

Case Study Questions Class 10 Science Chapter 8 How Do Organisms Reproduce
- Post author: studyrate
- Post published:
- Post category: class 10th
- Post comments: 0 Comments
Case study Questions Class 10 Science Chapter 8 are very important to solve for your exam. Class 10 Science Chapter 8 Case Study Questions have been prepared for the latest exam pattern. You can check your knowledge by solving case study-based questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 8 How Do Organisms Reproduce
Join our Telegram Channel, there you will get various e-books for CBSE 2024 Boards exams for Class 9th, 10th, 11th, and 12th.

In CBSE Class 10 Science Paper, Students will have to answer some questions based on Assertion and Reason . There will be a few questions based on case studies and passage-based as well. In that, a paragraph will be given, and then the MCQ questions based on it will be asked.
How Do Organisms Reproduce Case Study Questions With Answers
Here, we have provided case-based/passage-based questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 8 How Do Organisms Reproduce
Case Study/Passage-Based Questions
Question 1:
The male reproductive system consists of portions that produce the germ cells and other portions that deliver the germ cells to the site of fertilization. Testes are located outside the abdominal cavity in the scrotum because sperm formation requires a lower temperature than normal body temperature. It also has a role of secretion of male sex hormone which brings changes in appearance seen in boys at the time of puberty. Vas deferens unites with a tube coming from the urinary bladder. The urethra is a common passage for sperms and urine. The prostate gland and seminal vesicles add their secretions so that sperms are now in a fluid.

(i) Name the sex hormone associated with males. (a) Testosterone (b) Progesterone (c) Oestrogen (d) None of these
Answer: (a) Testosterone
(ii) Which of the following statements is incorrect ? (a) Sperms are present in a fluid (b) Fluid provides nutrition to sperms (c) Fluid makes easier transportation of sperms (d) Fluid helps to bind the sperms together
(iii) Testes are located outside the abdominal cavity in scrotum because (a) sperms formation requires higher temperature than body temperature (b) sperms formation requires lower temperature than body temperature (c) it is easier to transport sperms from the scrotum (d) None of these
Answer: (b) sperms formation requires lower temperature than body temperature
(iv) Which of the following statement is incorrect? (a) Sperms and urine has a common passage from urethra.
(b) Sperms have long tail that helps them to move forward. (c) Sperms contain genetic material. (d) Sperms formation requires 1–3°C higher temperature than normal body temperature.
Answer: (d) Sperms formation requires 1–3°C higher temperature than normal body temperature.
(v) What is the nature of semen? (a) slightly acidic (b) Neutral (c) Slightly basic (d) Strongly basic
Answer: (c) Slightly basic
Question 2:
Rohit collected some pond water which was dark green in color in a test tube. She took out green-colored mass from it and separated its filaments by using needles. She broke some filaments into small fragments and put them in a Petri dish containing clean water. She observed that after a few days the small fragments gave rise to complete filaments.
2.1) What do you think the mass of green filament was ? (a) It was a mass of Spirogyra filament. (b) It was a colony of Volvox algae. (c) It was large brown algae. (d) It was a mass of fungal filaments
Answer:(a) It was a mass of Spirogyra filament.
2.2) Organisms that reproduces in similar ways as Spirogyra is : (a) yeast (b) hydra (c) Planaria (d) Sea anemone
Answer: (d) Sea anemone
2.3) The small fragment gave rise to new filament. What does it indicate ? (a) Spirogyra reproduces asexually through budding. (b) Spirogyra reproduces asexually through spore formation. (c) Spirogyra reproduces asexually through fragmentation. (d) Spirogyra reproduces asexually through fission
Answer: (c) Spirogyra reproduces asexually through fragmentation.
2.4) Which among the following organisms do not reproduce by fragmentation ? (a) Riccia (b) Selaginella (c) Aurelia (d) Marchantia
Answer: (c) Aurelia.
2.5) Select the correct statement from the following. (a) Only multicellular organisms can undergo fragmentation. (b) Both unicellular and multicellular organisms can undergo fragmentation. (c) Fragmentation is sexual mode of reproduction. (d) Fragmentation is found only in algae
Answer: (a) Only multicellular organisms can undergo fragmentation
Question 3:
In humans, if the egg is not fertilized, it lives for about one day. Since the ovary releases one egg every month, the uterus also prepares itself every month to receive a fertilized egg. Thus its lining becomes thick and spongy. This would be required for nourishing the embryo if fertilization had taken place. Now, however, this lining is not needed any longer. So, the lining slowly breaks and comes out through the vagina as blood and mucous. This cycle takes place roughly every month and is known as menstruation. It usually lasts for about two to eight days.
3.1) What is the sexual cycle in human female that takes place every 28 days and marked by bleeding ? (a) Sexual cycle (b) Reproductive cycle (c) Menstrual cycle (d) Blood cycle
Answer: (c) Menstrual cycle
3.2) If fertilisation takes place, it results in the formation of : (a) an embryo (b) a zygote (c) a foetus (d) a placenta
Answer: (b) a zygote
3.3) Why does vaginal bleeding occur in human females on attaining puberty ? (a) Unfertilised egg along with thick uterus lining come out of vagina in form of bleeding. (b) In human females, ovaries start releasing egg or ovum once every 28 days from the age of puberty. (c) If fertilisation does not occur then menstrual flow occurs at the end of cycle. (d) All of these
Answer: (d) All of these
3.4) In what conditions vaginal bleeding will not occur in a human female who has attained puberty ? (a) If the ovum is fertilised (b) If the ovum is not fertilised (c) If there is some hormonal imbalance in female (d) Both (a) and (b)
Answer: (d) Both (a) and (b)
3.5) Mark one change from the following associated with sexual maturation in boys ? (a) loss of milk teeth (b) weight gain (c) increase in height (d) cracking of voice
Answer: (d) cracking of voice
Question 4: A newly married couple does not want have children for few years. They consulted a doctor who advised them barrier method and chemical method of birth control. Yet another couple who already have two children and are middle aged also consulted doctor for some permanent solution to avoid unwanted pregnancy. Doctor advised them surgical method of birth control.
Another category of contraceptives acts by changing the hormonal balance of the body so that eggs are not released and fertilisation cannot occur. These drugs commonly need to be taken orally as pills. However, since they change hormonal balances, they can cause side-effects too. Other contraceptive devices such as the loop or the copper-T are placed in the uterus to prevent pregnancy. Again, they can cause side effects due to irritation of the uterus.
4.1) What are the barrier methods of birth control ? (a) Condoms (b) Oral pills (c) Surgery (d) Both (a) and (c)
Answer: (a) Condoms
4.2) How physical barrier prevent pregnancy ? (a) They kill the sperms. (b) They kill the ovum. (c) They prevent intercourse. (d) They prevent fertilisation
Answer: (d) They prevent fertilisation.
4.3) How chemical methods prevent pregnancy ? (a) Vaginal pills contain chemical called spermicides which kill the sperms. (b) Oral pills prevent ovulation so there will be no fertilisation. (c) Oral pills stop menstruation in females. (d) Both (a) and (b)
Answer: (d) Both (a) and (b)
4.4) Select the correct statement regarding surgical method of birth control. (a) It involves termination of pregnancies in women particularly after eight weeks of conception. (b) Small portion of sperm duct or vas deferences in males is removed by surgical operation and both cut ends are ligated properly. (c) Small portion of oviducts in females is removed by surgical operation and cut ends are ligated. (d) Both (b) and (c)
Answer: (d) Both (b) and (c)
4.5) Select the correct statement regarding birth control methods. (a) Barrier method of birth control also protects the couple from sexually transmitted diseases. (b) Some women experience unpleasant side effects on taking oral pills because of change in hormonal balance in body. (c) Surgical method in males is called vasectomy and in females is called tubectomy. (d) All of these
Answer: (d) All of these
Hope the information shed above regarding Case Study and Passage Based Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 8 How do Organisms Reproduce with Answers Pdf free download has been useful to an extent. If you have any other queries of CBSE Class 10 Science How do Organisms Reproduce Case Study and Passage Based Questions with Answers, feel free to comment below so that we can revert back to us at the earliest possible. By Team Study Rate
You Might Also Like
Assertion reason questions class 10 science chapter 5 periodic classification of elements, extra questions of class 10 social science geography chapter 2 forests and wildlife resources pdf download, case study questions class 10 science chapter 9 heredity and evolution, leave a reply cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

- Book Solutions
- State Boards
Case Study Questions Class 10 Science How do Organisms Reproduce
Case study questions class 10 science chapter 8 how do organisms reproduce.
CBSE Class 10 Case Study Questions Science How do Organisms Reproduce. Important Case Study Questions for Class 10 Board Exam Students. Here we have arranged some Important Case Base Questions for students who are searching for Paragraph Based Questions How do Organisms Reproduce.
At Case Study Questions there will given a Paragraph. In where some Important Questions will made on that respective Case Based Study. There will various types of marks will given 1 marks, 2 marks, 3 marks, 4 marks.
CBSE Case Study Questions Class 10 Science How do Organisms Reproduce
Case study : 1.
When a girl is born, the ovaries already contain thousands of immature eggs. On reaching puberty, some of these start maturing. One egg is produced every month by one of the ovaries. The egg is carried from the ovary to the womb through a thin oviduct or fallopian tube. The two oviducts unite into an elastic bag-like structure known as the uterus. The uterus opens into the vagina through the cervix.
I) What is fertilization?
Ans: The fusion of male gametes(sperms) and the female gametes(egg) to form zygote is called fertilization.
ii) Where does fertilization occur?
Ans: Fertilization occur in the oviduct or Fallopian tube.
iii) What is placenta?
Ans: It is an special tissue which provide nutrition from mother’s blood to developing embryo.
iv) What are the different parts of female reproductive system?
Ans: Fallopian tube, ovary, uterus, vagina and cervix.
v) What happens when egg is not fertilized?
Ans: If the egg is not fertilized, the thick lining of uterus is not needed. So, it breaks slowly and comes out through vagina as blood and vagina, which is called as menstruation.
CASE STUDY : 2
The reproductive parts of angiosperms are located in the flower. You have already studied the different parts of a flower – sepals, petals, stamens and pistil. Stamens and pistil are the reproductive parts of a flower which contain the germ-cells.The flower may be unisexual (papaya, watermelon) when it contains either stamens or pistil or bisexual (Hibiscus, mustard) when it contains both stamens and pistil.
I) What is the male reproductive parts of flower?
Ans: Stamen is the male reproductive part of flower and it consist of anther and filament.
ii) What are the different part of pistil?
Ans: Stigma, style and ovary.
iii) What is pollination?
Ans: The transfer of pollen grains from the stamen to the stigma of flower is called pollination.
iv) Where does fertilization occur in flower?
Ans: The fertilization takes place inside the ovule.
v) What are the two types of pollination?
Ans: Self pollination and cross pollination.
CASE STUDY : 3
There are many plants in which parts like the root, stem and leaves develop into new plants under appropriate conditions. Unlike in most animals, plants can indeed use such a mode for reproduction. This property of vegetative propagation is used in methods such as layering or grafting to grow many plants like sugarcane, roses, or grapes for agricultural purposes
I) What are the advantages of vegetative propagation?
Ans: • All plants that are produced by such method are genetically similar to their parent and have all its characteristics. easy, less expensive and a fast method.
ii) Give a example of vegetative propagation through buds?
Ans: Bryophyllum
iii) What is tissue culture?
Ans: New plants are grown first in suitable artificial medium and then placing it in the soil to grow into mature plants.
iv) What is grafting?
Ans: New plants are grown by joining a scion(upper portion of plant) to a stock of other plants in such a manner that they get united to each other.
v) What are the example of layering?
Ans: Jasmine or grapevine
CASE STUDY: 4
Chromosomes in the nucleus of a cell contain information for inheritance of features from parents to next generation in the form of DNA (Deoxyribo Nucleic Acid) molecules. The DNA in the cell nucleus is the information source for making proteins. If the information is changed, different proteins will be made. Different proteins will eventually lead to altered body designs. Therefore, a basic event in reproduction is the creation of a DNA copy. Cells use chemical reactions to build copies of their DNA.
1) What is the importance of variation?
Ans: Variation is important for the survival of species over time. Variation make the species resistant to the changing environment and hence, it make easy for their survival.
ii) Which mode of reproduction does not show much variation?
Ans: Generally, asexual reproduction show less variation which includes budding, fragmentation, fission etc.
iii) What are the different modes of reproduction of single celled organism?
Ans: Fission, fragmentation, Budding and regeneration.
iv) What are the features of sexual reproduction?
Ans: It includes both the parents to produce offsprings and DNA copy is a crucial part of it.
v) Which mode of reproduction is better and why?
Ans: Sexual reproduction is better than asexual reproduction as the chances of survival of the species is higher in sexual reproduction.
CASE STUDY : 5
The sexual act always has the potential to lead to pregnancy. Pregnancy will make major demands on the body and the mind of the woman, and if she is not ready for it, her health will be adversely affected. Therefore, many ways have been devised to avoid pregnancy.
1) What are the different methods to prevent pregnancy?
Ans: Uses of contraceptive such as condoms, pills, copper -T and surgical methods.
ii) What are the surgical methods to prevent pregnancy?
Ans: Tubectomy in females and vasecotomy in males.
iii) Why the female sex ratio is declining day by day?
Ans: Due to female foeticides by doing illegal sex selective abortion of female foetuses.
iv) Which contraceptive methods have large side effects?
Ans: Oral pills and by changing the hormonal balance leads to high side effect.
v) Why should one have the knowledge about sexual act and the disease causing by it?
Ans: To stay healthy and free free from sexually transmitted disease one should be aware of the disease cause by bacteria and viruses such as gonorrhoea, syphilis and HIV- AIDS.
For more update follow net explanations page
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
We have a strong team of experienced Teachers who are here to solve all your exam preparation doubts
Amader poribesh class 4 solutions chapter 10 sthapotya, bhaskorjo o songrohoshala, seba board solution class 9 10 english grammar chapter 16 transformation of sentences, amader poribesh class 4 solutions chapter 9 adhunik sovvota o poribesher songrokkhon.

WBBSE Class 10 Notes on Ammonia from Inorganic Chemistry
Sign in to your account
Username or Email Address
Remember Me

Gurukul of Excellence
Classes for Physics, Chemistry and Mathematics by IITians
Join our Telegram Channel for Free PDF Download
Case Study and Passage Based Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 8 How Do Organisms Reproduce
- Last modified on: 1 year ago
- Reading Time: 5 Minutes
Case Study Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 8 How Do Organisms Reproduce
In CBSE Class 10 Science Paper, Students will have to answer some questions based on Assertion and Reason . There will be a few questions based on case studies and passage based as well. In that, a paragraph will be given, and then the MCQ questions based on it will be asked.
Here, we have provided case based/passage based questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 8 How Do Organisms Reproduce
Case Study/Passage Based Questions
Question 1:
The male reproductive system consist of portions which produce the germ-cells and other portions that deliver the germ-cells to the site of fertilisation. Testes are located outside the abdominal cavity in scrotum because sperm formation requires a lower temperature than normal body temperature. It also has a role of secretion of male sex hormone which brings changes in appearance seen in boys at the time of puberty. Vas deferens unites with a tube coming from urinary bladder. Urethra is a common passage for sperms and urine. Prostate gland and seminal vesicles add their secretions so that sperms are now in fluid.

