

Sign up to our Newsletter
Vet school personal statement: how to write + examples.

Reviewed by:
Jonathan Preminger
Former Admissions Committee Member, Hofstra-Northwell School of Medicine
Reviewed: 4/26/24
Writing your personal statement for vet school is no easy feat, but we’ve got you covered! Follow along for expert tips and successful examples of vet school personal statements.
When it comes to your vet school application, one of the main requirements is your personal statement, which can hold a lot of weight. This essay is your first opportunity to demonstrate your personality and why you would be an excellent candidate beyond your grades.
For some, an excellent personal statement can even help make up for low grades or test scores, so it’s important to get it right.
Luckily, we’ve compiled our best tips and successful vet school personal statement examples to help you through the process. We’ll review tips from our experts on how to write a stand-out essay, examine each of our essay samples, and explain what made them successful.
If you’re currently applying for vet school and are looking for assistance on any part of the application process, don’t hesitate to reach out to one of our experienced admissions advisors at any time. We know how hard it is to get into vet school ; we can help!
Let’s get started!
Get The Ultimate Guide on Writing an Unforgettable Personal Statement

How to Write a Personal Statement for Vet School
Here are some of our top tips when writing a personal statement for vet school.
Write Now, Edit Later
In most writing scenarios, getting started is the hardest part. The best way to relieve that stress is to start writing and keep going. It doesn’t have to be perfect; it can be longer or shorter than the word count initially. The purpose of this method is to pull out all the information and review it later on.
Try writing out your entire story, front to back, of how you grew up and developed an interest in vet school . Make sure to include two to three relevant work experiences.
Once you have nothing left to say, look at what you’ve written and highlight the best, most relevant parts. Then, you can begin editing backward and pull out your best ideas.
Consider Your Unique Perspective
Your story, no matter what it is, has value. Vet schools are competitive, and your admissions committee will see hundreds of applications. Finding a way to frame your unique perspective in your personal statement can help to create a memorable essay that will leave a lasting impression on readers.
Consider your hometown, culture, family, passions, etc. Some students compare their passion for learning a challenging skill like playing the piano to the commitment and dedication required for vet school.
There are no wrong answers here, as long as you can connect what makes you unique to your work experiences and why you would be an excellent vet school candidate.
Revise, Revise, Revise!
It may sound obvious, but there has never been a more important time to revise an essay repeatedly. Remember, vet school is competitive. Something as small as a spelling or grammatical error could make the difference between getting in or not.
Run your work by your teachers, family, and friends for revisions - not rewrites! Every word should sound like something you would authentically say. It would help if you had others help you edit, but ensure the paper still sounds like you.
Vet School Personal Statement Examples
Here are three excellent examples of vet school personal statements. Below you’ll find veterinary school personal statement samples and our explanations of why the essay was successful.
1. Example From the Veterinary School at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign
“Living with my single mother, a nurse who often works over 60 hours a week to support my family, has taught me the value of hard work. From her, I have learned to be passionate and meticulous in all the work that I do. She instilled in me the need to constantly stay busy and involved. I thrive in an environment that challenges me and requires quick thinking. Due to the influence of my mother, I have developed a strong perseverance and sense of determination. My parents’ divorce kept me in a changing environment growing up–I had to adapt to a variety of living situations with little finances to support us. From this, I acquired the skills of being thrifty and knowing how to make sacrifices. The characteristics I have developed through my home environment growing up made me into an ideal candidate for vet school and a future veterinarian – a person who is passionate and dedicated to their work, but who also can cope with a fast-paced environment and problematic situations. For the past seven years, I have applied these qualities to volunteering and caring for animals, developing my interest in veterinary medicine further. When I was thirteen, I volunteered at Birmingham Zoo in Alabama. A large part of my role there included guest education about the animals on exhibit, usually using artifacts such as animal hides and skulls to explain various topics. I worked mainly in the lorikeet exhibit, where I stayed in the exhibit with the birds while guests walked through. My jobs were to watch over the interactions between the birds and the guests, as well as to educate the guests about the birds. From working there, I realized that I really liked getting to educate people about animals, a large portion of the job of a veterinarian. The most influential experience I’ve had on my decision to become a veterinarian was working at Elk Grove Pet Clinic. I have been a kennel attendant there since 2007, where my job is to take care of all the in-house pets, care for the boarding animals, assist in appointments, give medications, and help with the cleaning of the clinic. I have observed numerous surgeries, including routine spay and neuter surgeries, but also more unusual surgeries such as a 6 pound tumor removal from a dog and a surgery on the clinic’s ferret to remove tumors from his pancreas. I have handled and cared for not only cats and dogs, but also macaws, cockatoos, snakes, ferrets, chinchillas, and tortoises. Through working there, I had the opportunity to observe the duties of a private practice vet and see how they normally handle appointments, surgeries, and client communication in difficult situations. I have observed the doctor discussing with clients care options and the possibility of euthanasia, as well as assisted in euthanasia. I have also assisted during emergencies, such as immediate care for a dog hit by a car. Through working at Elk Grove Pet Clinic, I have seen the responsibilities of a vet in caring for an animal in appointments and emergencies, as well as the importance of educating and discussing options with the pet owners. I spent my junior year of college interning at the Champaign County Humane Society. I did an Animal Care Internship in the fall and a Medical/Lab Internship in the spring. The Medical/Lab Internship reaffirmed my decision of wanting to go to veterinary school. While interning, I was able to gain experience performing physical exams, drawing blood, giving treatments and medications, restraining animals, microchipping animals, trimming nails, and learning what signs to look for in a sick animal. I learned how to make and read an ear cytology slide, as well as how to tell if an animal has a bacterial ear infection or ear mites. The animals that I worked with were mainly cats and dogs, but also included guinea pigs, rabbits, ferrets, hamsters, chinchillas, and bearded dragons. I was able to compare the duties of a shelter veterinarian and a private practice veterinarian, which varied due to the financial constraints of a shelter and the fact that the animals in the shelter do not have owners for the veterinarian to consult with. Through my internships, I learned how much I enjoy doing physical exams, finding out what is wrong with an animal, and learning how to treat it. As a veterinarian, I would be able to apply all of these experiences by working in a science that is continually advancing, while contributing to the field through research and public education. The skills that I have developed and the knowledge I have gained through working with animals have strengthened my interest in veterinary medicine. Overall, my experiences with animals, my profound passion for science, and the characteristics I have developed through my home environment have shaped me into an excellent candidate for veterinary school.”
Why this essay works:
In this example, the student begins by connecting their passion for vet school to her childhood experiences. The applicant then lists their valuable experience to demonstrate continued investment in their chosen career path.
They conclude by summarizing their writing - mentioning their passions for animals, science, and experience, all as reasons to accept them into the program.
This essay is strong overall; however, it lacks a bit of reading flow. While it’s good to remind the admissions committee of your achievements and how they helped you grow, keep in mind that they’ve already seen these accomplishments on your CV.
Your personal statement should be focused on telling your story rather than simply listing your achievements. Still, this student wrote a successful essay.
2. Example from the University College Dublin’s Veterinary Medicine Program (Graduate)
“From an early age, it was clear to me that my career path would involve working with animals in a clinical context, as I have always had a passion for science, animal health, and welfare. My first exposure to the veterinary clinical environment was through a high school program, which provided me with the insight into how rewarding and fulfilling it was to be able to use scientific knowledge in order to diagnose, treat, prevent and ideally cure diseases. This has led me to study Biochemistry for my undergraduate degree, as I wanted to have a solid basis for a comprehensive understanding of the metabolism and function of animals in health and disease. During my postgraduate studies, I had conducted a one-year research project working with Trypanosoma brucei, the causative agents for African Trypanosomiasis, an infectious disease of wild and domestic animals and humans of sub-Saharan Africa. As African Trypanosomiasis is a zoonotic disease, this research experience had introduced me to the ‘One Health’ transdisciplinary approach and increased my awareness of the intricate relationship between human and animal health. I have developed a strong appreciation on the importance of both veterinarians and human health professionals working together in order to detect, prevent and control disease outbreaks, as well as the key role that veterinarians play in the bigger picture of society. My latest internship at a companion animal veterinary clinic has taught me the importance of high-quality animal care and optimal health maintenance by providing routine treatments and the appropriate vaccinations. I thoroughly enjoyed working in a veterinary clinical setting, from communicating with the clients to determine the animal’s medical history, aiding during the clinical examinations, using the various laboratory equipment for diagnostics, to the hands-on component of the job such as dental cleaning and assisting during surgical procedures. I want to become a veterinarian because I am dedicated to improving public health goals and outcomes by assessing, investigating and managing animal health and zoonotic disease risks. I will enjoy collaborating with other veterinarians and various health professionals, such as epidemiologists and pathologists, to understand and identify new and emerging diseases and control them, reducing the time they circulate in the animal population. Working as a public health veterinarian would also involve protecting the welfare of animals by ensuring that the standards of animal-keeping are met. This would ensure that the animals, especially livestock, would be healthy, and diseases that could have repercussions on human health will be reduced as much as possible. In this regard, I would also like to foster better collaboration with human health professionals so that future interdisciplinary public health issues can be tackled more efficiently. I believe that my educational background and experience have prepared me well for a veterinary medicine program and I would be honoured to be able to attend the University College Dublin’s Veterinary Medicine (Graduate Entry) program to pursue my career as a veterinarian.”
This applicant displays a passion for veterinary medicine through their unique initiatives and career experiences. Something unique that this student focuses on in their personal statement is how they intend to improve the world of veterinary medicine.
This is an excellent perspective to present in your personal statement! Consider the specific shortcomings you’ve noticed in veterinary medicine and how you intend to improve upon those areas. It’s not essential if you don’t have any ideas, but it looks great on an application.
3. Example from the University of Scranton
“Ever since I can remember I have always had a passion for animals. Their beauty and ability to comfort me are only outmatched by their honesty, loyalty and faithfulness. My path to realizing that my true calling lies in veterinary medicine began when I took a life biology course in high school. In this course I realized my intrigue with animals went far beyond their cute and cuddly parts. I was interested in how they worked from the inside and realized that I should be their doctor. Ever since that first high school class I have focused my educational path in pursuit of becoming a veterinarian. I have volunteered at animal shelters, worked in clinics, shadowed veterinarians and participated in basic science research. Now that I stand at the doorstep of college graduation I cannot imagine my life if I do not attend veterinary school. I shadowed my veterinarian Dr. Henry Nebzydoski and was amazed by his precision, immense knowledge and skill. I learned that in medicine many things can go wrong in a situation, but there are also many ways to solve problems. I loved being able to meet clients whose love for their pets was apparent. That love between an animal and its owner drew me further into the love of veterinary medicine. This shared compassion and love for animals helped me relate to clients. Volunteering at local shelters, I gained more perspective on a career as a veterinarian. I learned how to care for abused and homeless animals and to let go of the animals I had grown to love when it was in their best interest. While shadowing Dr. Michelle Falzone, I observed that each veterinary practice was different. Doctors bring their own personality to make each experience unique; it is never just a routine doctor's visit. I believe that I, too, will bring individuality to the field of veterinary medicine that will benefit my clients. I obtained a job at an emergency animal hospital where the number of patients and the variety of problems presented was vastly different from daytime practices. Veterinarians have to work under time constraints and I learned about the hard choices a family often makes. At first, I thought the patient-doctor bond was absent in these cases, but the doctors make sure the connection is still present by spending time talking to clients and personally calling them to disclose test results. I learn a great deal everyday at the emergency clinic, such as filling medications, diagnosing symptoms and caring for patients and animals in difficult situations. Seeing many prognoses, I learned that there is hope for even the worst one and that a doctor's optimism is important. Most importantly this experience taught me the value of communication skills in veterinary medicine. I have to explain procedures and calm down many patients in order to be able to understand the problems involved with their pets. I will never forget the first time I watched a pet euthanized. Distraught, I thought for a time I would refuse to perform euthanasia in my practice. As I took in more of the doctor-patient interactions, I realized this would not be fair. The bond between a veterinarian and a pet owner becomes very important and is needed throughout the animal's life. The doctor, who has been there throughout the good and difficult times, needs to be there for the owner and the pet when the only choice left is to end the suffering of the animal. For more than a year I have been interning at The Commonwealth Medical College. I am conducting a research study with Dr. John Arnott on the expression of connective tissue growth factor in osteoblasts. This experience provided me with new insights into the importance of the basic sciences and I have developed great respect for their study and place in clinical medicine. More than anything scientific research has taught me humility and that success requires tenacity. This experience has helped me grow as an individual and to find that I am capable of doing things I never dreamed. With my help, we are one step closer to figuring out the steps in the cellular pathway to bone growth and thus are closer to potentially identifying molecules that will enhance bone growth. Veterinary medicine is a love of the science used to care and treat animals. This coincides with the compassion for and communication with pet owners. As these animals are unable to communicate as a human might, veterinarians become dependent on the owner's ability to detect and describe problems. This challenge continues to fascinate me and I look forward to devoting my life to the field of veterinary science. Becoming a veterinarian began as a dream many years ago for me, and is now close to a reality. My dream has always been a simple one - to pursue a love I have harbored since a youth, carrying it from a fascination and love of animals, to creating a successful veterinary practice. I am ready for the next step to fulfill this dream.”
Why this essay works:
This essay is the most successful example we’ve shown due to its readability. Notice how the applicant includes descriptive language when they mention their previous experiences.
They present their personal statement as a cohesive, flowing story from when they first became interested in veterinary medicine to now. It’s simple, compelling, honest, and - perhaps most importantly - easy to read.
These examples of personal statements for vet school should guide you in the right direction when creating yours.
FAQs: Personal Statement for Vet School
Here are our answers to some of the most frequently asked questions about personal statements for vet school.
1. What Should A Vet School Personal Statement Include?
Your vet school personal statement should describe how your passion for veterinary medicine began, and two to three experiences you’ve had that demonstrate how you’ve improved upon that passion. It should flow nicely, be easy to read, and conclude by reinstating your passion for the profession and how you intend to improve the field.
2. How Long Is A Personal Statement For Vet School?
Personal statements for vet school are typically one page or 3,000 words long. However, schools will often give you specific parameters for your essay. Pay close attention to the prompts given to you throughout your application process.
3. How Do You End a Vet School Personal Statement?
There are several ways to end a vet school personal statement successfully. You should always reinstate your passion for veterinary medicine and end on a high note. Suppose you have a specific way you intend to improve veterinary medicine. In that case, the end of your personal statement is an excellent place to state your intentions.
4. What Makes a Good Personal Statement for Vet School?
A good veterinary medicine personal statement must include your passion for the field, showcases unique experiences and qualities, exhibits a strong connection to animals, and utilizes effective storytelling and structure.
It must also exhibit strong and concise writing and attention to detail. It should authentically convey your motivation and leave a lasting impression on the admissions committee.
5. How Important Are Personal Statements for Veterinary Schools?
A personal statement for veterinary school is extremely important. It provides applicants a platform to showcase their individuality, express their motivation, and demonstrate their suitability for the veterinary profession.
Personal statements offer insights into applicants' personal and professional qualities that may not be apparent from other application components.
Final Thoughts
Your vet school personal statement should be thoughtful, heartfelt, and informative. You should ensure that your story is easy to read by using descriptive language and lining up the highlights of your work experience in order.
Consider your unique perspective. Remember, these programs are competitive. Putting your unique twist on your essay will help you stand out from the pack and remain in the minds of the admissions committee.
Good luck!
Schedule A Free Consultation
You may also like.

