An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- v.12(6); 2020 Jun


Social Media Use and Its Connection to Mental Health: A Systematic Review
Fazida karim.
1 Psychology, California Institute of Behavioral Neurosciences and Psychology, Fairfield, USA
2 Business & Management, University Sultan Zainal Abidin, Terengganu, MYS
Azeezat A Oyewande
3 Family Medicine, California Institute of Behavioral Neurosciences and Psychology, Fairfield, USA
4 Family Medicine, Lagos State Health Service Commission/Alimosho General Hospital, Lagos, NGA
Lamis F Abdalla
5 Internal Medicine, California Institute of Behavioral Neurosciences and Psychology, Fairfield, USA
Reem Chaudhry Ehsanullah
Safeera khan.
Social media are responsible for aggravating mental health problems. This systematic study summarizes the effects of social network usage on mental health. Fifty papers were shortlisted from google scholar databases, and after the application of various inclusion and exclusion criteria, 16 papers were chosen and all papers were evaluated for quality. Eight papers were cross-sectional studies, three were longitudinal studies, two were qualitative studies, and others were systematic reviews. Findings were classified into two outcomes of mental health: anxiety and depression. Social media activity such as time spent to have a positive effect on the mental health domain. However, due to the cross-sectional design and methodological limitations of sampling, there are considerable differences. The structure of social media influences on mental health needs to be further analyzed through qualitative research and vertical cohort studies.
Introduction and background
Human beings are social creatures that require the companionship of others to make progress in life. Thus, being socially connected with other people can relieve stress, anxiety, and sadness, but lack of social connection can pose serious risks to mental health [ 1 ].
Social media
Social media has recently become part of people's daily activities; many of them spend hours each day on Messenger, Instagram, Facebook, and other popular social media. Thus, many researchers and scholars study the impact of social media and applications on various aspects of people’s lives [ 2 ]. Moreover, the number of social media users worldwide in 2019 is 3.484 billion, up 9% year-on-year [ 3 - 5 ]. A statistic in Figure 1 shows the gender distribution of social media audiences worldwide as of January 2020, sorted by platform. It was found that only 38% of Twitter users were male but 61% were using Snapchat. In contrast, females were more likely to use LinkedIn and Facebook. There is no denying that social media has now become an important part of many people's lives. Social media has many positive and enjoyable benefits, but it can also lead to mental health problems. Previous research found that age did not have an effect but gender did; females were much more likely to experience mental health than males [ 6 , 7 ].

Impact on mental health
Mental health is defined as a state of well-being in which people understand their abilities, solve everyday life problems, work well, and make a significant contribution to the lives of their communities [ 8 ]. There is debated presently going on regarding the benefits and negative impacts of social media on mental health [ 9 , 10 ]. Social networking is a crucial element in protecting our mental health. Both the quantity and quality of social relationships affect mental health, health behavior, physical health, and mortality risk [ 9 ]. The Displaced Behavior Theory may help explain why social media shows a connection with mental health. According to the theory, people who spend more time in sedentary behaviors such as social media use have less time for face-to-face social interaction, both of which have been proven to be protective against mental disorders [ 11 , 12 ]. On the other hand, social theories found how social media use affects mental health by influencing how people view, maintain, and interact with their social network [ 13 ]. A number of studies have been conducted on the impacts of social media, and it has been indicated that the prolonged use of social media platforms such as Facebook may be related to negative signs and symptoms of depression, anxiety, and stress [ 10 - 15 ]. Furthermore, social media can create a lot of pressure to create the stereotype that others want to see and also being as popular as others.
The need for a systematic review
Systematic studies can quantitatively and qualitatively identify, aggregate, and evaluate all accessible data to generate a warm and accurate response to the research questions involved [ 4 ]. In addition, many existing systematic studies related to mental health studies have been conducted worldwide. However, only a limited number of studies are integrated with social media and conducted in the context of social science because the available literature heavily focused on medical science [ 6 ]. Because social media is a relatively new phenomenon, the potential links between their use and mental health have not been widely investigated.
This paper attempt to systematically review all the relevant literature with the aim of filling the gap by examining social media impact on mental health, which is sedentary behavior, which, if in excess, raises the risk of health problems [ 7 , 9 , 12 ]. This study is important because it provides information on the extent of the focus of peer review literature, which can assist the researchers in delivering a prospect with the aim of understanding the future attention related to climate change strategies that require scholarly attention. This study is very useful because it provides information on the extent to which peer review literature can assist researchers in presenting prospects with a view to understanding future concerns related to mental health strategies that require scientific attention. The development of the current systematic review is based on the main research question: how does social media affect mental health?
Research strategy
The research was conducted to identify studies analyzing the role of social media on mental health. Google Scholar was used as our main database to find the relevant articles. Keywords that were used for the search were: (1) “social media”, (2) “mental health”, (3) “social media” AND “mental health”, (4) “social networking” AND “mental health”, and (5) “social networking” OR “social media” AND “mental health” (Table 1 ).
Out of the results in Table 1 , a total of 50 articles relevant to the research question were selected. After applying the inclusion and exclusion criteria, duplicate papers were removed, and, finally, a total of 28 articles were selected for review (Figure 2 ).

PRISMA, Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses
Inclusion and exclusion criteria
Peer-reviewed, full-text research papers from the past five years were included in the review. All selected articles were in English language and any non-peer-reviewed and duplicate papers were excluded from finally selected articles.
Of the 16 selected research papers, there were a research focus on adults, gender, and preadolescents [ 10 - 19 ]. In the design, there were qualitative and quantitative studies [ 15 , 16 ]. There were three systematic reviews and one thematic analysis that explored the better or worse of using social media among adolescents [ 20 - 23 ]. In addition, eight were cross-sectional studies and only three were longitudinal studies [ 24 - 29 ].The meta-analyses included studies published beyond the last five years in this population. Table 2 presents a selection of studies from the review.
IGU, internet gaming disorder; PSMU, problematic social media use
This study has attempted to systematically analyze the existing literature on the effect of social media use on mental health. Although the results of the study were not completely consistent, this review found a general association between social media use and mental health issues. Although there is positive evidence for a link between social media and mental health, the opposite has been reported.
For example, a previous study found no relationship between the amount of time spent on social media and depression or between social media-related activities, such as the number of online friends and the number of “selfies”, and depression [ 29 ]. Similarly, Neira and Barber found that while higher investment in social media (e.g. active social media use) predicted adolescents’ depressive symptoms, no relationship was found between the frequency of social media use and depressed mood [ 28 ].
In the 16 studies, anxiety and depression were the most commonly measured outcome. The prominent risk factors for anxiety and depression emerging from this study comprised time spent, activity, and addiction to social media. In today's world, anxiety is one of the basic mental health problems. People liked and commented on their uploaded photos and videos. In today's age, everyone is immune to the social media context. Some teens experience anxiety from social media related to fear of loss, which causes teens to try to respond and check all their friends' messages and messages on a regular basis.
On the contrary, depression is one of the unintended significances of unnecessary use of social media. In detail, depression is limited not only to Facebooks but also to other social networking sites, which causes psychological problems. A new study found that individuals who are involved in social media, games, texts, mobile phones, etc. are more likely to experience depression.
The previous study found a 70% increase in self-reported depressive symptoms among the group using social media. The other social media influence that causes depression is sexual fun [ 12 ]. The intimacy fun happens when social media promotes putting on a facade that highlights the fun and excitement but does not tell us much about where we are struggling in our daily lives at a deeper level [ 28 ]. Another study revealed that depression and time spent on Facebook by adolescents are positively correlated [ 22 ]. More importantly, symptoms of major depression have been found among the individuals who spent most of their time in online activities and performing image management on social networking sites [ 14 ].
Another study assessed gender differences in associations between social media use and mental health. Females were found to be more addicted to social media as compared with males [ 26 ]. Passive activity in social media use such as reading posts is more strongly associated with depression than doing active use like making posts [ 23 ]. Other important findings of this review suggest that other factors such as interpersonal trust and family functioning may have a greater influence on the symptoms of depression than the frequency of social media use [ 28 , 29 ].
Limitation and suggestion
The limitations and suggestions were identified by the evidence involved in the study and review process. Previously, 7 of the 16 studies were cross-sectional and slightly failed to determine the causal relationship between the variables of interest. Given the evidence from cross-sectional studies, it is not possible to conclude that the use of social networks causes mental health problems. Only three longitudinal studies examined the causal relationship between social media and mental health, which is hard to examine if the mental health problem appeared more pronounced in those who use social media more compared with those who use it less or do not use at all [ 19 , 20 , 24 ]. Next, despite the fact that the proposed relationship between social media and mental health is complex, a few studies investigated mediating factors that may contribute or exacerbate this relationship. Further investigations are required to clarify the underlying factors that help examine why social media has a negative impact on some peoples’ mental health, whereas it has no or positive effect on others’ mental health.
Conclusions
Social media is a new study that is rapidly growing and gaining popularity. Thus, there are many unexplored and unexpected constructive answers associated with it. Lately, studies have found that using social media platforms can have a detrimental effect on the psychological health of its users. However, the extent to which the use of social media impacts the public is yet to be determined. This systematic review has found that social media envy can affect the level of anxiety and depression in individuals. In addition, other potential causes of anxiety and depression have been identified, which require further exploration.
The importance of such findings is to facilitate further research on social media and mental health. In addition, the information obtained from this study can be helpful not only to medical professionals but also to social science research. The findings of this study suggest that potential causal factors from social media can be considered when cooperating with patients who have been diagnosed with anxiety or depression. Also, if the results from this study were used to explore more relationships with another construct, this could potentially enhance the findings to reduce anxiety and depression rates and prevent suicide rates from occurring.
The content published in Cureus is the result of clinical experience and/or research by independent individuals or organizations. Cureus is not responsible for the scientific accuracy or reliability of data or conclusions published herein. All content published within Cureus is intended only for educational, research and reference purposes. Additionally, articles published within Cureus should not be deemed a suitable substitute for the advice of a qualified health care professional. Do not disregard or avoid professional medical advice due to content published within Cureus.
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Subscribe or renew today
Every print subscription comes with full digital access
Science News
Social media harms teens’ mental health, mounting evidence shows. what now.
Understanding what is going on in teens’ minds is necessary for targeted policy suggestions

Most teens use social media, often for hours on end. Some social scientists are confident that such use is harming their mental health. Now they want to pinpoint what explains the link.
Carol Yepes/Getty Images
Share this:
By Sujata Gupta
February 20, 2024 at 7:30 am
In January, Mark Zuckerberg, CEO of Facebook’s parent company Meta, appeared at a congressional hearing to answer questions about how social media potentially harms children. Zuckerberg opened by saying: “The existing body of scientific work has not shown a causal link between using social media and young people having worse mental health.”
But many social scientists would disagree with that statement. In recent years, studies have started to show a causal link between teen social media use and reduced well-being or mood disorders, chiefly depression and anxiety.
Ironically, one of the most cited studies into this link focused on Facebook.
Researchers delved into whether the platform’s introduction across college campuses in the mid 2000s increased symptoms associated with depression and anxiety. The answer was a clear yes , says MIT economist Alexey Makarin, a coauthor of the study, which appeared in the November 2022 American Economic Review . “There is still a lot to be explored,” Makarin says, but “[to say] there is no causal evidence that social media causes mental health issues, to that I definitely object.”
The concern, and the studies, come from statistics showing that social media use in teens ages 13 to 17 is now almost ubiquitous. Two-thirds of teens report using TikTok, and some 60 percent of teens report using Instagram or Snapchat, a 2022 survey found. (Only 30 percent said they used Facebook.) Another survey showed that girls, on average, allot roughly 3.4 hours per day to TikTok, Instagram and Facebook, compared with roughly 2.1 hours among boys. At the same time, more teens are showing signs of depression than ever, especially girls ( SN: 6/30/23 ).
As more studies show a strong link between these phenomena, some researchers are starting to shift their attention to possible mechanisms. Why does social media use seem to trigger mental health problems? Why are those effects unevenly distributed among different groups, such as girls or young adults? And can the positives of social media be teased out from the negatives to provide more targeted guidance to teens, their caregivers and policymakers?
“You can’t design good public policy if you don’t know why things are happening,” says Scott Cunningham, an economist at Baylor University in Waco, Texas.
Increasing rigor
Concerns over the effects of social media use in children have been circulating for years, resulting in a massive body of scientific literature. But those mostly correlational studies could not show if teen social media use was harming mental health or if teens with mental health problems were using more social media.
Moreover, the findings from such studies were often inconclusive, or the effects on mental health so small as to be inconsequential. In one study that received considerable media attention, psychologists Amy Orben and Andrew Przybylski combined data from three surveys to see if they could find a link between technology use, including social media, and reduced well-being. The duo gauged the well-being of over 355,000 teenagers by focusing on questions around depression, suicidal thinking and self-esteem.
Digital technology use was associated with a slight decrease in adolescent well-being , Orben, now of the University of Cambridge, and Przybylski, of the University of Oxford, reported in 2019 in Nature Human Behaviour . But the duo downplayed that finding, noting that researchers have observed similar drops in adolescent well-being associated with drinking milk, going to the movies or eating potatoes.
Holes have begun to appear in that narrative thanks to newer, more rigorous studies.
In one longitudinal study, researchers — including Orben and Przybylski — used survey data on social media use and well-being from over 17,400 teens and young adults to look at how individuals’ responses to a question gauging life satisfaction changed between 2011 and 2018. And they dug into how the responses varied by gender, age and time spent on social media.
Social media use was associated with a drop in well-being among teens during certain developmental periods, chiefly puberty and young adulthood, the team reported in 2022 in Nature Communications . That translated to lower well-being scores around ages 11 to 13 for girls and ages 14 to 15 for boys. Both groups also reported a drop in well-being around age 19. Moreover, among the older teens, the team found evidence for the Goldilocks Hypothesis: the idea that both too much and too little time spent on social media can harm mental health.
“There’s hardly any effect if you look over everybody. But if you look at specific age groups, at particularly what [Orben] calls ‘windows of sensitivity’ … you see these clear effects,” says L.J. Shrum, a consumer psychologist at HEC Paris who was not involved with this research. His review of studies related to teen social media use and mental health is forthcoming in the Journal of the Association for Consumer Research.
Cause and effect
That longitudinal study hints at causation, researchers say. But one of the clearest ways to pin down cause and effect is through natural or quasi-experiments. For these in-the-wild experiments, researchers must identify situations where the rollout of a societal “treatment” is staggered across space and time. They can then compare outcomes among members of the group who received the treatment to those still in the queue — the control group.
That was the approach Makarin and his team used in their study of Facebook. The researchers homed in on the staggered rollout of Facebook across 775 college campuses from 2004 to 2006. They combined that rollout data with student responses to the National College Health Assessment, a widely used survey of college students’ mental and physical health.
The team then sought to understand if those survey questions captured diagnosable mental health problems. Specifically, they had roughly 500 undergraduate students respond to questions both in the National College Health Assessment and in validated screening tools for depression and anxiety. They found that mental health scores on the assessment predicted scores on the screenings. That suggested that a drop in well-being on the college survey was a good proxy for a corresponding increase in diagnosable mental health disorders.
Compared with campuses that had not yet gained access to Facebook, college campuses with Facebook experienced a 2 percentage point increase in the number of students who met the diagnostic criteria for anxiety or depression, the team found.
When it comes to showing a causal link between social media use in teens and worse mental health, “that study really is the crown jewel right now,” says Cunningham, who was not involved in that research.
A need for nuance
The social media landscape today is vastly different than the landscape of 20 years ago. Facebook is now optimized for maximum addiction, Shrum says, and other newer platforms, such as Snapchat, Instagram and TikTok, have since copied and built on those features. Paired with the ubiquity of social media in general, the negative effects on mental health may well be larger now.
Moreover, social media research tends to focus on young adults — an easier cohort to study than minors. That needs to change, Cunningham says. “Most of us are worried about our high school kids and younger.”
And so, researchers must pivot accordingly. Crucially, simple comparisons of social media users and nonusers no longer make sense. As Orben and Przybylski’s 2022 work suggested, a teen not on social media might well feel worse than one who briefly logs on.
Researchers must also dig into why, and under what circumstances, social media use can harm mental health, Cunningham says. Explanations for this link abound. For instance, social media is thought to crowd out other activities or increase people’s likelihood of comparing themselves unfavorably with others. But big data studies, with their reliance on existing surveys and statistical analyses, cannot address those deeper questions. “These kinds of papers, there’s nothing you can really ask … to find these plausible mechanisms,” Cunningham says.
One ongoing effort to understand social media use from this more nuanced vantage point is the SMART Schools project out of the University of Birmingham in England. Pedagogical expert Victoria Goodyear and her team are comparing mental and physical health outcomes among children who attend schools that have restricted cell phone use to those attending schools without such a policy. The researchers described the protocol of that study of 30 schools and over 1,000 students in the July BMJ Open.
Goodyear and colleagues are also combining that natural experiment with qualitative research. They met with 36 five-person focus groups each consisting of all students, all parents or all educators at six of those schools. The team hopes to learn how students use their phones during the day, how usage practices make students feel, and what the various parties think of restrictions on cell phone use during the school day.
Talking to teens and those in their orbit is the best way to get at the mechanisms by which social media influences well-being — for better or worse, Goodyear says. Moving beyond big data to this more personal approach, however, takes considerable time and effort. “Social media has increased in pace and momentum very, very quickly,” she says. “And research takes a long time to catch up with that process.”
Until that catch-up occurs, though, researchers cannot dole out much advice. “What guidance could we provide to young people, parents and schools to help maintain the positives of social media use?” Goodyear asks. “There’s not concrete evidence yet.”
More Stories from Science News on Science & Society

Privacy remains an issue with several women’s health apps

Should we use AI to resurrect digital ‘ghosts’ of the dead?

