A Guide to Literature Reviews
Importance of a good literature review.
- Conducting the Literature Review
- Structure and Writing Style
- Types of Literature Reviews
- Citation Management Software This link opens in a new window
- Acknowledgements
A literature review is not only a summary of key sources, but has an organizational pattern which combines both summary and synthesis, often within specific conceptual categories . A summary is a recap of the important information of the source, but a synthesis is a re-organization, or a reshuffling, of that information in a way that informs how you are planning to investigate a research problem. The analytical features of a literature review might:
- Give a new interpretation of old material or combine new with old interpretations,
- Trace the intellectual progression of the field, including major debates,
- Depending on the situation, evaluate the sources and advise the reader on the most pertinent or relevant research, or
- Usually in the conclusion of a literature review, identify where gaps exist in how a problem has been researched to date.
The purpose of a literature review is to:
- Place each work in the context of its contribution to understanding the research problem being studied.
- Describe the relationship of each work to the others under consideration.
- Identify new ways to interpret prior research.
- Reveal any gaps that exist in the literature.
- Resolve conflicts amongst seemingly contradictory previous studies.
- Identify areas of prior scholarship to prevent duplication of effort.
- Point the way in fulfilling a need for additional research.
- Locate your own research within the context of existing literature [very important].
- << Previous: Definition
- Next: Conducting the Literature Review >>
- Last Updated: May 10, 2024 11:34 AM
- URL: https://libguides.mcmaster.ca/litreview
News alert: UC Berkeley has announced its next university librarian

Secondary menu
- Log in to your Library account
- Hours and Maps
- Connect from Off Campus
- UC Berkeley Home
Search form
Conducting a literature review: why do a literature review, why do a literature review.
- How To Find "The Literature"
- Found it -- Now What?
Besides the obvious reason for students -- because it is assigned! -- a literature review helps you explore the research that has come before you, to see how your research question has (or has not) already been addressed.
You identify:
- core research in the field
- experts in the subject area
- methodology you may want to use (or avoid)
- gaps in knowledge -- or where your research would fit in
It Also Helps You:
- Publish and share your findings
- Justify requests for grants and other funding
- Identify best practices to inform practice
- Set wider context for a program evaluation
- Compile information to support community organizing
Great brief overview, from NCSU
Want To Know More?
- Next: How To Find "The Literature" >>
- Last Updated: Apr 25, 2024 1:10 PM
- URL: https://guides.lib.berkeley.edu/litreview

- University of Texas Libraries
Literature Reviews
- What is a literature review?
- Steps in the Literature Review Process
- Define your research question
- Determine inclusion and exclusion criteria
- Choose databases and search
- Review Results
- Synthesize Results
- Analyze Results
- Librarian Support
What is a Literature Review?
A literature or narrative review is a comprehensive review and analysis of the published literature on a specific topic or research question. The literature that is reviewed contains: books, articles, academic articles, conference proceedings, association papers, and dissertations. It contains the most pertinent studies and points to important past and current research and practices. It provides background and context, and shows how your research will contribute to the field.
A literature review should:
- Provide a comprehensive and updated review of the literature;
- Explain why this review has taken place;
- Articulate a position or hypothesis;
- Acknowledge and account for conflicting and corroborating points of view
From S age Research Methods
Purpose of a Literature Review
A literature review can be written as an introduction to a study to:
- Demonstrate how a study fills a gap in research
- Compare a study with other research that's been done
Or it can be a separate work (a research article on its own) which:
- Organizes or describes a topic
- Describes variables within a particular issue/problem
Limitations of a Literature Review
Some of the limitations of a literature review are:
- It's a snapshot in time. Unlike other reviews, this one has beginning, a middle and an end. There may be future developments that could make your work less relevant.
- It may be too focused. Some niche studies may miss the bigger picture.
- It can be difficult to be comprehensive. There is no way to make sure all the literature on a topic was considered.
- It is easy to be biased if you stick to top tier journals. There may be other places where people are publishing exemplary research. Look to open access publications and conferences to reflect a more inclusive collection. Also, make sure to include opposing views (and not just supporting evidence).
Source: Grant, Maria J., and Andrew Booth. “A Typology of Reviews: An Analysis of 14 Review Types and Associated Methodologies.” Health Information & Libraries Journal, vol. 26, no. 2, June 2009, pp. 91–108. Wiley Online Library, doi:10.1111/j.1471-1842.2009.00848.x.
Meryl Brodsky : Communication and Information Studies
Hannah Chapman Tripp : Biology, Neuroscience
Carolyn Cunningham : Human Development & Family Sciences, Psychology, Sociology
Larayne Dallas : Engineering
Janelle Hedstrom : Special Education, Curriculum & Instruction, Ed Leadership & Policy
Susan Macicak : Linguistics
Imelda Vetter : Dell Medical School
For help in other subject areas, please see the guide to library specialists by subject .
Periodically, UT Libraries runs a workshop covering the basics and library support for literature reviews. While we try to offer these once per academic year, we find providing the recording to be helpful to community members who have missed the session. Following is the most recent recording of the workshop, Conducting a Literature Review. To view the recording, a UT login is required.
- October 26, 2022 recording
- Last Updated: Oct 26, 2022 2:49 PM
- URL: https://guides.lib.utexas.edu/literaturereviews

- Library Homepage
Literature Review: The What, Why and How-to Guide: Literature Reviews?
- Literature Reviews?
- Strategies to Finding Sources
- Keeping up with Research!
- Evaluating Sources & Literature Reviews
- Organizing for Writing
- Writing Literature Review
- Other Academic Writings
What is a Literature Review?
So, what is a literature review .
"A literature review is an account of what has been published on a topic by accredited scholars and researchers. In writing the literature review, your purpose is to convey to your reader what knowledge and ideas have been established on a topic, and what their strengths and weaknesses are. As a piece of writing, the literature review must be defined by a guiding concept (e.g., your research objective, the problem or issue you are discussing, or your argumentative thesis). It is not just a descriptive list of the material available or a set of summaries." - Quote from Taylor, D. (n.d)."The Literature Review: A Few Tips on Conducting it".
- Citation: "The Literature Review: A Few Tips on Conducting it"
What kinds of literature reviews are written?
Each field has a particular way to do reviews for academic research literature. In the social sciences and humanities the most common are:
- Narrative Reviews: The purpose of this type of review is to describe the current state of the research on a specific research topic and to offer a critical analysis of the literature reviewed. Studies are grouped by research/theoretical categories, and themes and trends, strengths and weaknesses, and gaps are identified. The review ends with a conclusion section that summarizes the findings regarding the state of the research of the specific study, the gaps identify and if applicable, explains how the author's research will address gaps identify in the review and expand the knowledge on the topic reviewed.
- Book review essays/ Historiographical review essays : A type of literature review typical in History and related fields, e.g., Latin American studies. For example, the Latin American Research Review explains that the purpose of this type of review is to “(1) to familiarize readers with the subject, approach, arguments, and conclusions found in a group of books whose common focus is a historical period; a country or region within Latin America; or a practice, development, or issue of interest to specialists and others; (2) to locate these books within current scholarship, critical methodologies, and approaches; and (3) to probe the relation of these new books to previous work on the subject, especially canonical texts. Unlike individual book reviews, the cluster reviews found in LARR seek to address the state of the field or discipline and not solely the works at issue.” - LARR
What are the Goals of Creating a Literature Review?
- To develop a theory or evaluate an existing theory
- To summarize the historical or existing state of a research topic
- Identify a problem in a field of research
- Baumeister, R.F. & Leary, M.R. (1997). "Writing narrative literature reviews," Review of General Psychology , 1(3), 311-320.
When do you need to write a Literature Review?
- When writing a prospectus or a thesis/dissertation
- When writing a research paper
- When writing a grant proposal
In all these cases you need to dedicate a chapter in these works to showcase what has been written about your research topic and to point out how your own research will shed new light into a body of scholarship.
Where I can find examples of Literature Reviews?
Note: In the humanities, even if they don't use the term "literature review", they may have a dedicated chapter that reviewed the "critical bibliography" or they incorporated that review in the introduction or first chapter of the dissertation, book, or article.
- UCSB electronic theses and dissertations In partnership with the Graduate Division, the UC Santa Barbara Library is making available theses and dissertations produced by UCSB students. Currently included in ADRL are theses and dissertations that were originally filed electronically, starting in 2011. In future phases of ADRL, all theses and dissertations created by UCSB students may be digitized and made available.
Where to Find Standalone Literature Reviews
Literature reviews are also written as standalone articles as a way to survey a particular research topic in-depth. This type of literature review looks at a topic from a historical perspective to see how the understanding of the topic has changed over time.
- Find e-Journals for Standalone Literature Reviews The best way to get familiar with and to learn how to write literature reviews is by reading them. You can use our Journal Search option to find journals that specialize in publishing literature reviews from major disciplines like anthropology, sociology, etc. Usually these titles are called, "Annual Review of [discipline name] OR [Discipline name] Review. This option works best if you know the title of the publication you are looking for. Below are some examples of these journals! more... less... Journal Search can be found by hovering over the link for Research on the library website.
Social Sciences
- Annual Review of Anthropology
- Annual Review of Political Science
- Annual Review of Sociology
- Ethnic Studies Review
Hard science and health sciences:
- Annual Review of Biomedical Data Science
- Annual Review of Materials Science
- Systematic Review From journal site: "The journal Systematic Reviews encompasses all aspects of the design, conduct, and reporting of systematic reviews" in the health sciences.
- << Previous: Overview
- Next: Strategies to Finding Sources >>
- Last Updated: Mar 5, 2024 11:44 AM
- URL: https://guides.library.ucsb.edu/litreview
Libraries | Research Guides
Literature reviews, what is a literature review, learning more about how to do a literature review.
- Planning the Review
- The Research Question
- Choosing Where to Search
- Organizing the Review
- Writing the Review
A literature review is a review and synthesis of existing research on a topic or research question. A literature review is meant to analyze the scholarly literature, make connections across writings and identify strengths, weaknesses, trends, and missing conversations. A literature review should address different aspects of a topic as it relates to your research question. A literature review goes beyond a description or summary of the literature you have read.
- Sage Research Methods Core Collection This link opens in a new window SAGE Research Methods supports research at all levels by providing material to guide users through every step of the research process. SAGE Research Methods is the ultimate methods library with more than 1000 books, reference works, journal articles, and instructional videos by world-leading academics from across the social sciences, including the largest collection of qualitative methods books available online from any scholarly publisher. – Publisher
- Next: Planning the Review >>
- Last Updated: May 2, 2024 10:39 AM
- URL: https://libguides.northwestern.edu/literaturereviews
Research Methods
- Getting Started
- Literature Review Research
- Research Design
- Research Design By Discipline
- SAGE Research Methods
- Teaching with SAGE Research Methods
Literature Review
- What is a Literature Review?
- What is NOT a Literature Review?
- Purposes of a Literature Review
- Types of Literature Reviews
- Literature Reviews vs. Systematic Reviews
- Systematic vs. Meta-Analysis
Literature Review is a comprehensive survey of the works published in a particular field of study or line of research, usually over a specific period of time, in the form of an in-depth, critical bibliographic essay or annotated list in which attention is drawn to the most significant works.
Also, we can define a literature review as the collected body of scholarly works related to a topic:
- Summarizes and analyzes previous research relevant to a topic
- Includes scholarly books and articles published in academic journals
- Can be an specific scholarly paper or a section in a research paper
The objective of a Literature Review is to find previous published scholarly works relevant to an specific topic
- Help gather ideas or information
- Keep up to date in current trends and findings
- Help develop new questions
A literature review is important because it:
- Explains the background of research on a topic.
- Demonstrates why a topic is significant to a subject area.
- Helps focus your own research questions or problems
- Discovers relationships between research studies/ideas.
- Suggests unexplored ideas or populations
- Identifies major themes, concepts, and researchers on a topic.
- Tests assumptions; may help counter preconceived ideas and remove unconscious bias.
- Identifies critical gaps, points of disagreement, or potentially flawed methodology or theoretical approaches.
- Indicates potential directions for future research.
All content in this section is from Literature Review Research from Old Dominion University
Keep in mind the following, a literature review is NOT:
Not an essay
Not an annotated bibliography in which you summarize each article that you have reviewed. A literature review goes beyond basic summarizing to focus on the critical analysis of the reviewed works and their relationship to your research question.
Not a research paper where you select resources to support one side of an issue versus another. A lit review should explain and consider all sides of an argument in order to avoid bias, and areas of agreement and disagreement should be highlighted.
A literature review serves several purposes. For example, it
- provides thorough knowledge of previous studies; introduces seminal works.
- helps focus one’s own research topic.
- identifies a conceptual framework for one’s own research questions or problems; indicates potential directions for future research.
- suggests previously unused or underused methodologies, designs, quantitative and qualitative strategies.
- identifies gaps in previous studies; identifies flawed methodologies and/or theoretical approaches; avoids replication of mistakes.
- helps the researcher avoid repetition of earlier research.
- suggests unexplored populations.
- determines whether past studies agree or disagree; identifies controversy in the literature.
- tests assumptions; may help counter preconceived ideas and remove unconscious bias.
As Kennedy (2007) notes*, it is important to think of knowledge in a given field as consisting of three layers. First, there are the primary studies that researchers conduct and publish. Second are the reviews of those studies that summarize and offer new interpretations built from and often extending beyond the original studies. Third, there are the perceptions, conclusions, opinion, and interpretations that are shared informally that become part of the lore of field. In composing a literature review, it is important to note that it is often this third layer of knowledge that is cited as "true" even though it often has only a loose relationship to the primary studies and secondary literature reviews.
Given this, while literature reviews are designed to provide an overview and synthesis of pertinent sources you have explored, there are several approaches to how they can be done, depending upon the type of analysis underpinning your study. Listed below are definitions of types of literature reviews:
Argumentative Review This form examines literature selectively in order to support or refute an argument, deeply imbedded assumption, or philosophical problem already established in the literature. The purpose is to develop a body of literature that establishes a contrarian viewpoint. Given the value-laden nature of some social science research [e.g., educational reform; immigration control], argumentative approaches to analyzing the literature can be a legitimate and important form of discourse. However, note that they can also introduce problems of bias when they are used to to make summary claims of the sort found in systematic reviews.
Integrative Review Considered a form of research that reviews, critiques, and synthesizes representative literature on a topic in an integrated way such that new frameworks and perspectives on the topic are generated. The body of literature includes all studies that address related or identical hypotheses. A well-done integrative review meets the same standards as primary research in regard to clarity, rigor, and replication.
Historical Review Few things rest in isolation from historical precedent. Historical reviews are focused on examining research throughout a period of time, often starting with the first time an issue, concept, theory, phenomena emerged in the literature, then tracing its evolution within the scholarship of a discipline. The purpose is to place research in a historical context to show familiarity with state-of-the-art developments and to identify the likely directions for future research.
Methodological Review A review does not always focus on what someone said [content], but how they said it [method of analysis]. This approach provides a framework of understanding at different levels (i.e. those of theory, substantive fields, research approaches and data collection and analysis techniques), enables researchers to draw on a wide variety of knowledge ranging from the conceptual level to practical documents for use in fieldwork in the areas of ontological and epistemological consideration, quantitative and qualitative integration, sampling, interviewing, data collection and data analysis, and helps highlight many ethical issues which we should be aware of and consider as we go through our study.
Systematic Review This form consists of an overview of existing evidence pertinent to a clearly formulated research question, which uses pre-specified and standardized methods to identify and critically appraise relevant research, and to collect, report, and analyse data from the studies that are included in the review. Typically it focuses on a very specific empirical question, often posed in a cause-and-effect form, such as "To what extent does A contribute to B?"
Theoretical Review The purpose of this form is to concretely examine the corpus of theory that has accumulated in regard to an issue, concept, theory, phenomena. The theoretical literature review help establish what theories already exist, the relationships between them, to what degree the existing theories have been investigated, and to develop new hypotheses to be tested. Often this form is used to help establish a lack of appropriate theories or reveal that current theories are inadequate for explaining new or emerging research problems. The unit of analysis can focus on a theoretical concept or a whole theory or framework.
* Kennedy, Mary M. "Defining a Literature." Educational Researcher 36 (April 2007): 139-147.
All content in this section is from The Literature Review created by Dr. Robert Larabee USC
Robinson, P. and Lowe, J. (2015), Literature reviews vs systematic reviews. Australian and New Zealand Journal of Public Health, 39: 103-103. doi: 10.1111/1753-6405.12393

What's in the name? The difference between a Systematic Review and a Literature Review, and why it matters . By Lynn Kysh from University of Southern California

Systematic review or meta-analysis?
A systematic review answers a defined research question by collecting and summarizing all empirical evidence that fits pre-specified eligibility criteria.
A meta-analysis is the use of statistical methods to summarize the results of these studies.
Systematic reviews, just like other research articles, can be of varying quality. They are a significant piece of work (the Centre for Reviews and Dissemination at York estimates that a team will take 9-24 months), and to be useful to other researchers and practitioners they should have:
- clearly stated objectives with pre-defined eligibility criteria for studies
- explicit, reproducible methodology
- a systematic search that attempts to identify all studies
- assessment of the validity of the findings of the included studies (e.g. risk of bias)
- systematic presentation, and synthesis, of the characteristics and findings of the included studies
Not all systematic reviews contain meta-analysis.
Meta-analysis is the use of statistical methods to summarize the results of independent studies. By combining information from all relevant studies, meta-analysis can provide more precise estimates of the effects of health care than those derived from the individual studies included within a review. More information on meta-analyses can be found in Cochrane Handbook, Chapter 9 .
A meta-analysis goes beyond critique and integration and conducts secondary statistical analysis on the outcomes of similar studies. It is a systematic review that uses quantitative methods to synthesize and summarize the results.
An advantage of a meta-analysis is the ability to be completely objective in evaluating research findings. Not all topics, however, have sufficient research evidence to allow a meta-analysis to be conducted. In that case, an integrative review is an appropriate strategy.
Some of the content in this section is from Systematic reviews and meta-analyses: step by step guide created by Kate McAllister.
- << Previous: Getting Started
- Next: Research Design >>
- Last Updated: Aug 21, 2023 4:07 PM
- URL: https://guides.lib.udel.edu/researchmethods
- Link to facebook
- Link to linkedin
- Link to twitter
- Link to youtube
- Writing Tips
What is the Purpose of a Literature Review?

