Something went wrong!
Some error occured while loading page for you. Please try again.

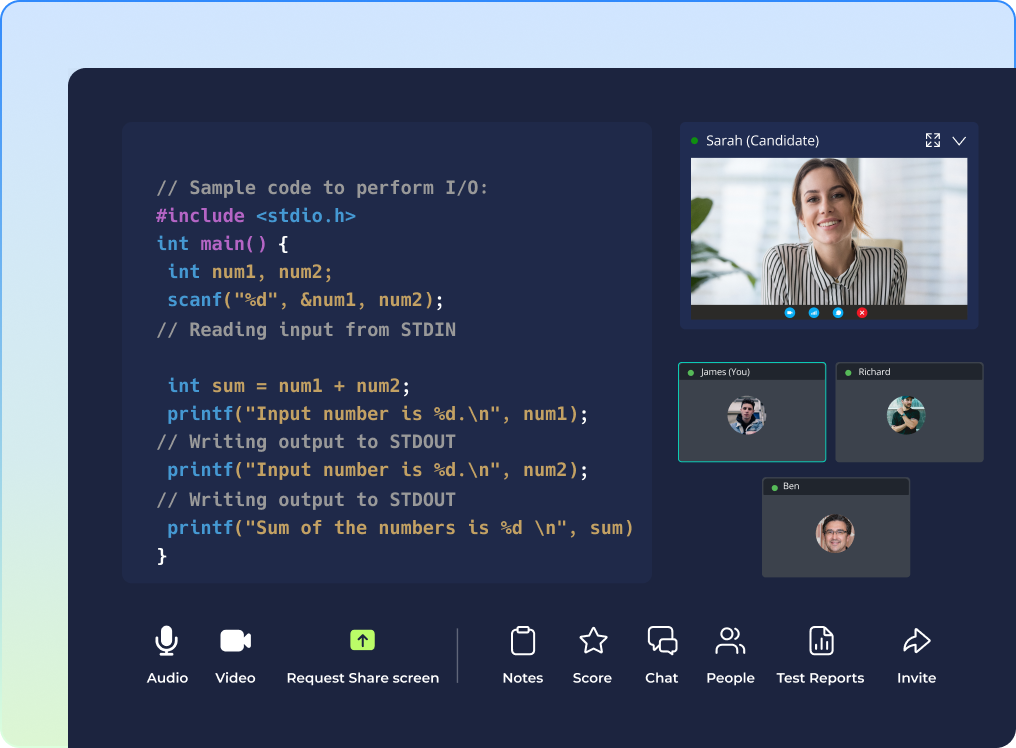
Challenge Walkthrough
Review the problem statement, choose a language, enter your code, test your code, submit to see results.
- Check your score

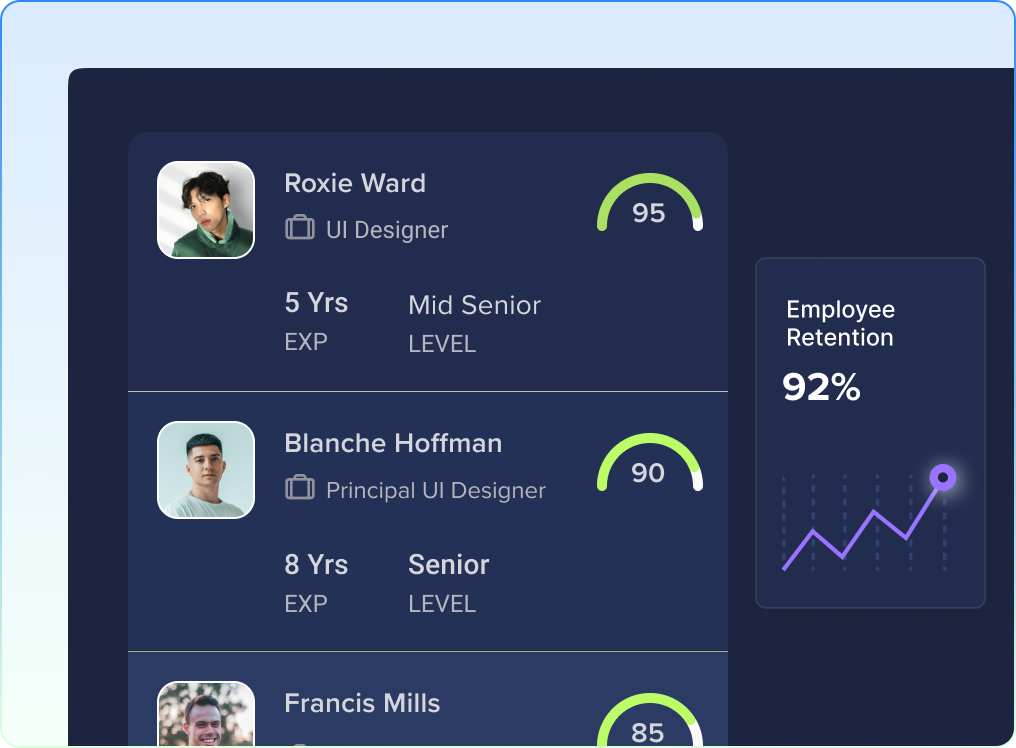
How to Solve Coding Problems: Step-by-Step Guide (2024)
May 20, 2024 · 13 min read
Coding challenges are a common obstacle for many programmers, whether they are just starting or have years of experience.
In this complete guide, we will provide expert tips and strategies for effectively solving coding problems.
By following these valuable tips, you can confidently enhance your problem-solving skills and conquer even the most challenging coding tasks.
Let's get started.
Read the Problem Statement Carefully

Identify key constraints
One imperative step in solving coding problems is identifying the key constraints in the problem statement. These constraints define the boundaries within which your solution must operate and can greatly influence your approach.
Note important variables
Carefully note down important variables mentioned in the problem statement as they often hold crucial information for solving the problem efficiently.
Understanding the significance of these variables can guide you toward the right solution approach.
Remember to consider any implicit variables that might affect your solution but are not explicitly mentioned in the problem statement.
Attention to all variables will ensure a more comprehensive understanding of the problem.
Tip: Here, you can learn about key programming definitions and terms
Create your next presentation
snappify will help you to create stunning presentations and videos.
This video was created using snappify 🤩
Break Down Complexity

Divide into smaller Tasks
You'll find that breaking down a complex coding problem into smaller tasks makes it more manageable.
Start by identifying the different components of the problem and breaking them down into smaller subproblems. This approach will help you tackle each subproblem individually and eventually solve the larger problem.
Focus on one task
The key to successfully breaking down a complex coding problem is to focus on one task at a time.
Concentrating all your efforts on solving one specific subproblem can help you avoid feeling overwhelmed by the complexity of the overall task.
This focused approach will improve your problem-solving skills and allow you to make steady progress toward the final solution.
When focusing on one task, setting clear goals and objectives for that specific subproblem is vital. It will help you stay on track and prevent distractions derailing your problem-solving process.
By dedicating your full attention and energy to each task, you can efficiently work through the complexities of the coding problem and find an effective solution.
Tip: The Feynman learning technique is the best solution for learning how to break down complex concepts.
Research and Learn

Study similar problems
Research shows that one of the best strategies to solve coding problems easily is to study similar problems.
By analyzing how others have approached and solved comparable issues, you can gain valuable insights and techniques to apply to your challenges.
Learn new concepts
Learning new concepts is imperative for continuous improvement in coding.
By staying updated with the latest technologies, algorithms, and best practices, you can enhance your problem-solving skills and broaden your understanding of different coding techniques.
Any aspiring coder should regularly explore new concepts through online courses, tutorials, and coding challenges.
This proactive approach helps solve current problems more effectively and prepares you for future challenges in the ever-evolving tech industry.
Tip: The fastest way to learn any new concept is to share what you learn. For example, you can learn a piece of code and then use code sharing tools to share your knowledge with the audience.
Write Pseudocode First

Plan out Algorithm Steps
For effective problem-solving, it is crucial to plan out the steps of your algorithm before writing actual code.
Pseudocode helps break down the problem into smaller, manageable steps, making it easier to implement the solution in the chosen programming language.
Visualize solution flow
While writing pseudocode, visualize how the solution will flow from one step to another.
This visualization helps in understanding the logic of the algorithm and can highlight any potential issues or optimizations that can be made before writing actual code.
For instance, if you are working on a sorting algorithm, visualizing the flow can help you determine the most efficient way to arrange the elements and identify any redundant steps that you can eliminate to improve performance.
Start with Simple

Implement basic solution
Unlike complex problems, coding problems are best tackled with a straightforward approach.
Begin by implementing a basic solution that may not be the most efficient but solves the problem correctly.
This helps in understanding the problem better and getting a working solution.
Refine as needed
Implementing a basic solution is just the beginning.
As you progress, refine your code by optimizing it for performance, readability, and scalability.
Refactoring code to improve efficiency and incorporating best practices will boost your solution to the next level.
A key strategy for refining your code is to analyze its complexity and identify areas for optimization. This may involve revisiting your algorithm choices and data structures or breaking down the problem into smaller, manageable parts.
By continuously refining your solution, you improve your coding skills and enhance the quality of your code.
Use Online Resources

Leverage coding communities
Despite the various challenges of coding problems, the process becomes easier when you tap into the wealth of knowledge available in coding communities.
These online platforms, such as Stack Overflow and GitHub, offer a supportive environment where you can seek solutions, ask questions, and learn from experienced programmers.
Consult online tutorials
These resources provide step-by-step guidance on various programming concepts and problem-solving techniques, making grasping complex algorithms and data structures easier.
The abundance of online tutorials ranges from beginner to advanced, and they are fit for programmers of all proficiency levels.
By consulting these tutorials, you can enhance your understanding of coding principles and develop effective strategies for solving various coding problems.
Any aspiring coder should take advantage of the vast array of online resources that can facilitate the process of solving coding problems.
By leveraging coding communities, consulting online tutorials, and exploring other online platforms, you can quickly sharpen your problem-solving skills and become a more proficient programmer.
Tip: Resources like YouTube and Udemy are great ways. But you can also read the best development books to enhance your coding skills further.
Debug Thoroughly

Identify common mistakes
Unlike overlooking small errors, identifying common mistakes is crucial in debugging code efficiently.
Any coder should be aware of recurring issues like:
- Syntax Errors
- Logical mistakes
- Incorrect variable usage
By recognizing these patterns, programmers can initiate debugging and write cleaner code.
Test edge cases
Any comprehensive debugging strategy should include testing edge cases to ensure code reliability and robustness.
By intentionally pushing the boundaries of input values or conditions, developers can uncover potential mistakes that might go unnoticed during regular testing.
This practice helps programmers anticipate and address unexpected scenarios, leading to more resilient code.
Testing edge cases involves evaluating the extremes of input data or conditions to verify the code's behavior under challenging circumstances.
By examining how the program handles unusual or extreme values, developers can identify vulnerabilities or inefficiencies that may occur in real-world usage.
Practice Regularly

Build problem-solving muscle
Your coding skills are like a muscle that needs regular exercise to strengthen. Make a habit of solving coding problems daily to enhance your problem-solving abilities.
Develop coding instincts
Build a strong intuition for coding by practicing regularly.
As you solve more problems, you'll notice patterns and common strategies that can help you tackle new problems more efficiently.
Developing coding instincts involves understanding different approaches to problem-solving and knowing when to apply them. This initiative will guide you in choosing the most effective solutions and optimizing your code for better performance.
Review and Refine

Analyze solution efficiency
Unlike simply finding a solution, it is imperative to analyze its efficiency.
Evaluate the time complexity, space complexity, and overall performance of the code.
This step will help you understand how the code will perform with larger inputs and whether there are any bottlenecks that need to be addressed.
Optimize code quality
Coding problems are not just about finding a solution but also about writing clean and efficient code.
Pay attention to coding standards, readability, and best practices.
Refactor the code to make it more concise, understandable, and maintainable. This step is crucial in ensuring that your code is not only functional but also of high quality.
You can use tools like linters and code formatters to check and improve your code's quality automatically.
These tools can help you catch potential errors, enforce coding standards, and enhance the overall readability of your codebase.
By optimizing your code quality, you can make it easier for yourself and others to understand and work with the code in the future.
Tip: You can use a code review checklist to optimize code efficiency quickly.
Learn from Others

Study open-source code
Study open-source code to truly enhance your coding skills.
By studying the work of experienced developers, you can gain insight into different perspectives, problem-solving techniques, and coding styles.
This exposure can broaden your knowledge and inspire innovative solutions to coding problems.
Learn from mentors
Some of the most effective learning experiences come from mentors who can provide guidance, feedback, and real-world insights.
Connecting with experienced professionals in the field can offer valuable advice, help you navigate challenges, and accelerate your learning process.
Learn from mentors who have expertise in your specific area of interest.
Their guidance can help you grasp complex concepts, avoid common pitfalls, and stay updated on industry trends.
Building a strong mentorship relationship can significantly impact your coding journey and foster professional growth.
Stay Calm and Patient

