
How it works
Transform your enterprise with the scalable mindsets, skills, & behavior change that drive performance.
Explore how BetterUp connects to your core business systems.
We pair AI with the latest in human-centered coaching to drive powerful, lasting learning and behavior change.
Build leaders that accelerate team performance and engagement.
Unlock performance potential at scale with AI-powered curated growth journeys.
Build resilience, well-being and agility to drive performance across your entire enterprise.
Transform your business, starting with your sales leaders.
Unlock business impact from the top with executive coaching.
Foster a culture of inclusion and belonging.
Accelerate the performance and potential of your agencies and employees.
See how innovative organizations use BetterUp to build a thriving workforce.
Discover how BetterUp measurably impacts key business outcomes for organizations like yours.
A demo is the first step to transforming your business. Meet with us to develop a plan for attaining your goals.

- What is coaching?
Learn how 1:1 coaching works, who its for, and if it's right for you.
Accelerate your personal and professional growth with the expert guidance of a BetterUp Coach.
Types of Coaching
Navigate career transitions, accelerate your professional growth, and achieve your career goals with expert coaching.
Enhance your communication skills for better personal and professional relationships, with tailored coaching that focuses on your needs.
Find balance, resilience, and well-being in all areas of your life with holistic coaching designed to empower you.
Discover your perfect match : Take our 5-minute assessment and let us pair you with one of our top Coaches tailored just for you.

Research, expert insights, and resources to develop courageous leaders within your organization.
Best practices, research, and tools to fuel individual and business growth.
View on-demand BetterUp events and learn about upcoming live discussions.
The latest insights and ideas for building a high-performing workplace.
- BetterUp Briefing
The online magazine that helps you understand tomorrow's workforce trends, today.
Innovative research featured in peer-reviewed journals, press, and more.
Founded in 2022 to deepen the understanding of the intersection of well-being, purpose, and performance
We're on a mission to help everyone live with clarity, purpose, and passion.
Join us and create impactful change.
Read the buzz about BetterUp.
Meet the leadership that's passionate about empowering your workforce.

For Business
For Individuals

How to write a speech that your audience remembers

Whether in a work meeting or at an investor panel, you might give a speech at some point. And no matter how excited you are about the opportunity, the experience can be nerve-wracking .
But feeling butterflies doesn’t mean you can’t give a great speech. With the proper preparation and a clear outline, apprehensive public speakers and natural wordsmiths alike can write and present a compelling message. Here’s how to write a good speech you’ll be proud to deliver.
What is good speech writing?
Good speech writing is the art of crafting words and ideas into a compelling, coherent, and memorable message that resonates with the audience. Here are some key elements of great speech writing:
- It begins with clearly understanding the speech's purpose and the audience it seeks to engage.
- A well-written speech clearly conveys its central message, ensuring that the audience understands and retains the key points.
- It is structured thoughtfully, with a captivating opening, a well-organized body, and a conclusion that reinforces the main message.
- Good speech writing embraces the power of engaging content, weaving in stories, examples, and relatable anecdotes to connect with the audience on both intellectual and emotional levels.
Ultimately, it is the combination of these elements, along with the authenticity and delivery of the speaker , that transforms words on a page into a powerful and impactful spoken narrative.
What makes a good speech?
A great speech includes several key qualities, but three fundamental elements make a speech truly effective:
Clarity and purpose
Remembering the audience, cohesive structure.
While other important factors make a speech a home run, these three elements are essential for writing an effective speech.
The main elements of a good speech
The main elements of a speech typically include:
- Introduction: The introduction sets the stage for your speech and grabs the audience's attention. It should include a hook or attention-grabbing opening, introduce the topic, and provide an overview of what will be covered.
- Opening/captivating statement: This is a strong statement that immediately engages the audience and creates curiosity about the speech topics.
- Thesis statement/central idea: The thesis statement or central idea is a concise statement that summarizes the main point or argument of your speech. It serves as a roadmap for the audience to understand what your speech is about.
- Body: The body of the speech is where you elaborate on your main points or arguments. Each point is typically supported by evidence, examples, statistics, or anecdotes. The body should be organized logically and coherently, with smooth transitions between the main points.
- Supporting evidence: This includes facts, data, research findings, expert opinions, or personal stories that support and strengthen your main points. Well-chosen and credible evidence enhances the persuasive power of your speech.
- Transitions: Transitions are phrases or statements that connect different parts of your speech, guiding the audience from one idea to the next. Effective transitions signal the shifts in topics or ideas and help maintain a smooth flow throughout the speech.
- Counterarguments and rebuttals (if applicable): If your speech involves addressing opposing viewpoints or counterarguments, you should acknowledge and address them. Presenting counterarguments makes your speech more persuasive and demonstrates critical thinking.
- Conclusion: The conclusion is the final part of your speech and should bring your message to a satisfying close. Summarize your main points, restate your thesis statement, and leave the audience with a memorable closing thought or call to action.
- Closing statement: This is the final statement that leaves a lasting impression and reinforces the main message of your speech. It can be a call to action, a thought-provoking question, a powerful quote, or a memorable anecdote.
- Delivery and presentation: How you deliver your speech is also an essential element to consider. Pay attention to your tone, body language, eye contact , voice modulation, and timing. Practice and rehearse your speech, and try using the 7-38-55 rule to ensure confident and effective delivery.
While the order and emphasis of these elements may vary depending on the type of speech and audience, these elements provide a framework for organizing and delivering a successful speech.

How to structure a good speech
You know what message you want to transmit, who you’re delivering it to, and even how you want to say it. But you need to know how to start, develop, and close a speech before writing it.
Think of a speech like an essay. It should have an introduction, conclusion, and body sections in between. This places ideas in a logical order that the audience can better understand and follow them. Learning how to make a speech with an outline gives your storytelling the scaffolding it needs to get its point across.
Here’s a general speech structure to guide your writing process:
- Explanation 1
- Explanation 2
- Explanation 3
How to write a compelling speech opener
Some research shows that engaged audiences pay attention for only 15 to 20 minutes at a time. Other estimates are even lower, citing that people stop listening intently in fewer than 10 minutes . If you make a good first impression at the beginning of your speech, you have a better chance of interesting your audience through the middle when attention spans fade.
Implementing the INTRO model can help grab and keep your audience’s attention as soon as you start speaking. This acronym stands for interest, need, timing, roadmap, and objectives, and it represents the key points you should hit in an opening.
Here’s what to include for each of these points:
- Interest : Introduce yourself or your topic concisely and speak with confidence . Write a compelling opening statement using relevant data or an anecdote that the audience can relate to.
- Needs : The audience is listening to you because they have something to learn. If you’re pitching a new app idea to a panel of investors, those potential partners want to discover more about your product and what they can earn from it. Read the room and gently remind them of the purpose of your speech.
- Timing : When appropriate, let your audience know how long you’ll speak. This lets listeners set expectations and keep tabs on their own attention span. If a weary audience member knows you’ll talk for 40 minutes, they can better manage their energy as that time goes on.
- Routemap : Give a brief overview of the three main points you’ll cover in your speech. If an audience member’s attention starts to drop off and they miss a few sentences, they can more easily get their bearings if they know the general outline of the presentation.
- Objectives : Tell the audience what you hope to achieve, encouraging them to listen to the end for the payout.
Writing the middle of a speech
The body of your speech is the most information-dense section. Facts, visual aids, PowerPoints — all this information meets an audience with a waning attention span. Sticking to the speech structure gives your message focus and keeps you from going off track, making everything you say as useful as possible.
Limit the middle of your speech to three points, and support them with no more than three explanations. Following this model organizes your thoughts and prevents you from offering more information than the audience can retain.
Using this section of the speech to make your presentation interactive can add interest and engage your audience. Try including a video or demonstration to break the monotony. A quick poll or survey also keeps the audience on their toes.
Wrapping the speech up
To you, restating your points at the end can feel repetitive and dull. You’ve practiced countless times and heard it all before. But repetition aids memory and learning , helping your audience retain what you’ve told them. Use your speech’s conclusion to summarize the main points with a few short sentences.
Try to end on a memorable note, like posing a motivational quote or a thoughtful question the audience can contemplate once they leave. In proposal or pitch-style speeches, consider landing on a call to action (CTA) that invites your audience to take the next step.

