The Barriers to Effective Communication
Effective communication is crucial in any professional setting.
Whether you’re participating in a meeting, conversing with your colleagues, or attending a presentation, navigating through communication barriers can be challenging. These barriers often obstruct the smooth flow of information, leading to misunderstandings that waste valuable time and resources.
Therefore, it is vital to identify these barriers and find ways to minimize their impact.
In this article, we’ll explore common communication barriers across different industries and provide practical solutions to bridge these gaps. So, let’s dive in and see how you can enhance communication within your team!

Table of Contents

What is a communication barrier?
Before we dive deep into the 8 types of communication barriers, we’ll look at how communication barriers are defined in the professional world.
In essence, any problem or obstacle that gets in the way of the communication process qualifies as a communication barrier .
The truth is, rarely any communication situation is devoid of communication barriers, as they can occur at any stage of the interaction. For this reason, it’s essential that we become familiar with specific causes and learn how to overcome communication barriers in the workplace.
Although classifications vary, the most common communication barriers are:
- Physical barriers,
- Perceptual barriers,
- Emotional barriers,
- Cultural barriers,
- Language barriers,
- Gender barriers,
- Interpersonal barriers , and
- Organizational barriers .
Given that each of the above barriers has its own challenges, merely knowing the classification isn’t enough to optimize workplace communication.
As we’ve mentioned, we’re bound to run into obstacles in professional communication.
But, this doesn’t mean that barriers to communication doom all business interactions to failure. By learning more detail about communication barriers, you’ll get a clear overview of how they impact conversation and understand which preventative measures to take.
Physical barriers to effective team communication + solutions
Physical barriers to communication represent the various environmental and natural conditions that act as barriers between the senders and receivers of information .
These physical barriers include challenges related to:
- Time and distance,
- Personal space,
- Workplace design,
- Work environment, and
- Background noise.
Physical barrier #1: Time and distance
The barriers related to time and distance typically affect remote teams whose members work from home.
Remote teammates do not work in the same office or even at the same time. Instead, they may operate on a different continent and time zone . This makes real-time communication difficult and in-person communication inconvenient or near impossible — unless one teammate is willing to accommodate the other, work at night, or fly across the globe regularly.
Example of a communication barrier based on time and distance
Let’s look at a remote software developer team consisting of 5 software developers who live across the globe.
The developers are already geographically apart — and the time difference means they are unlikely to work at the same time.
For example, the project manager may start working at 9 a.m. EST when their teammates have started wrapping up work at 3 p.m. CET.
Because of these time differences, the team can rarely work together at the same time — and they need to find other ways to collaborate .
Top solutions for problems with time and distance
Embracing asynchronous communication can help prevent time and distance from causing communication barriers in the workplace. Consider using specialized apps, such as:
- A team communication app : It allows for direct messaging, audio/video calls , topic-based channels, and scheduling messages.
- A project management tool : You can use it to communicate project details.
- A time tracker : You can use it to indicate and track everyone’s work hours.
- A time converter app: It helps you see everyone’s time zones and organize meetings accordingly.
By taking advantage of the above tools, you’ll be able to make in-person work more efficient and address the challenges of remote and hybrid work.
Physical barrier #2: Personal space
In verbal, face-to-face communication , personal space plays a crucial role.
Namely, the distance that applies only to in-person communication may act as a facilitator to good communication or as a barrier to effective communication — depending on whether it’s adequately interpreted and arranged.
We can recognize 4 types of distance between in-person communicators:
- Intimate space : The distance between the communicators is less than 18 inches (0.45 meters). It’s usually reserved for close relationships, such as between a parent and child or between partners.
- Personal space : The distance between communicators is 2–3 feet (0.6–0.9 meters). It’s typically associated with friends and peer groups.
- Official space : The distance between communicators is 4–5 feet (1.2–1.5 meters), depending on the type of information transmitted. This type of space is associated with official situations, such as most communication situations at work .
- Public space : The distance between communicators is over 10 feet (3 meters). Public space is associated with speakers and listeners in public situations, like speaking events.
Reducing these space requirements may lead to awkward or embarrassing situations.
But, this depends on a person’s culture .
Namely, people from the US and Northern Europe dislike having their personal space violated.
But, people from South American countries and the Middle East belong to so-called “contact cultures.” This means they’re more comfortable with people coming closer, even if they’re not close friends.
This makes space not only a physical barrier to effective communication but often a cultural one as well.
Free business communication tool
Secure, real-time communication for professionals.
FREE FOREVER • UNLIMITED COMMUNICATION

Example of a communication barrier based on personal space
In the conference room of a marketing agency, employees Steve and Manuel are sitting in the front row listening to the company’s head of HR, Charlotte, deliver a speech about the company’s planned cultural development.
The conference room is relatively small, but there are a lot of employees — they needed to squeeze in 10 rows, so the front row is only 3 feet away from Charlotte.
Charlotte needs to keep her voice loud so that the people in the back row can hear her clearly.
Because of this, she appears too loud to Steve and Manuel, who are thus more focused on the discomfort they are feeling because of Charlotte’s voice volume than on the message she is trying to convey.
Top solutions for problems with personal space
In a professional setting, always maintain a moderate distance from the people you are speaking with.
When it comes to public speeches in smaller spaces, consider organizing a virtual meeting instead.
🎓 Pumble Pro Tip
To learn how to better run both in-person and virtual meetings, check out this blog post:
- How to run effective meetings
Physical barrier #3: Workplace design
Workplace design has a crucial influence on communication effectiveness in the workplace.
For example, the seating arrangements can facilitate effective communication — when team members who need to communicate and collaborate daily are seated at connected desks.
But, the seating arrangement can also become a barrier to communication, primarily when it isn’t addressed promptly.
Example of a communication barrier based on workplace design
What do difficulties with office layout look like in practice? We’ll look at a customer support team whose workstations are in the same area to learn more.
Although the team members work from the same room, their desks are separated by cubicles.
Whenever an emergency arises or teammates want to speak to each other, they need to go from cubicle to cubicle to pass on information. They face similar difficulties when they want to ask or answer a question.
This practice slows down their response time for customers and lowers their overall efficacy.
Top solutions for problems with workplace design
An open office plan can go a long way in fixing a subpar layout.
After swapping out separate offices and cubicles for open tables, it becomes much easier to communicate in person.
But, in companies with a remote or hybrid model, reaching someone in person isn’t always possible.
In that case, use threads in your team communication app to keep all team members posted and on top of the latest developments.
Physical barrier #4: Work environment
The chief element of a work environment that may hinder effective communication is comfort — or, more precisely, the potential lack of it .
Namely, if the company or home office is too hot or cold , people may not be able to fully focus on the information being communicated in business situations. The same applies if the desks and chairs are too low or high or the office lighting is too bright or dim.
Example of a communication barrier based on work environment
Have you ever shared an office with a coworker? If so, you may have found yourself in Matt or David’s shoes.
Matt and David are 2 sales specialists that work in a shared office.
The desks in their office are too low for their liking, while the comfortableness of their chairs leaves a lot to be desired.
Moreover, they often have disputes about the thermostat. Matt often finds that it is too hot, while David often finds that it is too cold.
Because of these work environment issues, the 2 sales specialists are occasionally unfocused while conversing with customers, each other, and colleagues.
Top solutions for problems with work environment
While you can’t always completely change your work environment, small tweaks can make your time in the office more enjoyable.
First, try to adjust what you can and learn how to adapt to what you can’t adjust. For example, if the office is too cold for one colleague but too hot for the other, dress accordingly — wear short sleeves or bring a jacket.
And, if you’re after more long-term changes, you can organize an informal meeting with your colleagues and see if you can all reach a compromise.
Physical barrier #5: Background noise
Noise is a common barrier to communication in the workplace. Background noise can stem from several reasons, including:
- Colleagues talking nearby (often experienced by people who work in an office),
- Family members, roommates, or partners talking nearby (often experienced by people who work from home),
- Copy machines, kitchen noise, and other inside noises, and
- Outside noises from thunderstorms, traffic, or lawn equipment.
While some people can tune out and ignore the above distractions, most struggle to maintain their cognitive performance when exposed to loud intermittent noises.
Interestingly, introverts may have more problems focusing in noisy environments. A study from a research center in Glasgow examined the effect of background noise on both extroverts and introverts.
Although both groups performed poorly when background noise was present, the noise distractions significantly impacted the introverted participants. Since introverts are more sensitive to external stimuli, it’s unsurprising that loud environments prevent them from doing their best work.
So, the extent to which noises prevent us from focusing on our tasks may be down to our personality type.
Example of a communication barrier based on background noise
To glean just how distracting background noise can be in the workplace, we’ll look at Adam, Leila, and Craig, who are all members of the content team.
Since their workstations are close together, even the slightest noise can be a major disturbance — especially when Adam cranks up the volume.
While creating content, Adam likes to listen to popular music. He uses headphones, but the music is loud enough for Craig and Leila to hear everything.
Leila and Craig often need to talk about the content she writes. But, the fact they can hear Adam’s music often distracts them from the points they are trying to make.
Top solutions for problems with background noise
First, research the best ways to manage background noise.
Perhaps you’ll find that noise-canceling headphones are a great all-encompassing solution.
Or, maybe you’ll find that playing a noise generator app via regular headphones blocks most noise.
If the problem is noisy colleagues, talk with them — try to find a suitable noise-reducing solution together.
Perceptual barriers to effective team communication + solutions

