seriously seek points of view other than their own. The ability to think “dialogically” would include the abilities to: analyze, synthesize, compare and contrast, explain, evaluate, justify, recognize valid and invalid conclusions, identify or anticipate or pose problems, look for alternatives, apply logical principles, and solve conventional or novel problems. These are many of the skills of critically thinkers.
Stephen Brookfield in his book, Challenging Adults to Explore Alternative Ways of Thinking, writes,
“Critical thinking is only possible when people probe their habitual ways of thinking, for their underlying assumptions, those taken-for-granted values, common-sense ideas, and stereotypical notions about human nature that underlie our actions.” 2
We are looking at the process of argumentation and the type of person who can be most effective in an argumentative situation. You as a critical thinker will be both involved in an argument and an observer of an argument. We can improve our abilities to do both.
- Thomas Oppong "F. Scott Fitzgerald on first Rate Intelligence," 2018, medium.com/personal-growth/f...e-7cf8ea002794 (accessed on November 6, 2019)
- Brookfield, Stephen. Developing Critical Thinkers : Challenging Adults to Explore Alternative Ways of Thinking and Acting. (Baltimore: Laureate Education, 2010)
Improving Social Studies Students’ Critical Thinking
- First Online: 01 January 2014
Cite this chapter

- Khe Foon Hew 3 &
- Wing Sum Cheung 4
Part of the book series: SpringerBriefs in Education ((BRIEFSEDUCAT))
2538 Accesses
2 Citations
The ability to think critically along with an awareness of local and global issues have been identified as important competencies that could benefit students as they journey through life in the 21st century (Voogt and Roblin 2012 ). Social studies, as a subject discipline, could serve as a conducive environment for the development of such competencies because it not only aims to equip students with information about important social-cultural issues within and without a country but also to inculcate critical thinking ability whereby students review, analyze, and make appropriate judgments based on particular evidences or ideas presented. This chapter reports a study that examines the effect of using blended learning approaches on social studies students’ critical thinking. This study relied on objective measurements of students’ critical thinking such as their actual performance scores, rather than students’ self-report data of their critical thinking levels. It employed a one-group pre- and post-test research design to examine the impact of a Socratic question-blogcast model on grade 10 students’ ability to critically evaluate controversial social studies issues. A paired-samples t -test was conducted to determine the potential critical thinking gain using a validated rubric. There was a significant difference in critical thinking between pre-intervention ( M = 2.33 SD = 1.240) and post-intervention ( M = 3.19 SD = 1.388), t (26) = −3.690, p < 0.001, with an effect size of 0.67. We also reported students’ perceptions of the Socratic question-blogcast blended learning approach to provide additional qualitative insights into how the approach was particularly helpful to the students.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Compact, lightweight edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
Abrami, P. C., Bernard, R. M., Borokhovski, E., Wade, A., Surkes, M. A., Tamim, R., & Zhang, D. (2008). Instructional interventions affecting critical thinking skills and dispositions: A stage 1 meta-analysis. Review of Educational Research, 78 (4), 1102–1134.
Google Scholar
Allen, J. (1994). If this is history, why isn’t it boring? In S. Steffey & W. J. Hood (Eds.), If this is social studies, why isn’t it boring? (pp. 1–12). York: Stenhouse.
Bjork, R. A. (1999). Assessing our own competence: Heuristics and illusions. In D. Gopher, A. Koriat (Eds.), Attention and performance XVII. Cognitive regulation of performance: Interaction of theory and application (pp. 435–459). Cambridge: MIT Press.
Black, M. S., & Blake, M. E. (2001). Knitting local history together: Collaborating to construct curriculum. The Social Studies, 92 (6), 243–247.
Article Google Scholar
Buckley, M. (1979). The development of verbal thinking and Its implications for teaching. Theory Into Practice, 18 (4), 295–297.
Burack, J. (2014). Interpreting political cartoons in the history classroom. Retrieved on 24 Feb 2014 from http://teachinghistory.org/teaching-materials/teaching-guides/21733 .
Case, R., & Wright, L. (1997). Taking seriously the teaching of critical thinking. In R. Case & P. Clark (Eds.), The Canadian anthology of social studies . Burnaby, BC: Field Relations and Teacher In-service Education, Simon Fraser University.
Chaffee, J. (1998). The thinker’s way: 8 steps to a richer life . USA: Little, Brown & Company.
Chance, P. (1986). Thinking in the classroom: A survey of programs . New York: Teachers College, Columbia University.
Colley, B. M., Bilics, A. R., & Lerch, C. M. (2012). Reflection: A key component to thinking critically. The Canadian Journal for the Scholarship of Teaching and Learning , 3 (1). Retrieved on 25 Feb 2014 from http://ir.lib.uwo.ca/cjsotl_rcacea/vol3/iss1/2 .
Diem, R. A. (2000). Can it make a difference? Technology and the social studies. Theory and Research in Social Education, 28 (4), 493–501.
Dillon, J. T. (1988). Questioning and teaching: A manual of practice . New York: Teachers College Press.
Ellison, N. B., & Wu, Y. (2008). Blogging in the classroom: A preliminary exploration of student attitudes and impact on comprehension. Journal of Educational Multimedia and Hypermedia, 17 (1), 99–122.
Ennis, R. (1989). Critical thinking and subject specificity: Clarification and needed research. Educational Researcher, 18 (3), 4–10.
Falchikov, N., & Boud, D. (1989). Student self-assessment in higher education: A meta-analysis. Review of Educational Research, 59 (4), 395–430.
Fertig, G. (2005). Teaching elementary students how to interpret the past. The Social Studies, 96 (1), 2–8.
Flammer, A. (1981). Towards a theory of question asking. Psychological Research 4 , 407–420.
Friedman, A. M., & Hicks, D. (2006). Guest editorial: The state of the field: Technology, social studies, and teacher education. Contemporary Issues in Technology in Teacher Education, 6 , 246–258.
Heitzmann, W. R. (1998). The power of political cartoons in teaching history . Westlake: National Council for History Education.
Henri, F. (1992). Computer conferencing and content analysis. In A. R. Kaye (Ed.), Collaborative learning through computer conferencing: The Najaden Papers (pp. 117–136). Berlin: Springer.
Chapter Google Scholar
Hew, K. F., & Cheung, W. S. (2013). Audio-based versus text-based asynchronous online discussion: Two case studies. Instructional Science, 41 (2), 365–380.
Jensen, M. (2001). Bring the past to life. The Writer, 114 (11), 30.
Kassirer, J. P., & Kopelman, R. I. (1991). Learning clinical reasoning . Baltimore: Williams and Wilkins.
King, A. (1990). Enhancing peer interaction and learning in classroom through reciprocal questioning. American Educational Research Journal, 27 (4), 664–687
Levans, N. E. (2007). Critical thinking in the secondary social studies classroom. Unpublished master project. Evergreen State College.
Maiorana, V. P. (1990–1991). The road from rote to critical thinking. Community Review, 11 (1–2), 53–63.
Martindale, T., & Wiley, D. A. (2004). An Introduction to Teaching with Weblogs. Retrieved March 15, 2008, from http://teachable.org/papers/2004_techtrends_bloglinks.htm
McLoughlin, C., & Lee, M. (2007). Listen and learn: A systematic review of the evidence that podcasting supports learning in higher education. In C. Montgomerie & J. Seale (Eds.), Proceedings of World Conference on Educational Multimedia, Hypermedia and Telecommunications 2007 (pp. 1669–1677). Chesapeake, VA: AACE.
Mezirow, J. (1990). Fostering critical reflection in adulthood: A guide to transformative and emancipatory learning . San Francisco: Jossey-Bass.
National Council for the Social Studies (NCSS) (1994). Expectations of excellence: Curriculum standards for Social Studies . Washington, DC: NCSS.
Newman, D. R., Johnson, C., Webb, B., & Cochrane, C. (1997). Evaluating the quality of learning in computer supported cooperative learning. Journal of the American Society of Information Science, 48 , 484–495.
Ng, J. Y. (2012). Social Studies syllabus revamped to train critical thinking. Today . Retrieved from http://www.todayonline.com/Focus/Education/EDC121023-0000026/Social-Studies-syllabus-revamped-to-train-critical-thinking .
Paul, R. W. (1993). Critical thinking: What every person needs to survive in a rapidly changing world . CA: Foundation for Critical Thinking, Sonoma Valley University.
Phaneuf, M. (2009). The think-aloud protocol, adjunct or substitute for the nursing process . Retrieved on 25 Feb 2014 from http://www.infiressources.ca/fer/Depotdocument_anglais/The_think-aloud_protocol_adjunct_or_substitute_for_the_nursing_process.pdf .
Salam, S., & Hew, K. F. (2010). Enhancing social studies students’ critical thinking through blogcast and Socratic questioning: A Singapore case study. International Journal of Instructional Media, 37 (4), 391–401.
Schafersman, S.D. (1991). An introduction to critical thinking . Retrieved on 26 Aug 2011 from http://smartcollegeplanning.org/wp-content/uploads/2010/03/Critical-Thinking.pdf .
Schellens, T., Keer, H. V., De Wever, B., & Valcke, M. (2009). Tagging thinking types in asynchronous discussion groups: Effects on critical thinking. Interactive Learning Environments, 17 (1), 77–94.
Siegel, H. (1988). Educating reason: Rationality, critical thinking, and education . New York: Routledge.
Steinbrink, J. E., & Bliss, D. (1988). Using political cartoons to teach thinking skills. The Social Studies, 79 (5), 217–220.
Swartz, R. J. & Parks, S. (1994). Infusing the teaching of critical and creative thinking into content instruction. A lesson design handbook for the elementary grades. Critical Thinking Press & Software.
Taylor, L. (1992). Mathematics attitude development from a Vygotskian perspective. Mathematics Education Research Journal, 4 , 8–23.
Vogler, K. (2004). Using political cartoons to improve your verbal questioning. Social Studies, 95 (1), 11–15.
Voogt, J., & Roblin, N. P. (2012). A comparative analysis of international frameworks for 21st century competences: Implications for national curriculum policies. Journal of Curriculum Studies, 44 (3), 299–321.
Wade, S., Niederhauser, D. S., Cannon, M., & Long, T. (2001). Electronic discussions in an issues course. Expanding the boundaries of the classroom. Journal of Computing in Teacher Education, 17 (3), 4–9.
Waring, S. M., & Robinson, K. S. (2010). Developing critical historical thinking skills in middle grades social studies. Middle School Journal , 22–28.
White, C. W. (1999). Transforming social studies education: A critical perspective . Springfield: Charles C. Thomas.
White, J. E., Nativio, D. G., Kobert, S. N., & Engberg, S. J. (1992). Content and process in clinical decision-making by nurse practitioners. IMAGE, 24 , 153–158.
Wright, I. (2002a). Challenging students with the tools of critical thinking. The Social Studies, 93 (6), 257–261.
Wright, I. (2002b). Critical thinking in the schools: Why doesn’t much happen? Informal Logic, 22 (2), 137–154.
Yang, S. C., & Chung, T.-Y. (2009). Experimental study of teaching critical thinking in civic education in Taiwanese junior high school. British Journal of Educational Psychology, 79 , 29–55.
Yang, Y.-T. C., Newby, T. J., & Bill, R. L. (2005). Using Socratic questioning to promote critical thinking skills through asynchronous discussion forums in distance learning environments. American Journal of Distance Education, 19 (3), 163–181.
Zhao, Y., & Hoge, J. D. (2005). What elementary students and teachers say about social studies. The Social Studies, 96 (5), 216–221.
Zohar, A., Weinberger, Y., & Tamir, P. (1994). The effect of the biology critical thinking project on the development of critical thinking. Journal of Research in Science Teaching, 31 (2), 183–196.
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Faculty of Education, Division of Information and Technology Studies, The University of Hong Kong, Pok Fu Lam, Hong Kong SAR
Khe Foon Hew
Learning Sciences and Technologies, NIE, Nanyang Technological University, Singapore, Singapore
Wing Sum Cheung
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Khe Foon Hew .
4.1.1 Activity 1
1. Instructions
Getting started:

Podcast your answer:
Study the background information, sources and question. Then answer the question orally and record it to audacity. Just say out whatever comes to mind. Do not worry if your ideas do not flow. This is only your first draft. You will be given a chance to improve on your answers later. Upload your podcast onto your blogcast account, which have been created for you. Do not spend more than 15 min on this activity!
2. The Question
Study this question carefully.
Study Source A
How reliable is the source as evidence to suggest that the Tamils formed a militant group due to the unfair university admission criteria? Explain your answer.
3. The Background Information
Read this carefully. It may help you to answer the questions.
After 1970, the government introduced new university admission criteria. Tamil students had to score higher marks than the Sinhalese students to enter the same courses in the universities. A fixed number of places were also reserved for the Sinhalese. Admission was no longer based solely on academic results. This became the main point of the conflict between the government and Tamil leaders. Tamil youths, resentful by what they considered discrimination against them, formed a militant group, the Liberation Tigers of Tamil Eelam (LTTE), more popularly known as Tamil Tigers, and resorted to violence to achieve its aim.
4. The Sources
A cartoon about university admission in Sri Lanka by a Tamil artist.
http://www.slideshare.net/khooky/srilanka-conflict-v09
A view expressed by a Sinhalese about the Tamils in Sri Lanka, 1995.
The LTTE terrorists complain that the Tamils have been treated unfairly. This is unfair. This is no longer true. They say they have been the victims of discrimination in university education, employment and in other matters controlled by the government. But most of their demands were met long ago. Discrimination exists in every society but in Sri Lanka it is less serious than in some countries. It certainly does not give them the right to kill people. The Tamils do not need to be freed by a group of terrorists. Discrimination is not the real reason for terrorism, it is just an excuse.
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2014 The Author(s)
About this chapter
Hew, K.F., Cheung, W.S. (2014). Improving Social Studies Students’ Critical Thinking. In: Using Blended Learning. SpringerBriefs in Education. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-287-089-6_4
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-287-089-6_4
Published : 02 August 2014
Publisher Name : Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN : 978-981-287-088-9
Online ISBN : 978-981-287-089-6
eBook Packages : Humanities, Social Sciences and Law Education (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
- International Center for the Assessment of Higher Order Thinking
- Our Team of Presenters
- Fellows of the Foundation
- Dr. Richard Paul
- Dr. Linda Elder
- Dr. Gerald Nosich
- Permission to Use Our Work
- Create a CriticalThinking.Org Account
- Contributions to the Foundation for Critical Thinking
- Contact Us - Office Information
- Testimonials
- Center for Critical Thinking
- The National Council for Excellence in Critical Thinking
- Library of Critical Thinking Resources
- The Center for Critical Thinking Community Online
- Customized Webinars and Online Courses for Faculty
- Certification in the Paul-Elder Approach to Critical Thinking
- Consulting for Leaders and Key Personnel at Your Organization
- K-12 Instruction
- Higher Education
- Business & Professional Groups
- Build a Local Critical Thinking Town Hall
- Critical Thinking Training for Law Enforcement
- Online Courses for Instructors
- Critical Thinking Therapy
- Bring Critical Thinking Into Your Website's Discussion
- The State of Critical Thinking Today
- Professional Development Model for K-12
- Professional Development Model - College and University
- Workshop Descriptions
- Mentor Program
- Inservice Information Request Form
- Institutions Using Our Approach to Critical Thinking
- Upcoming Events in Critical Thinking
- 44th Annual International Conference on Critical Thinking
- Focal Session Descriptions
- Daily Schedule
- Call for Proposals
- Presuppositions of the 44th Annual International Conference on Critical Thinking
- Recommended Reading
- 2024 Fall Academy on Critical Thinking
- Transportation, Lodging, and Leisure
- Academy Presuppositions
- Conference Archives
- 43rd Annual International Conference on Critical Thinking
- Guest Presentation Program
- Register as an Ambassador
- Testimonials from Past Attendees
- Thank You to Our Donors
- Presuppositions of the Conference
- 42nd Annual International Conference on Critical Thinking
- Overview of Sessions (Flyer)
- Presuppositions of the Annual International Conference
- Testimonials from Past Conferences
- 41st Annual International Conference on Critical Thinking
- Recommended Publications
- Dedication to Our Donors
- 40th Annual International Conference on Critical Thinking
- Session Descriptions
- Testimonials from Prior Conferences
- International Critical Thinking Manifesto
- Scholarships Available
- 39th Annual International Conference on Critical Thinking
- Travel and Lodging Info
- FAQ & General Announcements
- Focal and Plenary Session Descriptions
- Program and Proceedings of the 39th Annual International Conference on Critical Thinking
- The Venue: KU Leuven
- Call for Critical Thinking Ambassadors
- Conference Background Information
- 38th Annual International Conference on Critical Thinking
- Call for Ambassadors for Critical Thinking
- Conference Focal Session Descriptions
- Conference Concurrent Session Descriptions
- Conference Roundtable Discussions
- Conference Announcements and FAQ
- Conference Program and Proceedings
- Conference Daily Schedule
- Conference Hotel Information
- Conference Academic Credit
- Conference Presuppositions
- What Participants Have Said About the Conference
- 37th Annual International Conference on Critical Thinking
- Registration & Fees
- FAQ and Announcements
- Conference Presenters
- 37th Conference Flyer
- Program and Proceedings of the 37th Conference
- 36th International Conference
- Conference Sessions
- Conference Flyer
- Program and Proceedings
- Academic Credit
- 35th International Conference
- Conference Session Descriptions
- Available Online Sessions
- Bertrand Russell Distinguished Scholar - Daniel Ellsberg
- 35th International Conference Program
- Concurrent Sessions
- Posthumous Bertrand Russell Scholar
- Hotel Information
- Conference FAQs
- Visiting UC Berkeley
- 34th INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE
- Bertrand Russell Distinguished Scholar - Ralph Nader
- Conference Concurrent Presenters
- Conference Program
- Conference Theme
- Roundtable Discussions
- Flyer for Bulletin Boards
- 33rd INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE
- 33rd International Conference Program
- 33rd International Conference Sessions
- 33rd International Conference Presenters
- The Bertrand Russell Distinguished Scholars Critical Thinking Conversations
- 33rd International Conference - Fees & Registration
- 33rd International Conference Concurrent Presenters
- 33rd International Conference - Hotel Information
- 33rd International Conference Flyer
- 32nd INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE
- 32nd Annual Conference Sessions
- 32nd Annual Conference Presenter Information
- 32nd Conference Program
- The Bertrand Russell Distinguished Scholars Critical Thinking Lecture Series
- 32nd Annual Conference Concurrent Presenters
- 32nd Annual Conference Academic Credit
- 31st INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE
- 31st Conference Sessions
- Comments about previous conferences
- Conference Hotel (2011)
- 31st Concurrent Presenters
- Registration Fees
- 31st International Conference
- 30th INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON CRITICAL THINKING
- 30th International Conference Theme
- 30th Conference Sessions
- PreConference Sessions
- 30th Concurrent Presenters
- 30th Conference Presuppositions
- Hilton Garden Inn
- 29th International Conference
- 29th Conference Theme
- 29th Conference Sessions
- 29th Preconference Sessions
- 29th Conference Concurrent Sessions
- 2008 International Conference on Critical Thinking
- 2008 Preconference Sessions (28th Intl. Conference)
- 2007 Conference on Critical Thinking (Main Page)
- 2007 Conference Theme and sessions
- 2007 Pre-Conference Workshops
- 2006 Annual International Conference (archived)
- 2006 International Conference Theme
- 2005 International Conference (archived)
- Prior Conference Programs (Pre 2000)
- Workshop Archives
- Spring 2022 Online Workshops
- 2021 Online Workshops for Winter & Spring
- 2019 Seminar for Military and Intelligence Trainers and Instructors
- Transportation, Lodging, and Recreation
- Seminar Flyer
- 2013 Spring Workshops
- Our Presenters
- 2013 Spring Workshops - Hotel Information
- 2013 Spring Workshops Flyer
- 2013 Spring Workshops - Schedule
- Spring Workshop 2012
- 2012 Spring Workshop Strands
