- How to Write a Great PhD Research Proposal | FindAPhD.com

How to Write a Great PhD Research Proposal
Written by Mark Bennett
You'll need to write a research proposal if you're submitting your own project plan as part of a PhD application. A good PhD proposal outlines the scope and significance of your topic and explains how you plan to research it.
It's helpful to think about the proposal like this: if the rest of your application explains your ability to do a PhD, the proposal demonstrates the actual PhD you plan to do. Of course, being able to effectively plan and explain a research project is one of the key qualifications for being able to complete one, which is why the proposal is such an important part of the PhD application process.
Thankfully, the secret to writing a good research proposal isn't complicated. It's simply a case of understanding what the proposal is for, what it needs to do and how it needs to be put together.
On this page
What is a phd research proposal.
First things first, do you need a research proposal for your PhD? It depends on the kind of project you want to do:
- If your PhD is advertised by a university, you probably won't need to submit a research proposal for it. The broad aims and objectives for your PhD will already be defined: you just need to prove you're the right person to do it.
- But, if you're proposing your own research topic to research within a university's PhD programme, you will need to write a proposal for it (the clue is in the word "proposing")
As a rule, advertised PhDs are very common in STEM subjects, whereas Arts, Humanities and Social Science students are more likely to propose their own PhDs.
Some PhD programmes actually wait and ask students to develop their research proposal during the degree (usually after they've completed some initial training). This is normal in the USA , but it's becoming more common for some UKRI-funded UK PhDs.
For the purposes of this guide we're going to assume that you do need to write a good research proposal for your PhD application. So let's explore what's involved in that.
Pick the right programme for you
There are lots of choices, let us help you to make the right one. Sign up to our weekly newsletter for the latest advice and guidance from our team of experts.
What should a research proposal for PhD admission include?
It's natural to be a little intimidated at the thought of structuring a PhD proposal, particularly if you've never written anything like this before.
But here's the thing: a research proposal isn't a fiendish test designed to catch you out and stop you ever doing a PhD. It's actually much more boring than that.
All a research proposal really is is a document that demonstrates three things:
- Your PhD is worthwhile
- Your PhD is feasible
- You are capable of completing it at this university
Or to put it even more simply: the PhD is worth doing, it's doable and you can do it.
Demonstrate your PhD is worthwhile (the what and the why)
A successful PhD project has to make a significant original contribution to knowledge. If it doesn't, it won't meet the criteria for a doctoral degree and will probably fail the viva exam .
Your PhD proposal itself doesn't have to meet those criteria (or pass a viva!) but it does need to indicate that your PhD project eventually will.
It does that by first demonstrating that your research topic is original. That means nobody else has studied this same topic (or one very similar) before.
There are all sorts of ways a PhD can be original. You might examine new data or primary sources, to look at existing material from a fresh perspective, or deal with the impact of new events. It doesn't matter how your project is original, so long as your proposal is really specific about what makes it original.
You also need to explain why your proposed research will be academically significant. To do this properly, you'll need to acknowledge relevant existing scholarship and explain how your research will relate to it. You don't need to be exhaustive at this point, but you should be able to show how your PhD will contribute to its field and – ideally – indicate some of the gaps in knowledge it will aim to fill.
The final step in demonstrating your PhD is worthwhile is to suggest what will become possible as a result of your research. How could other researchers use or build upon your results? What might closing those gaps in academic knowledge mean for audiences outside the unviversity?
Demonstrate your PhD is feasible (the how)
It isn't enough just to show that your research is worth doing; it also needs to actually be doable.
The length of a full-time PhD is around three to four years in most countries (it's longer in for a PhD in the USA , but you don't spend all that time doing research).
Three years may seem like a long time, but researching a PhD is a lot of work and you'll probably spend at least some of your time on other activities like teaching, conference presentations or even publication.
So, one of the things your proposal needs to do is demonstrate that your project is feasible: that it fits within the scope of a PhD.
The most important criteria for this is to be clear about what you plan to do. It should be obvious from your proposal what the scope of your project is – what is and isn't included within it.
You also need to outline how you plan to go about your research. Where will you start and what order do you expect to proceed in? Is the logic for that obvious? If not, it's probably a good idea to explain it.
Finally, you need to explain the methodology you plan to use. This could include techniques for collecting data and sources, theoretical perspectives for analysing them – or both. You may also need to detail specific equipment you expect to use or fieldwork you'll need to undertake (including trips to archives or other external resources).
None of this needs to be exact or completely final. The key word here is 'plan' – but you do need to have one.
Demonstrate that you can complete it at this university (the who and the where)
So far we've thought about the project itself: what makes it worth doing and how it's going to get done. But your proposal also needs to address the who and the where: why are you the right person to carry out this research, and why do you want to do it at this particular university?
The first part of this is easier than it probably looks. Writing a good research proposal demonstrates enthusiasm for your project much more convincingly than simply saying you're very interested in it (a classic case of 'show, don't tell').
You also don't need to repeat your grades and academic achievements (other parts of your PhD application will cover those). Instead, try to underline experiences that relate to this project. Has a particular module or Masters dissertation topic prepared you with useful subject knowledge or methodological skills? If so, highlight it.
It's also fine, within reason, to be honest about the skills you don't have and to identify your training needs. This shows you're being practical about your project and thinking seriously about what it will require. Just make sure you can realistically acquire the skills and training you need within the time available (this goes back to the feasibility).
Showing your project is a good fit for the university is also relatively simple. There should already be some reasons why you've chosen this university for your PhD so make sure you explain what they are. Perhaps there's a particular supervisor you'd like to work with , or facilities and resources your research could use. The key is to emphasise the fit between the project and the university – so don't just say you want to research there because it's highly ranked .
PhD research proposal structure
Hopefully the above sections have given you a few ideas for the things your proposal needs to include. Let's be honest though, the scariest thing about a proposal isn't deciding what to include: it's actually writing it.
But, if we flip that on its head, we remember that all a research proposal really is is a piece of writing that follows a pretty standard format. And that's a lot less scary.
Research proposal structure
Because proposals for PhD all have to do the same things, they mostly follow a similar structure. Yours will probably go something like this:
- Title – Keep it simple and descriptive: the clever alliteration and quotes can come later when you write up your thesis. For now, you just want the person reading this to know exactly what your research is about and, perhaps, which prospective supervisor to send it to.
- Overview – Start by defining your research question (the what) and explaining how it contributes to current work in your field (the why). This is also a good place to reference one or two pieces of scholarship: the full literature review can wait until your PhD begins, but you should show that you have some understanding of relevant academic research.
- Methodology – Make sure the reader understands the practical and / or theoretical approaches you'll take to your research. What data will you collect, how will you collect it and how will you analyse it? Ideally refer to relevant research methods and models. It's also a good idea to provide some sort of roadmap for how you'll go about things. Don't worry, you can change it later (and you will).
- Outcomes and impact – What will exist as a result of your research (other than just another PhD on a library shelf) and what will it make possible? You don't need to identify every specific outcome from your project (blue sky research is fine) but you should think about what some potential outcomes might be.
You probably won't need to include a specific conclusion - it should be obvious, by now, what your project is doing, how you're going to do it and why that matters. A quick summary sentence is fine though, if you think it will help.
Writing tips
Being able to effectively communicate academic concepts, ideas and results is a key skill for PhD research in all subjects . Think of your proposal as a chance to demonstrate this.
The good news is that the key principles of good proposal writing aren't that different from other work you've probably done as a Bachelors or Masters student:
- Be clear – The person reading your research proposal should know exactly what it is you're proposing to research, with no room for ambiguity and confusion. This is important on a practical level (they need to know where to send it) but it's also important to the success of your application: a confusing proposal suggests a confused project. Try having a friend read it and ask them "do you know what it is I'm proposing to do here?" (even if they don't understand the details).
- Be concise – You will have more ideas than you can include in your proposal. That's fine. Choose the best ones and leave the others for your interview .
- be coherent – Follow something like the structure above. Don't start with your methodology, then say what it is you want to research.
How long should a PhD research proposal be?
Honestly? As long as the university asks for it to be. Most will have guidelines and you should follow them closely if so.
If you honestly can't find a suggested word count for your proposal, then consider asking a prospective supervisor . If you still aren't sure, aim for somewhere between 1,000-2,000 words .
As a very general rule, Arts, Humanities and Social Sciences are a bit longer than STEM proposals (and a lot of STEM students don't have to write one anyway, as we've explained).
Research proposal for PhD admission - dos and don'ts
Research proposals are a popular topic over on the FindAPhD blog , where we've shared stories of how students wrote theirs , along with mistakes to avoid and a counter-intuitive look at the things a PhD proposal doesn't actually need to do .
Here are a few general tips and mistakes to avoid:
#1 Give yourself enough time to do a good job
Preparing to write a PhD proposal takes time and effort. None of this is wasted as the process of evaluating and framing your ideas for a proposal will improve your project plan immensely. So will the need to decide which ideas to include.
But you need time and space to do that, so make sure you get it. How long it will take to write your PhD proposal is heavily dependent on your personal working style, but you'll likely need to give yourself at least a few weeks to do a good job.
#2 Set out to impress
A good proposal isn't a begging letter. You're approaching the university with a great idea that's going to contribute to and enhance their research. Be honest, be realistic, but don't be unnecessarily humble. They should want you and your project.
#3 Demonstrate original thinking!
You may not need to present original research findings yet, but your proposal does need to present original ideas – and it should be clear why and how those ideas are original.
Make sure you indicate how your project is going to expand, enhance or even correct existing work in your field. Remember that making an "original contribution to knowledge" is a key part of what a PhD is .
#1 Send the same proposal to several universities
A good proposal needs to explain why you want to do your research at a particular university. That's a big part of the feasibility (the fit between project, person and place) and methodology (how are you going to use this university's equipment and archives; when and where will you need to travel).
It's OK to apply to more than one university in parallel, but, in that case, you're writing research proposals .
#2 Use online proposal templates (without evaluating them first!)
It can be tempting to search for PhD proposal samples on the internet, but make sure you evaluate what you find. Some websites may host old proposals from previous PhD students, but there's no way of knowing how relevant these are to your subject and university – or if they were even successful! More 'generic' research proposal examples can offer guidance, but they won't be tailored to your specific project.
The best place to look for a PhD proposal sample is your university. Consider asking your supervisor if they can share a good proposal from a previous student in your subject – or put you in touch with a current student you can ask.
#3 Confuse the proposal with the PhD
We've covered this on the blog , but it's simple enough to include here too.
You're setting out to do a PhD, but you (probably!) haven't done one yet. So you don't need to include research findings, in-depth analysis or a comprehesive literature review. You need to make a case for the research and analysis you want to do.
#4 Ignore your university's help and guidance
The advice on this page is necessarily quite general. We're considering adding guides to writing PhD proposals in specific subjects in future but, for now, the best place to get specific advice for your academic field is probably the university you're applying to.
See if you can get some subject-specific tips by contacting a supervisor , or just checking with the admissions team for your department.
And remember: if they give you a structure and a word count, stick to it.
Ready to apply for a PhD?
Find out what PhD opportunities are currently available with our FindAPhD course listings .
Our postgrad newsletter shares courses, funding news, stories and advice
You may also like....

We've answered some of the most frequently asked questions about PhDs, covering course types, applications, funding and the benefits of further study.

Getting ready to apply for a PhD? Our guides explain research proposals, references and entry tests for doctoral programmes.

Our guide explains how to contact a potential PhD supervisor to discuss your proposal or ideas with them before applying.

A checklist of the things you'll need to do when making an international PhD application, from meeting the entry requirements to sorting out your visa.
FindAPhD. Copyright 2005-2024 All rights reserved.
Unknown ( change )
Have you got time to answer some quick questions about PhD study?
Select your nearest city
You haven’t completed your profile yet. To get the most out of FindAPhD, finish your profile and receive these benefits:
- Monthly chance to win one of ten £10 Amazon vouchers ; winners will be notified every month.*
- The latest PhD projects delivered straight to your inbox
- Access to our £6,000 scholarship competition
- Weekly newsletter with funding opportunities, research proposal tips and much more
- Early access to our physical and virtual postgraduate study fairs
Or begin browsing FindAPhD.com
or begin browsing FindAPhD.com
*Offer only available for the duration of your active subscription, and subject to change. You MUST claim your prize within 72 hours, if not we will redraw.

Do you want hassle-free information and advice?
Create your FindAPhD account and sign up to our newsletter:
- Find out about funding opportunities and application tips
- Receive weekly advice, student stories and the latest PhD news
- Hear about our upcoming study fairs
- Save your favourite projects, track enquiries and get personalised subject updates

Create your account
Looking to list your PhD opportunities? Log in here .
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Starting the research process
- How to Write a Research Proposal | Examples & Templates
How to Write a Research Proposal | Examples & Templates
Published on October 12, 2022 by Shona McCombes and Tegan George. Revised on November 21, 2023.