Perceptual barriers to communication represent the mental blocks people may have that influence their perceptions about specific people, topics, or events .
These perceptions form intra-personal barriers that affect how people send, receive, or interpret messages in conversations.
Perceptual barriers to effective communication include perceptual filters but also nonverbal language .
Perceptual barrier #1: Perceptual filters
Perceptual filters to effective communication include our:
- Thoughts,
- Cognitive biases ,
- Assumptions,
- Preferences,
- Values, and
- Attitudes.
Unfortunately, these “filters” may lead to misunderstandings, stereotyping, and assumptions in communication. Such “filters” often make us closed-minded to opinions that are different from our own or ideas that go beyond what we consider “ usual ,” “ expected ,” or “ normal .”
Example of a communication barrier based on perceptual filters
We all construct our model of the world based on past experiences, which means that our filters usually lead to a few blind spots.
Consequently, these blind spots can negatively affect the people around us, as is the case with Erica, who has just joined a team of medical surgeons.
She just finished her specialization and is the daughter of the head of the hospital. Because of this, Erica’s colleagues assume she is inexperienced and, even worse, admitted to the team simply because her father appoints the staff.
Erica is also a staunch supporter of new surgical research — research her colleagues are still wary of.
Because of their assumptions and differences in values, the rest of the surgical team tends to ignore Erica during breaks.
As a result, Erica is often left in the dark about important happenings in the hospital.
Top solutions for problems with perceptual filters
Just because you perceive someone in a certain way doesn’t mean your perceptions hold true in reality.
Before declaring that you know exactly what someone thinks or feels, gaining all the relevant information is essential. This requires a certain level of flexibility, which can be hard when we refuse to question our own beliefs.
In the book Big Ideas: Putting the Zest Into Creativity & Innovation at Work , Jonne Ceserani touches on perceptual position. The author defines them as the outlooks we use as starting positions when thinking about specific topics and circumstances. Ceserani also goes on to describe 4 perceptual positions:
- The “ I ” position : We base our worldview on our past experiences, assumptions, and beliefs.
- The “ You ” position : We step into someone else’s shoes and try to understand where they’re coming from.
- The “ They ” position : We detach ourselves from our emotions and the feelings of everyone involved in the situation. The goal is to become an impartial observer who comes in from a factual standpoint.
- The “ We ” position : We consider the bigger picture and adopt the perspective of a larger entity, such as a company or similar institution.
When we make a conscious effort to leave the “ I ” position and change our outlook, we can:
- Identify the shortcomings in our perspective,
- Get a clearer understanding of the people around us,
- Participate in more win-win situations,
- Learn how to overcome communication barriers, and
- Become more flexible and creative.
Of course, this is only possible if we’re willing to show up in our personal and professional lives with more empathy .
Perceptual barrier #2: Nonverbal language
Nonverbal facial expressions, triggers, and cues represent the body language people emit while communicating.
This body language may be connected with the intended meaning of the messages the communicator is trying to convey. But, it may also be intentionally or unintentionally misleading.
In line with that, other people may perceive the nonverbal language of their fellow communicators correctly, or they might misinterpret it.
Example of a nonverbal language challenge
How can nonverbal language give rise to problems in the workplace? Let’s take Noah and Larissa, the only customer support specialists in an online fashion shop, as an example.
Recently, a customer has returned a valuable shipment, asking for a full refund. The reason cited is that a customer support specialist led her on about the color of the dresses ordered.
Julia, the head of customer support, calls up Noah and Larissa to discuss the matter and find the person responsible.
During the separate interviews, both Noah and Larissa deny it was them — but both display deceptive behavior, including:
- Averting their eyes when answering questions,
- Showing signs of alarm and panic,
- Fake smiling, and
- Fidgeting and looking stressed.
In truth, Noah is the one to blame.
Larissa is just nervous because she’s being interrogated on such an important matter.
The problem is that Julia cannot immediately spot the liar because her perception of Noah’s and Larrisa’s nonverbal language tells her they are both lying.
Top solutions for problems with nonverbal language
Observing nonverbal language can help you decide whether someone is lying, trying to conceal information or to mislead you.
But, it shouldn’t be the sole reason you decide to distrust someone.
So, don’t just look for disparities between people’s words and facial expressions.
Instead, always focus on what they are saying first . Don’t be shy to ask more questions if you cannot decide whether someone’s words match your perception of their nonverbal language.
These questions should be specific open-ended questions and direct “Yes/No” questions a person cannot evade.
The more questions you ask, the closer you will be to discovering what you want.
🎓 Pumble Pro Tip
To learn how to ask better questions at work, read this blog post:
- How to ask better questions at work
Emotional barriers to effective team communication + solutions
Emotional barriers to communication represent the emotions that may hold you back from communicating what you want to your teammates . These emotions might also stop you from listening to others attentively and accepting their point of view.
These key emotional barriers include:
Emotional barrier #1: Anger
Anger is an emotional barrier to communication that affects how your brain processes information.
Because of anger, you are less likely to be logical in discussions.
Moreover, you are less likely to contribute productively to solving problems — and more likely to oppose other people’s ideas.
The people you are projecting your anger to will usually become defensive, scared, or hurt.
As a result, people may hesitate to contact you in case of an emergency — even if you objectively are the best person to solve the problem.
Example of a communication barrier based on anger
Emotional barriers to communication can be detrimental to team collaboration . When those in leadership positions don’t know how to manage their anger , teamwork suffers the brunt of this emotion, as evidenced by Ginny’s situation below.
Ginny is a project manager at a software development company.
The project she is currently working on is late, and she has organized an emergency meeting to discuss what can be done to speed up and re-organize work.
During the discussion, Ginny becomes frustrated with her team’s perceived lack of urgency and starts calling on individual teammates to explain their work processes.
A couple of teammates become defensive, and Ginny angrily rejects their explanations. She even dismisses the fact-based reasons that show Ginny herself disregarded the original deadline estimates and defined an overly ambitious project deadline on her own.
After the meeting, the team goes back to work.
They may work with more focus in the future, but they now feel wary of Ginny and are reluctant to ask for help in the future — even if they think that they need to.
Top solutions for overcoming problems with anger
The fundamental solution to handling anger while communicating is removing yourself from the problematic situation until you can manage and respond to it appropriately.
Preferably, you should do this before you snap at someone. Then, once you’ve calmed yourself and collected your thoughts, address the matter again.
This time, think clearly about what you want to say before you say it, and refrain from making potentially hurtful comments.
Emotional barrier #2: Pride
Pride is an emotional barrier that inhibits healthy communication in several ways.
For one, pride as an emotion implies you take pride in what you say and do. When this feeling gets the better of you, you might talk more than you listen — and active listening is an essential skill of effective communicators.
As a result, teammates become wary of inviting you to brainstorming sessions — because your idea always needs to be the best one, or else you become difficult to work with.
Example of a communication barrier based on pride
Are you unsure how pride could impede successful teamwork and collaboration ? To get more insight, we’ll turn to Oliver, a social media marketer at a marketing agency.
At every brainstorming session, he is the loudest when presenting his ideas. He is quick to dismiss the opinions of others with methodical flair.
His accomplishments are celebrated the longest, and he never makes mistakes (at least, not mistakes he owns up to).
Consequently, his teammates have come to dread daily meetings. They tend to let Oliver talk and often feel unmotivated to outtalk him. This dreary cycle continues, even if they have something important to say or ask.
Top solutions for overcoming problems with pride
Pride is arguably one of the most challenging communication barriers to overcome because it leads us to believe we’re always in the right. However, when we take a step back and cool off, we quickly realize that no opinion is infallible, not even our own.
Work on accepting that your statements may not always be perfect — or even correct. And, don’t be afraid to admit to your mistakes instead of investing all your efforts into persuading others that you are not at fault.
If you have a particular emotional insecurity, don’t try to compensate for it with a false sense of superiority. Instead, identify the cause of your insecurities and try to address them. Thanks to these efforts, people will feel more at ease when communicating with you.
Emotional barrier #3: Anxiety
Anxiety is another emotional barrier to effective communication that can diminish the efficacy of your communication skills.
This emotion prevents you from becoming an effective communicator by eating away at your concentration. Instead of paying attention to others, you become increasingly preoccupied with what you want to say.
Moreover, anxiety may push you to avoid certain social situations and save yourself from embarrassment or difficult conversations , even in a professional setting.
Example of a communication barrier based on anxiety
Let’s delve deeper into how anxiety can generate persistent fear and worry and stop us from putting our best foot forward in the workplace.
That’s exactly what it does to Daniel, an HR specialist in charge of recruiting, screening, interviewing, and onboarding workers .
At the end of each month, he attends a meeting with the head of the HR department, the CEO, and the leaders of other departments. During this meeting, they discuss his progress with the job positions they’ve requested.
Daniel’s talent with most tasks is noteworthy. But, his meeting anxiety creeps up each time he needs to attend the said monthly meeting.
Due to his situational anxiety, he often forgets to highlight his accomplishments and struggles to articulate answers to the audience’s questions. Although his achievements are commendable, his less-than-confident presentations make people question his capacity to handle his HR duties and grow in the future.
Top solutions for overcoming problems with anxiety
Overcoming problems with anxiety is easier said than done, but there are ways you can try to keep the fear and worry at bay.
First, look into relaxation exercises and see whether meditation or breathwork can help you cope with stressful situations .
Also, consider why you feel anxious under certain circumstances— weigh down your reasons and decide whether they are worth the worries.
Finally, consult a medical professional for specialized advice if you have a more generalized anxiety problem.
Cultural barriers to effective team communication + solutions
According to Joynt & Warner (1996), culture is “ the pattern of taken-for-granted assumptions about how a given collection of people should think, act, and feel as they go about their daily affairs .”
In line with this definition, cultural barriers to communication represent the different culture-related behavior patterns that may arise as obstacles to well-balanced communication among teammates .
These culture-related behavior patterns may revolve around:
- Language,
- Nonverbal language, and
- Cultural norms, beliefs, and values.
They may also manifest as:
- Stereotypes or
- Status-based self-importance.
Cultural barrier #1: Language
Language barriers to communication can be detrimental, especially for teams across the globe. After all, it’s not uncommon to find people with different native languages in remote-first organizations .
For all their benefits, work-from-anywhere initiatives bring a unique set of drawbacks because if you don’t understand your teammates and they don’t understand you, communication breaks down .
Example of a communication barrier based on language
We’ve already discussed how physical barriers like time and distance prevent teams from collaborating smoothly. Now, what happens when you add a language barrier to the mix?
In a software development team, the manager notices persistent communication issues. Namely, two team members are French-Canadian and much better at speaking their minds in French than English.
However, the remaining two teammates are from the UK, and English is their mother tongue. Worried about the direction the team is heading, the manager holds an emergency meeting, where the group realizes that they have one language in common: French.
The manager took advanced French courses in university, and the coworkers from the UK got their degrees in Paris.
Because of this, the team decides to use French for all official correspondence.
Top solutions for problems with language
As evidenced by the example above, the top solution for overcoming the communication barrier of different languages is to identify the language the entire team is comfortable communicating in.
Once you do, define it as the official team language. Then, all official correspondence between team members should be handled in the selected language.
Cultural barrier #2: Nonverbal language
We already discussed nonverbal language when addressing the perceptual barriers to effective communication.
However, nonverbal language can also be connected with the speaker’s culture. The same gestures or facial expressions can have different meanings in different cultures.
In such cases, we regard nonverbal language as a crucial culture-based communication barrier.
Example of a nonverbal language challenge (as a cultural barrier)
Let’s look at a software development team with members from different cultural backgrounds.
During a video meeting, the group encounters a nonverbal language challenge. The team lead, Olivia, from Wales, accidentally mutes her microphone while Nicholas, a QA specialist from Greece, presents a new feature.
When Nicholas asks for Olivia’s approval, she nods her head once and gives a thumbs-up gesture. However, this unintentionally unnerves the team members from Greece, Turkey, and Bangladesh.
Olivia is unaware that a single nod signifies “ No ” in Greece and Turkey, and in Bangladesh, a thumbs-up is considered offensive.
It takes some time for Olivia to explain her intended meaning and bridge the communication gap caused by cultural differences.
The best way to avoid miscommunication and misunderstandings caused by these cultural differences is to learn about the nonverbal communication patterns of your teammates.
Ask if they’re comfortable sharing about their culture and beliefs so that you gain further context. And, if your company offers such programs, pay attention to cross-cultural training.
Cultural barrier #3: Cultural norms, beliefs, and values
Each culture holds its own cultural norms, beliefs, and values. These are shared standards within a given culture, as well as human behaviors that support them. Consequently, these behaviors are met with social approval or disapproval.
Holidays, religions, customs, signs of respect, and even rules for proper business conduct may differ from culture to culture.
As a result, people from different cultures may struggle to communicate effectively because they might perceive the behavior of their fellow communicators as unusual, uncomfortable, or simply disrespectful.
Of course, this is rarely the intention of the communicators, who have merely made an honest mistake.
Example of a communication barrier based on cultural norms, beliefs, and values
Cultural differences can bring us together with our teammates. But, without sufficient clarification, they can make professional situations uncomfortable and act as communication barriers.
Unfortunately, that’s how it turned out for Irene, an intern from Norway working in a firm in San Francisco.
She requested a day off on “Independence Day” and Catherine, her coordinator, approved it.
However, they failed to clarify which Independence Day — Irene celebrates Norway’s on May 17th, not the US’s on July 4th. Consequently, the mishap led to Irene missing work and a scheduling problem.
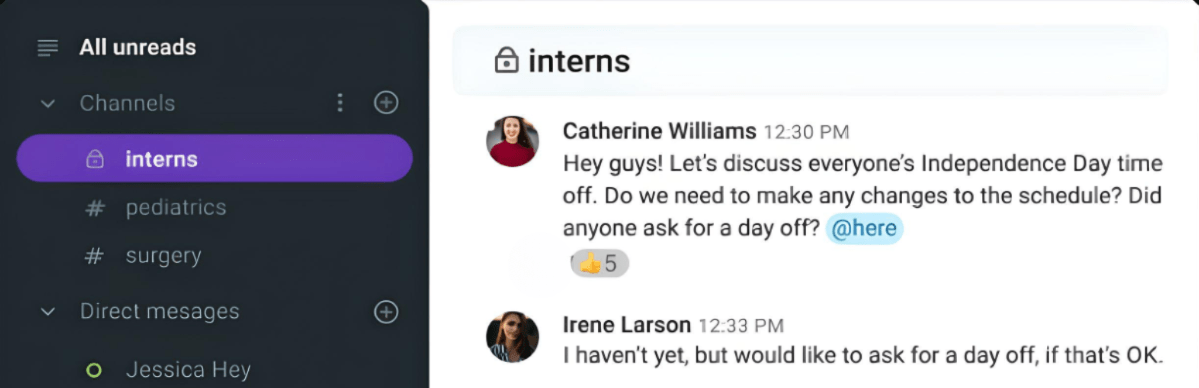
Top solutions for problems with cultural norms, beliefs, and values
Bridging cultural gaps is a top priority for global teams dedicated to achieving lasting success. To make sure everyone feels valued and comfortable, consider:
- Strengthening your soft skills ,
- Checking in with colleagues regularly,
- Attending cross-cultural training, and
- Keeping an open mind on diverse perspectives.
Cultural barrier #4: Stereotypes
According to social psychology, a stereotype represents a “ fixed, over-generalized belief about a particular group or class of people .”
In other words, we have a particular idea about how a specific group or class of people think or behave — and we assume that every member of that group or class thinks or acts similarly.
Such an approach to people who belong to different cultures builds prejudices and stops us from viewing members from other cultures as unique individuals.
Stereotypes come in different forms, but the most common ones that are disruptive to effective communication are:
- Microaggressions ,
- Biases , and
- Discrimination .
One particular source of stereotypes and prejudices is ethnocentrism.
According to the classic definition by Melville J. Herskovits, ethnocentrism represents “a feeling of superiority regarding one’s own culture or way of life.”
For ethnicism to arise, there must be an “in-group” and an “out-group.”
Social theorist Theodore W. Adorno and his colleagues have created a broader definition that defines ethnocentrism as a combination of “ a positive attitude toward one’s own ethnic/cultural group (the in-group) with a negative attitude toward the other ethnic/cultural group (the out-group) .”
For people with this type of outlook, it’s always “ us ” against “ them ,” which minimizes the effectiveness of many communication situations.
Example of a communication barrier based on stereotypes
A common type of stereotyping is based on generational prejudices.
In the modern workplace, exercising empathy ensures that such prejudices don’t get in the way of teamwork. However, when we don’t work on overcoming unconscious biases , they can lead to escalating microaggressions and the development of team silos .
Like Finn and Milo in the following example, we may hesitate to give older colleagues a chance to prove us wrong.
Finn and Milo are two new graduates who’ve just got jobs as production assistants at a bank. The majority of their colleagues are much older than them.
Finn and Milo believe the older generation is “ out of touch, inflexible, and closed-minded to new ideas, ” labeling their colleagues “Boomers.”
When their colleagues oppose their innovative solutions in meetings or dislike the use of new apps, it only reinforces Finn and Milo’s preconceived notions. Consequently, they take little notice when their older teammates support their ideas.
Top solutions for culture-based stereotypes
You can start embracing diversity and combating culture-based stereotypes by reconfiguring your perceptions.
If you’re part of a diverse workforce, go the extra mile and start a conversation with colleagues you haven’t spoken to that much.
Once you break the ice , it’ll be much easier to learn who they are and the central values of their culture. This way, you’ll relate to them more fully and better understand your mutual interdependence in the workplace.
Sharon Salzberg, a mindfulness coach and author of Real Happiness at Work , also emphasizes this idea:
“ We find ourselves filled with a new sense of responsibility toward the quality of our experience and its impact on others. The shift of awareness from ‘me’ to ‘we’ set the stage for a whole new life at work .”
Another way to remove these barriers is by calling out stereotyping when you see it. For example, don’t be afraid to speak up if you notice two colleagues speaking insensitively about another teammate.
Such seemingly minor actions stack up and positively impact the development of a well-connected workforce. Remember that advocating for your coworkers is as equally important as self-advocacy at work .
For a detailed look at cross-cultural communication and useful tips on how to improve it, check out this blog post:
- How to perfect cross-cultural communication at the workplace
Cultural barrier #5: Status
The perceived importance of someone’s status can also pose a culturally-based communication barrier.
Namely, workers accustomed to workplaces where seniority and status take precedence may find it challenging to adapt to workplaces that favor a more fluid work environment with less strict rules.
But, the opposite may also be true. For example, a worker used to a workplace where teammates are encouraged to treat each other as equals might have trouble navigating a workplace with a prominent hierarchy and rules.
Example of a communication barrier based on status
While rules can optimize a company’s internal organization, rigid regulations can send a message to employees that besides status, little else matters.
In the below example, Arya, who has landed a new job as a product manager, has ample experience working in such companies. Consequently, she has difficulty adjusting to a more relaxed environment in her new role.
Arya used to work in a company where hierarchy was strictly followed, and people had to be formal and wait to be spoken to by senior staff. She had many formal meetings with her subordinates.
However, her new company has a different culture where individual contributions matter more than titles, and people communicate and collaborate freely regardless of their position. Arya finds it hard to adjust to this new culture, as she is used to being treated as someone of higher rank.
She struggles to chat with junior staff and maintain a friendly relationship with them.
Top solutions for problems with status
Status in the workplace largely depends on an organization’s structure and internal policy.
Although a role is vital to business proceedings and grants an employee a lot of power, others may not necessarily regard it as a high-status role. This disparity may lead to job dissatisfaction and, in the worst-case scenario, workplace conflicts .
So, rather than going against rules of conduct just because they are not what you’re used to, learn to adapt to changes in how workplaces function.
Remember to do your best to adapt to the new atmosphere when you go from a rule-based workplace to a more relaxed work environment or vice versa.
You can even talk about this with someone from HR to help smoothen the transition.
Language barriers to effective team communication + solutions

