
- Tips & Guides

How To Avoid Using “We,” “You,” And “I” in an Essay
- Posted on October 27, 2022 October 27, 2022
Maintaining a formal voice while writing academic essays and papers is essential to sound objective.
One of the main rules of academic or formal writing is to avoid first-person pronouns like “we,” “you,” and “I.” These words pull focus away from the topic and shift it to the speaker – the opposite of your goal.
While it may seem difficult at first, some tricks can help you avoid personal language and keep a professional tone.
Let’s learn how to avoid using “we” in an essay.
What Is a Personal Pronoun?
Pronouns are words used to refer to a noun indirectly. Examples include “he,” “his,” “her,” and “hers.” Any time you refer to a noun – whether a person, object, or animal – without using its name, you use a pronoun.
Personal pronouns are a type of pronoun. A personal pronoun is a pronoun you use whenever you directly refer to the subject of the sentence.
Take the following short paragraph as an example:
“Mr. Smith told the class yesterday to work on our essays. Mr. Smith also said that Mr. Smith lost Mr. Smith’s laptop in the lunchroom.”
The above sentence contains no pronouns at all. There are three places where you would insert a pronoun, but only two where you would put a personal pronoun. See the revised sentence below:
“Mr. Smith told the class yesterday to work on our essays. He also said that he lost his laptop in the lunchroom.”
“He” is a personal pronoun because we are talking directly about Mr. Smith. “His” is not a personal pronoun (it’s a possessive pronoun) because we are not speaking directly about Mr. Smith. Rather, we are talking about Mr. Smith’s laptop.
If later on you talk about Mr. Smith’s laptop, you may say:
“Mr. Smith found it in his car, not the lunchroom!”
In this case, “it” is a personal pronoun because in this point of view we are making a reference to the laptop directly and not as something owned by Mr. Smith.
Why Avoid Personal Pronouns in Essay Writing
We’re teaching you how to avoid using “I” in writing, but why is this necessary? Academic writing aims to focus on a clear topic, sound objective, and paint the writer as a source of authority. Word choice can significantly impact your success in achieving these goals.
Writing that uses personal pronouns can unintentionally shift the reader’s focus onto the writer, pulling their focus away from the topic at hand.
Personal pronouns may also make your work seem less objective.
One of the most challenging parts of essay writing is learning which words to avoid and how to avoid them. Fortunately, following a few simple tricks, you can master the English Language and write like a pro in no time.
Alternatives To Using Personal Pronouns
How to not use “I” in a paper? What are the alternatives? There are many ways to avoid the use of personal pronouns in academic writing. By shifting your word choice and sentence structure, you can keep the overall meaning of your sentences while re-shaping your tone.
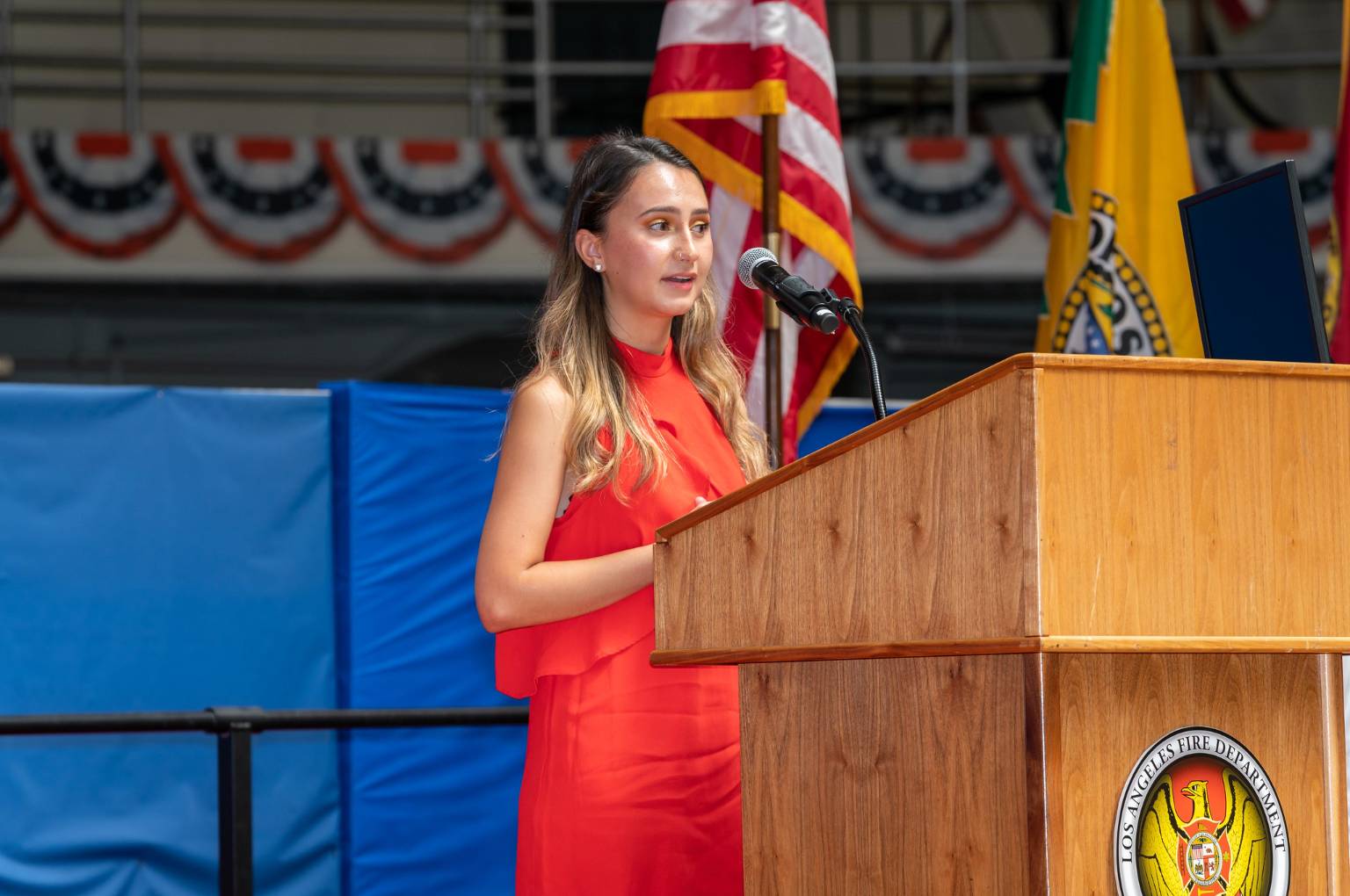
Utilize Passive Voice
In conventional writing, students are taught to avoid the passive voice as much as possible, but it can be an excellent way to avoid first-person pronouns in academic writing.
You can use the passive voice to avoid using pronouns. Take this sentence, for example:
“ We used 150 ml of HCl for the experiment.”
Instead of using “we” and the active voice, you can use a passive voice without a pronoun. The sentence above becomes:
“150 ml of HCl were used for the experiment.”
Using the passive voice removes your team from the experiment and makes your work sound more objective.
Take a Third-Person Perspective
Another answer to “how to avoid using ‘we’ in an essay?” is the use of a third-person perspective. Changing the perspective is a good way to take first-person pronouns out of a sentence. A third-person point of view will not use any first-person pronouns because the information is not given from the speaker’s perspective.
A third-person sentence is spoken entirely about the subject where the speaker is outside of the sentence.
Take a look at the sentence below:
“In this article you will learn about formal writing.”
The perspective in that sentence is second person, and it uses the personal pronoun “you.” You can change this sentence to sound more objective by using third-person pronouns:
“In this article the reader will learn about formal writing.”
The use of a third-person point of view makes the second sentence sound more academic and confident. Second-person pronouns, like those used in the first sentence, sound less formal and objective.
Be Specific With Word Choice
You can avoid first-personal pronouns by choosing your words carefully. Often, you may find that you are inserting unnecessary nouns into your work.
Take the following sentence as an example:
“ My research shows the students did poorly on the test.”
In this case, the first-person pronoun ‘my’ can be entirely cut out from the sentence. It then becomes:
“Research shows the students did poorly on the test.”
The second sentence is more succinct and sounds more authoritative without changing the sentence structure.
You should also make sure to watch out for the improper use of adverbs and nouns. Being careful with your word choice regarding nouns, adverbs, verbs, and adjectives can help mitigate your use of personal pronouns.
“They bravely started the French revolution in 1789.”
While this sentence might be fine in a story about the revolution, an essay or academic piece should only focus on the facts. The world ‘bravely’ is a good indicator that you are inserting unnecessary personal pronouns into your work.
We can revise this sentence into:
“The French revolution started in 1789.”
Avoid adverbs (adjectives that describe verbs), and you will find that you avoid personal pronouns by default.
Closing Thoughts
In academic writing, It is crucial to sound objective and focus on the topic. Using personal pronouns pulls the focus away from the subject and makes writing sound subjective.
Hopefully, this article has helped you learn how to avoid using “we” in an essay.
When working on any formal writing assignment, avoid personal pronouns and informal language as much as possible.
While getting the hang of academic writing, you will likely make some mistakes, so revising is vital. Always double-check for personal pronouns, plagiarism , spelling mistakes, and correctly cited pieces.
You can prevent and correct mistakes using a plagiarism checker at any time, completely for free.
Quetext is a platform that helps you with all those tasks. Check out all resources that are available to you today.
Sign Up for Quetext Today!
Click below to find a pricing plan that fits your needs.
You May Also Like

A Safer Learning Environment: The Impact of AI Detection on School Security
- Posted on May 17, 2024

Rethinking Academic Integrity Policies in the AI Era
- Posted on May 10, 2024 May 10, 2024

Jargon Phrases to Avoid in Business Writing
- Posted on May 3, 2024 May 3, 2024

Comparing Two Documents for Plagiarism: Everything You Need to Know
- Posted on April 26, 2024 April 26, 2024

Mastering Tone in Email Communication: A Guide to Professional Correspondence
- Posted on April 17, 2024

Mastering End-of-Sentence Punctuation: Periods, Question Marks, Exclamation Points, and More
- Posted on April 12, 2024

Mastering the Basics: Understanding the 4 Types of Sentences
- Posted on April 5, 2024

Can You Go to Jail for Plagiarism?
- Posted on March 22, 2024 March 22, 2024
Input your search keywords and press Enter.

Using You in Academic Writing

Using You in Academic Writing Podcast
Using you in academic writing transcript.
This is Kurtis Clements with another effective writing podcast. In this episode, I am going to talk about using the second person, you and your, in academic writing.
Many folks are confused when it comes to using the second person pronouns “you” and “your” in their academic writing, in large part because such pronouns are used often in other kinds of writing, so it seems natural to use such words in academic writing.
What is “academic writing”? Academic writing is writing that is generally formal; by and large, it’s the kind of writing produced in school when you are writing a report or an essay. Academic writing usually does not contain contractions or slang, nor does academic writing use emoticons or exclamation points. Academic writing sticks to a fairly objective point of view and avoids personal pronouns such as “I, we, us, our, you,” and “your,” for example. Now this is not to say that academic writing will never use such pronouns, but as a guiding general principle such pronouns are not used often in academic writing.
I don’t want to confuse you, but not all writing produced in school is “academic.” For example, if you were taking a creative writing course, while you may write essays that require a formal approach to writing, you will also be writing “creatively”—short stories and poems and other genres that would not require you to use “academic writing.”
Imagine a poem like Gwendolyn Brook’s “We Real Cool” in which the speaker, a thug without much of a future, says, “We real cool. We left school. We lurk late” written in formal academic writing like this: “They were indifferent to the conventional values of society. They left school. They lurked late at night.” Big difference, right? Of course. Academic writing is not the kind of writing to use when writing creatively.
Ok, so back to our discussion of second person. Second person is the use of the pronouns “you” and “your” in writing. In this podcast, I sometimes relate what I am talking about to my audience—to you folks listening right now—so I will make statements like “I don’t want to confuse you, but…” In my podcast, which is not a formal writing situation, it’s fine to use the pronouns “you” and “your.”
As a guiding principle, the second person pronouns “you” and “your” should not be used in academic writing. Using “you and your” is informal and lacks the kind of professional tone found in academic writing. “You” may work fine in some situations (like this podcast, for example), but in academic writing, such usage can be downright confusing. When I use “you” in my podcast, it’s clear that I am addressing my listeners.
But let’s say you were reading a paper about recycling, something that you already do. What would your reaction be if every now and then the writer included a sentence like “All you would need to do is set up a few extra bins in your home for glass, paper, metal, and plastic, and then put each item into its respective bin.” What would your response be? You would likely be confused, right? After all, you already recycle. And imagine other instances of the writer referring to “you” in a sentence. Every time you read “you,” you stop in your tracks and think, “Me?”
Let’s say the recycling paper’s purpose is to persuade and thus the logical audience would be folks who don’t recycle. Would “you” be appropriate then? No. While there would clearly be less confusion on the part of readers, writing of a more formal nature should be as objective as possible and not refer directly to readers.
Imagine reading a formal academic essay that is arguing for greater individual effort to recycle, and throughout the paper the writer uses the objective third person point of view, making such statements as “Individuals have a responsibility to future generations to do what they can to cut down on waste” and “Individuals must be proactive in recycling at home and work,” and then all of a sudden, out of the blue, the writing shifts to second person and makes a statement like “You might be busy, but if you make recycling a top priority then you would probably be successful.”
Whoa, right?
Where did that sentence come from? As a reader, you were engaged in the persuasive but objective discussion of the need to recycle, when all of a sudden the writing shifts to second person, and it seems like the writer is pointing a finger at you.
The use of second person can be confusing, awkward, and off-putting in academic writing, so it’s best to avoid the pronouns “you” and “your.”
A good way to ensure such pronouns don’t appear in your paper is to read your work slowly aloud. Mark each “you” or “your” you find and revise accordingly. With a little practice, keeping the second person out of your writing will come naturally.
Thanks for listening, everyone. Happy writing.
Share this:
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Reddit (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window)
- Click to print (Opens in new window)
Follow Blog via Email
Enter your email address to follow this blog and receive email notifications of new posts.
Email Address
- RSS - Posts
- RSS - Comments
- COLLEGE WRITING
- USING SOURCES & APA STYLE
- EFFECTIVE WRITING PODCASTS
- LEARNING FOR SUCCESS
- PLAGIARISM INFORMATION
- FACULTY RESOURCES
- Student Webinar Calendar
- Academic Success Center
- Writing Center
- About the ASC Tutors
- DIVERSITY TRAINING
- PG Peer Tutors
- PG Student Access
Subscribe to Blog via Email
Enter your email address to subscribe to this blog and receive notifications of new posts by email.
- College Writing
- Using Sources & APA Style
- Learning for Success
- Effective Writing Podcasts
- Plagiarism Information
- Faculty Resources
- Tutor Training
Twitter feed
- How it works

