

DECAVERSITY
10 business plan examples for students.

Are you thinking of starting a business? Let’s take a look at some business plan examples for students.
Starting a business as a student is exciting. But, like anyone else, students need support when venturing into entrepreneurship. One of the most important things to start with is learning how to create a strong business plan.
A business plan helps you set clear goals, strategies, and the necessary steps to succeed in the business world. However, not all business plans are the same. There are different types to consider, and choosing the right one depends on your specific business and goals.
In this guide, we'll walk you through the process of creating a solid business plan and introduce you to different plan types. So, let's get started and explore the world of entrepreneurship with a well-structured plan for success.
Writing the Business Plan
Crafting a business plan is a crucial move when you're starting or expanding your business, whether you’re working on a business plan project for students or a fully-fledged business person.
It helps you navigate your journey while also catching the attention of potential investors or lenders. In this guide, we'll break down every part of a business plan and share helpful tips.
What Goes in a Business Plan?
A good business plan typically has several important sections, each with its own job to do.
- Business Overview : Introduction and executive summary.
- Market Analysis : Understanding your target market and competition.
- Marketing and Sales : Strategies to reach and convert customers.
- Product/Service : Description of what you offer.
- Operations and Team : How your business operates and key team members.
- Financial Projection s: Future financial estimates and funding needs.
- Appendix : Supporting documents, if needed.
Now, let’s get into what these sections look like.
Develop a Business Plan Worksheet
Before you start writing your business plan, it's a good idea to start with a business plan worksheet. Think of it as the foundation for your plan—a tool to gather information and get your thoughts organized.
This worksheet will help you come up with your business vision, understand your target market better, and lay out your financial projections. It's the first step to building a solid plan that sets your business on the right track.
The Executive Summary
The executive summary is your business plan's attention-grabbing headline. It's a concise preview of your plan's most critical elements, designed to engage your reader. Here's what to include:
- Mission Statement : Clearly state your business's mission, describing the problem you solve and why your business exists. Define your core values and goals.
- Product/Service Description : Provide a brief, compelling description of your offering, emphasizing its unique features or benefits that set it apart.
- Leadership and Team : Introduce key team members and their qualifications, showcasing their expertise and their role in your business's success.
- Financial Information : Give an overview of your current financial status. Mention revenue and profits if your business is running. If you seek financing, explain how much you need and where you'll invest it.
- Growth Plans : Share your strategy for growth and long-term goals, outlining how you'll expand and achieve profitability.
The executive summary sets the stage for your business plan, making a strong first impression and sparking excitement for what follows.
The Products/Services
In this part, we'll dig deeper into the heart of your business—your products or services. We're going beyond the basics to look at three crucial aspects:
- Benefits to Customers : Discuss how your products or services help your customers. Explain how they solve specific problems or fulfill the needs of your target market. What makes them stand out? What's the unique value they bring compared to what competitors offer?
- Product Lifecycle : Every product or service has a journey. Tell us about the expected lifecycle of yours. Are you planning updates, new versions, or related offerings in the future? Knowing this helps us understand how your business will evolve.
- Intellectual Property : If it applies to your products or services, include any intellectual property rights you have. This might include copyrights, trademarks, or patents. These rights protect your creations and can be valuable assets.
Remember, this section is all about offering the essence of what you're offering and why it's special.
Target Market
Knowing your target market is a cornerstone of business success. Let's simplify:
Who Are Your Customers?
- Demographics : Basic info like age, gender, income, and location helps you target effectively.
What Makes Them Tick?
- Psychographics : Understand their interests, lifestyle, and buying habits to connect personally and tailor your marketing.
Market Trends
- Stay Updated : Keep an eye on industry trends and market shifts. Adapt to capitalize on opportunities.
Why does it matter? Think of it like knowing the weather—it helps you plan. Understanding your target market is your key to getting ahead.

The Marketing Strategy
Your marketing and sales strategies are crucial for attracting and retaining customers.
Marketing Mix
Here, we'll break down each element of your marketing mix—product, price, promotion, and place (distribution).
- Product : Describe your product offerings in detail. What are their unique features and benefits? Why would your target customers choose your products over others in the market? Be clear about what sets you apart.
- Price : Explain your pricing strategy. Will you compete on price, offering lower costs than competitors? Or will you position your products as premium and charge a higher price? Detail any discounts, bundles, or special offers you plan to implement.
- Promotion : Outline your promotional tactics. How will you create awareness and interest in your products? This can include advertising, public relations, content marketing, social media campaigns, and more. Specify your marketing budget and the platforms you'll utilize.
- Place (Distribution) : Describe your distribution strategy. How will your products reach your customers? Will you sell directly to consumers, through retailers, or online? Highlight your distribution channels and logistics. Explain how you'll ensure your products are readily available where your customers want them.
Sales Process
Now it’s time to discuss how you plan to turn potential leads into paying customers.
- Direct Sales : If your strategy involves direct sales, explain how your sales team will engage with potential customers. Provide insights into your sales force, their training, and how they will approach prospects.
- Online Sales : If online sales are a significant part of your strategy, detail your e-commerce platform. Discuss the user experience, payment processing, security measures, and any online marketing tactics to drive traffic and conversions.
- Conversion Strategy : Highlight how you plan to convert leads into paying customers. Will you offer free trials, consultations, or samples? Describe your approach to closing deals and fostering customer loyalty.
By going beyond the surface and addressing these elements in detail, you'll have a marketing and sales strategy that can effectively attract and retain customers for your business.
Discuss Your Distribution Strategy
Your distribution strategy is how you get your products or services to your customers effectively:
- Distribution Channels : These are the paths your products or services take, like physical stores or online platforms.
- Logistics and Transportation : This is how your products move, whether you do it yourself or use other companies.
- Inventory Management : It's about keeping the right amount of stock without having too much or too little.
- Geographic Reach : It's where your customers are, whether nearby, across the country, or worldwide.
- Efficiency and Costs : It's about being fast and not spending too much money.
- Customer Convenience : It means making it easy for customers to buy from you.
- Technology and Automation : Using tools and systems to make things work smoother.
- Scaling and Adaptation : It's about being ready for more customers or changes in the market.
Having a good distribution strategy helps make sure your products or services reach the right customers the right way.
The Competition
It's essential to have a solid grasp of your competitors and strategically position your business to thrive.
Competitive Analysis
To stay ahead of the game, make sure to conduct a thorough competitive analysis. This means rolling up your sleeves and diving deep into the strategies and operations of your rivals.
- In-Depth Examination : Start by examining your competitors meticulously. Look into their products or services, pricing strategies, marketing tactics, and customer base. The goal is to gain a comprehensive understanding of what they do and how they do it.
- Strengths and Weaknesses : Highlight your competitors' strengths and weaknesses. What are they exceptionally good at, and where do they fall short? Identifying these aspects will help them identify opportunities to capitalize on their weaknesses and leverage their strengths.
- Success Insights : Share your insights into what makes your competitors successful. Understand their unique selling propositions, customer engagement strategies, and market positioning. This knowledge will provide you with a foundation for your own strategies.
- Outperforming Plans : Once you've dissected your competitors, outline your plan to outperform them. Whether it's through innovation, superior customer service, or better pricing, make it clear how you intend to gain a competitive edge.
Competitive Advantage
Every business has something that sets it apart from the rest – these are your competitive advantages. In this section, it's time to highlight why customers should choose you over the competition.
- Expert Team : If you have experts on your team, let people know. Customers trust businesses with knowledgeable professionals who offer excellent products or services. If you're new, focus on any relevant experience to build trust as your business grows.
- Unique Partnerships : If your business has forged unique partnerships or collaborations that give you an edge, make it known. These alliances can lead to exclusive offerings, cost advantages, or increased visibility in the market.
- Ideal Location : If your business benefits from an ideal location that attracts foot traffic or serves a specific target demographic, this can be a powerful competitive advantage. Explain how your location enhances your business prospects.
By underlining your competitive advantages, you're essentially telling your audience why you're not just another player in the market.

The operations section is your day-to-day business plan. It helps your team understand how to make your business run smoothly. Here are the key parts:
- Objectives and Goals : State what you want to achieve, both short and long-term. Ensure they align with your overall plan.
- Procedures and Processes : Explain how things will get done, from making your product to customer service.
- Timeline and Milestones : Set dates and goals to track your progress.
- Resource Needs : List what you need to run your business, like equipment and people.
- Supply Chain : Describe how you'll get what you need and manage it.
- Quality Control : Detail how you'll ensure quality, whether through checks or testing.
- Regulations : Mention any rules you need to follow, like permits or licenses.
- Risk Planning : Identify potential problems and your backup plans.
- Growth Strategy : Explain how you'll handle growth, like hiring more people or expanding to new markets.
- Costs : Break down your expenses, both fixed and variable, and how you'll manage them.
By laying out these details, you'll be well-prepared to handle the challenges and growth opportunities that come your way.
The Management Team
In this section of your business plan, you'll want to cover a few key areas:
1. Personal Background : Start by introducing the key people in your management team, if there are any. If it’s just you—don't worry! Give some basic details like names, ages, where they live, their interests, and their educational background. Also, mention any special skills they bring to the table.
2. Business Experience : Talk about their history in the business world. Have they been involved in other businesses? Have they held important positions before? Share their past achievements and roles in previous companies.
3. Track Record : Highlight their successes, the responsibilities they've handled, and their capabilities. Show how their previous experiences have prepared them for the roles they'll play in your business.
4. Education : Mention their formal and informal education, like degrees, certifications, or courses they've taken that are relevant to your business.
5. Financial Standing : Include personal financial statements and supporting documents to demonstrate their financial stability and ability to contribute to the business if necessary.
6. Work History : Detail their direct experience in similar businesses and how it aligns with your current venture.
7. Roles and Responsibilities : Clearly define who does what on the management team. Explain why they're the right fit for their roles and who makes the final decisions.
8. Organization Chart : Create a simple chart that shows how your team is structured and lists each person's responsibilities.
9. Compensation and Benefits : Outline the pay and bonuses each management member will receive. Also, mention any benefits like health insurance or life insurance.
10. External Resources : Tell about any outside resources you can tap into, like lawyers, accountants, or support from organizations that help small businesses.
11. Board of Directors : If you have a board, introduce them and explain how they'll help guide your business.
12. Online Resources : Mention any useful internet resources you'll use for research and networking.
Including these details paints a picture of your team's qualifications and their role in making your business a success.
In this part of your business plan, focus on who will be working with you.
- Current and Future Needs : Start by saying how many people you have on your team right now, if any. Then, talk about how many team members you think you'll need in the near future (like the next year or two) and in the longer term (three to five years from now).
- Skills Required : Describe what skills your team members should have. Think about what makes them good at their jobs and what special skills might be needed for your business.
- Job Descriptions : Explain what each person on your team will be responsible for. This will help everyone better understand their roles. Keep in mind that your roles might change as your business grows.
- Finding People : Discuss how you plan to find and hire the right people. As students, you might use your school's resources and online job platforms or work with other students who have the skills you need.
- Pay and Benefits : Clarify if you'll be paying salaries, hourly wages, or both. You can also mention any extra rewards or bonuses based on performance. Since you're a student, you may not offer extensive benefits initially.
- Extras like Overtime : Say if you'll pay extra for overtime work and when that might happen. Being students, you'll want to manage your workload efficiently, especially during busy times.
By covering these points, you'll show that you've considered your team's needs and are ready to manage your business's human resources effectively, even as students.

Financial Analysis
Think of this section as the pulse of your business plan. It gives you a detailed look at your business's financial health and sustainability. This part is crucial for students because it helps them make informed decisions and attracts potential investors or lenders.
Balance Sheet
Get a certified public accountant (CPA) to help you create a balance sheet. This document paints a picture of your business's financial situation at a specific moment. It has three main parts:
- Assets : What your business owns ( cash, equipment, or inventory).
- Liabilities : What your business owes (such as loans or outstanding bills).
- Owner's Equity : The owner's stake in the business, which is assets minus liabilities. It's basically your business's net worth.
Break-Even Analysis
This is significant because it tells you when your business will start making money. It determines the minimum amount of sales revenue needed to cover both fixed costs (like rent and salaries) and variable costs (like materials and utilities). It's based on info from the income statement and cash flow projections.
Income Statement (Profit and Loss Statement)
The income statement gives you the lowdown on your business's financial performance over a specific time frame, usually monthly or annually. It shows how much money you made and how much you spent. Subtract the expenses from the income, and you've got your profit or loss. It's all about how well your business handles its cash.
Cash Flow Statement
Cash is king in business, and this statement forecasts how money will move in and out of your company. It predicts all cash coming in and going out, helping you ensure you have enough to cover day-to-day costs and investments and pay off any debts. A strong cash flow is crucial to keeping your business going.
As student entrepreneurs, having a CPA set up your accounting system is a smart move for accuracy. When you present these financial documents in your business plan, make sure they're clear and detailed.
These numbers prove the worth and profitability of your business idea, which can be a big draw for potential investors or lenders. So, be thorough and get the figures right.
Supporting Documentation
You'll also want to include various documents that back up the information you've presented in the main part of your plan. Keep in mind that this list might change depending on how far along your business is. Here's what to include:
- Resumes : Put in resumes of the people who are key to your business. Show off their qualifications and experience to give confidence to potential investors or lenders.
- Credit Information (appendix) : If relevant, add credit reports for yourself or your team members. This will prove that you're financially responsible.
- Quotes or Estimates : Include any quotes or cost estimates you've received from suppliers or service providers. This helps prove that you've done your homework on expenses.
- Letters of Intent from Prospective Customers : If you have letters from potential customers saying they want to use your products or services, toss those in. It shows there's a demand.
- Letters of Support from Credible References : If you have supportive letters from mentors, professors, or industry experts, add those. They can vouch for your idea.
- Leases or Buy/Sell Agreements : If you're renting space or buying equipment, include the agreements. It proves you have the physical assets and responsibilities in place.
- Legal Documents Relevant to the Business : If there are any legal papers like incorporation documents, partnership agreements, or licenses, include them. It shows you're following the rules.
- Census/Demographic Data : If your business relies on specific data about people, include statistics or reports from trustworthy sources. This information will support your market analysis and target audience information.
Remember to keep these documents well-organized in the appendix. This list covers the basics, but tailor it to your specific student business plan's needs and stage of development.
Business Plan Program
Creating a strong business plan is essential for any entrepreneur, and with the help of business plan programs and tools, you can make it more effective.
- LivePlan : LivePlan is a user-friendly business planning software that guides users through creating business plans and offers financial forecasting.
- Bizplan : Bizplan focuses on startups and small businesses, providing step-by-step planning, financial tools, and pitch deck creation.
- Enloop : Enloop automates business plan writing using data inputs and offers financial projection tools.
- PlanGuru : PlanGuru is for in-depth financial analysis and creating detailed financial projections.
- Upmetrics : Upmetrics offers customizable templates, financial forecasting, and collaboration features for various business stages.
- Tarkenton GoSmallBiz : Tarkenton GoSmallBiz provides business planning tools, legal resources, and marketing guidance.
- Bplans : Bplans offers free business plan templates and samples for those starting from scratch.
- Canva : Canva provides pitch deck templates and design tools to enhance presentations.
- QuickBooks : QuickBooks aids in financial tracking and management, complementing business planning.

14 Types of Business Plans with Examples
In this section, we'll explore 10 types of business plan examples for student entrepreneurship.
1. Traditional Business Plans
These classic business plans , often prepared on paper, provide a comprehensive overview of the business, detailing its identity, goals, and strategies for success.
2. Standard Plans
Similar to traditional plans, standard business plans are created digitally, typically using software like Microsoft Word or Excel, making them easier to edit and share.
3. One-Page Business Plans
Incredibly concise, these plans condense all crucial information onto a single page, often using bullet points for clarity and brevity.
4. Annual Business Plans
Tailored for a specific year, these plans outline a business's objectives and actions for that particular period, providing a focused strategy.
5. Lean Plans
Lean business plans are streamlined versions, intentionally omitting some details to protect confidential information while offering a concise yet informative summary.
6. Business Plans for Start-ups
Specifically designed for new ventures, these plans may incorporate surveys, customer insights, and visual aids to support their customized approach.
7. Feasibility Studies
These plans investigate the viability of new product or service ideas, helping businesses make informed decisions about their implementation by analyzing their potential success.
Understanding these various types of business plans is essential for your business management studies, as they serve different purposes and contexts within the business world.
8. Strategic Plans
Concentrating on marketing and branding strategies, these plans often involve extensive market research and prioritize effective brand promotion.
9. Operational Plans
Emphasizing practical steps, operational plans use data, charts, and graphs to guide a business's actions toward its goals, with a strong focus on execution.
10. Internal Plans
Highly detailed and meant exclusively for the company's internal team, these plans contain sensitive information and strategic insights for team members' use.
11. What-If plan
This type of plan explores various scenarios and their potential impact on the business. It helps a company prepare for unexpected situations by outlining strategies for different outcomes.
12. Expansion plan
An expansion plan outlines strategies for growing a business, whether through opening new locations, entering new markets, or diversifying product lines. It details the steps and resources needed for expansion.
14. Business Acquisition Plan
When a company intends to acquire another business, this plan outlines the acquisition strategy, financial considerations, and integration plans. It helps ensure a smooth transition and maximizes the value of the acquisition.
These plans cover a range of scenarios and goals, each serving a unique purpose in the world of business strategy. Hopefully, you can choose a business plan template for high school students that suits your needs.
Final Thoughts
Starting and running a business as a student is a journey. A well-structured business plan is essential for success, helping you define your goals and strategies. To create one, feel free to use these business plan examples for students as a source of inspiration.
It’s your tool to guide your entrepreneurial journey and increase your chances of success. So, get started, create your plan, and get started on your path to entrepreneurship with confidence.


- Entrepreneurship
- WordPress And Webdesign
- Sales Funnel
- Motivation And Affirmation
- Get in Touch
10 Business Plan Examples for Students (2024)
Written by Peter Keszegh
Starting a business isn’t just for the established entrepreneurs. If you’re a student with a great business idea, or if you’re just looking to earn extra money on the side, you can set up your own business with the right steps and preparation, too!
In this article, we’ll list some business plan examples for students and how you can turn your business ideas into reality.

What is a business plan?
In simple terms, a business plan is a detailed document that explains everything you need to know about your business idea. It includes your goals for your business and how exactly you plan to achieve them.
A business plan should be able to explain why your product or service is valuable, your target market for your business, and your future plans for the business.
Having a well-written business plan is important, especially if you’re looking at seeking external funding from investors. Even if you’re planning to use personal funds for your business, the business plan will help outline all your operational and management strategies.
Tailoring your plan to your business
While business plans have some standard sections used by all industries, it’s best to tailor your business plan depending on what your market is. For instance, if you’re planning to sell food products, you need to write sections on sourcing ingredients and quality control.
Think about what’s special about your business, and make sure to incorporate that in your business plan. Put yourselves in the shoes of an external investor – what would they want to know about your business? Don’t be afraid to think outside the box, too.

Parts of a business plan
You might be wondering – how should we structure a business plan? Here are some key sections you might want to include when writing your business plan:
Executive summary
An executive summary is exactly that – a summary of what your business is all about and your goals for the future. Make sure to include what your product or service plans to do, your target market, and key milestones you’d like to achieve. If you have plans to source external funding, mention this here, too.
Company description
You can use this section to expound on what you plan to achieve and what your business vision is . Use this section to highlight what makes your business unique , and why your product or service offers an innovative solution.
Market analysis
If you’re looking to start a business, you need to have a good understanding of the market and who your competitors are. Do the research to make sure there’s a real need for your product or service , and make sure you know what sets your business apart from competitors.
Organizational structure
If you’re working with a team and you all have different responsibilities, make sure to put that into writing. This doesn’t have to be too formal – all you have to do is make sure everyone’s tasks are clearly delineated so there’s no overstepping.
Product line or services offered
Talk about what you plan to sell or offer as a business. What exactly does your product or service do? What makes it so special, and what can your product or service do that isn’t already offered by your competitors?
Marketing and sales strategies
How do you plan to promote your business to attract customers and secure sales ? You can talk about where you plan to sell your products or offer your services, and how you plan to advertise your business.
Financial projections and funding requests
Set financial goals for your business and identify when your business will likely break even . If you need to secure external funding, make sure to mention this here, and mention how much money you’ll be needing and how you’ll be spending it.
Relevant documents that you mentioned earlier in your business plan should be included here. For instance, if you conducted market research via a survey, put your survey data here.
Of course, don’t be limited by the sections listed here. If there are other relevant details you’d like to talk about in your business plan, don’t be afraid to explore them. For instance, if you’re looking at using new technologies and tools for your product or service, you can write a relevant section in your business plan as well.

Why students need to master business plans
Businesses aren’t just for more seasoned entrepreneurs – starting a business can prove to be useful for students who want to hone their skills and become more business-minded.
Here’s how business plans can help students:
Enhancing strategic decision-making
You’ll have to make a lot of decisions when running a business, and business plans will force you to make smarter decisions. You don’t want to make things unnecessarily difficult for you and your team only to get mediocre results – you want to make sure you make the most out of your resources!
This kind of strategic decision-making isn’t something you learn in the classroom. Hands-on business experience will be useful for you to make wise decisions, even if it means learning from mistakes.
Improving market research and analysis skills
As students, you already do a lot of research for different school projects. When setting up a business, you’ll have to do research of your own to get a better understanding of the market your business plans to work in.
Having a good understanding of the market will also improve your analysis skills. For instance, doing enough research on the retail industry will give you a better idea of who the average retail customer is, allowing you to tweak your marketing and sales strategies to capture that target market.
Honing financial literacy and forecasting
Discussions about money and numbers can get pretty confusing. When you’re setting up a business and dealing with real, tangible figures, you’ll gain a better understanding of how finances work, how profitable your business might be, and what you’ll likely be spending money on.

Business plan examples for students
If you need a little help in thinking about the kind of business you want to set up, here are 10 business plan examples for students that you can use as inspiration:

Tu toring services
Some students will understand subjects better than others, which means there are a number of students who’ll need a little bit of help when it comes to their academic requirements and upcoming exams.
If you’re academically gifted and have a talent for teaching, you might want to consider offering tutoring services in your school.
- Executive summary : Mission, services offered, and target client demographic.
- Business description: Subjects covered, and technologies used (if applicable).
- Services provided: Individual tutoring, group workshops, and ongoing support options.
- Market analysis: Demographic trends, existing offerings, and unmet needs.
- Marketing strategy: Flyers, community center partnerships, and word-of-mouth referral programs .
- Operational plan: Scheduling system, session formats (in-person, online), and materials preparation.
- Management and organization: Tutor recruitment, training programs, and operational leadership.
- Financial summary: Basic costs, session pricing, financial goals, and sustainability plan.

Campus delivery service business
Especially during finals weeks, students can get pretty busy and can often forget to take care of themselves. How many all-nighters have you pulled as a student, and how many times have you skipped a meal to work on a deadline?
If this sounds like the kind of culture in your university, you might want to consider setting up a campus delivery service to cater to busy students. Here’s how you can set up your business plan:
- Executive summary: Service overview, mission, and objectives.
- Company description: Origins, campus focus, and service differentiation.
- Service offering: Types of delivery services offered (e.g., food, groceries).
- Market analysis: Campus demographics, needs assessment, and competitor analysis.
- Marketing strategy: Promotional tactics targeting students and staff, partnerships with local businesses.
- Operations plan: Delivery logistics, technology use (e.g., apps, GPS tracking), and hours of operation.
- Management and organization: Team roles, volunteer vs. paid staff, and management hierarchy.
- Financial plan: Start-up costs, pricing strategy, revenue projections, and break-even analysis.

Campus fitness and wellness programs
Another way you can help students in your school become healthier is to offer services that focus on fitness and wellness . If there’s a need for students in your school to become more physically active or to just take better care of their overall wellness, you could offer relevant programs on campus.
- Executive summary: Concept, target audience, and objectives of the fitness programs.
- Business description: Range of services (classes, personal training, wellness workshops).
- Market analysis: Campus health trends, competitor offerings, and student wellness needs.
- Services: Detailed look at program offerings, schedules, and customization options.
- Marketing plan: Engagement strategies, campus events, and partnership with student health services.
- Operational plan: Instructor qualifications, equipment needs, and location logistics.
- Management and organization: Structure of the team, roles, and experience in health and wellness.
- Financial overview: Initial setup costs, pricing strategy, revenue streams, and financial projections.

Student freelance platform
Freelancing is a popular way for students to earn extra income on the side, in the middle of their busy class schedules. If you have enough know-how when it comes to setting up websites or apps, you might want to consider launching a portal where student freelancers can conveniently find more freelance gigs.
- Executive summary: Platform purpose, target market, and value proposition.
- Business description: Niche focus (e.g., design, tutoring, programming), platform features.
- Market analysis: Demand for freelance work among students, analysis of existing platforms, gap identification.
- Service description: User interface, service categories, payment processing system.
- Marketing and sales strategy: Campus outreach, online presence, and user acquisition strategies.
- Technology plan: Website architecture, user security measures, and scalability.
- Operations plan: Customer support, dispute resolution process, and freelancer vetting process.
- Financial summary: Funding requirements, monetization strategy, and financial forecasts.

Mobile app for campus services and networking business
Maybe you’ve got an enormous campus that boasts a lot of helpful activities and services that most students might not already be aware of. If you want to promote these services in an innovative way, you could think about setting up a mobile app that students can use as a one-stop-shop for all their campus service needs.
- Executive summary: Introduction to the app, its core functionalities, and target user base.
- Business description: Insight into how the app facilitates campus life, services offered, and networking features.
- Market analysis: Current apps in the market, student needs analysis, and potential for growth.
- Product description: Detailed functionalities, user interface design, and privacy features.
- Marketing plan: Strategies for app launch, user acquisition, and partnerships with university departments.
- Technology plan: Development roadmap, platform compatibility, and maintenance plan.
- Management and operations: Team structure, developer roles, and operational milestones.
- Financial projections: Budget for app development, marketing costs, monetization strategies, and revenue forecasts.

Eco-friendly apparel brand
Everyone’s becoming more eco-conscious nowadays, and brands who often highlight their environmentally-friendly practices do get a good reputation. If you want to tap into that market and mix it with a bit of fashion design, you can choose to set up an eco-friendly apparel business.
- Executive summary: Brand mission, product range, and sustainability goals.
- Company background: Inspiration behind the brand, target demographic, and brand story.
- Products and services: Description of apparel line, materials used, and production process.
- Market analysis: Trends in sustainable fashion, target market behavior, and competitive landscape.
- Marketing strategy: Branding, social media campaigns, and collaborations with eco-conscious influencers.
- Operational plan: Supply chain management, ethical sourcing, and online versus physical sales approach.
- Management team: Roles, responsibilities, and background of team members.
- Financial plan: Initial investment, cost structure, sales forecast, and profitability analysis.

Sustainable campus living products
Maybe you’re not too keen on selling apparel, but you’d still like to tap into the market of students who prioritize sustainable brands and products.
If you also share the same passion for sustainability and have ideas on how to cater to students’ needs, you might want to consider selling sustainable products instead that dormers and other students will find useful for everyday life.
- Executive summary: Mission statement, product line overview, and sustainability goals.
- Company overview: Background on the inspiration for eco-friendly products targeted at students.
- Market analysis: Trends in sustainability, potential campus markets, and niche opportunities.
- Products offered: Description of eco-friendly living products (reusable containers, biodegradable goods).
- Marketing and sales strategy: Campus-based initiatives, eco-friendly partnerships, and social media.
- Operations: Sourcing of materials, product manufacturing, and logistics.
- Management team: Founder’s background, operational management, and advisory board.
- Financial projections: Cost analysis, sales forecast, funding requirements, and profitability timeline.

Student event planning service
A big part of student life is all about events and getting to meet new people. Not only is event planning a big thing for official student organizations, it’s also helpful for smaller communities who want to organize events to meet like-minded people.
If events are a popular thing in your school, you might benefit from setting up a student event planning service.
- Executive summary: Overview of services, unique selling points, and business goals.
- Company description: Types of events covered (e.g., academic, social, sporting).
- Service offering: Full event planning, day-of coordination, and consultation services.
- Market analysis: Campus event culture, demand for event planning services, competitor overview.
- Marketing plan: Outreach strategies, partnerships with campus organizations, and promotional materials.
- Operational strategy: Event logistics, vendor relationships, and event execution checklist.
- Management structure: Leadership team, volunteer opportunities, and staffing needs.
- Financial projections: Pricing model, expected expenses, revenue estimates, and growth potential.

Campus event photography service
Every big event needs good documentation to go with it. Even if your school isn’t big on events, you can choose to offer photography services to groups of friends who want cute little photoshoots in the most Instagrammable parts of your campus.
If you have a knack for photography, here’s how you can start offering photography services on campus:
- Executive summary: Concept and goals for providing photography services for campus events and personal photoshoots.
- Company description: Insights into the types of events covered (e.g., graduations, parties, portraits).
- Services offered: Packages available, including event coverage, individual portraits, and group sessions.
- Market analysis: Demand for photography services on campus, existing offerings, and unique selling points.
- Marketing strategy: Portfolio development, social media presence, partnerships with event organizers.
- Operational plan: Booking process, event execution, post-processing, and delivery of images.
- Management team: Background of the photographer(s), roles in business management, marketing, and customer service.
- Financial plan: Pricing strategy, cost of equipment and travel, revenue projections, and growth potential.

Student art gallery and workshop space
Maybe you’re from an art school, or your campus boasts a rich and talented artistic community. If your school’s artists are looking for a space to display their art, setting up a gallery and workshop space might be a profitable and sustainable business opportunity.
- Executive summary: Vision, goals, and unique aspects of the art gallery and workshop space.
- Company overview: Concept behind promoting student art, workshop themes, and community benefits.
- Market analysis: Interest in local art, campus cultural activities, and potential for art sales.
- Services and products: Exhibition schedules, workshop offerings, and art sales.
- Marketing strategy: Promotions through campus channels, local art scenes, and social media.
- Operations: Gallery setup, workshop logistics, and artist collaboration processes.
- Management team: Backgrounds in art management, curation, and education.
- Financials: Start-up expenses, pricing for art and workshops, expected revenue, and growth potential.

Common mistakes to avoid for student businesses
Setting up a business is no walk in the park, especially for young and inexperienced students. Here are some common mistakes that you can avoid when planning your own business, so you can steer clear of bigger problems down the road:
Lack of a well-defined business plan
It should go without saying that insufficient planning will make it difficult to get your business off the ground. Make sure you put down all important details in writing , and consult experts and get insights from successful small businesses if you need to.
Underestimating the importance of market research
You’ll need more than just a cool idea to start a business. There needs to be a real need or demand for your product or service, and if there’s another business already offering the same thing, you need to make sure your product or service is different or unique.
Familiarize yourself with the existing market and what the market gaps are. Once you identify what that market needs, you can tailor your business plans to try to fill in that gap.
Overlooking legal and financial regulations
Being a student doesn’t exempt you from following standard business regulations. Double check with experts and do extra research to make sure your business complies with all necessary regulations. For instance, you may need to officially register your business, or secure necessary permits.
Inadequate financial planning and management
Your business needs to be on financially stable ground for it to stay sustainable. Make sure you know if you’re in good financial standing to launch your business , and make sure you aren’t spending more than what you can actually afford.
Ignoring the importance of a strong team
It’s tempting to do everything yourself, especially if you lack funds or the ability to delegate tasks. However, you might benefit from having a team of members with various skills. A strong team will bring in more ideas to the table , and will be helpful in managing heavy workloads.
Overlooking customer feedback
You need to listen to what your customers are saying to adapt to their needs and wants. Are your products too expensive? Are people looking for different colors of your products? Engage with your customers so they can let you know how you can improve your business.
Neglecting online marketing
Social media is everything in today’s digital age! You’ll be able to reach a wider audience if you set up social media accounts on different platforms to advertise your services or products.

Future steps for student business owners
So you’ve made your business plan – congratulations! But where do you go from here?
If you want to know whether or not your business is taking off and what future opportunities you can secure, here are some ideas:
Evaluating business performance
Regularly review how well your business is performing by checking product sales, total profits, and how wide your customer base is. If you’ve been earning a good amount of money and are selling popular products or services, that’s a great sign!
Make sure to listen to customer feedback , too, as your customers might give you helpful insights that you might not immediately be aware of. You can do this via informal chats with your customers, or via more formal means like customer surveys.
Exploring growth strategies
Once you’ve evaluated how well your business is performing, you might want to consider growing your business if there’s a demand for a product or service you aren’t already offering, or if there’s an adjacent market you can tap into.
For instance, if you’re offering tutoring services for basic algebra classes, you might want to offer sessions for more complicated math subjects if your tutees need them. If you’ve set up an art space that can also be used as a venue for student events, you can consider expanding your offerings.
Scaling the business
Maybe your business has really taken off and has hit a point that you can no longer meet the customer demand with your tiny team. If that’s the case, you might want to consider scaling.
You can scale your business by adding more people to your team , or ramping up your production efforts.
Building a brand
Don’t be afraid to make a name for yourself! Explore how you can create a brand for your business. This is where you can let your creative juices flow – do you want to appear like a sophisticated and professional brand, or are you going for a more quirky approach?