Medical Schools in Nebraska: List + How to Get In

How to Succeed as a Johns Hopkins Premed


How to Write Great Personal Essays for Veterinary School
If you are getting ready to go to veterinary school, the first step in your formal acceptance process is preparing your application through the Veterinary Medical College Application Service (VMCAS). There are many sections to this application, from general demographic information to a list of your academic history and veterinary experience, and this application takes a lot of time to fill out. While most of the application is just about listing facts, one of the more daunting aspects for many hopeful applications is crafting the perfect personal statement for the VMCAS.
The VMCAS personal statement or essay portion has changed some over the years, from a one or two-page essay during my application cycle to the most recent three essay questions with specific prompts. The prompts from the 2020 application cycle were the following:
- There are many career choices within the veterinary profession. What are your future career goals and why?
- In what ways to veterinarians contribute to society and what do you hope to contribute?
- Consider the breadth of society which veterinarians serve. What attributes do you believe are essential to be successful within the veterinary profession? Of these attributes, which do you possess and how have you demonstrated these in the past?
Regardless of the format of the essay portion when you apply to veterinary school, the following tips are sure to help you create a great essay portion for your own VMCAS application.
1. Read the Requirements and Stick to Them!
This is an obvious suggestion, but it is important to adhere to the following requirements that VMCAS lists.
- Keep your topic general (not program-specific), as this application will be sent to multiple veterinary colleges.
- Stay within the character limits! Last year it was 2,000 characters per essay.
- Use your own words and DO NOT plagiarize.
- Use simple formatting.
2. Don’t Try to Re-List Your Experience and Achievements
The admissions committee members can see the rest of your application, where you will have plenty of space to list all of the bullet points on your resume up to this date. So when it comes to the essay questions, don’t waste time trying to re-highlight your previous experiences within your answers. Focus on answering the prompts directly without feeling the need to list your qualifications.
Except for your answer to question three, you do not even need to list any specific past examples. And when you do get to essay number three, keep in mind that you can think outside the box and are not limited to instances where you demonstrated these qualities in a veterinary-related capacity. Your attributes and personality traits outside of school and veterinary clinics are just as reflective of who you are. And who you are outside of a veterinary clinic or formal education setting can have a big impact on your personality and future success as a veterinarian.
3. Don’t Be Vague
Come up with specific examples for your essay answers that really help the admissions committee get to know you. Telling the admissions committee that you want to help improve the lives of animals doesn’t really tell them anything. You want to demonstrate insight, maturity, and depth in your essay. Show that you put a lot of thought into your answers.
Instead of generally helping animals, maybe you want to contribute to society by donating your time at a local humane society providing veterinary care at lower cost to qualifying low-income households. Maybe you want to work in rural Iowa to help decrease the barriers to accessing veterinary care for those that live in underserved regions of the United States.
Being specific will help you demonstrate more of who you are and help you stand out from the crowded pool of applications.
4. Avoid the Cliches
Another way to stand out with unique answers is to avoid cliches. For example, you probably don’t need to mention that an essential attribute to becoming a successful veterinarian is to “love animals.” Instead, think about things that are less cliche but just as essential and more specific, such as being a great communicator, so that you can improve the lives of animals by clearly discussing the importance of preventative care with a dog’s caretaker.
In addition to loving animals, it can be cliche to discuss that you have wanted to work with animals since you were young or that you feel that veterinary medicine your passion or calling. When you craft your answers to these essays it can help to write down multiple ideas for answers and get rid of the obvious responses. The more obvious the response, the less likely it will be to stand out from other applications.
5. Match Your Future Goals with Your Experience
Make sure your future goals are in line with the experience that you have listed on your VMCAS application. If not, explain why. For example, if most of your veterinary experience has been obtained working with cats and dogs, it would be expected that you are interested in working a small animal veterinary clinic after graduation.
If your future goals do not match your experience, let the admissions committee know why. Maybe you had a recent experience assisting with a research project and found purpose in research as a way to improve the lives of cats and dogs.
By explaining any discrepancy between your future goals and your past experience, you create a cohesive application and don’t leave the admissions committee wondering about the differences.
6. Set a Confident and Positive Tone
When you discuss your future goals, write about the good things that you are going to do WHEN you graduate from veterinary school. Not the things you will do IF you graduate from veterinary school. This will help you come across as confident and capable. Other people are more likely to believe in you when you also believe in your success.
And don’t make any excuses or focus on any negatives in these 3 short essays. You want to leave the admissions committees with a positive overall impression after they finish reading your essay responses.
7. Pick 3-5 Main Points for Each Answer
Since you only have 2,000 characters in which to write a great essay answer to each question, it can be helpful to list out your ideas and main points before you begin writing. Then you can review your ideas and pick the 3-5 strongest ideas for each answer. Throw out any ideas that seem cliche or vague.
By focusing your thoughts ahead of time, you can write a more clear and concise essay that clearly answers the question.
8. Write Your Essay Answers without Focusing on the Character Count
Once you have picked your main 3-5 points, write without focusing the character count. After you have written what you want to convey, read the essay and then cut out information that you don’t need and work on shortening sentences.
No fluff is needed, get straight to the point. Any sentence that isn’t directly supporting your answer can be shortened or removed. And limit descriptive words to help get as much information as possible across in your 2000 character limit.
That being said, if you have the opposite problem and your essay is not close to the 2000 character limit, consider adding another point to that essay. You do want to try and fill most of the space allowed.
9. Proofread, Proofread, Proofread!
Type your answers out in a program like Microsoft Word or Google Docs so that you can easily proofread your essays. I recommend having at least 3 other people read through your essays to look for any spelling or grammar mistakes.
When you proofread the essays yourself, read them aloud so that it is easier to catch any errors.
If you don’t have anyone in your life to help you proofread your personal statement, then head over to The Student Doctor Network Pre-Veterinary Forum . There is a whole topic thread of people willing to help read personal statements for the prospective class of 2025!
Time to Get Writing
Good luck in your journey to veterinary school! I remember how stressful the application process can be, but remember to take a deep breath and leave plenty of time to fill out your application in as stress-free a manner as possible.
And if you are looking for more advice on writing your personal essays, check out this great guide for writing a personal statement from Loop Abroad . It is very thorough and helpful!
The writer of this blog, Dr. Kate, has been practicing veterinary medicine since 2014. She works at a small animal practice, focusing on dogs and cats. In her free time, she enjoys hiking with her two dogs. You can find out more about her adventures with her pups on PawsitivelyIntrepid.com
Recent Posts
What are the typical work hours of a veterinarian?
There are many different careers a veterinarian can pursue, and therefore there are also many different work schedules that a veterinarian can have. But let's start by taking a look at the most...
How to Get Into Veterinary School with a Low GPA
Your grade point average (GPA) is an important part of your veterinary school application. But just how high does your GPA have to be? And what if your GPA isn't high enough? The answers to these...
- Veterinary School
VMCAS Essay Examples

VMCAS essay examples are a great place to start when you're preparing to apply to veterinary school. After researching vet school rankings and looking into the best vet schools in your chosen area, you’ve finally decided on the schools you would like to apply to. One of the items you’ll need to include in your VMCAS application is a personal essay. We’re here to show you how to highlight your personal story and provide you with some VMCAS essay examples to make the process easier.
>> Want us to help you get accepted? Schedule a free strategy call here . <<
Listen to the blog!
Article Contents 10 min read
Personal essay example 1.
I grew up in a family with no pets. An experimental goldfish or two, but there is no family dog I can look back on fondly. My parents were both immigrants who left their homes young and understandably focused on providing for their kids and ensuring we did well in school.
But like a lot of young kids, I developed a love and fascination for horses. My parents thought it was a phase, but when my requests for horseback riding lessons continued year after year, they finally relented and took me to a local farm for lessons. I remember my first connection with the pony. I felt like it could understand, hear, and accept me, without being able to say a word. That’s when I started to understand the relationship that people have with the animals in their lives, and I wanted nothing more than to experience it again.
Want to know how to answer the hardest MMI Questions? Watch this video:
Several years later, I jumped at the opportunity to help out at the riding camp during the summer break. I didn’t realize until then how different it is to participate in the care of the animals, instead of just passively riding them. Every chore was to make sure the horses were comfortable, healthy, and happy. I felt like they relied on me, and they, in turn, provided peace and enjoyment to the people around them.
Since then, I’ve volunteered at the Second Chances Animal Sanctuary for several years, developing and applying the knowledge I’ve gained from my biology and zoology classes. My proudest moments were when we were able to help a family’s beloved pony walk again after a leg fracture that might have otherwise resulted in euthanasia. Being able to give the family hope when they thought there was nothing we could do was amazing, and giving the animal a chance at a full life was incredibly fulfilling.
I developed a special interest in animal orthopedics while completing an internship at the Main Street Animal Hospital. What I want more than anything is to be a vet who works within the field of orthopedics for large animals, developing therapies and treatment programs to help regain mobility. These animals are often essential to rural businesses or farms and should get the care a partner deserves. The sense of responsibility I feel toward them and their quality of life continues to drive me to pursue the skills and knowledge I need to care for them as a practitioner of veterinary medicine.
My parents didn’t believe in going to conventional places when it came to vacations. They wanted to see places that were unusual and immerse themselves in everything the locals did while they were there.
This meant that my brother and I were regularly exposed to places that were very culturally different from ours, but also climates that were totally new to us. As I got older, what struck me wasn’t always the exotic animals and plants, but the relationship a lot of people had with wildlife, and how it was different from what I experienced at home. At home in the urban setting where I lived, “wildlife” was what got into your garbage if you didn’t secure the lid properly. It was what dug through your flower pots at night. But in a lot of countries I visited, wildlife was an inseparable part of everyday life, and vital to the local economies. The animals there were valued as pollinators, decomposers, and yes, food. It made me curious about how people could value and experience wildlife back in the city where I lived.
At the beginning of high school, a friend and I decided to volunteer at the city’s wildlife center. As untrained volunteers we would mostly be cleaning cages and measuring feed for the animals, but I had never been so excited. The vets and vet technicians were so dedicated and resourceful. They relied on local donations, and the center survived on a shoestring budget, but they made it work. To them, even the common sparrows deserved kindness and care. Witnessing that level of empathy from vets and vet techs is humbling and inspiring.
Since that experience, I’ve taken as many opportunities as possible to work with wildlife organizations as possible. I volunteered at a summer program that was specifically created to help and preserve local turtle species, treating and tracking injured animals to ensure their survival. I’ve also participated in local songbird data collection, aiding in gathering information about migration patterns and population decline.
What I want is to be one of those veterinarians who cares for animals that don’t have anyone to care for them, or are treated like nuisances. Dogs and cats are loved and cared for, but so many city-dwelling animals are displaced or trapped or impacted negatively by humans. Working at a wildlife organization has taught me to be creative and resourceful, making the most out of the materials and equipment we had. I want to show people that even the plainest city wildlife deserves respect and help when they need it.
The VMCAS essay is one of the application components required by the Veterinary Medical College Application Service when you use their process to apply to vet schools. This essay is intended to provide admissions committees with “a clear picture of who you are and, most importantly, why you want to pursue a career in veterinary medicine.” While they may have your credentials on paper through your vet school resume , they might not have a good idea of what your personality is like, or what your goals are. Even your veterinary school letters of recommendation only represent who you are through someone else’s eyes, not your own.
Different from your vet school letter of intent , which must make a clear connection between your background, training, areas of interest, and the objectives and mission of your chosen veterinary school program, the VMCAS essay is more personal. It’s your chance to show the admissions committee why you love veterinary medicine and why you think you will make a good veterinarian.
Requirements
The VMCAS essay or vet school personal statement can be a maximum of 3,000 characters (including spaces). This comes out to about one page of writing. It’s important to make sure your essay falls within the character count and contains all the listed requirements .
Note that the application site doesn’t have spell-check, and you can’t edit your work once you’ve submitted it. Making sure your punctuation and spelling is correct is the most basic way to show you’ve paid attention to the details in your essay. If you aren’t sure about a word or grammar choice, look it up so you know you’ve used it properly.
For help writing your essay, you could consider medical school personal statement editing services, which can easily be modified by an advisor to suit veterinary school requirements. Engaging an expert, such as those at BeMo Academic Consulting, is well worth it to improve your application documents and stand out from the crowd.
Is the VMCAS Essay Important?
The personal essay might not seem as formal or intensive as other parts of your application, but it’s still very important and can help or hurt your chances of being accepted into a program. A great essay showcases your personality traits, your sense of responsibility, as well as your motivations for going into veterinary medicine. A middling essay may be acceptable but fail to separate you from the pack, while a poor essay can show a want of attention to detail. One of the easiest ways to figure out what should be in yours is to look up VMCAS essay examples and see what you should aim for.
Want to learn more about vet school rankings? Check out this infographic:
What Should I Include in My Essay?
You may immediately think of a hundred things you want to tell the admissions committee, from your first pet hamster to your experience as an intern at the city zoo. However, keep in mind that you only have about 500 words, and you need to make them count. Here are some ideas of what you’ll want to include in your VMCAS essay.
- Career goals. Where do you ultimately want to be, and what is your dream job? Don’t just list a title – explain what appeals to you about it, or why you want this specific position over any others.
- What you want to contribute. You don’t need to make up a grand, world-altering contribution here, unless that is what you sincerely want to do. Your goal can be to simply bring joy and comfort to families by taking care of their pets. It can also be to make significant advancements to the field of veterinary science. Make sure you’re authentic.
- Characteristics that make you a good vet. Yes, you need good marks to get into vet school, but the admissions committee also wants to know that you have the right personality traits. For example, you may be a very motivated self-learner. This is a great attribute to have, but you need to highlight how being an excellent self-learner would help you in vet school and ultimately, as a vet.
- Always give examples. Remember that the committee doesn’t know you, so they will be wary of applicants who make claims without backing them up. It’s important to give examples so that the committee can see how you’ve used your skills and individual attributes in real-life situations: “show, don’t tell.” If you write that you’re an empathetic and caring person, write about a time when you demonstrated that empathy. This shows that you aren’t just listing what you think they want to hear.
- Set yourself apart. Any special experiences, personal revelations, or big life events that affected your desire to be in veterinary medicine are worth noting. You have a limited amount of space, so stick to the most important ones. These unique experiences are what will help the admissions committee remember you and set you apart from the crowd.
With only 500 or so words to make your case, what you don’t include can be just as vital as what you do include. The admissions committee likely doesn’t want an entire essay on your childhood pet, so be careful about getting stuck on one aspect. In fact, the VMCAS guide explains that while many applicants “have had meaningful experiences with animals or veterinarians as children … these should only be mentioned briefly.”
Here are some other things you’ll want to make sure you avoid when writing your VMCAS essay.
- Information they already have. At this point, the admissions committee already knows about your academic achievements. They may be familiar with the jobs you’ve had, based on your letter of intent or high school resume . They may have a list of any vet school extracurriculars in which you participated. In your essay, don’t repeat what they already know. Instead, tell them something they don’t have on paper, expand on one or two of those experiences, or explain how an event impacted your motivation to go into veterinary medicine.
- Vague, generalized information. Telling them that “you’ve always liked animals” is nice, but vague, and likely a trait that many applicants share. Make it more specific: What is it that draws you to animals? When, exactly, did you start taking a special interest in animals?
- Jargon, unless it’s necessary. The admissions committee is unfortunately not going to be impressed if you throw terms around or use 5-syllable words in every sentence. You aren’t a vet yet, and one of the more embarrassing things you can do is attempt to use a term and use it wrong. Stick with language that is used in everyday conversation.
- Make unnecessary explanations. The members of the admissions committee don’t need you to explain the process of getting into vet school or how medical procedures work. Explain something if it is very specific to you, like the type of club you were in at school, or an event that occurred in your year of study. Giving an example is a better way of showing the committee what you mean, instead of getting bogged down in explanations.
- Irrelevant things. If the event isn’t relevant to why you want to be a vet or what you are looking for in a school/program, you probably don’t need to write it here. Take note of the various parts of the application process that would allow you to go into more detail. For example, should you be invited to answer vet school interview questions , you will have such an opportunity. The “tell me about yourself” vet school interview question would be the perfect moment to discuss your personal background further. It’s a good idea to go back and examine each piece of information you’ve provided in your essay and make sure it ties into the main topic: why you want to have a career in veterinary medicine.
Language and Tone
Ideally, the tone in which you write your VMCAS essay is similar to the way you would talk with someone in person. Keep your word choice conversational. Writing in a way that is overly formal doesn’t give the admissions committee members a clear sense of your own voice, and doesn’t humanize you. You’re writing your story, so it helps to read the essay aloud and see if it sounds like an accurate representation of yourself. Having a friend or family member read it can also be beneficial.
Admission to vet school is challenging, as shown by veterinary school acceptance rates ; some schools are more difficult to get into than others. Applying is a long process with a lot of pieces to consider. Your VMCAS essay is perhaps one of the least restrictive parts, where you’re given the freedom to tell the admissions committee why you’re there and what you want to do. Being authentic and specific is your best approach to being accepted into the school of your choice.
It won’t make as much of an impact as your grades or your resume, but it can make you more memorable and more likeable to the committee members. An average essay likely won’t hurt you too much, but a bad one can.
The American Association of Veterinary Medical Colleges is a good place to start. There you’ll find all the pieces you’ll need to submit for the application as well as contacts if you need more help. You can also have a look at our list of the best vet schools, along with tips for getting in.
A letter of intent shows how serious you are about your application and emphasizes what sort of experience and education you have related to veterinary medicine. The personal essay is more about your personality, motivation, and goals.
You don’t need to list everything you’ve ever done that is related to the field. That is already outlined in other parts of the application. Highlight the personal impact certain experiences have had on you – be specific about how they made you feel, how they changed your perspective, and how they moved you in the direction of veterinary studies.
Admissions committee members aren’t expecting fine literature when you submit your personal essay. They know that not all candidates are natural writers. What they’re interested in is your ability to express yourself in a short piece of writing. Don’t worry about using fancy terms – write in a way that sounds natural and authentic to you.
The committee will want to know about your experiences if they’re specific to you and have impacted you in a tangible way. You don’t have to tell them about every interaction you’ve had with animals, just the ones that were special to you.
Use the language you would use in a normal conversation in your essay. Very few people speak in a formal tone, and it can end up sounding stilted and unnatural. Be expressive but stick to the requirements.
There is no editing once your VMCAS essay has been submitted. However, if there is a serious mistake in the essay, you can contact the admissions committee and forward them a corrected copy as soon as possible.
Want more free tips? Subscribe to our channels for more free and useful content!
Apple Podcasts
Like our blog? Write for us ! >>
Have a question ask our admissions experts below and we'll answer your questions, get started now.
Talk to one of our admissions experts
Our site uses cookies. By using our website, you agree with our cookie policy .