Manage problem-solving stress
After encountering a challenging coding problem, managing the stress that comes with it is imperative.
Take deep breaths, step back, and remind yourself that feeling stuck is okay.
Keeping a clear mind will help you approach the problem more effectively.
Take breaks when needed
If you find yourself hitting a wall and getting frustrated, it's time to take a break.
Stepping away from the problem for a few minutes or even an hour can improve your mental clarity.
Some fresh air or a quick walk can help reset your mind and improve focus when you return to the task.
When stress builds up, it can blur your thinking and make problem-solving even more challenging.
Taking breaks gives you a chance to relax and allows your brain to subconsciously work on the problem in the background, often leading to new insights and solutions.
Identify Patterns

Recognize common patterns
One vital skill in solving coding problems is recognizing common patterns.
By identifying recurring themes or structures in the problem you're trying to solve, you can apply similar solutions that have worked in the past. It can help simplify your problem-solving process and lead to more efficient coding.
Apply pattern-based solutions
To effectively apply pattern-based solutions, you need to understand different types of patterns commonly found in coding problems.
These patterns can include algorithms like sliding windows, two-pointers, or depth-first search.
By leveraging these patterns, you can quickly develop solutions that have been proven to work for similar problems.
Tip: You can explore different development frameworks to identify common patterns.
Draw Diagrams

Visualize problem structure
When faced with a complex coding problem, start by visualizing its structure.
Use diagrams to represent different components, their relationships, and data flow. This visual representation can clarify the problem and help you identify key areas to focus on.
Illustrate solution flow
While solving coding problems, illustrating the solution flow through diagrams can facilitate the problem-solving process.
Create a step-by-step flowchart or sequence diagram to map the logic and algorithm.
This visual aid can guide you through the implementation phase and help you identify potential errors or optimizations in the solution.
Diagrams can also serve as documentation for your code, making it easier for others to understand your thought process and approach.
By incorporating visual elements into your problem-solving strategies, you can enhance your efficiency and accuracy in coding.
Collaborate with Peers

Work with coding partners
For an effective problem-solving strategy, consider working with coding partners.
Collaborating with peers can help you bounce ideas off each other, share different approaches, and collectively develop innovative solutions.
By leveraging your peers diverse skills and perspectives, you can tackle coding problems more efficiently and effectively.
Learn from peer feedback
Even the most experienced coders can benefit from constructive feedback from their peers.
Peer feedback can provide valuable insights into alternative solutions, code optimization techniques, and potential pitfalls to avoid.
You can continuously improve your problem-solving skills and expand your coding knowledge by actively seeking and incorporating feedback from your coding peers.
Work with your coding partners to brainstorm ideas, discuss different approaches, and troubleshoot any challenges you encounter.
Creating a collaborative environment with your peers can enhance your problem-solving abilities and accelerate your learning process.
Final Words
Mastering the key skills mentioned above will help you solve coding problems more easily and efficiently.
Buffing your problem-solving skills, staying organized, and utilizing various techniques such as pseudocoding and debugging can help you tackle coding challenges with confidence and precision.
Keep practicing and implementing these strategies to enhance your problem-solving abilities and become a more skilled coder.
Why is code optimization important in the problem-solving process?
Code optimization is important in the problem-solving process because it improves the code's performance and efficiency. Optimized code runs faster, requires less memory, and performs better with large input sizes. Optimization reduces the code's time and space complexity and ensures that it meets performance requirements.
Why is testing your code with different test cases important in coding problem-solving?
Testing your code with different test cases helps ensure your solution works correctly for various scenarios. It also helps identify edge cases, errors, and potential bugs in the code. Thorough testing enhances the reliability and accuracy of your code.
Share Article
The 10 Most Popular Coding Challenge Websites [Updated for 2021]

A great way to improve your skills when learning to code is by solving coding challenges. Solving different types of challenges and puzzles can help you become a better problem solver, learn the intricacies of a programming language, prepare for job interviews, learn new algorithms, and more.
Below is a list of some popular coding challenge websites with a short description of what each one offers.
1. TopCoder

TopCoder is one of the original platforms for competitive programming online. It provides a list of algorithmic challenges from the past that you can complete on your own directly online using their code editor. Their popular Single Round Matches are offered a few times per month at a specific time where you compete against others to solve challenges the fastest with the best score.
The top ranked users on TopCoder are very good competitive programmers and regularly compete in programming competitions. The top ranked user maintains his own blog titled Algorithms weekly by Petr Mitrichev where he writes about coding competitions, algorithms, math, and more.
2. Coderbyte

Coderbyte provides 200+ coding challenges you can solve directly online in one of 10 programming languages (check out this example ). The challenges range from easy (finding the largest word in a string) to hard (print the maximum cardinality matching of a graph).
They also provide a collection of algorithm tutorials , introductory videos, and interview preparation courses . Unlike HackerRank and other similar websites, you are able to view the solutions other users provide for any challenge aside from the official solutions posted by Coderbyte.
3. Project Euler

Project Euler provides a large collection of challenges in the domain of computer science and mathematics. The challenges typically involve writing a small program to figure out the solution to a clever mathematical formula or equation, such as finding the sum of digits of all numbers preceding each number in a series.
You cannot directly code on the website in an editor, so you would need to write a solution on your own computer and then provide the solution on their website.
4. HackerRank

HackerRank provides challenges for several different domains such as Algorithms, Mathematics, SQL, Functional Programming, AI, and more. You can solve all the challenge directly online (check out this example ).
They provide a discussion and leaderboard for every challenge, and most challenges come with an editorial that explains more about the challenge and how to approach it to come up with a solution.
Currently, if you don't solve the problem, then you can't see the solution of others. If you also try to check the editorial before solving the problem, then you won't get the point for solving the problem at all.
As an example, here I haven't solved the problem, and I am trying to check others' submissions:
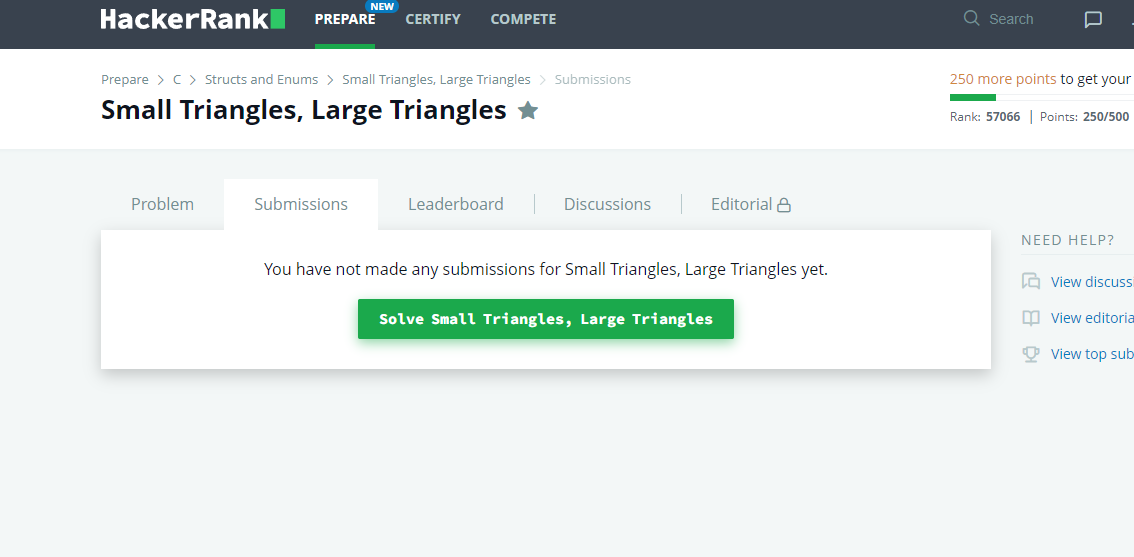
And here, I haven't solved the problem, and I am trying to check the editorial:
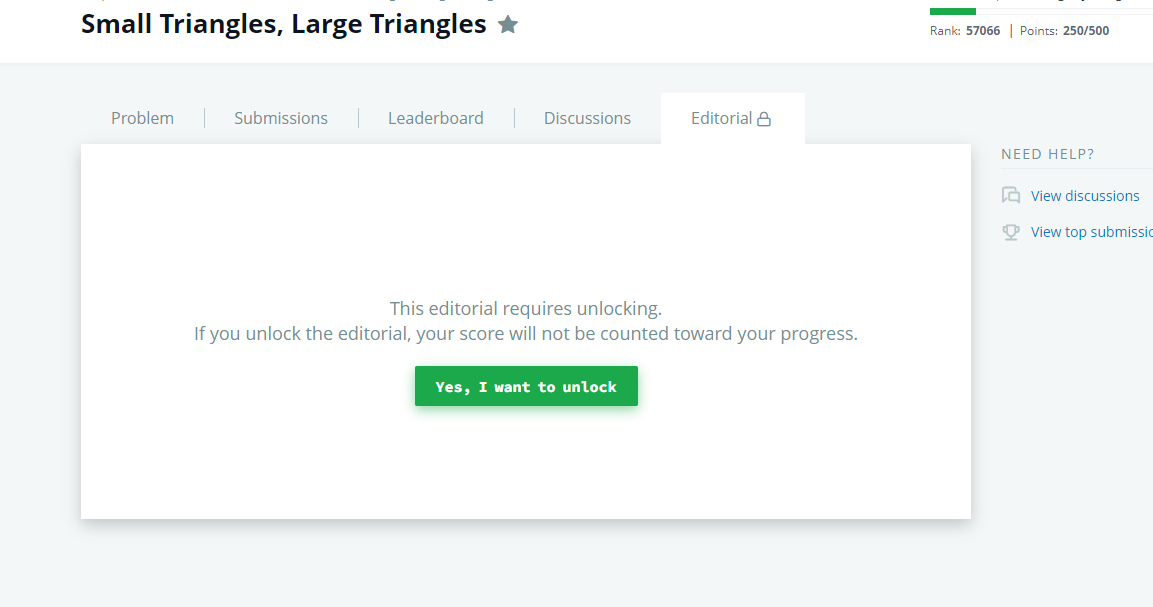
HackerRank also provides the ability for users to submit applications and apply to jobs by solving company-sponsored coding challenges.
5. CodeChef
CodeChef is an Indian-based competitive programming website that provides hundreds of challenges. You are able to write code in their online editor and view a collections of challenges that are separated into different categories depending on your skill level (check out this example ). They have a large community of coders that contribute to the forums, write tutorials , and take part in CodeChef’s coding competitions .
6. Exercism.io

Exercism is a coding challenge website that offers 3100+ challenges spanning 52 different programming languages. After picking a language that you'd like to master, you tackle the coding challenges right on your machine (Exercism has their own command line interface that you can download from GitHub).
It is a bit different from other challenge websites, however, because you work with a mentor after completing each challenge. The mentor reviews your answers online and helps you improve them if needed. Once your answers have been approved and submitted, you unlock more challenges.
7. Codewars
Codewars provides a large collection of coding challenges submitted and edited by their own community. You can solve the challenges directly online in their editor in one of several languages. You can view a discussion for each challenges as well as user solutions.
8. LeetCode
LeetCode is a popular Online Judge that provides a list of 190+ challenges that can help you prepare for technical job interviews. You can solve the challenges directly online in one of 9 programming languages. You are not able to view other users' solutions, but you are provided statistics for your own solutions such as how fast your code ran when compared to other users' code.
They also have a Mock Interview section that is specifically for job interview preparation, they host their own coding contests , and they have a section for articles to help you better understand certain problems.
Sphere Online Judge (SPOJ) is an online judge that provides over 20k coding challenges. You are able to submit your code in an online editor . SPOJ also hosts their own contests and has an area for users to discuss coding challenges. They do not currently provide any official solutions or editorials like some other websites do, though.
10. CodinGame
CodinGame is a bit different from the other websites, because instead of simply solving coding challenges in an editor, you actually take part in writing the code for games that you play directly online. You can see a list of games currently offered here and an example of one here . The game comes with a problem description, test cases, and an editor where you can write your code in one of 20+ programming languages.
Although this website is different than typical competitive programming websites such as the ones mentioned above, it is still popular amongst programmers who enjoy solving challenges and taking part in contests.
This list was based on a few things: my own experiences using the websites, some Google searches , Quora posts , and articles such as this one and this one . I also frequented some forums and subreddits such as r/learnprogramming to see what websites were usually recommended by the users there. Disclaimer: I work at Coderbyte which is one of the websites mentioned above.
CEO & Founder at Coderbyte.
If this article was helpful, share it .
Learn to code for free. freeCodeCamp's open source curriculum has helped more than 40,000 people get jobs as developers. Get started
Achieve mastery through challenge
Improve your development skills by training with your peers on code kata that continuously challenge and push your coding practice.