How to write a good speech
If public speaking gives you the jitters, you’re not alone. Roughly 80% of the population feels nervous before giving a speech, and another 10% percent experiences intense anxiety and sometimes even panic.
The fear of failure can cause procrastination and can cause you to put off your speechwriting process until the last minute. Finding the right words takes time and preparation, and if you’re already feeling nervous, starting from a blank page might seem even harder.
But putting in the effort despite your stress is worth it. Presenting a speech you worked hard on fosters authenticity and connects you to the subject matter, which can help your audience understand your points better. Human connection is all about honesty and vulnerability, and if you want to connect to the people you’re speaking to, they should see that in you.
1. Identify your objectives and target audience
Before diving into the writing process, find healthy coping strategies to help you stop worrying . Then you can define your speech’s purpose, think about your target audience, and start identifying your objectives. Here are some questions to ask yourself and ground your thinking :
- What purpose do I want my speech to achieve?
- What would it mean to me if I achieved the speech’s purpose?
- What audience am I writing for?
- What do I know about my audience?
- What values do I want to transmit?
- If the audience remembers one take-home message, what should it be?
- What do I want my audience to feel, think, or do after I finish speaking?
- What parts of my message could be confusing and require further explanation?
2. Know your audience
Understanding your audience is crucial for tailoring your speech effectively. Consider the demographics of your audience, their interests, and their expectations. For instance, if you're addressing a group of healthcare professionals, you'll want to use medical terminology and data that resonate with them. Conversely, if your audience is a group of young students, you'd adjust your content to be more relatable to their experiences and interests.
3. Choose a clear message
Your message should be the central idea that you want your audience to take away from your speech. Let's say you're giving a speech on climate change. Your clear message might be something like, "Individual actions can make a significant impact on mitigating climate change." Throughout your speech, all your points and examples should support this central message, reinforcing it for your audience.
4. Structure your speech
Organizing your speech properly keeps your audience engaged and helps them follow your ideas. The introduction should grab your audience's attention and introduce the topic. For example, if you're discussing space exploration, you could start with a fascinating fact about a recent space mission. In the body, you'd present your main points logically, such as the history of space exploration, its scientific significance, and future prospects. Finally, in the conclusion, you'd summarize your key points and reiterate the importance of space exploration in advancing human knowledge.
5. Use engaging content for clarity
Engaging content includes stories, anecdotes, statistics, and examples that illustrate your main points. For instance, if you're giving a speech about the importance of reading, you might share a personal story about how a particular book changed your perspective. You could also include statistics on the benefits of reading, such as improved cognitive abilities and empathy.
6. Maintain clarity and simplicity
It's essential to communicate your ideas clearly. Avoid using overly technical jargon or complex language that might confuse your audience. For example, if you're discussing a medical breakthrough with a non-medical audience, explain complex terms in simple, understandable language.
7. Practice and rehearse
Practice is key to delivering a great speech. Rehearse multiple times to refine your delivery, timing, and tone. Consider using a mirror or recording yourself to observe your body language and gestures. For instance, if you're giving a motivational speech, practice your gestures and expressions to convey enthusiasm and confidence.
8. Consider nonverbal communication
Your body language, tone of voice, and gestures should align with your message . If you're delivering a speech on leadership, maintain strong eye contact to convey authority and connection with your audience. A steady pace and varied tone can also enhance your speech's impact.
9. Engage your audience
Engaging your audience keeps them interested and attentive. Encourage interaction by asking thought-provoking questions or sharing relatable anecdotes. If you're giving a speech on teamwork, ask the audience to recall a time when teamwork led to a successful outcome, fostering engagement and connection.
10. Prepare for Q&A
Anticipate potential questions or objections your audience might have and prepare concise, well-informed responses. If you're delivering a speech on a controversial topic, such as healthcare reform, be ready to address common concerns, like the impact on healthcare costs or access to services, during the Q&A session.
By following these steps and incorporating examples that align with your specific speech topic and purpose, you can craft and deliver a compelling and impactful speech that resonates with your audience.

Tools for writing a great speech
There are several helpful tools available for speechwriting, both technological and communication-related. Here are a few examples:
- Word processing software: Tools like Microsoft Word, Google Docs, or other word processors provide a user-friendly environment for writing and editing speeches. They offer features like spell-checking, grammar correction, formatting options, and easy revision tracking.
- Presentation software: Software such as Microsoft PowerPoint or Google Slides is useful when creating visual aids to accompany your speech. These tools allow you to create engaging slideshows with text, images, charts, and videos to enhance your presentation.
- Speechwriting Templates: Online platforms or software offer pre-designed templates specifically for speechwriting. These templates provide guidance on structuring your speech and may include prompts for different sections like introductions, main points, and conclusions.
- Rhetorical devices and figures of speech: Rhetorical tools such as metaphors, similes, alliteration, and parallelism can add impact and persuasion to your speech. Resources like books, websites, or academic papers detailing various rhetorical devices can help you incorporate them effectively.
- Speechwriting apps: Mobile apps designed specifically for speechwriting can be helpful in organizing your thoughts, creating outlines, and composing a speech. These apps often provide features like voice recording, note-taking, and virtual prompts to keep you on track.
- Grammar and style checkers: Online tools or plugins like Grammarly or Hemingway Editor help improve the clarity and readability of your speech by checking for grammar, spelling, and style errors. They provide suggestions for sentence structure, word choice, and overall tone.
- Thesaurus and dictionary: Online or offline resources such as thesauruses and dictionaries help expand your vocabulary and find alternative words or phrases to express your ideas more effectively. They can also clarify meanings or provide context for unfamiliar terms.
- Online speechwriting communities: Joining online forums or communities focused on speechwriting can be beneficial for getting feedback, sharing ideas, and learning from experienced speechwriters. It's an opportunity to connect with like-minded individuals and improve your public speaking skills through collaboration.
Remember, while these tools can assist in the speechwriting process, it's essential to use them thoughtfully and adapt them to your specific needs and style. The most important aspect of speechwriting remains the creativity, authenticity, and connection with your audience that you bring to your speech.