Use of Pronouns in Academic Writing
Published by Alvin Nicolas at August 17th, 2021 , Revised On August 24, 2023
Pronouns are words that make reference to both specific and nonspecific things and people. They are used in place of nouns.
First-person pronouns (I, We) are rarely used in academic writing. They are primarily used in a reflective piece, such as a reflective essay or personal statement. You should avoid using second-person pronouns such as “you” and “yours”. The use of third-person pronouns (He, She, They) is allowed, but it is still recommended to consider gender bias when using them in academic writing.
The antecedent of a pronoun is the noun that the pronoun represents. In English, you will see the antecedent appear both before and after the pronoun, even though it is usually mentioned in the text before the pronoun. The students could not complete the work on time because they procrastinated for too long. Before he devoured a big burger, Michael looked a bit nervous.
The Antecedent of a Pronoun
Make sure the antecedent is evident and explicit whenever you use a pronoun in a sentence. You may want to replace the pronoun with the noun to eliminate any vagueness.
- After the production and the car’s mechanical inspection were complete, it was delivered to the owner.
In the above sentence, it is unclear what the pronoun “it” is referring to.
- After the production and the car’s mechanical inspection was complete, the car was delivered to the owner.
Use of First Person Pronouns (I, We) in Academic Writing
The use of first-person pronouns, such as “I” and “We”, is a widely debated topic in academic writing.
While some style guides, such as ‘APA” and “Harvard”, encourage first-person pronouns when describing the author’s actions, many other style guides discourage their use in academic writing to keep the attention to the information presented within rather than who describes it.
Similarly, you will find some leniency towards the use of first-person pronouns in some academic disciplines, while others strictly prohibit using them to maintain an impartial and neutral tone.
It will be fair to say that first-person pronouns are increasingly regular in many forms of academic writing. If ever in doubt whether or not you should use first-person pronouns in your essay or assignment, speak with your tutor to be entirely sure.
Avoid overusing first-person pronouns in academic papers regardless of the style guide used. It is recommended to use them only where required for improving the clarity of the text.
If you are writing about a situation involving only yourself or if you are the sole author of the paper, then use the singular pronouns (I, my). Use plural pronouns (We, They, Our) when there are coauthors to work.
Avoiding First Person Pronouns
You can avoid first-person pronouns by employing any of the following three methods.
There are advantages and disadvantages of each of these three strategies. For example, passive voice introduces dangling modifiers, which can make your text unclear and ambiguous. Therefore, it would be best to keep first-person pronouns in the text if you can use them.
In some forms of academic writing, such as a personal statement and reflective essay, it is completely acceptable to use first-person pronouns.
The Problem with the Editorial We
Avoid using the first person plural to refer to people in academic text, known as the “editorial we”. The use of the “editorial we” is quite common in newspapers when the author speaks on behalf of the people to express a shared experience or view.
Refrain from using broad generalizations in academic text. You have to be crystal clear and very specific about who you are making reference to. Use nouns in place of pronouns where possible.
- When we tested the data, we found that the hypothesis to be incorrect.
- When the researchers tested the data, they found the hypothesis to be incorrect.
- As we started to work on the project, we realized how complex the requirements were.
- As the students started to work on the project, they realized how complex the requirements were.
If you are talking on behalf of a specific group you belong to, then the use of “we” is acceptable.
- It is essential to be aware of our own
- It is essential for essayists to be aware of their own weaknesses.
- Essayists need to be aware of their own
Use of Second Person Pronouns (You) in Academic Writing
It is strictly prohibited to use the second-person pronoun “you” to address the audience in any form of academic writing. You can rephrase the sentence or introduce the impersonal pronoun “one” to avoid second-person pronouns in the text.
- To achieve the highest academic grade, you must avoid procrastination.
- To achieve the highest academic grade, one must avoid procrastination.
- As you can notice in below Table 2.1, all participants selected the first option.
- As shown in below Table 2.1, all participants selected the first option.
Use of Third Person Pronouns (He, She, They) in Academic Writing
Third-person pronouns in the English language are usually gendered (She/Her, He/Him). Educational institutes worldwide are increasingly advocating for gender-neutral language, so you should avoid using third-person pronouns in academic text.
In the older academic text, you will see gender-based nouns (Fishermen, Traitor) and pronouns (him, her, he, she) being commonly used. However, this style of writing is outdated and warned against in the present times.
You may also see some authors using both masculine and feminine pronouns, such as “he” or “she”, in the same text, but this generally results in unclear and inappropriate sentences.
Considering using gender-neutral pronouns, such as “they”, ‘there”, “them” for unknown people and undetermined people. The use of “they” in academic writing is highly encouraged. Many style guides, including Harvard, MLA, and APA, now endorse gender natural pronouns in academic writing.
On the other hand, you can also choose to avoid using pronouns altogether by either revising the sentence structure or pluralizing the sentence’s subject.
- When a student is asked to write an essay, he can take a specific position on the topic.
- When a student is asked to write an essay, they can take a specific position on the topic.
- When students are asked to write an essay, they are expected to take a specific position on the topic.
- Students are expected to take a specific position on the essay topic.
- The writer submitted his work for approval
- The writer submitted their work for approval.
- The writers submitted their work for approval.
- The writers’ work was submitted for approval.
Make sure it is clear who you are referring to with the singular “they” pronoun. You may want to rewrite the sentence or name the subject directly if the pronoun makes the sentence ambiguous.
For example, in the following example, you can see it is unclear who the plural pronoun “they” is referring to. To avoid confusion, the subject is named directly, and the context approves that “their paper” addresses the writer.
- If the writer doesn’t complete the client’s paper in time, they will be frustrated.
- The client will be frustrated if the writer doesn’t complete their paper in due time.
If you need to make reference to a specific person, it would be better to address them using self-identified pronouns. For example, in the following sentence, you can see that each person is referred to using a different possessive pronoun.
The students described their experience with different academic projects: Mike talked about his essay, James talked about their poster presentation, and Sara talked about her dissertation paper.
Ensure Consistency Throughout the Text
Avoid switching back and forth between first-person pronouns (I, We, Our) and third-person pronouns (The writers, the students) in a single piece. It is vitally important to maintain consistency throughout the text.
For example, The writers completed the work in due time, and our content quality is well above the standard expected. We completed the work in due time, and our content quality is well above the standard expected. The writers completed the work in due time, and the content quality is well above the standard expected.“
How to Use Demonstrative Pronouns (This, That, Those, These) in Academic Writing
Make sure it is clear who you are referring to when using demonstrative pronouns. Consider placing a descriptive word or phrase after the demonstrative pronouns to give more clarity to the sentence.
For example, The political relationship between Israel and Arab states has continued to worsen over the last few decades, contrary to the expectations of enthusiasts in the regional political sphere. This shows that a lot more needs to be done to tackle this. The political relationship between Israel and Arab states has continued to worsen over the last few decades, contrary to the expectations of enthusiasts in the regional political sphere. This situation shows that a lot more needs to be done to tackle this issue.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the 8 types of pronouns.
The 8 types of pronouns are:
- Personal: Refers to specific persons.
- Demonstrative: Points to specific things.
- Interrogative: Used for questioning.
- Possessive: Shows ownership.
- Reflexive: Reflects the subject.
- Reciprocal: Indicates mutual action.
- Relative: Introduces relative clauses.
- Indefinite: Refers vaguely or generally.
You May Also Like
Question marks are frequently used in academic writing, considering the number of questions we try to address.
You can introduce elaborations, descriptions, a list of items, phrases, words, clauses, and pointers using a colon. This article explains the use of colons with examples.
The subject-verb agreement is simple to apply in straightforward and short sentences, but it can be tricky in more complicated and longer sentences.
USEFUL LINKS
LEARNING RESOURCES

COMPANY DETAILS

- How It Works

Should I Use “I”?
What this handout is about.
This handout is about determining when to use first person pronouns (“I”, “we,” “me,” “us,” “my,” and “our”) and personal experience in academic writing. “First person” and “personal experience” might sound like two ways of saying the same thing, but first person and personal experience can work in very different ways in your writing. You might choose to use “I” but not make any reference to your individual experiences in a particular paper. Or you might include a brief description of an experience that could help illustrate a point you’re making without ever using the word “I.” So whether or not you should use first person and personal experience are really two separate questions, both of which this handout addresses. It also offers some alternatives if you decide that either “I” or personal experience isn’t appropriate for your project. If you’ve decided that you do want to use one of them, this handout offers some ideas about how to do so effectively, because in many cases using one or the other might strengthen your writing.
Expectations about academic writing
Students often arrive at college with strict lists of writing rules in mind. Often these are rather strict lists of absolutes, including rules both stated and unstated:
- Each essay should have exactly five paragraphs.
- Don’t begin a sentence with “and” or “because.”
- Never include personal opinion.
- Never use “I” in essays.
We get these ideas primarily from teachers and other students. Often these ideas are derived from good advice but have been turned into unnecessarily strict rules in our minds. The problem is that overly strict rules about writing can prevent us, as writers, from being flexible enough to learn to adapt to the writing styles of different fields, ranging from the sciences to the humanities, and different kinds of writing projects, ranging from reviews to research.
So when it suits your purpose as a scholar, you will probably need to break some of the old rules, particularly the rules that prohibit first person pronouns and personal experience. Although there are certainly some instructors who think that these rules should be followed (so it is a good idea to ask directly), many instructors in all kinds of fields are finding reason to depart from these rules. Avoiding “I” can lead to awkwardness and vagueness, whereas using it in your writing can improve style and clarity. Using personal experience, when relevant, can add concreteness and even authority to writing that might otherwise be vague and impersonal. Because college writing situations vary widely in terms of stylistic conventions, tone, audience, and purpose, the trick is deciphering the conventions of your writing context and determining how your purpose and audience affect the way you write. The rest of this handout is devoted to strategies for figuring out when to use “I” and personal experience.
Effective uses of “I”:
In many cases, using the first person pronoun can improve your writing, by offering the following benefits:
- Assertiveness: In some cases you might wish to emphasize agency (who is doing what), as for instance if you need to point out how valuable your particular project is to an academic discipline or to claim your unique perspective or argument.
- Clarity: Because trying to avoid the first person can lead to awkward constructions and vagueness, using the first person can improve your writing style.
- Positioning yourself in the essay: In some projects, you need to explain how your research or ideas build on or depart from the work of others, in which case you’ll need to say “I,” “we,” “my,” or “our”; if you wish to claim some kind of authority on the topic, first person may help you do so.
Deciding whether “I” will help your style
Here is an example of how using the first person can make the writing clearer and more assertive:
Original example:
In studying American popular culture of the 1980s, the question of to what degree materialism was a major characteristic of the cultural milieu was explored.
Better example using first person:
In our study of American popular culture of the 1980s, we explored the degree to which materialism characterized the cultural milieu.
The original example sounds less emphatic and direct than the revised version; using “I” allows the writers to avoid the convoluted construction of the original and clarifies who did what.
Here is an example in which alternatives to the first person would be more appropriate:
As I observed the communication styles of first-year Carolina women, I noticed frequent use of non-verbal cues.
Better example:
A study of the communication styles of first-year Carolina women revealed frequent use of non-verbal cues.
In the original example, using the first person grounds the experience heavily in the writer’s subjective, individual perspective, but the writer’s purpose is to describe a phenomenon that is in fact objective or independent of that perspective. Avoiding the first person here creates the desired impression of an observed phenomenon that could be reproduced and also creates a stronger, clearer statement.
Here’s another example in which an alternative to first person works better:
As I was reading this study of medieval village life, I noticed that social class tended to be clearly defined.
This study of medieval village life reveals that social class tended to be clearly defined.
Although you may run across instructors who find the casual style of the original example refreshing, they are probably rare. The revised version sounds more academic and renders the statement more assertive and direct.
Here’s a final example:
I think that Aristotle’s ethical arguments are logical and readily applicable to contemporary cases, or at least it seems that way to me.
Better example
Aristotle’s ethical arguments are logical and readily applicable to contemporary cases.
In this example, there is no real need to announce that that statement about Aristotle is your thought; this is your paper, so readers will assume that the ideas in it are yours.
Determining whether to use “I” according to the conventions of the academic field
Which fields allow “I”?
The rules for this are changing, so it’s always best to ask your instructor if you’re not sure about using first person. But here are some general guidelines.
Sciences: In the past, scientific writers avoided the use of “I” because scientists often view the first person as interfering with the impression of objectivity and impersonality they are seeking to create. But conventions seem to be changing in some cases—for instance, when a scientific writer is describing a project she is working on or positioning that project within the existing research on the topic. Check with your science instructor to find out whether it’s o.k. to use “I” in their class.
Social Sciences: Some social scientists try to avoid “I” for the same reasons that other scientists do. But first person is becoming more commonly accepted, especially when the writer is describing their project or perspective.
Humanities: Ask your instructor whether you should use “I.” The purpose of writing in the humanities is generally to offer your own analysis of language, ideas, or a work of art. Writers in these fields tend to value assertiveness and to emphasize agency (who’s doing what), so the first person is often—but not always—appropriate. Sometimes writers use the first person in a less effective way, preceding an assertion with “I think,” “I feel,” or “I believe” as if such a phrase could replace a real defense of an argument. While your audience is generally interested in your perspective in the humanities fields, readers do expect you to fully argue, support, and illustrate your assertions. Personal belief or opinion is generally not sufficient in itself; you will need evidence of some kind to convince your reader.
Other writing situations: If you’re writing a speech, use of the first and even the second person (“you”) is generally encouraged because these personal pronouns can create a desirable sense of connection between speaker and listener and can contribute to the sense that the speaker is sincere and involved in the issue. If you’re writing a resume, though, avoid the first person; describe your experience, education, and skills without using a personal pronoun (for example, under “Experience” you might write “Volunteered as a peer counselor”).
A note on the second person “you”:
In situations where your intention is to sound conversational and friendly because it suits your purpose, as it does in this handout intended to offer helpful advice, or in a letter or speech, “you” might help to create just the sense of familiarity you’re after. But in most academic writing situations, “you” sounds overly conversational, as for instance in a claim like “when you read the poem ‘The Wasteland,’ you feel a sense of emptiness.” In this case, the “you” sounds overly conversational. The statement would read better as “The poem ‘The Wasteland’ creates a sense of emptiness.” Academic writers almost always use alternatives to the second person pronoun, such as “one,” “the reader,” or “people.”
Personal experience in academic writing
The question of whether personal experience has a place in academic writing depends on context and purpose. In papers that seek to analyze an objective principle or data as in science papers, or in papers for a field that explicitly tries to minimize the effect of the researcher’s presence such as anthropology, personal experience would probably distract from your purpose. But sometimes you might need to explicitly situate your position as researcher in relation to your subject of study. Or if your purpose is to present your individual response to a work of art, to offer examples of how an idea or theory might apply to life, or to use experience as evidence or a demonstration of an abstract principle, personal experience might have a legitimate role to play in your academic writing. Using personal experience effectively usually means keeping it in the service of your argument, as opposed to letting it become an end in itself or take over the paper.
It’s also usually best to keep your real or hypothetical stories brief, but they can strengthen arguments in need of concrete illustrations or even just a little more vitality.
Here are some examples of effective ways to incorporate personal experience in academic writing:
- Anecdotes: In some cases, brief examples of experiences you’ve had or witnessed may serve as useful illustrations of a point you’re arguing or a theory you’re evaluating. For instance, in philosophical arguments, writers often use a real or hypothetical situation to illustrate abstract ideas and principles.
- References to your own experience can explain your interest in an issue or even help to establish your authority on a topic.
- Some specific writing situations, such as application essays, explicitly call for discussion of personal experience.
Here are some suggestions about including personal experience in writing for specific fields:
Philosophy: In philosophical writing, your purpose is generally to reconstruct or evaluate an existing argument, and/or to generate your own. Sometimes, doing this effectively may involve offering a hypothetical example or an illustration. In these cases, you might find that inventing or recounting a scenario that you’ve experienced or witnessed could help demonstrate your point. Personal experience can play a very useful role in your philosophy papers, as long as you always explain to the reader how the experience is related to your argument. (See our handout on writing in philosophy for more information.)
Religion: Religion courses might seem like a place where personal experience would be welcomed. But most religion courses take a cultural, historical, or textual approach, and these generally require objectivity and impersonality. So although you probably have very strong beliefs or powerful experiences in this area that might motivate your interest in the field, they shouldn’t supplant scholarly analysis. But ask your instructor, as it is possible that they are interested in your personal experiences with religion, especially in less formal assignments such as response papers. (See our handout on writing in religious studies for more information.)
Literature, Music, Fine Arts, and Film: Writing projects in these fields can sometimes benefit from the inclusion of personal experience, as long as it isn’t tangential. For instance, your annoyance over your roommate’s habits might not add much to an analysis of “Citizen Kane.” However, if you’re writing about Ridley Scott’s treatment of relationships between women in the movie “Thelma and Louise,” some reference your own observations about these relationships might be relevant if it adds to your analysis of the film. Personal experience can be especially appropriate in a response paper, or in any kind of assignment that asks about your experience of the work as a reader or viewer. Some film and literature scholars are interested in how a film or literary text is received by different audiences, so a discussion of how a particular viewer or reader experiences or identifies with the piece would probably be appropriate. (See our handouts on writing about fiction , art history , and drama for more information.)
Women’s Studies: Women’s Studies classes tend to be taught from a feminist perspective, a perspective which is generally interested in the ways in which individuals experience gender roles. So personal experience can often serve as evidence for your analytical and argumentative papers in this field. This field is also one in which you might be asked to keep a journal, a kind of writing that requires you to apply theoretical concepts to your experiences.
History: If you’re analyzing a historical period or issue, personal experience is less likely to advance your purpose of objectivity. However, some kinds of historical scholarship do involve the exploration of personal histories. So although you might not be referencing your own experience, you might very well be discussing other people’s experiences as illustrations of their historical contexts. (See our handout on writing in history for more information.)
Sciences: Because the primary purpose is to study data and fixed principles in an objective way, personal experience is less likely to have a place in this kind of writing. Often, as in a lab report, your goal is to describe observations in such a way that a reader could duplicate the experiment, so the less extra information, the better. Of course, if you’re working in the social sciences, case studies—accounts of the personal experiences of other people—are a crucial part of your scholarship. (See our handout on writing in the sciences for more information.)
You may reproduce it for non-commercial use if you use the entire handout and attribute the source: The Writing Center, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
Make a Gift