Sharpen your coding skills
Challenge yourself on small coding exercises called "kata". Each kata is crafted by the community to help you strengthen different coding techniques. Master your current language of choice, or quickly pick up any of the 55+ programming languages supported.

Get instant feedback
Solve kata with your coding style right in the browser and use test cases (TDD) to check it as you progress. Retrain with new, creative, and optimized approaches. Find all of the bugs in your programming practice.

Earn ranks and honor
Kata code challenges are ranked from beginner to expert level. As you complete higher-ranked kata, you level up your profile and push your software development skills to your highest potential.

An engaged software development community
Codewars is a collective effort by its users. They are creators—authoring kata to teach various techniques, solving kata with solutions that enlighten others, and commenting with constructive feedback.
Community members added every month
Kata completed every month
Kata created by our community
Tap into the collective wisdom
Compare your solution with others after each kata for greater understanding. Discuss kata, best practices, and innovative techniques with the community. Have your mind blown by how different other solutions can be from your own.

Create your own kata
Author kata that focus on your interests and train specific skill sets. Challenge the community with your insight and code understanding. Create everything from common developer interview questions to challenges that push the limits of your creativity. Gain honor within the coding dojo.

What can I use Codewars for?
From beginner to expert and beyond...
Get new perspectives
Solve challenges then view how others solved the same challenge. Pickup new techniques from some of the most skilled developers in the world.
Learn new languages
Solve challenges in a language you are comfortable with, then do it in a language you want to improve with. Level up across different languages.
Compete with peers
Compete against your friends, colleagues, and the community at large. Allow competition to motivate you towards mastering your craft.
Extremely well done and an excellent example of mastery learning.

Ahmed Omran
@this_ahmed
Accidentally got addicted to codewars, oops.

Kelly Williams
Build self-confidence
Not sure if you are progressing well as a programmer? Push yourself to your limits and show yourself what you are really made of.
Become a mentor
Lend your expertise to others, either indirectly by contributing great solutions or directly by creating your own kata and reviewing code.
Insights from Codewars staff and community.

What's new in Codewars: April highlights

Author's Corner, meet geoffp

Introducing the EPIC Challenge 2024
Codewars is built on.
The world's most advanced coding assessment platform for organizations looking to scale their hiring, upskilling, and certification programs.
Achieve mastery through challenge.
Top languages
40 Coding Challenges (SOLVED with CODE) To Kill Your Next Coding Interview
You may hate code challenges and coding interviews but reality is a lot of companies from Google to Amazon do care that you understand the difference between O(n log n) and O(n²) , that you do understand when different data structures are appropriate, and that you can leverage these (very basic) skills to solve simple problems. Follow along and check 40 most common Coding Challenges and Questions that solved with code on Java, C#, Python and JS to crack and close your next coding interview.
Q1 : Convert a Single Linked List to a Double Linked List
A doubly linked list is simply a linked list where every element has both next and prev mebers, pointing at the elements before and after it, not just the one after it in a single linked list.
so to convert your list to a doubly linked list, just change your node to be:
and when iterating the list, on each new node add a reference to the previous node.
Q2 : Convert a Singly Linked List to Circular Linked List
To convert a singly linked list to a circular linked list, we will set the next pointer of the tail node to the head pointer.
- Create a copy of the head pointer, let's say temp .
- Using a loop, traverse linked list till tail node (last node) using temp pointer.
- Now set the next pointer of the tail node to head node. temp->next = head
Q3 : Detect if a List is Cyclic using Hash Table
To detect if a list is cyclic, we can check whether a node had been visited before. A natural way is to use a hash table.
We go through each node one by one and record each node's reference (or memory address) in a hash table. If the current node is null , we have reached the end of the list and it must not be cyclic. If current node’s reference is in the hash table, then return true.
Space: O(n)
- Time complexity : O ( n ) . We visit each of the n elements in the list at most once. Adding a node to the hash table costs only O ( 1 ) time.
- Space complexity: O ( n ) . The space depends on the number of elements added to the hash table, which contains at most n elements.
Q4 : Implement Stack using Two Queues (with efficient push )
Given two queues with their standard operations ( enqueue , dequeue , isempty , size ), implement a stack with its standard operations ( pop , push , isempty , size ). The stack should be efficient when pushing an item.
Given we have queue1 and queue2 :
push - O(1) :
- enqueue in queue1
pop - O(n) :
- while size of queue1 is bigger than 1, pipe (dequeue + enqueue) dequeued items from queue1 into queue2
- dequeue and return the last item of queue1 , then switch the names of queue1 and queue2
Space: O(1)
If queue is implemented as linked list the enqueue operation has O(1) time complexity.
Q5 : Implement a Queue using two Stacks
Suppose we have two stacks and no other temporary variable. Is to possible to "construct" a queue data structure using only the two stacks?
Keep two stacks, let's call them inbox and outbox .
- Push the new element onto inbox
- If outbox is empty, refill it by popping each element from inbox and pushing it onto outbox
- Pop and return the top element from outbox
In the worst case scenario when outbox stack is empty, the algorithm pops n elements from inbox stack and pushes n elements to outbox, where n is the queue size. This gives 2*n operations, which is O(n) . But when outbox stack is not empty the algorithm has O(1) time complexity that gives amortised O(1) .
Q6 : Insert item into the Heap. Explain your actions.
Suppose I have a Heap Like the following:
Now, I want to insert another item 55 into this Heap. How to do this?
A binary heap is defined as a binary tree with two additional constraints:
- Shape property : a binary heap is a complete binary tree; that is, all levels of the tree, except possibly the last one (deepest) are fully filled, and, if the last level of the tree is not complete, the nodes of that level are filled from left to right.
- Heap property : the key stored in each node is either greater than or equal to (≥) or less than or equal to (≤) the keys in the node's children, according to some total order.
We start adding child from the most left node and if the parent is lower than the newly added child than we replace them. And like so will go on until the child got the parent having value greater than it.
Your initial tree is:
Now adding 55 according to the rule on most left side:
But you see 22 is lower than 55 so replaced it:
Now 55 has become the child of 50 which is still lower than 55 so replace them too:
Now it cant be sorted more because 77 is greater than 55.
Q7 : Return the N-th value of the Fibonacci sequence Recursively
Recursive solution looks pretty simple (see code).
Let’s look at the diagram that will help you understand what’s going on here with the rest of our code. Function fib is called with argument 5:
Basically our fib function will continue to recursively call itself creating more and more branches of the tree until it hits the base case, from which it will start summing up each branch’s return values bottom up, until it finally sums them all up and returns an integer equal to 5.
Time: O(2^n)
In case of recursion the solution take exponential time, that can be explained by the fact that the size of the tree exponentially grows when n increases. So for every additional element in the Fibonacci sequence we get an increase in function calls. Big O in this case is equal to O ( 2 n ) . Exponential Time complexity denotes an algorithm whose growth doubles with each addition to the input data set.
Q8 : Return the N-th value of the Fibonacci sequence. Solve in O(n) time
The easiest solution that comes to mind here is iteration:
And output:
Notice that two first numbers can not really be effectively generated by a for loop, because our loop will involve adding two numbers together, so instead of creating an empty array we assign our arr variable to [0, 1] that we know for a fact will always be there. After that we create a loop that starts iterating from i = 2 and adds numbers to the array until the length of the array is equal to n + 1 . Finally, we return the number at n index of array.
An algorithm in our iterative solution takes linear time to complete the task. Basically we iterate through the loop n-2 times, so Big O (notation used to describe our worst case scenario) would be simply equal to O (n) in this case. The space complexity is O(n) .
Q9 : Reverse a String using Stack
The followings are the steps to reversing a String using Stack:
- String to char[] .
- Create a Stack .
- Push all characters, one by one.
- Then Pop all characters, one by one and put into the char[] .
- Finally, convert to the String .
Q10 : What is complexity of push and pop for a Stack implemented using a LinkedList?
O ( 1 ) . Note, you don't have to insert at the end of the list. If you insert at the front of a (singly-linked) list, they are both O(1) .
Stack contains 1,2,3:
Q11 : What would the number 22 look like as a Byte?
A byte is made up of 8 bits and the highest value of a byte is 255, which would mean every bit is set.
Lets take it right to left and add up all those values together:
128 0 + 64 0 + 32 0 + 16 1 + 8 0 + 4 1 + 2 1 + 1 0 = 22
Q12 : Check if parentheses are balanced using Stack
One of the most important applications of stacks is to check if the parentheses are balanced in a given expression. The compiler generates an error if the parentheses are not matched.
Here are some of the balanced and unbalanced expressions:
- Declare a character stack which will hold an array of all the opening parenthesis.
- Now traverse the expression string exp.
- If the current character is a starting bracket ( ( or { or [ ) then push it to stack.
- If the current character is a closing bracket ( ) or } or ] ) then pop from stack and if the popped character is the matching starting bracket then fine else parenthesis are not balanced.
- After complete traversal, if there is some starting bracket left in stack then “not balanced”
- We are traversing through each character of string, Time complexity O ( n ) .
- We are storing the opposite parentheses characters in the stack, in the worst case there can be all the opposite characters in the string, Space complexity O ( n ) .
Q13 : Explain how Heap Sort works
Heapsort is a comparison-based sorting algorithm. Heapsort can be thought of as an improved selection sort : like that algorithm, it divides its input into a sorted and an unsorted region, and it iteratively shrinks the unsorted region by extracting the largest element and moving that to the sorted region. The improvement consists of the use of a heap data structure rather than a linear-time search to find the maximum.
A heap is a complete binary tree (every level filled as much as possible beginning at the left side of the tree) that follows this condition: the value of a parent element is always greater than the values of its left and right child elements. So, by taking advantage of this property, we can pop off the max of the heap repeatedly and establish a sorted array .
In an array representation of a heap binary tree, this essentially means that for a parent element with an index of i , its value must be greater than its left child [2i+1] and right child [2i+2] (if it has one).
The HeapSort steps are:
- Create a max heap from the unsorted list
- Swap the max element, located at the root, with the last element
- Re- heapify or rebalance the array again to establish the max heap order. The new root is likely not in its correct place.
- Repeat Steps 2–3 until complete (when the list size is 1)
Visualisation :
Complexity:
Time: O(n log n)
- Best : O ( n log n )
- Average : O ( n log n )
- Worst : O ( n log n )
Q14 : Find all the Permutations of a String
A permutation , also called an “arrangement number” or “order,” is a rearrangement of the elements of an ordered list S into a one-to-one correspondence with S itself (or in simple english: permutation is each of several possible ways in which a set or number of things can be ordered or arranged). A string of length n has n! permutation:
To print all permutations of a string use backtracking implemented via recursion :
- Try each of the letters in turn as the first letter and then find all the permutations of the remaining letters using a recursive call.
- The base case is when the input is an empty string the only permutation is the empty string.
- In other words, you simply traverse the tree, and when you reach the leaf you print the permutation. Then you backtrack one level up, and try another option. Moving one level up the tree is what we call the backtracking in this case.
Time: O(n!)
Space: O(n!)
For any given string of length n there are n! possible permutations, and we need to print all of them so Time complexity is O(n * n!) . The function will be called recursively and will be stored in call stack for all n! permutations, so Space complexity is O(n!) .
Q15 : Floyd's Cycle Detect Algorithm: Explain how to find a starting node of a Cycle in a Linked List?
This is Floyd's algorithm for cycle detection . Once you've found a node that's part of a cycle, how does one find the start of the cycle?
- In the first part of Floyd's algorithm, the hare moves two steps for every step of the tortoise. If the tortoise and hare ever meet, there is a cycle, and the meeting point is part of the cycle, but not necessarily the first node in the cycle.
- Once tortoise and hare meet, let's put tortoise back to the beginning of the list and keep hare where they met (which is k steps away from the cycle beginning). The hypothesis (see math explanation) is that if we let them move at the same speed (1 step for both), the first time they ever meet again will be the cycle beginning .
Another solution to mention is Hash Map :
- Traverse the nodes list.
- For each node encountered, add it to the identity hash map
- If the node already existed in the identity map then the list has a circular link and the node which was prior to this conflict is known (either check before moving or keep the "last node")
Q16 : Floyd's Cycle Detect Algorithm: How to detect a Cycle (or Loop) in a Linked List?
You can make use of Floyd's cycle-finding algorithm , also known as tortoise and hare algorithm . The idea is to have two references to the list and move them at different speeds . Move one forward by 1 node and the other by 2 nodes.
- If the linked list has a loop they will definitely meet.
- Else either of the two references(or their next ) will become null .
We only use two nodes (slow and fast) so the space complexity is O ( 1 ) .
Q17 : Floyd's Cycle Detect Algorithm: Remove Cycle (Loop) from a Linked List
Floyd's cycle detect algorithm, also called the tortoise and hare algorithm as it involves using two pointers/references that move at different speeds, is one way of detecting the cycle. If there is a cycle, the two pointers (say slow and fast ) will end up pointing to the same element after a finite number of steps. Interestingly, it can be proved that the element at which they meet will be the same distance to the start of the loop (continuing to traverse the list in the same, forward direction) as the start of the loop is to the head of the list . That is, if the linear part of the list has k elements, the two pointers will meet inside the loop of length m at a point m-k from the start of the loop or k elements to the 'end' of the loop (of course, it's a loop so it has no 'end' - it's just the 'start' once again). And that gives us a way to find the start of the loop:
Once a cycle has been detected, let fast remain pointing to the element where the loop for the step above terminated but reset slow so that it's pointing back to the head of the list. Now, move each pointer one element at a time. Since fast began inside the loop, it will continue looping. After k steps (equal to the distance of the start of the loop from the head of the list), slow and fast will meet again. This will give you a reference to the start of the loop.
It is now easy to set slow (or fast ) to point to the element starting the loop and traverse the loop until slow ends up pointing back to the starting element. At this point slow is referencing the 'last' element list and it's next pointer can be set to null .
Q18 : Get the N-th Fibonacci number with O(n) time and O(1) space complexity
This solution is in linear O(n) time complexity, and constant O(1) space complexity. The number of loops it takes to calculate the nth fib number will still increase at a linear rate as n increases, but we are overriding the previous numbers in the sequence as we build it out, making the space complexity constant for any input n. It's also called Iterative Top-Down Approach .
Q19 : How to check if String is a Palindrome?
A palindrome is a word, phrase, number or other sequence of units that can be read the same way in either direction . You can check if a string is a palindrome by comparing it to the reverse of itself either using simple loop or recursion .
The time complexity is O(n/2) that is still O ( n ) . We doing n comparisons, where n = s.length() . Each comparison takes O ( 1 ) time, as it is a single character comparison. You can cut the complexity of the function in half by stopping at i == (s.length() / 2)+1 . It is not relevant in Big O terms, but it is still a pretty decent gain. Loop approach has constant space complexity O ( 1 ) as we not allocating any new memory. Reverse string approach needs O ( n ) additional memory to create a reversed copy of a string. Recursion approach has O ( n ) space complexity due call stack.
Recursion :
You may want to solve the problem by inverting the original string in a whole but note the space complexity will be worst than for the loop solution ( O(n) instead of O(1) ):
Q20 : How to check if two Strings (words) are Anagrams ?
Explain what is space complexity of that solution?
Two words are anagrams of each other if they contain the same number of characters and the same characters. There are two solutions to mention:
- You should only need to sort the characters in lexicographic order, and determine if all the characters in one string are equal to and in the same order as all of the characters in the other string. If you sort either array, the solution becomes O(n log n) .
- Hashmap approach where key - letter and value - frequency of letter,
- for first string populate the hashmap O(n)
- for second string decrement count and remove element from hashmap O(n)
- if hashmap is empty, the string is anagram otherwise not.
The major space cost in your code is the hashmap which may contain a frequency counter for each lower case letter from a to z . So in this case, the space complexity is supposed to be constant O(26) .
To make it more general, the space complexity of this problem is related to the size of alphabet for your input string. If the input string only contains ASCII characters, then for the worst case you will have O(256) as your space cost. If the alphabet grows to the UNICODE set, then the space complexity will be much worse in the worst scenario.
So in general its O(size of alphabet) .
Q21 : How to find Nth element from the end of a singly Linked List?
Use lockstep solution. The key to this algorithm is to set two pointers p1 and p2 apart by n-1 nodes initially so we want p2 to point to the (n-1)th node from the start of the list then we move p2 till it reaches the last node of the list. Once p2 reaches end of the list p1 will be pointing to the Nth node from the end of the list.
This lockstep approach will generally give better cache utilization, because a node hit by the front pointer may still be in cache when the rear pointer reaches it. In a language implementation using tracing garbage collection, this approach also avoids unnecessarily keeping the beginning (thus entire) list live for the duration of the operation.
Another solution is to use circular buffer . Keep a circular buffer of size x and add the nodes to it as you traverse the list. When you reach the end of the list, the x'th one from the tail is equal to the next entry in the circular buffer.
The lockstep approach moves all array elements in every step, resulting in a O(n + x 2 ) running time, whereas circular buffer approach uses a circular array and runs in O(n) . The circular buffer solution requires an additional x in memory.
Circular buffer approach:
Q22 : How to merge two sorted Arrays into a Sorted Array ?
Let's look at the merge principle :
Given two separate lists A and B ordered from least to greatest, construct a list C by:
- repeatedly comparing the least value of A to the least value of B,
- removing (or moving a pointer) the lesser value, and appending it onto C.
- when one list is exhausted, append the remaining items in the other list onto C in order.
- The list C is then also a sorted list.
Space: None
This problem will have O(n) complexity at best.

