myCBSEguide
- Class 9 Science Case...

Class 9 Science Case Study Questions
Table of Contents
myCBSEguide App
Download the app to get CBSE Sample Papers 2023-24, NCERT Solutions (Revised), Most Important Questions, Previous Year Question Bank, Mock Tests, and Detailed Notes.
If you are wondering how to solve class 9 science case study questions, then myCBSEguide is the best platform to choose. With the help of our well-trained and experienced faculty, we provide solved examples and detailed explanations for the recently added Class 9 Science case study questions.
You can find a wide range of solved case studies on myCBSEguide, covering various topics and concepts. Class 9 Science case studies are designed to help you understand the application of various concepts in real-life situations.
The rationale behind Science
Science is crucial for Class 9 students’ cognitive, emotional, and psychomotor development. It encourages curiosity, inventiveness, objectivity, and aesthetic sense.
In the upper primary stage, students should be given a variety of opportunities to engage with scientific processes such as observing, recording observations, drawing, tabulating, plotting graphs, and so on, whereas in the secondary stage, abstraction and quantitative reasoning should take a more prominent role in science teaching and learning. As a result, the concept of atoms and molecules as matter’s building units, as well as Newton’s law of gravitation, emerges.
Science is important because it allows Class 9 Science students to understand the world around us. It helps to find out how things work and to find solutions to problems at the Class 9 Science level. Science is also a source of enjoyment for many people. It can be a hobby, a career, or a source of intellectual stimulation.
Case study questions in Class 9 Science
The inclusion of case study questions in Class 9 science CBSE is a great way to engage students in critical thinking and problem-solving. By working through real-world scenarios, Class 9 Science students will be better prepared to tackle challenges they may face in their future studies and careers. Class 9 Science Case study questions also promote higher-order thinking skills, such as analysis and synthesis. In addition, case study questions can help to foster creativity and innovation in students. As per the recent pattern of the Class 9 Science examination, a few questions based on case studies/passages will be included in the CBSE Class 9 Science Paper. There will be a paragraph presented, followed by questions based on it.
Examples of Class 9 science class case study questions
Class 9 science case study questions have been prepared by myCBSEguide’s qualified teachers. Class 9 case study questions are meant to evaluate students’ knowledge and comprehension of the material. They are not intended to be difficult, but they will require you to think critically about the material. We hope you find Class 9 science case study questions beneficial and that they assist you in your exam preparation.
The following are a few examples of Class 9 science case study questions.
Class 9 science case study question 1
- due to its high compressibility
- large volumes of a gas can be compressed into a small cylinder
- transported easily
- all of these
- shape, volume
- volume, shape
- shape, size
- size, shape
- the presence of dissolved carbon dioxide in water
- the presence of dissolved oxygen in the water
- the presence of dissolved Nitrogen in the water
- liquid particles move freely
- liquid have greater space between each other
- both (a) and (b)
- none of these
- Only gases behave like fluids
- Gases and solids behave like fluids
- Gases and liquids behave like fluids
- Only liquids are fluids
Answer Key:
- (d) all of these
- (a) shape, volume
- (b) the presence of dissolved oxygen in the water
- (c) both (a) and (b)
- (c) Gases and liquids behave like fluids
Class 9 science case study question 2
- 12/32 times
- 18 g of O 2
- 18 g of CO 2
- 18 g of CH 4
- 1 g of CO 2
- 1 g of CH 4 CH 4
- 2 moles of H2O
- 20 moles of water
- 6.022 × 1023 molecules of water
- 1.2044 × 1025 molecules of water
- (I) and (IV)
- (II) and (III)
- (II) and (IV)
- Sulphate molecule
- Ozone molecule
- Phosphorus molecule
- Methane molecule
- (c) 8/3 times
- (d) 18g of CH 4
- (c) 1g of H 2
- (d) (II) and (IV)
- (c) phosphorus molecule
Class 9 science case study question 3
- collenchyma
- chlorenchyma
- It performs photosynthesis
- It helps the aquatic plant to float
- It provides mechanical support
- Sclerenchyma
- Collenchyma
- Epithelial tissue
- Parenchyma tissues have intercellular spaces.
- Collenchymatous tissues are irregularly thickened at corners.
- Apical and intercalary meristems are permanent tissues.
- Meristematic tissues, in its early stage, lack vacuoles, muscles
- (I) and (II)
- (III) and (I)
- Transpiration
- Provides mechanical support
- Provides strength to the plant parts
- None of these
- (a) Collenchyma
- (b) help aquatic plant to float
- (b) Sclerenchyma
- (d) Only (III)
- (c) provide strength to plant parts
Cracking Class 9 Science Case Study Questions
There is no one definitive answer to Class 9 Science case study questions. Every case study is unique and will necessitate a unique strategy. There are, nevertheless, certain general guidelines to follow while answering case study questions.
- To begin, double-check that you understand the Class 9 science case study questions. Make sure you understand what is being asked by reading it carefully. If you’re unclear, seek clarification from your teacher or tutor.
- It’s critical to read the Class 9 Science case study material thoroughly once you’ve grasped the question. This will provide you with a thorough understanding of the problem as well as the various potential solutions.
- Brainstorming potential solutions with classmates or other students might also be beneficial. This might provide you with multiple viewpoints on the situation and assist you in determining the best solution.
- Finally, make sure your answer is presented simply and concisely. Make sure you clarify your rationale and back up your claim with evidence.
A look at the Class 9 Science Syllabus
The CBSE class 9 science syllabus provides a strong foundation for students who want to pursue a career in science. The topics are chosen in such a way that they build on the concepts learned in the previous classes and provide a strong foundation for further studies in science. The table below lists the topics covered in the Class 9 Science syllabus of the Central Board of Secondary Education (CBSE). As can be seen, the Class 9 science syllabus is divided into three sections: Physics, Chemistry and Biology. Each section contains a number of topics that Class 9 science students must study during the course.
CBSE Class 9 Science (Code No. 086)
Theme: Materials Unit I: Matter-Nature and Behaviour Definition of matter; solid, liquid and gas; characteristics – shape, volume, density; change of state-melting (absorption of heat), freezing, evaporation (cooling by evaporation), condensation, sublimation. Nature of matter: Elements, compounds and mixtures. Heterogeneous and homogenous mixtures, colloids and suspensions. Particle nature and their basic units: Atoms and molecules, Law of constant proportions, Atomic and molecular masses. Mole concept: Relationship of mole to mass of the particles and numbers. Structure of atoms: Electrons, protons and neutrons, valency, the chemical formula of common compounds. Isotopes and Isobars.
Theme: The World of the Living Unit II: Organization in the Living World Cell – Basic Unit of life: Cell as a basic unit of life; prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, multicellular organisms; cell membrane and cell wall, cell organelles and cell inclusions; chloroplast, mitochondria, vacuoles, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus; nucleus, chromosomes – basic structure, number. Tissues, Organs, Organ System, Organism: Structure and functions of animal and plant tissues (only four types of tissues in animals; Meristematic and Permanent tissues in plants).
Theme: Moving Things, People and Ideas Unit III: Motion, Force and Work Motion: Distance and displacement, velocity; uniform and non-uniform motion along a straight line; acceleration, distance-time and velocity-time graphs for uniform motion and uniformly accelerated motion, derivation of equations of motion by graphical method; elementary idea of uniform circular motion. Force and Newton’s laws: Force and Motion, Newton’s Laws of Motion, Action and Reaction forces, Inertia of a body, Inertia and mass, Momentum, Force and Acceleration. Elementary idea of conservation of Momentum. Gravitation: Gravitation; Universal Law of Gravitation, Force of Gravitation of the earth (gravity), Acceleration due to Gravity; Mass and Weight; Free fall. Floatation: Thrust and Pressure. Archimedes’ Principle; Buoyancy. Work, energy and power: Work done by a Force, Energy, power; Kinetic and Potential energy; Law of conservation of energy. Sound: Nature of sound and its propagation in various media, speed of sound, range of hearing in humans; ultrasound; reflection of sound; echo.
Theme: Food Unit IV: Food Production Plant and animal breeding and selection for quality improvement and management; Use of fertilizers and manures; Protection from pests and diseases; Organic farming.
PRESCRIBED BOOKS:
- Science-Textbook for class IX-NCERT Publication
- Assessment of Practical Skills in Science-Class IX – CBSE Publication
- Laboratory Manual-Science-Class IX, NCERT Publication
- Exemplar Problems Class IX – NCERT Publication
myCBSEguide: A true helper
There are numerous advantages to using myCBSEguide to achieve the highest results in Class 9 Science.
- myCBSEguide offers high-quality study materials that cover all of the topics in the Class 9 Science curriculum.
- myCBSEguide provides practice questions and mock examinations to assist students in the best possible preparation for their exams.
- On our myCBSEguide app, you’ll find a variety of solved Class 9 Science case study questions covering a variety of topics and concepts. These case studies are intended to help you understand how certain principles are applied in real-world settings
- myCBSEguide is that the study material and practice problems are developed by a team of specialists who are always accessible to assist students with any questions they may have. As a result, students may be confident that they will receive the finest possible assistance and support when studying for their exams.
So, if you’re seeking the most effective strategy to study for your Class 9 Science examinations, myCBSEguide is the place to go!
Test Generator
Create question paper PDF and online tests with your own name & logo in minutes.
Question Bank, Mock Tests, Exam Papers, NCERT Solutions, Sample Papers, Notes
Related Posts
- Competency Based Learning in CBSE Schools
- Class 11 Physical Education Case Study Questions
- Class 11 Sociology Case Study Questions
- Class 12 Applied Mathematics Case Study Questions
- Class 11 Applied Mathematics Case Study Questions
- Class 11 Mathematics Case Study Questions
- Class 11 Biology Case Study Questions
- Class 12 Physical Education Case Study Questions
Leave a Comment
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- New QB365-SLMS
- NEET Materials
- JEE Materials
- Banking first yr Materials
- TNPSC Materials
- DIPLOMA COURSE Materials
- 5th Standard Materials
- 12th Standard Materials
- 11th Standard Materials
- 10th Standard Materials
- 9th Standard Materials
- 8th Standard Materials
- 7th Standard Materials
- 6th Standard Materials
- 12th Standard CBSE Materials
- 11th Standard CBSE Materials
- 10th Standard CBSE Materials
- 9th Standard CBSE Materials
- 8th Standard CBSE Materials
- 7th Standard CBSE Materials
- 6th Standard CBSE Materials
- Tamilnadu Stateboard
- Scholarship Exams
- Scholarships