Language barriers represent characteristics of linguistic use that inhibit comprehension and thus prevent successful communication . Although we associate miscommunication issues with communicators who have a different native language, they may arise even if the communicators have the same mother tongue.
Language barriers to effective communication usually result from:
- Regional accents and dialects,
- Pidgin languages,
- Jargon,
- Slang,
- Word choice, and
- Literacy and linguistic ability.
Language barrier #1: Regional accents and dialects
Team members may have the same mother tongue but also speak in different regional accents and dialects. This can cause comprehension issues, as teammates could use different pronunciation, grammar, and vocabulary.
Example of a communication barrier based on regional accents and dialects
In teams where all members have English as their mother tongue, most people wouldn’t expect to find many instances of miscommunication and miscomprehension.
However, if the members come from both the US and the UK, regional differences in language use can pose a problem.
For example, when a product team with US and UK employees organizes an on-site meeting, the organizer states they’ll hold the session on “the first floor of the building.” For the organizer and the rest of the US employees, the “first floor” is the floor at street level.
But, for teammates from the UK, the “first floor” is the floor above street level.
A simple question would clear away any second thoughts, yet many attendees feel uncomfortable and too embarrassed to ask for further clarification. Consequently, the organization encounters workflow issues, and employees waste valuable time searching for the meeting on the wrong floors.
Language barrier #2: Pidgin languages
According to the International Encyclopedia of the Social and Behavioral Sciences , pidgin languages, along with creoles, are language varieties formed from two or more languages. These new varieties have a simpler grammatical structure and smaller vocabulary than regular languages.
Additionally, they grow out of necessity when two or more groups of people speak different languages but need to communicate on a regular basis.
Pidgin languages may represent a barrier to effective communication when the standard meaning of pidgin expressions is unclear to all communicators.
For example, a common universal form of pidgin is acronyms. But, visual representations like emojis can also serve as a pictorial pidgin language.
Using acronyms and emojis in pidgin may give rise to a communication roadblock if some group members share a different meaning for the same emojis and acronyms.
Example of a communication barrier based on pidgin languages
Pidgins are legitimate language varieties, and clearing up a communication mishap is typically done quickly. Still, using specific phrases can cause a temporary communication break, as seen in the below example with Tok Pisin .
Fay is an art director heading a program that organizes educational, extracurricular activities for high school and college students. Although she’s spent most of her career in the US, she was born in Papua New Guinea, so some pidgin wording occasionally finds its way into her daily communication.
When informing one of her coworkers they should visit the local college for an upcoming art event, she tells them they should visit the “big school.” She’s not wrong since many Tok Pisin speakers call universities “big schools.”
Yet, Fay’s coworker is unaware of this and is unsure whether Fay meant they should visit a high school or college.
Language barrier #3: Jargon
Jargon represents words and phrases used by a particular group of people (e.g., people in a specific industry or field of work).
Jargon is often difficult to understand for those outside of the group because it is laden with:
- Technical terms,
- Acronyms , and
- Abbreviations.
Furthermore, the overuse of jargon can lead to:
- Misinterpretation,
- Lack of understanding,
- Lack of collaboration, and
- Feelings of exclusion.
Example of a communication barrier based on jargon
For employees working with professionals from different industries, jargon can become one of the top reasons for unclear communication.
For instance, a doctor who contacts a financial advisor about settling a patient’s medical bill may slip into their usual way of expression.
The doctor uses medical terms such as “ sub-therapeutic ,” “ agonal, ” and “ iatrogenic .”
On the flip side, the financial adviser uses financial terms such as “ active-participant status, ” “ advance ,” and “ life annuity .” Neither can fully understand the other and what was supposed to be a 30-minute meeting drags on for over an hour.
There’s a place and time for using jargon in the workplace. To learn more about the topic, check out this blog post:
- The dos and don’ts for using industry jargon in internal communication
Language barrier #4: Slang
Slang is a type of informal language, and such expressions are traditionally tied to a specific region, community, or social group.
Slang consists of unconventional phrases, idioms, and vocabulary, usually absent from standardized dictionaries. These expressions can bring people together and foster a sense of belonging.
Yet, in cases where not all parties are familiar with slang expressions, it can lead to communication rifts.
Example of a communication barrier based on slang
Slang varies from language to language, and when two coworkers have a different mother tongue, they may be unable to grasp the meaning of each other’s regional slang.
To see how that plays out in practice, we’ll look at Jeffrey, who is talking to Jannine, a sales representative from France.
During their conversation, Jeffrey, the CEO of an American pharmaceutical company, praises Jannine for her impressive sales record.
To express his delight, he exclaims, “ Get outta here! ”.
Unfortunately, English is not Jeanne’s first language, and she took the expression literally. Thinking that Jeffrey was angry and didn’t believe her sales figures, she hastily left his office.
Language barrier #5: Word choice
Problems with word choice may arise if you use:
- Homophones , which are words that share the same pronunciation as other words but have different meanings. Problems with homophones may occur in verbal communication. A common homophone set includes the words there, their, and they’re .
- Homographs , which are words that share the same spelling as other words but have different pronunciations and meanings. Problems with homographs may arise in written communication. A common set of homographs consists of the past tense of the verb see ( saw ) and the noun saw (a tool used for cutting wood).
Example of a communication barrier based on word choice
If you’re not careful, your word choice can sometimes give coworkers the wrong impression. In those cases, you may end up as the person in the below example.
At lunch, a colleague mentions they want to “ right the wrong expressions ” in a report by Lexie. However, other colleagues interpret it as wanting to “ write ” the wrong expressions, which would be spiteful.
Language barrier #6: Literacy and linguistic ability
Issues with literacy and linguistic ability represent the problems that might arise due to grammar and vocabulary differences.
These issues may be especially prominent if the person is trying to communicate in a language that is not their mother tongue.
But, they may also be the result of typos.
Example of a communication barrier based on literacy and linguistic ability
In teams whose members come from different linguistic backgrounds, things like date grammar can lead to misinterpretation.
In such a scenario, Alan, who works in HR at a local school, asks Gabriella, a new Italian teacher, to send him some documents by 06/07/2021.
However, Gabriella doesn’t know that in the United States, this date means June 7th, not July 6th, as it does in Italy.
As a result, she misunderstands the message and has a false deadline in mind.
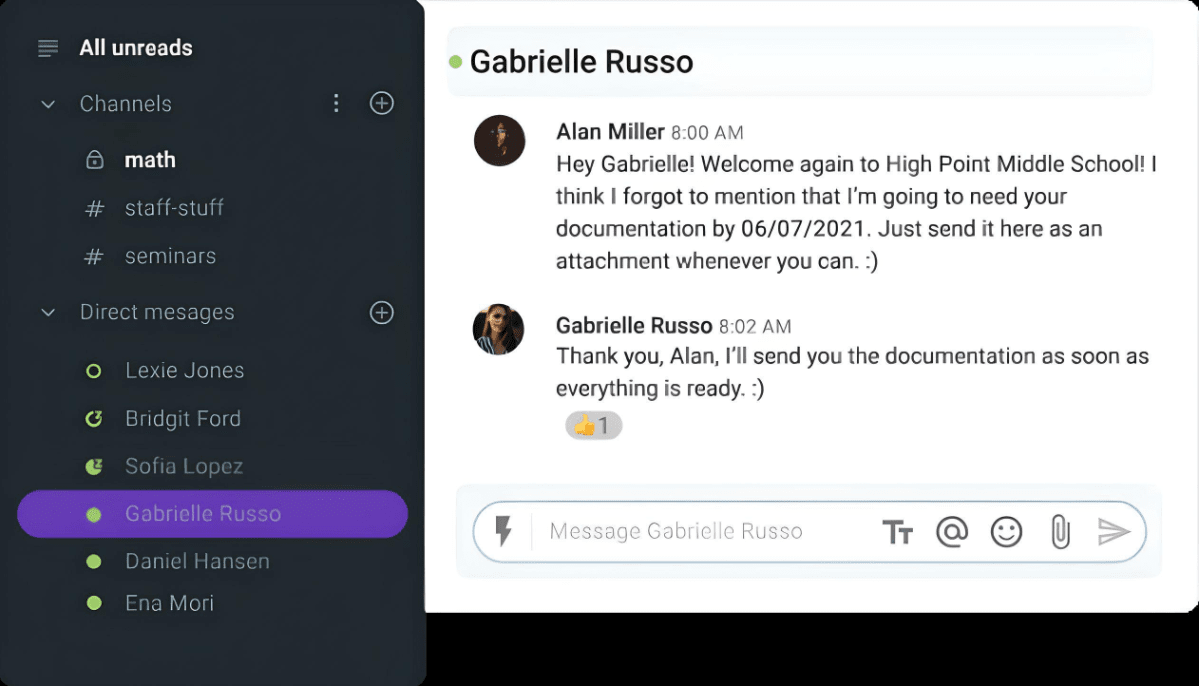
Top solutions for overcoming language barriers to effective communication
Effective communication can be challenging when language barriers are present. Here are some top solutions to help smooth out such issues:
- Keep it simple: Use straightforward and concise language a broader audience can easily understand.
- Use visuals: Incorporate diagrams, charts, or images to support written or verbal communication.
- Ask for feedback : Encourage feedback to ensure understanding and address any potential misunderstandings promptly.
- Be culturally sensitive: Recognize and respect cultural differences in communication styles , non-verbal cues, and social norms.
- Foster a supportive environment : Create an atmosphere that encourages respectful communication .
- Promote diversity: Building diverse teams with individuals from various language backgrounds can foster a collaborative environment where people learn from each other’s linguistic and cultural diversity.
Gender barriers to effective team communication + solutions

In recent years, workplace equity initiatives have helped many employees access new opportunities, regardless of gender or background. However, these policies serve to minimize conflict and motivate employees, not resolve miscommunication troubles altogether.
Thus, we still see communication issues stemming from gender differences, which may be a result of societal values or cultural norms.
Whatever the case, one of the most common gender barriers to communication is stereotyping. Preconceived notions can significantly impact how we view people, compelling us to link particular behavior and traits to gender differences.
These stereotypes can infringe on a person’s authenticity, preventing them from expressing themselves freely in the workplace.
Example of a communication barrier based on gender biases and stereotyping
Not only can gender biases contribute to a hostile work environment , but they can also create rifts between members of a team. If the tension persists, it might even have a long-lasting impact on employee mental health .
But, how exactly do gender differences make team members disconnected ? To learn more, we’ll turn to Charles, Peter, and Ainsley.
Charles, an ambulance driver, talks with Peter, an emergency medical technician, about their colleagues at the hospital. However, they exclude their female colleague, Ainsley, because they think she gossips too much.
This treatment makes Ainsley feel she can’t trust Charles and Peter since they don’t include her in their conversations.
Top solutions for overcoming gender barriers to effective team communication
Here are some steps you can take to tackle gender-based biases and stereotypes in a professional setting:
- Educate the team : Identify and acknowledge any biases and stereotypes that may be present. Do your best to encourage open and honest discussions about these topics and ensure everyone understands how they can contribute to positive change.
- Encourage diversity : When making decisions, involve everyone in the discussion and seek feedback from all team members. These actions will help ensure that diverse perspectives are considered and valued.
- Support the HR team : When dealing with gender-based issues, it’s crucial to have a well-prepared team that will handle them respectfully and effectively. Ensure your HR team has the training and resources they need to address these problems tactfully.
Interpersonal barriers to effective communication + solutions