- 2012 Spring Workshop Flier
- 2011 Spring Workshop
- Spring 2010 Workshop Strands
- 2009 Spring Workshops on Critical Thinking
- 2008 SPRING Workshops and Seminars on Critical Thinking
- 2008 Ethical Reasoning Workshop
- 2008 - On Richard Paul's Teaching Design
- 2008 Engineering Reasoning Workshop
- 2008 Academia sobre Formulando Preguntas Esenciales
- Fellows Academy Archives
- 2017 Fall International Fellows Academy
- 4th International Fellows Academy - 2016
- 3rd International Fellows Academy
- 2nd International Fellows Academy
- 1st International Fellows Academy
- Academy Archives
- October 2019 Critical Thinking Academy for Educators and Administrators
- Advanced Seminar: Oxford Tutorial
- Recreational Group Activities
- Limited Scholarships Available
- September 2019 Critical Thinking Educators and Administrators Academy
- 2019 Critical Thinking Training for Trainers and Advanced Academy
- Academy Flyer
- Seattle, WA 2017 Spring Academy
- San Diego, CA 2017 Spring Academy
- 2016 Spring Academy -- Washington D.C.
- 2016 Spring Academy -- Houston, TX
- The 2nd International Academy on Critical Thinking (Oxford 2008)
- 2007 National Academy on Critical Thinking Testing and Assessment
- 2006 Cambridge Academy (archived)
- 2006 Cambridge Academy Theme
- 2006 Cambridge Academy Sessions
- Accommodations at St. John's College
- A Model for the National Assessment of Higher Order Thinking
- International Critical Thinking Essay Test
- Online Critical Thinking Basic Concepts Test
- Online Critical Thinking Basic Concepts Sample Test
- Consequential Validity: Using Assessment to Drive Instruction
- News & Announcements
- Newest Pages Added to CriticalThinking.Org
- Critical Thinking Online Courses
- Critical Thinking Blog
- 2019 Blog Entries
- 2020 Blog Entries
- 2021 Blog Entries
- 2022 Blog Entries
- 2023 Blog Entries
- Online Courses for Your Students
- 2023 Webinar Archives
- 2022 Webinar Archives
- 2021 Webinar Archive
- 2020 Webinar Archive
- Guided Study Groups
- Critical Thinking Channel on YouTube
- CT800: Spring 2024
Translate this page from English...
*Machine translated pages not guaranteed for accuracy. Click Here for our professional translations.
Critical Thinking and Social Studies
Critical Thinking and the Social Studies Teacher
by Mike Yell
The advance of knowledge has been achieved not because the mind is capable of memorizing what teachers say but because it can be disciplined to ask probing questions and pursue them in a reasoned, self-critical way. Scholars pursuing knowledge submit their thinking to rigorous discipline.
~Richard Paul
One of the most used and highlighted books in my professional library is Critical Thinking: How to Prepare Students for a Rapidly Changing World by Richard Paul, an international leader in critical thinking movement. We often hear about the need for critical thinking, but we seldom hear sound definitions, or, in my opinion, see comprehensive models that we can apply to what we do in our classrooms. To my mind the works of Richard Paul, and his colleagues Linda Elder Gerald Nosich, and others at the Foundation for Critical Thinking put flesh on the bones of the concept of critical thinking; a concept all too rarely made substantive.
While there are many different approaches to, and definitions of, critical thinking, the Paul/Elder view is that critical thinking is the development of discipline organized thinking that monitors itself and is guided by intellectual standards . Further, they hold that reasoning must be at the heart of good teaching, sound learning, and preparation for college, career, and civic life. Rather than lectures, worksheets, and didactic instruction, it is through reasoning and thinking their way through the curriculum, that students really learn. This approach to critical thinking, I believe, puts this model of critical thinking head and shoulders above others.
To read the full article, join the Center for Critical Thinking Community Online – the world’s leading online community dedicated to teaching and advancing critical thinking. Featuring the world's largest library of critical thinking articles, videos, and books, as well as learning activities, study groups, and a social media component, this interactive learning platform is essential to anyone dedicated to developing as an effective reasoner in the classroom, in the professions, in business and government, and throughout personal life.
Join the community and learn explicit tools of critical thinking.
Critical Thinking Definition, Skills, and Examples
- Homework Help
- Private School
- College Admissions
- College Life
- Graduate School
- Business School
- Distance Learning
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/ADHeadshot-Cropped-b80e40469d5b4852a68f94ad69d6e8bd.jpg)
- Indiana University, Bloomington
- State University of New York at Oneonta
Critical thinking refers to the ability to analyze information objectively and make a reasoned judgment. It involves the evaluation of sources, such as data, facts, observable phenomena, and research findings.
Good critical thinkers can draw reasonable conclusions from a set of information, and discriminate between useful and less useful details to solve problems or make decisions. Employers prioritize the ability to think critically—find out why, plus see how you can demonstrate that you have this ability throughout the job application process.
Why Do Employers Value Critical Thinking Skills?
Employers want job candidates who can evaluate a situation using logical thought and offer the best solution.
Someone with critical thinking skills can be trusted to make decisions independently, and will not need constant handholding.
Hiring a critical thinker means that micromanaging won't be required. Critical thinking abilities are among the most sought-after skills in almost every industry and workplace. You can demonstrate critical thinking by using related keywords in your resume and cover letter, and during your interview.
Examples of Critical Thinking
The circumstances that demand critical thinking vary from industry to industry. Some examples include:
- A triage nurse analyzes the cases at hand and decides the order by which the patients should be treated.
- A plumber evaluates the materials that would best suit a particular job.
- An attorney reviews evidence and devises a strategy to win a case or to decide whether to settle out of court.
- A manager analyzes customer feedback forms and uses this information to develop a customer service training session for employees.
Promote Your Skills in Your Job Search
If critical thinking is a key phrase in the job listings you are applying for, be sure to emphasize your critical thinking skills throughout your job search.
Add Keywords to Your Resume
You can use critical thinking keywords (analytical, problem solving, creativity, etc.) in your resume. When describing your work history , include top critical thinking skills that accurately describe you. You can also include them in your resume summary , if you have one.
For example, your summary might read, “Marketing Associate with five years of experience in project management. Skilled in conducting thorough market research and competitor analysis to assess market trends and client needs, and to develop appropriate acquisition tactics.”
Mention Skills in Your Cover Letter
Include these critical thinking skills in your cover letter. In the body of your letter, mention one or two of these skills, and give specific examples of times when you have demonstrated them at work. Think about times when you had to analyze or evaluate materials to solve a problem.
Show the Interviewer Your Skills
You can use these skill words in an interview. Discuss a time when you were faced with a particular problem or challenge at work and explain how you applied critical thinking to solve it.
Some interviewers will give you a hypothetical scenario or problem, and ask you to use critical thinking skills to solve it. In this case, explain your thought process thoroughly to the interviewer. He or she is typically more focused on how you arrive at your solution rather than the solution itself. The interviewer wants to see you analyze and evaluate (key parts of critical thinking) the given scenario or problem.
Of course, each job will require different skills and experiences, so make sure you read the job description carefully and focus on the skills listed by the employer.
Top Critical Thinking Skills
Keep these in-demand critical thinking skills in mind as you update your resume and write your cover letter. As you've seen, you can also emphasize them at other points throughout the application process, such as your interview.
Part of critical thinking is the ability to carefully examine something, whether it is a problem, a set of data, or a text. People with analytical skills can examine information, understand what it means, and properly explain to others the implications of that information.
- Asking Thoughtful Questions
- Data Analysis
- Interpretation
- Questioning Evidence
- Recognizing Patterns