4-minute read
- 23rd October 2023
If you’re writing a research paper or dissertation , then you’ll most likely need to include a comprehensive literature review . In this post, we’ll review the purpose of literature reviews, why they are so significant, and the specific elements to include in one. Literature reviews can:
1. Provide a foundation for current research.
2. Define key concepts and theories.
3. Demonstrate critical evaluation.
4. Show how research and methodologies have evolved.
5. Identify gaps in existing research.
6. Support your argument.
Keep reading to enter the exciting world of literature reviews!
What is a Literature Review?
A literature review is a critical summary and evaluation of the existing research (e.g., academic journal articles and books) on a specific topic. It is typically included as a separate section or chapter of a research paper or dissertation, serving as a contextual framework for a study. Literature reviews can vary in length depending on the subject and nature of the study, with most being about equal length to other sections or chapters included in the paper. Essentially, the literature review highlights previous studies in the context of your research and summarizes your insights in a structured, organized format. Next, let’s look at the overall purpose of a literature review.
Find this useful?
Subscribe to our newsletter and get writing tips from our editors straight to your inbox.
Literature reviews are considered an integral part of research across most academic subjects and fields. The primary purpose of a literature review in your study is to:
Provide a Foundation for Current Research
Since the literature review provides a comprehensive evaluation of the existing research, it serves as a solid foundation for your current study. It’s a way to contextualize your work and show how your research fits into the broader landscape of your specific area of study.
Define Key Concepts and Theories
The literature review highlights the central theories and concepts that have arisen from previous research on your chosen topic. It gives your readers a more thorough understanding of the background of your study and why your research is particularly significant .
Demonstrate Critical Evaluation
A comprehensive literature review shows your ability to critically analyze and evaluate a broad range of source material. And since you’re considering and acknowledging the contribution of key scholars alongside your own, it establishes your own credibility and knowledge.
Show How Research and Methodologies Have Evolved
Another purpose of literature reviews is to provide a historical perspective and demonstrate how research and methodologies have changed over time, especially as data collection methods and technology have advanced. And studying past methodologies allows you, as the researcher, to understand what did and did not work and apply that knowledge to your own research.
Identify Gaps in Existing Research
Besides discussing current research and methodologies, the literature review should also address areas that are lacking in the existing literature. This helps further demonstrate the relevance of your own research by explaining why your study is necessary to fill the gaps.
Support Your Argument
A good literature review should provide evidence that supports your research questions and hypothesis. For example, your study may show that your research supports existing theories or builds on them in some way. Referencing previous related studies shows your work is grounded in established research and will ultimately be a contribution to the field.
Literature Review Editing Services
Ensure your literature review is polished and ready for submission by having it professionally proofread and edited by our expert team. Our literature review editing services will help your research stand out and make an impact. Not convinced yet? Send in your free sample today and see for yourself!
Share this article:
Post A New Comment
Got content that needs a quick turnaround? Let us polish your work. Explore our editorial business services.
9-minute read
How to Use Infographics to Boost Your Presentation
Is your content getting noticed? Capturing and maintaining an audience’s attention is a challenge when...
8-minute read
Why Interactive PDFs Are Better for Engagement
Are you looking to enhance engagement and captivate your audience through your professional documents? Interactive...
7-minute read
Seven Key Strategies for Voice Search Optimization
Voice search optimization is rapidly shaping the digital landscape, requiring content professionals to adapt their...
Five Creative Ways to Showcase Your Digital Portfolio
Are you a creative freelancer looking to make a lasting impression on potential clients or...
How to Ace Slack Messaging for Contractors and Freelancers
Effective professional communication is an important skill for contractors and freelancers navigating remote work environments....
3-minute read
How to Insert a Text Box in a Google Doc
Google Docs is a powerful collaborative tool, and mastering its features can significantly enhance your...

Make sure your writing is the best it can be with our expert English proofreading and editing.
- USC Libraries
- Research Guides
Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Paper
- 5. The Literature Review
- Purpose of Guide
- Design Flaws to Avoid
- Independent and Dependent Variables
- Glossary of Research Terms
- Reading Research Effectively
- Narrowing a Topic Idea
- Broadening a Topic Idea
- Extending the Timeliness of a Topic Idea
- Academic Writing Style
- Applying Critical Thinking
- Choosing a Title
- Making an Outline
- Paragraph Development
- Research Process Video Series
- Executive Summary
- The C.A.R.S. Model
- Background Information
- The Research Problem/Question
- Theoretical Framework
- Citation Tracking
- Content Alert Services
- Evaluating Sources
- Primary Sources
- Secondary Sources
- Tiertiary Sources
- Scholarly vs. Popular Publications
- Qualitative Methods
- Quantitative Methods
- Insiderness
- Using Non-Textual Elements
- Limitations of the Study
- Common Grammar Mistakes
- Writing Concisely
- Avoiding Plagiarism
- Footnotes or Endnotes?
- Further Readings
- Generative AI and Writing
- USC Libraries Tutorials and Other Guides
- Bibliography
A literature review surveys prior research published in books, scholarly articles, and any other sources relevant to a particular issue, area of research, or theory, and by so doing, provides a description, summary, and critical evaluation of these works in relation to the research problem being investigated. Literature reviews are designed to provide an overview of sources you have used in researching a particular topic and to demonstrate to your readers how your research fits within existing scholarship about the topic.
Fink, Arlene. Conducting Research Literature Reviews: From the Internet to Paper . Fourth edition. Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE, 2014.
Importance of a Good Literature Review
A literature review may consist of simply a summary of key sources, but in the social sciences, a literature review usually has an organizational pattern and combines both summary and synthesis, often within specific conceptual categories . A summary is a recap of the important information of the source, but a synthesis is a re-organization, or a reshuffling, of that information in a way that informs how you are planning to investigate a research problem. The analytical features of a literature review might:
- Give a new interpretation of old material or combine new with old interpretations,
- Trace the intellectual progression of the field, including major debates,
- Depending on the situation, evaluate the sources and advise the reader on the most pertinent or relevant research, or
- Usually in the conclusion of a literature review, identify where gaps exist in how a problem has been researched to date.
Given this, the purpose of a literature review is to:
- Place each work in the context of its contribution to understanding the research problem being studied.
- Describe the relationship of each work to the others under consideration.
- Identify new ways to interpret prior research.
- Reveal any gaps that exist in the literature.
- Resolve conflicts amongst seemingly contradictory previous studies.
- Identify areas of prior scholarship to prevent duplication of effort.
- Point the way in fulfilling a need for additional research.
- Locate your own research within the context of existing literature [very important].
Fink, Arlene. Conducting Research Literature Reviews: From the Internet to Paper. 2nd ed. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2005; Hart, Chris. Doing a Literature Review: Releasing the Social Science Research Imagination . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications, 1998; Jesson, Jill. Doing Your Literature Review: Traditional and Systematic Techniques . Los Angeles, CA: SAGE, 2011; Knopf, Jeffrey W. "Doing a Literature Review." PS: Political Science and Politics 39 (January 2006): 127-132; Ridley, Diana. The Literature Review: A Step-by-Step Guide for Students . 2nd ed. Los Angeles, CA: SAGE, 2012.
Types of Literature Reviews
It is important to think of knowledge in a given field as consisting of three layers. First, there are the primary studies that researchers conduct and publish. Second are the reviews of those studies that summarize and offer new interpretations built from and often extending beyond the primary studies. Third, there are the perceptions, conclusions, opinion, and interpretations that are shared informally among scholars that become part of the body of epistemological traditions within the field.
In composing a literature review, it is important to note that it is often this third layer of knowledge that is cited as "true" even though it often has only a loose relationship to the primary studies and secondary literature reviews. Given this, while literature reviews are designed to provide an overview and synthesis of pertinent sources you have explored, there are a number of approaches you could adopt depending upon the type of analysis underpinning your study.
Argumentative Review This form examines literature selectively in order to support or refute an argument, deeply embedded assumption, or philosophical problem already established in the literature. The purpose is to develop a body of literature that establishes a contrarian viewpoint. Given the value-laden nature of some social science research [e.g., educational reform; immigration control], argumentative approaches to analyzing the literature can be a legitimate and important form of discourse. However, note that they can also introduce problems of bias when they are used to make summary claims of the sort found in systematic reviews [see below].
Integrative Review Considered a form of research that reviews, critiques, and synthesizes representative literature on a topic in an integrated way such that new frameworks and perspectives on the topic are generated. The body of literature includes all studies that address related or identical hypotheses or research problems. A well-done integrative review meets the same standards as primary research in regard to clarity, rigor, and replication. This is the most common form of review in the social sciences.
Historical Review Few things rest in isolation from historical precedent. Historical literature reviews focus on examining research throughout a period of time, often starting with the first time an issue, concept, theory, phenomena emerged in the literature, then tracing its evolution within the scholarship of a discipline. The purpose is to place research in a historical context to show familiarity with state-of-the-art developments and to identify the likely directions for future research.
Methodological Review A review does not always focus on what someone said [findings], but how they came about saying what they say [method of analysis]. Reviewing methods of analysis provides a framework of understanding at different levels [i.e. those of theory, substantive fields, research approaches, and data collection and analysis techniques], how researchers draw upon a wide variety of knowledge ranging from the conceptual level to practical documents for use in fieldwork in the areas of ontological and epistemological consideration, quantitative and qualitative integration, sampling, interviewing, data collection, and data analysis. This approach helps highlight ethical issues which you should be aware of and consider as you go through your own study.
Systematic Review This form consists of an overview of existing evidence pertinent to a clearly formulated research question, which uses pre-specified and standardized methods to identify and critically appraise relevant research, and to collect, report, and analyze data from the studies that are included in the review. The goal is to deliberately document, critically evaluate, and summarize scientifically all of the research about a clearly defined research problem . Typically it focuses on a very specific empirical question, often posed in a cause-and-effect form, such as "To what extent does A contribute to B?" This type of literature review is primarily applied to examining prior research studies in clinical medicine and allied health fields, but it is increasingly being used in the social sciences.
Theoretical Review The purpose of this form is to examine the corpus of theory that has accumulated in regard to an issue, concept, theory, phenomena. The theoretical literature review helps to establish what theories already exist, the relationships between them, to what degree the existing theories have been investigated, and to develop new hypotheses to be tested. Often this form is used to help establish a lack of appropriate theories or reveal that current theories are inadequate for explaining new or emerging research problems. The unit of analysis can focus on a theoretical concept or a whole theory or framework.
NOTE: Most often the literature review will incorporate some combination of types. For example, a review that examines literature supporting or refuting an argument, assumption, or philosophical problem related to the research problem will also need to include writing supported by sources that establish the history of these arguments in the literature.
Baumeister, Roy F. and Mark R. Leary. "Writing Narrative Literature Reviews." Review of General Psychology 1 (September 1997): 311-320; Mark R. Fink, Arlene. Conducting Research Literature Reviews: From the Internet to Paper . 2nd ed. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2005; Hart, Chris. Doing a Literature Review: Releasing the Social Science Research Imagination . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications, 1998; Kennedy, Mary M. "Defining a Literature." Educational Researcher 36 (April 2007): 139-147; Petticrew, Mark and Helen Roberts. Systematic Reviews in the Social Sciences: A Practical Guide . Malden, MA: Blackwell Publishers, 2006; Torracro, Richard. "Writing Integrative Literature Reviews: Guidelines and Examples." Human Resource Development Review 4 (September 2005): 356-367; Rocco, Tonette S. and Maria S. Plakhotnik. "Literature Reviews, Conceptual Frameworks, and Theoretical Frameworks: Terms, Functions, and Distinctions." Human Ressource Development Review 8 (March 2008): 120-130; Sutton, Anthea. Systematic Approaches to a Successful Literature Review . Los Angeles, CA: Sage Publications, 2016.
Structure and Writing Style
I. Thinking About Your Literature Review
The structure of a literature review should include the following in support of understanding the research problem :
- An overview of the subject, issue, or theory under consideration, along with the objectives of the literature review,
- Division of works under review into themes or categories [e.g. works that support a particular position, those against, and those offering alternative approaches entirely],
- An explanation of how each work is similar to and how it varies from the others,
- Conclusions as to which pieces are best considered in their argument, are most convincing of their opinions, and make the greatest contribution to the understanding and development of their area of research.
The critical evaluation of each work should consider :
- Provenance -- what are the author's credentials? Are the author's arguments supported by evidence [e.g. primary historical material, case studies, narratives, statistics, recent scientific findings]?
- Methodology -- were the techniques used to identify, gather, and analyze the data appropriate to addressing the research problem? Was the sample size appropriate? Were the results effectively interpreted and reported?
- Objectivity -- is the author's perspective even-handed or prejudicial? Is contrary data considered or is certain pertinent information ignored to prove the author's point?
- Persuasiveness -- which of the author's theses are most convincing or least convincing?
- Validity -- are the author's arguments and conclusions convincing? Does the work ultimately contribute in any significant way to an understanding of the subject?
II. Development of the Literature Review
Four Basic Stages of Writing 1. Problem formulation -- which topic or field is being examined and what are its component issues? 2. Literature search -- finding materials relevant to the subject being explored. 3. Data evaluation -- determining which literature makes a significant contribution to the understanding of the topic. 4. Analysis and interpretation -- discussing the findings and conclusions of pertinent literature.
Consider the following issues before writing the literature review: Clarify If your assignment is not specific about what form your literature review should take, seek clarification from your professor by asking these questions: 1. Roughly how many sources would be appropriate to include? 2. What types of sources should I review (books, journal articles, websites; scholarly versus popular sources)? 3. Should I summarize, synthesize, or critique sources by discussing a common theme or issue? 4. Should I evaluate the sources in any way beyond evaluating how they relate to understanding the research problem? 5. Should I provide subheadings and other background information, such as definitions and/or a history? Find Models Use the exercise of reviewing the literature to examine how authors in your discipline or area of interest have composed their literature review sections. Read them to get a sense of the types of themes you might want to look for in your own research or to identify ways to organize your final review. The bibliography or reference section of sources you've already read, such as required readings in the course syllabus, are also excellent entry points into your own research. Narrow the Topic The narrower your topic, the easier it will be to limit the number of sources you need to read in order to obtain a good survey of relevant resources. Your professor will probably not expect you to read everything that's available about the topic, but you'll make the act of reviewing easier if you first limit scope of the research problem. A good strategy is to begin by searching the USC Libraries Catalog for recent books about the topic and review the table of contents for chapters that focuses on specific issues. You can also review the indexes of books to find references to specific issues that can serve as the focus of your research. For example, a book surveying the history of the Israeli-Palestinian conflict may include a chapter on the role Egypt has played in mediating the conflict, or look in the index for the pages where Egypt is mentioned in the text. Consider Whether Your Sources are Current Some disciplines require that you use information that is as current as possible. This is particularly true in disciplines in medicine and the sciences where research conducted becomes obsolete very quickly as new discoveries are made. However, when writing a review in the social sciences, a survey of the history of the literature may be required. In other words, a complete understanding the research problem requires you to deliberately examine how knowledge and perspectives have changed over time. Sort through other current bibliographies or literature reviews in the field to get a sense of what your discipline expects. You can also use this method to explore what is considered by scholars to be a "hot topic" and what is not.
III. Ways to Organize Your Literature Review
Chronology of Events If your review follows the chronological method, you could write about the materials according to when they were published. This approach should only be followed if a clear path of research building on previous research can be identified and that these trends follow a clear chronological order of development. For example, a literature review that focuses on continuing research about the emergence of German economic power after the fall of the Soviet Union. By Publication Order your sources by publication chronology, then, only if the order demonstrates a more important trend. For instance, you could order a review of literature on environmental studies of brown fields if the progression revealed, for example, a change in the soil collection practices of the researchers who wrote and/or conducted the studies. Thematic [“conceptual categories”] A thematic literature review is the most common approach to summarizing prior research in the social and behavioral sciences. Thematic reviews are organized around a topic or issue, rather than the progression of time, although the progression of time may still be incorporated into a thematic review. For example, a review of the Internet’s impact on American presidential politics could focus on the development of online political satire. While the study focuses on one topic, the Internet’s impact on American presidential politics, it would still be organized chronologically reflecting technological developments in media. The difference in this example between a "chronological" and a "thematic" approach is what is emphasized the most: themes related to the role of the Internet in presidential politics. Note that more authentic thematic reviews tend to break away from chronological order. A review organized in this manner would shift between time periods within each section according to the point being made. Methodological A methodological approach focuses on the methods utilized by the researcher. For the Internet in American presidential politics project, one methodological approach would be to look at cultural differences between the portrayal of American presidents on American, British, and French websites. Or the review might focus on the fundraising impact of the Internet on a particular political party. A methodological scope will influence either the types of documents in the review or the way in which these documents are discussed.
Other Sections of Your Literature Review Once you've decided on the organizational method for your literature review, the sections you need to include in the paper should be easy to figure out because they arise from your organizational strategy. In other words, a chronological review would have subsections for each vital time period; a thematic review would have subtopics based upon factors that relate to the theme or issue. However, sometimes you may need to add additional sections that are necessary for your study, but do not fit in the organizational strategy of the body. What other sections you include in the body is up to you. However, only include what is necessary for the reader to locate your study within the larger scholarship about the research problem.
Here are examples of other sections, usually in the form of a single paragraph, you may need to include depending on the type of review you write:
- Current Situation : Information necessary to understand the current topic or focus of the literature review.
- Sources Used : Describes the methods and resources [e.g., databases] you used to identify the literature you reviewed.
- History : The chronological progression of the field, the research literature, or an idea that is necessary to understand the literature review, if the body of the literature review is not already a chronology.
- Selection Methods : Criteria you used to select (and perhaps exclude) sources in your literature review. For instance, you might explain that your review includes only peer-reviewed [i.e., scholarly] sources.
- Standards : Description of the way in which you present your information.
- Questions for Further Research : What questions about the field has the review sparked? How will you further your research as a result of the review?
IV. Writing Your Literature Review
Once you've settled on how to organize your literature review, you're ready to write each section. When writing your review, keep in mind these issues.
Use Evidence A literature review section is, in this sense, just like any other academic research paper. Your interpretation of the available sources must be backed up with evidence [citations] that demonstrates that what you are saying is valid. Be Selective Select only the most important points in each source to highlight in the review. The type of information you choose to mention should relate directly to the research problem, whether it is thematic, methodological, or chronological. Related items that provide additional information, but that are not key to understanding the research problem, can be included in a list of further readings . Use Quotes Sparingly Some short quotes are appropriate if you want to emphasize a point, or if what an author stated cannot be easily paraphrased. Sometimes you may need to quote certain terminology that was coined by the author, is not common knowledge, or taken directly from the study. Do not use extensive quotes as a substitute for using your own words in reviewing the literature. Summarize and Synthesize Remember to summarize and synthesize your sources within each thematic paragraph as well as throughout the review. Recapitulate important features of a research study, but then synthesize it by rephrasing the study's significance and relating it to your own work and the work of others. Keep Your Own Voice While the literature review presents others' ideas, your voice [the writer's] should remain front and center. For example, weave references to other sources into what you are writing but maintain your own voice by starting and ending the paragraph with your own ideas and wording. Use Caution When Paraphrasing When paraphrasing a source that is not your own, be sure to represent the author's information or opinions accurately and in your own words. Even when paraphrasing an author’s work, you still must provide a citation to that work.
V. Common Mistakes to Avoid
These are the most common mistakes made in reviewing social science research literature.
- Sources in your literature review do not clearly relate to the research problem;
- You do not take sufficient time to define and identify the most relevant sources to use in the literature review related to the research problem;
- Relies exclusively on secondary analytical sources rather than including relevant primary research studies or data;
- Uncritically accepts another researcher's findings and interpretations as valid, rather than examining critically all aspects of the research design and analysis;
- Does not describe the search procedures that were used in identifying the literature to review;
- Reports isolated statistical results rather than synthesizing them in chi-squared or meta-analytic methods; and,
- Only includes research that validates assumptions and does not consider contrary findings and alternative interpretations found in the literature.
Cook, Kathleen E. and Elise Murowchick. “Do Literature Review Skills Transfer from One Course to Another?” Psychology Learning and Teaching 13 (March 2014): 3-11; Fink, Arlene. Conducting Research Literature Reviews: From the Internet to Paper . 2nd ed. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2005; Hart, Chris. Doing a Literature Review: Releasing the Social Science Research Imagination . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications, 1998; Jesson, Jill. Doing Your Literature Review: Traditional and Systematic Techniques . London: SAGE, 2011; Literature Review Handout. Online Writing Center. Liberty University; Literature Reviews. The Writing Center. University of North Carolina; Onwuegbuzie, Anthony J. and Rebecca Frels. Seven Steps to a Comprehensive Literature Review: A Multimodal and Cultural Approach . Los Angeles, CA: SAGE, 2016; Ridley, Diana. The Literature Review: A Step-by-Step Guide for Students . 2nd ed. Los Angeles, CA: SAGE, 2012; Randolph, Justus J. “A Guide to Writing the Dissertation Literature Review." Practical Assessment, Research, and Evaluation. vol. 14, June 2009; Sutton, Anthea. Systematic Approaches to a Successful Literature Review . Los Angeles, CA: Sage Publications, 2016; Taylor, Dena. The Literature Review: A Few Tips On Conducting It. University College Writing Centre. University of Toronto; Writing a Literature Review. Academic Skills Centre. University of Canberra.
Writing Tip
Break Out of Your Disciplinary Box!
Thinking interdisciplinarily about a research problem can be a rewarding exercise in applying new ideas, theories, or concepts to an old problem. For example, what might cultural anthropologists say about the continuing conflict in the Middle East? In what ways might geographers view the need for better distribution of social service agencies in large cities than how social workers might study the issue? You don’t want to substitute a thorough review of core research literature in your discipline for studies conducted in other fields of study. However, particularly in the social sciences, thinking about research problems from multiple vectors is a key strategy for finding new solutions to a problem or gaining a new perspective. Consult with a librarian about identifying research databases in other disciplines; almost every field of study has at least one comprehensive database devoted to indexing its research literature.
Frodeman, Robert. The Oxford Handbook of Interdisciplinarity . New York: Oxford University Press, 2010.
Another Writing Tip
Don't Just Review for Content!
While conducting a review of the literature, maximize the time you devote to writing this part of your paper by thinking broadly about what you should be looking for and evaluating. Review not just what scholars are saying, but how are they saying it. Some questions to ask:
- How are they organizing their ideas?
- What methods have they used to study the problem?
- What theories have been used to explain, predict, or understand their research problem?
- What sources have they cited to support their conclusions?
- How have they used non-textual elements [e.g., charts, graphs, figures, etc.] to illustrate key points?
When you begin to write your literature review section, you'll be glad you dug deeper into how the research was designed and constructed because it establishes a means for developing more substantial analysis and interpretation of the research problem.
Hart, Chris. Doing a Literature Review: Releasing the Social Science Research Imagination . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications, 1 998.
Yet Another Writing Tip
When Do I Know I Can Stop Looking and Move On?
Here are several strategies you can utilize to assess whether you've thoroughly reviewed the literature:
- Look for repeating patterns in the research findings . If the same thing is being said, just by different people, then this likely demonstrates that the research problem has hit a conceptual dead end. At this point consider: Does your study extend current research? Does it forge a new path? Or, does is merely add more of the same thing being said?
- Look at sources the authors cite to in their work . If you begin to see the same researchers cited again and again, then this is often an indication that no new ideas have been generated to address the research problem.
- Search Google Scholar to identify who has subsequently cited leading scholars already identified in your literature review [see next sub-tab]. This is called citation tracking and there are a number of sources that can help you identify who has cited whom, particularly scholars from outside of your discipline. Here again, if the same authors are being cited again and again, this may indicate no new literature has been written on the topic.
Onwuegbuzie, Anthony J. and Rebecca Frels. Seven Steps to a Comprehensive Literature Review: A Multimodal and Cultural Approach . Los Angeles, CA: Sage, 2016; Sutton, Anthea. Systematic Approaches to a Successful Literature Review . Los Angeles, CA: Sage Publications, 2016.
- << Previous: Theoretical Framework
- Next: Citation Tracking >>
- Last Updated: May 25, 2024 4:09 PM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide

- Become Involved |
- Give to the Library |
- Staff Directory |
- UNF Library
- Thomas G. Carpenter Library
Conducting a Literature Review
Benefits of conducting a literature review.
- Steps in Conducting a Literature Review
- Summary of the Process
- Additional Resources
- Literature Review Tutorial by American University Library
- The Literature Review: A Few Tips On Conducting It by University of Toronto
- Write a Literature Review by UC Santa Cruz University Library
While there might be many reasons for conducting a literature review, following are four key outcomes of doing the review.
Assessment of the current state of research on a topic . This is probably the most obvious value of the literature review. Once a researcher has determined an area to work with for a research project, a search of relevant information sources will help determine what is already known about the topic and how extensively the topic has already been researched.
Identification of the experts on a particular topic . One of the additional benefits derived from doing the literature review is that it will quickly reveal which researchers have written the most on a particular topic and are, therefore, probably the experts on the topic. Someone who has written twenty articles on a topic or on related topics is more than likely more knowledgeable than someone who has written a single article. This same writer will likely turn up as a reference in most of the other articles written on the same topic. From the number of articles written by the author and the number of times the writer has been cited by other authors, a researcher will be able to assume that the particular author is an expert in the area and, thus, a key resource for consultation in the current research to be undertaken.
Identification of key questions about a topic that need further research . In many cases a researcher may discover new angles that need further exploration by reviewing what has already been written on a topic. For example, research may suggest that listening to music while studying might lead to better retention of ideas, but the research might not have assessed whether a particular style of music is more beneficial than another. A researcher who is interested in pursuing this topic would then do well to follow up existing studies with a new study, based on previous research, that tries to identify which styles of music are most beneficial to retention.
Determination of methodologies used in past studies of the same or similar topics. It is often useful to review the types of studies that previous researchers have launched as a means of determining what approaches might be of most benefit in further developing a topic. By the same token, a review of previously conducted studies might lend itself to researchers determining a new angle for approaching research.
Upon completion of the literature review, a researcher should have a solid foundation of knowledge in the area and a good feel for the direction any new research should take. Should any additional questions arise during the course of the research, the researcher will know which experts to consult in order to quickly clear up those questions.
- << Previous: Home
- Next: Steps in Conducting a Literature Review >>
- Last Updated: Aug 29, 2022 8:54 AM
- URL: https://libguides.unf.edu/litreview

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
The objective of a literature review
Questions to Consider
B. In some fields or contexts, a literature review is referred to as the introduction or the background; why is this true, and does it matter?
The elements of a literature review • The first step in scholarly research is determining the “state of the art” on a topic. This is accomplished by gathering academic research and making sense of it. • The academic literature can be found in scholarly books and journals; the goal is to discover recurring themes, find the latest data, and identify any missing pieces. • The resulting literature review organizes the research in such a way that tells a story about the topic or issue.
The literature review tells a story in which one well-paraphrased summary from a relevant source contributes to and connects with the next in a logical manner, developing and fulfilling the message of the author. It includes analysis of the arguments from the literature, as well as revealing consistent and inconsistent findings. How do varying author insights differ from or conform to previous arguments?

Language in Action
A. How are the terms “critique” and “review” used in everyday life? How are they used in an academic context?
In terms of content, a literature review is intended to:
• Set up a theoretical framework for further research • Show a clear understanding of the key concepts/studies/models related to the topic • Demonstrate knowledge about the history of the research area and any related controversies • Clarify significant definitions and terminology • Develop a space in the existing work for new research
The literature consists of the published works that document a scholarly conversation or progression on a problem or topic in a field of study. Among these are documents that explain the background and show the loose ends in the established research on which a proposed project is based. Although a literature review focuses on primary, peer -reviewed resources, it may begin with background subject information generally found in secondary and tertiary sources such as books and encyclopedias. Following that essential overview, the seminal literature of the field is explored. As a result, while a literature review may consist of research articles tightly focused on a topic with secondary and tertiary sources used more sparingly, all three types of information (primary, secondary, tertiary) are critical.
The literature review, often referred to as the Background or Introduction to a research paper that presents methods, materials, results and discussion, exists in every field and serves many functions in research writing.
Adapted from Frederiksen, L., & Phelps, S. F. (2017). Literature Reviews for Education and Nursing Graduate Students. Open Textbook Library
Review and Reinforce
Two common approaches are simply outlined here. Which seems more common? Which more productive? Why? A. Forward exploration 1. Sources on a topic or problem are gathered. 2. Salient themes are discovered. 3. Research gaps are considered for future research. B. Backward exploration 1. Sources pertaining to an existing research project are gathered. 2. The justification of the research project’s methods or materials are explained and supported based on previously documented research.
Media Attributions
- 2589960988_3eeca91ba4_o © Untitled blue is licensed under a CC BY (Attribution) license
Sourcing, summarizing, and synthesizing: Skills for effective research writing Copyright © 2023 by Wendy L. McBride is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book

Why is it important to do a literature review in research?
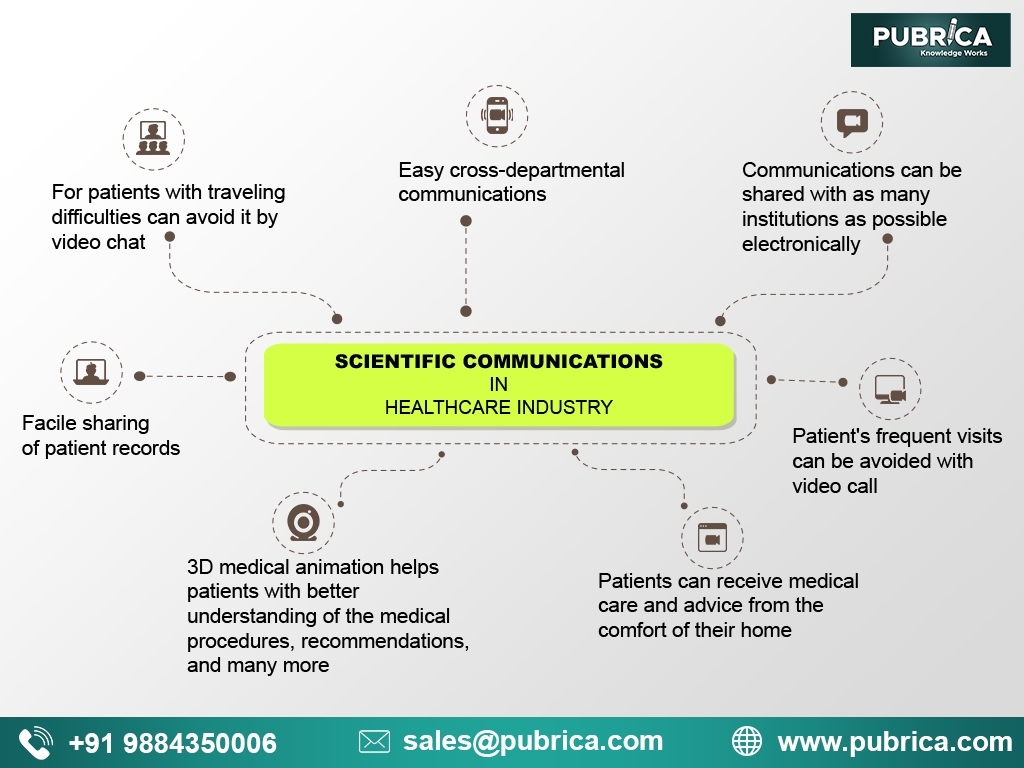
The importance of scientific communication in the healthcare industry
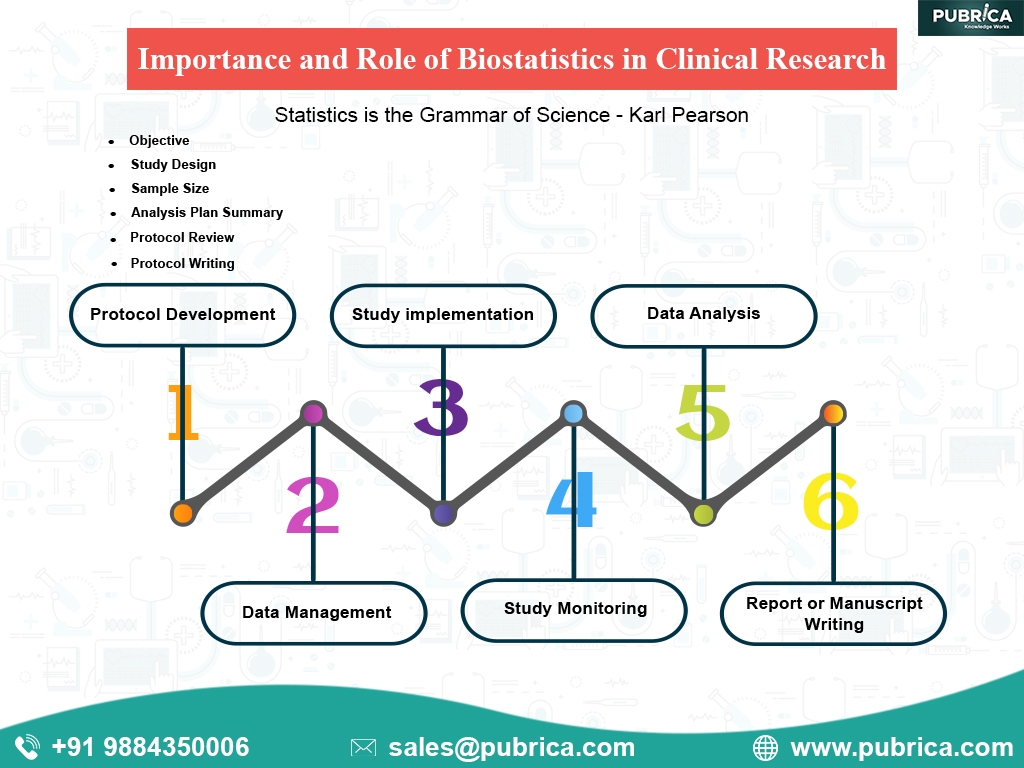
The Importance and Role of Biostatistics in Clinical Research
“A substantive, thorough, sophisticated literature review is a precondition for doing substantive, thorough, sophisticated research”. Boote and Baile 2005
Authors of manuscripts treat writing a literature review as a routine work or a mere formality. But a seasoned one knows the purpose and importance of a well-written literature review. Since it is one of the basic needs for researches at any level, they have to be done vigilantly. Only then the reader will know that the basics of research have not been neglected.
The aim of any literature review is to summarize and synthesize the arguments and ideas of existing knowledge in a particular field without adding any new contributions. Being built on existing knowledge they help the researcher to even turn the wheels of the topic of research. It is possible only with profound knowledge of what is wrong in the existing findings in detail to overpower them. For other researches, the literature review gives the direction to be headed for its success.
The common perception of literature review and reality:
As per the common belief, literature reviews are only a summary of the sources related to the research. And many authors of scientific manuscripts believe that they are only surveys of what are the researches are done on the chosen topic. But on the contrary, it uses published information from pertinent and relevant sources like
- Scholarly books
- Scientific papers
- Latest studies in the field
- Established school of thoughts
- Relevant articles from renowned scientific journals
and many more for a field of study or theory or a particular problem to do the following:
- Summarize into a brief account of all information
- Synthesize the information by restructuring and reorganizing
- Critical evaluation of a concept or a school of thought or ideas
- Familiarize the authors to the extent of knowledge in the particular field
- Encapsulate
- Compare & contrast
By doing the above on the relevant information, it provides the reader of the scientific manuscript with the following for a better understanding of it:
- It establishes the authors’ in-depth understanding and knowledge of their field subject
- It gives the background of the research
- Portrays the scientific manuscript plan of examining the research result
- Illuminates on how the knowledge has changed within the field
- Highlights what has already been done in a particular field
- Information of the generally accepted facts, emerging and current state of the topic of research
- Identifies the research gap that is still unexplored or under-researched fields
- Demonstrates how the research fits within a larger field of study
- Provides an overview of the sources explored during the research of a particular topic
Importance of literature review in research:
The importance of literature review in scientific manuscripts can be condensed into an analytical feature to enable the multifold reach of its significance. It adds value to the legitimacy of the research in many ways:
- Provides the interpretation of existing literature in light of updated developments in the field to help in establishing the consistency in knowledge and relevancy of existing materials
- It helps in calculating the impact of the latest information in the field by mapping their progress of knowledge.
- It brings out the dialects of contradictions between various thoughts within the field to establish facts
- The research gaps scrutinized initially are further explored to establish the latest facts of theories to add value to the field
- Indicates the current research place in the schema of a particular field
- Provides information for relevancy and coherency to check the research
- Apart from elucidating the continuance of knowledge, it also points out areas that require further investigation and thus aid as a starting point of any future research
- Justifies the research and sets up the research question
- Sets up a theoretical framework comprising the concepts and theories of the research upon which its success can be judged
- Helps to adopt a more appropriate methodology for the research by examining the strengths and weaknesses of existing research in the same field
- Increases the significance of the results by comparing it with the existing literature
- Provides a point of reference by writing the findings in the scientific manuscript
- Helps to get the due credit from the audience for having done the fact-finding and fact-checking mission in the scientific manuscripts
- The more the reference of relevant sources of it could increase more of its trustworthiness with the readers
- Helps to prevent plagiarism by tailoring and uniquely tweaking the scientific manuscript not to repeat other’s original idea
- By preventing plagiarism , it saves the scientific manuscript from rejection and thus also saves a lot of time and money
- Helps to evaluate, condense and synthesize gist in the author’s own words to sharpen the research focus
- Helps to compare and contrast to show the originality and uniqueness of the research than that of the existing other researches
- Rationalizes the need for conducting the particular research in a specified field
- Helps to collect data accurately for allowing any new methodology of research than the existing ones
- Enables the readers of the manuscript to answer the following questions of its readers for its better chances for publication
- What do the researchers know?
- What do they not know?
- Is the scientific manuscript reliable and trustworthy?
- What are the knowledge gaps of the researcher?
22. It helps the readers to identify the following for further reading of the scientific manuscript:
- What has been already established, discredited and accepted in the particular field of research
- Areas of controversy and conflicts among different schools of thought
- Unsolved problems and issues in the connected field of research
- The emerging trends and approaches
- How the research extends, builds upon and leaves behind from the previous research
A profound literature review with many relevant sources of reference will enhance the chances of the scientific manuscript publication in renowned and reputed scientific journals .
References:
http://www.math.montana.edu/jobo/phdprep/phd6.pdf
journal Publishing services | Scientific Editing Services | Medical Writing Services | scientific research writing service | Scientific communication services
Related Topics:
Meta Analysis
Scientific Research Paper Writing
Medical Research Paper Writing
Scientific Communication in healthcare
pubrica academy
Related posts.

