Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Methodology

Research Design | Step-by-Step Guide with Examples
Published on 5 May 2022 by Shona McCombes . Revised on 20 March 2023.
A research design is a strategy for answering your research question using empirical data. Creating a research design means making decisions about:
- Your overall aims and approach
- The type of research design you’ll use
- Your sampling methods or criteria for selecting subjects
- Your data collection methods
- The procedures you’ll follow to collect data
- Your data analysis methods
A well-planned research design helps ensure that your methods match your research aims and that you use the right kind of analysis for your data.
Table of contents
Step 1: consider your aims and approach, step 2: choose a type of research design, step 3: identify your population and sampling method, step 4: choose your data collection methods, step 5: plan your data collection procedures, step 6: decide on your data analysis strategies, frequently asked questions.
- Introduction
Before you can start designing your research, you should already have a clear idea of the research question you want to investigate.
There are many different ways you could go about answering this question. Your research design choices should be driven by your aims and priorities – start by thinking carefully about what you want to achieve.
The first choice you need to make is whether you’ll take a qualitative or quantitative approach.
Qualitative research designs tend to be more flexible and inductive , allowing you to adjust your approach based on what you find throughout the research process.
Quantitative research designs tend to be more fixed and deductive , with variables and hypotheses clearly defined in advance of data collection.
It’s also possible to use a mixed methods design that integrates aspects of both approaches. By combining qualitative and quantitative insights, you can gain a more complete picture of the problem you’re studying and strengthen the credibility of your conclusions.
Practical and ethical considerations when designing research
As well as scientific considerations, you need to think practically when designing your research. If your research involves people or animals, you also need to consider research ethics .
- How much time do you have to collect data and write up the research?
- Will you be able to gain access to the data you need (e.g., by travelling to a specific location or contacting specific people)?
- Do you have the necessary research skills (e.g., statistical analysis or interview techniques)?
- Will you need ethical approval ?
At each stage of the research design process, make sure that your choices are practically feasible.
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
Within both qualitative and quantitative approaches, there are several types of research design to choose from. Each type provides a framework for the overall shape of your research.
Types of quantitative research designs
Quantitative designs can be split into four main types. Experimental and quasi-experimental designs allow you to test cause-and-effect relationships, while descriptive and correlational designs allow you to measure variables and describe relationships between them.
With descriptive and correlational designs, you can get a clear picture of characteristics, trends, and relationships as they exist in the real world. However, you can’t draw conclusions about cause and effect (because correlation doesn’t imply causation ).
Experiments are the strongest way to test cause-and-effect relationships without the risk of other variables influencing the results. However, their controlled conditions may not always reflect how things work in the real world. They’re often also more difficult and expensive to implement.
Types of qualitative research designs
Qualitative designs are less strictly defined. This approach is about gaining a rich, detailed understanding of a specific context or phenomenon, and you can often be more creative and flexible in designing your research.
The table below shows some common types of qualitative design. They often have similar approaches in terms of data collection, but focus on different aspects when analysing the data.
Your research design should clearly define who or what your research will focus on, and how you’ll go about choosing your participants or subjects.
In research, a population is the entire group that you want to draw conclusions about, while a sample is the smaller group of individuals you’ll actually collect data from.
Defining the population
A population can be made up of anything you want to study – plants, animals, organisations, texts, countries, etc. In the social sciences, it most often refers to a group of people.
For example, will you focus on people from a specific demographic, region, or background? Are you interested in people with a certain job or medical condition, or users of a particular product?
The more precisely you define your population, the easier it will be to gather a representative sample.
Sampling methods
Even with a narrowly defined population, it’s rarely possible to collect data from every individual. Instead, you’ll collect data from a sample.
To select a sample, there are two main approaches: probability sampling and non-probability sampling . The sampling method you use affects how confidently you can generalise your results to the population as a whole.
Probability sampling is the most statistically valid option, but it’s often difficult to achieve unless you’re dealing with a very small and accessible population.
For practical reasons, many studies use non-probability sampling, but it’s important to be aware of the limitations and carefully consider potential biases. You should always make an effort to gather a sample that’s as representative as possible of the population.
Case selection in qualitative research
In some types of qualitative designs, sampling may not be relevant.
For example, in an ethnography or a case study, your aim is to deeply understand a specific context, not to generalise to a population. Instead of sampling, you may simply aim to collect as much data as possible about the context you are studying.
In these types of design, you still have to carefully consider your choice of case or community. You should have a clear rationale for why this particular case is suitable for answering your research question.
For example, you might choose a case study that reveals an unusual or neglected aspect of your research problem, or you might choose several very similar or very different cases in order to compare them.
Data collection methods are ways of directly measuring variables and gathering information. They allow you to gain first-hand knowledge and original insights into your research problem.
You can choose just one data collection method, or use several methods in the same study.
Survey methods
Surveys allow you to collect data about opinions, behaviours, experiences, and characteristics by asking people directly. There are two main survey methods to choose from: questionnaires and interviews.
Observation methods
Observations allow you to collect data unobtrusively, observing characteristics, behaviours, or social interactions without relying on self-reporting.
Observations may be conducted in real time, taking notes as you observe, or you might make audiovisual recordings for later analysis. They can be qualitative or quantitative.
Other methods of data collection
There are many other ways you might collect data depending on your field and topic.
If you’re not sure which methods will work best for your research design, try reading some papers in your field to see what data collection methods they used.
Secondary data
If you don’t have the time or resources to collect data from the population you’re interested in, you can also choose to use secondary data that other researchers already collected – for example, datasets from government surveys or previous studies on your topic.
With this raw data, you can do your own analysis to answer new research questions that weren’t addressed by the original study.
Using secondary data can expand the scope of your research, as you may be able to access much larger and more varied samples than you could collect yourself.
However, it also means you don’t have any control over which variables to measure or how to measure them, so the conclusions you can draw may be limited.
As well as deciding on your methods, you need to plan exactly how you’ll use these methods to collect data that’s consistent, accurate, and unbiased.
Planning systematic procedures is especially important in quantitative research, where you need to precisely define your variables and ensure your measurements are reliable and valid.
Operationalisation
Some variables, like height or age, are easily measured. But often you’ll be dealing with more abstract concepts, like satisfaction, anxiety, or competence. Operationalisation means turning these fuzzy ideas into measurable indicators.
If you’re using observations , which events or actions will you count?
If you’re using surveys , which questions will you ask and what range of responses will be offered?
You may also choose to use or adapt existing materials designed to measure the concept you’re interested in – for example, questionnaires or inventories whose reliability and validity has already been established.
Reliability and validity
Reliability means your results can be consistently reproduced , while validity means that you’re actually measuring the concept you’re interested in.
For valid and reliable results, your measurement materials should be thoroughly researched and carefully designed. Plan your procedures to make sure you carry out the same steps in the same way for each participant.
If you’re developing a new questionnaire or other instrument to measure a specific concept, running a pilot study allows you to check its validity and reliability in advance.
Sampling procedures
As well as choosing an appropriate sampling method, you need a concrete plan for how you’ll actually contact and recruit your selected sample.
That means making decisions about things like:
- How many participants do you need for an adequate sample size?
- What inclusion and exclusion criteria will you use to identify eligible participants?
- How will you contact your sample – by mail, online, by phone, or in person?
If you’re using a probability sampling method, it’s important that everyone who is randomly selected actually participates in the study. How will you ensure a high response rate?
If you’re using a non-probability method, how will you avoid bias and ensure a representative sample?
Data management
It’s also important to create a data management plan for organising and storing your data.
Will you need to transcribe interviews or perform data entry for observations? You should anonymise and safeguard any sensitive data, and make sure it’s backed up regularly.
Keeping your data well organised will save time when it comes to analysing them. It can also help other researchers validate and add to your findings.
On their own, raw data can’t answer your research question. The last step of designing your research is planning how you’ll analyse the data.
Quantitative data analysis
In quantitative research, you’ll most likely use some form of statistical analysis . With statistics, you can summarise your sample data, make estimates, and test hypotheses.
Using descriptive statistics , you can summarise your sample data in terms of:
- The distribution of the data (e.g., the frequency of each score on a test)
- The central tendency of the data (e.g., the mean to describe the average score)
- The variability of the data (e.g., the standard deviation to describe how spread out the scores are)
The specific calculations you can do depend on the level of measurement of your variables.
Using inferential statistics , you can:
- Make estimates about the population based on your sample data.
- Test hypotheses about a relationship between variables.
Regression and correlation tests look for associations between two or more variables, while comparison tests (such as t tests and ANOVAs ) look for differences in the outcomes of different groups.
Your choice of statistical test depends on various aspects of your research design, including the types of variables you’re dealing with and the distribution of your data.
Qualitative data analysis
In qualitative research, your data will usually be very dense with information and ideas. Instead of summing it up in numbers, you’ll need to comb through the data in detail, interpret its meanings, identify patterns, and extract the parts that are most relevant to your research question.
Two of the most common approaches to doing this are thematic analysis and discourse analysis .
There are many other ways of analysing qualitative data depending on the aims of your research. To get a sense of potential approaches, try reading some qualitative research papers in your field.
A sample is a subset of individuals from a larger population. Sampling means selecting the group that you will actually collect data from in your research.
For example, if you are researching the opinions of students in your university, you could survey a sample of 100 students.
Statistical sampling allows you to test a hypothesis about the characteristics of a population. There are various sampling methods you can use to ensure that your sample is representative of the population as a whole.
Operationalisation means turning abstract conceptual ideas into measurable observations.
For example, the concept of social anxiety isn’t directly observable, but it can be operationally defined in terms of self-rating scores, behavioural avoidance of crowded places, or physical anxiety symptoms in social situations.
Before collecting data , it’s important to consider how you will operationalise the variables that you want to measure.
The research methods you use depend on the type of data you need to answer your research question .
- If you want to measure something or test a hypothesis , use quantitative methods . If you want to explore ideas, thoughts, and meanings, use qualitative methods .
- If you want to analyse a large amount of readily available data, use secondary data. If you want data specific to your purposes with control over how they are generated, collect primary data.
- If you want to establish cause-and-effect relationships between variables , use experimental methods. If you want to understand the characteristics of a research subject, use descriptive methods.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, March 20). Research Design | Step-by-Step Guide with Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved 21 May 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/research-methods/research-design/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes

Experimental Research Design — 6 mistakes you should never make!
Since school days’ students perform scientific experiments that provide results that define and prove the laws and theorems in science. These experiments are laid on a strong foundation of experimental research designs.
An experimental research design helps researchers execute their research objectives with more clarity and transparency.
In this article, we will not only discuss the key aspects of experimental research designs but also the issues to avoid and problems to resolve while designing your research study.
Table of Contents
What Is Experimental Research Design?
Experimental research design is a framework of protocols and procedures created to conduct experimental research with a scientific approach using two sets of variables. Herein, the first set of variables acts as a constant, used to measure the differences of the second set. The best example of experimental research methods is quantitative research .
Experimental research helps a researcher gather the necessary data for making better research decisions and determining the facts of a research study.
When Can a Researcher Conduct Experimental Research?
A researcher can conduct experimental research in the following situations —
- When time is an important factor in establishing a relationship between the cause and effect.
- When there is an invariable or never-changing behavior between the cause and effect.
- Finally, when the researcher wishes to understand the importance of the cause and effect.
Importance of Experimental Research Design
To publish significant results, choosing a quality research design forms the foundation to build the research study. Moreover, effective research design helps establish quality decision-making procedures, structures the research to lead to easier data analysis, and addresses the main research question. Therefore, it is essential to cater undivided attention and time to create an experimental research design before beginning the practical experiment.
By creating a research design, a researcher is also giving oneself time to organize the research, set up relevant boundaries for the study, and increase the reliability of the results. Through all these efforts, one could also avoid inconclusive results. If any part of the research design is flawed, it will reflect on the quality of the results derived.
Types of Experimental Research Designs
Based on the methods used to collect data in experimental studies, the experimental research designs are of three primary types:
1. Pre-experimental Research Design
A research study could conduct pre-experimental research design when a group or many groups are under observation after implementing factors of cause and effect of the research. The pre-experimental design will help researchers understand whether further investigation is necessary for the groups under observation.
Pre-experimental research is of three types —
- One-shot Case Study Research Design
- One-group Pretest-posttest Research Design
- Static-group Comparison
2. True Experimental Research Design
A true experimental research design relies on statistical analysis to prove or disprove a researcher’s hypothesis. It is one of the most accurate forms of research because it provides specific scientific evidence. Furthermore, out of all the types of experimental designs, only a true experimental design can establish a cause-effect relationship within a group. However, in a true experiment, a researcher must satisfy these three factors —
- There is a control group that is not subjected to changes and an experimental group that will experience the changed variables
- A variable that can be manipulated by the researcher
- Random distribution of the variables
This type of experimental research is commonly observed in the physical sciences.
3. Quasi-experimental Research Design
The word “Quasi” means similarity. A quasi-experimental design is similar to a true experimental design. However, the difference between the two is the assignment of the control group. In this research design, an independent variable is manipulated, but the participants of a group are not randomly assigned. This type of research design is used in field settings where random assignment is either irrelevant or not required.
The classification of the research subjects, conditions, or groups determines the type of research design to be used.
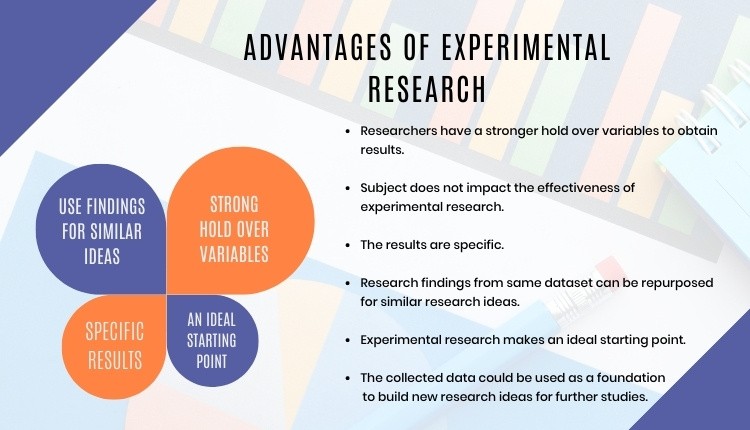
Advantages of Experimental Research
Experimental research allows you to test your idea in a controlled environment before taking the research to clinical trials. Moreover, it provides the best method to test your theory because of the following advantages:
- Researchers have firm control over variables to obtain results.
- The subject does not impact the effectiveness of experimental research. Anyone can implement it for research purposes.
- The results are specific.
- Post results analysis, research findings from the same dataset can be repurposed for similar research ideas.
- Researchers can identify the cause and effect of the hypothesis and further analyze this relationship to determine in-depth ideas.
- Experimental research makes an ideal starting point. The collected data could be used as a foundation to build new research ideas for further studies.
6 Mistakes to Avoid While Designing Your Research
There is no order to this list, and any one of these issues can seriously compromise the quality of your research. You could refer to the list as a checklist of what to avoid while designing your research.
1. Invalid Theoretical Framework
Usually, researchers miss out on checking if their hypothesis is logical to be tested. If your research design does not have basic assumptions or postulates, then it is fundamentally flawed and you need to rework on your research framework.
2. Inadequate Literature Study
Without a comprehensive research literature review , it is difficult to identify and fill the knowledge and information gaps. Furthermore, you need to clearly state how your research will contribute to the research field, either by adding value to the pertinent literature or challenging previous findings and assumptions.
3. Insufficient or Incorrect Statistical Analysis
Statistical results are one of the most trusted scientific evidence. The ultimate goal of a research experiment is to gain valid and sustainable evidence. Therefore, incorrect statistical analysis could affect the quality of any quantitative research.
4. Undefined Research Problem
This is one of the most basic aspects of research design. The research problem statement must be clear and to do that, you must set the framework for the development of research questions that address the core problems.
5. Research Limitations
Every study has some type of limitations . You should anticipate and incorporate those limitations into your conclusion, as well as the basic research design. Include a statement in your manuscript about any perceived limitations, and how you considered them while designing your experiment and drawing the conclusion.
6. Ethical Implications
The most important yet less talked about topic is the ethical issue. Your research design must include ways to minimize any risk for your participants and also address the research problem or question at hand. If you cannot manage the ethical norms along with your research study, your research objectives and validity could be questioned.
Experimental Research Design Example
In an experimental design, a researcher gathers plant samples and then randomly assigns half the samples to photosynthesize in sunlight and the other half to be kept in a dark box without sunlight, while controlling all the other variables (nutrients, water, soil, etc.)
By comparing their outcomes in biochemical tests, the researcher can confirm that the changes in the plants were due to the sunlight and not the other variables.
Experimental research is often the final form of a study conducted in the research process which is considered to provide conclusive and specific results. But it is not meant for every research. It involves a lot of resources, time, and money and is not easy to conduct, unless a foundation of research is built. Yet it is widely used in research institutes and commercial industries, for its most conclusive results in the scientific approach.
Have you worked on research designs? How was your experience creating an experimental design? What difficulties did you face? Do write to us or comment below and share your insights on experimental research designs!
Frequently Asked Questions
Randomization is important in an experimental research because it ensures unbiased results of the experiment. It also measures the cause-effect relationship on a particular group of interest.
Experimental research design lay the foundation of a research and structures the research to establish quality decision making process.
There are 3 types of experimental research designs. These are pre-experimental research design, true experimental research design, and quasi experimental research design.
The difference between an experimental and a quasi-experimental design are: 1. The assignment of the control group in quasi experimental research is non-random, unlike true experimental design, which is randomly assigned. 2. Experimental research group always has a control group; on the other hand, it may not be always present in quasi experimental research.
Experimental research establishes a cause-effect relationship by testing a theory or hypothesis using experimental groups or control variables. In contrast, descriptive research describes a study or a topic by defining the variables under it and answering the questions related to the same.
good and valuable
Very very good
Good presentation.
Rate this article Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published.