(i) Name the sex hormone associated with males. (a) Testosterone (b) Progesterone (c) Oestrogen (d) None of these
(ii) Which of the following statements is incorrect ? (a) Sperms are present in a fluid (b) Fluid provides nutrition to sperms (c) Fluid makes easier transportation of sperms (d) Fluid helps to bind the sperms together
(iii) Testes are located outside the abdominal cavity in scrotum because (a) sperms formation requires higher temperature than body temperature (b) sperms formation requires lower temperature than body temperature (c) it is easier to transport sperms from the scrotum (d) None of these
(iv) Which of the following statement is incorrect? (a) Sperms and urine has a common passage from urethra. (b) Sperms have long tail that helps them to move forward. (c) Sperms contain genetic material. (d) Sperms formation requires 1–3°C higher temperature than normal body temperature.
(v) What is the nature of semen? (a) slightly acidic (b) Neutral (c) Slightly basic (d) Strongly basic
Related Posts
Category lists (all posts).
All categories of this website are listed below with number of posts in each category for better navigation. Visitors can click on a particular category to see all posts related to that category.
- Full Form (1)
- Biography of Scientists (1)
- Assertion Reason Questions in Biology (37)
- Case Study Questions for Class 12 Biology (14)
- DPP Biology for NEET (12)
- Blog Posts (35)
- Career Guidance (1)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 10 Maths (14)
- Case Study Questions for Class 10 Maths (15)
- Extra Questions for Class 10 Maths (12)
- Maths Formulas for Class 10 (1)
- MCQ Questions for Class 10 Maths (15)
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths (4)
- Quick Revision Notes for Class 10 Maths (14)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 10 Science (16)
- Case Study Questions for Class 10 Science (14)
- Evergreen Science Book Solutions for Class 10 (17)
- Extra Questions for Class 10 Science (23)
- HOTS for Class 10 Science (17)
- Important Questions for Class 10 Science (10)
- Lakhmir Singh Class 10 Biology Solutions (4)
- Lakhmir Singh Class 10 Chemistry Solutions (5)
- Lakhmir Singh Class 10 Physics Solutions (5)
- MCQ Questions for Class 10 Science (20)
- NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 10 Science (16)
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science (15)
- Quick Revision Notes for Class 10 Science (4)
- Study Notes for Class 10 Science (17)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 10 Social Science (14)
- Case Study Questions for Class 10 Social Science (24)
- MCQ Questions for Class 10 Social Science (3)
- Topicwise Notes for Class 10 Social Science (4)
- CBSE CLASS 11 (1)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 11 Chemistry (14)
- Case Study Questions for Class 11 Chemistry (11)
- Free Assignments for Class 11 Chemistry (1)
- MCQ Questions for Class 11 Chemistry (8)
- Very Short Answer Questions for Class 11 Chemistry (7)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 11 Entrepreneurship (8)
- Important Questions for CBSE Class 11 Entrepreneurship (1)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 11 Geography (24)
- Case Study Questions for Class 11 Geography (24)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 11 History (12)
- Case Study Questions for Class 11 History (12)
- Assertion and Reason Questions for Class 11 Maths (16)
- Case Study Questions for Class 11 Maths (16)
- Formulas for Class 11 Maths (6)
- MCQ Questions for Class 11 Maths (17)
- NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Maths (8)
- Case Study Questions for Class 11 Physical Education (11)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 11 Physics (15)
- Case Study Questions for Class 11 Physics (12)
- Class 11 Physics Study Notes (5)
- Concept Based Notes for Class 11 Physics (2)
- Conceptual Questions for Class 11 Physics (10)
- Derivations for Class 11 Physics (3)
- Extra Questions for Class 11 Physics (13)
- MCQ Questions for Class 11 Physics (16)
- NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Physics (16)
- Numerical Problems for Class 11 Physics (4)
- Physics Formulas for Class 11 (7)
- Revision Notes for Class 11 Physics (11)
- Very Short Answer Questions for Class 11 Physics (11)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 11 Political Science (20)
- Case Study Questions for Class 11 Political Science (20)
- CBSE CLASS 12 (8)
- Extra Questions for Class 12 Biology (14)
- MCQ Questions for Class 12 Biology (13)
- Case Studies for CBSE Class 12 Business Studies (13)
- MCQ Questions for Class 12 Business Studies (1)
- Revision Notes for Class 12 Business Studies (10)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 12 Chemistry (15)
- Case Study Based Questions for Class 12 Chemistry (14)
- Extra Questions for Class 12 Chemistry (5)
- Important Questions for Class 12 Chemistry (15)
- MCQ Questions for Class 12 Chemistry (8)
- NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Chemistry (16)
- Revision Notes for Class 12 Chemistry (7)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 12 Economics (9)
- Case Study Questions for Class 12 Economics (9)
- MCQ Questions for Class 12 Economics (1)
- MCQ Questions for Class 12 English (2)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 12 Entrepreneurship (7)
- Case Study Questions for Class 12 Entrepreneurship (7)
- Case Study Questions for Class 12 Geography (18)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 12 History (8)
- Case Study Questions for Class 12 History (13)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 12 Informatics Practices (13)
- Case Study Questions for Class 12 Informatics Practices (11)
- MCQ Questions for Class 12 Informatics Practices (5)
- Assertion and Reason Questions for Class 12 Maths (14)
- Case Study Questions for Class 12 Maths (13)
- Maths Formulas for Class 12 (5)
- MCQ Questions for Class 12 Maths (14)
- Problems Based on Class 12 Maths (1)
- RD Sharma Solutions for Class 12 Maths (1)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 12 Physical Education (11)
- Case Study Questions for Class 12 Physical Education (11)
- MCQ Questions for Class 12 Physical Education (10)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 12 Physics (16)
- Case Study Based Questions for Class 12 Physics (14)
- Class 12 Physics Conceptual Questions (16)
- Class 12 Physics Discussion Questions (1)
- Class 12 Physics Latest Updates (2)
- Derivations for Class 12 Physics (8)
- Extra Questions for Class 12 Physics (4)
- Important Questions for Class 12 Physics (8)
- MCQ Questions for Class 12 Physics (14)
- NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Physics (18)
- Numerical Problems Based on Class 12 Physics (16)
- Physics Class 12 Viva Questions (1)
- Revision Notes for Class 12 Physics (7)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 12 Political Science (16)
- Case Study Questions for Class 12 Political Science (16)
- Notes for Class 12 Political Science (1)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 6 Maths (13)
- Case Study Questions for Class 6 Maths (13)
- Extra Questions for Class 6 Maths (1)
- Worksheets for Class 6 Maths (1)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 6 Science (16)
- Case Study Questions for Class 6 Science (16)
- Extra Questions for Class 6 Science (1)
- MCQ Questions for Class 6 Science (9)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 6 Social Science (1)
- Case Study Questions for Class 6 Social Science (26)
- NCERT Exemplar for Class 7 Maths (13)
- NCERT Exemplar for Class 7 Science (19)
- NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 7 Maths (12)
- NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 7 Science (18)
- NCERT Notes for Class 7 Science (18)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 7 Maths (14)
- Case Study Questions for Class 7 Maths (14)
- Extra Questions for Class 7 Maths (5)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 7 Science (18)
- Case Study Questions for Class 7 Science (17)
- Extra Questions for Class 7 Science (19)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 7 Social Science (1)
- Case Study Questions for Class 7 Social Science (30)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 8 Maths (7)
- Case Study Questions for Class 8 Maths (17)
- Extra Questions for Class 8 Maths (1)
- MCQ Questions for Class 8 Maths (6)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 8 Science (16)
- Case Study Questions for Class 8 Science (11)
- Extra Questions for Class 8 Science (2)
- MCQ Questions for Class 8 Science (4)
- Numerical Problems for Class 8 Science (1)
- Revision Notes for Class 8 Science (11)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 8 Social Science (27)
- Case Study Questions for Class 8 Social Science (23)
- CBSE Class 9 English Beehive Notes and Summary (2)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 9 Maths (14)
- Case Study Questions for Class 9 Maths (14)
- MCQ Questions for Class 9 Maths (11)
- NCERT Notes for Class 9 Maths (6)
- NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths (12)
- Revision Notes for Class 9 Maths (3)
- Study Notes for Class 9 Maths (10)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 9 Science (16)
- Case Study Questions for Class 9 Science (15)
- Evergreen Science Book Solutions for Class 9 (15)
- Extra Questions for Class 9 Science (22)
- MCQ Questions for Class 9 Science (11)
- NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science (15)
- Revision Notes for Class 9 Science (1)
- Study Notes for Class 9 Science (15)
- Topic wise MCQ Questions for Class 9 Science (2)
- Topicwise Questions and Answers for Class 9 Science (15)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 9 Social Science (15)
- Case Study Questions for Class 9 Social Science (19)
- CHEMISTRY (8)
- Chemistry Articles (2)
- Daily Practice Problems (DPP) (3)
- Books for CBSE Class 9 (1)
- Books for ICSE Class 10 (3)
- Editable Study Materials (8)
- Exam Special for CBSE Class 10 (3)
- H. C. Verma (Concepts of Physics) (13)
- Study Materials for ICSE Class 10 Biology (14)
- Extra Questions for ICSE Class 10 Chemistry (1)
- Study Materials for ICSE Class 10 Chemistry (5)
- Study Materials for ICSE Class 10 Maths (16)
- Important Questions for ICSE Class 10 Physics (13)
- MCQ Questions for ICSE Class 10 Physics (4)
- Study Materials for ICSE Class 10 Physics (8)
- Study Materials for ICSE Class 9 Maths (7)
- Study Materials for ICSE Class 9 Physics (10)
- Topicwise Problems for IIT Foundation Mathematics (4)
- Challenging Physics Problems for JEE Advanced (2)
- Topicwise Problems for JEE Physics (1)
- DPP for JEE Main (1)
- Integer Type Questions for JEE Main (1)
- Integer Type Questions for JEE Chemistry (6)
- Chapterwise Questions for JEE Main Physics (1)
- Integer Type Questions for JEE Main Physics (8)
- Physics Revision Notes for JEE Main (4)
- JEE Mock Test Physics (1)
- JEE Study Material (1)
- JEE/NEET Physics (6)
- CBSE Syllabus (1)
- Maths Articles (2)
- NCERT Books for Class 12 Physics (1)
- NEET Chemistry (13)
- Important Questions for NEET Physics (17)
- Topicwise DPP for NEET Physics (5)
- Topicwise MCQs for NEET Physics (32)
- NTSE MAT Questions (1)
- Physics (1)
- Alternating Current (1)
- Electrostatics (6)
- Fluid Mechanics (2)
- PowerPoint Presentations (13)
- Previous Years Question Paper (3)
- Products for CBSE Class 10 (15)
- Products for CBSE Class 11 (10)
- Products for CBSE Class 12 (6)
- Products for CBSE Class 6 (2)
- Products for CBSE Class 7 (5)
- Products for CBSE Class 8 (1)
- Products for CBSE Class 9 (3)
- Products for Commerce (3)
- Products for Foundation Courses (2)
- Products for JEE Main & Advanced (10)
- Products for NEET (6)
- Products for ICSE Class 6 (1)
- Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance (1)
- Topic Wise Study Notes (Physics) (2)
- Topicwise MCQs for Physics (2)
- Uncategorized (138)
Test series for students preparing for Engineering & Medical Entrance Exams are available. We also provide test series for School Level Exams. Tests for students studying in CBSE, ICSE or any state board are available here. Just click on the link and start test.
Download CBSE Books
Exam Special Series:
- Sample Question Paper for CBSE Class 10 Science (for 2024)
- Sample Question Paper for CBSE Class 10 Maths (for 2024)
- CBSE Most Repeated Questions for Class 10 Science Board Exams
- CBSE Important Diagram Based Questions Class 10 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Important Numericals Class 10 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Practical Based Questions for Class 10 Science Board Exams
- CBSE Important “Differentiate Between” Based Questions Class 10 Social Science
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Physics (for 2024)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Chemistry (for 2024)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Maths (for 2024)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Biology (for 2024)
- CBSE Important Diagrams & Graphs Asked in Board Exams Class 12 Physics
- Master Organic Conversions CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Board Exams
- CBSE Important Numericals Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Important Definitions Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Important Laws & Principles Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Physics Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Maths Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Biology Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- ICSE Important Numericals Class 10 Physics BOARD Exams (215 Numericals)
- ICSE Important Figure Based Questions Class 10 Physics BOARD Exams (230 Questions)
- ICSE Mole Concept and Stoichiometry Numericals Class 10 Chemistry (65 Numericals)
- ICSE Reasoning Based Questions Class 10 Chemistry BOARD Exams (150 Qs)
- ICSE Important Functions and Locations Based Questions Class 10 Biology
- ICSE Reasoning Based Questions Class 10 Biology BOARD Exams (100 Qs)
✨ Join our Online JEE Test Series for 499/- Only (Web + App) for 1 Year
✨ Join our Online NEET Test Series for 499/- Only for 1 Year
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Join our Online Test Series for CBSE, ICSE, JEE, NEET and Other Exams

Editable Study Materials for Your Institute - CBSE, ICSE, State Boards (Maharashtra & Karnataka), JEE, NEET, FOUNDATION, OLYMPIADS, PPTs
Discover more from Gurukul of Excellence
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Type your email…
Continue reading

- Andhra Pradesh
- Chhattisgarh
- West Bengal
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Jammu & Kashmir
- NCERT Books 2022-23
- NCERT Solutions
- NCERT Notes
- NCERT Exemplar Books
- NCERT Exemplar Solution
- States UT Book
- School Kits & Lab Manual
- NCERT Books 2021-22
- NCERT Books 2020-21
- NCERT Book 2019-2020
- NCERT Book 2015-2016
- RD Sharma Solution
- TS Grewal Solution
- TR Jain Solution
- Selina Solution
- Frank Solution
- ML Aggarwal Solution
- Lakhmir Singh and Manjit Kaur Solution
- I.E.Irodov solutions
- ICSE - Goyal Brothers Park
- ICSE - Dorothy M. Noronhe
- Sandeep Garg Textbook Solution
- Micheal Vaz Solution
- S.S. Krotov Solution
- Evergreen Science
- KC Sinha Solution
- ICSE - ISC Jayanti Sengupta, Oxford
- ICSE Focus on History
- ICSE GeoGraphy Voyage
- ICSE Hindi Solution
- ICSE Treasure Trove Solution
- Thomas & Finney Solution
- SL Loney Solution
- SB Mathur Solution
- P Bahadur Solution
- Narendra Awasthi Solution
- MS Chauhan Solution
- LA Sena Solution
- Integral Calculus Amit Agarwal Solution
- IA Maron Solution
- Hall & Knight Solution
- Errorless Solution
- Pradeep's KL Gogia Solution
- OP Tandon Solutions
- Sample Papers
- Previous Year Question Paper
- Value Based Questions
- CBSE Syllabus
- CBSE MCQs PDF
- Assertion & Reason
- New Revision Notes
- Revision Notes
- HOTS Question
- Marks Wise Question
- Toppers Answer Sheets
- Exam Paper Aalysis
- Concept Map
- CBSE Text Book
- Additional Practice Questions
- Vocational Book
- CBSE - Concept
- KVS NCERT CBSE Worksheets
- Formula Class Wise
- Formula Chapter Wise
- JEE Crash Course
- JEE Previous Year Paper
- Important Info
- JEE Mock Test
- JEE Sample Papers
- SRM-JEEE Mock Test
- VITEEE Mock Test
- BITSAT Mock Test
- Manipal Engineering Mock Test
- AP EAMCET Previous Year Paper
- COMEDK Previous Year Paper
- GUJCET Previous Year Paper
- KCET Previous Year Paper
- KEAM Previous Year Paper
- Manipal Previous Year Paper
- MHT CET Previous Year Paper
- WBJEE Previous Year Paper
- AMU Previous Year Paper
- TS EAMCET Previous Year Paper
- SRM-JEEE Previous Year Paper
- VITEEE Previous Year Paper
- BITSAT Previous Year Paper
- UPSEE Previous Year Paper
- CGPET Previous Year Paper
- CUSAT Previous Year Paper
- AEEE Previous Year Paper
- Crash Course
- Previous Year Paper
- NCERT Based Short Notes
- NCERT Based Tests
- NEET Sample Paper
- Previous Year Papers
- Quantitative Aptitude
- Numerical Aptitude Data Interpretation
- General Knowledge
- Mathematics
- Agriculture
- Accountancy
- Business Studies
- Political science
- Enviromental Studies
- Mass Media Communication
- Teaching Aptitude
- NAVODAYA VIDYALAYA
- SAINIK SCHOOL (AISSEE)
- Mechanical Engineering
- Electrical Engineering
- Electronics & Communication Engineering
- Civil Engineering
- Computer Science Engineering
- CBSE Board News
- Scholarship Olympiad
- School Admissions
- Entrance Exams
- All Board Updates
- Miscellaneous
- State Wise Books
- Engineering Exam
How Do Organisms Reproduce Case Study Based Questions Class 10
Students who are studying in CBSE class 10 board, need to get the knowledge about the How Do Organisms Reproduce Case Study Based Questions. Case based questions are generally based on the seen passages from the chapter How Do Organisms Reproduce. Through solving the case based questions, students can understand each and every concept.
With the help of How Do Organisms Reproduce Case Study Based Questions, students don’t need to memorise each answer. As answers for these case studies are already available in the given passage. Questions are asked through MCQs so student’s won’t take time to mark the answers. These multiple choice questions can help students to score the weightage of How Do Organisms Reproduce.
How Do Organisms Reproduce Case Study Based Questions with Solutions
Selfstudys provides case studies for the Class 10 Science chapter How Do Organisms Reproduce with solutions. The Solutions can be helpful for students to refer to if there is a doubt in any of the case studies problems. The solutions from the Selfstudys website are easily accessible and free of cost to download. This accessibility can help students to download case studies from anywhere with the help of the Internet.
How Do Organisms Reproduce Case Study Based Questions with solutions are in the form of PDF. Portable Document Format (PDF) can be downloaded through any of the devices: smart phone, laptop. Through this accessibility, students don't need to carry those case based questions everywhere.
Features of How Do Organisms Reproduce Case Study Based Questions
Before solving questions, students should understand the basic details of How Do Organisms Reproduce. Here are the features of case based questions on How Do Organisms Reproduce are:
- These case based questions start with short or long passages. In these passages some concepts included in the chapter can be explained.
- After reading the passage, students need to answer the given questions. These questions are asked in the Multiple Choice Questions (MCQ).
- These case based questions are a type of open book test. These case based questions can help students to score well in the particular subject.
- These How Do Organisms Reproduce Case Study Based Questions can also be asked in the form of CBSE Assertion and Reason .
Benefits of Solving How Do Organisms Reproduce Case Study Based Questions
According to the CBSE board, some part of the questions are asked in the board exam question papers according to the case studies. As some benefits of solving How Do Organisms Reproduce Case Study Based Questions can be obtained by the students. Those benefits are:
- Through solving case studies students will be able to understand every concept included in the chapter How Do Organisms Reproduce
- Passages included in the case study are seen passages, so students don’t need to struggle for getting answers. As these questions and answers can be discussed by their concerned teacher.
- Through these students can develop their observation skills. This skill can help students to study further concepts clearly.
- Case studies covers all the concepts which are included in the How Do Organisms Reproduce
How to Download How Do Organisms Reproduce Case Based Questions?
Students studying in CBSE class 10 board, need to solve questions based on case study. It is necessary for students to know the basic idea of How Do Organisms Reproduce Case Study Based Questions. Students can obtain the basic idea of case based questions through Selfstudys website. Easy steps to download it are:
- Open Selfstudys website.
- Bring the arrow towards CBSE which is visible in the navigation bar.
- A pop-up menu will appear, Select case study from the list.
- New page will appear, select 10 from the list of classes.
- Select Science from the subject list.
- And in the new page, you can access the How Do Organisms Reproduce Case Study Based Questions.
Tips to solve How Do Organisms Reproduce Case Study Questions-
Students should follow some basic tips to solve How Do Organisms Reproduce Case Study Based Questions. These tips can help students to score good marks in CBSE Class 10 Science.
- Generally, the case based questions are in the form of Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs).
- Students should start solving the case based questions through reading the given passage.
- Identify the questions and give the answers according to the case given.
- Read the passage again, so that you can easily answer the complex questions.
- Answer according to the options given below the questions provided in the How Do Organisms Reproduce Case Study Based Questions.

- NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Maths
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths
- CBSE Syllabus 2023-24
- Social Media Channels
- Login Customize Your Notification Preferences

One Last Step...

- Second click on the toggle icon

Provide prime members with unlimited access to all study materials in PDF format.
Allow prime members to attempt MCQ tests multiple times to enhance their learning and understanding.
Provide prime users with access to exclusive PDF study materials that are not available to regular users.