A hidden danger lurks beneath Yellowstone

Online spaces may intensify teens’ uncertainty in social interactions

Want to see butterflies in your backyard? Try doing less yardwork

Ximena Velez-Liendo is saving Andean bears with honey

‘Flavorama’ guides readers through the complex landscape of flavor

Rain Bosworth studies how deaf children experience the world
Subscribers, enter your e-mail address for full access to the Science News archives and digital editions.
Not a subscriber? Become one now .
- Open access
- Published: 06 July 2023
Pros & cons: impacts of social media on mental health
- Ágnes Zsila 1 , 2 &
- Marc Eric S. Reyes ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-5280-1315 3
BMC Psychology volume 11 , Article number: 201 ( 2023 ) Cite this article
454k Accesses
16 Citations
107 Altmetric
Metrics details
The use of social media significantly impacts mental health. It can enhance connection, increase self-esteem, and improve a sense of belonging. But it can also lead to tremendous stress, pressure to compare oneself to others, and increased sadness and isolation. Mindful use is essential to social media consumption.
Social media has become integral to our daily routines: we interact with family members and friends, accept invitations to public events, and join online communities to meet people who share similar preferences using these platforms. Social media has opened a new avenue for social experiences since the early 2000s, extending the possibilities for communication. According to recent research [ 1 ], people spend 2.3 h daily on social media. YouTube, TikTok, Instagram, and Snapchat have become increasingly popular among youth in 2022, and one-third think they spend too much time on these platforms [ 2 ]. The considerable time people spend on social media worldwide has directed researchers’ attention toward the potential benefits and risks. Research shows excessive use is mainly associated with lower psychological well-being [ 3 ]. However, findings also suggest that the quality rather than the quantity of social media use can determine whether the experience will enhance or deteriorate the user’s mental health [ 4 ]. In this collection, we will explore the impact of social media use on mental health by providing comprehensive research perspectives on positive and negative effects.
Social media can provide opportunities to enhance the mental health of users by facilitating social connections and peer support [ 5 ]. Indeed, online communities can provide a space for discussions regarding health conditions, adverse life events, or everyday challenges, which may decrease the sense of stigmatization and increase belongingness and perceived emotional support. Mutual friendships, rewarding social interactions, and humor on social media also reduced stress during the COVID-19 pandemic [ 4 ].
On the other hand, several studies have pointed out the potentially detrimental effects of social media use on mental health. Concerns have been raised that social media may lead to body image dissatisfaction [ 6 ], increase the risk of addiction and cyberbullying involvement [ 5 ], contribute to phubbing behaviors [ 7 ], and negatively affects mood [ 8 ]. Excessive use has increased loneliness, fear of missing out, and decreased subjective well-being and life satisfaction [ 8 ]. Users at risk of social media addiction often report depressive symptoms and lower self-esteem [ 9 ].
Overall, findings regarding the impact of social media on mental health pointed out some essential resources for psychological well-being through rewarding online social interactions. However, there is a need to raise awareness about the possible risks associated with excessive use, which can negatively affect mental health and everyday functioning [ 9 ]. There is neither a negative nor positive consensus regarding the effects of social media on people. However, by teaching people social media literacy, we can maximize their chances of having balanced, safe, and meaningful experiences on these platforms [ 10 ].
We encourage researchers to submit their research articles and contribute to a more differentiated overview of the impact of social media on mental health. BMC Psychology welcomes submissions to its new collection, which promises to present the latest findings in the emerging field of social media research. We seek research papers using qualitative and quantitative methods, focusing on social media users’ positive and negative aspects. We believe this collection will provide a more comprehensive picture of social media’s positive and negative effects on users’ mental health.
Data Availability
Not applicable.
Statista. (2022). Time spent on social media [Chart]. Accessed June 14, 2023, from https://www.statista.com/chart/18983/time-spent-on-social-media/ .
Pew Research Center. (2023). Teens and social media: Key findings from Pew Research Center surveys. Retrieved June 14, 2023, from https://www.pewresearch.org/short-reads/2023/04/24/teens-and-social-media-key-findings-from-pew-research-center-surveys/ .
Boer, M., Van Den Eijnden, R. J., Boniel-Nissim, M., Wong, S. L., Inchley, J. C.,Badura, P.,… Stevens, G. W. (2020). Adolescents’ intense and problematic social media use and their well-being in 29 countries. Journal of Adolescent Health , 66(6), S89-S99. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jadohealth.2020.02.011.
Marciano L, Ostroumova M, Schulz PJ, Camerini AL. Digital media use and adolescents’ mental health during the COVID-19 pandemic: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front Public Health. 2022;9:2208. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpubh.2021.641831 .
Article Google Scholar
Naslund JA, Bondre A, Torous J, Aschbrenner KA. Social media and mental health: benefits, risks, and opportunities for research and practice. J Technol Behav Sci. 2020;5:245–57. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41347-020-00094-8 .
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Harriger JA, Thompson JK, Tiggemann M. TikTok, TikTok, the time is now: future directions in social media and body image. Body Image. 2023;44:222–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bodyim.2021.12.005 .
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Chi LC, Tang TC, Tang E. The phubbing phenomenon: a cross-sectional study on the relationships among social media addiction, fear of missing out, personality traits, and phubbing behavior. Curr Psychol. 2022;41(2):1112–23. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12144-022-0135-4 .
Valkenburg PM. Social media use and well-being: what we know and what we need to know. Curr Opin Psychol. 2022;45:101294. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.copsyc.2020.101294 .
Bányai F, Zsila Á, Király O, Maraz A, Elekes Z, Griffiths MD, Urbán R, Farkas J, Rigó P Jr, Demetrovics Z. Problematic social media use: results from a large-scale nationally representative adolescent sample. PLoS ONE. 2017;12(1):e0169839. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0169839 .
American Psychological Association. (2023). APA panel issues recommendations for adolescent social media use. Retrieved from https://apa-panel-issues-recommendations-for-adolescent-social-media-use-774560.html .
Download references
Acknowledgements
Ágnes Zsila was supported by the ÚNKP-22-4 New National Excellence Program of the Ministry for Culture and Innovation from the source of the National Research, Development and Innovation Fund.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Institute of Psychology, Pázmány Péter Catholic University, Budapest, Hungary
Ágnes Zsila
Institute of Psychology, ELTE Eötvös Loránd University, Budapest, Hungary
Department of Psychology, College of Science, University of Santo Tomas, Manila, 1008, Philippines
Marc Eric S. Reyes
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
AZ conceived and drafted the Editorial. MESR wrote the abstract and revised the Editorial. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Marc Eric S. Reyes .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate, consent for publication, competing interests.
The authors have no competing interests to declare relevant to the content of this article.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Zsila, Á., Reyes, M.E.S. Pros & cons: impacts of social media on mental health. BMC Psychol 11 , 201 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40359-023-01243-x
Download citation
Received : 15 June 2023
Accepted : 03 July 2023
Published : 06 July 2023
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s40359-023-01243-x
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Social media
- Mental health
BMC Psychology
ISSN: 2050-7283
- General enquiries: [email protected]
- Bipolar Disorder
- Therapy Center
- When To See a Therapist
- Types of Therapy
- Best Online Therapy
- Best Couples Therapy
- Best Family Therapy
- Managing Stress
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Understanding Emotions
- Self-Improvement
- Healthy Relationships
- Student Resources
- Personality Types
- Guided Meditations
- Verywell Mind Insights
- 2024 Verywell Mind 25
- Mental Health in the Classroom
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
- Crisis Support
The Social Media and Mental Health Connection
Sherri Gordon, CLC is a published author, certified professional life coach, and bullying prevention expert. She's also the former editor of Columbus Parent and has countless years of experience writing and researching health and social issues.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/Sherri-Gordon-1000-9b857b46047148108c1f2fb50bee6e51.jpg)
Rachel Goldman, PhD FTOS, is a licensed psychologist, clinical assistant professor, speaker, wellness expert specializing in eating behaviors, stress management, and health behavior change.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/Rachel-Goldman-1000-a42451caacb6423abecbe6b74e628042.jpg)
Verywell / Catherine Song
Why Social Media Is Growing in Popularity
Social media and mental health concerns, signs social media is impacting your mental health.
In recent years, there has been a significant increase in social media use. According to the Pew Research Center, 72% of Americans in the U.S. use social media.
People use social networking tools to stay in touch with family and friends, get their news, and share their political views . This has some researchers wondering about the long-term effects of social media use.
Because social media use is still relatively new, there are no long-term studies documenting its effects. But several studies indicate that social media impacts mental health in a number of ways. The increasing reliance on and use of social media puts a large number of Americans at an increased risk for feeling anxious, depressed, lonely, envious, and even ill over social media use.
Aside from the fact that social media allows people to reconnect with family and friends that live far away or that they have lost touch with, it became a vital communication tool during the pandemic.
Social Media Supports Connections
People used social media to share information and connect with others when stay-at-home orders kept them from meeting in person. It became a vehicle for social support and connectedness that they would not otherwise have had.
Social Media Makes People Feel Good
Social media has a tendency to reinforce use. People quickly become hooked on checking their statuses for comments and likes, as well as perusing other people's posts.
Using social media sometimes activates the brain's reward center by releasing dopamine , also known as the feel-good chemical. This dopamine release, in turn, keeps people coming back because they want to repeat those feel-good experiences.
Social Media Boosts Self-Esteem
Social media also can boost self-esteem , especially if a person is viewed favorably online or gets a number of likes or interactions on their content. And social media allows some people to share parts of their identity that may be challenging to communicate in person.
Social media can be particularly helpful for people with social anxiety who struggle to interact with people in person.
Despite the above benefits, researchers are discovering that there are some downsides to social media, particularly with regard to mental health.
Social Media Use May Contribute to Depression
For a technology that's supposed to bring people closer together, it can have the opposite effect—especially when disagreements erupt online. Social media has been linked to depression , anxiety, and loneliness. It can make people feel isolated and alone.
One 2017 study found that young people who use social media more than two hours per day are much more likely to categorize their mental health as fair or poor compared to occasional social media users.
A large-scale study of young adults in the U.S. found that occasional users of social media are three times less likely to experience symptoms of depression than heavy users.
Social Media May Hurt Your Self-Esteem
While social media can sometimes be a self-esteem booster, it can also cause you to experience feelings of inadequacy about your life and your appearance. Even if you know that the images you see online are manipulated or represent someone else's highlight reel, they can still cause feelings of insecurity, envy, and dissatisfaction.
Fear of Missing Out
Another mental health phenomenon associated with social media is what is known as FOMO , or the "fear of missing out." Social media sites like Facebook and Instagram exacerbate the fear that you're missing something or that other people are living a better life than you are.
In extreme cases, FOMO can cause you to become tethered to your phone where you are constantly checking for updates or responding to every single alert.
Social Media Can Lead to Self-Absorption
Sharing endless selfies as well as your innermost thoughts on social media can create an unhealthy self-centeredness that causes you to focus on crafting your online image rather than making memories with your friends and family members in real life.
In fact, strenuous efforts to engage in impression management or get external validation can have psychological costs, especially if the approval you're seeking is never received. Ultimately, the lack of positive feedback online can lead to self-doubt and self-hatred .
Impulse Control Issues
Excessive social media use can lead to impulse control issues , especially if you access your social networks using a smartphone. This means that you have round-the-clock access to your accounts, which not only makes it easy for you always to be connected, but can affect your concentration and focus. It can even disturb your sleep and compromise your in-person relationships.
Social Media May Be Used As an Unhealthy Coping Mechanism
Social media can become an unhealthy way of coping with uncomfortable feelings or emotions . For instance, if you turn to social media when you're feeling down, lonely, or bored, you're potentially using it as a way to distract you from unpleasant feelings.
Ultimately, social media is a poor way to self-soothe, especially because perusing social media can often make you feel worse instead of better.
Press Play For Advice on Reducing Screen Time
Hosted by therapist Amy Morin, LCSW, this episode of The Verywell Mind Podcast shares effective ways to reduce screen time. Click below to listen now.
Follow Now : Apple Podcasts / Spotify / Google Podcasts
Because everyone is different, there is no set amount of time spent on social media that is recommended. Instead, you need to evaluate how your social media use is impacting your life, including how you feel when you don't use social media as well as how you feel after using it.
A 2018 University of Pennsylvania study suggests that self-monitoring can change one's perception of social media. According to the lead researcher, psychologist Melissa G. Hunt, PhD, using social media less than you normally do, can lead to significant decreases in loneliness and depression. By using self-monitoring and making adjustments, people can significantly improve their overall well-being.
Social Media Distracts You
If you find that your social media use is impacting your relationships or is distracting you from work or school, it may be problematic. Additionally, if scrolling through social media leaves you feeling envious, depressed, anxious, or angry, then you need to re-evaluate your use.
It could be that you need to detox from social media and spend some time offline in order to safeguard your mental health.
You Use Social Media to Avoid Negative Emotions
Social media also could be an issue if you tend to use it to fight boredom or to deal with loneliness. Although these feelings are uncomfortable and it's only natural to want to alleviate them, turning to social media for comfort or as a distraction is not a healthy way to cope with difficult feelings and emotions.
As a result, it may be time for you to reassess your social media habits. Here are some additional signs that social media may be having a negative impact on your life and your mental health:
- Your symptoms of anxiety, depression, and loneliness are increasing.
- You are spending more time on social media than with your real-world friends and family members.
- You tend to compare yourself unfavorably with others on social media or you find that are your frequently jealous of others.
- You are being trolled or cyberbullied by others online.
- You are engaging in risky behaviors or taking outrageous photos in order to gain likes.
- Your work obligations, family life, or school work is suffering because of the time you spend on social media.
- You have little time for self-care activities like mindfulness , self-reflection, exercise, and sleep.
If you're spending a significant amount of time on social media and you're beginning to notice feelings of sadness, dissatisfaction, frustration, and loneliness that are impacting your life and your relationships, it may be time to re-evaluate your online habits.
If you find that even after adjusting your social media use, you're still experiencing symptoms of depression or anxiety, it's important to talk with your healthcare provider so that you can be evaluated. With proper treatment, you will soon be feeling better.
If you or a loved one are struggling with [condition name], contact the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA) National Helpline at 1-800-662-4357 for information on support and treatment facilities in your area.
For more mental health resources, see our National Helpline Database .
Pew Research Center. Social media fact sheet .
Centre for Addiction and Mental Health. Social media use and mental health among students in Ontario . CAMH Population Studies eBulletin . 2018;19(2).
Lin LY, Sidani JE, Shensa A, et al. Association between social media use and depression among U.S. young adults . Depress Anxiety . 2016;33(4):323-31. doi:10.1002/da.22466.
Chou H-TG, Edge N. “They are happier and having better lives than i am”: The impact of using Facebook on perceptions of others’ lives . Cyberpsychol Behav Soc Netw . 2012;15(2):117-121. doi:10.1089/cyber.2011.0324
Hunt MG, Marx R, Lipson C, Young J. No more FOMO: limiting social media decreases loneliness and depression . J Soc Clin Psychol . 2018;37(10):751-768. doi:10.1521/jscp.2018.37.10.751
Karim F, Oyewande AA, Abdalla LF, Chaudhry Ehsanullah R, Khan S. Social media use and its connection to mental health: a systematic review . Cureus . 2020;12(6):e8627. doi:10.7759/cureus.8627
Pantic I. Online social networking and mental health . Cyberpsychol Behav Soc Netw . 2014;17(10):652-657. doi:10.1089/cyber.2014.0070
By Sherri Gordon Sherri Gordon, CLC is a published author, certified professional life coach, and bullying prevention expert. She's also the former editor of Columbus Parent and has countless years of experience writing and researching health and social issues.
Is social media use bad for young people’s mental health? It’s complicated.