Enago Academy's Most Popular Articles
![how to write an experimental research design What is Academic Integrity and How to Uphold it [FREE CHECKLIST]](https://www.enago.com/academy/wp-content/uploads/2024/05/FeatureImages-59-210x136.png)
Ensuring Academic Integrity and Transparency in Academic Research: A comprehensive checklist for researchers
Academic integrity is the foundation upon which the credibility and value of scientific findings are…

- Publishing Research
- Reporting Research
How to Optimize Your Research Process: A step-by-step guide
For researchers across disciplines, the path to uncovering novel findings and insights is often filled…

- Industry News
- Trending Now
Breaking Barriers: Sony and Nature unveil “Women in Technology Award”
Sony Group Corporation and the prestigious scientific journal Nature have collaborated to launch the inaugural…

Achieving Research Excellence: Checklist for good research practices
Academia is built on the foundation of trustworthy and high-quality research, supported by the pillars…

- Promoting Research
Plain Language Summary — Communicating your research to bridge the academic-lay gap
Science can be complex, but does that mean it should not be accessible to the…
Choosing the Right Analytical Approach: Thematic analysis vs. content analysis for…
Comparing Cross Sectional and Longitudinal Studies: 5 steps for choosing the right…
Research Recommendations – Guiding policy-makers for evidence-based decision making

Sign-up to read more
Subscribe for free to get unrestricted access to all our resources on research writing and academic publishing including:
- 2000+ blog articles
- 50+ Webinars
- 10+ Expert podcasts
- 50+ Infographics
- 10+ Checklists
- Research Guides
We hate spam too. We promise to protect your privacy and never spam you.
I am looking for Editing/ Proofreading services for my manuscript Tentative date of next journal submission:

As a researcher, what do you consider most when choosing an image manipulation detector?
Research Design 101
Everything You Need To Get Started (With Examples)
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) | Reviewers: Eunice Rautenbach (DTech) & Kerryn Warren (PhD) | April 2023

Navigating the world of research can be daunting, especially if you’re a first-time researcher. One concept you’re bound to run into fairly early in your research journey is that of “ research design ”. Here, we’ll guide you through the basics using practical examples , so that you can approach your research with confidence.
Overview: Research Design 101
What is research design.
- Research design types for quantitative studies
- Video explainer : quantitative research design
- Research design types for qualitative studies
- Video explainer : qualitative research design
- How to choose a research design
- Key takeaways
Research design refers to the overall plan, structure or strategy that guides a research project , from its conception to the final data analysis. A good research design serves as the blueprint for how you, as the researcher, will collect and analyse data while ensuring consistency, reliability and validity throughout your study.
Understanding different types of research designs is essential as helps ensure that your approach is suitable given your research aims, objectives and questions , as well as the resources you have available to you. Without a clear big-picture view of how you’ll design your research, you run the risk of potentially making misaligned choices in terms of your methodology – especially your sampling , data collection and data analysis decisions.
The problem with defining research design…
One of the reasons students struggle with a clear definition of research design is because the term is used very loosely across the internet, and even within academia.
Some sources claim that the three research design types are qualitative, quantitative and mixed methods , which isn’t quite accurate (these just refer to the type of data that you’ll collect and analyse). Other sources state that research design refers to the sum of all your design choices, suggesting it’s more like a research methodology . Others run off on other less common tangents. No wonder there’s confusion!
In this article, we’ll clear up the confusion. We’ll explain the most common research design types for both qualitative and quantitative research projects, whether that is for a full dissertation or thesis, or a smaller research paper or article.

Research Design: Quantitative Studies
Quantitative research involves collecting and analysing data in a numerical form. Broadly speaking, there are four types of quantitative research designs: descriptive , correlational , experimental , and quasi-experimental .
Descriptive Research Design
As the name suggests, descriptive research design focuses on describing existing conditions, behaviours, or characteristics by systematically gathering information without manipulating any variables. In other words, there is no intervention on the researcher’s part – only data collection.
For example, if you’re studying smartphone addiction among adolescents in your community, you could deploy a survey to a sample of teens asking them to rate their agreement with certain statements that relate to smartphone addiction. The collected data would then provide insight regarding how widespread the issue may be – in other words, it would describe the situation.
The key defining attribute of this type of research design is that it purely describes the situation . In other words, descriptive research design does not explore potential relationships between different variables or the causes that may underlie those relationships. Therefore, descriptive research is useful for generating insight into a research problem by describing its characteristics . By doing so, it can provide valuable insights and is often used as a precursor to other research design types.
Correlational Research Design
Correlational design is a popular choice for researchers aiming to identify and measure the relationship between two or more variables without manipulating them . In other words, this type of research design is useful when you want to know whether a change in one thing tends to be accompanied by a change in another thing.
For example, if you wanted to explore the relationship between exercise frequency and overall health, you could use a correlational design to help you achieve this. In this case, you might gather data on participants’ exercise habits, as well as records of their health indicators like blood pressure, heart rate, or body mass index. Thereafter, you’d use a statistical test to assess whether there’s a relationship between the two variables (exercise frequency and health).
As you can see, correlational research design is useful when you want to explore potential relationships between variables that cannot be manipulated or controlled for ethical, practical, or logistical reasons. It is particularly helpful in terms of developing predictions , and given that it doesn’t involve the manipulation of variables, it can be implemented at a large scale more easily than experimental designs (which will look at next).
That said, it’s important to keep in mind that correlational research design has limitations – most notably that it cannot be used to establish causality . In other words, correlation does not equal causation . To establish causality, you’ll need to move into the realm of experimental design, coming up next…
Need a helping hand?
Experimental Research Design
Experimental research design is used to determine if there is a causal relationship between two or more variables . With this type of research design, you, as the researcher, manipulate one variable (the independent variable) while controlling others (dependent variables). Doing so allows you to observe the effect of the former on the latter and draw conclusions about potential causality.
For example, if you wanted to measure if/how different types of fertiliser affect plant growth, you could set up several groups of plants, with each group receiving a different type of fertiliser, as well as one with no fertiliser at all. You could then measure how much each plant group grew (on average) over time and compare the results from the different groups to see which fertiliser was most effective.
Overall, experimental research design provides researchers with a powerful way to identify and measure causal relationships (and the direction of causality) between variables. However, developing a rigorous experimental design can be challenging as it’s not always easy to control all the variables in a study. This often results in smaller sample sizes , which can reduce the statistical power and generalisability of the results.
Moreover, experimental research design requires random assignment . This means that the researcher needs to assign participants to different groups or conditions in a way that each participant has an equal chance of being assigned to any group (note that this is not the same as random sampling ). Doing so helps reduce the potential for bias and confounding variables . This need for random assignment can lead to ethics-related issues . For example, withholding a potentially beneficial medical treatment from a control group may be considered unethical in certain situations.
Quasi-Experimental Research Design
Quasi-experimental research design is used when the research aims involve identifying causal relations , but one cannot (or doesn’t want to) randomly assign participants to different groups (for practical or ethical reasons). Instead, with a quasi-experimental research design, the researcher relies on existing groups or pre-existing conditions to form groups for comparison.
For example, if you were studying the effects of a new teaching method on student achievement in a particular school district, you may be unable to randomly assign students to either group and instead have to choose classes or schools that already use different teaching methods. This way, you still achieve separate groups, without having to assign participants to specific groups yourself.
Naturally, quasi-experimental research designs have limitations when compared to experimental designs. Given that participant assignment is not random, it’s more difficult to confidently establish causality between variables, and, as a researcher, you have less control over other variables that may impact findings.
All that said, quasi-experimental designs can still be valuable in research contexts where random assignment is not possible and can often be undertaken on a much larger scale than experimental research, thus increasing the statistical power of the results. What’s important is that you, as the researcher, understand the limitations of the design and conduct your quasi-experiment as rigorously as possible, paying careful attention to any potential confounding variables .

Research Design: Qualitative Studies
There are many different research design types when it comes to qualitative studies, but here we’ll narrow our focus to explore the “Big 4”. Specifically, we’ll look at phenomenological design, grounded theory design, ethnographic design, and case study design.
Phenomenological Research Design
Phenomenological design involves exploring the meaning of lived experiences and how they are perceived by individuals. This type of research design seeks to understand people’s perspectives , emotions, and behaviours in specific situations. Here, the aim for researchers is to uncover the essence of human experience without making any assumptions or imposing preconceived ideas on their subjects.
For example, you could adopt a phenomenological design to study why cancer survivors have such varied perceptions of their lives after overcoming their disease. This could be achieved by interviewing survivors and then analysing the data using a qualitative analysis method such as thematic analysis to identify commonalities and differences.
Phenomenological research design typically involves in-depth interviews or open-ended questionnaires to collect rich, detailed data about participants’ subjective experiences. This richness is one of the key strengths of phenomenological research design but, naturally, it also has limitations. These include potential biases in data collection and interpretation and the lack of generalisability of findings to broader populations.
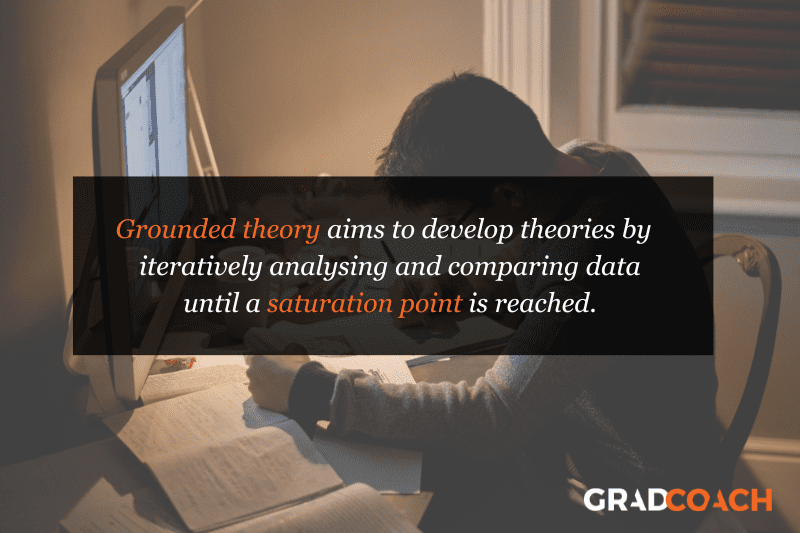
Grounded Theory Research Design
Grounded theory (also referred to as “GT”) aims to develop theories by continuously and iteratively analysing and comparing data collected from a relatively large number of participants in a study. It takes an inductive (bottom-up) approach, with a focus on letting the data “speak for itself”, without being influenced by preexisting theories or the researcher’s preconceptions.
As an example, let’s assume your research aims involved understanding how people cope with chronic pain from a specific medical condition, with a view to developing a theory around this. In this case, grounded theory design would allow you to explore this concept thoroughly without preconceptions about what coping mechanisms might exist. You may find that some patients prefer cognitive-behavioural therapy (CBT) while others prefer to rely on herbal remedies. Based on multiple, iterative rounds of analysis, you could then develop a theory in this regard, derived directly from the data (as opposed to other preexisting theories and models).
Grounded theory typically involves collecting data through interviews or observations and then analysing it to identify patterns and themes that emerge from the data. These emerging ideas are then validated by collecting more data until a saturation point is reached (i.e., no new information can be squeezed from the data). From that base, a theory can then be developed .
As you can see, grounded theory is ideally suited to studies where the research aims involve theory generation , especially in under-researched areas. Keep in mind though that this type of research design can be quite time-intensive , given the need for multiple rounds of data collection and analysis.
Ethnographic Research Design
Ethnographic design involves observing and studying a culture-sharing group of people in their natural setting to gain insight into their behaviours, beliefs, and values. The focus here is on observing participants in their natural environment (as opposed to a controlled environment). This typically involves the researcher spending an extended period of time with the participants in their environment, carefully observing and taking field notes .
All of this is not to say that ethnographic research design relies purely on observation. On the contrary, this design typically also involves in-depth interviews to explore participants’ views, beliefs, etc. However, unobtrusive observation is a core component of the ethnographic approach.
As an example, an ethnographer may study how different communities celebrate traditional festivals or how individuals from different generations interact with technology differently. This may involve a lengthy period of observation, combined with in-depth interviews to further explore specific areas of interest that emerge as a result of the observations that the researcher has made.
As you can probably imagine, ethnographic research design has the ability to provide rich, contextually embedded insights into the socio-cultural dynamics of human behaviour within a natural, uncontrived setting. Naturally, however, it does come with its own set of challenges, including researcher bias (since the researcher can become quite immersed in the group), participant confidentiality and, predictably, ethical complexities . All of these need to be carefully managed if you choose to adopt this type of research design.
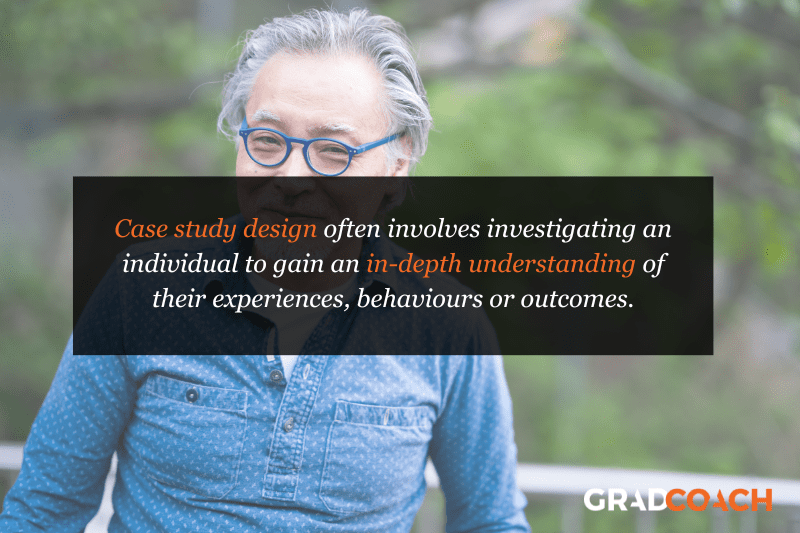
Case Study Design
With case study research design, you, as the researcher, investigate a single individual (or a single group of individuals) to gain an in-depth understanding of their experiences, behaviours or outcomes. Unlike other research designs that are aimed at larger sample sizes, case studies offer a deep dive into the specific circumstances surrounding a person, group of people, event or phenomenon, generally within a bounded setting or context .
As an example, a case study design could be used to explore the factors influencing the success of a specific small business. This would involve diving deeply into the organisation to explore and understand what makes it tick – from marketing to HR to finance. In terms of data collection, this could include interviews with staff and management, review of policy documents and financial statements, surveying customers, etc.
While the above example is focused squarely on one organisation, it’s worth noting that case study research designs can have different variation s, including single-case, multiple-case and longitudinal designs. As you can see in the example, a single-case design involves intensely examining a single entity to understand its unique characteristics and complexities. Conversely, in a multiple-case design , multiple cases are compared and contrasted to identify patterns and commonalities. Lastly, in a longitudinal case design , a single case or multiple cases are studied over an extended period of time to understand how factors develop over time.
As you can see, a case study research design is particularly useful where a deep and contextualised understanding of a specific phenomenon or issue is desired. However, this strength is also its weakness. In other words, you can’t generalise the findings from a case study to the broader population. So, keep this in mind if you’re considering going the case study route.
How To Choose A Research Design
Having worked through all of these potential research designs, you’d be forgiven for feeling a little overwhelmed and wondering, “ But how do I decide which research design to use? ”. While we could write an entire post covering that alone, here are a few factors to consider that will help you choose a suitable research design for your study.
Data type: The first determining factor is naturally the type of data you plan to be collecting – i.e., qualitative or quantitative. This may sound obvious, but we have to be clear about this – don’t try to use a quantitative research design on qualitative data (or vice versa)!
Research aim(s) and question(s): As with all methodological decisions, your research aim and research questions will heavily influence your research design. For example, if your research aims involve developing a theory from qualitative data, grounded theory would be a strong option. Similarly, if your research aims involve identifying and measuring relationships between variables, one of the experimental designs would likely be a better option.
Time: It’s essential that you consider any time constraints you have, as this will impact the type of research design you can choose. For example, if you’ve only got a month to complete your project, a lengthy design such as ethnography wouldn’t be a good fit.
Resources: Take into account the resources realistically available to you, as these need to factor into your research design choice. For example, if you require highly specialised lab equipment to execute an experimental design, you need to be sure that you’ll have access to that before you make a decision.
Keep in mind that when it comes to research, it’s important to manage your risks and play as conservatively as possible. If your entire project relies on you achieving a huge sample, having access to niche equipment or holding interviews with very difficult-to-reach participants, you’re creating risks that could kill your project. So, be sure to think through your choices carefully and make sure that you have backup plans for any existential risks. Remember that a relatively simple methodology executed well generally will typically earn better marks than a highly-complex methodology executed poorly.

Recap: Key Takeaways
We’ve covered a lot of ground here. Let’s recap by looking at the key takeaways:
- Research design refers to the overall plan, structure or strategy that guides a research project, from its conception to the final analysis of data.
- Research designs for quantitative studies include descriptive , correlational , experimental and quasi-experimenta l designs.
- Research designs for qualitative studies include phenomenological , grounded theory , ethnographic and case study designs.
- When choosing a research design, you need to consider a variety of factors, including the type of data you’ll be working with, your research aims and questions, your time and the resources available to you.
If you need a helping hand with your research design (or any other aspect of your research), check out our private coaching services .

Psst... there’s more!
This post was based on one of our popular Research Bootcamps . If you're working on a research project, you'll definitely want to check this out ...
You Might Also Like:

10 Comments
Is there any blog article explaining more on Case study research design? Is there a Case study write-up template? Thank you.
Thanks this was quite valuable to clarify such an important concept.
Thanks for this simplified explanations. it is quite very helpful.
This was really helpful. thanks
Thank you for your explanation. I think case study research design and the use of secondary data in researches needs to be talked about more in your videos and articles because there a lot of case studies research design tailored projects out there.
Please is there any template for a case study research design whose data type is a secondary data on your repository?
This post is very clear, comprehensive and has been very helpful to me. It has cleared the confusion I had in regard to research design and methodology.
This post is helpful, easy to understand, and deconstructs what a research design is. Thanks
how to cite this page
Thank you very much for the post. It is wonderful and has cleared many worries in my mind regarding research designs. I really appreciate .
how can I put this blog as my reference(APA style) in bibliography part?
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
- Experimental Research Designs: Types, Examples & Methods