A research proposal describes what you will investigate, why it’s important, and how you will conduct your research.
The format of a research proposal varies between fields, but most proposals will contain at least these elements:
Introduction
Literature review.
- Research design
Reference list
While the sections may vary, the overall objective is always the same. A research proposal serves as a blueprint and guide for your research plan, helping you get organized and feel confident in the path forward you choose to take.
Table of contents
Research proposal purpose, research proposal examples, research design and methods, contribution to knowledge, research schedule, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about research proposals.
Academics often have to write research proposals to get funding for their projects. As a student, you might have to write a research proposal as part of a grad school application , or prior to starting your thesis or dissertation .
In addition to helping you figure out what your research can look like, a proposal can also serve to demonstrate why your project is worth pursuing to a funder, educational institution, or supervisor.
| Show your reader why your project is interesting, original, and important. | |
| Demonstrate your comfort and familiarity with your field. Show that you understand the current state of research on your topic. | |
| Make a case for your . Demonstrate that you have carefully thought about the data, tools, and procedures necessary to conduct your research. | |
| Confirm that your project is feasible within the timeline of your program or funding deadline. |
Research proposal length
The length of a research proposal can vary quite a bit. A bachelor’s or master’s thesis proposal can be just a few pages, while proposals for PhD dissertations or research funding are usually much longer and more detailed. Your supervisor can help you determine the best length for your work.
One trick to get started is to think of your proposal’s structure as a shorter version of your thesis or dissertation , only without the results , conclusion and discussion sections.
Download our research proposal template
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
Writing a research proposal can be quite challenging, but a good starting point could be to look at some examples. We’ve included a few for you below.
- Example research proposal #1: “A Conceptual Framework for Scheduling Constraint Management”
- Example research proposal #2: “Medical Students as Mediators of Change in Tobacco Use”
Like your dissertation or thesis, the proposal will usually have a title page that includes:
- The proposed title of your project
- Your supervisor’s name
- Your institution and department
The first part of your proposal is the initial pitch for your project. Make sure it succinctly explains what you want to do and why.
Your introduction should:
- Introduce your topic
- Give necessary background and context
- Outline your problem statement and research questions
To guide your introduction , include information about:
- Who could have an interest in the topic (e.g., scientists, policymakers)
- How much is already known about the topic
- What is missing from this current knowledge
- What new insights your research will contribute
- Why you believe this research is worth doing
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
As you get started, it’s important to demonstrate that you’re familiar with the most important research on your topic. A strong literature review shows your reader that your project has a solid foundation in existing knowledge or theory. It also shows that you’re not simply repeating what other people have already done or said, but rather using existing research as a jumping-off point for your own.
In this section, share exactly how your project will contribute to ongoing conversations in the field by:
- Comparing and contrasting the main theories, methods, and debates
- Examining the strengths and weaknesses of different approaches
- Explaining how will you build on, challenge, or synthesize prior scholarship
Following the literature review, restate your main objectives . This brings the focus back to your own project. Next, your research design or methodology section will describe your overall approach, and the practical steps you will take to answer your research questions.
| ? or ? , , or research design? | |
| , )? ? | |
| , , , )? | |
| ? |
To finish your proposal on a strong note, explore the potential implications of your research for your field. Emphasize again what you aim to contribute and why it matters.
For example, your results might have implications for:
- Improving best practices
- Informing policymaking decisions
- Strengthening a theory or model
- Challenging popular or scientific beliefs
- Creating a basis for future research
Last but not least, your research proposal must include correct citations for every source you have used, compiled in a reference list . To create citations quickly and easily, you can use our free APA citation generator .
Some institutions or funders require a detailed timeline of the project, asking you to forecast what you will do at each stage and how long it may take. While not always required, be sure to check the requirements of your project.
Here’s an example schedule to help you get started. You can also download a template at the button below.
Download our research schedule template
| Research phase | Objectives | Deadline |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Background research and literature review | 20th January | |
| 2. Research design planning | and data analysis methods | 13th February |
| 3. Data collection and preparation | with selected participants and code interviews | 24th March |
| 4. Data analysis | of interview transcripts | 22nd April |
| 5. Writing | 17th June | |
| 6. Revision | final work | 28th July |
If you are applying for research funding, chances are you will have to include a detailed budget. This shows your estimates of how much each part of your project will cost.
Make sure to check what type of costs the funding body will agree to cover. For each item, include:
- Cost : exactly how much money do you need?
- Justification : why is this cost necessary to complete the research?
- Source : how did you calculate the amount?
To determine your budget, think about:
- Travel costs : do you need to go somewhere to collect your data? How will you get there, and how much time will you need? What will you do there (e.g., interviews, archival research)?
- Materials : do you need access to any tools or technologies?
- Help : do you need to hire any research assistants for the project? What will they do, and how much will you pay them?
If you want to know more about the research process , methodology , research bias , or statistics , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
Methodology
- Sampling methods
- Simple random sampling
- Stratified sampling
- Cluster sampling
- Likert scales
- Reproducibility
Statistics
- Null hypothesis
- Statistical power
- Probability distribution
- Effect size
- Poisson distribution
Research bias
- Optimism bias
- Cognitive bias
- Implicit bias
- Hawthorne effect
- Anchoring bias
- Explicit bias
Once you’ve decided on your research objectives , you need to explain them in your paper, at the end of your problem statement .
Keep your research objectives clear and concise, and use appropriate verbs to accurately convey the work that you will carry out for each one.
I will compare …
A research aim is a broad statement indicating the general purpose of your research project. It should appear in your introduction at the end of your problem statement , before your research objectives.
Research objectives are more specific than your research aim. They indicate the specific ways you’ll address the overarching aim.
A PhD, which is short for philosophiae doctor (doctor of philosophy in Latin), is the highest university degree that can be obtained. In a PhD, students spend 3–5 years writing a dissertation , which aims to make a significant, original contribution to current knowledge.
A PhD is intended to prepare students for a career as a researcher, whether that be in academia, the public sector, or the private sector.
A master’s is a 1- or 2-year graduate degree that can prepare you for a variety of careers.
All master’s involve graduate-level coursework. Some are research-intensive and intend to prepare students for further study in a PhD; these usually require their students to write a master’s thesis . Others focus on professional training for a specific career.
Critical thinking refers to the ability to evaluate information and to be aware of biases or assumptions, including your own.
Like information literacy , it involves evaluating arguments, identifying and solving problems in an objective and systematic way, and clearly communicating your ideas.
The best way to remember the difference between a research plan and a research proposal is that they have fundamentally different audiences. A research plan helps you, the researcher, organize your thoughts. On the other hand, a dissertation proposal or research proposal aims to convince others (e.g., a supervisor, a funding body, or a dissertation committee) that your research topic is relevant and worthy of being conducted.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. & George, T. (2023, November 21). How to Write a Research Proposal | Examples & Templates. Scribbr. Retrieved June 18, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/research-process/research-proposal/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, how to write a problem statement | guide & examples, writing strong research questions | criteria & examples, how to write a literature review | guide, examples, & templates, get unlimited documents corrected.
✔ Free APA citation check included ✔ Unlimited document corrections ✔ Specialized in correcting academic texts

