Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts

Footnotes & Appendices

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
APA style offers writers footnotes and appendices as spaces where additional, relevant information might be shared within a document; this resource offers a quick overview of format and content concerns for these segments of a document. Should additional clarification be necessary, it is always recommended that writers reach out to the individual overseeing their work (i.e., instructor, editor, etc.). For your convenience, a student sample paper is included below; please note the document is filled with Lorem Ipsum placeholder text and references to footnotes and appendices are highighlighted. Additional marginal notes also further explain specific portions of the example.
Footnotes
Footnotes are supplementary details printed at the bottom of the page pertaining to a paper’s content or copyright information. This supporting text can be utilized in any type of APA paper to support the body paragraphs.
Content-Based Footnotes
Utilizing footnotes to provide supplementary detail can enrich the body text and reinforce the main argument of the paper. Footnotes may also direct readers to an alternate source for more detail on a topic. Though content footnotes can be useful in providing additional context, it is detrimental to include tangential or convoluted information. Footnotes should detail a focused subject; lengthier sections of text are better suited for the body paragraphs.
Acknowledging Copyright
When citing long quotations, images, tables, data, or commercially published questionnaires in-text, it is important to credit the copyright information in a footnote. Functioning much like an in-text citation, a footnote copyright attribution provides credit to the original source and must also be included in a reference list. A copyright citation is needed for both direct reprinting as well as adaptations of content, and these may require express permission from the copyright owner.
Formatting Footnotes
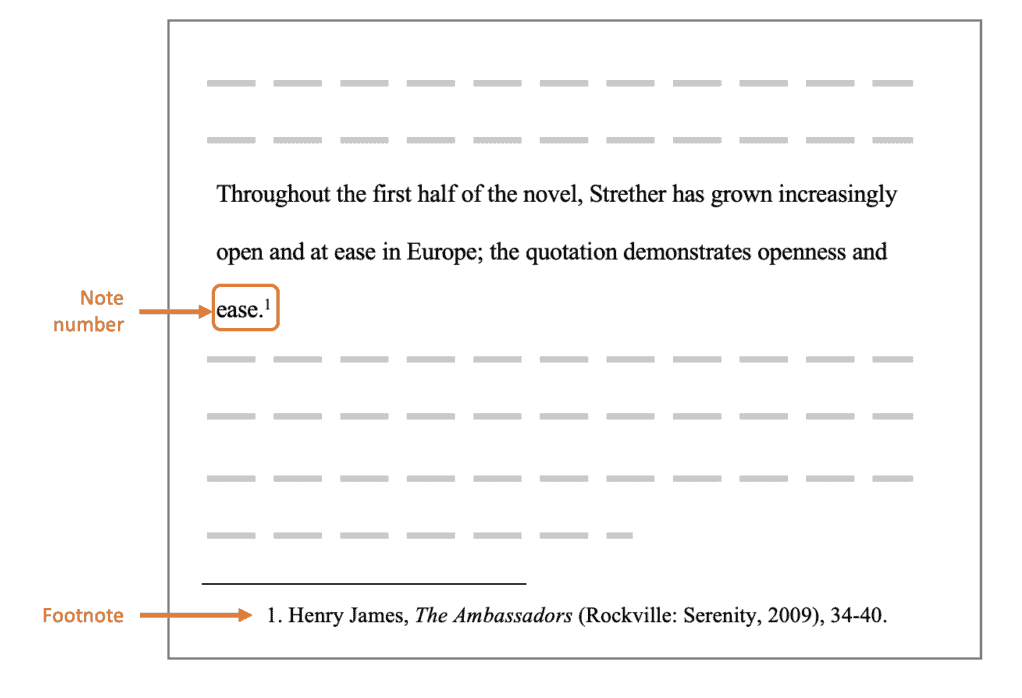
Each footnote and its corresponding in-text callout should be formatted in numerical order of appearance utilizing superscript. As demonstrated in the example below, the superscripted numerals should follow all punctuation with the exception of dashes and parentheses.
For example:
Footnote callouts should not be placed in headings and do not require a space between the callout and superscripted number. When reintroducing a footnote that has previously been called out, refrain from replicating the callout or footnote itself; rather, format such reference as “see Footnote 4”, for example. Footnotes should be placed at the bottom of the page on which the corresponding callout is referenced. Alternatively, a footnotes page could be created to follow the reference page. When formatting footnotes in the latter manner, center and bold the label “Footnotes” then record each footnote as a double-spaced and indented paragraph. Place the corresponding superscripted number in front of each footnote and separate the numeral from the following text with a single space.
Formatting Copyright Information
To provide credit for images, tables, or figures pulled from an outside source, include the accreditation statement at the end of the note for the visual. Copyright acknowledgements for long quotations or questionnaires should simply be placed in a footnote at the bottom of the page.
When formatting a copyright accreditation, utilize the following format:
- Establish if the content was reprinted or adapted by using language such as “from” for directly copied material or “adapted from” for material that has been modified
- Include the content’s title, author, year of publication, and source
- Cite the copyright holder and year of copyright or indicate that the source is public domain or licensed under Creative Commons
- If express permission was required to reprint the material, include a statement indicating that permission was acquired
Appendices
When introducing supplementary content that may not fit within the body of a paper, an appendix can be included to help readers better understand the material without distracting from the text itself. Primarily used to introduce research materials, specific details of a study, or participant demographics, appendices are generally concise and only incorporate relevant content. Much like with footnotes, appendices may require an acknowledgement of copyright and, if data is cited, an adherence to the privacy policies that protect participant identities.
Formatting Appendices
An appendix should be created on its own individual page labelled “Appendix” and followed by a title on the next line that describes the subject of the appendix. These headings should be centered and bolded at the top of the page and written in title case. If there are multiple appendices, each should be labelled with a capital letter and referenced in-text by its specific title (for example, “see Appendix B”). All appendices should follow references, footnotes, and any tables or figures included at the end of the document.
Text Appendices
Appendices should be formatted in traditional paragraph style and may incorporate text, figures, tables, equations, or footnotes. In an appendix, all figures, tables, and other visuals should be labelled with the letter of the corresponding appendix followed by a number indicating the order in which each appears. For example, a table labelled “Table B1” would be the first table in Appendix B. If there is only one appendix in the document, the visuals should still be labelled with the letter A and a number to differentiate them from those contained in the paper itself (for example, “Figure A3” is the third figure in the singular appendix, which is not labelled with a letter in the heading).
Table or Figure Appendices
When an appendix solely contains a table or figure, the title of the figure or table should be substituted with the title of the appendix. For example, if Appendix B only includes a figure, the figure should be labelled “Appendix B” rather than “Figure B1”, as it would be named if there were multiple figures included.
If an appendix does not contain text but includes numerous figures or table, the appendix should be formatted like a text appendix. The appendix would receive a name and label, and each figure or table would be given a corresponding letter and number. For example, if Appendix C contains two tables and one figure, these visuals would be labelled “Table C1”, “Table C2”, and “Figure C1” respectively.
Sample Paper
Media File: APA 7 - Student Sample Paper (Footnotes & Appendices)
How to Use Footnotes in Research Papers
edfuentesg / Getty Images
- An Introduction to Punctuation
- Ph.D., Rhetoric and English, University of Georgia
- M.A., Modern English and American Literature, University of Leicester
- B.A., English, State University of New York
A footnote is a reference, explanation, or comment 1 placed below the main text on a printed page. Footnotes are identified in the text by a numeral or a symbol .
In research papers and reports , footnotes commonly acknowledge the sources of facts and quotations that appear in the text.
" Footnotes are the mark of a scholar," says Bryan A. Garner. "Overabundant, overflowing footnotes are the mark of an insecure scholar — often one who gets lost in the byways of analysis and who wants to show off" ( Garner's Modern American Usage , 2009).
Examples and Observations
- " Footnotes: vices . In a work containing many long footnotes, it may be difficult to fit them onto the pages they pertain to, especially in an illustrated work."
- " Content footnotes supplement or simplify substantive information in the text; they should not include complicated, irrelevant, or nonessential information..." " Copyright permission footnotes acknowledge the source of lengthy quotations, scale and test items, and figures and tables that have been reprinted or adapted."
- Content Footnotes "What, after all, is a content footnote but material that one is either too lazy to integrate into the text or too reverent to discard? Reading a piece of prose that constantly dissolves into extended footnotes is profoundly disheartening. Hence my rule of thumb for footnotes is exactly the same as that for parentheses . One should regard them as symbols of failure. I hardly need to add that in this vale of tears failure is sometimes unavoidable."
- Footnote Forms All notes have the same general form: 1. Adrian Johns. The Nature of the Book: Print and Knowledge in the Making (Chicago: University of Chicago Press, 1998), 623. If you cite the same text again, you can shorten subsequent notes: 5. Johns. Nature of the Book , 384-85.
- The Disadvantages of Footnotes "More than one recent critic has pointed out that footnotes interrupt a narrative . References detract from the illusion of veracity and immediacy . . . . (Noel Coward made the same point more memorably when he remarked that having to read a footnote resembles having to go downstairs to answer the door while in the midst of making love.)"
- Belloc on Footnotes "[L]et a man put his foot-notes in very small print indeed at the end of a volume, and, if necessary, let him give specimens rather than a complete list. For instance, let a man who writes history as it should be written — with all the physical details in evidence, the weather, the dress, colors, everything — write on for the pleasure of his reader and not for his critic. But let him take sections here and there, and in an appendix show the critic how it is being done. Let him keep his notes and challenge criticism. I think he will be secure. He will not be secure from the anger of those who cannot write clearly, let alone vividly, and who have never in their lives been able to resurrect the past, but he will be secure from their destructive effect."
- The Lighter Side of Footnotes "A footnote is like running downstairs to answer the doorbell on your wedding night."
1 "The footnote has figured prominently in the fictions of such leading contemporary novelists as Nicholson Baker 2 , David Foster Wallace 3 , and Dave Eggers. These writers have largely revived the digressive function of the footnote." (L. Douglas and A. George, Sense and Nonsensibility: Lampoons of Learning and Literature . Simon and Schuster, 2004)
2 "[T]he great scholarly or anecdotal footnotes of Lecky, Gibbon, or Boswell, written by the author of the book himself to supplement, or even correct over several later editions, what he says in the primary text, are reassurances that the pursuit of truth doesn't have clear outer boundaries: it doesn't end with the book; restatement and self-disagreement and the enveloping sea of referenced authorities all continue. Footnotes are the finer-suckered surfaces that allow tentacular paragraphs to hold fast to the wider reality of the library." (Nicholson Baker, The Mezzanine . Weidenfeld and Nicholson, 1988)
3 "One of the odd pleasures in reading the work of the late David Foster Wallace is the opportunity to escape from the main text to explore epic footnotes , always rendered at the bottoms of pages in thickets of tiny type." (Roy Peter Clark, The Glamour of Grammar . Little, Brown, 2010)
- Hilaire Belloc, On , 1923
- Chicago Manual of Style , University of Chicago Press, 2003
- Anthony Grafton, The Footnote: A Curious History . Harvard University Press, 1999.
- Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association , 6th ed., 2010.
- Paul Robinson, "The Philosophy of Punctuation." Opera, Sex, and Other Vital Matters . University of Chicago Press, 2002.
- Kate Turabian, A Manual for Writers of Research Papers, Theses, and Dissertations , 7th ed. University of Chicago Press, 2007 .
- What Are Endnotes, Why Are They Needed, and How Are They Used?
- Formatting Papers in Chicago Style
- Top 10 Reference Works for Writers and Editors
- Definition of Appendix in a Book or Written Work
- Margin (Composition Format) Definition
- Turabian Style Guide With Examples
- What Is a Citation?
- What Is a Style Guide and Which One Do You Need?
- 140 Key Copyediting Terms and What They Mean
- Documentation in Reports and Research Papers
- What Is a Senior Thesis?
- Justification (Typesetting and Composition)
- What are Ellipsis Points?
- How to Write a Research Paper That Earns an A
- Examples of Epigraphs in English
- Definition and Examples of Title Case and Headline Style
Educational resources and simple solutions for your research journey

What are Footnotes and How to Use Them for Research?
The research process is inherently collaborative, involving the analysis of the collective body of knowledge developed over time. It is academically and ethically vital to acknowledge others’ contributions. Footnotes serve as subtle markers of acknowledgment while also providing supplementary details to enhance the reader’s understanding and engagement with your work.
Table of Contents
What are footnotes?
During your research, you’ll encounter inconspicuous superscript numbers at the end of some sentences, which link to corresponding notes at the page’s bottom or ‘foot.’ These notes serve as references to cited works and offer supplementary information to aid the reader’s understanding.
It’s important to note that not all references and supplementary notes are at the bottom of the page; some are placed at the end of the research paper as “endnotes.” This doesn’t lessen their significance; they still offer valuable context and insights.
Footnotes vs Endnotes
Footnotes and endnotes fulfill the same fundamental purpose in scholarly writing. However, the choice between them often reflects an author’s personal preference or aligns with specific style guidelines. Footnotes are frequently utilized for immediate comments or explanations related to the main text. On the other hand, endnotes are commonly reserved for citations of the works referenced within the text.
Let’s examine footnotes and endnotes more closely to understand the distinctions between these two citation methods:
Footnotes are highly effective due to their ease of access and their ability to direct readers to relevant citations or supplementary ideas swiftly. This approach increases the likelihood that readers will engage with the citation or additional information. However, the limited space at the bottom of the page necessitates caution. Overloading it with excessive other text can be overwhelming and potentially distracting for readers.
Endnotes, in contrast, offer the advantage of being located at the end of a paper within a designated section, giving authors the freedom to incorporate supplementary information liberally without the need to use up the limited space on a page. However, endnotes are often overlooked by readers. This oversight can be attributed to a mental justification that if information is not included in the main text, it may not hold significant value.¹²
Footnote Citation Styles
Incorporating footnotes into your research paper is crucial, but it’s equally important to grasp the specific footnote citation style required by your target journal or publication. The format and style of footnote citations can differ significantly based on the citation style guide in use. Below, you’ll find illustrative examples of how to use footnotes in essays according to the central style guides:¹
Chicago Style
The Chicago Style uses footnotes to provide full source details in the form of numbered notes at the bottom of each page. A corresponding bibliography is provided at the end of the research essay or document. Here is an example:
“The Apollo program was designed by men, for men. If we do not acknowledge the gender bias of the early space program, it becomes difficult to move past it.” ¹
1.1 Mary Robinette Kowal, To Make It to the Moon, Women Have to Escape Earth’s Gender Bias (New York Times, 17 July 1969).
In this example, the superscript “1” in the text corresponds to the first footnote, which provides complete source information for an article by Mary Robinette Kowal in The New York Times.
Modern Language Association (MLA) Style
The MLA Style does not typically use footnotes for citations. Instead, it relies on in-text citations with an author-page number format. However, the footnotes might be utilized for explanatory or supplementary information. Example:
“The protagonist’s transformation throughout the novel is central to its theme and character development.” 1
1 This analysis draws on the ideas of literary critic John Smith regarding character evolution in narrative fiction.
In this example, the superscript “1” in the main text points to a footnote that offers additional context and acknowledges the source, i.e., John Smith’s ideas.
American Psychological Association (APA) Style
APA Style typically uses in-text citations rather than footnotes. However, you may use footnotes for clarifications or additional information, not for standard source citations. Here is an example:
“The study’s results revealed a statistically significant correlation between the two variables^1^.”
^1^ Note that the p-value was set at 0.05 as the threshold for statistical significance.
In the example, the superscript “^1^” in the main text indicates a footnote, which is used to provide a brief explanation.
How to add Footnotes in Microsoft Word and Google Docs?
So, how do you make footnotes? Adding footnotes in both Microsoft Word and Google Docs is a straightforward process. Step-by-step instructions are provided below for adding footnotes in both applications:
Microsoft Word
- Position your cursor where you want to insert a footnote in the document.
- Navigate to the “References” tab and click on the “Insert Footnote” button.
- A small superscript number (typically “1”) will appear where you positioned the cursor, and a corresponding footnote area will appear at the bottom of the page. Enter your footnote content in this designated area.
- To insert additional footnotes, repeat the same steps. Microsoft Word will automatically manage the numbering of footnotes. (4)
Google Docs
- Place the cursor at the location where you wish to insert a footnote.
- In the menu bar, click on “Insert” and select “Footnote.”
- A superscript number (usually “1”) will appear where you placed your cursor, and a footnote section will be created at the bottom of the page. Type your footnote content in this section.
- Add more footnotes using the same steps. Google Docs will handle the footnotes numbering. (5)
References:
- Footnotes and Endnotes – Khalifa University
- Footnotes and Endnotes – University of Bristol
- Footnote Referencing Styles – Bibliography.com
- Add footnotes and endnotes – Microsoft Support
- Use headers, footers, page numbers, & footnotes – Google Docs Editors Help
R Discovery is a literature search and research reading app that uses your interests to instantly create personalized reading feeds. Researchers can stay updated on the latest, most relevant content from its continually expanding library of 115M+ research articles sourced from trusted aggregators like CrossRef, Unpaywall, PubMed, PubMed Central, Open Alex as well as prestigious publishing houses like Springer Nature, JAMA, IOP, Taylor & Francis, NEJM, BMJ, Karger, SAGE, Emerald Publishing and more. The top-rated app in its space, R Discovery’s carefully curated features give you the power to choose what, where, and how you read research.
Try the app for free or upgrade to R Discovery Prime, which unlocks unlimited access to app-only features that let you listen to research on the go, read in your language, invite collaborators, auto sync with reference managers and more. It’s like having the world of research at your fingertips! Choose a simpler, smarter way to find and read research – Get R Discovery Prime now at just US$39 a year!
Related Posts