Class 10 Science Chapter 7 Case Based Questions - How Do Organisms Reproduce
Case study - 1.
The sexual act always has the potential to lead to pregnancy. Pregnancy will make major demands on the body and the mind of the woman, and if she is not ready for it, her health will be adversely affected. Therefore, many ways have been devised to avoid pregnancy.
Q1: What are the different methods to prevent pregnancy? Ans: Uses of contraceptive such as condoms, pills, copper -T and surgical methods. Q2: What are the surgical methods to prevent pregnancy? Ans: Tubectomy in females and vasecotomy in males. Q3: Why the female sex ratio is declining day by day? Ans: Due to female foeticides by doing illegal sex selective abortion of female foetuses. Q4: Which contraceptive methods have large side effects? Ans: Oral pills and by changing the hormonal balance leads to high side effect. Q5: Why should one have the knowledge about sexual act and the disease causing by it? Ans: To stay healthy and free free from sexually transmitted disease one should be aware of the disease cause by bacteria and viruses such as gonorrhoea, syphilis and HIV- AIDS.
Case Study - 2
Chromosomes in the nucleus of a cell contain information for inheritance of features from parents to next generation in the form of DNA (Deoxyribo Nucleic Acid) molecules. The DNA in the cell nucleus is the information source for making proteins. If the information is changed, different proteins will be made. Different proteins will eventually lead to altered body designs. Therefore, a basic event in reproduction is the creation of a DNA copy. Cells use chemical reactions to build copies of their DNA.
Q1: What is the importance of variation? Ans: Variation is important for the survival of species over time. Variation make the species resistant to the changing environment and hence, it make easy for their survival. Q2: Which mode of reproduction does not show much variation? Ans: Generally, asexual reproduction show less variation which includes budding, fragmentation, fission etc. Q3: What are the different modes of reproduction of single celled organism? Ans: Fission, fragmentation, Budding and regeneration. Q4: What are the features of sexual reproduction? Ans: It includes both the parents to produce offsprings and DNA copy is a crucial part of it. Q5: Which mode of reproduction is better and why? Ans: Sexual reproduction is better than asexual reproduction as the chances of survival of the species is higher in sexual reproduction.
Case Study - 3
There are many plants in which parts like the root, stem and leaves develop into new plants under appropriate conditions. Unlike in most animals, plants can indeed use such a mode for reproduction. This property of vegetative propagation is used in methods such as layering or grafting to grow many plants like sugarcane, roses, or grapes for agricultural purposes
Q1: What are the advantages of vegetative propagation? Ans: All plants that are produced by such method are genetically similar to their parent and have all its characteristics. easy, less expensive and a fast method. Q2: Give a example of vegetative propagation through buds? Ans: Bryophyllum Q3: What is tissue culture? Ans: New plants are grown first in suitable artificial medium and then placing it in the soil to grow into mature plants. Q4: What is grafting? Ans: New plants are grown by joining a scion(upper portion of plant) to a stock of other plants in such a manner that they get united to each other. Example: Roses Q5: What are the examples of layering? Ans: Jasmine or Grapevine.
Case Study - 4
The reproductive parts of angiosperms are located in the flower. You have already studied the different parts of a flower – sepals, petals, stamens and pistil. Stamens and pistil are the reproductive parts of a flower which contain the germ-cells.The flower may be unisexual (papaya, watermelon) when it contains either stamens or pistil or bisexual (Hibiscus, mustard) when it contains both stamens and pistil.
Q1: What is the male reproductive parts of flower? Ans: Stamen is the male reproductive part of flower and it consist of anther and filament. Q2: What are the different part of pistil? Ans: Stigma, style and ovary. Q3: What is pollination? Ans: The transfer of pollen grains from the stamen to the stigma of flower is called pollination. Q4: Where does fertilization occur in flower? Ans: The fertilization takes place inside the ovule. Q5: What are the two types of pollination? Ans: Self pollination and cross pollination.
Case Study - 5
When a girl is born, the ovaries already contain thousands of immature eggs. On reaching puberty, some of these start maturing. One egg is produced every month by one of the ovaries. The egg is carried from the ovary to the womb through a thin oviduct or fallopian tube. The two oviducts unite into an elastic bag-like structure known as the uterus. The uterus opens into the vagina through the cervix.
Q1: What is fertilization? Ans: The fusion of male gametes(sperms) and the female gametes(egg) to form zygote is called fertilization. Q2: Where does fertilization occur? Ans: Fertilization occur in the oviduct or Fallopian tube. Q3: What is placenta? Ans: It is an special tissue which provide nutrition from mother’s blood to developing embryo. Q4: What are the different parts of female reproductive system? Ans: Fallopian tube, ovary, uterus, vagina and cervix. Q5: What happens when egg is not fertilized? Ans: If the egg is not fertilized, the thick lining of uterus is not needed. So, it breaks slowly and comes out through vagina as blood and vagina, which is called as menstruation.
Top Courses for Class 10
Mock tests for examination, viva questions, practice quizzes, past year papers, semester notes, sample paper, important questions, previous year questions with solutions, study material, objective type questions, shortcuts and tricks, extra questions, video lectures.

Case Based Questions: How do Organisms Reproduce? Free PDF Download
Importance of case based questions: how do organisms reproduce, case based questions: how do organisms reproduce notes, case based questions: how do organisms reproduce class 10, study case based questions: how do organisms reproduce on the app, welcome back, create your account for free.
Forgot Password
Unattempted tests, change country, practice & revise.
- Bihar Board
RBSE Result 2024
Srm university.
- Goa Board Result 2024
- Maharashtra HSC Result
- Maharashtra SSC Result
- RBSE 10th Result 2024
- RBSE 12th Result 2024
- CBSE Board Result 2024
- Shiv Khera Special
- Education News
- Web Stories
- Current Affairs
- नए भारत का नया उत्तर प्रदेश
- School & Boards
- College Admission
- Govt Jobs Alert & Prep
- GK & Aptitude
- CBSE Class 10
CBSE Class 10 Biology How Do Organisms Reproduce Important Questions and Answers for 2023
Cbse class 10 biology how do organisms reproduce important questions and answers: a ll important questions from the chapter how do organisms reproduce in cbse class 10 science. the questions are of all varieties: multiple choice questions, assertion reason questions, case study questions, and all descriptive questions such as very short answer questions, short answer questions and long answer questions..

CBSE Class 10 Biology How Do Organisms Reproduce Important Questions: In this article, we will cover all important questions from the chapter How do Organisms Reproduce in CBSE Class 10 Science. The questions are of all varieties: Multiple choice questions, Assertion Reason questions, Case Study questions, and all descriptive questions such as Very Short answer Questions, Short answer questions and Long answer questions. The answers to these questions are also provided here. These important questions and answers prepared by the subject experts are provided here for candidates of CBSE Class 10 Science board exam 2022-23 to help them prepare effectively. By practising these questions along with the sample paper questions and textbook exercises, students will be able to master the topics in the chapter.
How Do Organisms Reproduce is the third chapter in the second unit World of Living. Earlier it was the eighth chapter in the syllabus. Since the syllabus was updated during the pandemic years, it is now Chapter 7.
Chapter 7 How do Organisms Reproduce covers the following topics: Reproduction in animals and plants (asexual and sexual) reproductive health - need and methods of family planning. Safe sex vs HIV/AIDS. Child bearing and women’s health.
CBSE Class 10 Biology How Do Organisms Reproduce Important Questions
Multiple choice questions:.
Q.1. The two oviducts in a human female unite into an elastic bag like is known as
a. Vagina b. Uterus c. Fallopian tube d. Cervix
2. Where does fertilisation occur in human females?
a. Uterus b. Cervix c. Oviduct d. None of these
- Vegetative propagation
- Contraception
- Increasing fertility
- Avoiding miscarriage
4. Which is the portion on which grafting is done it provides the roots?
a. Stock b. Scion c. Both a and b d. None of these
5. When an animal is cut into pieces and each piece grows into a complex organism. What is the process?
a. Budding b. Fragmentation c. Spore formation d. Regeneration
6. Which among the following does not reproduce by spore formation:
(a) Penicillium fungus (b) Yeast fungus (c) Mucor fungus (d) Rhizopus fungus
7. What is the puberty age in human males?
a. 8-10 b. 10-12 c. 12-14 d. 14-16
8. Reason for the greater similarities among the off springs produced by asexual reproduction, is:
(i) Asexual reproduction involves only one parent
(ii) Asexual reproduction involves two parents
(iii) Asexual reproduction involves gametes
(iv) Asexual reproduction does not involve gametes
(a) (i) and (ii)
(b) (i) and (iii)
(c) (ii) and (iv)
(d) (i) and (iv)
9. Fruits are formed from
a. Stamen b. Stigma c. Ovary d. Ovule
10. An organism capable of reproducing by two asexual reproduction methods one similar to the reproduction in yeast and the other similar to the reproduction in Planaria is:
ASSERTION REASON QUESTIONS:
DIRECTION: Each of these questions contains an Assertion followed by Reason. Read them carefully and answer the question on the basis of following options. You have to select the one that best describes the two statements.
(a)Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b)Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c)A is true but R is false.
- Assertion: Unisexual flowers have separate male and female Organs.
- Assertion: Condom is a safe contraceptive method to prevent pregnancy
- Assertion: Testes lie outside the body.
- Assertion: Spores are unicellular bodies.
- Assertion: Ovary is not an organ in the female reproductive system.
- Assertion: Surgical methods are most effective methods of contraception.
- Assertion: Fertilisation will not occur in the absence of pollination.
- Assertion(A) : Asexual reproduction is a primitive type of reproduction.
- Assertion: Sexual reproduction involves two parents of different sexes, a male and a female
- Assertion: In internal fertilization male and female gametes fuse inside the female body
- Assertion: The size of human population is a cause for concern for many people .
- Assertion: Urethra in human male acts as urino-genital canal.
- Assertion(A) : The offspring produced by sexual reproduction is likely to adjust better in environmental fluctuation.
- Assertion : Ovary lies at the lower part of the stamen.
- Assertion: Warts is a sexually transmitted disease.
CASE STUDY BASED QUESTIONS:
1 Germination starts with the rapid intake of water by the seed through its micropyle. The first visible indication of germination is the swelling of the seed with a resultant increase in weight. It is also accompanied by the softening of the seed coat. Absorption of water causes a number of physiological changes in the seed. Germinating seeds exhibit increased respiratory activity. The embryo produces enzymes which convert the food materials stored in the cotyledons into soluble form usable by the growing embryo. Once the food is made available, cell division activity starts in the growing embryo. The growth of the embryonic tissue ruptures the seed coat.
(i) Which of the following is not connected with the germination of seed.
(a) It swells
(b) The seed coat softened
(c) It exhibits photosynthesis
(d) It exhibits respiration
(ii) Which among the following are true
(i) Radicle develops into root
(ii) Radicle develops into shoot
(iii) Plumule develops into root
(iii) Plumule develops into shoot
(c) (i) and (iv)
(d) (ii) and (iv)
(iii) Which of the following is a part of seed.
(b) Radicle
(c) Plumule
(d) All of the above
(iv) The condition needed for the germination of the seed
(a) Moisture
(b) Temperature
(c) Both (A)and (b)
(d) None of the above
2 The growing size of the human population is a cause of concern for all people. The rate of birth and death in a given population will determine its size. Reproduction is the process by which organisms increase their population. The process of sexual maturation for reproduction is gradual and takes place while general body growth is still going on. Some degree of sexual maturation does not n ecessarily mean that the mind or body is ready for sexual acts or for having and bringing up children. Various contraceptive devices are being used by human beings to control the size of population.
1) What should be maintained for healthy society?
a) Rate of birth and death rate
b) Male and female sex ratio
c) Child sex ratio
d) None of these
2) Which contraceptive method changes the hormonal balance of the body?
b) Diaphragms
c) Oral pills
d) Both a) and b)
3) Common sign of sexual maturation in girls is
a) Low pitch voice
b) Appearance of moustache and beard
c) Development of mammary glands
d) Broadening of shoulders
4) What are common signs of sexual maturation in boys?
a) Broadening of shoulders
b) Development of mammary glands
c) Broadening of waist
DESCRIPTIVE QUESTIONS:
1) Newly formed DNA copies may not be identical at times. Give one reason.
2) Where is the zygote located in the flower after fertilization?
3) How does Plasmodium reproduce? Is this method sexual or asexual?
4) Name the part of Bryophyllum where the buds are produced for vegetative propagation.
5) Name the method by which Spirogyra reproduces under favourable conditions. Is this method sexual or asexual?
6) Name the causative agent of the disease “kala- azar” and its mode of asexual reproduction
7) In a bisexual flower in spite of the young stamens removed artificially, the flower produces fruit. Provide a suitable explanation for the above situation.
8) Define vegetative propagation.
9) Name two sex hormones.
10) What are the agents of pollination?
11) Define the terms unisexual and bisexual giving one example of each.
12) What are the limitations of the asexual mode of reproduction? Differentiate between asexual reproduction and sexual reproduction.
13) Explain how human embryo get nourished in mother body?
14) How do Plasmodium and Leishmania reproduce? Write one difference in their mode of reproduction.
15) Name the female reproductive part of a flower. Which part of a flower develops into a seed and a fruit? Where are the male germ cell and female gamete present in the flower?
16.) Name the male and female gametes in animals. What is fertilisation and where does it take place in human females?
17) Name an organism which reproduces by spore formation. List three conditions favourable for spores to germinate and grow.
18) What is the importance of variation in the survival of individuals?
19) Name and explain any three methods of contraception?
20) List the advantages of vegetative propagation
21) Explain various steps of budding in yeast.
22) Draw a human male reproductive system of a human and label the parts. Mention the function of vas deferens and ureter?
23) Define reproduction. How does it help in providing stability to the population of species?
- a) We can develop new plants from the leaves of Bryophyllum. Comment.
- b) List two advantages of vegetative propagation over other modes of reproduction.
25) Draw a diagram showing germination of pollen on the stigma of a flower.
26) Draw a human female reproductive system of a human and label the parts.
By going through the important topics of Chapter 7 How Do Organisms Reproduce students will get a good idea of the topics from where the questions are expected and the types of questions to be asked in the CBSE Class 10 Science board exam paper.
To get the CBSE Class 10 Science Sample Question Paper and Marking Scheme, click below:
CBSE Class 10 Science Sample Question Paper and Marking Scheme
Get here latest School , CBSE and Govt Jobs notification in English and Hindi for Sarkari Naukari and Sarkari Result . Download the Jagran Josh Sarkari Naukri App . Check Board Result 2024 for Class 10 and Class 12 like CBSE Board Result , UP Board Result , Bihar Board Result , MP Board Result , Rajasthan Board Result and Other States Boards.
- JAC 9th, 11th रिजल्ट 2024
- JAC 9th रिजल्ट 2024
- JAC Result 2024
- jac.jharkhand.gov.in 11th Result 2024
- JAC 11वीं रिजल्ट 2024 रोल नंबर
- GBSHSE SSC Result 2024
- SSC Result 2024 Goa
- CDS 2 Notification 2024
- results.gbshsegoa.net Result 2024
- CBSE 10th Result 2024
- CBSE Class 10 QnA
Latest Education News
IPL 2024 Playoffs Teams: इन 4 टीमों का प्लेऑफ टिकट कन्फर्म! KKR, SRH और RR के बाद किसका नंबर
IPL 2024 RCB Players: रॉयल चैलेंजर्स बेंगलूरू के खिलाड़ियों की पूरी लिस्ट यहां देखें Today RCB vs CSK मैच
[रिजल्ट लिंक] JAC 9th Result 2024 OUT: कोडरमा जिला रहा अव्वल, jac.jharkhand.gov.in पर Result Link से तुरंत डाउनलोड करें Marksheet
CUET UG Answer Key May 18, 2024: Download Set Wise Answer Sheet PDF
CUET UG Exam Analysis 2024, May 18: Check Detailed Paper Review, Difficulty Level, and Good Attempts
CUET UG Question Paper 2024, May 18: Download Question Paper PDF (SET A, B, C, D)
RBSE Result 2024 Kab Aayega: आज आ सकता है राजस्थान बोर्ड 10वीं का रिजल्ट नोटिफिकेशन, rajresults.nic.in पर मिलेगा Result Link
VNSGU Result 2024 OUT at vnsgu.ac.in, Direct Link to Download UG and PG Marksheet
TS EAMCET Result 2024 Declared: Check TS EAPCET Rankcard at eapcet.tsche.ac.in
MSBSHSE Result 2024 LIVE: Maharashtra Board SSC, HSC Results Date, Time Soon at mahresult.nic.in, Check Direct Link and Past Year's Trends
DBRAU Result 2024 OUT at dbrau.ac.in; Download Agra University UG and PG Semester Marksheet PDF
TS TET Cut Off Marks 2024, Check Category-wise Telangana TET Minimum Passing Marks
Bihar STET Exam Analysis 18 May 2024: Check Paper Review, Difficulty Level, Good Attempts
Seek and Find Puzzle: Test Your Vision By Finding the Hidden Tiger in this Park Scene in 9 Seconds
[डायरेक्ट लिंक] jac.jharkhand.gov.in 9th, 11th Result 2024: झारखंड बोर्ड 9वीं, 11वीं का रिजल्ट jacresults.com पर घोषित, यहां Roll Number से तुरंत करें चेक
JAC 8th Result 2024: झारखंड बोर्ड क्लास 8वीं का रिजल्ट jacresults.com पर जल्द, इस Website पर मिलेगा Direct Link
[रिजल्ट लिंक] JAC Result 2024 LIVE: Jharkhand Board 8th Result Soon, 9th, 11th Declared at jacresults.com, Check Marks Online by Roll Number, Roll Code
NEET Paper Leak 2024: SC Rejects Plea to Halt Results Despite Alleged Leak, Check Details
[Fast Update] IPL Points Table 2024: आईपीएल 2024 अपडेटेड पॉइंट टेबल यहां देखें, KKR और RR, SRH Qualify
IPL 2024 Stats: आईपीएल में किसने फेंकी थी पहली गेंद, किसने लिया पहला विकेट और किसने जड़ा पहला छक्का