Q23 : Implement Double Linked List from Stack with min complexity
Imagine all items are organized into two stacks, draw them facing each other where face is where you put and peek:
now you can move 4 to 5:
and 3 to 4:
and you can go backwards.
You may also need another two stacks so that you can traverse List via the tail:
once current stack runs out
simply switch to the second pair of stacks!
Q24 : Merge two sorted singly Linked Lists without creating new nodes
You have two singly linked lists that are already sorted, you have to merge them and return a the head of the new list without creating any new extra nodes. The returned list should be sorted as well.
The method signature is:
Node class is below:
Here is the algorithm on how to merge two sorted linked lists A and B:
Here C will be the output list.
There are two solutions possible:
- Of the two nodes passed, keep the node with smaller value
- Point the smaller node's next to the next smaller value of remaining of the two linked lists
- Return the current node (which was smaller of the two nodes passed to the method)
- Treat one of the sorted linked lists as list, and treat the other sorted list as `bag of nodes'.
- Then we lookup for correct place for given node (from bag of nodes) in the list.
The run time complexity for the recursive and iterative solution here or the variant is O ( n ) .
Recursive solution:
Recursion should not be needed to avoid allocating a new node:
Q25 : Remove Invalid Parentheses
We all know how to check a string of parentheses is valid using a stack. Or even simpler use a counter. The counter will increase when it is ( and decrease when it is ) . Whenever the counter is negative, we have more ) than ( in the prefix.
To make the prefix valid, we need to remove a ) . The problem is: which one? The answer is any one in the prefix. However, if we remove any one, we will generate duplicate results, for example: s = ()), we can remove s[1] or s[2] but the result is the same (). Thus, we restrict ourself to remove the first ) in a series of concecutive )s.
After the removal, the prefix is then valid. We then call the function recursively to solve the rest of the string. However, we need to keep another information: the last removal position. If we do not have this position, we will generate duplicate by removing two ) in two steps only with a different order. For this, we keep tracking the last removal position and only remove ) after that.
Now one may ask. What about ( ? What if s = (()(() in which we need remove ( ? The answer is: do the same from right to left. However a cleverer idea is: reverse the string and reuse the code!
Q26 : Sort a Stack using Recursion
Note we can't use another stack or queue.
The idea of the solution is to hold all values in system stack until the stack becomes empty. When the stack becomes empty, insert all held items one by one in sorted order.
Time: O(n^2)
Q27 : Sort a Stack using another Stack
A stack performs push and pop operations. So, the push and pop operations are carried out between the input_stack and the auxilary_stack in such a way that the auxiliary stack contains the sorted input stack.
Solution Steps:
- Create a temporary stack say aux_stack .
- Repeat until the input_stack is not empty
- Pop an element from input_stack call it temp_value.
- While aux_stack is not empty and top of the aux_stack < temp_value , pop data from aux_stack and push it to the input_stack
- Push temp_value to the aux_stack
- return the aux_stack .
Q28 : Write a program for Recursive Binary Search
- The first difference is that the while loop from iterative approach is replaced by a recursive call back to the same method with the new values of low and high passed to the next recursive invocation along with Array and key or target element.
- The second difference is that instead of returning false when the while loop exits in the iterative version, in case of the recursive version, the condition of low > high is checked at the beginning of the next level of recursion and acts as the boundary condition for stopping further recursive calls by returning false.
- Also, note that the recursive invocations of binarySearch() return back the search result up the recursive call stack so that true or false return value is passed back up the call stack without any further processing.
- To further optimize the solution, in term of running time, we could consider implement the tail-recursive solution , where the stack trace of the algorithm would not pile up, which leads to a less memory footprint during the running time. To have the tail-recursive solution, the trick is to simply return the result from the next recursive function instead of further processing.
Q29 : Explain Knuth-Morris-Pratt (KMP) Algorithm in Plain English
The KMP algorithm is an efficient string matching algorithm due to Donald Knuth, Vaughan Pratt, and James H. Morris.
For the string matching problem (find p in S ) the naive approach would be to slide a window of size p all over S and check if it matches. That works but actually is inefficient. It takes O(p*S) time.
Instead of naive approach KMP is a linear time ( O ( n ) ) algorithm that exploits the observation that every time a match (or a mismatch) happens, the pattern itself contains enough information to dictate where the new examination should begin from. Every time the naive function fails (or succeeds), it starts matching over from the next character. This might not be necessary. We could use our knowledge of the point of last matching and the "structure" of the test string to know where the next matching should begin from.
How To Understand Prefix Function and Partial Match Table?
The "structure" of the string is encapsulated in the Prefix (or Failure) Function that we use to create Partial Match Table . Now, in order to talk about the meaning, we need to know about proper prefixes and proper suffixes.
- Proper prefix : All the characters in a string, with one or more cut off the end. “S”, “Sn”, “Sna”, and “Snap” are all the proper prefixes of “Snape”.
- Proper suffix : All the characters in a string, with one or more cut off the beginning. “agrid”, “grid”, “rid”, “id”, and “d” are all proper suffixes of “Hagrid”.
Saying that here’s the partial match table for the pattern abababca where each cell value is "The length of the longest proper prefix in the (sub)pattern that matches a proper suffix in the same (sub)pattern" .
Let’s also try it for cell five, which concerns “ababa”. We have four proper prefixes (“a”, “ab”, “aba”, and “abab”) and four proper suffixes (“a”, “ba”, “aba”, and “baba”). Now, we have two matches: “a” and “aba” are both proper prefixes and proper suffixes. Since “aba” is longer than “a”, it wins, and cell five gets value 3.
How To Use Partial Match Table?
We can use the values in the partial match table to skip ahead (rather than redoing unnecessary old comparisons) when we find partial matches. The formula works like this:
If a partial match of length partial_match_length is found and table[partial_match_length] > 1 , we may skip ahead partial_match_length - table[partial_match_length - 1] characters.*
Let’s say we’re matching the pattern “abababca” against the text “bacbababaabcbab”. Here’s our partial match table again for easy reference:
The first time we get a partial match is here:
This is a partial_match_length of 1. The value at table[partial_match_length - 1] (or table[0] ) is 0, so we don’t get to skip ahead any. The next partial match we get is here:
This is a partial_match_length of 5. The value at table[partial_match_length - 1] (or table[4] ) is 3. That means we get to skip ahead partial_match_length - table[partial_match_length - 1] (or 5 - table[4] or 5 - 3 or 2 ) characters:
This is a partial_match_length of 3. The value at table[partial_match_length - 1] (or table[2] ) is 1. That means we get to skip ahead partial_match_length - table[partial_match_length - 1] (or 3 - table[2] or 3 - 1 or 2 ) characters:
At this point, our pattern is longer than the remaining characters in the text, so we know there’s no match.
Things to remember:
- Once table is built, this algorithm has complexity O(n) even for binary alphabet (compare with O(m*n) for brute force).
- Table is built very quickly at start since pattern is usually very small.
- Table-building part is O(m) . Search part is O(n) . Total complexity O(m+n) even on binary alphabet.
- Compare with O(m*n) for brute force on binary alphabet.
- Because the prefix-function already tells us what needs to be done about the already matched parts, we do not need to check those parts again and hence, only one pass over the string is sufficient. So, the time complexity of the matching is O ( n ) .
- What about the pre-computation? It turns out that, if correctly implemented, it can be done in O(m) time where m is a length of a pattern.
- Overall, it takes O(m+ n) time. But since m≤ n , the time is bounded by O(n) . This is certainly better than the usual O ( n 2 )
- We only require as much space as the pattern. So, the space requirement is O(m) .
Q30 : Find Merge (Intersection) Point of Two Linked Lists
Say, there are two lists of different lengths, merging at a point ; how do we know where the merging point is?
Conditions:
- We don't know the length
This arguably violates the "parse each list only once" condition, but implement the tortoise and hare algorithm (used to find the merge point and cycle length of a cyclic list) so you start at List 1, and when you reach the NULL at the end you pretend it's a pointer to the beginning of List 2, thus creating the appearance of a cyclic list. The algorithm will then tell you exactly how far down List 1 the merge is.
Algorithm steps:
- it goes forward every time till the end, and then
- jumps to the beginning of the opposite list, and so on.
- Create two of these, pointing to two heads.
- Advance each of the pointers by 1 every time, until they meet in intersection point ( IP ). This will happen after either one or two passes.
To understand it count the number of nodes traveled from head1-> tail1 -> head2 -> intersection point and head2 -> tail2-> head1 -> intersection point . Both will be equal (Draw diff types of linked lists to verify this). Reason is both pointers have to travel same distances head1-> IP + head2->IP before reaching IP again. So by the time it reaches IP , both pointers will be equal and we have the merging point.
Q31 : Flip k least significant bits in an integer
The ~ unary operator is bitwise negation. If you need fewer bits than what fits in an int then you'll need to mask it with & after the fact.
To flip the k least significant bits, use the right mask.
or you can create a mask without loop:
Q32 : Given a singly Linked List, determine if it is a Palindrome
Could you do it in O ( 1 ) time and O ( 1 ) space?
Solution: is Reversed first half == Second half ?
Let's look to an example [1, 1, 2, 1] . In the beginning, set two pointers fast and slow starting at the head.
(1) Move: fast pointer goes to the end, and slow goes to the middle.
(2) Reverse: the right half is reversed, and slow pointer becomes the 2nd head.
(3) Compare: run the two pointers head and slow together and compare.
Q33 : How come that hash values are not reversible?
The input material can be an infinite length, where the output is always 128 bits long (for MD5 hash). This means that an infinite number of input strings will generate the same output.
If you pick a random number and divide it by 2 but only write down the remainder, you'll get either a 0 or 1 - even or odd, respectively. Is it possible to take that 0 or 1 and get the original number?
Q34 : How implement a Queue using only One (1) Stack?
I know how to do that with 2 stacks but how to implement it with one?
Tricky question.
You can "cheat" by using recursive function calls to pop the stack, then you push the item being queued, then as the recursive calls unwind you push what was popped. But this is really two stacks, because the function call stack counter is a stack .
Following is the implementation:
- During Enqueue operation, we can straight away push the element into the stack.
During Dequeue operation,
- Pop all the elements from a Stack recursively until Stack size is equal to 1 .
- If Stack size = 1 , Pop item from Stack , and return the same item.
- Push all popped element back to Stack .
Q35 : How to implement 3 Stacks with one Array ?
Find an algorithm/write pseudocode with high performance for a stack with only two operations, pop() and push() .