- Walden University
- Faculty Portal
Scholarly Voice: First-Person Point of View
First-person point of view.
Since 2007, Walden academic leadership has endorsed the APA manual guidance on appropriate use of the first-person singular pronoun "I," allowing the use of this pronoun in all Walden academic writing except doctoral capstone abstracts, which should not contain first person pronouns.
In addition to the pointers below, APA 7, Section 4.16 provides information on the appropriate use of first person in scholarly writing.
Inappropriate Uses: I feel that eating white bread causes cancer. The author feels that eating white bread causes cancer. I found several sources (Marks, 2011; Isaac, 2006; Stuart, in press) that showed a link between white bread consumption and cancer. Appropriate Use: I surveyed 2,900 adults who consumed white bread regularly. In this chapter, I present a literature review on research about how seasonal light changes affect depression.
Confusing Sentence: The researcher found that the authors had been accurate in their study of helium, which the researcher had hypothesized from the beginning of their project. Revision: I found that Johnson et al. (2011) had been accurate in their study of helium, which I had hypothesized since I began my project.
Passive voice: The surveys were distributed and the results were compiled after they were collected. Revision: I distributed the surveys, and then I collected and compiled the results.
Appropriate use of first person we and our : Two other nurses and I worked together to create a qualitative survey to measure patient satisfaction. Upon completion, we presented the results to our supervisor.
Make assumptions about your readers by putting them in a group to which they may not belong by using first person plural pronouns. Inappropriate use of first person "we" and "our":
- We can stop obesity in our society by changing our lifestyles.
- We need to help our patients recover faster.
In the first sentence above, the readers would not necessarily know who "we" are, and using a phrase such as "our society " can immediately exclude readers from outside your social group. In the second sentence, the author assumes that the reader is a nurse or medical professional, which may not be the case, and the sentence expresses the opinion of the author.
To write with more precision and clarity, hallmarks of scholarly writing, revise these sentences without the use of "we" and "our."
- Moderate activity can reduce the risk of obesity (Hu et al., 2003).
- Staff members in the health care industry can help improve the recovery rate for patients (Matthews, 2013).
Pronouns Video
- APA Formatting & Style: Pronouns (video transcript)
Related Resources
Didn't find what you need? Email us at [email protected] .
- Previous Page: Point of View
- Next Page: Second-Person Point of View
- Office of Student Disability Services
Walden Resources
Departments.
- Academic Residencies
- Academic Skills
- Career Planning and Development
- Customer Care Team
- Field Experience
- Military Services
- Student Success Advising
- Writing Skills
Centers and Offices
- Center for Social Change
- Office of Academic Support and Instructional Services
- Office of Degree Acceleration
- Office of Research and Doctoral Services
- Office of Student Affairs
Student Resources
- Doctoral Writing Assessment
- Form & Style Review
- Quick Answers
- ScholarWorks
- SKIL Courses and Workshops
- Walden Bookstore
- Walden Catalog & Student Handbook
- Student Safety/Title IX
- Legal & Consumer Information
- Website Terms and Conditions
- Cookie Policy
- Accessibility
- Accreditation
- State Authorization
- Net Price Calculator
- Contact Walden
Walden University is a member of Adtalem Global Education, Inc. www.adtalem.com Walden University is certified to operate by SCHEV © 2024 Walden University LLC. All rights reserved.

Get The "You" Outta Here: Home
Oh silly, you.
When you reach puberty, you grow hair on your chest.
Removing Second Person Handout and Practice
Download the Removing Second Person Handout and Practice:
For answers to the practice, visit a campus tutoring center near you.
Rule of Thumb for Academic Writing
- you, your, yours
- we, us, our, ours
Sounds harsh, but unless an instructor specifically says otherwise, assume second person is to be avoided.
Get the "You" Outta Here Video
Main Reasons to Avoid Second Person
- Causes confusion
- Addresses the reader
- Is imprecise
- Is inaccurate
- Shifts person
- Is too informal
Breaking the You Habit
- Use nouns instead
- Use indefinite pronouns (everyone, someone, anything) instead
- Cut the "you" out altogether
- Avoid giving commands (where "you" is the implied subject)
Spotting Second Person
- The best way to spot second person is to print paper and read it out loud.
- Another way is to use the Find/Replace feature in your word processing software.
- Last Updated: Oct 23, 2023 11:03 AM
- URL: https://spcollege.libguides.com/noyou
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Appropriate Pronoun Usage

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
Because English has no generic singular—or common-sex—pronoun, we have used HE, HIS, and HIM in such expressions as "the student needs HIS pencil." When we constantly personify "the judge," "the critic," "the executive," "the author," and so forth, as male by using the pronoun HE, we are subtly conditioning ourselves against the idea of a female judge, critic, executive, or author. There are several alternative approaches for ending the exclusion of women that results from the pervasive use of masculine pronouns.
Recast into the plural
- Original: Give each student his paper as soon as he is finished.
- Alternative: Give students their papers as soon as they are finished.
Reword to eliminate gender problems.
- Original: The average student is worried about his grade.
- Alternative: The average student is worried about grades.
Replace the masculine pronoun with ONE, YOU, or (sparingly) HE OR SHE, as appropriate.
- Original: If the student was satisfied with his performance on the pretest, he took the post-test.
- Alternative: A student who was satisfied with her or his performance on the pretest took the post-test.
Alternate male and female examples and expressions. (Be careful not to confuse the reader.)
- Original: Let each student participate. Has he had a chance to talk? Could he feel left out?
- Alternative: Let each student participate. Has she had a chance to talk? Could he feel left out?
Indefinite Pronouns
Using the masculine pronouns to refer to an indefinite pronoun ( everybody, everyone, anybody, anyone ) also has the effect of excluding women. In all but strictly formal uses, plural pronouns have become acceptable substitutes for the masculine singular.
- Original: Anyone who wants to go to the game should bring his money tomorrow.
- Alternative: Anyone who wants to go to the game should bring their money tomorrow.
An alternative to this is merely changing the sentence. English is very flexible, so there is little reason to "write yourself into a corner":
- Original: Anyone who wants to go to the game should bring his money.
- Alternative: People who want to go to the game should bring their money.
Table of Contents
Ai, ethics & human agency, collaboration, information literacy, writing process, using first person in an academic essay: when is it okay.
- CC BY-NC-ND 4.0 by Jenna Pack Sheffield

Related Concepts: Academic Writing – How to Write for the Academic Community ; First-Person Point of View ; Rhetorical Analysis; Rhetorical Stance ; The First Person ; Voice
In order to determine whether or not you can speak or write from the first-person point of view, you need to engage in rhetorical analysis. You need to question whether your audience values and accepts the first person as a legitimate rhetorical stance. Source:Many times, high school students are told not to use first person (“I,” “we,” “my,” “us,” and so forth) in their essays. As a college student, you should realize that this is a rule that can and should be broken—at the right time, of course.
By now, you’ve probably written a personal essay, memoir, or narrative that used first person. After all, how could you write a personal essay about yourself, for instance, without using the dreaded “I” word?
However, academic essays differ from personal essays; they are typically researched and use a formal tone . Because of these differences, when students write an academic essay, they quickly shy away from first person because of what they have been told in high school or because they believe that first person feels too informal for an intellectual, researched text. While first person can definitely be overused in academic essays (which is likely why your teachers tell you not to use it), there are moments in a paper when it is not only appropriate, but also more effective and/or persuasive to use first person. The following are a few instances in which it is appropriate to use first person in an academic essay:
- Including a personal anecdote: You have more than likely been told that you need a strong “hook” to draw your readers in during an introduction. Sometimes, the best hook is a personal anecdote, or a short amusing story about yourself. In this situation, it would seem unnatural not to use first-person pronouns such as “I” and “myself.” Your readers will appreciate the personal touch and will want to keep reading! (For more information about incorporating personal anecdotes into your writing, see “ Employing Narrative in an Essay .”)
- Establishing your credibility ( ethos ): Ethos is a term stemming back to Ancient Greece that essentially means “character” in the sense of trustworthiness or credibility. A writer can establish her ethos by convincing the reader that she is trustworthy source. Oftentimes, the best way to do that is to get personal—tell the reader a little bit about yourself. (For more information about ethos, see “ Ethos .”)For instance, let’s say you are writing an essay arguing that dance is a sport. Using the occasional personal pronoun to let your audience know that you, in fact, are a classically trained dancer—and have the muscles and scars to prove it—goes a long way in establishing your credibility and proving your argument. And this use of first person will not distract or annoy your readers because it is purposeful.
- Clarifying passive constructions : Often, when writers try to avoid using first person in essays, they end up creating confusing, passive sentences . For instance, let’s say I am writing an essay about different word processing technologies, and I want to make the point that I am using Microsoft Word to write this essay. If I tried to avoid first-person pronouns, my sentence might read: “Right now, this essay is being written in Microsoft Word.” While this sentence is not wrong, it is what we call passive—the subject of the sentence is being acted upon because there is no one performing the action. To most people, this sentence sounds better: “Right now, I am writing this essay in Microsoft Word.” Do you see the difference? In this case, using first person makes your writing clearer.
- Stating your position in relation to others: Sometimes, especially in an argumentative essay, it is necessary to state your opinion on the topic . Readers want to know where you stand, and it is sometimes helpful to assert yourself by putting your own opinions into the essay. You can imagine the passive sentences (see above) that might occur if you try to state your argument without using the word “I.” The key here is to use first person sparingly. Use personal pronouns enough to get your point across clearly without inundating your readers with this language.
Now, the above list is certainly not exhaustive. The best thing to do is to use your good judgment, and you can always check with your instructor if you are unsure of his or her perspective on the issue. Ultimately, if you feel that using first person has a purpose or will have a strategic effect on your audience, then it is probably fine to use first-person pronouns. Just be sure not to overuse this language, at the risk of sounding narcissistic, self-centered, or unaware of others’ opinions on a topic.
Recommended Readings:
- A Synthesis of Professor Perspectives on Using First and Third Person in Academic Writing
- Finding the Bunny: How to Make a Personal Connection to Your Writing
- First-Person Point of View

Brevity – Say More with Less

Clarity (in Speech and Writing)

Coherence – How to Achieve Coherence in Writing

Flow – How to Create Flow in Writing

Inclusivity – Inclusive Language

The Elements of Style – The DNA of Powerful Writing

Suggested Edits
- Please select the purpose of your message. * - Corrections, Typos, or Edits Technical Support/Problems using the site Advertising with Writing Commons Copyright Issues I am contacting you about something else
- Your full name
- Your email address *
- Page URL needing edits *
- Phone This field is for validation purposes and should be left unchanged.
Featured Articles

Academic Writing – How to Write for the Academic Community

Professional Writing – How to Write for the Professional World

Credibility & Authority – How to Be Credible & Authoritative in Speech & Writing
Using “I” in Academic Writing
Traditionally, some fields have frowned on the use of the first-person singular in an academic essay and others have encouraged that use, and both the frowning and the encouraging persist today—and there are good reasons for both positions (see “Should I”).
I recommend that you not look on the question of using “I” in an academic paper as a matter of a rule to follow, as part of a political agenda (see webb), or even as the need to create a strategy to avoid falling into Scylla-or-Charybdis error. Let the first-person singular be, instead, a tool that you take out when you think it’s needed and that you leave in the toolbox when you think it’s not.
Examples of When “I” May Be Needed
- You are narrating how you made a discovery, and the process of your discovering is important or at the very least entertaining.
- You are describing how you teach something and how your students have responded or respond.
- You disagree with another scholar and want to stress that you are not waving the banner of absolute truth.
- You need “I” for rhetorical effect, to be clear, simple, or direct.
Examples of When “I” Should Be Given a Rest
- It’s off-putting to readers, generally, when “I” appears too often. You may not feel one bit modest, but remember the advice of Benjamin Franklin, still excellent, on the wisdom of preserving the semblance of modesty when your purpose is to convince others.
- You are the author of your paper, so if an opinion is expressed in it, it is usually clear that this opinion is yours. You don’t have to add a phrase like, “I believe” or “it seems to me.”
Works Cited
Franklin, Benjamin. The Autobiography of Benjamin Franklin . Project Gutenberg , 28 Dec. 2006, www.gutenberg.org/app/uploads/sites/3/20203/20203-h/20203-h.htm#I.
“Should I Use “I”?” The Writing Center at UNC—Chapel Hill , writingcenter.unc.edu/handouts/should-i-use-i/.
webb, Christine. “The Use of the First Person in Academic Writing: Objectivity, Language, and Gatekeeping.” ResearchGate , July 1992, doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2648.1992.tb01974.x.
J.S.Beniwal 05 August 2017 AT 09:08 AM
I have borrowed MLA only yesterday, did my MAEnglish in May 2017.MLA is of immense help for scholars.An overview of the book really enlightened me.I should have read it at bachelor's degree level.
Your e-mail address will not be published
Dr. Raymond Harter 25 September 2017 AT 02:09 PM
I discourage the use of "I" in essays for undergraduates to reinforce a conversational tone and to "self-recognize" the writer as an authority or at least a thorough researcher. Writing a play is different than an essay with a purpose.
Osayimwense Osa 22 March 2023 AT 05:03 PM
When a student or writer is strongly and passionately interested in his or her stance and argument to persuade his or her audience, the use of personal pronoun srenghtens his or her passion for the subject. This passion should be clear in his/her expression. However, I encourage the use of the first-person, I, sparingly -- only when and where absolutely necessary.
Eleanor 25 March 2023 AT 04:03 PM
I once had a student use the word "eye" when writing about how to use pronouns. Her peers did not catch it. I made comments, but I think she never understood what eye was saying!
Join the Conversation
We invite you to comment on this post and exchange ideas with other site visitors. Comments are moderated and subject to terms of service.
If you have a question for the MLA's editors, submit it to Ask the MLA!
- Have your assignments done by seasoned writers. 24/7
- Contact us:
- +1 (213) 221-0069
- [email protected]

How to Replace I in Essays: Alternative 3rd Person Pronouns

replacing I in essays
Learning how to write an essay without using ‘I,’ ‘We,’ or ‘You,’ and other personal languages can be challenging for students. The best writing skills recommend not to use such pronouns. This guide explores how to replace ‘I,’ ‘We,’ or ‘You’ in an essay and the methods to avoid them.
For those of us who have been able to overcome this, you will agree that there was a time when you experienced a challenge when finding alternatives to clauses such as “I will argue” or “I think.”
The good thing is that there are several methods of communicating your point and writing an essay without using ‘I’ or related personal language.