How to Write a PhD Research Proposal
- Applying to a PhD
- A research proposal summarises your intended research.
- Your research proposal is used to confirm you understand the topic, and that the university has the expertise to support your study.
- The length of a research proposal varies. It is usually specified by either the programme requirements or the supervisor upon request. 1500 to 3500 words is common.
- The typical research proposal structure consists of: Title, Abstract, Background and Rationale, Research Aims and Objectives, Research Design and Methodology, Timetable, and a Bibliography.
What is a Research Proposal?
A research proposal is a supporting document that may be required when applying to a research degree. It summarises your intended research by outlining what your research questions are, why they’re important to your field and what knowledge gaps surround your topic. It also outlines your research in terms of your aims, methods and proposed timetable .
What Is It Used for and Why Is It Important?
A research proposal will be used to:
- Confirm whether you understand the topic and can communicate complex ideas.
- Confirm whether the university has adequate expertise to support you in your research topic.
- Apply for funding or research grants to external bodies.
How Long Should a PhD Research Proposal Be?
Some universities will specify a word count all students will need to adhere to. You will typically find these in the description of the PhD listing. If they haven’t stated a word count limit, you should contact the potential supervisor to clarify whether there are any requirements. If not, aim for 1500 to 3500 words (3 to 7 pages).
Your title should indicate clearly what your research question is. It needs to be simple and to the point; if the reader needs to read further into your proposal to understand your question, your working title isn’t clear enough.
Directly below your title, state the topic your research question relates to. Whether you include this information at the top of your proposal or insert a dedicated title page is your choice and will come down to personal preference.
2. Abstract
If your research proposal is over 2000 words, consider providing an abstract. Your abstract should summarise your question, why it’s important to your field and how you intend to answer it; in other words, explain your research context.
Only include crucial information in this section – 250 words should be sufficient to get across your main points.
3. Background & Rationale
First, specify which subject area your research problem falls in. This will help set the context of your study and will help the reader anticipate the direction of your proposed research.
Following this, include a literature review . A literature review summarises the existing knowledge which surrounds your research topic. This should include a discussion of the theories, models and bodies of text which directly relate to your research problem. As well as discussing the information available, discuss those which aren’t. In other words, identify what the current gaps in knowledge are and discuss how this will influence your research. Your aim here is to convince the potential supervisor and funding providers of why your intended research is worth investing time and money into.
Last, discuss the key debates and developments currently at the centre of your research area.
4. Research Aims & Objectives
Identify the aims and objectives of your research. The aims are the problems your project intends to solve; the objectives are the measurable steps and outcomes required to achieve the aim.
In outlining your aims and objectives, you will need to explain why your proposed research is worth exploring. Consider these aspects:
- Will your research solve a problem?
- Will your research address a current gap in knowledge?
- Will your research have any social or practical benefits?
If you fail to address the above questions, it’s unlikely they will accept your proposal – all PhD research projects must show originality and value to be considered.
5. Research Design and Methodology
The following structure is recommended when discussing your research design:
- Sample/Population – Discuss your sample size, target populations, specimen types etc.
- Methods – What research methods have you considered, how did you evaluate them and how did you decide on your chosen one?
- Data Collection – How are you going to collect and validate your data? Are there any limitations?
- Data Analysis – How are you going to interpret your results and obtain a meaningful conclusion from them?
- Ethical Considerations – Are there any potential implications associated with your research approach? This could either be to research participants or to your field as a whole on the outcome of your findings (i.e. if you’re researching a particularly controversial area). How are you going to monitor for these implications and what types of preventive steps will you need to put into place?
6. Timetable
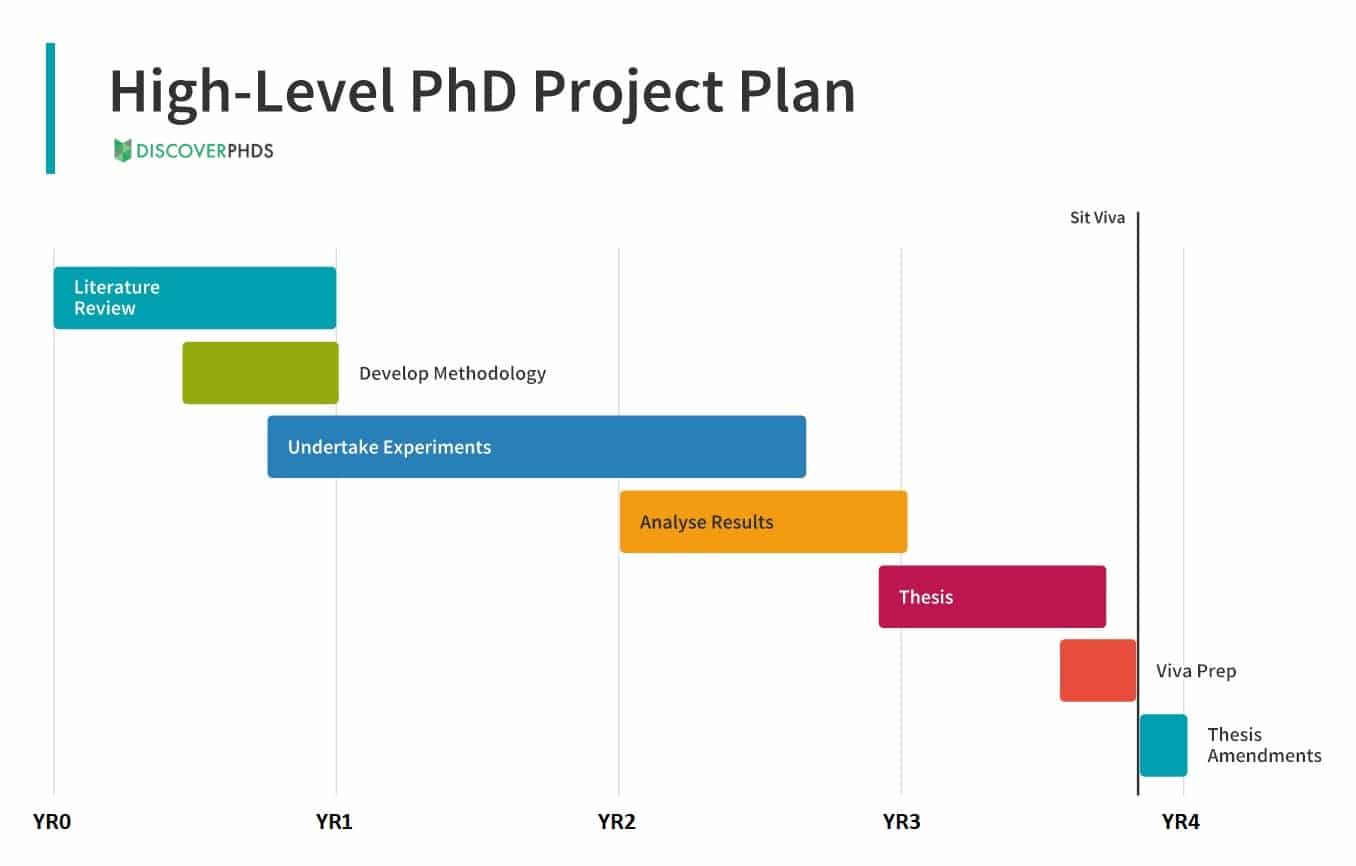
We’ve outlined the various stages of a PhD and the approximate duration of a PhD programme which you can refer to when designing your own research study.
7. Bibliography
Plagiarism is taken seriously across all academic levels, but even more so for doctorates. Therefore, ensure you reference the existing literature you have used in writing your PhD proposal. Besides this, try to adopt the same referencing style as the University you’re applying to uses. You can easily find this information in the PhD Thesis formatting guidelines published on the University’s website.
Finding a PhD has never been this easy – search for a PhD by keyword, location or academic area of interest.
Questions & Answers
Here are answers to some of the most common questions we’re asked about the Research Proposal:
Can You Change a Research Proposal?
Yes, your PhD research proposal outlines the start of your project only. It’s well accepted that the direction of your research will develop with time, therefore, you can revise it at later dates.
Can the Potential Supervisor Review My Draft Proposal?
Whether the potential supervisor will review your draft will depend on the individual. However, it is highly advisable that you at least attempt to discuss your draft with them. Even if they can’t review it, they may provide you with useful information regarding their department’s expertise which could help shape your PhD proposal. For example, you may amend your methodology should you come to learn that their laboratory is better equipped for an alternative method.
How Should I Structure and Format My Proposal?
Ensure you follow the same order as the headings given above. This is the most logical structure and will be the order your proposed supervisor will expect.
Most universities don’t provide formatting requirements for research proposals on the basis that they are a supporting document only, however, we recommend that you follow the same format they require for their PhD thesis submissions. This will give your reader familiarity and their guidelines should be readily available on their website.
Last, try to have someone within the same academic field or discipline area to review your proposal. The key is to confirm that they understand the importance of your work and how you intend to execute it. If they don’t, it’s likely a sign you need to rewrite some of your sections to be more coherent.
Browse PhDs Now
Join thousands of students.
Join thousands of other students and stay up to date with the latest PhD programmes, funding opportunities and advice.
How to write a research proposal
What is a research proposal.
A research proposal should present your idea or question and expected outcomes with clarity and definition – the what.
It should also make a case for why your question is significant and what value it will bring to your discipline – the why.
What it shouldn't do is answer the question – that's what your research will do.
Why is it important?
Research proposals are significant because Another reason why it formally outlines your intended research. Which means you need to provide details on how you will go about your research, including:
- your approach and methodology
- timeline and feasibility
- all other considerations needed to progress your research, such as resources.
Think of it as a tool that will help you clarify your idea and make conducting your research easier.
How long should it be?
Usually no more than 2000 words, but check the requirements of your degree, and your supervisor or research coordinator.
Presenting your idea clearly and concisely demonstrates that you can write this way – an attribute of a potential research candidate that is valued by assessors.
What should it include?
Project title.
Your title should clearly indicate what your proposed research is about.
Research supervisor
State the name, department and faculty or school of the academic who has agreed to supervise you. Rest assured, your research supervisor will work with you to refine your research proposal ahead of submission to ensure it meets the needs of your discipline.
Proposed mode of research
Describe your proposed mode of research. Which may be closely linked to your discipline, and is where you will describe the style or format of your research, e.g. data, field research, composition, written work, social performance and mixed media etc.
This is not required for research in the sciences, but your research supervisor will be able to guide you on discipline-specific requirements.
Aims and objectives
What are you trying to achieve with your research? What is the purpose? This section should reference why you're applying for a research degree. Are you addressing a gap in the current research? Do you want to look at a theory more closely and test it out? Is there something you're trying to prove or disprove? To help you clarify this, think about the potential outcome of your research if you were successful – that is your aim. Make sure that this is a focused statement.
Your objectives will be your aim broken down – the steps to achieving the intended outcome. They are the smaller proof points that will underpin your research's purpose. Be logical in the order of how you present these so that each succeeds the previous, i.e. if you need to achieve 'a' before 'b' before 'c', then make sure you order your objectives a, b, c.
A concise summary of what your research is about. It outlines the key aspects of what you will investigate as well as the expected outcomes. It briefly covers the what, why and how of your research.
A good way to evaluate if you have written a strong synopsis, is to get somebody to read it without reading the rest of your research proposal. Would they know what your research is about?
Now that you have your question clarified, it is time to explain the why. Here, you need to demonstrate an understanding of the current research climate in your area of interest.
Providing context around your research topic through a literature review will show the assessor that you understand current dialogue around your research, and what is published.
Demonstrate you have a strong understanding of the key topics, significant studies and notable researchers in your area of research and how these have contributed to the current landscape.
Expected research contribution
In this section, you should consider the following:
- Why is your research question or hypothesis worth asking?
- How is the current research lacking or falling short?
- What impact will your research have on the discipline?
- Will you be extending an area of knowledge, applying it to new contexts, solving a problem, testing a theory, or challenging an existing one?
- Establish why your research is important by convincing your audience there is a gap.
- What will be the outcome of your research contribution?
- Demonstrate both your current level of knowledge and how the pursuit of your question or hypothesis will create a new understanding and generate new information.
- Show how your research is innovative and original.
Draw links between your research and the faculty or school you are applying at, and explain why you have chosen your supervisor, and what research have they or their school done to reinforce and support your own work. Cite these reasons to demonstrate how your research will benefit and contribute to the current body of knowledge.
Proposed methodology
Provide an overview of the methodology and techniques you will use to conduct your research. Cover what materials and equipment you will use, what theoretical frameworks will you draw on, and how will you collect data.
Highlight why you have chosen this particular methodology, but also why others may not have been as suitable. You need to demonstrate that you have put thought into your approach and why it's the most appropriate way to carry out your research.
It should also highlight potential limitations you anticipate, feasibility within time and other constraints, ethical considerations and how you will address these, as well as general resources.
A work plan is a critical component of your research proposal because it indicates the feasibility of completion within the timeframe and supports you in achieving your objectives throughout your degree.
Consider the milestones you aim to achieve at each stage of your research. A PhD or master's degree by research can take two to four years of full-time study to complete. It might be helpful to offer year one in detail and the following years in broader terms. Ultimately you have to show that your research is likely to be both original and finished – and that you understand the time involved.
Provide details of the resources you will need to carry out your research project. Consider equipment, fieldwork expenses, travel and a proposed budget, to indicate how realistic your research proposal is in terms of financial requirements and whether any adjustments are needed.
Bibliography
Provide a list of references that you've made throughout your research proposal.
Apply for postgraduate study
New hdr curriculum, find a supervisor.
Search by keyword, topic, location, or supervisor name
- 1800 SYD UNI ( 1800 793 864 )
- or +61 2 8627 1444
- Open 9am to 5pm, Monday to Friday
- Student Centre Level 3 Jane Foss Russell Building Darlington Campus
Scholarships
Find the right scholarship for you
Research areas
Our research covers the spectrum – from linguistics to nanoscience
Our breadth of expertise across our faculties and schools is supported by deep disciplinary knowledge. We have significant capability in more than 20 major areas of research.
Research facilities
High-impact research through state-of-the-art infrastructure
School of Sociology, Politics and International Studies
How to write a phd research proposal.
In order to help you with your application, the information below aims to give some guidance on how a typical research proposal might look.
Your research proposal is a concise statement (up to 3,000 words) of the rationale for your research proposal, the research questions to be answered and how you propose to address them. We know that during the early stages of your PhD you are likely to refine your thinking and methodology in discussion with your supervisors.
However, we want to see that you can construct a fairly rigorous, high quality research proposal.
We use your research proposal to help us decide whether you would be a suitable candidate to study at PhD level. We therefore assess your proposal on its quality, originality, and coherence. It also helps us to decide if your research interests match those of academics in the School of Sociology, Politics and International Studies (SPAIS) and whether they would be able to provide suitably qualified supervision for your proposed research.
Format of the research proposal
Your proposal should include the following:
Title. A short, indicative title is best.
Abstract. This is a succinct summary of your research proposal (approximately 200-300 words) that will present a condensed outline, enabling the reader to get a very quick overview of your proposed project, lines of inquiry and possible outcomes. An abstract is often written last, after you have written the proposal and are able to summarise it effectively.
Rationale for the research project. This might include a description of the question/debate/phenomenon of interest; an explanation of why the topic is of interest to you; and an outline of the reasons why the topic should be of interest to research and/ or practice (the 'so what?' question).
Aims and initial research question. What are the aims and objectives of the research? State clearly the puzzle you are addressing, and the research question that you intend to pursue. It is acceptable to have multiple research questions, but it is a good idea to clarify which is the main research question. If you have hypotheses, discuss them here. A research proposal can and should make a positive and persuasive first impression and demonstrate your potential to become a good researcher. In particular, you need to demonstrate that you can think critically and analytically as well as communicate your ideas clearly.
Research context for your proposed project. Provide a short introduction to your area of interest with a succinct, selective and critical review of the relevant literature. Demonstrate that you understand the theoretical underpinnings and main debates and issues in your research area and how your proposed research will make an original and necessary contribution to this. You need to demonstrate how your proposed research will fill a gap in existing knowledge.
Intended methodology. Outline how you plan to conduct the research and the data sources that you will use. We do not expect you to have planned a very detailed methodology at this stage, but you need to provide an overview of how you will conduct your research (qualitative and/or quantitative methods) and why this methodology is suited for your proposed study. You need to be convincing about the appropriateness and feasibility of the approaches you are suggesting, and reflective about problems you might encounter (including ethical and data protection issues) in collecting and analysing your data.
Expected outcomes and impact. How do you think the research might add to existing knowledge; what might it enable organisations or interested parties to do differently? Increasingly in academia (and this is particularly so for ESRC-funded studentships), PhD students are being asked to consider how their research might contribute to both academic impact and/or economic and societal impact. (This is well explained on the ESRC website if you would like to find out more.) Please consider broader collaborations and partnerships (academic and non-academic) that will support your research. Collaborative activity can lead to a better understanding of the ways in which academic research can translate into practice and it can help to inform and improve the quality of your research and its impact.
Timetable. What is your initial estimation of the timetable of the dissertation? When will each of the key stages start and finish (refining proposal; literature review; developing research methods; fieldwork; analysis; writing the draft; final submission). There are likely to overlaps between the stages.
Why Bristol? Why – specifically – do you want to study for your PhD at Bristol ? How would you fit into the School's research themes and research culture . You do not need to identify supervisors at the application stage although it can be helpful if you do.
Bibliography. Do make sure that you cite what you see as the key readings in the field. This does not have to be comprehensive but you are illustrating the range of sources you might use in your research.
We expect your research proposal to be clear, concise and grammatically correct. Prior to submitting your research proposal, please make sure that you have addressed the following issues:
- Have you included a clear summary of what the proposed research is about and why it is significant?
- Have you clearly identified what your proposed research will add to our understanding of theory, knowledge or research design?
- Does it state what contributions it will make to policy and/or practice?
- Does the proposal clearly explain how you will do the research?
- Is the language clear and easy to understand by someone who is not an expert in the field?
- Is the grammar and spelling correct?
- Locations and Hours
- UCLA Library
- Research Guides
- Research Tips and Tools
Advanced Research Methods
- Writing a Research Proposal
- What Is Research?
- Library Research
What Is a Research Proposal?
Reference books.
- Writing the Research Paper
- Presenting the Research Paper
When applying for a research grant or scholarship, or, just before you start a major research project, you may be asked to write a preliminary document that includes basic information about your future research. This is the information that is usually needed in your proposal:
- The topic and goal of the research project.
- The kind of result expected from the research.
- The theory or framework in which the research will be done and presented.
- What kind of methods will be used (statistical, empirical, etc.).
- Short reference on the preliminary scholarship and why your research project is needed; how will it continue/justify/disprove the previous scholarship.
- How much will the research project cost; how will it be budgeted (what for the money will be spent).
- Why is it you who can do this research and not somebody else.
Most agencies that offer scholarships or grants provide information about the required format of the proposal. It may include filling out templates, types of information they need, suggested/maximum length of the proposal, etc.
Research proposal formats vary depending on the size of the planned research, the number of participants, the discipline, the characteristics of the research, etc. The following outline assumes an individual researcher. This is just a SAMPLE; several other ways are equally good and can be successful. If possible, discuss your research proposal with an expert in writing, a professor, your colleague, another student who already wrote successful proposals, etc.
- Author, author's affiliation
- Explain the topic and why you chose it. If possible explain your goal/outcome of the research . How much time you need to complete the research?
- Give a brief summary of previous scholarship and explain why your topic and goals are important.
- Relate your planned research to previous scholarship. What will your research add to our knowledge of the topic.
- Break down the main topic into smaller research questions. List them one by one and explain why these questions need to be investigated. Relate them to previous scholarship.
- Include your hypothesis into the descriptions of the detailed research issues if you have one. Explain why it is important to justify your hypothesis.
- This part depends of the methods conducted in the research process. List the methods; explain how the results will be presented; how they will be assessed.
- Explain what kind of results will justify or disprove your hypothesis.
- Explain how much money you need.
- Explain the details of the budget (how much you want to spend for what).
- Describe why your research is important.
- List the sources you have used for writing the research proposal, including a few main citations of the preliminary scholarship.
- << Previous: Library Research
- Next: Writing the Research Paper >>
- Last Updated: May 16, 2024 10:20 AM
- URL: https://guides.library.ucla.edu/research-methods
- Interesting for you
- My settings