How To Write a Vet School Personal Statement
Personal statements are one of the first big steps towards becoming a vet, but how do you write one? Find out in our detailed guide.
How to write a vet school personal statement
Getting into a great veterinary school can be tough. Vet course admissions are very competitive, so you need to do everything you can to prove that you are an exceptional candidate. This includes writing a great veterinary personal statement. We look at how to write a personal statement for vet school, key items to include, and why nailing your personal statement is important.
Why we have to write personal statements
Your personal statement is an important part of your application process, as veterinary school is highly competitive. This is the chance to add a personal touch to your application and make you stand out from the crowd. While your resume will list all of your accomplishments, educational background, and experience, your personal statement allows you to tie all of this together and let your passion, personality, and enthusiasm for veterinary medicine shine through. Your personal statement is also where you can mention anything that doesn’t fit into the other sections of your application, and it’s an ideal place to reinforce how you meet the admission requirements .
Here, you’ll introduce yourself and explain why you’ll be a great fit for the program, touch on what has inspired you to further your studies, and why you think you are good candidate to become a veterinarian. You might also want to include what you like about this particular program and how you think it will enrich your knowledge and understanding of veterinary medicine.
This means that when you get an interview for admission, the admissions officer should already know a bit about you and allows you to jump straight into answering their questions.
Demonstrate your passion for animals
Since you only have limited space on your personal statement, it’s important to use this space to convince the admissions team that your passion for animals would make you an excellent veterinarian.
In order to uniquely demonstrate your passion for animals, try to think outside of the box. Don’t just talk about family pets. Mention times you’ve been proactive, hands-on, and gained experience with animals. This might include helping with the birthing season on a local farm, volunteering in kennels, or helping strays find foster homes in animal shelters.
It’s also important to specify what type of animals you have interacted with. Did you grow up riding horses and love tending to large mammals? Or did your family raise small animals? Whatever your particular interest in the veterinary world, be sure to add it. Schools like to see students who have a plan of where to specialize and continue their education.
Of course, don’t forget that most vets have to work with people too, so it’s a good idea to include something that shows you can work as part of a team or with clients.
Highlight all relevant experience
Whatever you’ve done for animals outside your normal household, include it, especially if it’s something related to wellbeing and health. Even better, if you can remember a particular interaction that made you want to be a veterinarian, be sure to include it.
Your resume will list your experience and qualifications, but your vet school application personal statement is where you can say why your experience is relevant to the program. When you’re planning your statement, you can make notes of what experience you have, and what transferable skills you have gained. Then you can find ways to tie this into veterinary medicine. For example, if you’re an empathetic person who has worked in customer service, you can relate this to dealing with clients at a standard vet practice. If you have experience running a social group, this ties into leadership skills and motivation to go above and beyond for something you’re interested in.
Remember, you’ll have gained invaluable experience from almost everything you do, whether that’s education, work, voluntary roles, or hobbies. You just need to think about how it is relevant to what you want to do next.
Set yourself apart from the crowd
First, you should try to think about what makes you unique. Try to think about the things you’ve done that other people haven’t, or experiences you’ve had. Remember that you’ll be competing for a seat against people all over the country and potentially all over the world, so even the most basic things might be unusual compared to other applicants.
Just like in the previous section, think about how your background gives you a different perspective or relevant skills. Try to tie it into the topics you’ll be learning in vet school, and the challenges you would face in your daily life as a veterinarian.
While you might want a large portion of your statement to be positive, you can also bring up any difficulties you’ve had and how you’ve used problem-solving skills and resourcefulness to overcome them. It shows that you’re willing to do a lot to reach your dream, which suggests you’ll be a focused and dedicated student.
You should also be sure to be personable in your personal statement. Vet school committees will expect you to remain professional and precise in what you say with word limitations in mind. However, you should aim for a conversational, friendly tone. Your personal statement is about you, so it should give the admissions committee an insight into your personality. Try to find a happy medium where you don’t sound too stiff and formal, but also don’t use slang too much.
Preparation is key
There are a lot of different things you will want to cover in your personal statement for vet school, and it’s more than simply a ‘why I want to be a veterinarian’ essay. That’s why it’s vital to prepare and plan your statement before you write it.
Just like any other assignment, you should break the statement down into sections. Make sure you highlight the goal of each section – one section might be talking about your background, and one might be about your experience. Then plan out each section with some key points to include, such as the skills your experience has provided. Then you can write the actual contents without wavering too much – and you definitely don’t want to waste words.
Afterward, be sure to proofread it thoroughly. If you can, you should ask someone else to read it too. Ask them if it makes sense, as well as get them to note any errors they find.
If you’re ready to take the next step and start studying at a leading vet school, contact us to speak to one of our expert advisors. St. Matthew’s University School of Veterinary Medicine provides graduates with new knowledge, skills, and methods necessary to become caring, competent veterinarians.
Check out webinar events at St. Matthew’s School of Veterinary Medicine for more information about the application process, including your personal statement.
Get in touch for more information
- Share on Twitter
- Share on Facebook
- Share on Linkedin
Related Blogs
Complete guide: financing veterinary school for canadian students, how to prepare for a career in veterinary medicine, what is veterinary school like, nait partnership agreement.
- All News & Stories
- Berry College News
- Berry Stories
- Articles & Guest Blog Posts
- In The News
- Faculty & Staff
- Berry Magazine
- Athletic News
- SHARE A STORY
- Campus Life
- Student Enterprises

How to Get Into Vet School: 8 Application Tips for Aspiring Animal Doctors
While many students are interested in careers with animals, not all of them are meant for veterinary medicine. It takes someone like you with a knack for science and a drive to succeed. In fact, you’re already thinking about how to get into vet school.
There’s no tried-and-true method for gaining an acceptance letter to a veterinary medicine program, but these expert tips can help you put together the strongest possible application.
8 tips for students researching how to get into vet school
According to Dr. Laura Flatow, clinical assistant professor of animal science and pre-vet coordinator at Berry College, it’s wise to think about what’s motivating you to pursue a doctor of veterinary medicine (DVM) degree before you get started. “Really think about working on all your experiences and building a solid application based off what it is about the field that makes you want to be a vet,” she suggests.
1. Aim for academic excellence
Veterinary schools are explicit about the courses applicants need to complete, so you’ll want to identify which prerequisite classes you’ll need to take early on in your education. And it’s essential that you perform as well as you can in those required courses because vet schools carefully scrutinize your science GPA.
“That science GPA really tells schools if students have the ability to do well in a rigorous DVM curriculum,” Dr. Flatow explains.
When thinking about how to get into vet school, it’s also important to do well in your other classes. Dr. Flatow notes that some schools won’t look at the rest of your application if you don’t meet their minimum GPA standards. The only other chance you have to prove your academic prowess is the Graduate Record Examination (GRE), but that’s becoming less important to DVM programs.
2. Gain as much animal and veterinary experience as you can
Students need to accumulate both veterinary experience (work done under the supervision of a veterinarian) and animal experience (any activity that involves working with animals). Dr. Flatow suggests students think more about gaining a breadth of experiences than obsessing over the specific number of hours.
“Vet schools would prefer that students divide their time to get experience in different clinics and with different animals,” she explains.
Looking for a benchmark? The American Association of Veterinary Medical Colleges (AAVMC) reports veterinary students who began class in 2020 accumulated a mean of more than 1,600 veterinary experience hours and more than 1,100 animal experience hours.
3. Consider participating in research
Getting involved in research isn’t a requirement for veterinary schools, but participating in a project that you’re really passionate about can be beneficial. That said, it’s not always easy to find opportunities depending on your school.
“Berry College is a smaller school,” Dr. Flatow says. “There are no graduate students doing the research, so we have more opportunities for undergraduates to get that experience.”
4. Work closely with a pre-vet advisor
Students who have access to a dedicated pre-veterinary advisor should take full advantage. Most everyone knows that getting good grades and accumulating relevant experiences are both essential for getting into vet school, but Dr. Flatow says figuring out all the other nuances like how to approach letters of recommendation can be tricky.
“Pre-vet advisors keep up with the individual vet schools and what their admissions processes look like,” she points out. “That's not something you're going to get from just a typical advisor.”
5. Write a thoughtful essay
The essay portion of the Veterinary Medical College Application Service (VMCAS) asks students to compose a personal statement that illustrates who they are and why they want to pursue a veterinary medicine career. This composition must be 3,000 characters or less.
“Students need to show who they are, what experiences they had that shaped them and what their goals are,” Dr. Flatow explains.
6. Secure glowing letters of recommendation
Every vet school applicant needs to obtain at least three letters of recommendation . But don’t think of these evaluations as items you can check off a list. Most DVM programs expect at least one letter be written by a veterinarian. More importantly, letters should be composed by individuals who know you well.
“Admissions committees are looking for those letters to complement the application by telling them who the candidate is as a person,” Dr. Flatow elaborates. “They can provide insight that may not be in the rest of the application.”
7. Let your personality show through
It’s wise to focus on activities related to animals and veterinary medicine, but don’t forget to mention other valuable experiences in your vet school applications. The VMCAS help guide also lists extracurricular activities, volunteering and even paid work. Mentioning these experiences can give admissions committees a better sense of who you are and where your passions lie. Consider what your time playing sports or volunteering might say about you.
“Schools want students who have soft skills like communication and the ability to work well with others,” Dr. Flatow says. “Things like employment and extracurricular activities can show that.”
8. Be selective when choosing an undergraduate program
“Look for programs that offer courses that are going to be challenging,” Dr. Flatow urges. Berry College’s animal science program, for instance, has developed a reputation for pushing students to do their best. “Students who do well in our program are prepared for a rigorous DVM curriculum, and they end up doing quite well when they get there,” she adds.
Start your journey toward vet school
There’s no proven checklist on how to get into vet school. Remember that admissions committees are looking for candidates who would make good veterinarians, not just good students. Focusing on your studies and gathering experiences that can help you become a well-rounded person will go a long way toward helping you achieve your goal of becoming a veterinarian.
Curious about what else it takes to pursue this career? Learn more by checking out our article “ How to Become a Veterinarian: An Aspiring DVM’s All-Encompassing Guide .”
Related Articles