CBSE 10th Standard Science Subject How do Organisms Reproduce Chapter Case Study Questions 2021
QB365 Provides the updated CASE Study Questions for Class 10 , and also provide the detail solution for each and every case study questions . Case study questions are latest updated question pattern from NCERT, QB365 will helps to get more marks in Exams
QB365 - Question Bank Software
Cbse 10th standard science subject how do organisms reproduce case study questions 2021.
10th Standard CBSE
Final Semester - June 2015
A newly married couple does not want have children for few years. They consulted a doctor who advised them barrier method and chemical method of birth control. Yet another couple who already have two children and are middle aged also consulted doctor for some permanent solution to avoid unwanted pregnancy. Doctor advised them surgical method of birth control. (i) What are the barrier methods of birth control?
(ii) How physical barrier prevent pregnancy? (a) They kill the sperms (b) They kill the ovum (c) They prevent sperms from meeting the ovum (d) They prevent intercourse (iii) How chemical methods prevent pregnancy? (a) Vaginal pills contain chemical called spermicides which kill the sperms (b) Oral pills prevent ovulation so there will be no fertilisation (c) Oral pills stop menstruation in females (d) Both (a) and (b) (iv) Select the correct statement regarding surgical method of birth control. (a) It involves termination of pregnancies in women particularly after eight weeks of conception (b) Small portion of sperm duct or vas deferences in males is removed by surgical operation and both cut ends are ligated properly (c) Small portion of oviducts in females is removed by surgical operation and cut ends are ligated (d) Both (b) and (c) (v) Select the correct statement regarding birth control methods. (a) Barrier method of birth control also protects the couple from sexually transmitted diseases (b) Some women experience unpleasant side effects on taking oral pills because of change in hormonal balance in body (c) Surgical method in males is called vasectomy and in females is called tubectomy (d) All of these
A married woman used a device X made of common metal for preventing pregnancy. This device was put into her uterus by some trained medical professional. Unfortunately she got pregnant after two months of insertion of device. She was in shock to learn that her birth control device has failed. (i) What is the name of birth control device used by the woman?
(ii) Which metal is commonly used for making device X?
(iii) How does device X prevent pregnancy? (a) It prevents ovulation (b) It prevents copulation (c) It suppresses fertilising capacity of sperm (d) None of these (iv) Why do you think the woman got pregnant even after using device X? (a) Device X might have got expelled without the knowledge of woman (b) Device X might be defective and was not working from the beginning (c) Device X could have been destroyed by the uterine fluid (d) None of these (v) Select the correct statement regarding device X. (a) Device X is very effective in preventing sexually transmitted diseases (b) Device X can be inserted in uterus by woman herself (c) Device X prevents menstrual cycle in women (d) Device X can cause heavy painful and longer duration periods or menstruation
X, Y and Z are sexually reproducing organisms. Fertilisation occurs either in external medium (water) or inside the body of organism. Thus two types of gametic fusion are external fertlisation and internal fertilisation. X undergoes external fertilisation whereas Y and Z undergo internal fertilisation. X and Y both release their eggs outside their body. (i) Select the option that correctly identifies organisms X, Y and Z.
(ii) Select the correct statement regarding organisms X and Y. (a) Y produces large number of eggs where X produces single egg at a time. (b) Fertilisation in case of X occurs in water but fertilisation occurs inside the body of Y. (c) X could be a reptile whereas Y could be fish or amphibian. (d) Eggs of X are covered by hard calcareous shell whereas eggs ofY are covered in jelly. (iii) Select the incorrect statement regarding organisms Y and Z. (a) Y is oviparous whereas Z is viviparous. (b) Zygote develops to complete baby in the bodies of organism Y and Z. (c) Y could be a bird or reptile whereas Z could be a mammal. (d) Both Y and Z copulate with their female counterparts to transfer sperms in their bodies. (iv) Select the correct match. (a) Eggs with calcareous shells - Parrot, King Cobra, Salmon (b) Eggs with jelly covering - Toad, Eagle, Lizard (c) Eggs without shell - Cat, Dog, Human (d) Eggs produced in large numbers at a time - Rohu, Human, Python (v) Why are eggs of animal X covered in jelly? (a) To keep the eggs moist and offer some protection from predators (b) To prevent the egg from breaking (c) To prevent fertilisation of eggs (d) All of these
Menstrual cycle is the cycle of events taking place in female reproductive organs, under the control of sex hormones, in every 28 days. At an interval of 28 days, a single egg is released from either of two ovaries. Regular menstrual cycle stopped abruptly in a married women. She got herself tested and was happy to discover that she is pregnant with her first baby. (i) Why menstruation stops in a pregnant female? (a) The egg gets fertilised so need not to be expelled out of body (b) Ovulation stops during pregnancy and so do menstruation (c) Thick uterine lining is needed for proper development of embryo, so that it is retained (d) All of these (ii) Select the correct sequence of acts that leads to pregnancy in a female. A. Fertilisation of egg B. Ovulation C. Formation of zygote D. Implantation
(iii) How is a zygote different from embryo? (a) Zygote is formed by repeated division of embryo (b) Zygote is formed by fusion of sperm and egg whereas embryo is formed by fusion of zygote with other zygote (c) Zygote is single celled but embryo is multicellular (d) Zygote is formed by fertilisation but embryo is formed without fertilisation (iv) What change takes place in the uterus of a pregnant female? (a) Uterine lining becomes thick and vascular (b) Placenta develops which links the embryo to mother through umbilical cord (c) Uterus lining containing lots of blood capillaries breaks down (d) Both (a) and (b) (v) Select the correct statement. (a) The average duration of human pregnancy is about nine months (b) The time period from fertilisation up to the birth of baby is called gestation (c) If doctor finds any anomaly in the developing fetus then he may terminate pregnancy at an early stage, known as abortion (d) All of these
X, Y and Z are three sexually transmitted diseases (STDs). X and Z are caused by bacteria whereas Y is caused by virus P. Virus P lowers the immunity of a person and leads to an incurable disease. X starts as painless sores on genitals rectum or mouth. Z causes painful urination and abnormal discharge from genitals. (i) Select the option that correctly identifies disease X, Y and Z?
(ii) Identify virus P from the given paragraph. (a) Human papilloma virus (b) Human adenovirus (c) Human immunodeficiency virus (d) Human cytomegalovirus (iii) What are the symptoms of disease Y? (a) Weight loss (b) Fever or night sweats (c) Fatigue and weakness infections (d) All of these (iv) Select the incorrect statement regarding diseases X and Y. (a) Both X and Y can spread from infected mother to unborn baby during pregnancy (b) Both X and Y can spread from infected partner to healthy partner by unprotected sex (c) Y can also spread through use of contaminated needles and blood transfusion (d) None of these. (v) How can disease Y be prevented? (a) By following polygamy and having protected sex (b) Use of sterilised needles for injecting medicines, blood tests, etc (c) Collecting blood from unknown donors without background check by blood bank professionals (d) All of these.
*****************************************
Related 10th standard cbse science materials, other 10th standard cbse materials.

CBSE 10th Maths Probability Chapter Case Study Question with Answers
Cbse 10th maths statistics chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th maths surface areas and volumes chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th maths areas related to circles chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th maths circles chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th maths some applications of trigonometry chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th maths introduction to trigonometry chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th maths coordinate geometry chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th maths triangles chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th maths arithmetic progressions chapter case study questions with answers, cbse 10th maths quadratic equations chapter case study questions with answers.

CBSE 10th Social Science The Making Of A Global World Chapter Case Study Question with Answers
Cbse 10th social science nationalism in india chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th social science the rise of nationalism in europe chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th maths pair of linear equation in two variables chapter case study question with answers, tamilnadu stateboard 10th standard cbse study materials.

Tamilnadu Stateboard 10th Standard CBSE Subjects

Book a Trial With Our Experts
Hey there! We receieved your request
Stay Tuned as we are going to contact you within 1 Hour
Thank you for registering.
One of our academic counsellors will contact you within 1 working day.

Click to Chat
- 1800-5470-145
- +91 7353221155
- Login | Register
- My Classroom
- My Self Study Packages
- Batch Discussion
- My Forum Activity
- Refer a Friend
- Edit Profile
- Add Question
- Add Paragraph
- Search Coupon
Use Coupon: CART20 and get 20% off on all online Study Material
Complete Your Registration (Step 2 of 2 )

Register Now and Win Upto 25% Scholorship for a Full Academic Year !
Enter your details.

Registration done!
Sit and relax as our customer representative will contact you within 1 business day
Mobile Verification
OTP to be sent to Change
- Junior Hacker
- Junior Hacker New
- Self Study Packages
- JEE Advanced Coaching
- 1 Year Study Plan
- Rank Predictor
- Paper Pattern
- Important Books
- Sample Papers
- Past Papers
- Preparation Tips
- Latest News
- JEE Main Exams
- Online Coaching
- Branch Predictor
- JEE Main Syllabus
- Past Year Papers
- Math Preparation Tips
- IIT JEE Exam Details
- JEE Syllabus
- IIT JEE Toppers Tips
- IIT JEE Preparation Tips
- IIT JEE Preparation Tips for Class 11
- IIT JEE Preparation Tips for Class 9
- IIT JEE Preparation Tips for Class 8
- IIT JEE Preparation Time Table
- IIT JEE Online Coaching
- Correspondence Course For IIT JEE
- IIT JEE Coaching after 10th
- IIT JEE Coaching For Foundation Classes
- JEE Coaching Institutes
- IIT JEE Coaching in Kota
- IIT JEE Coaching Institutes In Kota
- BITSAT Examination
- View complete IIT JEE Section
- View All Engineering Exams
- Top Engineering Colleges
- Top Engineering Branches
- Engineering Exam Calendar
- NEET Entrance Exam
- NEET Online Coaching
- NEET Preparation Tips
- Participating States
- AIIMS Examination
- AIIMS Online Coaching
- View all Medical Exams
- Top Medical Colleges
- Medical Exam Coaching
- Best Medical Coaching In Kota
- Medical Exam Calendar
- NTSE Examination
- Notifications
- Application
- Important Dates
- Eligibility
- Study Material
- KVPY Examination
- Olympiads Examination
- Indian National Mathematics Olympiad
- Physics Olympiad
- Chemistry Olympiad
- Biology Olympiad
- Olympiads Sample Papers
- INMO Papers
- CBSE School Exams
- Solutions for Board Exam
- JEE Advanced
- Karnataka CET
- Manipal UGET
- NCERT Class 12 Solutions
- NCERT Class 11 Solutions
- NCERT Class 10 Solutions
- NCERT Class 9 Solutions
- NCERT Class 8 Solutions
- NCERT Class 7 Solutions
- NCERT Class 6 Solutions
- List of JEE Main & JEE Advanced Books
- R.D. Sharma Solutions PDFâ
- Concepts of Physics by HC Verma for JEE
- HC Verma Solutions Part 1
- HC Verma Solutions Part 2
- Most Scoring Topics in IIT JEE
- IIT JEE Entrance Exam
- Discuss with Colleagues and IITians
- Engineering Entrance Exams
- Branch Ranking of IIT
- Discuss with Askiitians Tutors
- NEET (AIPMT)
- Marks and Rank in IIT JEE
- Top Engineering Colleges in India
- AIEEE Entrance Exam
- Electric Current
- Wave Motion
- Modern Physics
- Thermal Physics
- Electromagnetic Induction
- General Physics
- Electrostatics
- Wave Optics
- Physical Chemistry
- Organic Chemistry
- Inorganic Chemistry
- Trigonometry
- Analytical Geometry
- Differential Calculus
- Integral Calculus
- Magical Mathematics
- Online Tutoring
- View complete NRI Section
- View Complete Study Material
- View Complete Revision Notes
- Ahmadi (FAIPS)
- Khaitan (Carmel School)
IIT JEE Courses

One Year IIT Programme
- Super Premium LIVE Classes
- Top IITian Faculties
- 955+ hrs of Prep
- Test Series & Analysis

Two Year IIT Programme
- 1,835+ hrs of Prep

Crash Course
- LIVE + Pre Recorded Sessions
- 300+ hrs of Prep
NEET Courses

One Year NEET Programme
- Top IITian & Medical Faculties
- 900+ hrs of Prep

Two Year NEET Programme
- 1,820+ hrs of Prep

- LIVE 1-1 Classes
- Personalized Sessions
- Design your own Courses
- Personalized Study Materials
School Board
Live online classes, class 11 & 12.
- Class 11 Engineering
- Class 11 Medical
Class 9 & 10
Class 6, 7 & 8, test series, jee test series.
- 2 Year Jee Test Series
- 1 Year Jee Test Series
NEET test series
- 2 Year NEET Test Series
- 1 Year NEET Test Series
C.B.S.E test series
- 11 Engineering
- 12 Engineering
Complete Self Study Packages
Full course.
- 2 year NEET
- Chemistry 11th & 12th
- Maths 11th & 12th
- Physics 11th & 12th
- Biology 11th & 12th
- View Complete List
For class 12th
- Chemistry class 12th
- Maths class 12th
- Physics class 12th
- Biology class 12 th
For class 11th
- Chemistry class 11th
- Maths class 11th
- Physics class 11th
- Biology class 11th
How Do Organisms Reproduce CBSE Class 10 Science Notes Chapter 8
CBSE Class 10 Science Revision Notes for Chapter 8 How do Organisms Reproduce are given below in a pointwise format. The notes are based on the current syllabus for Class 10 Science and are the best study resource for board exam preparation. With these notes, you can revise the whole chapter of How do Organisms Reproduce in just 15 minutes. The notes include all the important points, definitions and diagrams for your complete understanding.
Class 10 Science CBSE Chapter 8 How do Organisms Reproduce includes topics like sexual reproduction, asexual reproduction and reproduction in flowering plants, fission and fusion, sexual reproduction in animals, changes in the body at puberty, birth control methods, etc. You can revise every topic in detail with our online free revision notes for CBSE Class 10 Science.
Free Revision Notes for Class 10 Science How do Organisms Reproduce
The ability to produce a new organism is known as reproduction. There are two types of reproduction-asexual reproduction and sexual reproduction.
Do organisms create exact copies of themselves?
Reproduction at its most basic level involves making copies of the blueprints of body design.
The chromosomes in the nucleus of a cell contain information for the inheritance of features from parents to the next generation in the form of DNA (Deoxyribo Nucleic Acid) molecules.
The DNA in the cell nucleus is the information source for making proteins. If the information is changed, different proteins will be made. Different proteins will eventually lead to altered body designs.
The cells use chemical reactions to build copies of their DNA. This creates two copies of the DNA in a reproducing cell, and they will need to be separated from each other.
To ensure that, a cell divides itself into two cells, each cell containing its own DNA and cellular apparatus.
Now, both these cells will be identical, but we cannot say that copying of the DNA will be 100% identical.
There might be some variations in the chemical reaction which means organisms cannot create exact copies of themselves.
Different types of Reproduction
There are mainly two types of reproduction- asexual reproduction and sexual reproduction.
Asexual Reproduction
It is a mode of reproduction involving a single parent. There are different modes of asexual reproduction-
Fission is defined as the splitting of the organisms into two halves and each half gives rise to a new organism. For example, Amoeba, bacteria. The most common type of fission is binary fission. It is a division of organisms such as bacteria into two or more parts. Binary fission can be irregular (division can take place in any plane), longitudinal (division occurs longitudinally), transverse (division occurs transversely) and can also be oblique (division occurs obliquely).

Fig.1. Binary fission in Amoeba
Fragmentation is another mode of asexual reproduction in which organism breaks into pieces and each piece give rise to a new organism. For example, Spirogyra, Planaria.
Fig.2. Fragmentation in Planaria
Regeneration is the ability to form new organisms from body parts. Cut or broken part generates a new organism. For example, Hydra, Planarians

Fig. 3. Regeneration in Hydra
Budding is defined as an outgrowth from the body of the organism. This outgrowth then detaches from the body and forms a new independent organism. For example, Hydra and Yeast.

Fig .4. Budding in Hydra
Vegetative reproduction is another method of asexual reproduction. In this form of reproduction, stem, root and leaves are used to form plants when provided with suitable conditions. Layering and cutting are the two common methods used for vegetative propagation. For example, banana, rose, jasmine etc. The plant produced through vegetative propagation is genetically identical to the parent plant.
Cutting involves the rooting of the severed piece of the plant.
Layering involved rooting the piece of the plant and then severing it.
Grafting occurs when two plant parts are joined together such as stem and root. The stem of the plant to be grafted is known as the scion, and the root is called the stock. (NTSE)
Fig.5. Vegetative Propagation
Spore formation is another method of asexual reproduction that involves specific reproductive parts such as hyphae in Rhizopus and blob-on-a stick structure in Rhizopus are involved in reproduction.

Fig.6. Spore formation in Rhizopus
Sexual Reproduction
Sexual reproduction involved two different parent organisms involving a female and a male parent.
Significance of Sexual Reproduction
Sexual reproduction is the source of variation. The mixing of two organisms gives rise to new recombinants or variants. Sexual reproduction involves the mating of germ cells also known as gametes. These gametes are haploid, that is, they have a half set of chromosomes. These gametes are formed through the process of meiosis. When male gametes and female gametes each with a haploid set of chromosomes combine they will form a diploid zygote. Zygotes undergo repeated divisions to form a new organism.
In humans, the male gamete is small and motile whereas the female gamete is large and non-motile.
Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants
The flower is the reproductive structure found in angiosperms. The flower consists of sepals, petals, stamens and pistils.
Fig.7. Structure of flower
A flower is said to be unisexual if it contains either stamens or pistils whereas if both stamens and pistils are present, it is known as bisexual. Papaya and watermelon are unisexual whereas Hibiscus and mustard are bisexual.
Pistil/carpel is the female reproductive structure that consists of a swollen basal ovary, middle elongated style and terminal stigma. The ovary contains ovules and each ovule bears an egg cell. Stamen is the male reproductive part and it consists of the anther and the stigma. The anther contains pollen grains that fuse with a female gamete, that is, egg cells. Fusion leads to zygote formation which forms a new plant.
Transfer of pollen grains from the anther to the stigma of the flower is known as pollination. When the pollen and the stigma are of the same flower, it is known as self-pollination. When pollen from one flower lands on the stigma of another flower it is known as cross-pollination.
Gametogenesis
The formation of gametes is known as gametogenesis. The male gamete is pollen grains whereas the female gamete is present inside the ovary. The ovary contains an ovule. Ovule contains the female gametophyte. Ovule also consists of outer layers known as integuments, nucellus and female gametophyte. Male and female gametes are produced and they are haploid in nature. There are two types of gametes- homogametes and heterogametes. When male and female gametes cannot be differentiated morphologically. They are known as homogametes. For example, gametes in Cladophora, Algae. When male and female gametes can be differentiated morphologically, they are known as heterogametes.
Post Fertilisation Events
The most important post-fertilization structure is the embryo and seeds. Zygote forms the embryo. Zygote first forms a pro-embryo which later converts into a mature embryo. Seeds are the result of sexual reproduction. Ovules mature into seeds whereas the ovary develops into fruits.
Double Fertilisation
In flowering plants, one sperm fertilises the egg cell, whereas the other sperm fuses with the two polar nuclei forming the endosperm. This is known as double fertilisation as two fertilisation events are taking place. The zygote divides to form 7 celled and 8 nucleated embryo sacs. Out of these 7 cells and 8 nuclei, there are two synergids with egg cells, 3 antipodals and two polar nuclei. Two polar nuclei fuse with one sperm and the other sperm fuse with the egg cell to form the zygote.
Fig.8. Double fertilisation
Reproduction in Human Beings
Humans reproduce sexually. When girls and boys attain puberty (reproductively active) there occur lots of changes in their bodies. The development of hair in armpits and genital regions is common to both males and females. Girls have increased breast size, darkening of skin and tips of nipples etc. Some changes such as thick hairy facial growth, voice changes occur in males.
Male Reproductive System
The male reproductive system comprises a pair of the testis, glands, accessory ducts, and male genitalia.
The testis is the site where male gametes or germ cells are produced. They are located outside the abdominal cavity in a sac-like structure known as the scrotum. This is to maintain the lower temperature required for the formation of sperm. Testis produces the male hormone testosterone needed for the development of secondary sexual characteristics in males such as the formation of beard and moustaches and also in the development of sperm.
Vas deferens is a duct that transports sperm to the urethra, which is a common passage for both urine and sperm ejaculation.
Prostate glands and seminal vesicles are also found in males to nourish and for easy transport of sperm in the female genital tract. Cowper’s gland produces mucus-like fluid that neutralises the acidity of the female vagina. All these secretions along with sperm form the semen.

Fig.9. Male Reproductive System
The formation of male gametes or sperm in testes is known as spermatogenesis. Sperms are haploid in nature. Seminiferous tubules are the site for spermatogenesis.
Testis produces a male hormone known as testosterone needed for the male secondary sexual characteristics as well as for spermatogenesis.
Female Reproductive Tract
The female reproductive system consists of a pair of ovaries, uterus, cervix, vagina, and external genitalia.
Female eggs or ova are produced in the ovaries. The formation of ova in the ovaries is known as oogenesis. The ovary produces female hormones such as oestrogen, progesterone. These hormones are needed for female sexual development and well as for pregnancy. The fallopian tube carries ova from the ovary to the womb. Two oviducts joined to form the uterus. Uterus then opens into Vagina via the cervix.

Fig.10. Female Reproductive System
Sperm enter into the female vagina at the time of sexual intercourse. Then the sperm reaches the fallopian tube where it fuses the ova to form a zygote. This is known as fertilisation. Then the zygote divides to form an embryo. The embryo gets implanted into the uterus. The embryo development occurs in the uterus to form the foetus.
Mother supplies nutrition to the growing foetus via the placenta. The placenta helps in the exchange of nutrients, gases and the removal of excretory products. The development of a child inside the womb of the mother takes place for about 9 months. Then the rhythmic uterine contraction leads to the delivery of the baby outside the female body.
Fig.11. Human Placenta
If the egg is not fertilised, the uterine lining is shed off in the form of fluid known as menstrual fluid. The discharge occurs from the vagina as blood and mucus. This is known as menstruation. It lasts for about 2 to 8 days.
Reproductive Health
It is defined as the state of well being in terms of safe sex, reproductive fitness as well as the absence of any reproductive diseases. Unsafe sex leads to different diseases which are known as sexually transmitted diseases.
Some of the sexually transmitted diseases are as follows-
- Gonorrhoea is caused by bacteria
- Syphilis is caused by bacteria
- AIDS (acquired immunodeficiency syndrome) is caused by a virus HIV(human immunodeficiency virus)
In-vitro Fertilisation (IVF)
IVF is an infertility treatment method. In this case, the egg is fertilised with sperm outside the female body. Ovum is removed from the female body and is allowed to fertilise with sperm outside the body in In-vitro conditions.
Birth Control Methods
For a country like India where the population is increasing continuously, there is a need for birth control methods.
- Condoms and diaphragms are barrier methods for birth control. They prevent the binding of sperm to the ovum.
- The chemical method of birth control includes oral pills and vaginal pills.
- Intrauterine contraceptive devices are also there to prevent the implantation of embryos in the uterus.
- Surgical methods include vasectomy in males and tubectomy in females. Vasectomy is done by cutting the Vas deferens and then tying them up. Tubectomy involves cutting and tying a small portion of oviducts.