Space (not time) efficient. You could:
- Define two stacks beginning at the array endpoints and growing in opposite directions.
- Define the third stack as starting in the middle and growing in any direction you want.
- Redefine the Push op, so that when the operation is going to overwrite other stack, you shift the whole middle stack in the opposite direction before Pushing.
You need to store the stack top for the first two stacks, and the beginning and end of the third stack in some structure.
Above you may see an example. The shifting is done with an equal space partitioning policy, although other strategies could be chosen depending upon your problem heuristics.
the middle stack could be implemented using an alternating sequence for subsequent pushes. The resulting stack structure will be something like:
In this case, you'll need to store the number n of elements on the middle stack and use the function:
to know the next array element to use for this stack.
Although probably this will lead to less shifting, the implementation is not homogeneous for the three stacks, and inhomogeneity (you know) leads to special cases, more bugs and difficulties to maintain code.
Q36 : How to recursively reverse a Linked List?
Start from the bottom up by asking and answering tiny questions:
- What is the reverse of null (the empty list)? null .
- What is the reverse of a one element list? the element.
- What is the reverse of an n element list? the reverse of the rest of the list followed by the first element.
How to understand that part?
Think about the origin link list:
Now assume that the last node has been reversed. Just like this:
And this time you are at the node 3 , you want to change 3->4 to 3<-4 , means let 3->next->next = 3 (as 3->next is 4 and 4->next = 3 is to reverse it)
Assume that n is the list's length, the time complexity is O ( n ) . The extra space comes from implicit stack space due to recursion. The recursion could go up to n levels deep then space complexity is O ( n ) .
Q37 : How to use Memoization for N-th Fibonacci number?
Why? Any problems you may face with that solution?
Yes. It's called Memoization . Memoization is an optimization technique used primarily to speed up computer programs by storing the results of expensive function calls .
Let’s look at the diagram that will help you understand what’s going on here with the rest of our code. Function fib is called with argument 5. Can you see that we calculate the fib(2) results 3(!) times?
Basically, if we just store the value of each index in a hash , we will avoid the computational time of that value for the next N times. This change will increase the space complexity of our new algorithm to O ( n ) but will dramatically decrease the time complexity to 2N which will resolve to linear time since 2 is a constant O ( n ) .
There’s just one problem : With an infinite series, the memo array will have unbounded growth. Eventually, you’re going to run into heap size limits, and that will crash the JS engine. No worries though. With Fibonacci, you’ll run into the maximum exact JavaScript integer size first, which is 9007199254740991 . That’s over 9 quadrillion, which is a big number, but Fibonacci isn’t impressed. Fibonacci grows fast . You’ll burst that barrier after generating only 79 numbers.
Q38 : Copy a Linked List with Random (Arbitrary) Pointer using O ( 1 ) Space
Every node of the linked list has a random pointer (in addition to the next pointer) which could randomly point to another node or be null. How would you duplicate such a Linked List? Could you do that in O ( 1 ) space complexity?
Let's assume you have
An intuitive solution is to keep a hash table for each node in the list, via which we just need to iterate the list in 2 rounds ( 2N steps) respectively to create nodes and assign the values for their random pointers. As a result, the space complexity of this solution is O(N) , although with a linear time complexity.
- Walk the old list following the next pointers. For each node you visit, add a node to your new list, connect the previous node in your new list to the new node, store the old node random pointer in the new new node, then store a mapping of the old node pointer to the new node pointer in a map .
- Walk the new list, and for each random pointer, look it up in the map to find the associated node in the new list to replace it with.
As an optimised solution, we could reduce the space complexity into constant. The idea is to associate the original node with its copy node in a single linked list. In this way, we don't need extra space to keep track of the new nodes.
The algorithm is composed of the follow three steps which are also 3 iteration rounds.
- Iterate the original list and duplicate each node. The duplicate of each node follows its original immediately.
- Iterate the new list and assign the random pointer for each duplicated node.
- Restore the original list and extract the duplicated nodes.
Or mapped to code below:
Hash table version:
Q39 : Find all the repeating substrings in a given String (or DNA chromosome sequence)
Suffix Tree is the way to go.
- If you analyze the output for the string "AAAAAAAAAAAAAA" , then there are O ( n 2 ) characters in it, so the algorithm is at least O ( n 2 ) .
- To achieve O ( n 2 ) , just build the suffix tree for each suffix of s (indices 1..n , 2..n , 3..n , ..., n..n ). It doesn't matter if one of the strings has no own end node, just count how often each node is used.
- At the end, iterate over each node with count > 1 and print its path.
There are multiple way to construct the suffix tree:
- Using Ukkonen's algorithm.
- Using Suffix array and LCP (longest common prefix array)
Q40 : How to check for braces balance in a really large (1T) file in parallel?
There is a large file( 1TB) containing braces. How to check for braces balance? Make this process parallel.
If ( = 1 and ) = -1 . We should check the same two conditions:
- The total sum of the brackets is 0
- We never go negative at any point of time.
The first instinct to solving the parallel problem might be to split the work up into equal-sized chunks for each processor. If there are N characters in the file and K processors, give each processor a chunk of N/K characters. When processing a chunk, we can no longer simply return false when the count drops below 0, because there may be more opening braces in an earlier chunk processed by a different processor. We also can't return false if the counter is not 0 at the end, because it may be that there are more closing braces in later chunks. What we should calculate for each chunk, instead, is:
If we were doing a global brace counter as in the single-threaded approach, by how much would this chunk change the counter? This can be a positive or negative number. Call this the " brace delta ". This number is equal to the number of opening braces minus the number of closing braces in the chunk.
While we are calculating the " brace delta ", what is the lowest point to which the brace delta drops anytime during the processing of the chunk? Call that the " brace delta minimum ". This number is important because this is the point in the chunk where the global counter would be the smallest. We can check whether the global counter would have ever been negative by seeing whether (global counter before chunk) + (brace delta minimum in chunk) < 0 for any chunk.
These two things would be calculated by:
The complexity of the above code is O(N/K) for each of K processors. However, we can consider it O(N/K) time because all the processors can work in parallel.
After we process each chunk in parallel, we combine the results in a single-threaded way. We use the brace deltas to calculate the value of the global counter at the beginning of every chunk, and we use the brace delta min of the chunks to verify that the global counter never drops below 0. The global counter value should be 0 at the end of all the chunks as before.
The non-parallel part takes O(K) time, making the overall time for the solution O(N/K + K) .
Rust has been Stack Overflow’s most loved language for four years in a row and emerged as a compelling language choice for both backend and system developers, offering a unique combination of memory safety, performance, concurrency without Data races...
Clean Architecture provides a clear and modular structure for building software systems, separating business rules from implementation details. It promotes maintainability by allowing for easier updates and changes to specific components without affe...
Azure Service Bus is a crucial component for Azure cloud developers as it provides reliable and scalable messaging capabilities. It enables decoupled communication between different components of a distributed system, promoting flexibility and resili...
FullStack.Cafe is a biggest hand-picked collection of top Full-Stack, Coding, Data Structures & System Design Interview Questions to land 6-figure job offer in no time.
Coded with 🧡 using React in Australia 🇦🇺
by @aershov24 , Full Stack Cafe Pty Ltd 🤙, 2018-2023
Privacy • Terms of Service • Guest Posts • Contacts • MLStack.Cafe
- Trending Now
- Foundational Courses
- Data Science
- Practice Problem
- Machine Learning
- System Design
- DevOps Tutorial
Basic Programming Problems
- Learn Programming For Free
- Programming Tutorial | Introduction, Basic Concepts, Getting started, Problems
- Types of Issues and Errors in Programming/Coding
- What is Programming? A Handbook for Beginners
- Top 10 Programming Tips For Beginners
- C++ Programming Examples
- Best Courses on Competitive Programming
- CBSE Class 11 | Concepts of Programming Methodology
- How to begin with Competitive Programming?
- Programming | Question 1
- CBSE Class 11 | Problem Solving Methodologies
- C Program to Add Two Integers
- Top | MCQs on Dynamic Programming with Answers | Question 19
- C++ program for Solving Cryptarithmetic Puzzles
- Basic Coding Problems in DSA for Beginners
- Output of C programs | Set 49 (Operators)
- C Program to Make a Simple Calculator
- C | Pointer Basics | Question 13
Learn Programming – How To Code
In the world of programming , mastering the fundamentals is key to becoming a proficient developer. In this article, we will explore a variety of basic programming problems that are essential for every aspiring coder to understand. By delving into these foundational challenges, you will gain valuable insights into problem-solving techniques and build a strong foundation for your programming journey. Whether you’re a novice programmer or looking to refresh your skills, this guide will provide you with a solid introduction to essential programming problems
Why to Start with Basics Programming Problems?
Starting with basics is important because it helps you build a strong foundation. When you understand the basics well, it becomes easier to learn more advanced things later on. It’s like building a solid base for a tall building – if the base is strong, the building will be strong too. Mastering the basics also helps you become better at solving problems, which is really important in programming and other technical areas.
Benefits of Starting with Basic Programming Problems:
Foundation Building: Establishes a strong foundation in coding by introducing fundamental concepts.
- Improve Problem-Solving: Enhances problem-solving skills, preparing for more complex challenges.
- Language Proficiency: Fosters proficiency in a programming language, facilitating expression of thoughts and implementation of solutions.
- Debugging Skills: Provides practice in debugging techniques and understanding common errors.
- Algorithmic Thinking: Encourages efficient and optimized thinking, laying the groundwork for advanced problem-solving.
- Confidence Building: Boosts confidence in coding and problem-solving abilities through successful progression.
- Get Ready for Interviews: Prepares for coding job interviews by mastering fundamental concepts commonly assessed.
Basic Programming Problems:
Related Article:
- What is a Code in Programming?
- What Is Coding and What Is It Used For?
- How to Learn Programming?
Please Login to comment...
Similar reads.
- Programming
Improve your Coding Skills with Practice
What kind of Experience do you want to share?
1000+ Skills. 400+ Roles. One Platform
Resumes only tell you where a developer has worked, not how good they are writing code. Adopt skill-first hiring with HackerEarth.
4000+ tech leaders and 10M+ developers use HackerEarth