5 tips for writing a speech
Behind every great speech is an excellent idea and a speaker who refined it. But a successful speech is about more than the initial words on the page, and there are a few more things you can do to help it land.
Here are five more tips for writing and practicing your speech:
1. Structure first, write second
If you start the writing process before organizing your thoughts, you may have to re-order, cut, and scrap the sentences you worked hard on. Save yourself some time by using a speech structure, like the one above, to order your talking points first. This can also help you identify unclear points or moments that disrupt your flow.
2. Do your homework
Data strengthens your argument with a scientific edge. Research your topic with an eye for attention-grabbing statistics, or look for findings you can use to support each point. If you’re pitching a product or service, pull information from company metrics that demonstrate past or potential successes.
Audience members will likely have questions, so learn all talking points inside and out. If you tell investors that your product will provide 12% returns, for example, come prepared with projections that support that statement.
3. Sound like yourself
Memorable speakers have distinct voices. Think of Martin Luther King Jr’s urgent, inspiring timbre or Oprah’s empathetic, personal tone . Establish your voice — one that aligns with your personality and values — and stick with it. If you’re a motivational speaker, keep your tone upbeat to inspire your audience . If you’re the CEO of a startup, try sounding assured but approachable.
4. Practice
As you practice a speech, you become more confident , gain a better handle on the material, and learn the outline so well that unexpected questions are less likely to trip you up. Practice in front of a colleague or friend for honest feedback about what you could change, and speak in front of the mirror to tweak your nonverbal communication and body language .
5. Remember to breathe
When you’re stressed, you breathe more rapidly . It can be challenging to talk normally when you can’t regulate your breath. Before your presentation, try some mindful breathing exercises so that when the day comes, you already have strategies that will calm you down and remain present . This can also help you control your voice and avoid speaking too quickly.
How to ghostwrite a great speech for someone else
Ghostwriting a speech requires a unique set of skills, as you're essentially writing a piece that will be delivered by someone else. Here are some tips on how to effectively ghostwrite a speech:
- Understand the speaker's voice and style : Begin by thoroughly understanding the speaker's personality, speaking style, and preferences. This includes their tone, humor, and any personal anecdotes they may want to include.
- Interview the speaker : Have a detailed conversation with the speaker to gather information about their speech's purpose, target audience, key messages, and any specific points they want to emphasize. Ask for personal stories or examples they may want to include.
- Research thoroughly : Research the topic to ensure you have a strong foundation of knowledge. This helps you craft a well-informed and credible speech.
- Create an outline : Develop a clear outline that includes the introduction, main points, supporting evidence, and a conclusion. Share this outline with the speaker for their input and approval.
- Write in the speaker's voice : While crafting the speech, maintain the speaker's voice and style. Use language and phrasing that feel natural to them. If they have a particular way of expressing ideas, incorporate that into the speech.
- Craft a captivating opening : Begin the speech with a compelling opening that grabs the audience's attention. This could be a relevant quote, an interesting fact, a personal anecdote, or a thought-provoking question.
- Organize content logically : Ensure the speech flows logically, with each point building on the previous one. Use transitions to guide the audience from one idea to the next smoothly.
- Incorporate engaging stories and examples : Include anecdotes, stories, and real-life examples that illustrate key points and make the speech relatable and memorable.
- Edit and revise : Edit the speech carefully for clarity, grammar, and coherence. Ensure the speech is the right length and aligns with the speaker's time constraints.
- Seek feedback : Share drafts of the speech with the speaker for their feedback and revisions. They may have specific changes or additions they'd like to make.
- Practice delivery : If possible, work with the speaker on their delivery. Practice the speech together, allowing the speaker to become familiar with the content and your writing style.
- Maintain confidentiality : As a ghostwriter, it's essential to respect the confidentiality and anonymity of the work. Do not disclose that you wrote the speech unless you have the speaker's permission to do so.
- Be flexible : Be open to making changes and revisions as per the speaker's preferences. Your goal is to make them look good and effectively convey their message.
- Meet deadlines : Stick to agreed-upon deadlines for drafts and revisions. Punctuality and reliability are essential in ghostwriting.
- Provide support : Support the speaker during their preparation and rehearsal process. This can include helping with cue cards, speech notes, or any other materials they need.
Remember that successful ghostwriting is about capturing the essence of the speaker while delivering a well-structured and engaging speech. Collaboration, communication, and adaptability are key to achieving this.
Give your best speech yet
Learn how to make a speech that’ll hold an audience’s attention by structuring your thoughts and practicing frequently. Put the effort into writing and preparing your content, and aim to improve your breathing, eye contact , and body language as you practice. The more you work on your speech, the more confident you’ll become.
The energy you invest in writing an effective speech will help your audience remember and connect to every concept. Remember: some life-changing philosophies have come from good speeches, so give your words a chance to resonate with others. You might even change their thinking.
Boost your speech skills
Enhance your public speaking with personalized coaching tailored to your needs
Elizabeth Perry, ACC
Elizabeth Perry is a Coach Community Manager at BetterUp. She uses strategic engagement strategies to cultivate a learning community across a global network of Coaches through in-person and virtual experiences, technology-enabled platforms, and strategic coaching industry partnerships. With over 3 years of coaching experience and a certification in transformative leadership and life coaching from Sofia University, Elizabeth leverages transpersonal psychology expertise to help coaches and clients gain awareness of their behavioral and thought patterns, discover their purpose and passions, and elevate their potential. She is a lifelong student of psychology, personal growth, and human potential as well as an ICF-certified ACC transpersonal life and leadership Coach.
10+ interpersonal skills at work and ways to develop them
How to write an impactful cover letter for a career change, 6 presentation skills and how to improve them, what are analytical skills examples and how to level up, 18 effective strategies to improve your communication skills, the 11 tips that will improve your public speaking skills, what is gig work and does it make the dream work, how to be more persuasive: 6 tips for convincing others, self-management skills for a messy world, similar articles, how to write an executive summary in 10 steps, how to pitch ideas: 8 tips to captivate any audience, how to give a good presentation that captivates any audience, anxious about meetings learn how to run a meeting with these 10 tips, writing an elevator pitch about yourself: a how-to plus tips, 9 elevator pitch examples for making a strong first impression, how to write a memo: 8 steps with examples, stay connected with betterup, get our newsletter, event invites, plus product insights and research..
3100 E 5th Street, Suite 350 Austin, TX 78702
- Platform Overview
- Integrations
- Powered by AI
- BetterUp Lead™
- BetterUp Manage™
- BetterUp Care®
- Sales Performance
- Diversity & Inclusion
- Case Studies
- Why BetterUp?
- About Coaching
- Find your Coach
- Career Coaching
- Communication Coaching
- Life Coaching
- News and Press
- Leadership Team
- Become a BetterUp Coach
- BetterUp Labs
- Center for Purpose & Performance
- Leadership Training
- Business Coaching
- Contact Support
- Contact Sales
- Privacy Policy
- Acceptable Use Policy
- Trust & Security
- Cookie Preferences

A short speech – create a 3 minute speech that rocks
I’m in the Charles Pearson Theatre at the University of Melbourne, watching 12 short speeches. It’s a 3 minute speech competition called the 3 minute Thesis .
These annual, 3 minute speech competitions challenge Ph.D and Masters students to effectively communicate 3-1/2 years’ of technical research into a short speech. Their task is to convey only the most important ideas and findings to a non-technical audience – and with only a single slide.