Statistical analyses of case-control studies

PUB - Selecting material (e.g. excipient, active pharmaceutical ingredient) for drug development
Selecting material (e.g. excipient, active pharmaceutical ingredient, packaging material) for drug development

PUB - Health Economics of Data Modeling
Health economics in clinical trials
Comments are closed.
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Clinics (Sao Paulo)
Approaching literature review for academic purposes: The Literature Review Checklist
Debora f.b. leite.
I Departamento de Ginecologia e Obstetricia, Faculdade de Ciencias Medicas, Universidade Estadual de Campinas, Campinas, SP, BR
II Universidade Federal de Pernambuco, Pernambuco, PE, BR
III Hospital das Clinicas, Universidade Federal de Pernambuco, Pernambuco, PE, BR
Maria Auxiliadora Soares Padilha
Jose g. cecatti.
A sophisticated literature review (LR) can result in a robust dissertation/thesis by scrutinizing the main problem examined by the academic study; anticipating research hypotheses, methods and results; and maintaining the interest of the audience in how the dissertation/thesis will provide solutions for the current gaps in a particular field. Unfortunately, little guidance is available on elaborating LRs, and writing an LR chapter is not a linear process. An LR translates students’ abilities in information literacy, the language domain, and critical writing. Students in postgraduate programs should be systematically trained in these skills. Therefore, this paper discusses the purposes of LRs in dissertations and theses. Second, the paper considers five steps for developing a review: defining the main topic, searching the literature, analyzing the results, writing the review and reflecting on the writing. Ultimately, this study proposes a twelve-item LR checklist. By clearly stating the desired achievements, this checklist allows Masters and Ph.D. students to continuously assess their own progress in elaborating an LR. Institutions aiming to strengthen students’ necessary skills in critical academic writing should also use this tool.
INTRODUCTION
Writing the literature review (LR) is often viewed as a difficult task that can be a point of writer’s block and procrastination ( 1 ) in postgraduate life. Disagreements on the definitions or classifications of LRs ( 2 ) may confuse students about their purpose and scope, as well as how to perform an LR. Interestingly, at many universities, the LR is still an important element in any academic work, despite the more recent trend of producing scientific articles rather than classical theses.
The LR is not an isolated section of the thesis/dissertation or a copy of the background section of a research proposal. It identifies the state-of-the-art knowledge in a particular field, clarifies information that is already known, elucidates implications of the problem being analyzed, links theory and practice ( 3 - 5 ), highlights gaps in the current literature, and places the dissertation/thesis within the research agenda of that field. Additionally, by writing the LR, postgraduate students will comprehend the structure of the subject and elaborate on their cognitive connections ( 3 ) while analyzing and synthesizing data with increasing maturity.
At the same time, the LR transforms the student and hints at the contents of other chapters for the reader. First, the LR explains the research question; second, it supports the hypothesis, objectives, and methods of the research project; and finally, it facilitates a description of the student’s interpretation of the results and his/her conclusions. For scholars, the LR is an introductory chapter ( 6 ). If it is well written, it demonstrates the student’s understanding of and maturity in a particular topic. A sound and sophisticated LR can indicate a robust dissertation/thesis.
A consensus on the best method to elaborate a dissertation/thesis has not been achieved. The LR can be a distinct chapter or included in different sections; it can be part of the introduction chapter, part of each research topic, or part of each published paper ( 7 ). However, scholars view the LR as an integral part of the main body of an academic work because it is intrinsically connected to other sections ( Figure 1 ) and is frequently present. The structure of the LR depends on the conventions of a particular discipline, the rules of the department, and the student’s and supervisor’s areas of expertise, needs and interests.

Interestingly, many postgraduate students choose to submit their LR to peer-reviewed journals. As LRs are critical evaluations of current knowledge, they are indeed publishable material, even in the form of narrative or systematic reviews. However, systematic reviews have specific patterns 1 ( 8 ) that may not entirely fit with the questions posed in the dissertation/thesis. Additionally, the scope of a systematic review may be too narrow, and the strict criteria for study inclusion may omit important information from the dissertation/thesis. Therefore, this essay discusses the definition of an LR is and methods to develop an LR in the context of an academic dissertation/thesis. Finally, we suggest a checklist to evaluate an LR.
WHAT IS A LITERATURE REVIEW IN A THESIS?
Conducting research and writing a dissertation/thesis translates rational thinking and enthusiasm ( 9 ). While a strong body of literature that instructs students on research methodology, data analysis and writing scientific papers exists, little guidance on performing LRs is available. The LR is a unique opportunity to assess and contrast various arguments and theories, not just summarize them. The research results should not be discussed within the LR, but the postgraduate student tends to write a comprehensive LR while reflecting on his or her own findings ( 10 ).
Many people believe that writing an LR is a lonely and linear process. Supervisors or the institutions assume that the Ph.D. student has mastered the relevant techniques and vocabulary associated with his/her subject and conducts a self-reflection about previously published findings. Indeed, while elaborating the LR, the student should aggregate diverse skills, which mainly rely on his/her own commitment to mastering them. Thus, less supervision should be required ( 11 ). However, the parameters described above might not currently be the case for many students ( 11 , 12 ), and the lack of formal and systematic training on writing LRs is an important concern ( 11 ).
An institutional environment devoted to active learning will provide students the opportunity to continuously reflect on LRs, which will form a dialogue between the postgraduate student and the current literature in a particular field ( 13 ). Postgraduate students will be interpreting studies by other researchers, and, according to Hart (1998) ( 3 ), the outcomes of the LR in a dissertation/thesis include the following:
- To identify what research has been performed and what topics require further investigation in a particular field of knowledge;
- To determine the context of the problem;
- To recognize the main methodologies and techniques that have been used in the past;
- To place the current research project within the historical, methodological and theoretical context of a particular field;
- To identify significant aspects of the topic;
- To elucidate the implications of the topic;
- To offer an alternative perspective;
- To discern how the studied subject is structured;
- To improve the student’s subject vocabulary in a particular field; and
- To characterize the links between theory and practice.
A sound LR translates the postgraduate student’s expertise in academic and scientific writing: it expresses his/her level of comfort with synthesizing ideas ( 11 ). The LR reveals how well the postgraduate student has proceeded in three domains: an effective literature search, the language domain, and critical writing.
Effective literature search
All students should be trained in gathering appropriate data for specific purposes, and information literacy skills are a cornerstone. These skills are defined as “an individual’s ability to know when they need information, to identify information that can help them address the issue or problem at hand, and to locate, evaluate, and use that information effectively” ( 14 ). Librarian support is of vital importance in coaching the appropriate use of Boolean logic (AND, OR, NOT) and other tools for highly efficient literature searches (e.g., quotation marks and truncation), as is the appropriate management of electronic databases.
Language domain
Academic writing must be concise and precise: unnecessary words distract the reader from the essential content ( 15 ). In this context, reading about issues distant from the research topic ( 16 ) may increase students’ general vocabulary and familiarity with grammar. Ultimately, reading diverse materials facilitates and encourages the writing process itself.
Critical writing
Critical judgment includes critical reading, thinking and writing. It supposes a student’s analytical reflection about what he/she has read. The student should delineate the basic elements of the topic, characterize the most relevant claims, identify relationships, and finally contrast those relationships ( 17 ). Each scientific document highlights the perspective of the author, and students will become more confident in judging the supporting evidence and underlying premises of a study and constructing their own counterargument as they read more articles. A paucity of integration or contradictory perspectives indicates lower levels of cognitive complexity ( 12 ).
Thus, while elaborating an LR, the postgraduate student should achieve the highest category of Bloom’s cognitive skills: evaluation ( 12 ). The writer should not only summarize data and understand each topic but also be able to make judgments based on objective criteria, compare resources and findings, identify discrepancies due to methodology, and construct his/her own argument ( 12 ). As a result, the student will be sufficiently confident to show his/her own voice .
Writing a consistent LR is an intense and complex activity that reveals the training and long-lasting academic skills of a writer. It is not a lonely or linear process. However, students are unlikely to be prepared to write an LR if they have not mastered the aforementioned domains ( 10 ). An institutional environment that supports student learning is crucial.
Different institutions employ distinct methods to promote students’ learning processes. First, many universities propose modules to develop behind the scenes activities that enhance self-reflection about general skills (e.g., the skills we have mastered and the skills we need to develop further), behaviors that should be incorporated (e.g., self-criticism about one’s own thoughts), and each student’s role in the advancement of his/her field. Lectures or workshops about LRs themselves are useful because they describe the purposes of the LR and how it fits into the whole picture of a student’s work. These activities may explain what type of discussion an LR must involve, the importance of defining the correct scope, the reasons to include a particular resource, and the main role of critical reading.
Some pedagogic services that promote a continuous improvement in study and academic skills are equally important. Examples include workshops about time management, the accomplishment of personal objectives, active learning, and foreign languages for nonnative speakers. Additionally, opportunities to converse with other students promotes an awareness of others’ experiences and difficulties. Ultimately, the supervisor’s role in providing feedback and setting deadlines is crucial in developing students’ abilities and in strengthening students’ writing quality ( 12 ).
HOW SHOULD A LITERATURE REVIEW BE DEVELOPED?
A consensus on the appropriate method for elaborating an LR is not available, but four main steps are generally accepted: defining the main topic, searching the literature, analyzing the results, and writing ( 6 ). We suggest a fifth step: reflecting on the information that has been written in previous publications ( Figure 2 ).

First step: Defining the main topic
Planning an LR is directly linked to the research main question of the thesis and occurs in parallel to students’ training in the three domains discussed above. The planning stage helps organize ideas, delimit the scope of the LR ( 11 ), and avoid the wasting of time in the process. Planning includes the following steps:
- Reflecting on the scope of the LR: postgraduate students will have assumptions about what material must be addressed and what information is not essential to an LR ( 13 , 18 ). Cooper’s Taxonomy of Literature Reviews 2 systematizes the writing process through six characteristics and nonmutually exclusive categories. The focus refers to the reviewer’s most important points of interest, while the goals concern what students want to achieve with the LR. The perspective assumes answers to the student’s own view of the LR and how he/she presents a particular issue. The coverage defines how comprehensive the student is in presenting the literature, and the organization determines the sequence of arguments. The audience is defined as the group for whom the LR is written.
- Designating sections and subsections: Headings and subheadings should be specific, explanatory and have a coherent sequence throughout the text ( 4 ). They simulate an inverted pyramid, with an increasing level of reflection and depth of argument.
- Identifying keywords: The relevant keywords for each LR section should be listed to guide the literature search. This list should mirror what Hart (1998) ( 3 ) advocates as subject vocabulary . The keywords will also be useful when the student is writing the LR since they guide the reader through the text.
- Delineating the time interval and language of documents to be retrieved in the second step. The most recently published documents should be considered, but relevant texts published before a predefined cutoff year can be included if they are classic documents in that field. Extra care should be employed when translating documents.

Second step: Searching the literature
The ability to gather adequate information from the literature must be addressed in postgraduate programs. Librarian support is important, particularly for accessing difficult texts. This step comprises the following components:
- Searching the literature itself: This process consists of defining which databases (electronic or dissertation/thesis repositories), official documents, and books will be searched and then actively conducting the search. Information literacy skills have a central role in this stage. While searching electronic databases, controlled vocabulary (e.g., Medical Subject Headings, or MeSH, for the PubMed database) or specific standardized syntax rules may need to be applied.
In addition, two other approaches are suggested. First, a review of the reference list of each document might be useful for identifying relevant publications to be included and important opinions to be assessed. This step is also relevant for referencing the original studies and leading authors in that field. Moreover, students can directly contact the experts on a particular topic to consult with them regarding their experience or use them as a source of additional unpublished documents.
Before submitting a dissertation/thesis, the electronic search strategy should be repeated. This process will ensure that the most recently published papers will be considered in the LR.
- Selecting documents for inclusion: Generally, the most recent literature will be included in the form of published peer-reviewed papers. Assess books and unpublished material, such as conference abstracts, academic texts and government reports, are also important to assess since the gray literature also offers valuable information. However, since these materials are not peer-reviewed, we recommend that they are carefully added to the LR.
This task is an important exercise in time management. First, students should read the title and abstract to understand whether that document suits their purposes, addresses the research question, and helps develop the topic of interest. Then, they should scan the full text, determine how it is structured, group it with similar documents, and verify whether other arguments might be considered ( 5 ).
Third step: Analyzing the results
Critical reading and thinking skills are important in this step. This step consists of the following components:
- Reading documents: The student may read various texts in depth according to LR sections and subsections ( defining the main topic ), which is not a passive activity ( 1 ). Some questions should be asked to practice critical analysis skills, as listed below. Is the research question evident and articulated with previous knowledge? What are the authors’ research goals and theoretical orientations, and how do they interact? Are the authors’ claims related to other scholars’ research? Do the authors consider different perspectives? Was the research project designed and conducted properly? Are the results and discussion plausible, and are they consistent with the research objectives and methodology? What are the strengths and limitations of this work? How do the authors support their findings? How does this work contribute to the current research topic? ( 1 , 19 )
- Taking notes: Students who systematically take notes on each document are more readily able to establish similarities or differences with other documents and to highlight personal observations. This approach reinforces the student’s ideas about the next step and helps develop his/her own academic voice ( 1 , 13 ). Voice recognition software ( 16 ), mind maps ( 5 ), flowcharts, tables, spreadsheets, personal comments on the referenced texts, and note-taking apps are all available tools for managing these observations, and the student him/herself should use the tool that best improves his/her learning. Additionally, when a student is considering submitting an LR to a peer-reviewed journal, notes should be taken on the activities performed in all five steps to ensure that they are able to be replicated.
Fourth step: Writing
The recognition of when a student is able and ready to write after a sufficient period of reading and thinking is likely a difficult task. Some students can produce a review in a single long work session. However, as discussed above, writing is not a linear process, and students do not need to write LRs according to a specific sequence of sections. Writing an LR is a time-consuming task, and some scholars believe that a period of at least six months is sufficient ( 6 ). An LR, and academic writing in general, expresses the writer’s proper thoughts, conclusions about others’ work ( 6 , 10 , 13 , 16 ), and decisions about methods to progress in the chosen field of knowledge. Thus, each student is expected to present a different learning and writing trajectory.
In this step, writing methods should be considered; then, editing, citing and correct referencing should complete this stage, at least temporarily. Freewriting techniques may be a good starting point for brainstorming ideas and improving the understanding of the information that has been read ( 1 ). Students should consider the following parameters when creating an agenda for writing the LR: two-hour writing blocks (at minimum), with prespecified tasks that are possible to complete in one section; short (minutes) and long breaks (days or weeks) to allow sufficient time for mental rest and reflection; and short- and long-term goals to motivate the writing itself ( 20 ). With increasing experience, this scheme can vary widely, and it is not a straightforward rule. Importantly, each discipline has a different way of writing ( 1 ), and each department has its own preferred styles for citations and references.
Fifth step: Reflecting on the writing
In this step, the postgraduate student should ask him/herself the same questions as in the analyzing the results step, which can take more time than anticipated. Ambiguities, repeated ideas, and a lack of coherence may not be noted when the student is immersed in the writing task for long periods. The whole effort will likely be a work in progress, and continuous refinements in the written material will occur once the writing process has begun.
LITERATURE REVIEW CHECKLIST
In contrast to review papers, the LR of a dissertation/thesis should not be a standalone piece or work. Instead, it should present the student as a scholar and should maintain the interest of the audience in how that dissertation/thesis will provide solutions for the current gaps in a particular field.
A checklist for evaluating an LR is convenient for students’ continuous academic development and research transparency: it clearly states the desired achievements for the LR of a dissertation/thesis. Here, we present an LR checklist developed from an LR scoring rubric ( 11 ). For a critical analysis of an LR, we maintain the five categories but offer twelve criteria that are not scaled ( Figure 3 ). The criteria all have the same importance and are not mutually exclusive.