Simple Random Sampling: Definition, Methods, and Examples

What is a Case Study in Research? Definition, Methods, and Examples
- USC Libraries
- Research Guides
Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Paper
- Footnotes or Endnotes?
- Purpose of Guide
- Design Flaws to Avoid
- Independent and Dependent Variables
- Glossary of Research Terms
- Reading Research Effectively
- Narrowing a Topic Idea
- Broadening a Topic Idea
- Extending the Timeliness of a Topic Idea
- Academic Writing Style
- Applying Critical Thinking
- Choosing a Title
- Making an Outline
- Paragraph Development
- Research Process Video Series
- Executive Summary
- The C.A.R.S. Model
- Background Information
- The Research Problem/Question
- Theoretical Framework
- Citation Tracking
- Content Alert Services
- Evaluating Sources
- Primary Sources
- Secondary Sources
- Tiertiary Sources
- Scholarly vs. Popular Publications
- Qualitative Methods
- Quantitative Methods
- Insiderness
- Using Non-Textual Elements
- Limitations of the Study
- Common Grammar Mistakes
- Writing Concisely
- Avoiding Plagiarism
- Further Readings
- Generative AI and Writing
- USC Libraries Tutorials and Other Guides
- Bibliography
Endnote Note citing a particular source or making a brief explanatory comment placed at the end of a research paper and arranged sequentially in relation to where the reference appears in the paper.
Footnote Note citing a particular source or making a brief explanatory comment placed at the bottom of a page corresponding to the item cited in the corresponding text above.
Fiske, Robert Hartwell. To the Point: A Dictionary of Concise Writing . New York: W.W. Norton and Company, 2014.
Structure and Writing Style
Advantages of Using Endnotes
- Endnotes are less distracting to the reader and allows the narrative to flow better.
- Endnotes don't clutter up the page.
- As a separate section of a research paper, endnotes allow the reader to read and contemplate all the notes at once.
Disadvantages of Using Endnotes
- If you want to look at the text of a particular endnote, you have to flip to the end of the research paper to find the information.
- Depending on how they are created [i.e., continuous numbering or numbers that start over for each chapter], you may have to remember the chapter number as well as the endnote number in order to find the correct one.
- Endnotes may carry a negative connotation much like the proverbial "fine print" or hidden disclaimers in advertising. A reader may believe you are trying to hide something by burying it in a hard-to-find endnote.
Advantages of Using Footnotes
- Readers interested in identifying the source or note can quickly glance down the page to find what they are looking for.
- It allows the reader to immediately link the footnote to the subject of the text without having to take the time to find the note at the back of the paper.
- Footnotes are automatically included when printing off specific pages.
Disadvantages of Using Footnotes
- Footnotes can clutter up the page and, thus, negatively impact the overall look of the page.
- If there are multiple columns, charts, or tables below only a small segment of text that includes a footnote, then you must decide where the footnotes should appear.
- If the footnotes are lengthy, there's a risk they could dominate the page, although this issue is considered acceptable in legal scholarship.
- Adding lengthy footnotes after the paper has been completed can alter the page where other sources are located [i.e., a long footnote can push text to the next page].
- It is more difficult learning how to insert footnotes using your word processing program than simply adding endnotes at the end of your paper.
Things to keep in mind when considering using either endnotes or footnotes in your research paper :
1. Footnotes are numbered consecutively throughout a research paper, except for those notes accompanying special material (e.g., figures, tables, charts, etc.). Numbering of footnotes are "superscript"--Arabic numbers typed slightly above the line of text. Do not include periods, parentheses, or slashes. They can follow all punctuation marks except dashes. In general, to avoid interrupting the continuity of the text, footnote numbers are placed at the end of the sentence, clause, or phrase containing the quoted or paraphrased material. 2. Depending on the writing style used in your class, endnotes may take the place of a list of resources cited in your paper or they may represent non-bibliographic items, such as comments or observations, followed by a separate list of references to the sources you cited and arranged alphabetically by the author's last name. If you are unsure about how to use endnotes, consult with your professor. 3. In general, the use of footnotes in most academic writing is now considered a bit outdated and has been replaced by endnotes, which are much easier to place in your paper, even with the advent of word processing programs. However, some disciplines, such as law and history, still predominantly utilize footnotes. Consult with your professor about which form to use and always remember that, whichever style of citation you choose, apply it consistently throughout your paper.
NOTE: Always think critically about the information you place in a footnote or endnote. Ask yourself, is this supplementary or tangential information that would otherwise disrupt the narrative flow of the text or is this essential information that I should integrate into the main text? If you are not sure, it's better to work it into the text. Too many notes implies a disorganized paper.
Cermak, Bonni and Jennifer Troxell. A Guide to Footnotes and Endnotes for NASA History Authors . NASA History Program. History Division; Hale, Ali. Should You Use Footnotes or Endnotes? DailyWritingTips.com; Tables, Appendices, Footnotes and Endnotes. The Writing Lab and The OWL. Purdue University; Lunsford, Andrea A. and Robert Connors. The St. Martin's Handbook . New York: St. Martin's Press, 1989; Saller, Carol. “Endnotes or Footnotes? Some Considerations.” The Chronicle of Higher Education 58 (January 6, 2012): http://chronicle.com/blogs/linguafranca/2012/01/06/endnotes-or-footnotes-some-considerations/.
- << Previous: Avoiding Plagiarism
- Next: Further Readings >>
- Last Updated: Jun 18, 2024 10:45 AM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide
Footnotes in a Paper: How to Use Them Effectively in Your Writing
Discover the best way to use footnotes in a paper. Get expert tips on how to efficiently and effectively use footnotes in academic papers.
Footnotes in a paper can be a valuable tool in providing a way to supplement our writing with additional information, citations, and explanations without disrupting the flow of the main text. However, many writers may be unsure of when and how to use footnotes effectively. In this article, we will explore the importance and usage of footnotes in academic writing, and provide practical tips for incorporating footnotes into your own writing. Whether you are a seasoned academic writer or just starting out, understanding how to use footnotes can help you increase the clarity and credibility of your writing.
What Are Footnotes?
Footnotes are a useful tool in academic writing that allows for the inclusion of additional information or comments in a document or text. Typically denoted by a small number or symbol in the main text, footnotes in a paper appear at the bottom of the page and can serve a variety of purposes. For example, footnotes can be used to clarify a point, provide background information, or give credit to a source that is not directly quoted or referenced in the main text. They are also helpful in avoiding disruptions to the flow of the main text, particularly when lengthy citations or explanations are required. In short, footnotes provide readers with additional information or references related to specific sections of the text, making them a valuable tool for researchers.
How to Write a Footnote
To write a footnote for a paper, follow these general steps:
- Determine what information needs to be included in the footnote. This may include the author’s name, the title of the source, the publication date, the publisher, and the page number(s) you are referencing.
- Place the footnote number or symbol at the end of the sentence or clause that requires the footnote. The footnote number or symbol should be placed after the punctuation, such as a period or comma.
- Write the footnote itself at the bottom of the page. The first line of the footnote should be indented, and the subsequent lines should be flush with the left margin.
- Format the footnote according to the citation style you are using (e.g. MLA, APA , Chicago). Each citation style has specific rules for how footnotes should be formatted, so consult the appropriate style guide for details.
- If you are using a word processing program, such as Microsoft Word, you can use the “Insert Footnote” function to automatically insert footnotes and format them correctly.
Difference Between Footnotes and Endnotes
The main difference between footnotes and endnotes is their placement within a document. Footnotes appear at the bottom of the page on which they are referenced, while endnotes appear at the end of a document, chapter, or section.
Here are some other differences between footnotes and endnotes:
| Definition | Notes placed at the bottom of the same page as the reference. | Notes placed at the end of the document. |
| Placement | Below the text they reference, usually in smaller font sizes. | At the end of the document, usually in the same font size as the main text. |
| Usage | Used to provide additional information or explanation of a point in the text. | Used to provide additional information, explanation, or citation of a source. |
| Advantages | Easy to locate and read in the context of the text. | Keep the text clean and uncluttered. |
| Disadvantages | May clutter the page and distract the reader. | May require the reader to flip back and forth between the text and the endnotes. |
Chicago Style Footnotes
Chicago-style footnotes are a common citation style used in research papers. In this format, footnotes are used to provide information about a source within the text. There are two types of Chicago-style footnotes: short form and long form. Short form citations include only the basic details of a source if a full bibliography is provided, while long form citations include a full citation the first time a source is cited, with subsequent citations using the short form.
Here is an example of a Chicago-style footnote using the short form:
“The concept of social capital has been widely discussed in recent years, with Putnam’s Bowling Alone¹ being one of the most influential works in the field.” At the bottom of the page, the corresponding footnote would appear as: ¹ Putnam, Bowling Alone, 26.
Note that the author’s last name is listed first, followed by the abbreviated title of the work (in this case, “Bowling Alone”), and the page number where the information was found.
Here is a Chicago-style footnote using the short form example:
First reference: John Smith, The History of Chicago (Chicago: University of Chicago Press, 2005), 25. Subsequent reference: Smith, The History of Chicago, 30.
Here is an example of a Chicago footnote in text:
“According to Smith, the notion of human rights can be traced back to ancient Greek philosophy.¹”² Bottom of page: ¹John Smith, The Origins of Human Rights (New York: Oxford University Press, 2021), 15. ²Smith, Origins of Human Rights, 22.
Learn how to make citations in Chicago style in our blog “ Chicago Style Citation Made Easy: Formatting and Examples “.
APA Style Footnotes
APA format generally uses parenthetical in-text citations instead of footnotes. However, there are two exceptions to this rule: content footnotes and copyright attribution. Content footnotes provide additional information on a single topic that does not fit coherently in the text, while copyright attribution footnotes are used when a writer uses a lengthy quotation or other copyrighted material, such as a stock photograph. Footnotes are formatted similarly to Chicago style, with sequential superscript numbers coming after the passage and the corresponding footnote at the bottom of the page.
Here’s an example of an APA-style footnote for supplementary information:
In-text: According to recent studies, the COVID-19 vaccine is highly effective in preventing infection and transmission of the virus.¹ Footnote: ¹For more information on the studies cited, see Smith et al. (2021) and Jones et al. (2022).
Learn how to make citations in APA style in our blog “ How to Make Citations using APA Formatting: A Guide “.
MLA Style Footnotes
MLA (Modern Language Association) style does not typically use footnotes. Instead, in-text citations are used to indicate the source of information or quotations. However, if footnotes are required for a specific publication or assignment, the following guidelines can be followed:
Placement: Footnotes should be placed at the bottom of the page on which the reference appears.
Numbering: Footnotes should be numbered consecutively throughout the paper using Arabic numerals. The number should be placed after any punctuation marks, such as periods or commas.
Formatting: Footnotes should be single-spaced and in a smaller font size than the main text.
Content: Footnotes should include bibliographic information for the source being cited, as well as any additional information necessary to clarify the reference. For example, a footnote for a book might include the author, title, publisher, and year of publication, while a footnote for a website might include the URL and date of access.
Example of MLA Style Footnote for a book:
John Doe, The History of Art (New York: Penguin Books, 2000), 24. Example of MLA Style Footnote for a website: “The Benefits of Exercise,” National Institutes of Health, accessed May 15, 2023, https://www.nih.gov/health-information/benefits-exercise .
A MLA Style footnote text example:
Text: According to a recent study, the use of social media can have negative effects on mental health (Johnson 36).² Footnote citation: ² Johnson, Sarah. “The Impact of Social Media on Mental Health.” Journal of Health Psychology, vol. 22, no. 1, 2018, pp. 35-44.
Learn how to make citations in MLA style in our blog “ A Writer’s Guide to MLA Format: How to Get It Right “.
Improve your papers’ impact and visibility through quality visual communication
Mind the Graph is an innovative platform that provides a wide range of tools to help scientists improve their papers’ impact and visibility through quality visual communication. With Mind the Graph, scientists can easily create graphical abstracts, posters, and other visual aids that can effectively communicate their research findings to a wider audience.

Subscribe to our newsletter
Exclusive high quality content about effective visual communication in science.
Content tags

- Foundations
- Write Paper
Search form
- Experiments
- Anthropology
- Self-Esteem
- Social Anxiety

- Research Paper >
How to Write Footnotes
Information on how to write footnotes and endnotes. Footnotes, a type of citation format, are most often used for history and philosophy papers. As such, scientists rarely encounter it, but it is still useful to know how to follow the practice.
This article is a part of the guide:
- Outline Examples
- Example of a Paper
- Write a Hypothesis
- Introduction
Browse Full Outline
- 1 Write a Research Paper
- 2 Writing a Paper
- 3.1 Write an Outline
- 3.2 Outline Examples
- 4.1 Thesis Statement
- 4.2 Write a Hypothesis
- 5.2 Abstract
- 5.3 Introduction
- 5.4 Methods
- 5.5 Results
- 5.6 Discussion
- 5.7 Conclusion
- 5.8 Bibliography
- 6.1 Table of Contents
- 6.2 Acknowledgements
- 6.3 Appendix
- 7.1 In Text Citations
- 7.2 Footnotes
- 7.3.1 Floating Blocks
- 7.4 Example of a Paper
- 7.5 Example of a Paper 2
- 7.6.1 Citations
- 7.7.1 Writing Style
- 7.7.2 Citations
- 8.1.1 Sham Peer Review
- 8.1.2 Advantages
- 8.1.3 Disadvantages
- 8.2 Publication Bias
- 8.3.1 Journal Rejection
- 9.1 Article Writing
- 9.2 Ideas for Topics
Many biology journals, for example, prefer footnotes because they allow annotation of the in-text citation on the same page.
Whilst footnotes are a little more cumbersome than the 'author/date' system, they are useful where sources require elaboration and short explanatory notes.

What is a Footnote
The footnote takes the form of a superscripted number, just after a paraphrased piece of information. Subsequently, a cross-reference to this number is inserted at the bottom of the same page.
In fact, for dissertations and theses, many writers use footnotes to keep track of their citations , adding a short note of what exactly each one adds to the paper.
Once the paper is complete, the writer converts them to endnotes at the end or every chapter, or even removes them all together, and uses a standard APA or MLA bibliography instead.

Automatically Inserting Footnotes
The reason that footnotes are still popular in some fields is that most word processing programs now include a function that makes it very easy to include footnotes in any paper.
In Microsoft Word, clicking Insert > Reference > Footnote allows you to insert footnotes automatically, and automatically numbers them. This function is so useful, that even if you cut and paste, and swap information around, it automatically adjusts the footnotes.
This is why it is an excellent resource for keeping track of your sources during the course of a research paper .
How to Write Footnotes - Protocols
If you are using footnotes, the common convention is to insert a full citation, including author, year and the title of the book, followed by the page number. Afterwards, the surname of the author and the page number is sufficient.
Older journals often use the word ibid, to show that a footnote uses the same source as the previous one, but this has become much rarer.
- Psychology 101
- Flags and Countries
- Capitals and Countries
Martyn Shuttleworth (Nov 21, 2009). How to Write Footnotes. Retrieved Jun 28, 2024 from Explorable.com: https://explorable.com/how-to-write-footnotes
You Are Allowed To Copy The Text
The text in this article is licensed under the Creative Commons-License Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) .
This means you're free to copy, share and adapt any parts (or all) of the text in the article, as long as you give appropriate credit and provide a link/reference to this page.
That is it. You don't need our permission to copy the article; just include a link/reference back to this page. You can use it freely (with some kind of link), and we're also okay with people reprinting in publications like books, blogs, newsletters, course-material, papers, wikipedia and presentations (with clear attribution).
Want to stay up to date? Follow us!
Check out the official book.
Learn how to construct, style and format an Academic paper and take your skills to the next level.

(also available as ebook )
Save this course for later
Don't have time for it all now? No problem, save it as a course and come back to it later.
Footer bottom
- Privacy Policy

- Subscribe to our RSS Feed
- Like us on Facebook
- Follow us on Twitter

How to Format Your Research Paper
- APA 7 Paper Format
- MLA Paper Format
- Chicago Paper Format
How to Create Footnotes
- Hanging Indents
- Ask a Librarian
What Are They
Footnotes are short numbered notes that are placed at the bottom of the page in an essay or article. They are used for a variety of reasons including, citing materials, providing notes on a source or topic, and to acknowledge copyright status.
Although you will find footnotes in many journal articles, they are not typically required in APA or MLA formatted essays. They are most heavily used when applying the CMOS style.
For information on footnotes in the Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association see section 2.13 "Footnotes.". For information on using footnotes with MLA see the " Using Notes in MLA Style " article from the MLA Style Center . For information on footnotes in The Chicago Manual of Style see Chapter 14 "Notes and Bibliography."
Using Google Docs:
- Cómo incorporar notas al calce en Google Docs Vea éste video en español.
Using Microsoft Word:
- Cómo incorporar notas al calce en Microsoft Word Vea éste video en español.
- << Previous: Chicago Paper Format
- Next: Hanging Indents >>
- Last Updated: Jun 21, 2024 10:45 AM
- URL: https://necc.mass.libguides.com/formatting
To cite this LibGuide use the following templates:
APA : Northern Essex Community College Library. (Date updated). Title of page . Title of LibGuide. URL
MLA : Northern Essex Community College Library. "Title of Page." Title of LibGuide, Date updated, URL.
Generate accurate MLA citations for free
- Knowledge Base
- MLA footnotes and endnotes
MLA Footnotes & Endnotes | Format & Examples
Published on August 23, 2019 by Shona McCombes . Revised on March 5, 2024 by Jack Caulfield.
MLA style requires you to cite sources using MLA in-text citations , not notes. However, you can still use footnotes or endnotes in MLA style for other purposes:
Citing a lot of sources at once
- Providing any extra explanation needed about your citation or translation practice
- Elaborating on ideas
- Providing additional examples that don’t fit into the main text
Footnotes appear at the bottom of the relevant page, while endnotes appear at the end of the paper, just before the Works Cited list. MLA allows the use of either type, but stick to one or the other.
Any sources you cite in your footnotes or endnotes must also be included in your Works Cited list , just like sources in the main text. Scribbr’s free MLA Citation Generator can help you create accurate MLA citations.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
Formatting footnotes and endnotes in mla, explaining citation or translation practice, using notes to elaborate on ideas, providing more examples in notes, frequently asked questions about mla notes.
Both footnotes and endnotes are indicated by superscript numbers. The number usually appears at the end of a sentence, after the period.
If you need to use a note in the middle of a sentence to avoid ambiguity, place the number directly after a punctuation mark (with the exception of the dash , where the number comes before).
Four main factors have been determined as possible characteristics of any successful fictional work: 6 popularity, enduring fame, commercial success and scholarly appeal. Each of the case studies must possess at least one of these. 7
The note itself begins with the corresponding number, again in superscript, followed by a space, and then the content of the note. Notes should be in the same font as the rest of your document, but a smaller font size; the first line of each note is slightly indented.
Your word processing program should allow you to automatically insert footnotes .
Formatting the endnotes page
If you are using endnotes, list them on a separate page directly before the Works Cited list. The title (“Notes” or “Endnotes”) appears centered at the top of the page. Like the rest of an MLA format paper , the endnotes should be double-spaced.

Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

When you have a lot of sources to cite at once, you can save space in your text by placing them in a note instead. These can be sources for a statement you made in the text, or sources providing supplementary information relevant to the discussion.
Note that you don’t need to use parentheses around the page numbers when the note just consists of a list of sources.
When there’s any important information that might not be immediately obvious from your citations, you can explain it in a note at the first point where it comes up.
For example, you might use your own translations for some texts but not others, or you might cite different editions of a text in different ways. These details can be clarified in notes where relevant.
When you mention something in passing but think more information may be useful to the reader, you can add the extra information, as well as related sources if relevant, in a note.
Bear in mind that long notes with superfluous information can be distracting for readers. Use notes of this kind sparingly, and keep them brief. If a piece of information is essential to your point, you should usually include it in the main text.
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
Sometimes you have more examples than you can smoothly fit into your text. In those cases, it can be worth placing further examples in a note, if you think they add something to your point. You might also provide a counterexample to acknowledge the limitations of your argument.
No, you should use parenthetical MLA in-text citations to cite sources. Footnotes or endnotes can be used to add extra information that doesn’t fit into your main text, but they’re not needed for citations.
If you need to cite a lot of sources at the same point in the text, though, placing these citations in a note can be a good way to avoid cluttering your text.
In MLA style , footnotes or endnotes can be used to provide additional information that would interrupt the flow of your text.
This can be further examples or developments of ideas you only briefly discuss in the text. You can also use notes to provide additional sources or explain your citation practice.
You don’t have to use any notes at all; only use them to provide relevant information that complements your arguments or helps the reader to understand them.
Footnotes appear at the bottom of the relevant page. Endnotes appear in a list at the end of the text, just before the reference list or bibliography. Don’t mix footnotes and endnotes in the same document: choose one or the other and use them consistently.
In Chicago notes and bibliography style , you can use either footnotes or endnotes, and citations follow the same format in either case.
In APA and MLA style , footnotes or endnotes are not used for citations, but they can be used to provide additional information.
Some source types, such as books and journal articles , may contain footnotes (or endnotes) with additional information. The following rules apply when citing information from a note in an MLA in-text citation :
- To cite information from a single numbered note, write “n” after the page number, and then write the note number, e.g. (Smith 105n2)
- To cite information from multiple numbered notes, write “nn” and include a range, e.g. (Smith 77nn1–2)
- To cite information from an unnumbered note, write “un” after the page number, with a space in between, e.g. (Jones 250 un)
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. (2024, March 05). MLA Footnotes & Endnotes | Format & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved June 24, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/mla/footnotes-and-endnotes/
Is this article helpful?
Most Popular
11 days ago
How To Write A Conclusion For A Research Paper
12 days ago
How To Start A Scholarship Essay
How to focus on homework, how to write a rhetorical analysis essay, how to do footnotes.