Takeaways for business plan examples for students
The opportunities are endless if you want to set up a business as a student. Let your imagination run wild and look through business plan examples for students if you want to start selling or offering something new to your school’s community.
Don’t be intimidated by your lack of expertise or resources just yet – with the right mindset and enough determination, you’ll be able to set up your business for success and start your journey as a solid business owner!
Read More Articles:
Why Hire Marketing Consultants for Small Business? Pros and Cons
5 Principles of Motivational Interviewing for Successful Hires
Business Plan Template for College Students
- Great for beginners
- Ready-to-use, fully customizable Subcategory
- Get started in seconds

Starting a business as a college student can be both exciting and challenging. You have big dreams and innovative ideas, but how do you turn them into a successful reality? ClickUp's Business Plan Template for College Students is here to guide you every step of the way!
With this template, you can:
- Clearly define your business goals and strategies for success
- Create a comprehensive financial plan and projections to attract investors
- Identify potential obstacles and develop contingency plans
- Effectively communicate your business ideas to stakeholders and secure funding or resources
Don't let your entrepreneurial dreams fade away. Use ClickUp's Business Plan Template for College Students to bring your vision to life and make a lasting impact in the business world. Start planning and building your future today!
Business Plan Template for College Students Benefits
Starting a business as a college student is an exciting and challenging endeavor. With a Business Plan Template for College Students, you can:
- Clearly articulate your business goals and strategies, giving potential investors and partners a comprehensive understanding of your vision
- Create a solid financial forecast that demonstrates the potential profitability of your venture, increasing your chances of securing funding or resources
- Identify potential obstacles and develop contingency plans to mitigate risks, ensuring your business is well-prepared for any challenges that may arise
- Effectively communicate your business idea to others, including professors, mentors, and potential customers, gaining valuable feedback and support for your startup.
Main Elements of College Students Business Plan Template
ClickUp's Business Plan Template for College Students provides a comprehensive framework for college students to develop and present their business ideas effectively:
- Custom Statuses: Easily track the progress of each section of your business plan with statuses such as Complete, In Progress, Needs Revision, and To Do.
- Custom Fields: Use custom fields like Reference, Approved, and Section to add important details to your business plan, such as references, approval status, and specific sections.
- Custom Views: Access different views like Topics, Status, Timeline, Business Plan, and Getting Started Guide to organize your business plan information, track progress, create a timeline, and refer to a guide to get started.
- Collaboration Tools: Collaborate with team members, mentors, or advisors by assigning tasks, adding comments, and attaching files directly within the template.
- Goal Tracking: Set goals within your business plan and use ClickUp's Goals feature to track their progress and measure success.
- Document Management: Store important documents, financial projections, and market research within ClickUp's Docs feature for easy access and reference.
How To Use Business Plan Template for College Students
If you're a college student looking to start your own business, using ClickUp's Business Plan Template can help you get organized and create a solid plan for success. Just follow these six steps:
1. Define your business idea and goals
Start by clearly defining your business idea and the goals you want to achieve. What problem does your business solve? Who is your target audience? What are your short-term and long-term goals? Take the time to brainstorm and outline these key details.
Use a Doc in ClickUp to document your business idea and goals.
2. Conduct market research
Next, conduct thorough market research to understand your industry, competition, and target market. Identify trends, customer needs, and potential challenges. This research will help you refine your business idea, identify opportunities, and develop strategies to stand out in the market.
Use the Table view in ClickUp to organize and analyze your market research data.
3. Plan your products or services
Based on your market research, plan out the products or services you will offer. Determine their unique selling points, pricing strategy, and how they will meet the needs of your target market. Consider any additional features or benefits that will set you apart from competitors.
Create tasks in ClickUp to outline and organize your product or service plans.
4. Develop a marketing strategy
Now it's time to develop a comprehensive marketing strategy to promote your business and attract customers. Identify the most effective channels to reach your target audience, such as social media, content marketing, or email campaigns. Outline your branding, messaging, and promotional tactics.
Use the Board view in ClickUp to visually plan and track your marketing initiatives.
5. Create a financial plan
A solid financial plan is crucial for any business. Determine your startup costs, revenue projections, and expenses. Create a budget that includes marketing, operations, and any other necessary expenses. Consider different funding options and outline your financial goals for the first year and beyond.
Use custom fields in ClickUp to track and analyze your financial projections.
6. Review and revise
Once you have completed your business plan using ClickUp's template, review it thoroughly and make any necessary revisions. Share it with trusted mentors, advisors, or teammates for feedback. Continuously update and refine your plan as your business evolves.
Set recurring tasks in ClickUp to regularly review and update your business plan.
Get Started with ClickUp’s Business Plan Template for College Students
College students who are starting their own businesses or pursuing entrepreneurial ventures can use the ClickUp Business Plan Template to effectively communicate their business ideas and secure funding or resources for their startups.
First, hit “Add Template” to sign up for ClickUp and add the template to your Workspace. Make sure you designate which Space or location in your Workspace you’d like this template applied.
Next, invite relevant members or guests to your Workspace to start collaborating.
Now you can take advantage of the full potential of this template to create a comprehensive business plan:
- Use the Topics View to outline and organize different sections of your business plan, such as Executive Summary, Market Analysis, Marketing Strategy, Financial Projections, etc.
- The Status View will help you track the progress of each section, with statuses like Complete, In Progress, Needs Revision, and To Do
- The Timeline View will allow you to set deadlines and visualize the timeline for completing each section of your business plan
- The Business Plan View will provide a holistic overview of your entire business plan, allowing you to see how different sections fit together
- The Getting Started Guide View will provide step-by-step instructions and resources to help you navigate through the business planning process
- Utilize custom fields like Reference, Approved, and Section to add additional information and categorize different aspects of your business plan
- Regularly update and revise your business plan as you progress, ensuring that it reflects the most accurate and up-to-date information.
- Business Plan Template for Lululemon
- Business Plan Template for Hotel Industry
- Business Plan Template for Packaging Manufacturers
- Business Plan Template for Sales Teams
- Business Plan Template for Photography Business
Template details
Free forever with 100mb storage.
Free training & 24-hours support
Serious about security & privacy
Highest levels of uptime the last 12 months
- Product Roadmap
- Affiliate & Referrals
- On-Demand Demo
- Integrations
- Consultants
- Gantt Chart
- Native Time Tracking
- Automations
- Kanban Board
- vs Airtable
- vs Basecamp
- vs MS Project
- vs Smartsheet
- Software Team Hub
- PM Software Guide
Small Business Trends
How to create a business plan: examples & free template.
This guide has been designed to help you create a winning plan that stands out in the ever-evolving marketplace. U sing real-world examples and a free downloadable template, it will walk you through each step of the process.
Table of Contents
How to Write a Business Plan
Executive summary.

The Executive Summary serves as the gateway to your business plan, offering a snapshot of your venture’s core aspects. This section should captivate and inform, succinctly summarizing the essence of your plan.
Example: EcoTech is a technology company specializing in eco-friendly and sustainable products designed to reduce energy consumption and minimize waste. Our mission is to create innovative solutions that contribute to a cleaner, greener environment.
Overview and Business Objectives
This part of the plan demonstrates to investors and stakeholders your vision for growth and the practical steps you’ll take to get there.
Company Description
Include information about the company’s founders, their expertise, and why they are suited to lead the business to success. This section should paint a vivid picture of your business, its values, and its place in the industry.
Define Your Target Market
Example: Our target market comprises environmentally conscious consumers and businesses looking for innovative solutions to reduce their carbon footprint. Our ideal customers are those who prioritize sustainability and are willing to invest in eco-friendly products.
Market Analysis
Our research indicates a gap in the market for high-quality, innovative eco-friendly technology products that cater to both individual and business clients.
SWOT Analysis
Competitive analysis.
In this section, you’ll analyze your competitors in-depth, examining their products, services, market positioning, and pricing strategies. Understanding your competition allows you to identify gaps in the market and tailor your offerings to outperform them.
Organization and Management Team
Example: EcoTech’s organizational structure comprises the following key roles: CEO, CTO, CFO, Sales Director, Marketing Director, and R&D Manager. Our management team has extensive experience in technology, sustainability, and business development, ensuring that we are well-equipped to execute our business plan successfully.
Products and Services Offered
Marketing and sales strategy.
Describe the nature of your advertising campaigns and promotional activities, explaining how they will capture the attention of your target audience and convey the value of your products or services. Outline your sales strategy, including your sales process, team structure, and sales targets.
Logistics and Operations Plan
Inventory control is another crucial aspect, where you explain strategies for inventory management to ensure efficiency and reduce wastage. The section should also describe your production processes, emphasizing scalability and adaptability to meet changing market demands.
Financial Projections Plan
In the Financial Projections Plan, lay out a clear and realistic financial future for your business. This should include detailed projections for revenue, costs, and profitability over the next three to five years.
Income Statement
The income statement , also known as the profit and loss statement, provides a summary of your company’s revenues and expenses over a specified period. It helps you track your business’s financial performance and identify trends, ensuring you stay on track to achieve your financial goals.
Cash Flow Statement
| Section | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Executive Summary | Brief overview of the business plan | Overview of EcoTech and its mission |
| Overview & Objectives | Outline of company's goals and strategies | Market leadership in sustainable technology |
| Company Description | Detailed explanation of the company and its unique selling proposition | EcoTech's history, mission, and vision |
| Target Market | Description of ideal customers and their needs | Environmentally conscious consumers and businesses |
| Market Analysis | Examination of industry trends, customer needs, and competitors | Trends in eco-friendly technology market |
| SWOT Analysis | Evaluation of Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats | Strengths and weaknesses of EcoTech |
| Competitive Analysis | In-depth analysis of competitors and their strategies | Analysis of GreenTech and EarthSolutions |
| Organization & Management | Overview of the company's structure and management team | Key roles and team members at EcoTech |
| Products & Services | Description of offerings and their unique features | Energy-efficient lighting solutions, solar chargers |
| Marketing & Sales | Outline of marketing channels and sales strategies | Digital advertising, content marketing, influencer partnerships |
| Logistics & Operations | Details about daily operations, supply chain, inventory, and quality control | Partnerships with manufacturers, quality control |
| Financial Projections | Forecast of revenue, expenses, and profit for the next 3-5 years | Projected growth in revenue and net profit |
| Income Statement | Summary of company's revenues and expenses over a specified period | Revenue, Cost of Goods Sold, Gross Profit, Net Income |
| Cash Flow Statement | Overview of cash inflows and outflows within the business | Net Cash from Operating Activities, Investing Activities, Financing Activities |
Tips on Writing a Business Plan
3. Set realistic goals: Your business plan should outline achievable objectives that are specific, measurable, attainable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART). Setting realistic goals demonstrates your understanding of the market and increases the likelihood of success.
FREE Business Plan Template
To help you get started on your business plan, we have created a template that includes all the essential components discussed in the “How to Write a Business Plan” section. This easy-to-use template will guide you through each step of the process, ensuring you don’t miss any critical details.
What is a Business Plan?
Why you should write a business plan, what are the different types of business plans.
In today’s fast-paced business world, having a well-structured roadmap is more important than ever. A traditional business plan provides a comprehensive overview of your company’s goals and strategies, helping you make informed decisions and achieve long-term success. There are various types of business plans, each designed to suit different needs and purposes. Let’s explore the main types:
| Type of Business Plan | Purpose | Key Components | Target Audience |
|---|---|---|---|
| Startup Business Plan | Outlines the company's mission, objectives, target market, competition, marketing strategies, and financial projections. | Mission Statement, Company Description, Market Analysis, Competitive Analysis, Organizational Structure, Marketing and Sales Strategy, Financial Projections. | Entrepreneurs, Investors |
| Internal Business Plan | Serves as a management tool for guiding the company's growth, evaluating its progress, and ensuring that all departments are aligned with the overall vision. | Strategies, Milestones, Deadlines, Resource Allocation. | Internal Team Members |
| Strategic Business Plan | Outlines long-term goals and the steps to achieve them. | SWOT Analysis, Market Research, Competitive Analysis, Long-Term Goals. | Executives, Managers, Investors |
| Feasibility Business Plan | Assesses the viability of a business idea. | Market Demand, Competition, Financial Projections, Potential Obstacles. | Entrepreneurs, Investors |
| Growth Business Plan | Focuses on strategies for scaling up an existing business. | Market Analysis, New Product/Service Offerings, Financial Projections. | Business Owners, Investors |
| Operational Business Plan | Outlines the company's day-to-day operations. | Processes, Procedures, Organizational Structure. | Managers, Employees |
| Lean Business Plan | A simplified, agile version of a traditional plan, focusing on key elements. | Value Proposition, Customer Segments, Revenue Streams, Cost Structure. | Entrepreneurs, Startups |
| One-Page Business Plan | A concise summary of your company's key objectives, strategies, and milestones. | Key Objectives, Strategies, Milestones. | Entrepreneurs, Investors, Partners |
| Nonprofit Business Plan | Outlines the mission, goals, target audience, fundraising strategies, and budget allocation for nonprofit organizations. | Mission Statement, Goals, Target Audience, Fundraising Strategies, Budget. | Nonprofit Leaders, Board Members, Donors |
| Franchise Business Plan | Focuses on the franchisor's requirements, as well as the franchisee's goals, strategies, and financial projections. | Franchise Agreement, Brand Standards, Marketing Efforts, Operational Procedures, Financial Projections. | Franchisors, Franchisees, Investors |
Using Business Plan Software
Enloop is a robust business plan software that automatically generates a tailored plan based on your inputs. It provides industry-specific templates, financial forecasting, and a unique performance score that updates as you make changes to your plan. Enloop also offers a free version, making it accessible for businesses on a budget.
| Software | Key Features | User Interface | Additional Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| LivePlan | Over 500 sample plans, financial forecasting tools, progress tracking against KPIs | User-friendly, visually appealing | Allows creation of professional-looking business plans |
| Upmetrics | Customizable templates, financial forecasting tools, collaboration capabilities | Simple and intuitive | Provides a resource library for business planning |
| Bizplan | Drag-and-drop builder, modular sections, financial forecasting tools, progress tracking | Simple, visually engaging | Designed to simplify the business planning process |
| Enloop | Industry-specific templates, financial forecasting tools, automatic business plan generation, unique performance score | Robust, user-friendly | Offers a free version, making it accessible for businesses on a budget |
| Tarkenton GoSmallBiz | Guided business plan builder, customizable templates, financial projection tools | User-friendly | Offers CRM tools, legal document templates, and additional resources for small businesses |
Business Plan FAQs
What is a good business plan, what are the 3 main purposes of a business plan, can i write a business plan by myself.
We also have examples for specific industries, including a using food truck business plan , salon business plan , farm business plan , daycare business plan , and restaurant business plan .
Is it possible to create a one-page business plan?
How long should a business plan be, what is a business plan outline, what are the 5 most common business plan mistakes, what questions should be asked in a business plan.
A business plan should address questions such as: What problem does the business solve? Who is the specific target market ? What is the unique selling proposition? What are the company’s objectives? How will it achieve those objectives?
What’s the difference between a business plan and a strategic plan?
How is business planning for a nonprofit different.
How to Write a Business Plan (Plus Examples & Templates)

Have you ever wondered how to write a business plan step by step? Mike Andes, told us:
This guide will help you write a business plan to impress investors.
Throughout this process, we’ll get information from Mike Andes, who started Augusta Lawn Care Services when he was 12 and turned it into a franchise with over 90 locations. He has gone on to help others learn how to write business plans and start businesses. He knows a thing or two about writing business plans!
We’ll start by discussing the definition of a business plan. Then we’ll discuss how to come up with the idea, how to do the market research, and then the important elements in the business plan format. Keep reading to start your journey!
What Is a Business Plan?
A business plan is simply a road map of what you are trying to achieve with your business and how you will go about achieving it. It should cover all elements of your business including:
- Finding customers
- Plans for developing a team
- Competition
- Legal structures
- Key milestones you are pursuing
If you aren’t quite ready to create a business plan, consider starting by reading our business startup guide .
Get a Business Idea
Before you can write a business plan, you have to have a business idea. You may see a problem that needs to be solved and have an idea how to solve it, or you might start by evaluating your interests and skills.
Mike told us, “The three things I suggest asking yourself when thinking about starting a business are:
- What am I good at?
- What would I enjoy doing?
- What can I get paid for?”

If all three of these questions don’t lead to at least one common answer, it will probably be a much harder road to success. Either there is not much market for it, you won’t be good at it, or you won’t enjoy doing it.
As Mike told us, “There’s enough stress starting and running a business that if you don’t like it or aren’t good at it, it’s hard to succeed.”
If you’d like to hear more about Mike’s approach to starting a business, check out our YouTube video
Conduct Market Analysis
Market analysis is focused on establishing if there is a target market for your products and services, how large the target market is, and identifying the demographics of people or businesses that would be interested in the product or service. The goal here is to establish how much money your business concept can make.
Product and Service Demand

A search engine is your best friend when trying to figure out if there is demand for your products and services. Personally, I love using presearch.org because it lets you directly search on a ton of different platforms including Google, Youtube, Twitter, and more. Check out the screenshot for the full list of search options.
With quick web searches, you can find out how many competitors you have, look through their reviews, and see if there are common complaints about the competitors. Bad reviews are a great place to find opportunities to offer better products or services.
If there are no similar products or services, you may have stumbled upon something new, or there may just be no demand for it. To find out, go talk to your most honest friend about the idea and see what they think. If they tell you it’s dumb or stare at you vacantly, there’s probably no market for it.
You can also conduct a survey through social media to get public opinion on your idea. Using Facebook Business Manager , you could get a feel for who would be interested in your product or service.
I ran a quick test of how many people between 18-65 you could reach in the U.S. during a week. It returned an estimated 700-2,000 for the total number of leads, which is enough to do a fairly accurate statistical analysis.
Identify Demographics of Target Market
Depending on what type of business you want to run, your target market will be different. The narrower the demographic, the fewer potential customers you’ll have. If you did a survey, you’ll be able to use that data to help define your target audience. Some considerations you’ll want to consider are:
- Other Interests
- Marital Status
- Do they have kids?
Once you have this information, it can help you narrow down your options for location and help define your marketing further. One resource that Mike recommended using is the Census Bureau’s Quick Facts Map . He told us,
“It helps you quickly evaluate what the best areas are for your business to be located.”
How to Write a Business Plan

Now that you’ve developed your idea a little and established there is a market for it, you can begin writing a business plan. Getting started is easier with the business plan template we created for you to download. I strongly recommend using it as it is updated to make it easier to create an action plan.
Each of the following should be a section of your business plan:
- Business Plan Cover Page
- Table of Contents
- Executive Summary
- Company Description
- Description of Products and Services
SWOT Analysis
- Competitor Data
- Competitive Analysis
- Marketing Expenses Strategy
Pricing Strategy
- Distribution Channel Assessment
- Operational Plan
- Management and Organizational Strategy
- Financial Statements and/or Financial Projections
We’ll look into each of these. Don’t forget to download our free business plan template (mentioned just above) so you can follow along as we go.
How to Write a Business Plan Step 1. Create a Cover Page
The first thing investors will see is the cover page for your business plan. Make sure it looks professional. A great cover page shows that you think about first impressions.
A good business plan should have the following elements on a cover page:
- Professionally designed logo
- Company name
- Mission or Vision Statement
- Contact Info
Basically, think of a cover page for your business plan like a giant business card. It is meant to capture people’s attention but be quickly processed.
How to Write a Business Plan Step 2. Create a Table of Contents
Most people are busy enough that they don’t have a lot of time. Providing a table of contents makes it easy for them to find the pages of your plan that are meaningful to them.
A table of contents will be immediately after the cover page, but you can include it after the executive summary. Including the table of contents immediately after the executive summary will help investors know what section of your business plan they want to review more thoroughly.
Check out Canva’s article about creating a table of contents . It has a ton of great information about creating easy access to each section of your business plan. Just remember that you’ll want to use different strategies for digital and hard copy business plans.
How to Write a Business Plan Step 3. Write an Executive Summary

An executive summary is where your business plan should catch the readers interest. It doesn’t need to be long, but should be quick and easy to read.
Mike told us,
How long should an executive summary bein an informal business plan?
For casual use, an executive summary should be similar to an elevator pitch, no more than 150-160 words, just enough to get them interested and wanting more. Indeed has a great article on elevator pitches . This can also be used for the content of emails to get readers’ attention.
It consists of three basic parts:
- An introduction to you and your business.
- What your business is about.
- A call to action
Example of an informal executive summary
One of the best elevator pitches I’ve used is:
So far that pitch has achieved a 100% success rate in getting partnerships for the business.
What should I include in an executive summary for investors?
Investors are going to need a more detailed executive summary if you want to secure financing or sell equity. The executive summary should be a brief overview of your entire business plan and include:
- Introduction of yourself and company.
- An origin story (Recognition of a problem and how you came to solution)
- An introduction to your products or services.
- Your unique value proposition. Make sure to include intellectual property.
- Where you are in the business life cycle
- Request and why you need it.
Successful business plan examples
The owner of Urbanity told us he spent 2 months writing a 75-page business plan and received a $250,000 loan from the bank when he was 23. Make your business plan as detailed as possible when looking for financing. We’ve provided a template to help you prepare the portions of a business plan that banks expect.
Here’s the interview with the owner of Urbanity:
When to write an executive summary?
Even though the summary is near the beginning of a business plan, you should write it after you complete the rest of a business plan. You can’t talk about revenue, profits, and expected expenditures if you haven’t done the market research and created a financial plan.
What mistakes do people make when writing an executive summary?
Business owners commonly go into too much detail about the following items in an executive summary:
- Marketing and sales processes
- Financial statements
- Organizational structure
- Market analysis
These are things that people will want to know later, but they don’t hook the reader. They won’t spark interest in your small business, but they’ll close the deal.
How to Write a Business Plan Step 4. Company Description
Every business plan should include a company description. A great business plan will include the following elements while describing the company:
- Mission statement
- Philosophy and vision
- Company goals
Target market
- Legal structure
Let’s take a look at what each section includes in a good business plan.
Mission Statement
A mission statement is a brief explanation of why you started the company and what the company’s main focus is. It should be no more than one or two sentences. Check out HubSpot’s article 27 Inspiring Mission Statement for a great read on informative and inspiring mission and vision statements.
Company Philosophy and Vision

The company philosophy is what drives your company. You’ll normally hear them called core values. These are the building blocks that make your company different. You want to communicate your values to customers, business owners, and investors as often as possible to build a company culture, but make sure to back them up.
What makes your company different?
Each company is different. Your new business should rise above the standard company lines of honesty, integrity, fun, innovation, and community when communicating your business values. The standard answers are corporate jargon and lack authenticity.
Examples of core values
One of my clients decided to add a core values page to their website. As a tech company they emphasized the values:
- Prioritize communication.
- Never stop learning.
- Be transparent.
- Start small and grow incrementally.
These values communicate how the owner and the rest of the company operate. They also show a value proposition and competitive advantage because they specifically focus on delivering business value from the start. These values also genuinely show what the company is about and customers recognize the sincerity. Indeed has a great blog about how to identify your core values .
What is a vision statement?
A vision statement communicate the long lasting change a business pursues. The vision helps investors and customers understand what your company is trying to accomplish. The vision statement goes beyond a mission statement to provide something meaningful to the community, customer’s lives, or even the world.
Example vision statements
The Alzheimer’s Association is a great example of a vision statement:
A world without Alzheimer’s Disease and other dementia.
It clearly tells how they want to change the world. A world without Alzheimers might be unachievable, but that means they always have room for improvement.
Business Goals
You have to measure success against goals for a business plan to be meaningful. A business plan helps guide a company similar to how your GPS provides a road map to your favorite travel destination. A goal to make as much money as possible is not inspirational and sounds greedy.
Sure, business owners want to increase their profits and improve customer service, but they need to present an overview of what they consider success. The goals should help everyone prioritize their work.
How far in advance should a business plan?
Business planning should be done at least one year in advance, but many banks and investors prefer three to five year business plans. Longer plans show investors that the management team understands the market and knows the business is operating in a constantly shifting market. In addition, a plan helps businesses to adjust to changes because they have already considered how to handle them.
Example of great business goals
My all time-favorite long-term company goals are included in Tesla’s Master Plan, Part Deux . These goals were written in 2016 and drive the company’s decisions through 2026. They are the reason that investors are so forgiving when Elon Musk continually fails to meet his quarterly and annual goals.
If the progress aligns with the business plan investors are likely to continue to believe in the company. Just make sure the goals are reasonable or you’ll be discredited (unless you’re Elon Musk).

You did target market research before creating a business plan. Now it’s time to add it to the plan so others understand what your ideal customer looks like. As a new business owner, you may not be considered an expert in your field yet, so document everything. Make sure the references you use are from respectable sources.
Use information from the specific lender when you are applying for lending. Most lenders provide industry research reports and using their data can strengthen the position of your business plan.
A small business plan should include a section on the external environment. Understanding the industry is crucial because we don’t plan a business in a vacuum. Make sure to research the industry trends, competitors, and forecasts. I personally prefer IBIS World for my business research. Make sure to answer questions like:
- What is the industry outlook long-term and short-term?
- How will your business take advantage of projected industry changes and trends?
- What might happen to your competitors and how will your business successfully compete?
Industry resources
Some helpful resources to help you establish more about your industry are:
- Trade Associations
- Federal Reserve
- Bureau of Labor Statistics
Legal Structure
There are five basic types of legal structures that most people will utilize:
- Sole proprietorships
- Limited Liability Companies (LLC)
Partnerships
Corporations.
- Franchises.
Each business structure has their pros and cons. An LLC is the most common legal structure due to its protection of personal assets and ease of setting up. Make sure to specify how ownership is divided and what roles each owner plays when you have more than one business owner.
You’ll have to decide which structure is best for you, but we’ve gathered information on each to make it easier.
Sole Proprietorship
A sole proprietorship is the easiest legal structure to set up but doesn’t protect the owner’s personal assets from legal issues. That means if something goes wrong, you could lose both your company and your home.
To start a sole proprietorship, fill out a special tax form called a Schedule C . Sole proprietors can also join the American Independent Business Alliance .
Limited Liability Company (LLC)
An LLC is the most common business structure used in the United States because an LLC protects the owner’s personal assets. It’s similar to partnerships and corporations, but can be a single-member LLC in most states. An LLC requires a document called an operating agreement.
Each state has different requirements. Here’s a link to find your state’s requirements . Delaware and Nevada are common states to file an LLC because they are really business-friendly. Here’s a blog on the top 10 states to get an LLC.
Partnerships are typically for legal firms. If you choose to use a partnership choose a Limited Liability Partnership. Alternatively, you can just use an LLC.
Corporations are typically for massive organizations. Corporations have taxes on both corporate and income tax so unless you plan on selling stock, you are better off considering an LLC with S-Corp status . Investopedia has good information corporations here .

There are several opportunities to purchase successful franchises. TopFranchise.com has a list of companies in a variety of industries that offer franchise opportunities. This makes it where an entrepreneur can benefit from the reputation of an established business that has already worked out many of the kinks of starting from scratch.
How to Write a Business Plan Step 5. Products and Services
This section of the business plan should focus on what you sell, how you source it, and how you sell it. You should include:
- Unique features that differentiate your business products from competitors
- Intellectual property
- Your supply chain
- Cost and pricing structure
Questions to answer about your products and services
Mike gave us a list of the most important questions to answer about your product and services:
- How will you be selling the product? (in person, ecommerce, wholesale, direct to consumer)?
- How do you let them know they need a product?
- How do you communicate the message?
- How will you do transactions?
- How much will you be selling it for?
- How many do you think you’ll sell and why?
Make sure to use the worksheet on our business plan template .
How to Write a Business Plan Step 6. Sales and Marketing Plan
The marketing and sales plan is focused on the strategy to bring awareness to your company and guides how you will get the product to the consumer. It should contain the following sections:
SWOT Analysis stands for strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. Not only do you want to identify them, but you also want to document how the business plans to deal with them.
Business owners need to do a thorough job documenting how their service or product stacks up against the competition.
If proper research isn’t done, investors will be able to tell that the owner hasn’t researched the competition and is less likely to believe that the team can protect its service from threats by the more well-established competition. This is one of the most common parts of a presentation that trips up business owners presenting on Shark Tank .
SWOT Examples

Examples of strengths and weaknesses could be things like the lack of cash flow, intellectual property ownership, high costs of suppliers, and customers’ expectations on shipping times.
Opportunities could be ways to capitalize on your strengths or improve your weaknesses, but may also be gaps in the industry. This includes:
- Adding offerings that fit with your current small business
- Increase sales to current customers
- Reducing costs through bulk ordering
- Finding ways to reduce inventory
- And other areas you can improve
Threats will normally come from outside of the company but could also be things like losing a key member of the team. Threats normally come from competition, regulations, taxes, and unforeseen events.
The management team should use the SWOT analysis to guide other areas of business planning, but it absolutely has to be done before a business owner starts marketing.
Include Competitor Data in Your Business Plan
When you plan a business, taking into consideration the strengths and weaknesses of the competition is key to navigating the field. Providing an overview of your competition and where they are headed shows that you are invested in understanding the industry.
For smaller businesses, you’ll want to search both the company and the owners names to see what they are working on. For publicly held corporations, you can find their quarterly and annual reports on the SEC website .
What another business plans to do can impact your business. Make sure to include things that might make it attractive for bigger companies to outsource to a small business.
Marketing Strategy
The marketing and sales part of business plans should be focused on how you are going to make potential customers aware of your business and then sell to them.
If you haven’t already included it, Mike recommends:
“They’ll want to know about Demographics, ages, and wealth of your target market.”
Make sure to include the Total addressable market . The term refers to the value if you captured 100% of the market.
Advertising Strategy
You’ll explain what formats of advertising you’ll be using. Some possibilities are:
- Online: Facebook and Google are the big names to work with here.
- Print : Print can be used to reach broad groups or targeted markets. Check out this for tips .
- Radio : iHeartMedia is one of the best ways to advertise on the radio
- Cable television : High priced, hard to measure ROI, but here’s an explanation of the process
- Billboards: Attracting customers with billboards can be beneficial in high traffic areas.
You’ll want to define how you’ll be using each including frequency, duration, and cost. If you have the materials already created, including pictures or links to the marketing to show creative assets.
Mike told us “Most businesses are marketing digitally now due to Covid, but that’s not always the right answer.”
Make sure the marketing strategy will help team members or external marketing agencies stay within the brand guidelines .

This section of a business plan should be focused on pricing. There are a ton of pricing strategies that may work for different business plans. Which one will work for you depends on what kind of a business you run.
Some common pricing strategies are:
- Value-based pricing – Commonly used with home buying and selling or other products that are status symbols.
- Skimming pricing – Commonly seen in video game consoles, price starts off high to recoup expenses quickly, then reduces over time.
- Competition-based pricing – Pricing based on competitors’ pricing is commonly seen at gas stations.
- Freemium services – Commonly used for software, where there is a free plan, then purchase options for more functionality.
HubSpot has a great calculator and blog on pricing strategies.
Beyond explaining what strategy your business plans to use, you should include references for how you came to this pricing strategy and how it will impact your cash flow.
Distribution Plan
This part of a business plan is focused on how the product or service is going to go through the supply chain. These may include multiple divisions or multiple companies. Make sure to include any parts of the workflow that are automated so investors can see where cost savings are expected and when.
Supply Chain Examples
For instance, lawn care companies would need to cover aspects such as:
- Suppliers for lawn care equipment and tools
- Any chemicals or treatments needed
- Repair parts for sprinkler systems
- Vehicles to transport equipment and employees
- Insurance to protect the company vehicles and people.
Examples of Supply Chains
These are fairly flat supply chains compared to something like a clothing designer where the clothes would go through multiple vendors. A clothing company might have the following supply chain:
- Raw materials
- Shipping of raw materials
- Converting of raw materials to thread
- Shipping thread to produce garments
- Garment producer
- Shipping to company
- Company storage
- Shipping to retail stores
There have been advances such as print on demand that eliminate many of these steps. If you are designing completely custom clothing, all of this would need to be planned to keep from having business disruptions.
The main thing to include in the business plan is the list of suppliers, the path the supply chain follows, the time from order to the customer’s home, and the costs associated with each step of the process.
According to BizPlanReview , a business plan without this information is likely to get rejected because they have failed to research the key elements necessary to make sales to the customer.
How to Write a Business Plan Step 7. Company Organization and Operational Plan
This part of the business plan is focused on how the business model will function while serving customers. The business plan should provide an overview of how the team will manage the following aspects:
Quality Control
- Legal environment
Let’s look at each for some insight.
Production has already been discussed in previous sections so I won’t go into it much. When writing a business plan for investors, try to avoid repetition as it creates a more simple business plan.
If the organizational plan will be used by the team as an overview of how to perform the best services for the customer, then redundancy makes more sense as it communicates what is important to the business.