First category: Coverage
1. justified criteria exist for the inclusion and exclusion of literature in the review.
This criterion builds on the main topic and areas covered by the LR ( 18 ). While experts may be confident in retrieving and selecting literature, postgraduate students must convince their audience about the adequacy of their search strategy and their reasons for intentionally selecting what material to cover ( 11 ). References from different fields of knowledge provide distinct perspective, but narrowing the scope of coverage may be important in areas with a large body of existing knowledge.
Second category: Synthesis
2. a critical examination of the state of the field exists.
A critical examination is an assessment of distinct aspects in the field ( 1 ) along with a constructive argument. It is not a negative critique but an expression of the student’s understanding of how other scholars have added to the topic ( 1 ), and the student should analyze and contextualize contradictory statements. A writer’s personal bias (beliefs or political involvement) have been shown to influence the structure and writing of a document; therefore, the cultural and paradigmatic background guide how the theories are revised and presented ( 13 ). However, an honest judgment is important when considering different perspectives.
3. The topic or problem is clearly placed in the context of the broader scholarly literature
The broader scholarly literature should be related to the chosen main topic for the LR ( how to develop the literature review section). The LR can cover the literature from one or more disciplines, depending on its scope, but it should always offer a new perspective. In addition, students should be careful in citing and referencing previous publications. As a rule, original studies and primary references should generally be included. Systematic and narrative reviews present summarized data, and it may be important to cite them, particularly for issues that should be understood but do not require a detailed description. Similarly, quotations highlight the exact statement from another publication. However, excessive referencing may disclose lower levels of analysis and synthesis by the student.
4. The LR is critically placed in the historical context of the field
Situating the LR in its historical context shows the level of comfort of the student in addressing a particular topic. Instead of only presenting statements and theories in a temporal approach, which occasionally follows a linear timeline, the LR should authentically characterize the student’s academic work in the state-of-art techniques in their particular field of knowledge. Thus, the LR should reinforce why the dissertation/thesis represents original work in the chosen research field.
5. Ambiguities in definitions are considered and resolved
Distinct theories on the same topic may exist in different disciplines, and one discipline may consider multiple concepts to explain one topic. These misunderstandings should be addressed and contemplated. The LR should not synthesize all theories or concepts at the same time. Although this approach might demonstrate in-depth reading on a particular topic, it can reveal a student’s inability to comprehend and synthesize his/her research problem.
6. Important variables and phenomena relevant to the topic are articulated
The LR is a unique opportunity to articulate ideas and arguments and to purpose new relationships between them ( 10 , 11 ). More importantly, a sound LR will outline to the audience how these important variables and phenomena will be addressed in the current academic work. Indeed, the LR should build a bidirectional link with the remaining sections and ground the connections between all of the sections ( Figure 1 ).
7. A synthesized new perspective on the literature has been established
The LR is a ‘creative inquiry’ ( 13 ) in which the student elaborates his/her own discourse, builds on previous knowledge in the field, and describes his/her own perspective while interpreting others’ work ( 13 , 17 ). Thus, students should articulate the current knowledge, not accept the results at face value ( 11 , 13 , 17 ), and improve their own cognitive abilities ( 12 ).
Third category: Methodology
8. the main methodologies and research techniques that have been used in the field are identified and their advantages and disadvantages are discussed.
The LR is expected to distinguish the research that has been completed from investigations that remain to be performed, address the benefits and limitations of the main methods applied to date, and consider the strategies for addressing the expected limitations described above. While placing his/her research within the methodological context of a particular topic, the LR will justify the methodology of the study and substantiate the student’s interpretations.
9. Ideas and theories in the field are related to research methodologies
The audience expects the writer to analyze and synthesize methodological approaches in the field. The findings should be explained according to the strengths and limitations of previous research methods, and students must avoid interpretations that are not supported by the analyzed literature. This criterion translates to the student’s comprehension of the applicability and types of answers provided by different research methodologies, even those using a quantitative or qualitative research approach.
Fourth category: Significance
10. the scholarly significance of the research problem is rationalized.
The LR is an introductory section of a dissertation/thesis and will present the postgraduate student as a scholar in a particular field ( 11 ). Therefore, the LR should discuss how the research problem is currently addressed in the discipline being investigated or in different disciplines, depending on the scope of the LR. The LR explains the academic paradigms in the topic of interest ( 13 ) and methods to advance the field from these starting points. However, an excess number of personal citations—whether referencing the student’s research or studies by his/her research team—may reflect a narrow literature search and a lack of comprehensive synthesis of ideas and arguments.
11. The practical significance of the research problem is rationalized
The practical significance indicates a student’s comprehensive understanding of research terminology (e.g., risk versus associated factor), methodology (e.g., efficacy versus effectiveness) and plausible interpretations in the context of the field. Notably, the academic argument about a topic may not always reflect the debate in real life terms. For example, using a quantitative approach in epidemiology, statistically significant differences between groups do not explain all of the factors involved in a particular problem ( 21 ). Therefore, excessive faith in p -values may reflect lower levels of critical evaluation of the context and implications of a research problem by the student.
Fifth category: Rhetoric
12. the lr was written with a coherent, clear structure that supported the review.
This category strictly relates to the language domain: the text should be coherent and presented in a logical sequence, regardless of which organizational ( 18 ) approach is chosen. The beginning of each section/subsection should state what themes will be addressed, paragraphs should be carefully linked to each other ( 10 ), and the first sentence of each paragraph should generally summarize the content. Additionally, the student’s statements are clear, sound, and linked to other scholars’ works, and precise and concise language that follows standardized writing conventions (e.g., in terms of active/passive voice and verb tenses) is used. Attention to grammar, such as orthography and punctuation, indicates prudence and supports a robust dissertation/thesis. Ultimately, all of these strategies provide fluency and consistency for the text.
Although the scoring rubric was initially proposed for postgraduate programs in education research, we are convinced that this checklist is a valuable tool for all academic areas. It enables the monitoring of students’ learning curves and a concentrated effort on any criteria that are not yet achieved. For institutions, the checklist is a guide to support supervisors’ feedback, improve students’ writing skills, and highlight the learning goals of each program. These criteria do not form a linear sequence, but ideally, all twelve achievements should be perceived in the LR.
CONCLUSIONS
A single correct method to classify, evaluate and guide the elaboration of an LR has not been established. In this essay, we have suggested directions for planning, structuring and critically evaluating an LR. The planning of the scope of an LR and approaches to complete it is a valuable effort, and the five steps represent a rational starting point. An institutional environment devoted to active learning will support students in continuously reflecting on LRs, which will form a dialogue between the writer and the current literature in a particular field ( 13 ).
The completion of an LR is a challenging and necessary process for understanding one’s own field of expertise. Knowledge is always transitory, but our responsibility as scholars is to provide a critical contribution to our field, allowing others to think through our work. Good researchers are grounded in sophisticated LRs, which reveal a writer’s training and long-lasting academic skills. We recommend using the LR checklist as a tool for strengthening the skills necessary for critical academic writing.
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS
Leite DFB has initially conceived the idea and has written the first draft of this review. Padilha MAS and Cecatti JG have supervised data interpretation and critically reviewed the manuscript. All authors have read the draft and agreed with this submission. Authors are responsible for all aspects of this academic piece.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
We are grateful to all of the professors of the ‘Getting Started with Graduate Research and Generic Skills’ module at University College Cork, Cork, Ireland, for suggesting and supporting this article. Funding: DFBL has granted scholarship from Brazilian Federal Agency for Support and Evaluation of Graduate Education (CAPES) to take part of her Ph.D. studies in Ireland (process number 88881.134512/2016-01). There is no participation from sponsors on authors’ decision to write or to submit this manuscript.
No potential conflict of interest was reported.
1 The questions posed in systematic reviews usually follow the ‘PICOS’ acronym: Population, Intervention, Comparison, Outcomes, Study design.
2 In 1988, Cooper proposed a taxonomy that aims to facilitate students’ and institutions’ understanding of literature reviews. Six characteristics with specific categories are briefly described: Focus: research outcomes, research methodologies, theories, or practices and applications; Goals: integration (generalization, conflict resolution, and linguistic bridge-building), criticism, or identification of central issues; Perspective: neutral representation or espousal of a position; Coverage: exhaustive, exhaustive with selective citations, representative, central or pivotal; Organization: historical, conceptual, or methodological; and Audience: specialized scholars, general scholars, practitioners or policymakers, or the general public.

Literature Review: Purpose of a Literature Review
- Literature Review
- Purpose of a Literature Review
- Work in Progress
- Compiling & Writing
- Books, Articles, & Web Pages
- Types of Literature Reviews
- Departmental Differences
- Citation Styles & Plagiarism
- Know the Difference! Systematic Review vs. Literature Review
The purpose of a literature review is to:
- Provide a foundation of knowledge on a topic
- Identify areas of prior scholarship to prevent duplication and give credit to other researchers
- Identify inconstancies: gaps in research, conflicts in previous studies, open questions left from other research
- Identify the need for additional research (justifying your research)
- Identify the relationship of works in the context of their contribution to the topic and other works
- Place your own research within the context of existing literature, making a case for why further study is needed.
Videos & Tutorials
VIDEO: What is the role of a literature review in research? What's it mean to "review" the literature? Get the big picture of what to expect as part of the process. This video is published under a Creative Commons 3.0 BY-NC-SA US license. License, credits, and contact information can be found here: https://www.lib.ncsu.edu/tutorials/litreview/
Elements in a Literature Review
- Elements in a Literature Review txt of infographic
- << Previous: Literature Review
- Next: Searching >>
- Last Updated: Oct 19, 2023 12:07 PM
- URL: https://uscupstate.libguides.com/Literature_Review
Harvey Cushing/John Hay Whitney Medical Library
- Collections
- Research Help
YSN Doctoral Programs: Steps in Conducting a Literature Review
- Biomedical Databases
- Global (Public Health) Databases
- Soc. Sci., History, and Law Databases
- Grey Literature
- Trials Registers
- Data and Statistics
- Public Policy
- Google Tips
- Recommended Books
- Steps in Conducting a Literature Review
What is a literature review?
A literature review is an integrated analysis -- not just a summary-- of scholarly writings and other relevant evidence related directly to your research question. That is, it represents a synthesis of the evidence that provides background information on your topic and shows a association between the evidence and your research question.
A literature review may be a stand alone work or the introduction to a larger research paper, depending on the assignment. Rely heavily on the guidelines your instructor has given you.
Why is it important?
A literature review is important because it:
- Explains the background of research on a topic.
- Demonstrates why a topic is significant to a subject area.
- Discovers relationships between research studies/ideas.
- Identifies major themes, concepts, and researchers on a topic.
- Identifies critical gaps and points of disagreement.
- Discusses further research questions that logically come out of the previous studies.
APA7 Style resources
APA Style Blog - for those harder to find answers
1. Choose a topic. Define your research question.
Your literature review should be guided by your central research question. The literature represents background and research developments related to a specific research question, interpreted and analyzed by you in a synthesized way.
- Make sure your research question is not too broad or too narrow. Is it manageable?
- Begin writing down terms that are related to your question. These will be useful for searches later.
- If you have the opportunity, discuss your topic with your professor and your class mates.
2. Decide on the scope of your review
How many studies do you need to look at? How comprehensive should it be? How many years should it cover?
- This may depend on your assignment. How many sources does the assignment require?
3. Select the databases you will use to conduct your searches.
Make a list of the databases you will search.
Where to find databases:
- use the tabs on this guide
- Find other databases in the Nursing Information Resources web page
- More on the Medical Library web page
- ... and more on the Yale University Library web page
4. Conduct your searches to find the evidence. Keep track of your searches.
- Use the key words in your question, as well as synonyms for those words, as terms in your search. Use the database tutorials for help.
- Save the searches in the databases. This saves time when you want to redo, or modify, the searches. It is also helpful to use as a guide is the searches are not finding any useful results.
- Review the abstracts of research studies carefully. This will save you time.
- Use the bibliographies and references of research studies you find to locate others.
- Check with your professor, or a subject expert in the field, if you are missing any key works in the field.
- Ask your librarian for help at any time.
- Use a citation manager, such as EndNote as the repository for your citations. See the EndNote tutorials for help.
Review the literature
Some questions to help you analyze the research:
- What was the research question of the study you are reviewing? What were the authors trying to discover?
- Was the research funded by a source that could influence the findings?
- What were the research methodologies? Analyze its literature review, the samples and variables used, the results, and the conclusions.
- Does the research seem to be complete? Could it have been conducted more soundly? What further questions does it raise?
- If there are conflicting studies, why do you think that is?
- How are the authors viewed in the field? Has this study been cited? If so, how has it been analyzed?
Tips:
- Review the abstracts carefully.
- Keep careful notes so that you may track your thought processes during the research process.
- Create a matrix of the studies for easy analysis, and synthesis, across all of the studies.
- << Previous: Recommended Books
- Last Updated: Jan 4, 2024 10:52 AM
- URL: https://guides.library.yale.edu/YSNDoctoral

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
The Research Proposal
83 Components of the Literature Review
Krathwohl (2005) suggests and describes a variety of components to include in a research proposal. The following sections present these components in a suggested template for you to follow in the preparation of your research proposal.
Introduction
The introduction sets the tone for what follows in your research proposal – treat it as the initial pitch of your idea. After reading the introduction your reader should:
- Understand what it is you want to do;
- Have a sense of your passion for the topic;
- Be excited about the study´s possible outcomes.
As you begin writing your research proposal it is helpful to think of the introduction as a narrative of what it is you want to do, written in one to three paragraphs. Within those one to three paragraphs, it is important to briefly answer the following questions:
- What is the central research problem?
- How is the topic of your research proposal related to the problem?
- What methods will you utilize to analyze the research problem?
- Why is it important to undertake this research? What is the significance of your proposed research? Why are the outcomes of your proposed research important, and to whom or to what are they important?
Note : You may be asked by your instructor to include an abstract with your research proposal. In such cases, an abstract should provide an overview of what it is you plan to study, your main research question, a brief explanation of your methods to answer the research question, and your expected findings. All of this information must be carefully crafted in 150 to 250 words. A word of advice is to save the writing of your abstract until the very end of your research proposal preparation. If you are asked to provide an abstract, you should include 5-7 key words that are of most relevance to your study. List these in order of relevance.
Background and significance
The purpose of this section is to explain the context of your proposal and to describe, in detail, why it is important to undertake this research. Assume that the person or people who will read your research proposal know nothing or very little about the research problem. While you do not need to include all knowledge you have learned about your topic in this section, it is important to ensure that you include the most relevant material that will help to explain the goals of your research.
While there are no hard and fast rules, you should attempt to address some or all of the following key points:
- State the research problem and provide a more thorough explanation about the purpose of the study than what you stated in the introduction.
- Present the rationale for the proposed research study. Clearly indicate why this research is worth doing. Answer the “so what?” question.
- Describe the major issues or problems to be addressed by your research. Do not forget to explain how and in what ways your proposed research builds upon previous related research.
- Explain how you plan to go about conducting your research.
- Clearly identify the key or most relevant sources of research you intend to use and explain how they will contribute to your analysis of the topic.
- Set the boundaries of your proposed research, in order to provide a clear focus. Where appropriate, state not only what you will study, but what will be excluded from your study.
- Provide clear definitions of key concepts and terms. As key concepts and terms often have numerous definitions, make sure you state which definition you will be utilizing in your research.
Literature Review
This is the most time-consuming aspect in the preparation of your research proposal and it is a key component of the research proposal. As described in Chapter 5 , the literature review provides the background to your study and demonstrates the significance of the proposed research. Specifically, it is a review and synthesis of prior research that is related to the problem you are setting forth to investigate. Essentially, your goal in the literature review is to place your research study within the larger whole of what has been studied in the past, while demonstrating to your reader that your work is original, innovative, and adds to the larger whole.
As the literature review is information dense, it is essential that this section be intelligently structured to enable your reader to grasp the key arguments underpinning your study. However, this can be easier to state and harder to do, simply due to the fact there is usually a plethora of related research to sift through. Consequently, a good strategy for writing the literature review is to break the literature into conceptual categories or themes, rather than attempting to describe various groups of literature you reviewed. Chapter V, “ The Literature Review ,” describes a variety of methods to help you organize the themes.
Here are some suggestions on how to approach the writing of your literature review:
- Think about what questions other researchers have asked, what methods they used, what they found, and what they recommended based upon their findings.
- Do not be afraid to challenge previous related research findings and/or conclusions.
- Assess what you believe to be missing from previous research and explain how your research fills in this gap and/or extends previous research
It is important to note that a significant challenge related to undertaking a literature review is knowing when to stop. As such, it is important to know how to know when you have uncovered the key conceptual categories underlying your research topic. Generally, when you start to see repetition in the conclusions or recommendations, you can have confidence that you have covered all of the significant conceptual categories in your literature review. However, it is also important to acknowledge that researchers often find themselves returning to the literature as they collect and analyze their data. For example, an unexpected finding may develop as one collects and/or analyzes the data and it is important to take the time to step back and review the literature again, to ensure that no other researchers have found a similar finding. This may include looking to research outside your field.
This situation occurred with one of the authors of this textbook´s research related to community resilience. During the interviews, the researchers heard many participants discuss individual resilience factors and how they believed these individual factors helped make the community more resilient, overall. Sheppard and Williams (2016) had not discovered these individual factors in their original literature review on community and environmental resilience. However, when they returned to the literature to search for individual resilience factors, they discovered a small body of literature in the child and youth psychology field. Consequently, Sheppard and Williams had to go back and add a new section to their literature review on individual resilience factors. Interestingly, their research appeared to be the first research to link individual resilience factors with community resilience factors.
Research design and methods
The objective of this section of the research proposal is to convince the reader that your overall research design and methods of analysis will enable you to solve the research problem you have identified and also enable you to accurately and effectively interpret the results of your research. Consequently, it is critical that the research design and methods section is well-written, clear, and logically organized. This demonstrates to your reader that you know what you are going to do and how you are going to do it. Overall, you want to leave your reader feeling confident that you have what it takes to get this research study completed in a timely fashion.
Essentially, this section of the research proposal should be clearly tied to the specific objectives of your study; however, it is also important to draw upon and include examples from the literature review that relate to your design and intended methods. In other words, you must clearly demonstrate how your study utilizes and builds upon past studies, as it relates to the research design and intended methods. For example, what methods have been used by other researchers in similar studies?
While it is important to consider the methods that other researchers have employed, it is equally important, if not more so, to consider what methods have not been employed but could be. Remember, the methods section is not simply a list of tasks to be undertaken. It is also an argument as to why and how the tasks you have outlined will help you investigate the research problem and answer your research question(s).
Tips for writing the research design and methods section:
- Specify the methodological approaches you intend to employ to obtain information and the techniques you will use to analyze the data.
- Specify the research operations you will undertake and he way you will interpret the results of those operations in relation to the research problem.
- Go beyond stating what you hope to achieve through the methods you have chosen. State how you will actually do the methods (i.e. coding interview text, running regression analysis, etc.).
- Anticipate and acknowledge any potential barriers you may encounter when undertaking your research and describe how you will address these barriers.
- Explain where you believe you will find challenges related to data collection, including access to participants and information.
Preliminary suppositions and implications
The purpose of this section is to argue how and in what ways you anticipate that your research will refine, revise, or extend existing knowledge in the area of your study. Depending upon the aims and objectives of your study, you should also discuss how your anticipated findings may impact future research. For example, is it possible that your research may lead to a new policy, new theoretical understanding, or a new method for analyzing data? How might your study influence future studies? What might your study mean for future practitioners working in the field? Who or what may benefit from your study? How might your study contribute to social, economic, environmental issues? While it is important to think about and discuss possibilities such as these, it is equally important to be realistic in stating your anticipated findings. In other words, you do not want to delve into idle speculation. Rather, the purpose here is to reflect upon gaps in the current body of literature and to describe how and in what ways you anticipate your research will begin to fill in some or all of those gaps.
The conclusion reiterates the importance and significance of your research proposal and it provides a brief summary of the entire proposed study. Essentially, this section should only be one or two paragraphs in length. Here is a potential outline for your conclusion:
- Discuss why the study should be done. Specifically discuss how you expect your study will advance existing knowledge and how your study is unique.
- Explain the specific purpose of the study and the research questions that the study will answer.
- Explain why the research design and methods chosen for this study are appropriate, and why other design and methods were not chosen.
- State the potential implications you expect to emerge from your proposed study,
- Provide a sense of how your study fits within the broader scholarship currently in existence related to the research problem.
As with any scholarly research paper, you must cite the sources you used in composing your research proposal. In a research proposal, this can take two forms: a reference list or a bibliography. A reference list does what the name suggests, it lists the literature you referenced in the body of your research proposal. All references in the reference list, must appear in the body of the research proposal. Remember, it is not acceptable to say “as cited in …” As a researcher you must always go to the original source and check it for yourself. Many errors are made in referencing, even by top researchers, and so it is important not to perpetuate an error made by someone else. While this can be time consuming, it is the proper way to undertake a literature review.
In contrast, a bibliography , is a list of everything you used or cited in your research proposal, with additional citations to any key sources relevant to understanding the research problem. In other words, sources cited in your bibliography may not necessarily appear in the body of your research proposal. Make sure you check with your instructor to see which of the two you are expected to produce.
Overall, your list of citations should be a testament to the fact that you have done a sufficient level of preliminary research to ensure that your project will complement, but not duplicate, previous research efforts. For social sciences, the reference list or bibliography should be prepared in American Psychological Association (APA) referencing format. Usually, the reference list (or bibliography) is not included in the word count of the research proposal. Again, make sure you check with your instructor to confirm.
An Introduction to Research Methods in Sociology Copyright © 2019 by Valerie A. Sheppard is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
Explaining research performance: investigating the importance of motivation
- Original Paper
- Open access
- Published: 23 May 2024
- Volume 4 , article number 105 , ( 2024 )
Cite this article
You have full access to this open access article

- Silje Marie Svartefoss ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-5072-1293 1 nAff4 ,
- Jens Jungblut 2 ,
- Dag W. Aksnes 1 ,
- Kristoffer Kolltveit 2 &
- Thed van Leeuwen 3
421 Accesses
6 Altmetric
Explore all metrics
In this article, we study the motivation and performance of researchers. More specifically, we investigate what motivates researchers across different research fields and countries and how this motivation influences their research performance. The basis for our study is a large-N survey of economists, cardiologists, and physicists in Denmark, Norway, Sweden, the Netherlands, and the UK. The analysis shows that researchers are primarily motivated by scientific curiosity and practical application and less so by career considerations. There are limited differences across fields and countries, suggesting that the mix of motivational aspects has a common academic core less influenced by disciplinary standards or different national environments. Linking motivational factors to research performance, through bibliometric data on publication productivity and citation impact, our data show that those driven by practical application aspects of motivation have a higher probability for high productivity. Being driven by career considerations also increases productivity but only to a certain extent before it starts having a detrimental effect.
Similar content being viewed by others