July 17, 2023 – On May 23, U.S. Surgeon General Vivek Murthy issued an advisory warning about the potential dangers of social media for the mental health of children and teens . Laura Marciano , postdoctoral research fellow at the Lee Kum Sheung Center for Health and Happiness and in the Department of Social and Behavioral Sciences at Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, says that social media use might be detrimental for young people’s well-being but can also have positive effects.
Q: What are your thoughts on the Surgeon General’s advisory?
A: The advisory highlighted compelling evidence published during the last decade on the potential harmful impact of social media on children and adolescents. Some of what young people experience online—including cyberbullying, online harassment and abuse, predatory behaviors, and exposure to violent, sexual, and hate-based content—can undoubtedly be negative. But social media experiences are not limited to these types of content.
Much of the scientific literature on the effects of social media use has focused on negative outcomes. But the link between social media use and young people’s mental health is complicated. Literature reviews show that study results are mixed: Associations between social media use and well-being can be positive, negative, and even largely null when advanced data analyses are carried out, and the size of the effects is small. And positive and negative effects can co-exist in the same individual. We are still discovering how to compare the effect size of social media use with the effects of other behavioral habits—such as physical activity, sleep, food consumption, life events, and time spent in offline social connections—and psychological processes happening offline. We are also still studying how social media use may be linked positively with well-being.
It’s important to note that many of the existing studies relied on data from people living in so-called WEIRD countries (Western, Educated, Industrialized, Rich and Democratic), thus leaving out the majority of the worldwide population living in the Global South. In addition, we know that populations like minorities, people experiencing health disparities and chronic health conditions , and international students can find social media extremely helpful for creating and maintaining social communities to which they feel they belong.
A number of large cohort studies have measured social media use according to time spent on various platforms. But it’s important to consider not just time spent, but whether that time is displacing time for other activities promoting well-being, like physical activity and sleep. Finally, the effects of social media use are idiosyncratic, meaning that each child and adolescent might be affected differently, which makes it difficult to generalize about the effects.
Literature reviews on interventions limiting social media use present a more balanced picture. For example, one comprehensive review on the effects of digital detox—refraining from using devices such as smartphones—wasn’t able to draw any clear conclusions about whether such detox could be effective at promoting a healthy way of life in the digital era, because the findings were mixed and contradictory.
Q: What has your research found regarding the potential risks and benefits of social media use among young people?
A: In my work with Prof. Vish Viswanath , we have summarized all the papers on how social media use is related to positive well-being measures, to balance the ongoing bias of the literature on negative outcomes such as depression and anxiety. We found both positive and negative correlations between different social media activities and well-being. The most consistent results show a link between social media activities and hedonic well-being (positive emotions) and social well-being. We also found that social comparison—such as comparing how many likes you have with how many someone else has, or comparing yourself to digitally enhanced images online—drives the negative correlation with well-being.
Meanwhile, I am working on the “ HappyB ” project, a longitudinal project based in Switzerland, through which I have collected data from more than 1,500 adolescents on their smartphone and social media use and well-being. In a recent study using that cohort, we looked at how social media use affects flourishing , a construct that encompasses happiness, meaning and purpose, physical and mental health, character, close social relationships, and financial stability. We found that certain positive social media experiences are associated with flourishing. In particular, having someone to talk to online when feeling lonely was the item most related to well-being. That is not surprising, considering that happiness is related to the quality of social connections.
Our data suggest that homing in on the psychological processes triggered during social media use is key to determining links with well-being. For example, we should consider if a young person feels appreciated and part of a group in a particular online conversation. Such information can help us shed light on the dynamics that shape young people’s well-being through digital activities.
In our research, we work to account for the fact that social media time is a sedentary behavior. We need to consider that any behavior that risks diminishing the time spent on physical activity and sleep—crucial components of brain development and well-being—might be detrimental. Interestingly, some studies suggest that spending a short amount of time using social media, around 1-2 hours, is beneficial, but—as with any extreme behavior—it can cause harm if the time spent online dominates a child’s or adolescent’s day.
It’s also important to consider how long the effects of social media last. Social media use may have small ephemeral effects that can accumulate over time. A step for future research is to disentangle short- versus long-term effects and how long each last. In addition, we should better understand how digital media usage affects the adolescent brain. Colleagues and I have summarized existing neuroscientific studies on the topic, but more multidisciplinary research is needed.
Q: What are some steps you’d recommend to make social media use safer for kids?
A: I’ll use a metaphor to answer this question. Is a car safe for someone that is not able to drive? To drive safely, we need to learn how to accelerate, recognize road signs, make safe decisions according to certain rules, and wear safety belts. Similarly, to use social media safely, I think we as a society—including schools, educators, and health providers—should provide children and families with clear, science-based information on both its positive and negative potential impacts.
We can also ask social media companies to pay more attention to how some features—such as the number of “likes”—can modulate adolescent brain activity, and to think about ways to limit negative effects. We might even ask adolescents to advise designers on how to create social media platforms specifically for them. It would be extremely valuable to ask them which features would be best for them and which ones they would like to avoid. I think that co-designing apps and conducting research with the young people who use the platforms is a crucial step.
For parents, my suggestion is to communicate with your children and promote a climate of safety and empathy when it comes to social media use. Try to use these platforms along with them, for example by explaining how a platform works and commenting on the content. Also, I would encourage schools and parents to collaborate on sharing information with young people about social media and well-being.
Also, to offset children’s sedentary time spent on social media, parents could offer them alternative extracurricular activities to provide some balance. But it’s important to remember that social well-being depends on the quality of social connections, and that social media can help to promote this kind of well-being. So I’d recommend trying to keep what is good—according to my research that would include instant messaging, the chance to talk to people when someone is feeling lonely, and funny or inspirational content—and minimizing what’s negative, such as too much sedentary time or too much time spent on social comparison.
– Karen Feldscher
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- CORRESPONDENCE
- 21 May 2024
Social-media influence on teen mental health goes beyond just cause and effect
- Michael A. Spikes 0
Northwestern University Medill School, Evanston, Illinois, USA.
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
In her review of Jonathan Haidt’s book The Anxious Generation ( Nature 628 , 29–30; 2024 ), Candice Odgers focuses on whether there is a causal relationship between social-media use and poor social outcomes among young people. However, this gives an incomplete view of Haidt’s argument, which puts social-media use in a wider context.
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
24,99 € / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
185,98 € per year
only 3,65 € per issue
Rent or buy this article
Prices vary by article type
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Nature 629 , 757 (2024)
doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/d41586-024-01488-5
Competing Interests
The author declares no competing interests.
Related Articles
See more letters to the editor

‘I saw that discrimination wasn’t hearsay or rumours — it really did exist’
Career Q&A 05 JUN 24

Is AI misinformation influencing elections in India?
Comment 05 JUN 24

What we do — and don’t — know about how misinformation spreads online
Editorial 05 JUN 24
Need a policy for using ChatGPT in the classroom? Try asking students
Career Column 05 JUN 24

Meta AI system is a boost to endangered languages — as long as humans aren’t forgotten

MDMA therapy for PTSD rejected by FDA panel
News 05 JUN 24
Internet use and teen mental health: it’s about more than just screen time
Correspondence 21 MAY 24
Interpersonal therapy can be an effective tool against the devastating effects of loneliness
Correspondence 14 MAY 24
Sir Run Run Shaw Hospital, School of Medicine, Zhejiang University, Warmly Welcomes Talents Abroad
Qiushi Chair Professor; Qiushi Distinguished Scholar; ZJU 100 Young Researcher; Distinguished researcher
No. 3, Qingchun East Road, Hangzhou, Zhejiang (CN)
Sir Run Run Shaw Hospital Affiliated with Zhejiang University School of Medicine
Proteomics expert (postdoc or staff scientist)
We are looking for a (senior) postdoc or postdoc-level staff scientist from all areas of proteomics to become part of our Proteomics Center.
Frankfurt am Main, Hessen (DE)
Goethe University (GU) Frankfurt am Main - Institute of Molecular Systems Medicine
Tenured Position in Huzhou University School of Medicine (Professor/Associate Professor/Lecturer)
※Tenured Professor/Associate Professor/Lecturer Position in Huzhou University School of Medicine
Huzhou, Zhejiang (CN)
Huzhou University
Electron Microscopy (EM) Specialist
APPLICATION CLOSING DATE: July 5th, 2024 About the Institute Human Technopole (HT) is an interdisciplinary life science research institute, created...
Human Technopole
Post-Doctoral Fellow in Chemistry and Chemical Biology
We are seeking a highly motivated, interdisciplinary scientist to investigate the host-gut microbiota interactions that are associated with driving...
Cambridge, Massachusetts
Harvard University - Department of Chemistry and Chemical Biology
Sign up for the Nature Briefing newsletter — what matters in science, free to your inbox daily.
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
student opinion
How Does Social Media Affect Your Mental Health?
Facebook has delayed the development of an Instagram app for children amid questions about its harmful effects on young people’s mental health. Does social media have an impact on your well-being?

By Nicole Daniels
What is your relationship with social media like? Which platforms do you spend the most time on? Which do you stay away from? How often do you log on?
What do you notice about your mental health and well-being when spending time on social networks?
In “ Facebook Delays Instagram App for Users 13 and Younger ,” Adam Satariano and Ryan Mac write about the findings of an internal study conducted by Facebook and what they mean for the Instagram Kids app that the company was developing:
Facebook said on Monday that it had paused development of an Instagram Kids service that would be tailored for children 13 years old or younger, as the social network increasingly faces questions about the app’s effect on young people’s mental health. The pullback preceded a congressional hearing this week about internal research conducted by Facebook , and reported in The Wall Street Journal , that showed the company knew of the harmful mental health effects that Instagram was having on teenage girls. The revelations have set off a public relations crisis for the Silicon Valley company and led to a fresh round of calls for new regulation. Facebook said it still wanted to build an Instagram product intended for children that would have a more “age appropriate experience,” but was postponing the plans in the face of criticism.
The article continues:
With Instagram Kids, Facebook had argued that young people were using the photo-sharing app anyway, despite age-requirement rules, so it would be better to develop a version more suitable for them. Facebook said the “kids” app was intended for ages 10 to 12 and would require parental permission to join, forgo ads and carry more age-appropriate content and features. Parents would be able to control what accounts their child followed. YouTube, which Google owns, has released a children’s version of its app. But since BuzzFeed broke the news this year that Facebook was working on the app, the company has faced scrutiny. Policymakers, regulators, child safety groups and consumer rights groups have argued that it hooks children on the app at a younger age rather than protecting them from problems with the service, including child predatory grooming, bullying and body shaming.
The article goes on to quote Adam Mosseri, the head of Instagram:
Mr. Mosseri said on Monday that the “the project leaked way before we knew what it would be” and that the company had “few answers” for the public at the time. Opposition to Facebook’s plans gained momentum this month when The Journal published articles based on leaked internal documents that showed Facebook knew about many of the harms it was causing. Facebook’s internal research showed that Instagram, in particular, had caused teen girls to feel worse about their bodies and led to increased rates of anxiety and depression, even while company executives publicly tried to minimize the app’s downsides.
But concerns about the effect of social media on young people go beyond Instagram Kids, the article notes:
A children’s version of Instagram would not fix more systemic problems, said Al Mik, a spokesman for 5Rights Foundation, a London group focused on digital rights issues for children. The group published a report in July showing that children as young as 13 were targeted within 24 hours of creating an account with harmful content, including material related to eating disorders, extreme diets, sexualized imagery, body shaming, self-harm and suicide. “Big Tobacco understood that the younger you got to someone, the easier you could get them addicted to become a lifelong user,” Doug Peterson, Nebraska’s attorney general, said in an interview. “I see some comparisons to social media platforms.” In May, attorneys general from 44 states and jurisdictions had signed a letter to Facebook’s chief executive, Mark Zuckerberg, asking him to end plans for building an Instagram app for children. American policymakers should pass tougher laws to restrict how tech platforms target children, said Josh Golin, executive director of Fairplay, a Boston-based group that was part of an international coalition of children’s and consumer groups opposed to the new app. Last year, Britain adopted an Age Appropriate Design Code , which requires added privacy protections for digital services used by people under the age of 18.
Students, read the entire article , then tell us:
Do you think Facebook made the right decision in halting the development of the Instagram Kids app? Do you think there should be social media apps for children 13 and younger? Why or why not?
What is your reaction to the research that found that Instagram can have harmful mental health effects on teenagers, particularly teenage girls? Have you experienced body image issues, anxiety or depression tied to your use of the app? How do you think social media affects your mental health?
What has your experience been on different social media apps? Are there apps that have a more positive or negative effect on your well-being? What do you think could explain these differences?
Have you ever been targeted with inappropriate or harmful content on Instagram or other social media apps? What responsibility do you think social media companies have to address these issues? Do you think there should be more protections in place for users under 18? Why or why not?
What does healthy social media engagement look like for you? What habits do you have around social media that you feel proud of? What behaviors would you like to change? How involved are your parents in your social media use? How involved do you think they should be?
If you were in charge of making Instagram, or another social media app, safer for teenagers, what changes would you make?
Want more writing prompts? You can find all of our questions in our Student Opinion column . Teachers, check out this guide to learn how you can incorporate them into your classroom.
Students 13 and older in the United States and Britain, and 16 and older elsewhere, are invited to comment. All comments are moderated by the Learning Network staff, but please keep in mind that once your comment is accepted, it will be made public.
Nicole Daniels joined The Learning Network as a staff editor in 2019 after working in museum education, curriculum writing and bilingual education. More about Nicole Daniels
Limiting Social Media Use Decreases Depression, Anxiety, & FOMO In Youth
Olivia Guy-Evans, MSc
Associate Editor for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MSc Psychology of Education
Olivia Guy-Evans is a writer and associate editor for Simply Psychology. She has previously worked in healthcare and educational sectors.
Learn about our Editorial Process
Saul Mcleod, PhD
Editor-in-Chief for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MRes, PhD, University of Manchester
Saul Mcleod, PhD., is a qualified psychology teacher with over 18 years of experience in further and higher education. He has been published in peer-reviewed journals, including the Journal of Clinical Psychology.
Social media use (SMU) refers to the time spent engaging with social networking platforms. Fear of Missing Out ( FoMO ) is the apprehension that others are having rewarding experiences that one is missing out on, often leading to increased SMU. Excessive SMU has been associated with detrimental effects on mental health, such as increased symptoms of depression and anxiety . This may be due to factors like negative social comparisons, exposure to harmful content, and the displacement of healthier activities like sleep and in-person interactions. Emotionally distressed youth may be particularly vulnerable to these negative effects.