Footer Menu
- Applying to Uni
- Apprenticeships
- Health & Relationships
- Money & Finance
Personal Statements
- Postgraduate
- U.S Universities
University Interviews
- Vocational Qualifications
- Accommodation
- Budgeting, Money & Finance
- Health & Relationships
- Jobs & Careers
- Socialising
Studying Abroad
- Studying & Revision
- Technology
- University & College Admissions
Guide to GCSE Results Day
Finding a job after school or college
Retaking GCSEs
In this section
Choosing GCSE Subjects
Post-GCSE Options
GCSE Work Experience
GCSE Revision Tips
Why take an Apprenticeship?
Applying for an Apprenticeship
Apprenticeships Interviews
Apprenticeship Wage
Engineering Apprenticeships
What is an Apprenticeship?
Choosing an Apprenticeship
Real Life Apprentices
Degree Apprenticeships
Higher Apprenticeships
A Level Results Day 2024
AS Levels 2024
Clearing Guide 2024
Applying to University
SQA Results Day Guide 2024
BTEC Results Day Guide
Vocational Qualifications Guide
Sixth Form or College
International Baccalaureate
Post 18 options
Finding a Job
Should I take a Gap Year?
Travel Planning
Volunteering
Gap Year Blogs
Applying to Oxbridge
Applying to US Universities
Choosing a Degree
Choosing a University or College
Personal Statement Editing and Review Service
Guide to Freshers' Week
Student Guides
Student Cooking
Student Blogs
- Top Rated Personal Statements
Personal Statement Examples
Writing Your Personal Statement
- Postgraduate Personal Statements
- International Student Personal Statements
- Gap Year Personal Statements
Personal Statement Length Checker
Personal Statement Examples By University
Personal Statement Changes 2025
- Personal Statement Template
Job Interviews
Types of Postgraduate Course
Writing a Postgraduate Personal Statement
Postgraduate Funding
Postgraduate Study
Internships
Choosing A College
Ivy League Universities
Common App Essay Examples
Universal College Application Guide
How To Write A College Admissions Essay
College Rankings
Admissions Tests
Fees & Funding
Scholarships
Budgeting For College
Online Degree
Platinum Express Editing and Review Service
Gold Editing and Review Service
Silver Express Editing and Review Service
UCAS Personal Statement Editing and Review Service
Oxbridge Personal Statement Editing and Review Service
Postgraduate Personal Statement Editing and Review Service
You are here
- Mature Student Personal Statements

Personal Statements By University
- Accountancy and Finance Personal Statements
- Actuarial Science Personal Statements
- American Studies Personal Statements
- Anthropology Personal Statements
- Archaeology Personal Statements
- Architecture Personal Statements
- Art and Design Personal Statements
- Biochemistry Personal Statements
- Bioengineering Personal Statements
- Biology Personal Statements
- Biomedical Science Personal Statements
- Biotechnology Personal Statements
- Business Management Personal Statement Examples
- Business Personal Statements
- Catering and Food Personal Statements
- Chemistry Personal Statements
- Classics Personal Statements
- Computer Science Personal Statements
- Computing and IT Personal Statements
- Criminology Personal Statements
- Dance Personal Statements
- Dentistry Personal Statements
- Design Personal Statements
- Dietetics Personal Statements
- Drama Personal Statements
- Economics Personal Statement Examples
- Education Personal Statements
- Engineering Personal Statement Examples
- English Personal Statements
- Environment Personal Statements
- Environmental Science Personal Statements
- Event Management Personal Statements
- Fashion Personal Statements
- Film Personal Statements
- Finance Personal Statements
- Forensic Science Personal Statements
- Geography Personal Statements
- Geology Personal Statements
- Health Sciences Personal Statements
- History Personal Statements
- History of Art Personal Statements
- Hotel Management Personal Statements
- International Relations Personal Statements
- International Studies Personal Statements
- Islamic Studies Personal Statements
- Japanese Studies Personal Statements
- Journalism Personal Statements
- Land Economy Personal Statements
- Languages Personal Statements
- Law Personal Statement Examples
- Linguistics Personal Statements
- Management Personal Statements
- Marketing Personal Statements
- Mathematics Personal Statements
- Media Personal Statements
- Medicine Personal Statement Examples
- Midwifery Personal Statements
- Music Personal Statements
- Music Technology Personal Statements
- Natural Sciences Personal Statements
- Neuroscience Personal Statements
- Nursing Personal Statements
- Occupational Therapy Personal Statements
- Osteopathy Personal Statements
- Oxbridge Personal Statements
- Pharmacy Personal Statements
- Philosophy Personal Statements
- Photography Personal Statements
- Physics Personal Statements
- Physiology Personal Statements
- Physiotherapy Personal Statements
- Politics Personal Statements
- Psychology Personal Statement Examples
- Radiography Personal Statements
- Religious Studies Personal Statements
- Social Work Personal Statements
- Sociology Personal Statements
- Sports & Leisure Personal Statements
- Sports Science Personal Statements
- Surveying Personal Statements
- Teacher Training Personal Statements
- Theology Personal Statements
- Travel and Tourism Personal Statements
- Urban Planning Personal Statements
- Veterinary Science Personal Statements
- Zoology Personal Statements
- Personal Statement Editing Service
- Personal Statement Writing Guide
- Submit Your Personal Statement
- Personal Statement Questions 2025
- Personal Statement Changes 2024
Veterinary Science Personal Statement Examples

What is a veterinary medicine personal statement?
Your veterinary medicine personal statement is an opportunity to sell yourself to admissions tutors, and tell them why you would make a great candidate on their course.
Your statement should include how you meet all the entry requirements for a veterinary science degree and demands of the course. For example, your love of animals, patience, empathy, and your academic and practical skills.
How do I write a veterinary medicine personal statement?
Most veterinary medicine candidates open their personal statement with why they want to become a vet. Motivations for wanting to study any course at university are always important.
We recommend you write a series a notes about your skills, experience, hobbies, extracurricular activities, career plans and anything else that is relevant to your application.
When you have put an initial draft together, proofread it and leave yourself plenty of time to amend your statement.
Ask family, friends and tutors to read your veterinary medicine personal statement, and invite them to make suggestions, comments and any other feedback to help you improve it.
What should I include in my veterinary medicine personal statement?
- Your passion for animals should be obvious from the outset. Think about what made you want to pursue a career in veterinary medicine in the first place - was it a childhood experience or something you read or encountered? Were you inspired by a family member or friend who is already a qualified vet?
- Talk about any work experience (paid or unpaid) or voluntary roles that have helped you gain experience in the veterinary science field. This will help demonstrate your skills, commitment and ambition to the university admissions tutors.
- If you're applying to Oxbridge, your personal statement will need to be exemplary. Veterinary medicine is a highly competitive course, so you have to show that you are a talented, dedicated and enthusiastic student that meets all the academic and vocational requirements.
For more help and advice on what to write in your veterinary medicine personal statement, please see:
- Personal Statement Editing Services
- Personal Statement Tips From A Teacher
- Analysis Of A Personal Statement
- The 15th January UCAS Deadline: 4 Ways To Avoid Missing It
- Personal Statement FAQs
- Personal Statement Timeline
- 10 Top Personal Statement Writing Tips
- What To Do If You Miss The 15th January UCAS Deadline.
What can I do with a veterinary medicine degree?
There are many career options available to those wanting to study veterinary medicine, including:
- Animal nutritionist
- Veterinary surgeon
- Animal physiotherapist
However, there are other job roles where your veterinary science degree could be useful, such as:
- Animal technician
- Veterinary nurse
- Environmental consultant
- Nature conservation officer.
For more information about careers with a veterianary science degree, please see Prospects and The Times .
What are the best UK universities for veterinary medicine?
Currently the best UK universities for veterinary medicine are:
| 1. | |
| 2. | |
| 3. | |
| 4. | |
| 5. | |
| 6. | |
| 7. | |
| 8. |
For more information about UK university rankings for veterinary science, please see The Complete University Guide and The Guardian .
Related resources

Find out more
UCAS Personal Statement FAQs

Personal Statement Writing Tips

How To Write A Personal Statement

UCAS Extra: How Does It Work?