Footnotes are a reference tool for writers and researchers, allowing them to provide additional information, clarify sources, or share related insights without disrupting the flow of the main text. Footnotes are positioned at the bottom of the page and indicated within the text by a superscript number or symbol. Various academic and professional fields rely on footnotes to maintain the credibility of written work. They are prevalent in citation styles such as Chicago, often used in history and the humanities, and MLA, preferred in literature and some social sciences. Footnotes help maintain the integrity of the narrative while providing the reader with access to the source material for verification or deeper exploration.
What Is a Footnote?
A footnote, as the name suggests, is a special note or a comment placed at the bottom of a page within a document that provides additional information, clarification, or citation of sources related to the text referenced by a superscript number or symbol appearing in the main body of the document. The purpose of these messages is to explain, elaborate on, or complement the material without cluttering the main content. It helps readers stay on track of the story and just glance at the bottom of the page at a footnote to get more information, if necessary. Therefore, footnotes allow for a cleaner and more readable narrative.
Footnotes come in various forms, primarily categorized based on their purpose: content footnotes and citation footnotes.
Content footnotes give further details for better understanding or provide context to a statement made in the main text but are not directly linked to a citation. Informational footnotes are valuable in technical documents, encyclopedias, and detailed analytical works where extra information might be helpful for readers who seek deeper understanding or background knowledge about the discussed topic.
Citation footnotes , on the other hand, are implied when the referencing style of the document prefers footnotes for citation instead of in-text citations or endnotes. Bibliographic footnotes make all the citation details accessible without overcrowding the main text. This is particularly useful in disciplines like history and classical studies, where original sources may be extensively analyzed or critiqued.
Typically, footnotes appear at the bottom of the same page where their corresponding superscript is noted. This placement is very convenient as readers can easily find and refer to the additional information without having to flip through the pages. It maintains a smooth reading experience while providing depth and evidence where needed.
How to Use Footnotes
To use footnotes in your writing effectively, start by determining when a footnote is necessary or when you believe it may be helpful for readers. Generally, any supporting information that is too detailed for the main text but required for deeper understanding or source verification should be noted in a footnote. This includes direct citations, clarifications, and supplemental data.
Once you decide to add a footnote, insert a superscript number at the end of the sentence or clause related to the additional information. This number should follow any punctuation (except a dash) and be placed directly after the last word of the sentence. In your document’s footer, corresponding to each superscript, you’ll detail the footnote. Each footnote should be concise and directly relevant to the referenced text.
For example, consider a statement in an academic paper:
You might use a footnote to cite the sources of this claim or to provide a brief list of historians who support this viewpoint. The footnote might look like this:

Always start the footnote content flush left at the bottom of the page. If a footnote extends beyond one line, indent the subsequent lines. This formatting helps maintain clarity and improves readability.
Additionally, if you reference the same source multiple times throughout your document, you may use shortened forms of the citation after the first full one, or use “Ibid.” if it’s the immediately preceding citation. This keeps your footnotes focused.
How To Write A Footnote
Writing correct footnotes is a valuable skill and an important part of academic writing. Footnotes allow authors to make their writing more credible by providing additional context, source citations, and relevant commentary. There are several aspects to consider in creating informative and accurate footnotes, including clarity of expression, compliance with a consistent formatting style, and attention to detail in citing sources.
- Clarity : Each footnote should be concise. It’s important to provide thorough information, but it’s equally vital to be brief and to the point. Avoid overly complex sentences and focus on the essential details.
- Consistent Formatting : Stick to a consistent formatting style for your footnotes. This includes the font size, indentations, and the spacing of lines. Consistency in formatting helps maintain professionalism and readability.
- Use of Signals : Employ standard scholarly signals such as “see,” “cf.,” “compare,” and others to guide the reader on the nature of the citation or comment. For instance, “cf.” (confer) suggests a comparison, while “see” directs the reader to a source that supports your argument.
- Language Style : Maintain an academic tone that matches the rest of your document. Avoid colloquial language. Your footnotes should enhance the scholarly quality of your paper.
- Reference Accuracy : Double-check your references for accuracy. A footnote with a citation must include all necessary details, such as page numbers, authors’ names, and publication details, formatted according to the appropriate style guide.
- Integration with Text : Each footnote should correlate directly with a specific part of the text. This connection should be clear without the reader having to make assumptions about the relevance of the footnote.
All styles use a similar method for creating footnotes based on their purposes and functionalities that we already mentioned. But there are subtle variations and quirks everywhere, as is typically the case with citation issues.
The Modern Language Association style typically uses parenthetical in-text citations rather than footnotes. However, footnotes can still be used in MLA for supplementary comments, additional references, or explanatory notes that might be too wordy for the main text.
When you do need to use a footnote in MLA style, you would insert a superscript number at the end of the sentence containing the information that requires a footnote. This number corresponds to a footnote at the bottom of the page where you provide the additional information or citation. Footnotes in MLA are mainly used to provide readers with further explanations or to cite sources for quotations and factual statements where in-text citations would disrupt the flow of reading.
Consider a sentence from an academic paper:
| “Despite its initial failure, the treaty significantly influenced international policy in subsequent years.” |
Corresponding Footnote : At the bottom of the page, you would add:
3. While the treaty’s initial reception was lukewarm, historians like Thompson argue that its long-term impact was profound (Thompson 157).

Here, the superscript “1” directs the reader to the footnote at the bottom of the page, where further details and a source are provided. This helps keep the main text clean, while still offering a way to access extra information and detailed citations.
Similar to MLA, the American Psychological Association (APA) style includes in-text citations. However, footnotes may be used for additional material or private correspondence not included in the reference list. APA footnotes are also used for additional comments that expand on a point made in the text, define advanced terminology or present data.
For example, you might find a statement in a paper such as:
| “ |
Corresponding Footnote : A corresponding footnote might include:
4. See Smith (2020) for a detailed analysis of the data and trends from the past decade. The study outlines the variables influencing the outcomes.

In this case, the footnote provides additional source information that supports the statement. Unlike a reference list entry, a footnote in APA can provide direct commentary or specific page numbers, contributing to a more detailed or specific discussion.
Chicago Style
This style is the king of footnotes! The Chicago Manual of Style is widely used in the humanities and historical journals and is distinctive for its extensive use of footnotes for citation purposes. Chicago-style footnotes provide a comprehensive method for citing sources, enabling detailed commentary and source information directly accessible at the bottom of the page. Footnotes here are used for citing sources and providing additional comments or clarifications related to the text. This style is favored for its precision in citation and the ease with which readers can access source details.
Example in text: Consider a statement in a historical analysis:
Corresponding Footnote : At the bottom of the page, the footnote would appear as:
Abraham Lincoln, Speeches and Writings , 1859-1865 (New York: Library of America, 1989), 234.

How should footnotes be written?
Footnotes should be written clearly and concisely. They should provide the necessary information or citation without disrupting the flow of the main text. When writing a footnote, include a superscript number in the text that corresponds to a note at the bottom of the page. The content of the footnote should be directly relevant to the superscript reference, and it should be formatted according to the specific citation style being used (e.g., MLA, APA, Chicago).
How do you format a footnote?
Footnotes are formatted slightly differently depending on the citation style:
- MLA : Use footnotes for supplementary information or personal commentary, not typically for citations.
- APA : Similar to MLA, use footnotes for extra information or personal communications.
- Chicago : Use footnotes extensively for citations, formatting them with full citation details and a period at the end.
Generally, footnotes should start with the corresponding superscript number followed by the text of the footnote. This text should be single-spaced, with a first-line indent, and the same font size as the main text or slightly smaller.
What should a footnote look like?
A typical footnote contains the superscript number that corresponds to the reference in the text, followed by the detailed note or citation. The footnote itself should be at the bottom of the page, separated from the main body of text by a short line or space. It should be short and directly relevant to the reference number.
How do you write the first footnote?
- Insert a superscript number at the end of the sentence that requires additional information, clarification, or source citation. This number should ideally follow any punctuation (except dashes).
- Create the corresponding footnote at the bottom of the page. The footnote itself begins with the same superscript number, followed by the content of the note. Ensure it’s clearly separated from the main text, typically by a horizontal line across the column.
- Format the footnote content according to the guidelines of the citation style you are using. Generally, this includes the source’s author, title, and publication details for citations, or explanatory text for additional information.
What is the easiest footnote format?
The easiest footnote format involves the use of a simple numeric system, as seen in the Chicago Manual of Style. This system is straightforward:
- Numeric indicators : Use consecutive superscript numbers in the text to indicate footnotes.
- Footnote details : At the bottom of the page, the same number appears in superscript followed by the footnote content. This content could be as simple as a full citation or a brief explanatory note.
Chicago’s numeric system is straightforward because it consistently uses numbers for footnotes (as opposed to letters or symbols), which makes it easy to track and manage, especially in documents with many references.
Follow us on Reddit for more insights and updates.
Comments (0)
Welcome to A*Help comments!
We’re all about debate and discussion at A*Help.
We value the diverse opinions of users, so you may find points of view that you don’t agree with. And that’s cool. However, there are certain things we’re not OK with: attempts to manipulate our data in any way, for example, or the posting of discriminative, offensive, hateful, or disparaging material.
Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
More from How to Write an Academic Assignment

Remember Me
Is English your native language ? Yes No
What is your profession ? Student Teacher Writer Other
Forgotten Password?
Username or Email

- Master Your Homework
- Do My Homework
Footnotes for Research Papers: Tips and Tricks
When it comes to research papers, the use of footnotes can provide a useful and effective way to cite sources and add additional information for readers. This article provides an overview of tips and tricks that professors may wish to consider when incorporating footnotes into their research papers. The advantages, disadvantages, conventions used in certain disciplines such as the humanities or social sciences, best practices for referencing sources with accuracy and clarity, guidelines for avoiding plagiarism by properly citing others’ work – all these are important elements that will be discussed herein. In conclusion, this article offers advice on how students can correctly incorporate evidence from outside texts without compromising academic integrity.
I. Introduction to Footnotes in Research Papers
Ii. benefits of using footnotes, iii. guidelines for formatting footnote citations, iv. best practices for incorporating footnote sources into your writing, v. strategies for managing multiple sources with various citation requirements, vi. tips and tricks on how to avoid repetitive use of cited materials in your paper vii. conclusion: maximizing the impact of properly formatted footnotes.
Footnotes in research papers provide additional information to readers and give credit where it is due. They are a crucial component of any academic work as they demonstrate the credibility of an author’s claims. In this section, we will explain how to effectively use footnotes within your own paper so you can gain the most out of them.
- When citing sources, footnotes should always be used . This ensures that no plagiarism has been committed and also gives recognition to those who have influenced your work.
- Include only relevant details when adding footnotes; otherwise, readers may become overwhelmed with unnecessary facts . The footnote should include enough detail for a reader to locate the source being cited without taking away from the main points of your paper.
A well-written research paper contains both primary sources and secondary sources referenced through footnotes. Your professor may require you to cite using certain style guides like APA or MLA but there are also general guidelines which apply regardless of which one you choose:
- All quoted material must be properly attributed , whether it’s a direct quotation or paraphrasing.
The Expanded Academic Reach of Footnotes Footnotes provide an important reference and context to research papers, allowing authors to cite sources more readily. In addition, this method of citation offers a number of additional benefits that can help academics bolster their work. For example, footnotes may allow researchers to go beyond the usual conventions for citations and include details such as lengthier comments or extended discussion on a topic in order to give readers further understanding into their paper’s arguments. From primary source documents like letters from historical figures or data found within court records, citing those materials directly gives readers access not only to the original material but also allows them insight into how they have been used by the author – aiding comprehension and bolstering overall understanding. In his seminal 1995 essay “On Historical Evidence” Henry Flynn explains why utilizing footnotes is so essential for historians: “Historical knowledge requires evidence—the kinds of evidence that support our conclusions about what happened in some past time…footnoting provides information about [primary] source[s]. It makes clear which facts are founded upon direct observation rather than conjecture or hearsay” [1] .
By including appropriate referencing through footnote citation methods, scholars can often enhance both credibility and accessibility when it comes discussing complex topics with different audiences. Including detailed citations helps add depth while simultaneously providing verifiability – thus helping bridge disparate areas together along scholarly lines while still being comprehensible outside specific disciplines. This way one could discuss advances in computer science alongside archaeological findings without diminishing either field’s value due its complexity when referenced properly using footnotes. In summary, there is great potential contained within using footnote referencing correctly; whether it be an undergraduate dissertation cited with Harvard style notation or Phd thesis written according APA format guidelines — depending on content wise use will expand academic reach considerably where done right.
In-Text Citations
When citing sources in the body of your research paper, it is important to follow a few guidelines. Generally speaking, for works with multiple authors, include both surnames each time you cite their work. When mentioning an author’s name outside parentheses or brackets, you should spell out their full name (not just initials). Whenever possible use abbreviated titles instead of complete ones; this will keep your footnotes and endnotes from becoming too long.
For example: As Quigley explains in The Evolutionary Dynamics of Organizations , “Organizations do not act like rational agents attempting to maximize profit”1
Footnote Formats
- Your footnote citation should start at 1 on every page.
- Use superscript numbers after quotes and other reference material that needs a source attribution.
. For example: “Information technology has become central to modern life2”
The corresponding footnote might look something like this: 2 McAdams et al., “Impact of Technology,” 47–49.
Integrating Footnote Sources for Quality Writing The inclusion of external sources is an integral part of writing a research paper, providing facts and perspectives that support your main argument. For this reason, it’s important to incorporate them in the proper format so that they add maximum value to your piece. Here are some tips on best practices for using footnotes:
- Include a full reference at the bottom of each page where you include any source material.
- If multiple works by one author are used within the same footnote section, use short titles with abbreviations instead of repeating their full name.
- Keep all original punctuation from quoted text but omit quotation marks when quoting directly in-text.
Furthermore, make sure you understand what types of materials require citation. Common examples include published books or articles as well as online resources such as websites and blogs. But also consider if ideas have been paraphrased or copied word-for-word – these need citations too! Ultimately, no matter how small an idea might seem compared to others in the paper be mindful not to plagiarize without giving due credit – this will save yourself potential embarrassment and academic penalties down the line.
Harnessing the Power of Citation Management Software
Citing multiple sources in a research paper can be daunting, particularly if they come from different citation styles. To efficiently manage these requirements and resources, researchers should employ specialized software such as Zotero . It allows for easy organization and retrieval of information while providing handy templates for creating citations with various formats. 1
Using Zotero also makes it easier to craft an annotated bibliography. Annotated bibliographies offer brief summaries or evaluations on each source used by the author. This form of assessment helps demonstrate how different pieces of evidence support arguments within a paper. The annotations aid readers who are unfamiliar with the material; allowing them to quickly grasp its significance without having to read through every article individually. 2
VI. Tips and Tricks on How to Avoid Repetitive Use of Cited Materials in Your Paper
When you are writing a research paper with footnotes, it is important to be aware of the amount of repetition that can occur when citing your sources. To minimize the chances for this type of redundancy, here are some tips and tricks:
- Consider paraphrasing instead of directly quoting material.
- Mix up your source citations; try not to stick to one single author or work.
- Add additional commentary between quotations—this will help break up long strings that contain too many quotes.
It’s also useful if you keep track of which specific passages have been used before while working on a project; this allows for greater control over where each citation should go throughout the document. Additionally, look into alternative forms such as indirect citations or cited summaries, both viable options when avoiding repetitive use. VII. Conclusion: Maximizing the Impact Of Properly Formatted Footnotes Ultimately, proper formatting makes all the difference in ensuring accurate references without overusing certain materials. Being mindful about how often individual sources appear within a body text helps writers create an effective balance between original content and supporting evidence from reliable sources. Furthermore, by being conscious about their own knowledge versus what they take from external works helps researchers avoid plagiarism concerns stemming from unintentional copy-paste errors. With these ideas in mind – paraphrasing more than repeating phrases verbatim as well as keeping organized notes along with considering other kinds of referential formats – researchers can maximize their potential impact through correctly formatted footnotes!
English: The use of footnotes in research papers can be invaluable for providing an additional level of detail to support one’s conclusions. However, it is important to ensure that such notes are properly formatted and used correctly in order to maximize the effectiveness of the paper as a whole. This article has provided tips and tricks for those looking to make their footnotes more effective tools within their writing process. With this advice in hand, researchers should have a better understanding on how best utilize this style component within the scope of their work.

Citation & Reference Guide
- Getting Started
- In-Text Citations & Quotations
- Reference List
Footnotes & Quotations
- Bibliography
- Tools and Resources
Every time you use another person's ideas in your assignment, whether you present them in quotations or write them in your own words, you must cite and reference. This page demonstrates how to create citations using the Notes and Bibliography system of the Chicago Citation Style, and how to add quotations to your text. If you are interested in learning about creating references for your bibliography, please consult the Bibliography page.
For more information on citing in the Notes and Bibliography system, and quoting, please consult chapter 14 of The Chicago Manual of Style (17th edition, 2017).
Footnotes (to go to the Quotations section, click here )
General Information
The Chicago Notes and Bibliography Citation Style uses footnotes for the citation of sources in the text:
- Insert a superscript number after the clause or sentence you wish to cite in your assignment. This number refers the reader to a note starting with the same number at the bottom of the same page , also known as a footnote. A footnote offers information on the source being cited, such as the author's name, the title of the work, the year and place of publication, and the page(s) from which a specific piece of information originated.
- In the Chicago Notes and Bibliography style, it is also possible to use endnotes instead of footnotes. They are distinguished by their location. Footnotes can be found at the bottom of the relevant page, whereas endnotes are located at the end of a chapter or a document. Since footnotes are most commonly used by students at Saint Paul University, this guide focuses on that particular note style.
- When a superscript number is found at the end of a sentence, it is placed after the final punctuation mark. When a superscript number is found at the end of a quote, it is placed after the final quotation mark.
- Place an indent of 5 spaces (1 cm) on the first line of every footnote. Do not indent subsequent lines.
- Separate the different components of a footnote (author's name, title of the work, date of publication, etc.) by commas.
Single space footnotes internally. Put double spaces between footnotes.
For example:
In the body of your text:
Studies demonstrate that team building activities are essential to having a harmonious workplace. 1 Polish researchers, in particular, recommend “reserving an afternoon for employees during which they are able to enjoy and collaborate on an activity, whether it is playing board games or taking part in sports.” 2 This is a strategy (which is explained in great detail by Johnson) 3 that was very popular in the 1970s.
At the bottom of the same page:
_______________________________________
1. Jill E. Cumberland, An Introduction to Team Management (New York: MBA Press, 2005), 22.
2. Lara Bobienski and Anatol Kaczka, "Building Stronger Teams in the Corporate World," Management Monthly 34, no. 2 (2014): 134, doi:10.1045/rmh0000009.
3. Harold Johnson, "Team Building Games," in Increasing Team Spirit in the Workplace , eds. Juliet L. Burns and Cara Watson (Sudbury, ON: White Water, 2005), 334-50.
Full and Short Form of Footnotes
The first time you cite a source in your work, the full form of the footnote must be given, which includes the author's full name, the title of the work, and the publication information. A short form is presented in subsequent citations. In this case, the family name, a shortened version of the title (if longer than four words), and the page number(s) are given. Omit the initial A or The, and only include the significant words of the short form of the title.
Here's an example for an online journal article:
1. Trevor Devine, "Relations Between Europe and the Middle East During the Middle Ages: The Case of the Holy Roman Empire," World History and Archaeology Journal 118, no, 3 (2010): 364-65, http://www.whaj.com/issues/index.
14. Devine, "Relations Between Europe," 370.
In the case above, Devine's work was cited at the beginning of the research paper and, again, a few pages later.
Footnote Types
For footnote types, see the Chicago Citations and References page.
- Short direct quotations are quotes that are less than 100 words. You need to put short quotations in quotation marks, and indicate the quote by using a subscript number. You will then include a citation in your footnotes section for the quote. You will also need to create a full reference in your bibliography.
Mitchell investigates “possible causal pathways connecting genetic replicators and social behaviors.” 1
(taken from https://getproofed.com)
- Long direct quotations are quotes that are more than 100 words. You need to start a new paragraph for a long direct quotation, and you do not use quotation marks. The quote is indented 0.5 from the margin and is a freestanding block of text. You will also need to include a footnote and a full reference in your bibliography.
Discussing genetics and behavior, Mitchell writes that:
In order to evaluate the legitimacy of such explanations it is, thus, necessary to explicate the variety of possible causal pathways connecting genetic replicators and social behaviors. If phenotypic variation is the direct object of natural selection, one must understand the underlying relationship between the phenotypic expression and genetic replicators to argue that any such phenotypic trait is, or can be, an adaptation.¹
This suggests the relationship between genetics and behavior in animals is…
Sample Citations in Chicago
To find out what citations (footnotes) done in the Chicago Citation Style look like, consult the following link:
Chicago Style: Sample Notes & Bibliography Paper
Abbreviations
Certain words may be abbreviated in your footnotes.
Here is a list of commonly used abbreviations that are accepted in the Chicago Style. For full information on abbreviations, consult chapter 10 of the The Chicago Manual of Style, 17th Edition, 2017 .
Place Names
Here are guidelines for writing place names in your footnotes. A place name is normally found before the name of a publisher to indicate where a specific work was published. The guidelines for place names can be found in sections 8.44-8.59 (pp. 478-485) of The Chicago Manual of Style :
If the city of publication of a work is not well known or may be confused with another city of the same name, include the abbreviation for the state, province, or country in which that city is located. Use the two-letter postal codes for Canadian provinces and territories, and American states. The capital of the United States, Washington, is always followed by the abbreviation "DC". For example:
If the city of publication is well known, an abbreviation for the state, province, or country is not required. For example:
Digital Object Identifier (DOI)
A digital object identifier, or DOI, is a unique alphanumeric code assigned to an online article. This code helps you quickly identify and locate that article on the web. Some electronic books can also have DOIs.
A DOI is typically found on the first page of an article/book or in the article/book's record in a database. If you are unable to find it, use the free DOI lookup by crossref.org. Please note that not all online articles and e-books are assigned a DOI.
If a DOI is listed with an electronic article or an e-book, make sure to include it in your footnote. This piece of information will make it easier for readers of your research paper to find that article/book.
Here is an example of a DOI:
doi:10.1037/0278-6133.24.2.225
If you have a DOI number and want to find the article or book that it is associated with, simply enter it in the search box on crossref.org .
[Back to top]
- << Previous: Chicago
- Next: Bibliography >>
- Last Updated: May 1, 2024 2:59 PM
- URL: https://ustpaul.libguides.com/citationstyles
- Translation
How to use Footnotes and Endnotes in academic papers
By charlesworth author services.
- Charlesworth Author Services
- 28 January, 2022
How to use and write Footnotes and Endnotes in academic papers
Research papers and reports often include adjuncts such as charts and graphs, tables , diagrams, a hierarchy of headings, citations and references etc. Notes – whether footnotes or endnotes – are an important adjunct. They primarily serve the role of supplying additional information , which, if weaved into the main text, may reduce its ease of readability .
Footnotes vs. endnotes
- Location : By definition, footnotes appear at the foot of a page on which appears the text they support. Endnotes are placed at the end of a paper, a chapter or a book.
- Space : Footnotes, being located at the bottom of each individual page, are constrained by the amount of space available, whereas endnotes, located right at the end of the text, are afforded much more ample room.
- Amount of information (and flow) : The above point (space) is a useful distinction that tells readers what to expect. Footnotes offer small bits of information that you can choose to take in without breaking stride. You could take a quick look and return to the main text on the same page. On the other hand, endnotes may sometimes contain sizeable amounts of information, but you do not have to interrupt your reading of the main text. You can choose to read them once you have reached the end of the document.
Footnotes: Examples
As discussed, footnotes comprise small bits of information short enough to take in at a glance. Here are a couple of examples to illustrate the function of footnotes.
- A text may mention the name of an organisation and use a footnote to explain that the organisation had a different name in the past.
- A text may mention a certain sum of money in Korean Won, and the corresponding footnotes will indicate the equivalent sum in US dollars.
Endnotes: Examples
As discussed too, endnotes can comprise much longer parcels of information. Here too are a couple of examples to illustrate the use of endnotes.
- While you may describe a certain method in your main text, you might use an endnote to outline in more detail some other tangential studies , perhaps from a slightly different field, which used that same method , the results they produced and why this may be of interest.
- You might cite an important quotation within the main body of your text and then include in a related endnote the full paragraph or section from which that quotation was taken, thus enabling interested readers to explore the wider context and additional insights if they wish.
Usage in academic papers and digital documents
As an author of an academic paper, you can choose between footnotes and endnotes depending on how much additional information you want to give. Be aware, however, that footnotes and endnotes, especially endnotes, are virtually never used in research papers in the physical and biological sciences . They may sometimes be used in the social sciences and are more commonly seen in the humanities .
In digital documents, the distinction between footnotes and endnotes and their placement is less important, because the additional information can be connected to the main text with hyperlinks .