Class 9th Science - Motion Case Study Questions and Answers 2022 - 2023
By QB365 on 09 Sep, 2022
QB365 provides a detailed and simple solution for every Possible Case Study Questions in Class 9th Science Subject - Motion, CBSE. It will help Students to get more practice questions, Students can Practice these question papers in addition to score best marks.
QB365 - Question Bank Software
Motion case study questions with answer key.
9th Standard CBSE
Final Semester - June 2015
(ii) Find the Velocity of the boy.
(iii) A boy is sitting on a merry-go-round which is moving with a constant speed of 10m/s. This means that the boy is :
(iv) In which of the following cases of motion, the distance moved and the magnitude of displacement are equal ?
(ii) How far does it travel in 1 second ?
(iii) How far does it travel in 6 seconds ?
(iv) How long does it take to travel 240 m ?
(v) Which of the following statement is correct regarding velocity and speed of a moving body? (a) velocity of a moving body is always higher than its speed (b) speed of a moving body is always higher than its velocity (c) speed of a moving body is its velocity in a given direction (d) velocity of a moving body is its speed in a given direction
(ii) What type of motion is represented by BC ?
(iii) Find out the acceleration of the body.
(iv) Calculate the retardation of the body.
(v) Find out the distance travelled by the body from A to B.
*****************************************
Motion case study questions with answer key answer keys.
(i) (b) 2 m/s Total distance travelled is 100 m + 100 m = 200 m and the total time taken is 50 s + 50 s = 100 s. \(\text { Speed of boy }=\frac{\text { Distance travelled }}{\text { Time taken }}=\frac{200 \mathrm{~m}}{100 \mathrm{~s}}=2 \mathrm{~m} / \mathrm{s}\) (ii) (d) 0 m/s The boy runs 100 m towards East and then 100 m towards West and reaches at the starting point, his home. So, the displacement will be 100 m – 100 m = 0 m. The total time taken is 50 s + 50 s = 100 s. \(\text { Velocity of boy }=\frac{\text { Displacement }}{\text { Time taken }}=\frac{0 \mathrm{~m}}{100 \mathrm{~s}}=0 \mathrm{~m} / \mathrm{s}\) (iii) (c) in accelerated motion (iv) (a) if the car is moving on straight road (v) (c) 2r
(i) (b) 30 m/s Average speed = total distance travelled/total time taken = 150/5 = 30 m/s (ii) (b) 30 m Time = 1 s Distance = (average speed)(time) = 30 m/s x 1s = 30 m (iii) (c) 180 m Time = 6 s Distance = (average speed)(time) = 30 m/s x 6s = 180m (iv) (d) 8s Distance = 240m Time = Distance/average speed = 240/30 = 8s (v) (d) velocity of a moving body is its speed in a given direction
(i) (b) uniform acceleration OA is a straight line graph between speed and time, and it is sloping upwards from O to A. Therefore, the graph line OA represents uniform acceleration. (ii) (c) negative acceleration BC is a straight line graph between speed and time which is sloping downwards from B to C. Therefore, BC represents uniform retardation (or negative acceleration). (iii) (a) 1.5 m/s 2 The slope of speed-time graph OA will give us the acceleration of the body. Thus, Acceleration = Slope of line OA = AD/OD Now, in the given graph, we find that AD = 6 m/s and OD = 4 seconds. So, putting these values in the above relation, we get : Acceleration = 6 m/s / 4 s = 1.5 m/s 2 (iv) (d) 1 m/s 2 The slope of speed-time graph BC will be equal to the retardation of the body. So, Retardation = Slope of line BC = BE/EC Now, in the graph given to us, we find that BE = 6 m/s and EC = 16 – 10 = 6 seconds. So, putting these values in the above relation, we get : Retardation = 6m/s / 6 s = 1 m/s 2 (v) (c) 36 m Distance travelled from A to B = Area under the line AB and the time axis = Area of rectangle DABE = DA × DE Now, from the given graph, we find that DA = 6 m/s and DE = 10 – 4 = 6 s. Therefore, Distance travelled from A to B = 6 × 6 = 36 m
Related 9th Standard CBSE Science Materials
9th standard cbse syllabus & materials, class 10th social science - pastoralists case study questions and answers 2022 - 2023, class 9th social science - forest society and colonialism case study questions and answers 2022 - 2023, class 9th social science - nazism and the rise of hitler case study questions and answers 2022 - 2023, class 9th social science - socialism in europe and the russian revolution case study questions and answers 2022 - 2023, class 9th social science - the french revolution case study questions and answers 2022 - 2023, class 9th maths - probability case study questions and answers 2022 - 2023, class 9th maths - statistics case study questions and answers 2022 - 2023, class 9th maths - surface case study questions and answers 2022 - 2023, class 9th maths - linear equations in two variables case study questions and answers 2022 - 2023, class 9th maths - coordinate geometry case study questions and answers 2022 - 2023, rs aggarwal 9th standard maths ncert solutions for probability, rs aggarwal 9th standard maths ncert solutions for statistics, rs aggarwal 9th standard maths ncert solutions for surface areas volumes, rs aggarwal 9th standard maths ncert solutions for heron's formula, rs aggarwal 9th standard maths ncert solutions for constructions.

Class VI to XII
Tn state board / cbse, 3000+ q&a's per subject, score high marks.

9th Standard CBSE Study Materials

9th Standard CBSE Subjects

Class 9 Science Case Study Questions PDF Download
- Post author: studyrate
- Post published:
- Post category: class 9th
- Post comments: 0 Comments
Class 9 Science Case Study Questions play a crucial role in the field of science education as they provide real-life scenarios for students to analyze, apply their knowledge, and develop problem-solving skills. This article aims to present a comprehensive collection of case study questions for Class 9 Science , covering various topics and concepts.
Join our Telegram Channel, there you will get various e-books for CBSE 2024 Boards exams for Class 9th, 10th, 11th, and 12th.

CBSE Class 9 Science Exam will have a set of questions based on case studies in the form of MCQs. The CBSE Class 9 Science Question Bank on Case Studies, provided in this article, can be very helpful to understand the new format of questions. Share this link with your friends.
If you want to want to prepare all the tough, tricky & difficult questions for your upcoming exams, this is where you should hang out. CBSE Case Study Questions for Class 9 will provide you with detailed, latest, comprehensive & confidence-inspiring solutions to the maximum number of Case Study Questions covering all the topics from your NCERT Text Books !
Table of Contents
CBSE Class 9th SCIENCE Chapterwise Case Study Question & Solution
Case study questions provide students with real-life scenarios that require critical thinking and application of scientific concepts. They help students understand the practical application of scientific principles and develop problem-solving skills in various scientific disciplines.
Chapterwise Case Study Questions for Class 9 Science
Inboard exams, students will find the questions based on assertion and reasoning. Also, there will be a few questions based on case studies. In that, a paragraph will be given, and then the MCQ questions based on it will be asked. For Science subjects, there would be 5 case-based sub-part questions, wherein a student has to attempt 4 sub-part questions.
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 1 Matter in Our Surroundings
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 2 Is Matter Around Us Pure?
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 3 Atoms and Molecules
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 4 Structure of Atom
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 5 The Fundamental Unit of Life
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 6 Tissues
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 7 Diversity in Living Organisms
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 8 Motion
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 9 Force and Laws of Motion
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 10 Gravitation
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 11 Work and Energy
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 12 Sound
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 13 Why do we Fall ill
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 14 Natural Resources
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 15 Improvement in Food Resources
The above Case studies for Class 9 Science will help you to boost your scores as Case Study questions have been coming in your examinations. These CBSE Class 9 Science Case Studies have been developed by experienced teachers of schools.studyrate.in for the benefit of Class 10 students.
Class 9 Maths Case Study Questions
Benefits of Case Studies in Science Education
Case studies offer several advantages over traditional teaching methods. Here are some key benefits:
- Real-World Application : Case studies present authentic scenarios, enabling students to understand how scientific concepts are applied in real-life situations.
- Critical Thinking : Analyzing case studies requires students to think critically, make connections, and apply scientific knowledge to solve problems.
- Interdisciplinary Approach : Case studies often involve multiple scientific disciplines, fostering an interdisciplinary understanding of complex issues.
- Engagement and Active Learning : Case studies actively engage students in the learning process, promoting active participation, discussion, and collaboration.
- Skill Development : Case studies develop essential skills such as analytical thinking, problem-solving, and effective communication of scientific concepts.
Importance of Practicing Case Study Questions
Practicing case study questions is crucial for Class 9 Science students to enhance their understanding and application of scientific concepts. Here’s why it is important:
- Application of Knowledge : Case studies allow students to apply their theoretical knowledge to practical situations, bridging the gap between theory and real-world scenarios.
- Developing Analytical Skills : Analyzing case studies improves students’ ability to identify relevant information, make connections, and draw logical conclusions.
- Problem-Solving Skills : Case studies present complex problems that require students to think critically and develop effective problem-solving strategies.
- Enhanced Exam Performance : Practicing case study questions familiarizes students with the format and types of questions they may encounter in exams, leading to improved performance.
Subjects Covered in the Case Study Questions for Class 9 Science
The case study questions for Class 9 Science cover the following subjects:
- Motion and Forces
- Light and Reflection
- Electricity
- Matter and Its Properties
- Atoms and Molecules
- Structure of the Atom
- Chemical Reactions
- Cell: The Fundamental Unit of Life
- Diversity in Living Organisms
- Natural Resources
Tips for Approaching Case Study Questions
To tackle case study questions effectively, consider the following tips:
- Read Carefully : Pay close attention to the details provided in the case study, as they hold crucial information for solving the problem.
- Analyze Methodically : Break down the problem into smaller components and analyze each part systematically.
- Apply Relevant Concepts : Identify the scientific principles relevant to the case study and apply them appropriately.
- Consider Multiple Perspectives : Explore different angles and viewpoints while proposing solutions, taking into account various scientific factors.
- Provide Justifications : Support your answers with scientific explanations and logical reasoning to strengthen your responses.
The Class 9 Science Case Study Questions provided in this article serve as a valuable resource for students seeking to enhance their scientific knowledge and problem-solving skills. By practicing these case studies, students can develop a deeper understanding of scientific concepts and their practical applications. Embrace this opportunity to engage with real-world scenarios and strengthen your scientific acumen.
Q1: Are the Class 9 Science Case Study Questions aligned with the official curriculum?
Yes, the Class 9 Science Case Study Questions presented in this article are aligned with the official curriculum. They cover relevant topics and concepts that students need to study for their exams.
Q2: Can practicing case study questions alone guarantee success in Class 9 Science exams?
Practicing case study questions is an important part of exam preparation, but it should be complemented with a thorough understanding of the subject matter. It is advisable to study the concepts in detail, refer to textbooks, and engage in other learning activities to achieve success in exams.
Q3: Where I Can get Class 9 Science Case Study Questions ?
You can practice Class 9 Science Case Study Questions on schools.studyrate.in for free.
You Might Also Like
Mcq class 9 social science history the french revolution quiz with answers, mcq questions of class 9 maths chapter 15 probability with answers, mcq questions of class 9 social science history chapter 7 history and sport the story of cricket with answers, leave a reply cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Talk to our experts
1800-120-456-456
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 1 - Matters In Our Surroundings
- NCERT Solutions
- Chapter 1 Matters In Our Surroundings

NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 1 - Matter in Our Surroundings
The NCERT Answer for Class 9 Science Chapter 1 was written with the sole purpose of assisting students in obtaining more marks and improving their grades in mind. The answer for class 9 Science chapter 1 addresses students' academic expectations and needs. The themes in Chapter 1 on Matter in Our Surroundings are covered in accordance with the CBSE syllabus . The solution's strategy incorporates a step-by-step method that assists in improved knowledge of the issues.
NCERT Solution of class 9 Science chapter 1 has been created, keeping in mind the primary goal of helping students to secure more marks and improve grades. The academic requirements and needs of students have been addressed in the solution for class 9 Science chapter 1. The topics in chapter 1 related to Matter in Our Surrounding are discussed according to the CBSE syllabus. The approach in the solution involves a step-by-step process which aids in better comprehension of the topics.
CBSE class 9 Science chapter 1 solutions explain all the foundational concepts in detail for students to understand better. The solutions are made available to everybody over the Vedantu app. These free PDFs can be downloaded easily from Vedantu’s official portal.
You can also download NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths and NCERT Solution for Class 9 Science to help you to revise complete syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.

Access NCERT solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter – 1 Matter in our Surroundings
Intext exercise -1.
1. Which of the following are the matter?
Chair, air, love, smell, hate, almonds, thought, cold, cold drink, smell of perfume.
Ans: Matter is anything that occupies space and has some mass. There are three states of matter called Solid, Liquid and Gas. On the basis of these three states, we can define that which of this is a matter:
Chair and almond are said to be in a solid state of matter as these have fixed shape., cold drink is in liquid state as it has the tendency to flow., air and the smell of perfume have gaseous particles which are free to move so this will also be considered as a gaseous state of matter..
While Love, hate, cold, smell and thought are not having any mass or neither do they occupy space these are just emotions or sensations felt by human beings so they are not considered as matter.
2. Give reasons for the following observation:
The smell of hot sizzling food reaches you several meters away, but to get the smell from cold food you have to go close.
Ans: The smell of hot sizzling food prepared by our mom reaches to us in our room from kitchen but if the food gets cold after some time, we did not feel any smell of that food this phenomenon can be defined on the basis of rate of diffusion which gets increases when the temperature get increases as high temperature increases the kinetic energy of food particles to get diffused in air. The temperature of hot food particles is high as compared to old one so its molecules get easily diffused in the air as compared to cold ones.
3: a diver is able to cut through water in a swimming pool. which property of matter does this observation show, ans: this can be explained on the properties of matter to attract the particles towards themselves and this will also decide their shape and rigidity. the force of attraction is highest in case of solid as compared to liquid and gas this defines that particles of solid are tightly bound to each other. while in case of liquid particles they have less forces of attraction which defines that there is space between the particles and due to this reason that we can cut them easily. that is why we can say that due to less forces of attraction between water molecules a diver is able to cut through water in a swimming pool., 4: what are the characteristics of particles of matter, ans: matter is anything that occupies space and has some mass. there are three states of matter called solid, liquid and gas., the main characteristics of matter can be described as follows:, particles of matter have space between them and the order of spacing is highest in gas after that liquid and solid have very less space between their particles., particles of matter are continuously moving in all the three states of matter., particles of matter attract each other with strong forces which help them to bind with each other. in solid particles attraction is very high whereas in liquid it is low and in gases it is quite low. , intext exercise -2.
1: The mass per unit volume of a substance is called density (density = mass/volume). Arrange the following in order of increasing density − air, exhaust from chimney, honey, water, chalk, cotton, and iron.
Ans: Density is depending on mass and volume hence higher the mass higher will be the density and out of these heavier particles have higher mass as compare to lighter one so the order of increasing density of given substances can be written as follows:
Air < Exhaust from chimney < Cotton < Water < Honey < Chalk < Iron.
Tabulate the differences in the characteristics of states of matter.
Matter is anything that occupies space and has some mass. There are three states of matter called Solid, Liquid and Gas.
Comment upon the following: rigidity, compressibility, fluidity, filling a gas container, shape, kinetic energy, and density.
Ans:
Rigidity: it is defined as the tendency of matter to resist a change in shape..
Compressibility: The ability of matter to reduce in volume when any type of external force is applied on it.
Fluidity: Tendency of particles to flow this property can be seen in case of liquid and gases which can also be known as fluids.
Filling a Gas Container: Gases neither have definite shape nor have definite volume. Gases take the shape of that container in which it gets filled. Hence by filling a gas container, it means the attainment of shape of the container by the gas.
Shape: Shape corresponds to fixed volume and boundary. Only solids have a fixed shape.
Kinetic Energy: Particles which produce energy possessed due to its continuous motion.
Density: It is defined as the mass per unit volume.
3: Give Reasons:
A Gas Fills Completely the Vessel in Which it is Kept.
The gas particles have a tendency to move freely in all directions as they have very less force of attraction between their particles. Like water, gas can also take the shape of the container in which it is kept. Therefore, we can say that gas completely fills the vessel in which it is kept.
A Gas Exerts Pressure on the Walls of the Container.
The gas particles move freely due to its lesser forces of attraction between the particles. Therefore, these gaseous particles continuously collide with each other and with the walls of the container with a greater force. Pressure is known as the force produced by the gas particles per unit area. By this we can say that gas exerts pressure on the walls of the container.
A wooden table should be called a solid.
A wooden table is very rigid in nature which means that it has a definite shape and its shape cannot be changed easily and has definite volume too. The shape is fixed due to strong intermolecular forces hence it attains all the properties of solid therefore, it is considered as a solid.
We can easily move our hands in air, but to do the same through a solid block of wood, we need a karate expert.
Air particles have very less forces of attraction between their particles so they have large space in between them. But wood has very little space between the particles due to its high force of attraction therefore, wood is considered to be of rigid nature. Due to this reason, we can easily move our hands in air but the same will not happen through a solid block of wood. For this we need a karate expert.
4: Liquids generally have lower density as compared to solids. But you must have observed that ice floats on water. Find out why.
Ans: as we know that density is defined as the mass per unit volume. this corresponds with the increase of the volume of any substance density will decrease as they are inversely proportional to each other. .
Ice is solid in nature therefore it contains strong intermolecular forces which tightly bound them and they contain lesser volume but on the other hand liquid has tendency to move freely due to weak intermolecular forces and contain large volume.
From this we can say that water has larger volume and lesser density so it has a tendency to float on water.
Intext Exercise -3
1: convert the following temperature to celsius scale:.
Celsius and Kelvin are two main scales to measure the temperature. By subtracting the 273K from the given value we can get the value in degrees Celsius. The formula corresponds to degree Celsius can be shown as:
\[X{}^\circ C=(X-273)\]
\[300K=(300-273){}^\circ C=27{}^\circ C\]
573 K
$573K=(573-273){}^\circ C=300{}^\circ C$
2: What is the physical state of water at:
$\mathbf{\text{25}{{\text{0}}^{\text{o}}}\text{C}}$
Ans: Physical state corresponds to the state of matter whether it exists in solid, liquid or gas.
$\text{25}{{\text{0}}^{\text{o}}}\text{C}$– As we know that water starts boiling at 100°C and above this temperature water exists in gaseous state. So, this defines that water at 250°C exists in a gaseous state.
$\mathbf{{{100}^{o}}C}$
${{100}^{o}}C$ – It is the starting point where water starts boiling so at this temperature water exists in both liquid and gaseous states.
3: For any substance, why does the temperature remain constant during the change of state?