Quality control policies help to keep the team focused on how to verify that the company adheres to the business plan and meets or exceeds customer expectations.
Quality control can be anything from a standard that says “all labels on shirts can be no more than 1/16″ off center” to a defined checklist of steps that should be performed and filled out for every customer.
There are a variety of organizations that help define quality control including:
- International Organization for Standardization – Quality standards for energy, technology, food, production environments, and cybersecurity
- AICPA – Standard defined for accounting.
- The Joint Commission – Healthcare
- ASHRAE – HVAC best practices
You can find lists of the organizations that contribute most to the government regulation of industries on Open Secrets . Research what the leaders in your field are doing. Follow their example and implement it in your quality control plan.
For location, you should use information from the market research to establish where the location will be. Make sure to include the following in the location documentation.
- The size of your location
- The type of building (retail, industrial, commercial, etc.)
- Zoning restrictions – Urban Wire has a good map on how zoning works in each state
- Accessibility – Does it meet ADA requirements?
- Costs including rent, maintenance, utilities, insurance and any buildout or remodeling costs
- Utilities – b.e.f. has a good energy calculator .
Legal Environment
The legal requirement section is focused on defining how to meet the legal requirements for your industry. A good business plan should include all of the following:
- Any licenses and/or permits that are needed and whether you’ve obtained them
- Any trademarks, copyrights, or patents that you have or are in the process of applying for
- The insurance coverage your business requires and how much it costs
- Any environmental, health, or workplace regulations affecting your business
- Any special regulations affecting your industry
- Bonding requirements, if applicable
Your local SBA office can help you establish requirements in your area. I strongly recommend using them. They are a great resource.
Your business plan should include a plan for company organization and hiring. While you may be the only person with the company right now, down the road you’ll need more people. Make sure to consider and document the answers to the following questions:
- What is the current leadership structure and what will it look like in the future?
- What types of employees will you have? Are there any licensing or educational requirements?
- How many employees will you need?
- Will you ever hire freelancers or independent contractors?
- What is each position’s job description?
- What is the pay structure (hourly, salaried, base plus commission, etc.)?
- How do you plan to find qualified employees and contractors?
One of the most crucial parts of a business plan is the organizational chart. This simply shows the positions the company will need, who is in charge of them and the relationship of each of them. It will look similar to this:

Our small business plan template has a much more in-depth organizational chart you can edit to include when you include the organizational chart in your business plan.
How to Write a Business Plan Step 8. Financial Statements
No business plan is complete without financial statements or financial projections. The business plan format will be different based on whether you are writing a business plan to expand a business or a startup business plan. Let’s dig deeper into each.
Provide All Financial Income from an Existing Business
An existing business should use their past financial documents including the income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statement to find trends to estimate the next 3-5 years.
You can create easy trendlines in excel to predict future revenue, profit and loss, cash flow, and other changes in year-over-year performance. This will show your expected performance assuming business continues as normal.
If you are seeking an investment, then the business is probably not going to continue as normal. Depending on the financial plan and the purpose of getting financing, adjustments may be needed to the following:
- Higher Revenue if expanding business
- Lower Cost of Goods Sold if purchasing inventory with bulk discounts
- Adding interest if utilizing financing (not equity deal)
- Changes in expenses
- Addition of financing information to the cash flow statement
- Changes in Earnings per Share on the balance sheet
Financial modeling is a challenging subject, but there are plenty of low-cost courses on the subject. If you need help planning your business financial documentation take some time to watch some of them.
Make it a point to document how you calculated all the changes to the income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statement in your business plan so that key team members or investors can verify your research.
Financial Projections For A Startup Business Plan
Unlike an existing business, a startup doesn’t have previous success to model its future performance. In this scenario, you need to focus on how to make a business plan realistic through the use of industry research and averages.
Mike gave the following advice in his interview:
Financial Forecasting Mistakes
One of the things a lot of inexperienced people use is the argument, “If I get one percent of the market, it is worth $100 million.” If you use this, investors are likely to file the document under bad business plan examples.
Let’s use custom t-shirts as an example.
Credence Research estimated in 2018 there were 11,334,800,000 custom t-shirts sold for a total of $206.12 Billion, with a 6% compound annual growth rate.
With that data, you can calculate that the industry will grow to $270 Billion in 2023 and that the average shirt sold creates $18.18 in revenue.
Combine that with an IBIS World estimate of 11,094 custom screen printers and that means even if you become an average seller, you’ll get .009% of the market.
Here’s a table for easier viewing of that information.

The point here is to make sure your business proposal examples make sense.
You’ll need to know industry averages such as cost of customer acquisition, revenue per customer, the average cost of goods sold, and admin costs to be able to create accurate estimates.
Our simple business plan templates walk you through most of these processes. If you follow them you’ll have a good idea of how to write a business proposal.
How to Write a Business Plan Step 9. Business Plan Example of Funding Requests
What is a business plan without a plan on how to obtain funding?
The Small Business Administration has an example for a pizza restaurant that theoretically needed nearly $20k to make it through their first month.
In our video, How to Start a $500K/Year T-Shirt Business (Pt. 1 ), Sanford Booth told us he needed about $200,000 to start his franchise and broke even after 4 months.
Freshbooks estimates it takes on average 2-3 years for a business to be profitable, which means the fictitious pizza company from the SBA could need up to $330k to make it through that time and still pay their bills for their home and pizza shop.
Not every business needs that much to start, but realistically it’s a good idea to assume that you need a fairly large cushion.
Ways to get funding for a small business
There are a variety of ways to cover this. the most common are:
- Bootstrapping – Using your savings without external funding.
- Taking out debt – loans, credit cards
- Equity, Seed Funding – Ownership of a percentage of the company in exchange for current funds
- Crowdsourcing – Promising a good for funding to create the product
Keep reading for more tips on how to write a business plan.
How funding will be used
When asking for business financing make sure to include:
- How much to get started?
- What is the minimum viable product and how soon can you make money?
- How will the money be spent?
Mike emphasized two aspects that should be included in every plan,
How to Write a Business Plan Resources
Here are some links to a business plan sample and business plan outline.
- Sample plan
It’s also helpful to follow some of the leading influencers in the business plan writing community. Here’s a list:
- Wise Plans – Shares a lot of information on starting businesses and is a business plan writing company.
- Optimus Business Plans – Another business plan writing company.
- Venture Capital – A venture capital thread that can help give you ideas.
How to Write a Business Plan: What’s Next?
We hope this guide about how to write a simple business plan step by step has been helpful. We’ve covered:
- The definition of a business plan
- Coming up with a business idea
- Performing market research
- The critical components of a business plan
- An example business plan
In addition, we provided you with a simple business plan template to assist you in the process of writing your startup business plan. The startup business plan template also includes a business model template that will be the key to your success.
Don’t forget to check out the rest of our business hub .
Have you written a business plan before? How did it impact your ability to achieve your goals?
80% of businesses fail... Learn how not to.
Learn from business failures and successes in 5 min or less. The stories, frameworks, and tactics that will make you a 10x better founder.
Brandon Boushy
Related articles

698 Endearing Daycare Names (2024)

How to Start a Home Business (in 9 Steps)

Opening a Gas Station: The Ultimate Guide (2024)
nice work https://binarychemist.com/
My Name is PRETTY NGOMANE. A south African female. Aspiring to do farming. And finding a home away from home for the differently abled persons in their daily needs.
Become a business owner in less than 90 days
Start your 10-day free trial of the UpFlip Academy and learn how to start your own business from scratch.
Get business advice straight to your Inbox
Limited Time Offer:
Save Up to 25% on LivePlan today
What stage is your business at?
Tell us and we’ll match you with a special LivePlan discount:
New Business Idea
Startup Phase
Established Business
Enter your email address to unlock it.
Please enter a valid email address
We care about your privacy. See our Privacy Policy .
Samples & Examples
550+ business plan examples to inspire you
Jump-start your own business with real-world business plan examples created in LivePlan.

Trusted by over 1 million small business owners
4.8/5 Google reviews
35-day money-back guarantee Get started risk-free
Don’t start from scratch — get a headstart with real business plan examples

Real business plan library
No business plan experience required
Looking at real business plan examples can help you visualize what a successful plan looks like. With LivePlan you’ll have access to over 550 free example business plans to use as a starting point.
Browse real sample plans covering a broad range of businesses to see how others have written effective executive summaries, planned marketing activities, created financial forecasts, and more.

AI-Powered Planning
Welcome to a world without writers block
LivePlan asks you questions about your business, you simply plug in the answers. It's as easy as that. Get expert guidance, instructions, and examples at each step.
Not sure where to start? The AI-Powered LivePlan Assistant will automatically generate ideas for each section of the plan and offer improved versions of your writing, adjusting for tone, voice, and grammar or spelling errors.

Automatic Financials
Forget the formulas and focus on your vision
Forget the complex formulas and spreadsheets — with automatic financials and drag-and-drop forecasting you can finish faster and be confident your numbers are accurate.
Instantly get tailored revenue and expense suggestions to add to your forecast using the AI-Powered LivePlan Assistant.
Plus, access over 40 benchmark financial metrics so you can see how your key metrics (like net profit margin and marketing spend) stack up against other businesses within your same industry.

Select your Business Category

IT, Staffing & Customer Service (16)

Construction, Architecture & Engineering (17)

Food, Beverage & Restaurant (57)

Real Estate & Rentals (16)

Mobile Apps & Software (6)

Education & Training (14)

Beauty Salon & Fitness (19)

Medical & Health Care (39)

Retail, Consumers & E-commerce (80)

Entertainment & Media (43)

Transportation, Logistics & Travel (26)

Agriculture, Farm & Food Production (18)

Nonprofit & Community (9)
Manufacturing & Wholesale (33)

Services (213)

Clothing & Fashion (12)

Children & Pets (16)

Fine Art & Crafts (5)

Cleaning, Maintenance & Repair (22)

Hotel & Lodging (9)

Finance & Investing (13)

Consulting, Advertising & Marketing (22)

Accounting, Insurance & Compliance (5)
Didn't find what you are looking for.
The answer is simple.
It’s an informal business plan that can convince you that your idea makes sense to the outside world because you are investing your time, money, and everything into that idea.
To write a business plan, maybe you think you don’t need a step-by-step guide or a sample business plan . After all, some entrepreneurs achieved success without writing a business plan. With great timing, past business experiences, entrepreneurial ambitions, and a little luck, some entrepreneurs build successful businesses without even writing an informal business plan.
But the odds are greater than those entrepreneurs fail.
And that’s why writing a business plan will help you succeed .
The easiest way to simplify the work of writing a business plan is to start with sample business plans.
What is business plan sample?
Why you should refer a business plan example, who should use business plan examples, how to use sample business plans.

What is Business Plan Sample?
That’s why we created business plan examples to help you get started.

Use our 400+ business plan examples written for all industries and write your business plan in half of the time with twice the impact.

- Guidance on what to include in each section. If you’ve never attended business school, you might never have created a SWOT analysis or a balance sheet before. Business templates that give guidance — in plain language — about what to include and how to fill in each section and create a complete and effective plan.
- A business plan is vital to get an investment. If you’re seeking investment for your business, you’ll need to convince banks and investors why they should invest in your business . Lenders and investors will only risk their time and money if they’re certain that your business will be successful and profitable and they will get a great return on their investment.
- A business plan can help you prioritize. A complete, well-balanced business plan is one of the most valuable tools in assisting you to reach your long-term goals. It gives your business direction, defines your goals, outlines out strategies to reach your goals, and helps you to manage possible bumps in the way.
Who should use Business Plan Examples?
Well Everyone, who wants to write a business plan should use these sample business plans. These plans apply to almost all industries.
We have created a library of professional sample business plans from a wide variety of industries to help you start writing your business plan with minimum effort.
Use our Upmetrics — business plan software that offers step by step guide to start writing your business plan , especially if you’re writing an informal business plan to get a bank loan or outside investment.
Our extensive sample business plans library includes business plan templates and business plan examples for almost all business industries.
Make your plan in half the time & twice the impact with Upmetrics.

How to use Business Plan Examples to write your own?
Having real-life and industry-specific business plan examples by your side can be incredibly resourceful to help you write a business plan from scratch.
A well-planned structure helps you outline your plan, while content inspiration helps you set the tone for your business document.
Let’s dive deep and understand how to use these examples effectively to write your business plan.
1. Use examples as a guide
2. understanding the structure.
Traditional business plans generally follow a similar structure.
It starts with an executive summary followed by a company description, market analysis, product and services, sales and marketing strategies, operational plan, management team, financial plan, and appendix.
Using an example business plan is the best way to understand the structure and outline your plan.
3. Gaining Inspiration
Reading industry-specific business plan examples can help you gain inspiration for your plan. You can gain insights on presenting your business idea, vision, mission, and values and persuade investors to invest in your idea.
4. Learning Industry-Specific Language
There’s no universal template for business planning that fits all. An industry-specific template can help you learn and understand the business language for your industry and the best way to communicate your message to your investors.
5. Identifying Key Elements
Reading business plan examples of similar businesses can help you identify the key elements and information to include in your plan. You can keep note of these and ensure everything necessary for investors to consider is present in your final draft.
6. Crafting Financial Projections
A financial plan is a critical component of your business plan, and a good business plan example can help you better understand how they project their financials which can be incredibly helpful while forecasting yours.
7. Refining Your Executive Summary
As mentioned earlier, your executive summary is a key factor influencing potential investors and lenders to invest or lend you money. Analyzing free business plan templates can help you optimize your executive summary to make it more brief, persuasive, and attention-grabbing.
8. Realizing What Works and What Doesn’t
Analyzing industry-specific and real-life examples can help you determine what works best and what doesn’t within your industry. Understanding these factors can help you avoid many significant pitfalls.
While business plan examples can be incredibly helpful in writing a plan from scratch, ensure your plan is customized for your business and sends out a unique message. Your business plan must reflect its unique idea, vision, and target market.
Using your Business Plan as a Management Tool
It’s essential to have a business plan, but it’s also crucial to keep it up to date as your business progresses. A business plan is not merely a document that you write once and forget after you get started. It’s a business road map and vision that you should develop as your business progresses and evolves. It’s also important to update your business plan regularly as your business situation and position change.
How Business Plan Software can help you?
We have created Upmetrics — business plan software to simplify the process of business planning.
Our financial forecasting module will create all the essential reports automatically. You just need to enter numbers and the application will do all the math to generate your financial reports. Later you can embed those reports into your business plan.
After completing your business plan, you can download your business plan in PDF or DOC file using Upmetrics. Also, you can share it online with investors or with other important people just by a quick link.
Ready to take the next step?
Now that you have a business idea and you know how to write a business plan, it’s time to go for it . Our business plan software will take you through each step outlined above in more detail so there are no surprises on your journey.

Simplifying Business Planning through AI-Powered Insights.

Founder, CEO & Lead Scientist at Nanolyse Technologies
After trying Upmetrics, I wish to highly recommend this app to anyone who needs to write a business plan flexibly and to a high standard.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is sample business plan, how do i write a business plan.
In business plan writing you will need to write the following sections into your business plan. These sections include an Executive Summary, Company Overview, Problem Analysis, The Solution, Market Analysis, Customer Analysis, Competitive Analysis, SWOT Analysis, Marketing Plan, Operations Plan, and Financial Plan.
How long should my business plan be?
The length of your business plan depends on the type of plan you choose. There are one-page business plans that offer easy and practical planning. Then you have traditional business plans that usually vary from 20 to 50 pages. It’s worth noting that the quality of your business plan matters more than its length.
Should I hire someone to write my business plan for me?
Absolutely No, You as a business owner know all about your business idea, your business goals, target market and audience, and what you want to achieve by writing your plan. Don’t hire someone who doesn’t know what your readers will want, the reason is that, if you intend to raise funds, you are the best person that understands what investors will look out for in your business plan.
Consultants or business plan writers definitely can write a business plan but not better than you.
Looking for a faster way to finish your business plan?
No Risk – Cancel at Any Time – 15 Day Money Back Guarantee
BUSINESS STRATEGIES
12 business ideas for students to start at college
- Nirit Braun
- Dec 10, 2023
- 10 min read

A student business idea is an entrepreneurial endeavor initiated by a college student. College students may start businesses for various reasons and these ventures can range from small side hustles to full-fledged startups.
Learn more: How to choose a business idea
Why might students need to start a business?
There are many reasons why college students might choose to start a business . Some of the main ones include:
College students often face financial challenges, including high tuition fees, living expenses and student loan repayments. Starting a business can provide an additional income source and financial stability. Read more about how to make money as a student or how to make money as a teenager .
Entrepreneurship allows students to gain real-world job experience and build their resumes or portfolios. This practical experience and gained expertise can be valuable when seeking employment after graduation.
Running a business can offer flexibility in terms of work hours, which can be beneficial for students with irregular class schedules or other academic commitments.
Students may have unique talents, skills, or interests they want to pursue as a business. Entrepreneurship allows them to turn their passions and college studies into profitable ventures.
12 best business ideas for students to start while at college
Students at college can explore a range of business opportunities that fit into their busy schedules. Ideas like freelancing, dropshipping, tutoring, blogging and others offer them the chance to earn and learn simultaneously. Service businesses like pet care, landscaping and cleaning are great for part-time ventures that can accommodate academic commitments.
Freelancing
Dropshipping
Craft business
Start and monetize a blog
Marketing services
Pet sitting and care
Landscaping
Bookkeeping
Delivery services
01. Freelancing
Freelancing involves offering your skills and services to clients or businesses on a project-by-project basis. Freelancers work independently, often remotely and may provide services such as writing, graphic design, web development, social media management or digital marketing.
Learn more: Freelance ideas , how to make money as a graphic designer
Why is freelancing a good business idea for students?
Freelancing offers students the flexibility to work around their class schedules and other commitments, much like other side business ideas do. Students can leverage their skills and expertise to earn income in areas they are passionate about. Freelancing allows students to gain real-world experience, build a portfolio and network with potential clients. All of which can help them in their professional careers post-graduation.
What are some good freelancing businesses for students to start?
Content writing : this could be writing blog posts or freelance copywriting services for businesses.
Graphic design : creating logos, infographics or marketing materials for clients.
Web creation and development : build websites for individuals or businesses. You can use a website builder like Wix to easily build websites for clients.
Social media management : manage and grow social media profiles for small businesses. This can include creating posts and content, tracking users and building engagement.
02. Dropshipping
Dropshipping is an eCommerce business model where students can set up online stores and sell products without holding inventory. When a customer places an order, the products are shipped directly from the supplier to the customer.
Learn more: eCommerce business ideas , Dropshipping business ideas
Why is dropshipping a good business idea for students?
Dropshipping requires minimal upfront investment, making it accessible to students on a tight budget.
Learn more: Low-cost business ideas , How to sell online
The e-Commerce industry is continuously growing and dropshipping allows students to tap into this market without the hassles of inventory management. In 2022 global retail m-commerce sales topped $431.4 billion and are expected to top $511.8 billion in 2023.
Learn more: How to start a dropshipping business
What are some good dropshipping businesses for students to start?
Online clothing store: sell clothing, accessories, or niche-specific fashion items. Learn more: How to start a clothing business .
Electronics and gadgets: offer a range of tech gadgets and accessories.
Home decor: sell decorative items, furniture or interior design products.
Health and wellness: focus on products like supplements, fitness equipment or eco-friendly products.
03. Reselling
Reselling involves buying products at a lower price and reselling them at a profit. This can be done through various channels, including online marketplaces, thrift stores, or even college flea markets.
Why is reselling a good business idea for students?
Reselling can be started with a small investment, which is suitable for students. It provides students with valuable experience in sales, marketing and negotiation all of which are important professional skills to learn. Students can engage in reselling part-time or during breaks so it doesn’t conflict with their studies.
Learn more: Best businesses to start with little money
What are some good reselling businesses for students to start?
Thrift store finds: sell vintage clothing , collectibles or antiques.
Online bookstore: sell used or rare books through online marketplaces.
Tech accessories: offer phone cases, chargers, or tech gadgets.
Home decor: resell furniture, artwork or other decorative items.
04. Craft business
Selling crafts online involves creating and selling handmade crafts and products. This can include jewelry , candles , artwork, hand-knit scarves or personalized gifts.
Why is crafting a good business idea for students?
Craft businesses allow students to express their creativity and turn their hobbies into income. Operating from a dorm room or small workspace minimizes overhead costs.
Learn more: Home-based business ideas
Handcrafted items have a unique, artisanal appeal that can attract regular customers. Learn how to sell crafts online .
Learn more: Unique business ideas
What are some good crafting business ideas for students to start?
Handmade jewelry: create custom jewelry pieces or unique designs.
Candle making : craft scented or decorative candles.
Art and illustrations : sell original artwork, prints, or digital designs.
Personalized gifts : offer custom-made gifts, such as mugs, T-shirts or home decor.
05. Tutoring
Tutoring involves providing educational support to students or learners in specific subjects or skills. This can be done in person or online and subjects can range from math and science to languages and test preparation.
Learn more: How to start a tutoring business
Why is tutoring a good business idea for students?
Students can leverage their knowledge in subjects they’re passionate about and in turn, share them with other students. Tutors can schedule sessions around their class schedule and availability which makes this a flexible business idea to start. It can also be a great business idea for students looking to enter teaching or lecturing as a professional post-graduation.
Learn more: Business ideas for teachers
What are some good tutoring businesses for students to start?
Academic tutoring: offer assistance in subjects like math, science, or history.
Language lessons : teach foreign languages or provide English as a Second Language (ESL) lessons.
Test prep: help students prepare for standardized tests like the SAT or GRE.
Music or art lessons: provide music instruction or art lessons to aspiring learners.
06. Start and monetize a blog
Blogging involves creating and regularly updating an online platform where you share information, opinions, or expertise on a specific topic or niche. Monetizing a blog means earning income from it through various methods like advertising, affiliate marketing, sponsored content or selling digital products.
Learn more: How to start a blog
Why is a blog a good business idea for students?
Blogging allows students to work on their own schedules, making it easy to balance with classes. All you need to blog is a computer and an internet connection, making it possible to do from anywhere. It's an opportunity to express ideas, passions and knowledge. These are all important skills for a college student. Over time, a well-monetized blog can generate passive income.
Learn more: Passive income ideas .
What are some good blog ideas for students to start?
Travel blog : share travel experiences, tips and affiliate links to booking platforms.
Fitness blog : Discuss fitness nutrition and promote related products.
Tech blog: write reviews and recommendations for tech products.
Finance blog : offer financial advice, budgeting tips and promote financial tools.
Get started with the Wix blog maker and make your own blog.
07. Marketing services
These services encompass a wide range of activities, such as social media marketing, content creation, SEO and advertising, to help businesses reach and engage their target audience.
Learn more: How to start a marketing business
Why is marketing a good business idea for students?
Students often possess digital marketing skills, either from their studies or from their own use of social media and can leverage them to help businesses improve theirg online presence. Marketing is essential for businesses and there's a consistent demand for marketing services that students can tap intoStudents can offer marketing services on a freelance basis, which provides flexibility around their studies and extracurricular commitments..
What are some good marketing businesses for students to start?
Social media management : help businesses grow and manage their social media profiles.
Content creation : provide blog posts, articles or video content for companies.
Email marketing: helping to create the assets and strategy for email marketing campaigns.
08. Pet sitting and care
Pet sitting and care services involve taking care of pets when their owners are away. This includes pet sitting, dog walking, feeding and providing companionship or even boarding.
Why is pet care a good business idea for students?
Students who love animals can earn income doing what they enjoy. Pet sitting can be done part-time, at the weekend, in the evenings or during breaks. Minimal investment is needed for pet sitting and dog walking which suits most students' budgets.
What are some good pet-related businesses for students to start?
Dog walking: offering daily dog-walking services for pet owners.
In-home pet sitting : care for pets at the owner's home while they're away.
Pet boarding: provide boarding services for pets in your home or a rented space.
Pet grooming: offer grooming and spa services for pets.
09. Landscaping
Landscaping services involve tasks like lawn maintenance and gardening. This can include mowing, weeding, planting and landscape design.
Why is gardening a good business idea for students?
Landscaping provides a physical workout, which can be appealing to students who want to keep fit as part of their business. Landscaping can be seasonal, allowing students to work during breaks and avoiding conflict with their studies. The startup costs for basic landscaping services are relatively low, some lawn care services can be done with the lawn owner's tools or equipment.
Learn more: Business ideas for teens , Recession-proof business ideas
What are some good landscaping-related businesses for students to start?
Lawn care: offer services like mowing, edging and lawn treatment.
Gardening and planting: assist homeowners with garden design and planting.
Tree care: prune, trim and care for trees on residential properties.
Landscape design: create landscape plans and implement them for clients.
10. Cleaning services
Cleaning services involve cleaning and maintaining residential or commercial spaces. This can include house cleaning, office cleaning and specialized cleaning services.
Why is cleaning a good business idea for students?
Cleaning businesses can start with basic cleaning supplies, keeping initial costs low for students. Cleaning can be scheduled around classes and other commitments, a flexibility that is ideal for college students as a part-time business idea .
What are some good cleaning businesses for students to start?
House cleaning: offer regular house cleaning services for homeowners.
Office cleaning: provide cleaning services for small businesses or offices.
Specialized cleaning: focus on niche cleaning services like carpet cleaning, window washing, or post-construction cleaning.
Janitorial services: offer cleaning and maintenance services to commercial properties.
11. Bookkeeping
A bookkeeping business involves maintaining financial records and ensuring the accuracy of financial transactions for businesses. This includes tasks like data entry, reconciling accounts and preparing financial reports.
Why is bookkeeping a good business idea for students?
Students with accounting or finance knowledge can offer bookkeeping services to businesses who need it, this can be done on a freelance basis, providing flexibility for students. It’s also a great way for students to learn how to manage a business themselves.
What are some good bookkeeping businesses for students to start?
Small business: assist small businesses with their financial record-keeping.
Virtual services : provide remote and online bookkeeping services to clients.
Tax preparation : expand services to include tax preparation and filing.
Financial consulting: offer financial advice and consultation in addition to bookkeeping. Make sure you understand the risks and liabilities involved in providing businesses with financial advice that they may then act on.
12. Delivery services
Delivery services involve transporting goods or packages from one location to another. This can include food delivery, courier services or package delivery.
Why are delivery services a good business idea for students?
Delivery services can be scheduled around class hours and student availability. Basic delivery services can be started with a vehicle or even a bicycle, meaning minimal startup costs.
What are some good delivery services for students to start?
Food delivery: partner with local restaurants for food delivery services.
Package delivery : delivering parcels for courier companies or retailers.
How to turn a student business idea into a successful business?
Choose a business idea that aligns with your skills, interests and market demand. For example, if you have a special talent for animation, then you can learn how to make money as an animator . Conduct market research to identify unmet needs or niches within your target industry. You can also consider choosing from recession-proof business ideas , to ensure no matter what you're able to maintain your business.
Create a detailed business plan outlining your business goals, target market, competition, financial projections and marketing strategy.
Explore funding options, such as personal savings, grants, loans or crowdfunding, to finance your business.
Effectively manage your time to balance coursework, business operations and personal life. Create a schedule that accommodates your class schedule and business needs.
Build a network of mentors, peers and potential clients. Networking can provide valuable guidance and opportunities for collaboration.
Establish a strong online presence through a business website , social media and e-Commerce platforms (you can do this by making an eCommerce website of your own) if applicable. Online visibility is essential for attracting customers and clients via an eCommerce model.
Prioritize the quality of your products or services and provide excellent customer service. Satisfied customers are more likely to return and refer your business.
Ensure your business complies with all relevant laws and regulations. This includes registering your business and applying for business licenses, permits, taxes and intellectual property considerations.
Develop effective marketing strategies to reach your target audience. Consider digital marketing, social media, content marketing and traditional advertising methods too.
Be prepared to adapt to changes and challenges in the business landscape. Flexibility and the ability to pivot when necessary are key to success.
Keep accurate financial records and budget your expenses wisely. Monitor your business's financial health regularly.
Seek feedback from customers to identify areas for improvement. Be open to making necessary changes and enhancements to your business.
Consider seeking mentorship from experienced entrepreneurs or professors who can provide guidance and support. They can provide invaluable advice, such as this from Anegl Gregorio, Founder of the Spice Suite , "The best advice that I give to people is always 'Start now, perfect later,'” she says. “I never got so tied up in the need to perfect it all. I'm here to say, 'Just start it. You can fix it along the way. If you build your tribe and your community, they will go along the journey with you.’"
Explore more business ideas
Craft business ideas
Beauty business ideas
Reselling business ideas
DIY business ideas
Clothing business ideas
Small-town business ideas
Business ideas for couples
Rental business ideas
Family business ideas
B2B business ideas
Scalable business ideas
Related Posts
11 small business website examples to inspire you in 2024
Small business name ideas to consider
Best website builders for small businesses in 2024
Was this article helpful?
- Start free trial
Start selling with Shopify today
Start your free trial with Shopify today—then use these resources to guide you through every step of the process.

7 Business Plan Examples to Inspire Your Own (2024)
Need support creating your business plan? Check out these business plan examples for inspiration.

Any aspiring entrepreneur researching how to start a business will likely be advised to write a business plan. But few resources provide business plan examples to really guide you through writing one of your own.
Here are some real-world and illustrative business plan examples to help you craft your business plan .
7 business plan examples: section by section
The business plan examples in this article follow this template:
- Executive summary. An introductory overview of your business.
- Company description. A more in-depth and detailed description of your business and why it exists.
- Market analysis. Research-based information about the industry and your target market.
- Products and services. What you plan to offer in exchange for money.
- Marketing plan. The promotional strategy to introduce your business to the world and drive sales.
- Logistics and operations plan. Everything that happens in the background to make your business function properly.
- Financial plan. A breakdown of your numbers to show what you need to get started as well as to prove viability of profitability.
- Executive summary
Your executive summary is a page that gives a high-level overview of the rest of your business plan. It’s easiest to save this section for last.
In this free business plan template , the executive summary is four paragraphs and takes a little over half a page:

- Company description
You might repurpose your company description elsewhere, like on your About page, social media profile pages, or other properties that require a boilerplate description of your small business.
Soap brand ORRIS has a blurb on its About page that could easily be repurposed for the company description section of its business plan.

You can also go more in-depth with your company overview and include the following sections, like in the example for Paw Print Post:
- Business structure. This section outlines how you registered your business —as an LLC , sole proprietorship, corporation, or other business type . “Paw Print Post will operate as a sole proprietorship run by the owner, Jane Matthews.”
- Nature of the business. “Paw Print Post sells unique, one-of-a-kind digitally printed cards that are customized with a pet’s unique paw prints.”
- Industry. “Paw Print Post operates primarily in the pet industry and sells goods that could also be categorized as part of the greeting card industry.”
- Background information. “Jane Matthews, the founder of Paw Print Post, has a long history in the pet industry and working with animals, and was recently trained as a graphic designer. She’s combining those two loves to capture a niche in the market: unique greeting cards customized with a pet’s paw prints, without needing to resort to the traditional (and messy) options of casting your pet’s prints in plaster or using pet-safe ink to have them stamp their ‘signature.’”
- Business objectives. “Jane will have Paw Print Post ready to launch at the Big Important Pet Expo in Toronto to get the word out among industry players and consumers alike. After two years in business, Jane aims to drive $150,000 in annual revenue from the sale of Paw Print Post’s signature greeting cards and have expanded into two new product categories.”
- Team. “Jane Matthews is the sole full-time employee of Paw Print Post but hires contractors as needed to support her workflow and fill gaps in her skill set. Notably, Paw Print Post has a standing contract for five hours a week of virtual assistant support with Virtual Assistants Pro.”
Your mission statement may also make an appearance here. Passionfruit shares its mission statement on its company website, and it would also work well in its example business plan.
- Market analysis
The market analysis consists of research about supply and demand, your target demographics, industry trends, and the competitive landscape. You might run a SWOT analysis and include that in your business plan.
Here’s an example SWOT analysis for an online tailored-shirt business:
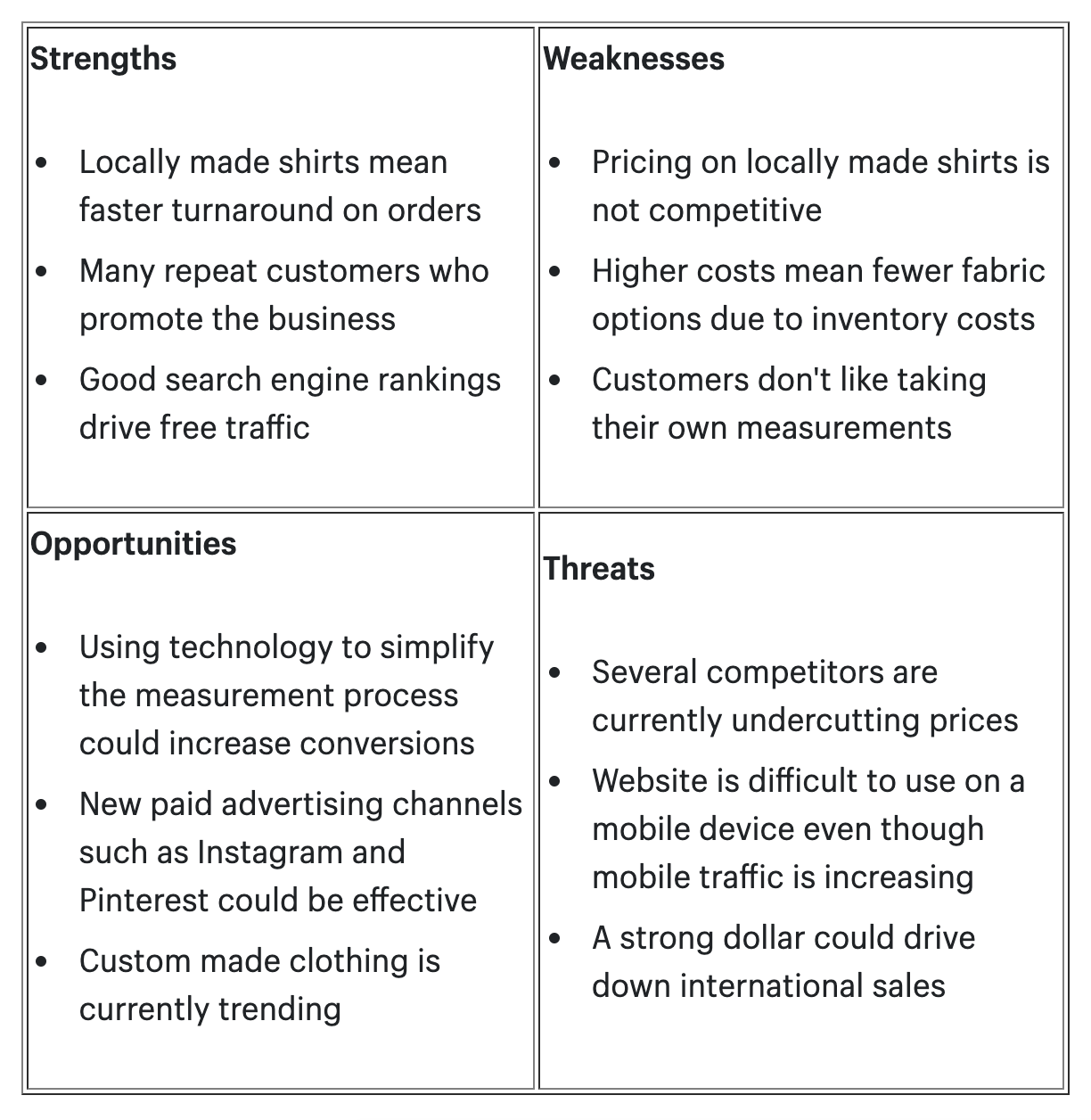
You’ll also want to do a competitive analysis as part of the market research component of your business plan. This will tell you who you’re up against and give you ideas on how to differentiate your brand. A broad competitive analysis might include:
- Target customers
- Unique value add or what sets their products apart
- Sales pitch
- Price points for products
- Shipping policy
- Products and services
This section of your business plan describes your offerings—which products and services do you sell to your customers? Here’s an example for Paw Print Post:

- Marketing plan
It’s always a good idea to develop a marketing plan before you launch your business. Your marketing plan shows how you’ll get the word out about your business, and it’s an essential component of your business plan as well.
The Paw Print Post focuses on four Ps: price, product, promotion, and place. However, you can take a different approach with your marketing plan. Maybe you can pull from your existing marketing strategy , or maybe you break it down by the different marketing channels. Whatever approach you take, your marketing plan should describe how you intend to promote your business and offerings to potential customers.
- Logistics and operations plan
The Paw Print Post example considered suppliers, production, facilities, equipment, shipping and fulfillment, and inventory.
Financial plan
The financial plan provides a breakdown of sales, revenue, profit, expenses, and other relevant financial metrics related to funding and profiting from your business.
Ecommerce brand Nature’s Candy’s financial plan breaks down predicted revenue, expenses, and net profit in graphs.
It then dives deeper into the financials to include:
- Funding needs
- Projected profit-and-loss statement
- Projected balance sheet
- Projected cash-flow statement
You can use this financial plan spreadsheet to build your own financial statements, including income statement, balance sheet, and cash-flow statement.
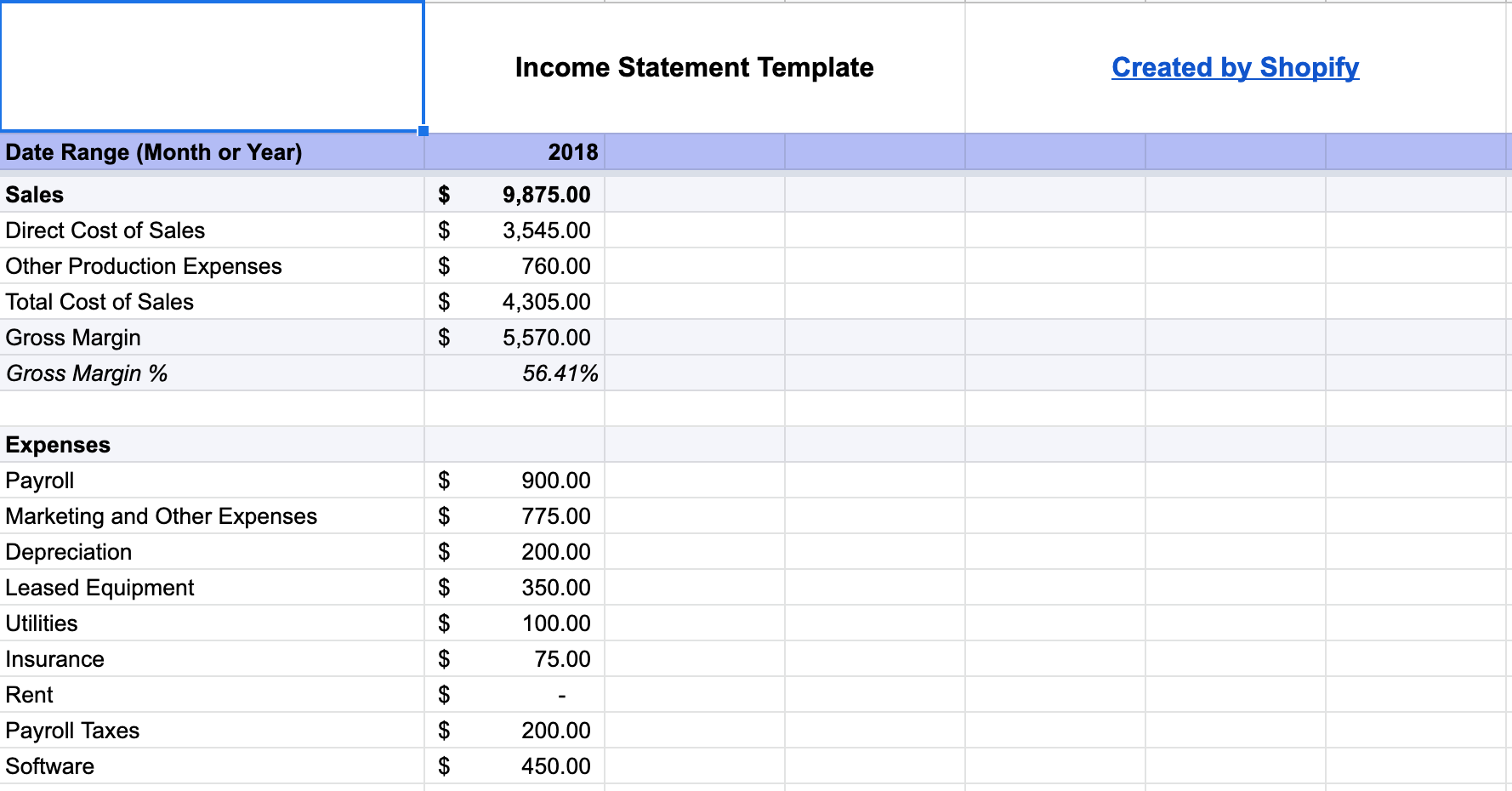
Types of business plans, and what to include for each
A one-page business plan is meant to be high level and easy to understand at a glance. You’ll want to include all of the sections, but make sure they’re truncated and summarized:
- Executive summary: truncated
- Market analysis: summarized
- Products and services: summarized
- Marketing plan: summarized
- Logistics and operations plan: summarized
- Financials: summarized
A startup business plan is for a new business. Typically, these plans are developed and shared to secure outside funding . As such, there’s a bigger focus on the financials, as well as on other sections that determine viability of your business idea—market research, for example.
- Market analysis: in-depth
- Financials: in-depth
Your internal business plan is meant to keep your team on the same page and aligned toward the same goal.
A strategic, or growth, business plan is a bigger picture, more-long-term look at your business. As such, the forecasts tend to look further into the future, and growth and revenue goals may be higher. Essentially, you want to use all the sections you would in a normal business plan and build upon each.
- Market analysis: comprehensive outlook
- Products and services: for launch and expansion
- Marketing plan: comprehensive outlook
- Logistics and operations plan: comprehensive outlook
- Financials: comprehensive outlook
Feasibility
Your feasibility business plan is sort of a pre-business plan—many refer to it as simply a feasibility study. This plan essentially lays the groundwork and validates that it’s worth the effort to make a full business plan for your idea. As such, it’s mostly centered around research.
Set yourself up for success as a business owner
Building a good business plan serves as a roadmap you can use for your ecommerce business at launch and as you reach each of your business goals. Business plans create accountability for entrepreneurs and synergy among teams, regardless of your business model .
Kickstart your ecommerce business and set yourself up for success with an intentional business planning process—and with the sample business plans above to guide your own path.
- How to Start a Dropshipping Business- A Complete Playbook for 2024
- The 13 Best Dropshipping Suppliers in 2024
- How To Source Products To Sell Online
- 25+ Ideas for Online Businesses To Start Now (2024)
- The Ultimate Guide To Dropshipping (2024)
- How to Build a Business Website for Beginners
- 7 Inspiring Marketing Plan Examples (and How You Can Implement Them)
- 10 Ways to Write Product Descriptions That Persuade (2024)
- Get Guidance- 6 Business Plan Software to Help Write Your Future
- Business Valuation- Learn the Value of Your Business
Business plan examples FAQ
How do i write a simple business plan, what is the best format to write a business plan, what are the 4 key elements of a business plan.
- Executive summary: A concise overview of the company's mission, goals, target audience, and financial objectives.
- Business description: A description of the company's purpose, operations, products and services, target markets, and competitive landscape.
- Market analysis: An analysis of the industry, market trends, potential customers, and competitors.
- Financial plan: A detailed description of the company's financial forecasts and strategies.
What are the 3 main points of a business plan?
- Concept: Your concept should explain the purpose of your business and provide an overall summary of what you intend to accomplish.
- Contents: Your content should include details about the products and services you provide, your target market, and your competition.
- Cashflow: Your cash flow section should include information about your expected cash inflows and outflows, such as capital investments, operating costs, and revenue projections.
Keep up with the latest from Shopify
Get free ecommerce tips, inspiration, and resources delivered directly to your inbox.
By entering your email, you agree to receive marketing emails from Shopify.
popular posts

The point of sale for every sale.

Subscribe to our blog and get free ecommerce tips, inspiration, and resources delivered directly to your inbox.
Unsubscribe anytime. By entering your email, you agree to receive marketing emails from Shopify.
Latest from Shopify
Jun 19, 2024
Jun 18, 2024
Learn on the go. Try Shopify for free, and explore all the tools you need to start, run, and grow your business.
Try Shopify for free, no credit card required.
24 of My Favorite Sample Business Plans & Examples For Your Inspiration
Published: February 06, 2024
I believe that reading sample business plans is essential when writing your own.

hbspt.cta._relativeUrls=true;hbspt.cta.load(53, 'e9d2eacb-6b01-423a-bf7a-19d42ba77eaa', {"useNewLoader":"true","region":"na1"});
As you explore business plan examples from real companies and brands, it’s easier for you to learn how to write a good one.
But what does a good business plan look like? And how do you write one that’s both viable and convincing. I’ll walk you through the ideal business plan format along with some examples to help you get started.
Table of Contents
Business Plan Format
Business plan types, sample business plan templates, top business plan examples.
Ask any successful sports coach how they win so many games, and they’ll tell you they have a unique plan for every single game. To me, the same logic applies to business.
If you want to build a thriving company that can pull ahead of the competition, you need to prepare for battle before breaking into a market.
Business plans guide you along the rocky journey of growing a company. And if your business plan is compelling enough, it can also convince investors to give you funding.
With so much at stake, I’m sure you’re wondering where to begin.
.webp)
Free Business Plan Template
The essential document for starting a business -- custom built for your needs.
- Outline your idea.
- Pitch to investors.
- Secure funding.
- Get to work!
Download Free
All fields are required.
You're all set!
Click this link to access this resource at any time.
Fill out the form to get your free template.
First, you’ll want to nail down your formatting. Most business plans include the following sections.
1. Executive Summary
I’d say the executive summary is the most important section of the entire business plan.
Why? Essentially, it's the overview or introduction, written in a way to grab readers' attention and guide them through the rest of the business plan. This is important, because a business plan can be dozens or hundreds of pages long.
There are two main elements I’d recommend including in your executive summary:
Company Description
This is the perfect space to highlight your company’s mission statement and goals, a brief overview of your history and leadership, and your top accomplishments as a business.
Tell potential investors who you are and why what you do matters. Naturally, they’re going to want to know who they’re getting into business with up front, and this is a great opportunity to showcase your impact.
Need some extra help firming up those business goals? Check out HubSpot Academy’s free course to help you set goals that matter — I’d highly recommend it
Products and Services
To piggyback off of the company description, be sure to incorporate an overview of your offerings. This doesn’t have to be extensive — just another chance to introduce your industry and overall purpose as a business.
In addition to the items above, I recommend including some information about your financial projections and competitive advantage here too.:
Keep in mind you'll cover many of these topics in more detail later on in the business plan. So, keep the executive summary clear and brief, and only include the most important takeaways.
Executive Summary Business Plan Examples
This example was created with HubSpot’s business plan template:

This executive summary is so good to me because it tells potential investors a short story while still covering all of the most important details.
.webp?width=500&height=418&name=executive-summary-business-plans-examples%20(1).webp)
Image Source

Tips for Writing Your Executive Summary
- Start with a strong introduction of your company, showcase your mission and impact, and outline the products and services you provide.
- Clearly define a problem, and explain how your product solves that problem, and show why the market needs your business.
- Be sure to highlight your value proposition, market opportunity, and growth potential.
- Keep it concise and support ideas with data.
- Customize your summary to your audience. For example, emphasize finances and return on investment for venture capitalists.
Check out our tips for writing an effective executive summary for more guidance.
2. Market Opportunity
This is where you'll detail the opportunity in the market.
The main question I’d ask myself here is this: Where is the gap in the current industry, and how will my product fill that gap?
More specifically, here’s what I’d include in this section:
- The size of the market
- Current or potential market share
- Trends in the industry and consumer behavior
- Where the gap is
- What caused the gap
- How you intend to fill it
To get a thorough understanding of the market opportunity, you'll want to conduct a TAM, SAM, and SOM analysis and perform market research on your industry.
You may also benefit from creating a SWOT analysis to get some of the insights for this section.
Market Opportunity Business Plan Example
I like this example because it uses critical data to underline the size of the potential market and what part of that market this service hopes to capture.

Tips for Writing Your Market Opportunity Section
- Focus on demand and potential for growth.
- Use market research, surveys, and industry trend data to support your market forecast and projections.
- Add a review of regulation shifts, tech advances, and consumer behavior changes.
- Refer to reliable sources.
- Showcase how your business can make the most of this opportunity.
3. Competitive Landscape
Since we’re already speaking of market share, you'll also need to create a section that shares details on who the top competitors are.
After all, your customers likely have more than one brand to choose from, and you'll want to understand exactly why they might choose one over another.
My favorite part of performing a competitive analysis is that it can help you uncover:
- Industry trends that other brands may not be utilizing
- Strengths in your competition that may be obstacles to handle
- Weaknesses in your competition that may help you develop selling points
- The unique proposition you bring to the market that may resonate with customers
Competitive Landscape Business Plan Example
I like how the competitive landscape section of this business plan below shows a clear outline of who the top competitors are.
.webp?width=500&height=405&name=competitive-landscape-business-plans-examples%20(1).webp)
It also highlights specific industry knowledge and the importance of location, which shows useful experience in this specific industry.
This can help build trust in your ability to execute your business plan.
Tips for Writing Your Competitive Landscape
- Complete in-depth research, then emphasize your most important findings.
- Compare your unique selling proposition (USP) to your direct and indirect competitors.
- Show a clear and realistic plan for product and brand differentiation.
- Look for specific advantages and barriers in the competitive landscape. Then, highlight how that information could impact your business.
- Outline growth opportunities from a competitive perspective.
- Add customer feedback and insights to support your competitive analysis.
4. Target Audience
Use this section to describe who your customer segments are in detail. What is the demographic and psychographic information of your audience?
If your immediate answer is "everyone," you'll need to dig deeper. Here are some questions I’d ask myself here:
- What demographics will most likely need/buy your product or service?
- What are the psychographics of this audience? (Desires, triggering events, etc.)
- Why are your offerings valuable to them?
I’d also recommend building a buyer persona to get in the mindset of your ideal customers and be clear on why you're targeting them.
Target Audience Business Plan Example
I like the example below because it uses in-depth research to draw conclusions about audience priorities. It also analyzes how to create the right content for this audience.
Tips for Writing Your Target Audience Section
- Include details on the size and growth potential of your target audience.
- Figure out and refine the pain points for your target audience , then show why your product is a useful solution.
- Describe your targeted customer acquisition strategy in detail.
- Share anticipated challenges your business may face in acquiring customers and how you plan to address them.
- Add case studies, testimonials, and other data to support your target audience ideas.
- Remember to consider niche audiences and segments of your target audience in your business plan.
5. Marketing Strategy
Here, you'll discuss how you'll acquire new customers with your marketing strategy. I’d suggest including information:
- Your brand positioning vision and how you'll cultivate it
- The goal targets you aim to achieve
- The metrics you'll use to measure success
- The channels and distribution tactics you'll use
I think it’s helpful to have a marketing plan built out in advance to make this part of your business plan easier.
Marketing Strategy Business Plan Example
This business plan example includes the marketing strategy for the town of Gawler.
In my opinion, it really works because it offers a comprehensive picture of how they plan to use digital marketing to promote the community.
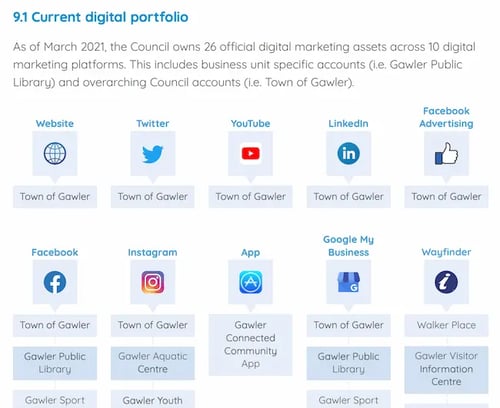
Tips for Writing Your Marketing Strategy
- Include a section about how you believe your brand vision will appeal to customers.
- Add the budget and resources you'll need to put your plan in place.
- Outline strategies for specific marketing segments.
- Connect strategies to earlier sections like target audience and competitive analysis.
- Review how your marketing strategy will scale with the growth of your business.
- Cover a range of channels and tactics to highlight your ability to adapt your plan in the face of change.
6. Key Features and Benefits
At some point in your business plan, you'll need to review the key features and benefits of your products and/or services.
Laying these out can give readers an idea of how you're positioning yourself in the market and the messaging you're likely to use. It can even help them gain better insight into your business model.
Key Features and Benefits Business Plan Example
In my opinion, the example below does a great job outlining products and services for this business, along with why these qualities will attract the audience.

Tips for Writing Your Key Features and Benefits
- Emphasize why and how your product or service offers value to customers.
- Use metrics and testimonials to support the ideas in this section.
- Talk about how your products and services have the potential to scale.
- Think about including a product roadmap.
- Focus on customer needs, and how the features and benefits you are sharing meet those needs.
- Offer proof of concept for your ideas, like case studies or pilot program feedback.
- Proofread this section carefully, and remove any jargon or complex language.
7. Pricing and Revenue
This is where you'll discuss your cost structure and various revenue streams. Your pricing strategy must be solid enough to turn a profit while staying competitive in the industry.
For this reason, here’s what I’d might outline in this section:
- The specific pricing breakdowns per product or service
- Why your pricing is higher or lower than your competition's
- (If higher) Why customers would be willing to pay more
- (If lower) How you're able to offer your products or services at a lower cost
- When you expect to break even, what margins do you expect, etc?
Pricing and Revenue Business Plan Example
I like how this business plan example begins with an overview of the business revenue model, then shows proposed pricing for key products.

Tips for Writing Your Pricing and Revenue Section
- Get specific about your pricing strategy. Specifically, how you connect that strategy to customer needs and product value.
- If you are asking a premium price, share unique features or innovations that justify that price point.
- Show how you plan to communicate pricing to customers.
- Create an overview of every revenue stream for your business and how each stream adds to your business model as a whole.
- Share plans to develop new revenue streams in the future.
- Show how and whether pricing will vary by customer segment and how pricing aligns with marketing strategies.
- Restate your value proposition and explain how it aligns with your revenue model.
8. Financials
To me, this section is particularly informative for investors and leadership teams to figure out funding strategies, investment opportunities, and more.
According to Forbes , you'll want to include three main things:
- Profit/Loss Statement - This answers the question of whether your business is currently profitable.
- Cash Flow Statement - This details exactly how much cash is incoming and outgoing to give insight into how much cash a business has on hand.
- Balance Sheet - This outlines assets, liabilities, and equity, which gives insight into how much a business is worth.
While some business plans might include more or less information, these are the key details I’d include in this section.
Financials Business Plan Example
This balance sheet is a great example of level of detail you’ll need to include in the financials section of your business plan.
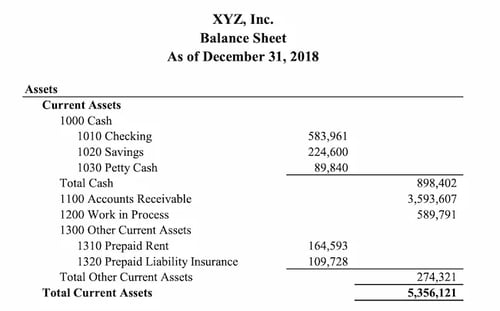
Tips for Writing Your Financials Section
- Growth potential is important in this section too. Using your data, create a forecast of financial performance in the next three to five years.
- Include any data that supports your projections to assure investors of the credibility of your proposal.
- Add a break-even analysis to show that your business plan is financially practical. This information can also help you pivot quickly as your business grows.
- Consider adding a section that reviews potential risks and how sensitive your plan is to changes in the market.
- Triple-check all financial information in your plan for accuracy.
- Show how any proposed funding needs align with your plans for growth.
As you create your business plan, keep in mind that each of these sections will be formatted differently. Some may be in paragraph format, while others could be charts or graphs.
The formats above apply to most types of business plans. That said, the format and structure of your plan will vary by your goals for that plan.
So, I’ve added a quick review of different business plan types. For a more detailed overview, check out this post .
1. Startups
Startup business plans are for proposing new business ideas.
If you’re planning to start a small business, preparing a business plan is crucial. The plan should include all the major factors of your business.
You can check out this guide for more detailed business plan inspiration .
2. Feasibility Studies
Feasibility business plans focus on that business's product or service. Feasibility plans are sometimes added to startup business plans. They can also be a new business plan for an already thriving organization.
3. Internal Use
You can use internal business plans to share goals, strategies, or performance updates with stakeholders. In my opinion, internal business plans are useful for alignment and building support for ambitious goals.
4. Strategic Initiatives
Another business plan that's often for sharing internally is a strategic business plan. This plan covers long-term business objectives that might not have been included in the startup business plan.
5. Business Acquisition or Repositioning
When a business is moving forward with an acquisition or repositioning, it may need extra structure and support. These types of business plans expand on a company's acquisition or repositioning strategy.
Growth sometimes just happens as a business continues operations. But more often, a business needs to create a structure with specific targets to meet set goals for expansion. This business plan type can help a business focus on short-term growth goals and align resources with those goals.
Now that you know what's included and how to format a business plan, let's review some of my favorite templates.
1. HubSpot's One-Page Business Plan
Download a free, editable one-page business plan template..
The business plan linked above was created here at HubSpot and is perfect for businesses of any size — no matter how many strategies we still have to develop.
Fields such as Company Description, Required Funding, and Implementation Timeline give this one-page business plan a framework for how to build your brand and what tasks to keep track of as you grow.
Then, as the business matures, you can expand on your original business plan with a new iteration of the above document.
Why I Like It
This one-page business plan is a fantastic choice for the new business owner who doesn’t have the time or resources to draft a full-blown business plan. It includes all the essential sections in an accessible, bullet-point-friendly format. That way, you can get the broad strokes down before honing in on the details.
2. HubSpot's Downloadable Business Plan Template

We also created a business plan template for entrepreneurs.
The template is designed as a guide and checklist for starting your own business. You’ll learn what to include in each section of your business plan and how to do it.
There’s also a list for you to check off when you finish each section of your business plan.
Strong game plans help coaches win games and help businesses rocket to the top of their industries. So if you dedicate the time and effort required to write a workable and convincing business plan, you’ll boost your chances of success and even dominance in your market.
This business plan kit is essential for the budding entrepreneur who needs a more extensive document to share with investors and other stakeholders.
It not only includes sections for your executive summary, product line, market analysis, marketing plan, and sales plan, but it also offers hands-on guidance for filling out those sections.
3. LiveFlow’s Financial Planning Template with built-in automation
This free template from LiveFlow aims to make it easy for businesses to create a financial plan and track their progress on a monthly basis.
The P&L Budget versus Actual format allows users to track their revenue, cost of sales, operating expenses, operating profit margin, net profit, and more.
The summary dashboard aggregates all of the data put into the financial plan sheet and will automatically update when changes are made.
Instead of wasting hours manually importing your data to your spreadsheet, LiveFlow can also help you to automatically connect your accounting and banking data directly to your spreadsheet, so your numbers are always up-to-date.
With the dashboard, you can view your runway, cash balance, burn rate, gross margins, and other metrics. Having a simple way to track everything in one place will make it easier to complete the financials section of your business plan.
This is a fantastic template to track performance and alignment internally and to create a dependable process for documenting financial information across the business. It’s highly versatile and beginner-friendly.
It’s especially useful if you don’t have an accountant on the team. (I always recommend you do, but for new businesses, having one might not be possible.)
4. ThoughtCo’s Sample Business Plan

One of the more financially oriented sample business plans in this list, BPlan’s free business plan template dedicates many of its pages to your business’s financial plan and financial statements.
After filling this business plan out, your company will truly understand its financial health and the steps you need to take to maintain or improve it.
I absolutely love this business plan template because of its ease-of-use and hands-on instructions (in addition to its finance-centric components). If you feel overwhelmed by the thought of writing an entire business plan, consider using this template to help you with the process.
6. Harvard Business Review’s "How to Write a Winning Business Plan"
Most sample business plans teach you what to include in your business plan, but this Harvard Business Review article will take your business plan to the next level — it teaches you the why and how behind writing a business plan.
With the guidance of Stanley Rich and Richard Gumpert, co-authors of " Business Plans That Win: Lessons From the MIT Enterprise Forum ", you'll learn how to write a convincing business plan that emphasizes the market demand for your product or service.
You’ll also learn the financial benefits investors can reap from putting money into your venture rather than trying to sell them on how great your product or service is.
This business plan guide focuses less on the individual parts of a business plan, and more on the overarching goal of writing one. For that reason, it’s one of my favorites to supplement any template you choose to use. Harvard Business Review’s guide is instrumental for both new and seasoned business owners.
7. HubSpot’s Complete Guide to Starting a Business
If you’re an entrepreneur, you know writing a business plan is one of the most challenging first steps to starting a business.
Fortunately, with HubSpot's comprehensive guide to starting a business, you'll learn how to map out all the details by understanding what to include in your business plan and why it’s important to include them. The guide also fleshes out an entire sample business plan for you.
If you need further guidance on starting a business, HubSpot's guide can teach you how to make your business legal, choose and register your business name, and fund your business. It will also give small business tax information and includes marketing, sales, and service tips.
This comprehensive guide will walk you through the process of starting a business, in addition to writing your business plan, with a high level of exactitude and detail. So if you’re in the midst of starting your business, this is an excellent guide for you.
It also offers other resources you might need, such as market analysis templates.
8. Panda Doc’s Free Business Plan Template

PandaDoc’s free business plan template is one of the more detailed and fleshed-out sample business plans on this list. It describes what you should include in each section, so you don't have to come up with everything from scratch.
Once you fill it out, you’ll fully understand your business’ nitty-gritty details and how all of its moving parts should work together to contribute to its success.
This template has two things I love: comprehensiveness and in-depth instructions. Plus, it’s synced with PandaDoc’s e-signature software so that you and other stakeholders can sign it with ease. For that reason, I especially love it for those starting a business with a partner or with a board of directors.
9. Small Business Administration Free Business Plan Template

The Small Business Administration (SBA) offers several free business plan templates that can be used to inspire your own plan.
Before you get started, you can decide what type of business plan you need — a traditional or lean start-up plan.
Then, you can review the format for both of those plans and view examples of what they might look like.
We love both of the SBA’s templates because of their versatility. You can choose between two options and use the existing content in the templates to flesh out your own plan. Plus, if needed, you can get a free business counselor to help you along the way.
I’ve compiled some completed business plan samples to help you get an idea of how to customize a plan for your business.
I chose different types of business plan ideas to expand your imagination. Some are extensive, while others are fairly simple.
Let’s take a look.
1. LiveFlow
One of the major business expenses is marketing. How you handle your marketing reflects your company’s revenue.
I included this business plan to show you how you can ensure your marketing team is aligned with your overall business plan to get results. The plan also shows you how to track even the smallest metrics of your campaigns, like ROI and payback periods instead of just focusing on big metrics like gross and revenue.
Fintech startup, LiveFlow, allows users to sync real-time data from its accounting services, payment platforms, and banks into custom reports. This eliminates the task of pulling reports together manually, saving teams time and helping automate workflows.
"Using this framework over a traditional marketing plan will help you set a profitable marketing strategy taking things like CAC, LTV, Payback period, and P&L into consideration," explains LiveFlow co-founder, Lasse Kalkar .
When it came to including marketing strategy in its business plan, LiveFlow created a separate marketing profit and loss statement (P&L) to track how well the company was doing with its marketing initiatives.
This is a great approach, allowing businesses to focus on where their marketing dollars are making the most impact. Having this information handy will enable you to build out your business plan’s marketing section with confidence. LiveFlow has shared the template here . You can test it for yourself.
2. Lula Body

Sometimes all you need is a solid mission statement and core values to guide you on how to go about everything. You do this by creating a business plan revolving around how to fulfill your statement best.
For example, Patagonia is an eco-friendly company, so their plan discusses how to make the best environmentally friendly products without causing harm.
A good mission statement should not only resonate with consumers but should also serve as a core value compass for employees as well.
Patagonia has one of the most compelling mission statements I’ve seen:
"Together, let’s prioritise purpose over profit and protect this wondrous planet, our only home."
It reels you in from the start, and the environmentally friendly theme continues throughout the rest of the statement.
This mission goes on to explain that they are out to "Build the best product, cause no unnecessary harm, and use business to protect nature."
Their mission statement is compelling and detailed, with each section outlining how they will accomplish their goal.
4. Vesta Home Automation

This executive summary for a smart home device startup is part of a business plan created by students at Mount Royal University .
While it lacks some of the sleek visuals of the templates above, its executive summary does a great job of demonstrating how invested they are in the business.
Right away, they mention they’ve invested $200,000 into the company already, which shows investors they have skin in the game and aren’t just looking for someone else to foot the bill.
This is the kind of business plan you need when applying for business funds. It clearly illustrates the expected future of the company and how the business has been coming along over the years.
5. NALB Creative Center
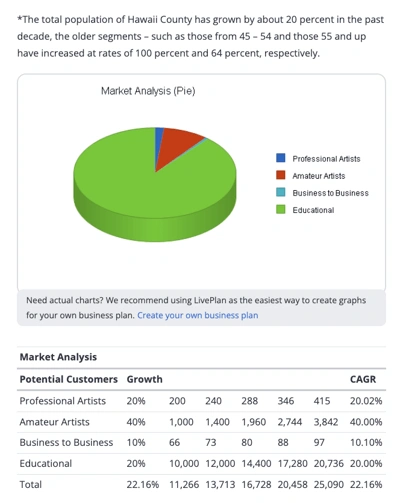
This fictional business plan for an art supply store includes everything one might need in a business plan: an executive summary, a company summary, a list of services, a market analysis summary, and more.
One of its most notable sections is its market analysis summary, which includes an overview of the population growth in the business’ target geographical area, as well as a breakdown of the types of potential customers they expect to welcome at the store.
This sort of granular insight is essential for understanding and communicating your business’s growth potential. Plus, it lays a strong foundation for creating relevant and useful buyer personas .
It’s essential to keep this information up-to-date as your market and target buyer changes. For that reason, you should carry out market research as often as possible to ensure that you’re targeting the correct audience and sharing accurate information with your investors.
Due to its comprehensiveness, it’s an excellent example to follow if you’re opening a brick-and-mortar store and need to get external funding to start your business .
6. Curriculum Companion Suites (CSS)
If you’re looking for a SaaS business plan example, look no further than this business plan for a fictional educational software company called Curriculum Companion Suites.
Like the business plan for the NALB Creative Center, it includes plenty of information for prospective investors and other key stakeholders in the business.
One of the most notable features of this business plan is the executive summary, which includes an overview of the product, market, and mission.
The first two are essential for software companies because the product offering is so often at the forefront of the company’s strategy. Without that information being immediately available to investors and executives, then you risk writing an unfocused business plan.
It’s essential to front-load your company’s mission if it explains your "Why?" and this example does just that. In other words, why do you do what you do, and why should stakeholders care? This is an important section to include if you feel that your mission will drive interest in the business and its offerings.
7. Culina Sample Business Plan

Culina's sample business plan is an excellent example of how to lay out your business plan so that it flows naturally, engages readers, and provides the critical information investors and stakeholders need.
You can use this template as a guide while you're gathering important information for your own business plan. You'll have a better understanding of the data and research you need to do since Culina’s plan outlines these details so flawlessly for inspiration.
8. Plum Sample Business Plan

Don't forget to share this post!
Related articles.
![examples of a business plan for students How to Write an Executive Summary Execs Can't Ignore [+ 5 Top Examples]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/executive-summary-example_5.webp)
How to Write an Executive Summary Execs Can't Ignore [+ 5 Top Examples]
20 Free & Paid Small Business Tools for Any Budget

What is a Business Plan? Definition, Tips, and Templates

Maximizing Your Social Media Strategy: The Top Aggregator Tools to Use

The Content Aggregator Guide for 2024
![examples of a business plan for students 7 Gantt Chart Examples You'll Want to Copy [+ 5 Steps to Make One]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/gantt-chart-example.jpg)
7 Gantt Chart Examples You'll Want to Copy [+ 5 Steps to Make One]
![examples of a business plan for students The 8 Best Free Flowchart Templates [+ Examples]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/flowchart%20templates.jpg)
The 8 Best Free Flowchart Templates [+ Examples]

16 Best Screen Recorders to Use for Collaboration

The 25 Best Google Chrome Extensions for SEO

Professional Invoice Design: 28 Samples & Templates to Inspire You
2 Essential Templates For Starting Your Business
Marketing software that helps you drive revenue, save time and resources, and measure and optimize your investments — all on one easy-to-use platform
Learn to Build a Better Business Plan

Sample Business Plan Gallery
Browse our library of over 550 free business plan examples to kickstart your own plan.
Browse our library of over 550 free business plan examples.

How to Write a Business Plan
Step-by-step guide to establish the foundation of your business quickly and efficiently.
Step-by-step guide to establish the foundation of your business.

Business Plan Template
Build your business using the proven planning template designed by the experts at Bplans.
Use the planning template designed by the experts at Bplans.

Subscribe to Bplans business insights
Stay up to date with the latest business planning, management, growth, and funding trends from bplans..
We care about your privacy. See our Privacy Policy .
Popular Downloads

SWOT Analysis
Easily evaluate your competitive position and develop effective growth strategies.
Refine your competitive strategy using a SWOT analysis.

Cash Flow Forecast
Improve the health of your business by easily estimating your business’s financial future.
Estimate and improve the financial health of your business.

Lean Business Plan Template
Fast, simple, and shareable. Start with a one-page plan to grow alongside your business.
Start with a simple one-page plan to grow alongside your business…
Start Your Business

Business Startup Guide
Get everything in order to start your business and write your business plan.
Get everything in order to start your business.

How to start a business with no money
Is it possible to start a business with no money? Check out this proven process to get your business…
Is it possible to start a business with no money? Check out this.…

Startup Checklist
Break down the startup process and check all the necessary boxes.