Let us Write your Essays! No Plagiarism
Get an expert writer to score an A in your next essay assignment. Place your order today, and you will enjoy it.
Why Avoid Using Pronouns in Formal Writing
Before identifying the communication methods without using personal language like “I,” it is best to know why we should avoid such language while writing essays.
The most important reason for avoiding such language is because it is not suitable for formal writing such as essays. Appropriate professional English should not include any form of personal pronouns or language.

The second and equally important reason to avoid using personal language while writing an essay is to sound impersonal, functional, and objective.
In formal English, personal pronouns conflict with the idea of being impersonal, functional, and objective because they make redundant references to the writer and other people.
Personal pronouns will make an essay seem to contain only the writer’s perspectives and others they have deliberately selected. Again, they will make the work appear subjective.
Another reason to avoid personal language while coming up with an essay is to avoid sounding as if you have an urgent need to impress the reader through wording.
Personal pronouns like “you” and “I” tend to suggest something important that is away from what the writing is all about.
By continually using “I,” “we,” or “you,” you are taking the reader’s attention from the essay to other personal issues. The essay becomes all about the writer.
That being said, let’s explore how to replace “I” in an essay.
Custom Essay Writing Service by vetted writers
Ways of avoiding pronouns “i,” “you,” and “we” in an essay.
You can replace the pronouns ‘I’, ‘You’, and ‘We’ by replacing them with acceptable wording, applying passive voice instead of pronouns, Using a third-person perspective, adopting an objective language, and including strong verbs and adjectives.
In our other guide, we explained the best practices to avoid using ‘you’ in essay writing and use academically sound words. Let us explore each of these strategies in detail.

1. Replacing it with an Acceptable Wording
This is a very good strategy for replacing “I” in an essay. The problem is that it is often difficult to find the right word to replace the personal pronoun. Though this is the case, “I” has some alternatives.
For example, if the verb that follows it revolves around writing and research, such as “…will present” or “…have described”, it is best to replace “I” with text-referencing nouns such as “the essay.”
If you wanted to say “I will present” or “I have described”, then the alternative will be “the essay will present,” or “as described in the essay.”
Another method of replacing “I” in an essay is using appropriate wording like “this writer” if the verb’s action is not within the text.
While this is sometimes acceptable, it is often advised to have no words here by using passive verbs or their equivalents.
A wording that may also be used but rarely suitable is “the researcher”. This alternative can only be used when your actions as a writer are completely detached from the writing.
2. Using Passive voice Instead of Pronouns
Another way to replace “I” and other personal pronouns in an essay is to use passive voice. This is achieved by transforming an active verb passive.
Though this is the case, the strategy is often difficult, and it may create sentence structures that are not acceptable in formal writing and language.
The sentences in which “I” can be successfully changed using this strategy is when an active verb describing an object is transformed into its passive form.
3. Using a Third-Person Perspective
This is a very important and applicable strategy when replacing “I” in an essay. This is where you avoid using first-person and second-person perspectives.
When referring to the subject matter, refer directly to them using the third person. For example, if you were to write, “I think regular exercise is good for mind and body”, you can replace it with “Regular exercise is good for mind and body”.
4. Use of Objective Language
Objective language is lost when a person uses informal expressions like colloquialisms, slang, contractions, and clichés. It is the reason why we discourage the use of contractions in essay writing so that you can keep things formal.
While informal language can be applicable in casual writing and speeches, it is not acceptable when writing essays. This is because you will be tempted to use a first-person perspective to convey your message.
5. Being Specific and using Strong Verbs and Adjectives
In most cases, essays that have been written using a lot of personal pronouns tend to be imprecise. When you want to avoid using “I” in your essay, try to be exact and straight to the point.
Personal pronouns tend to convey a subjective message, and it is up to the writer to explain their perspectives through writing.
Here, a writer will use a lot of “I think…” or “I believe…” to express their opinion. By doing so, the writer will end up wasting a lot of time explaining a concept.
Instead of doing that, it is best to look for appropriate verbs and adjectives to explain the points. Also, use objective language. Refer to the suggestions given by credible evidence instead of basing your arguments on what you think.
Get an essay written by a Team
Our team avoids plagiarism and ensures checks to guarantee a quality and ORIGINAL paper
Words to use Instead of Personal Pronouns like “You” and “I”
As noted, it is important to avoid using personal pronouns such as “You” and “I” when writing an essay.
By eliminating them or finding alternatives to them, your essay will be formal and objective. You can decide to eliminate them in a sentence.

For example, you could be having a sentence like “I think the author makes a valid point concerning capitalism.”
In this example, you can eliminate the personal language and write, “The author makes a valid point concerning capitalism.”
The second sentence goes straight to the point and is objective.
Other words to use instead of personal pronouns, like “You” and “I,” can be created when personal judgment words are avoided.
Instead, it is best to replace those words with those that refer to the evidence.
Examples of Ways to Replace Personal Pronouns
Below are examples of how personal judgment words can be replaced by words referring to the evidence.
- I feel – In light of the evidence
- From I think – According to the findings
- I agree – It is evident from the data that
- I am convinced – Considering the results
- You can see that – From the results, it is evident that
Using the third-person or “it” constructions can be used to replace personal pronouns like “You” and “I.” Such words also help to reduce the word count of your essay and make it short and precise.
For example, if you write “I conclude that, “replace those words with “it could be concluded that. ” Here, “it” constructions are helping replace personal pronouns to make the sentence more objective and precise.
To be more specific, words to replace personal pronouns like “I” include “one,” the viewer,” “the author,” “the reader,” “readers,” or something similar.
However, avoid overusing those words because your essay will seem stiff and awkward. For example, if you write, “I can perceive the plot’s confusion,” you can replace “I” by writing, “Readers can perceive the plot’s confusion.”
Words that can be used instead of personal pronouns like “You” include “one,” “the viewer,” reader,” “readers,” or any other similar phrases. It is similar to words that replace first-person pronouns.
For example, if you write “you can see that the poet’s tone is serious and urgent,” you can replace “You” by writing “readers/one can see that the poet’s tone is serious and urgent.”
Words to use Instead of “My” in an Essay
Since “My” demonstrates the possessiveness of something, in this case, the contents or thoughts within an essay, it makes the writing subjective. According to experts, writing should take an objective language . To do this, it is important to replace it.

You can replace the word “My” with “the”. For example, if you write, “My final thoughts concerning the issue are”, you can write, “The final thoughts concerning the issues are”.
In this case, the article “The” makes the sentence formal and objective.
Another method is eliminating the word “My” from the sentence to make it more objective and straight to the point.
In the same example above, if you write “My final thoughts concerning the issue are”, you can write “Final thoughts concerning the issue are”.
The major difference here is that the word “my” in the first example makes it subjective, and eliminating it from the sentence makes it sound formal and objective.
Final Advice
Therefore, when writing an essay, it is important to avoid personal pronouns like “You”, “I,” and “My.” Not all papers use third-person language. Different types of essays are formatted differently, a 5-paragraph essay is different from a 4-page paper , but all use third-person tones.
This is because an essay should be written in formal language, and using personal pronouns makes it appear and sound informal. Therefore, writing an essay without using ‘I’ is good.
Formal language makes your essay sound objective and precise. However, do not remove the first-person language when writing personal experiences in an essay or a paper. This is because it is acceptable and formal that way.
Order an Excellent Essay today!
Let us help you get that A in your next assignment. Place your order today, and you will enjoy the benefits.

With over 10 years in academia and academic assistance, Alicia Smart is the epitome of excellence in the writing industry. She is our managing editor and is in charge of the writing operations at Grade Bees.
Related posts

Overcoming the feeling and fear of writing essays
Overcoming the Feeling and Fear of Writing Essays
Spaces between Paragraphs in an Essay
How Many Spaces between Paragraphs in an Essay
Double Space an Essay
Should You Double Space an Essay: When and When Not To

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
Margin Size
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