Interpersonal barriers to effective communication stop people from reaching their full potential by restricting communication skills.
They may manifest as an inability to listen to others attentively or maintain the attention of the people you want to communicate with.
The reason for these communication problems mainly stems from a:
- Lack of participation and
- Lack of open-mindedness.
Interpersonal barrier #1: A lack of desire to participate in communication
A crucial interpersonal barrier to effective communication is a lack of a desire to participate in communication situations at the workplace.
Often, others will feel frustrated while trying to communicate with people who don’t want to interact with them.
Example of a communication barrier based on a lack of desire to participate
A lot of the time, it’s not that your coworker is avoiding interacting with you. It could be just that they’re not used to the communication model the company uses. However, this perceived lack of desire to engage in conversation can have dire consequences on team morale .
Let’s take John, an enterprise sales specialist at a company that builds software solutions, as an example.
An essential part of his duties is to conduct calls with prospective clients. But, he often needs the assistance of the software development team to answer technical questions.
However, rarely anyone from the software development team is enthusiastic about participating in these client calls.
In fact, John often has problems finding people to join him in these calls, which wastes a lot of time on futile persuasion and evasive answers.
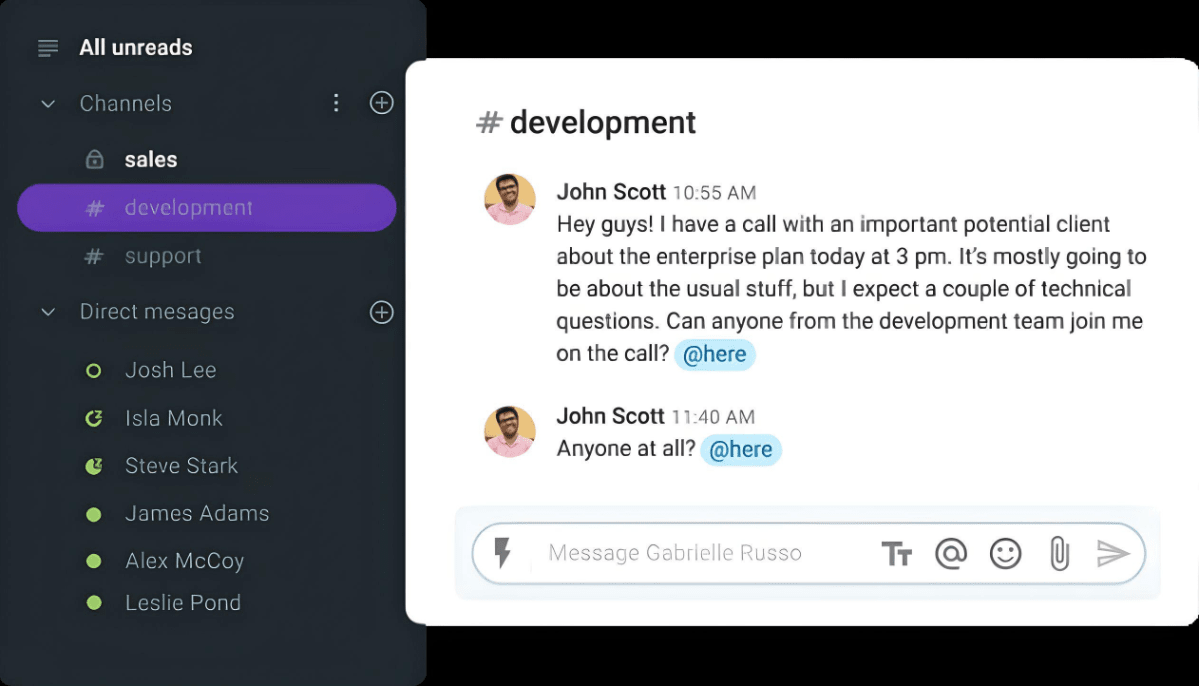
Interpersonal barrier #2: A lack of desire to explore new concepts
Another interpersonal barrier to effective communication is a lack of a desire to explore new ideas and opinions.
Closed-minded coworkers can make brainstorming sessions difficult and uncreative. Moreover, they frustrate teammates looking to dive deeper into new concepts.
Example of a communication barrier based on a lack of desire to explore new concepts
No matter how much you excel at your job, being stuck in your ways doesn’t make you a good team player. And, that’s precisely the case with Michael, a senior product designer at a product design studio.
He is experienced and renowned for his work ethic but dreaded at brainstorming meetings.
He shoots down every idea and opinion different from what he knows, even if it has great potential.
As a result, the team doesn’t look forward to meeting with him. They know he will always try to confine them to his old ways of thinking.

Top solutions for overcoming interpersonal barriers to effective communication
Overcoming interpersonal barriers to effective communication requires a range of tactics. Here are 3 key strategies you can try:
- Expand your horizons : To overcome reservations towards new concepts in meetings and brainstorming sessions, venture beyond typical business communication situations. You can explore new ideas on your own by reading about relevant findings. Additionally, challenge your previous knowledge and embrace the possibility that what you once believed may not hold up today.
- Step out of your comfort zone : To combat reluctance in communication, make a conscious effort to engage more frequently. Push yourself to participate in various communication situations, whether it’s actively contributing to meetings, asking questions during onboarding, or taking the lead in resolving conflicts between colleagues. The more you engage, the more comfortable you’ll become, paving the way for future communication success.
- Offer constructive feedback : Teammates can also play a crucial role in helping others overcome communication barriers. If you notice a colleague who seems aloof or hesitant, provide them with constructive feedback. Help them improve their approach to communication, collaboration, and overall work. You can contribute to a more communicative and productive team environment by offering support and guidance.
Remember that effective communication is a valuable skill you can develop through consistent effort and a willingness to break old patterns.
By implementing these tactics, you’ll be well on your way to achieving greater success in interacting with others and fostering solid work relationships .
Organizational barriers to effective communication + solutions
Sometimes, despite the employees’ willingness to become better communicators, they run into roadblocks in the form of organizational barriers.
These issues severely limit the flow of information within an organization, preventing people from getting urgent information on time.
The primary causes of organizational barriers include:
- Strict structure and rigid hierarchy,
- Lack of transparency, and
- Lack of communication channels.
Organizational barrier #1: Strict organizational structure and rigid hierarchies
In companies where leadership is inaccessible, meaningful interactions may become few and far between. Consequently, managers are urgently looking for the information their teams desperately need to complete their work.
This may work as a short-term solution, but eventually, it creates a mistrust of leadership and a culture where employees are reluctant to speak up.
The absence of open dialogue means the employee input gets lost because workers believe leadership isn’t interested in hearing them out. Besides, in such environments, employees often feel ill-equipped to deal with the possible repercussions.
Example of a communication barrier based on strict organizational structure and frigid hierarchies
How do rigid hierarchies prevent the effective exchange of ideas within an organization? To better answer this question, we’ll join a quarterly meeting at a software development firm.
Josh is a software developer whose team has regular monthly and weekly meetings. The members talk with each other about their progress and ask their manager about future steps and further guidance.
However, only the top executives and a few managers lead the conversation at the quarterly meetings. The few times John and his team have tried to suggest product improvements, they’ve been promptly shut down.
Due to these unpleasant experiences, John does not want to speak up at the upcoming meeting, although his idea about product improvements is objectively great.
Top solutions for problems with strict organizational structure and frigid hierarchies
Organizations facing communication issues due to a strict internal structure can improve operations through:
- Flattening hierarchies: Companies should try flattening internal hierarchies by moving part of the decision-making process to include more employees. Not only does this engender inclusivity, but it also fosters a feeling of professional autonomy.
- Promoting cross-level collaboration: When employees from different teams and hierarchical levels work together to achieve a shared goal, they develop stronger relationships. Consequently, they learn about each other’s abilities, build greater trust , and acquire new perspectives. All of this contributes to greater job satisfaction and enhanced productivity levels .
- Developing better feedback channels: Quarterly performance assessments, one-on-one meetings , and employee surveys are just a few possible ways businesses can take note of employee feedback. Workers who readily express their concerns and thoughts aid their employers in creating a positive professional environment.
Organizational barrier #2: Lack of transparency
In the modern workplace, a culture of transparency is one of the key ingredients for running a successful business.
Improving upward communication or resolving problems with lateral communication is impossible without transparency. Organizations that put a lot of value on transparency encourage employees to exchange information across different levels, which in turn makes them more:
- Trustworthy and
- Collaborative.
Yet, the 2023 Edelman Trust Barometer survey shows that most workers lack faith in their employers. Furthermore, the survey highlighted that 1 in 3 respondents stated they don’t trust their employer.
The absence of transparent communication can have long-term consequences on business operations, including:
- Lower engagement and motivation levels,
- Employees who are reluctant to self-advocate at work, and
- Higher turnover rates.
Example of a communication barrier based on a lack of transparency
Without transparency, employees have limited access to vital resources and expected outcomes, making it challenging to develop a feasible work strategy.
For example, Jacob, a team lead of a software development team in a tech company, is left in the dark after a few new stakeholders have joined the organization. He’s heard whispers that the company may head in a different direction, but each time he asks leadership for clarification, he’s told he’ll be informed in due time.
However, a few months have already passed, and Jacob’s team is frustrated with the runaround they’ve received. This puts him in an uncomfortable position because his hands are tied, and he feels bad for being unable to alleviate his team’s concerns.
Had the company taken steps to overcome barriers to communication, leadership would be more in tune with how the employees feel.
Top solutions for lack of transparency
Fostering a culture of transparency takes time and effort, and there are several practices businesses can implement to achieve this goal. Some of the ways you can do so are by:
- Providing adequate training and education : Communication is a skill, and not every professional starts out as an effective communicator. But, through workshops, seminars, and team-building activities , they can acquire the tools and skills that will allow them to excel in transparent communication.
- Being open about decision-making processes and strategies : Make sure that employees fully understand the organization’s core values and principles. Whenever there is a new initiative or practice, a company-wide meeting can help prevent teams from feeling like they’re left out of the decision-making process.
- Being clear about performance assessments : Taking employees through every step of their performance review is crucial to maintaining transparent communication. It ensures workers understand how and why their achievements contribute to the bigger picture and helps them better relate to strategic goals.
Organizational barrier #3: Lack of communication channels
Employee effort goes to waste if communication channels are insufficient or lacking.
For example, knowledge sharing is quicker and easier for teams that rely on video conferencing . However, when the organization adamantly insists on using an unsuitable communication channel, much of the information can get lost in the shuffle.
As a result, we see:
- Missed opportunities,
- Lack of timely feedback,
- Mistakes and miscommunication, and
- Dissatisfied customers.
For a deep dive into communication channels, check out this thorough guide:
- Channels of communication
Example of a communication barrier based on a lack of communication channels
Without clear and well-established communication pathways, no team can thrive for long, and coworkers feel isolated and disconnected.
But, how does this come about?
In the case of Thomas, an app developer working in a big tech company, his team has been struggling for weeks to solve a bug that’s been a problem for months. After much trial and error, he finally found the solution.
Yet, his happiness is short-lived. As his team has no central platform for communication and collaboration, informing his manager and coworkers about the breakthrough is a game of telephone, and no one seems to understand his urgency.
Finally, the manager tells Thomas to wait until the monthly team meeting to tell everyone about his progress. Thomas is deflated since this means other employees will have to work around the bug until he presents his solution.
Top solutions for lack of communication channels
Although a lack of communication channels can bring about a wide array of trouble for an organization, these steps can prevent long-term issues:
- Implementing new communication channels : User-friendly and intuitive team communication apps can unite all employees. Whether they prefer to come into the office or work remotely, they’ll know the person they need to contact is just a few clicks away. Also, project management tools can further optimize workflows by providing an overview of urgent and long-term tasks and goals.
- Holding regular meetings : In teams whose workflow involves dynamic and complex tasks, weekly team meetings and occasional one-on-one meetings prevent feelings of loneliness and the development of team silos.
- Providing comprehensive communication training : Workshops on active listening, communication planning , and business communication can help employees tackle different situations during their workday.
It takes collaboration to overcome communication barriers: Do it with Pumble!
No team can be successful without good communication, but sometimes several barriers may prevent us from reaching our goals.
To ensure you’re doing everything you can to overcome them, have your team use Pumble!
Pumble is a team communication and collaboration app that will allow you to:
- Overcome physical barriers, as it allows for both real-time and asynchronous communication,
- Overcome perceptual barriers as it allows for both verbal and non-verbal communication , thanks to features like voice calls and video conferencing ,
- Overcome organizational barriers, as it’s an ideal one-stop solution for team communication and collaboration .
Help your team overcome communication barriers — try Pumble today !
References :
- Baylor, E. (2012). Ethnocentrism . Oxford Bibliographies. https://www.oxfordbibliographies.com/view/document/obo-9780199766567/obo-9780199766567-0045.xml
- Ceserani J. (2003). Big ideas: putting the zest into creativity and innovation at work. Kogan Page.
- Daily Health Post. (2019). This is What Happens to Your Body When You Get Angry. https://dailyhealthpost.com/anger-negatively-affects-brain-and-heart/
- Erickson, A. (2017). What ‘personal space’ looks like around the world. The Washington Post. https://www.washingtonpost.com/news/worldviews/wp/2017/04/24/how-close-is-too-close-depends-on-where-you-live/
- Joynt, P. and Warner, M. (1996). Managing Across Cultures: Issues and Perspectives, International Thomson Business Press, London.
- McLeod, S. (2017). Stereotypes . Simply Psychology. https://www.simplypsychology.org/katz-braly.html
- Shofner, K. (n.d.) The Evolution of Pidgin Languages . United Language Group. https://www.unitedlanguagegroup.com/blog/evolution-pidgin-languages
- Salzberg S. (2011). Real happiness: the power of meditation: a 28-day program . Workman Pub.
- Siegel, J. (n.d.). Language Varieties: Tok Pisin . Language Varieties. https://www.hawaii.edu/satocenter/langnet/definitions/tokpisin.html
- Steinhilber, B. (2017). How to Tell if Someone is Lying to You, According to Researchers. NBS News. https://www.nbcnews.com/better/health/how-tell-if-someone-lying-according-behavioral-experts-ncna786326
- The Edelman Trust Institute (n.d.). The 2023 Edelman Trust Barometer . Edelman. https://www.edelman.com/trust/2023/trust-barometer
- (n.d.). Soft skills: What are they and how to develop them. Futurelearn. https://www.futurelearn.com/info/blog/soft-skills-what-they-are-and-how-to-develop-them
Explore further
Team Communication Fundamentals
Improving Team Communication