How to Write a Successful PhD Research Proposal
What is a research proposal.
A research proposal is a document of around 3,000-4,000 words outlining the research you are going to undertake. The majority of universities require PhD applicants to submit a research proposal when applying for a PhD position.
Find PhD programmes abroad
Why a research proposal?
Apart from being an essential requirement for PhD entry, a research proposal helps your future supervisors to better understand your line of thinking, experience in doing research and how you are planning to go about writing your thesis. In addition to this, a research proposal is a great tool that can help you to structure your thinking and outline the path you would like to follow during your PhD studies.
What should I include in a research proposal?
Before you start writing a research proposal, carefully check the website of the university you are applying for. Many universities provide guidelines on writing research proposals that will help you both to structure your thinking and meet the requirements of a specific university.
Regardless of university specific requirements, most of the research proposals usually include:
- Title and abstract: In case of predefined PhD projects, a title is usually provided by the university. In other cases, an applicant is expected to provide a preliminary title which will be further elaborated in the process of thesis writing. An abstract should usually be no longer than a page, and provide a brief summary of what you are going to cover in your research proposal.
- Literature review: The literature review demonstrates the applicant’s knowledge of the main research achievements in the area of study. You should pay attention to providing some of the key references in your area of research which requires doing extensive research on your part.
- Research problem, aim and objectives: As a result of your literature review, you should identify the main gap in your research area on which you are going to focus in your PhD project. Once the research problem is identified, you will be able to pose the main aim and objectives of your project.
- You should dedicate some space to Research methodology , or, in other words, explaining how you are going to go about doing your research. This section also demonstrates your knowledge of the existing research methodologies in your area of study.
- Ethical considerations: You should check some literature on ethics of conducting research in your area and outline some key ethical aspects related to the proposed project.
- Increasingly applicants are asked to outline the impact of their research studies . This can include both the impact on your research area and society in general. It is important to dedicate some time to this section since it will add more value to your proposal.
- References: Do not forget to specify all the references at the end of the proposal.
An obvious but very important point is the format of your research proposal. Make sure that the formatting of the document is consistent throughout and that the structure is clear. If possible, it can be a good idea to give the document to your academic tutor or colleague for revision.
It is important to remember that a research proposal is a provisional rather than a definitive document. It will most likely change extensively during the first several months of your PhD programme. Nevertheless, at the stage of application it is an essential document that helps evaluators make their decision in relation to your application. Therefore, it is worth investing time and effort in it! Good luck!
Interesting programmes for you
Explore more than 10000 Ph.D. Degrees from all around the world with Studyportals.
Go to your profile page to get personalised recommendations!
You're viewing this site as a domestic an international student
You're a domestic student if you are:
- a citizen of Australia or New Zealand,
- an Australian permanent resident, or
- a holder of an Australian permanent humanitarian visa.
You're an international student if you are:
- intending to study on a student visa,
- not a citizen of Australia or New Zealand,
- not an Australian permanent resident, or
- a temporary resident (visa status) of Australia.

How to write a good PhD proposal
Study tips Published 3 Mar, 2022 · 5-minute read
Want to make sure your research degree starts smoothly? We spoke with 2 PhD candidates about overcoming this initial hurdle. Here’s their advice for how to write a good PhD proposal.
Writing your research proposal is an integral part of commencing a PhD with many schools and institutes, so it can feel rather intimidating. After all, how you come up with your PhD proposal could be the difference between your supervisor getting on board or giving your project a miss.
Let’s explore how to make a PhD research proposal with UQ candidates Chelsea Janke and Sarah Kendall.
Look at PhD proposal examples

Look at other PhD proposals that have been successful. Ask current students if you can look at theirs.
Nobody’s asking you to reinvent the wheel when it comes to writing your PhD proposal – leave that for your actual thesis. For now, while you’re just working out how to write a PhD proposal, examples are a great starting point.
Chelsea knows this step is easier if you’ve got a friend who is already doing a PhD, but there are other ways to find a good example or template.
“Look at other PhD proposals that have been successful,” she says.
“Ask current students if you can look at theirs.”
“If you don’t know anyone doing their PhD, look online to get an idea of how they should be structured.”
What makes this tricky is that proposals can vary greatly by field and disciplinary norms, so you should check with your proposed supervisor to see if they have a specific format or list of criteria to follow. Part of writing a good PhD proposal is submitting it in a style that's familiar to the people who will read and (hopefully) become excited by it and want to bring you into their research area.
Here are some of the key factors to consider when structuring your proposal:
- meeting the expected word count (this can range from a 1-page maximum to a 3,000-word minimum depending on your supervisor and research area)
- making your bibliography as detailed as necessary
- outlining the research questions you’ll be trying to solve/answer
- discussing the impact your research could have on your field
- conducting preliminary analysis of existing research on the topic
- documenting details of the methods and data sources you’ll use in your research
- introducing your supervisor(s) and how their experience relates to your project.
Please note this isn't a universal list of things you need in your PhD research proposal. Depending on your supervisor's requirements, some of these items may be unnecessary or there may be other inclusions not listed here.
Ask your planned supervisor for advice
Alright, here’s the thing. If sending your research proposal is your first point of contact with your prospective supervisor, you’ve jumped the gun a little.
You should have at least one researcher partially on board with your project before delving too deep into your proposal. This ensures you’re not potentially spending time and effort on an idea that no one has any appetite for. Plus, it unlocks a helpful guide who can assist with your proposal.
PhD research isn’t like Shark Tank – you’re allowed to confer with academics and secure their support before you pitch your thesis to them. Discover how to choose the right PhD supervisor for you.
For a time-efficient strategy, Chelsea recommends you approach your potential supervisor(s) and find out if:
- they have time to supervise you
- they have any funds to help pay for your research (even with a stipend scholarship , your research activities may require extra money)
- their research interests align with yours (you’ll ideally discover a mutual ground where you both benefit from the project).
“The best way to approach would be to send an email briefly outlining who you are, your background, and what your research interests are,” says Chelsea.
“Once you’ve spoken to a potential supervisor, then you can start drafting a proposal and you can even ask for their input.”
Chelsea's approach here works well with some academics, but keep in mind that other supervisors will want to see a research proposal straight away. If you're not sure of your proposed supervisor's preferences, you may like to cover both bases with an introductory email that has a draft of your research proposal attached.
Sarah agrees that your prospective supervisor is your most valuable resource for understanding how to write a research proposal for a PhD application.
“My biggest tip for writing a research proposal is to ask your proposed supervisor for help,” says Sarah.
“Or if this isn’t possible, ask another academic who has had experience writing research proposals.”
“They’ll be able to tell you what to include or what you need to improve on.”
Find the 'why' and focus on it

One of the key aspects of your research proposal is emphasising why your project is important and should be funded.
Your PhD proposal should include your major question, your planned methods, the sources you’ll cite, and plenty of other nitty gritty details. But perhaps the most important element of your proposal is its purpose – the reason you want to do this research and why the results will be meaningful.
In Sarah’s opinion, highlighting the 'why' of your project is vital for your research proposal.
“From my perspective, one of the key aspects of your research proposal is emphasising why your project is important and should be funded,” she says.
“Not only does this impact whether your application is likely to be successful, but it could also impact your likelihood of getting a scholarship .”
Imagine you only had 60 seconds to explain your planned research to someone. Would you prefer they remember how your project could change the world, or the statistical models you’ll be using to do it? (Of course, you’ve got 2,000 words rather than 60 seconds, so do make sure to include those little details as well – just put the why stuff first.)
Proofread your proposal, then proof it again
As a PhD candidate, your attention to detail is going to be integral to your success. Start practising it now by making sure your research proposal is perfect.
Chelsea and Sarah both acknowledge that clarity and writing quality should never be overlooked in a PhD proposal. This starts with double-checking that the questions of your thesis are obvious and unambiguous, followed by revising the rest of your proposal.
“Make sure your research questions are really clear,” says Sarah.
“Ensure all the writing is clear and grammatically correct,” adds Chelsea.
“A supervisor is not going to be overly keen on a prospective student if their writing is poor.”
It might sound harsh, but it’s fair. So, proofread your proposal multiple times – including after you get it back from your supervisor with any feedback and notes. When you think you’ve got the final, FINAL draft saved, sleep on it and read it one more time the next morning.
Still feeling a little overwhelmed by your research proposal? Stay motivated with these reasons why a PhD is worth the effort .
Want to learn more from Chelsea and Sarah? Easy:
- Read about Chelsea’s award-winning PhD thesis on keeping crops healthy.
- Read Sarah’s series on becoming a law academic .
Share this Facebook Twitter LinkedIn Email
Related stories