A short speech is a great test
As you’d imagine, it can be difficult to condense all that research and knowledge into a 3 minute speech, yet still convey all the pertinent information .
But that’s exactly why it’s such a great exercise for all speakers .
That’s because, in order to be effective, your ideas must be able to be communicated in the most brief, simple and clear manner possible. You need them to stick in the listener’s mind.
Not everyone is good at this skill – indeed, few people are. But you need to be if you want other to see the value of your ideas.
By the way, if you think giving a good 3 minute speech is hard, try doing one in just 5 words! That’s what they do at the Webby awards .
What did the winning speakers do right?
Despite giving a short speech on very different topics, there were some common practices I noticed about the winning speakers.
- They presented an exceptionally clear message .
- They included a “ top and tail ” element.
- They made use of metaphor and other verbal illustrations to simplify a complex idea.
- They spoke like they were having a conversation with their audience – not ‘giving a formal speech’.
The losing speakers, by contrast, were more forced. Some were so unnatural they seemed to be giving a pantomime a speech for an audience of children. The engagement of conversation was missing. We’ve talked before about the importance of an unforced, natural style .
How to create a short speech.
1. use a simple structure..
Start by clearly saying the ‘headline’ and key idea underpinning your speech in simple, everyday language, and follow with a simple structure supporting your main point. Here are some examples:
A: Headline and 3 supporting reasons:
With this approach, follow your “headline” statement with 3 simple supporting reasons. State each reason clearly, and explain how each one helps achieve or support the objective.
“We must change the way we work – for 3 important reasons:
- Thwack …,
- Kapow…,
- Whamm. “
B: Problem – solution:
This is a simple structure of only 2 parts. It’s an easy yet powerful way to capture people’s attention and interest when done well. But you’ll want to avoid the trap of rushing through the problem, and spending too much time on your brilliant solution.
If you really want to hook people, take some time to paint a vivid picture of the problem first. Your audience will then be clambering for a solution with both ears open.
C: Timeline:
In this type of short speech, you might cover:
- The history of the issue …
- The current situation …
- What might happen in the future …
- And the ramifications of agreeing (or disagreeing) with your main argument.
D: Metaphor/Top & Tail:
To “top and tail” simply means starting with a story/quote that hints at your message. At the end, you recall that story and link it to your message.
This short speech from a 3 minute speech competition makes excellent use of this approach.
Start your speech (“the top”) with a compelling metaphor to make a memorable point, and end the speech (“the tail”) with the same metaphor — but adjusted to show the benefit of adopting your central argument.
2: End with a memorable message:
Just as important as how you begin and structure your speech, is how you end it .
Consider the same techniques at the end of your speech. A metaphor that links back to your original premise, or finishing with a thought-provoking question, are two ways to burnish your speech in your listener’s mind.
These videos of the 1st and 2nd place winners of a 3 minute speech competition show how effective these closing techniques can be: 1st Place: Sara Ciesielski 2nd Place: Samantha Lichter
People worry that time limitations mean they have to ‘dumb down’ their valuable research — this is not the case!
A vivid message and a compelling short speech can become a window to the depth of your research, and give clarity to the value of your ideas.
A 3 minute speech gives you a huge amount of time to do this – if you use the time wisely and structure your speech to maximum effect.
Want to be a great speaker? Get the kindle ebook from amazon.com: What’s Your Message? Public Speaking with Twice the Impact, Using Half the Effort
Memorable 2-Minute Speeches: How to Write & Deliver (With Examples)
Hrideep barot.
- Public Speaking , Speech Topics , Speech Writing