How To Apply To University

Loop Abroad

Mastering the VMCAS Personal Essay
Introduction.
This free guide to mastering the VMCAS Personal Essay is brought to you by Loop Abroad, the leader in pre-veterinary and veterinary study abroad programs. Go to www.LoopAbroad.com for info on all of our pre-veterinary programs around the world, including one- and two-week programs, pre-veterinary semesters, internships, and virtual programs.. If you’d like to organize a private group for your pre-vet club or school, you can travel with your group for free – contact [email protected] for more information. Programs for vet students, including an elephant medicine course, are also available.
The application to vet school, commonly referred to as the VMCAS, can be overwhelming. Vet school applications are competitive, and they only come after years of gathering experience, mastering science classes, tracking veterinary hours, and making sure that vet school is the path for you.
Many students who plan to attend vet school do not consider themselves writers. (If you do, lucky you!) As such, the VMCAS Personal Essay can feel like just one more thing that you have to do in the complicated process of completing your application to vet school.
But don’t be afraid! It’s actually pretty easy to write a compelling, convincing, successful personal essay on your application, if you know what to do. This little guide will take you through all the steps of writing a successful VMCAS essay, including important pitfalls to avoid.
And if you need extra help, from proofreading to brainstorming, we are there to assist you.
So let’s write a great personal essay!
The New Personal Essay
At the time of revising this ebook (July 2022), the personal essay prompt is as follows:
“Your personal statement is a one-page essay that gives veterinary admissions committees a clear picture of who you are and, most importantly, why you want to pursue a career in veterinary medicine. ”
The response is limited to 3,000 characters (less than a page – about 500 to 750 words). The instructions also give some ideas about how to write an effective personal statement.
Now, think from the perspective of the admissions committee members. Their goal is to pick the best collection of students for their incoming class. They are looking to the Personal Essay to give them information that they can’t learn elsewhere, and to help illuminate something about the applicants.
The prompt makes it clear that this is a chance to clearly articulate why you want to be a veterinarian and to tell the committee more about you that they don’t already know from your application. They don’t want you to re-list your resume or wax poetic, and vaguely, about your interest in being a vet . In other words, follow the directions and write about what the prompt asks.
So, now that we know what we’ll be writing about, let’s go ahead and get your essay ready. But, how much should we worry about it?
How Much Does the Personal Statement Matter?
The answer is: it depends. Your personal statement can’t outshine bad grades, and it can’t make up for a lack of experience. But it can do two things:
- It can set you apart if you are an otherwise “average” successful applicant, but your essay shows insight, maturity, care, and depth; or
- It can show that you haven’t taken the process seriously if it is sloppy, off-topic, or very poorly written.
In other words, a mediocre essay probably won’t hurt you, but it definitely won’t help you. In this way, it doesn’t matter as much as, for example, your Common Application essay when you applied to undergrad. After all, you’re applying to be a veterinarian, not a novelist.
However, a very bad essay can hurt you. If you were an admissions committee member and you reviewed an essay that was off-topic, full of typos, and in any way revealed ignorance of the profession, it would be hard for you to put those things aside in your mind when considering the rest of the application.
What’s more, a very good essay could help you by strengthening your application. If you can show more dimension to your understanding of veterinary medicine and make yourself stand out, you can humanize yourself to the reader a bit.
So, for short, it matters a lot that your essay is at least adequate. And it can help you a little if it’s really, really good.
Now that we know we should invest at least a little time and attention in the Personal Essay, we’re almost ready to start brainstorming and making a plan. But first, we have to go over what not to do.
Top Ten Mistakes to Avoid
Remember, our #1 goal is to not write a bad essay, so that means avoiding the following common mistakes. This list does not include grammar, spelling, punctuation, and the other basics of effective writing, but rather reviews ten mistakes of content that you want to avoid.
1. Stating the obvious.
You only get 3,000 characters to show yourself to the admissions committee and make sure you clearly articulate the reasons why you want to be a member of the veterinary profession.
You probably have a lot of thoughts on this topic; if you don’t, you will by the end of this book! So you don’t have space for anything that doesn’t help answer the questions or give the admissions committee a glimpse into what makes you special.
Here are some examples of obvious statements that you can erase from your essay right away:
- “I love animals.” Most people don’t become vets because they hate animals. The admissions committee is already pretty sure that you love animals.
- “The process of becoming a veterinarian takes a lot of schooling and hard work, and is very competitive.” What does this tell me about you? Nothing. Also, I promise the members of the admissions committee already know this.
- “It’s difficult to fit all the ways veterinarians contribute to society into just 3,000 characters.” Yes, it is. So don’t use 15 of them on that pointless sentence.
- “There’s no way I can explain all the attributes that are essential to success as a veterinarian.” Again, correct. They don’t want you to explain every single thing a successful person has to do every day.
- “I’m sure you’ve read lots of essays that say that focus is important.” They probably have, but there’s no need to say “I’m unoriginal” expressly in your word count. (Also, don’t use the word “you” in your essay. It’s about you , not the reader.)
2. Going off topic.
You have a lot of ground to cover if you want to write a convincing and interesting essay that introduces you to the admissions committee. This is the only place in the application they really get to hear your voice.
Now is not the time to talk about your childhood pet. Please don’t talk about how much you loved your childhood pet. Everyone loves their childhood pet; it doesn’t tell the admissions committee anything about you. In general, if you spend more than one sentence talking about your childhood, you have likely gone off-topic.
Now is not the time to talk about anything that doesn’t tell the admissions committee more about what makes you uniquely suited to be a member of the veterinary profession and why that’s your goal. If a sentence doesn’t help to do one of those things, cut it, or find a way to rewrite it that makes it refer directly to the prompt.
3. Using terminology incorrectly.
Here’s a guiding principle for your essay: the people reading your essay know more about veterinary medicine and vet school than you do. If you aren’t sure exactly how to use a medical term, look it up first or just don’t use it.
Using medical terminology incorrectly makes you look as if you are trying to pretend to know something you don’t. It can be off-putting to the reader.
Not sure if something’s capitalized? Look it up. Not sure if an abbreviation has punctuation or not? Look it up. Not sure if you’re using the correct name of an instrument? Look it up. Not sure the difference between a zoo vet or an exotics vet? Not sure if you’re describing the correct medication? At this point, you can probably guess that you should look it up .
4. Making generalizations and speaking in absolutes.
You should avoid making broad, sweeping statements that either can’t possibly be true or that you can’t possibly know are true. Often these are ideas that are meant rhetorically, but they end up feeling disingenuous and can make you sound pompous, ignorant, or just uninformed. At worst, they will make the reader find you arrogant or unlikeable; at best, they add nothing to your essay.
Here are some examples:
- “No one works harder than me.”
- “Every veterinarian faces this challenge in his or her career.”
- “Everyone knows that dealing with animals can be emotional.”
- “There is no job more important than being a veterinarian.”
- “Nothing could be more difficult than the choice I faced.”
- “I will be the best and most devoted student you have ever seen.”
- “I know I will love every moment of the challenge.”
- “I would never do that if I were making the same decision.”
- “I always think about the interests of others before my own.”
There’s a reason that the Star Wars franchise chose the sentence, “Only a Sith deals in absolutes.” Absolutes generally do not reflect a mature, moral, developing understanding of the world, so you should try to avoid them whenever possible.
To make sure you avoid statements such as these, you can do a quick search of your essay for the words “none”, “no one”, “everyone”, “every”, “all”, “always”, “never”, “most”, and pretty much any other superlatives (words ending in “est” such as “best” and “hardest”).
5. Explaining too much or too little.
The committee members reading your Personal Essay understand more about the veterinary profession and veterinary education than you do. However, they likely didn’t attend your school, and even if they did, they didn’t attend it this year.
That means you don’t need to explain:
- What certain medications do
- What certain surgeries are for
- How surgical instruments are used
- What common veterinary abbreviations stand for
- The process of becoming a veterinarian
But you do need to explain:
- The acronym for your school club or organization
- The purpose of your school event with a cute but unclear name
- The full name of a particular course at your school
- Any acronyms or abbreviations that are unique to your school or town
In short, you don’t want to waste words explaining something the committee members already know, but you don’t want to leave them confused as to what you’re talking about.
6. Making excuses.
Your essay is not the place to explain why you got an F in a class, or why you had to withdraw during your sophomore semester, or why you don’t have as many veterinary hours as some other applicants. Your essay is the place to make yourself sound like a strong applicant, not talk about the weaknesses of your application.
You can address a weakness if you mention it in passing in a way that informs your answer to one of the questions. It should not sound like you are making excuses for your failures.
No: “Once I retook the course with a professor who knew how to explain things in a way that made sense, I quickly mastered the content.”
Yes: “Retaking the course gave me the opportunity to master the material, and I know this tenacity will be a key to my success in my veterinary career.”
No: “Working two jobs meant that I was not able to collect the veterinary hours that some of my more affluent classmates could easily fit into their schedules.”
Yes: In every veterinary office where I have worked, resourcefulness has been an essential skill. Finding opportunities to volunteer and learn that fit my lean, self-supported budget has only helped me to build these skills.
No: “I had to withdraw because my school did not make me aware of the deadlines that were approaching, and I had no choice.”
Yes: “Because my school doesn’t have a pre-vet advisor, I have had to be organized and dedicated in pursuit of my educational goals.”
No: “Not everyone can afford to pursue fancy pre-veterinary volunteer programs all over the world.”
Yes: “I believe that veterinarians are an essential part of their communities, and I was grateful to be able to find opportunities to get involved close to home.”
It goes without saying that you shouldn’t use these exact sentences , but you get the idea. You don’t want to sound bitter or give off the impression that you don’t take ownership of your own successes and failures. You don’t have to ignore the weaknesses in your application, but you if you mention them, you should frame them in terms of what you learned and how you improved. Speaking of not using these exact sentences…
7. Plagiarizing.
This one doesn’t need a lot of reiteration. If you find a sample essay that seems to say just exactly what you wanted to say , and you feel like you’ve finally found the words, that’s great–but you can’t use it.
Put the sample essays down. Stop asking other people on the APVMA Facebook page to share their essay with you as a sample. Write your own work. All the time.
8. Restating other parts of your application.
The Personal Essay is the chance to include new information that isn’t already in your application. If you’ve already described the details of a class or activity elsewhere, you don’t need to include them here. If you already mentioned an award elsewhere, don’t mention it here.
You don’t want to waste your word count telling your reader something he or she already knows. This is your chance to share the qualitative aspects of your application: the things that can’t be measured in grades, hours, or ranks. This is your chance to talk about your values, your beliefs, your interests, and your ambitions. It’s your chance to show the kind of person you are, and the kind of person you are is never a grade or an award. (And even if it were, there are other places to include that information.)
9. Writing filler sentences.
You should view the word limit as a length guideline; while you can’t write more than that, you shouldn’t write much less.
That said, you have probably had lots of unique and interesting experiences in your life up to this point, so you don’t have room for lots of flowery introduction and conclusion sentences. Check out this grammatically correct, completely-on-topic opening:
“Veterinarians are an important part of every society around the world and throughout history, and they contribute in myriad ways. In considering all the ways they contribute to society, I realized that they may indeed be the cornerstone of progress in a culture.”
Uh, okay. But what does that tell me about the applicant? Exactly nothing. Use this space to tell the admissions committee about you. Skip the fluff.
10. Playing the expert.
Repeat after me: you are not a veterinarian . You don’t know what a veterinarian would or should do in a medical emergency. You don’t know what you would do as a veterinarian in any given setting. You don’t yet understand all the ins and outs of owning or running a veterinary practice. It’s important that you honor that truth in your essay.
Someday, you might know more about being a veterinarian than your reader does, but now is not that time . You cannot impress your reader with your knowledge of veterinary medicine, so don’t use your time trying. However, you are an expert in one thing: you . Luckily, that is exactly the one thing that your reader wants to know about. Don’t spend your essay trying to impress with what you know; spend your essay trying to share who you are.
Now You’re Ready to Brainstorm
Clear thirty or sixty minutes from your schedule. Turn off your computer, your TV, and your phone. Get a pen and paper (or use your computer if you prefer), put in some thought, and write down some answers to the following questions.
You don’t have to have the correct wording right now, or say things in the right way. Just get something down on paper that matches your real feelings and experiences. Even writing a couple words is great. Bullet points can make it easy to get your mind flowing.
- What are my future vet career goals? a. Do I want to practice, research, or teach? b. What kind of animals do I want to work with? c. Pets? Conservation? Wildlife? Food animals? What comes to mind? d. Where would be my dream to end up? Writing a book? Saving animals in the rainforest? Opening a free clinic? Discovering a new vaccine
- Why do I want those goals in my career? a. Am I more motivated by my talents or my aptitudes? b. What motivates me? c. Who motivates me? d. What do I believe is the measure of success? e. What’s the best thing a vet can do? f. What have I done so far that helped me choose these goals? g. What have been my favorite classes? Why? h. What has been my favorite work with animals? Why?
- What do I want to contribute as a vet? a. What kind of animals do I want to help? b. What kind of people do I want to help? c. What kind of difference do I want to make? d. Why is it important to me?
- What attributes are essential to the success of a vet? a. What am I good at that helps me be a vet? b. In what areas could I improve that would help me? c. Who are my professional role models? d. What traits do I admire in my professional role models?
- What are my strongest attributes? a. What do people say I’m good at? b. What do I find easy and enjoy? c. What am I proud of? d. What’s important for me to be good at?
- What are some examples of times I showed these attributes? a. What are some examples from work? b. From school? c. From my personal life and relationships? d. From childhood?
- Do I have special or unique experiences that informed my understanding of the veterinary profession, helped set my career goals, or gave me unique perspective? a. Personal growth moments that built positive attributes? b. Unique animal experiences? c. Diverse perspectives to share? d. Challenges I faced that show my capabilities? e. Role models in the profession that inspired me?
You won’t use everything you wrote above, but this is a good starting place.
Take a look over your brainstorming session. Are there any themes that stand out? Any great ideas? Any concepts that you didn’t realize mattered to you until now? Is there anything that sounds unique to you? Is there anything there that truly tells your story and sums up who you are?
You want to look for any themes or ideas that recur throughout the brainstorming session; that might help to guide your ideas and help your essay paint a picture of who you are. Review the list above now, and try to clarify and write down the top three things that you want the admissions committee to understand about you after reading your responses.
You don’t get a lot of words, so you want to stay on one message and make sure that all your answers are cohesive. You cannot possibly include everything you think or might want to say in your essay, so focus on making the points that are more important to you and that help tell the story of who you are as a candidate. This brings us to the most important concept of your Personal Essay: it should tell a story.
Think about what you identified as the three most important things you want the admissions committee to know about you from your essay. Everything you write should be directly related to one of those three things. You only get one page to share everything that makes you a good candidate for vet school, so make every sentence count
Remember: it’s very important to answer the prompt, but your real goal in answering the prompt is to show the admissions committee something about who you are as a person and a candidate. So you absolutely want to make sure you clearly answer the question of “why you want to pursue a career in veterinary medicine.”
The story you tell in your essay, ultimately, should match with the rest of your application. If all your volunteer work and vet experience is with dogs, but your entire essay is about elephants, you’ll need to explain how those two connect. If all your coursework and research is about reptiles, but your essay emphasizes that you want to work with horses, you should explain. It’s okay if your experiences and goals don’t match perfectly, as long as you can connect them.
For example, maybe you’ve been studying horses because learning about horses is a good way to prepare for a career with elephants, which is your goal. Maybe your volunteer hours are with dogs because that activity is supervised by a very experienced vet at your university, but in your summer internship at a zoo you fell in love with zoo medicine.
You don’t want to leave the reader wondering if your goals make sense and if you’re really informed about your educational plans. Think about the three things you most want to convey in your essay: do they match the rest of your application? If so, your only goal is to convey them clearly in a way that also answers the prompts. If not, you may need to reshape your application to make everything “match” and tell a cohesive story. Whether this means rearranging your resume, reshaping your essay, looking for a new recommendation letter, or some other combination of little changes, you will need to find a way to shape the application so that it’s clear to the admission committee exactly who you are and what you bring to their potential incoming class.
Making an Outline
With all the information from your brainstorming session, and an understanding of the story you want to tell, it’s time to make an outline.
It’s important that each paragraph has a key point. Then you can add support for the point you are trying to make. It’s easy to be all over the place when you feel like you have a lot to tell the admissions committee, but an outline can help you make sure that everything you write conveys your most important points.
Choosing the points you want to convey is more important than beautiful or poetic writing in this case. You have a short window in which to tell your story, so you want it to be concise, accurate, and interesting.
Now that you know what you want to include, the actual writing is the easy part. This doesn’t have to be the most beautiful thing you’ve ever written, but it should be grammatically correct and free of errors. It should also have the right tone.
What Tone to Use
Some of us naturally write in a more formal or informal tone, and it’s okay to sound like yourself. Your essay doesn’t have to sound just like everyone else’s — in fact, it shouldn’t!
Here are some general rules of thumb to follow in making sure that your tone doesn’t go too far either way.
- Don’t say “you”. Don’t address the reader as “you”. There’s no need to address the reader in any way.
- …But it’s okay to say “I”. Many of your college classes may have required that you avoid the first person in formal writing, never saying “I” or “me” in a paper. This isn’t an academic essay; it’s a personal essay that is asking questions about you and your beliefs. It’s perfectly fine to write in the first person; it would be kind of weird if you didn’t.
- Don’t try to write “fancy”. There’s no need to use words like “aforementioned” or use introductions such as, “Given the above, it is therefore commensurate that such results would ensue.” If you wouldn’t say it, don’t write it. Long, fancy words don’t make you a better writer, and they certainly don’t make you sound more like yourself.
- …But don’t use text-speak. While you don’t have to be fancy, you should be somewhat formal. This is a personal statement, not a text. You may think it goes without saying that LOLs and smiley faces don’t belong in your personal statement, and it’s a relief if you do. But if you aren’t sure if something belongs in your statement, then it doesn’t.
- You can use contractions. Very formal writing avoids contractions like “can’t” and “don’t”, but in the interest of saving space, you can use them in your personal statement if you’d like.
- …But what about things that are right but sound wrong? This area is a bit more tricky. Consider the sentence, “Zoo medicine is what I’ve chosen to devote my life to.” You would be more likely to say that than, “Zoo medicine is that to which I’ve chosen to devote my life,” but the second option is grammatically correct. (The first, in case you’re wondering, has a preposition at the end of the sentence.) In these cases, should you be formal but correct, or should you try to sound like yourself? My advice is to avoid making the choice by shuffling the order of your sentence whenever possible. “I’ve chosen to devote my life to zoo medicine” is both correct and normal sounding, and it has the added benefits of being more clear and more direct than your initial draft.
- Don’t give advice. Your readers are not looking for advice, so don’t tell them what they should or should not do. Remember who you’re talking to.
- …But don’t apologize. At the same time, you don’t have to apologize for not being an expert in veterinary medicine or not knowing exactly what you want to do with your life. The word “sorry” shouldn’t be anywhere in your essay.
Write, Then Cut
Now you’re ready to write! I suggest that you write first, not worrying about perfection but instead trying to convey all the main points of your outline in a way that answers the prompt. Your first step should be including everything you want to include in a way that answers the question and gives the reader some insight into your personality.
Then, you can worry about the length! Editing generally takes longer than writing. Start by shortening your introduction or conclusion–anything that doesn’t get right into answering the question and showing who you are.
Next, you can look for phrases that don’t add to your main point or that can be replaced with one or two more descriptive words. “The place I worked for many years” can become “my workplace”, or “the medications that we always stored in the cabinet” could just be “medications”. If something doesn’t contribute to one of your main bullet points, then cut it out.
The harder part of editing is choosing if one of your main points needs to be cut. It’s likely that it does. Choose the one that says the least about you, is the least unique, or has the least relevance to the rest of your application, and start deleting.
Your final answers should be very close to the word limit permitted.
Check for Grammar, Spelling, and Punctuation
You aren’t going to school to be a writer. That said, correct grammar, punctuation, and spelling are essential in your Personal Essay. Why?
- Grammar, punctuation, and spelling show attentiveness and care. For the purposes of vet school, this is the most important reason to care about your quality of writing. Correct grammar, punctuation, and spelling show that you have put time and thought into your application. They show that this is important to you. They show that you have learned a set of rules and know how to follow them. If you can imagine why those things would be important to a vet school admission committee, then you can take the time to make sure your essay is grammatically correct.
- Correct grammar makes reading easy. The purpose of grammar and punctuation is to make life easy for the reader, which is something you definitely want to do in an application.
- Correct grammar makes your message clear. Grammar, punctuation, and spelling are tools for ensuring that your message is conveyed clearly and correctly, which is an asset to you in this process.
- Correct grammar is concise. Good writing saves space and words, which you’ll find important with such a strict word limit.
- Correct grammar makes you sound smarter. Whether it should or not, it does. And who doesn’t want to sound smart in their application?
For these reasons, you should ensure that your grammar, punctuation, and spelling are correct. Microsoft Word or Google Docs spell-check is a good first start, but that red, squiggly line doesn’t know everything.
Please take at least one of the following three steps to ensure that your grammar, punctuation, and spelling are correct.
- Read it out loud. Reading something out loud (to yourself if necessary, but preferably to someone else) can help you discover typos, grammatical mistakes, repetitive word use, phrases that are unclear, or anything that doesn’t sound like you intended. This is a great first step to writing a solid Personal Essay.
- Ask someone to proofread for you. Asking a friend or family member to read over your essay can be a great way to catch typos or grammatical mistakes.
- Read it backwards. Read the last sentence. Then read the sentence before that. Continue until you get back to the beginning. This method will not help you with continuity or the sound of your writing, but it can be incredibly helpful for finding typos or misspellings.
Congrats, you’re done with this section of the VMCAS. If you find that your application is lacking in research hours, veterinary hours, or hands-on experience, or you otherwise want to have an amazing experience abroad working with animals, we encourage you to check out Loop Abroad for two-week pre-veterinary experiences around the world (generally 3 credits and 80 vet hours each) or a full semester abroad (300+ veterinary hours, 20 credits, designed specifically for pre-veterinary students) in Thailand, South Africa, or around the globe. Good luck on your vet school admissions journey!
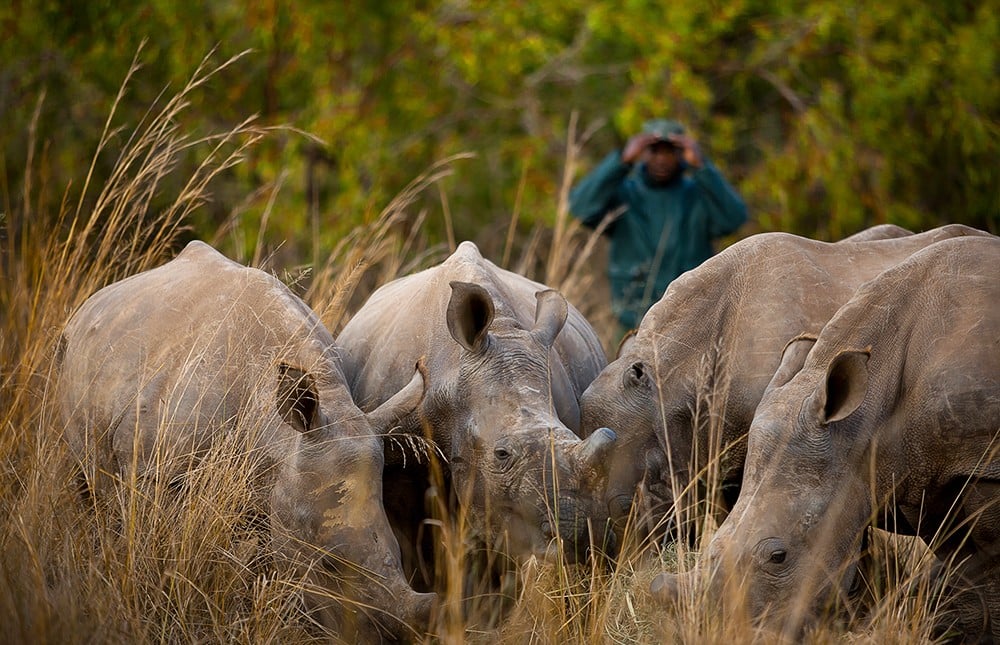