Are the strategic research agendas of researchers in the social sciences determinants of research productivity?
Research incentives and research output.
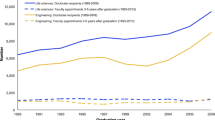
Exploring the determinants of research performance for early-career researchers: a literature review
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
Motivation and abilities are known to be as important factors in explaining employees’ job performance of employees (Van Iddekinge et al. 2018 ), and in the vast scientific literature on motivation, it is common to differentiate between intrinsic and extrinsic motivation factors (Ryan and Deci 2000 ). In this context, path-breaking individuals are said to often be intrinsically motivated (Jindal-Snape and Snape 2006 ; Thomas and Nedeva 2012 ; Vallerand et al. 1992 ), and it has been found that the importance of these of types of motivations differs across occupations and career stages (Duarte and Lopes 2018 ).
In this article, we address the issue of motivation for one specific occupation, namely: researchers working at universities. Specifically, we investigate what motivates researchers across fields and countries (RQ1) and how this motivation is linked to their research performance (RQ2). The question of why people are motivated to do their jobs is interesting to address in an academic context, where work is usually harder to control, and individuals tend to have a lot of much freedom in structuring their work. Moreover, there have been indications that academics possess an especially high level of motivation for their tasks that is not driven by a search for external rewards but by an intrinsic satisfaction from academic work (Evans and Meyer 2003 ; Leslie 2002 ). At the same time, elements of researchers’ performance are measurable through indicators of their publication activity: their productivity through the number of outputs they produce and the impact of their research through the number of citations their publications receive (Aksnes and Sivertsen 2019 ; Wilsdon et al. 2015 ).
Elevating research performance is high on the agenda of many research organisations (Hazelkorn 2015 ). How such performance may be linked to individuals’ motivational aspects has received little attention. Thus, a better understanding of this interrelation may be relevant for developing institutional strategies to foster environments that promote high-quality research and research productivity.
Previous qualitative research has shown that scientists are mainly intrinsically motivated (Jindal-Snape and Snape 2006 ). Other survey-based contributions suggest that there can be differences in motivations across disciplines (Atta-Owusu and Fitjar 2021 ; Lam 2011 ). Furthermore, the performance of individual scientists has been shown to be highly skewed in terms of publication productivity and citation rates (Larivière et al. 2010 ; Ruiz-Castillo and Costas 2014 ). There is a large body of literature explaining these differences. Some focus on national and institutional funding schemes (Hammarfelt and de Rijcke 2015 ; Melguizo and Strober 2007 ) and others on the research environment, such as the presence of research groups and international collaboration (Jeong et al. 2014 ), while many studies address the role of academic rank, age, and gender (see e.g. Baccini et al. 2014 ; Rørstad and Aksnes 2015 ). Until recently, less emphasis has been placed on the impact of researchers’ motivation. Some studies have found that different types of motivations drive high levels of research performance (see e.g. Horodnic and Zaiţ 2015 ; Ryan and Berbegal-Mirabent 2016 ). However, researchers are only starting to understand how this internal drive relates to research performance.
While some of the prior research on the impact of motivation depends on self-reported research performance evaluations (Ryan 2014 ), the present article combines survey responses with actual bibliometric data. To investigate variation in research motivation across scientific fields and countries, we draw on a large-N survey of economists, cardiologists, and physicists in Denmark, Norway, Sweden, the Netherlands, and the UK. To investigate how this motivation is linked to their research performance, we map the survey respondents’ publication and citation data from the Web of Science (WoS).
This article is organised as follows. First, we present relevant literature on research performance and motivation. Next, the scientific fields and countries are then presented before elaborating on our methodology. In the empirical analysis, we investigate variations in motivation across fields, gender, age, and academic position and then relate motivation to publications and citations as our two measures of research performance. In the concluding section, we discuss our findings and implications for national decision-makers and individual researchers.
Motivation and research performance
As noted above, the concepts of intrinsic and extrinsic motivation play an important role in the literature on motivation and performance. Here, intrinsic motivation refers to doing something for its inherent satisfaction rather than for some separable consequence. Extrinsic motivation refers to doing something because it leads to a separable outcome (Ryan and Deci 2000 ).
Some studies have found that scientists are mainly intrinsically motivated (Jindal-Snape and Snape 2006 ; Lounsbury et al. 2012 ). Research interests, curiosity, and a desire to contribute to new knowledge are examples of such motivational factors. Intrinsic motives have also been shown to be crucial when people select research as a career choice (Roach and Sauermann 2010 ). Nevertheless, scientists are also motivated by extrinsic factors. Several European countries have adopted performance-based research funding systems (Zacharewicz et al. 2019 ). In these systems, researchers do not receive direct financial bonuses when they publish, although such practices may occur at local levels (Stephan et al. 2017 ). Therefore, extrinsic motivation for such researchers may include salary increases, peer recognitions, promotion, or expanded access to research resources (Lam 2011 ). According to Tien and Blackburn ( 1996 ), both types of motivations operate simultaneously, and their importance vary and may depend on the individual’s circumstances, personal situation, and values.
The extent to which different kinds of motivations play a role in scientists’ performance has been investigated in several studies. In these studies, bibliometric indicators based on the number of publications are typically used as outcome measures. Such indicators play a critical role in various contexts in the research system (Wilsdon et al. 2015 ), although it has also been pointed out that individuals can have different motivations to publish (Hangel and Schmidt-Pfister 2017 ).
Based on a survey of Romanian economics and business administration academics combined with bibliometric data, Horodnic and Zait ( 2015 ) found that intrinsic motivation was positively correlated with research productivity, while extrinsic motivation was negatively correlated. Their interpretations of the results are that researchers motivated by scientific interest are more productive, while researchers motivated by extrinsic forces will shift their focus to more financially profitable activities. Similarly, based on the observation that professors continue to publish even after they have been promoted to full professor, Finkelstein ( 1984 ) concluded that intrinsic rather than extrinsic motivational factors have a decisive role regarding the productivity of academics.
Drawing on a survey of 405 research scientists working in biological, chemical, and biomedical research departments in UK universities, Ryan ( 2014 ) found that (self-reported) variations in research performance can be explained by instrumental motivation based on financial incentives and internal motivation based on the individual’s view of themselves (traits, competencies, and values). In the study, instrumental motivation was found to have a negative impact on research performance: As the desire for financial rewards increase, the level of research performance decreases. In other words, researchers mainly motivated by money will be less productive and effective in their research. Contrarily, internal motivation was found to have a positive impact on research performance. This was explained by highlighting that researchers motivated by their self-concept set internal standards that become a reference point that reinforces perceptions of competency in their environments.
Nevertheless, it has also been argued that intrinsic and extrinsic motivations for publishing are intertwined (Ma 2019 ). According to Tien and Blackburn ( 1996 ), research productivity is neither purely intrinsically nor purely extrinsically motivated. Publication activity is often a result of research, which may be intrinsically motivated or motivated by extrinsic factors such as a wish for promotion, where the number of publications is often a part of the assessment (Cruz-Castro and Sanz-Menendez 2021 ; Tien 2000 , 2008 ).
The negative relationship between external/instrumental motivation and performance and the positive relationship between internal/self-concept motivation and performance are underlined by Ryan and Berbegal-Mirabent ( 2016 ). Drawing on a fuzzy set qualitative comparative analysis of a random sampling of 300 of the original respondents from Ryan ( 2014 ), they find that scientists working towards the standards and values they identify with, combined with a lack of concern for instrumental rewards, contribute to higher levels of research performance.
Based on the above, this article will address two research questions concerning different forms of motivation and the relationship between motivation and research performance.
How does the motivation of researchers vary across fields and countries?
How do different types of motivations affect research performance?
In this study, the roles of three different motivational factors are analysed. These are scientific curiosity, practical and societal applications, and career progress. The study aims to assess the role of these specific motivational factors and not the intrinsic-extrinsic distinction more generally. Of the three factors, scientific curiosity most strongly relates to intrinsic motivation; practical and societal applications also entail strong intrinsic aspects. On the other hand, career progress is linked to extrinsic motivation.
In addition to variation in researchers’ motivations by field and country, we consider differences in relation to age, position and gender. Additionally, when investigating how motivation relates to scientific performance we control for the influence of age, gender, country and funding. These are dimensions where differences might be found in motivational factors given that scientific performance, particularly publication productivity, has been shown to differ along these dimensions (Rørstad and Aksnes 2015 ).
Research context: three fields, five countries
To address the research question about potential differences across fields and countries, the study is based on a sample consisting of researchers in three different fields (cardiology, economics, and physics) and five countries (Denmark, Norway, Sweden, the Netherlands, and the UK). Below, we describe this research context in greater detail.
The fields represent three different domains of science: medicine, social sciences, and the natural sciences, where different motivational factors may be at play. This means that the fields cover three main areas of scientific investigations: the understanding of the world, the functioning of the human body, and societies and their functions. The societal role and mission of the fields also differ. While a primary aim of cardiology research and practice is to reduce the burden of cardiovascular disease, physics research may drive technology advancements, which impacts society. Economics research may contribute to more effective use of limited resources and the management of people, businesses, markets, and governments. In addition, the fields also differ in publication patterns (Piro et al. 2013 ). The average number of publications per researcher is generally higher in cardiology and physics than in economics (Piro et al. 2013 ). Moreover, cardiologists and physicists mainly publish in international scientific journals (Moed 2005 ; Van Leeuwen 2013 ). In economics, researchers also tend to publish books, chapters, and articles in national languages, in addition to international journal articles (Aksnes and Sivertsen 2019 ; van Leeuwen et al. 2016 ).
We sampled the countries with a twofold aim. On the one hand, we wanted to have countries that are comparable so that differences in the development of the science systems, working conditions, or funding availability would not be too large. On the other hand, we also wanted to assure variation among the countries regarding these relevant framework conditions to ensure that our findings are not driven by a specific contextual condition.
The five countries in the study are all located in the northwestern part of Europe, with science systems that are foremost funded by block grant funding from the national governments (unlike, for example, the US, where research grants by national funding agencies are the most important funding mechanism) (Lepori et al. 2023 ).
In all five countries, the missions of the universities are composed of a blend of education, research, and outreach. Furthermore, the science systems in Norway, Denmark, Sweden, and the Netherlands have a relatively strong orientation towards the Anglo-Saxon world in the sense that publishing in the national language still exists, but publishing in English in internationally oriented journals in which English is the language of publications is the norm (Kulczycki et al. 2018 ). These framework conditions ensure that those working in the five countries have somewhat similar missions to fulfil in their professions while also belonging to a common mainly Anglophone science system.
However, in Norway, Denmark, Sweden, and the Netherlands, research findings in some social sciences, law, and the humanities are still oriented on publishing in various languages. Hence, we avoided selecting the humanities field for this study due to a potential issue with cross-country comparability (Sivertsen 2019 ; Sivertsen and Van Leeuwen 2014 ; Van Leeuwen 2013 ).
Finally, the chosen countries vary regarding their level of university autonomy. When combining the scores for organisational, financial, staffing, and academic autonomy presented in the latest University Autonomy in Europe Scorecard presented by the European University Association (EUA), the UK, the Netherlands, and Denmark have higher levels of autonomy compared to Norway and Sweden, with Swedish universities having less autonomy than their Norwegian counterparts (Pruvot et al. 2023 ). This variation is relevant for our study, as it ensures that our findings are not driven by response from a higher education system with especially high or low autonomy, which can influence the motivation and satisfaction of academics working in it (Daumiller et al. 2020 ).
Data and methods
The data used in this article are a combination of survey data and bibliometric data retrieved from the WoS. The WoS database was chosen for this study due to its comprehensive coverage of research literature across all disciplines, encompassing the three specific research areas under analysis. Additionally, the WoS database is well-suited for bibliometric analyses, offering citation counts essential for this study.
Two approaches were used to identify the sample for the survey. Initially, a bibliometric analysis of the WoS using journal categories (‘Cardiac & cardiovascular systems’, ‘Economics’, and ‘Physics’) enabled the identification of key institutions with a minimum number of publications within these journal categories. Following this, relevant organisational units and researchers within these units were identified through available information on the units’ webpages. Included were employees in relevant academic positions (tenured academic personnel, post-docs, and researchers, but not PhD students, adjunct positions, guest researchers, or administrative and technical personnel).
Second, based on the WoS data, people were added to this initial sample if they had a minimum number of publications within the field and belonged to any of the selected institutions, regardless of unit affiliation. For economics, the minimum was five publications within the selected period (2011–2016). For cardiology and physics, where the individual publication productivity is higher, the minimum was 10 publications within the same period. The selection of the minimum publication criteria was based on an analysis of publication outputs in these fields between 2011 and 2016. The thresholds were applied to include individuals who are more actively engaged in research while excluding those with more peripheral involvement. The higher thresholds for cardiology and physics reflect the greater frequency of publications (and co-authorship) observed in these fields.
The benefit of this dual-approach strategy to sampling is that we obtain a more comprehensive sample: the full scope of researchers within a unit and the full scope of researchers that publish within the relevant fields. Overall, 59% of the sample were identified through staff lists and 41% through the second step involving WoS data.
The survey data were collected through an online questionnaire first sent out in October 2017 and closed in December 2018. In this period, several reminders were sent to increase the response rate. Overall, the survey had a response rate of 26.1% ( N = 2,587 replies). There were only minor variations in response rates between scientific fields; the variations were larger between countries. Tables 1 and 2 provide an overview of the response rate by country and field.
Operationalisation of motivation
Motivation was measured by a question in the survey asking respondents what motivates or inspires them to conduct research, of which three dimensions are analysed in the present paper. The two first answer categories were related to intrinsic motivation (‘Curiosity/scientific discovery/understanding the world’ and ‘Application/practical aims/creating a better society’). The third answer category was more related to extrinsic motivation (‘Progress in my career [e.g. tenure/permanent position, higher salary, more interesting/independent work]’). Appendix Table A1 displays the distribution of respondents and the mean value and standard deviation for each item.
These three different aspects of motivation do not measure the same phenomenon but seem to capture different aspects of motivation (see Pearson’s correlation coefficients in Appendix Table A2 ). There is no correlation between curiosity/scientific discovery, career progress, and practical application. However, there is a weak but significant positive correlation between career progress and practical application. These findings indicate that those motivated by career considerations to some degrees also are motivated by practical application.
In addition to investigating how researchers’ motivation varies by field and country, we consider the differences in relation to age, position and gender as well. Field of science differentiates between economics, cardiology, physics, and other fields. The country variables differentiate between the five countries. Age is a nine-category variable. The position variable differentiates between full professors, associate professors, and assistant professors. The gender variable has two categories (male or female). For descriptive statistics on these additional variables, see Appendix Table A3 .
Publication productivity and citation impact
To analyse the respondents’ bibliometric performance, the Centre for Science and Technology Studies (CWTS) in-house WoS database was used. We identified the publication output of each respondent during 2011–2017 (limited to regular articles, reviews, and letters). For 16% of the respondents, no publications were identified in the database. These individuals had apparently not published in international journals covered by the database. However, in some cases, the lack of publications may be due to identification problems (e.g. change of names). Therefore, we decided not to include the latter respondents in the analysis.
Two main performance measures were calculated: publication productivity and citation impact. As an indicator of productivity, we counted the number of publications for each individual (as author or co-author) during the period. To analyse the citation impact, a composite measure using three different indicators was used: total number of citations (total citations counts for all articles they have contributed to during the period, counting citations up to and including 2017), normalised citation score (MNCS), and proportion of publications among the 10% most cited articles in their fields (Waltman and Schreiber 2013 ). Here, the MNCS is an indicator for which the citation count of each article is normalised by subject, article type, and year, where 1.00 corresponds to the world average (Waltman et al. 2011 ). Based on these data, averages for the total publication output of each respondent were calculated. By using three different indicators, we can avoid biases or limitations attached to each of them. For example, using the MNCS, a respondent with only one publication would appear as a high impact researcher if this article was highly cited. However, when considering the additional indicator, total citation counts, this individual would usually perform less well.
The bibliometric scores were skewedly distributed among the respondents. Rather than using the absolute numbers, in this paper, we have classified the respondents into three groups according to their scores on the indicators. Here, we have used percentile rank classes (tertiles). Percentile statistics are increasingly applied in bibliometrics (Bornmann et al. 2013 ; Waltman and Schreiber 2013 ) due to the presence of outliers and long tails, which characterise both productivity and citation distributions.
As the fields analysed have different publication patterns, the respondents within each field were ranked according to their scores on the indicators, and their percentile rank was determined. For the productivity measure, this means that there are three groups that are equal in terms of number of individuals included: 1: Low productivity (the group with the lowest publication numbers, 0–33 percentile), 2: Medium productivity (33–67 percentile), and 3: High productivity (67–100 percentile). For the citation impact measure, we conducted a similar percentile analysis for each of the three composite indicators. Then everyone was assigned to one of the three percentile groups based on their average score: 1: Low citation impact (the group with lowest citation impact, 0–33 percentile), 2: Medium citation impact (33–67 percentile), and 3: High citation impact (67–100 percentile), cf. Table 3 . Although it might be argued that the application of tertile groups rather than absolute numbers leads to a loss of information, the advantage is that the results are not influenced by extreme values and may be easier to interpret.
Via this approach, we can analyse the two important dimensions of the respondents’ performance. However, it should be noted that the WoS database does not cover the publication output of the fields equally. Generally, physics and cardiology are very well covered, while the coverage of economics is somewhat lower due to different publication practices (Aksnes and Sivertsen 2019 ). This problem is accounted for in our study by ranking the respondents in each field separately, as described above. In addition, not all respondents may have been active researchers during the entire 2011–2017 period, which we have not adjusted for. Despite these limitations, the analysis provides interesting information on the bibliometric performance of the respondents at an aggregated level.
Regression analysis
To analyse the relationship between motivation and performance, we apply multinomial logistic regression rather then ordered logistic regression because we assume that the odds for respondents belonging in each category of the dependent variables are not equal (Hilbe 2017 ). The implication of this choice of model is that the model tests the probability of respondents being in one category compared to another (Hilbe 2017 ). This means that a reference or baseline category must be selected for each of the dependent variables (productivity and citation impact). Furthermore, the coefficient estimates show how the probability of being in one of the other categories decreases or increases compared to being in the reference category.
For this analysis, we selected the medium performers as the reference or baseline category for both our dependent variables. This enables us to evaluate how the independent variables affect the probability of being in the low performers group compared to the medium performers and the high performers compared to the medium performers.
To evaluate model fit, we started with a baseline model where only types of motivations were included as independent variables. Subsequently, the additional variables were introduced into the model, and based on measures for model fit (Pseudo R 2 , -2LL, and Akaike Information Criterion (AIC)), we concluded that the model with all additional variables included provides the best fit to the data for both the dependent variables (see Appendix Tables A5 and A6 ). Additional control variables include age, gender, country, and funding. We include these variables as controls to obtain robust effects of motivation and not effects driven by other underlying factors. The type of funding was measured by variables where the respondent answered the following question: ‘How has your research been funded the last five years?’ The funding variable initially consisted of four categories: ‘No source’, ‘Minor source’, ‘Moderate source’, and ‘Major source’. In this analysis, we have combined ‘No source’ and ‘Minor source’ into one category (0) and ‘Moderate source’ and ‘Major source’ into another category (1). Descriptive statistics for the funding variables are available in Appendix Table A4 . We do not control for the influence of field due to how the scientific performance variables are operationalised, the field normalisation implies that there are no variations across fields. We also do not control for position, as this variable is highly correlated with age, and we are therefore unable to include these two variables in the same model.
The motivation of researchers
In the empirical analysis, we first investigate variation in motivation and then relate it to publications and citations as our two measures of research performance.
As Fig. 1 shows, the respondents are mainly driven by curiosity and the wish to make scientific discoveries. This is by far the most important motivation. Practical application is also an important source of motivation, while making career progress is not identified as being very important.