Writing footnotes and endnotes
- Superscripts and symbols : Within the main text, both footnotes and endnotes are typically signalled, or announced, using superscript numbers, although, for footnotes, other symbols such as a star or an asterisk (*), a dagger or obelisk (†), a double dagger or diesis (‡), a section mark (§), a pilcrow or blind p (¶), and so on are also employed, usually in that order. Do note that these symbols are never used with endnotes .
- Numbers : With numbered footnotes, the sequence either begins afresh on each page or can be continued throughout within a paper, a chapter (e.g. if the book has chapters by different contributors) or a book. Endnotes are always numbered and the sequence is always continuous .
- Heading for endnotes : Note that the heading for endnotes, when all of them are gathered at the end, is simply ‘Notes’ and not ‘Endnotes’.
- Footnotes for tables : Table titles, column or row headings, or specific cells within a table can all carry footnotes. Those footnotes are explained at the foot of the table in question and not at the foot of a page on which the table appears.
As a scholar, try to familiarise yourself with the idea of notes and their related mechanics as early on in your writing process as possible. These details can seem numerous at first, but once you master them, you will be able to spontaneously incorporate them into your writing.
Maximise your publication success with Charlesworth Author Services.
Charlesworth Author Services, a trusted brand supporting the world’s leading academic publishers, institutions and authors since 1928.
To know more about our services, visit: Our Services
Share with your colleagues
Scientific Editing Services
Sign up – stay updated.
We use cookies to offer you a personalized experience. By continuing to use this website, you consent to the use of cookies in accordance with our Cookie Policy.

Headnotes or Footnotes? A Quick Guide on Organizing Your Research Paper
In academic writing, footnotes, endnotes, and headnotes provide additional information on a particular topic. They are placed in the document as a supplement to the main text. These notes can be inserted into the document as a footer or at the end of a chapter.
The notes should be kept as brief as possible. The objective is to provide more information without distracting the reader. We discuss the different types of notes, how to use them, and their pros and cons.
What Are They and Why Use Them?
A footnote is a reference placed at the bottom of a page or footer. They are referenced in the text in the same way as a citation i.e. the referenced text is followed by a superscript numeral ( 1 ), which corresponds to the numbered footnote at the bottom of the page. When writing your research paper , you would use a footnote for two major reasons:
- To cite sources of facts or quotations
- Provide additional information
The two types of footnotes are:
- Content : Supplements or simplifies substantive information; not detailed.
- Copyright permission : Cites quoted text and any reprinted materials used in the text.
The format of footnotes is fairly standard (see below for specific rules) and is the same as that for references as follows:
Adrian Johns. The Nature of the Book: Print and Knowledge in the Making (Chicago: University of Chicago Press, 1998), 623.
When citing the same reference again, the footnote can be shortened as follows:
Johns. Nature of the Book , 384–85.
Some older journals use “ ibid ” instead of a shortened version of the reference. Ibid is short for the Latin “ ibidem” , which means “in the same place.” This format was previously used in most printed text but rarely used now.
Endnotes are much the same as footnotes except that they are placed at the end your research paper instead of at the bottom of a page. In books, they can be placed after each chapter or at the end of the book.
In many cases, the book publisher decides the best placement. Endnotes, as footnotes, are numerically noted in superscript. The format is the same as that for footnotes.
Headnotes are used as introductions in legal documents or as summaries of the text that follows them. In academic writing, headnotes are explanatory notes included with tables and figures. They are placed below the table itself or just below the figure title and typed in a font size that is smaller than the main text (e.g., 8- or 10-point font). Headnotes are used to define acronyms used, units of measure, significance, etc. Because tables and figures should be able to “stand alone” without the main text, headnotes should always be used.
Format for Footnotes, Endnotes, and Headnotes
Although the format for footnotes and endnotes is almost similar, there are specific rules depending on the journal where the paper is submitted. Most scientific journals use specific reference formats; however, some style guides do not allow footnotes and endnotes.
For example, the Modern Language Association (MLA), which deals specifically with disciplines in the humanities allows limited use of footnotes. These are to provide the reader with other sources for more information on the subject covered. The MLA style for these notes is shown in the example below and the number corresponds to the superscript number noted in the referenced text:
See [name of author], especially chapters 3 and 4, for an insightful analysis of this trend.
MLA suggests using “content” footnotes when necessary to avoid interrupting the text with an explanation or other details.
In contrast, the American Psychological Association (APA), the style for the behavioral and social sciences, does not usually allow footnotes. Your particular journal guidelines will provide that information.
A third style guide, the American Medical Association (AMA) , is used mostly with papers in the biological and medical sciences. AMA also discourages the use of footnotes but allows them on the title page. The information on the title page would include the authors’ names and affiliations, corresponding author, members of affiliated groups, etc.
Pros and Cons
Scientific papers do not usually include footnotes. Endnotes may be used sometimes, but sparingly. Other disciplines, such as law and history, still use them regularly . There are pros and cons to each.
The advantages of using footnotes are that they provide the reader with a fast reference and link to additional information. They are easy to insert and will automatically print. The advantage of using endnotes instead of footnotes is that their placement is less distracting. They also provide the reader with an easy reference list in one place.
According to the Chicago Manual of Style (CMOS), endnotes are preferred to footnotes simply because they don’t clutter up a page. CMOS does caution that it can seem disconcerting to a reader to see pages of notes at the end of a chapter or book, so use them sparingly.
Again, another disadvantage to footnotes is that they tend to interrupt the flow of the text. The reader might feel that he must stop and look at the note before moving on, which can be very distracting. Some disadvantages to endnotes are that the reader must turn to the end of the text or chapter to find the additional information. In books with several chapters, this can be tedious, especially if the endnotes are renumbered in each chapter.
As for headnotes, there are really no drawbacks to using them in tables and figures. They offer the reader helpful information that is readily available as they read the data or interpret a figure.
Bottom Line
The style to which you conform when writing your paper will ultimately depend on the journal’s guidelines. Pay careful attention to its protocols for citations and references and whether it will allow footnotes and endnotes. If allowed, be mindful of the disadvantages of both and consider either greatly limiting them or eliminating them altogether.
Rate this article Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published.

Enago Academy's Most Popular Articles

- Industry News
- Trending Now
ICMJE Updates Guidelines for Medical Journal Publication, Emphasizes on Inclusivity and AI Transparency
The International Committee of Medical Journal Editors (ICMJE) recently updated its recommendations for best practices…

- AI in Academia
- Infographic
- Manuscripts & Grants
- Reporting Research
Can AI Tools Prepare a Research Manuscript From Scratch? — A comprehensive guide
As technology continues to advance, the question of whether artificial intelligence (AI) tools can prepare…

- Manuscript Preparation
- Publishing Research
How to Choose Best Research Methodology for Your Study
Successful research conduction requires proper planning and execution. While there are multiple reasons and aspects…

- Journal Guidelines
How to Use CSE Style While Drafting Scientific Manuscripts
What is CSE Style Guide? CSE stands for Council of Science Editors. Originated in the…

How to Create Publication-ready Manuscripts Using AIP Style Guide
What is AIP Style Guide? The AIP style guide refers to a specific citation format…
What Are the Unique Characteristics of the AMA Style Guide?

Sign-up to read more
Subscribe for free to get unrestricted access to all our resources on research writing and academic publishing including:
- 2000+ blog articles
- 50+ Webinars
- 10+ Expert podcasts
- 50+ Infographics
- 10+ Checklists
- Research Guides
We hate spam too. We promise to protect your privacy and never spam you.
I am looking for Editing/ Proofreading services for my manuscript Tentative date of next journal submission:

What would be most effective in reducing research misconduct?
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- College University and Postgraduate
- Academic Writing
How to Do Footnotes
Last Updated: February 9, 2024 Fact Checked
Sample Footnotes
Placing citations, supplementing text, expert interview, expert q&a.
This article was co-authored by Noah Taxis and by wikiHow staff writer, Jennifer Mueller, JD . Noah Taxis is an English Teacher based in San Francisco, California. He has taught as a credentialed teacher for over four years: first at Mountain View High School as a 9th- and 11th-grade English Teacher, then at UISA (Ukiah Independent Study Academy) as a Middle School Independent Study Teacher. He is now a high school English teacher at St. Ignatius College Preparatory School in San Francisco. He received an MA in Secondary Education and Teaching from Stanford University’s Graduate School of Education. He also received an MA in Comparative and World Literature from the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign and a BA in International Literary & Visual Studies and English from Tufts University. There are 9 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 1,375,472 times.
Footnotes are used generally in academic and professional writing to cite sources or add supplemental information to the main text of a paper. Academic citation styles, such as the Modern Language Association (MLA) and the American Psychological Association (APA), discourage the use of extensive footnotes. Others, such as Chicago style, require them. [1] X Research source

Tip: Footnotes are typically a smaller font size than the main text of your paper. Typically, you won't need to change the default size on the word processing app you're using to write your paper – it will do this automatically when you create a footnote.

- You'll typically only have one footnote per sentence. If you need more than one footnote, place the other footnote at the end of the sentence clause it relates to, outside the closing punctuation. The only exception is if the sentence is broken up by a long dash, in which case, the superscript number goes before the beginning of the dash. [4] X Trustworthy Source Purdue Online Writing Lab Trusted resource for writing and citation guidelines Go to source
Footnote Number in Line with Text: It is well known that patients who suffer from Crohn's and Colitis can have many debilitating symptoms. 1.
Superscripted Footnote Number: It is well known that patients who suffer from Crohn's and Colitis can have many debilitating symptoms. 1

- For some longer papers, such as doctoral theses, footnote numbers may start over with each chapter. If you're unsure if this is appropriate for your project, discuss it with your editor or advisor.
- Most word processing apps will maintain sequential numbering for you, provided you use the app's function for inserting footnotes, rather than trying to type the numbers manually.

- You typically have formatting options that allow you to choose numbers, letters, or other symbols to indicate footnotes. You can also change the size or placement of footnotes, although the default option is usually appropriate.

- For most style guides, the use of footnotes does not replace the need for a list of references at the end of your paper. Even if a full list of references isn't strictly required, it can help place your paper in context.

- For example, suppose you've paraphrased information from a book by Reginald Daily, titled Timeless wikiHow Examples: Through the Ages. If you were using Chicago style, your footnote citation would look something like this: Reginald Daily, Timeless wikiHow Examples: Through the Ages (Minneapolis: St. Olaf Press, 2010), 115.

- For example, suppose later on in your paper you need to cite Reginald Daily's wikiHow book again. Your shortened citation might look something like this: Daily, wikiHow Examples , 130.
Tip: Some citation styles recommend using the abbreviation "id." or "ibid." if you cite to the same source in footnotes immediately following. Others, notably the Chicago Manual of Style, require the use of a shortened citation instead.

- For example, suppose you have a sentence in your text comparing the conclusions in Reginald Daily's book with the observations in another book on the same topic. Your footnote might look something like this: Reginald Daily, Timeless wikiHow Examples: Through the Ages (Minneapolis: St. Olaf Press, 2010), 115; Mary Beth Miller, The wiki Revolution (New York: New Tech Press, 2018), 48.

- For example, if Miller's work reached a conclusion that was contrary to the conclusion Daily reached, your footnote might look something like this: Reginald Daily, Timeless wikiHow Examples: Through the Ages (Minneapolis: St. Olaf Press, 2010), 115; but see Mary Beth Miller, The wiki Revolution (New York: New Tech Press, 2018), 48.
- If you believe it would be helpful to your readers, you can add a brief parenthetical comment after the second source that explains why you included it.

- For example, suppose you want to include a brief explanation as to why you're citing Daily's book, despite the fact that it was published in 2010. Your footnote might look something like this: Reginald Daily, Timeless wikiHow Examples: Through the Ages (Minneapolis: St. Olaf Press, 2010), 115. Although published in 2010, Daily's work provides a jumping-off point for research in this area.

- For example, there may be a basic concept that is beyond the scope of your paper, but important for your readers to understand. You could add a footnote that says "For an explanation of the theory of relativity, see generally" followed by a source or list of sources.
- Typically, these types of footnotes provide your reader with information on something that is tangential to your paper but could be important to help your readers understand the topic as a whole or place your paper in context.

- Some style guides, such as MLA and APA, instruct that parenthetical statements should be included in the main text of your paper, rather than in footnotes. [15] X Trustworthy Source Purdue Online Writing Lab Trusted resource for writing and citation guidelines Go to source
Tip: Keep your footnotes as brief as possible, especially with supplemental footnotes. Don't stray too far off topic or go into a tangent that is only marginally related to the topic of your paper.

- These types of footnotes frequently accompany a quote from a source and may include a citation to the source. For example, if you quoted a source that discussed wikiHow, and you wanted to clarify, you might add a footnote that says "wikiHow examples are used to clarify text in situations where it would be helpful to have a visual cue. Reginald Daily, Timeless wikiHow Examples: Through the Ages (Minneapolis: St. Olaf Press, 2010), 115."

- For example, suppose you are writing a paper about the use of wikiHow articles as sources, and you include a study finding that wikiHow articles are more accurate than articles on major news sites about similar topics. You might add a footnote that says "Despite this fact, the vast majority of professors at public universities in the US do not accept wikiHow articles as sources for research papers."
- You can also use footnotes to make a witty remark, which can add humor and lightheartedness to your paper. However, these types of footnotes should be used extremely rarely, and only when appropriate to the subject matter.