Your adventure is waiting. Start your application today!
Personal Statements
Your personal statement is a one-page essay that gives veterinary admissions committees a clear picture of who you are and, most importantly, why you want to pursue a career in veterinary medicine
UGA Supplemental Application questions for 2024-2025 application cycle:
- Veterinarians contribute to society in many different ways. Describe several roles they play in society and how you hope to contribute, including the qualities or traits you would bring to the profession. (3500 character limit)
- Describe a significant experience or challenge in your life that was unrelated to veterinary medicine, what you learned from that experience, and how you have grown from it. (3500 character limit)
- Personal Statement
What should be included?
Although there is no set of rules mandating what a strong personal statement should include, here are a few tips to help you successfully craft an effective personal statement:
- Explain a defining moment that helped steer you toward a career in veterinary medicine. Consider using that moment as the focal point of your essay.
- Be original and thoughtful: Discuss how you would contribute to the profession and patient care, all of which will help you stand out from other applicants.
- As you are telling us why you want to pursue a career in veterinary medicine , explain why you are good candidate for veterinary school. Ask yourself—in a pile of 100 applications, would I enjoy reading my statement? Be sure to convey your passion for veterinary medicine in your statement.
- Many of you have had meaningful experiences with animals or veterinarians as children and these are important but should only be mentioned briefly.
- Your application materials already contain a summary of your accomplishments, so avoid repeating information from your transcripts or reference letters.
- Give yourself time to organize your thoughts, write well and edit as necessary.
- Ask yourself if this essay is a good representation of your character, ideals and aspirations.
- Don’t forget to proofread!
What should NOT be included?
- Avoid cliches: How many times do you think admissions committees have read the phrase, “I love animals”?
- Avoid being vague: "[Insert experience] was challenging and rewarding." What does that mean? Be specific about what was impactful and how it affected you.
- Avoid brash decision-making: Your decision to become a veterinarian should be the result of a series of thoughtful, conscious, and reflective decisions. NOT an instantaneous realization. Similarly, you have not “always known” that you want to be a vet. No one is "born to be a vet." Nothing is innate, you have to work for it.
- Avoid excuses: In general, there are better uses for your essays than explaining away and justifying poor grades, incidents of misconduct, etc. However, if you choose to address these subjects, be sure to focus on what you have learned from those incidents and how your experiences have made you a stronger person. Never, ever blame anyone else for your mistakes.
- Avoid restating resume: Choose ONE or TWO significant and distinguishing experiences to elaborate upon.
- Avoid grandiosity: For example, claiming that you “know what it is like to be a vet from [shadowing/clinical volunteer experience].” No, you do not. That is precisely why you are hoping to go to vet school.
- Avoid inflammatory or controversial topics: You do not know the values, beliefs, and background of the person who is reading your essay. For these reasons, it is advisable to avoid making any strong statements regarding politics, religion, and other polarizing topics. Be extremely cautious to avoid expressing any views that could be construed as derogatory to any group. Additionally, your beliefs are not the only “correct” beliefs.
- Do not lie: Honesty and ethical behavior are the hallmarks of being a veterinarian. Do not include details that you are not prepared to talk about or are simply untrue.
When should I start writing?
You need to begin working on your essays early in the fall semester prior to the application opening in January. Remember that the people who are helping you with your essays will need time to review them and you will need time to work through multiple drafts. You should have several different people objectively read your personal essays and provide constructive feedback. There are also resources on campus that can assist you, such as the Career Center and UGA Writing Center . Consider the feedback you get carefully, but be sure that the essays are still written in your voice. In addition, some of your letter writers will want to see a copy of your essays before they write your letter, so you should strive to have competent drafts on hand by October or November. Your letter-writers are often a great option to help review your essays.

Princeton Pre-Veterinary Society
Princeton University
What are the vet school essay prompts and what are some useful tips and resources for writing the essays?
The personal statement for the VMCAS used to consist of a single prompt: Discuss briefly the development of your interest in veterinary medicine. Discuss those activities and unique experiences that have contributed to your preparation for a professional program. Discuss your understanding of the veterinary medical profession, and discuss your career goals and objectives (5000 characters)
Now, VMCAS asks students to answer each of the following prompts in less than 2000 characters (including spaces), which is roughly 300-350 words:
- There are many career choices within the veterinary profession. What are your future career goals and why?
- In what ways do veterinarians contribute to society and what do you hope to contribute?
- Considering the breadth of society we serve as veterinarians today; what attributes do you believe are essential to be successful within the veterinary profession? Of these attributes, which do you possess and how have you demonstrated these in the past?
Here are documents with tips and resources that you may find helpful. While some discuss the old prompt or a specific supplement, the information may still be relevant:
- https://prevet.princeton.edu/wp-content/uploads/sites/781/2020/07/Mastering-The-VMCAS-Personal-Essay.pdf
- https://prevet.princeton.edu/wp-content/uploads/sites/781/2020/07/Hamilton-Essay-Tips.pdf
- https://prevet.princeton.edu/wp-content/uploads/sites/781/2020/07/Univeristy-of-Florida-Tips.pdf
- https://hpa.princeton.edu/application-process/personal-statement
Remember, many schools also have their own supplemental prompts which may or may not be released on their websites. If you are thinking about applying during a certain year, you can create your account as soon as January of the same year so that you can access all the supplements before the summer and begin brainstorming/drafting asap.
Personal Statement
Admission committees look for applicants who capture the compassion as well as the passion for the field to which they wish to apply. The personal statement is your primary opportunity to distinguish yourself from the thousands of other applicants. Make a lasting impression by showing the admission committee who you are as a person and making the case that you possess the personality traits and characteristics to become a successful health care provider.
The Veterinary Medical College Application Service (VMCAS) prompt is:
Discuss briefly the development of your interest in veterinary medicine. Discuss those activities and unique experiences that have contributed to your preparation for a professional program. Discuss your understanding of the veterinary medical profession, and discuss your career goals and objectives.
Here are some tips specific to veterinary school personal statement:
- Do not regurgitate experiences and other data already existing on other parts of the application.
- Write about your knowledge of the veterinary profession.
- Include information about who you are as a person and what diversity you might bring to the institution.
- Include information about why you'd be a good candidate.
1. Brainstorm
Questions to ask yourself before you write.
- Who are the most influential people in your life? What did they do for you?
- What have been the pivotal moments in your life?
- What accomplishments are you most proud of?
- What obstacles have you overcome?
- What makes you different?
- How will your skills and personality traits add diversity to the class?
- Do you feel a passion for medicine? What is the source of that passion?
- What do you want medical schools to know about you that hasn't been disclosed in other sections of the application?
- How would your family and friends describe you?
- What are your goals and dreams?
Compile an inventory of all the activities, experiences, and relationships/influences that have helped to define the person you are today. Looking back, what can you recall having changed you? How were you affected? What lessons did you learn? What personality traits do they reflect in you? These notes will help you identify the topics or themes on which to focus your statement. As you are brainstorming, you may identify experiences that stir strong emotions. These experiences are likely to be meaningful to you and therefore may be good material for your personal statement. Speak from your heart.
2. Start Writing
Identify your word limit.
Word/character limits for personal statements vary across professions so it is important that you identify your word or character limit before you start writing. The limit for the veterinary school application (VMCAS) is 5000 characters. Generally speaking, this is roughly one page single-spaced. Character limits for common health professions' application services (all include spaces): Allopathic medicine (AMCAS): 5300 characters. For Texas schools (TMDSAS): 5000 characters Osteopathic medicine (AACOMAS): 4500 characters Dentistry (AADSAS): 4500 characters Veterinary (VMCAS): 5000 characters Physician Assistant (CASPA): 5000 characters Accelerated Nursing programs: varies by school; for schools using NursingCAS, the limit is 5000 characters Physical Therapy (PTCAS): 4500 characters Public Health (SOPHAS): 1500 words
Get It on the Page For your first draft, don't get hung up on your beginning or ending. Instead, just start writing. You may feel the urge to write a lot about your personal journey; if so, run with it. This may provide you with good material and you can edit it later.
- Identify the most significant aspects from your notes that will enable you to address one or more of the following standard topics:
- Your motivation for this career
- Influence of your family and early experiences on your life
- Influence of your extracurriculars, volunteer activities, and/or jobs on your life (what have you learned, how have you demonstrated leadership, and how have you matured?)
- Your qualifications (unique attributes, personal qualities, and/or skills that set you apart)
- Long term goals
Use your experiences to provide personal insight into your personal attributes. Weave a story that helps the reader understand who you are as a person rather than simply listing your achievements. Avoid repeating information that is included elsewhere on your application unless you are elaborating on how an experience has shaped you and your motivation for a career as a health professional.
Address Academic Irregularities If Necessary
You may wish to use a section of your personal statement to address academic irregularities such as withdrawals, incompletes, repeated courses, or significant fluctuations in your academic record. If applicable, you may mention special hardships, challenges, or obstacles that may have influenced your academic performance. Instead of making excuses, acknowledge and explain the situation, and if applicable, what you are doing differently and what you have learned.
Take Your Time and Take Breaks
- Take breaks from writing instead of trying to write everything in one sitting. Picking up your draft later can test whether your writing flows.
- Read your writing aloud and listen to what you hear to check for grammatical errors, flow, and clarity.
3. Organize Your Writing
Overall shape of the essay.
There is no one correct format for a personal statement. Strong personal statements often begin with a brief background that will serve as the foundation for the message you wish to convey. The bulk of the essay will illustrate the impression you wish to make on the reader, and will flow into a succinct conclusion. Always keep in mind that your essay must be interesting enough to immediately grab the reader's attention and compelling enough to hold it whether your essay is the first or fiftieth one the reader has seen that day. Though you are not limited to these examples, some people find it helpful to use one of the following approaches:
- I've always wanted to be a doctor/dentist/veterinarian
- My parents are health care providers
- Being a patient/having a sick family member made me want to become a health care provider
- My experiences in a clinical environment piqued/confirmed my interest in the health professions
- Through my [non-health care] experiences, I have developed the skills and personal qualities to be an effective health care provider.
Organizational Strategy
You may find it helpful to use one of the following types of organizational strategies with your outline:
Standard structure: This type of organization is one you are probably very familiar with from your academic writing. In your first paragraph, you introduce the main points of your essay. In the following paragraphs, you provide evidence to support each of your main points (usually defending one point per paragraph). In your final paragraph, you reiterate your main points in the context of the evidence you presented, possibly leaving the reader with some "big idea" that takes your message one step further.
Comparison: This organizational structure attempts to draw a comparison or analogy between two seemingly unrelated things. In the case of medical school applicants, these essays usually compare a non-medical life experience/talent/interest/famous quote with the field of medicine or the applicant's desire to pursue medicine. It is common for applicants to begin with a story, personal anecdote, quote as a lead and then spend the rest of the essay describing how the lead relates to or sheds light on medicine or their goal of becoming a physician.
If you use this structure, make sure that you provide adequate reflection on how your two disparate ideas connect (or don't connect) to each other. Make your arguments explicit; don't leave it up to the audience to figure out your points. Also, don't get too abstract or philosophical in your comparisons. You don't need to say something profound; rather, just be yourself. Remember, your discussion should always lead back to you and your motivations to enter your health profession of choice.
Chronology: In this type of outline, the writer takes the reader through the various steps in his/her life that led him/her to medicine. The introduction is usually the initial event that started the writer on his/her journey toward becoming a doctor. The writer then generally recounts the subsequent events in which he/she further explored and/or was further drawn into the medical profession before concluding with how all these events brought him/her to where he/she is today.
The advantage of this approach is that it allows for a more personal approach and helps the admissions committee to know you by turning the focus of the essay to you throughout the various stages of your life. The drawback is that the points you are trying to make can get lost in the narration of your life. To avoid this potential danger, make sure you clearly state how each of these events shaped you and your decision to pursue a health profession as well as the important lessons you learned along the way.
Opening Sentence
Your opening sentence can simultaneously set the theme of your essay and engage the reader. Here are some different types of leads you may wish to try out:
Standard: State what you will be talking about in the paper. This can take on the form of a "thesis" in many ways (i.e. "My interest in medicine began with my trip to Honduras"). This lead sets up the reader for a focused, well-structured essay and helps you to get the point quickly (infinitely useful in a short essay like the personal statement). Creative: Add interest by making the reader wonder what will come next (i.e. "I was awoken by the beating of African drums that filled the air"). Action: Take the reader into the middle of the action. This is useful if you're trying to conserve space or if your essay begins with a story (i.e. "Our car breaks screeched as the truck came hurtling toward us"). Personal: Reveal something about you (i.e. "My grandmother's words touched my soul like nothing else"). Quotation: Begin with a direct quotation or paraphrase whose meaning pertains to the main points you are trying to convey in your essay (i.e. "FDR once proclaimed that 'the only thing we have to fear is fear itself,' and I have frequently tried to follow his advice"). Avoid using clichés.
Dialogue: Put the reader into the middle of a conversation, whether it be an actual talk between two people or your own internal thoughts (i.e. "'I don't want to die,' cried the little girl"). Informative: State a fact that is relevant to the topic of your essay (i.e. "Every doctor remembers her first patient").
Ask yourself if your essay can stand without an introduction. It may be appropriate to simply begin with the action of the story (in media res as they say) and then move on to discussing how that story ties into the points you will be making throughout the rest of the essay.
Tie together the most important points you've made in your essay to bring the reader full-circle. The final sentence or two of your essay can be enough for a conclusion, especially if you're running low on space. The important thing is to make sure you bring your thoughts to their logical end and create a positive, memorable image in the reader's mind. Endings are the last experience the admissions committee will have with your essay, so your goal should be to leave them thinking that it was a satisfying read and wishing that there was more.
4. Get Feedback
Find someone to give you critical feedback who isn't afraid to hurt your feelings. Give your draft to multiple sources to get different perspectives. Ideally you should ask someone who is a good writer to help you with your writing, someone who knows you well enough to verify if your writing sounds like you, and someone who doesn't know you as well who can provide perspective on the impression you are making. Clarity in your writing will reflect good communication skills. By the end of the statement, the reader should be able to see the world through your eyes.
5. Refine Your Writing
The most important part of the personal statement is the impression of yourself that you are creating. After reading your personal statement, readers may ask themselves if you would be interesting to interview.
Quality of Writing
It is expected that your personal statement be error-free. Grammatical errors may reflect carelessness.
Further resources
For further advice on writing personal statements in general, visit the Writing Center Resources page.
Contact Name
Courtney Hance
Director of Health Professions Advising