Ans: this can be explained as the whole heat which we are providing to the substance to increase its temperature is used to break the intermolecular forces of attraction between them. this heat will also correspond to the latent heat i.e., the heat which gets absorbed or released during change of state. hence all the energy gets used so temperature remains constant. , 4: suggest a method to liquefy atmospheric gases., ans: atmospheric gases can be defined as the gases present in the atmosphere. it can be liquified i.e., converted into liquid by applying suitable conditions of applying pressure and by reducing their temperature., intext exercise -4, 1: why does a desert cooler cool better on a hot dry day, ans: this can be explained by the process called evaporation, this is the process in which the liquid particles absorb energy from the surroundings and cause cooling. the rate of evaporation generally depends on the amount of water vapour present in the air. if the amount of water vapor present in air is more than the rate of evaporation is more or vice-versa. on a hot dry day, the amount of water vapor present in air is quite low so this will evaporate easily and make its surroundings cooler. thus, from this we can say that a desert cooler cools better on a hot dry day as compared to rainy one., 2: how does water kept in an earthen pot (matka) become cool during summers, ans: an earthen pot or matka is generally made up of sand particles in which many tiny pores exist and this helps the water inside the pot to evaporate and surroundings makes the water cool. this is the reason why people kept the water in an earthen pot during summers., 3: why does our palm feel cold when we put some acetone or petrol or perfume on it, ans: acetone, petrol or perfume are considered as organic compounds which are volatile in nature whereas volatile substances are those which easily get vaporized and go through the process of evaporation. we know that during the process of evaporation particles of these organic liquids absorb energy from the surroundings or the surface of the palm and make the surroundings or surface of the palm somewhat cool. this is the reason why our palm feels cold when we put some acetone, petrol or perfume on it. , 4: why are we able to sip hot tea or milk faster from a saucer than a cup, ans: this can also be explained on the basis of rate of evaporation as we know that evaporation produces a cooling effect and evaporation depends on the surface area, larger the surface area higher the evaporation. as in saucer the area is larger as compared to cup so evaporation will be high in case of greater surface area. thus, we can say that liquid cools faster in a saucer than in a cup and due to this reason, we are able to sip hot tea or milk faster from a saucer than a cup., 5: what type of clothes should we wear in the summer, ans: in summer we usually sweat so we have to wear cotton or light-colored clothes because cotton or light-colored clothes can absorb more sweat from our body and transfers the sweat which is in the form of liquid to the atmosphere and makes the evaporation process faster. evaporation process causes a cooling effect which makes our body cool in cotton clothes as compared to synthetic or woolen ones. , ncert exercise, 2: convert the following temperature to kelvin scale:.
$\mathbf{25{}^\circ C}$
Celsius and Kelvin are two main scales to measure the temperature. By adding the 273K from the given value we can get the value in degrees Celsius. The formula corresponds to degree Celsius can be shown as:
\[0{}^\circ C=273K\]
\[{{27}^{o}}C=(27+273)K=300K\]
$\mathbf{373{}^\circ C}$
${{373}^{o}}C=(373+273)K=646K$
3: Give reason for the following observations.
Naphthalene balls disappear with time without leaving any solid.
This phenomenon can be explained on the basis of sublimation which defines that solid is directly converted into gaseous form without turning it into liquid. naphthalene is one that substances which undergo through the process of sublimation easily at room temperature. that is why we can say that naphthalene balls disappear after some time without leaving any solid., we can get the smell of perfume sitting several meters away., gaseous particles have very less internuclear forces due to which its molecules are very free to move and it possesses high kinetic energy. due to this reason particles of perfumes diffuse into the atmosphere and its molecules will mix in the environment which enables us to smell the perfume from several meters away., 4: arrange the following substances in increasing order of forces of attraction between particles − water, sugar, oxygen., ans: forces of attraction is the attracting power of molecules which keep them together and intermolecular forces are very strong in case of solid as compared to liquid or gas. , here sugar is said to be solid and contains higher forces of attraction., water is liquid comparatively containing lesser forces of attraction but higher as compared to gases., oxygen is a gas which contains very less attraction between forces., thus, the increasing order of forces of attraction between the particles of water, sugar and oxygen is.
Oxygen < Water < Sugar
5: What is the physical state of water at:
$\mathbf{{{25}^{o}}C}$
Ans: Physical state corresponds to the state of matter whether it exists in solid, liquid or gas.
$25{}^\circ C$– As we know that water melts at 0°C and above this temperature water exists in liquid state. So, this defines that water at 25°C exists in a liquid state
$\mathbf{{{0}^{o}}C}$
Ans: $0{}^\circ C$– It is the temperature at which water starts melting i.e., water gets converted into liquid from ice so at this temperature water exists as both solid and liquid state.
Ans: $100{}^\circ C$– It is the starting point where water starts boiling so at this temperature water exists in both liquid and gaseous states.
6: Give two reasons to justify:
water at room temperature is a liquid.
We find water is in liquid state at room temperature this can be justified as follows:
Water does not have any fixed shape; it can take the shape of the container in which it is kept and water has definite volume.
It has a tendency to flow.
Have weak intermolecular forces between their particles.
These all describe the property of liquid so we can say that water is liquid at room temperature.
An Iron Almirah is a Solid at Room Temperature.
Iron almirah kept in our room is said to be solid due to following reasons:
It has a fixed shape and definite volume.
It contains strong intermolecular forces between their particles.
Rigid in nature, difficult to compress.
These all describe the property of solid so we can say that almirah is solid at room temperature.
7: Why is ice at 273 K more effective in cooling than water at the same temperature?
Ans: here condition given that both ice and water are at same temperature i.e. 273 k. but ice at 273 k has less energy as compared to water this can be explained on the basis of latent heat of fusion which is possessed by water as an additional energy but ice does not have such type of energy. therefore, we can say that at 273 k ice is more effective in cooling as compared to water., 8: what produces more severe burns, boiling water or steam, ans: steam and water both are said to be at the same temperature i.e., 373 k. but steam contains more energy as compared to boiling water. this can be explained on the basis of latent heat of fusion which is possessed by water as an additional energy. therefore, steam produces more severe burns than boiling water., 9: name a, b, c, d, e and f in the following diagram showing change in its state..
A is the process of converting solid into liquid is called Melting.
B is the process which converts liquid into gaseous state, this is called vaporisation.
C in which gases get converted into liquid this is called condensation.
D is the process which converts liquid into solid. It is called solidification.
E and F are the processes which convert solid into gas or vice versa is known as sublimation.
You can opt for Chapter 1 - Matter in Our Surroundings NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science PDF for Upcoming Exams and also You can Find the Solutions of All the Maths Chapters below.
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science
Chapter 1 - Matter in Our Surroundings
Chapter 2 - Is Matter Around us Pure
Chapter 3 - Atoms and Molecules
Chapter 4 - Structure of Atom
Chapter 5 - The Fundamental Unit of Life
Chapter 6 - Tissues
Chapter 7 - Diversity in Living Organisms
Chapter 8 - Motion
Chapter 9 - Force and Laws of Motion
Chapter 10 - Gravitation
Chapter 11 - Work and Energy
Chapter 12 - Sound
Chapter 13 - Why do We Fall ill
Chapter 14 - Natural Resources
Chapter 15 - Improvement in Food Resources
Important Concepts Covered in Chapter 1 - Matter in Our Surroundings of Class 9 Science NCERT Solutions
The first chapter delves into the meaning of the matter, its definition, and the various physical states of matter. The matter is defined as everything that takes up space and has mass. For example, water and sugar, sand and sugar, hydrogen and oxygen, and so forth. The matter is made up of minuscule, microscopic particles. Because matter particles have space between them, they are attracted to one another.
Matter in Our Surrounding is the first chapter of Class 9 Science and it covers the following concepts.
Class 9 Science Chapter 1 Matter in Our Surroundings
Even though the topic of Matter in Our Surroundings can be very wide in scope, NCERT solution of Class 9 Science Chapter 1 strictly adheres to the CBSE syllabus. Here are the topics covered –
Matter in Our Surroundings
The introductory chapter elucidates the concept of matter, its definition and the and the physical states in which it exists in nature.
Physical State of Matter
The three physical states of matter are discussed – solid, liquid and gas. The point is elaborated with instances, one of which exemplifies the property of matter when a diver cuts through water.
Characteristics of Particles of Matter
In this chapter, students get to know various characteristics of particles of matter. It discusses that particles of matter – (1) have intermolecular spaces, (2) are in continuous motion and (3) experiences force between one another.
States of Matter
Chapter 4 deals with the features of states of matter – compressibility, rigidity, fluidity, kinetic energy, shape and density.
Can Matter Change its State?
The occurrence of change in state of matter is discussed through the example of ice converting into water and eventually into gaseous form.
Evaporation
The concept of evaporation is exemplified through the question as to why a desert cooler functions better on a hot, dry day as opposed to other weather conditions.
Why is it Beneficial for Students to Study from NCERT solutions class 9 Science Matter in Our Surroundings?
Teachers and mentors have always stressed on the importance of self-study in order for a student to succeed. The material that is referred to in the course of self-study also holds a critical value. Here are some of the benefits of studying NCERT solution of Class 9 Science Chapter 1 that would provide students with that much-needed competitive edge –
The solutions are framed by domain experts possessing much experience. The language of the material has been purposely kept lucid; however, the content remains comprehensive. It enables students to gain in-depth knowledge on the topic
If there is any concern about the relevance and accuracy of the Class 9 Science Ch 1 NCERT solutions, it can be put to rest. The solution strictly adheres to the CBSE curriculum, without any scope for deviation
It is ensured that the basic concepts are suitably explained so that students remain clear on the topic
Ample problem exercises are provided so that students get sufficient practice
The NCERT Solutions for Matter in Our Surroundings (Chapter 8) for Class 9 are given in this article.

Conclusion
This solution contains all of the chapter's questions so that students may prepare for their examinations properly. We have also provided NCERT activities to help pupils grasp the kind or pattern of questions in the CBSE Class 9 test.
While your devotion and constant practice will put you on the right track, NCERT answers will only pave the road. Therefore, get the answer right now and get started on your preparation!