Estimating Startup Costs
What will it cost to start your business? These are the expenses you will need to consider.
Do you know what it will cost to start your business?

Write Your Business Plan

Business Planning in Under an Hour
Learn how to write your business plan in under an hour.

1-Page Business Plan Template
A faster, more efficient way to develop your business strategy.
Perfect Your Elevator Pitch

Pitch Guide
Learn how to create a winning elevator pitch deck and speech that will impress investors.
Impress investors with a winning pitch deck and elevator pitch.

Elements of the Elevator Pitch
If you're pitching to investors or building a pitch deck, here are the 7 things you need.
Here are the 7 things you need to include in your elevator pitch.

Components of a Pitch Deck
Here are the 11 slides you must have in your pitch deck.

Investor Pitch Template
Start your pitch off right with a proven pitch deck template.

Get Your Business Funded

Funding Guide
Learn how to prepare your business plan and pitch to secure funding for your business.
Prepare your plan and pitch to secure funding for your business.

Ways to Fund Your Business
When it comes to funding, there isn't a one-size-fits-all method. Here are your options.
Find out what funding options are available for your business.
Grow Your Business

How to Grow Your Business
Growing your business can be just as difficult as starting. Here are proven ways to grow.
Try these proven methods to continue growing your business.

Grow Using Your Business Plan
Turn your business plan into a growth-oriented business strategy.

Set Clear and Actionable Goals
Grow your business by setting clear goals and establishing key metrics for success.
Learn to set clear and actionable goals to grow your business.

How to Forecast Cash Flow
Create a cash flow forecast to help keep your business healthy and plan for the future.
Keep your business healthy using a cash flow forecast.

Tim Berry Blog
Learn from renowned business planning expert and founder of Bplans, Tim Berry.

Business Glossary
Definitions for common terminology and acronyms that every small business owner should know.

The quickest way to turn a business idea into a business plan
Fill-in-the-blanks and automatic financials make it easy.
No thanks, I prefer writing 40-page documents.

Discover the world’s #1 plan building software

Business Plan Example
Writing the plan, what goes in a business plan, sample plans.
One of the best ways to learn about writing a business plan is to study the plans of established businesses in your industry.
http://www.bplans.com/sp/businessplans.cfm
Develop a Business Plan Worksheet
This worksheet describes the basic components of any business plan. Please note that every plan will be unique to its particular company.
The Executive Summary
Include crisp, clear descriptions of the following elements:
- Company history
- Company objectives
- Product/service offerings
- Competitive advantage (A persuasive statement of why and how the business will succeed)
- Projected growth for the company and the market
- Key management team members
- Funding requirements, including a timeline and details on how the funds will be used
The Products and Services
Answer the following questions in this section:
- Why is there a need for your offering?
- Is your product or service already on the market, or is it still in the research and development stage? If you are still in the development stage, what is the rollout strategy or timeline to bring the product to market?
- What makes your product or service unique? What competitive advantage does the product or service have over its competition?
- Can you price the product or service competitively and still maintain a healthy profit margin?
- What patents, copyrights and trademarks does your company currently own or plan to obtain?
- What confidential and non-disclosure protection have you secured?
- What barriers do you face in bringing the product to market, such as government regulations, competing products, high product-development costs, the need for manufacturing materials, etc.?
Include the following elements:
- A detailed description of your market
- A detailed description of your niche and why you chose it
- An explanation of the market demand for your product or service offering (Requires supporting documentation)
- What percentage of market share do you project you can capture?
- What is the growth potential of the market? (Requires supporting documentation)
- Will your share of the market increase or decrease as the market grows?
- How will you satisfy market growth?
- How will you price your goods or services to remain competitive in a growing market?
Note: If you are launching a new product, include your market research data. Likewise, if you have existing customers, provide a customer profile, detailing their purchasing habits and their buying cycle.
The Marketing Strategy
The following are some promotional options to consider:
- Social Media
- Direct mail
- Trade shows
- Public relations
- Promotional materials
- Telephone sales
- One-on-one sales
- Strategic alliances
If you have current samples of marketing materials or strategies that have proven successful for you, include them with your plan.
Discuss your distribution strategy:
- Will you mail order, personally deliver, hire sales reps, contract with distributors or resellers, or use some other method?
- What are the costs associated with your proposed delivery methods?
- How will you track the effectiveness of the methods you choose?
The Competition
Specific areas to address in this section are:
- Who are your closest competitors and what are their product/service offerings?
- Where are they located?
- What are their revenues?
- How long have they been in business?
- Who is their target market?
- What percentage of market share do they currently hold?
- Do they service a local, geographic market or a national customer base? Is that the same or different from your approach?
- In what other ways do your operations differ from each of them? How are they similar?
- What do your rivals do well? Where is there room for improvement?
- In what ways is your business superior to the competition?
- How is their business doing? Is it growing, declining or stable?
- Are there certain areas of the business where the competition surpasses you (management team, economies of scale, better distribution, volume discounts, etc.)? If so, what are those areas, and how do you plan on compensating for them?
This section of the plan should describe the following requirements of your business:
- Manufacturing
Note: Provide a rollout strategy as to when these requirements need to be purchased and implemented. In addition, describe the vendors you will need to build the business. Do you have current relationships, or do you need to establish new ones? Who will you choose and why?
The Management Team
When preparing this section of the business plan, you should address the following five areas:
- Business background of the principals
- Past experience — tracking successes, responsibilities and capabilities
- Educational background (formal and informal)
- Personal data: age, current address, past addresses, interests, education, special abilities, reasons for entering into business
- Personal financial statements with supporting documentation
- Direct operational and managerial experience in related businesses
- Indirect managerial experiences
- Who will do what and why? Who is responsible for final decisions?
- Organizational chart with chain of command and listing of duties
- A simple statement of what management members will be paid, by position
- Listing of bonuses in realistic terms
- Benefits (medical, life insurance, disability, etc.)
- Insurance brokers
- Accountants
- Consulting groups
- Small Business Association
- Local business information centers
- Chambers of Commerce
- Local colleges and universities
- Federal, state and local agencies
- Board of Directors
- World Wide Web (various search engines)
Consider the following questions in completing this section of the business plan:
- What are your current personnel needs (full- and/or part-time)? How many employees do you envision in the near future, and then in the next three to five years?
- What skills must your employees have?
- What will their job descriptions be?
- Are the people you need readily available? If not, how will you attract them?
- Will you pay salaries or hourly wages?
- Will you provide benefits? If so, what will they be, and at what cost?
- Will you pay overtime?
Financial Data
Have a certified public accountant establish your accounting system before the start of business to provide you with data in the following four areas:
- Balance Sheet – indicates what the cash position of the business is and what the owner’s equity is at any given point (the balance sheet will show assets, liabilities and retained earnings).
- Break-Even Analysis – Shows the volume of revenue from sales that are needed to balance the fixed and variable expenses. Without exception, all businesses should perform this analysis, which is based on the income statement and cash flow.
- Income Statement (also called the profit and loss statement) – Indicates how well the company is managing its cash, by subtracting disbursements from receipts.
- Cash Flow – Projects all cash receipts and disbursements. Healthy cash flow is critical to the survival of any business.
Supporting Documentation
You will need to include all documents that lend support to statements made in the body of your company’s business plan. Please be aware that this list is not complete and may vary depending on the stage of development of your business.
- Credit information (include in appendix)
- Quotes or estimates
- Letters of intent from prospective customers
- Letters of support from credible personal references
- Leases or buy/sell agreements
- Legal documents relevant to the business
- Census/demographic data
You are using an outdated browser. Please upgrade your browser to improve your experience.
- Online MBA Programs
- Advertising
- Artificial Intelligence
- Business Administration
- Business Analytics
- Big Data Analytics
- Business Intelligence
- Business Management
- Corporate Finance
- Computer Science
- Cybersecurity
- Data Science
- Entrepreneurship
- Financial Technology FINTECH
- Healthcare Administration
- Healthcare Management
- Health Information Management
- Hospitality Management
- Internet Marketing
- Non-Profit Management
- Public Administration
- Quantitative Analysis
Supply Chain Management
- Sustainability Management
- Sports Management
- Technology Management
- Business Certificate Programs Guide
- Military to MBA
- How to Pay for an MBA
- Is an Online MBA Worth It?
- 12 Month Online MBA
- Accounting MBA
- Best MBA Concentrations
- Cybersecurity MBA
- Best Online MBA Programs
- Entrepreneurship MBA
- Information Technology MBA
- Marketing MBA
- Risk Management MBA
- No GMAT Online MBA
- Human Resources MBA
- Best MBA Careers
- Dual Online MBA Options
- Entry Level MBA Salary
- Employer MBA Tips
- EMBA vs Regular MBA
- Online MBA Benefits
- Value of Online MBA
- MBA for Physicians
- MBA for CEO’s
- MBA for Product Management
- MBA for Entrepreneurs
- MBA Internships
- MBA for Veterans
- MBA for Nurses
- MBA for Private Equity
- MBA Scholarships
- MBA Networking
- Ace Your MBA Interview
- Your GMAT Score
- AACSB vs ACBSP Accreditation
- Brand Management
- Engineering
- Information Technology
- Management Consulting
- Non Profit Management
- Information Systems
- Marijuana Cannabis
- Operations Management
- Product Management
- Project Management
- Sports Marketing
How to Write the Perfect Business Plan
Created by Henry Steele
By Henry Steele - January 8, 2018

Are you planning to start a business or do you already own one ?
Sponsored School(s)
If the answer is yes, then you need a business plan .
This seems like an extremely daunting task, but if you understand your business, it won’t be hard at all. It’s simply a matter of organizing the information in a clear, concise manner.
The following article discusses how to write the perfect business plan, including the types of business plans most commonly used, top 10 do’s and don’ts, what goes into a business plan, the structure of your business, marketing and sales, your organizational and operational plan and much more.
What is a Business Plan?

To help you write the perfect business plan, we’ll provide you with an exact outline of everything you’ll need to include, so even if you think you’re too young, you’ll have no problem starting out.
The reason many business owners first decide to put together a business plan is that they simply have to. If you want to apply for a business loan, attract investors, or obtain any necessary licensing, business plans are a prerequisite.
Even if you don’t need financing or licensing, however, it’s still a good idea to have a well-thought-out business plan. If you need to hire any key employees, a strong business plan will help attract strong talent. Whenever you need to deal with professionals, such as a consultant or an accountant, your business plan gives them invaluable insight.
Finally, it’s a good idea to put a business plan together for your own sake . As you put the business plan together, you’ll have the chance to really conceptualize and evaluate your strategy. You’ll build proof that your idea makes both financial and logistic sense. Once you start working to get your business off of the ground, a strong business plan guides and helps you stay on-track.
Types of Business Plans
Business plans come in all shapes and sizes, but you can generally whittle them down to three key versions.
Shortened Business Plan
This is an easily digestible, much shorter version of your normal business plan. Typically, it will be between three and five pages. You should include your executive summary, financials, and any information pertinent to the person/s to whom you are presenting the plan. A shortened business plan is usually made with a specific purpose or recipient in mind, so it will be easy to figure out exactly what is and isn’t important enough to make the cut.
In-depth Business Plan
Your standard business plan, and the one we will be teaching you to write . Again, these come in handy when seeking to fund your business, attract employees or work with professionals, or simply to act as a guide.
Operational Business Plan
Unlike the other two business plans we have discussed, an operational business plan is meant for internal use only. This will not be distributed to anybody except for employees or professionals working on your company’s behalf. An operational business plan focuses on the company’s overarching goals, mission, and vision so that all department stay aligned. Your Marketing and Sales, Operational Plan, and Financial sections will be key here.
What Language Should I Use?

Top 10 Do’s and Don’ts
Before we dive into our business plan outline and describe each section, let’s go over some general do’s and don’ts you’ll want to keep in mind as you write your business plan:
Do: Provide Examples

Don’t: Overload the Reader
An in-depth business plan will contain lots of useful information and will likely end up being much more than ten pages. Because it’s so long by nature, you need to make sure to only include the most useful information in each section. Format everything carefully and correctly. Don’t use language that confuses or intimidates readers outside of your industry. The easier it is for the reader to absorb everything you’re presenting them, the more effective your business plan is.
Do: Proper Research

Don’t: Leave Any Stone Uncovered
Somebody who reads your business plan shouldn’t have any major questions left unanswered. Include complete information about what you are aiming to do, how you are going to do it, how much money is needed, etc. Use our full outline below to ensure everything is covered.
Do: Be Honest

Don’t: Hustle Just to ‘Get it Done’
Writing a business plan isn’t a task you’re completing and checking off your to-do list. Everything must be accurate, thoughtful, and well-articulated. Keep in mind: this will guide you as you operate your business and is the key to obtaining financing and/or pitching your business.
Do: Make it a Living Document

Don’t: Focus Solely on Your Product
You might think your business revolves around your particular product/s or service/s, but there’s so much more to it than that. Your business plan talks about how the actual business is run, so you might want to leave the technical specifications and granular details for another time.
Do: Show Your Passion
In the end, your business plan and your business are about you. While it’s important to maintain a professional tone, don’t be afraid to let your enthusiasm about your business seep through every page.
Don’t: Write Alone

How to Write a Business Plan

- Keep it concise.
- Know your audience.
- Perfect your executive summary.
- Focus and refine constantly.
- Gather and check all of your data.
- Be confident, but don’t go overboard.
- Be as clear and in-depth as possible.
- Enhance with graphics.
- Share and gather feedback from trusted advisors.
What Goes into a Business Plan?
When writing your business plan, you will need to put in a lot of time and research. Luckily, we’re here to walk you through all of that. A winning business plan contains the below sections, and you can use our sidebar to navigate to each of these:
- Introduction
Executive Summary
- Information About Your Business
- Industry Analysis
Marketing and Sales
- Operational Plan
Your Business Plan Introduction

Cover Letter
A cover letter is essential whenever you are presenting the business plan to somebody for a specific reason and should be tailored to each individual. Like any other letter, it should include names, dates, and a cordial greeting. In the first paragraph, explain exactly why you are presenting the business plan to the recipient. Take one or two paragraphs to discuss your business (an even more condensed executive summary, as we will cover in the next section). Finally, let the reader know you appreciate their consideration and would be happy to address any questions or concerns. Include any necessary contact information below your name and signature.
Your title page should be clean and simple. Here’s what to include in it:
- The title of the document (i.e. Business Plan, Business Proposal, Summary Business Plan).
- The name of your company.
- A sub-heading, if necessary (i.e. ‘Presented to ABC Investing Company’).
- Who the business plan was prepared by.
- The name of any other owners or key partners.
- Basic contact information.
Table of Contents
A table of contents is essential to make your business plan transparent and easy to navigate. It is unlikely that a serious potential partner or investor will read through your plan once and toss it aside, so you want to make it easy for them to return and pick up where they left off or revisit any key bits of information. If you are providing a digital copy, include clickable links to each section for the reader’s benefit.

The executive summary is exactly what it sounds like – a brief summary that describes the essence of what your business is and what it aims to do. Here’s how to write a winning executive summary:
- Begin with a single sentence that sums your business up. This is otherwise known as your value proposition.
- Describe what niche or problem your business fills or solves.
- Explain exactly how your business solves this problem in a way that the rest of the competition does not or cannot.
- A very brief (one or two sentences) summary of any other information from the following sections that would be critical to your business’ success.
Your Business / Company

Structure of Your Business
First and foremost, you’ll need to discuss the legal structure of your business:
- Sole-proprietorship: simple to set-up, but the owner is fully liable for any debts or obligations.
- Partnership: a general partnership is also simple to set-up, but all partners would be liable. Limited partnerships, or LPs, are a bit more complicated.
- Corporation: a corporation is owned by stockholders, so it is unlikely you will either want or need to structure as one. There are two types of corporations, which vary in terms of shareholder limitations and tax liabilities: S corporations and C corporations.
- Limited liability corporation (LLC): an LLC is generally the best of both worlds for small businesses. The owner’s’ liability is limited, and taxation is that of a partnership, which provides better flexibility over a corporation.
Once the legal structure is determined, you’ll need to break down the ownership of the business. Are you the sole owner? Do you have business partners? Has anybody purchased a share of the business in exchange for funding? Provide a brief introduction to any key executives or owners, outlining what strengths they have and how they will impact the business.
Finally, include a brief history (if any) of your business, and any pertinent location details.
Business Vision, Mission, and Values
This is one of the most important sections of your business plan. Here, you need to impart your passion for the business and really describe what you’re trying to achieve.
Business Vision
Your vision statement is all about the company’s goals. It serves as a template for exactly what you’re trying to achieve, both short-term and long-term. Don’t hold back when it comes to your vision: if your goal is to eventually dominate the Northeastern coffee shop scene, say that. A vision statement is your chance to think big.
Where a vision statement thinks big, a mission statement is more practical. Your mission statement should discuss your company’s purpose. Why does it even exist in the first place? This mission statement will act to provide organizational direction and help you achieve your vision.
The values are all about how you plan to operate your business in relation to the stakeholders. This includes investors, customers, and members of the local community. How do you plan to treat them? What are you doing to make their lives and the world they live in better?
Analyzing the Industry

Market Size
Here, you’ll describe exactly how large the market is. You should be able to find national figures with relatively little research. If you’re not serving a national or international market, discuss how large the population you plan to serve is. Extrapolating from the national information, how big do you expect your actual market size to be?
In addition, you should discuss any important trends. Is your market growing or retracting? If your market is growing, discuss how you project to fit into that growth and seize your market share. If your market is shrinking, discuss why you think entering the marketplace is worthwhile, and whether or not you project growth in the future.
Industry Focus and Trends

First, you’ll want to talk about the industry in general. This includes looping back to the market size and discussing whether it is growing, stagnant, or shrinking. Are there any overarching trends or cycles that will affect your business?
This is also a good opportunity to discuss pricing. What type of money does your average customer spend in your industry? What price point are you aiming for, and why is that a good strategy? If you aren’t competing on price, what reasons do you have to believe that somebody will be willing to spend more on your business?
Below, we will discuss two valuable business models you can and should use to discuss your industry further.
PEST Analysis
- Political: what impact could the government have on your business. Is there any pending legislation that could change how you operate? Would tax changes or tariffs cause a financial strain?
- Economic: would an economic downturn cause sales to tumble, or is your business relatively immune to economic factors? Furthermore, what do current economic trends (inflation, consumer demand, etc.) say about your short-term potential?
- Social: are there any relevant social or cultural trends that are shaping the industry? Is there a distinct seasonality to your business? Consider, for example, the impact of the Christmas season to retailers in the United States.
- Technological: how has technology shaped your industry over the past decade? Take a look at the future and make an educated guess on where the industry is headed, and how you’ll fit into that future.
Sometimes PEST is lengthened to PESTLE to include any legal or environmental factors as well. If you believe either will have a significant impact on your business, make sure to include it as well.
Porter’s 5 Forces Analysis
- Competition: we will go into this in more detail next, but for this model you should discuss how much competition there is, and how profitable they might be.
- Threat of new entrants: how easy is it for somebody to enter your industry? For a casino, it would be quite difficult (extensive significant licensing and upfront costs), but for a food truck, it would be quite minimal. The easier it is to enter your industry, the greater the threat is of somebody else entering and stealing your market share.
- Power of suppliers : if your industry has a low number of suppliers or suppliers that are dominated by much larger companies, you will have a problem sourcing on-budget and on-time. If you aren’t reliant on very specific suppliers, however, or if there is competition among suppliers, you can find yourself in an advantageous position.
- Power of customers: specifically, do your customers have the ability to drive prices down? If you expect to have a large number of small customers, your price will remain relatively stable. However, if you plan on having a small number of very important customers, they maintain the power to dramatically impact your pricing and profitability.
- Threat of substitutes: how likely is it that somebody will forego your offering for a comparable substitute. If you’re a restaurant, for example, Amazon’s grocery delivery business would be a substitute, since people may decide to stay home and cook for themselves.
Competition
It’s just as important to discuss how your competition is navigating the industry you plan on dominating. With a strong idea of where your competition is positioned and the strategic decisions they are making you will be able to determine where your own business fits in.
To begin, discuss what your competition looks like. Are there many small businesses vying for the same customers or are you competing against a couple of whales? List your most important competitors and summarize them. Discuss their location, products, pricing, market share, and any important strategic decisions they have made. Use this information to create a list of their strengths and weaknesses.
After discussing the competition, it’s time to think about where you fit among them. SWOT Analysis is the perfect model to do just that.
SWOT Analysis
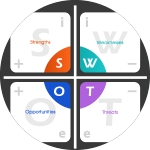
Here is what a complete SWOT Analysis looks like:
- Strengths: Exactly as it sounds. What do you do best? What do you do that the competition absolutely cannot?
- Weaknesses: Be honest. Are there any resources you lack? Any skillsets that are missing? What isn’t as efficient as it could be?
- Opportunities: Improving any of your weaknesses is a major opportunity. In addition to that, consider internal or external factors that might change and present a new business opportunity. Finally, are there any complementary products or services that you could consider offering to your customers?
- Threats: What potential is there for your business to be damaged? Are there any industry or economic trends? Could your competition change strategies and harm you? Do any obstacles to success stand in your way?
Once you have completed the SWOT analysis, wrap this section up by talking about your own competitive strategy. Given your industry, the competition, and your own SWOT analysis, what decisions are you making to position the company to succeed?
Readers of your business plan definitely need to know how you’ll be marketing and selling your product or service.There are going to be three key elements of your marketing plan.
Customer Segmentation

- Demographic information – age, gender.
- Psychographic profile – what do they care about? What motivates them? What do they value? Where do they get their information?
- Socioeconomic profile – income, lifestyle preference.
Describe your target audience in great detail. The more you know about your customer, the easier it will be to market to them.
Advertising and Promotion Plan
After building a strong customer profile of your target audience, you should know what your customer cares about. Think about how your business fits into that, and strategize how you’re going to market to them. Use their demographic and behavioral information to determine the most appropriate channels to focus on.

Your brand should seep into all aspects of your business – the website, advertisements, and even the tone of communications with customers. Whatever strategies you have for these elements, make sure to lay them out.
Finally, include your company logo and slogan, if they already exist. If not, you should begin to think about them and use the rest of this section as a guide.
Sales Distribution Plan
How exactly do you plan on getting your goods or services into somebody’s hands? Do you plan on hiring a sales staff or will you handle it all yourself initially? Do you plan on doing inbound or outbound sales? What does the sales process look at each step of the marketing funnel?
You’ll also need to think about and discuss pricing. Discuss your pricing strategy and why it’s a good value for your customers. If you are going low or moderately priced, discuss how you can stay profitable and remain differentiated from the competition. If you are a luxury brand, discuss why somebody will be willing to pay more for your business than the competition.
Lastly, consider distribution. Are you going to allow customers to purchase directly from you? Will they have to go through distributors? Do you have any retail partnerships to leverage? These are important decisions that have a profound impact on a business.
Organizational and Operational Plan

Production Process

Here are some ideas of what you’ll need to outline:
- Raw materials – how much do they cost? Do prices fluctuate? Is supply limited in quantity or how quickly it can be obtained in a pinch?
- What machines, technologies, etc., do you use for production? What costs are involved in these? Are you renting or do you own them?
- What is your estimated daily output?
- How easy is it to scale up or down as necessary? How does this impact the cost per unit?
- Which methods of quality control do you employ, both pre- and post-production?

If you’re a service business, you might not have any physical inventory, but your employees should be considered as your supply. After all, without them, you won’t be able to provide your services to your customers. What strategies do you have to recruit and retain the best talent possible? Can you scale quickly through recruiting and training, overtime, or an increase in part-time help?
You should also look back at your sales distribution plan and consider the logistics of shipping any physical products. How often will orders be fulfilled? Do you have the ability to rush orders if necessary? How will returns or incorrect shipments be handled in a way that keeps everybody happy?

Here are the components you must include in your business plan’s financial information:
Forecasted Sales
Use all of the marketing data you’ve put together to determine what a reasonable sales forecast looks like. Project your sales for a period of two or three years, going one month at a time. Include seasonality whenever applicable. As you forecast sales, include exactly how much revenue you expect to earn from those sales, and the total direct cost of those sales. You’ll be able to use these figures to determine revenue and gross margin, which you should use to compare to industry and competitive standards.
Projected Expenses

Fixed costs are going to stay the same whether you sell one widget or twenty. For example, rent, electricity, insurance, marketing costs, and payroll (with the exception of commission and bonuses), will mostly stay the same no matter what sales look like.
Variable costs, on the other hand, will vary by each unit sold. This includes the cost of materials, shipping, coupons, taxes, etc. Most of this should already be covered in your forecasted sales report, but make sure that nothing is overlooked.
Make sure to consider that as you scale, some fixed costs may become variable. As sales increase, you may have to hire more employees, or move into a bigger office. Keep this in mind by always referring back to your forecasted sales and estimating your business needs as best you can.
Balance Sheet
Everything comes together on your balance sheet. This includes your projected sales and expenses, but also deals with assets and liabilities.For example, if you take out a loan, you’ll need to include the capital in your assets and the repayments, including interest, in your liabilities. Non-monetary assets, such as the property and machinery must also be included.
You can find a sample balance sheet here .
Cash Flow Statement

Month by month, you’ll track exactly how much cash you expect to leave your hands and how much will come in. Keep in mind that not all sales are paid fully right away. Consider how many sales will be paid in full at the time of sale, how many will be paid in 30 days, 60 days, or go completely delinquent.
Once you have your cash flow statement completed, run some quick analysis. Compare your projected expenses each month to the projected cash coming in each month. For any months that project to have a negative cash flow, ensure you have enough money on hand to cover the difference.
You may find two examples of completed cash flow statements here and here .
Customer Lifetime Value
Customer Lifetime Value is an estimate of exactly how much each customer you acquire will be worth total. A simple way to calculate this is by determining how many purchases a customer makes before churning, and multiplying it by the average amount of their purchase. In other words, how many purchases will they make before moving on from your business, and how much will those purchases be worth?
Let’s take a look at a real-world example. Let’s assume you’re running an oil change business, and you know your average customer gets three oil changes per year. With premium options and add-ons, your average sale is $38.50. Each customer spends an average of three years with you before churning (perhaps they have moved away or found another service they prefer).
In this example, your expected CLV would be $346.50. You know each average customer will make 3 purchases per year, for 3 years, at $38.50 each. 3 x 3 x $38.50 = $346.50, which is your CLV.
Why is CLV so important? Let’s take a look at unit economics.
Unit Economics

The formula for cost of acquisition is simple. Divide your total marketing spend by the number of customers you have acquired through all marketing channels. If you spend $25,000 across all marketing channels and acquire 1,000 customers, your average cost per acquisition is $25.00.
Tracking your marketing expenses isn’t the tricky part. Attributing each user to a specific campaign, however, can be. If somebody walks into your store after seeing a TV ad, for example, it can be hard to properly attribute them. Digital campaigns are a bit easier, as there are typically tracking links that make everything easy to calculate. You’ll have to do your due diligence and make your best-educated guesses here, using industry standards whenever necessary and possible.
You should also take the time to break out your unit economics into each marketing channel. This allows you to track which channels are performing well and which ones aren’t. If Facebook is attracting lots of customers but you’re spending so much that your cost of acquisition is higher than expected CLV, you might actually need to stop spending money there.
It’s important to be very clear about exactly how your business has been funded so far. This includes what you have received through investments, series rounds, or personal loans. You will also need to mention any personal funds that you have put into the business, and how much you have saved that you are willing to put into it in the future.
Once you have discussed the funding your business has received, it is appropriate to lay out exactly how much you’ll need. Make sure to also discuss exactly what any loans or investments will be used for and how that spending will be tracked.
Business Plan Resources
Business plan samples.
To reinforce everything we’ve discussed above, let’s take a look at some sample business plans that have already been put together for your review. We’ll discuss some key takeaways from each plan, helping you consider how your business is unique and what you’ll need to emphasize.
Coffee Shop Business Plan
A coffee shop is a nice, simple business to start our samples with. A coffee shop requires a small storefront, and the location is critical. Most people will gladly stop in for a nice cup of coffee but are unlikely to drive miles out of their way for one. Notice that because of this, the sales forecast is relatively stagnant, even after several years.
Click here for the sample business plan.
Restaurant Business Plan
A restaurant business plan will be similar to a coffee shop, but is a little more involved. Start-up costs are higher as it requires a larger storefront and a larger variety of equipment. Variable costs are higher as a quality meal costs much more than a cup of coffee. The sales forecast shows more growth, as people are more willing to travel for a good meal than they are a simple cup of coffee.
Food Truck Business Plan
Let’s consider a third food-based business to really drive home how businesses that appear similar will have important differences. Food trucks have a much different fixed cost structure than a coffee shop or restaurant, as they don’t have a physical location. Seasonality and location will have a huge impact on salespeople won’t want to stand outside for a burrito when it’s cold and snowy outside. With a much smaller staff, a food truck is also more likely to be open for lunch only, or closed a couple days per week.
Startup Business Plan
It’s good to take a look at a general startup business plan to get an idea of how to estimate costs, sales, etc. This sample plan is a take-out pizza joint. Notice that trends are important, as the business plan notes their market is a growing area and they are aiming to fill a niche for low to middle-income families, which comprise the majority of residents in their service area. They use a mixture of studies and geographic data to make conservative estimates, giving potential investors confidence that the business can be profitable if the strategies are successfully executed.
Photography Business Plan
A photography business is a great example of a company that is minimal to the extreme. Mostly, you will be relying on your own skills and experience. Minus initial equipment and the cost of your own time, expenses are minimal. Still, you see that it’s important to have a strong plan in place so that you understand how to position your services and who exactly you’re aiming to serve.
Business Plan Tools
Here are a variety of tools that make both writing a business plan and getting your business off the ground much easier:
If you want to quickly build your idea into a business plan to validate its value or just to get started, LivePlan is perfect. The business planning process is made simple, as you simply need to answer questions and are given plenty of examples, videos, and tutorials along the way. You can even use LivePlan to collaborate with partners or investors, testing ideas on the fly and seeing its impact on your business’ health.
Click here to take a look at LivePlan.
Rocket Lawyer
When you’re starting a business, it’s extremely likely you’ll need quick legal help. You might need advice on licensing, permits, or zoning. Or perhaps you want to discuss how to structure your business as an LLC. Rocket Lawyer can help. You’ll have access to their services for a monthly fee that’s less than a cup of coffee each day. There’s an even option to help incorporate your business by filling out a couple of quick forms.
Click here to take a look at Rocket Lawyer.
Like LivePlan, StratPad offers a cloud-based chance to build your business plan and strategy on the fly. StratPad offers a demo for their services and if you’re looking for funding will even match you up automatically with a financial institution that makes sense for your business. Our suggestion is to take a look at both LivePlan and StratPad and select the one that you like best.
Click here to take a look at StratPad.
If you’re looking for a simple way to create a professional business plan without all the bells and whistles, BizPlan is perfect for you. You’ll be able to create a stylish, professional business plan using intuitive drag-and-drop templates. Financials are easy to create using a user-friendly dashboard.
Click here to take a look at BizPlan.
A typo can derail your business plan and make you look sloppy and unprepared, no matter how much effort you put into it. Grammarly is a world-class spell checker that also checks for many of the most common grammatical error for free. There’s even a browser-based version that you can use no matter where you are. For a fee, you can subscribe to Grammarly Premium, which provides an even more granular check.
Click here to take a look at Grammarly.
Business Plan Templates
Now that we have an idea of everything you need to include in your business plan and which tools you’ll need to get started, it’s time to get started. Here are some websites with sample business plan templates you may use to make writing the perfect business plan a bit easier:
- Score.org has a variety of business plan and financial statement templates, including ones for both start-ups and established businesses.
- Microsoft Office’s website has many valuable business plan templates, including a checklist and PowerPoint Presentation templates for pitching your business plan.
- The S. Small Business Administration allows you to create a business plan with a free account that you can download and distribute as a PDF.
- Santa Clara University provides a 15-section business plan that can be downloaded one section at a time or all at once.
- Law Depot offers a business plan template tailored for you. Simply answer some quick questions and your template is instantly ready to download.
How to Write a Business Plan Conclusion
In the end, a business plan is a highly unique and personalized document. A business plan that is right for your business won’t be right for any other business in the world. By closely following the outline and strategies above, however, you’ll have a great base to begin crafting your own perfect business plan.
Bibliography:
- Berry, T. 15 Reasons You Need a Business Plan. Entrepreneur. Retrieved from https://www.entrepreneur.com/article/83818.
- CBM Group. What Is The Right Tone And Writing Style For A Business Plan? Retrieved from http://www.cbmgroup.co.uk/blog/business-plan-writing/what-is-the-right-tone-and-writing-style-for-a-business-plan.
- Discover Business. How to Write a Business Plan. Retrieved from https://www.discoverbusiness.us/business-plans/.
- Fontinelle, A.How To Write A Business Plan. Investopedia. Retrieved from http://www.investopedia.com/university/business-plan/.
- Franklin, B. The Three General Types of Business Plans. Business Power Tools. Retrieved from http://www.businesspowertools.com/2016/06/management-2/the-three-general-types-of-business-plans/.
- Gregory, A. Comprehensive Business Plan Outline for Small Business. The Balance. Retrieved from https://www.thebalance.com/a-comprehensive-business-plan-outline-for-small-business-2951557.
- Gregory, A. How to Conduct a SWOT Analysis for Your Small Business. The Balance. Retrieved from https://www.thebalance.com/swot-analysis-for-small-business-2951706.
- Hazlett, M. Basics of Unit Economics. Medium. Retrieved from https://medium.com/@markhazlett/basic-of-unit-economics-79f1d6cae085.
- Investopedia. Porter’s 5 Forces. Retrieved from http://www.investopedia.com/terms/p/porter.asp.
- Johnson, J. How to Write a Cover Letter for a Business Plan. Small Business Chronicle. Retrieved from http://smallbusiness.chron.com/write-cover-letter-business-plan-43209.html.
- Katz, A. Determining the Best Legal Structure for Your Business. Entrepreneur. Retrieved from https://www.entrepreneur.com/article/236450.
- Kolowich, A. How to Write a Business Plan: A Bookmarkable Guide (With Examples). HubSpot. Retrieved from https://blog.hubspot.com/marketing/how-to-write-a-business-plan.
- Lavinsky, D. Marketing Plan Template: Exactly What To Include. Forbes. Retrieved from https://www.forbes.com/sites/davelavinsky/2013/09/30/marketing-plan-template-exactly-what-to-include/#1ddaeeb43503.
- My Own Business Institute. Session 2: The Business Plan. Retrieved from https://www.scu.edu/mobi/business-courses/starting-a-business/session-2-the-business-plan/.
- Parsons, N. How to Write a Business Plan [Updated for 2017]. Bplans. Retrieved from http://articles.bplans.com/how-to-write-a-business-plan/.
- PESTLE Analysis. What is PESTLE Analysis? A Tool for Business Analysis. Retrieved from http://pestleanalysis.com/what-is-pestle-analysis/,
- Robbins, S. Why You Must Have a Business Plan. Entrepreneur. Retrieved from https://www.entrepreneur.com/article/74194.
- Ronick, D. 10 Business Plan Dos and Don’ts. Inc. Retrieved from https://www.inc.com/articles/201104/business-plan-dos-and-donts.html.
- Ronick, D. 10 Things A Business Pitch Absolutely Does (And Does Not) Need. Business Insider. Retrieved from http://www.businessinsider.com/10-survival-tactics-for-a-successful-business-plan-pitch-2011-4/.
- Shopify. The Ultimate Guide to Business Plans, Chapter 3: The Company. Retrieved from https://www.shopify.com/guides/businessplan/the-company.
- Wasserman, E. How to Write the Financial Section of a Business Plan. Inc. Retrieved from https://www.inc.com/guides/business-plan-financial-section.html

FEATURED ARTICLES
- How AI Will Continue to Disrupt and Drive Business
- Do You Need a Business Degree to Get Your MBA?
- Leveraging Your New Master’s Degree
- Company Culture: The Future of Human Resource Management
- 10 Things Every Business Student Should Know
- 7 Ways To Make The Most of Your First Semester…
- How to Get an Employer to Sponsor Your MBA?
- The Big Question: Should You Go to College?
FEATURED INTERVIEWS
- Eastern Oregon University MBA Interview
- Adelphi University Business Analytics
- The Ohio State University MBA Interview
"It doesn't matter how many times you have failed, you only have to be right once." - Mark Cuban
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
Copyright © 2024, Business Student.com. All Rights Reserved.