Help us provide an accessible education, offer innovative resources and programs, and foster intellectual exploration.
Site Search
Life In Vet School & Tips On Getting In
So you want to become a veterinarian. Now what? Some people say that veterinary school is the hardest type of professional school to get accepted to. I disagree. Getting accepted in to veterinary school is not that hard, but it does take strategy! This blog will: 1) Provide information to aspiring veterinary students that will help them become the most competitive candidate they can be. 2) Provide a glimpse into what veterinary school is like at UC Davis. Enjoy! -Sharon

Veterinary School – Personal Statement Example
Posted on June 23, 2010 April 27, 2015 Author [email protected] 6 Comments
I know it helps to read a successful veterinary school applicant’s personal statement, so I am posting mine on this site.
*** Sharon now offers personal statement editing! *** See Career Coaching for details: http://www.lifeinvetschool.com/coaching/
Please do not attempt to copy or use this statement in any way, shape, or form — plagiarism is a serious issue and it is one way to make sure you never get into veterinary school.
Sharon Ostermann’s Personal Statement from VMCAS Application in 2008
Brakes screeched, tires squealed, and the car abruptly came to a halt. My heart was pounding. My father opened his door and, without hesitation, darted across the highway, dodging cars to rescue a defenseless turtle from the next car’s tire. Throughout my childhood in New York, rescuing turtles was a common practice for me and my father. Looking back, my father’s heroic sprints into oncoming traffic were not his most intelligent moves, but through them he communicated a very strong message – the value of an animal’s life. That message continues to motivate me today.
I have consistently devoted my life to giving animals another chance at theirs-be it rescuing turtles from roads, frogs from pools, or injured birds from dogs. Often I have been able to release the animals into their natural habitat; other times my efforts are too little, too late; and, occasionally, I end up raising an abandoned baby rabbit. My home has also been a refuge for rats, hamsters, birds, fish, turtles, and chinchillas, but never a dog and, until recently, never a cat. It almost goes without saying that my desire to care for animals led me to want to become a veterinarian, but the untraditional and circuitous path I have taken toward that goal is worthy of note.
A year ago a pre-vet student asked me a very frank question: “What’s stopping you?” At the time I was in graduate school, studying psychology, while concurrently running my own photography business. I did not have the time or money-much less courage-to change course. Yet, finding a deeper answer to her question became a driving force in my life. In time, I realized that animals have been the most important and most consistent facet of my life. So, what was keeping me from pursuing my dream? In the end, it was fear.
Fear of change kept me on an unfulfilling path where as courage, along with family support, freed me to pursue my dream. Realizing that a career in veterinary medicine best fit my values and lifestyle felt both liberating and daunting. While ready to change fields I faced intense coursework and the task of accumulating experience. Even so, without hesitation, I dove right in. With the support of Dr. ____ at the _____ Humane Society (_HS), I transitioned from helping hand at the _HS clinic to intern, a role requiring responsibility and participation in all situations, emergencies included. On my first day I helped treat the degloved leg of a dog that was hit by a car. And, by accepting all animals, _HS gives me experience in small animal, exotic, avian, and wildlife medicine. I love the challenges I face and my ability to learn quickly helps me to act competently in this setting. However, there are other aspects of veterinary work.
Since I knew my experience at _HS only gave me insight into one type of veterinary practice, I began volunteering at the ___ Zoo. There, I am involved in the health care and training of wild animals. Unlike _HS, where wildlife is given short-term care, rehabilitated and released, the zoo does not generally intend to release animals and, thus, invests in long-term care by way of regular health exams and medication. Facets of each of these environments attract me. I value the rehabilitative aspect of _HS, yet desire the rapport between animals and their caretakers that is achieved with long term care.
I also value community service on a global scale. Living in Ecuador and traveling abroad made me aware of the need for veterinary care in developing countries. To help fill this need, I will join a team to provide free veterinary care in Central America, where my Spanish language skills will be of use. I am excited for the opportunity to perform surgery and vaccinate under veterinary supervision and I am sure it will be the first of many trips of this nature for me. I can think of nothing more rewarding than putting my skills to work in the places that need my help most.
Ultimately, my journey makes me unique. Dabbling in other fields and work settings let me develop as an individual, reflect upon my decisions and finally choose veterinary medicine as a career. Through my indirect path, I gained a better understanding of myself, confidence in my chosen profession, and skills that may prove as valuable to a veterinarian as they are to a psychologist. In particular, the interpersonal skills that I have honed in the field of psychology will allow me to counsel and communicate with the owners of my future patients, an invaluable asset.
After many years, I am on track toward becoming a veterinarian. Experience has taught me that some things change and others do not, while that which remains the same defines us, drives us, and makes us who we are. Though I no longer live in New York, my father still rescues turtles; and my love and commitment to animals, which he inspired, remains intact. Whenever I see a turtle I smile as I am reminded of how I got to where I am today.
*** Sharon now offers personal statement editing! ***
See career coaching for details: http://www.lifeinvetschool.com/coaching/, share this:, 6 thoughts on “veterinary school – personal statement example”.
Thank you 🙂 Always helps reading some things x
This helped me a lot! Thank you for posting 🙂
That’s a sweet story.
Thank you so much for sharing your personal statement with the rest of is. It always helps to read some samples before assembling our own!
I really appreciate you posting this! This personal statement is stressing me out and it is helpful to see what other people have written.
Nice post, I love the website.
Comments are closed.
- Admission Essay
- Statement of Purpose Editing
- Personal Statement Editing
- Recommendation Letter
- Motivation Letter
- Cover Letter
- Supplemental Essay
- Letter of Continued Interest
- Scholarship Essay
- Role Model Essay
- Our Editors
- College Admission Essay Examples
- College Cover Letter Examples
- College Personal Statement Examples
- Graduate Personal Statement Examples
- Graduate Statement of Purpose Examples
- MBA Essay Examples
- MBA Personal Statement Examples
- MBA Resume Examples
- MBA Recommendation Letter Examples
- Medical School Personal Statement Examples
- Medical School Recommendation Letter Examples
- Pricing Plans
- Public Health
- Dissertation
- Research Paper
- Thesis Editing
- Academic Editing
- Motivation letter
- Letter of Recommendation
- Personal Statement
- Statement of Purpose
Vet School Personal Statement Sample Essay EDITED
EssayEdge > Blog > Vet School Personal Statement Sample Essay EDITED
EssayEdge significantly improves each essay using the same voice as the author. The only way to evaluate editing is to compare the original essay with the edited version. We significantly improve essays both for clients who write poorly and for clients who write well.
Table of Contents:
Edited Essay
Was it Jane Goodall’s In the Shadow of Man that changed my mind? How about the rush of excitement surrounding Earth Day in junior high? Was it my high school science teacher who revealed the truth about endangered species, habitat loss, acid rain, and ozone layer depletion?
When I look back and try to pinpoint the moment when I started to see things differently, too many events come to mind. I know that it did not happen in one day. From the time I saw David Suzuki talk on deforestation and our ecological footprint, to the time I euthanized my first litter of kittens because of pet overpopulation, my life has been a process of continual learning and discovery. Not all the lessons have been pleasant. Sometime while studying the harmful effects of large-scale farming during college, I realized that I needed to do more than merely recycle cola bottles, avoid aerosol cans, and make sure that my animals were neutered. I needed to do more.
This process of discovery began in rural Canada, where I spent the first six years of my life as an only child. My pets were my constant companions. I played make-believe not with dolls or with other little girls, but with the barn cats who were nice enough to tolerate the dresses and baby carriages. My sheep dog, Charlie, treated me as one of his flock, herding me from place to place as he saw fit. When my sister and cousins were born, they became part of my circle of friends, but Charlie and the other animals were never excluded from our games. I simply assumed everyone loved animals as much as I did.
Need help? Check out EssayEdge editing services:
My realization that this was not true came in the fourth grade when I witnessed a harrowing act of animal cruelty. Two older children with a sadistic streak tied one of my classmates to a tree and tortured his kitten in front of him. I still remember the description of the torture from the newspaper–the kitten’s eyes were gouged out, and he had sticks shoved through his body. I cried for weeks. I do not know what happened to the two boys, but I suspect that the incident was treated as yet another case of “boys will be boys.”
I have since encountered numerous other cases of atrocities committed against animals, especially through my work at an SPCA. In disbelief, I have witnessed the results of dogs being dragged behind snowmobiles, cats left out to freeze, horses starved to death, and innumerable puppies and kittens being thrown away like so much garbage. Determined to help stop the abuse, I became involved with activism and policy, assisting in fundraising and letter writing campaigns to protest the unfair treatment of animals.
While earning my B.Sc. in Agriculture, I learned that the family farm is an antiquated and outmoded ideal. Farming has become big business. The result of large-scale industrial farming is the overcrowding of animals in inhumane conditions, excessive antibiotic and pesticide use, and devastating clearcutting of the rainforest. Knowing that I had to contribute to environmental protection on a personal level, I made the decision to eat only free range meat. Limiting my meat consumption proved no easy task, particularly since free range meat is often hard to obtain in small quantities and is prohibitively expensive for most college students. Finally, convinced by the literature on animal welfare and the environmental movement, I decided to give vegetarianism a try. Giving up meat was perhaps the most difficult thing I have ever done, yet I knew that proper policy-making had to start with personal sacrifices. It took me two full years to master my cravings and become a lacto-ovo vegetarian.
Vegetarianism complemented my ever-increasing interest in animal rights and environmentalism. From the time I was a little girl, I have always known that I wanted to be a veterinarian. Nonetheless, my newfound concern for policy suddenly opened up several previously unconsidered career paths. At first, I found the abundance of possibilities daunting. Not wanting to take a year off school, I decided to enroll in a few graduate courses to see where they led me. After taking additional classes and time off to work and regroup, I finally came across a poster for a master’s degree program in Animals and Public Policy. I thought it was too good to be true; the program seemed to match my background, interests, and aspirations perfectly. I had no idea that such a program actually existed.
Although I have not renounced my ultimate ambition of becoming a veterinarian, I know that XXX’s program will allow me to develop expertise in an area that is personally important to me. My interest in animal welfare is not restricted to helping individual animals–I believe that I can complement my veterinary practice by opening people’s eyes and by helping them remember the wonder they felt as children when they saw their first giraffe. We have become dangerously blasé about the ecological diversity surrounding us, and I believe that, in order to preserve what is left, cases of animal abuse must be treated as serious crimes. By understanding and shaping animal welfare policy, I believe that I will be able to leverage my knowledge of veterinary medicine to make a powerful case in defense of animal rights. I believe that one person can make a difference, and I have no doubt that XXX’s program is the most efficient way for me to attain my objective.
Customer’s Comments
“I cannot thank you enough for editing my essay. You took what I said, kept the same tone and modified it to make it sound great!! I will keep you posted on how I make out.”
The essay is colorful and comprehensive–I am impressed with your ability to enumerate your qualifications for a master’s degree while retaining a descriptive, engaging style. Your essay is packed with interesting details, and it was a pleasure to work on this piece.
Despite its comprehensive and engaging style, your essay did contain a few weaknesses. Your grammar and phrasing were awkward in parts, and a few of your transitions were too abrupt or were missing altogether. In addition, your conclusion was too abstract; you should always anchor your arguments in concrete detail.
In your note, you inquired about the desirability of giving a title to your essay. Titles are unnecessary in application essays, and admissions officials generally prefer that they be omitted. If you print your essay on a separate sheet of paper, I suggest that you simply include the question in italics at the top of the sheet.
Your revised essay is well within the word limit, and I have illustrated a few places in which you might want to add additional information to make your passages more concrete.
As for sentence level changes, I concentrated on refining your language, highlighting your most vivid and interesting ideas, and making the logic of your ideas stand out more clearly. I rephrased passages that contained slightly awkward English, eliminated phrases or sentences that seemed extraneous or repetitive, and varied vocabulary to render the text more lucid and interesting.
The following are specific comments on the individual paragraphs of your essay:
Paragraph 1
Your use of rhetorical questions is effective in this introduction, but I have reworked your original first paragraph to give it more style and verve.
I transformed two of your original questions into a statement, since having too many questions in a row makes the rhythm of your introduction uninteresting. By varying sentence structure, and by breaking up your first paragraph into two parts, I have provided a new introduction that is compelling and vivid without bogging the reader down in a swamp of interrogatives.
Paragraph 2
The description of your childhood connection to animals is strong, but I have shown how you can make the passage even more compelling. For instance, I suggest interjecting new details that cement your images into the reader’s mind. Here is one such suggestion: “My sheep dog, Charlie, treated me as one of his flock, herding me from place to place as he saw fit.”
Paragraph 3
You were missing a strong transition between the second and third paragraphs. See the transition I have provided.
Paragraph 4
The description of your developing social conscience is very effective. Nonetheless, I suggest slight adjustments to verbiage to make your points more powerful. Instead of saying, “I helped with fund-raising and wrote letters,” for instance, I suggest, “I became involved with activism and policy, assisting in fundraising and letter writing campaigns.”
Paragraph 5
You need to draw out the logic of why it is bad that farming has become big business. See the new sentence I have proposed which addresses the new ecological concerns raised by industrial farming.
Paragraph 6
You should add a word or two about the graduate courses you took. What did you study? I have streamlined the discussion of your indecision to avoid the impression that your interests were unfocused.
“Though I’ve always wanted to be a veterinarian, my newfound concern for animal issues and the environment were pulling me in another direction.”
The logic of this transition sentence is not entirely clear. Your activism complements your vegetarianism, so I rephrased this transition to better highlight the synergy between your two activities.
Paragraph 7Â
Since you assert that your master’s degree will be useful in your eventual work as a veterinarian, you need to explain why. Apart from the obvious fact that through both activities you will be helping animals, it was not very clear from the original essay how you plan to combine veterinary science and policy. I have addressed this by connecting the two ideas with the following sentence:
“By understanding and shaping animal welfare policy, I believe that I will be able to leverage my knowledge of veterinary medicine to make a powerful case in defense of animal rights.”
Paragraph 8
Your original final paragraph was too abstract and dreamy. It is best to avoid waxing poetic at the end of your essay. Instead, I suggest ending your essay with the previous paragraph, ensuring that it concludes on a concrete and memorable note.
Congratulations on a great essay and on a very interesting career path. I wish you the best of luck in the admissions process.
Sincerely, Your EssayEdge Editor
This paper sample is one of the orders completed by EssayEdge editors. The amount of information you get depends on your chosen pricing plan, but we never deliver papers with no comments. The critique and feedback help clients see their mistakes and improve writing quality. Order personal statement editing on EssayEdge to evaluate the performance of editor
Popular Posts
June 2, 2022 How To Start a Scholarship Essay: Catch Reader’s Attention Fast
May 16, 2022 My Role Model Essay: A Few Ways to Elaborate on The Subject
May 3, 2022 How To Start a Personal Statement? | Writing Tips and Samples
Related Posts
July 14, 2021 Personal Statement Sample: How Can It Help You With Writing?
June 3, 2021 Clichés in College Essay Examples: How To Recognize Them?
October 26, 2020 Alternative Medicine Application Essay Sample – Edited
©2024 Student Media LLC. All rights reserved.
EssayEdge: Essay Editing & Proofreading Service.
Our mission is to prepare you for academic and career success.
- Log In
- Sign Up
- Forgot password
Unable to log in? Please clear your browser's cache and then refresh this page and try again
Reset password Please enter your email address to request a password reset.
Check your email We’ve just sent a password reset link to your email.
This information is used to create your account
Get the Reddit app
All things Vet school
Vet School Essays
Can I get some example essays? I'm having trouble with the flow of my stories, especially with the personal statement because reasons why I want to be a vet have grown and developed throughout my entire life. Writing my life chronologically seems boring, but I'm not sure how to write it any differently. Thank you in advance
- Go To Content
- Press releases
Rethinking English essay scores: The argument for argument over grammar
- Linguistics
- Foreign language education
To get high scores at essay writing tests, learners of English as a foreign language need to focus on good arguments more than on complex grammar. The Kobe University finding challenges conventional approaches to test preparation and scoring rubrics.