8.7: Tips for Writing Academic Persuasive Essays
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 250473
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
The previous chapters in this section offer an overview of what it means to formulate an argument in an academic situation. The purpose of this chapter is to offer more concrete, actionable tips for drafting an academic persuasive essay. Keep in mind that preparing to draft a persuasive essay relies on the strategies for any other thesis-driven essay, covered by the section in this textbook, The Writing Process. The following chapters can be read in concert with this one:
- Critical Reading and other research strategies helps writers identify the exigence (issue) that demands a response, as well as what kinds of research to use.
- Generate Ideas covers prewriting models (such as brainstorming techniques) that allow students to make interesting connections and develop comprehensive thesis statements. These connections and main points will allow a writer to outline their core argument.
- Organizing is important for understanding why an argument essay needs a detailed plan, before the drafting stage. For an argument essay, start with a basic outline that identifies the claim, reasoning, and evidence, but be prepared to develop more detailed outlines that include counterarguments and rebuttals, warrants, additional backing, etc., as needed.
- Drafting introduces students to basic compositional strategies that they must be familiar with before beginning an argument essay. This current chapter offers more details about what kinds of paragraphs to practice in an argument essay, but it assumes the writer is familiar with basic strategies such as coherence and cohesion.
Classical structure of an argument essay
Academic persuasive essays tend to follow what’s known as the “classical” structure, based on techniques that derive from ancient Roman and Medieval rhetoricians. John D. Ramage, et. al outline this structure in Writing Arguments :
This very detailed table can be simplified. Most academic persuasive essays include the following basic elements:
- Introduction that explains why the situation is important and presents your argument (aka the claim or thesis).
- Reasons the thesis is correct or at least reasonable.
- Evidence that supports each reason, often occurring right after the reason the evidence supports.
- Acknowledgement of objections.
- Response to objections.
Keep in mind that the structure above is just a conventional starting point. The previous chapters of this section suggest how different kinds of arguments (Classical/Aristotelian, Toulmin, Rogerian) involve slightly different approaches, and your course, instructor, and specific assignment prompt may include its own specific instructions on how to complete the assignment. There are many different variations. At the same time, however, most academic argumentative/persuasive essays expect you to practice the techniques mentioned below. These tips overlap with the elements of argumentation, covered in that chapter, but they offer more explicit examples for how they might look in paragraph form, beginning with the introduction to your essay.
Persuasive introductions should move from context to thesis
Since one of the main goals of a persuasive essay introduction is to forecast the broader argument, it’s important to keep in mind that the legibility of the argument depends on the ability of the writer to provide sufficient information to the reader. If a basic high school essay moves from general topic to specific argument (the funnel technique), a more sophisticated academic persuasive essay is more likely to move from context to thesis.
The great stylist of clear writing, Joseph W. Williams, suggests that one of the key rhetorical moves a writer can make in a persuasive introduction is to not only provide enough background information (the context), but to frame that information in terms of a problem or issue, what the section on Reading and Writing Rhetorically terms the exigence . The ability to present a clearly defined problem and then the thesis as a solution creates a motivating introduction. The reader is more likely to be gripped by it, because we naturally want to see problems solved.
Consider these two persuasive introductions, both of which end with an argumentative thesis statement:
A. In America we often hold to the belief that our country is steadily progressing. topic This is a place where dreams come true. With enough hard work, we tell ourselves (and our children), we can do anything. I argue that, when progress is more carefully defined, our current period is actually one of decline. claim
B . Two years ago my dad developed Type 2 diabetes, and the doctors explained to him that it was due in large part to his heavy consumption of sugar. For him, the primary form of sugar consumption was soda. hook His experience is echoed by millions of Americans today. According to the most recent research, “Sugary drink portion sizes have risen dramatically over the past forty years, and children and adults are drinking more soft drinks than ever,” while two out of three adults in the United States are now considered either overweight or obese. This statistic correlates with reduced life expectancy by many years. Studies have shown that those who are overweight in this generation will live a lot fewer years than those who are already elderly. And those consumers who don’t become overweight remain at risk for developing Type 2 diabetes (like my dad), known as one of the most serious global health concerns (“Sugary Drinks and Obesity Fact Sheet”). problem In response to this problem, some political journalists, such as Alexandra Le Tellier, argue that sodas should be banned. On the opposite end of the political spectrum, politically conservative journalists such as Ernest Istook argue that absolutely nothing should be done because that would interfere with consumer freedom. debate I suggest something in between: a “soda tax,” which would balance concerns over the public welfare with concerns over consumer freedom. claim
Example B feels richer, more dramatic, and much more targeted not only because it’s longer, but because it’s structured in a “motivating” way. Here’s an outline of that structure:
- Hook: It opens with a brief hook that illustrates an emerging issue. This concrete, personal anecdote grips the reader’s attention.
- Problem: The anecdote is connected with the emerging issue, phrased as a problem that needs to be addressed.
- Debate: The writer briefly alludes to a debate over how to respond to the problem.
- Claim: The introduction ends by hinting at how the writer intends to address the problem, and it’s phrased conversationally, as part of an ongoing dialogue.
Not every persuasive introduction needs all of these elements. Not all introductions will have an obvious problem. Sometimes a “problem,” or the exigence, will be as subtle as an ambiguity in a text that needs to be cleared up (as in literary analysis essays). Other times it will indeed be an obvious problem, such as in a problem-solution argument essay.
In most cases, however, a clear introduction will proceed from context to thesis . The most attention-grabbing and motivating introductions will also include things like hooks and problem-oriented issues.
Here’s a very simple and streamlined template that can serve as rudimentary scaffolding for a persuasive introduction, inspired by the excellent book, They Say / I Say: The Moves That Matter in Academic Writing : Definition: Term
In discussions of __________, an emerging issue is _____________________. issue When addressing this issue, some experts suggest ________________. debate In my view, however, _______________________________. claim
Each aspect of the template will need to be developed, but it can serve as training wheels for how to craft a nicely structured context-to-thesis introduction, including things like an issue, debate, and claim. You can try filling in the blanks below, and then export your attempt as a document.
Define key terms, as needed
Much of an academic persuasive essay is dedicated to supporting the claim. A traditional thesis-driven essay has an introduction, body, and conclusion, and the support constitutes much of the body. In a persuasive essay, most of the support is dedicated to reasoning and evidence (more on that below). However, depending on what your claim does, a careful writer may dedicate the beginning (or other parts of the essay body) to defining key terms.
Suppose I wish to construct an argument that enters the debate over euthanasia. When researching the issue, I notice that much of the debate circles around the notion of rights, specifically what a “legal right” actually means. Clearly defining that term will help reduce some of the confusion and clarify my own argument. In Vancouver Island University’s resource “ Defining key terms ,” Ian Johnston offers this example for how to define “legal right” for an academic reader:
Before discussing the notion of a right to die, we need to clarify precisely what the term legal right means. In common language, the term “right” tends often to mean something good, something people ought to have (e.g., a right to a good home, a right to a meaningful job, and so on). In law, however, the term has a much more specific meaning. It refers to something to which people are legally entitled. Thus, a “legal” right also confers a legal obligation on someone or some institution to make sure the right is conferred. For instance, in Canada, children of a certain age have a right to a free public education. This right confers on society the obligation to provide that education, and society cannot refuse without breaking the law. Hence, when we use the term right to die in a legal sense, we are describing something to which a citizen is legally entitled, and we are insisting that someone in society has an obligation to provide the services which will confer that right on anyone who wants it.
As the example above shows, academics often dedicate space to providing nuanced and technical definitions that correct common misconceptions. Johnston’s definition relies on research, but it’s not always necessary to use research to define your terms. Here are some tips for crafting definitions in persuasive essays, from “Defining key terms”:
- Fit the descriptive detail in the definition to the knowledge of the intended audience. The definition of, say, AIDS for a general readership will be different from the definition for a group of doctors (the latter will be much more technical). It often helps to distinguish between common sense or popular definitions and more technical ones.
- Make sure definitions are full and complete; do not rush them unduly. And do not assume that just because the term is quite common that everyone knows just what it means (e.g., alcoholism ). If you are using the term in a very specific sense, then let the reader know what that is. The amount of detail you include in a definition should cover what is essential for the reader to know, in order to follow the argument. By the same token, do not overload the definition, providing too much detail or using far too technical a language for those who will be reading the essay.
- It’s unhelpful to simply quote the google or dictionary.com definition of a word. Dictionaries contain a few or several definitions for important terms, and the correct definition is informed by the context in which it’s being employed. It’s up to the writer to explain that context and how the word is usually understood within it.
- You do not always need to research a definition. Depending on the writing situation and audience, you may be able to develop your own understanding of certain terms.
Use P-E-A-S or M-E-A-L to support your claim
The heart of a persuasive essay is a claim supported by reasoning and evidence. Thus, much of the essay body is often devoted to the supporting reasons, which in turn are proved by evidence. One of the formulas commonly taught in K-12 and even college writing programs is known as PEAS, which overlaps strongly with the MEAL formula introduced by the chapter, “ Basic Integration “:
Point : State the reasoning as a single point: “One reason why a soda tax would be effective is that…” or “One way an individual can control their happiness is by…”
Evidence : After stating the supporting reason, prove that reason with related evidence. There can be more than one piece of evidence. “According to …” or “In the article, ‘…,’ the author shows that …”
Analysis : There a different levels of analysis. At the most basic level, a writer should clearly explain how the evidence proves the point, in their own words: “In other words…,” “What this data shows is that…” Sometimes the “A” part of PEAS becomes simple paraphrasing. Higher-level analysis will use more sophisticated techniques such as Toulmin’s warrants to explore deeper terrain. For more tips on how to discuss and analyze, refer to the previous chapter’s section, “ Analyze and discuss the evidence .”
Summary/So what? : Tie together all of the components (PEA) succinctly, before transitioning to the next idea. If necessary, remind the reader how the evidence and reasoning relates to the broader claim (the thesis argument).
PEAS and MEAL are very similar; in fact they are identical except for how they refer to the first and last part. In theory, it shouldn’t matter which acronym you choose. Both versions are effective because they translate the basic structure of a supporting reason (reasoning and evidence) into paragraph form.
Here’s an example of a PEAS paragraph in an academic persuasive essay that argues for a soda tax:
A soda tax would also provide more revenue for the federal government, thereby reducing its debt. point Despite Ernest Istook’s concerns about eroding American freedom, the United States has long supported the ability of government to leverage taxes in order to both curb unhealthy lifestyles and add revenue. According to Peter Ubel’s “Would the Founding Fathers Approve of a Sugar Tax?”, in 1791 the US government was heavily in debt and needed stable revenue. In response, the federal government taxed what most people viewed as a “sin” at that time: alcohol. This single tax increased government revenue by at least 20% on average, and in some years more than 40% . The effect was that only the people who really wanted alcohol purchased it, and those who could no longer afford it were getting rid of what they already viewed as a bad habit (Ubel). evidence Just as alcohol (and later, cigarettes) was viewed as a superfluous “sin” in the Early Republic, so today do many health experts and an increasing amount of Americans view sugar as extremely unhealthy, even addictive. If our society accepts taxes on other consumer sins as a way to improve government revenue, a tax on sugar is entirely consistent. analysis We could apply this to the soda tax and try to do something like this to help knock out two problems at once: help people lose their addiction towards soda and help reduce our government’s debt. summary/so what?
The paragraph above was written by a student who was taught the PEAS formula. However, we can see versions of this formula in professional writing. Here’s a more sophisticated example of PEAS, this time from a non-academic article. In Nicholas Carr’s extremely popular article, “ Is Google Making Us Stupid? “, he argues that Google is altering how we think. To prove that broader claim, Carr offers a variety of reasons and evidence. Here’s part of his reasoning:
Thanks to the ubiquity of text on the Internet, not to mention the popularity of text-messaging on cell phones, we may well be reading more today than we did in the 1970s or 1980s, when television was our medium of choice. But it’s a different kind of reading, and behind it lies a different kind of thinking—perhaps even a new sense of the self. point “We are not only what we read,” says Maryanne Wolf, a developmental psychologist at Tufts University and the author of Proust and the Squid: The Story and Science of the Reading Brain . “We are how we read.” Wolf worries that the style of reading promoted by the Net, a style that puts “efficiency” and “immediacy” above all else, may be weakening our capacity for the kind of deep reading that emerged when an earlier technology, the printing press, made long and complex works of prose commonplace. When we read online, she says, we tend to become “mere decoders of information.” evidence Our ability to interpret text, to make the rich mental connections that form when we read deeply and without distraction, remains largely disengaged. analysis
This excerpt only contains the first three elements, PEA, and the analysis part is very brief (it’s more like paraphrase), but it shows how professional writers often employ some version of the formula. It tends to appear in persuasive texts written by experienced writers because it reinforces writing techniques mentioned elsewhere in this textbook. A block of text structured according to PEA will practice coherence, because opening with a point (P) forecasts the main idea of that section. Embedding the evidence (E) within a topic sentence and follow-up commentary or analysis (A) is part of the “quote sandwich” strategy we cover in the section on “Writing With Sources.”
Use “they say / i say” strategies for Counterarguments and rebuttals
Another element that’s unique to persuasive essays is embedding a counterargument. Sometimes called naysayers or opposing positions, counterarguments are points of view that challenge our own.
Why embed a naysayer?
Recall above how a helpful strategy for beginning a persuasive essay (the introduction) is to briefly mention a debate—what some writing textbooks call “joining the conversation.” Gerald Graff and Cathy Birkenstein’s They Say / I Say explains why engaging other points of view is so crucial:
Not long ago we attended a talk at an academic conference where the speaker’s central claim seemed to be that a certain sociologist—call him Dr. X—had done very good work in a number of areas of the discipline. The speaker proceeded to illustrate his thesis by referring extensively and in great detail to various books and articles by Dr. X and by quoting long pas-sages from them. The speaker was obviously both learned and impassioned, but as we listened to his talk we found ourselves somewhat puzzled: the argument—that Dr. X’s work was very important—was clear enough, but why did the speaker need to make it in the first place? Did anyone dispute it? Were there commentators in the field who had argued against X’s work or challenged its value? Was the speaker’s interpretation of what X had done somehow novel or revolutionary? Since the speaker gave no hint of an answer to any of these questions, we could only wonder why he was going on and on about X. It was only after the speaker finished and took questions from the audience that we got a clue: in response to one questioner, he referred to several critics who had vigorously questioned Dr. X’s ideas and convinced many sociologists that Dr. X’s work was unsound.
When writing for an academic audience, one of the most important moves a writer can make is to demonstrate how their ideas compare to others. It serves as part of the context. Your essay might be offering a highly original solution to a certain problem you’ve researched the entire semester, but the reader will only understand that if existing arguments are presented in your draft. Or, on the other hand, you might be synthesizing or connecting a variety of opinions in order to arrive at a more comprehensive solution. That’s also fine, but the creativity of your synthesis and its unique contribution to existing research will only be known if those other voices are included.
Aristotelian argumentation embeds counterarguments in order to refute them. Rogerian arguments present oppositional stances in order to synthesize and integrate them. No matter what your strategy is, the essay should be conversational.
Notice how Ana Mari Cauce opens her essay on free speech in higher education, “ Messy but Essential “:
Over the past year or two, issues surrounding the exercise of free speech and expression have come to the forefront at colleges around the country. The common narrative about free speech issues that we so often read goes something like this: today’s college students — overprotected and coddled by parents, poorly educated in high school and exposed to primarily left-leaning faculty — have become soft “snowflakes” who are easily offended by mere words and the slightest of insults, unable or unwilling to tolerate opinions that veer away from some politically correct orthodoxy and unable to engage in hard-hitting debate. counterargument
This is false in so many ways, and even insulting when you consider the reality of students’ experiences today. claim
The introduction to her article is essentially a counteragument (which serves as her introductory context) followed by a response. Embedding naysayers like this can appear anywhere in an essay, not just the introduction. Notice, furthermore, how Cauce’s naysayer isn’t gleaned from any research she did. It’s just a general, trendy naysayer, something one might hear nowadays, in the ether. It shows she’s attuned to an ongoing conversation, but it doesn’t require her to cite anything specific. As the previous chapter on using rhetorical appeals in arguments explained, this kind of attunement with an emerging problem (or exigence) is known as the appeal to kairos . A compelling, engaging introduction will demonstrate that the argument “kairotically” addresses a pressing concern.
Below is a brief overview of what counterarguments are and how you might respond to them in your arguments. This section was developed by Robin Jeffrey, in “ Counterargument and Response “:
Common Types of counterarguments
- Could someone disagree with your claim? If so, why? Explain this opposing perspective in your own argument, and then respond to it.
- Could someone draw a different conclusion from any of the facts or examples you present? If so, what is that different conclusion? Explain this different conclusion and then respond to it.
- Could a reader question any of your assumptions or claims? If so, which ones would they question? Explain and then respond.
- Could a reader offer a different explanation of an issue? If so, what might their explanation be? Describe this different explanation, and then respond to it.
- Is there any evidence out there that could weaken your position? If so, what is it? Cite and discuss this evidence and then respond to it.
If the answer to any of these questions is yes, that does not necessarily mean that you have a weak argument. It means, ideally and as long as your argument is logical and valid, that you have a counterargument. Good arguments can and do have counterarguments; it is important to discuss them. But you must also discuss and then respond to those counterarguments.
Responding to counterarguments
You do not need to attempt to do all of these things as a way to respond; instead, choose the response strategy that makes the most sense to you, for the counterargument that you have.
- If you agree with some of the counterargument perspectives, you can concede some of their points. (“I do agree that ….”, “Some of the points made by ____ are valid…..”) You could then challenge the importance/usefulness of those points. “However, this information does not apply to our topic because…”
- If the counterargument perspective is one that contains different evidence than you have in your own argument, you can explain why a reader should not accept the evidence that the counterarguer presents.
- If the counterargument perspective is one that contains a different interpretation of evidence than you have in your own argument, you can explain why a reader should not accept the interpretation of the evidence that that your opponent (counterarguer) presents.
- If the counterargument is an acknowledgement of evidence that threatens to weaken your argument, you must explain why and how that evidence does not, in fact invalidate your claim.
It is important to use transitional phrases in your paper to alert readers when you’re about to present an counterargument. It’s usually best to put this phrase at the beginning of a paragraph such as:
- Researchers have challenged these claims with…
- Critics argue that this view…
- Some readers may point to…
- A perspective that challenges the idea that . . .
Transitional phrases will again be useful to highlight your shift from counterargument to response:
- Indeed, some of those points are valid. However, . . .
- While I agree that . . . , it is more important to consider . . .
- These are all compelling points. Still, other information suggests that . .
- While I understand . . . , I cannot accept the evidence because . . .
Further reading
To read more about the importance of counterarguments in academic writing, read Steven D. Krause’s “ On the Other Hand: The Role of Antithetical Writing in First Year Composition Courses .”
When concluding, address the “so what?” challenge
As Joseph W. Williams mentions in his chapter on concluding persuasive essays in Style ,
a good introduction motivates your readers to keep reading, introduces your key themes, and states your main point … [but] a good conclusion serves a different end: as the last thing your reader reads, it should bring together your point, its significance, and its implications for thinking further about the ideas your explored.
At the very least, a good persuasive conclusion will
- Summarize the main points
- Address the So what? or Now what? challenge.
When summarizing the main points of longer essays, Williams suggests it’s fine to use “metadiscourse,” such as, “I have argued that.” If the essay is short enough, however, such metadiscourses may not be necessary, since the reader will already have those ideas fresh in their mind.
After summarizing your essay’s main points, imagine a friendly reader thinking,
“OK, I’m persuaded and entertained by everything you’ve laid out in your essay. But remind me what’s so important about these ideas? What are the implications? What kind of impact do you expect your ideas to have? Do you expect something to change?”
It’s sometimes appropriate to offer brief action points, based on the implications of your essay. When addressing the “So what?” challenge, however, it’s important to first consider whether your essay is primarily targeted towards changing the way people think or act . Do you expect the audience to do something, based on what you’ve argued in your essay? Or, do you expect the audience to think differently? Traditional academic essays tend to propose changes in how the reader thinks more than acts, but your essay may do both.
Finally, Williams suggests that it’s sometimes appropriate to end a persuasive essay with an anecdote, illustrative fact, or key quote that emphasizes the significance of the argument. We can see a good example of this in Carr’s article, “ Is Google Making Us Stupid? ” Here are the introduction and conclusion, side-by-side: Definition: Term
[Introduction] “Dave, stop. Stop, will you? Stop, Dave. Will you stop, Dave?” So the supercomputer HAL pleads with the implacable astronaut Dave Bowman in a famous and weirdly poignant scene toward the end of Stanley Kubrick’s 2001: A Space Odyssey . Bowman, having nearly been sent to a deep-space death by the malfunctioning machine, is calmly, coldly disconnecting the memory circuits that control its artificial “ brain. “Dave, my mind is going,” HAL says, forlornly. “I can feel it. I can feel it.”
I can feel it, too. Over the past few years I’ve had an uncomfortable sense that someone, or something, has been tinkering with my brain, remapping the neural circuitry, reprogramming the memory. …
[Conclusion] I’m haunted by that scene in 2001 . What makes it so poignant, and so weird, is the computer’s emotional response to the disassembly of its mind: its despair as one circuit after another goes dark, its childlike pleading with the astronaut—“I can feel it. I can feel it. I’m afraid”—and its final reversion to what can only be called a state of innocence. HAL’s outpouring of feeling contrasts with the emotionlessness that characterizes the human figures in the film, who go about their business with an almost robotic efficiency. Their thoughts and actions feel scripted, as if they’re following the steps of an algorithm. In the world of 2001 , people have become so machinelike that the most human character turns out to be a machine. That’s the essence of Kubrick’s dark prophecy: as we come to rely on computers to mediate our understanding of the world, it is our own intelligence that flattens into artificial intelligence.
Instead of merely rehashing all of the article’s main points, Carr returns to the same movie scene from 2001 that he opened with. The final lines interpret the scene according to the argument he just dedicated the entire essay to presenting.
The entire essay should use rhetorical appeals strategically
The chapter “ Persuasive Appeals ” introduces students to logos, pathos, ethos, and kairos. Becoming familiar with each of those persuasive appeals can add much to an essay. It also reinforces the idea that writing argumentative essays is not a straightforward process of jotting down proofs. It’s not a computer algorithm.
- Logos (appeals to evidence and reasoning) is the foundational appeal of an argument essay. Clearly identifying the claim, then supporting that claim with reasoning and evidence will appeal to the reader’s logos demands. As the previous chapter on argumentation mentions, however, what constitutes solid evidence will vary depending on the audience. Make sure your evidence is indeed convincing to your intended reader.
- Pathos (appeals to emotion) are a crucial component and should permeate should every section of the essay. Personal anecdotes are an effective way to illustrate important ideas, and they connect with the reader at an emotional level. Personal examples also cultivate voice .
- Ethos (appeals to character, image, and values) is essential to gaining the reader’s trust and assent. The tone of your essay (snarky, sincere, ironic, sarcastic, empathetic) is immensely important for its overall effect, and it helps build the reader’s image of you. A careful attention to high-quality research reinforces a sincere and empathetic tone. When supporting certain claims and sub-claims, it’s also important to identify implied beliefs (warrants) that your reader is most likely to agree with, and to undermine beliefs that might seem repugnant.
- Kairos (appeals to timeliness) impresses the reader with your attunement to the situation. This should be practiced especially in the introduction, but it can appear throughout the essay as you engage with research and other voices that have recently weighed in on the topic.
All of these appeals are already happening, whether or not they’re recognized. If they are missed, the audience will often use them against you, judging your essay as not being personable enough (pathos), or not in touch with commonly accepted values (ethos), or out of touch with what’s going on (kairos). These non-logical appeals aren’t irrational. They are crucial components to writing that matters.
Argument Outline Exercise
To get started on your argument essay, practice adopting from of the outlines from this Persuasive Essay Outline worksheet .
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
Letter of Recommendation
What I’ve Learned From My Students’ College Essays
The genre is often maligned for being formulaic and melodramatic, but it’s more important than you think.