Improving Communication Effectiveness

Additional Materials

Free team chat app
Improve collaboration and cut down on emails by moving your team communication to Pumble.
Effective Communication: Barriers and Strategies
Some basic skills can help you to be a more effective communicator in the classroom. This Teaching Tip explores barriers and strategies for active listening, accurate perception, and effective verbal communication.
Barriers to active listening
- Focusing on a personal agenda. When we spend our listening time formulating our next response, we cannot be fully attentive to what the speaker is saying.
- Experiencing information overload. Too much stimulation or information can make it very difficult to listen with full attention. Try to focus on the relevant information, and the central points that are being conveyed.
- Criticizing the speaker. Do not be distracted by critical evaluations of the speaker. Focus on what they are saying - the message - rather than the messenger.
- Being distracted by strong emotional responses. When you have strong emotional response, acknowledge the emotion and shift your focus back to listening. Make a conscious effort not to get lost in your emotional response.
- Getting distracted by external “noise”. Audible noise may be extremely distracting. Some things can be minimized – e.g., turn down the ringer on your phone, and notifications on your phone or computer while meeting with someone. Other noises may be unavoidable – e.g., construction, other people. Also, there may be figurative “noise” from the external environment, such as distracting or inappropriate decor in a room, or environmental conditions such as the room being too hot or cold.
- Experiencing physical illness or pain. Feeling physically unwell, or experiencing pain can make it very difficult to listen effectively. You may wish to communicate that this is not a good time, and reschedule the discussion.
Strategies for active listening
The following strategies are intended to promote active listening, or a type of listening with the goal to “develop a clear understanding of the speaker’s concern and also to clearly communicate the listener’s interest in the speaker’s message” (McNaughton, Hamlin, McCarthy, Head-Reeves, & Schreiner, 2008, p. 224).
- Stop. Focus on the other person, their thoughts and feelings. Consciously focus on quieting your own internal commentary, and step away from your own concerns to think about those of the speaker. Give your full attention to the speaker.
- Look. Pay attention to non-verbal messages, without letting yourself be distracted. Notice body language and non-verbal cues to allow for a richer understanding of the speaker’s point. Remember that “active listeners need to communicate to the speaker that they are involved and giving the person unconditional attention” (Weger, Castle, & Emmett, 2010, p. 35).
- Listen. Listen for the essence of the speaker’s thoughts: details, major ideas and their meanings. Seek an overall understanding of what the speaker is trying to communicate, rather than reacting to the individual words or terms that they use to express themselves.
- Be empathetic. Imagine how you would feel in their circumstances. Be empathetic to the feelings of the speaker, while maintaining a calm centre within yourself. You need not be drawn into all of their problems or issues, as long as you acknowledge what they are experiencing.
- Ask questions. Use questions to clarify your understanding, as well as to demonstrate interest in what is being said.
- Paraphrase. If you don’t have any specific questions to ask, you may choose to repeat back to the speaker, in your own words, what you have taken away, in order to allow the speaker to clarify any points (Weger et al., 2010).
Barriers to accurate perception
- Stereotyping and generalizing. Be careful not to hold on to preconceptions about people or things. We often have a tendency to see what we want to see, forming an impression from a small amount of information or one experience, and assuming that to be highly representative of the whole person or situation.
- Not investing time. Making assumptions and ignoring details or circumstances can lead to misconceptions. When we fail to look in-depth for causes or circumstances, we miss important details, and do not allow for the complexity of the situation.
- Negativity bias. Focusing on the negative aspects of a conversation or a situation is a habit common to many people. Even though we may recognize the positive things, we often give more weight to the negative, allowing one negative comment to overshadow numerous positive ones.
- Assuming similar interpretations. Not everyone will draw the same conclusions from a given situation or set of information. Everybody interprets things differently. Make sure to check for other people’s interpretations, and be explicit about your own.
- Experiencing incongruent cues. As speakers, and as listeners, we are constantly and simultaneously sending cues and receiving them from other people. Try to be consistent with your verbal cues and your body language. Do not say one thing and express something else through your body language. Be aware of how your non-verbal communication relates to your spoken words. If someone else seems to be sending a double message — by saying one thing and expressing something else in their body language — ask for clarification.
Strategies for accurate perception
- Analyze your own perceptions. Question your perceptions, and think about how they are formed. Check in with others around you regularly, and be aware of assumptions that you are making. Seek additional information and observations. You may just need to ask people if your perceptions are accurate.
- Work on improving your perception. Increase your awareness of barriers to perception, and which ones you tend towards. Check in with yourself regularly. Seek honest, constructive feedback from others regarding their perceptions of you as a means of increasing your selfawareness.
- Focus on others. Develop your ability to focus on other people, and understand them better by trying to gather knowledge about them, listening to them actively, and imagining how you would feel in their situation.
Verbal Communication
Barriers to effective verbal communication.
- Lacking clarity. Avoid abstract, overly-formal language, colloquialisms, and jargon, which obscure your message more than they serve to impress people.
- Using stereotypes and generalizations . Speakers who make unqualified generalizations undermine their own clarity and credibility. Be careful not to get stuck in the habit of using stereotypes, or making generalizations about complex systems or situations. Another form of generalization is “polarization” or creating extremes. Try to be sensitive to the complexities of situations, rather than viewing the world in black and white.
- Jumping to conclusions. Confusing facts with inferences is a common tendency. Do not assume you know the reasons behind events, or that certain facts necessarily have certain implications. Make sure you have all the information you can get, and then speak clearly about the facts versus the meanings or interpretations you attach to those.
- Dysfunctional responses. Ignoring or not responding to a comment or question quickly undermines effective communication. Likewise, responding with an irrelevant comment -- one that isn't connected to the topic at hand -- will quash genuine communication. Interrupting others while they are speaking also creates a poor environment for communication.
- Lacking confidence. Lacking confidence can be a major barrier to effective communication. Shyness, difficulty being assertive, or low self-worth can hinder your ability to make your needs and opinions known. Also, a lack of awareness of your own rights and opportunities in a given situation can prevent you from expressing your needs openly.
Strategies for effective verbal communication
- Focus on the issue, not the person. Try not to take everything personally, and similarly, express your own needs and opinions in terms of the job at hand. Solve problems rather than attempt to control others. For example, rather than ignoring a student who routinely answers questions in class with inappropriate tangents, speak with the student outside of class about how this might disrupt the class and distract other students.
- Be genuine. Be yourself, honestly and openly. Be honest with yourself, and focus on working well with the people around you, and acting with integrity.
- Empathize rather than remain detached. Although professional relationships entail some boundaries when it comes to interaction with colleagues, it is important to demonstrate sensitivity, and to really care about the people you work with. If you don’t care about them, it will be difficult for them to care about you when it comes to working together.
- Be flexible towards others. Allow for other points of view, and be open to other ways of doing things. Diversity brings creativity and innovation.
- Value yourself and your own experiences. Be firm about your own rights and needs. Undervaluing yourself encourages others to undervalue you, too. Offer your ideas and expect to be treated well.
- Use affirming responses. Respond to other in ways that acknowledge their experiences. Thank them for their input. Affirm their right to their feelings, even if you disagree. Ask questions, express positive feeling; and provide positive feedback when you can.
If you would like support applying these tips to your own teaching, CTE staff members are here to help. View the CTE Support page to find the most relevant staff member to contact.
McNaughton, D., Hamlin, D., McCarthy, J., Head-Reeves, D., & Schreiner, M. (2008). Learning to listen: Teaching an active listening strategy to preservice education professionals. Topics in Early Childhood Special Education, 27 , 223-231.
Weger, H., Jr., Castle, G. R., & Emmett, M. C. (2010). Active listening in peer interviews: The influence of message paraphrasing on perceptions of listening skill. International Journal of Listening, 24 , 34-49.
CTE teaching tips
- Question Strategies
- Facilitating Effective Discussions
- When Things Go Wrong
Other CTE resources
Consider participating in the CTE’s Instructional Skills Workshop , an intensive, collaborative learning model that uses videotaped micro-teaching and peer feedback sessions to support participants' teaching reflection and growth.
Other resources
- Beebe et al. Interpersonal Communication: Relating to Others 2nd Canadian Edition. (Scarborough, Ontario: Allyn and Bacon, 2000).
- Gordon, T. (2003). Teacher Effectiveness Training . First Revised Edition. New York: Three Rivers Press.
- Wood, J. T. (2015). Interpersonal communication: Everyday encounters . Nelson Education.
This Creative Commons license lets others remix, tweak, and build upon our work non-commercially, as long as they credit us and indicate if changes were made. Use this citation format: Effective Communication: Barriers and Strategies. Centre for Teaching Excellence, University of Waterloo
Catalog search
Teaching tip categories.
- Assessment and feedback
- Blended Learning and Educational Technologies
- Career Development
- Course Design
- Course Implementation
- Inclusive Teaching and Learning
- Learning activities
- Support for Student Learning
- Support for TAs
- Course Implementation ,

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
Margin Size
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

14.11: Introduction to Barriers to Effective Communication
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 47805
- Lumen Learning
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
What you’ll learn to do: explain barriers to effective communication
Barriers to communication are things that get in the way of a message being received. They could be physical, such as loud music playing, or emotional, such as when a person is too angry or fearful to listen to what another individual is saying. Culture, language, and social status can also represent barriers to effective communication. Managers need to be aware of barriers and how to overcome them to improve the communication process.
Contributors and Attributions
- Introduction to Barriers to Effective Communication. Authored by : John/Lynn Bruton and Lumen Learning. License : CC BY: Attribution
- Undergraduate
- High School
- Architecture
- American History
- Asian History
- Antique Literature
- American Literature
- Asian Literature
- Classic English Literature
- World Literature
- Creative Writing
- Linguistics
- Criminal Justice
- Legal Issues
- Anthropology
- Archaeology
- Political Science
- World Affairs
- African-American Studies
- East European Studies
- Latin-American Studies
- Native-American Studies
- West European Studies
- Family and Consumer Science
- Social Issues
- Women and Gender Studies
- Social Work
- Natural Sciences
- Pharmacology
- Earth science
- Agriculture
- Agricultural Studies
- Computer Science
- IT Management
- Mathematics
- Investments
- Engineering and Technology
- Engineering
- Aeronautics
- Medicine and Health
- Alternative Medicine
- Communications and Media
- Advertising
- Communication Strategies
- Public Relations
- Educational Theories
- Teacher's Career
- Chicago/Turabian
- Company Analysis
- Education Theories
- Shakespeare
- Canadian Studies
- Food Safety
- Relation of Global Warming and Extreme Weather Condition
- Movie Review
- Admission Essay
- Annotated Bibliography
- Application Essay
- Article Critique
- Article Review
- Article Writing
- Book Review
- Business Plan
- Business Proposal
- Capstone Project
- Cover Letter
- Creative Essay
- Dissertation
- Dissertation - Abstract
- Dissertation - Conclusion
- Dissertation - Discussion
- Dissertation - Hypothesis
- Dissertation - Introduction
- Dissertation - Literature
- Dissertation - Methodology
- Dissertation - Results
- GCSE Coursework
- Grant Proposal
- Marketing Plan
- Multiple Choice Quiz
- Personal Statement
- Power Point Presentation
- Power Point Presentation With Speaker Notes
- Questionnaire
- Reaction Paper
Research Paper
- Research Proposal
- SWOT analysis
- Thesis Paper
- Online Quiz
- Literature Review
- Movie Analysis
- Statistics problem
- Math Problem
- All papers examples
- How It Works
- Money Back Policy
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- We Are Hiring
Overcoming Barriers to Communication, Essay Example
Pages: 4
Words: 1084
Hire a Writer for Custom Essay
Use 10% Off Discount: "custom10" in 1 Click 👇
You are free to use it as an inspiration or a source for your own work.
Problems of communication diminish the success of principles in the performance of their function. If messages are poorly transmitted or misinterpreted and if action is not effected, managers can not plan and monitor activities properly. Managers can do several things to improve communications in organizations. In general, these center around understand the barriers to communication and knowing how to overcome them.
The sender, the receiver, and the medium are the essential elements of the communication process. But unless a message is interpreted as it was meant, one still does not have communication. Misinterpretation is always possible when two individual in the organizational environment interact. The four types of communication barriers are (a) process barriers, (b) physical barriers, (c) semantic barriers, and (d) personal barriers.
Process barriers may arise in many situations. They stem from unwieldy procedural approaches that limit teams’ ability to do their work. Cumbersome approve processes and communication channels that follow the chain of command are incompatible with effective team operation.
Physical barriers are environmental factors which prevent or reduce the sending or receiving of communication. They include distance, walls, distracting background noise, and similar interferences. For example, in a hospital setting, which functions round the clock in three shifts, the senior officers may not see their subordinates for several days at a time. These are usually obvious barriers.
Personal barriers arise from judgments, emotions and the social values of people and are less obvious. These factors cause a psychological distance between people, which can be just as real as a physical barrier.Managers see and hear what they want to see and hear, and they remain selectively “tuned out” to that which they do not wish to see or hear. Psychological distance may entirely prevent communication, filter part of it or cause misinterpretation. For example, three doctors were discussing the serious condition of a patient. The sister-in-charge, who was working in the duty room, thought that they were talking about her incompetence. She rushed to the matron and requested her to transfer the patient to another floor because the doctors felt that she could not give sufficient nursing care to their patient.
Semantic barriers arise from the limitations of language. Language may take any of the three forms: words, picture and actions. Words have several meanings and they become meaningless if not they are put in the proper sense . One of the basic problems in communication is that the sense and meaning which is actually understood by one person may not be what the other intended to imply.
In a case, an employee noticed a banana peel lying on the floor of the office. She instructed the sweeper on duty to remove it immediately as it was a safety hazard. The sweeper, who was busy mopping up the floor, nodded his head to indicate that he would remove the banana peel. Just as the sweeper had finished mopping up the floor, another employee slipped on that same banana peel. The employee was furious at this mishapwhich could be avoided . She decided to report about the sweeper for disobeying her instructions. She was informed by the sweeper that he was going to pick up the peel just after completing the job in hand, i.e. mopping up the floor. By the word “immediate” the employee meant at once, whereas the sweeper understood he could do the job after completing the one in hand. This example clearly shows that even simple words carry different meanings to different people. Employees have to be told what managers want them to do. The speaker and the listener should understand the words in the same sense.
Managers must be clear about what they wish to communicate as wellas the objective of that communication. Before communicating, it is necessary to be clear about the problem and the information sought to be communicated to solve this problem. Therefore, it is necessary to decide what the receiver should know. If the objective is clear, communication is likely to succeed.
It is preferable to speak in the vernacular language of the receiver, because this is more effective. This is often not practicable in organizational setting because most of the employees belong to different regions and speak different languages. Though English is the most common language used in organizations, its use for communication still causes a language barrier because the majority of employees lack fluency and mastery over it.
Managers should use the right medium of communication, such as diagrams, charts, visual aids; according to the requirements because these can help the receiver achieve a better perception of the content of the communication.
In cases of upward communication, it is necessary to remove the organizational and intentional blocks. While communicating, it is desirable for managers to consider a complete physical and human setting. Even the tone of the communication matters. Therefore, the right climate should be created for communication in terms of the subject matter, the medium used, the situation and the persons involved.
The amount of communication must be adequate so that the recipient gets the complete message. The message should neither be unnecessarily lengthy nor too short.
For written communication, clarity, brevity, and style are important to make reading easier and the content is understandable.
One of the biggest assets of any organization is its human resources. Therefore, it is essential for managers to have interaction with them. The manager any organization should make it a point to meet employees occasionally, ask their problems and try to know whether they know the developments that are taking place in the organization.
Managers can control the choice of words; the use of technical terms, acronyms, or trade jargon; and the speed of delivery. They can sometimes control the time and place of the communication. They also can enhance understanding and retention by repeating vital information and showing the same information in some graphic form. All of these techniques will have considerable impact on the listeners.
A successful system of communication must operate not only from the Chief Executive’s office downwards but must consist of four interlocking circuits transmitting information, opinions, etc. downward, upward, horizontal and grapevine. It is manager’s responsibility that the management of an organization should realize the importance of effective communication within the organization. The management should find from their senior managers and lower employees the difficulties involved in communicating. They should know what information the employees would like to know from the management and what they should know from the employees through upward communication so that unnecessary bottlenecks of communication may be eliminated in the interest of the organization and for the free flow of communication.
Stuck with your Essay?
Get in touch with one of our experts for instant help!
Online Learning vs. the Traditional College Classrooms, Research Paper Example
Hamiltonianism and Jeffersonianism Era, Outline Example
Time is precious
don’t waste it!
Plagiarism-free guarantee
Privacy guarantee
Secure checkout
Money back guarantee