Communication
Often, you will need to share your conclusions with your employers or with a group of colleagues. You need to be able to communicate with others to share your ideas effectively. You might also need to engage in critical thinking in a group. In this case, you will need to work with others and communicate effectively to figure out solutions to complex problems.
- Active Listening
- Collaboration
- Explanation
- Interpersonal
- Presentation
- Verbal Communication
- Written Communication
Critical thinking often involves creativity and innovation. You might need to spot patterns in the information you are looking at or come up with a solution that no one else has thought of before. All of this involves a creative eye that can take a different approach from all other approaches.
- Flexibility
- Conceptualization
- Imagination
- Drawing Connections
- Synthesizing
Open-Mindedness
To think critically, you need to be able to put aside any assumptions or judgments and merely analyze the information you receive. You need to be objective, evaluating ideas without bias.
- Objectivity
- Observation
Problem Solving
Problem-solving is another critical thinking skill that involves analyzing a problem, generating and implementing a solution, and assessing the success of the plan. Employers don’t simply want employees who can think about information critically. They also need to be able to come up with practical solutions.
- Attention to Detail
- Clarification
- Decision Making
- Groundedness
- Identifying Patterns
More Critical Thinking Skills
- Inductive Reasoning
- Deductive Reasoning
- Noticing Outliers
- Adaptability
- Emotional Intelligence
- Brainstorming
- Optimization
- Restructuring
- Integration
- Strategic Planning
- Project Management
- Ongoing Improvement
- Causal Relationships
- Case Analysis
- Diagnostics
- SWOT Analysis
- Business Intelligence
- Quantitative Data Management
- Qualitative Data Management
- Risk Management
- Scientific Method
- Consumer Behavior
Key Takeaways
- Demonstrate that you have critical thinking skills by adding relevant keywords to your resume.
- Mention pertinent critical thinking skills in your cover letter, too, and include an example of a time when you demonstrated them at work.
- Finally, highlight critical thinking skills during your interview. For instance, you might discuss a time when you were faced with a challenge at work and explain how you applied critical thinking skills to solve it.
University of Louisville. " What is Critical Thinking ."
American Management Association. " AMA Critical Skills Survey: Workers Need Higher Level Skills to Succeed in the 21st Century ."
- Questions for Each Level of Bloom's Taxonomy
- Critical Thinking in Reading and Composition
- Bloom's Taxonomy in the Classroom
- Introduction to Critical Thinking
- How To Become an Effective Problem Solver
- Creativity & Creative Thinking
- Higher-Order Thinking Skills (HOTS) in Education
- 2020-21 Common Application Essay Option 4—Solving a Problem
- 6 Skills Students Need to Succeed in Social Studies Classes
- College Interview Tips: "Tell Me About a Challenge You Overcame"
- Types of Medical School Interviews and What to Expect
- The Horse Problem: A Math Challenge
- What to Do When the Technology Fails in Class
- What Are Your Strengths and Weaknesses? Interview Tips for Teachers
- A Guide to Business Letters Types
- Landing Your First Teaching Job