Writing essays is a well-established tool for monitoring progress in learning English as a foreign language, as it provides a snapshot of a student’s mastery of grammar and vocabulary. Especially in Japan, where English language tests are often required for university admission and students closely follow advice on how to achieve high scores on these tests, a “good essay” is often seen as one that demonstrates a high level of grammatical complexity. But is this actually reflected in test scores?
Kobe University linguist YASUDA Sachiko expresses her doubts: “Based on my experience of teaching academic writing to students at various levels in Japan, I believe that linguistically complex texts do not always result in better writing.” She therefore decided to conduct an experiment with over 100 Japanese high school students. Yasuda had them write a short essay on a given topic and looked at the relationship between the linguistic complexity of the texts and the writers’ ability to present complex arguments, and how these two related to how the texts were graded according to official rubrics. She adds, “This study is the first to focus on the relationship between features of linguistic complexity and features of meaning complexity; no one else in the relevant fields has looked at the relationship between these two.”
The results, published in the journal Assessing Writing , confirmed her suspicions. She found that high-scoring essays shared features related more to the ability to express complex meaning, such as lexical diversity, noun modification, and soundness and number of arguments, than to structural complexity. “Interestingly, low scoring essays showed the highest level of complexity in finite adverbial dependent clauses,” the linguist writes in her paper. Emphasizing this point, the ability to express complex meaning was strongly correlated only with using diverse expressions and the ability to modify their meaning, but not with grammatical features. Yasuda concludes, “Simply having complex sentence structures does not necessarily lead to a better essay.”
The findings have implications for how essay writing tests are scored. The Kobe University researcher explains: “Current rubrics for writing questions on language tests instruct test-takers to ‘use complex grammar appropriately’ or ‘a variety of complex structures.’ However, since sentence complexity does not significantly affect overall essay quality, it may be more appropriate to use terms such as ‘contextually appropriate grammar’ or ‘genre-appropriate grammar.’” Thus arguing that the ability to express one’s opinion in varied and complex ways is a marker of students’ writing ability, she advocates that this characteristic should be more represented both in the way tests are scored and how feedback is provided to students.
This so-called washback effect of test scoring rubrics on the way language is taught is at the heart of what drives Yasuda. She says: “I am committed to using the results of this study for practical applications, such as refining assessment criteria for evaluating students’ writing, developing tasks and materials to improve their writing skills, and identifying the key knowledge that teachers need to help students become better writers. The ability to write in English has become increasingly important in the 21 st century, as it is a crucial medium that allows us to connect with others around the world.”
Acknowledgements
This research was funded by the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (grant JP24K04031JSPS).
Original publication
S. Yasuda: Does “more complexity” equal “better writing”? Investigating the relationship between form-based complexity and meaning-based complexity in EFL learners’ argumentative writing . Assessing Writing (2024). DOI: 10.1016/j.asw.2024.100867
Release on EurekAlert!
Researchers.
Yasuda Sachiko

- Institute for Promotion of Higher Education
- Graduate School of Intercultural Studies
More about these topics

What Makes a Class Attractive to University Students?
- Subscribe Digital Print

- Tokyo governor race
- Kim-Putin summit
- Japan economy
- Latest News
- Deep Dive Podcast
Today's print edition
Home Delivery
- Crime & Legal
- Science & Health
- More sports
- CLIMATE CHANGE
- SUSTAINABILITY
- EARTH SCIENCE
- Food & Drink
- Style & Design
- TV & Streaming
- Entertainment news
Japan study downplays complex grammar in improving English writing skills

English learners may improve their writing skills in the language if they focus on making good arguments rather than mastering complex grammar and vocabulary, according to new Japanese research.
In 2023, Yasuda conducted an experiment in which she had 102 students at a public secondary school in Japan write an argumentative essay on an assigned topic in English. She then let two writing experts — who did not know the purpose of the experiment — grade their essays.
In a time of both misinformation and too much information, quality journalism is more crucial than ever. By subscribing, you can help us get the story right.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Vet Personal Statement Example #1. "Saddle up," is my favorite phrase of all time and it conveys with it a sense of adventure that few other phrases ever can. I suppose a lot of this comes from my early years where I loved cowboy stories, but it continued on through my life once I started learning about horses.
Your vet school personal statement should be thoughtful, heartfelt, and informative. You should ensure that your story is easy to read by using descriptive language and lining up the highlights of your work experience in order. Consider your unique perspective. Remember, these programs are competitive.
6. Set a Confident and Positive Tone. When you discuss your future goals, write about the good things that you are going to do WHEN you graduate from veterinary school. Not the things you will do IF you graduate from veterinary school. This will help you come across as confident and capable.
1. Give Yourself Time. Most students apply for vet school through the Veterinary Medical College Application Service (VMCAS), but you should prepare your VMCAS personal statement well in advance. Good writing takes time. Demonstrate your communication skills, which play an important part in how applicants — and veterinarians — are evaluated.
Ethical behavior, sound judgement, communication, and critical/creative thinking were ranked as the top four characteristics (Conlon et al., 2012). Veterinary school candidates should keep those four characteristics in mind throughout their writing process and showcase experiences that exemplify these characteristics.
VMCAS essay examples are a great place to start when you're preparing to apply to veterinary school. After researching vet school rankings and looking into the best vet schools in your chosen area, you've finally decided on the schools you would like to apply to. One of the items you'll need to include in your VMCAS application is a personal essay.
Vet school committees will expect you to remain professional and precise in what you say with word limitations in mind. However, you should aim for a conversational, friendly tone. Your personal statement is about you, so it should give the admissions committee an insight into your personality. Try to find a happy medium where you don't sound ...
Don't expect to write the entire statement in one, two, or even three sittings. Sure it can be done, but you really don't want that to be the case for you. The amount of time and thought you put into your statement will be readily apparent in the finished product. Sit down to write when inspiration strikes and stop when you're feeling ...
Here are some tips to help you make your essays the best possible representation of you as a qualified applicant to the University of Florida College of Veterinary Medicine: Start writing early. Give yourself time to think about what you want to write. Spend a few days away from it and read it again. Allow yourself the opportunity to think of ...
Here are some tips to help you make your essays the best possible representation of you as a qualified applicant to the University of Florida College of Veterinary Medicine: Start writing early. Give yourself time to think about what you want to write. Spend a few days away from it and read it again. Allow yourself the opportunity to think of ...
6. Secure glowing letters of recommendation. Every vet school applicant needs to obtain at least three letters of recommendation. But don't think of these evaluations as items you can check off a list. Most DVM programs expect at least one letter be written by a veterinarian.
Most veterinary medicine candidates open their personal statement with why they want to become a vet. Motivations for wanting to study any course at university are always important. We recommend you write a series a notes about your skills, experience, hobbies, extracurricular activities, career plans and anything else that is relevant to your ...
Mastering the VMCAS Personal Essay. The application to vet school, commonly referred to as the VMCAS, can be overwhelming. Vet school applications are competitive, and they only come after years of gathering experience, mastering science classes, tracking veterinary hours, and making sure that vet school is the path for you.
Your application materials already contain a summary of your accomplishments, so avoid repeating information from your transcripts or reference letters. Give yourself time to organize your thoughts, write well and edit as necessary. Ask yourself if this essay is a good representation of your character, ideals and aspirations.
Applicants can show their potential for success in vet school by writing excellent personal statements or acing interviews. Admissions reviewers do not expect perfection. They want to see determination, resilience, growth, and triumph over adversity. ... Ask yourself if this essay is a good representation of your character, ideals, and aspirations.
What are the vet school essay prompts and what are some useful tips and resources for writing the essays? The personal statement for the VMCAS used to consist of a single prompt: Discuss briefly the development of your interest in veterinary medicine. Discuss those activities and unique experiences that have contributed to your preparation for ...
Word/character limits for personal statements vary across professions so it is important that you identify your word or character limit before you start writing. The limit for the veterinary school application (VMCAS) is 5000 characters. Generally speaking, this is roughly one page single-spaced. Character limits for common health professions ...
Sharon Ostermann's Personal Statement from VMCAS Application in 2008. Brakes screeched, tires squealed, and the car abruptly came to a halt. My heart was pounding. My father opened his door and, without hesitation, darted across the highway, dodging cars to rescue a defenseless turtle from the next car's tire.
The TL;DR of my vet school application essay would read as follows: After 4 years of working in different areas of research, that included neuroscience, human exposure, toxicology, and pathology, I discovered that I loved pathology and wanted to become an anatomic pathology veterinarian. I know exactly what I want to do in vet school and what ...
EssayEdge > Blog > Vet School Personal Statement Sample Essay EDITED. Updated: April 8, 2024. EssayEdge significantly improves each essay using the same voice as the author. The only way to evaluate editing is to compare the original essay with the edited version. We significantly improve essays both for clients who write poorly and for clients ...
Bonus points if you want to include why you want to go to a particular school (such as on a school-specific supplemental essay) Overall, you are trying to show them you have an understanding of the profession you want to enter, and give them an understanding of who you are so that they will think you'd make a good doctor and want to train you ...
Your personal statement is your opportunity to talk about not only why you want to be a vet, but what kind of vet you want to be. Unless it specifically says not to mention animals or veterinary experiences (like Tufts' essay prompt did last year), those things are totally fair game. I hope all that made sense. 4. Reply.
To get high scores on essay writing tests, learners of English as a foreign language need to focus on good arguments more than on complex grammar. The Kobe University finding challenges ...
Those feelings of knowing that I made a difference in the life of that dog and his owner….that feeling was something I'll never forget . I knew that was my calling. I sent in my story along with photos. The admissions committee called me personally to accept me while they were reviewing my application.
She therefore decided to conduct an experiment with over 100 Japanese high school students. Yasuda had them write a short essay on a given topic and looked at the relationship between the linguistic complexity of the texts and the writers' ability to present complex arguments, and how these two related to how the texts were graded according ...
English learners may improve their writing skills in the language if they focus on making good arguments rather than mastering complex grammar and vocabulary, according to new Japanese research.