Related Essay Samples & Examples
Voting as a civic responsibility, essay example.
Pages: 1
Words: 287
Utilitarianism and Its Applications, Essay Example
Words: 356
The Age-Related Changes of the Older Person, Essay Example
Pages: 2
Words: 448
The Problems ESOL Teachers Face, Essay Example
Pages: 8
Words: 2293
Should English Be the Primary Language? Essay Example
Words: 999
The Term “Social Construction of Reality”, Essay Example
Words: 371

Essay on Communication Barriers
Students are often asked to write an essay on Communication Barriers in their schools and colleges. And if you’re also looking for the same, we have created 100-word, 250-word, and 500-word essays on the topic.
Let’s take a look…
100 Words Essay on Communication Barriers
What are communication barriers.
Communication barriers are like walls that stop people from sharing ideas clearly. Imagine trying to talk to someone through a thick glass wall. Just like the wall makes it hard to hear, these barriers make understanding each other difficult.
Types of Barriers
There are many types of barriers. Language differences, loud noises, and even our emotions can be barriers. If you speak English and your friend speaks Spanish, language is a barrier. If you’re trying to talk at a noisy party, sound is a barrier.
Overcoming Barriers
To break down these walls, we need to be patient and try different ways to share our thoughts. Maybe we can use pictures or learn a few words in another language. It’s all about finding a way to connect.
250 Words Essay on Communication Barriers
Communication is when people exchange thoughts, messages, or information. Sometimes, this process doesn’t work well because of barriers. Communication barriers are like walls that stop messages from being understood correctly.
Types of Communication Barriers
First, there are language barriers. When people don’t speak the same language or use very different words, they might not understand each other. Next, there are physical barriers. This can be as simple as a bad phone connection or being too far away to hear.
Emotional and Cultural Walls
Feelings can also be a barrier. If someone is angry or sad, they might not listen well or speak clearly. Culture can be a wall too. People from different places might have their own ways of talking or understanding things, which can lead to confusion.
To break down these walls, we can learn other languages or find better ways to connect, like video calls instead of just voice calls. We should also pay attention to our feelings and try to be clear when we talk or write. Understanding other cultures can help a lot, too.
In summary, communication barriers are like obstacles that make it hard to share messages. They can be because of language, distance, emotions, or culture. By knowing about these barriers, we can try to fix them and talk to each other better.
500 Words Essay on Communication Barriers
Communication is like a bridge between people. It lets us share ideas, feelings, and information. But sometimes, this bridge can have problems, called communication barriers. These barriers make it hard to send and understand messages clearly. Imagine trying to talk to someone with a wall between you. That’s what these barriers are like. They can be caused by many things, such as language differences, loud noises, or even our emotions.
There are several types of barriers that can mess up communication. First, there are physical barriers. These are real, like walls, or distance between people. If you’re trying to talk to a friend across a noisy playground, it’s tough to hear each other.
Next, there are language barriers. When people don’t speak the same language or use very difficult words, it’s like they’re speaking a code that the other person can’t crack.
Another type is emotional barriers. If someone is feeling sad, angry, or scared, it can be hard for them to listen or explain their thoughts well.
Cultural barriers are also important. People from different places can have different ways of talking and understanding things. This can lead to confusion if they don’t know about each other’s customs.
Why Do These Barriers Matter?
Communication barriers are a big deal because they can cause misunderstandings. If you’re playing a game and you can’t understand the rules because they’re explained in a confusing way, you won’t be able to play properly. In real life, this can lead to arguments, mistakes, or people feeling bad because they think they’re not being listened to.
Overcoming Communication Barriers
So, what can we do about these barriers? To start, we can try to be clear when we talk or write. Using simple words and short sentences can help a lot. Also, paying attention to the person you’re talking to is important. Look at their face and body to see if they understand you.
If there’s noise, try to find a quieter place to talk. If you’re dealing with language barriers, pictures or hand signs can help. And if emotions are high, taking a break to calm down before talking can make things easier.
Communication barriers can be tricky, but knowing about them is the first step to breaking them down. By being patient, clear, and kind, we can get better at sharing our thoughts and understanding others. Just like fixing a bridge, it takes work to fix communication, but it’s worth it to connect with friends and family. With practice, we can all become super communicators, even when barriers pop up.
That’s it! I hope the essay helped you.
If you’re looking for more, here are essays on other interesting topics:
- Essay on Communication
- Essay on Communication And Globalization
- Essay on Communicable Diseases
Apart from these, you can look at all the essays by clicking here .
Happy studying!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

Home — Essay Samples — Sociology — Effective Communication — Effective Communication: The Key to Building Strong Connections
Effective Communication: The Key to Building Strong Connections
- Categories: Connection Effective Communication
About this sample

Words: 791 |
Published: Sep 12, 2023
Words: 791 | Pages: 2 | 4 min read
Table of contents
The importance of effective communication, key elements of effective communication, barriers to effective communication, strategies for improving communication, 1. building relationships:, 2. resolving conflicts:, 3. achieving goals:, 4. personal development:, 5. success in the workplace:, 1. clarity:, 2. active listening:, 3. empathy:, 4. nonverbal communication:, 5. respect:, 1. misunderstandings:, 2. lack of active listening:, 3. emotional barriers:, 4. assumptions and stereotypes:, 5. lack of feedback:, 1. practice active listening:, 2. foster empathy:, 3. be mindful of nonverbal cues:, 4. seek feedback:, 5. adapt to your audience: h3>, 6. practice constructive communication:, 7. educate yourself:.

Cite this Essay
Let us write you an essay from scratch
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
Get high-quality help

Dr Jacklynne
Verified writer
- Expert in: Sociology

+ 120 experts online
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
Related Essays
2 pages / 1109 words
2 pages / 878 words
1 pages / 439 words
2 pages / 727 words
Remember! This is just a sample.
You can get your custom paper by one of our expert writers.
121 writers online
Still can’t find what you need?
Browse our vast selection of original essay samples, each expertly formatted and styled
Related Essays on Effective Communication
Soft skills are known as combinations of social skills and personality characteristics. Soft skills influence how someone functions in a working environment with others (Doyle, 2019). The term 'soft skill” refers to various [...]
In a world where globalization and multiculturalism are becoming increasingly prevalent, the ability to speak more than one language is a valuable asset. Being bilingual opens up a world of opportunities, both personally and [...]
Communication is a complex process that involves the exchange of information, ideas, and emotions between individuals. In order to ensure that communication is effective, it is crucial for individuals to engage in perception [...]
Shannon, C. E., & Weaver, W. (1949). The Mathematical Theory of Communication. University of Illinois Press.Lasswell, H. D. (1948). The Structure and Function of Communication in Society. In L. Bryson (Ed.), The Communication of [...]
In an organization, the flow of communication can either be formal or informal. Communication that flows through normal channels can be upward, horizontal or downward. Communication that flows through informal organizational [...]
Effective communication involves effective speaking and active listening. Verbal exchanges in discussions are not sufficient in relaying messages. Other factors such as tonal variations and non-verbal cues are also crucial. [...]
Related Topics
By clicking “Send”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement . We will occasionally send you account related emails.
Where do you want us to send this sample?
By clicking “Continue”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy.
Be careful. This essay is not unique
This essay was donated by a student and is likely to have been used and submitted before
Download this Sample
Free samples may contain mistakes and not unique parts
Sorry, we could not paraphrase this essay. Our professional writers can rewrite it and get you a unique paper.
Please check your inbox.
We can write you a custom essay that will follow your exact instructions and meet the deadlines. Let's fix your grades together!
Get Your Personalized Essay in 3 Hours or Less!
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free
BUS209: Organizational Behavior
Communication
This chapter reading is a great resource to highlight and reinforce the concepts we learned in the previous video. The chapter begins with the Radio Shack case, which exemplifies the wrong way to communicate bad news. Consider the message, as well as the medium that you would choose in this situation. Also, take a look at the "communication freezers", words that essentially shut down effective communication within your workplace. Do you use these words? What might you say instead to create bridges instead of barriers?
In this chapter we have reviewed why effective communication matters to organizations. Communication may break down as a result of many communication barriers that may be attributed to the sender or receiver. Therefore, effective communication requires familiarity with the barriers. Choosing the right channel for communication is also important, because choosing the wrong medium undermines the message. When communication occurs in the cross-cultural context, extra caution is needed, given that different cultures have different norms regarding nonverbal communication, and different words will be interpreted differently across cultures. By being sensitive to the errors outlined in this chapter and adopting active listening skills, you may increase your communication effectiveness.
Essay on Importance of Communication for Students and Children
500+ words essay on importance of communication:.
Communication is one of the important tools that aid us to connect with people. Either you are a student or a working professional, good communication is something that will connect you far ahead. Proper communication can help you to solve a number of issues and resolve problems. This is the reason that one must know how to communicate well. The skills of communication essential to be developed so that you are able to interact with people. And able to share your thoughts and reach out to them. All this needs the correct guidance and self-analysis as well.

Meaning of Communication
The word communication is basically a process of interaction with the people and their environment . Through such type of interactions, two or more individuals influence the ideas, beliefs, and attitudes of each other.
Such interactions happen through the exchange of information through words, gestures, signs, symbols, and expressions. In organizations, communication is an endless process of giving and receiving information and to build social relationships.
Importance of Communication
Communication is not merely essential but the need of the hour. It allows you to get the trust of the people and at the same time carry better opportunities before you. Some important points are as follows –
Help to Build Relationships
No matter either you are studying or working, communication can aid you to build a relationship with the people. If you are studying you communicate with classmates and teachers to build a relationship with them. Likewise in offices and organizations too, you make relationships with the staff, your boss and other people around.
Improve the Working Environment
There are a number of issues which can be handled through the right and effective communication. Even planning needs communication both written as well as verbal. Hence it is essential to be good in them so as to fill in the communication gap.
Foster strong team
Communication helps to build a strong team environment in the office and other places. Any work which requires to be done in a team. It is only possible if the head communicates everything well and in the right direction.
Find the right solutions
Through communication, anyone can find solutions to even serious problems. When we talk, we get ideas from people that aid us to solve the issues. This is where communication comes into play. Powerful communication is the strength of any organization and can help it in many ways.
Earns more respect
If your communication skills are admirable, people will love and give you respect. If there is any problem, you will be the first person to be contacted. Thus it will increase your importance. Hence you can say that communications skills can make a big change to your reputation in society.
Get the huge list of more than 500 Essay Topics and Ideas
Don’t Go Overboard With Your Point
The conversation is about to express your thoughts. And to let the other person know what you feel. It is not mean to prove that your point is correct and the other person is wrong. Don’t Overboard other With Your Point.
Watch Your Words
Before you say something to Watch Your Words. At times, out of anger or anxiousness, we say somethings that we must not say. Whenever you are in a professional meeting or in some formal place, where there is a necessity of communicating about your product or work then it is advised to practice the same beforehand
Communication is the greatest importance. It is important to sharing out one’s thoughts and feelings to live a fuller and happier life. The more we communicate the less we suffer and the better we feel about everything around. However, it is all the more necessary to learn the art of effective communication to put across ones point well.
Customize your course in 30 seconds
Which class are you in.