How to get a PhD
4-minute read

How to find a PhD supervisor
5-minute read

How long does a PhD take?
3-minute read


Tips for PhD students from Samantha and Glenn
7-minute read
- Log in
- Site search
How to write a successful research proposal
As the competition for PhD places is incredibly fierce, your research proposal can have a strong bearing on the success of your application - so discover how to make the best impression
What is a research proposal?
Research proposals are used to persuade potential supervisors and funders that your work is worthy of their support. These documents set out your proposed research that will result in a Doctoral thesis. They are typically between 1,500 and 3,000 words.
Your PhD research proposal must passionately articulate what you want to research and why, convey your understanding of existing literature, and clearly define at least one research question that could lead to new or original knowledge and how you propose to answer it.
Professor Leigh Wilson, head of the graduate school at the University of Westminster , explains that while the research proposal is about work that hasn't been done yet, what prospective supervisors and funders are focusing on just as strongly is evidence of what you've done.
This includes how well you know existing literature in the area, including very recent publications and debates, and how clearly you've seen what's missing from this and so what your research can do that's new. Giving a strong sense of this background or frame for the proposed work is crucial.
'Although it's tempting to make large claims and propose research that sweeps across time and space, narrower, more focused research is much more convincing,' she adds. 'To be thorough and rigorous in the way that academic work needs to be, even something as long as a PhD thesis can only cover a fairly narrow topic. Depth not breadth is called for.'
The structure of your research proposal is therefore important to achieving this goal, yet it should still retain sufficient flexibility to comfortably accommodate any changes you need to make as your PhD progresses.
Layout and formats vary, so it's advisable to consult your potential PhD supervisor before you begin. Here's what to bear in mind when writing a research proposal.
Your provisional title should be around ten words in length, and clearly and accurately indicate your area of study and/or proposed approach. It should be catchy, informative and interesting.
The title page should also include personal information, such as:
- academic title
- date of birth
- nationality
- contact details.
Aims and objectives
This is a summary of your project. Your aims should be two or three broad statements that emphasise what you want to achieve, complemented by several focused, feasible and measurable objectives - the steps that you'll take to answer each of your research questions.
You'll need to clearly and briefly outline:
- how your research addresses a gap in, or builds upon, existing knowledge
- how your research links to the department that you're applying to
- the academic, cultural, political and/or social significance of your research questions.
Literature review
This section of your PhD proposal discusses the most important theories, models and texts that surround and influence your research questions, conveying your understanding and awareness of the key issues and debates.
It should focus on the theoretical and practical knowledge gaps that your work aims to address, as this ultimately justifies and provides the motivation for your project.
Methodology
Here, you're expected to outline how you'll answer each of your research questions. A strong, well-written methodology is crucial, but especially so if your project involves extensive collection and significant analysis of primary data.
In disciplines such as humanities, the research proposal methodology identifies the data collection and analytical techniques available to you, before justifying the ones you'll use in greater detail. You'll also define the population that you're intending to examine.
You should also show that you're aware of the limitations of your research, qualifying the parameters you plan to introduce. Remember, it's more impressive to do a fantastic job of exploring a narrower topic than a decent job of exploring a wider one.
Concluding or following on from your methodology, your timetable should identify how long you'll need to complete each step - perhaps using bi-weekly or monthly timeslots. This helps the reader to evaluate the feasibility of your project and shows that you've considered how you'll go about putting the PhD proposal into practice.
Bibliography
Finally, you'll provide a list of the most significant texts, plus any attachments such as your academic CV .
Demonstrate your skills in critical reflection by selecting only those resources that are most appropriate.
Final checks
Before submitting this document along with your PhD application, you'll need to ensure that you've adhered to the research proposal format. This means that:
- every page is numbered
- it's professional, interesting and informative
- the research proposal has been proofread by both an experienced academic (to confirm that it conforms to academic standards) and a layperson (to correct any grammatical or spelling errors)
- it has a contents page
- you've used a clear and easy-to-read structure, with appropriate headings.
Research proposal examples
To get a better idea of how your PhD proposal may look, some universities have provided examples of research proposals for specific subjects, including:
- The Open University - Social Policy and Criminology
- Queen's University Belfast - Nursing and Midwifery
- University of Sheffield - Sociological Studies
- University of Sussex
- University of York - Politics
- York St John University
Find out more
- Explore PhD studentships .
- For tips on writing a thesis, see 7 steps to writing a dissertation .
- Consider your PhD, what next?
How would you rate this page?
On a scale where 1 is dislike and 5 is like
- Dislike 1 unhappy-very
- Like 5 happy-very
Thank you for rating the page
- Postgraduate Research

How to write a PhD research proposal
Creating a focused and well-written research proposal - a concise and coherent summary of your proposed research - is an essential part of a successful PhD application.
A research proposal is normally required for self-funded PhDs (where you develop your own idea for a thesis), but isn't usually needed for funded studentships or pre-defined research projects.
What is a research proposal?
A research proposal sets out the central issues or questions that you intend to address. It outlines the general area of study within which your research falls, referring to the current state of knowledge and any recent debates on the topic. It should also demonstrate the originality of your proposed research.
What it should include
As a guide, research proposals should be around 2,000-3,000 words and contain:
- A title – this is just tentative and can be revised over the course of your research
- An abstract – a concise statement of your intended research
- Context - a brief overview of the general area of study within which your proposed research falls, summarising the current state of knowledge and recent debates on the topic
- Research questions - central aims and questions that will guide your research
- Research methods - outline of how you are going to conduct your research, for example, visiting particular libraries or archives, field work or interviews
- Research significance - demonstrate the originality of your intended research
- A bibliography.
Crucially, it is also an opportunity for you to communicate your passion for the subject area and to make a persuasive argument about the impact your project can achieve.
Your research proposal will be assessed by our academic schools to assess the quality of your proposed research and to establish whether they have the expertise to support your proposed area of PhD study.
Thesis writing classes and support for international research students
The University’s English Language Centre (ELC) provides thesis writing support for international PhD students. Classes run throughout semesters one and two and are designed to help develop the academic writing skills needed to write up research effectively.
The sessions are taught by tutors with their own research experience. They have PhDs themselves and have many years of experience in analysing writing in different disciplines.
The course also provides an opportunity for students to receive individual feedback on samples of their own writing.
The following classes are available:
- Thesis Writing for Science, Technology, Engineering and Medicine
- Thesis Writing for Humanities and Social Sciences
In addition to these thesis writing classes, the ELC also provides a 1:1 Academic Writing Consultation service.
Back to: Study
Find a course
- A-Z of courses /
- Studentship vacancies
Undergraduate enquiries
International enquiries
Postgraduate taught enquiries
Postgraduate research enquiries
Ask the University of Liverpool a question
- Undergraduate
- Postgraduate Taught
- Online programmes
- Welcome to Liverpool
Learn about...
- Visits and Open Days
- Accommodation
- Student support
- Careers and Employability
- Continuing Education
- Continuing Professional Development
Information for...
- International students
- Mature students and access courses
- Parents and supporters
- School and careers advisors

- Schools & departments

Writing your PhD research proposal
Find guidance on how to write your PhD research proposal and a template form for you to use to submit your research proposal.
By asking you for an outline research proposal we hope to get a good picture of your research interests and your understanding of what such research is likely to entail.
The University's application form is designed to enable you to give an overview of your academic experience and qualifications for study at postgraduate level. Your outline research proposal then gives us an idea of the kind of research you want to undertake. This, together with information from your referees, will help us assess whether the Moray House School of Education and Sport would be the appropriate place for you to pursue your research interests.
At the application stage, you are unlikely to be in a position to provide a comprehensive research proposal; the detailed shaping up of a research plan would be done in conjunction with your supervisor(s). But it is important for us to appreciate what you are hoping to investigate, how you plan to carry out the research, and what the results might be expected to contribute to current knowledge and understanding in the relevant academic field(s) of study. In writing your proposal, please indicate any prior academic or employment experience relevant to your planned research.
In your research proposal, please also ensure that you clearly identify the Moray House research cluster your proposal falls under, as well as two to three staff members with expertise in this area. We also encourage you to contact potential supervisors within your area of proposed research before submitting your application to gauge their interest and availability.
How to write your research proposal
The description of your proposed research should consist of 4-5 typed A4 sheets. It can take whatever form seems best, but should include some information about the following:
- The general area within which you wish to conduct research, and why (you might find it helpful to explain what stimulated your interest in your chosen research field, and any study or research in the area that you have already undertaken)
- The kind of research questions that you would hope to address, and why (in explaining what is likely to be the main focus of your research, it may be helpful to indicate, for example, why these issues are of particular concern and the way in which they relate to existing literature)
- The sources of information and type of research methods you plan to use (for example, how you plan to collect your data, which sources you will be targeting and how you will access these data sources).
In addition to the above, please include any comments you are able to make concerning:
- The approach that you will take to analyse your research data
- The general timetable you would follow for carrying out and writing up your research
- Any plans you may have for undertaking fieldwork away from Edinburgh
- Any problems that might be anticipated in carrying out your proposed research
Please note: This guidance applies to all candidates, except those applying to conduct PhD research as part of a larger, already established research project (for example, in the Institute for Sport, Physical Education & Health Sciences).
In this case, you should provide a two- to three-page description of a research project you have undertaken, to complement information in the application form. If you are in any doubt as to what is appropriate, please contact us:
Email: Education@[email protected]
All doctoral proposals submitted as part of an application will be run through plagiarism detection software.
Template form for your research proposal
All applicants for a PhD or MSc by Research must submit a research proposal as part of their application. Applicants must use the template form below for their research proposal. This research proposal should then be submitted online as part of your application. Please use Calibri size 11 font size and do not change the paragraph spacing (single, with 6pt after each paragraph) or the page margins.
Research Proposal Example/Sample
Detailed Walkthrough + Free Proposal Template
If you’re getting started crafting your research proposal and are looking for a few examples of research proposals , you’ve come to the right place.
In this video, we walk you through two successful (approved) research proposals , one for a Master’s-level project, and one for a PhD-level dissertation. We also start off by unpacking our free research proposal template and discussing the four core sections of a research proposal, so that you have a clear understanding of the basics before diving into the actual proposals.
- Research proposal example/sample – Master’s-level (PDF/Word)
- Research proposal example/sample – PhD-level (PDF/Word)
- Proposal template (Fully editable)
If you’re working on a research proposal for a dissertation or thesis, you may also find the following useful:
- Research Proposal Bootcamp : Learn how to write a research proposal as efficiently and effectively as possible
- 1:1 Proposal Coaching : Get hands-on help with your research proposal

PS – If you’re working on a dissertation, be sure to also check out our collection of dissertation and thesis examples here .
FAQ: Research Proposal Example
Research proposal example: frequently asked questions, are the sample proposals real.
Yes. The proposals are real and were approved by the respective universities.
Can I copy one of these proposals for my own research?
As we discuss in the video, every research proposal will be slightly different, depending on the university’s unique requirements, as well as the nature of the research itself. Therefore, you’ll need to tailor your research proposal to suit your specific context.
You can learn more about the basics of writing a research proposal here .
How do I get the research proposal template?
You can access our free proposal template here .
Is the proposal template really free?
Yes. There is no cost for the proposal template and you are free to use it as a foundation for your research proposal.
Where can I learn more about proposal writing?
For self-directed learners, our Research Proposal Bootcamp is a great starting point.
For students that want hands-on guidance, our private coaching service is recommended.