FAQs on NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 1 - Matters In Our Surroundings
1. What are the different characteristics of state of matter explained in NCERT solutions class 9 Science chapter 1?
The different characteristics as elaborated in CBSE Class 9 Science Chapter 1 solutions are based on six parameters - (1) Shape, (2) Volume, (3) Rigidity or Fluidity, (4) Intermolecular force, (5) Intermolecular space, and (6) Compressibility.
A few of the properties listed in Matter in Our Surroundings Class 9 NCERT answers suggest that solids have a set form, volume, and are rigid, whereas liquids have no fixed shape or volume and are less rigid than solids. Gas, on the other hand, has no definite shape or volume and is not hard.
2. Which are the chapters included in Class 9 Science as per the NCERT Science Book?
There are altogether fifteen chapters included in CBSE class 9 Science – (1) Matter in Our Surroundings, (2) Is Matter Around Us Pure, (3) Atoms and Molecules, (4) Structure of Atom, (5) The Fundamental Unit of Life, (6) Tissues, (7) Diversity in Living Organisms, (8) Motion, (9) Force and Laws of Motion, (10) Gravitation, (11) Work and Energy, (12) Sound, (13) Why do We Fall Ill, (14) Natural Resources, (15) Improvement in Food Resources.
3. Can NCERT Solutions be an effective way to prepare Science Class 9 Chapter 1?
Yes, NCERT Solutions will help the studnets to prepare for chapter 1 of Class 9 pretty well. While there can be a multitude of ways to prepare Ch 1 Class 9 Science, it is only when such preparation is done in a systematic manner, can an optimal output be gained. It is advised that instead of starting with a topic in Class 9 Chapter 1 solution of one’s preference, proceed according to the flow of the chapter.
4. How many questions are present in each exercise of NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 1?
There are five exercises in the NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 1. In Exercise 1, there are four questions. In Exercise 2, there are four questions. Exercise 3 also consists of four questions. In Exercise 4, there are four questions. Lastly, the NCERT exercise has nine questions. All of these questions are provided along with their solutions in the NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 1.
5. Are the NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 1 sufficient for the exam preparation?
Yes. To do well in the test, students must study and prepare through self-study in addition to what is given in school. Students must use the best study resources provided on Vedantu for self-study. Students should refer to NCERT Answers for Class 9 Science Chapter 1 and others when studying for the Class 9 Science test. They are developed by qualified teachers and are simple to grasp.
6. What is the matter in our surroundings?
Matter in our surroundings is the first topic covered in Chapter 1 of Class 9 Science. In this chapter, students learn what matter is and which entities can not be considered as matter. The five basic elements that constitute matters in our surroundings are fire, earth, sky, water and air. The building blocks of matter are very small particles that can only be seen under a microscope.
7. Write in short answer format what is matter according to the syllabus of Class 9.
Matter is defined as everything that fills space and has mass. Matter may be perceived by humans through their senses. Water, earth, fire, sky, and air are components that make up matter. It is made up of microscopic particles that can only be seen under a microscope. These are the fundamental building components of matter. Light, heat, electricity, and magnetism are not considered matter since they do not occupy space or have mass.
8. How to download the NCERT Solutions Class 9 Science Chapter 1?
Students can use NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 1 to download the NCERT Solutions Class 9 Science Chapter 1 from Vedantu (vedantu.com). These solutions contain the answers to all the questions from Chapter 1 of the Class 9 Science NCERT textbook in a concise and structured manner. These are available free of cost on Vedantu (vedantu.com). Students can download these using the Vedantu app as well. By going through the solutions, students can learn how to write their answers in the exam. Apart from the solutions, students can also find other study material on Vedantu, including important questions, revision notes and previous year question papers.
NCERT Solutions for Class 9
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Physics Free PDF Download
Ncert solutions for class 9 physics.
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Physics will help you to ace the unsolved problems in the Class 9 Science book prescribed by the NCERT for all the schools of CBSE. A thorough understanding of the NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Physics helps you in understanding Physics concepts to the point. The NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Physics cover all the 5 chapters of the prescribed Physics syllabus and are the best alternative.
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Physics breaks down the solutions into detailed steps and explains the answer thoroughly, which helps you understand the pattern of questioning and a way to increase your score in exams.
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Physics are prepared by our team of highly professional, qualified and experienced faculties. These NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Physics helps you to quickly grasp all the basic concepts of physics. In case you have a doubt while you are studying NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Physics, we have a team of teachers who are just a click away to solve your doubt any time.
Download NCERT Solutions for Class 9 of all subjects here .
Toppr provides free video lectures on each and every topic of physics, chemistry, and maths, free study materials and last 10 years of question papers. Download Toppr app for Android and iOS or sign up for free.
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Physics Chapterwise
Class 9 Physics Chapter 1 – Motion
Class 9 Physics Chapter 2 – Force And Laws Of Motion
Class 9 Physics Chapter 3 – Gravitation
Class 9 Physics Chapter 4 – Work and Energy
Class 9 Physics Chapter 5 – Sound

Class 9 Chapterwise NCERT Solutions for Physics
Ncert solutions for class 9 physics chapter 1 motion.
Here, you will learn about motion including motion along a straight line, types of motion, the difference between Vector & Scalar, Speed & Velocity, Distance & Displacement, Acceleration – Rate of change of velocity and average speed and velocity, Graphical representation of motion and derivation of three equation of motion. Download NCERT Solutions for Motion here .
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Physics Chapter 2 Force and Laws of Motion
In this chapter, you will learn the concept of balance and unbalance forces. Starting with the First law of motion, the Galileo’s concept, the law of inertia. You will also learn the Second law of motion and Third law of motion, momentum, rate of change of momentum. And applications on first, second and third laws of motion. Download NCERT Solutions for Force And Laws Of Motion here .
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Physics Chapter 3 Gravitation
This chapter gravitation takes you through the depths of motion of objects under the influence of gravitational force on the earth. Gravitational force and Newton’s universal law of gravitation. Download NCERT Solutions for Gravitation here .
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Physics Chapter 4 Work and Energy
In this chapter, you will learn about the relationship between work and energy, scientific conception of work and also different forms of energy such as Kinetic energy, Potential energy, application of kinetic and potential energy, and energy of an object at a certain height. Download NCERT Solutions for Work and Energy here .
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Physics Chapter 5 Sound
This chapter is a very interesting one as you will get to learn about the Reflection of Sound i.e ECHO, reverberation, and applications of multiple reflections of sound. All these concepts are taught by implementing various activities needed to be done in the Physics laboratory that makes the learning process more effective and interactive. Download NCERT Solutions for Sound here .
Why choose Toppr?
With Toppr App, you get free online classes with conceptual videos. You will also have access to all the free pdf downloads of study materials and solutions along with absolutely free online tests to enhance your problem-solving speed. So, Download Toppr App for Android and iOS or sign up for free.
Solved Questions For You:
Question 1. What is the acceleration of free fall?
Answer: Acceleration of free fall is the acceleration experienced by the freely falling body the effect of gravitation of earth alone. It is also called acceleration due to gravity.
Answer: The gravitation force between the earth and object is called weight.
Answer: By crumpling the paper into a ball, the volume of the object decreases but the mass remains the same. Hence its density increases.
Answer: The Importance of Universal law of gravitation lies in the fact, that it was successful in explaining many phenomena such as.
Customize your course in 30 seconds
Which class are you in.

NCERT Solutions for Class 9
- NCERT Solutions for Class 9 History Chapter 3 Free PDF Download
- NCERT Solutions for Class 9 History Chapter 6 Free PDF Download
- NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 15 Free PDF Download
- NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 7 Free PDF Download
- NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 14 Free PDF Download
- NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 12 Free PDF Download
- NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 1 Free PDF Download
- NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 9 Free PDF Download
- NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 4 Free PDF Download
- NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 11 Free PDF Download
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Download the App

CBSE Expert

Case Study Questions of Class 9 Science PDF Download
Download PDF Case Study Questions of Class 9 Science to prepare for the upcoming CBSE Class 9 Exams Exam 2023-24. With the help of our well-trained and experienced faculty, we provide solved examples and detailed explanations for the recently added Class 9 Science case study questions .

Case study questions are based on real or hypothetical scenarios that require students to analyze, evaluate, and apply scientific concepts to solve problems or make informed decisions. They often present a detailed context, providing students with the opportunity to demonstrate their understanding of the subject matter beyond basic recall.
Table of Contents
Class 9 Science: Case Study Questions
The inclusion of case study questions in Class 9 science CBSE is a great way to engage students in critical thinking and problem-solving. By working through real-world scenarios, Class 9 Science students will be better prepared to tackle challenges they may face in their future studies and careers. Class 9 Science Case study questions also promote higher-order thinking skills, such as analysis and synthesis. In addition, case study questions can help to foster creativity and innovation in students. As per the recent pattern of the Class 9 Science examination, a few questions based on case studies/passages will be included in the CBSE Class 9 Science Paper. There will be a paragraph presented, followed by questions based on it.
Chapterwise Case Study Questions of Class 9 Science
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 1 Matter in Our Surroundings
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 2 Is Matter Around Us Pure?
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 3 Atoms and Molecules
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 4 Structure of Atom
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 5 The Fundamental Unit of Life
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 6 Tissues
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 7 Diversity in Living Organisms
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 8 Motion
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 9 Force and Laws of Motion
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 10 Gravitation
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 11 Work and Energy
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 12 Sound
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 13 Why do we Fall ill
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 14 Natural Resources
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 15 Improvement in Food Resources
You can find a wide range of solved case studies on cbseexperts, covering various topics and concepts. Class 9 Science case studies are designed to help you understand the application of various concepts in real-life situations.
Class 9 Science Syllabus
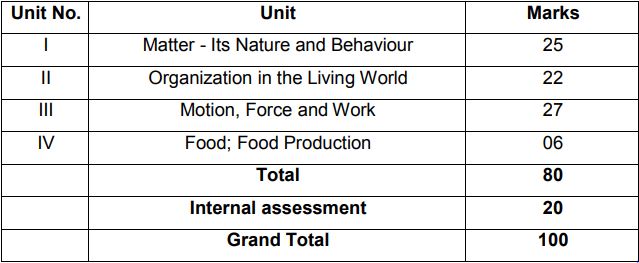
Unit I: Matter-Nature and Behaviour
Definition of matter; solid, liquid, and gas; characteristics – shape, volume, density; change of statementing (absorption of heat), freezing, evaporation (cooling by evaporation), condensation, sublimation.
Nature of matter: Elements, compounds, and mixtures. Heterogeneous and homogenous mixtures, colloids, and suspensions. Physical and chemical changes (excluding separating the components of a mixture).
Particle nature and their basic units: Atoms and molecules, Law of Chemical Combination, Chemical formula of common compounds, Atomic and molecular masses.
Structure of atoms: Electrons, protons and neutrons, Valency, Atomic Number and Mass Number, Isotopes and Isobars.
Unit II: Organization in the Living World
Cell – Basic Unit of life: Cell as a basic unit of life; prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, multicellular organisms; cell membrane and cell wall, cell organelles and cell inclusions; chloroplast, mitochondria, vacuoles, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus; nucleus, chromosomes – basic structure, number.
Tissues, Organs, Organ System, Organism: Structure and functions of animal and plant tissues (only four types of tissues in animals; Meristematic and Permanent tissues in plants).
Unit III: Motio n, Force, and Work
Motion: Distance and displacement, velocity; uniform and non-uniform motion along a straight line; acceleration, distance-time and velocity-time graphs for uniform motion and uniformly accelerated motion, elementary idea of uniform circular motion.
Force and Newton’s laws: Force and Motion, Newton’s Laws of Motion, Action and Reaction forces, Inertia of a body, Inertia and mass, Momentum, Force and Acceleration.
Gravitation: Gravitation; Universal Law of Gravitation, Force of Gravitation of the earth (gravity), Acceleration due to Gravity; Mass and Weight; Free fall. Floatation: Thrust and Pressure. Archimedes’ Principle; Buoyancy.
Work, Energy and Power: Work done by a Force, Energy, power; Kinetic and Potential energy; Law of conservation of energy (excluding commercial unit of Energy).
Sound: Nature of sound and its propagation in various media, speed of sound, range of hearing in humans; ultrasound; reflection of sound; echo.
Unit IV: Food Production
Plant and animal breeding and selection for quality improvement and management; Use of fertilizers and manures; Protection from pests and diseases; Organic farming.
Books for Class 9 Science Exams