- Before writing, confirm with your professor or organization what style guide you should be using to write your paper. Make sure your use of footnotes follows the rules for that style. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0
- If a footnote includes both a citation and supplemental information, the citation usually comes first. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0

You Might Also Like

Thanks for reading our article! If you’d like to learn more about academic writing, check out our in-depth interview with Noah Taxis .
- ↑ https://www.plagiarism.org/article/what-are-footnotes
- ↑ https://stpauls-mb.libguides.com/citations/footnotes
- ↑ https://www.library.georgetown.edu/tutorials/research-guides/turabian-footnote-guide
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/research_and_citation/mla_style/mla_formatting_and_style_guide/mla_endnotes_and_footnotes.html
- ↑ https://libguides.stonehill.edu/c.php?g=884839&p=6358739
- ↑ https://www.law.cornell.edu/citation/6-300
- ↑ https://libguides.utep.edu/c.php?g=429690&p=2930768
- ↑ https://jle.aals.org/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=1243&context=home
- ↑ https://libguides.liberty.edu/c.php?g=864199&p=6197236
About This Article

To use footnotes as citations, find a sentence you want to cite and insert a "1" at the end of it using the footnote setting in your word processor. Then, insert your citation next to the corresponding "1" at the bottom of the page, like "Reginald Daily, Timeless wikiHow Examples: Through the Ages (Minneapolis: St. Olaf Press, 2010), 115." When you're finished, move onto the next sentence you need to cite and repeat the process. To learn how to use footnotes to clarify information in your paper, read the article! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Ntando Malandela
Aug 29, 2017
Did this article help you?
Kevin Nesbit
Mar 24, 2017
Violet Black
May 21, 2017
Brandi Bumgardner
Dec 9, 2017

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Don’t miss out! Sign up for
wikiHow’s newsletter
- +44 (0) 207 391 9032
Recent Posts
- Academic Integrity vs. Academic Dishonesty: Understanding the Key Differences
- How to Use AI to Enhance Your Thesis
- Guide to Structuring Your Narrative Essay for Success
- How to Hook Your Readers with a Compelling Topic Sentence
- Is a Thesis Writing Format Easy? A Comprehensive Guide to Thesis Writing
- The Complete Guide to Copy Editing: Roles, Rates, Skills, and Process
- How to Write a Paragraph: Successful Essay Writing Strategies
- Everything You Should Know About Academic Writing: Types, Importance, and Structure
- Concise Writing: Tips, Importance, and Exercises for a Clear Writing Style
- How to Write a PhD Thesis: A Step-by-Step Guide for Success
- Academic News
- Custom Essays
- Dissertation Writing
- Essay Marking
- Essay Writing
- Essay Writing Companies
- Model Essays
- Model Exam Answers
- Oxbridge Essays Updates
- PhD Writing
- Significant Academics
- Student News
- Study Skills
- University Applications
- University Essays
- University Life
- Writing Tips

Using Footnotes: The Dos And Don’ts
(Last updated: 29 August 2018)
Since 2006, Oxbridge Essays has been the UK’s leading paid essay-writing and dissertation service
We have helped 10,000s of undergraduate, Masters and PhD students to maximise their grades in essays, dissertations, model-exam answers, applications and other materials. If you would like a free chat about your project with one of our UK staff, then please just reach out on one of the methods below.
In university, your ability to reference sources correctly will have a considerable impact on the mark you receive. The rules you must follow can be tricky to grasp initially, but if you do ever need a quick recap then Oxbridge Essays are always happy to help and give your work a going over to pick up any tiny errors.
The difference between a footnote and a bibliography
Mistakes with footnotes are common . Some students choose to use footnotes without having a firm grasp of how they should be used, or what they should be used for. As a general rule, if you’re not 100 percent sure how a footnote should be used, it’s best not to use one at all.
Footnotes should be included to provide the reader with additional information about the content. The footnote is found at the bottom of the page, and is referenced through a superscript number within the main body of your copy.
The bibliography page is the last section of your essay or dissertation and includes the full citation information for any source cited or referenced through the course of your work. The information contained within a bibliography will provide the reader with full details of the work, including when and where the source was published. A footnote might only include the title of the source.
How to use footnotes correctly
Write your footnotes last – A footnote is commonly, but not always, a shortened version of a citation contained in your bibliography. Whatever content you choose to include, it’s usually best to leave your footnotes until the essay is finished and your bibliography is complete. Place a short reminder in the form of a comment or even a brief footnote to prompt you to fill these in later.
You still need a bibliography – With the occasional exception found in the Oxford referencing system, the use of footnotes does not replace the need for a bibliography at the end of your essay, despite the fact that extensive footnotes can make them seem superfluous. Remember that your bibliography should include all of your reading, and everything that has informed your essay, even if they are not directly referenced. Doing so will prove you’ve done your research too.
Double-check footnotes can be used – Different universities and referencing styles all have their own take on footnotes, so before you start listing footnote citations, check they are actually allowed. Typically, British universities prefer the use of in-text citations.
Footnotes and different referencing styles
Using the Harvard system , which is the predominant form of referencing at universities in the UK, sources are cited in short, parenthetical notes within the text. Footnotes are not allowed. Citations within the text should include the name of the author, the date of the source, and, if necessary, the page numbers you used. The rest of the information, such as the title and publication details, should be included in the bibliography.
Using the Oxford system , citations in the text usually consist of a superscript number which relates to a footnote at the bottom of the page. If you write full bibliographic information in the footnote, you may not have to include a bibliography. However, it’s well worth checking with your tutor beforehand.
When you reference a source in a footnote for the first time using the Oxford system, you must provide full bibliographic information, which includes:
- Author’s initials and surname, title of the article, book or journal, editor (if applicable), publisher name, location and year published
The Chicago citation style , established by the University of Chicago Press, is probably the most commonly used footnote format. Guidelines to help you avoid mistakes with footnotes include: always include a full citation the first time you reference a source; cite author’s names as they appear with texts; don’t replace names with initials; and if no author is listed, organise the entry by title.
A Chicago style footnote citation will take the following form:
- Author’s first name and last name, title in italics, city of publication, publisher and year, page number if relevant.
Don’t forget footnotes
It’s easy to get caught up in the act of writing your essay, but it’s imperative that you include full footnotes and proper referencing whenever possible , as that is what separates academic writing from opinion. At Oxbridge Essays, we know a thing or two about how to use footnotes. And if you have an essay you need a little help with, we can provide full referencing in your chosen style, so get in touch for help.

How to Write an Appendix for your Essay

10 Tips for Polishing your Essays to Achieve Higher Grades

A guide to mature finance, funding and affordability
- dissertation help
- referencing
- writing a good essay
- writing tips
Writing Services
- Essay Plans
- Critical Reviews
- Literature Reviews
- Presentations
- Dissertation Title Creation
- Dissertation Proposals
- Dissertation Chapters
- PhD Proposals
- Journal Publication
- CV Writing Service
- Business Proofreading Services
Editing Services
- Proofreading Service
- Editing Service
- Academic Editing Service
Additional Services
- Marking Services
- Consultation Calls
- Personal Statements
- Tutoring Services
Our Company
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Become a Writer
Terms & Policies
- Fair Use Policy
- Policy for Students in England
- Privacy Policy
- Terms & Conditions
- [email protected]
- Contact Form
Payment Methods
Cryptocurrency payments.
More From Forbes
7 chatgpt prompts to improve your writing.
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter
- Share to Linkedin
Photo by NICOLAS MAETERLINCK/BELGA MAG/AFP via Getty Images
On writing , author David Sedaris once said, “You need to do the best that you can do, and then you need to take the best that you can do and you need to rewrite it, and rewrite it, and rewrite it.” That’s the dynamic essence of the writing process. Writers refine their drafts, just like they continually refine their craft. I didn’t study writing or literature, so I was intimidated when I began contributing to major publications. But my confidence grew with each byline, and I began to find my voice.
While ChatGPT can be an impressive imitator, it can never generate your unique voice and perspective. It can, however, be a powerful tool for improving your writing, whether you’re penning business articles or important emails. It all starts with the right prompts.
Here are seven that you can use to level up your writing skills.
Automate Your Busywork
There are no shortcuts to becoming a better writer. The prolific author Stephen King once said, “If you want to be a writer, you must do two things above all others: read a lot and write a lot.” That said, you can use AI tools to eliminate some of the tedious tasks involved in writing and leave more time for honing your craft. Here are some prompts to delegate your writing “busywork” to ChatGPT.
1. Generating Ideas And Topics
AI shouldn’t do your writing for you. It lacks the necessary human context and isn’t immune to errors. But it can be a powerful writing partner. As Wharton professor Christian Terwiesch (who challenged ChatGPT to come up with product ideas and compared those ideas to student ideas —ChatGPT won), has said , “Everybody should be using ChatGPT to help them generate ideas.” At worst, you reject all of them. At best, you enrich your pool of ideas.
Best High-Yield Savings Accounts Of 2024
Best 5% interest savings accounts of 2024.
Here is a prompt you can use to help get the idea wheels turning:
"I'm an [role/title] writing for [outlet description] targeting [target audience]. Can you suggest some fresh and engaging topics that would appeal to this audience?"
If you’d like ideas related to a certain topic or tailored to a specific style (e.g., a “hot take” versus a personal essay), remember: the more context you provide, the more concise the results.
2. Editing For Grammar And Style
Whether you’re sending an email or publishing an article on a high-traffic website, typos are an embarrassing—and avoidable—faux pas. In today’s world, where internet content exists in perpetuity, anything attached to your name should be error-free. ChatGPT can be a near-instantaneous proofreader. Test out the following prompt:
"Can you proofread this [content] for grammar, punctuation, and style consistency? The intended audience is [audience/recipient]. Please provide a list of any suggested improvements.”
3. Hitting The Right Tone
Spelling and grammar are a crucial part of editing, but they’re relatively objective. Perfecting the tone is more subjective and sometimes more challenging—but just as crucial.
The proper tone can ensure that your text is engaging. It can foster trust and understanding with colleagues and business partners. It can persuade your audience to get on board with your viewpoint. Writing that misses the mark on tone, however, can cause misunderstandings, hurt feelings, damage your credibility, and lose your reader’s interest.
With that in mind, here’s a prompt that can help you achieve the right tone in your writing:
"Can you help me rewrite this [content] for [audience], ensuring it maintains a [describe the desired tone]?
Add context to make ChatGPT’s reply more helpful. For example, if your content should show sensitivity to a certain issue or audience, add it to the prompt.
4. Adding Data And Research
One lesson I’ve learned from contributing to Forbes and other widely-read publications is that my word alone is rarely enough. I can share my personal experiences, but research and data can strengthen any piece of writing.
Instead of researching the traditional way—reviewing your writing and identifying facts that need outside sourcing, then Googling for relevant insight—ChatGPT can speed up the process, leaving you more time to polish those personal anecdotes. Try this prompt:
"I’m writing [describe the content and subject matter] for [target audience] and want to include relevant data and research. Can you review the following text and provide researched-backed statistics and insights on this topic?"
Importantly, always check the sources that ChatGPT generates. It will almost certainly come up with helpful results but they’re not always accurate—that’s where you, human editor, come into play.
Refine Your Craft
To continually improve your writing skills, you can take a page from the habits of professional writers. The following prompts can help you develop practices to become a stronger writer.
5. Daily Writing Prompts
I’ve written before about my morning pages . It’s a great way to clear my head before the day begins and to practice fluidly translating my thoughts into words on paper. If a blank page feels intimidating, writing prompts are a great way to get started. ChatGPT can generate writing prompts in an instant. You can keep it general:
“Can you suggest a couple of writing prompts that I can use to practice the craft of writing?”
Or, if you have a goal in mind, add more context. For example:
“I'm trying to improve engagement with my readers. Can you generate a couple of writing prompts to practice writing engaging content?”
6. Experiment With Different Styles And Voices
If you call your grandmother on the telephone, I’d bet your voice and speaking style sound vastly different from when you’re chatting with your best friend. Writing is the same.
ChatGPT can help you practice toggling between different styles and voices, and in doing so, help you find yours. You can ask ChatGPT for writing prompts to practice a certain style. For example:
“Can you generate three short exercises to help me practice writing in different voices and styles?”
ChatGPT will not only generate exercises, it will also break down the structure and elements of different writing styles and specify the tone.
Or, you can submit text to ChatGPT and ask it to analyze the style and voice. Try this prompt:
“Can you analyze the voice and style of the following text: [insert text].”
I used this prompt to assess the introduction to one of my recent Forbes stories, and ChatGPT said it was “Conversational and Relatable,” “Encouraging and Reassuring,” and “Informative and Practical”—encouraging feedback from my AI editor.
7. Rewrite, Rewrite, Rewrite
In A Moveable Feast , Ernest Hemingway wrote, “The only kind of writing is rewriting.”
If you want to become a writer, you have to embrace rewriting, whether you’re retyping every word or pouring over (and over) a Google Doc draft. Here are a couple of prompts you can use so that ChatGPT can assist in the rewriting process, one excerpt at a time:
“Rewrite this paragraph in the style of [Ernest Hemingway or any other author]."
“Rewrite this introduction so that it sounds like a story in [publication]”
“Rewrite this email so that it will resonate with [audience].”
“Rewrite this paragraph for clarity and concision.”
Importantly, ChatGPT only does part of the work. It falls to the writer to analyze the results, apply those lessons in future drafts, and, of course, to keep writing.

- Editorial Standards
- Reprints & Permissions
Join The Conversation
One Community. Many Voices. Create a free account to share your thoughts.
Forbes Community Guidelines
Our community is about connecting people through open and thoughtful conversations. We want our readers to share their views and exchange ideas and facts in a safe space.
In order to do so, please follow the posting rules in our site's Terms of Service. We've summarized some of those key rules below. Simply put, keep it civil.
Your post will be rejected if we notice that it seems to contain:
- False or intentionally out-of-context or misleading information
- Insults, profanity, incoherent, obscene or inflammatory language or threats of any kind
- Attacks on the identity of other commenters or the article's author
- Content that otherwise violates our site's terms.
User accounts will be blocked if we notice or believe that users are engaged in:
- Continuous attempts to re-post comments that have been previously moderated/rejected
- Racist, sexist, homophobic or other discriminatory comments
- Attempts or tactics that put the site security at risk
- Actions that otherwise violate our site's terms.
So, how can you be a power user?
- Stay on topic and share your insights
- Feel free to be clear and thoughtful to get your point across
- ‘Like’ or ‘Dislike’ to show your point of view.
- Protect your community.
- Use the report tool to alert us when someone breaks the rules.
Thanks for reading our community guidelines. Please read the full list of posting rules found in our site's Terms of Service.
- - Google Chrome
Intended for healthcare professionals
- My email alerts
- BMA member login
- Username * Password * Forgot your log in details? Need to activate BMA Member Log In Log in via OpenAthens Log in via your institution

Search form
- Advanced search
- Search responses
- Search blogs
- Trends in...
Trends in cardiovascular disease incidence among 22 million people in the UK over 20 years: population based study
- Related content
- Peer review
- Geert Molenberghs , professor 4 ,
- Geert Verbeke , professor 4 ,
- Francesco Zaccardi , associate professor 5 ,
- Claire Lawson , associate professor 5 ,
- Jocelyn M Friday , data scientist 1 ,
- Huimin Su , PhD student 2 ,
- Pardeep S Jhund , professor 1 ,
- Naveed Sattar , professor 6 ,
- Kazem Rahimi , professor 3 ,
- John G Cleland , professor 1 ,
- Kamlesh Khunti , professor 5 ,
- Werner Budts , professor 1 7 ,
- John J V McMurray , professor 1
- 1 School of Cardiovascular and Metabolic Health, British Heart Foundation Cardiovascular Research Centre, University of Glasgow, Glasgow, UK
- 2 Department of Cardiovascular Sciences, KU Leuven, Leuven, Belgium
- 3 Deep Medicine, Nuffield Department of Women’s and Reproductive Health, University of Oxford, Oxford, UK
- 4 Interuniversity Institute for Biostatistics and statistical Bioinformatics (I-BioStat), Hasselt University and KU Leuven, Belgium
- 5 Leicester Real World Evidence Unit, Diabetes Research Centre, University of Leicester, Leicester, UK
- 6 College of Medical, Veterinary and Life Sciences, University of Glasgow, Glasgow, UK
- 7 Congenital and Structural Cardiology, University Hospitals Leuven, Belgium
- Correspondence to: N Conrad nathalie.conrad{at}kuleuven.be (or @nathalie_conrad on X)
- Accepted 1 May 2024
Objective To investigate the incidence of cardiovascular disease (CVD) overall and by age, sex, and socioeconomic status, and its variation over time, in the UK during 2000-19.
Design Population based study.
Setting UK.
Participants 1 650 052 individuals registered with a general practice contributing to Clinical Practice Research Datalink and newly diagnosed with at least one CVD from 1 January 2000 to 30 June 2019.
Main outcome measures The primary outcome was incident diagnosis of CVD, comprising acute coronary syndrome, aortic aneurysm, aortic stenosis, atrial fibrillation or flutter, chronic ischaemic heart disease, heart failure, peripheral artery disease, second or third degree heart block, stroke (ischaemic, haemorrhagic, and unspecified), and venous thromboembolism (deep vein thrombosis or pulmonary embolism). Disease incidence rates were calculated individually and as a composite outcome of all 10 CVDs combined and were standardised for age and sex using the 2013 European standard population. Negative binomial regression models investigated temporal trends and variation by age, sex, and socioeconomic status.
Results The mean age of the population was 70.5 years and 47.6% (n=784 904) were women. The age and sex standardised incidence of all 10 prespecified CVDs declined by 19% during 2000-19 (incidence rate ratio 2017-19 v 2000-02: 0.80, 95% confidence interval 0.73 to 0.88). The incidence of coronary heart disease and stroke decreased by about 30% (incidence rate ratios for acute coronary syndrome, chronic ischaemic heart disease, and stroke were 0.70 (0.69 to 0.70), 0.67 (0.66 to 0.67), and 0.75 (0.67 to 0.83), respectively). In parallel, an increasing number of diagnoses of cardiac arrhythmias, valve disease, and thromboembolic diseases were observed. As a result, the overall incidence of CVDs across the 10 conditions remained relatively stable from the mid-2000s. Age stratified analyses further showed that the observed decline in coronary heart disease incidence was largely restricted to age groups older than 60 years, with little or no improvement in younger age groups. Trends were generally similar between men and women. A socioeconomic gradient was observed for almost every CVD investigated. The gradient did not decrease over time and was most noticeable for peripheral artery disease (incidence rate ratio most deprived v least deprived: 1.98 (1.87 to 2.09)), acute coronary syndrome (1.55 (1.54 to 1.57)), and heart failure (1.50 (1.41 to 1.59)).
Conclusions Despite substantial improvements in the prevention of atherosclerotic diseases in the UK, the overall burden of CVDs remained high during 2000-19. For CVDs to decrease further, future prevention strategies might need to consider a broader spectrum of conditions, including arrhythmias, valve diseases, and thromboembolism, and examine the specific needs of younger age groups and socioeconomically deprived populations.
Introduction
Since the 1970s, the prevention of coronary disease, both primary and secondary, has improved considerably, largely attributable to public health efforts to control risk factors, such as antismoking legislation, and the widespread use of drugs such as statins. 1 2
Improvements in mortality due to heart disease have, however, stalled in several high income countries, 3 and reports suggest that the incidence of heart disease might even be increasing among younger people. 4 5 6 Conversely, along with coronary heart disease, other cardiovascular conditions are becoming relatively more prominent in older people, altering the profile of cardiovascular disease (CVD) in ageing societies. The importance of non-traditional risk factors for atherosclerotic diseases, such as socioeconomic deprivation, has also been increasingly recognised. Whether socioeconomic deprivation is as strongly associated with other CVDs as with atherosclerosis is uncertain, but it is important to understand as many countries have reported an increase in socioeconomic inequalities. 7
Large scale epidemiological studies are therefore needed to investigate secular trends in CVDs to target future preventive efforts, highlight the focus for future clinical trials, and identify healthcare resources required to manage emerging problems. Existing comprehensive efforts, such as statistics on CVD from leading medical societies or the Global Burden of Diseases studies, have helped toward this goal, but reliable age standardised incidence rates for all CVDs, how these vary by population subgroups, and changes over time are currently not available. 8 9 10
We used a large longitudinal database of linked primary care, secondary care, and death registry records from a representative sample of the UK population 11 12 to assess trends in the incidence of 10 of the most common CVDs in the UK during 2000-19, and how these differed by sex, age, socioeconomic status, and region.
Data source and study population
We used anonymised electronic health records from the GOLD and AURUM datasets of Clinical Practice Research Datalink (CPRD). CPRD contains information on about 20% of the UK population and is broadly representative of age, sex, ethnicity, geographical spread, and socioeconomic deprivation. 11 12 It is also one of the largest databases of longitudinal medical records from primary care in the world and has been validated for epidemiological research for a wide range of conditions. 11 We used the subset of CPRD records that linked information from primary care, secondary care from Hospital Episodes Statistics (HES admitted patient care and HES outpatient) data, and death certificates from the Office for National Statistics (ONS). Linkage was possible for a subset of English practices, covering about 50% of the CPRD records. Data coverage dates were 1 January 1985 to 31 December 2019 for primary care data (including drug prescription data), 1 April 1997 to 30 June 2019 for secondary care data, and 2 January 1998 to 30 May 2019 for death certificates.
Included in the study were men and women registered with a general practice for at least one year during the study period (1 January 2000 to 30 June 2019) whose records were classified by CPRD as acceptable for use in research and approved for HES and ONS linkage.
Study endpoints
The primary endpoint was the first presentation of CVD as recorded in primary or secondary care. We investigated 10 CVDs: acute coronary syndrome, aortic aneurysm, aortic stenosis, atrial fibrillation or flutter, chronic ischaemic heart disease, heart failure, peripheral artery disease, second or third degree heart block, stroke (ischaemic, haemorrhagic, or unspecified), and venous thromboembolism (deep vein thrombosis or pulmonary embolism). We defined incident diagnoses as the first record of that condition in primary care or secondary care regardless of its order in the patient’s record.
Diseases were considered individually and as a composite outcome of all 10 CVDs combined. For the combined analyses, we calculated the primary incidence (considering only the first recorded CVD in each patient, reflecting the number of patients affected by CVDs) and the total incidence (considering all incident CVD diagnoses in each patient, reflecting the cumulative number of CVD diagnoses). We performed sensitivity analyses including diagnoses recorded on death certificates.
To identify diagnoses, we compiled a list of diagnostic codes based on the coding schemes in use in each data source following previously established methods. 13 14 15 We used ICD-10 (international classification of diseases, 10th revision) codes for diagnoses recorded in secondary care, ICD-9 (international classification of diseases, ninth revision) (in use until 31 December 2000) and ICD-10 codes for diagnoses recorded on death certificates (used in sensitivity analyses only), the UK Office of Population Censuses and Surveys classification (OPCS-4) for procedures performed in secondary care settings, and a combination of Read, SNOMED, and local EMIS codes for diagnoses recorded in primary care records (see supplementary table S1). 16 Supplementary texts S1, S2, and S3 describe our approach to the generation of the diagnostic code list as well as considerations and sensitivity analyses into the validity of diagnoses recorded in UK electronic health records.
We selected covariates to represent a range of known cardiovascular risk factors. For clinical data, including systolic and diastolic blood pressure, smoking status, cholesterol (total:high density lipoprotein ratio), and body mass index (BMI), we abstracted data from primary care records as the most recent measurement within two years before the incident CVD diagnosis. BMI was categorised as underweight (<18.5), normal (18.5-24.9), overweight (25-29.9), and obesity (≥30). Information on the prevalence of chronic kidney disease, dyslipidaemia, hypertension, and type 2 diabetes was obtained as the percentage of patients with a diagnosis recorded in their primary care or secondary care record at any time up to and including the date of a first CVD diagnosis. Patients’ socioeconomic status was described using the index of multiple deprivation 2015, 17 a composite measure of seven dimensions (income, employment, education, health, crime, housing, living environment) and provided by CPRD. Measures of deprivation are calculated at small area level, covering an average population of 1500 people, and are presented in fifths, with the first 20% and last 20% representing the least and most deprived areas, respectively. We extracted information on ethnicity from both primary and secondary care records, and we used secondary care data when records differed. Ethnicity was grouped into four categories: African/Caribbean, Asian, white, and mixed/other. Finally, we extracted information on cardiovascular treatments (ie, aspirin and other antiplatelets, alpha adrenoceptor antagonists, aldosterone antagonists/mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists, angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors, angiotensin II receptor antagonists, beta blockers, calcium channel blockers, diuretics, nitrates, oral anticoagulants, and statins) as the number of patients with at least two prescriptions of each drug class within six months after incident CVD, among patients alive and registered with a general practitioner 30 days after the diagnosis. Supplementary table S2 provides a list of substances included in each drug class. Prescriptions were extracted from primary care records up to 31 December 2019.
Statistical analyses
Categorical data for patient characteristics are presented as frequencies (percentages), and continuous data are presented as means and standard deviations (SDs) for symmetrically distributed data or medians and interquartile ranges (IQRs) for non-symmetrically distributed data, over the whole CVD cohort and stratified by age, sex, socioeconomic status, region, and calendar year of diagnosis. For variables with missing entries, we present numbers and percentages of records with missing data. For categorical variables, frequencies refer to complete cases.
Incidence rates of CVD were calculated by dividing the number of incident diagnoses by the number of patient years in the cohort. Category specific rates were computed separately for subgroups of age, sex, socioeconomic status, region, and calendar year of diagnosis. Age calculations were updated for each calendar year. To ensure calculations referred to incident diagnoses, we excluded individuals, from both the numerator and the denominator populations, with a disease of interest diagnosed before the study start date (1 January 2000), or within the first 12 months of registration with their general practice. Time at risk started at the latest of the patient’s registration date plus 12 months, 30 June of their birth year, or study start date; and stopped at the earliest of death, transfer out of practice, last collection date of the practice, incidence of the disease of interest, or linkage end date (30 June 2019). Disease incidence was standardised for age and sex 18 using the 2013 European standard population 19 in five year age bands up to age 90 years.
Negative binomial regression models were used to calculate overall and category specific incidence rate ratios and corresponding 95% confidence intervals (CIs). 20 Models were adjusted for calendar year of diagnosis, age (categorised into five years age bands), sex, socioeconomic status, and region. We chose negative binomial models over Poisson models to account for potential overdispersion in the data. Sensitivity analyses comparing Poisson and negative binomial models showed similar results.
Study findings are reported according to the RECORD (reporting of studies conducted using observational routinely collected health data) recommendations. 21 We performed statistical analyses in R, version 4.3.3 (R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria).
Patient and public involvement
No patients or members of the public were directly involved in this study owing to constraints on funding and time.
A total of 22 009 375 individuals contributed data between 1 January 2000 and 30 June 2019, with 146 929 629 patient years of follow-up. Among those we identified 2 906 770 new CVD diagnoses, affecting 1 650 052 patients. Mean age at first CVD diagnosis was 70.5 (SD 15.0) years, 47.6% (n=784 904) of patients were women, and 11.6% (n=191 421), 18.0% (n=296 554), 49.7% (n=820 892), and 14.2% (n=233 833) of patients had a history of chronic kidney disease, dyslipidaemia, hypertension, and type 2 diabetes, respectively, at the time of their first CVD diagnosis ( table 1 ).
Characteristics of patients with a first diagnosis of CVD, 2000-19. Values are number (percentage) unless stated otherwise
- View inline
During 2017-19, the most common CVDs were atrial fibrillation or flutter (age-sex standardised incidence 478 per 100 000 person years), heart failure (367 per 100 000 person years), and chronic ischaemic heart disease (351 per 100 000 person years), followed by acute coronary syndrome (190 per 100 000 person years), venous thromboembolism (183 per 100 000 person years), and stroke (181 per 100 000 patient years) ( fig 1 ).