Psst… there’s more!
This post is an extract from our bestselling short course, Research Proposal Bootcamp . If you want to work smart, you don't want to miss this .
You Might Also Like:
10 Comments
I am at the stage of writing my thesis proposal for a PhD in Management at Altantic International University. I checked on the coaching services, but it indicates that it’s not available in my area. I am in South Sudan. My proposed topic is: “Leadership Behavior in Local Government Governance Ecosystem and Service Delivery Effectiveness in Post Conflict Districts of Northern Uganda”. I will appreciate your guidance and support
GRADCOCH is very grateful motivated and helpful for all students etc. it is very accorporated and provide easy access way strongly agree from GRADCOCH.
Proposal research departemet management
I am at the stage of writing my thesis proposal for a masters in Analysis of w heat commercialisation by small holders householdrs at Hawassa International University. I will appreciate your guidance and support
please provide a attractive proposal about foreign universities .It would be your highness.
comparative constitutional law
Kindly guide me through writing a good proposal on the thesis topic; Impact of Artificial Intelligence on Financial Inclusion in Nigeria. Thank you
Kindly help me write a research proposal on the topic of impacts of artisanal gold panning on the environment
I am in the process of research proposal for my Master of Art with a topic : “factors influence on first-year students’s academic adjustment”. I am absorbing in GRADCOACH and interested in such proposal sample. However, it is great for me to learn and seeking for more new updated proposal framework from GRADCAOCH.
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
Cookies on our website
We use some essential cookies to make this website work.
We'd like to set additional cookies to understand how you use our site. And we'd like to serve you some cookies set by other services to show you relevant content.
Writing your research proposal
Your proposal is your chance to tell us why you want to study your PhD at Sussex. Follow our guide to making your research proposal as strong as possible.
Your research proposal
If you are considering studying a PhD, there are two options available to you.
- apply for a funded PhD where you research a set project
- design your own research project, which you can either fund yourself, or apply for external funding.
If you decide to design your own research project, you need to write a research proposal which will form a central part of your PhD application.
Follow our step-by-step guide below to help you through the process of writing your research proposal.
Plan your research proposal
You should contact the relevant academic department before applying to Sussex and check if there are any additional requirements for your research proposal.
Even at this early stage, you may be asked questions regarding your research, and so you should start thinking about:
- the questions driving your research
- how your research makes 'an original contribution' to your field and how will you achieve this
- if your research provides new knowledge, or reinterprets existing ideas in an original way
- how you intend to do the research i.e. the methodology you'll use and how you'll structure your work
- how Sussex can aid you in your research and what you want to study here.
Ask for advice
If you need further advice you can contact our academic staff working in your field.
You can also ask research students and academic staff at your current university for help. It is good practice to discuss your ideas with others in your research area and use their suggestions to further your understanding and strengthen your proposal.
During this process you should start making detailed notes. You might also want to start planning your research proposal. If so, breaking it down into the traditional sections below may help you organise and manage your thoughts:
- introduction
- research background
- research methods
- bibliography.
Find a supervisor
Choosing the right supervisor is one of the most important steps towards a successful and rewarding PhD.
Before approaching a supervisor, you'll need to have a clear idea of the research you hope to undertake.
Once you have established a relationship with a potential supervisor, you can ask them to read the first draft of your research proposal. They can give you valuable feedback and help you refine your ideas before you submit your application.
Discover how to find a supervisor
Write your proposal
You may now be in a position to start writing your proposal. This is central to your final application.
A strong research proposal:
- formulates a precise, interesting research question
- establishes the relevance and value of the proposed research question in the context of current academic thinking
- describes the data or source material your research requires
- outlines a clear and practical methodology, which enables you to answer the research question
- states clearly what you hope to discover at the end of your research and what new areas it might open up.
The exact content and structure of your research proposal will depend on your subject area.
Below you can see information from each academic school which shows what they expect a research proposal to contain:
Length: 8-10 pages
Your research proposal should include the following sections:
Introduction
You should:
- include a short summary of the central question behind your research
- explain the background of your proposed project
- describe the expected outcome of your project.
Thesis statement
Write a summary of your overarching research question and include:
- why your research area is of academic and practical interest
- how your research builds on existing work
- what has inspired you to pursue your area of research
- your knowledge of the research area.
Literature review
You must show you have the ability to review current research (literature and papers) within your field of study. Your literature review should demonstrate that your research question is relevant, you are aware of the work of others in your field, and how your research will contribute new findings to the subject area.
Theoretical Framework
The theoretical framework provides the rationale behind your research proposal. You must provide a critical review of existing theories, which are closely related to your research topic. Show how these theories frame your research questions and the overall structure of your research proposal.
Methodology
You must show how you will carry out the research and analyse your findings. Include potential sources, how data will be collected, and any difficulties there may be in conducting your research.
Ethical considerations
Outline any ethical concerns which arise from your research topic or your proposed methods. Read the existing codes of conduct in the social sciences before writing this part of your research proposal.
Bibliography
List the sources you have used in your literature review and any potential sources you may use for your research.
For more information visit the Business School .
Length: 2,000 - 3,000 words excluding references
Your research proposal should describe what you want to research, why it is important to do this research, and how you plan to conduct your study. Here is a suggested structure:
Provide a clear working title for your research.
The introduction will indicate the focus of your research and your main research question. It should also address:
- why this topic is an important area of research
- why the subject is important to you
- how your research will contribute to our knowledge and understanding.
Research context
Provide a concise overview of the context in which you plan to conduct your research.
This section provides a concise review of related research within your field of study. It demonstrates that you are aware of the work of others and how your research will contribute new knowledge. It should also demonstrate critical engagement with relevant conceptual and theoretical frameworks and make clear your theoretical position about the issues you are researching, how this frames your research questions and your methodological approach.
Methodology and methods
Indicate your methodological approach, followed by details of how you plan to answer your research questions. This should include information about:
- how you plan to collect data (through which research methods)
- how you plan to select participants
- how you plan to analyse the data
- how you will address ethical considerations.
Provide a timeline, including time to conduct the research, process and analyse your data and write your final thesis.
Provide a bibliography of all citations used in your proposal.
For more information visit the School of Education and Social Work .
Length: 2,000 words
You should identify which research group you want to work with and check that we can support your area of research before writing your research proposal.
Your research proposal should include:
- your interest in the particular research area and the topic you want to study
- the specific research questions you want to investigate
- a description of your knowledge of the subject
- the relevant research literature you have read
- the methods and techniques you will use for your research
- an explanation of your motivations for applying for a PhD degree and an outline of your career aspirations
- a timetable for your project (monthly for the first year, and quarterly for subsequent years).
For more information visit the School of Engineering and Informatics
Length: about 2,000 words
You must provide a working title for your research. This is likely to change over time, but provides a good starting point.
You should introduce the questions and issues central to your research and explain how your research will benefit the field.
Research background
Expand on the information you have given in your introduction and try to answer the following questions:
- what are the key texts already existing in your field?
- how does your proposal differ from existing research?
- what will your project contribute to existing work in the field?
- how does your project expand our understanding and knowledge of the subject?
You must set out your research questions as clearly as possible and explain the problems you want to explore.
Research methods
Show how you plan to carry out your research:
- does your project involve archives, databases or specialist libraries?
- is your study interdisciplinary?
- what are the theoretical resources you intend to use and why?
- is your research based on a single author or a group of writers and texts?
Set out your timescale for completing your study. You need to think about dividing your research into sections and indicate how you plan to write up each section.
Include a bibliography, which lists the books and articles, you have referred to in the proposal.
Extra information
Some of these sections will be easier to write than others at this preliminary stage. The selectors who read your proposal know that it is a provisional statement and that your ideas, questions, and approaches will change during the course of your research.
You should treat the proposal as an opportunity to show that you have begun to explore an important area of study and that you have a question, or questions, that challenge and develop that area. It is also necessary to demonstrate that you can express your ideas in clear and precise English, accessible to a non-specialist.
For more information visit the Department of English
Length: 1,000-2,000 words
Include a short summary of your central question. You should tell us what you are attempting to research and why it is significant.
Thesis statement and literature review
Explain the subject matter of your project, and why you think the issues raised are important. You should also show us you are familiar with texts in the field, and can show how your research area is relevant, and in context to current academic thinking.
You must explain how your proposed project is original and will increase our understanding of the subject matter.
You must state clearly what you hope to discover at the end of your research.
Theoretical framework
Show how you plan to carry out your research and how you will analyse the findings.
Outline any ethical concerns which arise from either your research topic or your proposed methods of collating data.
List the sources you have used in your literature review and point to potential sources for your research.
For more information visit the School of Global Studies
You must provide a working title for your research, this is likely to change over time, but provides a good starting point for your proposal.
Include a bibliography, which lists the books and articles you have referred to in the proposal.
For more information visit the School of History, Art History and Philosophy
Length: 2000-3500 words (excluding bibliography)
Your title should give a clear indication of your proposed research approach or key question.
Include a short summary of your central question. You should tell us what you are attempting to research and why it is significant. You must state clearly what you hope to discover at the end of your research.
Explain the subject matter of your project and why you think the issues raised are important. Provide a summary of the key debates and developments in your chosen area and demonstrate your knowledge and grasp of the specific literature (global) that you will be engaging with during your research. You should show that you are familiar with texts in your chosen area, and what are the gaps in the literature that your research is attempting to fill, i.e., how your proposed research is original and will increase our understanding of the subject matter. Through this, you should detail how your research area fits into current academic thinking and/or policy discourse.
The theoretical framework provides the rationale behind your research proposal. You must provide a critical review of existing theories or concepts (global), which are closely related to your research topic. Show how these theories/concepts frame your research questions and the overall structure of your research proposal, and clearly state the specific theoretical concepts/analytical frameworks that you are engaging with.
You should outline your draft overall research question and any relevant sub-research questions and hypotheses through engagement with the theoretical literature.
State to what extent your approach is distinctive or new or builds on/deepens existing theoretical literature in your chosen area.
Research Design
Show how you plan to carry out your research (including fieldwork) and how you will analyse the findings. You should also show how this relates to your hypothesis. Put details of your research design in terms of approaches, methods and tools, along with some indication of specifics such as sample size (i.e., give an idea of the scope of your research project).
Outline any ethical concerns that arise from either your research topic or your proposed methods of collecting and collating data.
List the sources you have used in your literature review. Also, separately, point to potential sources that will be appropriate for your proposed research.
For more information about the PhD in Development Studies by Research visit the Institute of Development Studies website .
Length: 2,000-3,000 words
- what has inspired you to pursue your area of research.
You must show you have the ability to review current research within your field of study. Your literature review should demonstrate that your research question is relevant, you are aware of the work of others in your field, and show how your research will contribute new findings to the subject area.
Outline any ethical concerns which arise from your research topic or your proposed methods.
For more information visit the School of Law, Politics and Sociology
Length: 1,500-2,000 words
You should identify the research group you want to work with and ensure that we can support your area of research before writing your research proposal.
- a general personal statement, which describes a broad topic of interest to you and how your areas of academic strength would benefit the topic
- a specific personal statement, which shows us why you are the right person for one of our advertised research projects
- explain your motivation for applying for a PhD degree and outline your career aspirations
- your knowledge of the subject and relevant research literature you have read
- the methods and techniques you will use for your research.
If you are applying for an advertised research project you should tell us:
- which project or PhD scholarship you want to be considered for in the financial information session
- if you have another way of funding your studies if we are unable to offer you a place on a funded project
- the name of your sponsor, if you will be funded by a third party.
For more information visit the School of Life Sciences
You should identify the research area (and/or the researchers) you want to be involved with.
You should either:
- write a new research proposal
- write a general personal statement, which describes a broad topic of interest to you and how your areas of academic strength would benefit the topic
- write a specific personal statement, which shows us why you are the right person for one of our advertised research projects.
- explain your interest in the research area, your motivation for carrying out the research and your career aspirations
- describe the questions you want to investigate
- describe your knowledge of the subject and relevant previous research experience and skills
- tell us about the relevant research literature you've read
- describe the methods and techniques you will use to achieve your aims.
If you are applying for advertised funding you should tell us:
- which project or PhD scholarship you want to be considered for in the financial information section
For more information visit the School of Mathematical and Physical Sciences
Length: about 2,000 words (not including bibliography)
You must provide a working title for your research. This is likely to change over time but provides a good starting point for your proposal.
Brief abstract
Write a paragraph summarising your proposed project.
Research questions and rationale
Introduce your main research questions and why you think your research matters. Indicate how you think your research will be an original contribution to the knowledge and understanding of the subject. Describe the form of your anticipated outputs if your proposal includes creative practice. You may want to explain how you think your research will connect with existing research interests at Sussex.
Conceptual framework
The conceptual framework should elaborate the rationale behind your research proposal. You should demonstrate a critical engagement with theories and secondary literature or other artefacts that are relevant to your research topic. Show how these theories frame your research questions and the overall structure of your research proposal. If relevant, reflect on the research dimension of your creative practice.
Methodology and Research Ethics
Show us how you intend to achieve your research aims and outcomes and how you will answer your research questions. Include information about specific methods and access to relevant sources. If your project involves creative practice in some way, it is important that you describe what facilities you will need and indicate your experience in the relevant production techniques. You may want to include a practice portfolio, or provide links to online examples of your work. Reflect on any ethical considerations relevant to the conduct of your research.
Indicative timeline
Provide an account of how you envisage conducting your research to completion within the period of registration. Note that we fully expect proposals and attendant timelines to evolve in practice, but we are keen to see your ability to design a research project, bearing this in mind.
Include any literature, audiovisual or online resources you have referenced in the proposal.
For more information visit the School of Media, Film and Music
Length: 1,000-1,500 words Your research proposal should contain the following sections:
- why your research topic is interesting and important
- what we know already about the research area and how your study will expand our knowledge of it.
You should assume you are writing your research proposal for someone who has a good understanding of psychology, but not an expert in your area of research.
You should identify any gaps in our knowledge in your research area, and how your research will fill them. At the end of the section outline your aims and hypotheses.
We are interested in your ability to think critically. You should answer the following questions:
- what kind of control conditions are needed for your research?
- what do you need to measure and how?
- do you need to run any pilot studies?
- what difficulties might you have carrying out your research, and how can these be overcome?
You are expected to show how your initial idea can be developed and expanded over the duration of your PhD degree.
Reference list
You must add in a reference list in American Psychological Association format.
For more information visit the School of Psychology.
Proofread your research proposal
Once you have completed your proposal, check it through thoroughly. You should make sure all the information you have cited is accurate. Correct spelling and punctuation is also essential.
Write in clear sentences and structure your research proposal in a logical format that is easy for the reader to follow.
It is easy to miss errors in your own work, so ask someone else to proofread your research proposal before submitting it to Sussex.
You might also be interested in:
- finding a supervisor
- using our postgraduate application system
- how to apply for a PhD
- Department of Sociological Studies
Writing a research proposal
Guidelines on preparing a thesis proposal to support your application.