Benefits of Case Study Questions
- Enhancing Analytical Skills : Case study questions challenge students to analyze complex scenarios, identify relevant information, and derive meaningful insights. By engaging with these questions, students develop critical analytical skills that are essential for scientific thinking and problem-solving.
- Promoting Critical Thinking : Case study questions encourage students to think critically and evaluate different perspectives. They require students to reason, make logical deductions, and justify their answers with supporting evidence. This process helps in honing their critical thinking abilities, enabling them to approach problems from multiple angles.
- Encouraging Practical Application of Concepts : By presenting real-world or hypothetical situations, case study questions promote the application of scientific concepts in practical scenarios. This application-based approach fosters a deeper understanding of the subject matter and helps students see the relevance of what they learn in the classroom to everyday life.
Case study questions of Class 9 Science provide students with an opportunity to apply their knowledge, enhance analytical skills, and think critically. By understanding the format, benefits, and effective strategies for answering case study questions, students can excel in this form of assessment. While challenges may arise, practicing time management, improving information extraction skills, and enhancing observation abilities will enable students to overcome these obstacles and perform well. Embracing case study questions as a valuable learning tool can contribute to a holistic understanding of scientific concepts and foster problem-solving abilities.
1. What is the purpose of case study questions in Class 9 Science?
Case study questions serve the purpose of evaluating a student’s understanding of scientific concepts, their ability to apply knowledge in real-life situations, and their analytical and critical thinking skills.
2. How can case study questions help improve analytical skills?
Case study questions require students to analyze complex scenarios, identify relevant information, and derive meaningful insights. Regular practice with such questions can significantly enhance analytical skills.
3. Are case study questions difficult to answer?
Case study questions can be challenging due to their comprehensive nature and the need for critical thinking. However, with practice and effective strategies, students can develop the skills necessary to answer them effectively.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Download India's best Exam Preparation App Now.
Key Features
- Revision Notes
- Important Questions
- Previous Years Questions
- Case-Based Questions
- Assertion and Reason Questions
No thanks, I’m not interested!
- NCERT Solutions
- NCERT Class 9
- NCERT 9 Science
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science
Ncert solutions for class 9 science updated for 2023-24 free chapterwise pdf download.
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science help students to clear any doubts instantly and efficiently. These NCERT Solutions guide students to learn the important concepts which are included in the CBSE Class 9 Science syllabus. Students are required to solve the exercise questions included in the textbook to create a proper understanding of the topics.
While solving the textbook questions, doubts arise among students. The NCERT Solutions for Class 9 come in handy at such times, as they include precise explanations and detailed answers to those questions. These CBSE Science NCERT Solutions for Class 9 cover solutions to all the important chapters included in the textbook, like Matter, Atoms, Tissues, Living Organisms, Motion, Force, Laws of Motion, Gravitation, Energy and Work, Sound, Natural Resources, etc.
Along with answers to the textbook questions, these solutions provide you with extra questions, exemplar problems, the important questions from previous year question papers, sample papers , worksheets, MCQs, short answering questions, descriptive type questions, their solutions, as well as tips and tricks.
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter-Wise PDFs
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science are provided in a format for better accessibility to the students. These solutions serve as an important studying tool for students who are preparing for their board examinations and assignments.