Experimental research is the most familiar type of research design for individuals in the physical sciences and a host of other fields. This is mainly because experimental research is a classical scientific experiment, similar to those performed in high school science classes.
Imagine taking 2 samples of the same plant and exposing one of them to sunlight, while the other is kept away from sunlight. Let the plant exposed to sunlight be called sample A, while the latter is called sample B.
If after the duration of the research, we find out that sample A grows and sample B dies, even though they are both regularly wetted and given the same treatment. Therefore, we can conclude that sunlight will aid growth in all similar plants.
What is Experimental Research?
Experimental research is a scientific approach to research, where one or more independent variables are manipulated and applied to one or more dependent variables to measure their effect on the latter. The effect of the independent variables on the dependent variables is usually observed and recorded over some time, to aid researchers in drawing a reasonable conclusion regarding the relationship between these 2 variable types.
The experimental research method is widely used in physical and social sciences, psychology, and education. It is based on the comparison between two or more groups with a straightforward logic, which may, however, be difficult to execute.
Mostly related to a laboratory test procedure, experimental research designs involve collecting quantitative data and performing statistical analysis on them during research. Therefore, making it an example of quantitative research method .
What are The Types of Experimental Research Design?
The types of experimental research design are determined by the way the researcher assigns subjects to different conditions and groups. They are of 3 types, namely; pre-experimental, quasi-experimental, and true experimental research.
Pre-experimental Research Design
In pre-experimental research design, either a group or various dependent groups are observed for the effect of the application of an independent variable which is presumed to cause change. It is the simplest form of experimental research design and is treated with no control group.
Although very practical, experimental research is lacking in several areas of the true-experimental criteria. The pre-experimental research design is further divided into three types
- One-shot Case Study Research Design
In this type of experimental study, only one dependent group or variable is considered. The study is carried out after some treatment which was presumed to cause change, making it a posttest study.
- One-group Pretest-posttest Research Design:
This research design combines both posttest and pretest study by carrying out a test on a single group before the treatment is administered and after the treatment is administered. With the former being administered at the beginning of treatment and later at the end.
- Static-group Comparison:
In a static-group comparison study, 2 or more groups are placed under observation, where only one of the groups is subjected to some treatment while the other groups are held static. All the groups are post-tested, and the observed differences between the groups are assumed to be a result of the treatment.
Quasi-experimental Research Design
The word “quasi” means partial, half, or pseudo. Therefore, the quasi-experimental research bearing a resemblance to the true experimental research, but not the same. In quasi-experiments, the participants are not randomly assigned, and as such, they are used in settings where randomization is difficult or impossible.
This is very common in educational research, where administrators are unwilling to allow the random selection of students for experimental samples.
Some examples of quasi-experimental research design include; the time series, no equivalent control group design, and the counterbalanced design.
True Experimental Research Design
The true experimental research design relies on statistical analysis to approve or disprove a hypothesis. It is the most accurate type of experimental design and may be carried out with or without a pretest on at least 2 randomly assigned dependent subjects.
The true experimental research design must contain a control group, a variable that can be manipulated by the researcher, and the distribution must be random. The classification of true experimental design include:
- The posttest-only Control Group Design: In this design, subjects are randomly selected and assigned to the 2 groups (control and experimental), and only the experimental group is treated. After close observation, both groups are post-tested, and a conclusion is drawn from the difference between these groups.
- The pretest-posttest Control Group Design: For this control group design, subjects are randomly assigned to the 2 groups, both are presented, but only the experimental group is treated. After close observation, both groups are post-tested to measure the degree of change in each group.
- Solomon four-group Design: This is the combination of the pretest-only and the pretest-posttest control groups. In this case, the randomly selected subjects are placed into 4 groups.
The first two of these groups are tested using the posttest-only method, while the other two are tested using the pretest-posttest method.
Examples of Experimental Research
Experimental research examples are different, depending on the type of experimental research design that is being considered. The most basic example of experimental research is laboratory experiments, which may differ in nature depending on the subject of research.
Administering Exams After The End of Semester
During the semester, students in a class are lectured on particular courses and an exam is administered at the end of the semester. In this case, the students are the subjects or dependent variables while the lectures are the independent variables treated on the subjects.
Only one group of carefully selected subjects are considered in this research, making it a pre-experimental research design example. We will also notice that tests are only carried out at the end of the semester, and not at the beginning.
Further making it easy for us to conclude that it is a one-shot case study research.
Employee Skill Evaluation
Before employing a job seeker, organizations conduct tests that are used to screen out less qualified candidates from the pool of qualified applicants. This way, organizations can determine an employee’s skill set at the point of employment.
In the course of employment, organizations also carry out employee training to improve employee productivity and generally grow the organization. Further evaluation is carried out at the end of each training to test the impact of the training on employee skills, and test for improvement.
Here, the subject is the employee, while the treatment is the training conducted. This is a pretest-posttest control group experimental research example.
Evaluation of Teaching Method
Let us consider an academic institution that wants to evaluate the teaching method of 2 teachers to determine which is best. Imagine a case whereby the students assigned to each teacher is carefully selected probably due to personal request by parents or due to stubbornness and smartness.
This is a no equivalent group design example because the samples are not equal. By evaluating the effectiveness of each teacher’s teaching method this way, we may conclude after a post-test has been carried out.
However, this may be influenced by factors like the natural sweetness of a student. For example, a very smart student will grab more easily than his or her peers irrespective of the method of teaching.
What are the Characteristics of Experimental Research?
Experimental research contains dependent, independent and extraneous variables. The dependent variables are the variables being treated or manipulated and are sometimes called the subject of the research.
The independent variables are the experimental treatment being exerted on the dependent variables. Extraneous variables, on the other hand, are other factors affecting the experiment that may also contribute to the change.
The setting is where the experiment is carried out. Many experiments are carried out in the laboratory, where control can be exerted on the extraneous variables, thereby eliminating them.
Other experiments are carried out in a less controllable setting. The choice of setting used in research depends on the nature of the experiment being carried out.
- Multivariable
Experimental research may include multiple independent variables, e.g. time, skills, test scores, etc.
Why Use Experimental Research Design?
Experimental research design can be majorly used in physical sciences, social sciences, education, and psychology. It is used to make predictions and draw conclusions on a subject matter.
Some uses of experimental research design are highlighted below.
- Medicine: Experimental research is used to provide the proper treatment for diseases. In most cases, rather than directly using patients as the research subject, researchers take a sample of the bacteria from the patient’s body and are treated with the developed antibacterial
The changes observed during this period are recorded and evaluated to determine its effectiveness. This process can be carried out using different experimental research methods.
- Education: Asides from science subjects like Chemistry and Physics which involves teaching students how to perform experimental research, it can also be used in improving the standard of an academic institution. This includes testing students’ knowledge on different topics, coming up with better teaching methods, and the implementation of other programs that will aid student learning.
- Human Behavior: Social scientists are the ones who mostly use experimental research to test human behaviour. For example, consider 2 people randomly chosen to be the subject of the social interaction research where one person is placed in a room without human interaction for 1 year.
The other person is placed in a room with a few other people, enjoying human interaction. There will be a difference in their behaviour at the end of the experiment.
- UI/UX: During the product development phase, one of the major aims of the product team is to create a great user experience with the product. Therefore, before launching the final product design, potential are brought in to interact with the product.
For example, when finding it difficult to choose how to position a button or feature on the app interface, a random sample of product testers are allowed to test the 2 samples and how the button positioning influences the user interaction is recorded.
What are the Disadvantages of Experimental Research?
- It is highly prone to human error due to its dependency on variable control which may not be properly implemented. These errors could eliminate the validity of the experiment and the research being conducted.
- Exerting control of extraneous variables may create unrealistic situations. Eliminating real-life variables will result in inaccurate conclusions. This may also result in researchers controlling the variables to suit his or her personal preferences.
- It is a time-consuming process. So much time is spent on testing dependent variables and waiting for the effect of the manipulation of dependent variables to manifest.
- It is expensive.
- It is very risky and may have ethical complications that cannot be ignored. This is common in medical research, where failed trials may lead to a patient’s death or a deteriorating health condition.
- Experimental research results are not descriptive.
- Response bias can also be supplied by the subject of the conversation.
- Human responses in experimental research can be difficult to measure.
What are the Data Collection Methods in Experimental Research?
Data collection methods in experimental research are the different ways in which data can be collected for experimental research. They are used in different cases, depending on the type of research being carried out.
1. Observational Study
This type of study is carried out over a long period. It measures and observes the variables of interest without changing existing conditions.
When researching the effect of social interaction on human behavior, the subjects who are placed in 2 different environments are observed throughout the research. No matter the kind of absurd behavior that is exhibited by the subject during this period, its condition will not be changed.
This may be a very risky thing to do in medical cases because it may lead to death or worse medical conditions.
2. Simulations
This procedure uses mathematical, physical, or computer models to replicate a real-life process or situation. It is frequently used when the actual situation is too expensive, dangerous, or impractical to replicate in real life.
This method is commonly used in engineering and operational research for learning purposes and sometimes as a tool to estimate possible outcomes of real research. Some common situation software are Simulink, MATLAB, and Simul8.
Not all kinds of experimental research can be carried out using simulation as a data collection tool . It is very impractical for a lot of laboratory-based research that involves chemical processes.
A survey is a tool used to gather relevant data about the characteristics of a population and is one of the most common data collection tools. A survey consists of a group of questions prepared by the researcher, to be answered by the research subject.
Surveys can be shared with the respondents both physically and electronically. When collecting data through surveys, the kind of data collected depends on the respondent, and researchers have limited control over it.
Formplus is the best tool for collecting experimental data using survey s. It has relevant features that will aid the data collection process and can also be used in other aspects of experimental research.
Differences between Experimental and Non-Experimental Research
1. In experimental research, the researcher can control and manipulate the environment of the research, including the predictor variable which can be changed. On the other hand, non-experimental research cannot be controlled or manipulated by the researcher at will.
This is because it takes place in a real-life setting, where extraneous variables cannot be eliminated. Therefore, it is more difficult to conclude non-experimental studies, even though they are much more flexible and allow for a greater range of study fields.
2. The relationship between cause and effect cannot be established in non-experimental research, while it can be established in experimental research. This may be because many extraneous variables also influence the changes in the research subject, making it difficult to point at a particular variable as the cause of a particular change
3. Independent variables are not introduced, withdrawn, or manipulated in non-experimental designs, but the same may not be said about experimental research.
Conclusion
Experimental research designs are often considered to be the standard in research designs. This is partly due to the common misconception that research is equivalent to scientific experiments—a component of experimental research design.
In this research design, one or more subjects or dependent variables are randomly assigned to different treatments (i.e. independent variables manipulated by the researcher) and the results are observed to conclude. One of the uniqueness of experimental research is in its ability to control the effect of extraneous variables.
Experimental research is suitable for research whose goal is to examine cause-effect relationships, e.g. explanatory research. It can be conducted in the laboratory or field settings, depending on the aim of the research that is being carried out.

Connect to Formplus, Get Started Now - It's Free!
- examples of experimental research
- experimental research methods
- types of experimental research
- busayo.longe

You may also like:
Experimental Vs Non-Experimental Research: 15 Key Differences
Differences between experimental and non experimental research on definitions, types, examples, data collection tools, uses, advantages etc.

Response vs Explanatory Variables: Definition & Examples
In this article, we’ll be comparing the two types of variables, what they both mean and see some of their real-life applications in research
What is Experimenter Bias? Definition, Types & Mitigation
In this article, we will look into the concept of experimental bias and how it can be identified in your research
Simpson’s Paradox & How to Avoid it in Experimental Research
In this article, we are going to look at Simpson’s Paradox from its historical point and later, we’ll consider its effect in...
Formplus - For Seamless Data Collection
Collect data the right way with a versatile data collection tool. try formplus and transform your work productivity today..
Experimental Design: Types, Examples & Methods
Saul Mcleod, PhD
Editor-in-Chief for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MRes, PhD, University of Manchester
Saul Mcleod, PhD., is a qualified psychology teacher with over 18 years of experience in further and higher education. He has been published in peer-reviewed journals, including the Journal of Clinical Psychology.
Learn about our Editorial Process
Olivia Guy-Evans, MSc
Associate Editor for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MSc Psychology of Education
Olivia Guy-Evans is a writer and associate editor for Simply Psychology. She has previously worked in healthcare and educational sectors.
On This Page:
Experimental design refers to how participants are allocated to different groups in an experiment. Types of design include repeated measures, independent groups, and matched pairs designs.
Probably the most common way to design an experiment in psychology is to divide the participants into two groups, the experimental group and the control group, and then introduce a change to the experimental group, not the control group.
The researcher must decide how he/she will allocate their sample to the different experimental groups. For example, if there are 10 participants, will all 10 participants participate in both groups (e.g., repeated measures), or will the participants be split in half and take part in only one group each?
Three types of experimental designs are commonly used:
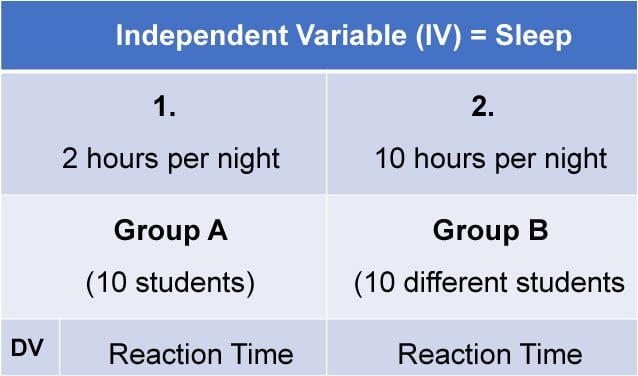
1. Independent Measures
Independent measures design, also known as between-groups , is an experimental design where different participants are used in each condition of the independent variable. This means that each condition of the experiment includes a different group of participants.
This should be done by random allocation, ensuring that each participant has an equal chance of being assigned to one group.
Independent measures involve using two separate groups of participants, one in each condition. For example:
- Con : More people are needed than with the repeated measures design (i.e., more time-consuming).
- Pro : Avoids order effects (such as practice or fatigue) as people participate in one condition only. If a person is involved in several conditions, they may become bored, tired, and fed up by the time they come to the second condition or become wise to the requirements of the experiment!
- Con : Differences between participants in the groups may affect results, for example, variations in age, gender, or social background. These differences are known as participant variables (i.e., a type of extraneous variable ).
- Control : After the participants have been recruited, they should be randomly assigned to their groups. This should ensure the groups are similar, on average (reducing participant variables).
2. Repeated Measures Design
Repeated Measures design is an experimental design where the same participants participate in each independent variable condition. This means that each experiment condition includes the same group of participants.
Repeated Measures design is also known as within-groups or within-subjects design .
- Pro : As the same participants are used in each condition, participant variables (i.e., individual differences) are reduced.
- Con : There may be order effects. Order effects refer to the order of the conditions affecting the participants’ behavior. Performance in the second condition may be better because the participants know what to do (i.e., practice effect). Or their performance might be worse in the second condition because they are tired (i.e., fatigue effect). This limitation can be controlled using counterbalancing.
- Pro : Fewer people are needed as they participate in all conditions (i.e., saves time).
- Control : To combat order effects, the researcher counter-balances the order of the conditions for the participants. Alternating the order in which participants perform in different conditions of an experiment.
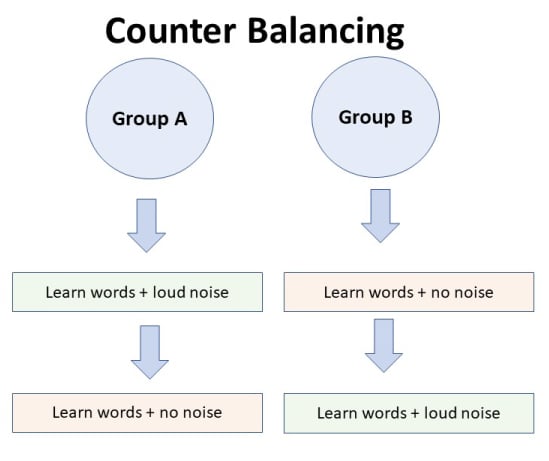
Counterbalancing
Suppose we used a repeated measures design in which all of the participants first learned words in “loud noise” and then learned them in “no noise.”
We expect the participants to learn better in “no noise” because of order effects, such as practice. However, a researcher can control for order effects using counterbalancing.
The sample would be split into two groups: experimental (A) and control (B). For example, group 1 does ‘A’ then ‘B,’ and group 2 does ‘B’ then ‘A.’ This is to eliminate order effects.
Although order effects occur for each participant, they balance each other out in the results because they occur equally in both groups.
3. Matched Pairs Design
A matched pairs design is an experimental design where pairs of participants are matched in terms of key variables, such as age or socioeconomic status. One member of each pair is then placed into the experimental group and the other member into the control group .
One member of each matched pair must be randomly assigned to the experimental group and the other to the control group.
- Con : If one participant drops out, you lose 2 PPs’ data.
- Pro : Reduces participant variables because the researcher has tried to pair up the participants so that each condition has people with similar abilities and characteristics.
- Con : Very time-consuming trying to find closely matched pairs.
- Pro : It avoids order effects, so counterbalancing is not necessary.
- Con : Impossible to match people exactly unless they are identical twins!
- Control : Members of each pair should be randomly assigned to conditions. However, this does not solve all these problems.
Experimental design refers to how participants are allocated to an experiment’s different conditions (or IV levels). There are three types:
1. Independent measures / between-groups : Different participants are used in each condition of the independent variable.
2. Repeated measures /within groups : The same participants take part in each condition of the independent variable.
3. Matched pairs : Each condition uses different participants, but they are matched in terms of important characteristics, e.g., gender, age, intelligence, etc.
Learning Check
Read about each of the experiments below. For each experiment, identify (1) which experimental design was used; and (2) why the researcher might have used that design.
1 . To compare the effectiveness of two different types of therapy for depression, depressed patients were assigned to receive either cognitive therapy or behavior therapy for a 12-week period.
The researchers attempted to ensure that the patients in the two groups had similar severity of depressed symptoms by administering a standardized test of depression to each participant, then pairing them according to the severity of their symptoms.
2 . To assess the difference in reading comprehension between 7 and 9-year-olds, a researcher recruited each group from a local primary school. They were given the same passage of text to read and then asked a series of questions to assess their understanding.
3 . To assess the effectiveness of two different ways of teaching reading, a group of 5-year-olds was recruited from a primary school. Their level of reading ability was assessed, and then they were taught using scheme one for 20 weeks.
At the end of this period, their reading was reassessed, and a reading improvement score was calculated. They were then taught using scheme two for a further 20 weeks, and another reading improvement score for this period was calculated. The reading improvement scores for each child were then compared.
4 . To assess the effect of the organization on recall, a researcher randomly assigned student volunteers to two conditions.
Condition one attempted to recall a list of words that were organized into meaningful categories; condition two attempted to recall the same words, randomly grouped on the page.
Experiment Terminology
Ecological validity.
The degree to which an investigation represents real-life experiences.
Experimenter effects
These are the ways that the experimenter can accidentally influence the participant through their appearance or behavior.
Demand characteristics
The clues in an experiment lead the participants to think they know what the researcher is looking for (e.g., the experimenter’s body language).
Independent variable (IV)
The variable the experimenter manipulates (i.e., changes) is assumed to have a direct effect on the dependent variable.
Dependent variable (DV)
Variable the experimenter measures. This is the outcome (i.e., the result) of a study.
Extraneous variables (EV)
All variables which are not independent variables but could affect the results (DV) of the experiment. Extraneous variables should be controlled where possible.
Confounding variables
Variable(s) that have affected the results (DV), apart from the IV. A confounding variable could be an extraneous variable that has not been controlled.
Random Allocation
Randomly allocating participants to independent variable conditions means that all participants should have an equal chance of taking part in each condition.
The principle of random allocation is to avoid bias in how the experiment is carried out and limit the effects of participant variables.
Order effects
Changes in participants’ performance due to their repeating the same or similar test more than once. Examples of order effects include:
(i) practice effect: an improvement in performance on a task due to repetition, for example, because of familiarity with the task;
(ii) fatigue effect: a decrease in performance of a task due to repetition, for example, because of boredom or tiredness.
Related Articles

Research Methodology
Qualitative Data Coding

What Is a Focus Group?

Cross-Cultural Research Methodology In Psychology

What Is Internal Validity In Research?