These guidelines are intended to assist you in developing and writing a thesis proposal. Applications for admission to a research degree cannot be dealt with unless they contain a proposal.
Your proposal will help us to make sure that:
- The topic is viable
- That the department can provide appropriate supervision and other necessary support
- You have thought through your interest in and commitment to a piece of research
- You are a suitable candidate for admission
The process of producing a proposal is usually also essential if you need to apply for funding to pay your fees or support yourself whilst doing your research. Funding bodies will often need to be reassured that you are committed to a viable project at a suitable university.
The research proposal – an outline
Your proposal should be typed double-spaced, if possible, and be between 1,000 and 2,000 words. Your PhD proposal can be added under the 'Supporting Documents' section of the Postgraduate Applications Online System .
Your proposal should contain at least the following elements:
- A provisional title
- A key question, hypothesis or the broad topic for investigation
- An outline of the key aims of the research
- A brief outline of key literature in the area [what we already know]
- A description of the topic and an explanation of why further research in the area is important [the gap in the literature - what we need to know]
- Details of how the research will be carried out, including any special facilities / resources etc. which would be required and any necessary skills which you either have already or would need to acquire [the tools that will enable us to fill the gap you have identified]
- A plan and timetable of the work you will carry out
For more detailed information on each element of your research proposal, see our extended guidance document .
Three additional points:
- Try to be concise. Do not write too much – be as specific as you can but not wordy. It is a difficult balance to strike.
- Bear in mind that the proposal is a starting point. If you are registered to read for a PhD you will be able to work the proposal through with your supervisor in more detail in the early months.
- Take a look at the Department’s staff profiles, research centres, and research clusters. Can you identify possible supervisors and intellectual support networks within the Department?
Examples of Successful PhD Proposals
- PhD sample proposal 1
- PhD sample proposal 2
- PhD sample proposal 3
- PhD sample proposal 4
- PhD sample proposal 5
- PhD sample proposal 6
- PhD sample proposal 7
- PhD sample proposal 8
Related information
Applying for a PhD
Our Research Themes
Our Research Areas
Search for PhD opportunities at Sheffield and be part of our world-leading research.

Learn how to write a PhD proposal that will stand out from the rest
Feb 27, 2019

Here, we show you how to write a PhD proposal that will stand out from the hundreds of others that are submitted each day.
Before we do though, know one thing :
The research you describe when you write your PhD proposal won’t look anything like the research you finally write up in your PhD thesis.
Wait, what ?
That’s not a typo. Everyone’s research changes over time. If you knew everything when you were writing up your proposal there wouldn’t be any point doing the PhD at all.
So, what’s the point of the proposal?
Your proposal is a guide, not a contract . It is a plan for your research that is necessarily flexible. That’s why it changes over time.
This means that the proposal is less about the robustness of your proposed research design and more about showing that you have
1. Critical thinking skills
2. An adequate grasp of the existing literature and know how your research will contribute to it
3. Clear direction and objectives. You get this by formulating clear research questions
4. Appropriate methods. This shows that you can link your understanding of the literature, research design and theory
5. An understanding of what’s required in a PhD
6. Designed a project that is feasible

Your PhD thesis. All on one page.
Use our free PhD structure template to quickly visualise every element of your thesis.
What is a PhD proposal?
Your PhD proposal is submitted as part of your application to a PhD program. It is a standard means of assessing your potential as a doctoral researcher.
When stripped down to its basic components, it does two things:
Explains the ‘what’- t hese are the questions you will address and the outcomes you expect
Explains the ‘why’- t his is the case for your research, with a focus on why the research is significant and what the contributions will be.
It is used by potential supervisors and department admission tutors to assess the quality and originality of your research ideas, how good you are at critical thinking and how feasible your proposed study is.
This means that it needs to showcase your expertise and your knowledge of the existing field and how your research contributes to it. You use it to make a persuasive case that your research is interesting and significant enough to warrant the university’s investment.
Above all though, it is about showcasing your passion for your discipline . A PhD is a hard, long journey. The admissions tutor want to know that you have both the skills and the resilience required.
What needs to be included in a PhD proposal?
Exactly what needs to be included when you write your PhD proposal will vary from university to university. How long your proposal needs to be may also be specified by your university, but if it isn’t, aim for three thousand words.
Check the requirements for each university you are applying for carefully.
Having said that, almost all proposals will need to have four distinct sections.
1. Introduction
2. the research context.
3. The approach you take
4. Conclusion
In the first few paragraphs of your proposal, you need to clearly and concisely state your research questions, the gap in the literature your study will address, the significance of your research and the contribution that the study makes.
Be as clear and concise as you can be. Make the reader’s job as easy as possible by clearly stating what the proposed research will investigate, what the contribution is and why the study is worthwhile.
This isn’t the place for lots of explanatory detail. You don’t need to justify particular design decisions in the introduction, just state what they are. The justification comes later.
In this section, you discuss the existing literature and the gaps that exist within it.
The goal here is to show that you understand the existing literature in your field, what the gaps are and how your proposed study will address them. We’ve written a guide that will help you to conduct and write a literature review .
Chances are, you won’t have conducted a complete literature review, so the emphasis here should be on the more important and well-known research in your field. Don’t worry that you haven’t read everything. Your admissions officer won’t have expected you to. Instead, they want to see that you know the following:
1. What are the most important authors, findings, concepts, schools, debates and hypotheses?
2. What gaps exist in the literature?
3. How does your thesis fill these gaps?
Once you have laid out the context, you will be in a position to make your thesis statement . A thesis statement is a sentence that summarises your argument to the reader. It is the ‘point’ you will want to make with your proposed research.
Remember, the emphasis in the PhD proposal is on what you intend to do, not on results. You won’t have results until you finish your study. That means that your thesis statement will be speculative, rather than a statement of fact.
For more on how to construct thesis statements, read this excellent guide from the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill who, incidentally, run a great academic writing blog you should definitely visit.
3. The approach you will take
This is the section in which you discuss the overall research design and is the most important component of the proposal. The emphasis here is on five things.
1. The overall approach taken (is it purely theoretical, or does it involve primary or empirical research? Maybe it’s both theoretical and empirical?)
2. The theoretical perspective you will use when you design and conduct your research
3. Why you have chosen this approach over others and what implications this choice has for your methods and the robustness of the study
4. Your specific aims and objectives
5. Your research methodology
In the previous section you outlined the context. In this section you explain the specific detail of what your research will look like.
You take the brief research design statements you made in the introduction and go into much more detail. You need to be relating your design decisions back to the literature and context discussion in the previous section.
The emphasis here is on showing that there is a logical flow. There’s no point highlighting a gap in the literature and then designing a study that doesn’t fill it.
Some of the detail here will only become clear once you have started the actual research. That’s fine. The emphasis in your proposal should be on showing that you understand what goes into a PhD.
So, keep it general.
For example, when talking about your methodology, keep things deliberately broad and focus on the overarching strategy. For example, if you are using interviews, you don’t need to list every single proposed interview question. Instead, you can talk about the rough themes you will discuss (which will relate to your literature review and thesis/project statement). Similarly, unless your research is specifically focusing on particular individuals, you don’t need to list exactly who you will interview. Instead, just state the types of people you will interview (for example: local politicians, or athletes, or academics in the UK, and so on).
4. Concluding paragraphs
There are a number of key elements to a proposal that you will need to put in the final paragraphs.
These include:
1. A discussion on the limitations of the study
2. A reiteration of your contribution
3. A proposed chapter structure (this can be an appendix)
4. Proposed month-by-month timetable (this can also be an appendix). The purpose of this timetable is to show that you understand every stage required and how long each stage takes relative to others.
Tips to turn an average proposal into one that will be accepted
1. be critical.
When you are making your design decisions in section three, you need to do so critically. Critical thinking is a key requirement of entry onto a PhD programme. In brief, it means not taking things at face value and questioning what you read or do. You can read our guide to being critical for help (it focuses on the literature review, but the take home points are the same).
2. Don’t go into too much detail too soon in your proposal
This is something that many people get wrong. You need to ease the reader in gradually . Present a brief, clear statement in the introduction and then gradually introduce more information as the pages roll on.
You will see that the outline we have suggested above follows an inverted pyramid shape.
1. In section one, you present the headlines in the introductory paragraphs. These are the research questions, aims, objectives, contribution and problem statement. State these without context or explanation.
2. When discussing the research context in section two, you provide a little more background. The goal here is to introduce the reader to the literature and highlight the gaps.
3. When describing the approach you will take, you present more detailed information. The goal here is to talk in very precise terms about how your research will address these gaps, the implications of these choices and your expected findings.
3. Be realistic
Don’t pretend you know more than you do and don’t try to reinvent your discipline .
A good proposal is one that is very focused and that describes research that is very feasible. If you try to design a study to revolutionise your field, you will not be accepted because doing so shows that you don’t understand what is feasible in the context of a PhD and you haven’t understood the literature.
4. Use clear, concise sentences
Describe your research as clearly as possible in the opening couple of paragraphs. Then write in short, clear sentences. Avoid using complex sentences where possible. If you need to introduce technical terminology, clearly define things.
In other words, make the reader’s job as easy as possible.
5. Get it proofread by someone else
We’ve written a post on why you need a proofreader .
Simple: you are the worst person to proofread your own work.
6. Work with your proposed supervisor, if you’re allowed
A lot of students fail to do this. Your supervisor isn’t your enemy. You can work with them to refine your proposal. Don’t be afraid to reach out for comments and suggestions. Be careful though. Don’t expect them to come up with topics or questions for you. Their input should be focused on refining your ideas, not helping you come up with them.
7. Tailor your proposal to each department and institution you are applying to
Admissions tutors can spot when you have submitted a one-size-fits-all proposal. Try and tailor it to the individual department. You can do this by talking about how you will contribute to the department and why you have chosen to apply there.
Follow this guide and you’ll be on a PhD programme in no time at all.
If you’re struggling for inspiration on topics or research design, try writing a rough draft of your proposal. Often the act of writing is enough for us to brainstorm new ideas and relate existing ideas to one another.
If you’re still struggling, send your idea to us in an email to us and we’ll give you our feedback.
Hello, Doctor…
Sounds good, doesn’t it? Be able to call yourself Doctor sooner with our five-star rated How to Write A PhD email-course. Learn everything your supervisor should have taught you about planning and completing a PhD.
Now half price. Join hundreds of other students and become a better thesis writer, or your money back.
Share this:
13 comments.
A wonderful guide. I must say not only well written but very well thought out and very efficient.
Great. I’m glad you think so.
Thanks for sharing. Makes navigating through the proposal lot easier
Great. Glad you think so!
An excellent guide, I learned a lot thank you
Great job and guide for a PhD proposal. Thank you!
You’re welcome!
I am going to start writing my Ph.D. proposal. This has been so helpful in instructing me on what to do. Thanks
Thanks! Glad you thought so.
A very reassuring guide to the process. Thank you, Max
I appreciate the practical advice and actionable steps you provide in your posts.
Glad to hear it. Many thanks.
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

Search The PhD Knowledge Base
Most popular articles from the phd knowlege base.
The PhD Knowledge Base Categories
- Your PhD and Covid
- Mastering your theory and literature review chapters
- How to structure and write every chapter of the PhD
- How to stay motivated and productive
- Techniques to improve your writing and fluency
- Advice on maintaining good mental health
- Resources designed for non-native English speakers
- PhD Writing Template
- Explore our back-catalogue of motivational advice

How to structure your PhD thesis
Organising your PhD thesis in a logical order is one of the crucial stages of your writing process. Here is a list of the individual components to include
Shama Prasada Kabekkodu