NCERT Solutions of Class 9 Science Book Chapter Brief
Chapter 1: matter in our surrounding.
The Class 9 science textbook starts with the chapter “Matter in Our Surroundings”. Everything that we see around us is made up of material which is called matter. These things occupy space and have mass. Earlier, Indian philosophers had classified matter into 5 basic elements called Panch Tatva – air, water, earth, sky and fire. Now, modern scientists have come up with 2 types of classification, i.e., based on physical property and chemical nature. In this chapter, students will learn about the physical properties of matter .
The matter is made up of particles and these particulars are very small. The particles of matter have space between them, they are continuously moving and attract each other. The matter around us exists in 3 different states – solids, liquids and gases. These states of matter arise due to variation in the characteristic of the particles of matter. All the 3 states of matters have been explained in-depth with the help of activities. Further, the textbook explains that the state of matter is inter-convertible. The state of matter can be changed by changing temperature or pressure. The phenomenon of change of a liquid into vapour at any temperature below its boiling point is called evaporation. The rate of evaporation depends upon the surface area exposed to the atmosphere, the temperature, the humidity and the wind speed. Evaporation also causes cooling.
Topics Covered in Class 9 Science Chapter 1 Matter in Our Surrounding :
Definition of matter; solid, liquid and gas; characteristics – shape, volume, density; change of state – melting (absorption of heat), freezing, evaporation (cooling by evaporation), condensation, sublimation.
Also access the following resources for Class 9 Chapter 1 Matter in Our Surrounding at BYJU’S:
- Matter in Our Surroundings Class 9 Notes – Chapter 1
- CBSE Class 9 Science Chapter 1 Matter in Our Surroundings Important Questions
- NCERT Exemplar Class 9 Science Solutions for Chapter 1 – Matter in Our Surroundings
Chapter 2: Is Matter Around Us Pure?
This chapter of NCERT Class 9 Science students will teach about mixtures, solutions, properties of solutions, separation of mixtures, and physical and chemical changes. Along with this, they will also learn about compounds and their properties, the difference between mixtures and compounds, the classification of matter, etc.
Topics Covered in Class 9 Science Chapter 2 Is Matter Around Us Pure? :
Nature of matter: Elements, compounds and mixtures. Heterogeneous and homogenous mixtures, colloids and suspensions. Physical and chemical changes (excluding separating the components of a mixture).
Also, access the following resources for Class 9 Chapter 2 Is Matter Around Us Pure? at BYJU’S:
- CBSE Class 9 Science Chapter 2 Is Matter Around Us Pure? Notes
- Important Questions for CBSE Class 9 Science Chapter 2 – Is Matter Around Us Pure?
- NCERT Exemplar Class 9 Science Solutions for Chapter 2 – Is Matter Around Us Pure?
Chapter 3: Atoms and Molecules
In NCERT Class 9 Science Chapter 3, students will learn the laws of chemical combination , atoms and molecules. They will get to know how to write a chemical formula, molecular mass and mole concepts and some numerical problems related to these concepts.
Topics Covered in Class 9 Science Chapter 3 Atoms and Molecules :
Particle nature and their basic units: Atoms and molecules, Law of Chemical Combination, Chemical formula of common compounds, Atomic and molecular masses.
Also, access the following resources for Class 9 Chapter 3 Atoms and Molecules, at BYJU’S:
- Atoms And Molecules Class 9 Notes – Chapter 3
- Important Questions for Class 9 Science Chapter 3 – Atoms and Molecules
- NCERT Exemplar Class 9 Science Solutions for Chapter 3 – Atoms And Molecules
Chapter 4: Structure of the Atom
This chapter of NCERT Class 9 Science deals with the various atomic models of atoms that were proposed by different scientists. In addition to it, this chapter also covers electrons’ distribution in different orbits, calculation of valency , atomic number and mass number.
Topics Covered in Class 9 Science Chapter 4 Structure of the Atom :
Structure of atoms: Electrons, protons and neutrons, Valency, Atomic Number and Mass Number, Isotopes and Isobars.
Also, access the following resources for Class 9 Chapter 4 Structure of the Atom at BYJU’S:
- Structure of the Atom Class 9 CBSE Notes – Chapter 4
- Important Questions of CBSE Class 9 Science Chapter 4 – Structure of the Atom
- NCERT Exemplar Class 9 Science Solutions for Chapter 4 – Structure of the Atom
Chapter 5: The Fundamental Unit of Life
This chapter is related to Biology. In this chapter, students will get to know that the cell is the fundamental unit of life. The whole chapter revolves around the cell and its structural organisation, in which students will learn about the plasma membrane , cell wall, nucleus, cytoplasm and structure of an animal cell.
Topics Covered in Class 9 Science Chapter 5 The Fundamental Unit of Life :
Cell – Basic Unit of life: Cell as a basic unit of life; prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, multicellular organisms; cell membrane and cell wall, cell organelles and cell inclusions; chloroplast, mitochondria, vacuoles, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus; nucleus, chromosomes – basic structure, number.
Also, access the following resources for Class 9 Chapter 5 The Fundamental Unit of Life at BYJU’S:
- The Fundamental Unit of Life Class 9 CBSE Notes – Chapter 5
- Revision Notes For Class 9 Science Chapter 5 The Fundamental Unit of Life
- NCERT Exemplar Class 9 Science Solutions for Chapter 5 – The Fundamental Unit of Life
Chapter 6: Tissues
This chapter pertains to the basic definition of tissue and then elaborates on Plant and Animal tissue with proper diagrams. Students will get to know the different types of plant and animal tissues with a detailed explanation of each.
Topics Covered in Class 9 Science Chapter 6 Tissues :
Tissues, Organs, Organ System, Organism: Structure and functions of animal and plant tissues (only four types of tissues in animals; Meristematic and Permanent tissues in plants).
Also, access the following resources for Class 9 Chapter 6 Tissues at BYJU’S:
- Tissues Class 9 CBSE Notes – Chapter 6
- Revision Notes For Class 9 Science Chapter 6 Tissues
- NCERT Exemplar Class 9 Science Solutions for Chapter 6 – Tissues
Chapter 7: Diversity in Living Organism
This chapter deals with the classification of plants and animals. Students get to know that all living organisms are divided into 5 kingdoms namely Monera, Protista, Fungi, Plantae and Animalia. It also describes the classification and evolution, the hierarchy of classification.
Also access the following resources for Class 9 Chapter 7 Diversity in Living Organism at BYJU’S:
- Diversity in Living Organisms Class 9 CBSE Notes – Chapter 7
- Important Questions for CBSE Class 9 Science Chapter 7 – Diversity in Living Organisms
- NCERT Exemplar Class 9 Science Solutions for Chapter 7 – Diversity In Living Organisms
Chapter 8: Motion
NCERT Class 9 Science Chapter 8 describes motion, the speed with direction, rate of change of velocity , and graphical representation of motion. Also, students will find the 3 equations of motion and numerical problems related to them. Overall, this chapter will be a mix of theory as well as the numerical part.
Topics Covered in Class 9 Science Chapter 8 Motion :
Motion: Distance and displacement, velocity; uniform and non-uniform motion along a straight line; acceleration, distance-time and velocity-time graphs for uniform motion and uniformly accelerated motion, elementary idea of uniform circular motion.
Also, access the following resources for Class 9 Chapter 8 Motion at BYJU’S:
- CBSE Class 9 Physics Motion Notes
- NCERT Exemplar Class 9 Science Solutions for Chapter 8 – Motion
Chapter 9: Force and Law of Motion
This chapter explains the 3 laws of motion with the help of diagrams and examples. Below are the 3 laws of motion:
- First law of motion: An object continues to be in a state of rest or of uniform motion along a straight line unless acted upon by an unbalanced force.
- Second law of motion: The rate of change of momentum of an object is proportional to the applied unbalanced force in the direction of the force .
- Third law of motion: To every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction, and they act on two different bodies.
Topics Covered in Class 9 Science Chapter 9 Force and Law of Motion :
Force and Newton’s laws: Force and Motion, Newton’s Laws of Motion, Action and Reaction forces, Inertia of a body, Inertia and mass, Momentum, Force and Acceleration.
Also, access the following resources for Class 9 Chapter 9 Force and Law of Motion at BYJU’S:
- Force and Laws Of Motion Class 9 CBSE Notes – Chapter 9
- Revision Notes For Class 9 Science Chapter 9 Force and Laws of Motion
- NCERT Exemplar Class 9 Science Solutions for Chapter 9 – Force and Laws Of Motion
Chapter 10: Gravitation
In chapter 10 of NCERT Class 9 Science, students will learn the universal law of gravitation and its importance, free fall, mass, weight, thrust and pressure, Archimedes’ principle and relative density. Students will also find numerical problems related to these topics.
Topics Covered in Class 9 Science Chapter 10 Gravitation :
Gravitation: Gravitation; Universal Law of Gravitation, Force of Gravitation of the earth (gravity), Acceleration due to Gravity; Mass and Weight; Free fall.
Floatation: Thrust and Pressure. Archimedes’ Principle; Buoyancy.
Also, access the following resources for Class 9 Chapter 10 Gravitation at BYJU’S:
- Gravitation Class 9 CBSE Notes – Chapter 10
- Revision Notes For Class 9 Science Chapter 10 Gravitation
- NCERT Exemplar Class 9 Science Solutions for Chapter 10 – Gravitation
Chapter 11: Work and Energy
In this chapter, the concept of work is defined with different activities, numerical and examples. The chapter also deals with energy and its different forms. Examples are given to explain all types of energy. The chapter ends with the topic “rate of doing work”.
Topics Covered in Class 9 Science Chapter 11 Work and Energy :
Work, Energy and Power: Work done by a Force, Energy, power; Kinetic and Potential energy; Law of conservation of energy (excluding commercial unit of Energy).
Also, access the following resources for Class 9 Chapter 11 Work and Energy at BYJU’S:
- Work And Energy Class 9 CBSE Notes – Chapter 11
- Revision Notes For Class 9 Science Chapter 11 Work and Energy
- NCERT Exemplar Class 9 Science Solutions for Chapter 11 – Work And Energy
Chapter 12: Sound
Chapter 12 of CBSE Class 9 Science, deals with concepts such as the production of sound, propagation of sound, the reflection of sound, range of hearing, applications of ultrasound, and the structure of the human ear . A few numericals are also there in the chapter which can only be solved after understanding the concepts. So, students must grasp and study the chapter carefully.
Topics Covered in Class 9 Science Chapter 12 Sound :
Sound: Nature of sound and its propagation in various media, speed of sound, range of hearing in humans; ultrasound; reflection of sound; echo.
Also access the following resources for Class 9 Chapter 12 Sound at BYJU’S:
- CBSE Class 9 Science Chapter 12 Sound Notes
- Important Questions for CBSE Class 9 Science Chapter 12 – Sound
- NCERT Exemplar Class 9 Science Solutions for Chapter 12 – Sound
Chapter 13: Why Do We Fall Ill?
NCERT Class 9 Science chapter 13 deals with health issues and different types of diseases. It covers topics like; Health and its failure , disease and its cause, infectious diseases. This chapter is added to make students aware of different types of diseases so that they take care of their health and be fit and healthy.
Also access the following resources for Class 9 Chapter 13 Why Do We Fall Ill? at BYJU’S:
- Why Do We Fall Ill? Class 9 CBSE Notes – Chapter 13
- Important Questions for CBSE Class 9 Science Chapter 13 – Why Do We Fall Ill?
- NCERT Exemplar Class 9 Science Solutions for Chapter 13 – Why Do We Fall Ill?
Chapter 14: Natural Resources
We are blessed with natural resources. These are essential to meet the basic requirements of all forms of life on Earth. So, this chapter has been included by NCERT to provide knowledge on the types of resources available on the Earth. This chapter deals with the topics like air, water, soil, the biogeochemical cycle and the ozone layer, its importance and how humans are polluting them.
Also access the following resources for Class 9 Chapter 14 Natural Resources at BYJU’S:
- Natural Resources Class 9 CBSE Notes – Chapter 14
- Revision Notes For Class 9 Science Chapter 14 Natural Resources
- NCERT Exemplar Class 9 Science Solutions for Chapter 14 – Natural Resources
Chapter 15: Improvement in Food Resources
The last chapter of NCERT Class 9 Science covers topics like Improvement in crop yields, manure, fertilizer, storage of grains, and animal husbandry . This chapter provides knowledge regarding agriculture, farming and dairy.
Also access the following resources for Class 9 Chapter 15 Improvement in Food Resources at BYJU’S:
- Improvement in Food Resources Class 9 CBSE Notes – Chapter 15
- Important Questions for CBSE Class 9 Science Chapter 15 – Improvement in Food Resources
- Revision Notes For Class 9 Science Chapter 15 Improvement in Food Resources
- NCERT Exemplar Class 9 Science Solutions for Chapter 15 – Improvement In Food Resources
To download the complete book in PDF format, visit NCERT Science Book Class 9 . For more practice tests and mock tests, sign up on BYJU’S the learning app. Apart from Science, get NCERT Solutions for all the subjects. Students can download worksheets, assignments, NCERT Books , notes and study materials for exam preparation and for a better understanding of the topics.
CBSE Class 9 Science Evaluation Scheme (Theory) –
Features of ncert 9 th class science book solutions.
The book has a wide variety of features which are listed below:
- CBSE Class 9 Science NCERT Solutions are available to everyone for free.
- Covers all the exercise problems from the Class 9 textbook.
- Consists of extra questions, exemplar problems, the important questions from previous year question papers and sample papers, worksheets, MCQs, short answering questions, descriptive type questions, their solutions and tips and tricks.
- CBSE Class 9 Science Solutions files are available for download in PDF format for easy access.
- Diagrams are included to help students visualize the topics.
- Most effective solutions are given which can help to score well in the exams.
Frequently Asked Questions on NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science
How many chapters are there in the ncert solutions for class 9 science , can i expect the questions from ncert solutions for class 9 science to be asked in the annual exam, is the ncert solutions for class 9 science sufficient for the exam preparation, why should students refer to the ncert solutions for class 9 science , leave a comment cancel reply.
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
Very good app
I am a subscriber and my feedback is that it really helped me to understand how the question’s answers came. Thank you Byju’s
Very nice app
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.

- Book Solutions
- State Boards
Case Study Questions Class 9 Science Motion
Case study questions class 9 science chapter 8 motion.
CBSE Class 9 Case Study Questions Science Motion. Important Case Study Questions for Class 9 Exam. Here we have arranged some Important Case Base Questions for students who are searching for Paragraph Based Questions Motion.
At Case Study Questions there will given a Paragraph. In where some Questions will made on that respective Case Based Study. There will various types of marks will given 1 marks, 2 marks, 3 marks or 4 marks.
CBSE Case Study Questions Class 9 Science – Motion
(1) Distance and displacement are two quantities that seem to mean the same but are different with different meanings and definitions. Distance is the measure of “how much distance an object has covered during its motion” while displacement refers to the measure of“how far the abject actually from initial place.” using this data answer following questions.
(i)Which of the following relation is always true when object moves in straight line
(a)distance is always equal to displacement
(b)distance is always greater than or equal to displacement
(c)distance is always lesser than or equal to displacement
(d)none of the above
(ii) Kapiltravels 20 km to North but then come back to South for 40 km to pick up a friend. Whatis kapil’s total distance?
(d) none of the above
(iii) Rahul travels 20 km to East but then come back to West for 10 km. Find displacement.
(iv) Define distance and displacement of particle.
(v) Write difference between distance and displacement
Answer key -1
(iv) Distance and displacement are two quantities that seem to mean the same but are different with different meanings and definitions. Distance is the measure of “how much distance an object has covered during its motion” while displacement refers to the measure of “how far the abject actually from initial place.”
(v) difference between distance and displacement is given by
(2 ) Answer the following questions by observing following diagram