Work Life is Atlassian’s flagship publication dedicated to unleashing the potential of every team through real-life advice, inspiring stories, and thoughtful perspectives from leaders around the world.

Contributing Writer
Work Futurist

Senior Quantitative Researcher, People Insights
Principal Writer

How to build critical thinking skills for better decision-making
It’s simple in theory, but tougher in practice – here are five tips to get you started.
Get stories like this in your inbox
Have you heard the riddle about two coins that equal thirty cents, but one of them is not a nickel? What about the one where a surgeon says they can’t operate on their own son?
Those brain teasers tap into your critical thinking skills. But your ability to think critically isn’t just helpful for solving those random puzzles – it plays a big role in your career.
An impressive 81% of employers say critical thinking carries a lot of weight when they’re evaluating job candidates. It ranks as the top competency companies consider when hiring recent graduates (even ahead of communication ). Plus, once you’re hired, several studies show that critical thinking skills are highly correlated with better job performance.
So what exactly are critical thinking skills? And even more importantly, how do you build and improve them?
What is critical thinking?
Critical thinking is the ability to evaluate facts and information, remain objective, and make a sound decision about how to move forward.
Does that sound like how you approach every decision or problem? Not so fast. Critical thinking seems simple in theory but is much tougher in practice, which helps explain why 65% of employers say their organization has a need for more critical thinking.
In reality, critical thinking doesn’t come naturally to a lot of us. In order to do it well, you need to:
- Remain open-minded and inquisitive, rather than relying on assumptions or jumping to conclusions
- Ask questions and dig deep, rather than accepting information at face value
- Keep your own biases and perceptions in check to stay as objective as possible
- Rely on your emotional intelligence to fill in the blanks and gain a more well-rounded understanding of a situation
So, critical thinking isn’t just being intelligent or analytical. In many ways, it requires you to step outside of yourself, let go of your own preconceived notions, and approach a problem or situation with curiosity and fairness.
It’s a challenge, but it’s well worth it. Critical thinking skills will help you connect ideas, make reasonable decisions, and solve complex problems.
7 critical thinking skills to help you dig deeper
Critical thinking is often labeled as a skill itself (you’ll see it bulleted as a desired trait in a variety of job descriptions). But it’s better to think of critical thinking less as a distinct skill and more as a collection or category of skills.
To think critically, you’ll need to tap into a bunch of your other soft skills. Here are seven of the most important.
Open-mindedness
It’s important to kick off the critical thinking process with the idea that anything is possible. The more you’re able to set aside your own suspicions, beliefs, and agenda, the better prepared you are to approach the situation with the level of inquisitiveness you need.
That means not closing yourself off to any possibilities and allowing yourself the space to pull on every thread – yes, even the ones that seem totally implausible.
As Christopher Dwyer, Ph.D. writes in a piece for Psychology Today , “Even if an idea appears foolish, sometimes its consideration can lead to an intelligent, critically considered conclusion.” He goes on to compare the critical thinking process to brainstorming . Sometimes the “bad” ideas are what lay the foundation for the good ones.
Open-mindedness is challenging because it requires more effort and mental bandwidth than sticking with your own perceptions. Approaching problems or situations with true impartiality often means:
- Practicing self-regulation : Giving yourself a pause between when you feel something and when you actually react or take action.
- Challenging your own biases: Acknowledging your biases and seeking feedback are two powerful ways to get a broader understanding.
Critical thinking example
In a team meeting, your boss mentioned that your company newsletter signups have been decreasing and she wants to figure out why.
At first, you feel offended and defensive – it feels like she’s blaming you for the dip in subscribers. You recognize and rationalize that emotion before thinking about potential causes. You have a hunch about what’s happening, but you will explore all possibilities and contributions from your team members.
Observation
Observation is, of course, your ability to notice and process the details all around you (even the subtle or seemingly inconsequential ones). Critical thinking demands that you’re flexible and willing to go beyond surface-level information, and solid observation skills help you do that.
Your observations help you pick up on clues from a variety of sources and experiences, all of which help you draw a final conclusion. After all, sometimes it’s the most minuscule realization that leads you to the strongest conclusion.
Over the next week or so, you keep a close eye on your company’s website and newsletter analytics to see if numbers are in fact declining or if your boss’s concerns were just a fluke.
Critical thinking hinges on objectivity. And, to be objective, you need to base your judgments on the facts – which you collect through research. You’ll lean on your research skills to gather as much information as possible that’s relevant to your problem or situation.
Keep in mind that this isn’t just about the quantity of information – quality matters too. You want to find data and details from a variety of trusted sources to drill past the surface and build a deeper understanding of what’s happening.
You dig into your email and website analytics to identify trends in bounce rates, time on page, conversions, and more. You also review recent newsletters and email promotions to understand what customers have received, look through current customer feedback, and connect with your customer support team to learn what they’re hearing in their conversations with customers.
The critical thinking process is sort of like a treasure hunt – you’ll find some nuggets that are fundamental for your final conclusion and some that might be interesting but aren’t pertinent to the problem at hand.
That’s why you need analytical skills. They’re what help you separate the wheat from the chaff, prioritize information, identify trends or themes, and draw conclusions based on the most relevant and influential facts.
It’s easy to confuse analytical thinking with critical thinking itself, and it’s true there is a lot of overlap between the two. But analytical thinking is just a piece of critical thinking. It focuses strictly on the facts and data, while critical thinking incorporates other factors like emotions, opinions, and experiences.
As you analyze your research, you notice that one specific webpage has contributed to a significant decline in newsletter signups. While all of the other sources have stayed fairly steady with regard to conversions, that one has sharply decreased.
You decide to move on from your other hypotheses about newsletter quality and dig deeper into the analytics.
One of the traps of critical thinking is that it’s easy to feel like you’re never done. There’s always more information you could collect and more rabbit holes you could fall down.
But at some point, you need to accept that you’ve done your due diligence and make a decision about how to move forward. That’s where inference comes in. It’s your ability to look at the evidence and facts available to you and draw an informed conclusion based on those.
When you’re so focused on staying objective and pursuing all possibilities, inference can feel like the antithesis of critical thinking. But ultimately, it’s your inference skills that allow you to move out of the thinking process and onto the action steps.
You dig deeper into the analytics for the page that hasn’t been converting and notice that the sharp drop-off happened around the same time you switched email providers.
After looking more into the backend, you realize that the signup form on that page isn’t correctly connected to your newsletter platform. It seems like anybody who has signed up on that page hasn’t been fed to your email list.
Communication