- Travelling Essay
- Picnic Essay
- Our Country Essay
- My Parents Essay
- Essay on Favourite Personality
- Essay on Memorable Day of My Life
- Essay on Knowledge is Power
- Essay on Gurpurab
- Essay on My Favourite Season
- Essay on Types of Sports
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Download the App

Power of Effective Communication Essay
- To find inspiration for your paper and overcome writer’s block
- As a source of information (ensure proper referencing)
- As a template for you assignment
Introduction
What is effective communication, models of effective communication, the mbi communication model, barriers to effective communication, how to communicate effectively, effective communication in the global context.
Communicating effectively has been one of the important factors that help a person to succeed in the chosen profession. Studies have estimated that employees typically spend about 75% of their time communicating with colleagues or customers. Personnel who interface with their clients need exceptionally effective communicating skills. Various features related to effective communications are discussed in this paper. Issues and opportunities such as what is effective communication, models of effective communication, global communication strategies, and others are examined.
Keane (July 2007) has suggested that effective communication is the skill of stating ideas, thoughts, instructions, or reports, in an unambiguous manner and with clarity so that the audience understands the intended meaning. Effective Communication is the process where information and ideas are relayed and received. Ideas are conveyed in spoken, written, or visual contexts and when a person is speaking, the tone of voice and the body language are very important. According to Keane, words make up for 7 percent of the communicated information, tone accounts for 55 %, and body language for 38 %. To be effective communicators, people should be aware of these forms, their use, and possible communication barriers The author rates effective communication along with skills such as delegation, time management, motivation, and leadership skills. To work or lead effectively, a manager or supervisor has to know how to explain clearly what needs to be done and how it has to be done. Keane has argued that an organization in effect acts like a human decision-making system and the quality and depth of the decisions that are taken depend on the effectiveness of the system used for communication.
Blitefield (2006) has presented a detailed discussion of the process of communication. According to the author, the process of communication has one communicator and at least one or more receivers. Effective communication starts with how completely the communicator can relate the information and how much of the information that is relayed is understood by the receivers. Effective communication between different disciplines has become one key aspect in organizations. In many cases, the communication process becomes complex when the subjects are controversial or there are multiple and diverse teams. The author speaks of the need to bridge the differences and this is one of the most important factors. The author has defined effective communication as the transmission of subjects and meaning between people and minimizing any misunderstand between them. Several models have been proposed for effective communications and some of them are discussed in the next paragraphs.
Robbins (2003) has suggested that the models of effective communication essentially start with a clear understanding of how people bridge their communication differences or the communication gap as it is called. The author argues that people tend to interpret information by using their reference frame and these references have been shaped by cultural backgrounds or group associations. The process of bridging is an try to minimize the inherent differences by trying to understand the reference frame that others are using. The process of bridging again needs to be a two-way process and both the sender and receiver have to attempt to remove any obstacles. The process of bridging the cultural differences among different groups becomes very important in business contexts such as management. Hofstede (1980) had proposed a framework that would help to assess the cultures by identifying 5 important value dimensions of the national cultures. The model was later expanded by other research organizations till no dimensions were identified. Myers (1985) has proposed the Myer Briggs Type Indicator that makes up the personality framework and explains the behavior of individuals and the concepts can be used to explain the different relationships between cultures.
The Map-Bridge-Integrate model has three interacting components and provides a means to bridge the cultural differences (DiStefano et all, 2002)
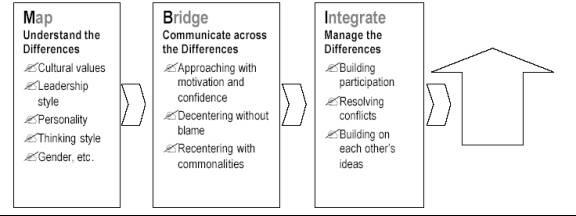
Map – Understand the Differences: The Map component is used in describing and understanding any differences between team members and also specifying the impact that these differences have on team objectives. There are three aspects and they are: selecting the characteristics to be mapped; description of members’ characteristics and identification of the impact of the characteristics.
Bridging – Communicate across the Differences: The Bridging component deals with communicating effectively across the group differences to bring ideas and people together. The main aim of this component is to stop miscommunication There are three aspects to this component: preparing and motivating members to build confidence and communicate so that problems are overcome. This is important since there is a possibility that because of lack of motivation, communication may not happen even after the differences are understood. Decentring where the team members try to explain their understanding of the difference in the process of communication by altering their behavior and thought process. This allows other cultures to be accommodated in their understanding. Re-centring is another aspect and team members try to create a new basis on which interactions can be created. A good understanding of differences is required and consent on shared norms has to be agreed upon.
Integrating – manage the Differences: The integrating component ensures that people use their differences to make good decisions. The understanding developed in the mapping component is converted to obtain positive results. There are three aspects for this component and they are: managing the participation to ensure that all members have an equal opportunity to participate by accommodating different norms for participation that would result from cultural differences; resolving disagreements or possible conflicts so that any disputes are addressed before they increase. The mapping component helps to detect early any probable areas and conflict zones while the bridging component helps to make manageable any personal conflicts. The third aspect is the building on ideas which is the final aspect. Individual ideas are taken as the starting point for any discussion and the concept of ownership needs to be left.
McAteer (March 2007) speaks of certain barriers to communication and the author defines barriers as Barriers are factors that break down or impede a continuous relay of information. These barriers tend to disrupt the process and act of communication. The author has suggested several factors that act as barriers and they are: Nonassertive behavior, Task preoccupation, frustration and anger at the communicator, any personal enmity or bias, diversity in the team with little areas of common interest, lack of confidence in self or on the communicator; complex organizational structure, distractions, tunnel vision, external and internal interruptions and so on.
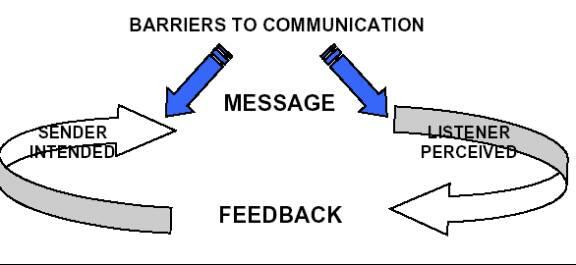
Smith (December 2007) has pointed that two types of major differences create barriers to effective communication and they are: Cultural differences and Group differences. Cultural differences occur when people from different cultures are involved in the communication process. Culture is defined informally as a set of shared traditions, values, and beliefs that control the formation and behavior of different social groups. The author argues that cultures have a strong influence on how people communicate and relate with each other. The cultural differences often create a bias or a barrier between the communicator and the receivers. Group differences on the other hand are due to peer pressure among group members and it is the predominant group mentality that creates a barrier against communication. The author argues that groups can be based according to work natures, ethnicity, and nationality, profession, and gender. Groups can also be formed as per the roles they play such as engineers, doctors, students, teachers, and so on and in many cases, the groups may even form associations. Groups with whom people are associated are called in-groups while groups with which people are not associated are called out-groups. The author suggests that these groups often have their vocabulary, mannerisms, and code of conduct and when one such group tries to communicate with the others, these mannerisms are not carried through and it can result in miscommunications.
Taylor (July 2006) has stressed that effective communications have to be a two-way process and begin with the communicator or the sender who would convey the required information necessary. The sender must have to be proactive and ensure that the receiver can understand the information. Certain key factors that need to be followed are: stating one idea at a time; putting forward the ideas in a medium that is understood; take extra care to elaborate and repeat if required, understand the body language of the audience and ask questions now and then to keep them involved in the discussion. Taylor has defined the four A’s of successful communication and they are Attention; Appreciation, Action, and Assimilation. The Four A’s are illustrated in Figure 3.
Attention: this is the first step in the process of effective communication and it deals with getting the receiver’s attention. This can be achieved by: overcoming distractions such as disturbing mannerisms, noise, emotional and attitude problems, negative and sarcastic attitude, and so on; using an appropriate greeting, showing respect and empathy for the people
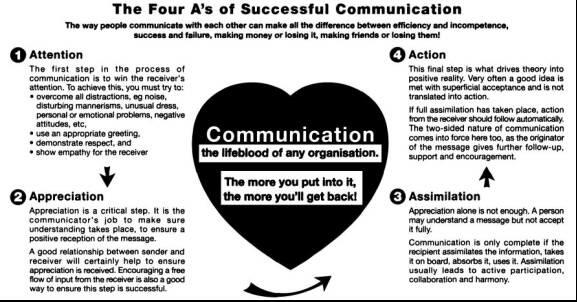
Appreciation: Appreciation is a critical step and it is the responsibility of the communicator to ensure that understanding takes place and that there is a positive reception of the message. A good relationship between the sender and the receiver will help to ensure that appreciation is received. Encouraging a free flow of input from the receiver is also a good way to ensure that this step is carried out properly.
Assimilation: This is the third step and though a person understands a message, it may not be accepted fully. Communication is considered only after the recipient assimilates the information, takes and uses it. It leads to active participation, collaboration, and harmony.
Action: This is the final step and moves the theory of communication into reality. In some cases, a good idea or a meaningful message is accepted superficially but is not translated into action. If complete assimilation takes place, the action from the receiver has to follow. A two-sided communication is brought into action and results in the required activity.
Yates (et all, 2006) have stressed the importance of effective communication for organizations that operate globally. Such organizations operate in different time zones and have employees who have different backgrounds and nationalities. In such a scenario, a proper communication strategy has to be in place to ensure that the messages given out by management are not distorted and the true intent is assimilated. The authors surveyed some leading global organizations to understand how they managed the communication strategy. They used a survey instrument to identify the best practices and the response percentages are shown in Figure 4.
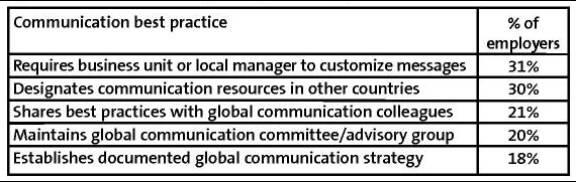
The study showed that only about 18% of the organizations had an established and documented global communication strategy. What many enterprises are learning is that the traditional approach to global communication – translating messages into several languages and shipping them to local managers for dissemination – simply doesn’t work. This approach often results in messages that are misunderstood, miscommunicated, and sometimes not communicated at all. Several multinationals have recognized the value of bringing a global perspective to their communication strategies. The author has reported several steps that such companies are taking up and they are:
Getting global participation: One of the biggest challenges in developing a global strategy is ensuring that the strategy supports and drives corporate goals without overlooking the distinct needs of separate regions, countries, and business areas. Inputs from people around the world are needed to strike the right balance (Maznevski, M. L., 1994).
Making global teams effective: Enterprises that put together effective global teams to develop and maintain the communication strategy are achieving some very positive results. The keyword here, though, is effective. Research into the performance of global teams – and this is not just global communication teams – shows that such teams don’t always deliver the value the enterprise expects. Cultural differences represented in multicultural teams provide great potential for creating value.
Creating messages with a global appeal: Global input provides insight into cultural sensitivities, compliance and legislative differences, and the unique characteristics of each market. Effective communicators use this insight to craft messages that are easy to interpret, translate and adapt to local needs. They also look at the type and content of messages to determine how widely they need to be communicated. The best global communicators determine which messages cannot be tinkered with and which areas of content are open for local customization. Moreover, they make it clear to local managers, which messages must be delivered exactly as presented and which ones can be adapted or expanded to address local needs.
Training local managers to communicate: While some multinationals have dedicated internal communicators on a regional basis, some of them have dedicated communicators on a country or local basis. Some companies rely on local managers to interpret and deliver messages. Functionally, these managers might be responsible for HR, plant management, or operations, so they often don’t have expertise in communication. Unfortunately, few companies provide training and support for these local managers and fewer still have processes in place to ensure that messages were delivered and understood.
Choosing the right delivery mechanisms: Effective internal communicators take advantage of a variety of media and technologies to communicate corporate messages. Options enable local managers to select the tools and information that work best for local employees. Face-to-face presentations work better in some parts of the world, while self-learning tools work better in others.
Measuring success: There are a variety of ways to measure, from focus groups and comprehensive annual employee surveys to quarterly targeted surveys, short feedback questionnaires for forums and workshops, and phone calls to local managers and employees. Such activities help to keep a pulse on whether or not people are receiving, understanding, and embracing messages. As the measurement processes are developed, the ultimate goal should be to identify the links between communication effectiveness and improved productivity and business performance.
The paper has discussed various issues related to effective communication. Effective communication is the process where the exchange of information takes place clearly and unambiguously. Global companies are facing an increasing challenge in inputting into a place an effective communication strategy that would reach employees from different cultural backgrounds.
Blitefield Jerry. (2006). The Rhetoric of RHETORIC: The Quest for Effective Communication. Journal of Rhetoric & Public Affairs. East Lansing. Volume 9. Issue 4. pp: 710-714.
DiStefano, J. J. Ekelund, B. Z. (2002). The MBI Model of Managing Differences Effectively. In Heritage & Management: Identity as a Competitive Tool, J. M. Fladmark (ed.), Donhead Publishing, Edinburgh.
Hofstede, G. (1980). Cultural Consequences: International Differences in Work-Related Values. Sage, Beverly Hills, CA.
Keane Tess. (2007). Power of effective communication. Nursing Standard: Harrow on the Hill. Volume 21. Issue 45. pp: 78-80.
Maznevski, M. L. (1994). Synergy and Performance in Multicultural Teams, Ph.D. dissertation. The University of Western Ontario.
McAteer Teal. (2007). Strategic Organizational Change. Canadian Journal of Administrative Sciences. Halifax. Volume. 24. Issue 1. pp: 74-76.
Robbins, S. P. (2003). Organizational Behavior. Prentice-Hall, Upper Saddle River, NJ.
Smith Marolee Beaumont. (December 2006). A Study on South African Corporate Business Failures. Journal of The Business Review, Cambridge. Hollywood. Volume 6. Issue 1. pp: 168-173.
Taylor Shirley. (2006). Communicating across Cultures. The British Journal of Administrative Management. Orpington. pp: 12-15.
Yates Kathryn. Beech Roger. (2006). Six crucial steps to effective global communication. Journal of Strategic Communication Management. Chicago. Volume 10. Issue 5. pp: 26-30.
- Bridging the Gap in Meeting Customer Expectations
- Role Model as a Communicator
- Bridging Uncertainty in Management Consulting
- How Instant Messages Have Changed Communication
- The Power of Propaganda
- Organizational Communication and Its Definition
- Concepts of Speech: Critique
- Communication in a Relationship and Maslow’s Need Hierarchy Theory
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2021, September 18). Power of Effective Communication. https://ivypanda.com/essays/power-of-effective-communication/
"Power of Effective Communication." IvyPanda , 18 Sept. 2021, ivypanda.com/essays/power-of-effective-communication/.
IvyPanda . (2021) 'Power of Effective Communication'. 18 September.
IvyPanda . 2021. "Power of Effective Communication." September 18, 2021. https://ivypanda.com/essays/power-of-effective-communication/.
1. IvyPanda . "Power of Effective Communication." September 18, 2021. https://ivypanda.com/essays/power-of-effective-communication/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "Power of Effective Communication." September 18, 2021. https://ivypanda.com/essays/power-of-effective-communication/.
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
Guest Essay
Mexico’s Women Are Speaking. Will a Female President Listen?