Research Methodology , Statistics
What Is Face Validity In Research? Importance & How To Measure

Criterion Validity: Definition & Examples
- USC Libraries
- Research Guides
Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Paper
- Types of Research Designs
- Purpose of Guide
- Design Flaws to Avoid
- Independent and Dependent Variables
- Glossary of Research Terms
- Reading Research Effectively
- Narrowing a Topic Idea
- Broadening a Topic Idea
- Extending the Timeliness of a Topic Idea
- Academic Writing Style
- Applying Critical Thinking
- Choosing a Title
- Making an Outline
- Paragraph Development
- Research Process Video Series
- Executive Summary
- The C.A.R.S. Model
- Background Information
- The Research Problem/Question
- Theoretical Framework
- Citation Tracking
- Content Alert Services
- Evaluating Sources
- Primary Sources
- Secondary Sources
- Tiertiary Sources
- Scholarly vs. Popular Publications
- Qualitative Methods
- Quantitative Methods
- Insiderness
- Using Non-Textual Elements
- Limitations of the Study
- Common Grammar Mistakes
- Writing Concisely
- Avoiding Plagiarism
- Footnotes or Endnotes?
- Further Readings
- Generative AI and Writing
- USC Libraries Tutorials and Other Guides
- Bibliography
Introduction
Before beginning your paper, you need to decide how you plan to design the study .
The research design refers to the overall strategy and analytical approach that you have chosen in order to integrate, in a coherent and logical way, the different components of the study, thus ensuring that the research problem will be thoroughly investigated. It constitutes the blueprint for the collection, measurement, and interpretation of information and data. Note that the research problem determines the type of design you choose, not the other way around!
De Vaus, D. A. Research Design in Social Research . London: SAGE, 2001; Trochim, William M.K. Research Methods Knowledge Base. 2006.
General Structure and Writing Style
The function of a research design is to ensure that the evidence obtained enables you to effectively address the research problem logically and as unambiguously as possible . In social sciences research, obtaining information relevant to the research problem generally entails specifying the type of evidence needed to test the underlying assumptions of a theory, to evaluate a program, or to accurately describe and assess meaning related to an observable phenomenon.
With this in mind, a common mistake made by researchers is that they begin their investigations before they have thought critically about what information is required to address the research problem. Without attending to these design issues beforehand, the overall research problem will not be adequately addressed and any conclusions drawn will run the risk of being weak and unconvincing. As a consequence, the overall validity of the study will be undermined.
The length and complexity of describing the research design in your paper can vary considerably, but any well-developed description will achieve the following :
- Identify the research problem clearly and justify its selection, particularly in relation to any valid alternative designs that could have been used,
- Review and synthesize previously published literature associated with the research problem,
- Clearly and explicitly specify hypotheses [i.e., research questions] central to the problem,
- Effectively describe the information and/or data which will be necessary for an adequate testing of the hypotheses and explain how such information and/or data will be obtained, and
- Describe the methods of analysis to be applied to the data in determining whether or not the hypotheses are true or false.
The research design is usually incorporated into the introduction of your paper . You can obtain an overall sense of what to do by reviewing studies that have utilized the same research design [e.g., using a case study approach]. This can help you develop an outline to follow for your own paper.
NOTE : Use the SAGE Research Methods Online and Cases and the SAGE Research Methods Videos databases to search for scholarly resources on how to apply specific research designs and methods . The Research Methods Online database contains links to more than 175,000 pages of SAGE publisher's book, journal, and reference content on quantitative, qualitative, and mixed research methodologies. Also included is a collection of case studies of social research projects that can be used to help you better understand abstract or complex methodological concepts. The Research Methods Videos database contains hours of tutorials, interviews, video case studies, and mini-documentaries covering the entire research process.
Creswell, John W. and J. David Creswell. Research Design: Qualitative, Quantitative, and Mixed Methods Approaches . 5th edition. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2018; De Vaus, D. A. Research Design in Social Research . London: SAGE, 2001; Gorard, Stephen. Research Design: Creating Robust Approaches for the Social Sciences . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2013; Leedy, Paul D. and Jeanne Ellis Ormrod. Practical Research: Planning and Design . Tenth edition. Boston, MA: Pearson, 2013; Vogt, W. Paul, Dianna C. Gardner, and Lynne M. Haeffele. When to Use What Research Design . New York: Guilford, 2012.
Action Research Design
Definition and Purpose
The essentials of action research design follow a characteristic cycle whereby initially an exploratory stance is adopted, where an understanding of a problem is developed and plans are made for some form of interventionary strategy. Then the intervention is carried out [the "action" in action research] during which time, pertinent observations are collected in various forms. The new interventional strategies are carried out, and this cyclic process repeats, continuing until a sufficient understanding of [or a valid implementation solution for] the problem is achieved. The protocol is iterative or cyclical in nature and is intended to foster deeper understanding of a given situation, starting with conceptualizing and particularizing the problem and moving through several interventions and evaluations.
What do these studies tell you ?
- This is a collaborative and adaptive research design that lends itself to use in work or community situations.
- Design focuses on pragmatic and solution-driven research outcomes rather than testing theories.
- When practitioners use action research, it has the potential to increase the amount they learn consciously from their experience; the action research cycle can be regarded as a learning cycle.
- Action research studies often have direct and obvious relevance to improving practice and advocating for change.
- There are no hidden controls or preemption of direction by the researcher.
What these studies don't tell you ?
- It is harder to do than conducting conventional research because the researcher takes on responsibilities of advocating for change as well as for researching the topic.
- Action research is much harder to write up because it is less likely that you can use a standard format to report your findings effectively [i.e., data is often in the form of stories or observation].
- Personal over-involvement of the researcher may bias research results.
- The cyclic nature of action research to achieve its twin outcomes of action [e.g. change] and research [e.g. understanding] is time-consuming and complex to conduct.
- Advocating for change usually requires buy-in from study participants.
Coghlan, David and Mary Brydon-Miller. The Sage Encyclopedia of Action Research . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2014; Efron, Sara Efrat and Ruth Ravid. Action Research in Education: A Practical Guide . New York: Guilford, 2013; Gall, Meredith. Educational Research: An Introduction . Chapter 18, Action Research. 8th ed. Boston, MA: Pearson/Allyn and Bacon, 2007; Gorard, Stephen. Research Design: Creating Robust Approaches for the Social Sciences . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2013; Kemmis, Stephen and Robin McTaggart. “Participatory Action Research.” In Handbook of Qualitative Research . Norman Denzin and Yvonna S. Lincoln, eds. 2nd ed. (Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE, 2000), pp. 567-605; McNiff, Jean. Writing and Doing Action Research . London: Sage, 2014; Reason, Peter and Hilary Bradbury. Handbook of Action Research: Participative Inquiry and Practice . Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE, 2001.
Case Study Design
A case study is an in-depth study of a particular research problem rather than a sweeping statistical survey or comprehensive comparative inquiry. It is often used to narrow down a very broad field of research into one or a few easily researchable examples. The case study research design is also useful for testing whether a specific theory and model actually applies to phenomena in the real world. It is a useful design when not much is known about an issue or phenomenon.
- Approach excels at bringing us to an understanding of a complex issue through detailed contextual analysis of a limited number of events or conditions and their relationships.
- A researcher using a case study design can apply a variety of methodologies and rely on a variety of sources to investigate a research problem.
- Design can extend experience or add strength to what is already known through previous research.
- Social scientists, in particular, make wide use of this research design to examine contemporary real-life situations and provide the basis for the application of concepts and theories and the extension of methodologies.
- The design can provide detailed descriptions of specific and rare cases.
- A single or small number of cases offers little basis for establishing reliability or to generalize the findings to a wider population of people, places, or things.
- Intense exposure to the study of a case may bias a researcher's interpretation of the findings.
- Design does not facilitate assessment of cause and effect relationships.
- Vital information may be missing, making the case hard to interpret.
- The case may not be representative or typical of the larger problem being investigated.
- If the criteria for selecting a case is because it represents a very unusual or unique phenomenon or problem for study, then your interpretation of the findings can only apply to that particular case.
Case Studies. Writing@CSU. Colorado State University; Anastas, Jeane W. Research Design for Social Work and the Human Services . Chapter 4, Flexible Methods: Case Study Design. 2nd ed. New York: Columbia University Press, 1999; Gerring, John. “What Is a Case Study and What Is It Good for?” American Political Science Review 98 (May 2004): 341-354; Greenhalgh, Trisha, editor. Case Study Evaluation: Past, Present and Future Challenges . Bingley, UK: Emerald Group Publishing, 2015; Mills, Albert J. , Gabrielle Durepos, and Eiden Wiebe, editors. Encyclopedia of Case Study Research . Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publications, 2010; Stake, Robert E. The Art of Case Study Research . Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE, 1995; Yin, Robert K. Case Study Research: Design and Theory . Applied Social Research Methods Series, no. 5. 3rd ed. Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE, 2003.
Causal Design
Causality studies may be thought of as understanding a phenomenon in terms of conditional statements in the form, “If X, then Y.” This type of research is used to measure what impact a specific change will have on existing norms and assumptions. Most social scientists seek causal explanations that reflect tests of hypotheses. Causal effect (nomothetic perspective) occurs when variation in one phenomenon, an independent variable, leads to or results, on average, in variation in another phenomenon, the dependent variable.
Conditions necessary for determining causality:
- Empirical association -- a valid conclusion is based on finding an association between the independent variable and the dependent variable.
- Appropriate time order -- to conclude that causation was involved, one must see that cases were exposed to variation in the independent variable before variation in the dependent variable.
- Nonspuriousness -- a relationship between two variables that is not due to variation in a third variable.
- Causality research designs assist researchers in understanding why the world works the way it does through the process of proving a causal link between variables and by the process of eliminating other possibilities.
- Replication is possible.
- There is greater confidence the study has internal validity due to the systematic subject selection and equity of groups being compared.
- Not all relationships are causal! The possibility always exists that, by sheer coincidence, two unrelated events appear to be related [e.g., Punxatawney Phil could accurately predict the duration of Winter for five consecutive years but, the fact remains, he's just a big, furry rodent].
- Conclusions about causal relationships are difficult to determine due to a variety of extraneous and confounding variables that exist in a social environment. This means causality can only be inferred, never proven.
- If two variables are correlated, the cause must come before the effect. However, even though two variables might be causally related, it can sometimes be difficult to determine which variable comes first and, therefore, to establish which variable is the actual cause and which is the actual effect.
Beach, Derek and Rasmus Brun Pedersen. Causal Case Study Methods: Foundations and Guidelines for Comparing, Matching, and Tracing . Ann Arbor, MI: University of Michigan Press, 2016; Bachman, Ronet. The Practice of Research in Criminology and Criminal Justice . Chapter 5, Causation and Research Designs. 3rd ed. Thousand Oaks, CA: Pine Forge Press, 2007; Brewer, Ernest W. and Jennifer Kubn. “Causal-Comparative Design.” In Encyclopedia of Research Design . Neil J. Salkind, editor. (Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2010), pp. 125-132; Causal Research Design: Experimentation. Anonymous SlideShare Presentation; Gall, Meredith. Educational Research: An Introduction . Chapter 11, Nonexperimental Research: Correlational Designs. 8th ed. Boston, MA: Pearson/Allyn and Bacon, 2007; Trochim, William M.K. Research Methods Knowledge Base. 2006.
Cohort Design
Often used in the medical sciences, but also found in the applied social sciences, a cohort study generally refers to a study conducted over a period of time involving members of a population which the subject or representative member comes from, and who are united by some commonality or similarity. Using a quantitative framework, a cohort study makes note of statistical occurrence within a specialized subgroup, united by same or similar characteristics that are relevant to the research problem being investigated, rather than studying statistical occurrence within the general population. Using a qualitative framework, cohort studies generally gather data using methods of observation. Cohorts can be either "open" or "closed."
- Open Cohort Studies [dynamic populations, such as the population of Los Angeles] involve a population that is defined just by the state of being a part of the study in question (and being monitored for the outcome). Date of entry and exit from the study is individually defined, therefore, the size of the study population is not constant. In open cohort studies, researchers can only calculate rate based data, such as, incidence rates and variants thereof.
- Closed Cohort Studies [static populations, such as patients entered into a clinical trial] involve participants who enter into the study at one defining point in time and where it is presumed that no new participants can enter the cohort. Given this, the number of study participants remains constant (or can only decrease).
- The use of cohorts is often mandatory because a randomized control study may be unethical. For example, you cannot deliberately expose people to asbestos, you can only study its effects on those who have already been exposed. Research that measures risk factors often relies upon cohort designs.
- Because cohort studies measure potential causes before the outcome has occurred, they can demonstrate that these “causes” preceded the outcome, thereby avoiding the debate as to which is the cause and which is the effect.
- Cohort analysis is highly flexible and can provide insight into effects over time and related to a variety of different types of changes [e.g., social, cultural, political, economic, etc.].
- Either original data or secondary data can be used in this design.
- In cases where a comparative analysis of two cohorts is made [e.g., studying the effects of one group exposed to asbestos and one that has not], a researcher cannot control for all other factors that might differ between the two groups. These factors are known as confounding variables.
- Cohort studies can end up taking a long time to complete if the researcher must wait for the conditions of interest to develop within the group. This also increases the chance that key variables change during the course of the study, potentially impacting the validity of the findings.
- Due to the lack of randominization in the cohort design, its external validity is lower than that of study designs where the researcher randomly assigns participants.
Healy P, Devane D. “Methodological Considerations in Cohort Study Designs.” Nurse Researcher 18 (2011): 32-36; Glenn, Norval D, editor. Cohort Analysis . 2nd edition. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2005; Levin, Kate Ann. Study Design IV: Cohort Studies. Evidence-Based Dentistry 7 (2003): 51–52; Payne, Geoff. “Cohort Study.” In The SAGE Dictionary of Social Research Methods . Victor Jupp, editor. (Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2006), pp. 31-33; Study Design 101. Himmelfarb Health Sciences Library. George Washington University, November 2011; Cohort Study. Wikipedia.
Cross-Sectional Design
Cross-sectional research designs have three distinctive features: no time dimension; a reliance on existing differences rather than change following intervention; and, groups are selected based on existing differences rather than random allocation. The cross-sectional design can only measure differences between or from among a variety of people, subjects, or phenomena rather than a process of change. As such, researchers using this design can only employ a relatively passive approach to making causal inferences based on findings.
- Cross-sectional studies provide a clear 'snapshot' of the outcome and the characteristics associated with it, at a specific point in time.
- Unlike an experimental design, where there is an active intervention by the researcher to produce and measure change or to create differences, cross-sectional designs focus on studying and drawing inferences from existing differences between people, subjects, or phenomena.
- Entails collecting data at and concerning one point in time. While longitudinal studies involve taking multiple measures over an extended period of time, cross-sectional research is focused on finding relationships between variables at one moment in time.
- Groups identified for study are purposely selected based upon existing differences in the sample rather than seeking random sampling.
- Cross-section studies are capable of using data from a large number of subjects and, unlike observational studies, is not geographically bound.
- Can estimate prevalence of an outcome of interest because the sample is usually taken from the whole population.
- Because cross-sectional designs generally use survey techniques to gather data, they are relatively inexpensive and take up little time to conduct.
- Finding people, subjects, or phenomena to study that are very similar except in one specific variable can be difficult.
- Results are static and time bound and, therefore, give no indication of a sequence of events or reveal historical or temporal contexts.
- Studies cannot be utilized to establish cause and effect relationships.
- This design only provides a snapshot of analysis so there is always the possibility that a study could have differing results if another time-frame had been chosen.
- There is no follow up to the findings.
Bethlehem, Jelke. "7: Cross-sectional Research." In Research Methodology in the Social, Behavioural and Life Sciences . Herman J Adèr and Gideon J Mellenbergh, editors. (London, England: Sage, 1999), pp. 110-43; Bourque, Linda B. “Cross-Sectional Design.” In The SAGE Encyclopedia of Social Science Research Methods . Michael S. Lewis-Beck, Alan Bryman, and Tim Futing Liao. (Thousand Oaks, CA: 2004), pp. 230-231; Hall, John. “Cross-Sectional Survey Design.” In Encyclopedia of Survey Research Methods . Paul J. Lavrakas, ed. (Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2008), pp. 173-174; Helen Barratt, Maria Kirwan. Cross-Sectional Studies: Design Application, Strengths and Weaknesses of Cross-Sectional Studies. Healthknowledge, 2009. Cross-Sectional Study. Wikipedia.
Descriptive Design
Descriptive research designs help provide answers to the questions of who, what, when, where, and how associated with a particular research problem; a descriptive study cannot conclusively ascertain answers to why. Descriptive research is used to obtain information concerning the current status of the phenomena and to describe "what exists" with respect to variables or conditions in a situation.
- The subject is being observed in a completely natural and unchanged natural environment. True experiments, whilst giving analyzable data, often adversely influence the normal behavior of the subject [a.k.a., the Heisenberg effect whereby measurements of certain systems cannot be made without affecting the systems].
- Descriptive research is often used as a pre-cursor to more quantitative research designs with the general overview giving some valuable pointers as to what variables are worth testing quantitatively.
- If the limitations are understood, they can be a useful tool in developing a more focused study.
- Descriptive studies can yield rich data that lead to important recommendations in practice.
- Appoach collects a large amount of data for detailed analysis.
- The results from a descriptive research cannot be used to discover a definitive answer or to disprove a hypothesis.
- Because descriptive designs often utilize observational methods [as opposed to quantitative methods], the results cannot be replicated.
- The descriptive function of research is heavily dependent on instrumentation for measurement and observation.
Anastas, Jeane W. Research Design for Social Work and the Human Services . Chapter 5, Flexible Methods: Descriptive Research. 2nd ed. New York: Columbia University Press, 1999; Given, Lisa M. "Descriptive Research." In Encyclopedia of Measurement and Statistics . Neil J. Salkind and Kristin Rasmussen, editors. (Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2007), pp. 251-254; McNabb, Connie. Descriptive Research Methodologies. Powerpoint Presentation; Shuttleworth, Martyn. Descriptive Research Design, September 26, 2008; Erickson, G. Scott. "Descriptive Research Design." In New Methods of Market Research and Analysis . (Northampton, MA: Edward Elgar Publishing, 2017), pp. 51-77; Sahin, Sagufta, and Jayanta Mete. "A Brief Study on Descriptive Research: Its Nature and Application in Social Science." International Journal of Research and Analysis in Humanities 1 (2021): 11; K. Swatzell and P. Jennings. “Descriptive Research: The Nuts and Bolts.” Journal of the American Academy of Physician Assistants 20 (2007), pp. 55-56; Kane, E. Doing Your Own Research: Basic Descriptive Research in the Social Sciences and Humanities . London: Marion Boyars, 1985.
Experimental Design
A blueprint of the procedure that enables the researcher to maintain control over all factors that may affect the result of an experiment. In doing this, the researcher attempts to determine or predict what may occur. Experimental research is often used where there is time priority in a causal relationship (cause precedes effect), there is consistency in a causal relationship (a cause will always lead to the same effect), and the magnitude of the correlation is great. The classic experimental design specifies an experimental group and a control group. The independent variable is administered to the experimental group and not to the control group, and both groups are measured on the same dependent variable. Subsequent experimental designs have used more groups and more measurements over longer periods. True experiments must have control, randomization, and manipulation.
- Experimental research allows the researcher to control the situation. In so doing, it allows researchers to answer the question, “What causes something to occur?”
- Permits the researcher to identify cause and effect relationships between variables and to distinguish placebo effects from treatment effects.
- Experimental research designs support the ability to limit alternative explanations and to infer direct causal relationships in the study.
- Approach provides the highest level of evidence for single studies.
- The design is artificial, and results may not generalize well to the real world.
- The artificial settings of experiments may alter the behaviors or responses of participants.
- Experimental designs can be costly if special equipment or facilities are needed.
- Some research problems cannot be studied using an experiment because of ethical or technical reasons.
- Difficult to apply ethnographic and other qualitative methods to experimentally designed studies.
Anastas, Jeane W. Research Design for Social Work and the Human Services . Chapter 7, Flexible Methods: Experimental Research. 2nd ed. New York: Columbia University Press, 1999; Chapter 2: Research Design, Experimental Designs. School of Psychology, University of New England, 2000; Chow, Siu L. "Experimental Design." In Encyclopedia of Research Design . Neil J. Salkind, editor. (Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2010), pp. 448-453; "Experimental Design." In Social Research Methods . Nicholas Walliman, editor. (London, England: Sage, 2006), pp, 101-110; Experimental Research. Research Methods by Dummies. Department of Psychology. California State University, Fresno, 2006; Kirk, Roger E. Experimental Design: Procedures for the Behavioral Sciences . 4th edition. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2013; Trochim, William M.K. Experimental Design. Research Methods Knowledge Base. 2006; Rasool, Shafqat. Experimental Research. Slideshare presentation.
Exploratory Design
An exploratory design is conducted about a research problem when there are few or no earlier studies to refer to or rely upon to predict an outcome . The focus is on gaining insights and familiarity for later investigation or undertaken when research problems are in a preliminary stage of investigation. Exploratory designs are often used to establish an understanding of how best to proceed in studying an issue or what methodology would effectively apply to gathering information about the issue.
The goals of exploratory research are intended to produce the following possible insights:
- Familiarity with basic details, settings, and concerns.
- Well grounded picture of the situation being developed.
- Generation of new ideas and assumptions.
- Development of tentative theories or hypotheses.
- Determination about whether a study is feasible in the future.
- Issues get refined for more systematic investigation and formulation of new research questions.
- Direction for future research and techniques get developed.
- Design is a useful approach for gaining background information on a particular topic.
- Exploratory research is flexible and can address research questions of all types (what, why, how).
- Provides an opportunity to define new terms and clarify existing concepts.
- Exploratory research is often used to generate formal hypotheses and develop more precise research problems.
- In the policy arena or applied to practice, exploratory studies help establish research priorities and where resources should be allocated.
- Exploratory research generally utilizes small sample sizes and, thus, findings are typically not generalizable to the population at large.
- The exploratory nature of the research inhibits an ability to make definitive conclusions about the findings. They provide insight but not definitive conclusions.
- The research process underpinning exploratory studies is flexible but often unstructured, leading to only tentative results that have limited value to decision-makers.
- Design lacks rigorous standards applied to methods of data gathering and analysis because one of the areas for exploration could be to determine what method or methodologies could best fit the research problem.
Cuthill, Michael. “Exploratory Research: Citizen Participation, Local Government, and Sustainable Development in Australia.” Sustainable Development 10 (2002): 79-89; Streb, Christoph K. "Exploratory Case Study." In Encyclopedia of Case Study Research . Albert J. Mills, Gabrielle Durepos and Eiden Wiebe, editors. (Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2010), pp. 372-374; Taylor, P. J., G. Catalano, and D.R.F. Walker. “Exploratory Analysis of the World City Network.” Urban Studies 39 (December 2002): 2377-2394; Exploratory Research. Wikipedia.
Field Research Design
Sometimes referred to as ethnography or participant observation, designs around field research encompass a variety of interpretative procedures [e.g., observation and interviews] rooted in qualitative approaches to studying people individually or in groups while inhabiting their natural environment as opposed to using survey instruments or other forms of impersonal methods of data gathering. Information acquired from observational research takes the form of “ field notes ” that involves documenting what the researcher actually sees and hears while in the field. Findings do not consist of conclusive statements derived from numbers and statistics because field research involves analysis of words and observations of behavior. Conclusions, therefore, are developed from an interpretation of findings that reveal overriding themes, concepts, and ideas. More information can be found HERE .
- Field research is often necessary to fill gaps in understanding the research problem applied to local conditions or to specific groups of people that cannot be ascertained from existing data.
- The research helps contextualize already known information about a research problem, thereby facilitating ways to assess the origins, scope, and scale of a problem and to gage the causes, consequences, and means to resolve an issue based on deliberate interaction with people in their natural inhabited spaces.
- Enables the researcher to corroborate or confirm data by gathering additional information that supports or refutes findings reported in prior studies of the topic.
- Because the researcher in embedded in the field, they are better able to make observations or ask questions that reflect the specific cultural context of the setting being investigated.
- Observing the local reality offers the opportunity to gain new perspectives or obtain unique data that challenges existing theoretical propositions or long-standing assumptions found in the literature.
What these studies don't tell you
- A field research study requires extensive time and resources to carry out the multiple steps involved with preparing for the gathering of information, including for example, examining background information about the study site, obtaining permission to access the study site, and building trust and rapport with subjects.
- Requires a commitment to staying engaged in the field to ensure that you can adequately document events and behaviors as they unfold.
- The unpredictable nature of fieldwork means that researchers can never fully control the process of data gathering. They must maintain a flexible approach to studying the setting because events and circumstances can change quickly or unexpectedly.
- Findings can be difficult to interpret and verify without access to documents and other source materials that help to enhance the credibility of information obtained from the field [i.e., the act of triangulating the data].
- Linking the research problem to the selection of study participants inhabiting their natural environment is critical. However, this specificity limits the ability to generalize findings to different situations or in other contexts or to infer courses of action applied to other settings or groups of people.
- The reporting of findings must take into account how the researcher themselves may have inadvertently affected respondents and their behaviors.
Historical Design
The purpose of a historical research design is to collect, verify, and synthesize evidence from the past to establish facts that defend or refute a hypothesis. It uses secondary sources and a variety of primary documentary evidence, such as, diaries, official records, reports, archives, and non-textual information [maps, pictures, audio and visual recordings]. The limitation is that the sources must be both authentic and valid.
- The historical research design is unobtrusive; the act of research does not affect the results of the study.
- The historical approach is well suited for trend analysis.
- Historical records can add important contextual background required to more fully understand and interpret a research problem.
- There is often no possibility of researcher-subject interaction that could affect the findings.
- Historical sources can be used over and over to study different research problems or to replicate a previous study.
- The ability to fulfill the aims of your research are directly related to the amount and quality of documentation available to understand the research problem.
- Since historical research relies on data from the past, there is no way to manipulate it to control for contemporary contexts.
- Interpreting historical sources can be very time consuming.
- The sources of historical materials must be archived consistently to ensure access. This may especially challenging for digital or online-only sources.
- Original authors bring their own perspectives and biases to the interpretation of past events and these biases are more difficult to ascertain in historical resources.
- Due to the lack of control over external variables, historical research is very weak with regard to the demands of internal validity.
- It is rare that the entirety of historical documentation needed to fully address a research problem is available for interpretation, therefore, gaps need to be acknowledged.
Howell, Martha C. and Walter Prevenier. From Reliable Sources: An Introduction to Historical Methods . Ithaca, NY: Cornell University Press, 2001; Lundy, Karen Saucier. "Historical Research." In The Sage Encyclopedia of Qualitative Research Methods . Lisa M. Given, editor. (Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2008), pp. 396-400; Marius, Richard. and Melvin E. Page. A Short Guide to Writing about History . 9th edition. Boston, MA: Pearson, 2015; Savitt, Ronald. “Historical Research in Marketing.” Journal of Marketing 44 (Autumn, 1980): 52-58; Gall, Meredith. Educational Research: An Introduction . Chapter 16, Historical Research. 8th ed. Boston, MA: Pearson/Allyn and Bacon, 2007.
Longitudinal Design
A longitudinal study follows the same sample over time and makes repeated observations. For example, with longitudinal surveys, the same group of people is interviewed at regular intervals, enabling researchers to track changes over time and to relate them to variables that might explain why the changes occur. Longitudinal research designs describe patterns of change and help establish the direction and magnitude of causal relationships. Measurements are taken on each variable over two or more distinct time periods. This allows the researcher to measure change in variables over time. It is a type of observational study sometimes referred to as a panel study.
- Longitudinal data facilitate the analysis of the duration of a particular phenomenon.
- Enables survey researchers to get close to the kinds of causal explanations usually attainable only with experiments.
- The design permits the measurement of differences or change in a variable from one period to another [i.e., the description of patterns of change over time].
- Longitudinal studies facilitate the prediction of future outcomes based upon earlier factors.
- The data collection method may change over time.
- Maintaining the integrity of the original sample can be difficult over an extended period of time.
- It can be difficult to show more than one variable at a time.
- This design often needs qualitative research data to explain fluctuations in the results.
- A longitudinal research design assumes present trends will continue unchanged.
- It can take a long period of time to gather results.
- There is a need to have a large sample size and accurate sampling to reach representativness.
Anastas, Jeane W. Research Design for Social Work and the Human Services . Chapter 6, Flexible Methods: Relational and Longitudinal Research. 2nd ed. New York: Columbia University Press, 1999; Forgues, Bernard, and Isabelle Vandangeon-Derumez. "Longitudinal Analyses." In Doing Management Research . Raymond-Alain Thiétart and Samantha Wauchope, editors. (London, England: Sage, 2001), pp. 332-351; Kalaian, Sema A. and Rafa M. Kasim. "Longitudinal Studies." In Encyclopedia of Survey Research Methods . Paul J. Lavrakas, ed. (Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2008), pp. 440-441; Menard, Scott, editor. Longitudinal Research . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2002; Ployhart, Robert E. and Robert J. Vandenberg. "Longitudinal Research: The Theory, Design, and Analysis of Change.” Journal of Management 36 (January 2010): 94-120; Longitudinal Study. Wikipedia.
Meta-Analysis Design
Meta-analysis is an analytical methodology designed to systematically evaluate and summarize the results from a number of individual studies, thereby, increasing the overall sample size and the ability of the researcher to study effects of interest. The purpose is to not simply summarize existing knowledge, but to develop a new understanding of a research problem using synoptic reasoning. The main objectives of meta-analysis include analyzing differences in the results among studies and increasing the precision by which effects are estimated. A well-designed meta-analysis depends upon strict adherence to the criteria used for selecting studies and the availability of information in each study to properly analyze their findings. Lack of information can severely limit the type of analyzes and conclusions that can be reached. In addition, the more dissimilarity there is in the results among individual studies [heterogeneity], the more difficult it is to justify interpretations that govern a valid synopsis of results. A meta-analysis needs to fulfill the following requirements to ensure the validity of your findings:
- Clearly defined description of objectives, including precise definitions of the variables and outcomes that are being evaluated;
- A well-reasoned and well-documented justification for identification and selection of the studies;
- Assessment and explicit acknowledgment of any researcher bias in the identification and selection of those studies;
- Description and evaluation of the degree of heterogeneity among the sample size of studies reviewed; and,
- Justification of the techniques used to evaluate the studies.
- Can be an effective strategy for determining gaps in the literature.
- Provides a means of reviewing research published about a particular topic over an extended period of time and from a variety of sources.
- Is useful in clarifying what policy or programmatic actions can be justified on the basis of analyzing research results from multiple studies.
- Provides a method for overcoming small sample sizes in individual studies that previously may have had little relationship to each other.
- Can be used to generate new hypotheses or highlight research problems for future studies.
- Small violations in defining the criteria used for content analysis can lead to difficult to interpret and/or meaningless findings.
- A large sample size can yield reliable, but not necessarily valid, results.
- A lack of uniformity regarding, for example, the type of literature reviewed, how methods are applied, and how findings are measured within the sample of studies you are analyzing, can make the process of synthesis difficult to perform.
- Depending on the sample size, the process of reviewing and synthesizing multiple studies can be very time consuming.
Beck, Lewis W. "The Synoptic Method." The Journal of Philosophy 36 (1939): 337-345; Cooper, Harris, Larry V. Hedges, and Jeffrey C. Valentine, eds. The Handbook of Research Synthesis and Meta-Analysis . 2nd edition. New York: Russell Sage Foundation, 2009; Guzzo, Richard A., Susan E. Jackson and Raymond A. Katzell. “Meta-Analysis Analysis.” In Research in Organizational Behavior , Volume 9. (Greenwich, CT: JAI Press, 1987), pp 407-442; Lipsey, Mark W. and David B. Wilson. Practical Meta-Analysis . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications, 2001; Study Design 101. Meta-Analysis. The Himmelfarb Health Sciences Library, George Washington University; Timulak, Ladislav. “Qualitative Meta-Analysis.” In The SAGE Handbook of Qualitative Data Analysis . Uwe Flick, editor. (Los Angeles, CA: Sage, 2013), pp. 481-495; Walker, Esteban, Adrian V. Hernandez, and Micheal W. Kattan. "Meta-Analysis: It's Strengths and Limitations." Cleveland Clinic Journal of Medicine 75 (June 2008): 431-439.
Mixed-Method Design
- Narrative and non-textual information can add meaning to numeric data, while numeric data can add precision to narrative and non-textual information.
- Can utilize existing data while at the same time generating and testing a grounded theory approach to describe and explain the phenomenon under study.
- A broader, more complex research problem can be investigated because the researcher is not constrained by using only one method.
- The strengths of one method can be used to overcome the inherent weaknesses of another method.
- Can provide stronger, more robust evidence to support a conclusion or set of recommendations.
- May generate new knowledge new insights or uncover hidden insights, patterns, or relationships that a single methodological approach might not reveal.
- Produces more complete knowledge and understanding of the research problem that can be used to increase the generalizability of findings applied to theory or practice.
- A researcher must be proficient in understanding how to apply multiple methods to investigating a research problem as well as be proficient in optimizing how to design a study that coherently melds them together.
- Can increase the likelihood of conflicting results or ambiguous findings that inhibit drawing a valid conclusion or setting forth a recommended course of action [e.g., sample interview responses do not support existing statistical data].
- Because the research design can be very complex, reporting the findings requires a well-organized narrative, clear writing style, and precise word choice.
- Design invites collaboration among experts. However, merging different investigative approaches and writing styles requires more attention to the overall research process than studies conducted using only one methodological paradigm.
- Concurrent merging of quantitative and qualitative research requires greater attention to having adequate sample sizes, using comparable samples, and applying a consistent unit of analysis. For sequential designs where one phase of qualitative research builds on the quantitative phase or vice versa, decisions about what results from the first phase to use in the next phase, the choice of samples and estimating reasonable sample sizes for both phases, and the interpretation of results from both phases can be difficult.
- Due to multiple forms of data being collected and analyzed, this design requires extensive time and resources to carry out the multiple steps involved in data gathering and interpretation.
Burch, Patricia and Carolyn J. Heinrich. Mixed Methods for Policy Research and Program Evaluation . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2016; Creswell, John w. et al. Best Practices for Mixed Methods Research in the Health Sciences . Bethesda, MD: Office of Behavioral and Social Sciences Research, National Institutes of Health, 2010Creswell, John W. Research Design: Qualitative, Quantitative, and Mixed Methods Approaches . 4th edition. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications, 2014; Domínguez, Silvia, editor. Mixed Methods Social Networks Research . Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press, 2014; Hesse-Biber, Sharlene Nagy. Mixed Methods Research: Merging Theory with Practice . New York: Guilford Press, 2010; Niglas, Katrin. “How the Novice Researcher Can Make Sense of Mixed Methods Designs.” International Journal of Multiple Research Approaches 3 (2009): 34-46; Onwuegbuzie, Anthony J. and Nancy L. Leech. “Linking Research Questions to Mixed Methods Data Analysis Procedures.” The Qualitative Report 11 (September 2006): 474-498; Tashakorri, Abbas and John W. Creswell. “The New Era of Mixed Methods.” Journal of Mixed Methods Research 1 (January 2007): 3-7; Zhanga, Wanqing. “Mixed Methods Application in Health Intervention Research: A Multiple Case Study.” International Journal of Multiple Research Approaches 8 (2014): 24-35 .
Observational Design
This type of research design draws a conclusion by comparing subjects against a control group, in cases where the researcher has no control over the experiment. There are two general types of observational designs. In direct observations, people know that you are watching them. Unobtrusive measures involve any method for studying behavior where individuals do not know they are being observed. An observational study allows a useful insight into a phenomenon and avoids the ethical and practical difficulties of setting up a large and cumbersome research project.
- Observational studies are usually flexible and do not necessarily need to be structured around a hypothesis about what you expect to observe [data is emergent rather than pre-existing].
- The researcher is able to collect in-depth information about a particular behavior.
- Can reveal interrelationships among multifaceted dimensions of group interactions.
- You can generalize your results to real life situations.
- Observational research is useful for discovering what variables may be important before applying other methods like experiments.
- Observation research designs account for the complexity of group behaviors.
- Reliability of data is low because seeing behaviors occur over and over again may be a time consuming task and are difficult to replicate.
- In observational research, findings may only reflect a unique sample population and, thus, cannot be generalized to other groups.
- There can be problems with bias as the researcher may only "see what they want to see."
- There is no possibility to determine "cause and effect" relationships since nothing is manipulated.
- Sources or subjects may not all be equally credible.
- Any group that is knowingly studied is altered to some degree by the presence of the researcher, therefore, potentially skewing any data collected.
Atkinson, Paul and Martyn Hammersley. “Ethnography and Participant Observation.” In Handbook of Qualitative Research . Norman K. Denzin and Yvonna S. Lincoln, eds. (Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 1994), pp. 248-261; Observational Research. Research Methods by Dummies. Department of Psychology. California State University, Fresno, 2006; Patton Michael Quinn. Qualitiative Research and Evaluation Methods . Chapter 6, Fieldwork Strategies and Observational Methods. 3rd ed. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2002; Payne, Geoff and Judy Payne. "Observation." In Key Concepts in Social Research . The SAGE Key Concepts series. (London, England: Sage, 2004), pp. 158-162; Rosenbaum, Paul R. Design of Observational Studies . New York: Springer, 2010;Williams, J. Patrick. "Nonparticipant Observation." In The Sage Encyclopedia of Qualitative Research Methods . Lisa M. Given, editor.(Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2008), pp. 562-563.
Philosophical Design
Understood more as an broad approach to examining a research problem than a methodological design, philosophical analysis and argumentation is intended to challenge deeply embedded, often intractable, assumptions underpinning an area of study. This approach uses the tools of argumentation derived from philosophical traditions, concepts, models, and theories to critically explore and challenge, for example, the relevance of logic and evidence in academic debates, to analyze arguments about fundamental issues, or to discuss the root of existing discourse about a research problem. These overarching tools of analysis can be framed in three ways:
- Ontology -- the study that describes the nature of reality; for example, what is real and what is not, what is fundamental and what is derivative?
- Epistemology -- the study that explores the nature of knowledge; for example, by what means does knowledge and understanding depend upon and how can we be certain of what we know?
- Axiology -- the study of values; for example, what values does an individual or group hold and why? How are values related to interest, desire, will, experience, and means-to-end? And, what is the difference between a matter of fact and a matter of value?
- Can provide a basis for applying ethical decision-making to practice.
- Functions as a means of gaining greater self-understanding and self-knowledge about the purposes of research.
- Brings clarity to general guiding practices and principles of an individual or group.
- Philosophy informs methodology.
- Refine concepts and theories that are invoked in relatively unreflective modes of thought and discourse.
- Beyond methodology, philosophy also informs critical thinking about epistemology and the structure of reality (metaphysics).
- Offers clarity and definition to the practical and theoretical uses of terms, concepts, and ideas.
- Limited application to specific research problems [answering the "So What?" question in social science research].
- Analysis can be abstract, argumentative, and limited in its practical application to real-life issues.
- While a philosophical analysis may render problematic that which was once simple or taken-for-granted, the writing can be dense and subject to unnecessary jargon, overstatement, and/or excessive quotation and documentation.
- There are limitations in the use of metaphor as a vehicle of philosophical analysis.
- There can be analytical difficulties in moving from philosophy to advocacy and between abstract thought and application to the phenomenal world.
Burton, Dawn. "Part I, Philosophy of the Social Sciences." In Research Training for Social Scientists . (London, England: Sage, 2000), pp. 1-5; Chapter 4, Research Methodology and Design. Unisa Institutional Repository (UnisaIR), University of South Africa; Jarvie, Ian C., and Jesús Zamora-Bonilla, editors. The SAGE Handbook of the Philosophy of Social Sciences . London: Sage, 2011; Labaree, Robert V. and Ross Scimeca. “The Philosophical Problem of Truth in Librarianship.” The Library Quarterly 78 (January 2008): 43-70; Maykut, Pamela S. Beginning Qualitative Research: A Philosophic and Practical Guide . Washington, DC: Falmer Press, 1994; McLaughlin, Hugh. "The Philosophy of Social Research." In Understanding Social Work Research . 2nd edition. (London: SAGE Publications Ltd., 2012), pp. 24-47; Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy . Metaphysics Research Lab, CSLI, Stanford University, 2013.
Sequential Design
- The researcher has a limitless option when it comes to sample size and the sampling schedule.
- Due to the repetitive nature of this research design, minor changes and adjustments can be done during the initial parts of the study to correct and hone the research method.
- This is a useful design for exploratory studies.
- There is very little effort on the part of the researcher when performing this technique. It is generally not expensive, time consuming, or workforce intensive.
- Because the study is conducted serially, the results of one sample are known before the next sample is taken and analyzed. This provides opportunities for continuous improvement of sampling and methods of analysis.
- The sampling method is not representative of the entire population. The only possibility of approaching representativeness is when the researcher chooses to use a very large sample size significant enough to represent a significant portion of the entire population. In this case, moving on to study a second or more specific sample can be difficult.
- The design cannot be used to create conclusions and interpretations that pertain to an entire population because the sampling technique is not randomized. Generalizability from findings is, therefore, limited.
- Difficult to account for and interpret variation from one sample to another over time, particularly when using qualitative methods of data collection.
Betensky, Rebecca. Harvard University, Course Lecture Note slides; Bovaird, James A. and Kevin A. Kupzyk. "Sequential Design." In Encyclopedia of Research Design . Neil J. Salkind, editor. (Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2010), pp. 1347-1352; Cresswell, John W. Et al. “Advanced Mixed-Methods Research Designs.” In Handbook of Mixed Methods in Social and Behavioral Research . Abbas Tashakkori and Charles Teddle, eds. (Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2003), pp. 209-240; Henry, Gary T. "Sequential Sampling." In The SAGE Encyclopedia of Social Science Research Methods . Michael S. Lewis-Beck, Alan Bryman and Tim Futing Liao, editors. (Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2004), pp. 1027-1028; Nataliya V. Ivankova. “Using Mixed-Methods Sequential Explanatory Design: From Theory to Practice.” Field Methods 18 (February 2006): 3-20; Bovaird, James A. and Kevin A. Kupzyk. “Sequential Design.” In Encyclopedia of Research Design . Neil J. Salkind, ed. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2010; Sequential Analysis. Wikipedia.