300+ Business Plan Examples

With over two decades of experience, Growthink has assisted more than 1 million companies in developing effective business plans to launch and expand their businesses. Trust in our expertise to guide you through developing a business plan that drives your success. In addition to our sample plans, below you’ll learn the answers to key business plan questions and gain insightful tips on writing your business plan.
Quick Links to Sections On this Page:
- Sample Business Plans By Business Category
Answers to Key Sample Business Plan Questions
Shoutmouth business plan example, business plan examples by business category.
Clothing & Fashion Business Plan Templates & Samples
Clothing Store Business Plan
Embroidery Business Plan
Fashion Business Plan
Jewelry Business Plan
Construction, Interior Design & Home Services Business Plan Templates & Samples
|
|
|
Consumer Services Business Plan Templates & Samples
|
|
|
Business Services Business Plan Templates & Samples
|
|
|
Events Business Plan Templates & Samples
Banquet Hall Business Plan
Event Planning Business Plan
Event Venue Business Plan
Sample Event Venue Business Plan
Party Rental Business Plan
Photo Booth Business Plan
Table and Chair Rental Business Plan
Wedding Planning Business Plan
Farm Business Plan Templates & Samples
|
|
|
Financial Services Business Plan Templates & Samples
|
|
|
Fitness & Beauty Business Plan Templates & Samples
|
|
|
Food & Beverage Business Plan Templates & Samples
|
|
|
Medical & Health Business Plan Templates & Samples
|
|
|
Music & Entertainment Business Plan Templates & Samples
Music Business Plan
Party Bus Business Plan
Podcast Business Plan
Production Company Business Plan
Record Label Business Plan
Recording Studio Business Plan
Nonprofit Business Plan Templates & Samples
Sample Non-Profit Business Plan
Charity Business Plan
Sample Nonprofit Business Plan PDF
Social Enterprise Business Plan
Real Estate Business Plan Templates & Samples
Sample Airbnb Business Plan
House Flipping Business Plan
Property Development Business Plan
Property Management Business Plan
Real Estate Business Plan
Real Estate Agent Business Plan
Real Estate Business Plan PDF
Real Estate Development Business Plan
Real Estate Investment Business Plan
Retail & Ecommerce Business Plan Templates & Samples
|
|
|
Technology Business Plan Templates & Samples
Biodiesel Business Plan
Blogging Business Plan
Clean Tech Business Plan
Mobile App Business Plan
Saas Business Plan
Software Company Business Plan
Technology Business Plan
Transportation Business Plan Templates & Samples
|
|
|
Travel and Lodging Business Plan Templates & Samples
Bed and Breakfast Business Plan
Campground Business Plan
Glamping Business Plan
Hotel Business Plan
Mobile Home Park Business Plan
Resort Business Plan
RV Park Business Plan
Travel Agency Business Plan
1. Why is utilizing an example business plan a good idea?
Sample business plans can help you quickly and easily write a business plan for your own business. Business plans are an important tool for any business, but they can be challenging to create. A sample business plan will help you understand the business plan format , the benefit of market research, and how to write a compelling executive summary. It can also serve as a guide for creating your own business plan, outlining the key sections and providing examples of successful plans. Utilizing the best business plan template can save you time and ensure that your plan is well-structured and comprehensive.
Business plan examples may even help you with the different sections of a plan, including market analysis, business description, cash flow statements/business financial statements, and more. Business plans can also show you how a quality plan in your exact business plan category is organized and shows you the appropriate business communications style to use when writing your business plan.
2. Who would benefit from using an example business plan?
Any entrepreneur or business owner who has never written a business plan before can benefit from an example or sample plan. New business owners often start with business plan templates , which are helpful but are sometimes more useful after reviewing other sample business plans.
A good sample plan can be a step-by-step guide as you work on your business planning and business idea. Once you have a sense for the flow, specs, and details, etc. that business plans have, utilizing a business plan template will help you pull everything together, helping you create a plan investors and other stakeholders will value. A solid business plan will also help you if you need a bank loan, which may require a startup business plan. Download our free business plan template to help you get started on your own business plan.
Free Download : Free Business Plan Template PDF
3. How do you get started with a sample business plan and maximize its benefit?
First you should read the business plan thoroughly. Study both the type of information provided in key sections like the executive summary, target market analysis, summary, etc., as well as the format and style of the plan. As you read, you may find yourself thinking through things such as improving or evaluating your business planning process, your business idea, or reconsidering who you want to write your business plan for. This is OK and part of the process. In fact, when you start writing a business plan for the first time, it will be much easier because you’ve gone through this process.
After this initial read, outline your business plan and copy in from the sample plan sections that apply to your business. For instance, if the sample plan included public relations in their marketing strategy and sales plan, and you will also use this tactic, you can copy it into your plan and edit it as appropriate. Finally, answer the other questions answered in the sample plan in ways that reflect your unique business and target customers.
Writing a business plan can seem daunting. Starting your business plan writing process by reviewing a plan that’s already been created can remove a lot of mental and emotional barriers while helping you craft the best plan you can.
4. When should you not use a sample business plan?
If your business is unlike any other, using a sample business plan will not be as effective. In this situation, writing a business plan from scratch utilizing a business plan template is probably your best path forward.
As an example, Facebook’s early business plan was unlike others since it was paving a new path and way of doing business. But, groundbreaking new businesses like Facebook are not the norm, and the vast majority of companies will benefit from utilizing sample business plans.
5. How do you choose the right type of business plan for your venture?
Selecting the appropriate type of business plan depends on your business’s stage, needs, and goals. Let’s explore the different types of business plans and how to determine which business plan format is right for you.
- Startup Business Plan : This type of plan is for businesses just starting out and seeking funding or investment. It typically includes a detailed analysis of the market, target audience, competition, and financial projections.
- Traditional Business Plan : Traditional business plans are the most common type of business plan, used by established businesses to outline their goals and strategies. It includes all the key sections such as market analysis, company description, and financial statements.
- Internal Business Plan : Internal business plans are used for internal purposes, to guide the day-to-day operations and decision making of the business. It may not be as detailed as a traditional business plan, but still includes important information such as company mission, objectives, and key performance indicators.
- Feasibility Business Plan : A feasibility business plan is used to assess the viability of a new product or service in the market. It includes detailed research and analysis to determine if the business idea is feasible and profitable.
- One-Page Business Plan : As the name suggests, this type of business plan is condensed into one page and includes the most critical information about the business. It can be a useful tool for pitching to potential investors or partners.
- Strategic Business Plan : A strategic plan looks at the big picture and long-term business goals of a company. It may include the company’s mission statement, core values, and overarching strategies for achieving success.
Ultimately, the type of business plan you choose will depend on your business’s specific needs and goals. It may also be beneficial to combine elements from different types of plans to create a customized plan that best fits your business. Carefully consider your objectives and resources before deciding on the right type of plan for your venture.
Finish Your Business Plan in 1 Day!
Don’t you wish there was a faster, easier way to finish your business plan?
With Growthink’s Ultimate Business Plan Template you can finish your plan in just 8 hours or less!
The business plan example below is for Shoutmouth, a company that enjoyed much success in the early 2000’s and which was able to raise funding. While the plan’s premise (social networking) is not as unique now as it was then, the format and structure of this business plan still holds.
I. Executive Summary
Business Overview
Launched in late February 2007, Shoutmouth.com is the most comprehensive music news website on the Internet .
Music is one of the most searched and accessed interests on the Internet. Top music artists like Akon receive over 3 million searches each month. In addition, over 500 music artists each receive over 25,000 searches a month.
However, music fans are largely unsatisfied when it comes to the news and information they seek on the artists they love. This is because most music websites (e.g., RollingStone.com, MTV.com, Billboard.com, etc.) cover only the top eight to ten music stories each day – the stories with mass appeal. This type of generic coverage does not satisfy the needs of serious music fans. Music fans generally listen to many different artists and genres of music. By publishing over 100 music stories each day, Shoutmouth enables these fans to read news on all their favorite artists.
In addition to publishing comprehensive music news on over 1200 music artists, Shoutmouth is a social network that allows fans to meet and communicate with other fans about music, and allows them to:
- Create personal profiles
- Interact with other members
- Provide comments on news stories and music videos
- Submit news stories and videos
- Recommend new music artists to add to the community
- Receive customized news and email alerts on their favorite artists
Success Factors
Shoutmouth is uniquely qualified to succeed due to the following reasons:
- Entrepreneurial track record : Shoutmouth’s CEO and team have helped launch numerous successful ventures.
- Affiliate marketing track record : Online affiliate marketing expertise has been cited as one of MySpace’s key success factors. Over the past two years, Shoutmouth’s founders have run one of the most successful online affiliate marketing programs, having sold products to over 500,000 music customers online.
- Key milestones completed : Shoutmouth’s founders have invested $500,000 to-date to staff the company (we currently have an 11-person full-time team), build the core technology, and launch the site. We have succeeded in gaining initial customer traction with 50,000 unique visitors in March, 100,000 unique visitors in April, and 200,000 unique visitors in May 2007.
Unique Investment Metrics
The Shoutmouth investment opportunity is very exciting due to the metrics of the business.
To begin, over the past two years, over twenty social networks have been acquired. The value in these networks is their relationships with large numbers of customers, which allow acquirers to effectively sell to this audience.
The sales price of these social networks has ranged from $25 to $137 per member. Shoutmouth has the ability to enroll members at less than $1 each, thus providing an extraordinary return on marketing expenditures. In fact, during an April 2007 test, we were able to sign-up 2,000 members to artist-specific Shoutmouth newsletters at a cost of only 43 cents per member.
While we are building Shoutmouth to last, potential acquirers include many types of companies that seek relationships with music fans such as music media/publishing (e.g., MTV, Rolling Stone), ticketing (e.g., Ticketmaster, LiveNation) and digital music sales firms (e.g., iTunes, The Orchard).
Financial Strategy, Needs and Exit Strategy
While Shoutmouth’s technological, marketing and operational infrastructure has been developed, we currently require $3 million to execute on our marketing and technology plan over the next 24 months until we hit profitability.
Shoutmouth will primarily generate revenues from selling advertising space. As technologies evolve that allow us to seamlessly integrate music sampling and purchasing on our site, sales of downloadable music are also expected to become a significant revenue source. To a lesser extent, we may sell other music-related items such as ringtones, concert tickets, and apparel.
Topline projections over the next three years are as follows:
| 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | |
| Shoutmouth Members | 626,876 | 4,289,580 | 9,577,020 |
| Unique Visitors | 2,348,050 | 8,390,187 | 18,633,659 |
| Total Page Views (Millions) | 20.7 | 273.5 | 781.0 |
| Revenues | $165,431 | $2,461,127 | $7,810,354 |
| Expenses | $1,407,958 | $2,591,978 | $2,838,423 |
| EBITDA | ($1,242,527) | ($130,851) | $4,971,931 |
II. Shoutmouth Overview
What is Shoutmouth?
Shoutmouth is an operating company of The Kisco Group Inc. (TKG). Since 2003, TKG has capitalized on web-based marketing opportunities via launching targeted websites and generating web-based leads. TKG revenues in 2005 exceeded $1.3 million and grew to $3.5 million in 2006. Shoutmouth is currently the sole focus of TKG; all other TKG business units have been divested.
Development of Shoutmouth began in August 2006 and the site officially launched on February 21, 2007. Shoutmouth (located at www.shoutmouth.com) is the most comprehensive music news community on the Internet. The website covers 1,200 popular bands and music artists and offers more than 100 new music articles each day. In addition to providing news, Shoutmouth is a web community. That is, Shoutmouth members can actively participate on the site, by doing things such as commenting on news stories and submitting their own stories.
The Market Size and Need for Shoutmouth
The music market is clearly vast. According to IFPI, which represents the recording industry worldwide, global music sales were $33.5 billion in 2005, with the U.S. accounting for $12.3 billion of that amount. Importantly, digitally music sales are seeing substantial growth, with IFPI reporting sales of $400 million in 2004, $1.1 billion in 2005 and $2 billion in 2006.
Online, music is the one of the most frequently searched and accessed interests. For example, according to Wordtracker, the music artist Eminem received over 1.7 million web searches in December 2006, while band Green Day received 534,000 searches.
To put these figures in perspective, top celebrities in other entertainment fields receive but a fraction of this search volume. For example, December 2006 search volumes for select sports stars and actors were as follows: Kobe Bryant, 122K; Tiger Woods, 88K; Cameron Diaz, 332K; and Tom Cruise, 82K.
Conversely, 225 music artists received over 100,000 searches in December 2006, and over 500 music artists received over 25,000 searches.
This data is corroborated by Nielsen BuzzMetrics which plots the most popular topics bloggers are posting about. The chart to the right plots September 25, 2006 to March 25, 2007 and shows how music dominates other entertainment sectors online.
When searching for music artists online, fans, which are primarily between the ages of 13 and 35, are looking for news, pictures, lyrics, videos and audio files. In addition, fans enjoy publicly voicing their opinions about music and interacting with other fans.
There is currently no website besides Shoutmouth that provides comprehensive music news. Currently, to get the latest news on their favorite artists, fans must visit the official websites or fan websites of each of the artists they like . Even then, it is unlikely that the fan will get all the news that has occurred. To solve this problem, Shoutmouth scours the web and uncovers news from thousands of web sites.
What Shoutmouth Does and Will Offer
As of May 2007, the site covers the 1,200 most popular music artists (popularity primarily based on the number of web searches over the past 12 months for each artist).
Shoutmouth currently offers members the ability to:
- Read over 500 new music articles each week
- Read special features such as album reviews, interviews, new album release dates, top quotes of the week and other special reports
- Watch and rate music videos
- Listen to select music audio clips
- Comment on news stories and music videos
- Submit news stories that they see/hear of elsewhere
- Suggest new music artists to add to the site
- View articles by music artist or by genre (current genres include Rock, Pop, Rap, R&B, Country, and Electronic)
- Create a user profile that includes their favorite music artists, Shoutmouth friends, news stories submitted to Shoutmouth, and comments made. Members have the ability to find other members based on their favorite artists and via our search functions.
- Receive customized news and email alerts. Members can customize their “My News” page to include only artists they specify. Likewise, they can choose to receive email alerts whenever there is a new story on one of their favorite artists.
While establishing itself as the premier music news community, Shoutmouth will embark on the more aggressive goal of becoming the premier music community online . To accomplish this, Shoutmouth will begin to offer additional content (more videos, audio, pictures, lyrics, etc.) and additional functionality (music compatibility testing (e.g., if you like this, you’ll like this), voting capabilities, member-to-member messaging, etc.). We have already begun mapping out our content and technology growths plans to achieve this goal upon financing.
Importantly, Shoutmouth expects to be able to add massive amounts of relevant content (e.g., lyrics, reviews, pictures, video files, audio files, etc.) via member submissions and moderation. This is the same way that YouTube has been able to quickly add millions of videos and Wikipedia has been able to add millions of articles. Importantly, since established music websites (e.g., MTV, RollingStone.com, Billboard.com, etc.) are not community based, they would have to hire thousands of staff members to rival the content that Shoutmouth will have.
How We Get and Publish Our News
Currently, news stories that appear on Shoutmouth are gathered from numerous online sources. Shoutmouth’s staff writers find these stories by using RSS and News feeds that cover thousands of websites. In addition, Shoutmouth community members have the ability to submit stories they find elsewhere.
Typical stories include factual information plus the insight of the author. Shoutmouth editors ensure that all stories are properly classified by artist and genre, and that duplicate articles are filtered out.
Over the past three months, Shoutmouth has developed a solid infrastructure, which we consider a core competitive advantage, that that allows us to provide comprehensive music news . This infrastructure includes:
- Setting up hundreds of RSS feeds based on comprehensive research regarding sites from which to receive feeds
- Training our editorial team regarding identifying a story and weeding out duplicates
- Assigning music artists among our five-person editorial team to better manage work flow and avoid duplicate articles
We are working on a system to ensure that member-submitted articles are automatically routed to the appropriate member of Shoutmouth’s editorial team to improve our efficiencies further.
Shoutmouth’s Goal to Break News First
The majority (approximately 90%) of Shoutmouth’s articles are currently developed by our in-house editorial team, while the balance is submitted by members. In addition, virtually all of our articles are based on information gleaned from other websites. As such, we are generally not the first to publish news; however we are the first and only site to publish all the news in one easily-accessible place. The one current exception is news which is published on bands’ official MySpace pages; Shoutmouth generally publishes articles on this news 24 to 48 hours before it is reported by other news or music sites (due to our efficiencies in finding news).
Shoutmouth realizes that it will gain a key competitive advantage, and will generate significant market buzz, if it is able to report on music news stories before other media sources . To accomplish this, we have begun contacting publicity departments at record labels to gain direct access to music news. We expect these contacts to enable us to gain immediate and sometimes exclusive access to news which will help further establish Shoutmouth as the canonical source for music news. We also plan to more aggressively solicit member submissions of new, buzzworthy news events and will consider offering rewards for unique substantiated news (much the way paparazzi are compensated).
III. Competition in the Online Music Market
This section of the business plan provides a competitive analysis, which is an overview of the competitive landscape, discusses both indirect and direct competitors and then details Shoutmouth’s competitive advantages.
Because consumer demand for music on the Internet is so great, there are a vast number of music websites. In summary, we consider most sectors of the online music market (which are discussed below) to be indirect competitors and potentially partners, rather than direct competitors, because none of them focus on music news.
The reason we believe that no one focuses on music news is that it is very difficult to do. Because news is very important to music fans, most music websites offer news. However, they primarily get their news from organizations such as CNN, Reuters, the Associated Press and BBC. These large organizations only write about the music stories that have mass appeal, which traditionally amounts to 8-10 music news stories per day. However, since music fans are often zealots when it comes to their favorite artists, they are not merely interested in cover stories. For instance, a U2 fan cares about any U2 news, particularly news that a non-U2 fan might consider insignificant.
In fact, because Shoutmouth is the sole one-stop shop for getting comprehensive music news, there might be an opportunity to license our content to other music websites.
Sectors of the Online Music Market
Shoutmouth specifically comPs in the community-based music news market. While players in this market represent direct competitors, Shoutmouth faces indirect competitors in the following markets:
- Community-Based Sites
- Community-Based News Sites
- Community-Based Music Sites
- Traditional Music Websites
- Official Artist and Fan Sites
Each of these markets is described below.
A. Community-Based Sites
Community-based sites, also known as social networking sites, are websites in which members can create profiles, leave comments throughout the site, and communicate with other members among other features.
A June 2006 report by Piper Jaffray entitled “Silk Road: Social Networking is Here to Stay” effectively sums up the power and longevity of social networking:
“We believe social networking sites have become a permanent part of the fabric of web applications and are rapidly becoming one of the most popular activities online, potentially impacting how other popular services such as email, IM, and maybe even search are accessed.
As a clear indication of the growth rate and scale of social networking, consider this: MySpace monthly page views have now surpassed MSN or AOL in the U.S. and are nearly 75% of the size of Yahoo!. Social networking has filled a gap that was left by all the existing portals and web services and it is fulfilling a very important and basic function for millions of users: allowing them to express themselves and connect with their friends, with the two functions tightly integrated.
The leading sites such as MySpace (News Corp), Facebook, and others are amassing significant power in the new landscape of the Internet and the existing Internet companies are likely to have to work with these newcomers as they may yield material control on the flow of traffic to other applications.”
Social networking sites such as MySpace.com, Facebook.com, Tagged.com, and TagWorld.com have educated consumers regarding the value of these sites and how to use them. Their success has spurred genre-specific social networks such as community-based/social networking news sites and music sites, which are discussed below.
Shoutmouth doesn’t view established social networking sites as competitors since these sites have a general focus. That is, members talk about all aspects of life, from dating to music to movies, etc. Conversely, Shoutmouth is solely focused on music.
B. Community-Based News Sites
Community-based news sites are sites in which members decide what’s newsworthy and what’s not. For instance, on Digg.com, the most prominent community-based news site, members “Digg” stories that they feel are most newsworthy. The stories that the community feels are most important rise to Digg’s homepage, while less important stories get little attention.
Digg’s one million members can submit stories, “digg” stories, and comment on stories. Digg focuses on general news with a slant towards technology, gaming and unique/sensational news. While Digg does have a Music area within its Entertainment section, this receives little focus. In fact, at the time of the writing of this plan, Digg’s music home page only includes one article submitted within the past 48 hours. Furthermore, Digg doesn’t pare down the music category into sub-categories such as Rock and individual music artists. Conversely, these sub-categories are the entire focus of Shoutmouth.
Other sites that are similar to Digg include Newsvine.com, Spotback.com and Gabbr.com. Of most relevance is the Digg-like site for music, Noisetap.com, which was launched by Ticketmaster in January 2007.
Like Digg, Noisetap.com allows members to submit and vote for music stories. Noisetap.com is organized by music genre and not by music artist. This most likely will not satisfy the needs of many music fans since they don’t have the ability to find news on the specific artists they care most about. Likewise, without a full-time staff actively researching and publishing news stories at the artist-level, Noisetap.com will never be able to offer the comprehensive news that Shoutmouth does.
While Shoutmouth is currently similar to community-based news sites in that members can submit stories and comment on the news they find most interesting, no established player in the market provides a comprehensive focus on music. In addition, Shoutmouth sees these sites as marketing partners as we have and will continue to submit our stories on them to increase our readership.
C. Community-Based Music Sites
There are many community-based music websites, although none focuses on music news such as Shoutmouth. Conversely, these sites generally give members the ability to create and listen to song play lists. The community acts to help individual members find new music and new friends based on similarities in their music tastes. Prominent sites in this genre include Last.fm, Finetune, Pandora, RadioBlogClub, MyStrands, iLike[1] and iJigg.
Last.fm is the most prominent community-based music site and is a good model with which to compare Shoutmouth. Likewise, we will benchmark our performance against Last.fm as we reach of goal of becoming the premier music news community and focus on becoming the premier music community.
According to Alexa, Last.fm is the 359th most visited site on the Internet. While Last.fm focuses on allowing members to create customized Internet stations based on their music tastes, the site has much additional content and social networking features. For instance, for each artist, Last.fm includes pictures, a bio, concert dates, discography, fans on Last.fm, and similar artists. Fans are also able to create journals and communicate with other fans. Key features that Last.fm doesn’t currently focus on include news and video.
D. Traditional Music Websites
Traditional music websites such as MTV.com, RollingStone.com, Billboard.com, NME.com, AOL Music, and Yahoo! Music tend to have many features such as news, reviews, pictures, videos and audio. While these sites are generally very well done and extremely popular, they are under-serving visitors in two core areas: music news and community .
These sites’ lack of music news stems from the difficulty in creating this news, specifically that it requires filtering through thousands of articles and websites to find relevant stories. Likewise, as discussed, these firms might wish to license our news content in the future.
Regarding community , none of the top music sites are thriving communities. Rather, either these sites offer no community features or they recently began offering select features (e.g., submitting reviews or commenting on articles). Even when available, the community features on these sites are afterthoughts and are not engrained within the core fabric of the sites.
While they haven’t been able to transform their current sites into communities, top music websites clearly understand the power of online music communities and have an appetite for them. For example, in January 2007, MTV invested in social networking website TagWorld. MTV also acquired RateMyProfessors.com and Quizilla.com (teen social network) in January 2007 and October 2006 respectively.
As mentioned previously, our vision is to build and incorporate additional technologies, and use our “army” of members to publish vast amounts of music content on Shoutmouth, in order to fully satisfy music fans and leapfrog traditional music sites in terms of their music content.
E. Official Artist and Fan Sites
Shoutmouth com’s with official music artist websites and fan websites. These sites often include news about the specific artist as well as pictures, videos and other relevant information.
On one hand, official music artist and fan websites are direct competitors to Shoutmouth. This is because some of these sites offer comprehensive news on the specific artist they cover. In addition, many offer forums, discussion boards or other ways to communicate with other fans.
However, two factors separate Shoutmouth from these types of sites: 1) breadth and 2) sophistication.
- Breadth : Most music fans love more than one artist. As such, in order to get the news they want, they would have to visit/join multiple fan or artist websites rather than getting all of their news from Shoutmouth.
- Sophistication : While some official music artist websites are technologically sophisticated, offering forums, networking and other worthwhile features, the majority of artist and fan websites have limited usability, functionality and networking ability. In fact, this deficiency has lead to the success of MusicToday, which provides front and back-end technology to power artist websites.
Specifically, MusicToday offers web design and hosting, develops sophisticated online stores, builds online fan clubs and offers web ticketing among other services to select top music artists such as Dave Matthews Band, Christina Aguilera, Kenny Chesney, Britney Spears and Usher. While offering sophisticated tools for select music artist websites, MusicToday offers little to no music news nor advanced social networking functions. For instance, the official Dave Matthews Band website offers less than one news story per month.
F. Direct Competitors: Community-Based Music News Sites
Shoutmouth’s direct competitors are other music news websites that have social or community features that allow users to join the site, submit articles, comment on articles, create public profiles and/or communicate with other members. Shoutmouth has identified one significant player who offers this service, AbsolutePunk.net.
AbsolutePunk.net has done a good job of building a user base (the site claims 125,000+ registered members and nearly 500,000 un-registered members). In addition, the user base is very active — the average story on their site receives approximately 20 comments. AbsolutePunk.net offers music news, reviews, pictures and interviews among other features.
On the negative side, AbsolutePunk.net’s articles are generally posted by one staff writer (as opposed to Shoutmouth’s five writers), most articles are simply one sentence posts rather than full articles, and no attempt seems to have been made to cover all news stories. In addition, the site only covers the punk music genre. Although “punk” is broadly defined on the site, the site doesn’t cater to genres such as R&B, rap and country among others, failing to satisfy the broader market.
AbsolutePunk.net is owned by Indieclick, a Los Angeles-based media company. According to the AbsolutePunk.net website, the site:
- Has developed a loyal (72% return rate) reader base
- 5,182,147 Posts
- 163,535 Threads
- 126,448 Members
- 1,711 Artist Profiles
- 20,774 Multimedia Files
- Approx 76,000 visits per day.
- Approx 276,000 pageviews per day.
Shoutmouth’s Competitive Advantage
In addition to being the first to fill the untapped market void for comprehensive music news, Shoutmouth’s competitive advantage in the market primarily includes the following:
Online Marketing Sophistication
Content Development Experience and Expertise
Shoutmouth’s team, primarily team members DL and PF, has operated an affiliate marketing business focusing on music for the past four years. Affiliate marketing is defined as a system of revenue sharing between one site (the affiliate) which features an ad or content designed to drive traffic to another site (the merchant). The affiliate receives a fee based on traffic to the merchant which converts to sales.
Our affiliate business has focused on connecting music fans, primarily aged 13 to 30, with music offers such as iPods and ringtones. Over the past two years, we have successful sold affiliated offers to over 500,000 customers. We have become a significant online advertiser, receiving Google’s “over 1 million leads” award, and are recognized as a major player among the top affiliate networks.
It is important to note that affiliate marketing success has been credited with part of MySpace’s success. This is because effective affiliate marketers understand how to drive and convert on Internet traffic.
Shoutmouth will employ its affiliate marketing techniques to drive traffic to Shoutmouth.com and enroll members. We will utilize technologies and proprietary techniques that allow us to monitor multiple metrics such as the cost per visitor, cost per member sign-up, etc., so that we can set and maintain profitable metrics.
Another venture that Shoutmouth team members, primarily PK and DL, launched was the development of over 3,000 niche websites. To create the content for these websites, we employed a virtual work force of over 90 researchers in India and 30 writers and editors in the US.
This experience taught us how to manage a large workforce, train writers to improve content quality and motivate a large group of people. These skill sets will be critical in allowing Shoutmouth to grow the content of the site, as developed by both staff and members, while maintaining quality standards.
IV. Marketing Plan
Shoutmouth’s marketing plan includes the following:
Online Advertising : Shoutmouth will initiate pay-per-click advertising campaigns on Google and Yahoo! in order to inexpensively drive traffic to the site. Specifically, Shoutmouth believes it can drive qualified traffic to the site for 20 cents per visitor and achieve a 20% member conversion rate, thus generating members at a cost of $1.00 per member.
Keys to Shoutmouth’s success in achieving this metric include:
- Conducting thorough keyword research and advertising on appropriate keywords and keyword groups
- Creating advertising text that maximizes click through rates
- Creating landing pages that maximize conversions while maintaining the highest Google AdWords quality score possible
- Closely monitoring conversions to quickly stop and/or modify unprofitable campaigns
- Getting individuals to enter their email address to join the newsletter is much easier than getting them to join a site where they have to create a username, select a password, etc. As such, step one will be to get visitors to sign up for artist-specific newsletters.
- Once on the newsletter distribution list, members will constantly receive messages (embedded in their daily newsletter) regarding the benefits of participating more on Shoutmouth.
- Active Shoutmouth Membership: the constant reminders regarding Shoutmouth’s value proposition in the daily newsletters will influence members to participate more actively on the site (e.g., customize their profile, visit the site more often, etc.).
Invite-A-Friend : Shoutmouth is in the process of creating an aggressive invite-a-friend/member referral program. In doing so, we are following the lead of social movie community, Flixster, which grew to 5 million members within 10 months. It did this by encouraging members, during their initial registration process, to upload and send an invitation to multiple contacts in their email address books. The technology to develop this process is fairly complex and we expect to be completed with and to rollout this program in June 2007.
Direct Email Marketing : Shoutmouth will directly contact bloggers and prominent music fans we find online to tell them about Shoutmouth, encourage them to join, and encourage them to write about Shoutmouth on their blogs and online journals .
Creating/Distributing Buzzworthy/Viral Content : Shoutmouth plans to have several buzzworthy/viral articles (i.e., content that people would want to email to their friends since it is funny, interesting, etc.) on the site each day. With a single click, visitors will be able to send these articles to social bookmarking sites such as Digg.com or Fark.com, where these articles could receive widespread attention. In addition to our traditional news stories, Shoutmouth will also periodically create special reports/features in order to satisfy our members and visitors and to try to get widespread exposure.
An example of the power of such buzzworthy content, Shoutmouth has already succeeded in having two stories accepted by Fark and Digg, which have brought in over 50,000 unique visitors.
Super Fans/Street Team Development : Shoutmouth also plans to recruit “super fans.” Super fans are individuals who are passionate about a certain music artist/band and actively contribute articles and/or comments on Shoutmouth. We will recruit these fans, reward them with status (e.g., adding a gold Shoutmouth headphones image to their profile page) and encourage them to more aggressively promote the site by:
- Submitting more news to Shoutmouth
- Commenting on more articles on Shoutmouth
- Growing the Shoutmouth community around their favorite artist(s) by actively recruiting new members to join the site (such as actively posting Shoutmouth-related comments on their MySpace pages, on other music forums, etc.)
Public Relations : Upon financing, Shoutmouth will hire a public relations firm to help us get mentions in media sources ranging from magazines, newspapers, radio, television and blogs. To date, we have developed and issued press releases via Billboard Publicity Wire which have been syndicated throughout the web. An effective PR firm will enable Shoutmouth to quickly reach a wide audience.
Widgets : Shoutmouth will create artist-specific and genre-specific music news widgets. For example, our U2 widget (see example on right) would include all of the recent U2 articles published on Shoutmouth. The widget can easily be placed on MySpace pages, blogs, etc. Each story title in the widget links to the full article on Shoutmouth.
Shoutmouth has great expectations for our widget. To begin, no such widget currently exists as there is no one place to get comprehensive news for specific music artists. Secondly, each time someone places a Shoutmouth widget on their blog or social networking page, it will effectively market Shoutmouth to a wide audience at zero cost to us.
V. Technology/Site Development Plan
This section provides a brief roadmap of the initial and future functionality of Shoutmouth.
Initial Site Functionality
The initial Shoutmouth website will include the following features:
- Ability to submit and comment on news stories
- Ability to suggest new music artists to add to the site
- Ability to create user profiles
- Ability to receive customized news and email alerts
- Articles categorized by artist and core genre (e.g., Rock, Rap, Pop, etc.)
- Music artist sections which includes News, Bio and Fans
Future Site Functionality
Shoutmouth will use news and basic functionality as the platform though which we will build a thriving music community. After initial launch, the Shoutmouth technology team will work on incorporating additional features such as:
- Ability to message other members via the site (e.g., members will have an Inbox on the site)
- Event calendars: members will receive online calendars. With the click of a button, the member will be able to add tour dates of their favorite artists/bands to their calendar.
- Articles also categorized by sub-genre (e.g., Alternative Rock, West Coast Rap, etc.)
- Music artist sections to also include videos, audio files, photo galleries, reviews and event calendars to which members can upload files and vote on top content.
- Forums and member blogs
- Music compatibility testing (suggestions on song/artists members might like)
- Trivia quizzes
- Music playlists
VI. Financial Plan
Revenue Model
During the first six months, Shoutmouth will not generate any revenues as it will not sell advertising space nor offer products for sale. This decision has been made to spur the growth of the Shoutmouth community. By initially positioning Shoutmouth more as a non-profit, for-the-people-by-the-people venture, members will be more prone to promote the site and invite their friends than if the site looks too commercial.
Starting in September 2007, Shoutmouth will primarily generate revenues from selling advertising space. As technologies (such as the Snocap music widget) evolve that allow us to seamlessly integrate music sampling and purchasing on our site, sales of downloadable music are also expected to be a significant revenue source. To a lesser extent, we may sell other music-related items such as ringtones, concert tickets, and apparel.
Funding To Date
To date, Shoutmouth’s founders have invested $500,000 in Shoutmouth, with which we have accomplished the following:
- Built the site’s core technology
- Hired and trained our core staff (we currently maintain an 11-person full-time team)
- Populated the website with content (over 10,000 articles and 1,200 artist bios)
- Generated brand awareness among music fans, including driving 50,000 unique visitors in March, 100,000 unique visitors in April, and 200,000 unique visitors in May 2007.
Funding Requirements/Use of Funds
Shoutmouth is currently seeking $3 million to provide funding for the next 24 months. At this point, the site will be profitable and can grow organically, or additional capital may be sought to more aggressively expand our member base.
The capital will be used as follows:
- Execution of Marketing plan : in order for Shoutmouth to grow its visitor and member base, we need to invest dollars in online advertising and public relations. With regards to online advertising, we are confident that we can enroll members at a cost of $1 per member, which is a fraction of the value of the members to an acquirer (minimum $25 per member), thus providing a significant return on our marketing investments.
- Execution of Technology plan : in order to build a thriving community, Shoutmouth needs to offer its visitors a “stickier” website and enhanced features. We currently maintain a vast “wish list” of features, such as members uploading and rating pictures and videos, trivia quizzes, and member-to-member messaging, that will significantly improve the site’s functionality and value proposition.
- Staffing : In order to reach our goals, we will have to hire additional technical and operations personnel.
Financial Projections
Below is an overview of Shoutmouth’s Financial Projections for the next three years. Please see the Appendix for the full financial projections and key assumptions.
Exit Strategy / Valuation Metric
Shoutmouth’s most likely exit strategy is to be acquired by a traditional music website or property (e.g., Viacom/MTV, Ticketmaster, Rolling Stone), an entertainment/media conglomerate (e.g., Yahoo!, IAC/InterActiveCorp, NBC), or a large social networking site (e.g., News Corp/MySpace).
This strategy is supported by the significant M&A activity in the social networking market, which includes the following transactions over the past 24 months:
| Del.icio.us | social bookmarking | 12/05 | $30-$35 million | Yahoo! |
| eCrush Inc. | teen social network | 01/07 | Undisclosed | Hearst Magazines Digital Media |
| FanNation | sports social networking | 01/07 | $20+ million | Sports Illustrated |
| Five Across Inc. | social networking | 02/07 | Undisclosed | Cisco Systems Inc. |
| Flickr | photo uploading and sharing community | 03/05 | $15-35 million (rumored) | Yahoo! |
| Grouper | video creating, uploading and sharing community | 08/06 | $65 million | Sony Pictures |
| Jumpcut | video creating, uploading and sharing community | 09/06 | $15 million (rumored) | Yahoo! |
| KiwiBox.com | teen social network | 02/07 | Undisclosed | Magnitude Information Systems, Inc. |
| MyBlogLog | blog community tool | 01/07 | $10 million (rumored) | Yahoo! |
| MySpace | social networking | 07/05 | $580 million | News Corp. |
| Quizilla.com | teen social network | 10/06 | Undisclosed | Viacom/MTV Networks |
| RateMyProfessors.com | community focused on rating college professors | 01/07 | Undisclosed | Viacom/MTV Networks |
| social news site | 10/06 | Undisclosed | Conde Nast/ Wired Digital | |
| Sconex.com | social network for high school students | 03/06 | $6.1 million | Alloy Inc. |
| TelevisionWithoutPity.com | TV fan site | 03/07 | Undisclosed | Bravo |
| Weblogs Inc. | blogging network | 10/05 | $25 million (rumored) | AOL |
| YouTube | video community | 10/06 | $1.65 billion | Google Inc. |
Regarding valuation, below are the estimated valuations of social networking companies on a per member basis upon exit:
- Del.icio.us: $50 – $100 per member
- MySpace: $25 per member
- Xing (business social network): $137 per member at IPO in 10/06
- Flickr: $56 – $130 per member
- Grouper: $130 per member
Based on this data, not only are social networking sites a promising investment, but sites that can acquire members for less than $25 each (a conservative valuation estimate based on the figures above), should earn a solid return on investment. As discussed above, Shoutmouth’s goal is to acquire members for no more than $1 each.
In addition, per the membership projections above, Shoutmouth’s valuation at the end of 2009, at a $25 valuation per member, is expected to be $239 million. A more conservative, using a 24.4 time EBITDA multiple (the average multiple of tech M&A deals in 2006 according to The M&A Advisor), yields a $121 million valuation in 2009.
Shoutmouth’s founding team includes entrepreneurs and managers with a track record of success and a history of successfully working together.
Management Team
DL, Co-Founder and CEO
D has a history of successfully launching and growing businesses of all sizes. As president and co-founder of an entrepreneurial services firm., D has personally assisted in the launch and development of over 100 ventures.
Over the past three years, D founded and has managed The Kisco Group which includes an affiliate marketing division (2006 revenues exceeded $3 million), a search engine optimization business which includes a network of 3,000 websites (2006 revenues exceeded $500,000) and an e-commerce business (which includes TopPayingKeywords.com and ShowerHeadsEtc.com).
D earned his Bachelors degree from the University of South Carolina.
PK, Co-Founder and Vice President of Operations
For the past two years, P has managed The Kisco Group’s search engine optimization business where he hired, trained and managed nearly 100 employees and a dozen outside firms. During this time, P has honed his management skills with regards to content development, marketing and operations.
P has had a passion for music since childhood and has been a semi-professional drummer for the past 15 years.
P earned his Bachelors of Arts degree, magna cum laude, from Clemson University.
PF, Co-Founder and Vice President of Technology
For the past year, P has managed The Kisco Group’s affiliate marketing business. In addition to setting up and managing widespread marketing campaigns, P has developed sophisticated analytic techniques to precisely analyze web traffic in order to optimize profitability.
Since August 2006, P has shifted his efforts and leveraged his technology skills in developing the Shoutmouth website. P has been instrumental in selecting the Content Management Platform upon which Shoutmouth is built, and finding and managing the technology team.
P earned his Bachelor of Arts degree from Swarthmore College.
AB, Marketing Manager
A’s background in music includes being a singer, songwriter, guitarist and producer. He has also worked on the marketing side of music, having marketed Veritas Records through the development and distribution of promotional materials.
A’s career also includes psychological research and administration, having served as a Research Assistant with the Interpersonal Perception And Communication Laboratory in Cambridge, MA.
A earned his Bachelor of Arts degree in Psychology from Ohio State University.
M, Lead Technology Developer
M is an experienced web programmer with expertise in web design, application development and database development among others.
M’s work experience includes serving as a Senior Developer at Spheres. M has also engaged in multiple, long term freelance projects including serving as a Database Developer Consultant with The Penn Group and a Web Developer Consultant with Volution Media Group and Allied Online Consulting Group.
M earned his Bachelors degree in Computer Science with a minor in Cognitive Science from Rutgers University.
Content Development Team
Shoutmouth’s writing team, managed by PK, includes the following members:
- JS, Editorial Manager: former content manager and copywriter for Scholastic Inc. and Promotions.com.
- TZ: former music intern (Virgin Records and WRRV) and author of the blog, The Tom Z Show .
- ML: former assistant editor for Adventure Publishing; author of the blog Certified Gangsta ; and former editor-in-chief of Fordham University’s newspaper The Paper .
- SB: former staff writer for Paste Magazine , The Clarion Ledger , and Nightclub and Bar Magazine among others.
- CSJ: former editorial intern for Rolling Stone and Editorial Assistant for Psychology Today .
Outsourced Technology Team
Shoutmouth works very closely with 2skies, a technology firm based in Australia with staff in Australia and the United States. 2skies is run by JDN, one of the co-founding developers of XE, the platform upon which Shoutmouth is built.
XE is an extensible, Open Source web application framework written in PHP and licensed under the GNU General Public License. XE delivers the requisite infrastructure and tools to create custom web applications that include fully dynamic multi-platform Content Management Solutions (CMS).
VIII. Appendix: Shoutmouth Financial Projections 3-Year Income Statement
| Total Page Views (MILLIONS) | |||
| Revenues | $165,431 | $2,461,127 | $7,810,354 |
| Staffing | $891,058 | $1,328,078 | $1,522,923 |
| Outsourced Technology | $115,000 | $60,000 | $60,000 |
| Office Space | $26,400 | $90,000 | $90,000 |
| Advertising | $254,000 | $900,000 | $900,000 |
| Other Marketing/Public Relations | $72,000 | $120,000 | $150,000 |
| Web Hosting | $11,500 | $33,900 | $55,500 |
| Other | $38,000 | $60,000 | $60,000 |
| $1,407,958 | $2,591,978 | $2,838,423 | |
| ($1,242,527) | ($130,851) | $4,971,931 | |
| Depreciation | $1,600 | $4,200 | $5,800 |
| ($1,244,127) | ($135,051) | $4,966,131 | |
| Income Taxes @ (40%) | ($497,651) | ($54,020) | $1,986,452 |
| Income Taxes Paid | $0 | $0 | $1,434,781 |
| Income Tax Credit | ($497,651) | ($551,671) | $0 |
| ($1,244,127) | ($135,051) | $3,531,350 |
3-Year Balance Sheet
As of December 31
| Cash | $1,845,206 | $1,614,336 | $4,726,360 |
| Accounts Receivable (30 days) | $13,597 | $202,284 | $641,947 |
| Inventory | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Current Assets | $1,858,803 | $1,816,620 | $5,368,307 |
| Other Assets | |||
| Equipment (Computer systems, office equipment, etc.) | $16,000 | $26,000 | $32,000 |
| Accumulated Depreciation | ($1,600) | ($5,800) | ($11,600) |
| Total Long-Term Assets | $14,400 | $20,200 | $20,400 |
| $1,873,203 | $1,836,820 | $5,388,707 | |
| Accounts Payable (30 days) | $117,330 | $215,998 | $236,535 |
| Total Current Liabilities | $117,330 | $215,998 | $236,535 |
| Long Term Debt | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Paid In Capital | $3,000,000 | $3,000,000 | $3,000,000 |
| Retained Earnings | ($1,244,127) | ($1,379,178) | $2,152,172 |
| Total Equity | $1,755,873 | $1,620,822 | $5,152,172 |
| $1,873,203 | $1,836,820 | $5,388,707 |
3-Year Cash Flow Statement
| Net Income/Loss | ($1,244,127) | ($135,051) | $3,531,350 |
| Depreciation | $1,600 | $4,200 | $5,800 |
| Minus Increase in Accounts Receivable | ($13,597) | ($188,687) | ($439,663) |
| Plus Change in Current Liabilities | $117,330 | $98,668 | $20,537 |
| Net Cash Flow from Operating | ($1,138,794) | ($220,870) | $3,118,024 |
| Purchases of Property & Equipment | ($16,000) | ($10,000) | ($6,000) |
| Net Cash Flow from Investing | ($16,000) | ($10,000) | ($6,000) |
| Cash Received from Investors | $3,000,000 | $0 | $0 |
| Net Cash Flow from Financing | $3,000,000 | $0 | $0 |
| $1,845,206 | ($230,870) | $3,112,024 | |
| $1,845,206 | $1,614,336 | $4,726,360 |