Refine talent management with our Assessment suite
Building a tech team requires an intricate interplay between internal Talent Acquisition, Human Resources, and the Engineering teams. Our product suite helps you navigate the developer hiring lifecycle effortlessly.
Tech Assessments
Screen and benchmark talent based on skills.
Ditch the GPA, embrace the code. Create job-relevant coding assessment tests with HackerEarth Assessments. Eliminate human bias with our AI-powered test evaluation and skill benchmarking, reduce acquisition effort, and screen the best tech talent for your hiring pipeline.
Coding Interviews
Collaborative platform with data-rich insights.
Unstructured developer interviews are so 2023! HackerEarth elevates developer experience with its built-in IDE, custom question library, interview rubrics, and integrated feedback mechanism. It's time to look beyond the inverted binary tree!
Learning and Development
Empower growth through tailored learning.
Learning programs without measurable outcomes have no defined ROI or effectiveness. Help developers build hands-on skills through experiential learning. HackerEarth lets you apply learning to real-world tasks and create transparent upskilling journeys for your team.
Your talent pipeline, powered by skills
A bad hire can derail months of product development. Cut out the guesswork in tech hiring with powerful data-driven insights. When it comes to good developers, only skills matter!

Unlock creativity and code: Experience Hackathon excellence
A hackathon is to a developer what a laboratory is to a scientist-an experimental playground where breakthroughs are made. Add to your talent pipeline, improve product innovation, and ignite meaningful dialogues with our end-to-end managed hackathons.
Branded Hackathons
Ignite innovation, improve brand recall.
Build a global talent pool of seasoned developers with our turnkey hiring challenges. Target specific skills and find the perfect fit for your team. Improve your employer brand by getting in front of our 10M+ strong community. Get direct access sets wrong expectation.
Internal Hackathons
Cultivate and reward creativity within your team.
Spark innovation. Foster collaboration. Leverage the power of Open Innovation. Drive creative ideation, solve business problems and drive product adoption through our end-to-end managed hackathons.
Hiring Challenges
Uncover top talent through competitive challenges.
Unearth hidden potential and discover internal talent ready for new challenges, with our Internal Hackathons. Recognize and reward the dreamers in your tech team, and encourage creative thinking and skill development.
HackerEarth as your Hackathon partner
No matter your goal, HackerEarth has the perfect hackathon solution. We take care of the entire logistics of hosting an event, while you focus on the skills that matter.
Challenge design and development
Marketing and promotion
Platform management
Data and insights
Hey there, developer!
Join our global community. Prep for tech interviews and upskill yourself. Get access to coveted tech jobs through and collaborate to build the future of tech in our hackathons.
Use our practice platform to hone your coding skills and light up the leaderboard!
Need help with an interview? These developer-friendly resources will help you land that dream job!
Participate in hackathons and hiring challenges to showcase your coding skills and to win cool prizes.
Loved by 20,000+ global tech recruiting leaders.

We use FaceCode to assess developers in real-time using actual tasks which they would perform day-to-day.

The ease with which a recruiter can create a test on HackerEarth and assess a candidate on a vast skill-set is simply amazing. The analytics that the platform provides gives an accurate measure of the candidate performance, which helps in hiring top-quality talent.

By using HackerEarth Assessments, we are giving our candidates an equal opportunity to prove their technical knowledge and skills, making the recruiting process fairer.
Skills first. Talent, always.
The future of hiring is skill-based. We are committed to leading the change. Are you?
HackerEarth is built for engineering teams, by an engineering team that hates a broken tech process and the inherent biases.
Top 100+ SQL Interview Questions and Practice Exercises

- jobs and career
- sql practice
- sql interview questions
Table of Contents
Review Your SQL Knowledge
Practice regularly, familiarize yourself with the testing platform, prepare for different types of questions, additional tips, explore 55+ general sql interview questions, practice, practice, practice, …, sql cheat sheet, data analysis in sql, window functions, common table expressions, advanced sql, good luck with your interview.
Are you gearing up for a SQL interview? This article is packed with over 100 SQL interview questions and practical exercises, organized by topic, to help you prepare thoroughly and approach your interview with confidence.
SQL is essential for many jobs, like data analysis, data science, software engineering, data engineering, testing, and many others. Preparing well for a SQL interview is crucial, no matter what role you're aiming for.
Searching for a new job can be really stressful, whether you're choosing to switch, have been laid off, or are looking for your first job. That's why being well-prepared is essential.
In this article, I've gathered over 100 SQL interview questions and exercises. These questions are spread across various articles published at LearnSQL.com. I have organized the articles by topic. Feel free to explore only the topics related to your specific job. I've also included tips to help you prepare for your interview.
SQL Interview Preparation Tips
Start preparing for your SQL interview well in advance. Once you're invited to an interview (Congratulations!), ask your recruiter what to expect and what is the format of the interview. For the SQL part you can usually expect coding exercises on an automated testing platform, a take-home assignment, or a whiteboard session.
The key to performing well in a SQL interview is practice. You'll likely be nervous, so the more familiar you are with SQL, the more instinctive your responses will become. Practice a variety of SQL problems so that querying becomes second nature to you.
If your interview involves using a specific coding platform, try to get comfortable with it beforehand. Many platforms offer a demo or practice session, so take advantage of this feature to familiarize yourself with the interface. This familiarity can help reduce stress and improve your performance during the actual interview.

- Coding Platform Questions: Whether during the interview or as a take-home task, make sure you understand the typical questions and problems that might appear on these platforms. Practice solving similar problems under timed conditions.
- Whiteboard Interviews: Be ready to write code in pseudocode and discuss your thought process. Focus on explaining the concepts and logic behind your solutions more than the exact syntax, which demonstrates a deeper understanding of the problem-solving process.
- Review Key SQL Concepts: Make sure you're comfortable with all fundamental SQL operations such as joins, subqueries, window functions, and aggregation. Also, review more advanced topics if the job role demands it.
- Mock Interviews: Consider doing mock interviews with friends or mentors to simulate the interview environment. This practice can help you manage time and stress effectively.
- Rest Well: Ensure you're well-rested before the interview day; a clear mind will help you think and perform better.
By incorporating these strategies into your preparation, you can approach your SQL interview with confidence and increase your chances of success.
Begin by refreshing your SQL knowledge, particularly if you haven't used it in a while. In this section we have collected some resources to assist you.
Our "SQL Basics" course is perfect for beginners or anyone needing a brief review. It covers both basic and intermediate SQL topics. In this course, you will actively write SQL code in various exercises, which will help you grow more confident in your SQL skills as you advance.

After you have refreshed the basics, check out these articles filled with SQL interview questions to help you prepare:
- Complete SQL Practice for Interviews — includes 16 SQL interview questions with practical exercises.
- 16 SQL Interview Questions for Business Analysts — SQL interview questions tailored for analysts.
- 8 Common Entry Level SQL Developer Interview Questions — great for beginners.
- Top 15 SQL Interview Questions in 2021 — a compilation of recent and relevant questions.
After refreshing your SQL skills, it’s important to keep practicing. Interviews can be stressful, and even straightforward topics can become challenging under pressure. The more you practice, the more confidently you can handle questions and problem-solving during an interview.
Here are some practice resources we recommend:
- SQL Practice track – This series includes 10 comprehensive SQL practice courses to sharpen your skills, perfect for those looking for hands-on practice. Key courses in this track include:
- SQL Practice Set – Provides a range of exercises across various SQL topics and databases.
- SQL Practice: A Store – Specifically designed for data analysts, this course offers practical SQL tasks using a database from an online store.
- SQL Practice: Blog & Traffic Data – Perfect for marketers and data analysts, this course focuses on analyzing traffic data from a pet store blog.
You can find many SQL practice materials and premium resources in Your Guide to SQL Practice at LearnSQL.com .
Lastly, we recommend our SQL Basics Cheat Sheet . It is a quick reference guide that covers basic SQL syntax. Keep it handy as you review your SQL knowledge and practice your skills.

Explore 50+ Specific SQL Topic Interview Questions
After you have refreshed your basic SQL knowledge, you might notice certain topics that are trickier for you or more relevant to your specific job role. In this section we've compiled resources that help you prepare for interview questions on specific SQL topics.
JOINs are a fundamental SQL construction used to combine data from multiple tables. They are also an essential topic at any SQL interview.
In our article The Top 10 SQL JOIN Interview Questions with Answers we've gathered the 10 most common questions about SQL JOINs that you might encounter in interviews. For each question we give you a detailed answer that will highlight what the interviewer is looking for in each question.
If you want to practice SQL JOINs, we recommend our interactive SQL JOINs course . It focuses on exercises specifically about SQL JOINs and contains 93 practice exercises to help you get confidence in your joining skills.
Additionally, we recommend Your Complete Guide to SQL JOINs , a comprehensive article that covers the basic knowledge of SQL JOINs, with additional articles and other resources on our platform.
The GROUP BY clause, paired with aggregate functions, is fundamental in SQL for calculating statistics like counts, averages, and sums from your data. This topic is essential for any SQL interview.
Our article Top 9 SQL GROUP BY Interview Questions provides a collection of the most frequently asked interview questions about GROUP BY . Each question includes a detailed answer, making sure you're prepared to discuss these topics during an interview.
If you are looking for an intermediate-level practice of GROUP BY topics, we recommend our Creating Basic SQL Reports course. It offers 100 exercises that focus on nuances of GROUP BY that can be asked about during an interview. It’s a hands-on course where you write your own SQL queries to help you better understand the issues and commit them to memory.
Furthermore, our article GROUP BY and Aggregate Functions: A Complete Overview gives a thorough explanation of GROUP BY and aggregate functions. This comprehensive guide is an excellent resource to round out your study, ensuring you have a robust understanding of how these functions work and how they can be applied in various scenarios.
We know that many of our users work specifically in the domain of data analysis. For these users, we have prepared an article 25 SQL Interview Questions for Data Analysts , which collects common SQL interview questions that can be asked for a role of data analyst. The article covers intermediate and advanced topics, like CTEs or window functions.
Window functions are an advanced SQL topic. Window functions are particularly useful when writing complex reports in SQL. For this reason, they are essential in data analysis and will come up in any data analysis interview.
Our article Top 10 SQL Window Functions Interview Questions contains the most common interview questions you might encounter regarding window functions. Each question has a detailed answer and links to further resources to help you dive deeper into each topic.
For those looking to refresh their knowledge through practice, we recommend our specialized courses:
- Window Functions – Covers the entire syntax of SQL window functions through interactive, hands-on exercises, making it ideal for those new to window functions or needing a refresher.
- Window Functions Practice Set - Aimed at those already familiar with window functions, this course provides additional practice to help refine your skills and prepare for more complex interview questions.
Additionally, we recommend our Window Functions Cheat Sheet , a handy quick reference guide for window functions. For a more thorough review, SQL Window Functions Guide is a comprehensive article that covers the basics of window functions with links to additional resources.
Common Table Expressions, or CTEs, is another advanced topic crucial for SQL interviews. CTEs help you organize and manage long and complex queries, make writing complex reports easier, and help you query hierarchical structures through recursive queries.
Our article Top 5 SQL CTE Interview Questions compiles essential CTE-related questions you're likely to face in interviews.in an article. Each question in the article is paired with a detailed answer to help you understand what is the most important in each response.
We also recommend our interactive Recursive Queries course that covers the syntax of CTEs through practice. The course is designed to teach the syntax and use of CTEs, including recursive CTEs, through hands-on exercises.
Finally, check out these articles to help you get ready for an advanced SQL interview:
- How to Prepare for an Advanced SQL Interview
- Top 27 Advanced SQL Interview Questions with Answers
- 15 Tricky SQL Interview Questions for Experienced Users
We also suggest our Advanced SQL Practice track, which is an online series of SQL practice courses designed for advanced users.
In this article we have gathered over 100 SQL interview questions and 20 additional resources compiled here to ensure you're thoroughly prepared. To further enhance your preparation, we recommend our All Forever SQL Package . It provides access to all our current and future courses in a single purchase, making it an excellent investment for your ongoing SQL education and interview readiness.
Sign up for free at LearnSQL.com and explore our SQL courses offer . Each month, we offer one of our courses—typically a practical, hands-on course—for free . This gives you a perfect opportunity to try out our resources without any commitment and see how they can help you succeed in your SQL interview. Take advantage of these offers to boost your confidence and sharpen your SQL skills effectively.
You may also like

How Do You Write a SELECT Statement in SQL?

What Is a Foreign Key in SQL?

Enumerate and Explain All the Basic Elements of an SQL Query
Subscribe to the PwC Newsletter
Join the community, edit social preview.