Systematic Review
- A systematic review synthesizes the findings of multiple studies related to each other by incorporating strategies of analysis and interpretation intended to reduce biases and random errors.
- The application of critical exploration, evaluation, and synthesis methods separates insignificant, unsound, or redundant research from the most salient and relevant studies worthy of reflection.
- They can be use to identify, justify, and refine hypotheses, recognize and avoid hidden problems in prior studies, and explain data inconsistencies and conflicts in data.
- Systematic reviews can be used to help policy makers formulate evidence-based guidelines and regulations.
- The use of strict, explicit, and pre-determined methods of synthesis, when applied appropriately, provide reliable estimates about the effects of interventions, evaluations, and effects related to the overarching research problem investigated by each study under review.
- Systematic reviews illuminate where knowledge or thorough understanding of a research problem is lacking and, therefore, can then be used to guide future research.
- The accepted inclusion of unpublished studies [i.e., grey literature] ensures the broadest possible way to analyze and interpret research on a topic.
- Results of the synthesis can be generalized and the findings extrapolated into the general population with more validity than most other types of studies .
- Systematic reviews do not create new knowledge per se; they are a method for synthesizing existing studies about a research problem in order to gain new insights and determine gaps in the literature.
- The way researchers have carried out their investigations [e.g., the period of time covered, number of participants, sources of data analyzed, etc.] can make it difficult to effectively synthesize studies.
- The inclusion of unpublished studies can introduce bias into the review because they may not have undergone a rigorous peer-review process prior to publication. Examples may include conference presentations or proceedings, publications from government agencies, white papers, working papers, and internal documents from organizations, and doctoral dissertations and Master's theses.
Denyer, David and David Tranfield. "Producing a Systematic Review." In The Sage Handbook of Organizational Research Methods . David A. Buchanan and Alan Bryman, editors. ( Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications, 2009), pp. 671-689; Foster, Margaret J. and Sarah T. Jewell, editors. Assembling the Pieces of a Systematic Review: A Guide for Librarians . Lanham, MD: Rowman and Littlefield, 2017; Gough, David, Sandy Oliver, James Thomas, editors. Introduction to Systematic Reviews . 2nd edition. Los Angeles, CA: Sage Publications, 2017; Gopalakrishnan, S. and P. Ganeshkumar. “Systematic Reviews and Meta-analysis: Understanding the Best Evidence in Primary Healthcare.” Journal of Family Medicine and Primary Care 2 (2013): 9-14; Gough, David, James Thomas, and Sandy Oliver. "Clarifying Differences between Review Designs and Methods." Systematic Reviews 1 (2012): 1-9; Khan, Khalid S., Regina Kunz, Jos Kleijnen, and Gerd Antes. “Five Steps to Conducting a Systematic Review.” Journal of the Royal Society of Medicine 96 (2003): 118-121; Mulrow, C. D. “Systematic Reviews: Rationale for Systematic Reviews.” BMJ 309:597 (September 1994); O'Dwyer, Linda C., and Q. Eileen Wafford. "Addressing Challenges with Systematic Review Teams through Effective Communication: A Case Report." Journal of the Medical Library Association 109 (October 2021): 643-647; Okoli, Chitu, and Kira Schabram. "A Guide to Conducting a Systematic Literature Review of Information Systems Research." Sprouts: Working Papers on Information Systems 10 (2010); Siddaway, Andy P., Alex M. Wood, and Larry V. Hedges. "How to Do a Systematic Review: A Best Practice Guide for Conducting and Reporting Narrative Reviews, Meta-analyses, and Meta-syntheses." Annual Review of Psychology 70 (2019): 747-770; Torgerson, Carole J. “Publication Bias: The Achilles’ Heel of Systematic Reviews?” British Journal of Educational Studies 54 (March 2006): 89-102; Torgerson, Carole. Systematic Reviews . New York: Continuum, 2003.
- << Previous: Purpose of Guide
- Next: Design Flaws to Avoid >>
- Last Updated: May 21, 2024 11:14 AM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- J Athl Train
- v.45(1); Jan-Feb 2010
Study/Experimental/Research Design: Much More Than Statistics
Kenneth l. knight.
Brigham Young University, Provo, UT
The purpose of study, experimental, or research design in scientific manuscripts has changed significantly over the years. It has evolved from an explanation of the design of the experiment (ie, data gathering or acquisition) to an explanation of the statistical analysis. This practice makes “Methods” sections hard to read and understand.
To clarify the difference between study design and statistical analysis, to show the advantages of a properly written study design on article comprehension, and to encourage authors to correctly describe study designs.
Description:
The role of study design is explored from the introduction of the concept by Fisher through modern-day scientists and the AMA Manual of Style . At one time, when experiments were simpler, the study design and statistical design were identical or very similar. With the complex research that is common today, which often includes manipulating variables to create new variables and the multiple (and different) analyses of a single data set, data collection is very different than statistical design. Thus, both a study design and a statistical design are necessary.
Advantages:
Scientific manuscripts will be much easier to read and comprehend. A proper experimental design serves as a road map to the study methods, helping readers to understand more clearly how the data were obtained and, therefore, assisting them in properly analyzing the results.
Study, experimental, or research design is the backbone of good research. It directs the experiment by orchestrating data collection, defines the statistical analysis of the resultant data, and guides the interpretation of the results. When properly described in the written report of the experiment, it serves as a road map to readers, 1 helping them negotiate the “Methods” section, and, thus, it improves the clarity of communication between authors and readers.
A growing trend is to equate study design with only the statistical analysis of the data. The design statement typically is placed at the end of the “Methods” section as a subsection called “Experimental Design” or as part of a subsection called “Data Analysis.” This placement, however, equates experimental design and statistical analysis, minimizing the effect of experimental design on the planning and reporting of an experiment. This linkage is inappropriate, because some of the elements of the study design that should be described at the beginning of the “Methods” section are instead placed in the “Statistical Analysis” section or, worse, are absent from the manuscript entirely.
Have you ever interrupted your reading of the “Methods” to sketch out the variables in the margins of the paper as you attempt to understand how they all fit together? Or have you jumped back and forth from the early paragraphs of the “Methods” section to the “Statistics” section to try to understand which variables were collected and when? These efforts would be unnecessary if a road map at the beginning of the “Methods” section outlined how the independent variables were related, which dependent variables were measured, and when they were measured. When they were measured is especially important if the variables used in the statistical analysis were a subset of the measured variables or were computed from measured variables (such as change scores).
The purpose of this Communications article is to clarify the purpose and placement of study design elements in an experimental manuscript. Adopting these ideas may improve your science and surely will enhance the communication of that science. These ideas will make experimental manuscripts easier to read and understand and, therefore, will allow them to become part of readers' clinical decision making.
WHAT IS A STUDY (OR EXPERIMENTAL OR RESEARCH) DESIGN?
The terms study design, experimental design, and research design are often thought to be synonymous and are sometimes used interchangeably in a single paper. Avoid doing so. Use the term that is preferred by the style manual of the journal for which you are writing. Study design is the preferred term in the AMA Manual of Style , 2 so I will use it here.
A study design is the architecture of an experimental study 3 and a description of how the study was conducted, 4 including all elements of how the data were obtained. 5 The study design should be the first subsection of the “Methods” section in an experimental manuscript (see the Table ). “Statistical Design” or, preferably, “Statistical Analysis” or “Data Analysis” should be the last subsection of the “Methods” section.
Table. Elements of a “Methods” Section

The “Study Design” subsection describes how the variables and participants interacted. It begins with a general statement of how the study was conducted (eg, crossover trials, parallel, or observational study). 2 The second element, which usually begins with the second sentence, details the number of independent variables or factors, the levels of each variable, and their names. A shorthand way of doing so is with a statement such as “A 2 × 4 × 8 factorial guided data collection.” This tells us that there were 3 independent variables (factors), with 2 levels of the first factor, 4 levels of the second factor, and 8 levels of the third factor. Following is a sentence that names the levels of each factor: for example, “The independent variables were sex (male or female), training program (eg, walking, running, weight lifting, or plyometrics), and time (2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 15, 20, or 30 weeks).” Such an approach clearly outlines for readers how the various procedures fit into the overall structure and, therefore, enhances their understanding of how the data were collected. Thus, the design statement is a road map of the methods.
The dependent (or measurement or outcome) variables are then named. Details of how they were measured are not given at this point in the manuscript but are explained later in the “Instruments” and “Procedures” subsections.
Next is a paragraph detailing who the participants were and how they were selected, placed into groups, and assigned to a particular treatment order, if the experiment was a repeated-measures design. And although not a part of the design per se, a statement about obtaining written informed consent from participants and institutional review board approval is usually included in this subsection.
The nuts and bolts of the “Methods” section follow, including such things as equipment, materials, protocols, etc. These are beyond the scope of this commentary, however, and so will not be discussed.
The last part of the “Methods” section and last part of the “Study Design” section is the “Data Analysis” subsection. It begins with an explanation of any data manipulation, such as how data were combined or how new variables (eg, ratios or differences between collected variables) were calculated. Next, readers are told of the statistical measures used to analyze the data, such as a mixed 2 × 4 × 8 analysis of variance (ANOVA) with 2 between-groups factors (sex and training program) and 1 within-groups factor (time of measurement). Researchers should state and reference the statistical package and procedure(s) within the package used to compute the statistics. (Various statistical packages perform analyses slightly differently, so it is important to know the package and specific procedure used.) This detail allows readers to judge the appropriateness of the statistical measures and the conclusions drawn from the data.
STATISTICAL DESIGN VERSUS STATISTICAL ANALYSIS
Avoid using the term statistical design . Statistical methods are only part of the overall design. The term gives too much emphasis to the statistics, which are important, but only one of many tools used in interpreting data and only part of the study design:
The most important issues in biostatistics are not expressed with statistical procedures. The issues are inherently scientific, rather than purely statistical, and relate to the architectural design of the research, not the numbers with which the data are cited and interpreted. 6
Stated another way, “The justification for the analysis lies not in the data collected but in the manner in which the data were collected.” 3 “Without the solid foundation of a good design, the edifice of statistical analysis is unsafe.” 7 (pp4–5)
The intertwining of study design and statistical analysis may have been caused (unintentionally) by R.A. Fisher, “… a genius who almost single-handedly created the foundations for modern statistical science.” 8 Most research did not involve statistics until Fisher invented the concepts and procedures of ANOVA (in 1921) 9 , 10 and experimental design (in 1935). 11 His books became standard references for scientists in many disciplines. As a result, many ANOVA books were titled Experimental Design (see, for example, Edwards 12 ), and ANOVA courses taught in psychology and education departments included the words experimental design in their course titles.
Before the widespread use of computers to analyze data, designs were much simpler, and often there was little difference between study design and statistical analysis. So combining the 2 elements did not cause serious problems. This is no longer true, however, for 3 reasons: (1) Research studies are becoming more complex, with multiple independent and dependent variables. The procedures sections of these complex studies can be difficult to understand if your only reference point is the statistical analysis and design. (2) Dependent variables are frequently measured at different times. (3) How the data were collected is often not directly correlated with the statistical design.
For example, assume the goal is to determine the strength gain in novice and experienced athletes as a result of 3 strength training programs. Rate of change in strength is not a measurable variable; rather, it is calculated from strength measurements taken at various time intervals during the training. So the study design would be a 2 × 2 × 3 factorial with independent variables of time (pretest or posttest), experience (novice or advanced), and training (isokinetic, isotonic, or isometric) and a dependent variable of strength. The statistical design , however, would be a 2 × 3 factorial with independent variables of experience (novice or advanced) and training (isokinetic, isotonic, or isometric) and a dependent variable of strength gain. Note that data were collected according to a 3-factor design but were analyzed according to a 2-factor design and that the dependent variables were different. So a single design statement, usually a statistical design statement, would not communicate which data were collected or how. Readers would be left to figure out on their own how the data were collected.
MULTIVARIATE RESEARCH AND THE NEED FOR STUDY DESIGNS
With the advent of electronic data gathering and computerized data handling and analysis, research projects have increased in complexity. Many projects involve multiple dependent variables measured at different times, and, therefore, multiple design statements may be needed for both data collection and statistical analysis. Consider, for example, a study of the effects of heat and cold on neural inhibition. The variables of H max and M max are measured 3 times each: before, immediately after, and 30 minutes after a 20-minute treatment with heat or cold. Muscle temperature might be measured each minute before, during, and after the treatment. Although the minute-by-minute data are important for graphing temperature fluctuations during the procedure, only 3 temperatures (time 0, time 20, and time 50) are used for statistical analysis. A single dependent variable H max :M max ratio is computed to illustrate neural inhibition. Again, a single statistical design statement would tell little about how the data were obtained. And in this example, separate design statements would be needed for temperature measurement and H max :M max measurements.
As stated earlier, drawing conclusions from the data depends more on how the data were measured than on how they were analyzed. 3 , 6 , 7 , 13 So a single study design statement (or multiple such statements) at the beginning of the “Methods” section acts as a road map to the study and, thus, increases scientists' and readers' comprehension of how the experiment was conducted (ie, how the data were collected). Appropriate study design statements also increase the accuracy of conclusions drawn from the study.
CONCLUSIONS
The goal of scientific writing, or any writing, for that matter, is to communicate information. Including 2 design statements or subsections in scientific papers—one to explain how the data were collected and another to explain how they were statistically analyzed—will improve the clarity of communication and bring praise from readers. To summarize:
- Purge from your thoughts and vocabulary the idea that experimental design and statistical design are synonymous.
- Study or experimental design plays a much broader role than simply defining and directing the statistical analysis of an experiment.
- A properly written study design serves as a road map to the “Methods” section of an experiment and, therefore, improves communication with the reader.
- Study design should include a description of the type of design used, each factor (and each level) involved in the experiment, and the time at which each measurement was made.
- Clarify when the variables involved in data collection and data analysis are different, such as when data analysis involves only a subset of a collected variable or a resultant variable from the mathematical manipulation of 2 or more collected variables.
Acknowledgments
Thanks to Thomas A. Cappaert, PhD, ATC, CSCS, CSE, for suggesting the link between R.A. Fisher and the melding of the concepts of research design and statistics.
- How it works

A Complete Guide to Experimental Research
Published by Carmen Troy at August 14th, 2021 , Revised On August 25, 2023
A Quick Guide to Experimental Research
Experimental research refers to the experiments conducted in the laboratory or observation under controlled conditions. Researchers try to find out the cause-and-effect relationship between two or more variables.
The subjects/participants in the experiment are selected and observed. They receive treatments such as changes in room temperature, diet, atmosphere, or given a new drug to observe the changes. Experiments can vary from personal and informal natural comparisons. It includes three types of variables ;
- Independent variable
- Dependent variable
- Controlled variable
Before conducting experimental research, you need to have a clear understanding of the experimental design. A true experimental design includes identifying a problem , formulating a hypothesis , determining the number of variables, selecting and assigning the participants, types of research designs , meeting ethical values, etc.
There are many types of research methods that can be classified based on:
- The nature of the problem to be studied
- Number of participants (individual or groups)
- Number of groups involved (Single group or multiple groups)
- Types of data collection methods (Qualitative/Quantitative/Mixed methods)
- Number of variables (single independent variable/ factorial two independent variables)
- The experimental design
Types of Experimental Research

Laboratory Experiment
It is also called experimental research. This type of research is conducted in the laboratory. A researcher can manipulate and control the variables of the experiment.
Example: Milgram’s experiment on obedience.
Field Experiment
Field experiments are conducted in the participants’ open field and the environment by incorporating a few artificial changes. Researchers do not have control over variables under measurement. Participants know that they are taking part in the experiment.
Natural Experiments
The experiment is conducted in the natural environment of the participants. The participants are generally not informed about the experiment being conducted on them.
Examples: Estimating the health condition of the population. Did the increase in tobacco prices decrease the sale of tobacco? Did the usage of helmets decrease the number of head injuries of the bikers?
Quasi-Experiments
A quasi-experiment is an experiment that takes advantage of natural occurrences. Researchers cannot assign random participants to groups.
Example: Comparing the academic performance of the two schools.
Does your Research Methodology Have the Following?
- Great Research/Sources
- Perfect Language
- Accurate Sources
If not, we can help. Our panel of experts makes sure to keep the 3 pillars of Research Methodology strong.