Motivation of researchers– percentage
As Table 4 shows, at the level of fields, there are no large differences, and the motivational profiles are relatively similar. However, physicists tend to view practical application as somewhat less important than cardiologists and economists. Moreover, career progress is emphasised most by economists. Furthermore, as table 5 shows, there are some differences in motivation between countries. For curiosity/scientific discovery and practical application, the variations across countries are minor, but researchers in Denmark tend to view career progress as somewhat more important than researchers in the other countries.
Furthermore, as table 6 shows, women seem to view practical application and career progress as a more important motivation than men; these differences are also significant. Similar gender disparities have also been reported in a previous study (Zhang et al. 2021 ).
There are also some differences in motivation across the additional variables worth mentioning, as Table 7 shows. Unsurprisingly, perhaps, there is a significant moderate negative correlation between age, position, and career progress. This means that the importance of career progress as a motivation seems to decrease with increased age or a move up the position hierarchy.
In the second part of the analysis, we relate motivation to research performance. We first investigate publications and productivity using the percentile groups. Here, we present the results we use using predicted probabilities because they are more easily interpretable than coefficient estimates. For the model with productivity percentile groups as the dependent variable, the estimates for career progress were negative when comparing the medium productivity group to the high productivity group and the medium productivity group to the low productivity group. This result indicates that the probability of being in the high and low productivity groups decreases compared to the medium productivity group as the value of career progress increases, which may point towards a curvilinear relationship between the variables. A similar pattern was also found in the model with the citation impact group as the dependent variable, although it was not as apparent.
As a result of this apparent curvilinear relationship, we included quadric terms for career progress in both models, and these were significant. Likelihood ratio tests also show that the models with quadric terms included have a significant better fit to the data. Furthermore, the AIC was also lower for these models compared to the initial models where quadric terms were not included (see Appendix Tables A5 – A7 ). Consequently, we base our results on these models, which can be found in Appendix Table A7 . Due to a low number of respondents in the low categories of the scientific curiosity/discovery variable, we also combined the first three values into one to include it as a variable in the regression analysis, which results in a reduced three-value variable for scientific curiosity/discovery.
Results– productivity percentile group
Using the productivity percentile group as the dependent variable, we find that the motivational aspects of practical application and career progress have a significant effect on the probability of being in the low, medium, or high productivity group but not curiosity/scientific discovery. In Figs. 2 and 3 , each line represents the probability of being in each group across the scale of each motivational aspect.
Predicted probability for being in each of the productivity groups according to the value on the ‘practical application’ variable
Predicted probability of being in the low and high productivity groups according to the value on the ‘progress in my career’ variable
Figure 2 shows that at low values of application, there are no significant differences between the probability of being in either of the groups. However, from around value 3 of application, the differences between the probability of being in each group increases, and these are also significant. As a result, we concluded that high scores on practical application is related to increased probability of being in the high productivity group.
In Fig. 3 , we excluded the medium productivity group from the figure because there are no significant differences between this group and the high and low productivity group. Nevertheless, we found significant differences between the low productivity and the high productivity group. Since we added a quadric term for career progress, the two lines in Fig. 3 have a curvilinear shape. Figure 3 shows that there are only significant differences between the probability of being in the low or high productivity group at mid and high values of career progress. In addition, the probability of being in the high productivity group is at its highest value at mid values of career progress. This indicates that being motivated by career progress increases the probability of being in the high productivity group but only up to a certain point before it begins to have a negative effect on the probability of being in this group.
We also included age and gender as variables in the model, and Figs. 4 and 5 show the results. Figure 4 shows that age especially impacts the probability of being in the high productivity and low productivity groups. The lowest age category (< 30–34 years) has the highest probability for being in the low productivity group, while from the mid age category (50 years and above), the probability is highest for being in the high productivity group. This means that increased age is related to an increased probability of high productivity. The variable controlling for the effect of funding also showed some significant results (see Appendix Table A7 ). The most relevant finding is that receiving competitive grants from external public sources had a very strong and significant positive effect on being in the high productivity group and a medium-sized significant negative effect on being in the low productivity group. This shows that receiving external funding in the form of competitive grants has a strong effect on productivity.
Predicted probability of being in each of the productivity groups according to age
Figure 5 shows that there is a difference between male and female respondents. For females, there are no differences in the probability of being in either of the groups, while males have a higher probability of being in the high productivity group compared to the medium and low productivity groups.
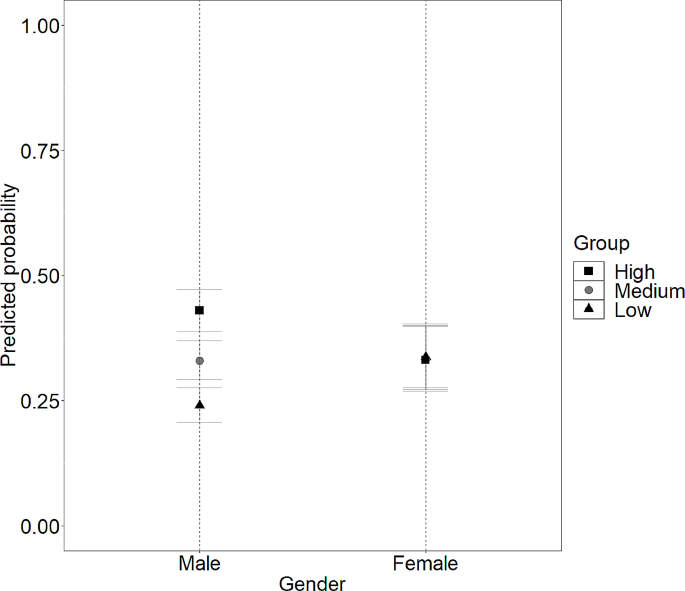
Results– citation impact group
For the citation impact group as the dependent variable, we found that career progress has a significant effect on the probability of being in the low citation impact group or the high citation group but not curiosity/scientific discovery or practical application. Figure 6 shows how the probability of being in the high citation impact group increases as the value on career progress increases and is higher than that of being in the low citation impact group, but only up to a certain point. This indicates that career progress increases the probability of being in the high citation impact group to some degree but that too high values are not beneficial for high citation impact. However, it should also be noted that the effect of career progress is weak and that it is difficult to conclude on how very low or very high values of career progress affect the probability of being in the two groups.
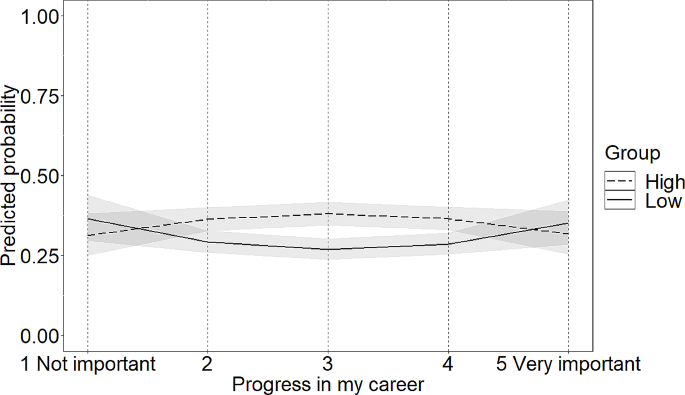
Predicted probability for being in each of the citation impact groups according to the value on the ‘progress in my career’ variable
We also included age and gender as variables in the model, and we found a similar pattern as in the model with productivity percentile group as the dependent variable. However, the relationship between the variables is weaker in this model with the citation impact group as the dependent variable. Figure 7 shows that the probability of being in the high citation impact group increases with age, but there is no significant difference between the probability of being in the high citation impact group and the medium citation impact group. We only see significant differences when each of these groups is compared to the low citation impact group. In addition, the increase in probability is more moderate in this model.
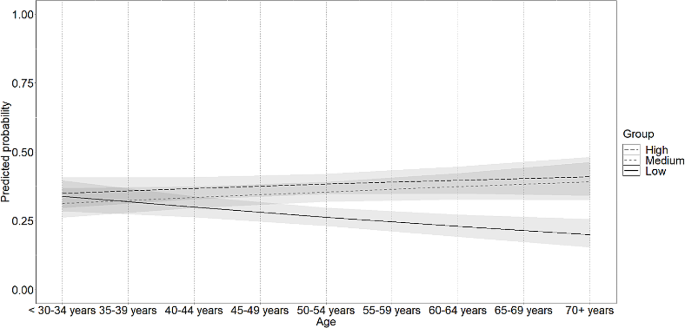
Predicted probability of being in each of the citation impact groups according to age
Figure 8 shows that there are differences between male and female respondents. Male respondents have a significant higher probability of being in the medium or high citation impact group compared to the low citation impact group, but there is no significant difference in the probability between the high and medium citation impact groups. For female respondents, there are no significant differences. Similarly, for age, the effect also seems to be more moderate in this model compared to the model with productivity percentile groups as the dependent variable. In addition, the effect of funding sources is more moderate on citation impact compared to productivity (see Appendix Table A7 ). Competitive grants from external public sources still have the most relevant effect, but the effect size and level of significance is lower than for the model where productivity groups are the dependent variable. Respondents who received a large amount of external funding through competitive grants are more likely to be highly cited, but the effect size is much smaller, and the result is only significant at p < 0.1. Those who do not receive much funding from this source are more likely to be in the low impact group. Here, the effect size is large, and the coefficient is highly significant.
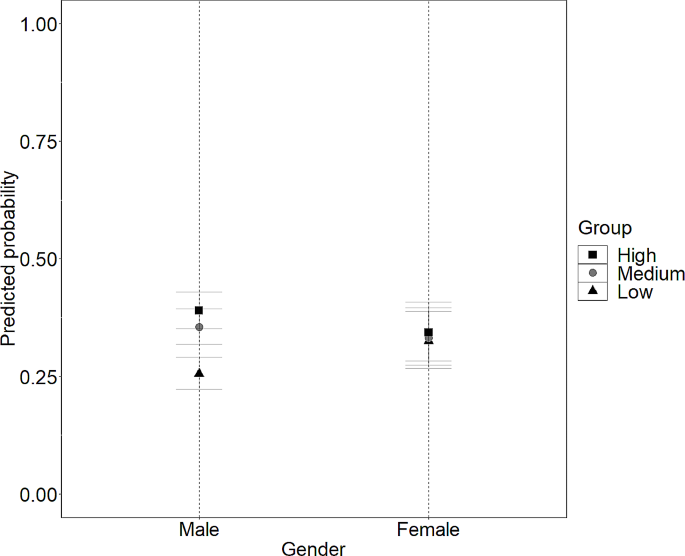
Predicted probability for being in each of the citation impact groups according to gender
Concluding discussion
This article aimed to explore researchers’ motivations and investigate the impact of motivation on research performance. By addressing these issues across several fields and countries, we provided new evidence on the motivation and performance of researchers.
Most researchers in our large-N survey found curiosity/scientific discovery to be a crucial motivational factor, with practical application being the second most supported aspect. Only a smaller number of respondents saw career progress as an important inspiration to conduct their research. This supports the notion that researchers are mainly motivated by core aspects of academic work such as curiosity, discoveries, and practical application of their knowledge and less so by personal gains (see Evans and Meyer 2003 ). Therefore, our results align with earlier research on motivation. In their interview study of scientists working at a government research institute in the UK, Jindal-Snape and Snape ( 2006 ) found that the scientists were typically motivated by the ability to conduct high quality, curiosity-driven research and de-motivated by the lack of feedback from management, difficulty in collaborating with colleagues, and constant review and change. Salaries, incentive schemes, and prospects for promotion were not considered a motivator for most scientists. Kivistö and colleagues ( 2017 ) also observed similar patterns in more recent survey data from Finnish academics.
As noted in the introduction, the issue of motivation has often been analysed in the literature using the intrinsic-extrinsic distinction. In our study, we have not applied these concepts directly. However, it is clear that the curiosity/scientific discovery item should be considered a type of intrinsic motivation, as it involves performing the activity for its inherent satisfaction. Moreover, the practical application item should probably be considered mainly intrinsic, as it involves creating a better society (for others) without primarily focusing on gains for oneself. The career progress item explicitly mentions personal gains such as position and higher salary and is, therefore, a type of extrinsic motivation. This means that our results support the notion that there are very strong elements of intrinsic motivation among researchers (Jindal-Snape and Snape 2006 ).
When analysing the three aspects of motivation, we found some differences. Physicists tend to view practical application as less important than researchers in the two other fields, while career progress was most emphasised by economists. Regarding country differences, our data suggest that career progress is most important for researchers in Denmark. Nevertheless, given the limited effect sizes, the overall picture is that motivational factors seem to be relatively similar regarding disciplinary and country dimensions.
Regarding gender aspects of motivation, our data show that women seem to view practical application and career progress as more important than men. One explanation for this could be the continued gender differences in academic careers, which tend to disadvantage women, thus creating a greater incentive for female scholars to focus on and be motivated by career progress aspects (Huang et al. 2020 ; Lerchenmueller and Sorenson 2018 ). Unsurprisingly, respondents’ age and academic position influenced the importance of different aspects of motivation, especially regarding career progress. Here, increased age and moving up the positional hierarchy are linked to a decrease in importance. This highlights that older academics and those in more senior positions drew more motivation from other sources that are not directly linked to their personal career gains. This can probably be explained by the academic career ladder plateauing at a certain point in time, as there are often no additional titles and very limited recognition beyond becoming a full professor. Finally, the type of funding that scholars received also had an influence on their productivity and, to a certain extent, citation impact.
Overall, there is little support that researchers across various fields and countries are very different when it comes to their motivation for conducting research. Rather, there seems to be a strong common core of academic motivation that varies mainly by gender and age/position. Rather than talking about researchers’ motivation per se, our study, therefore, suggests that one should talk about motivation across gender, at different stages of the career, and, to a certain degree, in different fields. Thus, motivation seems to be a multi-faceted construct, and the importance of different aspects of motivation vary between different groups.
In the second step of our analysis, we linked motivation to performance. Here, we focused on both scientific productivity and citation impact. Regarding the former, our data show that both practical application and career progress have a significant effect on productivity. The relationship between practical application aspects and productivity is linear, meaning that those who indicate that this aspect of motivation is very important to them have a higher probability of being in the high productivity group. The relationship between career aspects of motivation and productivity is curve linear, and we found only significant differences between the high and low productivity groups at mid and high values of the motivation scale. This indicates that being more motivated by career progress increases productivity but only to a certain extent before it starts having a detrimental effect. A common assumption has been that intrinsic motivation has a positive and instrumental effect and extrinsic motivation has a negative effect on the performance of scientists (Peng and Gao 2019 ; Ryan and Berbegal-Mirabent 2016 ). Our results do not generally support this, as motives related to career progress are positively linked with productivity only to a certain point. Possibly, this can be explained by the fact that the number of publications is often especially important in the context of recruitment and promotion (Langfeldt et al. 2021 ; Reymert et al. 2021 ). Thus, it will be beneficial from a scientific career perspective to have many publications when trying to get hired or promoted.
Regarding citation impact, our analysis highlights that only the career aspects of motivation have a significant effect. Similar to the results regarding productivity, being more motivated by career progress increases the probability of being in the high citation impact group, but only to a certain value when the difference stops being significant. It needs to be pointed out that the effect strength is weaker than in the analysis that focused on productivity. Thus, these results should be treated with greater caution.
Overall, our results shed light on some important aspects regarding the motivation of academics and how this translates into research performance. Regarding our first research question, it seems to be the case that there is not one type of motivation but rather different contextual mixes of motivational aspects that are strongly driven by gender and the academic position/age. We found only limited effects of research fields and even less pronounced country effects, suggesting that while situational, the mix of motivational aspects also has a common academic core that is less influenced by different national environments or disciplinary standards. Regarding our second research question, our results challenge the common assumption that intrinsic motivation has a positive effect and extrinsic motivation has a negative effect on the performance of scientists. Instead, we show that motives related to career are positively linked to productivity at least to a certain point. Our analysis regarding citation patterns achieved similar results. Combined with the finding regarding the importance of current academic position and age for specific patterns of motivation, it could be argued that the fact that the number of publications is often used as a measurement in recruitment and promotion makes academics that are more driven by career aspects publish more, as this is perceived as a necessary condition for success.
Our study has a clear focus on the research side of academic work. However, most academics do both teaching and research, which raises the question of how far our results can also inform our knowledge regarding the motivation for teaching. On the one hand, previous studies have highlighted that intrinsic motivation is also of high importance for the quality of teaching (see e.g. Wilkesmann and Lauer 2020 ), which fits well with our findings. At the same time, the literature also highlights persistent goal conflicts of academics (see e.g. Daumiller et al. 2020 ), given that extra time devoted to teaching often comes at the costs of publications and research. Given that other findings in the literature show that research performance continues to be of higher importance than teaching in academic hiring processes (Reymert et al. 2021 ), the interplay between research performance, teaching performance, and different types of motivation is most likely more complicated and demands further investigation.
While offering several relevant insights, our study still comes with certain limitations that must be considered. First, motivation is a complex construct. Thus, there are many ways one could operationalise it, and not one specific understanding so far seems to have emerged as best practice. Therefore, our approach to operationalisation and measurement should be seen as an addition to this broader field of measurement approaches, and we do not claim that this is the only sensible way of doing it. Second, we rely on self-reported survey data to measure the different aspects of motivation in our study. This means that aspects such as social desirability could influence how far academics claim to be motivated by certain aspects. For example, claiming to be mainly motivated by personal career gains may be considered a dubious motive among academics.
With respect to the bibliometric analyses, it is important to realise that we have lumped researchers into categories, thereby ‘smoothening’ the individual performances into group performances under the various variables. This has an effect that some extraordinary scores might have become invisible in our study, which might have been interesting to analyse separately, throwing light on the relationships we studied. However, breaking the material down to the lower level of analysis of individual researchers also comes with a limitation, namely that at the level of the individual academic, bibliometrics tend to become quite sensitive for the underlying numbers, which in itself is then hampered by the coverage of the database used, the publishing cultures in various countries and fields, and the age and position of the individuals. Therefore, the level of the individual academic has not been analysed in our study, how interesting and promising outcomes might have been. even though we acknowledge that such a study could yield interesting results.
Finally, our sample is drawn from northwestern European countries and a limited set of disciplines. We would argue that we have sufficient variation in countries and disciplines to make the results relevant for a broader audience context. While our results show rather small country or discipline differences, we are aware that there might be country- or discipline-specific effects that we cannot capture due to the sampling approach we used. Moreover, as we had to balance sufficient variation in framework conditions with the comparability of cases, the geographical generalisation of our results has limitations.
This article investigated what motivates researchers across different research fields and countries and how this motivation influences their research performance. The analysis showed that the researchers are mainly motivated by scientific curiosity and practical application and less so by career considerations. Furthermore, the analysis shows that researchers driven by practical application aspects of motivation have a higher probability of high productivity. Being driven by career considerations also increases productivity but only to a certain extent before it starts having a detrimental effect.
The article is based on a large-N survey of economists, cardiologists, and physicists in Denmark, Norway, Sweden, the Netherlands, and the UK. Building on this study, future research should expand the scope and study the relationship between motivation and productivity as well as citation impact in a broader disciplinary and geographical context. In addition, we encourage studies that develop and validate our measurement and operationalisation of aspects of researchers’ motivation.
Finally, a long-term panel study design that follows respondents throughout their academic careers and investigates how far their motivational patterns shift over time would allow for more fine-grained analysis and thereby a richer understanding of the important relationship between motivation and performance in academia.
Data availability
The data set for this study is available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Aksnes DW, Sivertsen G (2019) A criteria-based assessment of the coverage of Scopus and web of Science. J Data Inform Sci 4(1):1–21. https://doi.org/10.2478/jdis-2019-0001
Article Google Scholar
Atta-Owusu K, Fitjar RD (2021) What motivates academics for external engagement? Exploring the effects of motivational drivers and organizational fairness. Sci Public Policy. https://doi.org/10.1093/scipol/scab075 . November, scab075
Baccini A, Barabesi L, Cioni M, Pisani C (2014) Crossing the hurdle: the determinants of individual. Sci Perform Scientometrics 101(3):2035–2062. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-014-1395-3
Bornmann L, Leydesdorff L, Mutz R (2013) The use of percentiles and percentile rank classes in the analysis of bibliometric data: opportunities and limits. J Informetrics 7(1):158–165. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joi.2012.10.001
Cruz-Castro L, Sanz-Menendez L (2021) What should be rewarded? Gender and evaluation criteria for tenure and promotion. J Informetrics 15(3):1–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joi.2021.101196
Daumiller M, Stupnisky R, Janke S (2020) Motivation of higher education faculty: theoretical approaches, empirical evidence, and future directions. Int J Educational Res 99:101502. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijer.2019.101502
Duarte H, Lopes D (2018) Career stages and occupations impacts on workers motivations. Int J Manpow 39(5):746–763. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJM-02-2017-0026
Evans IM, Meyer LH (2003) Motivating the professoriate: why sticks and carrots are only for donkeys. High Educ Manage Policy 15(3):151–167. https://doi.org/10.1787/hemp-v15-art29-en
Finkelstein MJ (1984) The American academic profession: a synthesis of social scientific inquiry since World War II. Ohio State University, Columbus
Google Scholar
Hammarfelt B, de Rijcke S (2015) Accountability in context: effects of research evaluation systems on publication practices, disciplinary norms, and individual working routines in the Faculty of arts at Uppsala University. Res Evaluation 24(1):63–77. https://doi.org/10.1093/reseval/rvu029
Hangel N, Schmidt-Pfister D (2017) Why do you publish? On the tensions between generating scientific knowledge and publication pressure. Aslib J Inform Manage 69(5):529–544. https://doi.org/10.1108/AJIM-01-2017-0019
Hazelkorn E (2015) Rankings and the reshaping of higher education: the battle for world-class excellence. Palgrave McMillan, Basingstoke
Book Google Scholar
Hilbe JM (2017) Logistic regression models. Taylor & Francis Ltd, London
Horodnic IA, Zaiţ A (2015) Motivation and research productivity in a university system undergoing transition. Res Evaluation 24(3):282–292
Huang J, Gates AJ, Sinatra R, Barabási A-L (2020) Historical comparison of gender inequality in scientific careers across countries and disciplines. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 117(9):4609–4616. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1914221117
Jeong S, Choi JY, Kim J-Y (2014) On the drivers of international collaboration: the impact of informal communication, motivation, and research resources. Sci Public Policy 41(4):520–531. https://doi.org/10.1093/scipol/sct079
Jindal-Snape D, Snape JB (2006) Motivation of scientists in a government research institute: scientists’ perceptions and the role of management. Manag Decis 44(10):1325–1343. https://doi.org/10.1108/00251740610715678
Kivistö J, Pekkola E, Lyytinen A (2017) The influence of performance-based management on teaching and research performance of Finnish senior academics. Tert Educ Manag 23(3):260–275. https://doi.org/10.1080/13583883.2017.1328529
Kulczycki E, Engels TCE, Pölönen J, Bruun K, Dušková M, Guns R et al (2018) Publication patterns in the social sciences and humanities: evidence from eight European countries. Scientometrics 116(1):463–486. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-018-2711-0
Lam A (2011) What motivates academic scientists to engage in research commercialization: gold, ribbon or puzzle? Res Policy 40(10):1354–1368. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.respol.2011.09.002
Langfeldt L, Reymert I, Aksnes DW (2021) The role of metrics in peer assessments. Res Evaluation 30(1):112–126. https://doi.org/10.1093/reseval/rvaa032
Larivière V, Macaluso B, Archambault É, Gingras Y (2010) Which scientific elites? On the concentration of research funds, publications and citations. Res Evaluation 19(1):45–53. https://doi.org/10.3152/095820210X492495
Lepori B, Jongbloed B, Hicks D (2023) Introduction to the handbook of public funding of research: understanding vertical and horizontal complexities. In: Lepori B, Hicks BJ D (eds) Handbook of public funding of research. Edward Elgar Publishing, Cheltenham, pp 1–19
Chapter Google Scholar
Lerchenmueller MJ, Sorenson O (2018) The gender gap in early career transitions in the life sciences. Res Policy 47(6):1007–1017. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.respol.2018.02.009
Leslie DW (2002) Resolving the dispute: teaching is academe’s core value. J High Educ 73(1):49–73
Lounsbury JW, Foster N, Patel H, Carmody P, Gibson LW, Stairs DR (2012) An investigation of the personality traits of scientists versus nonscientists and their relationship with career satisfaction: relationship of personality traits and career satisfaction of scientists and nonscientists. R&D Manage 42(1):47–59. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-9310.2011.00665.x
Ma L (2019) Money, morale, and motivation: a study of the output-based research support scheme. Univ Coll Dublin Res Evaluation 28(4):304–312. https://doi.org/10.1093/reseval/rvz017
Melguizo T, Strober MH (2007) Faculty salaries and the maximization of prestige. Res High Educt 48(6):633–668
Moed HF (2005) Citation analysis in research evaluation. Springer, Dordrecht
Netherlands Observatory of Science (NOWT) (2012) Report to the Dutch Ministry of Science, Education and Culture (OC&W). Den Haag 1998
Peng J-E, Gao XA (2019) Understanding TEFL academics’ research motivation and its relations with research productivity. SAGE Open 9(3):215824401986629. https://doi.org/10.1177/2158244019866295
Piro FN, Aksnes DW, Rørstad K (2013) A macro analysis of productivity differences across fields: challenges in the measurement of scientific publishing. J Am Soc Inform Sci Technol 64(2):307–320. https://doi.org/10.1002/asi.22746
Pruvot EB, Estermann T, Popkhadze N (2023) University autonomy in Europe IV. The scorecard 2023. Retrieved from Brussels. https://eua.eu/downloads/publications/eua autonomy scorecard.pdf
Reymert I, Jungblut J, Borlaug SB (2021) Are evaluative cultures national or global? A cross-national study on evaluative cultures in academic recruitment processes in Europe. High Educ 82(5):823–843. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10734-020-00659-3
Roach M, Sauermann H (2010) A taste for science? PhD scientists’ academic orientation and self-selection into research careers in industry. Res Policy 39(3):422–434. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.respol.2010.01.004
Rørstad K, Aksnes DW (2015) Publication rate expressed by age, gender and academic position– A large-scale analysis of Norwegian academic staff. J Informetrics 9(2):317–333. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joi.2015.02.003
Ruiz-Castillo J, Costas R (2014) The skewness of scientific productivity. J Informetrics 8(4):917–934. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joi.2014.09.006
Ryan JC (2014) The work motivation of research scientists and its effect on research performance: work motivation of research scientists. R&D Manage 44(4):355–369. https://doi.org/10.1111/radm.12063
Ryan JC, Berbegal-Mirabent J (2016) Motivational recipes and research performance: a fuzzy set analysis of the motivational profile of high-performing research scientists. J Bus Res 69(11):5299–5304. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2016.04.128
Ryan RM, Deci EL (2000) Intrinsic and extrinsic motivations: classic definitions and new directions. Contemp Educ Psychol 25(1):54–67. https://doi.org/10.1006/ceps.1999.1020
Sivertsen G (2019) Understanding and evaluating research and scholarly publishing in the social sciences and humanities (SSH). Data Inform Manage 3(2):61–71. https://doi.org/10.2478/dim-2019-0008
Sivertsen G, Van Leeuwen T (2014) Scholarly publication patterns in the social sciences and humanities and their relationship with research assessment
Stephan P, Veugelers R, Wang J (2017) Reviewers are blinkered by bibliometrics. Nature 544(7651):411–412. https://doi.org/10.1038/544411a
Thomas D, Nedeva M (2012) Characterizing researchers to study research funding agency impacts: the case of the European Research Council’s starting grants. Res Evaluation 21(4):257–269. https://doi.org/10.1093/reseval/rvs020
Tien FF (2000) To what degree does the desire for promotion motivate faculty to perform research? Testing the expectancy theory. Res High Educt 41(6):723–752. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1007020721531
Tien FF (2008) What kind of faculty are motivated to perform research by the desire for promotion? High Educ 55(1):17–32. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10734-006-9033-5
Tien FF, Blackburn RT (1996) Faculty rank system, research motivation, and faculty research productivity: measure refinement and theory testing. J High Educ 67(1):2. https://doi.org/10.2307/2943901
Vallerand RJ, Pelletier LG, Blais MR, Briere NM, Senecal C, Vallieres EF (1992) The academic motivation scale: a measure of intrinsic, extrinsic, and amotivation in education. Educ Psychol Meas 52(4):1003–1017. https://doi.org/10.1177/0013164492052004025
Van Iddekinge CH, Aguinis H, Mackey JD, DeOrtentiis PS (2018) A meta-analysis of the interactive, additive, and relative effects of cognitive ability and motivation on performance. J Manag 44(1):249–279. https://doi.org/10.1177/0149206317702220
Van Leeuwen T (2013) Bibliometric research evaluations, Web of Science and the social sciences and humanities: A problematic relationship? Bibliometrie - Praxis Und Forschung, September, Bd. 2(2013). https://doi.org/10.5283/BPF.173
Van Leeuwen T, van Wijk E, Wouters PF (2016) Bibliometric analysis of output and impact based on CRIS data: a case study on the registered output of a Dutch university. Scientometrics 106(1):1–16. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-015-1788-y
Waltman L, Schreiber M (2013) On the calculation of percentile-based bibliometric indicators. J Am Soc Inform Sci Technol 64(2):372–379. https://doi.org/10.1002/asi.22775
Waltman L, van Eck NJ, van Leeuwen TN, Visser MS, van Raan AFJ (2011) Towards a new crown indicator: an empirical analysis. Scientometrics 87(3):467–481. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-011-0354-5
Wilkesmann U, Lauer S (2020) The influence of teaching motivation and new public management on academic teaching. Stud High Educ 45(2):434–451. https://doi.org/10.1080/03075079.2018.1539960
Wilsdon J, Allen L, Belfiore E, Campbell P, Curry S, Hill S, Jones R et al (2015) The metric tide: report of the independent review of the role of metrics in research assessment and management. https://doi.org/10.13140/RG.2.1.4929.1363
Zacharewicz T, Lepori B, Reale E, Jonkers K (2019) Performance-based research funding in EU member states—A comparative assessment. Sci Public Policy 46(1):105–115. https://doi.org/10.1093/scipol/scy041
Zhang L, Sivertsen G, Du H, Huang Y, Glänzel W (2021) Gender differences in the aims and impacts of research. Scientometrics 126(11):8861–8886. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-021-04171-y
Download references
Acknowledgements
We are thankful to the R-QUEST team for input and comments to the paper.
The authors disclosed the receipt of the following financial support for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article: This work was supported by the Research Council Norway (RCN) [grant number 256223] (R-QUEST).
Open access funding provided by University of Oslo (incl Oslo University Hospital)
Author information
Silje Marie Svartefoss
Present address: TIK Centre for Technology, Innovation and Culture, University of Oslo, 0317, Oslo, Norway
Authors and Affiliations
Nordic Institute for Studies in Innovation, Research and Education (NIFU), Økernveien 9, 0608, Oslo, Norway
Silje Marie Svartefoss & Dag W. Aksnes
Department of Political Science, University of Oslo, 0315, Oslo, Norway
Jens Jungblut & Kristoffer Kolltveit
Centre for Science and Technology Studies (CWTS), Leiden University, 2311, Leiden, The Netherlands
Thed van Leeuwen
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection, and analysis were performed by Silje Marie Svartefoss, Jens Jungblut, Dag W. Aksnes, Kristoffer Kolltveit, and Thed van Leeuwen. The first draft of the manuscript was written by all authors in collaboration, and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Silje Marie Svartefoss .
Ethics declarations
Competing interests.
The authors have no competing interests to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Informed consent
was retrieved from the participants in this study.
Electronic Supplementary Material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary Material 1
Rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Svartefoss, S.M., Jungblut, J., Aksnes, D.W. et al. Explaining research performance: investigating the importance of motivation. SN Soc Sci 4 , 105 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s43545-024-00895-9
Download citation
Received : 14 December 2023
Accepted : 15 April 2024
Published : 23 May 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s43545-024-00895-9
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Performance
- Productivity
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research