- Limiting social media use (SMU) to 1 hour per day for 3 weeks in youth with emotional distress led to significant reductions in symptoms of depression, anxiety, and fear of missing out (FoMO) compared to a control group.
- Reducing SMU also led to an increase in sleep duration of about 30 minutes per night in the intervention group, while sleep declined by 15 minutes per night in the control group.
- The beneficial effects of reducing SMU on mental health outcomes were not moderated by gender.
- Reducing SMU may be a feasible, low-cost intervention for improving mental health in emotionally distressed youth who are heavy social media users.
Previous research has found correlations between heavy SMU and poorer mental health in youth, with distressed youth potentially being more vulnerable to the negative effects (Keles et al., 2020; Twenge & Campbell, 2019).
Experimental studies on the effects of reducing SMU have had mixed results (Agadullina et al., 2020; Hunt et al., 2018; Tromholt, 2016).
This study aimed to test if reducing SMU to 1 hr/day for 3 weeks would improve depression, anxiety, FoMO, and sleep in emotionally distressed youth.
Parallel-group randomized controlled trial, the gold standard for assessing intervention efficacy.
1-week baseline period followed by 3-week intervention. Intervention group limited SMU to 1 hr/day, control group used social media as usual. Pre and post measures taken.
220 university students aged 17-25 (168 women, 50 men, 2 “other”) with emotional distress and heavy SMU (>2 hrs/day).
SMU objectively tracked via smartphone. Validated self-report scales used: CES-D (depression), GAD-7 (anxiety), FoMO, and self-reported sleep duration.
2×2 mixed ANOVAs tested intervention effects on each outcome. Gender examined as a moderator.
The study’s hypotheses were supported by the results.
Compared to the control group, the intervention group showed significantly greater reductions in symptoms of depression, anxiety, and FoMO, as well as a significant increase in sleep duration.
These findings demonstrate the beneficial effects of reducing SMU on mental health and sleep outcomes in emotionally distressed youth.
Importantly, the effects were not moderated by gender, suggesting that both men and women benefited equally from the intervention.
This study provides strong evidence for a causal link between SMU and mental health, using a well-controlled experimental design.
By randomly assigning participants to either reduce their SMU or continue as usual, the researchers were able to isolate the effects of SMU on depression, anxiety, FoMO, and sleep.
The findings suggest that the benefits of reducing SMU may come from decreased exposure to negative social comparisons and the displacement of healthy offline activities, such as sleep.
These results highlight the potential of reducing SMU as a low-cost, accessible intervention for improving mental health in emotionally distressed youth, a population that may be particularly vulnerable to the negative effects of excessive SMU.
Future research should aim to replicate these findings with longer intervention periods and explore the specific mechanisms underlying the benefits of SMU reduction.
This study had several methodological strengths, including:
- Randomized controlled design allowed for strong causal inferences about the effects of the intervention
- Objective measurement of SMU using smartphone tracking data provided a reliable and accurate assessment of actual use
- Good compliance with the intervention, with the intervention group reducing their SMU by approximately 50% on average
- Use of well-validated measures of mental health outcomes increases confidence in the findings
Limitations
This study also had some limitations, including:
- Short 3-week intervention period, unclear whether benefits would be maintained over a longer period
- Sample limited to university students interested in changing SMU, may limit generalizability to other populations
- Intervention group still averaged 78 minutes of SMU per day, which may be higher than ideal for maximizing mental health benefits
Implications
The results of this study have important implications for the treatment of anxiety and depression in youth.
They suggest that reducing SMU could be an effective component of interventions for these common mental health problems.
Encouraging youth to track their SMU and set goals for reducing it may help heavy users to regulate their use and improve their well-being.
The findings also highlight the need for further research to test the effectiveness of SMU reduction interventions in clinical samples and to explore the optimal level of SMU for mental health.
Overall, this study provides promising evidence for a simple, low-cost intervention that could have significant public health benefits for emotionally distressed youth.
Primary reference
Davis, C. G., & Goldfield, G. S. (2024). Limiting social media use decreases depression, anxiety, and fear of missing out in youth with emotional distress: A randomized controlled trial. Psychology of Popular Media. Advance online publication. https://doi.org/10.1037/ppm0000536
Other references
Agadullina, E. R., Lovakov, A., & Kiselnikova, N. V. (2020). Does quitting social networks change feelings of loneliness among freshmen? An experimental study. Journal of Applied Research in Higher Education, 13 (1), 149–163. https://doi.org/10.1108/JARHE-11-2019-0283
Hunt, M. G., Marx, R., Lipson, C., & Young, J. (2018). No more FOMO: Limiting social media decreases loneliness and depression. Journal of Social and Clinical Psychology, 37 (10), 751–768. https://doi.org/10.1521/jscp.2018.37.10.751
Keles, B., McCrae, N., & Grealish, A. (2020). A systematic review: The influence of social media on depression, anxiety and psychological distress in adolescents. International Journal of Adolescence and Youth, 25 (1), 79–93. https://doi.org/10.1080/02673843.2019.1590851
Tromholt, M. (2016). The Facebook experiment: Quitting Facebook leads to higher levels of well-being. Cyberpsychology, Behavior and Social Networking, 19 (11), 661–666. https://doi.org/10.1089/cyber.2016.0259
Twenge, J. M., & Campbell, W. K. (2019). Media use is linked to lower psychological well-being: Evidence from three datasets. The Psychiatric Quarterly, 90 (2), 311–331. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11126-019-09630-7
Keep Learning
Here are some potential discussion questions for a college class on this paper:
- What are some healthy alternative activities that youth could engage in to replace time spent on social media?
- How might social media platforms be designed differently to mitigate potential negative impacts on mental health?
- Are there certain types of SMU content or usage patterns that are more detrimental to wellbeing? How could this be studied?
- What barriers might prevent distressed youth from successfully reducing their SMU? How could these be addressed?
Related Articles

Clinical Psychology
Unprompted Thought and Affective Well-Being: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis

Executive Function Deficits Mediate The Relationship Between Employee’s ADHD And Job Burnout

Identification Of Exceptional Skills In Autistic Children

Social Attention, Physiological Arousal, And Familiarity In Autistic Children

Thematic Analysis Of Autistic Burnout On Online Platforms

The ‘Revolving Door’ of Mental Illness: A Meta-Analysis & Systematic Review

Social Media Can Damage Mental Health
Here’s how we can change that..
Posted September 9, 2021 | Reviewed by Tyler Woods
- There is a connection between poor mental health and social media usage.
- We need to lessen the impact social media use is having on our health, particularly that of our teens.
- Many people know that social media use is correlated to increased anxiety, depression, and low self-esteem, yet few want to make any changes.
With alarming frequency, the research reports hit my inbox, my newspaper, and—yes—my Twitter feed.
“ Excess screen time impacting teen mental health ”
“ Teens around the world are lonelier than a decade ago. The reason may be smartphones. ”
“ This Is Our Chance to Pull Teenagers Out of the Smartphone Trap ”
And that’s just from the last few weeks.

As a parent and as a professional who works in the field of education , the connection between poor mental health and smartphone usage—and more specifically, social media apps—is downright scary. That more doctors, schools, governments, and community groups aren’t speaking out is disheartening.
A recent piece from Helen Lee Bouygues recommends we declare social media a public mental health crisis and wage a campaign against it, much like we did with tobacco. I often work with Bouygues’s Reboot Foundation and wondered: What would that look like? What would it be like to have a public campaign?
For starters, it would include PSAs, educational outreach, both short-term and long-term research, and age restrictions on who can use social media platforms, according to Bouygues.
While I’m not sure that would work in my house, or with the teens I know—they’re too practiced to be dissuaded by a warning label, and too tech savvy to be defeated by an age restriction—I do think Bouygues is generally right. We need to mitigate the impact social media is having on our children’s mental health.
What we must do is give technology users, and teenagers especially, the critical thinking skills necessary to interpret what they see online, so that they can contextualize it and ultimately assess whether the latest meme or trending topic is worth their time or consideration.
This past spring the Reboot Foundation surveyed more than 1,000 Americans on their social media usage and its impact on their mental health, and the results were alarming. More than half of the people who took part in the survey acknowledged that their social media use intensified their feelings of anxiety , depression , or loneliness . They also knew that it contributed to feelings of low self-esteem and made it harder for them to concentrate.
So what did users do about this? Basically, nothing. Only about a third said that they took steps to limit their social media use. That same survey revealed that 40 percent of the respondents said they would give up their cars, TV, and their pets before they would give up their social media accounts.
See what we're up against?
Critical thinking begins with reflective thinking. This requires us to step back and examine our own thinking process, and to notice when we are thinking irrationally or unproductively. This type of thinking is also called “ metacognition .”
Social media apps and platforms were designed to discourage reflective thinking. The algorithms that control our feeds have been perfected to supply their users high octane emotional content that’s easy to share and amplify, regardless if it’s good for society, or for your mental health.
Teaching young people to be reflective thinkers would give them tools to resist conclusions based on raw emotion or knee-jerk reactions. This would go a long way to helping slow the spread of harmful content online.
Another way improved critical thinking skills would help address the mental health crisis teens face online is by giving them the confidence to think independently and to resist group pressure. This cool, rational thought is often called objective thinking and allows users to free themselves of the “hivemind” and to recognize that just because something is trending on Twitter doesn’t mean it’s worthy of your attention .
In short, good critical thinkers reflect on and correct their thinking. They’re objective and rational, even when things get heated or the facts get muddy.
Heated arguments and muddy facts. Doesn’t that sound like social media these days?
The good news is that these critical thinking skills can be taught and there is overwhelming public support for doing so . The bad news is that most schools don’t teach these skills very well.
That needs to change. Our’s kids’ mental health depends on it.

Ulrich Boser is the founder of The Learning Agency and a senior fellow at the Center for American Progress. He is the author of Learn Better, which Amazon called “the best science book of the year.”
- Find a Therapist
- Find a Treatment Center
- Find a Psychiatrist
- Find a Support Group
- Find Online Therapy
- United States
- Brooklyn, NY
- Chicago, IL
- Houston, TX
- Los Angeles, CA
- New York, NY
- Portland, OR
- San Diego, CA
- San Francisco, CA
- Seattle, WA
- Washington, DC
- Asperger's
- Bipolar Disorder
- Chronic Pain
- Eating Disorders
- Passive Aggression
- Personality
- Goal Setting
- Positive Psychology
- Stopping Smoking
- Low Sexual Desire
- Relationships
- Child Development
- Self Tests NEW
- Therapy Center
- Diagnosis Dictionary
- Types of Therapy

At any moment, someone’s aggravating behavior or our own bad luck can set us off on an emotional spiral that threatens to derail our entire day. Here’s how we can face our triggers with less reactivity so that we can get on with our lives.
- Emotional Intelligence
- Gaslighting
- Affective Forecasting
- Neuroscience
- - Google Chrome
Intended for healthcare professionals
- Access provided by Google Indexer
- My email alerts
- BMA member login
- Username * Password * Forgot your log in details? Need to activate BMA Member Log In Log in via OpenAthens Log in via your institution