Giving memorable 2-minute speeches are tricker than giving 2-minute speeches.
Speeches are an effective way to share your understanding, opinion, or perspective on a topic. It doesn’t matter if your speech is for 2 minutes, 10 minutes, or 50 minutes, the main essence of any speech is to reach the audience .
2-minute speeches are quite effective if presented in a well-structured manner. In fact, giving 2-minute speeches can also help you improve your public speaking skills. And that is the reason why schools ask the students to give 2-minute speeches for every assignment!
Now we understand you might have tons of questions when it comes to 2-minute speeches, but fret not, we’ve got you covered. Read till the end of the blog to get a more comprehensive idea about 2-minute speeches.
Also, check out our video here if you want a very short glimpse of the article:
Is a 2-minute speech too short?
2-minute speeches come under the category of short speeches. So ideally 2 minute speeches are short speeches . But when we say is it too short? Then the answer will be subjective.
For instance, If you are to present your research findings then a 2-minute speech would not do justice to years of your work. But at the same time if you are giving a self-introduction then 2 minute speeches are more than enough!
How long is a 2-minute speech?
To understand how long 2-minute speeches should be, you need to understand your pace of speaking which is the number of words spoken per minute. An average person usually speaks about 130-150 words per minute . So for 2-minute speeches, 260-300 words should be sufficient.
When it comes to the number of pages for a 2-minute speech, then your speech can be half to one page long . It all depends on the font size that you use!
Similarly, the number of sentences that would make up a 2-minute speech can vary depending on the font size that you use or your handwriting.
Writing 2-minute speeches
1. choose a topic.
The very first step in writing your speech is to know what you want to talk about, which is your topic !
You can either come up with the topic yourself or you can search for a broad topic on the internet and then narrow it down as per your liking.
So if for example, you are writing a 2-minute speech on unity as strength , you may want to focus on a particular instance wherein unity shown by people worked as their strength and helped them achieve a goal, like a freedom struggle.
2. Decide on your takeaway
If you are wondering what takeaways are, then they are your answer to the question “why are you presenting this particular topic to the audience?”
For some the answer could be, to educate, give another perspective on a widely studied topic, or even awaken the audience to take action .
In 2 minute speeches, the clock ticks faster so you should ideally focus on only 1 takeaway .
Once you have figured out why you want to present the topic to your audience or listeners, you can then move to the next stage of research.
3. Research for your speech
When you begin researching for 2 minutes speeches, you don’t have to get into tons of details . The idea is to give the audience enough information to understand your topic within a short time.
For starters, you can browse your topic on Google , YouTube , Instagram , and other social media channels. You might also want to research some facts or statistics related to your topic as it increases the credibility of your speech.
4. Structure your speech
There are 3 things to be kept in mind while structuring your speech. They are ethos, pathos, and logos.
Ethos means credibility . It is concerned with giving the audience a reason to believe in you. So, if your speech is about the impact of gaming on violent behavior, mentioning that you are a psychologist would add credibility to your speech.
Pathos is related to emotions . The idea is to connect with the listeners through emotions. And the easiest way to do that is through stories !
In the example above, you can share a story of a client who developed violent behavior patterns after spending a considerable amount of time on gaming and how they are doing now.
Logos means logic . Adding logical elements like facts, statistics, and quotes by famous personalities helps drive your main idea forward in a more rational sense.
Again, taking the example of the impact of gaming on violent behavior, logos could include a sentence like:
School shootings have increased from 11 in 2009 to 93 in 2021. It is a staggering number and when you take a deeper look into it, you’ll find that a considerable number of these shooters were addicted to gaming.
Editing is something we believe is a very crucial part of giving a memorable 2-minute speech. Why?
Because 2-minute speeches aren’t only about what you say but also about what you choose not to say.
Editing also helps you focus on your topic more clearly rather than drifting or diversifying your topic.
Delivering 2-minute Speeches
1. establish your takeaway.
Since you had already decided on your takeaway while writing the speech, you are well aware of it. But does your audience have any idea yet? No!
While they might infer why you are presenting the particular topic after listening to your speech, you cannot leave it to that.
Establish your takeaway right at the beginning of your speech , so that the audience also understands what they can expect from your speech.
2. How to begin a 2 minute Speech (Simple beginning)
This might come as a shocker, especially because we are always told to begin with a Bang!
For 2-minute speeches, if you end up spending a lot of your time on the beginning, you will have to shorten the main content of your speech.
Starting in a simple and direct manner suits best in such cases.
A few ways in which you can begin your 2-minute speeches are given below:
If you are to introduce yourself, you can begin simply by saying your name. “Good afternoon everyone, I am Xyz…”
You can also use ethos, pathos, and logos to begin your 2-minute speeches.
“Mumbai is known for 2 things gateway of India and potholes. Being someone who has lost a close friend of mine due to the careless work done towards these potholes , I’m here to address the issue we so conveniently drive over”
“About a year ago, in this very month of July, it was raining heavily in Mumbai. I remember this because there happened to be a friend of mine who was supposed to meet me for a meeting, we had that day, but he didn’t make it. The reason? Heavily flooded roads covered with potholes that he couldn’t see. A tragic accident or a convenient murder?”
“In 2018, Mumbai alone witnessed 522 accidents caused by potholes”
3. Emphasize
Repeating or rather stressing certain words gives rhythm to your speech. It also helps in easy learning and increases the chance of easy recall among the audience.
4. How to End a 2 Minute Speech
When it comes to 2-minute speeches, your conclusion or closing lines are very important. The reason is that your audience will mostly remember the last part of your speech better than the rest .
Make sure to restate the takeaway and main crux of your speech . You can also end your speech by quoting some famous personalities . In many speeches, the speaker asks the audience to take action or to think about a question that they leave the audience with.
So, we now know how your phone helps you socialize but keeps you away from the same people physically. We have been living in this virtual world for quite some time now. The least you can do is to keep your technology aside especially when you are with people you care about. An hour without your phone won’t hurt, will it?
Impromptu 2-minute speeches
Impromptu speeches are ones where you are given the topic on the spot with little to no time to prepare for the speech. In such cases, you barely have any time to go about carrying out thorough research and structuring your speech.
Rather you can keep a few frameworks in your mind and then structure the speech accordingly on the spot. This is the most convenient way of delivering effective impromptu 2-minute speeches.
A few frameworks that you can use for your 2-minute impromptu speeches are:
1. PREP model
PREP stands for Point, Reason, Example, and Point . This essentially means that you begin by talking about something, then give a reason that justifies that point. You then follow it with an example to back your point and end by repeating the point to reach your audience in a structured manner.
2. WWW model
No, WWW doesn’t stand for World Wide Web. Rather it means answering 3 questions,
- Who are you?
- What do you do?
- Where are you going from here?
WWW works best when you have to give an impromptu introduction of yourself .
An example of using the WWW model to introduce yourself is given below.
Hello everyone, I am Arsh M, a fashion designer, and advocate of sustainability. During my college years, I was astonished by the amount of cloth waste produced each day. Upon researching, I realized that the fashion industry happens to be one of the biggest polluters in the world. This motivated me to work towards bringing more sustainable styling choices for everyone. That is when I began my venture in Sustainaesthetic. We are a completely sustainable and animal cruelty-free brand that aims to provide you with diverse sustainable styling options at a very affordable rate so that saving the planet doesn’t hurt your pockets!
3. Pointer Format
As the name suggests, the pointer format involves dividing your content into 3-5 points . This will make it easier for you to talk about each point for a couple of seconds before moving to the next. At the same time, it sounds very structured and may be easy to recall.
An example of a pointer format is a speech given the by CEO of Pepsico Indra Nooyi .
Famous 2-minute speeches
1. indra nooyi.
The speech given by Pepsico’s CEO is well-written and spoken . She begins by appreciating India, her home country, and then moves on to briefly talk about her 3 life lessons. Diving her speech into such crisp segments with an introduction, 3 pointers and finally, a conclusion, makes the speech very comprehensive and structured .
2. Denzel Washington
The speech given by Denzel Washington is one of the most motivating speeches of all time . It is because of the way he calmly delivers the speech by taking required pauses to stress the important lines.
2-minute speeches from movies
Speeches in movies usually bring out the emotion of awe, inspiration, or sympathy . We will look at two such 2-minute inspirational speeches from movies.
1. Any Given Sunday
The scene on any given day is worth noting for its storytelling approach . Al Pacino begins his speech with brutal honesty when he says “ We are in hell gentlemen.”