By Nell Freudenberger
Most high school seniors approach the college essay with dread. Either their upbringing hasn’t supplied them with several hundred words of adversity, or worse, they’re afraid that packaging the genuine trauma they’ve experienced is the only way to secure their future. The college counselor at the Brooklyn high school where I’m a writing tutor advises against trauma porn. “Keep it brief , ” she says, “and show how you rose above it.”
I started volunteering in New York City schools in my 20s, before I had kids of my own. At the time, I liked hanging out with teenagers, whom I sometimes had more interesting conversations with than I did my peers. Often I worked with students who spoke English as a second language or who used slang in their writing, and at first I was hung up on grammar. Should I correct any deviation from “standard English” to appeal to some Wizard of Oz behind the curtains of a college admissions office? Or should I encourage students to write the way they speak, in pursuit of an authentic voice, that most elusive of literary qualities?
In fact, I was missing the point. One of many lessons the students have taught me is to let the story dictate the voice of the essay. A few years ago, I worked with a boy who claimed to have nothing to write about. His life had been ordinary, he said; nothing had happened to him. I asked if he wanted to try writing about a family member, his favorite school subject, a summer job? He glanced at his phone, his posture and expression suggesting that he’d rather be anywhere but in front of a computer with me. “Hobbies?” I suggested, without much hope. He gave me a shy glance. “I like to box,” he said.
I’ve had this experience with reluctant writers again and again — when a topic clicks with a student, an essay can unfurl spontaneously. Of course the primary goal of a college essay is to help its author get an education that leads to a career. Changes in testing policies and financial aid have made applying to college more confusing than ever, but essays have remained basically the same. I would argue that they’re much more than an onerous task or rote exercise, and that unlike standardized tests they are infinitely variable and sometimes beautiful. College essays also provide an opportunity to learn precision, clarity and the process of working toward the truth through multiple revisions.
When a topic clicks with a student, an essay can unfurl spontaneously.
Even if writing doesn’t end up being fundamental to their future professions, students learn to choose language carefully and to be suspicious of the first words that come to mind. Especially now, as college students shoulder so much of the country’s ethical responsibility for war with their protest movement, essay writing teaches prospective students an increasingly urgent lesson: that choosing their own words over ready-made phrases is the only reliable way to ensure they’re thinking for themselves.
Teenagers are ideal writers for several reasons. They’re usually free of preconceptions about writing, and they tend not to use self-consciously ‘‘literary’’ language. They’re allergic to hypocrisy and are generally unfiltered: They overshare, ask personal questions and call you out for microaggressions as well as less egregious (but still mortifying) verbal errors, such as referring to weed as ‘‘pot.’’ Most important, they have yet to put down their best stories in a finished form.
I can imagine an essay taking a risk and distinguishing itself formally — a poem or a one-act play — but most kids use a more straightforward model: a hook followed by a narrative built around “small moments” that lead to a concluding lesson or aspiration for the future. I never get tired of working with students on these essays because each one is different, and the short, rigid form sometimes makes an emotional story even more powerful. Before I read Javier Zamora’s wrenching “Solito,” I worked with a student who had been transported by a coyote into the U.S. and was reunited with his mother in the parking lot of a big-box store. I don’t remember whether this essay focused on specific skills or coping mechanisms that he gained from his ordeal. I remember only the bliss of the parent-and-child reunion in that uninspiring setting. If I were making a case to an admissions officer, I would suggest that simply being able to convey that experience demonstrates the kind of resilience that any college should admire.
The essays that have stayed with me over the years don’t follow a pattern. There are some narratives on very predictable topics — living up to the expectations of immigrant parents, or suffering from depression in 2020 — that are moving because of the attention with which the student describes the experience. One girl determined to become an engineer while watching her father build furniture from scraps after work; a boy, grieving for his mother during lockdown, began taking pictures of the sky.
If, as Lorrie Moore said, “a short story is a love affair; a novel is a marriage,” what is a college essay? Every once in a while I sit down next to a student and start reading, and I have to suppress my excitement, because there on the Google Doc in front of me is a real writer’s voice. One of the first students I ever worked with wrote about falling in love with another girl in dance class, the absolute magic of watching her move and the terror in the conflict between her feelings and the instruction of her religious middle school. She made me think that college essays are less like love than limerence: one-sided, obsessive, idiosyncratic but profound, the first draft of the most personal story their writers will ever tell.
Nell Freudenberger’s novel “The Limits” was published by Knopf last month. She volunteers through the PEN America Writers in the Schools program.
What is ChatGPT? Here's everything you need to know about ChatGPT, the chatbot everyone's still talking about
- ChatGPT is getting a futuristic human update.
- ChatGPT has drawn users at a feverish pace and spurred Big Tech to release other AI chatbots.
- Here's how ChatGPT works — and what's coming next.

OpenAI's blockbuster chatbot ChatGPT is getting a new update.
On Monday, OpenAI unveiled GPT-4o for ChatGPT, a new version of the bot that can hold conversations with users in a very human tone. The new version of the chatbot will also have vision abilities.
The futuristic reveal quickly prompted jokes about parallels to the movie "Her," with some calling the chatbot's new voice " cringe ."
The move is a big step for the future of AI-powered virtual assistants, which tech companies have been racing to develop.
Since its release in 2022, hundreds of millions of people have experimented with the tool, which is already changing how the internet looks and feels to users.
Users have flocked to ChatGPT to improve their personal lives and boost productivity . Some workers have used the AI chatbot to develop code , write real estate listings , and create lesson plans, while others have made teaching the best ways to use ChatGPT a career all to itself.
ChatGPT offers dozens of plug-ins to those who subscribe to ChatGPT Plus subscription. An Expedia one can help you book a trip, while an OpenTable one will get nab you a dinner reservation. And last month, OpenAI launched Code Interpreter, a version of ChatGPT that can code and analyze data .
While the personal tone of conversations with an AI bot like ChatGPT can evoke the experience of chatting with a human, the technology, which runs on " large language model tools, " doesn't speak with sentience and doesn't "think" the way people do.
That means that even though ChatGPT can explain quantum physics or write a poem on command, a full AI takeover isn't exactly imminent , according to experts.
"There's a saying that an infinite number of monkeys will eventually give you Shakespeare," said Matthew Sag, a law professor at Emory University who studies copyright implications for training and using large language models like ChatGPT.
"There's a large number of monkeys here, giving you things that are impressive — but there is intrinsically a difference between the way that humans produce language, and the way that large language models do it," he said.
Chatbots like ChatGPT are powered by large amounts of data and computing techniques to make predictions to string words together in a meaningful way. They not only tap into a vast amount of vocabulary and information, but also understand words in context. This helps them mimic speech patterns while dispatching an encyclopedic knowledge.
Other tech companies like Google and Meta have developed their own large language model tools, which use programs that take in human prompts and devise sophisticated responses.
Despite the AI's impressive capabilities, some have called out OpenAI's chatbot for spewing misinformation , stealing personal data for training purposes , and even encouraging students to cheat and plagiarize on their assignments.
Some recent efforts to use chatbots for real-world services have proved troubling. In 2023, the mental health company Koko came under fire after its founder wrote about how the company used GPT-3 in an experiment to reply to users.
Koko cofounder Rob Morris hastened to clarify on Twitter that users weren't speaking directly to a chatbot, but that AI was used to "help craft" responses.
Read Insider's coverage on ChatGPT and some of the strange new ways that both people and companies are using chat bots:
The tech world's reception to ChatGPT:
Microsoft is chill with employees using ChatGPT — just don't share 'sensitive data' with it.
Microsoft's investment into ChatGPT's creator may be the smartest $1 billion ever spent
ChatGPT and generative AI look like tech's next boom. They could be the next bubble.
The ChatGPT and generative-AI 'gold rush' has founders flocking to San Francisco's 'Cerebral Valley'
Insider's experiments:
I asked ChatGPT to do my work and write an Insider article for me. It quickly generated an alarmingly convincing article filled with misinformation.
I asked ChatGPT and a human matchmaker to redo my Hinge and Bumble profiles. They helped show me what works.
I asked ChatGPT to reply to my Hinge matches. No one responded.
I used ChatGPT to write a resignation letter. A lawyer said it made one crucial error that could have invalidated the whole thing .
Read ChatGPT's 'insulting' and 'garbage' 'Succession' finale script
An Iowa school district asked ChatGPT if a list of books contains sex scenes, and banned them if it said yes. We put the system to the test and found a bunch of problems.
Developments in detecting ChatGPT:
Teachers rejoice! ChatGPT creators have released a tool to help detect AI-generated writing
A Princeton student built an app which can detect if ChatGPT wrote an essay to combat AI-based plagiarism
Professors want to 'ChatGPT-proof' assignments, and are returning to paper exams and requesting editing history to curb AI cheating
ChatGPT in society:
BuzzFeed writers react with a mix of disappointment and excitement at news that AI-generated content is coming to the website
ChatGPT is testing a paid version — here's what that means for free users
A top UK private school is changing its approach to homework amid the rise of ChatGPT, as educators around the world adapt to AI
Princeton computer science professor says don't panic over 'bullshit generator' ChatGPT
DoNotPay's CEO says threat of 'jail for 6 months' means plan to debut AI 'robot lawyer' in courtroom is on ice
It might be possible to fight a traffic ticket with an AI 'robot lawyer' secretly feeding you lines to your AirPods, but it could go off the rails
Online mental health company uses ChatGPT to help respond to users in experiment — raising ethical concerns around healthcare and AI technology
What public figures think about ChatGPT and other AI tools:
What Elon Musk, Bill Gates, and 12 other business leaders think about AI tools like ChatGPT
Elon Musk was reportedly 'furious' at ChatGPT's popularity after he left the company behind it, OpenAI, years ago
CEO of ChatGPT maker responds to schools' plagiarism concerns: 'We adapted to calculators and changed what we tested in math class'
A theoretical physicist says AI is just a 'glorified tape recorder' and people's fears about it are overblown
'The most stunning demo I've ever seen in my life': ChatGPT impressed Bill Gates
Ashton Kutcher says your company will probably be 'out of business' if you're 'sleeping' on AI
ChatGPT's impact on jobs:
AI systems like ChatGPT could impact 300 million full-time jobs worldwide, with administrative and legal roles some of the most at risk, Goldman Sachs report says
Jobs are now requiring experience with ChatGPT — and they'll pay as much as $800,000 a year for the skill
Related stories
ChatGPT may be coming for our jobs. Here are the 10 roles that AI is most likely to replace.
AI is going to eliminate way more jobs than anyone realizes
It's not AI that is going to take your job, but someone who knows how to use AI might, economist says
4 careers where workers will have to change jobs by 2030 due to AI and shifts in how we shop, a McKinsey study says
Companies like Amazon, Netflix, and Meta are paying salaries as high as $900,000 to attract generative AI talent
How AI tools like ChatGPT are changing the workforce:
10 ways artificial intelligence is changing the workplace, from writing performance reviews to making the 4-day workweek possible
Managers who use AI will replace managers who don't, says an IBM exec
How ChatGPT is shaping industries:
ChatGPT is coming for classrooms, hospitals, marketing departments, and everything else as the next great startup boom emerges
Marketing teams are using AI to generate content, boost SEO, and develop branding to help save time and money, study finds
AI is coming for Hollywood. 'It's amazing to see the sophistication of the images,' one of Christopher Nolan's VFX guy says.
AI is going to offer every student a personalized tutor, founder of Khan Academy says
A law firm was fined $5,000 after one of its lawyers used ChatGPT to write a court brief riddled with fake case references
How workers are using ChatGPT to boost productivity:
CheatGPT: The hidden wave of employees using AI on the sly
I used ChatGPT to talk to my boss for a week and she didn't notice. Here are the other ways I use it daily to get work done.
I'm a high school math and science teacher who uses ChatGPT, and it's made my job much easier
Amazon employees are already using ChatGPT for software coding. They also found the AI chatbot can answer tricky AWS customer questions and write cloud training materials.
How 6 workers are using ChatGPT to make their jobs easier
I'm a freelance editor who's embraced working with AI content. Here's how I do it and what I charge.
How people are using ChatGPT to make money:
How ChatGPT and other AI tools are helping workers make more money
Here are 5 ways ChatGPT helps me make money and complete time-consuming tasks for my business
ChatGPT course instruction is the newest side hustle on the market. Meet the teachers making thousands from the lucrative gig.
People are using ChatGPT and other AI bots to work side hustles and earn thousands of dollars — check out these 8 freelancing gigs
A guy tried using ChatGPT to turn $100 into a business making 'as much money as possible.' Here are the first 4 steps the AI chatbot gave him
We used ChatGPT to build a 7-figure newsletter. Here's how it makes our jobs easier.
I use ChatGPT and it's like having a 24/7 personal assistant for $20 a month. Here are 5 ways it's helping me make more money.
A worker who uses AI for a $670 monthly side hustle says ChatGPT has 'cut her research time in half'
How companies are navigating ChatGPT:
From Salesforce to Air India, here are the companies that are using ChatGPT
Amazon, Apple, and 12 other major companies that have restricted employees from using ChatGPT
A consultant used ChatGPT to free up time so she could focus on pitching clients. She landed $128,000 worth of new contracts in just 3 months.
Luminary, an AI-generated pop-up restaurant, just opened in Australia. Here's what's on the menu, from bioluminescent calamari to chocolate mousse.
A CEO is spending more than $2,000 a month on ChatGPT Plus accounts for all of his employees, and he says it's saving 'hours' of time
How people are using ChatGPT in their personal lives:
ChatGPT planned a family vacation to Costa Rica. A travel adviser found 3 glaring reasons why AI won't replace experts anytime soon.
A man who hated cardio asked ChatGPT to get him into running. Now, he's hooked — and he's lost 26 pounds.
A computer engineering student is using ChatGPT to overcome learning challenges linked to her dyslexia
How a coder used ChatGPT to find an apartment in Berlin in 2 weeks after struggling for months
Food blogger Nisha Vora tried ChatGPT to create a curry recipe. She says it's clear the instructions lacked a human touch — here's how.
Men are using AI to land more dates with better profiles and personalized messages, study finds
Lawsuits against OpenAI:
OpenAI could face a plagiarism lawsuit from The New York Times as tense negotiations threaten to boil over, report says
This is why comedian Sarah Silverman is suing OpenAI, the company behind ChatGPT
2 authors say OpenAI 'ingested' their books to train ChatGPT. Now they're suing, and a 'wave' of similar court cases may follow.
A lawsuit claims OpenAI stole 'massive amounts of personal data,' including medical records and information about children, to train ChatGPT
A radio host is suing OpenAI for defamation, alleging that ChatGPT created a false legal document that accused him of 'defrauding and embezzling funds'
Tips on how to write better ChatGPT prompts:
7 ways to use ChatGPT at work to boost your productivity, make your job easier, and save a ton of time
I'm an AI prompt engineer. Here are 3 ways I use ChatGPT to get the best results.
12 ways to get better at using ChatGPT: Comprehensive prompt guide
Here's 9 ways to turn ChatGPT Plus into your personal data analyst with the new Code Interpreter plug-in
OpenAI's ChatGPT can write impressive code. Here are the prompts you should use for the best results, experts say.
Axel Springer, Business Insider's parent company, has a global deal to allow OpenAI to train its models on its media brands' reporting.
Watch: What is ChatGPT, and should we be afraid of AI chatbots?
- Main content
- Skip to main content
- Keyboard shortcuts for audio player
TikTok challenges U.S. ban in court, calling it unconstitutional

Bobby Allyn

TikTok's suit is in response to a law passed by Congress giving ByteDance up to a year to divest from TikTok and find a new buyer, or face a nationwide ban. Kiichiro Sato/AP hide caption
TikTok's suit is in response to a law passed by Congress giving ByteDance up to a year to divest from TikTok and find a new buyer, or face a nationwide ban.
TikTok and its parent company on Tuesday filed a legal challenge against the United States over a law that President Biden signed last month outlawing the app nationwide unless it finds a buyer within a year.
In the petition filed in the Court of Appeals for the District of Columbia Circuit, the company said the legislation exceeds the bounds of the constitution and suppresses the speech of millions of Americans.
"Banning TikTok is so obviously unconstitutional, in fact, that even the Act's sponsors recognized that reality, and therefore have tried mightily to depict the law not as a ban at all, but merely a regulation of TikTok's ownership," according to the filing.
The law, passed through Congress at lightning speed, which caught many inside TikTok off guard, is intended to force TikTok to be sold to a non-Chinese company in nine months, with the possibility of a three month extension if a possible sale is in play.
Yet lawyers for TikTok say the law offers the company a false choice, since fully divesting from its parent company, ByteDance, is "simply not possible: not commercially, not technologically, not legally," the challenge states. "And certainly not on the 270-day timeline required by the Act."
Anupam Chander, a law professor at Georgetown University who specializes in technology regulations, said if TikTok loses this legal fight, it will likely shut down in the U.S.
"The problem for TikTok is that they have a parent company that has these obligation in China, but they're trying to live by free speech rules by the United States," Chander said in an interview. "The question is whether American courts will believe that that's even possible."
TikTok says law based on "speculative and analytically flawed concerns"
Lawmakers in Washington have long been suspicious of TikTok, fearing its Chinese owner could use the popular app to spy on Americans or spread dangerous disinformation.
But in the company's legal petition, lawyers for TikTok say invoking "national security" does not give the government a free pass to violate the First Amendment, especially, TikTok, argues, when no public evidence has been presented of the Chinese government using the app as a weapon against Americans.