Search form
- Advanced search
- Search responses
- Search blogs
- News & Views
- Smartphones, social...
Smartphones, social media, and teenage mental health
- Related content
- Peer review
- Greg Hartwell , clinical assistant professor 1 ,
- Maeve Gill , specialty registrar in public health 2 ,
- Marco Zenone , research associate 3 ,
- Martin McKee , professor of European public health 1
- 1 London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine, London, UK
- 2 Royal Free Hospital NHS Foundation Trust, London, UK
- 3 Health Law Institute, University of Alberta, Canada
- Correspondence to: G Hartwell gregory.hartwell{at}lshtm.ac.uk
A precautionary public health response is needed
The tragic deaths of two UK teenagers continue to raise debate about the challenges that smartphones—and the unlimited access to social media they provide—may pose for adolescent mental health. 1 Molly Russell took her own life in 2017 aged 14 after being exposed on Instagram to what her father has described as a constant stream of “dark harmful material.” 1 Sixteen year old Brianna Ghey was murdered by two fellow pupils in 2023. Her mother believes that Brianna’s heavy mobile phone use increased her vulnerability before her death, and recently called for alerts on parents’ phones when their children use their own devices to search for violent material, as her daughter’s killers did. 1 2
This debate lies within broader concerns about the parlous state of adolescent mental health, with decreasing happiness reported among UK teenagers for a decade, alongside sharp increases in depression and anxiety, particularly among older girls. 3 4 These findings cannot easily be dismissed as artefact arising from changes to diagnostic criteria, reduced stigma, or greater willingness to seek help; they have coincided with marked rises in other measures such as teenage self-harm and suicidal behaviours, especially among teenage girls. 3 5
But can smartphones and social media be blamed? Population based data suggest a dose-response relationship between social media use and depressive symptoms in teenagers, especially girls. Systematic reviews report links to other harmful behaviours, 6 7 8 9 and heavy adolescent smartphone use has been associated with sleep deprivation and poorer socioemotional functioning. 9 10 Nonetheless, by age 12, smartphone ownership is near universal in the UK, and almost two thirds of 8-11 year olds already use social media. 11
Yet many macroeconomic, environmental, and social factors contribute to mental health at all ages. The relationships between social media, smartphones, and mental health are also vexed by a suite of potential confounders and questions of reverse causality. 12 13 Furthermore, young people are adept at harnessing technology’s power to make positive changes in their lives, connecting with peers across borders, mobilising youth movements, or advocating for social change. 14 15 Social media can facilitate engagement with health services, provide access to safe online spaces, and support help seeking in crises. 16
A precautionary response
So how should we protect children from harms linked to smartphones and social media, while maximising potential benefits? Three groups have roles to play: technology producers, parliamentarians who regulate them, and the public who use these products.
Firstly, the argument that social media firms simply provide a communication medium is wearing thin. The EU has launched various investigations into platforms’ addictiveness for young people, 17 while a US Senate committee recently condemned social media chief executives as having “blood on their hands,” 18 partly reflecting Meta’s research showing Instagram had toxic effects on girls. 19 Inevitably, these companies advocate self-regulation, yet we know this is ineffective. 20 21
Smartphones and social media should instead be seen as products to be regulated, like all commercial goods and services with potential to harm. 22 23 Restricting sales or advertising of cigarettes, vapes, alcoholic drinks, and gambling products is relatively uncontroversial, even though producers work to circumvent restrictions. Conversely, in the UK, the US, and elsewhere, social media access is permitted from age 13 across major platforms, a threshold with no health rationale, stemming instead from US legislation allowing collection of personal data from that age without parental consent. 24
Secondly, while parliamentarians must balance risks and benefits, the current UK government’s flagship Online Safety Act and Data Protection and Digital Information Bill have not allayed concerns. 2 25 Its non-statutory guidance recommending banning smartphones in schools also had a lukewarm reception 26 ; many schools already have such policies, and the guidance echoes a classic industry narrative emphasising individual responsibility, which shifts accountability for harm from policy makers or manufacturers to schools, parents, and pupils.
Thirdly, the public clearly have doubts about children and young people’s access to smartphones and social media, but parents also fear their children being excluded from online friendship groups and want to maintain contact for safety reasons. 11 Seeking to square this circle, an impromptu grassroots movement has recently grown across the UK calling on parents to collectively delay smartphone and social media uptake. 27 The UK’s children’s commissioner has voiced similar frustrations, while stressing the importance of involving young people themselves in shaping ways forward. 28
Debate will continue about exact associations between smartphones, social media, and mental health, 29 and further experimental research must be an urgent priority for funders and the academic community. But in the meantime, we must adopt the precautionary principle: measures to prevent harm should not be delayed where evidence is still contested. Health professionals and their organisations must act and advocate to ensure that smartphones and social media are framed clearly as commercial determinants of health; to guide advocacy efforts based on systematic syntheses of high quality evidence; and to amplify the voices of young people in research and policy. All will be critical if we are to facilitate technology’s potential positives while firmly safeguarding our young people’s mental health.
Competing interests: The BMJ has judged that there are no disqualifying financial ties to commercial companies. The authors declare the following other interests: MM is past president of the BMA. Further details of The BMJ policy on financial interests are here: https://www.bmj.com/sites/default/files/attachments/resources/2016/03/16-current-bmj-education-coi-form.pdf .
Provenance and peer review: Not commissioned; externally peer reviewed.
- ↵ Burns J, Crawford A. Brianna Ghey’s mother and Molly Russell’s father join forces to combat online harm. BBC News, 15 Feb 2024. https://www.bbc.com/news/uk-68309102
- ↵ Gillespie T. Brianna Ghey’s mum says mobile phones should be made specifically for children under 16 to protect them from online harms. Sky News, 15 Feb 2024. https://news.sky.com/story/brianna-gheys-mum-says-mobile-phones-should-be-made-specifically-for-children-under-16-to-protect-them-from-online-harms-13072291
- ↵ Royal College of Paediatrics and Child Health. State of child health. 2020. https://stateofchildhealth.rcpch.ac.uk/
- ↵ Children’s Society. The good childhood report. 2023. https://www.childrenssociety.org.uk/good-childhood
- Cybulski L ,
- Ashcroft DM ,
- Zilanawala A ,
- Thomson RM ,
- Henery PM ,
- Henderson M ,
- Katikireddi SV
- Blanchard L ,
- Conway-Moore K ,
- Abi-Jaoude E ,
- Naylor KT ,
- Pignatiello A
- ↵ Sapien Labs. Age of first smartphone/tablet and mental wellbeing outcomes. 2023. https://sapienlabs.org/whats_new/study-out-from-sapien-labs-links-age-of-first-smartphone-to-mental-wellbeing/
- ↵ Ofcom. Children and parents: media use and attitudes. 2023. https://www.ofcom.org.uk/__data/assets/pdf_file/0027/255852/childrens-media-use-and-attitudes-report-2023.pdf
- McCarthy S ,
- Cordedda C ,
- Kenworthy N ,
- ↵ Rankin J. EU investigates Facebook owner Meta over child safety and mental health concerns. Guardian 2024 May 16. https://www.theguardian.com/technology/article/2024/may/16/eu-investigates-facebook-owner-meta-over-child-safety-and-mental-health-concerns
- ↵ Gibson K. Mark Zuckerberg accused of having “blood on his hands” in fiery Senate hearing on internet child safety. CBS News, 31 Jan 2024. https://www.cbsnews.com/news/mark-zuckerberg-meta-x-child-exploitation/
- ↵ Wells G, Horwitz J, Seetharaman D. Facebook knows Instagram is toxic for teen girls, company documents show. Wall Street Journal 2021 Sep 14. https://www.wsj.com/articles/the-facebook-files-11631713039
- Stuckler D ,
- Monteiro C ,
- Lancet NCD Action Group
- Freudenberg N
- ↵ Federal Trade Commission. Complying with COPPA: frequently asked questions. 2020. https://www.ftc.gov/business-guidance/resources/complying-coppa-frequently-asked-questions
- ↵ Zeffman H. Bereaved parents’ anger at “broken” online safety promise. BBC News, 15 Dec 2023. https://www.bbc.com/news/uk-politics-67714572
- ↵ Department for Education. Mobile phones in schools. 2024. https://www.gov.uk/government/publications/mobile-phones-in-schools
- ↵ Banfield-Nwachi M. ‘It went nuts’: thousands join UK parents calling for smartphone-free childhood. Guardian 2024 Feb 17. https://www.theguardian.com/technology/2024/feb/17/thousands-join-uk-parents-calling-for-smartphone-free-childhood
- ↵ BBC. Woman’s hour, 8 Feb 2024. https://www.bbc.co.uk/programmes/m001w105
- ↵ Haidt J. Yes, social media really is a cause of the epidemic of teenage mental illness. After Babel, 2024. https://www.afterbabel.com/p/phone-based-childhood-cause-epidemic?utm_source=profile&utm_medium=reader2
The Impact of Social Media on Mental Health: Understanding Depression
This essay is about how social media can contribute to depression. It examines factors such as the culture of comparison, cyberbullying, and the impact on sleep and self-esteem. Social media often promotes idealized images that lead to unfavorable comparisons, causing feelings of inadequacy. Cyberbullying on these platforms can result in severe emotional distress. Additionally, social media can disrupt sleep patterns, a known risk factor for depression, and affect self-esteem and body image by setting unrealistic beauty standards. The essay suggests that mindful and moderated use of social media can help mitigate these negative effects.
How it works
The ubiquitous presence of social media in contemporary society has intricately woven itself into the fabric of everyday life, serving as a conduit for global connectivity and facilitating instantaneous communication and dissemination of information. Nonetheless, amidst its myriad benefits, mounting evidence suggests that the excessive consumption of social media may exacerbate mental health concerns, notably depression. Comprehending the mechanisms through which social media engenders depression entails a nuanced examination of several interconnected factors, including the culture of comparison, cyberbullying, and the ramifications on sleep patterns and self-esteem.
One of the foremost conduits through which social media precipitates depression is the pervasive culture of comparison it cultivates. Platforms such as Instagram, Facebook, and TikTok incentivize users to showcase the highlights of their lives, often presenting a curated facade of reality. Consequently, this engenders a distorted perception wherein others appear perpetually happier, more accomplished, and aesthetically superior. Prolonged exposure to these meticulously curated portrayals fosters a proclivity among individuals to unfavorably juxtapose their own lives, thereby instigating sentiments of inadequacy, diminished self-worth, and ultimately, depression. Empirical research indicates that individuals who frequently engage in social comparisons on social media platforms exhibit heightened susceptibility to depressive symptomatology.
Cyberbullying stands as another salient factor linking social media utilization to depression. Unlike conventional forms of bullying, cyberbullying transcends temporal and spatial barriers, manifesting as relentless dissemination of derogatory messages or imagery that can rapidly achieve wide circulation. Victims of cyberbullying often experience a profound sense of powerlessness and isolation, precipitating acute emotional anguish. The anonymity afforded by the digital realm emboldens individuals to engage in callous conduct that they might eschew in face-to-face interactions. Particularly among adolescents and young adults, who constitute among the most avid consumers of social media, cyberbullying poses deleterious repercussions on mental well-being, escalating the risk of depression and even suicidal ideation.
Moreover, the deleterious impact of social media on sleep patterns assumes a pivotal role in precipitating depression. A considerable cohort, notably adolescents, habitually devote extensive nocturnal hours to digital engagement, thereby impinging upon their sleep hygiene. The emission of blue light by screens disrupts the secretion of melatonin, a hormone pivotal in regulating circadian rhythms. Poor sleep quality and inadequate sleep duration are well-documented precursors to depression. Furthermore, the addictive allure of social media imparts formidable impediments to disengagement, precipitating chronic sleep deprivation and attendant mental health adversities.
Furthermore, social media exerts a pernicious influence on self-esteem and body image, thereby fostering a milieu conducive to depression. The proliferation of retouched and embellished imagery propounds unrealistic benchmarks of beauty and flawlessness. Particularly among young women, users contend with heightened pressure to conform to these idealized standards, thereby incurring dissatisfaction with body image and diminished self-regard. The incessant exposure to idealized portrayals engenders a warped conception of normalcy and attainability, exacerbating sentiments of inadequacy and fostering depressive symptomatology.
Social media’s role in fomenting depression is further compounded by the phenomenon colloquially termed “FOMO,” or fear of missing out. The incessant deluge of updates pertaining to peers’ engagements and experiences breeds a palpable anxiety and a pervasive sense of exclusion among those who perceive themselves as peripheral to the fray. This apprehension precipitates compulsive monitoring of social media platforms, thereby reinforcing feelings of isolation and despondency. The compulsive need for perpetual connectivity engenders a preclusion from authentic, real-world interactions, thereby further alienating individuals and precipitating deleterious effects on mental well-being.
Notwithstanding these perils, it behooves us to acknowledge that social media is not inherently deleterious. Indeed, it avails invaluable opportunities for social interconnectedness, communal support, and expressive freedom. However, judicious moderation and discerning engagement are imperative to ameliorating its adverse consequences. Encouraging individuals to cultivate intermittent reprieves from social media, partake in offline pursuits, and avail themselves of support networks can redound to a mitigation of depression risk. Parents and educators wield pivotal agency in cultivating healthy social media habits among youths, underscoring the primacy of genuine interpersonal connections and self-care.
In summation, whilst social media has revolutionized interpersonal dynamics and communication modalities, it concurrently engenders a panoply of challenges for mental well-being, particularly in the realm of depression. The culture of comparison, cyberbullying, disrupted sleep patterns, and impacts on self-esteem and body image coalesce as multifaceted factors that precipitate depressive symptomatology. By comprehensively delineating these mechanisms and advocating for judicious social media utilization, we can attenuate its deleterious repercussions and foster enhanced mental health outcomes for all stakeholders.

Cite this page
The Impact of Social Media on Mental Health: Understanding Depression. (2024, Jun 01). Retrieved from https://papersowl.com/examples/the-impact-of-social-media-on-mental-health-understanding-depression/
"The Impact of Social Media on Mental Health: Understanding Depression." PapersOwl.com , 1 Jun 2024, https://papersowl.com/examples/the-impact-of-social-media-on-mental-health-understanding-depression/
PapersOwl.com. (2024). The Impact of Social Media on Mental Health: Understanding Depression . [Online]. Available at: https://papersowl.com/examples/the-impact-of-social-media-on-mental-health-understanding-depression/ [Accessed: 6 Jun. 2024]
"The Impact of Social Media on Mental Health: Understanding Depression." PapersOwl.com, Jun 01, 2024. Accessed June 6, 2024. https://papersowl.com/examples/the-impact-of-social-media-on-mental-health-understanding-depression/
"The Impact of Social Media on Mental Health: Understanding Depression," PapersOwl.com , 01-Jun-2024. [Online]. Available: https://papersowl.com/examples/the-impact-of-social-media-on-mental-health-understanding-depression/. [Accessed: 6-Jun-2024]
PapersOwl.com. (2024). The Impact of Social Media on Mental Health: Understanding Depression . [Online]. Available at: https://papersowl.com/examples/the-impact-of-social-media-on-mental-health-understanding-depression/ [Accessed: 6-Jun-2024]
Don't let plagiarism ruin your grade
Hire a writer to get a unique paper crafted to your needs.