Fig. 12. Birth Control Methods
CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 8 How do Organisms Reproduce Revision Notes FAQs
Why should I download revision notes from askIITians?
- The revision notes are prepared by askIITians Science experts.
- The notes include pointwise explanations for all the topics of the chapter.
- There are labelled diagrams included to help students understand the concepts better.
- The notes help in quick revision of the chapter before exams and are the best study material for conceptual understanding as well.
- The free revision notes are based on the latest CBSE syllabus.
How to study CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 8 How do Organisms Reproduce for board exams?
- Read the chapter carefully from the NCERT textbook and underline the important points.
- Make your own notes and refer to the revision notes prepared by askIITians experts to understand every concept of the chapter clearly.
- Practise all the exercise questions from the chapter. In case you have any doubts, refer to the NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science from our experts.
I need more help with CBSE Class 10 Science. What should I do?
You should join online CBSE coaching at askIITians and study in live classes from our experts. Their innovative and clear teaching methodologies are proven to help students solidify their conceptual understanding. Besides, you will get a plethora of study resources for CBSE Class 10 Science including mind maps, practice worksheets, flashcards, previous year papers, and more!
TOP Your EXAMS!
Upto 50% scholarship on live classes, course features.
- Video Lectures
- Revision Notes
- Previous Year Papers
- Study Planner
- NCERT Solutions
- Discussion Forum
- Test paper with Video Solution

Book Free demo of askIITians Live class
View courses by askiitians.

Design classes One-on-One in your own way with Top IITians/Medical Professionals

Complete Self Study Package designed by Industry Leading Experts

Live 1-1 coding classes to unleash the Creator in your Child

a Complete All-in-One Study package Fully Loaded inside a Tablet!
Ask question.
Get your questions answered by the expert for free

Your Question has been posted!
You will get reply from our expert in sometime.
We will notify you when Our expert answers your question. To View your Question
POST QUESTION
Select the tag for question.

Our Environment CBSE Class 10 Science Revision...
Management of Natural Resources CBSE Class 10...
Electricity CBSE Class 10 Science Revision Notes...
Acid Bases and Salts CBSE Class 10 Science...
Metals and Non Metals CBSE Class 10 Science Notes...
Carbon and its Compounds CBSE Class 10 Science...
Revision Notes on Control and Coordination...
Revision Notes on Chemical Reactions and Equations...
Revision Notes on Sources of Energy The largest...
Heredity and Evolution CBSE Class 10 Science...
Periodic Classification of Elements CBSE Class 10...
Revision Notes on Magnetic Effect of Electric...
Light Reflection and Refraction CBSE Class 10...
Life Processes CBSE Class 10 Science Revision...
Human Eye and Colourful World CBSE Class 10...
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 7 How do Organisms Reproduce
Class 10 Science Chapter 7 Solutions Class 10 Science Chapter 7 Exercises Solutions Class 10 Science Chapter 7 Intext Exercises Class 10 Science Chapter 7 in Hindi Medium Class 10 Science Book Download in PDF Class 10 Science Chapter 7 Board Questions Class 10 Science Chapter 7 MCQ Class 10 Science Chapter 7 Extra Questions Class 10 Science NCERT Solutions Class 10 all Subjects Solutions
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 7 How do Organisms Reproduce? in Hindi and English Medium updated for CBSE 2024-25. Get the revise solutions of class 10th science chapter 7 based on latest textbooks and syllabus for academic year 2024-25.
In NCERT Class 10 Science, Chapter 7 is how do Organisms Reproduce? This chapter explains in detail about reproduction in organisms. Here are the main topics covered in this chapter introduction to Reproduction.
Class 10 Science Chapter 7 Questions in Detail
What is the importance of dna copying in reproduction, why is variation beneficial to the species but not necessarily for the individual.
- How does binary fission differ from multiple fission?
- How will an organism be benefited if it reproduces through spores?
- Can you think of reasons why more complex organisms cannot give rise to new individuals through regeneration?
- Why is vegetative propagation practised for growing some types of plants?
- Why is DNA copying an essential part of the process of reproduction?
- How is the process of pollination different from fertilisation?
- What is the role of the seminal vesicles and the prostate gland?
- What are the changes seen in girls at the time of puberty?
- How does the embryo get nourishment inside the mother’s body?
- If a woman is using a copper-T, will it help in protecting her from sexually transmitted diseases?
What are the advantages of sexual reproduction over asexual reproduction?
What are the functions performed by the testis in human beings, why does menstruation occur.
- Draw a labelled diagram of the longitudinal section of a flower.
What are the different methods of contraception?
- How are the modes for reproduction different in unicellular and multicellular organisms?
- How does reproduction help in providing stability to populations of species?
What could be the reasons for adopting contraceptive methods?
An overview of the concept of reproduction in living organisms. The significance of reproduction for the continuation of species, detailed explanation of asexual reproduction, various methods of asexual reproduction, including fission, budding, fragmentation, and spore formation are examples of organisms that reproduce asexually.
Class 10 Science Chapter 7 Answers in Hindi and English Medium
- Class 10 Science Chapter 7 Exercises
- Class 10 Science Chapter 7 Intext Questions
- Class 10 Science Chapter 7 in Hindi
- Class 10 Science Chapter 7 in PDF
- Class 10 Science Chapter 7 Board Questions
- Class 10 Science Chapter 7 MCQ
- Class 10 Science Chapter 7 Extra Questions
- Class 10 Science NCERT Solutions
- Class 10 all Subjects Solutions
A brief introduction of chapter 7 in 10th Science Basic Concepts of Reproduction : Class 10 Science chapter 7 begins by discussing the fundamental aspects of reproduction, emphasizing the role of DNA in inheritance and the importance of creating DNA copies for reproduction. It explains how changes in DNA can lead to different proteins and ultimately result in varied body designs.
Reproductive Methods in Various Organisms : Class 10 Science chapter 7 covers different reproductive strategies in organisms, including asexual methods like fission in single-celled organisms (e.g., Plasmodium) and fragmentation in multicellular organisms like Spirogyra. The chapter also discusses sexual reproduction in humans, detailing the changes that occur during puberty and the functioning of male and female reproductive systems.
Human Reproductive System : The 10th Science chapter 7 provides detailed descriptions of the male and female reproductive systems, explaining the process of egg and sperm production, fertilization, and embryo development. It also discusses menstrual cycles and reproductive health.
Pregnancy and Embryo Development : The process of embryo implantation in the uterus, the role of the placenta in nourishment, and the overall development of the embryo are explained. Class 10 Science chapter 7 also touches on the physical and hormonal changes that occur during pregnancy.
Reproductive Health and Social Aspects : Class 10 Science chapter 7 addresses the importance of reproductive health and the societal pressures related to sexual activity, marriage, and childbearing. The chapter 7 of 10th science encourages thoughtful consideration of these pressures and the importance of making informed choices.
Exercises and Questions : The chapter 7 of 10th science concludes with a series of exercises and questions designed to test understanding of the concepts covered, including the differences between various reproductive processes, the structure of reproductive systems, and the significance of reproductive health.
Class 10 Science chapter 7 explains about the detailed explanation of sexual reproduction, the role of male and female reproductive organs in sexual reproduction. It also describes fertilization and the formation of zygotes, structure and functions of the male and female reproductive systems. Students can learn here about the process of gametogenesis (formation of sperm and egg cells) in males and females and menstrual cycle and ovulation in females.
The main topics to learn for exams are development of the zygote into an embryo, pregnancy and the stages of embryonic development, the importance of reproductive health and hygiene, common reproductive health issues and their prevention, family planning methods and their significance.

We will learn here that the role of genes and DNA in inheritance. The occurrence of variation in offspring. Explanation of how sex is determined in different organisms. Human sex determination and the role of sex chromosomes. Structure and functions of the male and female reproductive organs in flowering plants (stamen and pistil). The process of pollination and fertilization in plants. Formation of seeds and fruits.
Class 10 Science chapter 7 helps to know the different reproductive strategies adopted by animals, examples of oviparous and viviparous animals, advantages and disadvantages of various reproductive strategies. This chapter provides a comprehensive understanding of the various ways in which organisms reproduce, from simple asexual methods to complex sexual reproduction. It also introduces students to the human reproductive system and the basics of genetics and heredity. Understanding these concepts is essential for a strong foundation in biology.
Extra important questions related to Chapter 7 of 10th Science are also given with previous years CBSE Board questions and answers. CBSE Solutions Apps based on latest NCERT Books download for offline use.
Class X Science NCERT textbook chapter 7 intext question answers of Page 128 or Page 133 or Page 140 or Exercises in English Medium updated for new academic session. All the contents in dual Medium on this website are free to use without any login or password.
Hindi Medium NCERT Solutions of 10th Science chapter 7 Hindi Medium Solution are given to view online or free download in PDF format. UP Board Students are also using NCERT Books in the session 2024-25, so download UP Board Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 7 from here in Hindi or English Medium.
Preparing for NCERT Class 10 Science Chapter 7 , how do Organisms Reproduce, here’s a step-by-step plan to help students prepare this chapter effectively. Begin by reading the entire chapter carefully to get an overview of the topics covered. Pay special attention to the definitions, terms, and processes related to reproduction, both asexual and sexual. While reading, take notes that summarize each section. Include important definitions, processes, and examples. These notes will be useful for quick revision.
To prepare the chapter 7 of 10th Science , create diagrams and flowcharts to visualize the processes of reproduction, especially those involving human reproductive systems and flower structures. Diagrams can help in understanding and retention. Understand the differences between asexual and sexual reproduction.
Be able to identify examples of organisms that reproduce using each method. Pay close attention to the structure and functions of the male and female reproductive systems in humans. Understand the processes of gametogenesis, fertilization, and embryo development.

Learn about Reproductive Health- Study the importance of reproductive health and hygiene. Be aware of common reproductive health issues and family planning methods. Understand the basics of genetics, genes, DNA, and inheritance. Comprehend how variation occurs in offspring. Solve the questions provided at the end of the chapter. This includes both multiple-choice and descriptive questions. Pay attention to numerical problems and their solutions.
If you find certain concepts, in chapter 7 of 10th Science , challenging, refer to supplementary resources such as online tutorials, videos, or reference books to gain a deeper understanding. Periodically review your notes and practice questions to reinforce your memory of the chapter’s content. Practice labeling diagrams related to flower structures, human reproductive organs, and other key concepts. This can help you score well in exams.
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 7 How do Organisms Reproduce? Intext question as well as chapter end exercises question answers are given below updated for new academic year. Ask your doubts through Discussion Forum and answer the questions asked by the other users.
Engage in discussions with classmates or study groups to clarify doubts and reinforce your understanding of the material. Allocate specific time slots for studying this chapter in your overall study schedule. Consistency in studying is crucial. Solve previous years’ question papers to become familiar with the types of questions that may appear in the board exams.
Remember that understanding the concepts and processes related to reproduction is crucial for both your board exams and for building a strong foundation in biology. Take a systematic approach, and don’t rush through the material.
Class 10 Science Chapter 7 Extra Question Answers
DNA found in chromosomes in the nucleus of the cell has the information to create proteins which lead to body design of an organisms. If the organisms are to make exact copies of themselves, the DNA should replicate to make an exact copy of itself. DNA replicate in the cell with the help of various enzymes and this is accompanied by division of the basic unit of every organism, i.e., the cell.
What are sexually transmitted diseases? Name an STD which damages the immune system of human body.
The sexually act is very intimate connection of bodies and thus many diseases can be sexually transmitted. These include bacterial infections like gonorrhoea and syphilis and viral infection like warts and HIV-AIDS (Human Immunodeficiency Virus-Acquired Immuno Deficiency Syndrome). HIV-AIDS causes damages to the immune system of human body.
Variations are useful for the survival of species in changed environmental situations. For example, if a population of reproducing organisms were suited to a particular niche (well defined place of abode) and if the niche is drastically changed, the population could be wiped out. However, if some variations were to be present in a few individuals in these populations, there would be some chance for them to survive. Thus, if there is a population of bacteria living in temperate waters and if water temperature increases by global warming, most of bacteria would die. But few a variants resistant to heat would survive and grow further. Variation is thus useful for the survival of species over time.
What are the three categories of contraception methods? Write briefly about each.
The methods used for regulation of child birth are: (i) Barrier method: In this method physical devices like condoms, cervical cap and diaphragm are used to prevent sperms to reach up to the ovum. (ii) Chemical method: In this method specific drugs are used by females. These drugs may be (a) oral pills or (b) vaginal pills. Oral pills mainly contains hormones and are called oral contraceptives. They disturb hormonal balance so that eggs are not released and fertilised. (iii) Intrauterine contraceptive devices (IUCDs): ICUD like copper-T is placed safely in the uterus by skill doctor. ICUDs prevents implantation of the fertilized ovum inside the uterus. (iv) Surgical method: this method is applicable to both male and female. In males, a small portion of vas deferens and the fallopian tube in female is surgically removed or ligated (tied). It is known as vasectomy in males which prevents release of sperms from the testes. In females, it is called tubectomy.
“Multicellular organisms cannot divide cell by cell.” List two reasons to justify this statement.
Multi cellular organisms cannot simply divide cell by cell because: (i) Many multi cellular organism are not simply a random collection of cells. Specialised cell are organised as tissues and tissues are organised into organs which are placed at a definite position in the body. (ii) Each organ performs a specific function/functions. In such a carefully organised situation, cell by cell division (for reproduction) would be impracticable.
Describe menstrual cycle.
The uterus develops thick and spongy lining to receive fertilised egg. When the egg is not fertilised, uterine lining slowly break and comes out as blood and mucous. This cycle takes place roughly every month and is known as menstrual cycle (menstruation).
Define the process of fragmentation in some organisms. Which category of organisms are involved in this process? Give one example.
Fragmentation: The mode of reproduction of simple multicellular organisms in which body simply breaks up into smaller pieces upon maturity and each piece or fragment grows into a new individual is called fragmentation. The relatively simple multicellular organisms which are simply a random collection of cells are involved in fragmentation type of reproduction. Example: Spirogyra.
What is the role of seminal vesicle and the prostate gland?
Role of seminal vesicle and Prostate gland. Along the path of the vas deferens, these glands add their secretions so that the sperms are now in a fluid which makes their transport easier and this fluid also provides nutrition to sperms.
What is pollination? List the modes of pollination and define each of them?
The transfer of pollen grains form anther of stamen to stigma is called pollination. The transfer of pollen from the anther of one flower to the stigma of another flower of a different plant of the same species is called cross pollination. In this case, pollen grains of the same flower do not pollinate its stigma. In cross pollination, the transfer of pollen grains may take place through some agency like wind, insect, bird, water, mammals etc. Transfer of pollen from the anther of a flower to the stigma of the same flower or a flower on the same plant is called self pollination.
Tiwari Academy provides a variety of practice questions and exercises related to 10th Science Chapter 7 . These questions can help students test their understanding of the material and improve their problem-solving skills.
To help students prepare for exams, the platform offer sample papers and previous years’ question papers. Solving these papers can help students familiarize themselves with the exam pattern and practice answering questions effectively.
Question 1: (a) Name the following: (i) Thread like non-reproductive structures present in Rhizopus. (ii) ‘Blob’ that develops at tips of the non-reproductive threads in Rhizopus. (b)Explain the structure and function of the structures released from the ‘blobs’ in Rhizopus. Answer 1: (a) (i) Hyphae (ii) Sporangia (b) On maturity sporangia ruptures and release spores. Each spore contains a nucleus and cytoplasm enclosed in a thick wall for protection. Function: Spores disperse far and wide. Each spore grows into new Rhizopus when come in contact of moist surface and other suitable conditions.
Question 2: Differentiate between pollen gains and ovule? Answer 2: Pollen grain produces male germs-cell (male gamete) in the plants. The ovule contains a female gamete (female germ cell or egg).
Question 1: Name the plant that reproduces through leaves. List two advantages of this way of reproduction. Answer 1: Bryophyllum Advantages: (i) Many buds are produced in the notches along the margin of a single leaf. Each leaf-bud of Bryophyllum produces a plant. (ii) The plants from the buds are exactly similar to the parent plant. (iii) A large number of young plants are produced by a single leaf of a plant that helps in survival of the species.
Important Questions on 10th Science Chapter 7
Name the plant that reproduces through leaves. list two advantages of this way of reproduction..
Bryophyllum Advantages: (i) Many buds are produced in the notches along the margin of a single leaf. Each leaf-bud of Bryophyllum produces a plant. (ii) The plants from the buds are exactly similar to the parent plant. (iii) A large number of young plants are produced by a single leaf of a plant that helps in survival of the species.
How does the process of budding is differ from the process of spore formation?
Budding: A bud, as in Hydra, develops as an outgrowth due to replicated cell division at a specific site. These buds when mature detach from the parent body and become new individual. Spore Formation: In spore formation, as in Rhizopus, a specific part called Sporangia that produce spores. The spores are covered by thick walls that protect them until a spore gets favourable conditions to grow into a new (Rhizopus) plant.
Advantages of sexual reproduction: In sexual reproduction, more variations are produced. Thus, it ensures survival of species in a population. The new formed individual has characteristics of both the parents. Variations are more viable in sexual mode than in asexual one. This is because in asexual reproduction, DNA has to function inside the inherited cellular apparatus.
The testes are the male reproductive organs that are located outside the abdominal cavity within a pouch called scrotum. Functions of testes: Produce sperms Produce a hormone called testosterone, which brings about secondary sexual characters in boys.
Menstruation is a process in which blood and mucous flows out every month through the vagina. This process occurs every month because one egg is released from the ovary every month and at the same time, the uterus (womb) prepares itself to receive the fertilized egg. Thus, the inner lining of the uterus gets thickened and is supplied with blood to nourish the embryo. If the egg does not get fertilised, then the lining of the uterus breaks down slowly and gets released in the form of blood and mucous from the vagina.
The contraceptive methods can be broadly divided into the following types: Natural method: It involves avoiding the chances of meeting of sperms and ovum. In this method, the sexual act is avoided from day 10th to 17th of the menstrual cycle because during this period, ovulation is expected and therefore, the chances of fertilization are very high. Barrier method: In this method, the fertilization of ovum and sperm is prevented with the help of barriers. Barriers are available for both males and females. Condoms are barriers made of thin rubber that are used to cover penis in males and vagina in females. Oral contraceptives: In this method, tablets or drugs are taken orally. These contain small doses of hormones that prevent the release of eggs and thus fertilization cannot occur. Implants and surgical methods: Contraceptive devices such as the loop or Copper-T are placed in uterus to prevent pregnancy. Some surgical methods can also be used to block the gamete transfer. It includes the blocking of vas deferens to prevent the transfer of sperms known as vasectomy. Similarly, fallopian tubes of the female can be blocked so that the egg will not reach the uterus known as tubectomy.
Contraceptive methods are mainly adopted because of the following reasons: (i) To prevent unwanted pregnancies. (ii) To control population rise or birth rate. (iii) To prevent the transfer of sexually transmitted diseases.
Question 2: Give functions of the following organs of the human male reproductive system. (a) Scrotum (b) Testes Answer 2: (a) Testes are placed in scrotum which are located outside the abdominal cavity. It keeps the temperature lower than the normal body temperature that is required for the formation of sperm. (b) Testes produce sperm and male hormone testosterone.
Tiwari Academy’s Discussion platforms have doubt-clearing sessions where students can ask questions related to the chapter, and educators or experts will provide explanations and clarifications. Interactive quizzes and tests can help students assess their knowledge and track their progress. These quizzes designed to simulate the format of actual exams. Class 10 Science chapter 7 involve complex diagrams and illustrations related to reproductive processes in plants and animals.
The chapter 7 of 10th Science includes diagrams related to flower structures, human reproductive organs, and other concepts. Students may be asked to label these diagrams or explain specific parts and their functions, making diagram-based questions important. Examination questions present scenarios or case studies related to reproduction in organisms. Students may need to apply their knowledge to analyze these situations and explain the outcomes.
Understanding the human reproductive system, including the structure and functions of male and female reproductive organs, processes like gametogenesis, fertilization, and embryonic development, is crucial. Questions related to human reproduction are common in exams. Reproductive health is a significant component of this chapter. Questions may focus on the importance of reproductive health, common reproductive health issues, and family planning methods.
The 10th Science chapter 7 briefly introduces students to the concepts of genetics and heredity, which are fundamental in biology. Questions may assess a student’s understanding of how genes, DNA, and variation play a role in reproduction. Some questions require practical knowledge, such as understanding the steps involved in the menstrual cycle in females or the process of fertilization. Mastery of Chapter 7 serves as a foundation for understanding more advanced concepts related to reproduction, genetics, and evolution in higher classes. It is essential for students who plan to pursue biology in their future studies.
In summary, NCERT Class 10 Science Chapter 7 is vital for both board examinations and future studies in biology. It covers fundamental biological concepts and practical knowledge related to reproduction in organisms, making it an important topic for students to prepare thoroughly.
How is Tiwari Academy helpful in preparation for NCERT Class 10 Science Chapter 7?
Tiwari Academy is an online education platform that offers resources and assistance to students preparing for various exams, including NCERT Class 10 Science. Tiwari Academy’s offerings for NCERT Class 10 Science Chapter 7, how do Organisms reproduce? It provides comprehensive chapter notes that summarize key concepts, definitions, and important points from Chapter 7. These notes can serve as a quick reference for students. The platform may offer video tutorials that explain complex topics from the chapter in an easy-to-understand manner. Visual aids can help students grasp concepts more effectively.
From an exam perspective, how is NCERT Class 10 Science Chapter 7 important?
From an exam perspective, NCERT Class 10 Science Chapter 7, how do organisms reproduce?’ is important for several reasons. This chapter typically carries a significant weightage in the Class 10 Science examination conducted by various educational boards, including the Central Board of Secondary Education (CBSE) in Bharat. This means that a substantial portion of the exam paper is dedicated to questions from this chapter.
Understanding the process of reproduction is a fundamental concept in biology. It is a crucial topic that serves as the basis for more advanced topics in biology and genetics in higher classes. Mastery of this chapter is essential for building a strong foundation. Class 10 Science chapter 7 covers a wide range of topics, including asexual and sexual reproduction in plants and animals, the human reproductive system, fertilization, pregnancy, reproductive health, heredity, variation, and more.
Which section of 10th Science Chapter 7 belongs to?
No, chapter 7 of grade 10th Science doesn’t belong to Physics or Chemistry. Chapter 7 of 10th Science contained the contents related to biology section. For Class 10 we can say that chapter 7 is a biology chapter.
In which term chapter 7 (How do organisms reproduce) of class 10th Science comes?
Chapter 7 (How do organisms reproduce) of class 10th Science comes in terminal exams. This chapter may come in term 1 also. This chapter is unique and interesting. Students should study this chapter patiently.
Which main topics do teachers cover under chapter 7 of 10th standard Science?
Teachers cover the following topics under chapter 7 of 10th standard Science: 1. Do organisms create exact copies of themselves? 2. The Importance of Variation 3. Modes of reproduction used by single organisms 4. Fission 5. Fragmentation 6. Regeneration 7. Budding 8. Vegetative Propagation 9. Spore Formation 10. Sexual reproduction 11. Why the Sexual Mode of Reproduction? 12. Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants 13. Reproduction in Human Beings 14. Male Reproductive System 15. Female Reproductive System 16. What happens when the Egg is not Fertilised? 17. Reproductive Health
Which extra materials can students use to prepare chapter 7 of class 10th Science?
Extra materials that students can use to prepare chapter 7 of class 10th Science are: 1. NCERT Exemplar 2. Book by Lakhmir Singh and Manjit Kaur 3. Sample papers released by CBSE and Previous years Board papers.