Possible TikTok ban could be 'an extinction-level event' for the creator economy
According to the filing, the law is based on "speculative and analytically flawed concerns about data security and content manipulation — concerns that, even if grounded in fact, could be addressed through far less restrictive and more narrowly tailored means."

New DOJ Filing: TikTok's Owner Is 'A Mouthpiece' Of Chinese Communist Party
Constitutional scholars say there are few ways for the government to restrict speech in a way that would survive a legal challenge. One of those ways is if the government can demonstrate a national security risk. Also key, legal experts say, is the government showing the speech suppression was the least restrictive option on the table.
TikTok said Congress ignored less restrictive ways of addressing the government's national security concerns.
"If Congress can do this, it can circumvent the First Amendment by invoking national security and ordering the publisher of any individual newspaper or website to sell to avoid being shut down," the filing states. "And for TikTok, any such divestiture would disconnect Americans from the rest of the global community."
Since more than 90% of TikTok's users are outside of America, Georgetown's Chander said selling the U.S.-based app to a different owner would cannibalize its own business.
"You can't really create a TikTok U.S., while having a different company manage TikTok Canada," Chander said in an interview. "What you're doing essentially is creating a rival between two TikToks," he said. " It may be better to take your marbles out of the United States and hope to make money outside of the U.S., rather than sell it at a fire-sale price."
TikTok critics call app a 'spy balloon on your phone'
The filing sets off what could be the most important battle for TikTok. It has been fending off legal challenges to its existence since former President Trump first sought to ban the app through an executive order in the summer of 2020. That effort was blocked by federal courts.
Since then, Democrats and Republicans have shown a rare moment of unity around calls to pressure TikTok to sever its ties with ByteDance, the Beijing-based tech giant that owns the video-streaming app.
Trump's Ban On TikTok Suffers Another Legal Setback
Congress has never before passed legislation that could outright ban a wildly popular social media app, a gesture the U.S. government has criticized authoritarian nations for doing.
In the case of TikTok, however, lawmakers have called the app a "spy balloon on your phone," emphasizing how the Chinese government could gain access to the personal data of U.S. citizens.
Worries also persist in Washington that Beijing could influence the views of Americans by dictating what videos are boosted on the platform. That concern has only become heightened seven months before a presidential election.
Yet the fears so far indeed remain hypothetical.
There is no publicly available example of the Chinese government attempting to use TikTok as an espionage or data collection tool. And no proof that the Chinese government has ever had a hand over what TikTok's 170 million American users see every day on the app.
TikTok says it offers U.S. a plan that would shut app down if it violated agreement
TikTok, for its part, says it has invested $2 billion on a plan, dubbed Project Texas, to separate its U.S. operation from its Chinese parent company. It deleted all of Americans' data from foreign servers and relocated all of the data to servers on U.S. soil overseen by the Austin-based tech company Oracle.
While the plan was intended to build trust with U.S. lawmakers and users, reports surfaced showing that data was still moving between staff in California and Beijing.
In the filing on Tuesday, TikTok said it submitted an agreement to the Committee on Foreign Investment in the United States, which has been probing the app for five years, that would allow the U.S. to suspend TikTok if it violated terms set forth in a national security plan.
But, lawyers for TikTok say, the deal was swept aside, "in favor of the politically expedient and punitive approach," the petition states.
Mnuchin claims he will place a bid to buy TikTok, even though app is not for sale
Despite the new law giving TikTok the ultimatum of selling or being shut down, there are many questions around how the app could even be bought by another company or group of investors.
Former Treasury Secretary Steven Mnuchin told NPR on Monday, he is planning to assemble a group of investors to try to purchase TikTok without the app's algorithm.
Mnuchin, who declined to answer additional questions, said in between sessions at the Milken Institute Global Conference in Los Angeles that the proposal to buy the app is still in the works, but he would not say when it would be formally submitted.
One major obstacle in any possible sale of TikTok is a glaring problem: The app is not for sale.