By Cristina Rivera Garza
Ms. Rivera Garza’s book “Liliana’s Invincible Summer: A Sister’s Search for Justice” is about one of the many women killed by femicide in Mexico.
My mother was born in 1943 in a country where she was not allowed to vote. The Mexican government did not grant women the right to vote in national elections — or the right to hold public office on a national level — until Oct. 17, 1953. Now, almost 71 years later, for the first time two women are leading the race to be Mexico’s next president: Claudia Sheinbaum, who is the front-runner, and Xóchitl Gálvez. It is no small feat for a country with a longstanding and complex relationship with machismo , and where every day some 10 women or girls are killed on average.
And yet this accomplishment has often felt like an afterthought during this historic election. Ms. Sheinbaum, a scientist running on the ticket of the ruling Morena party, and Ms. Gálvez, a businesswoman representing a mix of parties from the political establishment, have nodded at the achievements of feminism and its influence on Mexico’s public life. But they have been cautious about lingering too long on women’s issues in their campaigns, conspicuously tiptoeing around abortion and reproductive rights, seemingly out of deference to conservative voters. Neither candidate has put forth a strong agenda to serve the women who put them where they are today.
For as Mexico descended into its nightmare of generalized violence, from the U.S.-backed war on drugs to the government of Felipe Calderón and the administration of outgoing President Andrés Manuel López Obrador, it has been women — their tireless work, infinite rage and deepening sorrow — who have provided a moral compass to this nation. Women’s mobilizations have grown stronger and louder in the face of government indifference and repression, mounting the only serious opposition against the status quo and making women’s issues and gender justice central to any discussion of our shared future.
To be fair, male candidates have not historically been required to present their agenda for women either. They are seldom even asked about it. But women constitute a little over half of the Mexican electorate; it is imperative that Ms. Sheinbaum and Ms. Gálvez discuss their views and positions on issues that will affect women’s bodies, security and everyday life — not because they are women, but because they are presidential candidates, striving to represent all of us in the highest political office in the country.
On June 2, a woman will almost certainly be given a mandate to govern all of us. She will preside over an electorate that is deeply concerned about insecurity and corruption. The security policy of the current administration — known as “Hugs Not Bullets” — has failed to meaningfully de-escalate the violence unleashed by America’s failed drug policy, a fact painfully brought home by the ever-growing number of disappearances and high rates of gender-related violence. A staggering number of victims’ collectives, made up mostly of the mothers, wives, sisters and daughters of the disappeared, travel the nation with little to no funding or institutional support, sometimes unearthing the remains of their loved ones.
The women in my family tell more than the story of suffrage in Mexico. We are also among the countless families seeking justice for their murdered daughters in a country where impunity and corruption regularly obstruct them, particularly in cases of femicide. One among the many pending cases in Mexico today is that of Liliana Rivera Garza , my younger sister, who was killed on July 16, 1990. The man who is presumed to have killed her has never been arrested, despite a warrant.
But this is only part of the picture. The next president of Mexico will also run a country that is home to a vocal and energized women’s movement. In Mexico, femicide is a distinct crime; a specialized prosecutor’s office for the crime of femicide was created in Mexico City in 2019, when Ms. Sheinbaum was mayor. While the United States Supreme Court overturned Roe v. Wade in 2022, Mexico’s Supreme Court decriminalized abortion in 2023. There is much work to be done — for economic justice, equal access to education, and labor rights, and against racism and homo- and transphobia. But this young generation of Mexican women has made genuine progress, helping find language that is precise, compassionate and forceful enough to dismantle the narratives that have forcibly silenced them and normalized gender violence for too long.
Their success is part of something bigger. Across Latin America, women have been at the forefront of the fight against military dictatorships in Chile (the arpillera movement, for example) and Argentina (the Mothers of Plaza de Mayo). Today, they are holding states responsible for violence and reclaiming public space to remind us that they — that all of us — have the right to live and thrive in safety. On Nov. 25, 2019, during a celebration of the International Day for the Elimination of Violence Against Women, the Chilean feminist collective Las Tesis performed the protest song “Un violador en tu camino” (“A rapist in Your Path”), rallying thousands of us to chant against our governments. The next president of Mexico should be aware that the energy unleashed by these actions, which reverberate in Latin America and beyond, is here to stay.
It is these struggles and demands that have shaped the political arena in which Ms. Sheinbaum and Ms. Gálvez now stand. Will the first female president of Mexico be willing and able to honor such history, acknowledging that women’s equality and gender justice are not peripheral issues but crucial to the country’s future? Will she be ready to face the immense challenge of organized crime, both within and outside the government, to secure a violence-free life for all? Will she preserve and defend the safety of the journalists and activists who risk their lives as they hurl hard questions at power? Unlike former presidents, will she listen?
I believe women are complex human beings “with the full range of saintly and demonic behaviors this entails, including criminal ones,” as Margaret Atwood once wrote. And many female leaders — Margaret Thatcher and Corazón Aquino, to mention just two — demonstrated that a woman running the country does not necessarily translate into support for women. Like all presidents in the past, and in the future, the next leader of Mexico will be judged not by her gender but for the decisions and actions of her government.
My mother’s story is part of one Mexico — the one where women have worked together to lift two female candidates to this moment. My sister Liliana’s story warns of another Mexico, one where violence ends things before they get started. Two years before her death, Liliana exercised her right to vote, on July 6, 1988, and enthusiastically joined the crowds that congregated at the main square in Mexico City afterward. She was ready to defend our emerging democracy and oppose the pervasive electoral fraud that kept the Institutional Revolutionary Party in office at the time.
She, like the countless other victims of violence against women in Mexico, cannot vote this week. We can cast our vote only if we are alive.
Cristina Rivera Garza is the author of “Liliana’s Invincible Summer: A Sister’s Search for Justice,” which won a Pulitzer Prize this year.
The Times is committed to publishing a diversity of letters to the editor. We’d like to hear what you think about this or any of our articles. Here are some tips . And here’s our email: [email protected] .
Follow the New York Times Opinion section on Facebook , Instagram , TikTok , WhatsApp , X and Threads .

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
250 Words Essay on Barriers To Effective Communication Understanding Communication. ... For example, in English, the word "biscuit" means different things in the UK and the US. Emotional Barriers. Emotional barriers are the third type. These happen when feelings get in the way of communication. For example, if someone is angry, they might ...
They include; physical barriers, emotions, language, lack of subject knowledge and stress. Physical barrier to communication can be viewed from different perspectives. It may be in the form of a large working area that is physically separated from the other (Barnlund, 2008, p. 28). As a matter of fact, it will not be easy for communication to ...
Barriers to effective communication include cultural differences, language barrier, organizational barriers, attitudinal barriers, interpersonal barriers, and communication channel barriers (Shewan, 1998). If a sender and recipient do not use a similar language, then effective communication is impossible. In addition, if the sender uses complex ...
24273. Communication, a seemingly simple process, often transforms into a labyrinth of frustration, leaving us feeling misunderstood and unable to convey our thoughts effectively. This essay delves into the intricacies of communication barriers, emphasizing the impact of cultural differences, language disparities, and environmental factors on ...
PDF | On Mar 16, 2018, Radhika Kapur published Barriers to Effective Communication | Find, read and cite all the research you need on ResearchGate
Interference in communications known as communication barriers is defined as any factor that interferes with the success of the communication process (Krizan et al 2005). Communication barriers exist due to much interference in communication such as culture, religion, personalities, and perceptions. In this essay, briefing on general causes of ...
Physical barrier #2: Personal space. In verbal, face-to-face communication, personal space plays a crucial role.. Namely, the distance that applies only to in-person communication may act as a facilitator to good communication or as a barrier to effective communication — depending on whether it's adequately interpreted and arranged.. We can recognize 4 types of distance between in-person ...
Interrupting others while they are speaking also creates a poor environment for communication. Lacking confidence. Lacking confidence can be a major barrier to effective communication. Shyness, difficulty being assertive, or low self-worth can hinder your ability to make your needs and opinions known.
The communication barrier is the absence of a communication channel through which the aide can report the occurrence of pressure ulcers among patients to the authority. Robinson, Gorman, Slimmer, and Yudkowsky (2010) cite the nature of hierarchical authority structure as a barrier to effective communication between healthcare providers and ...
Barriers to communication are things that get in the way of a message being received. They could be physical, such as loud music playing, or emotional, such as when a person is too angry or fearful to listen to what another individual is saying. Culture, language, and social status can also represent barriers to effective communication. ...
The four types of communication barriers are (a) process barriers, (b) physical barriers, (c) semantic barriers, and (d) personal barriers. Process barriers may arise in many situations. They stem from unwieldy procedural approaches that limit teams' ability to do their work. Cumbersome approve processes and communication channels that follow ...
Communication is like a bridge between people. It lets us share ideas, feelings, and information. But sometimes, this bridge can have problems, called communication barriers. These barriers make it hard to send and understand messages clearly. Imagine trying to talk to someone with a wall between you. That's what these barriers are like.
Effective communication is a fundamental aspect of human interaction, serving as the foundation for building strong relationships, resolving conflicts, and achieving shared goals. It encompasses a wide range of skills and practices that enable individuals to convey their thoughts, feelings, and ideas clearly and empathetically while actively listening to others.
Abstract. This discourse analyses the prominen t barriers to speaking in English while conducting online English Language. classes during the pandemic, COVID-19. T h e study is conducted among ...
There are five of these types of barriers to. effective communication, including: Attitudinal Barriers, Behavioral Barriers, Cultural Barriers, Language Barriers and Environment Barriers.A common ...
Conclusion. In this chapter we have reviewed why effective communication matters to organizations. Communication may break down as a result of many communication barriers that may be attributed to the sender or receiver. Therefore, effective communication requires familiarity with the barriers. Choosing the right channel for communication is ...
This study was an effort to explore the barriers of communication faced by the teachers and students in the English language classroom that cause problems in knowledge sharing. Effective communication is necessary to make teaching effective and successful as if the information is conveyed in a poor way would not result in effective teaching.
Language continues to remain a barrier to convey our messages to people in the globalization and communication era. Language barriers are a common challenge in international business, aviation and social settings. ey affect our daily life. Language barriers are the root causes of many problems or obstacles in health care, aviation, maritime ...
Abstract. This research paper delves into the significant language barriers that arise in cross-cultural communication, with a particular focus on the indispensable role of translation strategies ...
Communication is the greatest importance. It is important to sharing out one's thoughts and feelings to live a fuller and happier life. The more we communicate the less we suffer and the better we feel about everything around. However, it is all the more necessary to learn the art of effective communication to put across ones point well.
Keane (July 2007) has suggested that effective communication is the skill of stating ideas, thoughts, instructions, or reports, in an unambiguous manner and with clarity so that the audience understands the intended meaning. Effective Communication is the process where information and ideas are relayed and received.
stereotyping can cause communication barriers. Empathy is important for overcoming barriers to communication based on culture.Language barriers occur when people do not speak the same language, or do not have the same level of ability in a language. There are many environmental factors affecting the effective communication process.
The Mexican government did not grant women the right to vote in national elections — or the right to hold public office on a national level — until Oct. 17, 1953. Now, almost 71 years later ...