He then goes on to talk about how the game is very similar to everyone’s life and emphasizes being at the right place at the right time.
“One second early or one second late, you miss a catch,” he says. In the latter half of his speech, he increases his voice as if trying to reach his player’s very core, in an attempt to motivate them to do their level best in the game.
2. Coach Carter
This speech scene of Coach Carter is unlike other traditional scenes where the coach inspires his students. Rather, one of the students gives a very short speech that moves not only his teammates but also his teacher.
It can also be counted as a very effective thank you speech!
Monologues happen to be yet another powerful tool used in 2-minute speeches from movies. Monologues are long dialogues given by a single character. Let’s take a look at some of the most striking monologues given in movies
2-minute dramatic monologue for male
When it comes to dramatic monologues for males, the dialogue is often very inspiring or tries to instill the right amount of motivation among the team players or the soldiers. Let us take a look at 2 such dramatic monologues given by male characters in movies that had an amazing impact on their audience.
1. V for Vendetta
V for vendetta isn’t only an amazing movie, but this monologue by V is out of the ordinary. In the scene, V introduces himself to a woman whom he had just saved.
He uses alliteration by introducing himself with words that start with V. Check out the exact dialogue to get a clearer idea about the monologue.
V oila! In v iew, a humble v audevillian v eteran is cast v icariously as both v ictim and v illain by the v icissitudes of fate. This v isage, no mere v eneer of v anity, is a v estige of v ox populi, now v acant, v anished. However, this v alorous v isitation of a bygone v exation stands v ivified and had v owed to v anquish these v enal and v irulent v ermin v anguarding v ice and v ouchsafing the v iolently v icarious and v iolation of v olition…. You may call me V.
2. Wolf of Wallstreet
Who hasn’t heard of this amazing movie, wolf of wall street? One thing that we will observe when it comes to this movie is that the main lead had amazing public speaking skills . He had the power to persuade his listeners and encourage them to chip in at their level best for the growth of the organization.
In one such speech, he talks about how he isn’t leaving them and that he is here to stay.
The use of dramatic suspense followed by his change in tone and voice is something worth noting.
2-minute dramatic monologue for female
When it comes to dramatic monologues given by female characters in movies, 2 of these scenes come into our minds. The scenes are both beautifully written and executed by the actors.
1. Devil Wears Prada
In the movie Devil Wears Prada, the monologue is given by Meryl Streep who plays the role of Miranda Priestly. The speech is worth noting as she dramatically explains how even a small difference between two pieces of clothing to a lay person is a big difference for the fashion moguls as it is their opportunity to create millions!
Her passion for the industry is quite evident from the 2-minute speech. Further, the way her character picks up the pace when she talks about the reality of the fashion industry brings out her annoyance at the assistant and acts as a way of showing authority through words.
The movie 300 features a small scene where the queen requests the councilmen to send more men to war, to help not only her husband but also all the others who are already a part of it.
We see the use of ethos in the speech when the queen says the following statement:
I come to you as a mother. I come to you as a wife. I come to you as a spartan woman.
Examples of 2-minute speeches
If you are looking for some examples for your next 2-minute speech or 2-minute speeches to memorize, check out the ones given below!
How to introduce yourself in 2 minutes?
When you have to introduce yourself in 2-minutes, it is better to follow a simple structure of past, and present.
An example of introducing yourself as a fresher for a job interview has been given below
Good afternoon, I am Arya Rose. I recently graduated from ABC college, majoring in Analytics. Growing up I had always found immense interest in math and had also won Olympiads at the school level. During my under graduation, I had taken up a course in tools for Data Analysis which made me realize my inclination toward analytics. It also encouraged me to pursue my major in the field of analytics.
Being an active member of my college, I made sure to participate in and represent my college across various events and intercollegiate festivals. I also had the chance to be a part of Hackin which is ABC’s elite Hackathon team. With the Team, we stood 2nd at Hackified, a hackathon organized by QPR college.
I was further able to put my theoretical knowledge to use by interning with this amazing organization called ANAlysis. The internship spanned over 3 months and I was able to gain an in-depth understanding of software like R and Python.
I now look forward to gaining more practical experience in the field by working and growing with your esteemed organization.
2 minute thank you speech
There are a few things that you must keep in your mind while you are giving a thank you speech.
- Acknowledge the people around you
- Thank them
- Introduce yourself or why you are giving this speech.
- Individually thank every person required.
- Add some inspiring or heartfelt closing marks
An example of a 2-minute thank you speech for an event is given below.
I’d like to first thank every one of you present here, for joining us to make this event an absolute success. To those of you who might not know, I am Shiya M, the editor of the XYZ club and the coordinator of this amazing open mic event “Mehar.” Mehar means blessing in Punjabi, and there is a reason behind it.
On my very first day at XYZ, I was stunned to see the company ritual. Before leaving we were to recall one blessing that we received that day from our colleagues. As unusual as it felt, it was beyond measure one of the most beautiful rituals I had come across. You see in this fast-moving world, we tend to focus a lot on our busy schedule for the things we don’t have. And in all that chaos, we forget to take a look at the n number of blessings showered our way.
So, we wanted to provide a platform where you could do that, even if it was for a couple of hours.
I’d like to thank Ms. T, founder of XYZ, and her immense support and encouragement throughout, Arya and Daven for working closely with all the participants and audience members, ensuring that all your needs were met. I’d also like to thank Mr. Ajay for the technical support provided to him and how can we not thank Jay for being our lead guitarist, tuning in the vibe of this small room as per each participant’s requirement, Jay thank you!
Thank you to all the participants for presenting such beautifully written pieces, we enjoyed them all. A great round of applause for our participants!
Last, I’d like to thank our dear audience for being patient and for motivating all our speakers today you have been the most amazing audience we have ever seen!
Thank you again all of you, it was a great pleasure interacting with every one of you.
meher rakhi!
Humorous 2-minute speeches
If you are trying to understand how to add humor to your speech and make it more fun as well as casual, check out the 2-minute speech example given below.
2-minute humorous speech by bridesmaid
“Hello everyone, first of all, I’d like to begin quite humbly by thanking everyone present for gathering here to celebrate the union of this beautiful couple Jess and Jim.
Now if you know jess, you know me. Because I pretty much tag along with her everywhere. Just like those lice in your hair, can’t leave her alone!
At 5, I had taken up responsibility. It was to protect this absolutely beautiful soul. But as we grew up, it turned out that she was the one who protected me. What the turn tables!
Jess, I’m grateful every day to have such an amazing sister like you in my life who motivates me to do better and talk to “decent” guys..pst they are just not my type!
You’ve been my mom at times, waiting at the door every time I’d get late which makes me wonder if mom outsourced her strictness to you? And if yes, why not me? I was the broke kid!
I’m going to miss those small things you know? How you told me it was chocolate powder when it was coffee, how I never won a game I played with you because you never played it fair, and oh how you never missed complimenting my outfit when I was wearing your clothes!
But seriously, I’m going to miss you tons. I hope you get your fairytale happily ever after! To Jess and Jim!
if you have been asking yourself which topic is best for a 2-minute speech? what are some good topics to speak on? or what should I do for my school speech?
Here is a list of various topics you can choose from!
Common topics for 2-minute speeches
- Environment
- Domestic Violence
- Women’s Day
- Teachers’ Day
- Importance of Cleanliness
2-minute speech topics for students
- Failure: A blessing in disguise
- The best attitude to have is gratitude
- Is there value in homework?
- Impact of technology on mental health
- The authenticity of online degrees
- The future is sustainability
- Social media detox
- Blended learning and its benefits
- Residential programs and their benefits
- New education policy
- Value of time
- Importance of education
- Discipline and its importance.
- 2-minute speech on any freedom fighter
- Ban on school uniforms
2-minute speech topics for adults
- Work-life balance for remote employees
- Fields that can turn completely virtual
- Slow living: beyond the hustle
- Impact of diet on mental health
- Unhealthy patterns that cost you in your 40s
- Advice to an 18-year-old
- How colors affect people
- Consistency over motivation
- Future of automobile
- Metaverse: the new shopping hub
- The power of fake news
- Ban on animal testing
- Adopt, don’t shop!
- Social media diet fads or eating disorders?
- Can money buy happiness?
Final words
2-minute speeches are short, crisp speeches that help in conveying your ideas or opinions to the people effectively. As the time is short, focusing too much on the opening lines or in-depth research will steal your time. Instead, focus on a takeaway and chip in extra efforts to give a memorable conclusion.
At the end of the day, there are no strict rules that you must follow for 2-minute speeches, and hence you are open to writing it and delivering it the way that suits best for you.
Enroll in our transformative 1:1 Coaching Program
Schedule a call with our expert communication coach to know if this program would be the right fit for you