Add a new code entry for this paper
Remove a code repository from this paper, mark the official implementation from paper authors, add a new evaluation result row, remove a task, add a method, remove a method, edit datasets, bayesian methods for solving estimation and forecasting problems in the high-frequency trading environment.
SSRN 2016 · Paul Alexander Bilokon · Edit social preview
We examine modern stochastic filtering and Markov chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) methods and consider their applications in finance, especially electronic trading. Stochastic filtering methods have found many applications, from Space Shuttles to self-driving cars. We review some classical and modern algorithms and show how they can be used to estimate and forecast econometric models, stochastic volatility and term structure of risky bonds. We discuss the practicalities, such as outlier filtering, parameter estimation, and diagnostics. We focus on one particular application, stochastic volatility with leverage, and show how recent advances in filtering methods can help in this application: kernel density estimation can be used to estimate the predicted observation, filter out outliers, detect structural change, and improve the root mean square error while preventing discontinuities due to the resampling step. We then take a closer look at the discretisation of the continuous-time stochastic volatility models and show how an alternative discretisation, based on what we call a filtering Euler--Maruyama scheme, together with our generalisation of Gaussian assumed density filters to arbitrary (not necessarily additive) correlated process and observation noises, gives rise to a new, very fast approximate filter for stochastic volatility with leverage. Its accuracy falls short of particle filters but beats the unscented Kalman filter. Due to its speed and reliance exclusively on scalar computations this filter will be particularly useful in a high-frequency trading environment. In the final chapter we examine the leverage effect in high-frequency trade data, using last data point interpolation, tick and wall-clock time and generalise the models to take into account the time intervals between the ticks. We use a combination of MCMC methods and particle filtering methods. The robustness of the latter helps estimate parameters and compute Bayes factors. The speed and precision of modern filtering algorithms enables real-time filtering and prediction of the state.
Code Edit Add Remove Mark official
Tasks edit add remove, datasets edit, results from the paper edit add remove, methods edit add remove.
- Skip to content
- Skip to search
- Skip to footer
Products, Solutions, and Services
Want some help finding the Cisco products that fit your needs? You're in the right place. If you want troubleshooting help, documentation, other support, or downloads, visit our technical support area .
Contact Cisco
- Get a call from Sales
Call Sales:
- 1-800-553-6387
- US/CAN | 5am-5pm PT
- Product / Technical Support
- Training & Certification
Products by technology

- Software-defined networking
- Cisco Silicon One
- Cloud and network management
- Interfaces and modules
- Optical networking
- See all Networking

Wireless and Mobility
- Access points
- Outdoor and industrial access points
- Controllers
- See all Wireless and Mobility

- Secure Firewall
- Secure Endpoint
- Secure Email
- Secure Access
- Multicloud Defense
- See all Security

Collaboration
- Collaboration endpoints
- Conferencing
- Cisco Contact Center
- Unified communications
- Experience Management
- See all Collaboration

Data Center
- Servers: Cisco Unified Computing System
- Cloud Networking
- Hyperconverged infrastructure
- Storage networking
- See all Data Center
- Nexus Dashboard Insights
- Network analytics
- Cisco Secure Network Analytics (Stealthwatch)

- Video endpoints
- Cisco Vision
- See all Video

Internet of Things (IoT)
- Industrial Networking
- Industrial Routers and Gateways
- Industrial Security
- Industrial Switching
- Industrial Wireless
- Industrial Connectivity Management
- Extended Enterprise
- Data Management
- See all industrial IoT
- Cisco+ (as-a-service)
- Cisco buying programs
- Cisco Nexus Dashboard
- Cisco Networking Software
- Cisco DNA Software for Wireless
- Cisco DNA Software for Switching
- Cisco DNA Software for SD-WAN and Routing
- Cisco Intersight for Compute and Cloud
- Cisco ONE for Data Center Compute and Cloud
- See all Software
- Product index
Products by business type

Service providers

Small business

Midsize business
Cisco can provide your organization with solutions for everything from networking and data center to collaboration and security. Find the options best suited to your business needs.
- By technology
- By industry
- See all solutions
CX Services
Cisco and our partners can help you transform with less risk and effort while making sure your technology delivers tangible business value.
- See all services
Design Zone: Cisco design guides by category
Data center
- See all Cisco design guides
End-of-sale and end-of-life
- End-of-sale and end-of-life products
- End-of-Life Policy
- Cisco Commerce Build & Price
- Cisco Software Central
- Cisco Feature Navigator
- See all product tools
- Cisco Mobile Apps
- Design Zone: Cisco design guides
- Cisco DevNet
- Marketplace Solutions Catalog
- Product approvals
- Product identification standard
- Product warranties
- Cisco Security Advisories
- Security Vulnerability Policy
- Visio stencils
- Local Resellers
- Technical Support

- Toys & Games
- Learning & Education
- Science Kits & Toys

Enjoy fast, free delivery, exclusive deals, and award-winning movies & TV shows with Prime Try Prime and start saving today with fast, free delivery
Amazon Prime includes:
Fast, FREE Delivery is available to Prime members. To join, select "Try Amazon Prime and start saving today with Fast, FREE Delivery" below the Add to Cart button.
- Cardmembers earn 5% Back at Amazon.com with a Prime Credit Card.
- Unlimited Free Two-Day Delivery
- Streaming of thousands of movies and TV shows with limited ads on Prime Video.
- A Kindle book to borrow for free each month - with no due dates
- Listen to over 2 million songs and hundreds of playlists
- Unlimited photo storage with anywhere access
Important: Your credit card will NOT be charged when you start your free trial or if you cancel during the trial period. If you're happy with Amazon Prime, do nothing. At the end of the free trial, your membership will automatically upgrade to a monthly membership.
Return this item for free
Free returns are available for the shipping address you chose. You can return the item for any reason in new and unused condition: no shipping charges
- Go to your orders and start the return
- Select your preferred free shipping option
- Drop off and leave!

Image Unavailable

- To view this video download Flash Player
Color Code Magnets Base Kit: Interactive Coding Learning Tool for Kids Ages 3+, Enhances Logic & Problem-Solving Skills, Classroom Education, 36 Tiles, Evo Required Not Included
Purchase options and add-ons, about this item.
- INTERACTIVE CODING FOR YOUNG MINDS: The Ozobot Color Code Magnets Base Kit offers an engaging introduction to coding for students as young as Pre-K. With the magnetic board, wet erase marker and 36 puzzle pieces, it provides a hands-on learning experience that is both fun and educational, setting it apart from traditional coding tools. Evo robot is required and sold separately.
- FOUNDATIONAL CODING CONCEPTS MADE EASY: This kit simplifies complex coding concepts with a mix of Color Codes and line-following pieces. It's designed to help young learners grasp the basics of sequencing and logic, enhancing their problem-solving skills in a way that is accessible and enjoyable.
- DURABLE AND CLASSROOM-READY: Crafted with durability in mind, the Color Code Magnets are built to withstand regular classroom use. Their robust construction ensures longevity, making them a reliable educational resource for educators looking to invest in long-lasting teaching tools.
- EXPANDABLE LEARNING EXPERIENCE: While the Base Kit offers a complete coding experience, the Special Moves Kit and Speed Kit (sold separately) can be added for even more coding fun. This expandability makes the Ozobot Color Code Magnets a versatile tool for growing with the student's learning journey.
- SUPPORTS VARIOUS LEARNING ENVIRONMENTS: Perfect for both individual and group learning, the Color Code Magnets engage up to 3-4 students per kit. Their size and ease of use make them ideal for a range of educational settings, from classrooms to homeschooling, offering more flexibility than many other educational coding products.
Additional Details

Consider a similar item

Frequently bought together

Videos for similar products

Product information
Warranty & support, from the brand.

Ozobot makes award-winning programmable robots, patented screen-free coding programs and STEAM-based education solutions that transform the way students learn and create across all grades, subjects, and environments.

Evo Robots & Accessories
Visit the Store

Evo Compatible Kits

Product Description

What's in the box
- Magnetic Board: 25.2" x 12" Wet Erase Marker Straight Line - 16 Round Turn - 6 3-Way Intersection - 3 4-Way Intersection - 3 Right at Intersection - 2 Left at Intersection - 2 Straight at Intersection - 2 Start - 1 Win/Exit (Play Again) - 1
Videos for this product

Click to play video

Evo Classroom Kit Ozobot - Robotics
Product Review Show

Looking for specific info?
Customer reviews.
Customer Reviews, including Product Star Ratings help customers to learn more about the product and decide whether it is the right product for them.
To calculate the overall star rating and percentage breakdown by star, we don’t use a simple average. Instead, our system considers things like how recent a review is and if the reviewer bought the item on Amazon. It also analyzed reviews to verify trustworthiness.
No customer reviews
- Amazon Newsletter
- About Amazon
- Accessibility
- Sustainability
- Press Center
- Investor Relations
- Amazon Devices
- Amazon Science
- Sell on Amazon
- Sell apps on Amazon
- Supply to Amazon
- Protect & Build Your Brand
- Become an Affiliate
- Become a Delivery Driver
- Start a Package Delivery Business
- Advertise Your Products
- Self-Publish with Us
- Become an Amazon Hub Partner
- › See More Ways to Make Money
- Amazon Visa
- Amazon Store Card
- Amazon Secured Card
- Amazon Business Card
- Shop with Points
- Credit Card Marketplace
- Reload Your Balance
- Amazon Currency Converter
- Your Account
- Your Orders
- Shipping Rates & Policies
- Amazon Prime
- Returns & Replacements
- Manage Your Content and Devices
- Recalls and Product Safety Alerts
- Conditions of Use
- Privacy Notice
- Consumer Health Data Privacy Disclosure
- Your Ads Privacy Choices
Navigation Menu
Search code, repositories, users, issues, pull requests..., provide feedback.
We read every piece of feedback, and take your input very seriously.
Saved searches
Use saved searches to filter your results more quickly.
To see all available qualifiers, see our documentation .
- Notifications You must be signed in to change notification settings
Have a question about this project? Sign up for a free GitHub account to open an issue and contact its maintainers and the community.
By clicking “Sign up for GitHub”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy statement . We’ll occasionally send you account related emails.
Already on GitHub? Sign in to your account
An error message appears when running the front-end command yarn. How can I solve this problem? #346
ganganngannn commented May 29, 2024
abi commented May 29, 2024
Sorry, something went wrong.
ganganngannn commented May 30, 2024
- 👍 1 reaction
No branches or pull requests
Help | Advanced Search
Quantum Physics
Title: training-efficient density quantum machine learning.
Abstract: Quantum machine learning requires powerful, flexible and efficiently trainable models to be successful in solving challenging problems. In this work, we present density quantum neural networks, a learning model incorporating randomisation over a set of trainable unitaries. These models generalise quantum neural networks using parameterised quantum circuits, and allow a trade-off between expressibility and efficient trainability, particularly on quantum hardware. We demonstrate the flexibility of the formalism by applying it to two recently proposed model families. The first are commuting-block quantum neural networks (QNNs) which are efficiently trainable but may be limited in expressibility. The second are orthogonal (Hamming-weight preserving) quantum neural networks which provide well-defined and interpretable transformations on data but are challenging to train at scale on quantum devices. Density commuting QNNs improve capacity with minimal gradient complexity overhead, and density orthogonal neural networks admit a quadratic-to-constant gradient query advantage with minimal to no performance loss. We conduct numerical experiments on synthetic translationally invariant data and MNIST image data with hyperparameter optimisation to support our findings. Finally, we discuss the connection to post-variational quantum neural networks, measurement-based quantum machine learning and the dropout mechanism.
Submission history
Access paper:.
- HTML (experimental)
- Other Formats
References & Citations
- INSPIRE HEP
- Google Scholar
- Semantic Scholar
BibTeX formatted citation
Bibliographic and Citation Tools
Code, data and media associated with this article, recommenders and search tools.
- Institution
arXivLabs: experimental projects with community collaborators
arXivLabs is a framework that allows collaborators to develop and share new arXiv features directly on our website.
Both individuals and organizations that work with arXivLabs have embraced and accepted our values of openness, community, excellence, and user data privacy. arXiv is committed to these values and only works with partners that adhere to them.
Have an idea for a project that will add value for arXiv's community? Learn more about arXivLabs .
Screen Rant
Genshin impact 4.7's resin increase doesn't solve the game's biggest problem.