Our writers will help you fix any mistakes and get an A+!
Please check your inbox.
You can order an original essay written according to your instructions.
Trusted by over 1 million students worldwide
1. Tell Us Your Requirements
2. Pick your perfect writer
3. Get Your Paper and Pay
Hi! I'm Amy, your personal assistant!
Don't know where to start? Give me your paper requirements and I connect you to an academic expert.
short deadlines
100% Plagiarism-Free
Certified writers
Social Media and Mental Health Essay
- To find inspiration for your paper and overcome writer’s block
- As a source of information (ensure proper referencing)
- As a template for you assignment
The role of social media in people’s lives has increased exponentially over the past decade. The online personas that people create matter to them nearly just as much as their real-life image due to the constant communication and the opportunity to track down their responses to specific posts at any time. As a result, the impact of social media on the mental well-being of its users is worth considering. Sumner et al. point to the positive effects of social media, clarifying that the specified technological innovation can be used as the tool for improving mental health of its users. Namely, the research states that social media allows spreading useful and positive information about health-related issues much faster than traditional media. As a result, the opportunities for increasing the levels of public health and addressing some of the most common public health issues emerge.
The connection between the positivity of a message and its reception in social media is a crucial piece of information that needs to be incorporated into the current approach toward increasing the levels of public health, citizens’ health literacy, and the accessibility of health services. Namely, the conclusions that Sumner et al. make concerning the direct correlation between the positivity of a message and the likelihood of it being transmitted to a greater number of people should be used as the tool fro encouraging better health management: “Sheer volume of supportive content provided by produced by organizations or individuals may be less important than creating higher-quality messages” (p. 143). Thus, the conclusion that the authors provide should be used to enhance the efficacy and accessibility of the current health services.
One could argue that the general research outcomes should be seen as quite upsetting given the implications that they provide. Namely, the fact that the work of health professionals, who perform meticulous studies and arrange the data as carefully as possible to provide accurate and concise guidelines may be less important than an upbeat yet empty message is a rather sad idea. The specified conclusions may lead to a drop in the extent of health practitioners’ and nurse educators’ enthusiasm in providing the services of the highest quality.
However, the message that Sumner et al. convey could also be seen as an opportunity for enhancing health education and raising health literacy within the community by building a better rapport with its members. Namely, the data about the significance of the use of positivity in social networks as the tool for attracting the attention of patients and target audiences should be utilized to shape the current approach toward promoting health literacy. Specifically, healthcare practitioners and registered nurses, especially those that address the issues of patient education directly, need to create the strategy for the online conversation with patients through social media. The specified dialogue could be based on a combination of positive messages and clear visuals that inform patients about key issues in health management and provide them with an opportunity to improve their health literacy.
Additionally, the authors have provided an important tool for the development of a campaign aimed at public health management and improvement. Namely, based on the outcomes of the research carried out by Sumner et al. have informed the strategies for improving communication between patients and nurse educators. The specified change in how people perceive health management is especially important in the context of the present-day epidemic of coronavirus. Given the rapid spread of the epidemic and its recent transformation into the pandemic, reinforcing the instructions for people to remain safe is an essential task for APRNs and healthcare experts worldwide. In turn, the application of social media suits perfectly for the described purpose since it allows sharing information instantly and providing people with clear and concise guidelines for them to follow. Although social media mostly do not allow for detailed descriptions of specific health concerns and profound analysis of these issues, they serve their purpose of bulletin boards with clear and distinct guidelines that the members of the global community can apply to their daily routine.
Specifically, the use of positive messages in social media will reinforce the importance of guidelines and ensuring that people will follow them properly. For instance, Sumner et al. mention that the use of social networks has helped to promote social sharing. As the authors explain, “In topic areas such as cancer support, investigators found that the degree of positive sentiment in a message is associated with increased message spread” (Summer et al, p. 143). Therefore, the inclusion of positive thinking and positive emotions into the process of knowledge sharing enhances the extent to which people are willing to engage in the discussion. Moreover, the rise in the inclination to share a message that is positive will allow fighting some of the most severe health concerns that the global community is facing presently, primarily, the coronavirus.
Furthermore, the discussion sparked by the authors raises the question of inaccurate health-related information in social media and the means of filtering data. Indeed, for an uninitiated user of social media, discerning between accurate health-related information and the posts that reinforce health-associated myths is virtually impossible. Although some indicators such as the identity of the user posting the information could provide hints regarding the veracity of data, social media users have to rely on their intuition for the most part. Therefore, it is also critical for nurses to develop strategies for shielding social media users from the data that provides a distorted picture of health management.
Finally, the issue of addressing serious health concerns in social media should be discussed as a contentious subject. Given the outcomes of the research performed by Summer et al., it is critical to focus on delivering positive messages to target audiences to increase compliance with the established health management strategies. However, when tackling a serious health concern that has led or may potentially lead to a rapid rise in lethal outcomes, remaining positive becomes quite challenging. Not only will a message sound false in the specified circumstances, but it is also likely to be perceived in a negative light due to the dissonance between the subject matter and the tone of its delivery. Therefore, the outcomes of the study pose a difficult dilemma for educators and healthcare providers to resolve when addressing their target audiences via social media. Namely, retaining positivity while talking about serious issues is likely to become a major stumbling block for most healthcare service members.
The outcomes of the study performed by Summer et al. have offered a range of important insights, the significance of positivity in modern media as the means of encouraging citizens to accept healthy behaviors being one of the key conclusions. However, to apply the specified results to the management of current public health concerns, one will have to shape the existing framework for communicating with patients significantly. Therefore, the research should be seen as the basis for redesigning the present health education strategy, as well as the approach toward conversing with patients.
Sumner, Steven A., et al. “Factors Associated with Increased Dissemination of Positive Mental Health Messaging on Social Media.” Crisis: The Journal of Crisis Intervention and Suicide Prevention , vol. 41, no. 2, 2019, pp. 141-145. doi:10.1027/0227-5910/a000598.
- The Importance of Positivity at Work and in Life
- Social Darwinism Through the History
- How Do Social Media Influencers Convey the Message of Body Positivity?
- Technological Determinism Perspective Discussion
- Cyberbullying as a Major Problem in Contemporary Society
- Self-Disclosure and Social Media
- Social Media Satirical Cartoon by M. Wuerker
- “Westside Today” and “Gazette Newspapers”: Comparative Characteristics
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2022, February 17). Social Media and Mental Health. https://ivypanda.com/essays/social-media-and-mental-health/
"Social Media and Mental Health." IvyPanda , 17 Feb. 2022, ivypanda.com/essays/social-media-and-mental-health/.
IvyPanda . (2022) 'Social Media and Mental Health'. 17 February.
IvyPanda . 2022. "Social Media and Mental Health." February 17, 2022. https://ivypanda.com/essays/social-media-and-mental-health/.
1. IvyPanda . "Social Media and Mental Health." February 17, 2022. https://ivypanda.com/essays/social-media-and-mental-health/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "Social Media and Mental Health." February 17, 2022. https://ivypanda.com/essays/social-media-and-mental-health/.
More than just social media use may be causing depression in young adults, study shows
Over the past few decades, there has been a significant increase in the prevalence of depression in adolescents and young adults -- and a simultaneous uptick in the inclusion of technology and social media in everyday life. However, it is unclear how exactly social media use and depression are associated and relate to other behaviors, such as physical activity, green space exposure, cannabis use and eveningness (the tendency to stay up late).
In a study published May 15 in the International Journal of Mental Health and Addiction , a team of researchers, led by experts at Johns Hopkins Children's Center, investigated the association among social media use, depression and other health-related behaviors of young adults over time.
"Research shows that when social media use is high, depression is also high. But the question is -- is that because social media caused that person to be depressed? Or is it because people who are depressed tend to also use social media more, and spend less time exercising and being in green spaces? That is what we wanted to understand," says Carol Vidal, M.D., Ph.D., M.P.H., the first author of the study, a child and adolescent psychiatrist at Johns Hopkins Children's Center and an assistant professor of psychiatry and behavioral sciences at the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine.
In their study, 376 young adults in Canada (82.4% women) were asked to complete three online questionnaires between May 2021 and January 2022. At each point, participants self-reported depressive symptoms based on the Patient Health Questionnaire (PHQ-9) -- a nine-item scale that is commonly used to measure depression -- as well as social media use, greenspace exposure, physical activity and cannabis use.
The researchers found that most study participants had at least mild depressive symptoms. Findings showed that participants who had higher social media use tended to be more depressed, and people who were more depressed also tended to use social media more. However, researchers found that social media use did not cause an increase or decrease in depressive symptom levels over time.
"We found that if you tended to be a person who was depressed, you were a person also spending more time on social media," explains Vidal.
Researchers also found that higher levels of social media use and higher levels of depressive symptoms were associated with lower levels of green space exposure. In addition, cannabis use and higher eveningness were also associated with higher depressive levels.
The study authors say these results show social media use and depression are associated, but do not provide evidence that greater social media use predicts an increase in depressive symptoms over time. The team also says these findings indicate people who suffer from depression should be cautious about the amount of time they spend on social media and should be encouraged to incorporate other healthy habits into their lifestyle.
"Being indoors and not exercising, staying up late and using cannabis has its risks," says Vidal. "It is important for providers to educate patients and for parents to instill healthy habits in their kids -- having a balance of moderate social media use and other outdoor activities and exercise is what people should strive for in today's digital age."
Vidal and other investigators believe there are many aspects to social media, and there are important next steps to learn more about its impact on the mental health of people of all ages, including younger children and adolescents.
- Mental Health
- Media and Entertainment
- Popular Culture
- STEM Education
- Social Issues
- Clinical depression
- Social psychology
- Adult attention-deficit disorder
- Cognitive bias
- Social inequality
- Public health
- Mental illness
Story Source:
Materials provided by Johns Hopkins Medicine . Note: Content may be edited for style and length.
Journal Reference :
- Carol Vidal, Frederick L. Philippe, Marie-Claude Geoffroy, Vincent Paquin. The Role of Social Media Use and Associated Risk and Protective Behaviors on Depression in Youth Adults: A Longitudinal and Network Perspective . International Journal of Mental Health and Addiction , 2024; DOI: 10.1007/s11469-024-01313-0
Cite This Page :
Explore More
- Babies and AI Both Learn Key Foundation Models
- Myelination May Drive Drug Addiction
- Freshwater On Earth 4 Billion Years Ago
- Extended Battle: 3,500-Year-Old Mycenaean Armor
- Oral Insulin Drops: Relief for Diabetes Patients
- AIs Are Irrational, but Not Like Humans
- Bronze Age Cuisine of Mongolian Nomads
- Poor Quality Diet Makes Our Brains Sad
- AI Improves Performance Across Fusion Devices
- New Explanation for Why Earthquakes Happen
Trending Topics
Strange & offbeat.
- Alzheimer's disease & dementia
- Arthritis & Rheumatism
- Attention deficit disorders
- Autism spectrum disorders
- Biomedical technology
- Diseases, Conditions, Syndromes
- Endocrinology & Metabolism
- Gastroenterology
- Gerontology & Geriatrics
- Health informatics
- Inflammatory disorders
- Medical economics
- Medical research
- Medications
- Neuroscience
- Obstetrics & gynaecology
- Oncology & Cancer
- Ophthalmology
- Overweight & Obesity
- Parkinson's & Movement disorders
- Psychology & Psychiatry
- Radiology & Imaging
- Sleep disorders
- Sports medicine & Kinesiology
- Vaccination
- Breast cancer
- Cardiovascular disease
- Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- Colon cancer
- Coronary artery disease
- Heart attack
- Heart disease
- High blood pressure
- Kidney disease
- Lung cancer
- Multiple sclerosis
- Myocardial infarction
- Ovarian cancer
- Post traumatic stress disorder
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Schizophrenia
- Skin cancer
- Type 2 diabetes
- Full List »
share this!
May 29, 2024
This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies . Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
Study shows more than just social media use may be causing depression in young adults
by Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine
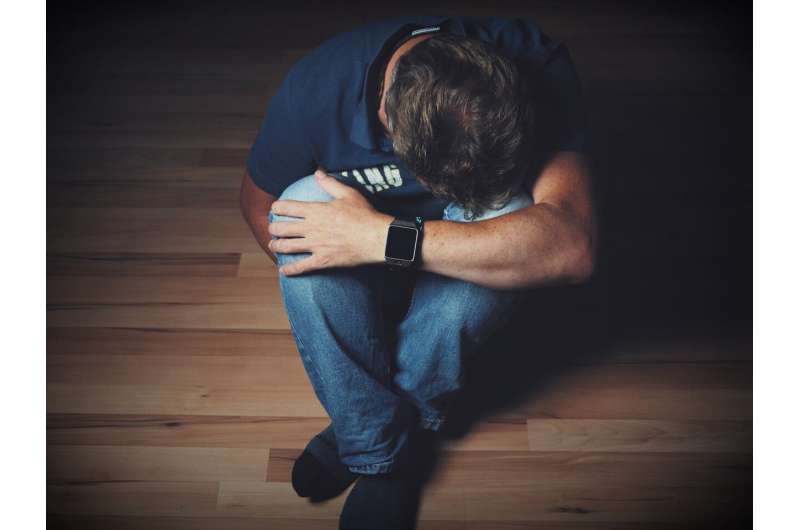

Over the past few decades, there has been a significant increase in the prevalence of depression in adolescents and young adults—and a simultaneous uptick in the inclusion of technology and social media in everyday life. However, it is unclear how exactly social media use and depression are associated and relate to other behaviors, such as physical activity, green space exposure, cannabis use and eveningness (the tendency to stay up late).
In a study published in the International Journal of Mental Health and Addiction , a team of researchers, led by experts at Johns Hopkins Children's Center, investigated the association among social media use, depression and other health-related behaviors of young adults over time.
"Research shows that when social media use is high, depression is also high. But the question is—is that because social media caused that person to be depressed? Or is it because people who are depressed tend to also use social media more, and spend less time exercising and being in green spaces? That is what we wanted to understand," says Carol Vidal, M.D., Ph.D., M.P.H., the first author of the study, a child and adolescent psychiatrist at Johns Hopkins Children's Center and an assistant professor of psychiatry and behavioral sciences at the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine.
In their study, 376 young adults in Canada (82.4% women) were asked to complete three online questionnaires between May 2021 and January 2022. At each point, participants self-reported depressive symptoms based on the Patient Health Questionnaire (PHQ-9)—a nine-item scale that is commonly used to measure depression—as well as social media use, greenspace exposure, physical activity and cannabis use .
The researchers found that most study participants had at least mild depressive symptoms. Findings showed that participants who had higher social media use tended to be more depressed, and people who were more depressed also tended to use social media more. However, researchers found that social media use did not cause an increase or decrease in depressive symptom levels over time.
"We found that if you tended to be a person who was depressed, you were a person also spending more time on social media," explains Vidal.
Researchers also found that higher levels of social media use and higher levels of depressive symptoms were associated with lower levels of green space exposure. In addition, cannabis use and higher eveningness were also associated with higher depressive levels.
The study authors say these results show social media use and depression are associated, but do not provide evidence that greater social media use predicts an increase in depressive symptoms over time. The team also says these findings indicate people who suffer from depression should be cautious about the amount of time they spend on social media and should be encouraged to incorporate other healthy habits into their lifestyle.
"Being indoors and not exercising, staying up late and using cannabis has its risks," says Vidal. "It is important for providers to educate patients and for parents to instill healthy habits in their kids—having a balance of moderate social media use and other outdoor activities and exercise is what people should strive for in today's digital age."
Vidal and other investigators believe there are many aspects to social media, and there are important next steps to learn more about its impact on the mental health of people of all ages, including younger children and adolescents.
Explore further
Feedback to editors

Lifesaving childbirth blood loss intervention is highly cost-effective, finds 78-hospital analysis
Research team develops searchable database for Alzheimer's research

First-of-its-kind test can predict dementia up to nine years before diagnosis

New glioblastoma treatment reaches human brain tumor and helps immune cells recognize cancer cells

Man in Mexico died of a bird flu strain that hadn't been confirmed before in a human, WHO says
2 hours ago

One in six people who stop antidepressants will experience discontinuation symptoms as a direct result, says study
12 hours ago

Immunotherapy before surgery very successful in treating colorectal cancer, trial finds
13 hours ago

Early life experiences linked to racial disparities in cognition
14 hours ago

Oral insulin drops offer relief for diabetes patients
15 hours ago
New study redefines how antidepressants aid in treating major depressive disorder
Related stories.

Social media-related nightmares: Study explores links between social media use, mental health and sleep quality
May 20, 2024

Social media program helps ease symptoms of postpartum depression
Feb 21, 2023

The people who are most active on social media are also the most active offline, shows study
May 2, 2024

Data show no evidence that teens' social media use predicts depression over time
Jan 30, 2019

Negative vs. positive social media experiences and depressive symptoms
Jun 7, 2018

What does the research say about social media and children's mental health?
Jun 19, 2023
Recommended for you

Evidence-based design or Feng Shui in hospital rooms might benefit patients, online study finds
16 hours ago

Babies use 'helpless' infant period to learn powerful foundation models, just as ChatGPT does
19 hours ago
Retina indicates severity of schizophrenia, scientists discover

Training cognitive control in children does not change brain or behavior, finds study
Let us know if there is a problem with our content.
Use this form if you have come across a typo, inaccuracy or would like to send an edit request for the content on this page. For general inquiries, please use our contact form . For general feedback, use the public comments section below (please adhere to guidelines ).
Please select the most appropriate category to facilitate processing of your request
Thank you for taking time to provide your feedback to the editors.
Your feedback is important to us. However, we do not guarantee individual replies due to the high volume of messages.
E-mail the story
Your email address is used only to let the recipient know who sent the email. Neither your address nor the recipient's address will be used for any other purpose. The information you enter will appear in your e-mail message and is not retained by Medical Xpress in any form.
Newsletter sign up
Get weekly and/or daily updates delivered to your inbox. You can unsubscribe at any time and we'll never share your details to third parties.
More information Privacy policy
Donate and enjoy an ad-free experience
We keep our content available to everyone. Consider supporting Science X's mission by getting a premium account.
E-mail newsletter
Resources for Students
Emory News Center
Emory University Home
Emory Forward
Campus Life
Academic Calendars
Emory Libraries
Emory Report
Past Issues

Essay on Effects Of Social Media On Mental Health
Students are often asked to write an essay on Effects Of Social Media On Mental Health in their schools and colleges. And if you’re also looking for the same, we have created 100-word, 250-word, and 500-word essays on the topic.
Let’s take a look…
100 Words Essay on Effects Of Social Media On Mental Health
Introduction.
Social media is a tool that lets us communicate and share with people around the world. It’s very popular, especially with young people. But, it can also affect our mental health in different ways.
Positive Impact
Social media can have a good effect on our mental health. It allows us to connect with friends and family, even if they live far away. It can also help us find groups of people who share our interests. This can make us feel less alone and more understood.
Negative Impact
On the other hand, social media can also have a bad effect on our mental health. Seeing other people’s “perfect” lives can make us feel bad about our own. It can also lead to cyberbullying, which can hurt our self-esteem and cause stress.
Importance of Balance
Like most things, balance is key when using social media. Spending too much time online can make us feel isolated in real life. It’s important to take breaks and spend time doing other things we enjoy.
In conclusion, social media can have both positive and negative effects on our mental health. It’s important to use it wisely and remember that it’s okay to take a break if it’s making us feel bad.
250 Words Essay on Effects Of Social Media On Mental Health
Social media is a powerful tool that connects people from all corners of the world. It is a platform where we share our thoughts, ideas, and daily life activities. But, it also has a great impact on our mental health.
Impacts on Self-Esteem
One of the main effects of social media on mental health is on our self-esteem. When we see our friends having fun, achieving things, or looking happy, we often compare ourselves with them. This comparison can make us feel less confident and happy about our own lives.
Loneliness and Isolation
Another effect is the feeling of loneliness and isolation. Even though we are connected with many people online, we can still feel alone. This is because social media interactions are not the same as real-life interactions. This feeling can lead to sadness and depression.
Anxiety and Fear
Social media can also cause anxiety and fear. We often worry about what others will think of our posts. We fear negative comments and judgments. This constant worry can lead to stress and anxiety.
In conclusion, while social media has its benefits, it can also have negative effects on our mental health. It can affect our self-esteem, make us feel lonely, and cause anxiety. Therefore, it is important to use social media wisely and not let it control our lives. We need to remember that what we see on social media is not always the full picture of someone’s life.
500 Words Essay on Effects Of Social Media On Mental Health
Social media is a big part of our lives. We use it to chat with friends, share photos, and learn about the world. But, it can also affect our mental health in both good and bad ways. This essay will explore these effects.
Positive Effects
First, let’s talk about the good things. Social media can make us feel connected. It allows us to keep in touch with friends and family, even if they live far away. This can make us feel less lonely. It can also help us find people who share our interests. For example, if you love painting, you can join an art group online. This can boost your confidence and make you feel part of a community.
Negative Effects
Now, let’s look at the negative side. Spending too much time on social media can make us feel sad or anxious. This is because we often compare our lives to the perfect ones we see online. This can make us feel like we are not good enough.
Another problem is cyberbullying. Some people use social media to hurt others by sending mean messages or spreading rumors. This can lead to stress, anxiety, and even depression.
Impact on Sleep
Social media can also affect our sleep. Many of us check our phones before bed. The bright screen can make it harder for us to fall asleep. Lack of sleep can lead to mood swings, trouble focusing, and feeling tired all the time.
Ways to Stay Healthy
The good news is there are ways to use social media without hurting our mental health. One way is to limit our time online. We can set a timer or use an app that reminds us to take a break.
We should also remember that what we see online is not always real. Many people only share the best parts of their lives, not the hard parts.
If someone is being mean to us online, we should tell a trusted adult. We can also block or report the person.
In conclusion, social media has both good and bad effects on our mental health. It can make us feel connected, but it can also make us feel sad, anxious, and tired. To stay healthy, we need to use social media in a balanced way, remember that what we see online is not always real, and speak up if someone is being mean to us.
That’s it! I hope the essay helped you.
If you’re looking for more, here are essays on other interesting topics:
- Essay on Effects Of Social Media On Family Relationships
- Essay on Effects Of Social Media
- Essay on Effects Of Poverty On Health
Apart from these, you can look at all the essays by clicking here .
Happy studying!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