3 ways to improve your communication skills at work
If and when you identify a solution or answer, you can’t keep it close to the vest. You’ll need to use your communication skills to share your findings with the relevant stakeholders – like your boss, team members, or anybody who needs to be involved in the next steps.
Your analysis skills will come in handy here too, as they’ll help you determine what information other people need to know so you can avoid bogging them down with unnecessary details.
In your next team meeting, you pull up the analytics and show your team the sharp drop-off as well as the missing connection between that page and your email platform. You ask the web team to reinstall and double-check that connection and you also ask a member of the marketing team to draft an apology email to the subscribers who were missed.
Problem-solving
Critical thinking and problem-solving are two more terms that are frequently confused. After all, when you think critically, you’re often doing so with the objective of solving a problem.
The best way to understand how problem-solving and critical thinking differ is to think of problem-solving as much more narrow. You’re focused on finding a solution.
In contrast, you can use critical thinking for a variety of use cases beyond solving a problem – like answering questions or identifying opportunities for improvement. Even so, within the critical thinking process, you’ll flex your problem-solving skills when it comes time to take action.
Once the fix is implemented, you monitor the analytics to see if subscribers continue to increase. If not (or if they increase at a slower rate than you anticipated), you’ll roll out some other tests like changing the CTA language or the placement of the subscribe form on the page.
5 ways to improve your critical thinking skills

Beyond the buzzwords: Why interpersonal skills matter at work
Think critically about critical thinking and you’ll quickly realize that it’s not as instinctive as you’d like it to be. Fortunately, your critical thinking skills are learned competencies and not inherent gifts – and that means you can improve them. Here’s how:
- Practice active listening: Active listening helps you process and understand what other people share. That’s crucial as you aim to be open-minded and inquisitive.
- Ask open-ended questions: If your critical thinking process involves collecting feedback and opinions from others, ask open-ended questions (meaning, questions that can’t be answered with “yes” or “no”). Doing so will give you more valuable information and also prevent your own biases from influencing people’s input.
- Scrutinize your sources: Figuring out what to trust and prioritize is crucial for critical thinking. Boosting your media literacy and asking more questions will help you be more discerning about what to factor in. It’s hard to strike a balance between skepticism and open-mindedness, but approaching information with questions (rather than unquestioning trust) will help you draw better conclusions.
- Play a game: Remember those riddles we mentioned at the beginning? As trivial as they might seem, games and exercises like those can help you boost your critical thinking skills. There are plenty of critical thinking exercises you can do individually or as a team .
- Give yourself time: Research shows that rushed decisions are often regrettable ones. That’s likely because critical thinking takes time – you can’t do it under the wire. So, for big decisions or hairy problems, give yourself enough time and breathing room to work through the process. It’s hard enough to think critically without a countdown ticking in your brain.
Critical thinking really is critical
The ability to think critically is important, but it doesn’t come naturally to most of us. It’s just easier to stick with biases, assumptions, and surface-level information.
But that route often leads you to rash judgments, shaky conclusions, and disappointing decisions. So here’s a conclusion we can draw without any more noodling: Even if it is more demanding on your mental resources, critical thinking is well worth the effort.
Advice, stories, and expertise about work life today.
- Key Activities
- Minnesota Adult Education
- MN ABE Connect
- Applications
- Submit Invoice
Find resources for online meetings/presentations/classes/events !
Teaching critical thinking skills through a social justice lens.
What a year 2020 has been so far. We have been navigating a worldwide pandemic, experiencing a racial injustice reckoning, and watching a presidential campaign that will shape our future. It is safe to say that 2020 has left us with a lot to unpack as individuals and as educators.
As our classes continue to look so different as they take place online, I am thinking about the need to find and use materials that help my students and me to process everything that is going on around us. I want to find materials that will help us to put current events into a historical context, and will help us to process the information that we receive through a critical lens. I want to explore issues of inequality and power, and I want my students to know that “We the people” have a voice in shaping our collective future.