How to Conduct Experimental Research?
Step 1. identify and define the problem.
You need to identify a problem as per your field of study and describe your research question .
Example: You want to know about the effects of social media on the behavior of youngsters. It would help if you found out how much time students spend on the internet daily.
Example: You want to find out the adverse effects of junk food on human health. It would help if you found out how junk food frequent consumption can affect an individual’s health.
Step 2. Determine the Number of Levels of Variables
You need to determine the number of variables . The independent variable is the predictor and manipulated by the researcher. At the same time, the dependent variable is the result of the independent variable.
In the first example, we predicted that increased social media usage negatively correlates with youngsters’ negative behaviour.
In the second example, we predicted the positive correlation between a balanced diet and a good healthy and negative relationship between junk food consumption and multiple health issues.
Step 3. Formulate the Hypothesis
One of the essential aspects of experimental research is formulating a hypothesis . A researcher studies the cause and effect between the independent and dependent variables and eliminates the confounding variables. A null hypothesis is when there is no significant relationship between the dependent variable and the participants’ independent variables. A researcher aims to disprove the theory. H0 denotes it. The Alternative hypothesis is the theory that a researcher seeks to prove. H1or HA denotes it.
Why should you use a Plagiarism Detector for your Paper?
It ensures:
- Original work
- Structure and Clarity
- Zero Spelling Errors
- No Punctuation Faults
Step 4. Selection and Assignment of the Subjects
It’s an essential feature that differentiates the experimental design from other research designs . You need to select the number of participants based on the requirements of your experiment. Then the participants are assigned to the treatment group. There should be a control group without any treatment to study the outcomes without applying any changes compared to the experimental group.
Randomisation: The participants are selected randomly and assigned to the experimental group. It is known as probability sampling. If the selection is not random, it’s considered non-probability sampling.
Stratified sampling : It’s a type of random selection of the participants by dividing them into strata and randomly selecting them from each level.
Matching: Even though participants are selected randomly, they can be assigned to the various comparison groups. Another procedure for selecting the participants is ‘matching.’ The participants are selected from the controlled group to match the experimental groups’ participants in all aspects based on the dependent variables.
What is Replicability?
When a researcher uses the same methodology and subject groups to carry out the experiments, it’s called ‘replicability.’ The results will be similar each time. Researchers usually replicate their own work to strengthen external validity.
Step 5. Select a Research Design
You need to select a research design according to the requirements of your experiment. There are many types of experimental designs as follows.
Step 6. Meet Ethical and Legal Requirements
- Participants of the research should not be harmed.
- The dignity and confidentiality of the research should be maintained.
- The consent of the participants should be taken before experimenting.
- The privacy of the participants should be ensured.
- Research data should remain confidential.
- The anonymity of the participants should be ensured.
- The rules and objectives of the experiments should be followed strictly.
- Any wrong information or data should be avoided.
Tips for Meeting the Ethical Considerations
To meet the ethical considerations, you need to ensure that.
- Participants have the right to withdraw from the experiment.
- They should be aware of the required information about the experiment.
- It would help if you avoided offensive or unacceptable language while framing the questions of interviews, questionnaires, or Focus groups.
- You should ensure the privacy and anonymity of the participants.
- You should acknowledge the sources and authors in your dissertation using any referencing styles such as APA/MLA/Harvard referencing style.
Step 7. Collect and Analyse Data.
Collect the data by using suitable data collection according to your experiment’s requirement, such as observations, case studies , surveys , interviews , questionnaires, etc. Analyse the obtained information.
Step 8. Present and Conclude the Findings of the Study.
Write the report of your research. Present, conclude, and explain the outcomes of your study .
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the first step in conducting an experimental research.
The first step in conducting experimental research is to define your research question or hypothesis. Clearly outline the purpose and expectations of your experiment to guide the entire research process.
You May Also Like
ANOVA is a statistical test for assessing how the levels of one or more categorical independent variables affect the changes in a quantitative dependent variable.
Analysis of Variance or ANOVA is a statistical test that uses means of two or more groups to analyse the difference. Here is all you need to know about it.
In historical research, a researcher collects and analyse the data, and explain the events that occurred in the past to test the truthfulness of observations.
USEFUL LINKS
LEARNING RESOURCES

COMPANY DETAILS

- How It Works
- Privacy Policy

Home » Experimental Design – Types, Methods, Guide
Experimental Design – Types, Methods, Guide
Table of Contents

Experimental Design
Experimental design is a process of planning and conducting scientific experiments to investigate a hypothesis or research question. It involves carefully designing an experiment that can test the hypothesis, and controlling for other variables that may influence the results.
Experimental design typically includes identifying the variables that will be manipulated or measured, defining the sample or population to be studied, selecting an appropriate method of sampling, choosing a method for data collection and analysis, and determining the appropriate statistical tests to use.
Types of Experimental Design
Here are the different types of experimental design:
Completely Randomized Design
In this design, participants are randomly assigned to one of two or more groups, and each group is exposed to a different treatment or condition.
Randomized Block Design
This design involves dividing participants into blocks based on a specific characteristic, such as age or gender, and then randomly assigning participants within each block to one of two or more treatment groups.
Factorial Design
In a factorial design, participants are randomly assigned to one of several groups, each of which receives a different combination of two or more independent variables.
Repeated Measures Design
In this design, each participant is exposed to all of the different treatments or conditions, either in a random order or in a predetermined order.
Crossover Design
This design involves randomly assigning participants to one of two or more treatment groups, with each group receiving one treatment during the first phase of the study and then switching to a different treatment during the second phase.
Split-plot Design
In this design, the researcher manipulates one or more variables at different levels and uses a randomized block design to control for other variables.
Nested Design
This design involves grouping participants within larger units, such as schools or households, and then randomly assigning these units to different treatment groups.
Laboratory Experiment
Laboratory experiments are conducted under controlled conditions, which allows for greater precision and accuracy. However, because laboratory conditions are not always representative of real-world conditions, the results of these experiments may not be generalizable to the population at large.
Field Experiment
Field experiments are conducted in naturalistic settings and allow for more realistic observations. However, because field experiments are not as controlled as laboratory experiments, they may be subject to more sources of error.
Experimental Design Methods
Experimental design methods refer to the techniques and procedures used to design and conduct experiments in scientific research. Here are some common experimental design methods:
Randomization
This involves randomly assigning participants to different groups or treatments to ensure that any observed differences between groups are due to the treatment and not to other factors.
Control Group
The use of a control group is an important experimental design method that involves having a group of participants that do not receive the treatment or intervention being studied. The control group is used as a baseline to compare the effects of the treatment group.
Blinding involves keeping participants, researchers, or both unaware of which treatment group participants are in, in order to reduce the risk of bias in the results.
Counterbalancing
This involves systematically varying the order in which participants receive treatments or interventions in order to control for order effects.
Replication
Replication involves conducting the same experiment with different samples or under different conditions to increase the reliability and validity of the results.
This experimental design method involves manipulating multiple independent variables simultaneously to investigate their combined effects on the dependent variable.
This involves dividing participants into subgroups or blocks based on specific characteristics, such as age or gender, in order to reduce the risk of confounding variables.
Data Collection Method
Experimental design data collection methods are techniques and procedures used to collect data in experimental research. Here are some common experimental design data collection methods:
Direct Observation
This method involves observing and recording the behavior or phenomenon of interest in real time. It may involve the use of structured or unstructured observation, and may be conducted in a laboratory or naturalistic setting.
Self-report Measures
Self-report measures involve asking participants to report their thoughts, feelings, or behaviors using questionnaires, surveys, or interviews. These measures may be administered in person or online.
Behavioral Measures
Behavioral measures involve measuring participants’ behavior directly, such as through reaction time tasks or performance tests. These measures may be administered using specialized equipment or software.
Physiological Measures
Physiological measures involve measuring participants’ physiological responses, such as heart rate, blood pressure, or brain activity, using specialized equipment. These measures may be invasive or non-invasive, and may be administered in a laboratory or clinical setting.
Archival Data
Archival data involves using existing records or data, such as medical records, administrative records, or historical documents, as a source of information. These data may be collected from public or private sources.
Computerized Measures
Computerized measures involve using software or computer programs to collect data on participants’ behavior or responses. These measures may include reaction time tasks, cognitive tests, or other types of computer-based assessments.
Video Recording
Video recording involves recording participants’ behavior or interactions using cameras or other recording equipment. This method can be used to capture detailed information about participants’ behavior or to analyze social interactions.
Data Analysis Method
Experimental design data analysis methods refer to the statistical techniques and procedures used to analyze data collected in experimental research. Here are some common experimental design data analysis methods:
Descriptive Statistics
Descriptive statistics are used to summarize and describe the data collected in the study. This includes measures such as mean, median, mode, range, and standard deviation.
Inferential Statistics
Inferential statistics are used to make inferences or generalizations about a larger population based on the data collected in the study. This includes hypothesis testing and estimation.
Analysis of Variance (ANOVA)
ANOVA is a statistical technique used to compare means across two or more groups in order to determine whether there are significant differences between the groups. There are several types of ANOVA, including one-way ANOVA, two-way ANOVA, and repeated measures ANOVA.
Regression Analysis
Regression analysis is used to model the relationship between two or more variables in order to determine the strength and direction of the relationship. There are several types of regression analysis, including linear regression, logistic regression, and multiple regression.
Factor Analysis
Factor analysis is used to identify underlying factors or dimensions in a set of variables. This can be used to reduce the complexity of the data and identify patterns in the data.
Structural Equation Modeling (SEM)
SEM is a statistical technique used to model complex relationships between variables. It can be used to test complex theories and models of causality.
Cluster Analysis
Cluster analysis is used to group similar cases or observations together based on similarities or differences in their characteristics.
Time Series Analysis
Time series analysis is used to analyze data collected over time in order to identify trends, patterns, or changes in the data.
Multilevel Modeling
Multilevel modeling is used to analyze data that is nested within multiple levels, such as students nested within schools or employees nested within companies.
Applications of Experimental Design
Experimental design is a versatile research methodology that can be applied in many fields. Here are some applications of experimental design:
- Medical Research: Experimental design is commonly used to test new treatments or medications for various medical conditions. This includes clinical trials to evaluate the safety and effectiveness of new drugs or medical devices.
- Agriculture : Experimental design is used to test new crop varieties, fertilizers, and other agricultural practices. This includes randomized field trials to evaluate the effects of different treatments on crop yield, quality, and pest resistance.
- Environmental science: Experimental design is used to study the effects of environmental factors, such as pollution or climate change, on ecosystems and wildlife. This includes controlled experiments to study the effects of pollutants on plant growth or animal behavior.
- Psychology : Experimental design is used to study human behavior and cognitive processes. This includes experiments to test the effects of different interventions, such as therapy or medication, on mental health outcomes.
- Engineering : Experimental design is used to test new materials, designs, and manufacturing processes in engineering applications. This includes laboratory experiments to test the strength and durability of new materials, or field experiments to test the performance of new technologies.
- Education : Experimental design is used to evaluate the effectiveness of teaching methods, educational interventions, and programs. This includes randomized controlled trials to compare different teaching methods or evaluate the impact of educational programs on student outcomes.
- Marketing : Experimental design is used to test the effectiveness of marketing campaigns, pricing strategies, and product designs. This includes experiments to test the impact of different marketing messages or pricing schemes on consumer behavior.
Examples of Experimental Design
Here are some examples of experimental design in different fields:
- Example in Medical research : A study that investigates the effectiveness of a new drug treatment for a particular condition. Patients are randomly assigned to either a treatment group or a control group, with the treatment group receiving the new drug and the control group receiving a placebo. The outcomes, such as improvement in symptoms or side effects, are measured and compared between the two groups.
- Example in Education research: A study that examines the impact of a new teaching method on student learning outcomes. Students are randomly assigned to either a group that receives the new teaching method or a group that receives the traditional teaching method. Student achievement is measured before and after the intervention, and the results are compared between the two groups.
- Example in Environmental science: A study that tests the effectiveness of a new method for reducing pollution in a river. Two sections of the river are selected, with one section treated with the new method and the other section left untreated. The water quality is measured before and after the intervention, and the results are compared between the two sections.
- Example in Marketing research: A study that investigates the impact of a new advertising campaign on consumer behavior. Participants are randomly assigned to either a group that is exposed to the new campaign or a group that is not. Their behavior, such as purchasing or product awareness, is measured and compared between the two groups.
- Example in Social psychology: A study that examines the effect of a new social intervention on reducing prejudice towards a marginalized group. Participants are randomly assigned to either a group that receives the intervention or a control group that does not. Their attitudes and behavior towards the marginalized group are measured before and after the intervention, and the results are compared between the two groups.
When to use Experimental Research Design
Experimental research design should be used when a researcher wants to establish a cause-and-effect relationship between variables. It is particularly useful when studying the impact of an intervention or treatment on a particular outcome.
Here are some situations where experimental research design may be appropriate:
- When studying the effects of a new drug or medical treatment: Experimental research design is commonly used in medical research to test the effectiveness and safety of new drugs or medical treatments. By randomly assigning patients to treatment and control groups, researchers can determine whether the treatment is effective in improving health outcomes.
- When evaluating the effectiveness of an educational intervention: An experimental research design can be used to evaluate the impact of a new teaching method or educational program on student learning outcomes. By randomly assigning students to treatment and control groups, researchers can determine whether the intervention is effective in improving academic performance.
- When testing the effectiveness of a marketing campaign: An experimental research design can be used to test the effectiveness of different marketing messages or strategies. By randomly assigning participants to treatment and control groups, researchers can determine whether the marketing campaign is effective in changing consumer behavior.
- When studying the effects of an environmental intervention: Experimental research design can be used to study the impact of environmental interventions, such as pollution reduction programs or conservation efforts. By randomly assigning locations or areas to treatment and control groups, researchers can determine whether the intervention is effective in improving environmental outcomes.
- When testing the effects of a new technology: An experimental research design can be used to test the effectiveness and safety of new technologies or engineering designs. By randomly assigning participants or locations to treatment and control groups, researchers can determine whether the new technology is effective in achieving its intended purpose.
How to Conduct Experimental Research
Here are the steps to conduct Experimental Research:
- Identify a Research Question : Start by identifying a research question that you want to answer through the experiment. The question should be clear, specific, and testable.
- Develop a Hypothesis: Based on your research question, develop a hypothesis that predicts the relationship between the independent and dependent variables. The hypothesis should be clear and testable.
- Design the Experiment : Determine the type of experimental design you will use, such as a between-subjects design or a within-subjects design. Also, decide on the experimental conditions, such as the number of independent variables, the levels of the independent variable, and the dependent variable to be measured.
- Select Participants: Select the participants who will take part in the experiment. They should be representative of the population you are interested in studying.
- Randomly Assign Participants to Groups: If you are using a between-subjects design, randomly assign participants to groups to control for individual differences.
- Conduct the Experiment : Conduct the experiment by manipulating the independent variable(s) and measuring the dependent variable(s) across the different conditions.
- Analyze the Data: Analyze the data using appropriate statistical methods to determine if there is a significant effect of the independent variable(s) on the dependent variable(s).
- Draw Conclusions: Based on the data analysis, draw conclusions about the relationship between the independent and dependent variables. If the results support the hypothesis, then it is accepted. If the results do not support the hypothesis, then it is rejected.
- Communicate the Results: Finally, communicate the results of the experiment through a research report or presentation. Include the purpose of the study, the methods used, the results obtained, and the conclusions drawn.
Purpose of Experimental Design
The purpose of experimental design is to control and manipulate one or more independent variables to determine their effect on a dependent variable. Experimental design allows researchers to systematically investigate causal relationships between variables, and to establish cause-and-effect relationships between the independent and dependent variables. Through experimental design, researchers can test hypotheses and make inferences about the population from which the sample was drawn.
Experimental design provides a structured approach to designing and conducting experiments, ensuring that the results are reliable and valid. By carefully controlling for extraneous variables that may affect the outcome of the study, experimental design allows researchers to isolate the effect of the independent variable(s) on the dependent variable(s), and to minimize the influence of other factors that may confound the results.
Experimental design also allows researchers to generalize their findings to the larger population from which the sample was drawn. By randomly selecting participants and using statistical techniques to analyze the data, researchers can make inferences about the larger population with a high degree of confidence.
Overall, the purpose of experimental design is to provide a rigorous, systematic, and scientific method for testing hypotheses and establishing cause-and-effect relationships between variables. Experimental design is a powerful tool for advancing scientific knowledge and informing evidence-based practice in various fields, including psychology, biology, medicine, engineering, and social sciences.
Advantages of Experimental Design
Experimental design offers several advantages in research. Here are some of the main advantages:
- Control over extraneous variables: Experimental design allows researchers to control for extraneous variables that may affect the outcome of the study. By manipulating the independent variable and holding all other variables constant, researchers can isolate the effect of the independent variable on the dependent variable.
- Establishing causality: Experimental design allows researchers to establish causality by manipulating the independent variable and observing its effect on the dependent variable. This allows researchers to determine whether changes in the independent variable cause changes in the dependent variable.
- Replication : Experimental design allows researchers to replicate their experiments to ensure that the findings are consistent and reliable. Replication is important for establishing the validity and generalizability of the findings.
- Random assignment: Experimental design often involves randomly assigning participants to conditions. This helps to ensure that individual differences between participants are evenly distributed across conditions, which increases the internal validity of the study.
- Precision : Experimental design allows researchers to measure variables with precision, which can increase the accuracy and reliability of the data.
- Generalizability : If the study is well-designed, experimental design can increase the generalizability of the findings. By controlling for extraneous variables and using random assignment, researchers can increase the likelihood that the findings will apply to other populations and contexts.
Limitations of Experimental Design
Experimental design has some limitations that researchers should be aware of. Here are some of the main limitations:
- Artificiality : Experimental design often involves creating artificial situations that may not reflect real-world situations. This can limit the external validity of the findings, or the extent to which the findings can be generalized to real-world settings.
- Ethical concerns: Some experimental designs may raise ethical concerns, particularly if they involve manipulating variables that could cause harm to participants or if they involve deception.
- Participant bias : Participants in experimental studies may modify their behavior in response to the experiment, which can lead to participant bias.
- Limited generalizability: The conditions of the experiment may not reflect the complexities of real-world situations. As a result, the findings may not be applicable to all populations and contexts.
- Cost and time : Experimental design can be expensive and time-consuming, particularly if the experiment requires specialized equipment or if the sample size is large.
- Researcher bias : Researchers may unintentionally bias the results of the experiment if they have expectations or preferences for certain outcomes.
- Lack of feasibility : Experimental design may not be feasible in some cases, particularly if the research question involves variables that cannot be manipulated or controlled.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Questionnaire – Definition, Types, and Examples

Case Study – Methods, Examples and Guide

Observational Research – Methods and Guide

Quantitative Research – Methods, Types and...