- Grades 6-12
- School Leaders
FREE Ice Cream Coloring Pages! 🍦
30 Lesson Plan Examples for Every Grade Level and Subject
Lots of ways to prepare for top-notch learning.

Lesson planning: Most teachers either love it or hate it. Either way, it’s something every teacher has to spend at least some time doing, so it’s worth learning to do well. Whether you’re a brand-new teacher or an experienced educator looking for some new ideas, these lesson plan examples offer inspiration for every subject and every grade level.
Lesson Plan Sections
Preschool lesson plan examples, elementary school lesson plan examples, middle and high school lesson plan examples.
Many lesson plans include some or all of the following sections.
- Objective : These should be specific and measurable. Often they align with Common Core or other learning standards.
- Materials: List any items you’ll need, including worksheets or handouts, school supplies, etc.
- Activities: This is usually the longest section, where you’ll lay out what the lesson and its activities look like. Some teachers write these in great detail. Others include just an overview to help them plan.
- Assessment : How will you assess your students’ learning? This could be a formal assessment or something simple like an exit ticket.
- Differentiation : Describe how you’ll vary the level of difficulty for students at all levels, including any enrichment for early finishers.
Some people think preschool is just playtime, but pre-K teachers know better! Here are some of the ways preschool teachers plan for their lessons.
Weekly Lesson Plan
Weekly preschool lesson planning helps you plan each day and ensure you’re tackling all the most important skills.
Learn more: Pre-K Weekly Lesson Plan
Pre-K Theme Lesson Plan
If you like to plan by theme, try a template like this. It includes space for a variety of activities that fit your topic.
Learn more: Pre-K Theme Lesson Plan
Alphabet Letter Lesson Plan
If you’re focusing on a new letter of the alphabet each week, try lesson planning like this. You can see the week at a glance, including all the materials and books you’ll need.
Learn more: Alphabet Letter Lesson Plan

Centers Lesson Plan
Your centers need some planning too! Whether you change them out weekly, monthly, or as needed, use plans like these to stay prepared.
Learn more: Centers Lesson Plan

Weekly Unit Lesson Plan
Adding pops of color and a few images can make it easier to locate the lesson plan you’re looking for in a snap.
Learn more: Weekly Weather Unit Lesson Plan
Since elementary teachers tackle multiple subjects every day, their lesson plans might look like a general overview. Or they may prepare more detailed lesson plans for each topic to help them stay on track. The choice is up to you.
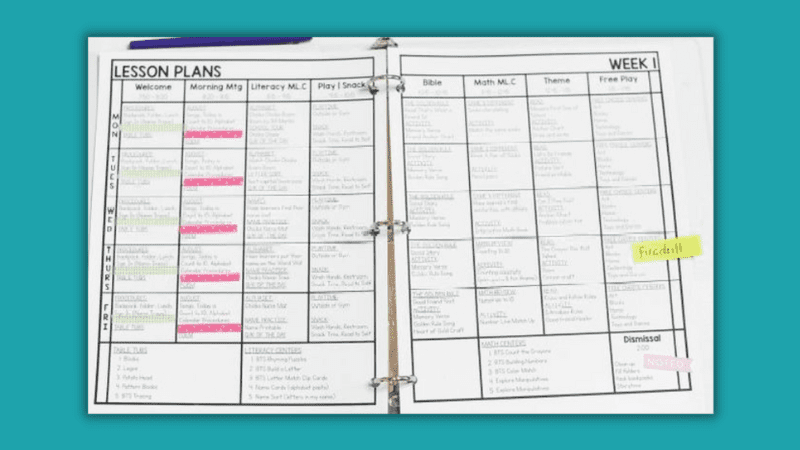
Weekly Overview Lesson Plan
Don’t be afraid to write out your lesson plans by hand! A side-by-side setup like this lets you see a whole week at once. We love the use of color to highlight special things like fire drills.
Learn more: Elementary Weekly Overview Lesson Plan
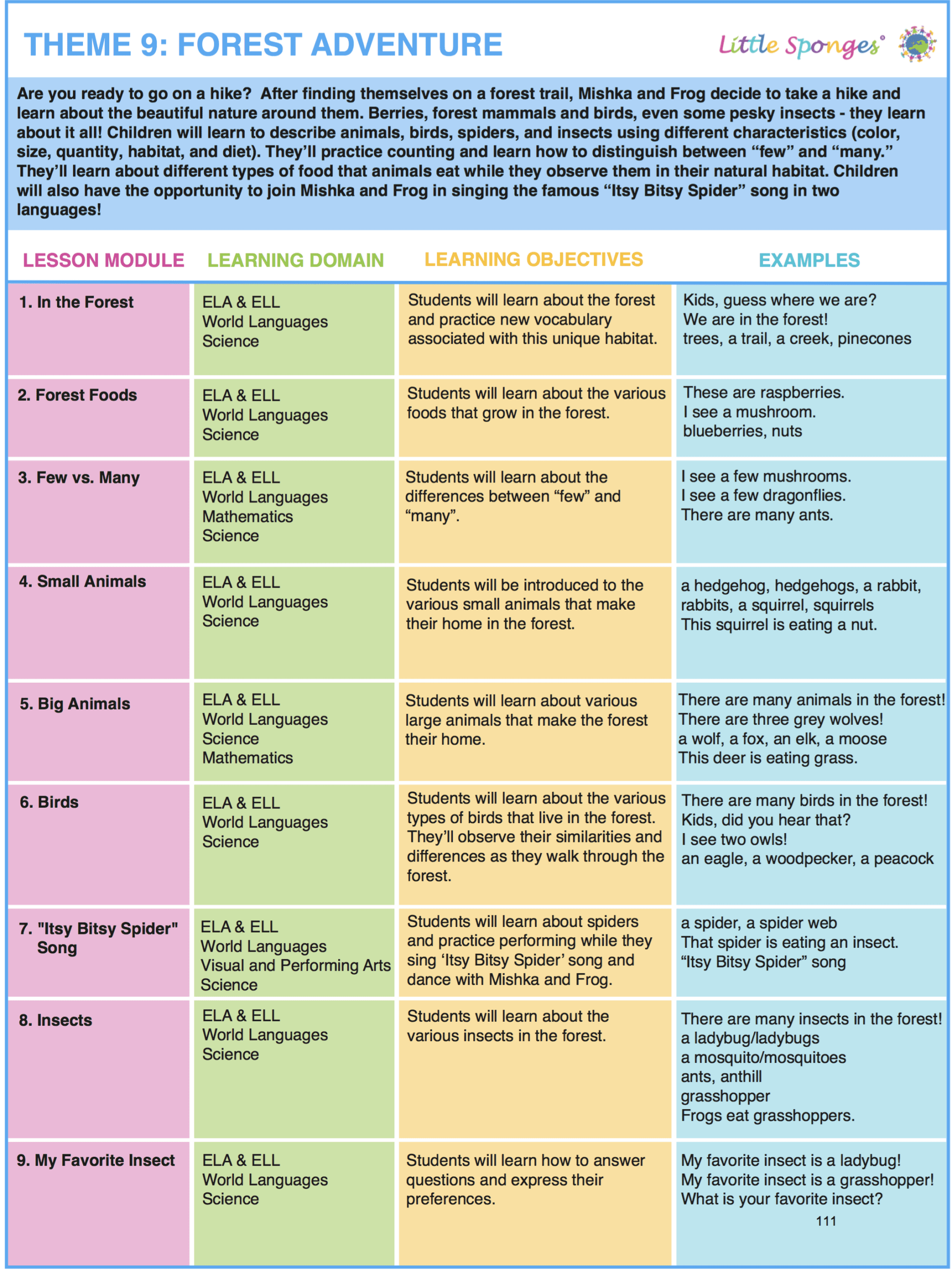
Unit Lesson Plan
Planning out a unit helps ensure you cover all the important topics and meet your learning objectives.
Learn more: Unit Lesson Plan
Yearlong Schedule
Planning a whole year may seem daunting, but it can show you where you’re going to need to stretch a unit and where you can circle back and review. Mrs. D from Mrs. D’s Corner has ideas on how to structure a yearlong lesson plan using Google Sheets.

Guided Math Lesson Plan
This example on adding three numbers together can be altered to fit any math lesson plan.
Learn more: Guided Math Lesson Plan

Art Lesson Plan
While these are elementary art lesson plan examples, you can easily use this style for teaching art at upper levels too.
Learn more: Art Lesson Plans
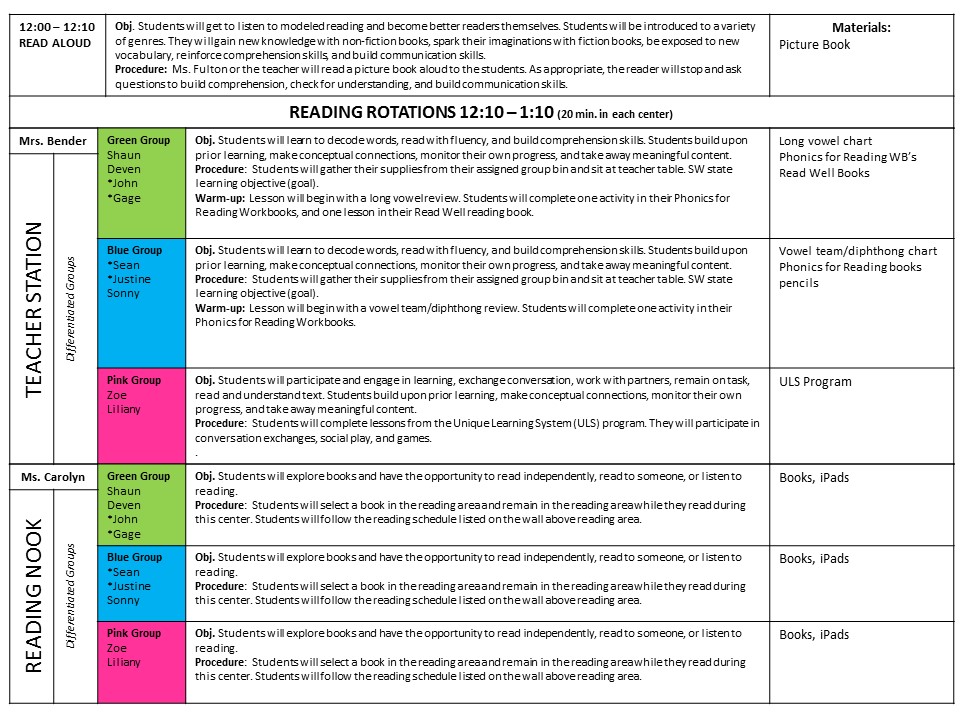
Special Education Lesson Plans
Lesson planning for special education looks different than general classroom lessons in that the lessons have to cover specific IEP goals and include lots and lots of progress monitoring. The Bender Bunch starts each lesson with independent work (read: IEP practice) and then heads into mini-lessons and group work.
Learn more: Special Education Lesson Plan
Interactive Read-Aloud Plan
Interactive read-alouds take some careful planning. The Colorful Apple explains how to choose a book, get to know it, and get ready to teach it. Once you’re in the book, sticky notes may be the best lesson-planning tool you have for marking questions and vocabulary words you want to point out to students.
Learn more: Interactive Read-Aloud Plan

Social Studies Lesson Plan
Including images of your anchor charts is a great idea! That way, you can pull one out and have it ready to go in advance.
Learn more: Social Studies Lesson Plan
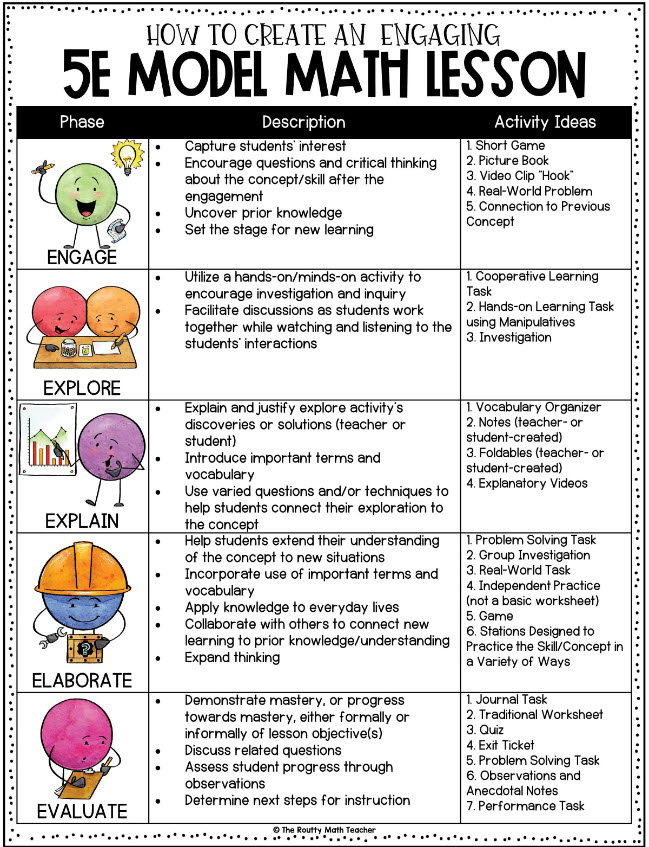
5E Lesson Plan for Elementary School
The 5Es stand for Engagement, Exploration, Explanation, Elaborate, and Evaluate. This type of lesson planning can be helpful for students as they work through each of the 5Es related to the topic you’re studying.
Learn more: 5E Lesson Plan for Elementary Math

Science Lesson Plans
If you like to plan your lessons in more detail, take a look at this elementary science lesson plan example.
Learn more: Science Lesson Plan Template
Reading Group Lesson Plan
Lots of elementary schools have differentiated reading groups. Use a template like this one to plan for each one, all on one page.

P.E. Lesson Plan
Gym teachers will love this lesson plan idea, which includes directions for playing the games.
Learn more: PE Lesson Plan
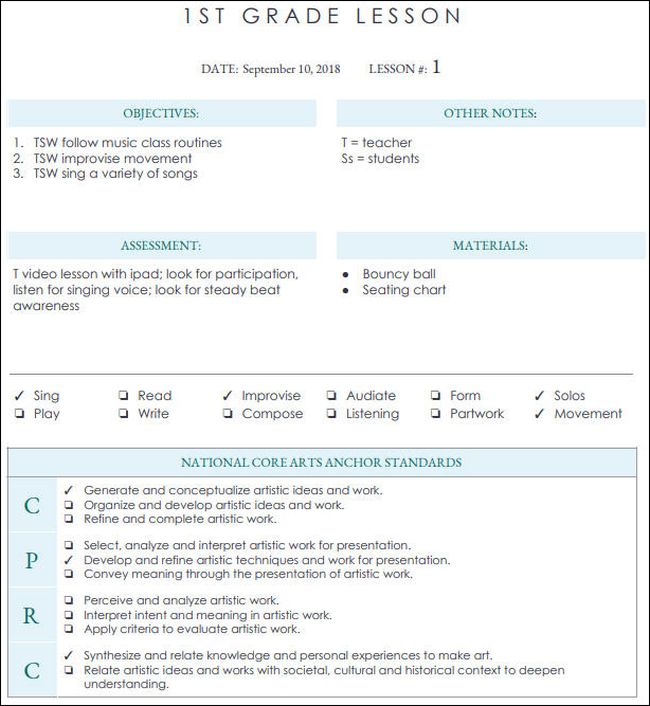
Music Class Lesson Plan
Plan out the skills and songs you’ll need for a meaningful music class with a lesson plan like this one.
Learn more: Music Class Lesson Plan
At the middle and high school levels, teachers often need more detailed plans for each class, which they may teach multiple times a day. Here are some examples to try.
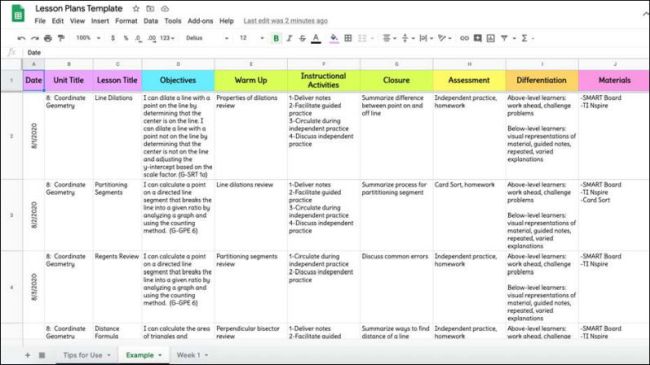
Google Sheets Lesson Plans
Google Sheets (or Excel) is terrific for lesson planning! Create a new tab for each week, unit, or class.
Learn more: Google Sheets Lesson Plan

Handwritten Lesson Plan
Some people really prefer to write things out by hand, highlighting important parts and making notes as they go. You can always convert this kind of plan to a digital format later if you need to.
Learn more: Handwritten Lesson Plan
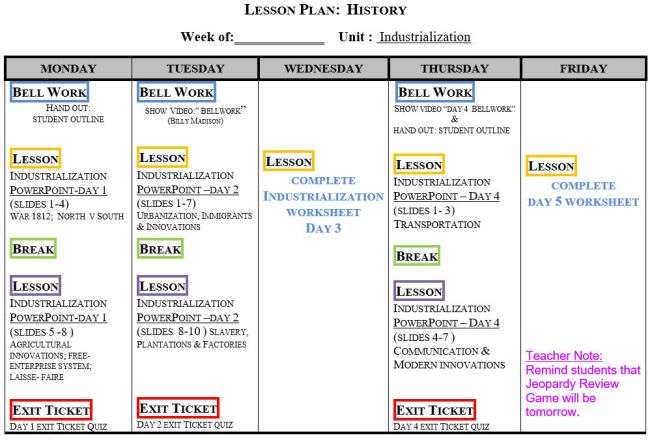
Weekly History Plan
This example shows how you can plan out a week’s worth of lessons at once, and see the entire week all in one spot. This example is for history, but you could use this for math, ELA, or social studies too.
Learn more: Weekly History Plan
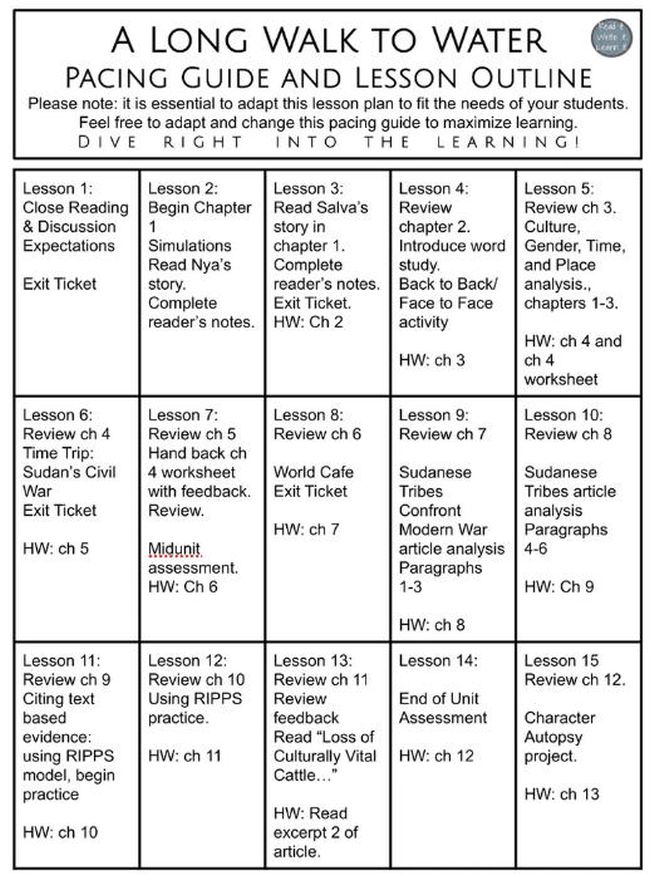
Outline and Pacing Guide Lesson Plan
A pacing guide or outline works for both you and your students. Share it at the beginning of a unit to let them know what’s ahead.
Learn more: Outline and Pacing Guide

5E Lessons in Middle and High School
5E lesson plans (Engagement, Exploration, Explanation, Elaborate, Evaluate) are great for middle and high school as well. This example is for science, but you can use the 5E structure across all lessons.
Learn more: Middle and High School 5E Lesson Plans

Sticky-Note Lesson Plan
At some point, you’ll know what students are doing each day, you’ll just need some reminders for questions to ask and key points to cover. The nice thing about using sticky notes for lesson planning is if you get ahead or behind schedule, you can move the entire sticky-note lesson to another day. ( Find more ways to use sticky notes in the classroom here .)
Learn more: Sticky Note Lesson Plan

Backwards Planning Lesson Plan
If your school uses backwards planning, you’ll be thinking about the outcome first and working back from there (rather than forward from an activity or task). Backwards planning lesson plans are intensive, but they’re also something you can use over and over, modifying them slightly for each group of students you have.
Learn more: Backwards Planning Lesson Plan

Visual Arts Lesson Plan
Detailed lesson plans take longer to prepare, but they make it easier on the day (especially if you wind up needing a sub).
Learn more: Visual Arts Lesson Plan Template

ELL or World Language Lesson Plan
Whether you’re teaching English-language learners (ELL) or a world language to English speakers, this lesson plan style is perfect.
Learn more: ELL/World Language Lesson Plan
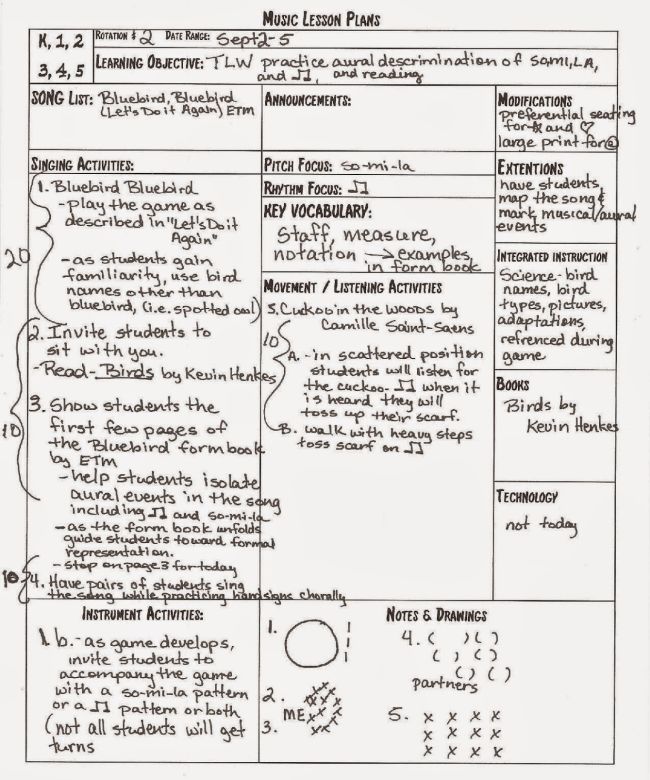
Music Lesson Plan
Use a lesson plan like this for choir, orchestra, band, or individual music lessons.
Learn more: HS Music Lesson Plan
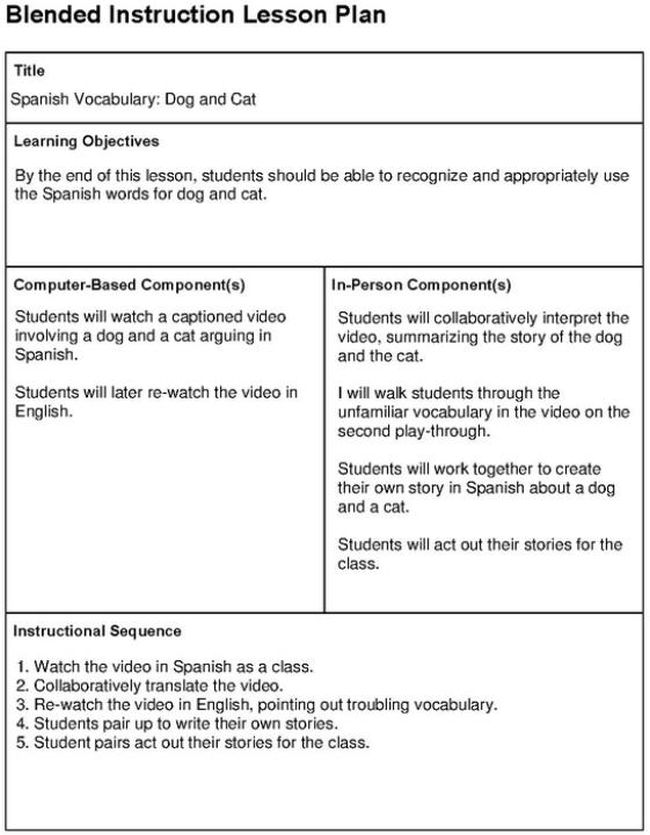
Blended Learning Lesson Plan
If your instruction includes both computer-based and in-person elements, this lesson plan idea might be just what you need.
Learn more: Hot Lunch Tray

One-Sentence Lesson Plan
This kind of lesson planning isn’t for everyone, but the extreme simplicity works well for some. Describe what students will learn, how they will learn it, and how they’ll demonstrate their knowledge.
Learn more: One-Sentence Lesson Plan
Need more help with lesson planning? Come ask for ideas in the We Are Teachers HELPLINE group on Facebook !
Plus, check out ways to make time for more creativity in your lesson plans ..