« Chapter 6: Control and Coordination
Chapter 8: heredity and evolution ».
Copyright 2024 by Tiwari Academy | A step towards Free Education

Talk to our experts
1800-120-456-456
- How Do Organisms Reproduce Class 10 Notes CBSE Science Chapter 8 (Free PDF Download)
- Revision Notes

CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 8 - How do Organisms Reproduce? Revision Notes - Free PDF Download
Chapter 10 in Science deals with the topic of 'How do organisms reproduce'. This chapter primarily discusses the reproductive system in living organisms and the types of reproductive systems, in particular. It shows the different methods of reproductive systems in plants and animals and distinguishes between asexual reproduction and sexual reproduction.
Reproduction Class 10 notes further elaborates on the male reproductive system and the female reproductive system. The chapter lays down the various intricacies associated with it and other related aspects. Vedantu is a platform that provides free CBSE Solutions (NCERT) and other study materials for students. Maths Students who are looking for the better solutions, they can download Class 10 Maths NCERT Solutions to help you to revise complete syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Download CBSE Class 10 Science Revision Notes 2024-25 PDF
Also, check CBSE Class 10 Science revision notes for All chapters:

Related Chapters
Access Class 10 Science Chapter 8 – How do Organisms Reproduce?
1. do organisms create exact copies of themselves .
The organisms are similar in their looks due to having similar body designs, which in turn indicates that the source for these designs must be similar. And hence reproduction is that process where these designs are created.
The nucleus of a cell contains the chromosomes, which carry the information for the inheritance of features from parents to the next generation. It is present in the form of DNA molecules.
The DNA present in the nucleus of a cell is the source of information for making proteins. If this information changes, then a different set of proteins will be synthesised which will eventually lead to altered body designs in the organisms.
Hence it can be noted that a basic event in reproduction involves the creation of a DNA copy.
This copying of DNA is accompanied by the creation of an additional cellular apparatus, after which the DNA copies separate with each of them having its own cellular apparatus. Thus, a cell divides to give rise to two cells.
Since this process of copying DNA is a biochemical process, it may not be reliable and it will lead to some variations each time.
If the created new DNA copy is not viable, then the cell will not survive. And the surviving cells will be similar but may not be identical to the original and will subtly differ from each other.
1.1 The Importance of Variation
The consistent DNA copying that happens during reproduction is essential to maintain the features of body design of an organism so that it can occupy its well-defined space or niche in the ecosystem.
Hence reproduction is very much linked with the stability of a population of a species.
The variations become important here as an organism may be suited for a specific niche and a drastic change in that due to unforeseen environmental conditions makes their survival difficult.
Hence in such situations when a few among the species have some variations, they stand a chance of survival in the new niche. And thus, these species adapt themselves to the new conditions and the species are maintained over a period of time.
It can be understood with an example. If a species of bacteria is living in the temperate waters and suddenly the temperatures rise due to global warming, then most of the bacteria in that water would not survive. But maybe a few variants among them who are able to resist the heat may survive and grow. In case the variations were not present, that entire species of bacteria would have become extinct.
Thus, the importance of variation lies in the survival of a species over time.
2. Modes of Reproduction
Reproduction can be defined as a process that involves the production of an offspring by a particular individual or individuals with the aim of propagating their species. Generally, reproduction happens during the reproductive phase of an organism. The mode of reproduction may vary in organisms. They can be broadly categorised as:
Asexual Mode of Reproduction:
The mode of reproduction by means of which a single individual creates a new generation of species is termed as asexual reproduction.
Generally unicellular organisms exhibit asexual mode of reproduction, though some of them exhibit sexual mode too.
Sexual Mode of Reproduction:
The mode of reproduction by means of which two individuals take art in the creation of a new generation of species is termed as sexual reproduction.
Types of Asexual Mode of Reproduction:
2.1.Fission:
In unicellular organisms the new individuals are created by the process of cell division or fission.
The nucleus of the cell divides into new individual cells under favourable conditions.
Fission can be of two types depending on the number of new individuals created.
Binary Fission: This division leads to the formation of two new individuals. These can be further divided based on their plane of division as:
Irregular binary fission: In this type of fission the plane of division of a cell is irregular, it can be in any plane. Example - Amoeba.
Transverse binary fission: In this type of fission the cells divide along a transverse plane. Example - Paramecium.
Longitudinal binary fission: In this type of fission the plane of cell division is longitudinal. Example - Euglena.
Multiple fission: This is the Division of a Single Cell into Many New Daughter Cells. Example - Plasmodium.
2.2.fragmentation: .
This is a process where an organism simply breaks up into smaller pieces when they are mature.
Each of the fragments or broken pieces grow into a new individual. There should be a cell that is capable of growing into a new individual in such organisms.
Example - Spirogyra.
2.3. Regeneration:
This is a process where some fully differentiated organisms can be cut or broken into pieces and each of their body parts have the ability to grow into a new individual.
Different cells in this mass of cut cells undergo a lot of changes in an organised manner to become different cells and tissues.
Example - Planaria, Hydra.
2.4. Budding:
This is a process where a protuberance like outgrowth which is called as bud grows by repeated cell division at a specific site and then they detach from the parent body to develop into a separate individual organism.
Example - Hydra.
2.5.Vegetative Propagation
This is the mode of reproduction by which plants reproduce asexually. In this mode, new plants are developed from a plant’s vegetative parts like stem, leaf, root. There are different methods of vegetative propagation that are carried out in plants which are as follows:
Stem Cutting: This involves cutting the stem into small pieces having internodes and axillary buds. These are then planted in the soil to propagate into new plants. This method is used in sugarcane, hibiscus, drumstick etc.
Layering: This is a method where the young stem of a plant is bent and buried in the soil to develop roots and thus a new plant. Once the new plant develops, the stem is detached from the parent plant. This is used in jasmine, bougainvillaea.
Grafting: This is a method wherein the stems of two different plants are cut and joined together to unite and start developing into a new plant. This is used in nutmeg, roses etc.
Leaf buds: This is a method in which the buds in the notches of leaves develop into new plants. This can be seen in bryophyllum.
Advantages of the Vegetative Propagation, Which are as Follows:
The plants that are grown by vegetative propagation bear flowers and fruits earlier as compared to the plants produced from seeds.
All plants that are produced this way are genetically similar to the parent plant and have all its characteristics.
2.6. Spore Formation:
Many multicellular organisms have specific reproductive parts.
They have tiny thread-like structures with a blob called sporangia.
These contain cells or spores which eventually develop into new individuals. The spores are very light and covered by a thick wall to protect them and when they come in contact with a moist surface they start to grow.
Example - Rhizopus.
3.Sexual Reproduction:
3.1. Why the Sexual Mode of Reproduction?
The sexual mode of reproduction involves two organisms, a male and a female to create a new organism or offspring.
The sexual reproduction allows greater variations in a species as the two individuals involved in producing the offspring would have different patterns of variations. This process includes the combination of DNA of two different individuals and the resultant combination and variation would be unique.
Hence this ensures a mixing of the gene pool of the species within a population and it also ensures the survival of the species as this process generates more variations due to the genetic recombination.
The process of combining DNA of two different individuals during sexual reproduction will lead to an offspring with twice the amount of DNA than their previous generation.
The solution to this lies in the fact that there are certain specialised cells in such organisms called germ cells or gametes. These have half the number of chromosomes and, therefore half the amount of DNA in comparison to the other non-reproductive cells. The combination of these germ cells from two different individuals during the process of sexual reproduction restores the original number of chromosomes and DNA content in the new offspring.
The germ cells may be similar and not much different from each other in simple organisms. With the complexity of the organisms the germ cell also becomes specialised. One of the germ cells becomes large and stores food. This is known as the female gamete. The other germ cell which is small and motile is called the male gamete. These gametes lead to the differences in the bodies and reproductive systems of males and females.
3.2. Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants
The process of sexual reproduction in plants involves the fusion of gametes to produce offspring. The reproductive parts in angiosperms (plants that flower and produce fruits and seeds) are located in the flower. The parts of a flower consist of sepals, petals, stamens and pistils.
The reproductive parts of the flower are stamen which contains the male gamete and the pistil containing the female gametes.
Stamen: This is the male reproductive part and is also known as the androecium. It consists of a filament and an anther that encloses the pollen grains. The pollen grains produce the male germ-cells or gametes.
Pistil: This is the female reproductive part of the flower and is also known as gynoecium. This is made of three parts, namely, stigma, style and ovary. The enlarged portion at the bottom of a pistil is the ovary that contains an ovule with an egg cell. The middle long part of the pistil is the style and the terminal sticky part is the stigma.
Based on the presence of the stamen or pistil, flowers can be classified as:
Unisexual: These are the flowers that contain either stamens or pistils. These are also called incomplete flowers. Example - papaya, mulberry, watermelon etc.
Bisexual: These are flowers that contains stamens as well as pistils. Example - Hibiscus, mustard, rose etc.
The process of sexual reproduction in plants starts with the fusion of the male and the female gametes, followed by the formation of a zygote that eventually develops into a new plant. The process is explained as follows:
Pollination:
The process of sexual reproduction in plants starts with the transfer of pollen grains from the anther of the stamen to the stigma of the pistil. This process is termed as pollination.
This is facilitated by pollinating agents like wind, birds, animals, water etc. which transfer the pollen grains.
There can be two types of pollination as follows:
Self-Pollination: This involves the transfer of pollen grains from the anther to the stigma of the same flower. Example - wheat, peanut, etc.
Cross-Pollination: This type of pollination involves the transfer of the pollen grains from the anther of one flower to the stigma of another flower of the same species. Example - apples, pumpkin etc.
Fertilization:
Through the process of pollination, the pollen is deposited in the style of the pistil. For the next process in reproduction, it needs to reach the female germ-cells which are present in the ovary.
To facilitate this, a tube grows out of the pollen grain and reaches the ovule in the ovary of the pistil.
Here in the ovule the male germ-cell fuses with a female germ-cell to form a zygote. This process of fusion of the gametes is termed as fertilisation.
After the process of fertilization, the zygote thus formed, divides repeatedly to form an embryo inside the ovule. The ovule later develops into a seed.
And meanwhile the ovary grows and ripens into a fruit and the other parts of the flower, namely the petals, sepals, stamens, style and stigma may be shed off.
The seed present inside the fruit encloses the future plant in its embryo.
Germination:
The seed that contains the new plant or embryo develops into a seedling when the conditions are suitable. This process is termed as germination. Certain conditions like nutrients, water and proper temperature are necessary for the process of germination.
The embryo gets its food from the reserve food material stored in the cotyledons. It also has a protective outer covering known as seed coat.
3.3. Reproduction in Human Beings.
The mode of reproduction in human beings is sexual mode. The reproductive phase of an individual is that phase of life when the individual is ready to reproduce an offspring. Changes are noticed at every phase of growth right from birth.
But there are some changes that begin in the teenage age that start to prepare us for the reproductive phase of life. This period of adolescence leads to sexual maturation. The body needs to create specialised germ-cells to take part in the sexual reproduction. The period of maturation of the reproductive tissues in the body is termed as puberty.
Numerous changes are noticed in both boys and girls during this period. The boys start to have hair growth on their face and body, voice change, active functioning of sweat and sebaceous glands, enlargement of penis etc. The changes in the girls include growth of pubic hair, enlargement of breasts, oily skin leading to pimples, onset of menstruation etc. Both of them undergo changes in their body appearance and they become more conscious of these bodily changes.
The process of fusion of germ-cells in sexual reproduction, the actual transfer of these germ-cells needs to be done. For the same special organs need to be present like penis in males and uterus in females for carrying the baby.
3.3.1. Male Reproductive System
The male reproductive system consists of organs that produce and transport the male germ-cell or gamete, male hormone testosterone and the organs which facilitate the discharge of male germ-cells into the female reproductive system for fertilization.
The male gamete is the sperm which is a tiny body containing the genetic material and they have a long tail for motility to help them reach the female germ-cell for fertilization.
The system consists of some external organs like penis, scrotum, testes and internal organs like urethra, prostate and seminal vesicles.
Testes: Testes is the part that is responsible for the production of the male germ-cell or sperms and the male hormone testosterone. Testes are present in a structure known as scrotum, located outside the abdominal cavity. This is thus located because the formation of sperm requires a temperature that is lower than the normal body temperature. The hormone testosterone plays a role in regulating the formation of sperms and also the development of the secondary sexual characteristics that are seen in boys during puberty.
Vas Deferens: The sperms that are produced in the testes are stored in the epididymis. Vas deferens is a tube that transports these sperm to the urethra.
Urethra: This is a common passage for the sperm as well as urine. The same passage connects the urinary bladder and the vas deferens.
Prostate Gland and Seminal Vesicles: These glands are located along the vas deferens. They secrete a fluid, called semen that nourishes the sperm. This semen helps in the easier movement of sperms.
3.3.2. Female Reproductive System.
The female reproductive system includes the organs that produce the female germ-cells, provides site for fertilization of the gametes and development of the embryo into a new individual.
The female gametes are the eggs that are produced in the ovaries.
They also produce some hormones like estrogen and progesterone that are responsible for the onset of secondary sexual characteristics in girls at puberty.
This system includes a pair of ovaries, a pair of oviducts, uterus and vagina that opens externally through the urethra.
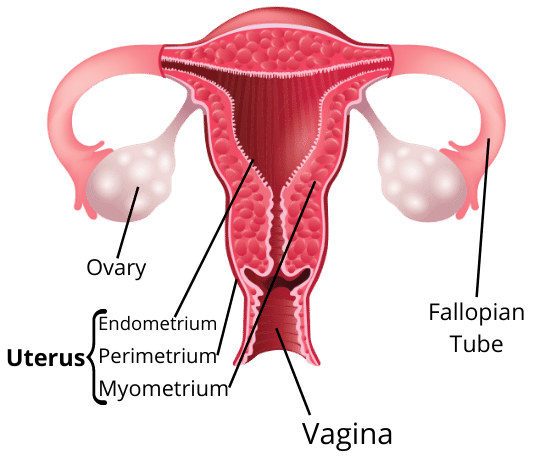
Ovaries: The ovaries are a pair of glands that are located on either side of the uterus. The ovaries protect the female gametes or eggs and make them suitable for fertilization. At birth the ovary of a girl contains thousands of eggs that are immature. After puberty, when the eggs mature, the ovaries release one egg every month. The ovaries also produce the hormones oestrogen and progesterone that are essential in bringing the secondary sexual changes in a girl at puberty.
Fallopian tube: This is also known as oviduct. This is a thin tube that connects the ovaries to the uterus. The eggs that are released by the ovary are transported through this tube.
Uterus: This is a bag-like muscular elastic structure into which the two oviducts open. The uterus is the site where the fertilized egg is implanted and it grows into a foetus. It is made of 3 tissues, outer perimetrium, middle layer of myometrium and the inner endometrium. This is also responsible for supporting the developing foetus during the entire gestation period.
Cervix: This is the site where the uterus opens into vagina. This facilitates a passage for the entry of the sperm into the uterus.
Fertilization and Development:
The process of fertilization of a male and female gamete or sperm and egg starts when the sperm enters the female reproductive system through the vaginal passage during a sexual intercourse. From the vaginal passage they move up through the uterus towards the fallopian tubes.
The eggs are present in the fallopian tube, meet the sperm and get fertilized.
The fertilized egg, which is known as the zygote, starts dividing repeatedly and travels down the fallopian tube to the uterus.
The ball of cells or embryo gets implanted in the endometrial lining of the uterus and continues to grow into a foetus. The embryo gets its nourishment from the mother through a special tissue called the placenta which acts as a connection between the mother and the developing embryo. It helps to transport glucose and oxygen to the embryo and remove the wastes generated by the embryo.
It takes about nine months for the complete development of the child inside the mother’s body. The child is born due to the rhythmic contractions of the uterine muscles.
3.3.3. What Happens When the Egg is Not Fertilized?
An egg is released by the ovary every month in anticipation of it getting fertilised. In case the egg does not get fertilized, it can survive for only a day. Similar to the ovary releasing an egg every month, every month, the uterus too prepares itself to the fertilized egg by creating a thick and spongy lining in order to provide nourishment to the embryo.
When the fertilization does not occur, this lining too is not required and this lining and the egg is shed as blood and mucous through the vagina. This is called menstruation. This cycle occurs every month and lasts for about 2 - 8 days roughly.
3.3.4. Reproductive Health.
The process of sexual maturation is a gradual one which happens while the general body growth is ongoing. Some amount of sexual maturation does not prepare a young person to be sexually active or get married and bear children and bring them up.
Reproductive health deals with all these aspects concerned with healthy and safe sexual practices. It becomes difficult for the young people to make the correct choice given the various types of pressure they face from peers, family, society.
Lack of proper information and unhealthy sexual practices can lead them to contract some diseases from one partner to another and even to the offspring as a sexual act is an intimate physical contact between them. The diseases transmitted in this manner are termed as sexually transmitted diseases (STDs), like bacterial infections such as gonorrhoea and syphilis, viral infections such as warts and HIV. These can lead to health complications and be fatal too if left untreated.
Reproductive health covers the area of safe sex to help young people. Pregnancy is a risk in a sexual act. As pregnancy is very demanding for the body and mind and has to be planned, unwanted pregnancies and abortions can be avoided by using some contraceptive methods.
The contraceptive methods can be by using physical barriers that block the entry of sperm into oviducts and not letting fertilization take place. Examples are condoms or coverings on the penis.
Contraceptive devices like Copper-T or intrauterine contraceptive device (IUCD) that are implanted in the uterus which does not allow the sperm to travel ahead.
The other contraceptive method changes the hormonal balance of the body, preventing fertilization. These are mostly in the form of drugs which can be taken orally in a scheduled manner. Examples are pills like Mala D, I-pill etc.
Another method is the surgical one like vasectomy in males in which the vas deferens is blocked to prevent the transfer of sperm. In females, tubectomy is done which blocks the fallopian tube and thus prevents the egg from reaching the uterus. The surgical methods are more reliable and safer as compared to the other methods.
Though surgery is used to abort unwanted pregnancies, it has been widely misused by the people, especially for illegally aborting a female foetus.
There is a law in place to prevent this female foeticide (killing of a foetus), which states that prenatal sex determination is prohibited.
A proper ratio of males to females is essential to maintain a balance in the society and to have a healthy population too.
Chapter-wise CBSE Class 10 Science Revision Notes Free PDFs
The links to Class 10 Science chapter-wise Revision Notes are given below.
Chapter 1 - Chemical Reactions and Equations Revision Notes
Chapter 2 - Acids, Bases and Salts Revision Note s
Chapter 3 - Metals and Non-metals Revision Note s
Chapter 4 - Carbon and Its Compounds Revision Note s
Chapter 5 - Periodic Classification of Elements Revision Notes
Chapter 6 Life Processes Revision Note s
Chapter 7 - Control and Coordination Revision Notes
Chapter 8 - How do Organisms Reproduce? Revision Notes
Chapter 9 - Heredity and Evolution Revision Notes
Chapter 10 - Light Reflection and Refraction Revision Notes
Chapter 11 - Human Eye and Colourful World Revision Notes
Chapter 12 - Electricity Revision Notes
Chapter 13 - Magnetic Effects of Electric Current Revision Notes
Chapter 14 - Sources of Energy Revision Notes
Chapter 15 - Our Environment Revision Notes
Chapter 16 - Management of Natural Resources Revision Note s
How do Organisms Reproduce Class 10 PDF Download
The chapter on reproduction of organisms will be introduced to the students for the first time. It becomes necessary that students gain a clear idea about the relevant concepts. While preparing, students may require short keynotes or revision notes. Further reference materials may be needed to make the understanding of concepts easier. Should a student feel the need for such materials, one can easily download the free PDF materials available over Vedantu's website.
Class 10 Science How do Organisms Reproduce Notes
Several important aspects of the chapter are discussed in Class 10th Science Chapter 8 notes. Some of those are:
Importance of Variation in Species
Body design features from parent to offspring are preserved with the consistency present in DNA copying. However, it may so happen that changes in existing environmental conditions may need variation to occur in species. Without that, it could be that a particular species may go extinct. Hence, variation is also important for species for survival.
Types of Reproduction
There are two types of reproduction – (1) asexual mode of reproduction, and (2) sexual mode of reproduction.
In the asexual mode of reproduction, it is a single organism that creates the next generation of species. On the other hand, in sexual reproduction, two organisms are needed for creating the offspring.
It is important to note that reproduction in unicellular organisms and multicellular organisms is markedly different. More often than not, asexual reproduction takes place unicellular organisms. Such reproduction can happen through any of the following methods:
Fission – DNA is duplicated into two parts.
Fragmentation – Organisms when mature break up into smaller pieces.
Regeneration – Fully differentiated organisms are giving rise to individual organisms.
Budding – Detachment of bud for developing into a separate organism.
Vegetative Propagation – New plants created from vegetative parts of existing plants.
Spore Formation – Spores bursting out of sporangia develop into new individuals.
Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants
Sexual reproduction in flowering plants takes place with the joining of male pollen and female eggs. The male reproductive part is the stamen which produced pollen grains. The female reproductive part is the carpel, from which ovules generate from the ovary.
Reproduction in Human Beings
As mentioned in reproduction class 10 notes, the male reproductive system includes testis, vas deferens and the muscular organ, penis. The male gamete, sperms, are generated from testes. The movement of sperm happens through the vas deferens.
On the other hand, the female reproductive system consists of ovaries, oviducts, uterus and vagina opening out through the urethra. The female gametes, eggs, are developed within the ovaries. The movement of eggs happens through a thin oviduct or fallopian tube.
If you are seeking expert guidance on Class 10 reproduction notes or seek solutions to the doubts that you may have while preparing the chapter, reach out to us today! All you have to do is download the app, and get started.
What are the Benefits of Referring to Vedantu’s Revision Notes for Class 10 Science Chapter 8 - How Do Organisms Reproduce
Provides quick, clear summaries of key concepts.
Simplifies complex topics for better understanding.
Efficient tool for last-minute exam prep.
Enhances retention of crucial information.
Supports effective exam preparation with key points and tips.
Saves time by consolidating information.
Prioritizes important topics and questions.
Offers practical examples for real-world connections.
Boosts student confidence for exams.
Related Study Materials for CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 8 How Do Organisms Reproduce?
The links given below are for the various other study resources prepared by the subject experts at Vedantu on Class 10 Science Chapter 8 How Do Organisms Reproduce. These study materials are available for free download on Vedantu’s website and students can refer to them for their exam preparation.
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 8
Important Questions for CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 8 - How do Organisms Reproduce?
NCERT Exemplar for Class 10 Science Chapter 8 - How do Organisms Reproduce? (Book Solutions)
CBSE Sample Paper for Class 10 Science
CBSE Class 10 Science: Previous Year Question Paper and Solutions Free Download (2007-2023)
For an enhanced comprehension of this subject, NCERT - Class 10 Science Chapter 8 - How Do Organisms Reproduce thoughtfully prepared by experienced educators at Vedantu is your invaluable companion. These notes break down the complexities of “How Do Organisms Reproduce” into easily digestible sections, helping you grasp new concepts and navigate through questions effortlessly quickly at the last minute as well. By immersing yourself in these notes, you not only prepare for your studies more efficiently but also develop a profound understanding of the subject matter.