Incidence of a first diagnosis of cardiovascular disease per 100 000 person years, 2000-19. Incidence rates are age-sex standardised to the 2013 European standard population. Any cardiovascular disease refers to the primary incidence of cardiovascular disease across the10 conditions investigated (ie, number of patients with a first diagnosis of cardiovascular disease). See supplementary table S4 for crude incidence rates by age and sex groups. IRR=incidence rate ratio
- Download figure
- Open in new tab
- Download powerpoint
Temporal trends
The primary incidence of CVDs (ie, the number of patients with CVD) decreased by 20% during 2000-19 (age-sex standardised incidence rate ratio 2017-19 v 2000-02: 0.80 (95% CI 0.73 to 0.88)). However, the total incidence of CVD (ie, the total number of new CVD diagnoses) remained relatively stable owing to an increasing number of subsequent diagnoses among patients already affected by a first CVD (incidence rate ratio 2017-19 v 2000-02: 1.00 (0.91 to 1.10)).
The observed decline in CVD incidence was largely due to declining rates of atherosclerotic diseases, in particular acute coronary syndrome, chronic ischaemic heart disease, and stroke, which decreased by about 30% during 2000-19. The incidence of peripheral artery disease also declined, although more modestly (incidence rate ratio 2017-19 v 2000-02: 0.89 (0.80 to 0.98)) ( fig 1 ).
The incidence of non-atherosclerotic heart diseases increased at varying rates, with incidence of aortic stenosis and heart block more than doubling over the study period (2017-19 v 2000-02: 2.42 (2.13 to 2.74) and 2.22 (1.99 to 2.46), respectively) ( fig 1 ). These increasing rates of non-atherosclerotic heart diseases balanced the reductions in ischaemic diseases so that the overall incidence of CVD across the 10 conditions appeared to reach a plateau and to remain relatively stable from 2007-08 (incidence rate ratio 2017-19 v 2005-07: 1.00 (0.91 to 1.10)) ( fig 2 ).

Age standardised incidence of cardiovascular disease by sex, 2000-19. Any cardiovascular disease refers to the primary incidence of cardiovascular disease across the 10 conditions investigated (ie, number of patients with a first diagnosis of cardiovascular disease). IRR=incidence rate ratio
Age stratified analyses further showed that the observed decrease in incidence of chronic ischaemic heart disease, acute coronary syndrome, and stroke was largely due to a reduced incidence in those aged >60 years, whereas incidence rates in those aged <60 years remained relatively stable ( fig 3 and fig 4 ).

Sex standardised incidence of cardiovascular disease in all age groups. Any cardiovascular disease refers to the primary incidence of cardiovascular disease across the 10 conditions investigated (ie, number of patients with a first diagnosis of cardiovascular disease)

Sex standardised incidence of cardiovascular diseases by age subgroups <69 years. Any cardiovascular disease refers to the primary incidence of cardiovascular disease across the 10 conditions investigated (ie, number of patients with a first diagnosis of cardiovascular disease)
Age at diagnosis
CVD incidence was largely concentrated towards the end of the life span, with a median age at diagnosis generally between 65 and 80 years. Only venous thromboembolism was commonly diagnosed before age 45 years ( fig 5 ). Over the study period, age at first CVD diagnosis declined for several conditions, including stroke (on average diagnosed 1.9 years earlier in 2019 than in 2000), heart block (1.3 years earlier in 2019 than in 2000), and peripheral artery disease (1 year earlier in 2019 than in 2000) (see supplementary figure S1). Adults with a diagnosis before age 60 years were more likely to be from lower socioeconomic groups and to have a higher prevalence of several risk factors, including obesity, smoking, and high cholesterol levels (see supplementary table S3).

Incidence rates of cardiovascular diseases calculated by one year age bands and divided into a colour gradient of 20 quantiles to reflect incidence density by age. IQR=interquartile range
Incidence by sex
Age adjusted incidence of all CVDs combined was higher in men (incidence rate ratio for women v men: 1.46 (1.41 to 1.51)), with the notable exception of venous thromboembolism, which was similar between men and women. The incidence of aortic aneurysms was higher in men (3.49 (3.33 to 3.65)) ( fig 2 ). The crude incidence of CVD, however, was similar between men and women (1069 per 100 000 patient years and 1176 per 100 000 patient years, respectively), owing to the higher number of women in older age groups. Temporal trends in disease incidence were generally similar between men and women ( fig 2 ).
Incidence by socioeconomic status
The most deprived socioeconomic groups had a higher incidence of any CVDs (incidence rate ratio most deprived v least deprived: 1.37 (1.30 to 1.44)) ( fig 6 ). A socioeconomic gradient was observed across almost every condition investigated. That gradient did not decrease over time, and it was most noticeable for peripheral artery disease (incidence rate ratio most deprived v least deprived: 1.98 (1.87 to 2.09)), acute coronary syndrome (1.55 (1.54 to 1.57)), and heart failure (1.50 (1.41 to 1.59)). For aortic aneurysms, atrial fibrillation, heart failure, and aortic stenosis, socioeconomic inequalities in disease incidence appeared to increase over time.