Home — Essay Samples — Sociology — Effects of Social Media — The Impact of Social Media on Mental Health
The Impact of Social Media on Mental Health
- Categories: Effects of Social Media Mental Health
About this sample

Words: 657 |
Published: Feb 7, 2024
Words: 657 | Page: 1 | 4 min read
Table of contents
The allure of social media, the pressure to present a perfect life, the loneliness behind the screens, the filtered reality, the echo chamber effect, the fear of missing out and anxiety, finding balance and positive experiences, conclusion and reflection.

Cite this Essay
Let us write you an essay from scratch
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
Get high-quality help

Prof Ernest (PhD)
Verified writer
- Expert in: Sociology Nursing & Health

+ 120 experts online
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
Related Essays
3 pages / 1430 words
3 pages / 1269 words
2 pages / 960 words
2 pages / 793 words
Remember! This is just a sample.
You can get your custom paper by one of our expert writers.
121 writers online
Still can’t find what you need?
Browse our vast selection of original essay samples, each expertly formatted and styled
Related Essays on Effects of Social Media
I will not stand here and pretend to understand what other people need in terms of self acceptance, but if there is one thing that my personal experience has taught me, it is that appreciating all of what makes me me and not [...]
Alton, L. (2017, May 15). Is Working From Home Making You Feel Miserable?. NBC news. Retrieved from https://www.inc.com/amy-morin/heres-why-internet-has-made-us-lonelier-than-ever.html
Social media has emerged as a transformative force in the modern world, reshaping the way individuals interact, communicate, and perceive themselves and others. In this essay, we explore the multifaceted influence of social [...]
Rabin, Ruhani. 'Social Media - Impact on Society.' International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications, vol. 2, no. 5, May 2012.Subrahmanyam, K., and Smahel, D. 'Digital Youth: The Role of Media in Development.' [...]
Social media creates a dopamine-driven feedback loop to condition young adults to stay online, stripping them of important social skills and further keeping them on social media, leading them to feel socially isolated. Annotated [...]
Social media is consisted of platforms such as facebook, twitter, and Instagram, basically anything where people could share a piece of their minds or their lives. It can also be considered as a place for creativity, freedom of [...]
Related Topics
By clicking “Send”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement . We will occasionally send you account related emails.
Where do you want us to send this sample?
By clicking “Continue”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy.
Be careful. This essay is not unique
This essay was donated by a student and is likely to have been used and submitted before
Download this Sample
Free samples may contain mistakes and not unique parts
Sorry, we could not paraphrase this essay. Our professional writers can rewrite it and get you a unique paper.
Please check your inbox.
We can write you a custom essay that will follow your exact instructions and meet the deadlines. Let's fix your grades together!
Get Your Personalized Essay in 3 Hours or Less!
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free
The Impact of Social Media on Mental Health
Introduction, the popularity of social media, feelings of depression and anxiety, social media and the fear of missing out, distraction turns into chaos, the potential benefits of social media, works cited.
Human beings are inherently social creatures who crave companionship and communication. It seems as though cooperating with others is the only way to make progress in life, according to lifestyle gurus and networking coaches. Being socially connected to others has never been more important, which explains the immense success of social media networking platforms. Despite the associated risks and dangers of this new invention, people use social media daily and rely on it in various aspects of their lives. Since the concept is relatively new, there are a limited number of studies, which would assess the impact of Instagram, Facebook, or any other platform on users’ mental health. Nevertheless, recent research indicates that the unnecessary and excessive use of social media can lead to depression, anxiety, and low self-esteem (Hunt et al. 751; Lyall et al. 507). The evidence paints a clear picture of the threats people might face as a result of social media use.
The purpose of this speech is to analyze the latest research to identify the main dangers of this new medium of communication. The intended audience is everyone interested in learning more about the impact of social media on mental health and gaining insights into the correlation between depression, self-hate, anxiety, and excessive social media use. However, it targets young people, in particular, since they are some of the most active users who are impressionable and persuadable.
Relatively recently, social media platforms have become an indispensable part of many people’s daily lives. Billions spend hours on Instagram and Facebook although just 50 years ago, no one could have predicted the existence of these new communication channels. The number of users is around 3.5 billion as of 2019, according to Karim et al. (1). Furthermore, it is projected to grow by 0.9 billion in only 6 years (Tankovska). The percentage of American adults who use social media platforms has increased by 74% since 2005 (Ortiz-Ospina). The penetration of social media is constantly expanding and intensifying in various regions worldwide. Tankovska notes that the global rate of using social media is at 49%, which is expected to increase significantly due to the economic development of less wealthy regions in sub-Saharan Africa and Asia. Although the U.S. and Europe remain the most prominent digital powerhouses, Eastern Asia starts to become the most penetrated market.
The most serious concern related to the use of social networking sites and their impact on mental health is depression and anxiety. While one might feel anxious because of daily problems or situations out of their comfort zone, clinical depression is an actual mood disorder. Depressive episodes often imply prolonged feelings of sadness and suicidal thoughts. Studies reveal a clear correlation between the disorder and social media use. The researchers often go a bit further and suggest that platforms such as Instagram and Facebook may cause depression, to begin with (Hunt et al. 751). For instance, The Lancet Psychiatry published a study linking the feelings of unhappiness and disappointment with late-night Facebook surfing (Lyall et al. 507). Melissa G. Hunt and her colleagues concluded that people generally feel happier and less lonely if they spend less time on social media networking sites (751). This suggests that there is a causal link between social media and mental health. By presenting the evidence of this experimental study, the researchers demonstrated the association between emotional well-being and the use of platforms such as Facebook and Instagram.
It is crucial to acknowledge that not social media itself, but the quality and quantity of the time spent using it affects mental health and behavioral patterns. According to Karim et al. (2), the Displaced Behavior Theory can provide an accurate explanation of the connection between emotional well-being and social networking. Thus, individuals who spend more of their time “in sedentary behaviors such as social media users have less time for face-to-face social interaction, both of which have been proven to be protective against mental disorders” (Karim et al. 2). In addition, the design of platforms such as Facebook and Instagram impacts the social patterns people tend to rely on during the process of maintaining their close relationships. As a result, they start to feel more anxious and disappointed once they recognize their inability to connect with others in real life.
The unnecessary use of social media platforms leads to feelings of depression and anxiety, which poses a threat to the global population’s mental well-being. The most common risk factors associated with such issues in the context of social media use include the excess of time spent, the quality of activities engaged in, and the overall addiction to social media.
When discussing the impact of social media on mental health, one of the most important concepts is the fear of missing out, which is simply referred to as FOMO online. In the study conducted by Hunt et al., the main reason why the participants were more likely to feel less depressed if they spent less time on social media platforms was the absence of stress-inducing content. Young people were simply spared from observing celebrities, influencers, or just their friends going on vacations, succeeding career-wise, or showcasing their affectionate relationships with significant others. Individuals fall into depressive episodes and develop suicidal thoughts due to the feelings of envy and disappointment fueled by looking at the pictures of someone’s seemingly perfect life. This leads to social media users questioning their own choices, which, in turn, affects their self-worth. Ultimately, by limiting the time spent on Instagram or Facebook, people consume less content. Therefore, by extension, they spend less time comparing themselves to others, which reduces the risk of developing depression.
It is no wonder why so many people use social media primarily as a certain form of escapism to distract themselves from the less-than-perfect reality. Unfortunately, this often results in their inability to accept and cope with the tragedies of life, including terrorist attacks, bombings, and natural disasters. Elisa Shearer from the Pew Research Center notes that approximately 20% of Americans receive all of their news from social media sites. It becomes apparent that while trying to escape, people still have to face the vicious cycle of negativity perpetuated by news media platforms online.
Despite the aforementioned arguments supported by reliable academic research, some still agree that social media is an overall positive invention. Mesfin Awoke Bekalu, a researcher at Harvard T. H. Chan School of Public Health, suggests that routine social media use positively affects primary health-related outcomes, including social well-being, self-rated health, and mental health. Visiting sites such as Facebook and Instagram to respond to others’ content and post personal images can be beneficial, according to Bekalu. However, it is important to recognize that social media use is usually accompanied by a destructive emotional connection to the content shared by others, which results in excessive time spent on apps.
Thus, a person is vulnerable to feelings of disappointment, self-hatred, and isolation, which often results in depression and anxiety disorders. Therefore, it is crucial to keep the statistics and scholarly research in mind before praising the platforms such as Facebook and Instagram. On the one hand, they are practical and beneficial since they allow people to connect easily and find a community of like-minded individuals. On the other hand, the sites should be used in moderation to avoid social comparison and escapist patterns in behavior.
In conclusion, social media is not necessarily the enemy. If used in moderation, the opportunities it provides to people are countless. With the recent growth in popularity and penetration of social networking sites, the impact of platforms such as Instagram and Facebook is bigger than ever. With regards to the latest research, it is evident that excessive use of such apps poses a threat of developing mental health disorders and feelings of loneliness and self-hatred. Isolation, fear of missing out, and anxiety are concepts often associated with excessive social media use. Therefore, the time spent online should be limited and controlled to limit the amount of stress from the content posted on these platforms.
Bekalu, Mesfin Awoke. “Social Media Use Can Be Positive for Mental Health and Well-Being.” Harvard T. H. Chan School of Public Health , 2020, Web.
Hunt, Melissa G., et al. “No More FOMO: Limiting Social Media Decreases Loneliness and Depression.” Journal of Social and Clinical Psychology , vol. 37, no. 10, 2018, pp. 751-768, Web.
Karim, Fazida, et al. “Social Media Use and Its Connection to Mental Health: A Systematic Review.” Cureus , vol. 12, no. 6, 2020. NCBI , Web.
Lyall, Laura M., et al. Association of Disrupted Circadian Rhythmicity with Mood Disorders, Subjective Wellbeing, and Cognitive Function: A Cross-Sectional Study of 91 105 Participants from the UK Biobank.” The Lancet Psychiatry , vol. 5, no. 6, 2019, pp. 507-514, Web.
Ortiz-Ospina, Esteban. “The Rise of Social Media.” Our World in Data , 2019, Web.
Shearer, Elisa. “Social Media Outpaces Print Newspapers in the U.S. as a News Source.” Pew Research Center , 2018, Web.
Tankovska, Hana. Number of Social Network Users Worldwide from 2017 to 2025. Statista , Web.
Cite this paper
- Chicago (N-B)
- Chicago (A-D)
StudyCorgi. (2022, August 14). The Impact of Social Media on Mental Health. https://studycorgi.com/the-impact-of-social-media-on-mental-health/
"The Impact of Social Media on Mental Health." StudyCorgi , 14 Aug. 2022, studycorgi.com/the-impact-of-social-media-on-mental-health/.
StudyCorgi . (2022) 'The Impact of Social Media on Mental Health'. 14 August.
1. StudyCorgi . "The Impact of Social Media on Mental Health." August 14, 2022. https://studycorgi.com/the-impact-of-social-media-on-mental-health/.
Bibliography
StudyCorgi . "The Impact of Social Media on Mental Health." August 14, 2022. https://studycorgi.com/the-impact-of-social-media-on-mental-health/.
StudyCorgi . 2022. "The Impact of Social Media on Mental Health." August 14, 2022. https://studycorgi.com/the-impact-of-social-media-on-mental-health/.
This paper, “The Impact of Social Media on Mental Health”, was written and voluntary submitted to our free essay database by a straight-A student. Please ensure you properly reference the paper if you're using it to write your assignment.
Before publication, the StudyCorgi editorial team proofread and checked the paper to make sure it meets the highest standards in terms of grammar, punctuation, style, fact accuracy, copyright issues, and inclusive language. Last updated: November 6, 2022 .
If you are the author of this paper and no longer wish to have it published on StudyCorgi, request the removal . Please use the “ Donate your paper ” form to submit an essay.
Many blame social media for poor mental health among teenagers, but the science is murky
If Jordy had a switch to instantly shut down social media, she would flip it.
"I'd switch it off, 100 per cent, even if it was for a week, just so people could have that taste of what it would be like," she said.
Now in her first year out of school, the 18-year-old studies nursing at university and works at a local cafe in Charleville, a small town 745 kilometres west of Brisbane, where she has lived most of her life.
Like Australian teenagers everywhere, she has another life online.
"It's like a second world, really," she said.
"You have reality and then you have social media — two extremely different things."
At the moment, she spends an average of five-and-a-half hours a day on her phone, but it's lower than her peak during high school.
"When I first got a phone I was on it constantly, probably like seven hours, eight hours a day," she said.
She has cut back since then because that second world was not always kind, especially when it came to body image — and despite the fact her parents were always strict about phone usage.
"Growing up, I've always been a big girl … and a sporty person — I'm pretty healthy," she said.
"But when we see images, it tends to be just very thin, skinny people.
"It can just take you down, with the click of your fingers."
Jordy was also being bullied at school, but social media meant it could happen around the clock, no matter where she was.
"A group of boys at my school had tagged me on TikTok telling me to go kill myself," she said.
"It was just so heartbreaking. I was just like, 'I go to school with you every day, we've never had an issue in the past.' That's probably the worst thing that's happened."
Jordy's mental health was tanking, and she began to withdraw from activities she used to love, like footy training or seeing friends.
"I just felt so scared to talk to my mum … I was just like, 'I don't want my mum to think I'm using social media the wrong way'," she said.
No matter how bad things got, logging off still felt impossible.
"It was like that fear of missing out, I guess. I think that's the addiction thing, right?" she said.
"You sort of just have to be on your phone to socialise."
Does more screen time cause worse mental health in teenagers?
Teen mental health has deteriorated at an accelerating rate in the last two decades — more or less exactly since social media and smartphones started to become widespread in 2007.
For obvious reasons, many people, especially concerned parents, have leapt to the conclusion that tech is the culprit.
But the science is surprisingly murky, even though there is a link — research shows more screen time is associated with higher rates of depression in adolescents.
"What we know about the link is there's a link, and that's pretty much what we know," said Aliza Werner-Seidler, a senior researcher at the Black Dog Institute.
"We have really good correlational data, there is a strong linear relationship, particularly in young girls.
"What we don't know is about causation — so is young people's mental health leading them to spend more time on social media and screens, or is it actually the other way around?
"We don't know the direction of the effect."
Dr Werner-Seidler is one of thousands of researchers around the world trying to solve that mystery.
Even if many people are convinced they already know the answer because of their own experience online.
"Personally I would say that it's both," Jordy said.
After a session doomscrolling perfect bodies on TikTok, she "would feel horrible" about herself.
"But then I'd continue to use it and then it made me feel even worse."
After 17 years, why don't we have the answers yet?
Despite 17 years of widespread smartphones and social media, researchers still don't have enough data to definitively say whether they're to blame for deteriorating teen mental health.
Getting those long-term studies done is particularly difficult because trends, algorithms and habits change so quickly.
"When I started this work, TikTok wasn't even a thing … Snapchat, really has only taken off in the last decade or so," Dr Werner-Seidler said.
"It's a very fast-moving field. And so it's very, very difficult to get a handle on it before the next thing comes out."
Part of the problem is that studies have focused on overall screen time, instead of looking at what people were doing online.
"Are they FaceTiming with Grandma? Are they viewing distressing content? Are they being groomed online?" Dr Werner-Seidler said.
"This idea of nuance and it matters what people do and how they do it and how long for and with whom.
"We can't tell any of this information just by looking at how long young people spend on screens."
What social media companies know but don't say
The National Mental Health Commission has been investigating the relationship between digital tech and teen mental health.
On Friday it released its findings after months of consultation, noting the lack of longitudinal evidence and calling for further research to be made a "top priority".
Frustratingly for Dr Werner-Seidler, and other researchers in this area, the data that might solve the mystery does exist — but they can't access it.
"Big tech companies have all of this information," she said.
"If they were to share it with academics and scientists, we would be able to learn so much more, so much more quickly."
The data that has so far emerged in other ways, courtesy of lawsuits and whistleblowers such as Frances Haugen in 2021, has been disturbing.
Ms Haugen, a former Facebook employee, revealed detailed internal research showing Instagram was harmful for teenage girls.
One slide from an in-house presentation reportedly said: "We make body image issues worse for one in three teen girls."
The peak body for Australia's technology industry — whose members include social media companies Meta, Snapchat and TikTok — has defended the sector's contribution to public research.
"DIGI's relevant members have long-standing research and community partnerships in mental health and online safety, and specific policies … informed by that work," a spokesperson said.
Depending on the platform, those policies might include parental controls, avenues to report inappropriate content and seek help, customisable settings, and age limits.
Adherence to those age limits has been mostly voluntary, and the federal government is spending $6.5 million on an age verification trial in the hopes of introducing a higher standard of proof.
Some social media companies are trying to get ahead of any future legislation.
Facebook's parent company Meta announced this week it would no longer allow Facebook users to edit their birthdate to say they're over 18 without verification — a feature that's been in place on Instagram in Australia since last year.
A window for change
The public and political mood when it comes to big tech has rarely been darker.
"I've never seen the appetite [for change] as strong as it is right now," said Alice Dawkins, executive director of Reset Tech Australia.
She says there's a window for change with the federal government currently reviewing its key legislation, the Online Safety Act.
"Our online safety laws are geared at protecting people from [one] another online … [but] there's virtually nothing that can be done about protecting people from the tech itself."
As it stands, companies are rarely obliged to share information on how their products, and not just the people using them, may cause harm.
"It's highly exceptional — think about other sectors, like food, like medicine, like toys — it's incredibly routine in those sectors to have risk assessment and risk mitigation of products," Ms Dawkins said.
"There's compounding public awareness of the problem … it's never been a more appropriate time for the government to legislate."
Dr Werner-Seidler said that for now, internal data was being used by big tech to keep users scrolling for as long as possible.
"These are commercial big companies [and] they use a whole bunch of engagement strategies to keep people coming back, and that is their goal," she said.
The conversation you need to have with your kids
Jordy eventually found the courage to tell her mum what was happening to her online.
"When it got really bad I was just like, 'Mum, I need to show you … this is what's happening.'"
After that, her parents insisted she cut back her screen time but, despite everything that had already happened, she still fought it.
"I was so mean to her … I would get so angry, I'd be like, 'Mum, it's not your life,'" she said.
But that was before Jordy noticed a big improvement in her mood and her grades.
"I'm thankful every day that my mum did what she did.
"You can't ever change the fact that your kids are going to use social media," said Jordy, although boundaries were useful in her case.
"Saying to your kids, 'What are you using social media for? Why do you have to be on social media?'
"For parents out there that are struggling, I think it's that conversation you need to have with your kids.
"As a kid, you're going to get frustrated, but it's really just parents trying to protect their kids from what's out there."
Mental health disorders among young people have soared by nearly 50 per cent in 15 years. The ABC is talking to youth, parents, and researchers about what's driving this pattern, and what can be done to turn things around.
- X (formerly Twitter)
Related Stories
'there's a radicalisation happening online': fears hardcore porn could be behind rising rates of teen sexual assaults.
Why are girls suffering so much right now? The problem is bigger than you think
Teen circadian rhythms are different to the rest of us and could be key to improving their sleep and wellbeing
- Federal Government
- Mental Health
- Mental Wellbeing
- Social Media