You Might Also Like
15 Inspiring Teaching Portfolio Examples (Plus How To Create Your Own)
Show them what you've got. Continue Reading
Copyright © 2024. All rights reserved. 5335 Gate Parkway, Jacksonville, FL 32256

Bookstore Business Plan PDF Example
- June 15, 2024
- Business Plan

Creating a comprehensive business plan is crucial for launching and running a successful bookstore. This plan serves as your roadmap, detailing your vision, operational strategies, and financial plan. It helps establish your bookstore business’s identity, navigate the competitive market, and secure funding for growth.
This article not only breaks down the critical components of a bookstore business plan, but also provides an example of a business plan to help you craft your own.
Whether you’re an experienced entrepreneur or new to the retail industry, this guide, complete with a business plan example, lays the groundwork for turning your bookstore business concept into reality. Let’s dive in!
Our bookstore business plan is structured to cover all essential aspects needed for a comprehensive strategy. It outlines the store’s operations, marketing strategy , market environment, competitors, management team, and financial forecasts.
- Executive Summary : Offers an overview of your bookstore’s business concept, market analysis , management, and financial strategy.
- Store & Location : Describes the store’s design, amenities, and why its location is appealing to potential clients.
- Supply & Products : Lists the types of books and related products provided by your bookstore, including pricing structure.
- Key Stats : Shares industry size , growth trends, and relevant statistics for the bookstore market.
- Key Trends : Highlights recent trends affecting the bookstore sector.
- Key Competitors : Analyzes main competitors nearby and how your bookstore differs from them.
- SWOT Analysis : Strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats analysis.
- Marketing Plan : Strategies for attracting and retaining customers.
- Timeline : Key milestones and objectives from start-up through the first year of operation.
- Management: Information on who manages the bookstore and their roles.
- Financial Plan: Projects the store’s 5-year financial performance, including revenue, profits, and expected expenses.

Bookstore Business Plan

Fully editable 30+ slides Powerpoint presentation business plan template.
Download an expert-built 30+ slides Powerpoint business plan template
Executive Summary
The Executive Summary introduces your bookstore’s business plan, offering a concise overview of your bookstore and its services. It should detail your market positioning, the range of books and related products you offer, its location, size, and an outline of day-to-day operations.
This section should also explore how your bookstore will integrate into the local market, including the number of direct competitors within the area, identifying who they are, along with your bookstore’s unique selling points that differentiate it from these competitors.
Furthermore, you should include information about the management and co-founding team, detailing their roles and contributions to the bookstore’s success. Additionally, a summary of your financial projections, including revenue and profits over the next five years, should be presented here to provide a clear picture of your bookstore’s financial plan.
Make sure to cover here _ Business Overview _ Market Overview _ Management Team _ Financial Plan
Business Overview
For a Bookstore, the Business Overview section can be concisely divided into 2 main slides:
Store & Location
Describe the bookstore’s design, comfort, and welcoming atmosphere. Highlight its location, accessibility, and convenience, such as proximity to public transportation, shopping centers, or ample parking. Explain why this location is ideal for attracting your target clientele.
Supply & Products
Detail the range of books and related products offered, including bestsellers, niche genres, and local authors. Include items like stationery, book-related merchandise, and e-books. Outline your pricing strategy , ensuring it reflects the market and quality of products. Highlight special offers, membership deals, and loyalty programs to encourage repeat visits and customer loyalty. Mention partnerships with local authors, book clubs, or schools to enhance community engagement.
Make sure to cover here _Store & Location _ Supply & Products
Market Overview
Industry size & growth.
In the Market Overview of your bookstore business plan, start by examining the size of the book retail industry and its growth potential. This analysis is crucial for understanding the market’s scope and identifying expansion opportunities.
Key Market Trends
Proceed to discuss recent market trends , such as the increasing consumer interest in diverse book genres, e-books, audiobooks, and sustainable products. Highlight the demand for personalized book recommendations, book clubs, and community events, alongside the rising popularity of independent and local bookstores.
Key Competitors
Then, consider the competitive landscape, which includes a range of bookstores from large chain stores to independent shops, as well as online book retailers. Emphasize what makes your bookstore distinctive, whether it’s through exceptional customer service, a unique selection of books, or community engagement activities. This section will help articulate the demand for bookstore services, the competitive environment, and how your bookstore is positioned to thrive within this dynamic market.
Make sure to cover here _ Industry size & growth _ Key competitors _ Key market trends

Dive deeper into Key competitors
First, conduct a SWOT analysis for the bookstore , highlighting Strengths (such as a unique book selection and knowledgeable staff), Weaknesses (including high operational costs or strong competition from online retailers), Opportunities (for example, increasing interest in local and independent bookstores and community events), and Threats (such as economic downturns that may decrease consumer spending on non-essential items).
Marketing Plan
Next, develop a marketing strategy that outlines how to attract and retain customers through targeted advertising, promotional discounts, engaging social media presence, and community involvement.
Finally, create a detailed timeline that outlines critical milestones for the bookstore’s opening, marketing efforts, customer base growth, and expansion objectives, ensuring the business moves forward with clear direction and purpose.
Make sure to cover here _ SWOT _ Marketing Plan _ Timeline

Dive deeper into SWOT
Dive deeper into Marketing Plan
The Management section focuses on the bookstore business’s management and their direct roles in daily operations and strategic direction. This part is crucial for understanding who is responsible for making key decisions and driving the bookstore business toward its financial and operational goals.
For your bookstore business plan, list the core team members, their specific responsibilities, and how their expertise supports the business.

Financial Plan
The Financial Plan section is a comprehensive analysis of your financial projections for revenue, expenses, and profitability. It lays out your bookstore business’s approach to securing funding, managing cash flow, and achieving breakeven.
This section typically includes detailed forecasts for the first 5 years of operation, highlighting expected revenue, operating costs and capital expenditures.
For your bookstore business plan, provide a snapshot of your financial statement (profit and loss, balance sheet, cash flow statement), as well as your key assumptions (e.g. number of customers and prices, expenses, etc.).
Make sure to cover here _ Profit and Loss _ Cash Flow Statement _ Balance Sheet _ Use of Funds

Related Posts

Bridal Shop Business Plan PDF Example
Bicycle Rental Business Plan PDF Example

Fashion Store Business Plan PDF Example
Privacy overview.
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| BIGipServerwww_ou_edu_cms_servers | session | This cookie is associated with a computer network load balancer by the website host to ensure requests are routed to the correct endpoint and required sessions are managed. |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-advertisement | 1 year | Set by the GDPR Cookie Consent plugin, this cookie is used to record the user consent for the cookies in the "Advertisement" category . |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-analytics | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Analytics". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-functional | 11 months | The cookie is set by GDPR cookie consent to record the user consent for the cookies in the category "Functional". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-necessary | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookies is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Necessary". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-others | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Other. |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-performance | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Performance". |
| CookieLawInfoConsent | 1 year | Records the default button state of the corresponding category & the status of CCPA. It works only in coordination with the primary cookie. |
| elementor | never | This cookie is used by the website's WordPress theme. It allows the website owner to implement or change the website's content in real-time. |
| viewed_cookie_policy | 11 months | The cookie is set by the GDPR Cookie Consent plugin and is used to store whether or not user has consented to the use of cookies. It does not store any personal data. |
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| __cf_bm | 30 minutes | This cookie, set by Cloudflare, is used to support Cloudflare Bot Management. |
| language | session | This cookie is used to store the language preference of the user. |
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| _ga | 2 years | The _ga cookie, installed by Google Analytics, calculates visitor, session and campaign data and also keeps track of site usage for the site's analytics report. The cookie stores information anonymously and assigns a randomly generated number to recognize unique visitors. |
| _ga_QP2X5FY328 | 2 years | This cookie is installed by Google Analytics. |
| _gat_UA-189374473-1 | 1 minute | A variation of the _gat cookie set by Google Analytics and Google Tag Manager to allow website owners to track visitor behaviour and measure site performance. The pattern element in the name contains the unique identity number of the account or website it relates to. |
| _gid | 1 day | Installed by Google Analytics, _gid cookie stores information on how visitors use a website, while also creating an analytics report of the website's performance. Some of the data that are collected include the number of visitors, their source, and the pages they visit anonymously. |
| browser_id | 5 years | This cookie is used for identifying the visitor browser on re-visit to the website. |
| WMF-Last-Access | 1 month 18 hours 11 minutes | This cookie is used to calculate unique devices accessing the website. |
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Welcome to the Purdue Online Writing Lab

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
The Online Writing Lab (the Purdue OWL) at Purdue University houses writing resources and instructional material, and we provide these as a free service at Purdue. Students, members of the community, and users worldwide will find information to assist with many writing projects. Teachers and trainers may use this material for in-class and out-of-class instruction.
The On-Campus and Online versions of Purdue OWL assist clients in their development as writers—no matter what their skill level—with on-campus consultations, online participation, and community engagement. The Purdue OWL serves the Purdue West Lafayette and Indianapolis campuses and coordinates with local literacy initiatives. The Purdue OWL offers global support through online reference materials and services.
Social Media
Facebook twitter.

Can we help you?

Supercharge your AI experience with Copilot Pro. Learn more
Maximize the everyday

- For business
Save 16% when you pay yearly for Microsoft 365
- Paid yearly
- Paid monthly
Microsoft 365 Family

- For one to six people
- Sign in to five devices at once
- Use on PCs, Macs, phones, and tablets
- Up to 6 TB of secure cloud storage
- Apps with premium features and offline access
- Identity, 1 data, and device security
- Ad-free secure email
Microsoft 365 Personal

- For one person
- 1 TB of cloud storage
Subscription automatically renews. Cancel anytime to stop future charges. 2 Already have a subscription?
Explore even more benefits of Microsoft 365

Simplify your online security
Keep you and your family safer online with continuous monitoring for threats, real-time alerts, tips, and expert guidance from Microsoft Defender.
Powerful productivity apps
Use Word, Excel, and PowerPoint to collaborate in real time or work offline.
Trusted storage for priceless memories
Quickly save, share, and edit your photos and files with OneDrive and Microsoft 365.
Make the most of your day
With Outlook as command central, you can spend less time organizing your life and more time enjoying it.

All your ideas in one place
Capture inspiration in text, audio, photos, and videos to create your next big idea with OneNote.

Tell your story, your way
Easily turn captured memories into beautiful videos with Clipchamp and Microsoft 365.
Compare Microsoft 365 with Office
Office home & student 2021.
Save with an annual subscription
Switch to an annual subscription and enjoy the full power of Microsoft 365 for less than paying monthly.
Office Home & Business 2021
- One-time purchase for 1 PC or Mac
- Classic 2021 versions of Word, Excel, PowerPoint, and Outlook
- Access to support experts

Frequently asked questions
What’s the difference between office 2021 (one-time purchase) and microsoft 365 (subscription).
Office 2021 is sold as a one-time purchase, which means you pay a single, up-front cost to get Office apps for one computer. One-time purchases are available for both PCs and Macs. However, there are no upgrade options, which means if you plan to upgrade to the next major release, you'll have to buy it at full price.
Microsoft 365 is a subscription that includes the most collaborative, up-to-date features in one seamless, integrated experience. Microsoft 365 includes the robust Office desktop apps that you’re familiar with, like Word, PowerPoint, and Excel. You also get extra online storage and cloud-connected features that let you collaborate on files in real time. With a subscription, you'll always have the latest features, fixes, and security updates along with ongoing tech support at no extra cost. You can choose to pay for your subscription on a monthly or yearly basis, and the Microsoft 365 Family plan lets you share your subscription with your family for up to 6 people, and use your apps on multiple PCs, Macs, tablets, and phones.
How do I know if my PC or Mac can run Microsoft 365?
Will microsoft 365 be identical on a pc and on a mac, do i keep control of my documents with a microsoft 365 subscription, is internet access required for microsoft 365.
Internet access is required to install and activate all the latest releases of apps and services included in all Microsoft 365 subscription plans. Note that if you are an existing subscriber, you do not need to reinstall or purchase another subscription.
For Microsoft 365 plans, Internet access is also needed to manage your subscription account, for example to install Office apps on other PCs or to change billing options. Internet access is also required to access documents stored on OneDrive, unless you install the OneDrive desktop app .
You should also connect to the Internet regularly to keep your version of Microsoft 365 up to date and to benefit from automatic upgrades. If you do not connect to the Internet at least every 31 days, your apps will go into reduced functionality mode, which means that you can view or print your documents but cannot edit the documents or create new ones. To reactivate your apps, simply reconnect to the Internet.
You do not need to be connected to the Internet to use the Office apps, such as Word, Excel, and PowerPoint, because the apps are fully installed on your computer.
What is a Microsoft account and why do I need it for Microsoft 365?
Your Microsoft account is the combination of an email address and password that you use to sign in to services like OneDrive, Xbox LIVE, and Outlook.com. If you use any of these services, you already have a Microsoft account that you can use or you can create a new account. Learn more about a Microsoft account .
As part of signing up for a trial or purchasing Microsoft 365, you will be prompted to sign in with a Microsoft account. You must be signed in with this account to install and manage your Microsoft 365 subscription, or to use some subscription benefits, including cloud storage.
How many people can use a Microsoft 365 subscription?
How do i share my subscription benefits with members of my family, if i’m not paying for a subscription, what do i get for free, what is microsoft defender, what is the difference between microsoft defender and windows security.
Microsoft Defender is a new cross-device app that helps people and families stay safer online. Microsoft Defender adds new features and a simplified, user interface. Microsoft Defender also brings valuable device protection to iOS, Android, Windows, and Mac, with malware protection, web protection, real-time security notifications, and security tips. 1,2 Microsoft Defender is available in the Apple, Google, and Microsoft app stores and requires a Microsoft 365 Personal or Family subscription to use.
Windows Security, formerly known as Windows Defender Security Center, is built-in security on Windows PCs to protect your device and data. Windows Security is pre-installed and automatically enabled. Windows Security includes Microsoft Defender Antivirus software that protects your Windows device and data against viruses, ransomware, trojans, and other malware unless non-Microsoft Antivirus software is active.
What is Clipchamp?
- App availability varies by device/language. Features vary by platform.
- Features and app availability may vary by region.
- [1] Identity theft monitoring is only available in the United States and US territories.
- [2] You can cancel online by visiting the Microsoft Account site . Sign in with the Microsoft account that you used to buy your subscription, and then turn off recurring billing. Then, your subscription will automatically expire when your remaining subscription time is up. For details, see “ How to cancel your Microsoft subscription ” at the Microsoft Support site .
Election latest: More polls forecast huge Tory losses - with one projecting just 53 seats
Labour are on course for their best-ever election result and the Tories their worst since before the First World War, according to a new YouGov poll for Sky News. It also shows several cabinet casualties, a win for Nigel Farage, and huge gains for the Liberal Democrats across the UK.
Wednesday 19 June 2024 23:03, UK
- General Election 2024
Please use Chrome browser for a more accessible video player
New YouGov poll for Sky News
- Catch up on the day's politics news with our 10pm bulletin
- Labour on course for best-ever election result
- 'Real collapse' in Tory support after 'uplift' for Reform
- Top Tories tipped to lose - with more than half of cabinet at risk
- Look up the projected result where you live
- Sam Coates: Tory wipeout on the cards in multiple regions
- Sky News Daily: What could change before election day?
Other election news
- PM welcomes fall in inflation
- More polls project huge Tory losses
- Police officer in Sunak's close protection team arrested
- Lib Dem leader opens up about caring for late mother and teen son
- Latest manifestos: Sinn Fein | SNP | Workers Party
Election essentials
- Manifesto pledges: Conservatives | Greens | Labour | Lib Dems | Plaid Cymru | Reform | SNP
- Trackers: Who's leading polls? | Is PM keeping promises?
- Campaign Heritage: Memorable moments from elections gone by
- Follow Sky's politics podcasts: Electoral Dysfunction | Politics At Jack And Sam's
- Read more: Who is standing down? | Key seats to watch | What counts as voter ID? | Check if your constituency is changing | Guide to election lingo | Sky's election night plans
It's 10pm and here's your rundown of the day.
It's been a day of manifesto launches and another YouGov poll for Sky News has projected Labour is on course for its best-ever election result - and the Tories set for their worst since 1906.
Here are the main things you need to know:
- The poll projects Labour will win a historic majority of 200 with 425 seats, more than double the 202 won in 2019;
- While the Tories would slump to their lowest number of parliamentary seats since the party's formation with 108, down from the 365 won in 2019;
- Some 15 out of 28 Tory cabinet members still standing in the election are projected to lose , including Chancellor Jeremy Hunt, Defence Secretary Grant Shapps, and Commons leader Penny Mordaunt.
- The Liberal Democrats would win 67 seats under the projection, the SNP 20, Plaid Cymru four and the Greens two;
- Nigel Farage's Reform UK is on course to win five seats, with the party leader becoming an MP for the first time after winning Clacton;
- History teaches us polls tend to narrow during election campaigns, but Patrick English, director of political analytics at YouGov, says "we're just not seeing that at the moment" .
- A police officer in Rishi Sunak's close protection team has been arrested and suspended over alleged bets about the timing of the general election.
- We had an in-depth interview with Lib Dem leader Sir Ed Davey , who discussed topics taking in migration, Brexit and social care, and his experience looking after his son;
- The SNP's economy spokesperson also told Sophy Ridge the party is "fighting for every vote" in response to the YouGov projection showing the party would lose half of its seats;
- The SNP launched its manifesto with a promise to continue its quest for another independence referendum, which the party claims could pave the way for Scotland to rejoin the EU;
- Sinn Fein launched its manifesto, as did George Galloway's Workers Party of Britain .
- Inflation falling back to the Bank of England's 2% target for the first time in three years has been welcomed by Rishi Sunak , but Sir Keir Starmer said people's lives wouldn't "suddenly get easier;
- The prime minister and Labour leader condemned Just Stop Oil members spraying Stonehenge with orange paint;
- Sir Keir's wife also said a protest outside their house - which involved a banner saying "Starmer stop the killing" in reference to the war in Gaza - made her feel "a bit sick".
On today's Sky News Daily podcast, Niall Paterson analyses the implications of today’s poll with our deputy political editor Sam Coates , while Sky’s political correspondent Tamara Cohen joins us from Edinburgh where she was at the launch of the SNP manifesto.
Thank you for following our coverage of the day's political events.
See our 10pm bulletin for the key points from today.
Join us again tomorrow from 7am for the latest updates.
Earlier, YouGov pollsters asked 2,238 people how they felt about various party leaders - and who would make the prime minister.
In a series of head to heads, Sir Keir Starmer came ahead of all the other leaders.
He beat Rishi Sunak by 41 points to 21 points, Nigel Farage by 50 points to 25, and Sir Ed Davey by 40 points to 14.
The rest of the 100% in each case was made up by "don't knows".
Out of the other match-ups, Mr Farage came second in them all - and Mr Sunak lost out to Sir Ed.
The grim news for the Tories in the latest Sky News/YouGov poll begs another question about Rishi Sunak's political judgement. Was a long election campaign a blunder?
The prime minister is already under fire from Conservative MPs and activists for gambling on an election in July rather than waiting for October or November.
The conventional wisdom was that economic news would be better by the autumn and deportation flights to Rwanda would help stop the boats bringing migrants across the Channel.
But as well as doubts about a July poll, the big slump in Tory support since the last Sky News/YouGov poll on 3 June, suggests a long campaign of six weeks may also have backfired.
On 22 May, the day the prime minister made his shock general election announcement, some veteran Tory MPs privately questioned Mr Sunak's decision to fight a long campaign.
But with the Tories trailing badly behind Labour in the polls for months, Mr Sunak clearly hoped a long election campaign would give his party more time to recover and close the gap.
However, the opposite appears to have happened. As the campaign continues, with polling day still two weeks away, opinion polls are suggesting bigger Conservative losses, not smaller.
Read the full analysis here ...
Our live poll tracker collates the results of opinion surveys carried out by all the main polling organisations - and allows you to see how the political parties are performing in the run-up to the general election.
Read more about the tracker here .
By Tamara Cohen , political correspondent
John Swinney has now been on the campaign trail for most of his short time as Scotland's first minister, which began just six weeks ago.
After a turbulent 15 months for the SNP following the resignation of Nicola Sturgeon and then Humza Yousaf, the party of independence is fighting for its life against a resurgent Labour poised to win back some old heartlands.
For the nationalists, this is existential. Having won 48 seats in the 2019 election, they could - according to today's YouGov poll- end up with just 20 seats.
With many seats too close to call, especially in the tightly-contested central belt, other polls have put the SNP far lower, and that leaves its central goal of independence at serious risk.
Read more below:
As well as our mammoth YouGov poll projecting 425 seats for Labour and 108 for the Conservatives, two other polls have been released today showing Labour maintaining its comfortable lead.
A poll by More In Common projected a Labour majority of 162, just shy of its 1997 and 2001 landslides, with the Conservatives falling just 155 seats, their worst total since 1906.
High profile losses forecast in the projection include Chancellor Jeremy Hunt and Defence Secretary Grant Shapps.
But the results were the most favourable for the Conservatives of the recent large-scale polls.
Meanwhile a poll by Savanta projects a drastic result for the Conservatives, with Labour winning 516 seats and the Tories falling to 53 MPs.
It puts Labour 19 percentage points ahead of the Tories, with Labour on 40%, the Tories 21%, Reform 14%, Lib Dems 11%, Green 4%, SNP 3% and other parties 5%.
The More In Common survey forecasts Reform UK winning no seats, with the Tories holding Clacton against Nigel Farage, but the poll is based on data collected between 22 May and 17 June and so includes the period before Mr Farage announced his decision to stand in the seat.
Sinn Fein were one of the parties to launch their manifesto today - but they don't actually sit in parliament.
Why is that? And what role do they have in the general election?
Our senior Ireland correspondent David Blevins explains:
Our deputy political editor Sam Coates praises Sir Ed Davey for his unique way of getting the Liberal Democrats' policies across.
He says he is able to "knit together a policy programme... that people understand why he cares about it, because he links it back to both his son and his mother who he cared for when he was a teenager".
Sam adds: "I think that relatability, along with the stunts everyone has seen, has been the core of his campaign, and it has caught the imagination by being something different."
He says he wondered what role the Lib Dems would play if there was a huge Labour supermajority, "because they don't feel like they are going to go on the attack, they don't feel like they're going to be particularly pugnacious".
"They're an anti-Tory outfit under this guy, Ed Davey. So what really is their role going to be from 5 July onwards?"
That concludes our coverage of tonight's Politics Hub With Sophy Ridge - it'll return tomorrow from 7pm. In the meantime, stick with us here for the latest general election news and analysis.
Ending on a lighter note, Sophy asks Sir Ed which politician he would most like to push off a paddleboard.
"There's just too many they won't fit on," Sir Ed says.
The Liberal Democrat leader has pulled several attention-grabbing stunts during the campaign, including repeatedly tumbling off a paddle board into Lake Windermere… as well as screaming on a rollercoaster, splashing down a waterslide, careening downhill on a bike, tackling an assault course, building sandcastles and competing in wheelbarrow races.
Who deserves a knighthood more?
Sophy asks Sir Ed who deserves a knighthood more, himself or Post Office campaigner Alan Bates, who was knighted in the King's Birthday Honours list last week.
Sir Ed has come under scrutiny for his previous work as the postal affairs minister in light of the scandal.
"I think Alan Bates does," Sir Ed says.
"I'm very proud of my knighthood though, which I was very fortunate to get from her late Majesty because of the work I've done on climate change."
Be the first to get Breaking News
Install the Sky News app for free


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
3. SBA Business Plan Example. Following an SBA-recommended business plan format is key to securing bank loans and business grants. Since it can be time-consuming to find a template that follows a similar outline as the SBA, this SBA-approved business plan example is the way to get started.. This SBA business plan template has nine primary sections, that include executive summary, company ...
LivePlan's business plan examples help students turn ideas into top-notch business plans for class projects and startups. The tools, features, and instructional content allow you to focus on bringing out the best in your students for every plan and project. Before using LivePlan, my students were intimidated by the business planning process.
In this section, we'll explore 10 types of business plan examples for student entrepreneurship. 1. Traditional Business Plans. These classic business plans, often prepared on paper, provide a comprehensive overview of the business, detailing its identity, goals, and strategies for success. 2.
Takeaways for business plan examples for students. The opportunities are endless if you want to set up a business as a student. Let your imagination run wild and look through business plan examples for students if you want to start selling or offering something new to your school's community.
Creating a business plan as a student can be a daunting task, but with the help of ClickUp's Business Plan Template, you can break it down into manageable steps. Follow these six steps to create a comprehensive business plan that sets you up for success: 1. Define your business idea. Start by clearly defining your business idea.
The business model canvas is a one-page template designed to demystify the business planning process. It removes the need for a traditional, copy-heavy business plan, in favor of a single-page outline that can help you and outside parties better explore your business idea. The structure ditches a linear format in favor of a cell-based template.
ClickUp's Business Plan Template for College Students is here to guide you every step of the way! With this template, you can: Clearly define your business goals and strategies for success. Create a comprehensive financial plan and projections to attract investors. Identify potential obstacles and develop contingency plans.
Tips on Writing a Business Plan. 1. Be clear and concise: Keep your language simple and straightforward. Avoid jargon and overly technical terms. A clear and concise business plan is easier for investors and stakeholders to understand and demonstrates your ability to communicate effectively. 2.
How to Write a Business Plan Step 8. Financial Statements. No business plan is complete without financial statements or financial projections. The business plan format will be different based on whether you are writing a business plan to expand a business or a startup business plan. Let's dig deeper into each.
A sample business plan is an example/template document that outlines the key sections and elements that are typically included in a plan used to start and/or operate a business venture. It provides a structured format and sample content that you can use as a guide when writing your own specific business plan tailored to your company's details.
Identifying Key Elements. Reading business plan examples of similar businesses can help you identify the key elements and information to include in your plan. You can keep note of these and ensure everything necessary for investors to consider is present in your final draft. 6. Crafting Financial Projections.
Ideas like freelancing, dropshipping, tutoring, blogging and others offer them the chance to earn and learn simultaneously. Service businesses like pet care, landscaping and cleaning are great for part-time ventures that can accommodate academic commitments. 01. Freelancing.
7 business plan examples: section by section. The business plan examples in this article follow this template: Executive summary. An introductory overview of your business. Company description. A more in-depth and detailed description of your business and why it exists. Market analysis.
8. Write up your financial forecast. This is one of the trickier parts of writing a business plan and requires a good understanding of business finance and accounting. If your business has been trading for a while, you'll want to start off by outlining some historical data, such as sales and gross margin.
8. Panda Doc's Free Business Plan Template. PandaDoc's free business plan template is one of the more detailed and fleshed-out sample business plans on this list. It describes what you should include in each section, so you don't have to come up with everything from scratch.
A complete business plan Unlike other blank templates, our business plan examples are complete business plans with all of the text and financial forecasts already filled out. Edit the text to make the plan your own and save hundreds of hours. A professional business plan template All 550 of our business plans are in the SBA-approved format that ...
Business Glossary. Definitions for common terminology and acronyms that every small business owner should know. Bplans offers free business plan samples and templates, business planning resources, how-to articles, financial calculators, industry reports and entrepreneurship webinars.
Sample Business Plan mindanao state university iligan institute of technology college of business administration and accountancy department of marketing alibata. ... Students also viewed. M6 Explorer project plan; 2nd Quarter Exam Math 8; Table for revised WHT 2018-2022; English 6 Q3 Week 1; Abaigarlessonplan-3 - Grade 9Lesson plan ...
This section of the plan should describe the following requirements of your business: Manufacturing. R&D. Purchasing. Staffing. Equipment. Facilities. Note: Provide a rollout strategy as to when these requirements need to be purchased and implemented. In addition, describe the vendors you will need to build the business.
Click here for the sample business plan. Restaurant Business Plan. A restaurant business plan will be similar to a coffee shop, but is a little more involved. Start-up costs are higher as it requires a larger storefront and a larger variety of equipment. Variable costs are higher as a quality meal costs much more than a cup of coffee.
Download over 300 free business plan examples to help you write a winning business plan to start and/or grow your business in 2024. Download over 300 free business plan examples to help you write a winning business plan to start and/or grow your business in 2024. ... social network for high school students: 03/06: $6.1 million: Alloy Inc ...
Business Plan Template for Students - Free download as Word Doc (.doc / .docx), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or read online for free. Business Plan Guide For Students
This business plan is for BambooS Sdn. Bhd., a company started by 10 students at University Putra Malaysia to produce and sell bamboo straws. Their products are bamboo straws that are reusable, customizable in size, affordable, and eco-friendly. Their target market is the UPM community. They will advertise on social media and sell at campus cafes, stores, and food establishments. Their ...
business plan for abm students department of education division of city taneo memorial high school senior high school department pe from the (business plan) Skip to document. University; High School; Books; Discovery. ... This is an image of the sample product. The team will create a heart shape waffle- not like the regular circle-shaped waffle ...
Plan out the skills and songs you'll need for a meaningful music class with a lesson plan like this one. Learn more: Victoria Boler. Middle and High School Lesson Plan Examples. At the middle and high school levels, teachers often need more detailed plans for each class, which they may teach multiple times a day. Here are some examples to try.
Whether you're an experienced entrepreneur or new to the retail industry, this guide, complete with a business plan example, lays the groundwork for turning your bookstore business concept into reality. Let's dive in! The Plan. Our bookstore business plan is structured to cover all essential aspects needed for a comprehensive strategy.
The Online Writing Lab (the Purdue OWL) at Purdue University houses writing resources and instructional material, and we provide these as a free service at Purdue. Students, members of the community, and users worldwide will find information to assist with many writing projects.
Find the right Microsoft 365 Family or Personal plan for all your devices. Includes AI-powered Office apps, 1 TB of cloud storage, and premium mobile features. ... Office Home & Student 2021 One-time purchase for PC or Mac. $149.99. Buy now. ... for example to install Office apps on other PCs or to change billing options.
Labour are on course for their best-ever election result and the Tories their worst since before the First World War, according to a new YouGov poll for Sky News. It also shows several cabinet ...