Age-sex standardised incidence rates of cardiovascular diseases by socioeconomic status (index of multiple deprivation 2015). Any cardiovascular disease refers to the primary incidence of cardiovascular disease across the 10 conditions investigated (ie, number of patients with a first diagnosis of cardiovascular disease). Yearly incidence estimates were smoothed using loess (locally estimated scatterplot smoothing) regression lines
Regional differences
Higher incidence rates were seen in northern regions (north west, north east, Yorkshire and the Humber) of England for all 10 conditions investigated, even after adjusting for socioeconomic status. Aortic aneurysms and aortic stenosis had the strongest regional gradients, with incidence rates about 30% higher in northern regions compared with London. Geographical variations remained modest, however, and did not appear to change considerably over time (see supplementary figure S2).
Sensitivity analyses
In sensitivity analyses that used broader disease definitions, that included diagnoses recorded on death certificates, that relied on longer lookback periods for exclusion of potentially prevalent diagnoses, or that were restricted to diagnoses recorded during hospital admissions, temporal trends in disease incidence appeared similar (see supplementary figures S3-S6).
Secondary prevention treatments
The proportion of patients using statins and antihypertensive drugs after a first CVD diagnosis increased over time, whereas the use of non-dihydropyridines calcium channel blockers, nitrates, and diuretics decreased over time. Non-vitamin K antagonist oral anticoagulants increasingly replaced vitamin K anticoagulants (see supplementary figure S7).
The findings of this study suggest that important changes occurred in the distribution of CVDs during 2000-19 and that several areas are of concern. The incidence of non-atherosclerotic heart diseases was shown to increase, the decline in atherosclerotic disease in younger people was stalling, and socioeconomic inequalities had a substantial association across almost every CVD investigated.
Implications for clinical practice and policy
Although no causal inference can be made from our data, the decline in rates of ischaemic diseases coincided with reductions in the prevalence of risk factors such as smoking, hypertension, and raised cholesterol levels in the general population over the same period, 22 and this finding suggests that efforts in the primary and secondary prevention of atherosclerotic diseases have been successful. The decline in stroke was not as noticeable as that for coronary heart disease, which may reflect the rising incidence of atrial fibrillation. The variation in trends for peripheral artery disease could be due to differences in risk factors (eg, a stronger association with diabetes), the multifaceted presentations and causes, and the introduction of systematic leg examinations for people with diabetes. 23 24
All the non-atherosclerotic diseases, however, appeared to increase during 2000-19. For some conditions, such as heart failure, the observed increase remained modest, whereas for others, such as aortic stenosis and heart block, incidence rates doubled. All analyses in this study were standardised for age and sex, to illustrate changes in disease incidence independently of changes in population demographics. Whether these trends solely reflect increased awareness, access to diagnostic tests, or even screening (eg, for abdominal aortic aneurysm 25 ) and coding practices, is uncertain. Reductions in premature death from coronary heart disease may have contributed to the emergence of these other non-atherosclerotic CVDs. Regardless, the identification of increasing numbers of people with these problems has important implications for health services, especially the provision of more surgical and transcatheter valve replacement, pacemaker implantation, and catheter ablation for atrial fibrillation. Importantly, these findings highlight the fact that for many cardiovascular conditions such as heart block, aortic aneurysms, and non-rheumatic valvular diseases, current medical practice remains essentially focused on the management of symptoms and secondary prevention and that more research into underlying causes and possible primary prevention strategies is needed. 26 27
These varying trends also mean that the contribution of individual CVDs towards the overall burden has changed. For example, atrial fibrillation or flutter are now the most common CVDs in the UK. Atrial fibrillation is also a cause (and consequence) of heart failure, and these two increasingly common problems may amplify the incidence of each other. Venous thromboembolism and heart block also appeared as important contributors to overall CVD burden, with incidence rates similar to those of stroke and acute coronary syndrome, yet both receive less attention in terms of prevention efforts.
The stalling decline in the rate of coronary heart disease in younger age groups is of concern, has also been observed in several other high income countries, and may reflect rising rates of physical inactivity, obesity, and type 2 diabetes in young adults. 4 6 28 The stalled decline suggests prevention approaches may need to be expanded beyond antismoking legislation, blood pressure control, and lipid lowering interventions to include the promotion of physical activity, weight control, and use of new treatments shown to reduce cardiovascular risk in people with type 2 diabetes. 29 Although CVD incidence is generally low in people aged <60 years, identifying those at high risk of developing CVD at a young age and intervening before problems occur could reduce premature morbidity and mortality and have important economic implications.
Our study further found that socioeconomic inequalities may contribute to CVD burden, and that this association is not restricted to selected conditions but is visible across most CVDs. The reasons behind the observed increase in risk in relation to socioeconomic inequalities are likely to be multifactorial and to include environmental, occupational, psychosocial, and behavioural risk factors, including established cardiovascular risk factors such as smoking, obesity, nutrition, air pollution, substance misuse, and access to care. 30 How these findings apply to different countries is likely to be influenced by socioeconomic structures and healthcare systems, although health inequalities have been reported in numerous countries. 30 One important factor in the present study is that access to care is free at the point of care in the UK, 31 and yet socioeconomic inequalities persist despite universal health coverage and they did not appear to improve over time. Independently of the specificities of individual countries, our findings highlight the importance of measuring and considering health inequalities and suggest that dealing with the social determinants of health—the conditions under which people are born, live, work, and age—could potentially bring substantial health improvements across a broad range of chronic conditions.
Finally, our results reflect disease incidence based on diagnostic criteria, screening practices, availability, and accuracy of diagnostic tests in place at a particular time and therefore must be interpreted within this context. 32 Several of the health conditions investigated are likely to being sought and detected with increased intensity over the study period. For example, during the study period the definition of myocardial infarction was revised several times, 33 34 35 and high sensitivity troponins were progressively introduced in the UK from 2010. These more sensitive markers of cardiac injury are thought to have increased the detection rates for less severe disease. 36 37 Similarly, increased availability of computed tomography may have increased detection rates for stroke. 38 These changes could have masked an even greater decline in these conditions than observed in the present study. Conversely, increased use of other biochemical tests (such as natriuretic peptides) and more sensitive imaging techniques might have increased the detection of other conditions. 39 40 41 The implementation of a screening programme for aortic aneurysm and incentive programmes aimed at improving coding practices, including the documentation of CVD, associated risk factors and comorbidities, and treatment of these, are also likely to have contributed to the observed trends. 25 42 43 As a result, the difference in incidence estimates and prevalence of comorbidities over time may not reflect solely changes in the true incidence but also differences in ascertainment of people with CVD. 44 Nonetheless, long term trends in large and unconstrained populations offer valuable insights for healthcare resource planning and for the design of more targeted prevention strategies that could otherwise not be answered by using smaller cohorts, cross sectional surveys, or clinical trials; and precisely because they are based on routinely reported diagnoses they are more likely to capture the burden of disease as experienced by doctors and health services.
Strengths and limitations of this study
A key strength of this study is its statistical power, with >140 million person years of data. The large size of the cohort allowed us to perform incidence calculations for a broad spectrum of conditions, and to examine the influence of age, sex, and socioeconomic status as well as trends over 20 years. One important limitation of our study was the modest ethnic diversity in our cohort and the lack of information on ethnicity for the denominator population, which precluded us from stratifying incidence estimates by ethnic group. Our analyses were also limited by the unavailability or considerable missingness of additional variables potentially relevant to the development of CVD, such as smoking, body mass index, imaging data, women specific cardiovascular risk factors (eg, pregnancy associated hypertension and gestational diabetes), and blood biomarkers. Further research may also need to consider an even wider spectrum of CVDs, including individual types of valve disease, pregnancy related conditions, and infection related heart diseases. Research using databases with electronic health records is also reliant on the accuracy of clinical coding input by doctors in primary care as part of a consultation, or in secondary care as part of a hospital admission. We therefore assessed the validity of diagnoses in UK electronic health records data and considered it to be appropriate in accordance with the >200 independent validation studies reporting an average positive predictive value of about 90% for recorded diagnoses. 45 Observed age distributions were also consistent with previous studies and added to the validity of our approach. Nevertheless, our results must be interpreted within the context and limitations of routinely collected data from health records, diagnostic criteria, screening practices, the availability and accuracy of diagnostic tests in place at that time, and the possibility that some level of miscoding is present or that some bias could have been introduced by restricting the cohort to those patients with at least 12 months of continuous data.
Conclusions
Efforts to challenge the notion of the inevitability of vascular events with ageing, and evidence based recommendations for coronary heart disease prevention, have been successful and can serve as a model for other non-communicable diseases. Our findings show that it is time to expand efforts to improve the prevention of CVDs. Broadening research and implementation efforts in both primary and secondary prevention to non-atherosclerotic diseases, tackling socioeconomic inequalities, and introducing better risk prediction and management among younger people appear to be important opportunities to tackle CVDs.
What is already known on this topic
Recent data show that despite decades of declining rates of cardiovascular mortality, the burden from cardiovascular disease (CVD) appears to have stalled in several high income countries
What this study adds
This observational study of a representative sample of 22 million people from the UK during 2000-19 found reductions in CVD incidence to have been largely restricted to ischaemic heart disease and stroke, and were paralleled by a rising number of diagnoses of cardiac arrhythmias, valve disease, and thromboembolic events
Venous thromboembolism and heart block were important contributors to the overall burden of CVDs, with incidence rates similar to stroke and acute coronary syndromes
Improvements in rates of coronary heart disease almost exclusively appeared to benefit those aged >60 years, and the CVD burden in younger age groups appeared not to improve
Ethics statements
Ethical approval.
This study was approved by the Clinical Practice Research Datalink Independent Scientific Advisory Committee.
Data availability statement
Access to Clinical Practice Research Datalink (CPRD) data is subject to a license agreement and protocol approval process that is overseen by CPRD’s research data governance process. A guide to access is provided on the CPRD website ( https://www.cprd.com/data-access ) To facilitate the subsequent use and replication of the findings from this study, aggregated data tables are provided with number of events and person years at risk by individual condition and by calendar year, age (by five year age band), sex, socioeconomic status, and region (masking field with fewer than five events, as per CPRD data security and privacy regulations) on our GitHub repository ( https://github.com/nathalieconrad/CVD_incidence ).
Acknowledgments
We thank Hilary Shepherd, Sonia Coton, and Eleanor L Axson from the Clinical Practice Research Datalink for their support and expertise in preparing the dataset underlying these analyses.
Contributors: NC and JJVM conceived and designed the study. NC, JJVM, GM, and GV designed the statistical analysis plan and NC performed the statistical analysis. All authors contributed to interpreting the results, drafting the manuscript, and the revisions. NC, GM, and GV had permission to access the raw data and NC and GM verified the raw data. All authors gave final approval of the version to be published and accept responsibility to submit the manuscript for publication. NC and JJVM accept full responsibility for the conduct of the study, had access to aggregated data, and controlled the decision to publish. They are the guarantors. The corresponding author attests that all listed authors meet authorship criteria and that no others meeting the criteria have been omitted.
Funding: This study was funded by a personal fellowship from the Research Foundation Flanders (grant No 12ZU922N), a research grant from the European Society of Cardiology (grant No App000037070), and the British Heart Foundation Centre of Research Excellence (grant No RE/18/6/34217). The funders had no role in considering the study design or in the collection, analysis, interpretation of data, writing of the report, or decision to submit the article for publication.
Competing interests: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form at www.icmje.org/disclosure-of-interest/ and declare: NC is funded by a personal fellowship from the Research Foundation Flanders and a research grant from the European Society of Cardiology. JMF, PSJ, JGC, NS, and JJVM are supported by British Heart Foundation Centre of Research Excellence. PSJ and JJVM are further supported by the Vera Melrose Heart Failure Research Fund. JJVM has received funding to his institution from Amgen and Cytokinetics for his participation in the steering sommittee for the ATOMIC-HF, COSMIC-HF, and GALACTIC-HF trials and meetings and other activities related to these trials; has received payments through Glasgow University from work on clinical trials, consulting, and other activities from Alnylam, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol Myers Squibb, Cardurion, Dal-Cor, GlaxoSmithKline, Ionis, KBP Biosciences, Novartis, Pfizer, and Theracos; and has received personal lecture fees from the Corpus, Abbott, Hikma, Sun Pharmaceuticals, Medscape/Heart.Org, Radcliffe Cardiology, Alkem Metabolics, Eris Lifesciences, Lupin, ProAdWise Communications, Servier Director, and Global Clinical Trial Partners. NS declares consulting fees or speaker honorariums, or both, from Abbott Laboratories, Afimmune, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Lilly, Hanmi Pharmaceuticals, Janssen, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Novartis, Novo Nordisk, Pfizer, Roche Diagnostics, and Sanofi; and grant support paid to his university from AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Novartis, and Roche Diagnostics. KK has acted as a consultant or speaker or received grants for investigator initiated studies for Astra Zeneca, Bayer, Novartis, Novo Nordisk, Sanofi-Aventis, Lilly, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Boehringer Ingelheim, Oramed Pharmaceuticals, Roche, and Applied Therapeutics. KK is supported by the National Institute for Health and Care Research (NIHR) Applied Research Collaboration East Midlands (ARC EM) and the NIHR Leicester Biomedical Research Centre (BRC). CL is funded by an NIHR Advanced Research Fellowship (NIHR-300111) and supported by the Leicester BRC. PSJ has received speaker fees from AstraZeneca, Novartis, Alkem Metabolics, ProAdWise Communications, Sun Pharmaceuticals, and Intas Pharmaceuticals; has received advisory board fees from AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, and Novartis; has received research funding from AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Analog Devices; his employer, the University of Glasgow, has been remunerated for clinical trial work from AstraZeneca, Bayer, Novartis, and Novo Nordisk; and is the Director of Global Clinical Trial Partners. HS is supported by the China Scholarship Council. Other authors report no support from any organisation for the submitted work, no financial relationships with any organisations that might have an interest in the submitted work in the previous three years, and no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Transparency: The lead author (NC) affirms that the manuscript is an honest, accurate, and transparent account of the study being reported; that no important aspects of the study have been omitted; and that any discrepancies from the study as planned (and, if relevant, registered) have been explained.
Dissemination to participants and related patient and public communities: Results from this study will be shared with patient associations and foundations dedicated to preventing cardiovascular diseases, such as the European Heart Network and the American Heart Association. To reach the public, findings will also be press released alongside publication of this manuscript. Social media (eg, X) will be used to draw attention to the work and stimulate debate about its findings. Finally, the underlying developed algorithms will be freely available for academic use at https://github.com/nathalieconrad/CVD_incidence .
Provenance and peer review: Not commissioned; externally peer reviewed.
This is an Open Access article distributed in accordance with the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY 4.0) license, which permits others to distribute, remix, adapt and build upon this work, for commercial use, provided the original work is properly cited. See: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
- ↵ Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation. Gobal Burden of Diseases Viz Hub. 2023. https://vizhub.healthdata.org/gbd-compare/
- Ananth CV ,
- Rutherford C ,
- Rosenfeld EB ,
- O’Flaherty M ,
- Allender S ,
- Scarborough P ,
- Andersson C ,
- Abdalla SM ,
- Mensah GA ,
- Johnson CO ,
- GBD-NHLBI-JACC Global Burden of Cardiovascular Diseases Writing Group
- Almarzooq ZI ,
- American Heart Association Council on Epidemiology and Prevention Statistics Committee and Stroke Statistics Subcommittee
- Townsend N ,
- Atlas Writing Group, European Society of Cardiology
- Herrett E ,
- Gallagher AM ,
- Bhaskaran K ,
- ↵ Wolf A, Dedman D, Campbell J, et al. Data resource profile: Clinical Practice Research Datalink (CPRD) Aurum. International Journal of Epidemiology. 2019 Mar 11 [cited 2019 Mar 22]; https://academic.oup.com/ije/advance-article/doi/10.1093/ije/dyz034/5374844
- Verbeke G ,
- Molenberghs G ,
- Ferguson LD ,
- ↵ Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency. What coding systems are used in CPRD data? 2023. https://www.cprd.com/defining-your-study-population
- ↵ Department for Communities and Local Government (DCLG). The English Index of Multiple Deprivation 2015: Guidance. 2015; pp1-7. https://www.gov.uk/government/statistics/english-indices-of-deprivation-2015
- ↵ Kirkwood B, Sterne J. Essential medical statistics. 2010.
- ↵ Eurostat’s task force. Revision of the European Standard Population Report. 2013.
- Benchimol EI ,
- Guttmann A ,
- RECORD Working Committee
- ↵ NHS Digital. Health Survey for England, 2021 part 1. https://digital.nhs.uk/data-and-information/publications/statistical/health-survey-for-england/2021
- Criqui MH ,
- ↵ Health and Social Care Information Centre. Quality and Outcomes Framework - Indicators 2011-12. 2011. https://digital.nhs.uk/data-and-information/publications/statistical/quality-and-outcomes-framework-achievement-prevalence-and-exceptions-data/quality-and-outcomes-framework-2011-12
- Jacomelli J ,
- Summers L ,
- Stevenson A ,
- Earnshaw JJ
- Vahanian A ,
- Beyersdorf F ,
- ESC/EACTS Scientific Document Group
- Glikson M ,
- Nielsen JC ,
- Kronborg MB ,
- ESC Scientific Document Group
- Stevenson C ,
- Peeters A ,
- Federici M ,
- Schultz WM ,
- Verbakel JY ,
- Thygesen K ,
- Alpert JS ,
- Joint ESC/ACCF/AHA/WHF Task Force for the Redefinition of Myocardial Infarction
- Joint ESC/ACCF/AHA/WHF Task Force for the Universal Definition of Myocardial Infarction
- Sandoval Y ,
- High-STEACS investigators
- Camargo ECS ,
- Singhal AB ,
- Wiener RS ,
- Schwartz LM ,
- Sappler N ,
- Roalfe AK ,
- Lay-Flurrie SL ,
- Ordóñez-Mena JM ,
- Herbert A ,
- Wijlaars L ,
- Zylbersztejn A ,
- Cromwell D ,
- ↵ NHS Digital. Quality and Outcomes Framework (QOF), 2019-20. Indicator definitions. 2020. https://digital.nhs.uk/data-and-information/publications/statistical/quality-and-outcomes-framework-achievement-prevalence-and-exceptions-data/2019-20
- Pronovost PJ
- Thomas SL ,
- Schoonen WM ,
- Environment
- Science & Technology
- Business & Industry
- Health & Public Welfare
- Topics (CFR Indexing Terms)
- Public Inspection
- Presidential Documents
- Document Search
- Advanced Document Search
- Public Inspection Search
- Reader Aids Home
- Office of the Federal Register Announcements
- Using FederalRegister.Gov
- Understanding the Federal Register
- Recent Site Updates
- Federal Register & CFR Statistics
- Videos & Tutorials
- Developer Resources
- Government Policy and OFR Procedures
- Congressional Review
- My Clipboard
- My Comments
- My Subscriptions
- Sign In / Sign Up
- Site Feedback
- Search the Federal Register
The Federal Register
The daily journal of the united states government.
- Legal Status
This site displays a prototype of a “Web 2.0” version of the daily Federal Register. It is not an official legal edition of the Federal Register, and does not replace the official print version or the official electronic version on GPO’s govinfo.gov.
The documents posted on this site are XML renditions of published Federal Register documents. Each document posted on the site includes a link to the corresponding official PDF file on govinfo.gov. This prototype edition of the daily Federal Register on FederalRegister.gov will remain an unofficial informational resource until the Administrative Committee of the Federal Register (ACFR) issues a regulation granting it official legal status. For complete information about, and access to, our official publications and services, go to About the Federal Register on NARA's archives.gov.
The OFR/GPO partnership is committed to presenting accurate and reliable regulatory information on FederalRegister.gov with the objective of establishing the XML-based Federal Register as an ACFR-sanctioned publication in the future. While every effort has been made to ensure that the material on FederalRegister.gov is accurately displayed, consistent with the official SGML-based PDF version on govinfo.gov, those relying on it for legal research should verify their results against an official edition of the Federal Register. Until the ACFR grants it official status, the XML rendition of the daily Federal Register on FederalRegister.gov does not provide legal notice to the public or judicial notice to the courts.
Proposed Rule
Expanded federal use of the non-federal fss and mss bands.
A Proposed Rule by the Federal Communications Commission on 07/01/2024
This document has a comment period that ends in 62 days. (08/30/2024) Submit a formal comment
Thank you for taking the time to create a comment. Your input is important.
Once you have filled in the required fields below you can preview and/or submit your comment to the Federal Communications Commission for review. All comments are considered public and will be posted online once the Federal Communications Commission has reviewed them.
You can view alternative ways to comment or you may also comment via Regulations.gov at /documents/2024/07/01/2024-14196/expanded-federal-use-of-the-non-federal-fss-and-mss-bands .
- What is your comment about?
Note: You can attach your comment as a file and/or attach supporting documents to your comment. Attachment Requirements .
this will NOT be posted on regulations.gov
- Opt to receive email confirmation of submission and tracking number?
- Tell us about yourself! I am... *
- First Name *
- Last Name *
- State Alabama Alaska American Samoa Arizona Arkansas California Colorado Connecticut Delaware District of Columbia Florida Georgia Guam Hawaii Idaho Illinois Indiana Iowa Kansas Kentucky Louisiana Maine Maryland Massachusetts Michigan Minnesota Mississippi Missouri Montana Nebraska Nevada New Hampshire New Jersey New Mexico New York North Carolina North Dakota Ohio Oklahoma Oregon Pennsylvania Puerto Rico Rhode Island South Carolina South Dakota Tennessee Texas Utah Vermont Virgin Islands Virginia Washington West Virginia Wisconsin Wyoming
- Country Afghanistan Åland Islands Albania Algeria American Samoa Andorra Angola Anguilla Antarctica Antigua and Barbuda Argentina Armenia Aruba Australia Austria Azerbaijan Bahamas Bahrain Bangladesh Barbados Belarus Belgium Belize Benin Bermuda Bhutan Bolivia, Plurinational State of Bonaire, Sint Eustatius and Saba Bosnia and Herzegovina Botswana Bouvet Island Brazil British Indian Ocean Territory Brunei Darussalam Bulgaria Burkina Faso Burundi Cambodia Cameroon Canada Cape Verde Cayman Islands Central African Republic Chad Chile China Christmas Island Cocos (Keeling) Islands Colombia Comoros Congo Congo, the Democratic Republic of the Cook Islands Costa Rica Côte d'Ivoire Croatia Cuba Curaçao Cyprus Czech Republic Denmark Djibouti Dominica Dominican Republic Ecuador Egypt El Salvador Equatorial Guinea Eritrea Estonia Ethiopia Falkland Islands (Malvinas) Faroe Islands Fiji Finland France French Guiana French Polynesia French Southern Territories Gabon Gambia Georgia Germany Ghana Gibraltar Greece Greenland Grenada Guadeloupe Guam Guatemala Guernsey Guinea Guinea-Bissau Guyana Haiti Heard Island and McDonald Islands Holy See (Vatican City State) Honduras Hong Kong Hungary Iceland India Indonesia Iran, Islamic Republic of Iraq Ireland Isle of Man Israel Italy Jamaica Japan Jersey Jordan Kazakhstan Kenya Kiribati Korea, Democratic People's Republic of Korea, Republic of Kuwait Kyrgyzstan Lao People's Democratic Republic Latvia Lebanon Lesotho Liberia Libya Liechtenstein Lithuania Luxembourg Macao Macedonia, the Former Yugoslav Republic of Madagascar Malawi Malaysia Maldives Mali Malta Marshall Islands Martinique Mauritania Mauritius Mayotte Mexico Micronesia, Federated States of Moldova, Republic of Monaco Mongolia Montenegro Montserrat Morocco Mozambique Myanmar Namibia Nauru Nepal Netherlands New Caledonia New Zealand Nicaragua Niger Nigeria Niue Norfolk Island Northern Mariana Islands Norway Oman Pakistan Palau Palestine, State of Panama Papua New Guinea Paraguay Peru Philippines Pitcairn Poland Portugal Puerto Rico Qatar Réunion Romania Russian Federation Rwanda Saint Barthélemy Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha Saint Kitts and Nevis Saint Lucia Saint Martin (French part) Saint Pierre and Miquelon Saint Vincent and the Grenadines Samoa San Marino Sao Tome and Principe Saudi Arabia Senegal Serbia Seychelles Sierra Leone Singapore Sint Maarten (Dutch part) Slovakia Slovenia Solomon Islands Somalia South Africa South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands South Sudan Spain Sri Lanka Sudan Suriname Svalbard and Jan Mayen Swaziland Sweden Switzerland Syrian Arab Republic Taiwan, Province of China Tajikistan Tanzania, United Republic of Thailand Timor-Leste Togo Tokelau Tonga Trinidad and Tobago Tunisia Turkey Turkmenistan Turks and Caicos Islands Tuvalu Uganda Ukraine United Arab Emirates United Kingdom United States United States Minor Outlying Islands Uruguay Uzbekistan Vanuatu Venezuela, Bolivarian Republic of Viet Nam Virgin Islands, British Virgin Islands, U.S. Wallis and Futuna Western Sahara Yemen Zambia Zimbabwe
- Organization Type * Company Organization Federal State Local Tribal Regional Foreign U.S. House of Representatives U.S. Senate
- Organization Name *
- You are filing a document into an official docket. Any personal information included in your comment text and/or uploaded attachment(s) may be publicly viewable on the web.
- I read and understand the statement above.
- Preview Comment
Document Details
Information about this document as published in the Federal Register .
Document Statistics
Published document.
This document has been published in the Federal Register . Use the PDF linked in the document sidebar for the official electronic format.
Enhanced Content - Table of Contents
This table of contents is a navigational tool, processed from the headings within the legal text of Federal Register documents. This repetition of headings to form internal navigation links has no substantive legal effect.
FOR FURTHER INFORMATION CONTACT:
Supplementary information:, enhanced content - submit public comment.
- Submit a public comment on this document
Enhanced Content - Read Public Comments
- This feature is not available for this document.
Enhanced Content - Sharing
- Email this document to a friend
Enhanced Content - Document Print View
- Print this document
Enhanced Content - Document Tools
These tools are designed to help you understand the official document better and aid in comparing the online edition to the print edition.
These markup elements allow the user to see how the document follows the Document Drafting Handbook that agencies use to create their documents. These can be useful for better understanding how a document is structured but are not part of the published document itself.
Enhanced Content - Developer Tools
This document is available in the following developer friendly formats:.
- JSON: Normalized attributes and metadata
- XML: Original full text XML
- MODS: Government Publishing Office metadata
More information and documentation can be found in our developer tools pages .
Official Content
- View printed version (PDF)
This PDF is the current document as it appeared on Public Inspection on 06/28/2024 at 8:45 am. It was viewed 21 times while on Public Inspection.
If you are using public inspection listings for legal research, you should verify the contents of the documents against a final, official edition of the Federal Register. Only official editions of the Federal Register provide legal notice of publication to the public and judicial notice to the courts under 44 U.S.C. 1503 & 1507 . Learn more here .
Federal Communications Commission.
Proposed rule.
In this document, the Office of Engineering and Technology opens a new docket and seeks comment on ways to potentially expand Federal access to non-Federal, including commercial, satellite services.
Interested parties may file comments on or before July 31, 2024; and reply comments on or before August 30, 2024. All filings must refer to ET Docket No. 24-121.
Pursuant to sections 1.415 and 1.419 of the Commission's rules, 47 CFR 1.415 , 1.419 , interested parties may file comments on or before the dates provided in the DATES section of this Proposed Rule. Comments may be filed using the Commission's Electronic Comment Filing System (ECFS). You may submit comments, identified by ET Docket No. 24-121 and referencing this public notice, by any of the following methods:
- Electronic Filers: Comments may be filed electronically using the internet by accessing the ECFS: https://www.fcc.gov/ecfs/ .
- Paper Filers: Parties who choose to file by paper must file an original and one copy of each filing.
- Filings can be sent by hand or messenger delivery, by commercial overnight courier, or by First-Class or overnight U.S. Postal Service mail. All filings must be addressed to the Commission's Secretary, Office of the Secretary, Federal Communications Commission.
- All hand-delivered or messenger-delivered paper filings for the Commission's Secretary are accepted between 8:00 a.m. and 4:00 p.m. at 9050 Junction Drive, Annapolis Junction, MD 20701. All hand deliveries must be held together with rubber bands or fasteners. Any envelopes and boxes must be disposed of before entering the building.
- Commercial overnight deliveries (other than U.S. Postal Service Express Mail and Priority Mail) must be sent to 9050 Junction Drive, Annapolis Junction, MD 20701.
- U.S. Postal Service First-Class, Express, and Priority mail must be addressed to Secretary, Federal Communications Commission, 45 L Street NE, Washington, DC 20554.
- People with Disabilities: Contact the Commission to request reasonable accommodations (accessible format documents, sign language interpreters, CART, etc.) by email: [email protected] or phone: 202-418-0530 or TTY: 202-418-0432.
- Availability of Documents: Comments and ex parte submissions will be available via ECFS. Documents will be available electronically in ASCII, Microsoft Word, and/or Adobe Acrobat.
Nicholas Oros of the Office of Engineering and Technology, at [email protected] or 202-418-0636.
This is a summary of the Office of Engineering and Technology's Public Notice in ET Docket No. 24-121, DA 24-396, released April 26, 2024. The full text of this document is available for public inspection at the following internet address: https://www.fcc.gov/document/oet-seeks-comment-expanded-federal-use-non-federal-bands .
Initial Regulatory Flexibility Act Analysis. The 2013 NPRM (FCC 13-65, 78 FR 39200 ) and 2021 FNPRM (FCC 21-44, 86 FR 30860 ) included Initial Regulatory Flexibility Analyses (IRFA) pursuant to 5 U.S.C. 603 , exploring the potential impact on small entities of the Commission's proposals. The Office of Engineering and Technology invite parties to file comments on the IRFAs in light of this request for supplemental comments.
Paperwork Reduction Act Analysis. This document does not contain any new or modified information collection requirements subject to the Paperwork Reduction Act of 1995, Public Law 104-13 . Thus, it does not contain any new or modified information collection burden for small business concerns with fewer than 25 employees, pursuant to the Small Business Paperwork Relief Act of 2002, Public Law 107-198 , see 44 U.S.C. 3506(c)(4) . Start Printed Page 54403
Ex Parte Presentations. The Commission has treated this proceeding as a “permit-but-disclose” proceeding in accordance with the Commission's ex parte rules. Persons making ex parte presentations must file a copy of any written presentation or a memorandum summarizing any oral presentation within two business days after the presentation (unless a different deadline applicable to the Sunshine period applies). Persons making oral ex parte presentations are reminded that memoranda summarizing the presentation must (1) list all persons attending or otherwise participating in the meeting at which the ex parte presentation was made, and (2) summarize all data presented and arguments made during the presentation. If the presentation consisted in whole or in part of the presentation of data or arguments already reflected in the presenter's written comments, memoranda or other filings in the proceeding, the presenter may provide citations to such data or arguments in his or her prior comments, memoranda, or other filings (specifying the relevant page and/or paragraph numbers where such data or arguments can be found) in lieu of summarizing them in the memorandum. Documents shown or given to Commission staff during ex parte meetings are deemed to be written ex parte presentations and must be filed consistent with rule 1.1206(b). In proceedings governed by rule 1.49(f) or for which the Commission has made available a method of electronic filing, written ex parte presentations and memoranda summarizing oral ex parte presentations, and all attachments thereto, must be filed through the electronic comment filing system available for that proceeding, and must be filed in their native format ( e.g., .doc, .xml, .ppt, searchable .pdf). Participants in this proceeding should familiarize themselves with the Commission's ex parte rules.
Providing Accountability Through Transparency Act: The Providing Accountability Through Transparency Act, Public Law 118-9 , requires each agency, in providing notice of a rulemaking, to post online a brief plain-language summary of the proposed rule. The required summary of this Public Notice is available at https://www.fcc.gov/proposedrulemakings .
The Office of Engineering and Technology invites interested parties to supplement the record with additional comments in this new docket, ET Docket No. 24-121, on possible mechanisms to expand Federal use of the bands used by commercial satellite networks that are not currently allocated for the Federal fixed satellite service (FSS) and mobile satellite service (MSS). Consistent with the Commission's direction to OET in the 2023 Second Report and Order (FCC 23-76, adopted Sept. 21, 2023), the record compiled in response to this Public Notice will be considered in conjunction with the existing record on this issue compiled in ET Docket No. 13-115 and RM-11341, which the Office of Engineering and Technology incorporates herein by reference. In particular, the Office of Engineering and Technology invites commenters to supplement the record on possible approaches to providing Federal earth stations with interference protection when those earth stations are communicating with commercial satellites in bands that are not allocated for Federal FSS and MSS. As noted above, the 2013 NPRM (FCC 13-65, 78 FR 39200 ) proposed to add a co-primary Federal FSS or MSS allocation to several bands together with an allocation table footnote that limits primary Federal use of the bands to earth stations communicating with non-Federal space stations. The 2013 NPRM alternatively proposed to add a footnote to the Allocation Table outlining circumstances under which Federal earth stations operating with non-Federal space stations would be entitled to interference protection. The Office of Engineering and Technology seeks renewed comment on these proposals. The Office of Engineering and Technology also seeks comment on whether there should be any additional modifications to the Allocation Table in connection with either proposal.
The Satellite Industry Association (SIA) suggested an alternative to the 2013 NPRM' s two proposals for providing Federal earth stations with interference protected access to spectrum bands that lack a Federal FSS and MSS allocation. SIA proposed that FSS and MSS allocations be added to the Federal portion of the Allocation Table for these bands along with an indication that the Federal allocation is limited to earth stations only. In addition, SIA proposed adding a footnote to the Allocation Table for these bands indicating that the Commission has exclusive regulatory jurisdiction over the co-primary allocations and that NTIA is responsible for assignments for Federal earth stations authorized to operate in the bands pursuant to the Commission's Part 25 rules. The Office of Engineering and Technology invites commenters to address SIA's proposal as well as any alternative approaches that could be used to provide Federal earth stations with interference-protected access to commercial satellite services. Finally, the Office of Engineering and Technology seeks comment on whether implementing any of these proposals might inhibit future repurposing of these bands or expansion of non-Federal operations and, if so, any approaches that might avoid such inhibition.
As the 2021 FNPRM (FCC 21-44, 86 FR 30860 ) recognized, the spectral landscape in non-Federal FSS and MSS allocations has significantly changed since the 2013 NPRM. As a result, the Office of Engineering and Technology seeks to refresh the record on which FSS and MSS frequency bands that are not allocated for Federal FSS and MSS might meet the needs of Federal agencies for communications with non-Federal satellites. As the Commission first noted in 2013, providing Federal earth stations with interference protection may require that new non-Federal stations, whether satellite earth stations or terrestrial stations, be coordinated with existing Federal earth stations in the FSS and MSS frequency bands to which any new rules would apply. This coordination may require additional effort by non-Federal station applicants and could restrict the locations and operating parameters of new non-Federal stations. Does any future impact on non-Federal operations outweigh the benefits of expanding Federal users' access to these bands? The 2013 NPRM proposed to implement agreed-upon procedures that would be followed by the Commission and NTIA to ensure parity between Federal and non-Federal earth stations that are similar to the procedures currently used by the Commission to coordinate new non-Federal earth stations. Would the procedures discussed in the 2013 NPRM be appropriate for coordination between Federal earth stations and non-Federal stations?
Ronald T. Repasi,
Chief, Office of Engineering and Technology.
[ FR Doc. 2024-14196 Filed 6-28-24; 8:45 am]
BILLING CODE 6712-01-P
- Executive Orders
Reader Aids
Information.
- About This Site
- Accessibility
- No Fear Act
- Continuity Information
Log in using your username and password
- Search More Search for this keyword Advanced search
- Latest content
- Current issue
- JME Commentaries
- BMJ Journals
You are here
- Online First
- Reviewing past and present consent practices in unplanned obstetric interventions: an eye towards the future
- Article Text
- Article info
- Citation Tools
- Rapid Responses
- Article metrics
- http://orcid.org/0000-0002-2780-7897 Morganne Wilbourne 1 ,
- http://orcid.org/0000-0002-9347-8702 Frances Hand 2 ,
- Sophie McAllister 3 ,
- Louise Print-Lyons 4 ,
- Meena Bhatia 3
- 1 Women's and Reproductive Health , Oxford University , Oxford , UK
- 2 Faculty of Law , University of Oxford , Oxford , UK
- 3 Obstetrics and Gynaecology , Oxford University Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust , Oxford , UK
- 4 Oxfordshire Maternity and Neonatal Voices Partnership , Oxford , UK
- Correspondence to Morganne Wilbourne, Women's and Reproductive Health, Oxford University, Oxford OX3 9DU, UK; morganne.wilbourne{at}spc.ox.ac.uk
Many first-time mothers (primiparous) within UK National Health Service (NHS) settings require an obstetric intervention to deliver their babies safely. While the antepartum period allows time for conversations about consent for planned interventions, such as elective caesarean section, current practice is that, in emergencies, consent is addressed in the moments before the intervention takes place. This paper explores whether there are limitations on the validity of consent offered in time-pressured and emotionally charged circumstances, specifically concerning emergency obstetric interventions. Using the legal framework of the Mental Capacity Act, Montgomery v. Lanarkshire Health Board (2015) and McCulloch v Forth Valley Health Board (2023), we argue that while women have the capacity to consent during labour, their autonomy is best supported by providing more information about instrumental delivery (ID) during the antepartum period. This conclusion is supported by some national guidelines, including those developed by the Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists, but not all. Further, we examine the extent to which these principles are upheld in modern-day practice. Data suggest there is relatively little antepartum information provision regarding ID within NHS settings, and that primiparous women do not report a thorough understanding of ID before labour. Based on these results, and bearing in mind the pressures under which NHS obstetric services currently operate, we recommend further research into patient and clinician perceptions of the consent process for ID. Pending these results, we discuss possible modes of information delivery in future practice.
- Decision Making
- Ethics- Medical
Data availability statement
No data are available.
https://doi.org/10.1136/jme-2024-109997
Statistics from Altmetric.com
Request permissions.
If you wish to reuse any or all of this article please use the link below which will take you to the Copyright Clearance Center’s RightsLink service. You will be able to get a quick price and instant permission to reuse the content in many different ways.
X @FrancesHand_
Contributors FH and MW have contributed equally to this project and should be considered to have joint first authorship. They are entitled to reference their own name first on curricula vitae. They have planned the project and drafted the original manuscript. SA, LP-L and MB provided revisions to the original manuscript. LP-L provided data from the Oxfordshire Maternity and Neonatal Voices Partnership. MB and SM provided supervision. MB and SM provided clinical insight and ensured accuracy with respect to current NHS practice in obstetrics. MB is the guarantor and accepts full responsibility for the finished work and the conduct of the study, had access to the data and controlled the decision to publish.
Funding The authors have not declared a specific grant for this research from any funding agency in the public, commercial or not-for-profit sectors.
Competing interests None declared.
Provenance and peer review Not commissioned; externally peer reviewed.
Read the full text or download the PDF:

In silico screening identifies SHPRH as a novel nucleosome acidic patch interactor
- Find this author on Google Scholar
- Find this author on PubMed
- Search for this author on this site
- ORCID record for Allison M. James
- ORCID record for Ernst W. Schmid
- ORCID record for Johannes C. Walter
- For correspondence: [email protected] [email protected]
- ORCID record for Lucas Farnung
- Info/History
- Supplementary material
- Preview PDF
Nucleosomes are the fundamental unit of eukaryotic chromatin. Diverse factors interact with nucleosomes to modulate chromatin architecture and facilitate DNA repair, replication, transcription, and other cellular processes. An important platform for chromatin binding is the H2A–H2B acidic patch. Here, we used AlphaFold-Multimer to screen over 7000 human proteins for nucleosomal acidic patch binding and identify 41 potential acidic patch binders. We determined the cryo-EM structure of one hit, SHPRH, with the nucleosome at 2.8 Å. The structure confirms the predicted acidic patch interaction, reveals that the SHPRH ATPase engages a different nucleosomal DNA location than other SF2-type ATPases, and clarifies the roles of SHPRH’s domains in nucleosome recognition. Our results illustrate the use of in silico screening as a high throughput method to identify specific interaction types and expands the set of potential acidic patch binding factors.
All the screening data is freely available at https://predictomes.org/view/acidicpatch
Competing Interest Statement
J.C.W. is a co-founder of MOMA Therapeutics, in which he has financial interest. All other authors do not declare any competing interests. Read-ers are welcome to comment on the online version of the paper.
https://predictomes.org/view/acidicpatch
https://github.com/walterlab-HMS/2024_af_h2ah2b_acidic_patch_screen
View the discussion thread.
Supplementary Material
Thank you for your interest in spreading the word about bioRxiv.
NOTE: Your email address is requested solely to identify you as the sender of this article.

Citation Manager Formats
- EndNote (tagged)
- EndNote 8 (xml)
- RefWorks Tagged
- Ref Manager
- Tweet Widget
- Facebook Like
- Google Plus One
Subject Area
- Molecular Biology
- Animal Behavior and Cognition (5414)
- Biochemistry (12217)
- Bioengineering (9145)
- Bioinformatics (30165)
- Biophysics (15487)
- Cancer Biology (12593)
- Cell Biology (18082)
- Clinical Trials (138)
- Developmental Biology (9755)
- Ecology (14627)
- Epidemiology (2067)
- Evolutionary Biology (18783)
- Genetics (12554)
- Genomics (17230)
- Immunology (12321)
- Microbiology (29051)
- Molecular Biology (12055)
- Neuroscience (63262)
- Paleontology (463)
- Pathology (1938)
- Pharmacology and Toxicology (3372)
- Physiology (5189)
- Plant Biology (10815)
- Scientific Communication and Education (1710)
- Synthetic Biology (3006)
- Systems Biology (7543)
- Zoology (1692)

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Utilizing footnotes to provide supplementary detail can enrich the body text and reinforce the main argument of the paper. Footnotes may also direct readers to an alternate source for more detail on a topic. Though content footnotes can be useful in providing additional context, it is detrimental to include tangential or convoluted information ...
A footnote is a reference, explanation, or comment 1 placed below the main text on a printed page. Footnotes are identified in the text by a numeral or a symbol . In research papers and reports, footnotes commonly acknowledge the sources of facts and quotations that appear in the text. " Footnotes are the mark of a scholar," says Bryan A. Garner.
APA footnotes use superscript numbers and should appear in numerical order. You can place footnotes at the bottom of the relevant pages, or on a separate footnotes page at the end: For footnotes at the bottom of the page, you can use your word processor to automatically insert footnotes.; For footnotes at the end of the text in APA, place them on a separate page entitled "Footnotes," after ...
Published on March 28, 2022 by Jack Caulfield . Revised on June 7, 2022. Footnotes are notes placed at the bottom of the page in a piece of academic writing and indicated in the text with superscript numbers (or sometimes letters or other symbols). You can insert footnotes automatically in Word or Google Docs.
Navigate to the "References" tab and click on the "Insert Footnote" button. A small superscript number (typically "1") will appear where you positioned the cursor, and a corresponding footnote area will appear at the bottom of the page. Enter your footnote content in this designated area. To insert additional footnotes, repeat the ...
When utilized effectively, footnotes can be used to add depth and perspective to an academic paper. This guide will provide readers with a detailed overview on how to write research papers using footnotes, as well as tips on best practices for utilizing them most effectively within their work. I. Introduction to Research Papers and Footnotes.
Adding lengthy footnotes after the paper has been completed can alter the page where other sources are located [i.e., a long footnote can push text to the next page]. ... Things to keep in mind when considering using either endnotes or footnotes in your research paper: 1. Footnotes are numbered consecutively throughout a research paper, except ...
When looking at research papers with footnotes, three primary types will be encountered: bibliographic notes (or endnotes), explanatory or content notes, and citations. Bibliographic Notes: Also known as "endnotes" these include basic information regarding cited sources such as author name (s), year published, title etc.
Footnotes are a useful tool in academic writing that allows for the inclusion of additional information or comments in a document or text. Typically denoted by a small number or symbol in the main text, footnotes in a paper appear at the bottom of the page and can serve a variety of purposes. For example, footnotes can be used to clarify a ...
Automatically Inserting Footnotes. The reason that footnotes are still popular in some fields is that most word processing programs now include a function that makes it very easy to include footnotes in any paper. In Microsoft Word, clicking Insert > Reference > Footnote allows you to insert footnotes automatically, and automatically numbers them.
For information on footnotes in the Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association see section 2.13 "Footnotes.". For information on using footnotes with MLA see the "Using Notes in MLA Style" article from the MLA Style Center. For information on footnotes in The Chicago Manual of Style see Chapter 14 "Notes and Bibliography."
Elaborating on ideas. Providing additional examples that don't fit into the main text. Footnotes appear at the bottom of the relevant page, while endnotes appear at the end of the paper, just before the Works Cited list. MLA allows the use of either type, but stick to one or the other. Any sources you cite in your footnotes or endnotes must ...
Insert a superscript number at the end of the sentence that requires additional information, clarification, or source citation. This number should ideally follow any punctuation (except dashes). Create the corresponding footnote at the bottom of the page. The footnote itself begins with the same superscript number, followed by the content of ...
Mastering Footnotes in Research Papers • Footnote Tips • Learn how to seamlessly add footnotes to your research paper using the footnote function in your wor...
When it comes to research papers, the use of footnotes can provide a useful and effective way to cite sources and add additional information for readers. This article provides an overview of tips and tricks that professors may wish to consider when incorporating footnotes into their research papers.
Footnotes go at the bottom of the page where the reference occurs; endnotes go on a separate page after the body of the paper. Both use the same formatting guidelines. Within the essay text: put the note number at the end of the sentence where the reference occurs, even if the cited material is mentioned at the beginning of the sentence.
The Chicago Notes and Bibliography Citation Style uses footnotes for the citation of sources in the text: Insert a superscript number after the clause or sentence you wish to cite in your assignment. This number refers the reader to a note starting with the same number at the bottom of the same page, also known as a footnote. A footnote offers ...
Footnotes vs. endnotes. Location: By definition, footnotes appear at the foot of a page on which appears the text they support. Endnotes are placed at the end of a paper, a chapter or a book. Space: Footnotes, being located at the bottom of each individual page, are constrained by the amount of space available, whereas endnotes, located right ...
Mastering Footnotes in Research Papers • Footnote Basics • Learn the simple steps to insert footnotes in your research paper and enhance your citations with ...
In academic writing, footnotes, endnotes, and headnotes provide additional information on a particular topic. They are placed in the document as a supplement to the main text. These notes can be inserted into the document as a footer or at the end of a chapter. The notes should be kept as brief as possible.
1. Use the same font for footnotes as the rest of the paper. Generally, you should use the same font for your entire paper rather than using several different fonts. The default font on your word processing app is usually fine. [2] Tip: Footnotes are typically a smaller font size than the main text of your paper.
How to use footnotes correctly. Write your footnotes last - A footnote is commonly, but not always, a shortened version of a citation contained in your bibliography. Whatever content you choose to include, it's usually best to leave your footnotes until the essay is finished and your bibliography is complete. Place a short reminder in the ...
1. Generating Ideas And Topics. AI shouldn't do your writing for you. It lacks the necessary human context and isn't immune to errors. But it can be a powerful writing partner.
Objective To investigate the incidence of cardiovascular disease (CVD) overall and by age, sex, and socioeconomic status, and its variation over time, in the UK during 2000-19. Design Population based study. Setting UK. Participants 1 650 052 individuals registered with a general practice contributing to Clinical Practice Research Datalink and newly diagnosed with at least one CVD from 1 ...
In addition, SIA proposed adding a footnote to the Allocation Table for these bands indicating that the Commission has exclusive regulatory jurisdiction over the co-primary allocations and that NTIA is responsible for assignments for Federal earth stations authorized to operate in the bands pursuant to the Commission's Part 25 rules.
Save & Close Corporate Research & Development Report 2022. Deloitte's ongoing focus on research and development (R&D) is what has inspired us to carry out this survey - our first research project of this kind since the outbreak of COVID-19 in 2020. Dealmaking in Central Europe. What is the most frequently used purchase price mechanism for M ...
Many first-time mothers (primiparous) within UK National Health Service (NHS) settings require an obstetric intervention to deliver their babies safely. While the antepartum period allows time for conversations about consent for planned interventions, such as elective caesarean section, current practice is that, in emergencies, consent is addressed in the moments before the intervention takes ...
Footnote 8 The early sketches show small houses in either stone or timber, but calculations written in the corners of the sketch papers indicate an insufficient number of dwellings. The first proper version was a three-storey stone house of apartments surrounding the plot, and its castle-like appearance also seems to have pleased the developer.
Nucleosomes are the fundamental unit of eukaryotic chromatin. Diverse factors interact with nucleosomes to modulate chromatin architecture and facilitate DNA repair, replication, transcription, and other cellular processes. An important platform for chromatin binding is the H2A-H2B acidic patch. Here, we used AlphaFold-Multimer to screen over 7000 human proteins for nucleosomal acidic patch ...
Drive, P.O. Box 13528, Research Triangle Park, NC 27709, requests to establish a tolerance in 40 CFR part 180 for residues of the fungicide, boscalid (3-pyridinecarboxamide, 2-chloro-N-(4′- chloro[1,1′-biphenyl]-2-yl)), in or on cereal grain, field corn subgroup 15-22C at 0.2 ppm; cereal grain, sweet corn