The impact of social media on mental health
Online mental wellbeing.
S ocial media has become an integral part of our lives, allowing us to connect with friends, share experiences, and access information in ways that were unimaginable just a few decades ago. However, as social media usage has soared, concerns about its impact on mental health have also emerged. The constant exposure to curated and often idealized versions of other people’s lives, the fear of missing out (FOMO), and the addictive nature of scrolling through endless feeds have all been linked to negative effects on mental wellbeing.
Research has shown that excessive social media use can contribute to feelings of anxiety, depression, loneliness, and decreased self-esteem. The constant comparisons to others, the pressure to present a perfect life online, and the never-ending stream of news and updates can easily overwhelm individuals and affect their mental health.
However, despite the potential for harm, social media can also provide a platform for support and connection. When used mindfully and in moderation, it can serve as a tool for seeking help, sharing experiences, and building communities. In this article, we will explore the impact of social media on mental health and provide some digital wellness tips to help you navigate the online world in a way that promotes mental wellbeing.
Digital wellness tips
1. Set boundaries: Establish designated times for social media use and avoid checking your accounts during work or personal time. Being intentional about your online activities can help prevent excessive use and create a healthier balance between the virtual and physical world.
2. Practice mindfulness: When using social media, be aware of your emotions and reactions. Notice how certain posts or interactions make you feel and take breaks if you find yourself becoming overwhelmed or anxious. Engaging in mindfulness exercises, such as deep breathing or meditation, can also help you stay present and grounded while navigating the online space.
3. Curate your feed: Take control of your social media experience by unfollowing accounts that make you feel inadequate or trigger negative emotions. Instead, follow accounts that promote positivity, creativity, and mental health awareness. Surrounding yourself with uplifting content can have a significant impact on your overall mood and mental wellbeing.
4. Connect with others: Use social media as a tool for building genuine connections rather than just passively consuming content. Engage in meaningful conversations, participate in online support groups, and reach out to friends and family. Actively seeking connection and support can help counteract the potential loneliness and isolation that excessive social media use may bring.
5. Take breaks: Regularly disconnecting from social media can be beneficial for your mental health. Plan digital detoxes and allocate dedicated time for hobbies, outdoor activities, or quality time with loved ones. Creating space for offline experiences can help maintain perspective and reduce the risks of falling into a social media spiral.
Social media addiction
One of the most concerning aspects of social media’s impact on mental health is the potential for addiction. The constant availability and the dopamine-inducing nature of social media platforms can lead to compulsive use and a diminished sense of control over one’s online behavior.
Social media addiction, also known as problematic internet use, has been linked to various negative consequences, including poor sleep quality, low self-esteem, heightened anxiety, and decreased productivity. Additionally, excessive social media use has been associated with the development or exacerbation of mental health disorders such as depression and anxiety disorders.
Recognizing the signs of social media addiction is a crucial step towards addressing and managing the issue. Some common indicators include:
- Feeling a constant need to check social media accounts
- Difficulty in cutting back on social media use despite wanting to do so
- Neglecting personal responsibilities or relationships due to excessive social media use
- Feeling anxious or irritable when unable to access social media
- Using social media as a coping mechanism for stress or negative emotions
If you suspect that you or someone you know may be struggling with social media addiction, it is essential to seek support. Professional help from therapists specializing in digital addiction can provide valuable guidance and strategies to regain control over online habits and promote mental wellbeing.
Mindfulness in social media
Mindfulness, the practice of intentionally focusing one’s attention on the present moment, can be a powerful tool for managing the impact of social media on mental health. By cultivating mindfulness in our online interactions, we can develop a healthier relationship with social media and mitigate its potential negative effects.
Here are some strategies to incorporate mindfulness into your social media usage:
1. Set intentions: Before opening a social media app, take a moment to reflect on your intentions. Are you looking to connect with friends, gain information, or simply pass the time? Setting clear intentions can help you use social media more consciously and avoid mindless scrolling.
2. Practice self-compassion: Remember that social media is often a highlight reel of people’s lives and is not an accurate representation of reality. Be kind to yourself and practice self-compassion when comparing yourself to others. Remind yourself that everyone has ups and downs, and no one’s life is perfect.
3. Engage mindfully: Rather than mindlessly scrolling through an endless feed, engage mindfully with the content you encounter. Reflect on how certain posts or articles make you feel and question whether they align with your values or contribute to your wellbeing. This awareness can help you curate a more supportive online environment.
4. Take media breaks: Set regular intervals during the day where you disconnect from social media and engage in activities that promote relaxation and self-care. Whether it’s taking a walk in nature, practicing a hobby, or spending time with loved ones, intentional breaks can rejuvenate your mind and prevent social media from consuming your thoughts.
5. Seek offline connections: While social media can facilitate connections, it should not be a substitute for real-life interactions. Make an effort to foster meaningful relationships offline and engage in activities that bring you joy and fulfillment. Remember to strike a balance between the digital and physical realms of your life.
By practicing mindfulness in our social media usage, we can reclaim control over our online experiences and prioritize mental wellbeing. Remember, social media is a tool that can be used for both positive and negative purposes. It is up to us to cultivate a healthy relationship with it and ensure that it enhances rather than hinders our mental health.
The post The impact of social media on mental health appeared first on Things That Make People Go Aww .


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Abstract. Social media are responsible for aggravating mental health problems. This systematic study summarizes the effects of social network usage on mental health. Fifty papers were shortlisted from google scholar databases, and after the application of various inclusion and exclusion criteria, 16 papers were chosen and all papers were ...
The concern, and the studies, come from statistics showing that social media use in teens ages 13 to 17 is now almost ubiquitous. Two-thirds of teens report using TikTok, and some 60 percent of ...
Benefits. The use of social media significantly impacts mental health. It can enhance connection, increase self-esteem, and improve a sense of belonging. But it can also lead to tremendous stress, pressure to compare oneself to others, and increased sadness and isolation. Mindful use is essential to social media consumption.
At least three recent papers 1,2,3 suggest this causal evidence is weaker than people may imagine. They suggest that: the observed relationship is very small; the measures of social media usage ...
Social media has been linked to depression, anxiety, and loneliness. It can make people feel isolated and alone. One 2017 study found that young people who use social media more than two hours per day are much more likely to categorize their mental health as fair or poor compared to occasional social media users.
But the link between social media use and young people's mental health is complicated. Literature reviews show that study results are mixed: Associations between social media use and well-being can be positive, negative, and even largely null when advanced data analyses are carried out, and the size of the effects is small.
Social-media influence on teen mental health goes beyond just cause and effect. By. Michael A. Spikes. In her review of Jonathan Haidt's book The Anxious Generation ( Nature 628, 29-30; 2024 ...
Abstract and Figures. This research paper titled "The Impact of Social Media on Mental Health and Well-being on Students" delves into the intricate relationship between the pervasive use of social ...
Facebook's internal research showed that Instagram, in particular, had caused teen girls to feel worse about their bodies and led to increased rates of anxiety and depression, even while company ...
Social media use (SMU) refers to the time spent engaging with social networking platforms. Fear of Missing Out is the apprehension that others are having rewarding experiences that one is missing out on, often leading to increased SMU.Excessive SMU has been associated with detrimental effects on mental health, such as increased symptoms of depression and anxiety.
Many people know that social media use is correlated to increased anxiety, depression, and low self-esteem, yet few want to make any changes. With alarming frequency, the research reports hit my ...
Although it has various positive effects, it can negatively affect users' mental health. Limiting the use of social media to 30 minutes a day can reduce FOMO and, in turn, relieve the loneliness ...
A precautionary public health response is needed The tragic deaths of two UK teenagers continue to raise debate about the challenges that smartphones—and the unlimited access to social media they provide—may pose for adolescent mental health.1 Molly Russell took her own life in 2017 aged 14 after being exposed on Instagram to what her father has described as a constant stream of "dark ...
High rates of negative reactions to the posts due to use of technology also contribute to the. adverse effects of social media on the mental health of the adolescents. Thus, positive. psychological influences of social media usage among adolescents are limited to cases where. there are no negative replies on the posts.
This essay is about how social media can contribute to depression. It examines factors such as the culture of comparison, cyberbullying, and the impact on sleep and self-esteem. Social media often promotes idealized images that lead to unfavorable comparisons, causing feelings of inadequacy. ... The Impact of Social Media on Mental Health ...
Social media is a technology with a lot of wonderful benefits. It allows people to share and connect, get news and information, and even meet new people. But there can be a downside too, especially for college-aged young adults who have grown up in a world of screens. Social media use has been linked to depression, anxiety and loneliness.
So far, most research investigating the effects of social media on mental health has focused on the potential negative aspects. For instance, a 2019 study involving 6,595 teenagers from the United ...
As a result, the impact of social media on the mental well-being of its users is worth considering. Sumner et al. point to the positive effects of social media, clarifying that the specified technological innovation can be used as the tool for improving mental health of its users. Namely, the research states that social media allows spreading ...
Vidal and other investigators believe there are many aspects to social media, and there are important next steps to learn more about its impact on the mental health of people of all ages ...
Social media-related nightmares: Study explores links between social media use, mental health and sleep quality May 20, 2024 Social media program helps ease symptoms of postpartum depression
Assessing the impacts of social media on Gen Z's mental health Gen Z is feeling the effects of social media, navigating its algorithms and forging online communities. Experts from the Rollins School of Public Health evaluate the positive and negative aspects of being raised on the internet.
The constant barrage of negative interactions on social media platforms can contribute to a sense of insecurity and isolation, amplifying the risk of developing mental health issues. The pervasive ...
250 Words Essay on Effects Of Social Media On Mental Health Introduction. Social media is a powerful tool that connects people from all corners of the world. It is a platform where we share our thoughts, ideas, and daily life activities. But, it also has a great impact on our mental health. Impacts on Self-Esteem. One of the main effects of ...
Social media has become an integral part of modern life, providing platforms for communication, connection, and self-expression.However, the implications of heavy social media use on mental health have raised concerns. In this essay, we will delve into the complex relationship between social media and mental health by examining real-life experiences and anecdotes from individuals who have ...
The number of users is around 3.5 billion as of 2019, according to Karim et al. (1). Furthermore, it is projected to grow by 0.9 billion in only 6 years (Tankovska). The percentage of American adults who use social media platforms has increased by 74% since 2005 (Ortiz-Ospina). The penetration of social media is constantly expanding and ...
The rise of social media and smartphones has coincided with an accelerating decline in teenagers' mental health — and researchers are trying to figure out whether the technology is to blame.
Social media addiction, also known as problematic internet use, has been linked to various negative consequences, including poor sleep quality, low self-esteem, heightened anxiety, and decreased ...