(i ) What is distance and displacement when particle moves from point A to B?
(a)distance is equal to displacement
(b)distance is greater than and equal to displacement
(c)distance is lesser than and equal to displacement
(ii)What is Displacement when particle moves from point A to D?
(iii) What is Displacement when particle moves from point A to C through A-B-C?
(c) 10√2 km
(iv) Find distance covered when particle moves in path ABCDA i.e. starts from A and ends at A?
(v) Find Displacement covered when particle moves in path ABCDA i.e. starts from A and ends at A?
ANSWER KEY-2
(3) The speed of an object is the distance covered per unit time,and velocity is the displacement per unit time.To specify the speed of anobject, we require only its magnitude while Velocity is the speed of an object moving in adefinite direction.
(i) S.I unit of speed is
(d) none of these
(ii) Which of the following is true
(a)speed is scalar
(b)velocity is vector
(c)both a and b
(d)none of these
(iii) To specify speed we require
(a)magnitude
(b)direction
(c)both magnitude and direction
(iv) Define speed and velocity of particle.
(v)Differentiate between speed and velocity.
Answer key-3
(iv)The speed of an object is the distance covered by object per unit time.Velocity is defined as the displacement by particle per unit time.
(v) Difference between speed and velocity.
(4) The speed of an object need not be constant. In most cases, objects will be in non-uniform
motion. Thereforewe describe the rate of motion of such objects in terms of their average speed. The average speed of an object is obtained by dividing the total distance travelled by the total time taken. That is, average speed =total distance travelled / total time taken. Answer the following.
(i)An object travels 20 m in 5 s and then another 20 m in 5s. What is the average speed in m/s of the object?
(d) None of these
(ii) An object travels 20 m in 5 s and then another 40 m in 5s. What is the average speed in m/s of the object?
(d)None of these
(iii)A man starts walking from a point P on a circular field of radius 7 km and after 1 hour later he comes to same point P after one complete round. find his speed. (take pi=22/7)
(a) 30km/hr
(b) 40km/hr
(c) 44km/hr
(d) 33km/hr
(iv) A man travelled on square field of side 10m .he completed one round of field by taking time 2s, 3s 1s and 2s respectively for each side. Find his average speed.
(v) Define average speed.write its formula and SI unit
Answer key-4
(v) The average speed of an object is obtained by dividing the total distance travelled by the total time taken. That is, average speed =total distance travelled / total time taken.Its SI unit is given by m/s.
(5) We know that the circumference of a circle of radius r is given by . If the body takes
t seconds to go once around the circular path of radius r, the speed v is given by
When an object moves in a circular path with uniform speed, its motion is called
uniform circular motion. Refer the paragraph and answer the following questions
(i) What happens when a body is moving with constant speed?
(a)acceleration is non uniform
(b)velocity is uniform
(c)velocity is changing
(ii) Cyclist on circular track with constant speed is example of
(a)uniform circular motion
(b)nonuniform circular motion
(iii) Which of the following changes whenbody performsuniform circular motion?
(b)direction of velocity
(iv) Define uniform circular motion. Give 2 examples of uniform circular motion
(v) Give the name of device used for measurement of speed of rotation
Answer key -5
(iv) When an object moves in a circular path with uniform speed, its motion is calleduniform circular motion. Rotation of hour hand of clock and motion of fan at constant speed are examples of uniform circular motion.
(v) Odometers and speedometers are two of the many instruments used to measure speed of rotation.
Plz put more difficult these all are very much easy.
But all over excellent
Yes we have think also it. This year we will put more hard.
A bit hard question may be helpful
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
We have a strong team of experienced Teachers who are here to solve all your exam preparation doubts
West bengal board class 6 solution, samacheer kalvi, assertion and reason questions class 7 maths chapter 2 fractions and decimals, assertion and reason questions class 7 maths chapter 1 integers.
Sign in to your account
Username or Email Address
Remember Me

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Class 9 science case study question 1. Read the passage and answer any four questions: Gases are highly compressible as compared to solids and liquids. The liquefied petroleum gas (LPG) cylinder that we get in our home for cooking or the oxygen supplied to hospitals in cylinders is compressed gas.
Case Study Questions for Class 9 Science Chapter 1 Matter in Our Surroundings. Here we are providing case study questions for class 9 science chapter 12 sound. Students are suggested to go through each and every case study questions for better understanding of the chapter. Case Study/Passage Based Questions: Question 1:
Class 9th Science - Motion Case Study Questions and Answers 2022 - 2023. QB365 provides a detailed and simple solution for every Possible Case Study Questions in Class 9th Science Subject - Motion, CBSE. It will help Students to get more practice questions, Students can Practice these question papers in addition to score best marks.
This article aims to present a comprehensive collection of case study questions for Class 9 Science, covering various topics and concepts. Join our Telegram Channel, there you will get various e-books for CBSE 2024 Boards exams for Class 9th, 10th, 11th, and 12th. CBSE Class 9 Science Exam will have a set of questions based on case studies in ...
At Case Study Questions there will given a Paragraph. In where some Questions will made on that respective Case Based Study. There will various types of marks will given 1 marks, 2 marks, 3 marks or 4 marks. CBSE Case Study Questions Class 9 Science - Matter in our Surroundings Case Study 1: 1.) A matter is anything that has mass and occupies ...
July 30, 2022 July 30, 2022 Physics Gurukul 1 Comment on Case Study Questions for Class 9 Science Chapter 15 Improvement In Food Resources. ... Case Study Questions for Class 9 Science Chapter 1 Matter in Our Surroundings; An Imperial Capital - Vijayanagara Assertion Reason Questions for CBSE Class 12 History Chapter 7 ...
Lakhmir Singh Solutions for Class 9 Physics Chapter 1 Motion are provided here, which can be downloaded in PDF for free. Motion is defined as the movement of an object from one place to another. When an object moves along a straight line, the motion is known as rectilinear motion. Distance, displacement, uniform motion, non-uniform motion ...
Case Study Based Questions Class 9 Science | Motion MCQs(Physics) | NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 8 | CBSE Class 9 Physics. Hey Students, We kn...
NCERT Solution of class 9 Science chapter 1 has been created, keeping in mind the primary goal of helping students to secure more marks and improve grades. The academic requirements and needs of students have been addressed in the solution for class 9 Science chapter 1. The topics in chapter 1 related to Matter in Our Surrounding are discussed according to the CBSE syllabus.
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Physics Chapterwise. Class 9 Physics Chapter 1 - Motion. Class 9 Physics Chapter 2 - Force And Laws Of Motion. Class 9 Physics Chapter 3 - Gravitation. Class 9 Physics Chapter 4 - Work and Energy. Class 9 Physics Chapter 5 - Sound.
Case 3: (3)The second law of motion is quantitative expression of force and it states that the rate of change of momentum of an object isproportional to the applied unbalanced force in the direction of force.Mathematically, F = ma, the unit of force is kg-m/s 2 or Newton,which has the symbol N. The second law ofmotion gives us a method to measure the force acting on an object as a product of ...
by experts. Download PDF Case Study Questions of Class 9 Science to prepare for the upcoming CBSE Class 9 Exams Exam 2023-24. With the help of our well-trained and experienced faculty, we provide solved examples and detailed explanations for the recently added Class 9 Science case study questions. Case study questions are based on real or ...
CBSE Case Study Questions Class 9 Science - Gravitation. Case 1: (1) Every object in the universe attracts every other object with a force which is proportional to the product of their masses (m1*m2) and inversely proportional to the square of the distance (d 2) between them. The force is along the line joining the centers of two objects.
1. A car travels a distance of 100 km in 2 hours. (a) Its average speed is 50 km/h. (b) The car did not travel at 50 km/h all the time. (c) The car travelled 50 km/h all the time. (d) all of the above. 2. If an object's speed and direction of motion changes. Then it is moving with.
Maths Case-Study Qs. Maths Case-Study Qs. VIEW ALL. TopperLearning offers an online platform to access case studies for CBSE Class 9 students. Explore your analytical and problem-solving skills by solving case studies with our expert guidance. Get started today!
Case Study/Passage Based Questions: Question 1: Read the following and answer any four questions from (i) to (v) given below : In the figure below the card is flicked with a push. It was observed that the card moves ahead while coin falls in glass. (i) Give reason for the above observation.(a) The coin possesses … Continue reading Case Study and Passage Based Questions for Class 9 Science ...
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science, latest edition, is available in PDF format, which can easily be downloaded. All questions are solved in detail and given here in a chapter-wise format. Visit BYJU'S to download the free NCERT Solutions Class 9 Science 2023-24 PDF.
CBSE Case Study Questions Class 9 Science - Motion. (1) Distance and displacement are two quantities that seem to mean the same but are different with different meanings and definitions. Distance is the measure of "how much distance an object has covered during its motion" while displacement refers to the measure of"how far the abject ...
There is Case Study Questions in class 12 Physics in session 2020-21. The first two questions in the board exam question paper will be based on Case Study and Assertion & Reason. Case Study Questions will have 5 MCQs out of which students will have to attempt any 4 questions. Here are the questions based on case study. Case Study Question 1:
Class 9 Science NCERT Solutions is given here. Students can click on the links of the particular chapter for which they are finding the solutions. Chapter 1 Matter in Our Surroundings. Chapter 2 Is Matter Around Us Pure. Chapter 3 Atoms and Molecules. Chapter 4 Structure of the Atom. Chapter 5 The Fundamental Unit of Life.
Question 1: Read the following and answer any four questions from (i) to (iv) given below : Sound bounces off a solid or a liquid like a rubber ball bounce off a wall. Like the light, sound gets reflected at the surface of a solid or liquid and follows the same laws of reflection. The directions in which the sound is incident and is reflected ...
Case Study/Passage Based Questions: Question 1: Read the following paragraph and any four questions from (i) to (v). Distance is the length of the actual path covered by an object, irrespective of its direction of motion. Displacement is the shortest distance between the initial and final positions of an object in a given direction.
Case Study Questions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 1 Real Numbers. Case Study Questions: Question 1: Himanshu has made a project on real numbers, where he finely explained the applicability of exponential laws and divisibility conditions on real numbers. He also included some assessment questions at the end of his project as listed below.