Qualitative Research Methods

Explanatory Research – Types, Methods, Guide
How to Write an Experimental Research Paper
- Conference paper
- Cite this conference paper

- M. N. Pamir M.D. 2 , 3
Part of the book series: Acta Neurochirurgica Supplements ((NEUROCHIRURGICA,volume 83))
453 Accesses
1 Citations
The art and practice of academic neurosurgery are mastered by defining and learning the pertinent basic principles and skills. This article aims to present general guidelines to one of the many roles of a neurosurgeon: Writing an experimental research paper.
Every research report must use the “IMRAD formula: introduction, methods, results and discussion”. After the IMRAD is finished, abstract should be written and the title should be “created”. Your abstract should answer these questions: “Why did you start?, what did you do?, what answer did you get?, and what does it mean?”. Title of the research paper should be short enough to catch glance and memory of the reader and be long enough to give the essential information of what the paper is about.
Writing about the results of the experiment is no easier than the research itself. As surgery, writing a scientific paper is also an improvisation, but general principles should be learned and used in practice. The most effective style of learning basic skills to construct a research paper is the “trial and error” type.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Compact, lightweight edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
- Durable hardcover edition
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Ad Hoc Working Group for Clinical Appraisal of the Medical Literature (1987) A proposal for more informative abstracts of clinical articles. Ann Intern Med 106: 598–604.
Google Scholar
Balch C, McKneally M, McPeek B, Mulder D, Spitzer W, Troidl H, Wechsler A (1997) Pentathlete: the many roles of academic surgeon. In: Troidl H, McKneally M, Mulder D, Wechsler A, McPeek B, Spitzer W (eds) Surgical research. New York: Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York Tokyo.
Condon R (1986) Type III Error. Arch Surg 121: 877–878.
PubMed CAS Google Scholar
Fleming A (1929) On the antimicrobial action of cultures of a penicillium, with special reference to their use in the isolation of B. influenzae. Br J Exper Pathol 10: 226–236.
CAS Google Scholar
Hill A (1965) The reasons for writing. Br Med J 2: 626–627.
Article Google Scholar
Hugh E (1987) Structured abstracts for papers reporting clinical articles. Ann Intern Med 106: 626–627.
International Committee of Medical Journal Editors (1997) Uniform requirements for manuscripts submitted to biomedical journals. New Engl J Med 336: 309–315.
Pollock A, Evans M (1997) Writing a scientific paper. In: Troidl H, McKneally M, Mulder D, Wechsler A, McPeek B, Spitzer W (eds) Surgical research. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York Tokyo.
Tufte E (1983) The visual display of quantitative information. CT: Graphics, Cheshire.
Watson J, Crick F (1953) Molecular structure of nucleic acids. A structure for deoxyribose nucleic acid. Nature 4356: 737–738.
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Institute of Neurological Sciences, Marmara University, Istanbul, Turkey
M. N. Pamir M.D.
Norolojik Bilimler Enstitusu, Marmara University, PK 53 Maltepe, Istanbul, Turkey
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Editor information
Editors and affiliations.
Ankara, Turkey
Y. Kanpolat
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2002 Springer-Verlag/Wien
About this paper
Cite this paper.
Pamir, M.N. (2002). How to Write an Experimental Research Paper. In: Kanpolat, Y. (eds) Research and Publishing in Neurosurgery. Acta Neurochirurgica Supplements, vol 83. Springer, Vienna. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-7091-6743-4_18
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-7091-6743-4_18
Publisher Name : Springer, Vienna
Print ISBN : 978-3-7091-7399-2
Online ISBN : 978-3-7091-6743-4
eBook Packages : Springer Book Archive
Share this paper
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
The use and interpretation of quasi-experimental design
Last updated
6 February 2023
Reviewed by
Miroslav Damyanov
- What is a quasi-experimental design?
Commonly used in medical informatics (a field that uses digital information to ensure better patient care), researchers generally use this design to evaluate the effectiveness of a treatment – perhaps a type of antibiotic or psychotherapy, or an educational or policy intervention.
Even though quasi-experimental design has been used for some time, relatively little is known about it. Read on to learn the ins and outs of this research design.
Make research less tedious
Dovetail streamlines research to help you uncover and share actionable insights
- When to use a quasi-experimental design
A quasi-experimental design is used when it's not logistically feasible or ethical to conduct randomized, controlled trials. As its name suggests, a quasi-experimental design is almost a true experiment. However, researchers don't randomly select elements or participants in this type of research.
Researchers prefer to apply quasi-experimental design when there are ethical or practical concerns. Let's look at these two reasons more closely.
Ethical reasons
In some situations, the use of randomly assigned elements can be unethical. For instance, providing public healthcare to one group and withholding it to another in research is unethical. A quasi-experimental design would examine the relationship between these two groups to avoid physical danger.
Practical reasons
Randomized controlled trials may not be the best approach in research. For instance, it's impractical to trawl through large sample sizes of participants without using a particular attribute to guide your data collection .
Recruiting participants and properly designing a data-collection attribute to make the research a true experiment requires a lot of time and effort, and can be expensive if you don’t have a large funding stream.
A quasi-experimental design allows researchers to take advantage of previously collected data and use it in their study.
- Examples of quasi-experimental designs
Quasi-experimental research design is common in medical research, but any researcher can use it for research that raises practical and ethical concerns. Here are a few examples of quasi-experimental designs used by different researchers:
Example 1: Determining the effectiveness of math apps in supplementing math classes
A school wanted to supplement its math classes with a math app. To select the best app, the school decided to conduct demo tests on two apps before selecting the one they will purchase.
Scope of the research
Since every grade had two math teachers, each teacher used one of the two apps for three months. They then gave the students the same math exams and compared the results to determine which app was most effective.
Reasons why this is a quasi-experimental study
This simple study is a quasi-experiment since the school didn't randomly assign its students to the applications. They used a pre-existing class structure to conduct the study since it was impractical to randomly assign the students to each app.
Example 2: Determining the effectiveness of teaching modern leadership techniques in start-up businesses
A hypothetical quasi-experimental study was conducted in an economically developing country in a mid-sized city.
Five start-ups in the textile industry and five in the tech industry participated in the study. The leaders attended a six-week workshop on leadership style, team management, and employee motivation.
After a year, the researchers assessed the performance of each start-up company to determine growth. The results indicated that the tech start-ups were further along in their growth than the textile companies.
The basis of quasi-experimental research is a non-randomized subject-selection process. This study didn't use specific aspects to determine which start-up companies should participate. Therefore, the results may seem straightforward, but several aspects may determine the growth of a specific company, apart from the variables used by the researchers.
Example 3: A study to determine the effects of policy reforms and of luring foreign investment on small businesses in two mid-size cities
In a study to determine the economic impact of government reforms in an economically developing country, the government decided to test whether creating reforms directed at small businesses or luring foreign investments would spur the most economic development.
The government selected two cities with similar population demographics and sizes. In one of the cities, they implemented specific policies that would directly impact small businesses, and in the other, they implemented policies to attract foreign investment.
After five years, they collected end-of-year economic growth data from both cities. They looked at elements like local GDP growth, unemployment rates, and housing sales.
The study used a non-randomized selection process to determine which city would participate in the research. Researchers left out certain variables that would play a crucial role in determining the growth of each city. They used pre-existing groups of people based on research conducted in each city, rather than random groups.
- Advantages of a quasi-experimental design
Some advantages of quasi-experimental designs are:
Researchers can manipulate variables to help them meet their study objectives.
It offers high external validity, making it suitable for real-world applications, specifically in social science experiments.
Integrating this methodology into other research designs is easier, especially in true experimental research. This cuts down on the time needed to determine your outcomes.
- Disadvantages of a quasi-experimental design
Despite the pros that come with a quasi-experimental design, there are several disadvantages associated with it, including the following:
It has a lower internal validity since researchers do not have full control over the comparison and intervention groups or between time periods because of differences in characteristics in people, places, or time involved. It may be challenging to determine whether all variables have been used or whether those used in the research impacted the results.
There is the risk of inaccurate data since the research design borrows information from other studies.
There is the possibility of bias since researchers select baseline elements and eligibility.
- What are the different quasi-experimental study designs?
There are three distinct types of quasi-experimental designs:
Nonequivalent
Regression discontinuity, natural experiment.
This is a hybrid of experimental and quasi-experimental methods and is used to leverage the best qualities of the two. Like the true experiment design, nonequivalent group design uses pre-existing groups believed to be comparable. However, it doesn't use randomization, the lack of which is a crucial element for quasi-experimental design.
Researchers usually ensure that no confounding variables impact them throughout the grouping process. This makes the groupings more comparable.
Example of a nonequivalent group design
A small study was conducted to determine whether after-school programs result in better grades. Researchers randomly selected two groups of students: one to implement the new program, the other not to. They then compared the results of the two groups.
This type of quasi-experimental research design calculates the impact of a specific treatment or intervention. It uses a criterion known as "cutoff" that assigns treatment according to eligibility.
Researchers often assign participants above the cutoff to the treatment group. This puts a negligible distinction between the two groups (treatment group and control group).
Example of regression discontinuity
Students must achieve a minimum score to be enrolled in specific US high schools. Since the cutoff score used to determine eligibility for enrollment is arbitrary, researchers can assume that the disparity between students who only just fail to achieve the cutoff point and those who barely pass is a small margin and is due to the difference in the schools that these students attend.
Researchers can then examine the long-term effects of these two groups of kids to determine the effect of attending certain schools. This information can be applied to increase the chances of students being enrolled in these high schools.
This research design is common in laboratory and field experiments where researchers control target subjects by assigning them to different groups. Researchers randomly assign subjects to a treatment group using nature or an external event or situation.
However, even with random assignment, this research design cannot be called a true experiment since nature aspects are observational. Researchers can also exploit these aspects despite having no control over the independent variables.
Example of the natural experiment approach
An example of a natural experiment is the 2008 Oregon Health Study.
Oregon intended to allow more low-income people to participate in Medicaid.
Since they couldn't afford to cover every person who qualified for the program, the state used a random lottery to allocate program slots.
Researchers assessed the program's effectiveness by assigning the selected subjects to a randomly assigned treatment group, while those that didn't win the lottery were considered the control group.
- Differences between quasi-experiments and true experiments
There are several differences between a quasi-experiment and a true experiment:
Participants in true experiments are randomly assigned to the treatment or control group, while participants in a quasi-experiment are not assigned randomly.
In a quasi-experimental design, the control and treatment groups differ in unknown or unknowable ways, apart from the experimental treatments that are carried out. Therefore, the researcher should try as much as possible to control these differences.
Quasi-experimental designs have several "competing hypotheses," which compete with experimental manipulation to explain the observed results.
Quasi-experiments tend to have lower internal validity (the degree of confidence in the research outcomes) than true experiments, but they may offer higher external validity (whether findings can be extended to other contexts) as they involve real-world interventions instead of controlled interventions in artificial laboratory settings.
Despite the distinct difference between true and quasi-experimental research designs, these two research methodologies share the following aspects:
Both study methods subject participants to some form of treatment or conditions.
Researchers have the freedom to measure some of the outcomes of interest.
Researchers can test whether the differences in the outcomes are associated with the treatment.
- An example comparing a true experiment and quasi-experiment
Imagine you wanted to study the effects of junk food on obese people. Here's how you would do this as a true experiment and a quasi-experiment:
How to carry out a true experiment
In a true experiment, some participants would eat junk foods, while the rest would be in the control group, adhering to a regular diet. At the end of the study, you would record the health and discomfort of each group.
This kind of experiment would raise ethical concerns since the participants assigned to the treatment group are required to eat junk food against their will throughout the experiment. This calls for a quasi-experimental design.
How to carry out a quasi-experiment
In quasi-experimental research, you would start by finding out which participants want to try junk food and which prefer to stick to a regular diet. This allows you to assign these two groups based on subject choice.
In this case, you didn't assign participants to a particular group, so you can confidently use the results from the study.
When is a quasi-experimental design used?
Quasi-experimental designs are used when researchers don’t want to use randomization when evaluating their intervention.
What are the characteristics of quasi-experimental designs?
Some of the characteristics of a quasi-experimental design are:
Researchers don't randomly assign participants into groups, but study their existing characteristics and assign them accordingly.
Researchers study the participants in pre- and post-testing to determine the progress of the groups.
Quasi-experimental design is ethical since it doesn’t involve offering or withholding treatment at random.
Quasi-experimental design encompasses a broad range of non-randomized intervention studies. This design is employed when it is not ethical or logistically feasible to conduct randomized controlled trials. Researchers typically employ it when evaluating policy or educational interventions, or in medical or therapy scenarios.
How do you analyze data in a quasi-experimental design?
You can use two-group tests, time-series analysis, and regression analysis to analyze data in a quasi-experiment design. Each option has specific assumptions, strengths, limitations, and data requirements.
Should you be using a customer insights hub?
Do you want to discover previous research faster?
Do you share your research findings with others?
Do you analyze research data?
Start for free today, add your research, and get to key insights faster
Editor’s picks
Last updated: 11 January 2024
Last updated: 15 January 2024
Last updated: 17 January 2024
Last updated: 25 November 2023
Last updated: 12 May 2023
Last updated: 30 April 2024
Last updated: 13 May 2024
Latest articles
Related topics, .css-je19u9{-webkit-align-items:flex-end;-webkit-box-align:flex-end;-ms-flex-align:flex-end;align-items:flex-end;display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-flex-direction:row;-ms-flex-direction:row;flex-direction:row;-webkit-box-flex-wrap:wrap;-webkit-flex-wrap:wrap;-ms-flex-wrap:wrap;flex-wrap:wrap;-webkit-box-pack:center;-ms-flex-pack:center;-webkit-justify-content:center;justify-content:center;row-gap:0;text-align:center;max-width:671px;}@media (max-width: 1079px){.css-je19u9{max-width:400px;}.css-je19u9>span{white-space:pre;}}@media (max-width: 799px){.css-je19u9{max-width:400px;}.css-je19u9>span{white-space:pre;}} decide what to .css-1kiodld{max-height:56px;display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;}@media (max-width: 1079px){.css-1kiodld{display:none;}} build next, decide what to build next.

Users report unexpectedly high data usage, especially during streaming sessions.

Users find it hard to navigate from the home page to relevant playlists in the app.

It would be great to have a sleep timer feature, especially for bedtime listening.

I need better filters to find the songs or artists I’m looking for.
Log in or sign up
Get started for free

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Table of contents. Step 1: Define your variables. Step 2: Write your hypothesis. Step 3: Design your experimental treatments. Step 4: Assign your subjects to treatment groups. Step 5: Measure your dependent variable. Other interesting articles. Frequently asked questions about experiments.
A good experimental design requires a strong understanding of the system you are studying. There are five key steps in designing an experiment: Consider your variables and how they are related. Write a specific, testable hypothesis. Design experimental treatments to manipulate your independent variable.
Table of contents. Step 1: Consider your aims and approach. Step 2: Choose a type of research design. Step 3: Identify your population and sampling method. Step 4: Choose your data collection methods. Step 5: Plan your data collection procedures. Step 6: Decide on your data analysis strategies.
There are 3 types of experimental research designs. These are pre-experimental research design, true experimental research design, and quasi experimental research design. 1. The assignment of the control group in quasi experimental research is non-random, unlike true experimental design, which is randomly assigned. 2.
Experimental design is a research method that enables researchers to assess the effect of multiple factors on an outcome.. You can determine the relationship between each of the variables by: Manipulating one or more independent variables (i.e., stimuli or treatments). Applying the changes to one or more dependent variables (i.e., test groups or outcomes)
Experimental Research Design. Experimental research design is used to determine if there is a causal relationship between two or more variables.With this type of research design, you, as the researcher, manipulate one variable (the independent variable) while controlling others (dependent variables). Doing so allows you to observe the effect of the former on the latter and draw conclusions ...
Step 2: build your hypothesis. Next, you should state your hypothesis. This should be a specific and testable statement that outlines what you expect to find, should emerge from your research question, and should be informed by the results of any previous research.
An experimental design is a detailed plan for collecting and using data to identify causal relationships. Through careful planning, the design of experiments allows your data collection efforts to have a reasonable chance of detecting effects and testing hypotheses that answer your research questions. An experiment is a data collection ...
Actually, a deeper knowledge on the topic could offer a different point of view. The aim of the present tutorial is to introduce the experimental design to beginners, by providing the theoretical basic principles as well as a practical guide to use the most common designs, from the experimental plan to the final optimization.
Step 2: Data Type you Need for Research. Decide on the type of data you need for your research. The type of data you need to collect depends on your research questions or research hypothesis. Two types of research data can be used to answer the research questions: Primary Data Vs. Secondary Data.
Abstract. This chapter addresses the peculiarities, characteristics, and major fallacies of experimental research designs. Experiments have a long and important history in the social, natural, and medicinal sciences. Unfortunately, in business and management this looks differently. This is astounding, as experiments are suitable for analyzing ...
This chapter addresses experimental research designs' peculiarities, characteristics, and significant fallacies. Experiments have a long and important history in the social, natural, and medicinal sciences. Unfortunately, in business and management, this looks different. This is astounding, as experiments are suitable for analyzing cause-and ...
The pre-experimental research design is further divided into three types. One-shot Case Study Research Design. In this type of experimental study, only one dependent group or variable is considered. The study is carried out after some treatment which was presumed to cause change, making it a posttest study.
Types of design include repeated measures, independent groups, and matched pairs designs. Probably the most common way to design an experiment in psychology is to divide the participants into two groups, the experimental group and the control group, and then introduce a change to the experimental group, not the control group.
Before beginning your paper, you need to decide how you plan to design the study.. The research design refers to the overall strategy and analytical approach that you have chosen in order to integrate, in a coherent and logical way, the different components of the study, thus ensuring that the research problem will be thoroughly investigated. It constitutes the blueprint for the collection ...
Study, experimental, or research design is the backbone of good research. It directs the experiment by orchestrating data collection, defines the statistical analysis of the resultant data, and guides the interpretation of the results. When properly described in the written report of the experiment, it serves as a road map to readers, 1 helping ...
Collect the data by using suitable data collection according to your experiment's requirement, such as observations, case studies , surveys , interviews, questionnaires, etc. Analyse the obtained information. Step 8. Present and Conclude the Findings of the Study. Write the report of your research.
Quasi-experimental research design is similar to experimental research design, but it lacks one or more of the features of a true experiment. For example, there may not be random assignment to groups or a control group. ... Writing a research design involves planning and outlining the methodology and approach that will be used to answer a ...
Experimental Design. Experimental design is a process of planning and conducting scientific experiments to investigate a hypothesis or research question. It involves carefully designing an experiment that can test the hypothesis, and controlling for other variables that may influence the results. Experimental design typically includes ...
This article aims to present general guidelines to one of the many roles of a neurosurgeon: Writing an experimental research paper. Every research report must use the "IMRAD formula: introduction, methods, results and discussion". After the IMRAD is finished, abstract should be written and the title should be "created".
A quasi-experimental design is used when it's not logistically feasible or ethical to conduct randomized, controlled trials. As its name suggests, a quasi-experimental design is almost a true experiment. However, researchers don't randomly select elements or participants in this type of research. Researchers prefer to apply quasi-experimental ...