It includes, among other things, posters, audio clips, film clips, songs and poems, and PDF copies of teaching materials. The materials very clearly relate to Social Studies topics and would be an excellent addition to any Adult Diploma teacher’s toolbox. However, they could also be used to craft rich, relevant units of instruction around a line of inquiry that would allow learners to explore these topics through reading, writing, speaking and listening, and deep critical thinking activities.

While the resources in the collection are all free, users do need to create an account in order to access them. After that, it’s just a matter of diving in to explore. There are a lot of teaching materials in the collection, but you can search them by time period , by theme , or by resource type .
Examples of activities
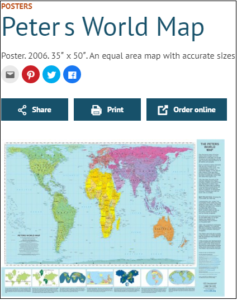
While searching by resource type, I started looking through the poster collection. I found something called the Peters World Map that I found very interesting. I’ve never spent much time thinking about maps and how they are drawn. If I had, I might have noticed that on some maps South America is drawn to appear smaller than Europe, when it is really more than twice Europe’s size.
Some of the other resources that stood out for me come from the PDF copies of teaching materials section. There are several role play and mixer activities that encourage students to explore issues from different points of view. Several of these activities relate to issues surrounding clean energy and climate change; “ Blockadia: Teaching How the Movement Against Fossil Fuels is Changing the World ” and “ The Climate Crisis Trial: A Roleplay on the Roots of Global Warming ” are two activities that look especially engaging. My writing teacher’s brain thinks these activities could be used as a lead in to helping students craft an argument essay about climate change, but they could also be used to develop speaking and listening skills in a class where students might be working up to delivering an oral presentation or poster session.
During this election year, I was also intrigued by something called “ Constitution Role Play: Whose ‘More Perfect Union’? ” and “ Who Gets to Vote? Teaching about the Struggle for Voting Rights in the United States .” Several of the role play activities include multiple perspective texts for students to read and then guided questions that help them to think about the issue from different points of view.
Adapting materials to various levels
I will caution that some of the texts are dense and the materials overall seem to be geared towards middle and high school level students, but I think they could be scaled back and adapted without too much effort. I would also argue that the activities that are presented provide a great framework and inspiration for teachers who want to create engaging, dynamic lessons with lower level materials. Seeing how the role plays are structured, for example, would allow a teacher to create a similar activity using different scenarios. I can imagine creating one in which students explore the protests that occurred after the death of George Floyd from multiple perspectives. To help create my role play activity, I could use the “ How to – and How Not to – Teach Role Plays ” guide that can found in the collection.
In conclusion, the Zinn Education Project provides educators with a large number of tools that can be used to teach from a social justice perspective, and there has never been a better time to use them.
Originally published 9/21/20
Newsletter Signup
Get MN ABE Connect —the official source for ABE events, activities, and resources!
Article Categories
- ABE Foundations/Staff Onboarding
- ACES/Transitions
- Adult Career Pathways
- CCR Standards
- Citizenship
- Cultural Competency
- Digital Literacy/Northstar
- Disabilities
- Distance Learning/Education
- Equity/Inclusion
- HSE/Adult Diploma
- Math/Numeracy
- Mental Health
- Minnesota ABE
- One-Room Schoolhouse/Multilevel
- Professional Development
- Program Management
- Remote Instruction
- Social Studies
- Speaking/Conversation
- Support Services
- Teaching Strategies
- Uncategorized
- Volunteers/Tutors
Join the Mailing List
Search the blog.
Input your search keywords and press Enter.

Alyssa Teaches
an Upper Elementary Blog
Critical Thinking in Your Social Studies Lessons

If your state is like mine, you’re expected to teach critical thinking skills in every subject. And it makes sense why! We want our students to be evaluating content and creating solutions – not just memorizing facts. Today, I want to share some easy ways to get your students using critical thinking skills in social studies.
What Critical Thinking Skills Can I Teach?
Practically all of them!
Here are just a few skills you can integrate into your history lessons:
- ask questions
- determine credibility and evaluate bias
- interpret sources
- recognize a variety of perspectives
- analyze choices
- compare and contrast
- determine relationships
- sequence events
- draw conclusions based on evidence
- differentiate facts from opinions
- explore impact
A lot of the social studies activities you’re using probably include some critical thinking skills! Let’s take a look at some simple strategies you can try to include more critical thinking opportunities in your lessons.

Ask Questions
A simple way to encourage students to dig a little deeper when they learn about history is to use higher-order thinking questions. Once they know the what, where, who, and when, you can guide students to explore the HOW and WHY. What were the causes of these events? What effects did they have? How did they impact different groups of people then and now?
Inquiry-based lessons are a great way to get students using these skills. Plus, they give them ownership of what they’re learning and help to increase engagement.
If you want to start a little more low-key, you can use some HOTS question prompts. A simple “parking lot” or bulletin board where students can record questions is also a good place to begin.
Analyze Primary Sources
I LOVE using primary sources to teach social studies. Primary source analysis requires students to use their background knowledge and observational skills to draw conclusions about history.
I almost always have students collaborate when they work with primary sources so they can bounce ideas off each other. I also usually use DBQs or question prompts so they have some direction. Afterward, I like to follow up with a whole-class discussion to debrief.

Compare & Contrast
A simple Venn diagram or t-chart is a great way for students to compare people, places, civilizations, artifacts, inventions, events, and time periods from history.

Plus, comparing helps students identify connections between people/places and over time.
Use Sorting Activities
Sorting activities are one of my favorite ways to get students thinking critically. They’re hands-on, interactive, and perfect for kids to do with a partner or in a small group.
You can assign an open sort, where students sort cards with words and/or pictures according to their own categories by looking for connections or patterns. I love this activity because it helps me see how students think.
Another option is to do a closed sort where you can ask students to sort according to specific rules. For example, they might sequence events into a timeline or sort them into cause-and-effect relationships. To make it more challenging, you can involve some inferencing scenarios. For instance, you can have them match quotes to the person or group that would’ve been likely to say them.
Explore Perspectives
We want students to consider a variety of perspectives and points of view when they learn about different historical events or periods. Primary sources are very helpful here, especially if you can find letters or diary entries. Picture books are another good option if you can find ones that provide different perspectives on a topic.
An easy activity is to use two different quotes about an event (that represent two points of view) and have students analyze their differences. Again, guiding questions or prompts will help them to understand the perspectives of different groups of people. One activity I’ve used is to explore the English colonization of Jamestown from Captain John Smith’s perspective compared to Chief Powhatan’s.