Created in partnership with

You may also like

Popular resources
.css-1txxx8u{overflow:hidden;max-height:81px;text-indent:0px;} The secrets to success as a provost
Using non verbal cues to build rapport with students, emotionally challenging research and researcher well-being, augmenting the doctoral thesis in preparation for a viva, how hard can it be testing ai detection tools.
The task of writing a PhD thesis is top of mind for many aspiring scholars. After all, completing one is no small task. And while these pieces of writing often share a standard format, this can differ slightly based on the requirements of your institution or subject. So what elements make up a PhD thesis?
A doctoral thesis usually contains:
- A title page
- Declarations from the candidate and supervisor
- A certificate from the candidate and supervisor
- A plagiarism report
- Acknowledgements
- A table of contents
- Abbreviations
- An abstract
Chapters typically cover:
- A general introduction
- Literature review
- Analysis of the gap in research with aims and objectives
- Materials and methods
- Summary and conclusion
- References or bibliography.
You should also include a list of papers you have published and any relevant achievements at the end.
An explanation of each of the components of a PhD dissertation
Title page: a PhD thesis starts with a title page that contains the complete title of the research work, the submitting university, names of the candidate and supervisor, affiliation and month and year of submission.
Abstract: this serves as a concise synopsis of the dissertation, covering the research context, purpose of the study or research questions, methodology, findings and conclusions. This section is usually one to two pages in length.
Table of contents: this page lists the thesis content and respective page numbers.
General introduction and literature review: this component is usually 20 to 40 pages long. It presents the readers with the primary material and discusses relevant published data. It provides an overview of pertinent literature related to the thesis such as texts that critically assess the existing literature to identify the gap in research and explain the need behind the study.
Aims and objectives: this section of the thesis is typically one to two pages long and describes the aims and objectives of the study. Structure them as three to four bullet points describing specific points that you will investigate. Approach this by thinking about what readers should understand by the end of the thesis. Ensure you:
- Give a clear explanation of the purpose and goals of your study
- Outline each aim concisely
- Explain how you will measure your objectives
- Ensure there is a clear connection between each aim
- Use verbs such as investigate, evaluate, explore, analyse and demonstrate.
Materials and methods: this section briefly explains how you have conducted the study and should include all the materials you used and procedures you implemented. For example, if your research involves working with chemicals, list the chemicals and instruments used, along with their catalogue numbers and manufacturers’ names. This section should also explicitly explain the methodology you used, step-by-step. Use the past tense while writing this section and do not describe any results or findings of the study yet.
Results: this section is sometimes called the “findings report” or “the experimental findings” (referring to data collection and analysis). Write the results concisely and in the past tense. Include text, figure and table infographics created with tools such as Microsoft PowerPoint, Adobe Illustrator and BioRender to visualise your data .
Discussion: this is a chance to discuss the results and compare the findings of your study with the initial hypothesis and existing knowledge. Focus on discussing interpretations, implications, limitations and recommendations here.
- Resources on academic writing for higher education staff
- Tips for writing a PhD dissertation: FAQs answered
- How to tackle the PhD dissertation
Summary and conclusion: this section should be shorter than the discussion and summarise your key findings. The summary and conclusion should be brief and engaging, allowing the reader to easily understand the major findings of the research work. Provide clear answers to the research questions, generate new knowledge and clarify the need for the study.
Future perspective: this section of the thesis (which is often combined with a summary or conclusion) talks about the study's limitations, if any, and indicates the directions for future studies based on your findings.
References or bibliography: the last section should include the list of articles, websites and other resources cited in the thesis.
Always remember that, depending on the department, university or field of study, you might have to follow specific guidelines on how to organise your PhD thesis. Ensure you consult your supervisor or academic department if you have any doubts.
Shama Prasada Kabekkodu is a professor and head of cell and molecular biology at Manipal School of Life Sciences, Manipal Academy of Higher Education, India.
If you would like advice and insight from academics and university staff delivered direct to your inbox each week, sign up for the Campus newsletter .
The secrets to success as a provost
Emotions and learning: what role do emotions play in how and why students learn, the podcast: bringing an outsider’s eye to primary sources, a diy guide to starting your own journal, formative, summative or diagnostic assessment a guide, harnessing the power of data to drive student success.
Register for free
and unlock a host of features on the THE site
We use cookies on reading.ac.uk to improve your experience, monitor site performance and tailor content to you
Read our cookie policy to find out how to manage your cookie settings
This site may not work correctly on Internet Explorer. We recommend switching to a different browser for a better experience.
Writing your research proposal
When applying to study for a PhD or MPhil in the School of Psychology and Clinical Language Sciences, you will typically need to send us an initial 500-word research proposal.
The content and structure of your research proposal will be influenced by the nature of the project you wish to pursue. The guidance and suggested headings provided here should help you to structure and present your ideas clearly.
Your initial research proposal
When writing your initial research proposal, you can either address it to the School generally, or to a specific supervisor if you have one in mind.
Potential supervisors in the School will review your initial research proposal, and get in touch with you to discuss it. Your proposal may change following this conversation. Depending on the supervisor and the outcome of this discussion, you may be asked to produce a longer research proposal of between 2,000 and 4,000 words.
Tips on writing a research proposal
Before you write your research proposal, we strongly recommend that you check our research page and individual supervisor profiles to view our areas of expertise.
- You should avoid the use of overly long sentences and technical jargon.
- It is important that the proposed research is realistic and feasible so that the outcomes can be achieved within the scale of a typical research degree programme. This is usually three years full-time for a PhD (or two years for an MPhil).
- A strong research proposal can and should make a positive first impression about your potential to become a good researcher. It should demonstrate that your ideas are focused, interesting and realistic.
Although you should write your proposal yourself, it is best if you discuss its contents with your proposed supervisor before you submit it. If this is not possible, then try to get someone else (such as an academic at your current or previous institution) to read and comment on it to ensure that it is sufficiently clear.
Your proposal needs a clear working title that gives an indication of what you want to study. You are not committed to continuing with the same title once you begin your studies.
Research question
For many projects, you'll usually address one main question, which can sometimes be broken down into several sub-questions. However, it's OK to have two or three research questions where appropriate.
In your research proposal, you'll need to state your main research question(s), explain its significance, and locate it within the relevant literature, in order to set out the context into which your research will fit. You should only refer to research that is directly relevant to your proposal.
Questions to address in your research proposal
You will need to address questions such as:
- What is the general area in which you will be working, and the specific aspect(s) of that area that will be your focus of inquiry?
- What is the problem, shortcoming, or gap in this area that you would like to address?
- What is the main research question or aim that you want to address?
- What are the specific objectives for the proposed research that follow from this?
- Why is the proposed research significant, why does it matter (either theoretically or practically), and why does it excite you?
- How does your work relate to other relevant research in the department?
Methodology
You will need to explain how you will go about answering your question (or achieving your aim), and why you will use your intended approach to address the question/aim.
Questions you might need to address include:
- What steps will you take and what methods will you use to address your question? For instance, do you plan to use quantitative or qualitative methods?
- How will your proposed method provide a reliable answer to your question?
- What sources or data will you use?
- If your project involves an experimental approach, what specific hypothesis or hypotheses will you address?
- What specific techniques will you use to test the hypothesis? For example, laboratory procedures, interviews, questionnaires, modelling, simulation, text analysis, use of secondary data sources.
- What practical considerations are there? For example, what equipment, facilities, and other resources will be required?
- What relevant skills and experience do you have with the proposed methods?
- Will you need to collaborate with other researchers and organisations?
- Are there particular ethical issues that will need to be considered (for example, all projects using human participants require ethical approval)?
- Are there any potential problems or difficulties that you foresee (for example, delays in gaining access to special populations or materials) that might affect your rate of progress?
You will need to provide a rough timeline for the completion of your research to show that the project is achievable (given the facilities and resources required) in no more than three years of full-time study (or part-time equivalent) for a PhD, and two years for an MPhil.
Expected outcomes
You need to say something about what the expected outcomes of your project would be.
How, for example, does it make a contribution to knowledge? How does it advance theoretical understanding? How might it contribute to policy or practice?
If you are aiming to study for a PhD, then you need to say how your proposed research will make an original contribution to knowledge. This is not essential if you are aiming to study for an MPhil, although you will still need to show originality in the application of knowledge.
List of references
You will need to provide a list of any key articles or texts that you have referred to in your proposal.
References should be listed in the appropriate style for your subject area (e.g. Harvard). You should only reference texts that you think are central to your proposed work, rather than a bibliography listing everything written on the subject.
Format and proofreading
Make sure that your proposal is well structured and clearly written. It is important that you carefully check your proposal for typographical and spelling errors, consistency of style, and accuracy of references, before submitting it.
The proposal should be aesthetically well presented, and look professional (e.g. no font inconsistencies, headings clearly identifiable). If you include figures, then they should be accompanied by captions underneath).
How to apply for a PhD

PhD opportunities
Our research

Take the next step
- How to apply
- Get a prospectus
- Ask us a question
- Learn about the Doctoral and Researcher College

COMMENTS
Written by Mark Bennett. You'll need to write a research proposal if you're submitting your own project plan as part of a PhD application. A good PhD proposal outlines the scope and significance of your topic and explains how you plan to research it. It's helpful to think about the proposal like this: if the rest of your application explains ...
Therefore, in a good research proposal you will need to demonstrate two main things: 1. that you are capable of independent critical thinking and analysis. 2. that you are capable of communicating your ideas clearly. Applying for a PhD is like applying for a job, you are not applying for a taught programme.
Research proposal length. The length of a research proposal can vary quite a bit. A bachelor's or master's thesis proposal can be just a few pages, while proposals for PhD dissertations or research funding are usually much longer and more detailed. Your supervisor can help you determine the best length for your work.
1. Title. Your title should indicate clearly what your research question is. It needs to be simple and to the point; if the reader needs to read further into your proposal to understand your question, your working title isn't clear enough. Directly below your title, state the topic your research question relates to.
When writing your PhD proposal you need to show that your PhD is worth it, achievable, and that you have the ability to do it at your chosen university. With all of that in mind, let's take a closer look at each section of a standard PhD research proposal and the overall structure. 1. Front matter.
Make sure you can ask the critical what, who, and how questions of your research before you put pen to paper. Your research proposal should include (at least) 5 essential components : Title - provides the first taste of your research, in broad terms. Introduction - explains what you'll be researching in more detail.
A research proposal should present your idea or question and expected outcomes with clarity and definition - the what. It should also make a case for why your question is significant and what value it will bring to your discipline - the why. What it shouldn't do is answer the question - that's what your research will do.
A PhD proposal is a focused document that int roduces your PhD study idea and seeks to. convince the reader that your idea is interesting, original and viable within the allocated study. period ...
Your research proposal is a concise statement (up to 3,000 words) of the rationale for your research proposal, the research questions to be answered and how you propose to address them. We know that during the early stages of your PhD you are likely to refine your thinking and methodology in discussion with your supervisors.
The new Third Edition covers every section of the proposal, telling you all you need to know on how to structure it, bring rigor to your methods section, impress your readers, and get your proposal accepted. Developing Effective Research Proposals provides an authoritative and accessible guide for anyone tackling a research proposal.
How To Structure A Research Proposal. ... As a rough guide, a formal research proposal at Masters-level often ranges between 2000-3000 words, while a PhD-level proposal can be far more detailed, ranging from 5000-8000 words. In some cases, a rough outline of the topic is all that's needed, while in other cases, universities expect a very ...
References: Do not forget to specify all the references at the end of the proposal. An obvious but very important point is the format of your research proposal. Make sure that the formatting of the document is consistent throughout and that the structure is clear. If possible, it can be a good idea to give the document to your academic tutor or ...
This starts with double-checking that the questions of your thesis are obvious and unambiguous, followed by revising the rest of your proposal. "Make sure your research questions are really clear," says Sarah. "Ensure all the writing is clear and grammatically correct," adds Chelsea. "A supervisor is not going to be overly keen on a ...
Research proposals are used to persuade potential supervisors and funders that your work is worthy of their support. These documents set out your proposed research that will result in a Doctoral thesis. They are typically between 1,500 and 3,000 words. Your PhD research proposal must passionately articulate what you want to research and why ...
Once your structure of a research proposal has been approved, the researcher gains the right time to conduct deep research. B. Key Questions to Be Asked ... Lyman, M., & Keyes, C. (2019). Peer-supported writing in graduate research courses: A mixed methods assessment. International Journal of Teaching and Learning in Higher Education, 31 (1 ...
As a guide, research proposals should be around 2,000-3,000 words and contain: A title - this is just tentative and can be revised over the course of your research. An abstract - a concise statement of your intended research. Context - a brief overview of the general area of study within which your proposed research falls, summarising the ...
All applicants for a PhD or MSc by Research must submit a research proposal as part of their application. Applicants must use the template form below for their research proposal. This research proposal should then be submitted online as part of your application. Please use Calibri size 11 font size and do not change the paragraph spacing ...
PhD proposal is an outline of your proposed project. It needs to: Define a clear question and approach to answering it. Highlight its originality and/or significance. Explain how it adds to, develops (or challenges) existing literature in the field. Persuade potential supervisors of the importance of the work, and why you are the right person ...
Detailed Walkthrough + Free Proposal Template. If you're getting started crafting your research proposal and are looking for a few examples of research proposals, you've come to the right place. In this video, we walk you through two successful (approved) research proposals, one for a Master's-level project, and one for a PhD-level ...
For more information about the PhD in Development Studies by Research visit the Institute of Development Studies website. Law, Politics and Sociology. Length: 2,000-3,000 words ... Write in clear sentences and structure your research proposal in a logical format that is easy for the reader to follow.
The research proposal - an outline. Your proposal should be typed double-spaced, if possible, and be between 1,000 and 2,000 words. Your PhD proposal can be added under the 'Supporting Documents' section of the Postgraduate Applications Online System. Your proposal should contain at least the following elements: A provisional title
This means that the proposal is less about the robustness of your proposed research design and more about showing that you have. 1. Critical thinking skills. 2. An adequate grasp of the existing literature and know how your research will contribute to it. 3. Clear direction and objectives.
Tips for writing a PhD dissertation: FAQs answered; How to tackle the PhD dissertation; Summary and conclusion: this section should be shorter than the discussion and summarise your key findings. The summary and conclusion should be brief and engaging, allowing the reader to easily understand the major findings of the research work.
When applying to study for a PhD or MPhil in the School of Psychology and Clinical Language Sciences, you will typically need to send us an initial 500-word research proposal. The content and structure of your research proposal will be influenced by the nature of the project you wish to pursue. The guidance and suggested headings provided here ...