COMMENTS
A literature review is not only a summary of key sources, but has an organizational pattern which combines both summary and synthesis, often within specific conceptual categories.A summary is a recap of the important information of the source, but a synthesis is a re-organization, or a reshuffling, of that information in a way that informs how you are planning to investigate a research problem.
Besides the obvious reason for students -- because it is assigned! -- a literature review helps you explore the research that has come before you, to see how your research question has (or has not) already been addressed. You identify: core research in the field. experts in the subject area. methodology you may want to use (or avoid)
Examples of literature reviews. Step 1 - Search for relevant literature. Step 2 - Evaluate and select sources. Step 3 - Identify themes, debates, and gaps. Step 4 - Outline your literature review's structure. Step 5 - Write your literature review.
This is why the literature review as a research method is more relevant than ever. Traditional literature reviews often lack thoroughness and rigor and are conducted ad hoc, rather than following a specific methodology. Therefore, questions can be raised about the quality and trustworthiness of these types of reviews.
A literature or narrative review is a comprehensive review and analysis of the published literature on a specific topic or research question. The literature that is reviewed contains: books, articles, academic articles, conference proceedings, association papers, and dissertations. It contains the most pertinent studies and points to important ...
Writing a literature review requires a range of skills to gather, sort, evaluate and summarise peer-reviewed published data into a relevant and informative unbiased narrative. Digital access to research papers, academic texts, review articles, reference databases and public data sets are all sources of information that are available to enrich ...
Most literature reviews are embedded in articles, books, and dissertations. In most research articles, there are set as a specific section, usually titled, "literature review", so they are hard to miss.But, sometimes, they are part of the narrative of the introduction of a book or article. This section is easily recognized since the author is engaging with other academics and experts by ...
A literature review is meant to analyze the scholarly literature, make connections across writings and identify strengths, weaknesses, trends, and missing conversations. A literature review should address different aspects of a topic as it relates to your research question. A literature review goes beyond a description or summary of the ...
Literature Review is a comprehensive survey of the works published in a particular field of study or line of research, usually over a specific period of time, in the form of an in-depth, critical bibliographic essay or annotated list in which attention is drawn to the most significant works.. Also, we can define a literature review as the collected body of scholarly works related to a topic:
Selecting the right quality of literature is the key to successful research literature review. The quality can be estimated by what is known as "The Evidence Pyramid.". The level of evidence of references obtained from the aforementioned search tools are depicted in Figure 9. Systematic reviews obtained from Cochrane library constitute ...
A literature review is a critical summary and evaluation of the existing research (e.g., academic journal articles and books) on a specific topic. It is typically included as a separate section or chapter of a research paper or dissertation, serving as a contextual framework for a study.
A literature review may consist of simply a summary of key sources, but in the social sciences, a literature review usually has an organizational pattern and combines both summary and synthesis, often within specific conceptual categories.A summary is a recap of the important information of the source, but a synthesis is a re-organization, or a reshuffling, of that information in a way that ...
Upon completion of the literature review, a researcher should have a solid foundation of knowledge in the area and a good feel for the direction any new research should take. Should any additional questions arise during the course of the research, the researcher will know which experts to consult in order to quickly clear up those questions.
A literature review can be a stand-alone work (often called a "review article") or it can be one part of a more substantial research paper. The focus of a literature review is to summarize and synthesize other authors' arguments and ideas (with only moderate contribution from the author of the review). Research papers, however, are larger ...
The importance of the literature review is directly related to its aims and purpose. Nursing and allied health disciplines contain a vast amount of ever increasing lit-erature and research that is important to the ongoing development of practice. The literature review is an aid to gathering and synthesising that information. The pur-
"A substantive, thorough, sophisticated literature review is a precondition for doing substantive, thorough, sophisticated research". Boote and Baile 2005 . Authors of manuscripts treat writing a literature review as a routine work or a mere formality. But a seasoned one knows the purpose and importance of a well-written literature review.
Purpose and Importance of the Literature Review. An understanding of the current literature is critical for all phases of a research study. Lingard 9 recently invoked the "journal-as-conversation" metaphor as a way of understanding how one's research fits into the larger medical education conversation. As she described it: "Imagine yourself joining a conversation at a social event.
A sophisticated literature review (LR) can result in a robust dissertation/thesis by scrutinizing the main problem examined by the academic study; anticipating research hypotheses, methods and results; and maintaining the interest of the audience in how the dissertation/thesis will provide solutions for the current gaps in a particular field.
The purpose of a literature review is to: Provide a foundation of knowledge on a topic; Identify areas of prior scholarship to prevent duplication and give credit to other researchers; Identify inconstancies: gaps in research, conflicts in previous studies, open questions left from other research
A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources (such as books, journal articles, and theses) related to a specific topic or research question. It is often written as part of a thesis, dissertation , or research paper , in order to situate your work in relation to existing knowledge.
Why is it important? A literature review is important because it: Explains the background of research on a topic. Demonstrates why a topic is significant to a subject area. Discovers relationships between research studies/ideas. Identifies major themes, concepts, and researchers on a topic. Identifies critical gaps and points of disagreement.
Literature Review. This is the most time-consuming aspect in the preparation of your research proposal and it is a key component of the research proposal. As described in Chapter 5, the literature review provides the background to your study and demonstrates the significance of the proposed research. Specifically, it is a review and synthesis ...
Some Issues in Liter ature R eview. 1. A continuous and time consuming process runs. through out r esearch work (more whil e selecting. a resear ch problem and writing 'r eview of. liter ature ...
Motivation and abilities are known to be as important factors in explaining employees' job performance of employees (Van Iddekinge et al. 2018), and in the vast scientific literature on motivation, it is common to differentiate between intrinsic and extrinsic motivation factors (Ryan and Deci 2000).In this context, path-breaking individuals are said to often be intrinsically motivated ...