Even creating a fake social media profile for a historical figure can help students think critically about someone’s needs, wants, and point-of-view.
Look at Cause and Effect
I think that exploring cause and effect relationships in history helps students understand the impact of events that have taken place. I like using a simple graphic organizer that has room for multiple causes and effects. (Cause and effect is also a good place to tie in perspectives and connections.)
Analyze Decision Making
Another critical thinking activity you can use is to analyze specific choices that people made.
A decision-making model graphic organizer helps students determine the costs and benefits of a choice or event. For example, they can weigh the costs and benefits of the 13 Colonies declaring independence from Great Britain.
A good extension activity is to have students discuss alternate decisions that could have been made. They can hypothesize how different choices would have changed history.
Investigate the Impact of Geography
Geography has played such a huge role in human history, but it’s not something our students always think about. It helps to use activities that encourage students to consider the specific ways geography has affected people. Comparing early maps to current maps is one option. And I love having students explore locations with Google Earth.
You can also practice this skill with the 5 themes of geography .

Research and Create Products
Finally, social studies research projects are a great way to use critical thinking skills. Students can take their research and create an artifact or product to apply their knowledge. They can also design solutions for the future based on what they’ve learned.
I’m all about finding ways to make social studies engaging . Incorporating critical thinking skills into your social studies lessons is a great way to challenge students, and it doesn’t have to be complicated. I hope you give some of these activities a try!
Related posts

Virtual Field Trips in Virginia: History and Social Studies

Teaching Social Studies with Picture Books

6 Easy Social Studies Anchor Charts for Any Unit
No comments, leave a reply cancel reply, join the mailing list for tips, ideas, and freebies.
- Mentor Teacher
- Organization
- Social Studies
- Teacher Tips
- Virginia Studies


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
According to the University of the People in California, having critical thinking skills is important because they are [ 1 ]: Universal. Crucial for the economy. Essential for improving language and presentation skills. Very helpful in promoting creativity. Important for self-reflection.
Validating the veracity of a claim. It is critical that teachers model this process for students: "Vetting social studies resources is important not just because we want to ensure students are learning from accurate, verifiable materials. It's important also because the ability to ask questions about sources, bias, and context are at the ...
In recent decades, approaches to critical thinking have generally taken a practical turn, pivoting away from more abstract accounts - such as emphasizing the logical relations that hold between statements (Ennis, 1964) - and moving toward an emphasis on belief and action.According to the definition that Robert Ennis (2018) has been advocating for the last few decades, critical thinking is ...
Brookfield (Citation 2012) maintains that the discussion taking place in collaborative learning is one way of identifying the critical thinking skills that the students use.He has introduced various forms of focused discussion groups (critical conversation, scenario analysis, circle of voices, circular response, and chalk-talk), in which students experience critical thinking, primarily as a ...
critical thinking further. We do not intend to cover the full range of critical thinking 'skills' (indeed, this would consider them to be something like a checklist, which is inappropriate for practice) but instead highlight a few basic principles to underpin the process of enhancing the critical aspects of your own learning and development.
Critical thinking is the discipline of rigorously and skillfully using information, experience, observation, and reasoning to guide your decisions, actions, and beliefs. You'll need to actively question every step of your thinking process to do it well. Collecting, analyzing and evaluating information is an important skill in life, and a highly ...
Critical Thinkers are independent Thinkers. They have the confidence to state their opinions and point of view to others who might disagree. They use the skills of critical thinking to support their positions and make their arguments. Critical thinkers seek a "dialogical" approach to the process of argument. "Dialogical" thinkers ...
views on promoting critical-thinking have shown more commonality than divergence. Conclusion: The result of this study revealed that the use of classroom discussions, writing activities, and questions should be utilized more in social studies classrooms to promote critical-thinking. However, more studies are needed to examine the effects of ...
The aforementioned aims of social studies clearly demonstrate the need for the development of critical thinking skills in students. This is particularly true in terms of student having to take multiple perspectives and make appropriate judgment when evaluating complex situations before acting especially in today's shared society (Levans 2007 ).
Critical thinking skills in tactical decision making: A model and a training strategy. In Cannon-Bowers J. A., Salas E. (Eds.), Making decisions under stress (pp. 155-189). Washington, DC: American Psychological Association. ... Critical social thinking and response training (Critical START): A conceptual framework for a critical social ...
'Critical thinking is one of the most sought-after skills in social work', is an introductory statement made by the authors who proceed to demonstrate powerfully that this skill is essential for safe, effective social work practice.
Critical Thinking and the Social Studies Teacher. by Mike Yell. The advance of knowledge has been achieved not because the mind is capable of memorizing what teachers say but because it can be disciplined to ask probing questions and pursue them in a reasoned, self-critical way. Scholars pursuing knowledge submit their thinking to rigorous ...
Critical thinking refers to the ability to analyze information objectively and make a reasoned judgment. It involves the evaluation of sources, such as data, facts, observable phenomena, and research findings. Good critical thinkers can draw reasonable conclusions from a set of information, and discriminate between useful and less useful ...
Critical thinking is the ability to effectively analyze information and form a judgment. To think critically, you must be aware of your own biases and assumptions when encountering information, and apply consistent standards when evaluating sources. Critical thinking skills help you to: Identify credible sources. Evaluate and respond to arguments.
ods for teaching critical thinking in gradu ate and undergraduate social work practice courses. Before exploring meth ods, however, it is important to specify the skills students should be taught. Critical Thinking Skills Paul (1992) lists the following abilities as components of critical thinking: The ability to formulate, analyze, and
Foster discussion and debate. Be the first to add your personal experience. 5. Integrate current events and issues. Be the first to add your personal experience. 6. Assess and reflect on critical ...
focused on using social media to develop critical thinking skills in undergraduates. In Critical Thinking Development: A Stage Theory, Paul and Elder (2014) define critical thinking as the habit of assessing thinking to improve one's problem-solving ability. Critical thinkers must practice critical thinking in all
Critical thinking is defined as more than a rational, step-by-step problem-solving process; it is seen as the systematic application of critical thinking skills to real life situations that can ...
Critical thinking skills will help you connect ideas, make reasonable decisions, and solve complex problems. 7 critical thinking skills to help you dig deeper. Critical thinking is often labeled as a skill itself (you'll see it bulleted as a desired trait in a variety of job descriptions). But it's better to think of critical thinking less ...
Teaching Critical Thinking Skills through a Social Justice Lens. What a year 2020 has been so far. We have been navigating a worldwide pandemic, experiencing a racial injustice reckoning, and watching a presidential campaign that will shape our future. It is safe to say that 2020 has left us with a lot to unpack as individuals and as educators.
compare and contrast. determine relationships. sequence events. draw conclusions based on evidence. differentiate facts from opinions. explore impact. A lot of the social studies activities you're using probably include some critical thinking skills! Let's take a look at some simple strategies you can try to include more critical thinking ...
The results showed critical thinking skills and social thinking skills together had a contribution to the development of students' character in the application of discovery learning models. This research can be a reference for readers about the contribution of students' critical thinking skills and social skills to developing
Top 5 critical thinking skills. Here are five common and impactful critical thinking skills you might consider highlighting on your resume or in an interview: 1. Observation. Observational skills are the starting point for critical thinking. People who are observant can quickly sense and identify a new problem.