Your changes have been saved
Email Is sent
Please verify your email address.
You’ve reached your account maximum for followed topics.
Genshin Impact 4.6 Unexpectedly Shines With Natlan Looming: Our Comprehensive Review
Every genshin impact 4.7 livestream code & reward, genshin impact natlan leaks: farming artifacts is about to get a lot easier, quick links, genshin impact's resin cap amount isn't the problem, how to fix genshin impact's resin problems, keeping up with genshin impact needs to be addressed.
- Genshin Impact's 4.7 update increases Resin cap from 160 to 200, attempting to address time-gating issues.
- Evaluating Resin efficiency is more important than simply raising the cap; Condensed Resin helps but has limits.
- The game's Resin economy may need a complete overhaul to cater to all player types and improve the overall experience.
The upcoming Genshin Impact 4.7 update is, presumably, one of the last the popular action-RPG will push out prior to the introduction of its next major region, Natlan. In general, the game cycles through one nation per year since its release, with most new version X.0 updates coming within a few months of the game's launch anniversary. With something so big in the pipeline, it makes sense for players to temper expectations for the next handful of updates and events.
However, Genshin Impact 4.7 will feature what many believe to be a major upgrade to a long-maligned system. Genshin Impact is an open world gacha action-RPG with an energy system - Resin - that dictates how players spend their time in-game. Resin is the "cap" on how fast players can progress their accounts - it's required to pursue artifact drops, materials for character ascensions, and more. The maximum amount of Resin will be changing from 160 to 200 as of 4.7 - but that won't solve Genshin Impact 's biggest problem when it comes to its time-gated resource acquisition.
Genshin Impact 4.8 Leaks: New Character May Provide A Much-Needed Reaction Buff
Details about a rumored new character in Genshin Impact have arisen, hinting at what may become a much-needed buff to an underused Elemental Reaction.
It's How Much Time There Is To Spend It
The best way to look at Genshin Impact 's Resin economy isn't necessarily in its total amount. It's best to evaluate Resin efficiency for the player; that is, how easy it is to maximize Resin usage relative to factors like time invested, resources acquired, and familiarity with the game's systems . In that sense, it doesn't matter how high the cap realistically gets, as it will still be constrained by other elements that HoYoverse can't alter with just a cap change - having 160 or 200 Resin, for instance, won't matter if a player is away for two days.
Of course, there is a way to help alleviate Resin inefficiency (the idea that every second spent with maximized Resin is a "waste") with Condensed Resin, but that's a capped inventory item as well. At a certain point, Resin just isn't efficiently stored anymore. Five Condensed Resin essentially works out to 200 "extra" Resin, which, as of Genshin Impact Version 4.7, will mirror the cap amount players have for their normal Resin.
Version 4.6 for Genshin Impact brings a surprising amount of remarkable playables to a game preparing for the launch of Natlan later this year.
Look at it this way: Resin cap increases are only valuable if a player is available to make good on them . For many who have to take extended breaks from the game through no desire of their own, these systems actively hinder their ability to catch back up on what they've missed - whether it be a new boss or new artifacts to acquire for a character they might be interested in wishing for.
Energy Resources Can Be Better Managed
Since simply increasing the cap is a short-term solution to a long-term problem (especially for new players in Genshin Impact ), HoYoverse should investigate better fixes for a system that actively hinders players from engaging with adventures in Teyvat - especially those returning to the game. The first and most obvious solution is borrowed from a game HoYoverse should be intimately familiar with . Honkai: Star Rail pre-solved this kind of issue early into its life cycle, allowing players to "bank" its energy resource passively to a whopping 2400 extra.
While it takes quite a long time to accumulate - 30 days - it provides a buffer for players who have fallen out of playing. While it's not a valuable option for people who are able to login daily and accomplish tasks while grinding for end-game materials and equipment, it's something . It's a drastically different amount to what Genshin Impact offers for lapsing between events or even update patches, and Honkai: Star Rail allows it passively - Genshin requires the actual crafting of Condensed Resin to fix it.
HoYoverse has shared three codes for Genshin Impact during the Version 4.7 livestream. Here are all of them and how to claim 300 free Primogems.
Another solution, albeit one that's significantly more work for the developer, is to completely overhaul the Resin economy in Genshin Impac t . This makes sense given the scale of the game and its roster of characters - the Resin refresh rate and its cap wasn't nearly as difficult to work with at launch, but the sheer number of options for both team building and artifact loadouts - and the grind for them - makes it far more daunting to farm. Given the amount of content available, it would make sense to reduce, or even halve, some of the Resin requirements for artifact domains or boss fights.
This would also have the side effect of increasing the amount of time it takes for a player to burn through their Resin for dailies, so its possible this option doesn't work for everyone . For some, using 160 Resin is a quick 10-minute daily option that is easy to keep up with, and having to do more to effectively spend their Resin might have the same effect on that demographic as the current system does on players who can't invest as much time in the game - and if HoYoverse is choosing between those two audiences, it makes sense the more consistently invested players are catered to.
The worst takeaway from the discussion of Genshin Impact 's biggest problem (at least currently) is to suggest that the game simply needs to tone down the amount of content it releases to give busy players more breathing room.
Finally, the best option - but also, perhaps, the most unlikely - would be to address how quickly Resin regenerates on top of increasing the cap. It currently regenerates at 1 Resin per 8 minutes, which is a stingy amount - increasing that number to 1 Resin per 4 minutes, even, would mean it only fully regenerates once every 10.5 hours or so . That would necessitate two daily logins for truly invested players looking to maximize their Resin spending, while giving basically double the amount of time per day for lapsed players to catch up with past content additions.
More Content Isn't Bad, But Requires Careful Consideration
The worst takeaway from the discussion of Genshin Impact 's biggest problem (at least currently) is to suggest that the game simply needs to tone down the amount of content it releases to give busy players more breathing room. Content droughts in live service games are brutal for player morale, and Genshin Impact has done an excellent job across the years to avoid this problem. By no means should Resin be made simpler to deal with by way of having less to do with it .
What Genshin Impact 's Resin issue is a symptom of, however, is the larger problem - that Genshin Impact has simply ballooned to such a scale that only the most invested, dedicated players can keep up with all of its updates, events, and character & weapon releases . The Resin system is an archaic failsafe to ensure people stay invested in daily logins and are enticed to spend money on banners or battle passes. Truthfully, that isn't needed.
According to a new leak, there may be a system update with Genshin Impact 5.0 and Natlan that will make Artifact grinding a bit easier.
The incredible amount of hours needed just to farm the right artifact substats and materials already means that those invested players would still need to log in every day to be efficient. While outright removing Resin as a resource would certainly be asking too much, it's not unreasonable to think that even doubling the cap would have a net positive effect on the amount players spend on Genshin Impact , both monetarily and with their time.
At the very least, the game has very little to lose in trying some of these more ambitious solutions out. Genshin Impact is one of the most successful and highest-earning live service games on the market today - it, more than any of its competitors, should be looking for ways to improve the player experience, as it has the luxury of doing so.
Genshin Impact

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Boost your coding interview skills and confidence by practicing real interview questions with LeetCode. Our platform offers a range of essential problems for practice, as well as the latest questions being asked by top-tier companies.
Accolite. + 7 more. Solve Problem. Easy 413K 31.49%. Platform to practice programming problems. Solve company interview questions and improve your coding intellect.
Practice over 5000+ problems in coding languages like Python, Java, JavaScript, C++, SQL and HTML. Start with beginner friendly problems and solve hard problems as you become better. Courses. Learn Python 10 courses. Learn C++ 9 courses. Learn C 9 courses. Learn Java 9 courses. Learn Javascript 9 courses. Data ...
This is an introduction to how challenges on Edabit work. In the Code tab above you'll see a starter function that looks like this: function hello () { } All you have to do is type return "hello edabit.com" between the curly braces { } and then click the Check button. If you did this correctly, the button will turn red and ….
In this post, we've gone over the four-step problem-solving strategy for solving coding problems. Let's review them here: Step 1: understand the problem. Step 2: create a step-by-step plan for how you'll solve it. Step 3: carry out the plan and write the actual code.
Simplest means you know the answer (or are closer to that answer). After that, simplest means this sub-problem being solved doesn't depend on others being solved. Once you solved every sub-problem, connect the dots. Connecting all your "sub-solutions" will give you the solution to the original problem. Congratulations!
Now, coding/programming isn't just about solving different kinds of problems using different programming languages, but it's a large part of what you'll do as a developer. The fields of Web development, Machine Learning, Artificial Intelligence, Augmented Reality, App Development, and many others require strong problem-solving skills.
These challenges are good for practicing your skills at using a programming language. Build a binary search tree. Write a program that prints the numbers from 1 to 100. But for multiples of three, print Fizz instead of the number, and multiples of five, print Buzz. For numbers that are multiples of both three and five, print FizzBuzz.
A better way to learn programming. Learn to code with 10,000+ interactive challenges. Gain XP, unlock achievements and level up. Our bite-sized challenges are a shortcut through the coding maze. Beginner Tutorials Explore Challenges.
Let's walk through this sample challenge and explore the features of the code editor. 1 of 6; Review the problem statement Each challenge has a problem statement that includes sample inputs and outputs. Some challenges include additional information to help you out. 2 of 6; Choose a language Select the language you wish to use to solve this ...
Buffing your problem-solving skills, staying organized, and utilizing various techniques such as pseudocoding and debugging can help you tackle coding challenges with confidence and precision. Keep practicing and implementing these strategies to enhance your problem-solving abilities and become a more skilled coder.
The technical part is always the easiest once you've clearly devised a clear plan of attack for how to solve the problem. "If I only had an hour to chop down a tree, I would spend the first 45 minutes sharpening my axe." — Abraham Lincoln. To demonstrate this we're going to work through a coding problem together.
6. Exercism.io. Exercism is a coding challenge website that offers 3100+ challenges spanning 52 different programming languages. After picking a language that you'd like to master, you tackle the coding challenges right on your machine (Exercism has their own command line interface that you can download from GitHub).
Return the Sum of Two Numbers. Create a function that takes two numbers as arguments and returns their sum. Examples addition (3, 2) 5 addition (-3, -6) -9 addition (7, 3) 10 Notes Don't forget to return the result. If you get stuck on a challenge, find help in the Resources tab.
Solve kata with your coding style right in the browser and use test cases (TDD) to check it as you progress. Retrain with new, creative, and optimized approaches. Find all of the bugs in your programming practice. Earn ranks and honor. Kata code challenges are ranked from beginner to expert level. As you complete higher-ranked kata, you level ...
CodinGame is a challenge-based training platform for programmers where you can play with the hottest programming topics. Solve games, code AI bots, learn from your peers, have fun.
You may hate code challenges and coding interviews but reality is a lot of companies from Google to Amazon do care that you understand the difference between O(n log n) and O(n²), that you do understand when different data structures are appropriate, and that you can leverage these (very basic) skills to solve simple problems. Follow along and check 40 most common Coding Challenges and ...
Learn Programming - How To Code. In the world of programming, mastering the fundamentals is key to becoming a proficient developer.In this article, we will explore a variety of basic programming problems that are essential for every aspiring coder to understand. By delving into these foundational challenges, you will gain valuable insights into problem-solving techniques and build a strong ...
Ditch the GPA, embrace the code. Create job-relevant coding assessment tests with HackerEarth Assessments. Eliminate human bias with our AI-powered test evaluation and skill benchmarking, reduce acquisition effort, and screen the best tech talent for your hiring pipeline. ... Drive creative ideation, solve business problems and drive product ...
Coding Platform Questions: Whether during the interview or as a take-home task, make sure you understand the typical questions and problems that might appear on these platforms. Practice solving similar problems under timed conditions. Whiteboard Interviews: Be ready to write code in pseudocode and discuss your thought process. Focus on ...
🚀 Day 91 of solving LeetCode & Coding Ninjas problems! Today's challenge dives into the realm of stacks, a fundamental data structure in computer science. The task at hand is to design and ...
Stay informed on the latest trending ML papers with code, research developments, libraries, methods, and datasets. Read previous issues. Subscribe. Join the community ... Bayesian methods for solving estimation and forecasting problems in the high-frequency trading environment
How Edabit Works. This is an introduction to how challenges on Edabit work. In the Code tab above you'll see a starter function that looks like this: public static boolean returnTrue () { } All you have to do is type return true; between the curly braces { } and then click the Check button. If you did this correctly, the button will turn re ….
Cisco+ (as-a-service) Cisco buying programs. Cisco Nexus Dashboard. Cisco Networking Software. Cisco DNA Software for Wireless. Cisco DNA Software for Switching. Cisco DNA Software for SD-WAN and Routing. Cisco Intersight for Compute and Cloud. Cisco ONE for Data Center Compute and Cloud.
INTERACTIVE CODING FOR YOUNG MINDS: The Ozobot Color Code Magnets Base Kit offers an engaging introduction to coding for students as young as Pre-K. With the magnetic board, wet erase marker and 36 puzzle pieces, it provides a hands-on learning experience that is both fun and educational, setting it apart from traditional coding tools.
The text was updated successfully, but these errors were encountered: Owner. abi commented May 29, 2024. I'll have to fix this issue. But as the logs indicate, can you set PUPPETEER_SKIP_DOWNLOAD=True yarn? Puppeteer is only needed for development of this project, not for simplify using it so you can remove it safely.
Quantum machine learning requires powerful, flexible and efficiently trainable models to be successful in solving challenging problems. In this work, we present density quantum neural networks, a learning model incorporating randomisation over a set of trainable unitaries. These models generalise quantum neural networks using parameterised quantum circuits, and allow a trade-off between ...
Genshin Impact's 4.7 update increases Resin cap from 160 to 200, attempting to address time-gating issues. Evaluating Resin efficiency is more important than simply raising the cap; Condensed Resin helps but has limits. The game's Resin economy may need a complete overhaul to cater to all player types and improve the overall experience.
Quantum computers could potentially reduce the distances travelers need to walk in airports by helping airlines assign planes to gates more efficiently. Vincent alban/Reuters. One day, you might ...
How Edabit Works. This is an introduction to how challenges on Edabit work. In the Code tab above you'll see a starter function that looks like this: bool returnTrue () { } All you have to do is type return true; between the curly braces { } and then click the Check button. If you did this correctly, the button will turn red and say SUBMIT ...