FAQs on How Do Organisms Reproduce Class 10 Notes CBSE Science Chapter 8 (Free PDF Download)
1. What is Fission in Reproduction?
Ans: Fission, as discussed in How do organisms reproduce Class 10 notes, is the separation of a single body into two new bodies by duplication of the genetic material of the organism. In the process of fission, deoxyribonucleic acid undergoes division to form two parts. The second process is termed as cytokinesis. Binary fission is an example of asexual reproduction and organisms falling under Bacteria and Archaea exhibits this type of reproduction process.
2. What are the Benefits of Vegetative Propagation?
Ans: The most prominent advantages of vegetative propagation have been outlined in Class 10 Science Chapter 8 notes. One of the major benefits is that the new plants will retain the genetic material of a single parent. It means that if specific desirable traits have been identified in the parent plant, the same will be replicated in the offspring as well. However, for that to happen, growing conditions have to be kept the same.
Notes of Chapter 8 Science Class 10 also mentions that in the case of vegetative propagation, the immature seedling phase is bypassed. Such development helps in reaching the mature phase faster.
3. What is Meant by Spore Formation?
Ans: Spore formation has been explained lucidly in Class 10 Chapter 8 Science notes. It is a process of asexual reproduction exhibited by plants such as moss, ferns, fungi etc.
Spores are essentially reproductive bodies which are unicellular. Those are present in a sac-like structure known as sporangia. On attaining maturity, spores burst out from sporangia and transmitted to various places with the help of wind, air or water.
4. What is the Function of Pollination in Plant Reproduction?
Ans: Class 10 Reproduction notes discuss pollination as the procedure of transmitting pollen from the male part of a flower, anther, to the female part of a flower, stigma. However, it must be noted in this regard that such happens between a male part of one flower to the female part of another flower. With pollination, a seed is produced from fertilised flowers, leading to the formation of fruit.
5. Where can I find Class 10 Chapter 8 How do organisms reproduce notes?
Ans: Vedantu offers students with revision notes of Chapter 8 How do organisms reproduce of Class 10 Science. These notes are beneficial to students as it helps them to understand all the important topics and concepts in the chapter better. These notes are written by subject experts in a simple and easy language. Students will be able to score well in their exams with the help of these revision notes. Some of the topics discussed in these notes include importance of variation, modes of reproduction, fragmentation, regeneration, spore formation, and many more. Most of these terms and concepts are important for students to learn and understand.
6. What are the various topics covered in Chapter 8 How do organisms reproduce of Class 10 Science?
Ans: There are many important topics and concepts that are discussed in Chapter 8 How do organisms reproduce of Class 10 Science. Some of these topics include various modes of reproduction like asexual reproduction, sexual reproduction, and reprodution in flowers. Students will even learn about the reproduction that involves cells, the process of DNA copy, and other additional cellular devices. Apart from this, students will learn about the DNA copying mechanisms as well. Other topics covered in Chapter 8 How do organisms reproduce of Class 10 Science Science include the understanding of the body design and use of reproductive modes by different organisms.
7. What are the advantages of sexual reproduction?
Ans: Sexual reproduction refers to the mode of reproduction between two individuals. Sexual reproduction has many advantages. Some of these include:
The offspring produced by the parents have characteristics of both of them
Sexual reproduction ensures that there are more variations of the species. This ensures the survival of the species as well
The offspring has the tendency to adapt to the environmental changes that the offspring may face around them
It is known that sexual reproduction improves the health of all human beings
8. What do you mean by asexual reproduction?
Ans: Asexual reproduction refers to the mode of reproduction that involves a single individual creating new generation of species. Under this mode of reproduction, a single parent generates/produces a new offspring. These offspring are physically and genetically identical to their parents. There are many unicellular and multicellular organism that follow asexual reproduction. However, not all of them follow this mode of reproduction. Some of these unicellular organisms exhibit the sexual mode of reproduction as well. Asexual mode of reproduction can include parthenogenesis, budding, fission, and fragmentation.
9. How is the process of pollination different from fertilization?
Ans: Pollination refers to the process of transferring pollen from the anther of one plant to the stigma. This process is done with the help of pollinators. Pollinators refer to the mode of transformation of pollen. These pollinators can include water, wind, and even a few insects. Whereas, fertilization refers to the process of a fusion between the male and female games. Fertilization takes place in the ovule. This further leads to the formation of zygote.
CBSE Previous Year Question Papers for Class 10
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 8 How do Organisms Reproduce
The Class 10 NCERT Solutions for Science Chapter 8 How do Organisms Reproduce includes all the intext and exercise questions. Class 10 Science Chapter 8 How do Organisms Reproduce NCERT questions and answers help students to clear their doubts and to obtain good marks in Class 10 board exam. All the solutions provided in this article are strictly based on the CBSE syllabus and curriculum.
Class 10 Science Chapter 8 NCERT Questions and Answers
Class 10 Science Chapter 8 How do Organisms Reproduce NCERT Questions and Answers are prepared by experts with a detailed explanation that will help students complete their assignments & homework. Having a good grasp over CBSE NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science will further help the students in their preparation for board exams and other competitive exams such as NTSE, Olympiad, etc.
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 8 Intext Questions
Intext Question (Page No. 128)
Question 1: What is the importance of DNA copying in reproduction?
Answer: DNA (Deoxyribonucleic acid) is the genetic material found in the chromosomes, which are present in the nucleus of a cell. The DNA is the information site for making proteins and each specific type of protein leads to a specific type of body design. Thus, it is the DNA molecule that determines the body design of an individual. Therefore, it can be concluded that it is the DNA that gets transferred from parents to off-springs and makes them look similar.
Question 2: Why is variation beneficial to the species but not necessarily for the individual?
Answer: The reason why the variation is beneficial to the species than individuals is because sometimes the climatic changes have a drastic effect on the species, which makes their survival difficult. For examples, if the temperature of the water body increases, then there might be certain species of microorganisms which might die. This may result in disturbance in the environment. So, variation is beneficial to species and not for the individuals.
Intext Question (Page No. 133)
Question 1: How does binary fission differ from multiple fission?
Question 2: How will an organism be benefited if it reproduces through spores?
Answer: There are many advantages, if an organism reproduces through spores.
Advantages of spore formation:
- Large numbers of spores are produced in one sporangium.
- Spores are distributed easily by air to far-off places to avoid competition at one place.
- Spores are covered by thick walls to prevent dehydration under unfavourable conditions.
Question 3: Can you think of reasons why more complex organisms cannot give rise to new individuals through regeneration?
Answer 3: Simple organisms such as Hydra and Planaria are capable of producing new individuals through the process of regeneration. The process of regeneration involves the formation of new organisms from its body parts. Simple organisms can utilize this method of reproduction as their entire body is made of similar kind of cells in which any part of their body can be formed by growth and development.
However, complex organisms have organ-system level of organization. All the organ systems of their body work together as an interconnected unit. They can regenerate their lost body parts such as skin, muscles, blood, etc. However, they cannot give rise to new individuals through regeneration.
Question 4: Why is vegetative propagation practised for growing some types of plants?
Answer: Following are the advantages of practising vegetative propagation for growing some types of plants:
- Crops like orange, banana, pineapple do not have viable seeds, so vegetative propagation can be used.
- It is a rapid, cheap and easier method to grow crops.
- It can be used in places where seed germination fails.
- A good quality of variety can be preserved.
Question 5: Why is DNA copying an essential part of the process of reproduction?
Answer: DNA (Deoxyribonucleic acid) copying is an essential part of reproduction as it passes genetic information from parents to offspring. It determines the body design of an individual. The reproducing cells produce a copy of their DNA through some chemical reactions and result in two copies of DNA. The copying of DNA always takes place along with the creation of additional cellular structure. This process is then followed by division of a cell to form two cells.
Intext Question (Page No. 140)
Question 1: How is the process of pollination different from fertilization?
Answer: Pollination is defined as the process of transfer of pollens from anther to stigma. The process takes place with the help of pollinators like air, water and some insects.
Fertilization is defined as the fusion of male and female gametes. It takes place in the ovule and leads to the formation of zygote.
Question 2: What is the role of the seminal vesicles and the prostate gland?
Answer: The secretions from seminal vesicles and prostate glands lubricate the sperms and provide a fluid medium for easy transport of sperms. Their secretion also provides nutrient in the form of fructose, calcium, and some enzymes.
Question 3: What are the changes seen in girls at the time of puberty?
Answer: Secondary sexual characteristics in girls:
- Increase in breast size and darkening of skin of the nipples present at the tips of the breasts.
- Appearance of hair in the genital area.
- Appearance of hair in other areas of skin like underarms, face, hands, and legs.
- Increase in the size of uterus and ovary.
- Beginning of menstrual cycle.
- More secretion of oil from the skin, which results in the appearance of pimples.
Question 4: How does the embryo get nourishment inside the mother’s body?
Answer: The embryo develops inside the mother’s body for about nine months. Inside the uterus, the outer tissue surrounding the embryo develops finger-like projections called villi. These villi are surrounded by uterine tissue and maternal blood. They provide a large surface area for exchange of oxygen and nutrients. Also, there is a special tissue called placenta, which is embedded in the uterine wall. The embryo receives the oxygen and nutrients from the mother’s blood via the placenta. The waste materials produced by the embryo are also removed through the placenta.
Question 5: If a woman is using a copper−T, will it help in protecting her from sexually transmitted diseases?
Answer: No, because usage of copper-T cannot stop the contact of body fluids. Hence, it cannot protect her from getting sexually transmitted diseases.
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 8 Exercise Questions
Question 1: Asexual reproduction takes place through budding in (a) amoeba (b) yeast (c) plasmodium (d) leishmania
Answer: (b) in yeast.
Question 2: Which of the following is not a part of the female reproductive system in human beings? (a) Ovary (b) Uterus (c) Vas deferens (d) Fallopian tube
Answer: (c) Vas deferens
Question 3: The anther contains (a) sepals (b) ovules (c) carpel (d) pollen grains
Answer: (d) pollen grains.
Question 4: What are the advantages of sexual reproduction over asexual reproduction?
Answer: Advantages of sexual reproduction:
- In sexual reproduction, more variations are produced. Thus, it ensures survival of species in a population.
- The new formed individual has characteristics of both the parents.
- Variations are more viable in sexual mode than in asexual one. This is because in asexual reproduction, DNA has to function inside the inherited cellular apparatus.
Question 5: What are the functions performed by the testis in human beings?
Answer: The testes are the male reproductive organs that are located outside the abdominal cavity within a pouch called scrotum.
Functions of testes:
- Produce sperms
- Produce a hormone called testosterone, which brings about secondary sexual characters in boys.
Question 6: Why does menstruation occur?
Answer: Menstruation is a process in which blood and mucous flows out every month through the vagina. This process occurs every month because one egg is released from the ovary every month and at the same time, the uterus (womb) prepares itself to receive the fertilized egg. Thus, the inner lining of the uterus gets thickened and is supplied with blood to nourish the embryo. If the egg does not get fertilized, then the lining of the uterus breaks down slowly and gets released in the form of blood and mucous from the vagina.
Question 7: Draw a labelled diagram of the longitudinal section of a flower.
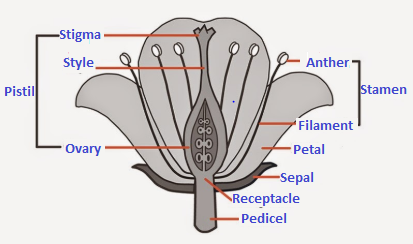
Question 8: What are the different methods of contraception?
Answer: The contraceptive methods can be broadly divided into the following types:
Natural method: It involves avoiding the chances of meeting of sperms and ovum. In this method, the sexual act is avoided from day 10th to 17th of the menstrual cycle because during this period, ovulation is expected and therefore, the chances of fertilization are very high.
Barrier method: In this method, the fertilization of ovum and sperm is prevented with the help of barriers. Barriers are available for both males and females. Condoms are barriers made of thin rubber that are used to cover penis in males and vagina in females.
Oral contraceptives: In this method, tablets or drugs are taken orally. These contain small doses of hormones that prevent the release of eggs and thus fertilization cannot occur.
Implants and surgical methods: Contraceptive devices such as the loop or Copper-T are placed in uterus to prevent pregnancy. Some surgical methods can also be used to block the gamete transfer. It includes the blocking of vas deferens to prevent the transfer of sperms known as vasectomy. Similarly, fallopian tubes of the female can be blocked so that the egg will not reach the uterus known as tubectomy.
Question 9: How are the modes for reproduction different in unicellular and multicellular organisms?
Question 10: How does reproduction help in providing stability to populations of species?
Answer: Living organisms reproduce for the continuation of a particular species. It helps in providing stability to the population of species by producing a new individual that resembles the parents. This is the reason why cats give birth to only cats or dogs give birth to only dogs. Therefore, reproduction provides stability to populations of dogs or cats or any other species.
Question 11: What could be the reasons for adopting contraceptive methods?
Answer: Following are the reasons for adopting contraceptive methods:
- To control population
- To avoid unplanned pregnancy
- To avoid transfer of sexually transmitted diseases
Topics covered under Class 10 Science Chapter 8 How do Organisms Reproduce
Below we have listed the topics discussed in NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 8. The list gives you a quick look at the different topics and subtopics of this chapter.
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 8 – A Brief Discussion
Chapter Overview: Have you ever wondered why do organisms reproduce? Whatever the answer to this question but it is obvious that we see organisms because they reproduce. In this chapter, you will learn about the modes of reproduction used by unicellular such as fission, fragmentation, regeneration, budding, vegetative propagation and spore formation. All these modes are the asexual modes of of reproduction. Mutlicellular organisms prefer sexual mode of reproduction over asexual mode. This chapter explains you the sexual mode of reproduction in plants and animals.

NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 8 How do Organisms Reproduce?

Chapter 8 How do Organisms Reproduce? Class 10 NCERT Solutions
Ncert solutions for class 10 science chapters:, where does fertilization take place in human females, what is cross-pollination, what is ovulation, what is menopause, what is asexual reproduction, contact form.
- Biology Article
- How Do Organisms Reproduce
How Do Organisms Reproduce?
Organisms reproduce to continue the chain of life, to pass on its genes which are acquired over millennia. Reproduction is essentially a process by which individuals produce new individuals of the same kind. And this process is very important for the existence of life on earth.
Different organisms reproduce in different ways. Let us have a detailed look at how different organisms reproduce.
How do Organisms Reproduce?
The organisms reproduce in two ways:
Asexual Reproduction – In this process, only a single parent is involved and no gamete formation takes place.
Sexual Reproduction – In this process, two parents are involved and gamete formation takes place. Meiosis is an important step in sexual reproduction.
Explore more about Reproduction
Asexual Reproduction
Asexual Reproduction is further divided into:
Vegetative propagation
Regeneration
Spore formation
This process takes place in unicellular organisms. It is of two types:
Binary Fission – The organisms reproduce by binary fission only when adequate amounts of food and moisture is available. In this, the mother cell divides into two daughter cells, each containing a nucleus. Amoeba divides by binary fission.
Multiple Fission – The unicellular organisms reproduce by multiple fission when the conditions are unfavourable with no proper amounts of food, moisture, and temperature. In this, the organism forms a cyst around itself. The nucleus divides, and each daughter nuclei is surrounded by a membrane. When the conditions are favourable again, the cyst dissolves and the daughter nuclei are released, which later develops into an individual cell. Plasmodium and Entamoeba undergo this process.
To know more about Reproduce in Organisms by Fission, watch the video given below:

In this process, an outgrowth is produced from the cell from which a new organism is developed. The developed organism remains attached to the parent organism and detaches only when it matures, leaving behind scar tissue. The process is prominent in yeast and hydra.
Also refer: Budding
In this, a new plant grows from the fragments of the parent plant or a specialized reproductive structure. The offspring are the exact clones of the original plant and there is no mixing of DNA. The common forms of vegetative propagations are grafting, layering, cutting, tuber, tissue culture, etc.
In organisms like Hydra and Planaria we had observed that if they are cut into several pieces, each part grows into a new organism. This is known as regeneration. The specialized cells proliferate and produce a large number of cells. These proliferated cells undergo changes and form different cells and tissues. The sequential process of these changes is known as development.
Spore Formation
During spore formation, the organisms form knob-like structures called a sporangium. This happens during unfavourable conditions in an inadequate supply of moisture and nutrients. When the conditions are favourable, they begin to grow.
The sporangia contain spores that develop into new individuals. The spores are covered by thick walls that protect the spores until they come in contact with moisture and begin to grow.
Sexual Reproduction
Sexual reproduction is a natural way of reproduction and takes place in all multicellular organisms . This process involves two individuals to produce offspring. In this, the male and the female gametes fuse together and give rise to a new cell.
Sexual reproduction in Plants
The angiosperms have both the male and female reproductive organs. The pollen grains produce male gametes which fuse with the egg cell of the female. The formation of gametes is known as gametogenesis. The pollen grains are transferred from the anther to the stigma of the flower. These pollens travel through the style and reach the female gametes present in the ovule. The two gametes fuse together and this process is known as fertilization. A zygote is formed which gets converted into an embryo. These give rise to a new seed which gradually turns into a fruit.
Sexual Reproduction in Humans
The testes in males and the ovaries in females are responsible for the production of sperm in males and eggs in females. The sperm fuses with the egg during fertilization, which results in the formation of a zygote and gets implanted in the wall of the uterus. It further divides and forms an embryo. The embryo starts developing week by week seeking nutrition from the mother with the help of the placenta. A new individual finally forms after a period of nine months.
Key Points on How do organisms reproduce
Reproduction is the process of producing new individuals of the same kind.
Organisms reproduce in two ways- asexually and sexually.
Asexual reproduction does not involve the fusion of male and female gametes. This takes place in bacteria, amoeba, hydra, etc.
Sexual reproduction involves the fusion of male and female gametes and can be seen in humans and many animals.
Fission, budding, vegetative propagation, fragmentation are some different types of asexual reproduction. It does not require any reproductive organs.
Sexual reproduction involves the reproductive organs of male and female.
Learn more in detail about reproduction, its importance, process, types and other related topics at BYJU’S Biology .
Related Links:-
Important Questions
Q.1. How do organisms reproduce?
A.1. The organisms reproduce in two ways-
Sexually where the fusion of male and female gametes takes place.
Asexually where the fusion of male and female gametes does not take place.
Q.2. What are the different modes of asexual reproduction?
A.2. The different modes of asexual reproduction include:
Fragmentation
Spore-formation
Q.3. How does sexual reproduction occur in plants?
A.3. Plants reproduce sexually through pollination. In this process, the pollen from the anther of the flower is transferred to the stigma. The fusion of the male and female gametes takes place. A zygote is then formed which gives rise to an embryo. This leads to the formation of seed which gradually turns into a fruit.
Q.4. What is budding?
A.4. This is a type of asexual reproduction in which a new organism grows from an outgrowth by cell division. It remains attached to the mother and derives nutrition from it. Once it matures it detaches itself from the mother and grows as an individual organism. This type of reproduction is seen in Hydra.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
Very nice 👌
yes best teaching app
Most Helpful APP
Very niceee
B Very nice
Best app for concept clarification 👌
Fine words ☺️
I want boad important question
Please refer to this link for important questions – https://byjus.com/biology/cbse-biology-important-questions/
Best for reads 👌✨
It’s best for study
- Share Share
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.

If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website.
If you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked.
To log in and use all the features of Khan Academy, please enable JavaScript in your browser.
Unit 7: How do organisms reproduce?
- Fission, fragmentation, regeneration, budding, spores (Opens a modal)
- Vegetative propagation (Opens a modal)
- Variation Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!
- Fission, Budding, Regeneration, Fragmentation and Spore formation Get 5 of 7 questions to level up!
- Vegetative propagation Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!
- Sexual reproduction in flowers (Opens a modal)
- Male reproductive system (Opens a modal)
- Female reproductive system (Opens a modal)
- Sexual reproduction in flowering plants Get 5 of 7 questions to level up!
- Male reproductive system Get 5 of 7 questions to level up!
- Female reproductive system Get 5 of 7 questions to level up!
- Reproductive health Get 5 of 6 questions to level up!
- Biotechnology
- Biochemistry
- Microbiology
- Cell Biology
- Cell Signaling
- Diversity in Life Form
- Molecular Biology
- Do Bacteria Reproduce Sexually or Asexually? - Bacteria Reproduction
- Difference Between Sexual And Asexual Reproduction
- Sexual Reproduction: An Overview
- Types of Asexual Reproduction
- Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants Notes Class 12
- Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants - Class 10 Notes
- Asexual Reproduction In Plants
- Ovary - Female Reproductive System
- Sexual Reproduction in Plants
- Female Reproductive System - Diagram, Functions, Organs
- How Do Organisms Reproduce For Class-10 CBSE Science Notes
- How Animals Reproduce?
- Diagram of Female Reproductive System
- Asexual Reproduction - Definition, Characteristics, Types, Examples
- Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants NCERT Solutions
- Male Reproductive System - Structure, Organs, Functions
- Diagram of Male Reproductive System
- How do organism Reproduce?
- Overview Of Reproductive System
Does corn reproduce sexually or asexually?
Yes, Corn, or maize, reproduces sexually through a process involving pollination and fertilization. It is a monoecious plant , meaning it has both male and female reproductive structures present in the same plant. The male flowers, located in the tassels at the top of the plant, produce pollen-containing sperm cells. The female flowers, found in the ears lower on the plant, contain ovules that develop into kernels once fertilized.
Pollination occurs when pollen grains are transferred from the tassels to the silks, the hair-like structures extending from the stamen. This transfer can happen through wind dispersal or due to the action of insects. Once the pollen reaches the stigma, it travels down to the ovules, where fertilization occurs. Each fertilized ovule develops into a kernel, which ultimately forms the edible seeds of the corn cob.
Sexual reproduction in corn ensures genetic diversity within the population, allowing for adaptation to changing environmental conditions and the evolution of new traits over time. Additionally, it contributes to the agricultural importance of corn, as sexual reproduction allows for the production of seeds that can be used for planting new crops in subsequent growing seasons.
Please Login to comment...
Similar reads.
- Biology Questions & Answers
- Plant-Physiology
- School Biology
- School Learning
Improve your Coding Skills with Practice
What kind of Experience do you want to share?

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Here, we have provided case-based/passage-based questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 8 How Do Organisms Reproduce. Case Study/Passage-Based Questions. Question 1: The male reproductive system consists of portions that produce the germ cells and other portions that deliver the germ cells to the site of fertilization.
CBSE Case Study Questions Class 10 Science How do Organisms Reproduce CASE STUDY : 1. When a girl is born, the ovaries already contain thousands of immature eggs. On reaching puberty, some of these start maturing. One egg is produced every month by one of the ovaries. The egg is carried from the ovary to the womb through a thin oviduct or ...
Case Study Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 8 How Do Organisms Reproduce. In CBSE Class 10 Science Paper, Students will have to answer some questions based on Assertion and Reason.There will be a few questions based on case studies and passage based as well. In that, a paragraph will be given, and then the MCQ questions based on it will be asked.
Students who are studying in CBSE class 10 board, need to get the knowledge about the How Do Organisms Reproduce Case Study Based Questions. Case based questions are generally based on the seen passages from the chapter How Do Organisms Reproduce. Through solving the case based questions, students can understand each and every concept.
CBSE Exam, class 10. About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How YouTube works Test new features NFL Sunday Ticket
The Case Based Questions: How do Organisms Reproduce? is an invaluable resource that delves deep into the core of the Class 10 exam. These study notes are curated by experts and cover all the essential topics and concepts, making your preparation more efficient and effective.
Practice. Male reproductive system. Female reproductive system. The reproductive system. Reproductive health. In this unit, we explore why organisms reproduce, sexual and asexual reproduction, and learn in detail about sexual reproduction in flowers and human beings. The unit is aligned to the CBSE class 10 curriculum.
How Do Organisms Reproduce? Case Study Questions (CSQ's) Select the number of questions for the test: TopperLearning provides a complete collection of case studies for CBSE Class 10 Biology How Do Organisms Reproduce? chapter. Improve your understanding of biological concepts and develop problem-solving skills with expert advice.
How do Organisms Reproduce? 129 Activity 8.2 8.2 MODES OF REPRODUCTION USED BY SINGLE ORGANISMS Activity 8.1 Dissolve about 10 gm of sugar in 100 mL of water. Take 20 mL of this solution in a test tube and add a pinch of yeast granules to it. Put a cotton plug on the mouth of the test tube and keep it in a warm place. After 1 or 2 hours, put a small drop of yeast culture from the test
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 8 explains the various reproduction modes like. Sexual reproduction. Sexual reproduction. Reproduction in flowering plants. It explains that reproduction involves the creation by the cell involved in the process of a DNA copy and additional cellular devices.
Assertion: Sexual reproduction involves two parents of different sexes, a male and a female. Reason: Male and female gametes fuse to form a zygote in sexual reproduction. Assertion: In internal ...
Fission is an asexual reproduction that is common in most unicellular organisms. When the fission results in two daughter cells, it is binary fission (e.g. paramecium). When fission results in many daughter cells, it is called multiple fission (e.g. Plasmodium). Planes of fission may be different for different organisms.
Ans: Fusion of male gamete with the egg cell is called syngamy. 10. Name the structure through which pollen tubes enter the ovule. Ans: Pollen tubes enter the ovule through stigma. 11. A common feature of reproduction in Amoeba, spirogyra and yeast is that -. Asexual reproduction occurs after sexual reproduction.
Fish. Duck-billed platypus. (ii) Select the correct statement regarding organisms X and Y. (a) Y produces large number of eggs where X produces single egg at a time. (b) Fertilisation in case of X occurs in water but fertilisation occurs inside the body of Y. (c) X could be a reptile whereas Y could be fish or amphibian.
Modes of Asexual Reproduction. Fission. → The parent cell divides into daughter cells. • Binary fission: 2 cells are formed. Example: amoeba. • Multiple fission: Many cells are formed. Example: Plasmodium. Fragmentation. → The organism breaks-up into smaller pieces upon maturation, each piece develops into new individual.
Fig.1. Binary fission in Amoeba. Fragmentation is another mode of asexual reproduction in which organism breaks into pieces and each piece give rise to a new organism. For example, Spirogyra, Planaria. Fig.2. Fragmentation in Planaria. Regeneration is the ability to form new organisms from body parts.
Answer: The organisms which have both male and female reproductive system within the same organism called bisexual organisms. For example: earthworm, leech, starfish etc. 11. Name those parts of the flower which server the same function as the following do in the animals. (i) Testis (ii) Ovary (iii) Eggs (iv) Sperms.
These quizzes designed to simulate the format of actual exams. Class 10 Science chapter 7 involve complex diagrams and illustrations related to reproductive processes in plants and animals. The chapter 7 of 10th Science includes diagrams related to flower structures, human reproductive organs, and other concepts.
Ans: Fission, as discussed in How do organisms reproduce Class 10 notes, is the separation of a single body into two new bodies by duplication of the genetic material of the organism. In the process of fission, deoxyribonucleic acid undergoes division to form two parts. The second process is termed as cytokinesis.
All these modes are the asexual modes of of reproduction. Mutlicellular organisms prefer sexual mode of reproduction over asexual mode. This chapter explains you the sexual mode of reproduction in plants and animals. The Class 10 NCERT Solutions for Science Chapter 8 How do Organisms Reproduce includes all the intext and exercise questions.
Chapter 8 How do Organisms Reproduce? NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science will be useful in fetching great marks in the examinations. You can figure out the latest marking scheme and prepare your answers as per the demand with the help of these Class 10 NCERT Solutions.In this chapter, you will get to learn about variety of topics like types of reproduction, asexual reproduction, female and ...
This process takes place in unicellular organisms. It is of two types: Binary Fission - The organisms reproduce by binary fission only when adequate amounts of food and moisture is available. In this, the mother cell divides into two daughter cells, each containing a nucleus. Amoeba divides by binary fission. Multiple Fission - The ...
UP Class 10th Science. 13 units · 80 skills. Unit 1. Chemical reactions and equations. Unit 2. Acids, Bases and Salts. Unit 3. Metals and Non-metals. Unit 4. ... How do organisms reproduce?: Unit test; Week 1. Learn. Fission, fragmentation, regeneration, budding, spores (Opens a modal) Vegetative propagation (Opens a modal)
class 10 science how do organisms reproduce notes
In this class Pooja will conduct How do Organisms reproduce. The class will 60 minutes long and will be conducted in Hindi whereas, notes will be shared in Hindi. Read more. Similar Classes. 399. ... Study material. UPSC Study Material NEET UG Study Material CA Foundation Study Material JEE Study Material SSC Study Material
Yes, Corn, or maize, reproduces sexually through a process involving pollination and fertilization. It is a monoecious plant, meaning it has both male and female reproductive structures present in the same plant. The male flowers, located in the tassels at the top of the plant, produce pollen-containing sperm cells.