Crisis Leadership 101: Cultivating Empathy While Exercising Authority

Lost Voice? Here’s How to Recover Sore Throat and Speak Again

7 Keys to Emcee Like a Pro: Unlock Your Hosting Potential

- [email protected]
- +91 98203 57888
Get our latest tips and tricks in your inbox always
Copyright © 2023 Frantically Speaking All rights reserved

Unsupported browser
This site was designed for modern browsers and tested with Internet Explorer version 10 and later.
It may not look or work correctly on your browser.
- Presentations
- Public Speaking
The Best Source for PowerPoint Templates (With Unlimited Use)
Before we dive into how to make a speech, let's look at a powerful tool that can help you design your presentation.
Envato Elements is a great place to find PowerPoint templates to use with your speech. These presentation templates are professionally designed to impress.

Envato Elements is an excellent value because you get unlimited access to digital elements once you become a subscriber. Envato Elements has more than just presentation templates . You get:
- stock images
- and much more
To become a subscriber, just sign up and pay a low monthly fee.

Sample Public Speaking Scenario
Here's a possible public speaking scenario:
You've just opened a small web design business in your town, and you join the town Chamber of Commerce. As a result, you're invited to give a short, five-minute presentation at the next Chamber of Commerce meeting.
Coming up with a public speaking speech for the scenario described above could be a challenge if you've never written or given a public speech before. Fortunately, there are some speech-writing steps that you can use that'll make speech writing easier.
Let's use this example and walk through the steps for writing a speech.
7 Steps for Writing a Speech
The steps for writing a speech for public speaking are like the steps for writing a presentation in general. But at each stage of the writing process, you need to keep your audience in mind:
1. Research Your Audience
Whenever you do any type of writing you need to consider who you're trying to reach with your writing. Speech writing is no different. The more you know about your target audience, the more effective your writing will be.
In the example above, you know that your audience is going to be the other members of the Chamber of Commerce. They're likely to be small business owners just like you are.

What to Do After You Research Your Audience:
Once you've defined your audience, you can gear your speech towards them. To do this, ask yourself questions like:
- What does this audience need?
- What problem can I solve for them?
- Is there anything else I need to consider about my listeners?
In the example we're using for this tutorial, most small businesses in your town fit one of the following three situations:
- They've got a website that works well.
- They've got a website, but the design is outdated or doesn't work well.
- They don't have a website.
2. Select a Topic
In this example your topic is already given. You've been invited to introduce your business. But you also know that the speech is going to be fairly short--only five minutes long.
While it's always a good idea to keep a speech focused, this is especially important for a short speech.
If I were writing the public speaking speech for the scenario we're working with, I'd narrow the topic down like this:
- Create a list of the strengths of my business.
- Compare the list of business strengths to the problems I observed with the other members' websites in the previous step.
- Focus my presentation on the areas where my business strengths meet weaknesses (needs) of other Chamber of Commerce members.
Let's say that I noticed that quite a few members of the chamber have websites that use outdated fonts, and the sites aren't mobile-friendly. Instead of listing everything my web design business could possibly do, I'd focus my short speech on those areas where I observed a need.
You can use a similar process to narrow the topic down any time you need to write a speech.
Avoid the temptation of trying to cover too much information. Most people are so overwhelmed by the sheer amount of new data they receive each day that they can't keep up with it all. Your listeners are more likely to remember your public speaking speech if it's tightly focused on one or two points.
3. Research Your Topic

In the example we've been going over, you probably don't need to do a lot of research. And you've already narrowed your topic down.
But some public speaking situations may require that that you cover a topic that you're less familiar with. For more detailed speech writing tips on how to study your subject (and other public speaking tips), review the tutorial:
.jpg)
4. Write Your Speech
Once you've completed the steps above, you're ready to write your speech. Here are some basic speech writing tips:
- Begin with an outline . To create a speech your audience will remember, you've got to be organized. An outline is one of the best ways to organize your thoughts.
- Use a conversational tone . Write your speech the way you would normally talk. Work in some small talk or humor, if appropriate.
- Use the speaker notes . Typically, speaker notes aren't seen by the audience. So, this is a good place to put reminders to yourself.
- Be specific . It's better to give examples or statistics to support a point than it is to make a vague statement.
- Use short sentences . It's likely you're not going to give your speech word for word anyway. Shorter sentences are easier to remember.
In this example scenario for the short speech we're preparing for the Chamber of Commerce, your outline could look something like this:
- Introduction . Give your name and the name of your business. (Show title slide of website home page with URL)
- Type of Business . Describe what you do in a sentence or two. (Show slide with bulleted list)
- Give example of a recent web design project . Emphasize areas that you know the other businesses need. (Show slides with examples)
- Conclusion. Let the audience know that you'd be happy to help with their web design needs. Offer to talk to anyone who's interested after the meeting. (Show closing slide that includes contact information)
- Give out handouts . Many presentation software packages allow you to print out your speech as a handout. For a networking-type presentation like the one in our example, this can be a good idea since it gives your listeners something to take with them that's got your contact information on it.
That simple speech format should be enough for the short speech in our example. If you find it's too short when you practice, you can always add more slides with examples.
If you've been asked to give a short speech, you can change the speech format above to fit your needs. If you're giving a longer speech, be sure to plan for audience breaks and question and answer sessions as you write.
5. Select a Presentation Tool
For most presentations, you'll want to use a professional presentation tool such as PowerPoint, Google Slides, or a similar package. A presentation tool allows you to add visual interest to your public speaking speech. Many of them allow you to add video or audio to further engage your audience.
If you don't already have a presentation tool, these tutorials can help you find the right one for your needs:

Once you've chosen a presentation tool, you're ready to choose a template for your presentation.
6. Select a Template and Finish
A presentation template controls the look and feel of your presentation. A good template design can make the difference between a memorable public speech with eye-catching graphics and a dull, forgettable talk.
You could design your own presentation template from scratch. But, if you've never designed a presentation template before, the result might look less than professional. And it could take a long time to get a good template. Plus, hiring a designer to create an original presentation template can be pricey.