TikTok Ban Averted: Trump Gives Oracle-Walmart Deal His 'Blessing'
Despite the new law in the U.S., ByteDance says it does not intend to let go of the service. Furthermore, winning the support of China would be necessary, and officials in Beijing are adamantly against any forced sale.
In 2020, amid the Trump administration's clamp down on the app, China added "content-recommendation algorithms" to its export-control list, effectively adding new regulations over how TikTok's all-powerful algorithm could ever be sold.
ByteDance, not TikTok, developed and controls the algorithm that determines what millions see on the app every day. The technology has become the envy of Silicon Valley, and no U.S. tech company has been able dislodge TikTok's firm hold on the short-form video market. Experts say key to its success is its highly engaging and hyper-personalized video-ranking algorithm.
The algorithm, which involves millions of lines of software code developed by thousands of engineers over many years, cannot be easily transferred to the U.S., even if China did allow it, TikTok's challenge states.
Lawyers for TikTok argue that "any severance [of the algorithm] would leave TikTok without access to the recommendation engine that has created a unique style and community that cannot be replicated on any other platform today."
Free All-in-One Office Suite with PDF Editor
Edit Word, Excel, and PPT for FREE.
Read, edit, and convert PDFs with the powerful PDF toolkit.
Microsoft-like interface, easy to use.
Windows • MacOS • Linux • iOS • Android
Select areas that need to improve
- Didn't match my interface
- Too technical or incomprehensible
- Incorrect operation instructions
- Incomplete instructions on this function
Fields marked * are required please
Please leave your suggestions below
- Quick Tutorials
- Practical Skills
Title Capitalization for Your Essays [For Students]
Many of us have experienced moments of confusion when unsure about which words to capitalize and which to leave lowercase, leading to questions about the underlying principles of title capitalization especially when you have a style guide to follow. If you are given the task of writing an essay, then you must know what to capitalize and how to capitalize the words for your headings. Title capitalization must be taken seriously because ultimately it is part of the formatting that you have to follow. I will show you how to do title capitalization for students and most importantly, what to capitalize and what you should keep in mind while title capitalization.
Challenges of Getting the Titles Right for Your Essays
Your concern regarding the title format typically revolves around capitalization accuracy. Here's a quick guide:
1.Confused About When to Use a Certain Type of Capitalization:
If you've got your title ready but find yourself unsure about what to capitalize and what not, remember these points:
Sentence case : This capitalization style capitalizes only the first letter of the first word in a sentence, along with any proper nouns or other words that are typically capitalized in English sentences. It's commonly used in writing sentences, paragraphs, and headings.
Title Case : Title Case is commonly used for titles, headings, and subtitles, where the first letter of most words is capitalized. Students are often provided with guidelines based on specific style manuals such as APA, MLA, or Chicago style, dictating how titles should be capitalized according to the rules of each style.
For example, in APA style, the first word of the title, the first word after a colon, and proper nouns are capitalized, while the rest of the words are in lowercase. In contrast, MLA style capitalizes the first letter of every major word in the title.
Uppercase : Uppercase formatting is typically used for abbreviations, acronyms, or initialisms to ensure clarity and consistency. On the other hand, lowercase formatting is generally used for regular text to maintain readability and conformity with standard writing conventions.
Lowercase : Students may use lowercase formatting when entering URLs, file paths, or coding snippets in their assignments or projects. This ensures that the text remains in the correct format, especially in technical or computer science-related fields.
2.Unsure About Which Words to Be Capitalized and Which Not:
One of the challenges of getting the titles right for your essays is understanding the grammar rules associated with capitalization. Students often grapple with deciding which words to capitalize and which to leave in lowercase, as there are specific conventions to follow depending on the context and style guide.
For instance, while proper nouns and the first word of a sentence are typically capitalized, the rules become more nuanced when dealing with titles and headings. There are specific guidelines outlined in style manuals such as APA, MLA, or Chicago style, which dictate the capitalization of titles based on the type of words used and their position within the title.
Also, certain words like articles (e.g., "a," "an," "the"), conjunctions (e.g., "and," "but," "or"), and prepositions (e.g., "of," "in," "to") are often left in lowercase unless they are the first or last word of the title. This can lead to confusion and uncertainty among students when creating titles for their essays or academic papers.
General Rules for Capitalizing the Titles of Your Essays
The rules for capitalization can be simplified using an easy technique. One effective method I've discovered for fixing these rules in my mind is by categorizing them into two distinct groups: what to capitalize and what not to capitalize. This approach allows for clear differentiation and easier retention of the capitalization rules.
Now, I'll demonstrate how I apply this technique, particularly when working on my thesis and adding headings.
In the title I’ve referenced from my paper, the capitalization follows the rules I have previously outlined. The first and last words, "Leader" and "Individual," are capitalized because they are nouns. Meanwhile, the words "as" and "an" in between are not capitalized, as they are a conjunction and an article, respectively.
The heading follows a similar pattern where two nouns are sandwiched between a conjunction like "and," the same capitalization rule applies. The nouns at the beginning and end of the title should be capitalized, while the conjunction "and" and any other non-capitalized words in the middle should not be capitalized.
Here a heading and subheading needs proper capitalization and it's done as such:
1.Reflection on Concepts and Theories
In this heading, "Reflection," "Concepts," and "Theories" are all nouns and should be capitalized according to the capitalization rule for nouns. "On" is a preposition and should not be capitalized.
Therefore, the correct capitalization for this heading would be: "Reflection on Concepts and Theories".
2.Hersey-Blanchard Situational Leadership Theory
In this heading, "Hersey-Blanchard" is a proper noun and should be capitalized. "Situational", "Leadership", and "Theory" are also nouns and should be capitalized. The hyphens between "Hersey" and "Blanchard" should not affect the capitalization.
Therefore, the correct capitalization for this heading would be: "Hersey-Blanchard Situational Leadership Theory".
If you're seeking a clear-cut capitalization rulebook to assist you in adhering to the style guide you're following, we've outlined the capitalization rules for APA, MLA, and Chicago below, ensuring you won't go wrong:
Title Capitalization Rules from Different Style Guides
The styles of APA, MLA, and Chicago are designed to provide clear guidelines for writing and formatting academic papers, articles, and other scholarly works. While they share common principles, such as the importance of clarity, accuracy, and professionalism, their differences become apparent in how they handle specific elements, particularly in terms of capitalization in titles.
1.Title Capitalization in APA Style
APA offers two clear-cut capitalization methods: title case and sentence case. Let's review the rules of title capitalization for APA style to ensure we adhere to the style correctly.
Title Case: Capitalizing the Important Stuff
Title case is all about highlighting the key words in your titles and headings. Here's what gets a capital letter:
The first word, even if it's a minor word like "a" or "the."
The first word of a subtitle.
The first word after a colon, em dash, or ending punctuation in a heading.
Major words, including nouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, pronouns, and any word with four or more letters.
The second part of hyphenated major words (e.g., "Self-Report").
Sentence Case: Keeping It Simple
Sentence case is a more relaxed approach, capitalizing only the first word and proper nouns. While rarely used for titles or headings, it might appear in certain instructions or figure captions.
When to Use Title Case
Now that you're equipped with the capitalization tools, let's explore where to use them:
Titles of essays, research papers, dissertations, and thesis.
Headings within your work (Levels 1-5, typically bolded or bold italicized).
Titles of referenced works (books, articles, reports) mentioned in your text.
Titles of tests or measures (e.g., Beck Depression Inventory–II).
Table and figure titles (italicized, along with axis labels and legends).
Knowing title capitalization in APA style is particularly handy when formatting titles in academic papers, articles, essays, reports, and other scholarly works. It's essential for headings and citations alike. APA capitalization guidelines ensure consistency and professionalism in presenting titles within the context of academic writing.
2.Title Capitalization in MLA Style
MLA uses title case for all major words within a title, regardless of whether it's a source you're citing or the title of your own work.
What Gets a Capital Letter?
The first word of the title, always.
All major words, including nouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, pronouns, and any word with four or more letters (e.g., "The" and "After" are capitalized, while "a" and "to" are lowercase).
The second part of hyphenated major words (e.g., "Long-Term Effects").
Italics vs. Quotation Marks
MLA uses two methods to present titles within your text and Works Cited list, depending on the type of source:
Italics : Used for complete works like books, films, journals, or websites.
Book : To Kill a Mockingbird
Film : The Shawshank Redemption
Journal : Journal of Applied Psychology
Website : Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy
Quotation Marks : Surround titles that are part of a larger work, such as chapters in a book, articles in a journal, or webpages.
Chapter in a Book : "The American Dream" in The Great Gatsby
Article in a Journal : "Climate Change and Its Impacts" in Nature
Webpage : "How to Create a Budget" on Investopedia
Remember, the capitalization rules remain the same regardless of italics or quotation marks.
Whether you're referencing a groundbreaking novel like "To Kill a Mockingbird" or citing a captivating news article titled "The Future of AI", MLA title capitalization ensures consistency and clarity in your writing.
3.Title Capitalization in Chicago Style
Chicago Style, a popular choice in various fields, uses a specific approach to title capitalization that might differ from what you're used to. But worry not! Let's break down the rules to ensure your essay titles and headings shine with clarity.
A Headline Approach
Chicago Style follows a headline-style capitalization method, making your titles stand out and grabbing the reader's attention. Here's what gets a capital letter:
The last word of the title, even if it's a minor word like "a" or "the".
All major words in between, including nouns, pronouns, adjectives, verbs (including phrasal verbs like "play with"), adverbs, and subordinate conjunctions (e.g., "because," "although").
Keeping It Lowercase:
While major words get the spotlight, some words take a backseat in Chicago Style:
Articles (a, an, the)
Coordinating conjunctions (and, but, or, for, nor, so, yet)
Prepositions (regardless of length), so even longer prepositions like "throughout" stay lowercase.
The second word after a hyphenated prefix (e.g., "Mid-term Exam," "Anti-government").
The "to" in an infinitive (e.g., "Learning to Code").
By following these Chicago Style capitalization guidelines, you'll ensure your titles are both informative and visually distinct, adding another layer of professionalism to your academic work.
APA vs. MLA vs. Chicago
The major differences in title capitalization among the style guides—APA, Chicago, MLA, and AP—lie in their treatment of certain words and expressions:
Titles of Works:
Chicago and MLA : Capitalize the first and last words and all other important words, regardless of length.
APA : Capitalize any word in a title, even a preposition, with five or more letters.
Internet Terms:
Chicago, APA, and MLA prefer "Internet" and "World Wide Web" but use "web" and "website".
Color Words for Race:
Chicago, and MLA recommend lowercase for "black" and "white" when referring to race, with Chicago allowing authors to capitalize them if preferred.
APA suggests capitalizing "Black" and "White".
Using WPS Writer for Effective Headings
WPS Office is widely recognized as the best suite for students for numerous reasons, and one of its standout features is its capability to simplify the process of capitalizing text. With WPS Office, capitalizing text can be made significantly easier through a few simple steps as such:
Step 1 : Open your thesis or dissertation in WPS Writer and navigate to a heading that needs capitalization correction.
Step 2 : Use your cursor to select the heading or title in your document.
Step 3 : Go to the Home tab and click on the " Change Case " icon represented by "Aa".
Step 4 : Users can now choose from five different options. Remember to consider the capitalization rules discussed in the article before making your selection, then click "OK" to proceed.
Step 5 : I decided to proceed with the "Capitalize Each Word" option to change the capitalization of my headings according to my academic requirements.
I find WPS Office the most user-friendly option for students, especially when it comes to capitalizing all letters in a word. Not only is it straightforward to follow formatting styles thanks to the intuitive features of WPS Office, but it's also incredibly easy to use. With just a simple click, WPS Office provides us with options on how to capitalize a title or word, making the process effortless.
Use Word, Excel, and PPT for FREE, No Ads.
Edit PDF files with the powerful PDF toolkit.
Microsoft-like interface. Easy to learn. 100% Compatibility.
Boost your productivity with WPS's abundant free Word, Excel, PPT, and CV templates.
WPS AI: Your Smart Writing Assistant
WPS Office is a student-friendly suite, primarily due to its accessibility—it's free of cost and offers all the essential features students might require. Its compatibility extends across all major operating systems and devices, ensuring seamless usage regardless of the platform. However, the latest addition to the WPS package is what truly sets it apart: the AI spell check feature. This innovative tool goes beyond traditional spell checking, as it not only identifies spelling errors but also corrects tone, fixes title capitalization, and enhances overall coherence and readability of documents.
Furthermore, AI plays a significant role in the AI Writer tool integrated into WPS Office. This tool serves as a valuable aid in composing articles by offering suggestions for improvement and ensuring clarity of expression. Additionally, it facilitates translation tasks by assisting in translating works into the target language, further enhancing the versatility and usability of WPS Office for students and professionals alike. With these AI-powered features, WPS Office provides a comprehensive solution for students' academic and writing needs, empowering them to create polished and professional documents effortlessly.
Converting Your Essays to PDF Without Losing Format
After completing your essay or thesis, which likely spanned a significant amount of time, the final step of converting it to PDF can be frustrating. Many PDF converters either demand payment or, worse yet, disrupt the carefully crafted formatting, which is key to your essay's presentation. However, WPS Office offers the best solution in this regard. It's free, and WPS PDF ensures that your formatting remains intact, sparing you the hassle and ensuring a seamless transition to PDF format.
Here's an easy way for students to change their papers to PDF using WPS Writer:
Step 1 : Open your paper in WPS Writer and click on the Menu button in the top-left corner.
Step 2 : Next, choose the "Export to PDF" option from the Menu.
Step 3 : In the Export to PDF dialog box, select "Common PDF" from the "Export Type" dropdown menu, and then click "Export to PDF" to convert your Word document to PDF .
FAQs About Title Capitalization
Q1. which words do you not capitalize in a title.
Certain words are not capitalized in titles, regardless of the writing style, such as AP Style, APA, Chicago Manual of Style, or MLA. These include:
Articles (a, an, the): These are not capitalized unless they are the first word of the title.
Prepositions: Most prepositions (such as "in," "on," "of," "by," "with," etc.) are not capitalized unless they are the first or last word of the title.
Conjunctions: Conjunctions (like "and," "but," "or," "nor," "for," "yet," and "so") are typically not capitalized unless they are the first or last word of the title.
Q2. Is “not” capitalized in a title?
The word "not" is capitalized in titles according to all style guides because it functions as an adverb.
Q3. How can I batch-change all the capitalizations on my reference page?
Yes, changing all the capitalizations on your reference page can easily be accomplished using the AI spell check feature in WPS Writer:
Step 1 : Open the document in WPS Writer.
Step 2 : Navigate to the Review tab and click on the "AI Spell Check" feature in the review ribbon.
Step 3 : The AI spell check feature will open on the right side of the WPS Writer interface. Click on the "Set Goals" button on the AI Spell Check window.
Step 4 : Now, set some goals by selecting the "Academic" option under "Domain".
Step 5 : Once you've chosen "Academic”, select the format you're following, such as "APA", "MLA", "Chicago", or "Other". After selection, WPS AI spell check will highlight all headings with incorrect capitalization.
Effortless Capitalization: Simplify Your Writing with WPS AI
The rules of title capitalization for students are simple to grasp. However, it's natural to forget these rules over time. WPS AI serves as an invaluable tool in this regard. Even if you happen to forget the rules, WPS AI remembers them for you. The AI checker meticulously scans through your text, ensuring that your capitalization adheres to the formatting standards you're employing. With WPS Office and its AI capabilities, you can streamline your work processes more effectively, eliminating the need to stress over title capitalization and other formatting nuances. Get WPS Office today to enhance your productivity and streamline your workflow effortlessly.
- 1. How to add title to excel chart
- 2. Fastest way to design a simple title slide in powerpoint
- 3. How to make a title page in WPS word
- 4. How to make title pages in word
- 5. How to add a title in excel spreadsheet 2016
- 6. How to Check Word Count for Your Essays in Word [For Students]
15 years of office industry experience, tech lover and copywriter. Follow me for product reviews, comparisons, and recommendations for new apps and software.
How-To Geek
How to make only one page landscape in a word document.
Sometimes landscape is just the way to go.
Quick Links
Turn specific pages landscape by inserting a break, change specific pages to landscape with page setup.
By default, Microsoft Word orients its pages in portrait view. While this is fine in most situations, you may have page or group of pages that would look better in landscape view. Here are two ways to make this happen.
Regardless of which method you use, be aware that if the text runs over to an extra page as a result of the rotation, that new page will also adopt the landscape orientation.
You can make a page or group of pages landscape by using section breaks , but there are slight differences in how to do this depending on the position of those pages in your document.
Enable Show/Hide
Unless you change your settings, section breaks are invisible pagination controls and can cause confusion if you forget where you've added them. To make them visible, click the Show/Hide (¶) icon in the Paragraph group of the Home tab.
Re-orientate the First Page or Pages
Place your cursor at the end of the page or pages you want to change to landscape. In the Layout tab, click "Breaks," and choose "Next Page." This inserts a next page section break in your document.
With your cursor on the first page (before the section break you just added), in the Layout tab, click "Orientation," and pick "Landscape."
This changes the first page or group of pages (depending on where you added your section break) to landscape.
Re-orientate Pages in the Middle of Your Document
If you have three or more pages, and you need to change the middle page or pages to landscape, place your cursor at the start of the first page you want to change. Then, as before, in the Layout tab, click "Breaks" and "Next Page." This inserts a section break at the start of the pages you want to re-orientate.
Next, with your cursor at the beginning of the new section you have just created, head to the Layout tab, click "Orientation," and then click "Landscape." This changes the current and all subsequent pages to landscape view.
But, as you only want certain pages in the middle of your document to be landscape, you'll need to add a second page break at the end of your landscape section.
Then, click anywhere after this new section break, and use the Orientation option in the Layout tab to turn the remaining pages to portrait, leaving the pages in between your section breaks in landscape view.
Re-orientate the Last Page or Pages
To change the end of your document to landscape, simply place your cursor at the start of this final section, add a next page section break here, and change the orientation accordingly (using the same steps as outlined above).
To delete a section break, place your cursor before the paragraph marker (¶), and press Delete.
Another way to convert a page or a number of adjacent pages from portrait to landscape in Word is to select the content and turn only those pages manually. This method works with text, images , tables, and other items you have on the page.
Select all items on the page or pages you want to rotate 90 degrees. If you have text, drag your cursor through all of it. If you have an image, table, chart, or another type of object, simply select it.
In the Layout tab, click the arrow in the bottom-right corner of the Page Setup group.
In the Page Setup dialog box that opens, confirm that you're on the Margins tab . In the Orientation section, choose "Landscape." Then, at the bottom, change the "Apply To" drop-down choice to "Selected Text," and click "OK."
When the dialog box closes, you will see the pages you selected turn to landscape view.
While this method is the simplest, you may run into difficulties. For instance, if you have an image or table with text wrapped around it , changing the page's orientation may alter its layout. Also, you might run into difficulties if you want to add more landscape pages to your document. The most structurally secure way to change page orientation is through the first method described at the top of this article.
If you use Google Docs, you can change the page orientation in Google Docs just as easily.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Learn the rules and preferences for using "you" or "one" in formal writing, with examples and explanations. Find out when to avoid "you" and when to use "one" to address a general reader or avoid the second person.
Learn why and how to avoid using "we," "you," and "I" in academic writing. Find out the alternatives to personal pronouns, such as passive voice, third-person perspective, and specific word choice.
Learn why you should avoid using the second person pronouns "you" and "your" in academic writing, and how they can be confusing, awkward, and off-putting. Find out how to revise your writing to avoid such pronouns and use more formal and objective language.
Learn how to use pronouns correctly in academic writing, avoiding first-person, second-person and gendered pronouns. Find out when and how to use third-person pronouns and gender-neutral pronouns in your essays and assignments.
Learn how to use first-person pronouns in APA Style to refer to yourself or your coauthors in your academic papers. Avoid using the third person or the editorial "we" to avoid ambiguity or confusion.
Learn when and how to use first person pronouns ("I", "we", etc.) and personal experience in academic writing. Find out the benefits, drawbacks, and conventions of using "I" in different fields and contexts.
Use the first person singular pronoun appropriately, for example, to describe research steps or to state what you will do in a chapter or section. Do not use first person "I" to state your opinions or feelings; cite credible sources to support your scholarly argument. Take a look at the following examples: Inappropriate Uses:
The use of "you" is acceptable in certain types of informal writing, such as personal letters and narratives. However, "you" is generally considered inappropriate in academic writing, such as papers or journals. "You" can be used... ⇒ To directly address the reader. "You" is often used in process of instructional essays, in ...
For all academic papers in all college classes, students should eliminate the use of second person pronouns: you, your, yours; we, us, our, ours; Sounds harsh, but unless an instructor specifically says otherwise, assume second person is to be avoided.
Learn how to use pronouns correctly and avoid gender bias in academic writing. Find out how to replace HE, HIS, and HIM with alternatives such as YOU, ONE, or (sparingly) HE OR SHE.
General Use of I or We. It is totally acceptable to write in the first person in an APA Style paper. If you did something, say, "I did it"—there's no reason to hide your own agency by saying "the author [meaning you] did X" or to convolute things by using the passive "X was done [meaning done by you].". If you're writing a ...
When you write an essay for a course you are taking, you are being asked not only to create a product (the essay) but, more importantly, to go through a process of thinking more deeply about a question or problem related to the course. By writing about a source or collection of sources, you will have the chance to wrestle with some of the
Learn why you should not use 'you' or other second-person pronouns in academic writing and how to replace them with third-person language. Find out when you can use 'I' or 'we' in your research paper and see examples of personal pronouns.
Learn when and how to use first person (I, we, my, us) in your academic essays. Find out when it is appropriate, effective, and persuasive to speak from your own perspective and experience.
Using "I" in Academic Writing. by Michael Kandel. Traditionally, some fields have frowned on the use of the first-person singular in an academic essay and others have encouraged that use, and both the frowning and the encouraging persist today—and there are good reasons for both positions (see "Should I"). I recommend that you not ...
Provide the grounds (evidence) for the claim. Explain the warrant (how the grounds support the claim) Discuss possible rebuttals to the claim, identifying the limits of the argument and showing that you have considered alternative perspectives. The Toulmin model is a common approach in academic essays. You don't have to use these specific ...
A wording that may also be used but rarely suitable is "the researcher". This alternative can only be used when your actions as a writer are completely detached from the writing. 2. Using Passive voice Instead of Pronouns. Another way to replace "I" and other personal pronouns in an essay is to use passive voice.
Words and Phrases to Avoid in Academic Writing. Published on February 6, 2016 by Sarah Vinz.Revised on September 11, 2023. When you are writing a dissertation, thesis, or research paper, many words and phrases that are acceptable in conversations or informal writing are considered inappropriate in academic writing.. You should try to avoid expressions that are too informal, unsophisticated ...
You can use first-person pronouns in your essays, but you probably shouldn't. But like I said, it's complicated. My sense is that teachers usually tell their students to avoid "I" or "me" (or "we," "us," "my," and "our") because these pronouns are often used poorly. The same goes for other "rules" that aren't ...
This very detailed table can be simplified. Most academic persuasive essays include the following basic elements: Introduction that explains why the situation is important and presents your argument (aka the claim or thesis). Support/Body. Reasons the thesis is correct or at least reasonable.
I personally use and/or when it is logically true. In some cases it is important to stress that BOTH options can be done, or a single option can be done (either or both can be done). Although it is often misused in cases where OR is sufficient. Otherwise, the use of OR may exclude BOTH options, when exclusion isn't the intent (that would be an ...
I can imagine an essay taking a risk and distinguishing itself formally — a poem or a one-act play — but most kids use a more straightforward model: a hook followed by a narrative built around ...
An Expedia one can help you book a trip, while an OpenTable one will get nab you a dinner reservation. ... A Princeton student built an app which can detect if ChatGPT wrote an essay to combat AI ...
The high-stakes legal battle could determine the future of the popular app in the U.S. TikTok's legal filing calls the ban law an unprecedented violation of First Amendment rights.
DON'T copy and paste. With upwards of 25 or more essays to write for a balanced college list of 10-12 schools, it's tempting for students to repurpose essays across applications if the prompts are similar, especially when working down to the wire. While students can use the same main essay on the Common App for multiple schools, we always ...
When to Use Title Case. Now that you're equipped with the capitalization tools, let's explore where to use them: Titles of essays, research papers, dissertations, and thesis. Headings within your work (Levels 1-5, typically bolded or bold italicized). Titles of referenced works (books, articles, reports) mentioned in your text.
An external keyboard if you use one. (You can use external keyboards only with a tablet—not a laptop.) Step 5: Taking the Test. Internet Connection: Bluebook is designed to work with an intermittent connection to the internet. An internet connection is required to start the test and to submit answers at the end of the test.
Introduction: "40 Days and 40 Nights," directed by Michael Lehmann, presents a modern-day portrayal of human sexuality, desire, and temptation. The film revolves around Matt Sullivan, who embarks on a 40-day celibacy vow following a series of failed relationships. As Matt navigates his journey of self-restraint, he encounters numerous ...
Place your cursor at the end of the page or pages you want to change to landscape. In the Layout tab, click "Breaks," and choose "Next Page." This inserts a next page section break in your document. With your cursor on the first page (before the section break you just added), in the Layout tab, click "Orientation," and pick "Landscape."