A smart shortcut for most small business owners is to invest in a professional presentation template. They can customize it to fit with their branding and marketing materials. If you choose this option, you'll save time and money. Plus, with a professional presentation template you get a proven result.
You can find some great-looking presentation templates at Envato Elements or GraphicRiver . To browse through some example templates, look at these articles:

Even a short speech like the one we've been using as an example in this tutorial could benefit from a good tutorial. If you've never used a template before, these PowerPoint tutorials can help:
7. How to Make a Public Speech

Now that you've completed all the steps above, you're ready to give your speech. Before you give your speech publicly, though, there are a few things you should remember:
- Don't read your speech . If you can, memorize your speech. If you can't, it's okay to use note cards or even your outline--but don't read those either. Just refer to them if you get stuck.
- Practice . Practice helps you get more comfortable with your speech. It'll also help you determine how your speech fits into the time slot you've been allotted.
- Do use visual aids . Of course, your presentation template adds a visual element to your public speech. But if other visual aids work with your presentation, they can be helpful as well.
- Dress comfortably, but professionally . The key is to fit in. If you're not sure how others at your meeting will be dressed, contact the organizer and ask.
- Speak and stand naturally . It's normal to be a little nervous but try to act as naturally as you can. Even if you make a mistake, keep going. Your audience probably won't even notice.
- Be enthusiastic . Excitement is contagious. If you're excited about your topic, your audience will likely be excited too.
In the example we're using in this tutorial (and with many public speaking opportunities), it's important not to disappear at the end of the meeting. Stick around and be prepared to interact individually with members of the audience. Have answers to questions anyone might have about your speech. And be sure to bring a stack of business cards to pass out.
5 Quick Tips to Make a Good Speech Great (& More Memorable)
After reading about the basics, here are some more tips on how to write a great speech really stand out:
1. Have a Strong Opening

Start your speech with a strong opening by presenting surprising facts or statistics. You could even start with a funny story or grand idea.
Another way to start your speech is to open with a question to spark your audience’s curiosity. If you engage your audience early in your speech, they're more likely to pay attention throughout your speech.
2. Connect With Your Audience
You want a speech that'll be memorable. One way to make your speech memorable is to connect with your audience. Using metaphors and analogies help your audience to connect and remember. For example, people use one writing tool to put the speech's theme in a 15-20 word short poem or memorable paragraph, then build your speech around it.
3. Have a Clear Structure

When writing your speech, have a clear path and a destination. Otherwise, you could have a disorganized speech. Messy speeches are unprofessional and forgettable. While writing your speech, leave out unnecessary information. Too many unnecessary details can cause people to lose focus.
4. Repeat Important Information
A key to writing memorable speeches is to repeat key phrases, words, and themes. When writing your speech, always bring your points back to your main point or theme. Repetition helps people remember your speech and drives home the topic of your speech.
5. Have a Strong Closing

Since the last thing that your audience listened to what your closing, they'll remember your closing the most. So, if your closing is forgettable, it can make your speech forgettable. So, recap your speech and repeat essential facts that you want the audience to remember in your closing.
Five PowerPoint Presentation Templates (From Envato Elements - For 2022)
If you’re writing a speech for a presentation, save time by using a premium presentation template:
1. Toetiec PowerPoint Presentation

Toetic PowerPoint Presentation has 90 unique slides and 1800 total slides that you can easily add your information onto. There are ten light and dark versions that come with this template. Also included in this template are vector icons, elements, and maps.
2. Suflen Multipurpose Presentation

Suflen Multipurpose Presentation template has a professional design that can work for any presentation topic. This template comes with over 450 total slides. With this template, you've got five color themes to choose from. Also, this template comes with illustrations, graphics, and picture placeholders.
3. Virtually PowerPoint

Virtually PowerPoint template is a modern and minimal style presentation template. This template comes with over 50 slides. You can use this template for any presentation theme.
4. Amarish PowerPoint Template

Amarish PowerPoint Template comes with five color themes that allow you to choose the color you want. This template is another multipurpose template that can work for any purpose. Also, this template comes with over 150 total slides and infographics, illustrations, and graphics.
5. Qubica PowerPoint Template

Qubica PowerPoint Template comes with over 150 total slides and five premade color themes. Easily add images into your presentation template by dragging the image of your choice into the picture placeholder. Everything in this template is entirely editable.
Learn More About How to Write a Great Speech
Here are some other tutorials that provide more information on giving a speech:

Learn More About Making Great Presentations

Download The Complete Guide to Making Great Presentations eBook now for FREE with a subscription to the Tuts+ Business Newsletter. Get your ideas formed into a powerful presentation that'll move your audience!
Make Your Next Speech Your Best Ever!
You've just learned how to write a good public speaking speech. You've been given a sample speech format and plenty of other speech writing tips and resources on how to write a good speech. You've seen some templates that'll really make a PowerPoint stand out.
Now, it's up to you to write the best speech for your needs. Good luck!
Editorial Note: This post has been updated with contributions from Sarah Joy . Sarah is a freelance instructor for Envato Tuts+.

- Testimonials

7 steps to prepare a speech in a surprisingly short time
Most of my clients are entrepreneurs, CEOs or working in other leadership positions. I also meet many small business entrepreneurs. One common thread is that they’re very busy. Successful leaders are mindful about how they spend every single minute.
It’s no surprise then, that when these leaders are asked to speak in public, the one thing they are thinking is:
How do I prepare a speech in as little time as possible?
They realise very well that speaking well is important , and that preparation is necessary to deal with speaking anxiety . They just want to do it efficiently.
Today I’d like to share with you an excerpt of my CEO playbook for delivering speeches. The section on preparation contains tips that are useful to anyone looking to prepare a speech in half the time while doubling their impact .
I’ve compiled them into a handy list of 7 steps:
The 7 steps to efficiently prepare a speech
The steps are:
- Identify your purpose . Why are you speaking?
- Know your audience. What are their aspirations, pains, …?
- Add significance. Why should the audience care?
- Define your clear message. What should your audience remember?
- Establish your structure . Develop a middle part with one or two points supported by an anecdote, story, and preferably backed up by facts and data.
- Prepare a strong opening and a strong ending .
1. Define your purpose
For a speech to be effective, it must have a clear goal. A goal also helps you focus while creating the speech.
Ask yourself: do you mainly want to…
Note: these goals may overlap, and one does not exclude another. But one must be your main goal.
2. Know your audience
In order to connect with your audience during speeches, it is important to be able to place yourself in their shoes. Only from this perspective can you truly communicate understanding and establish rapport.
To know your audience is to engage your audience.
The Empathy Map is a handy technique from the world of user experience and marketing, where it is used to better understand potential or existing customers. It works remarkably well when you prepare a speech, too.
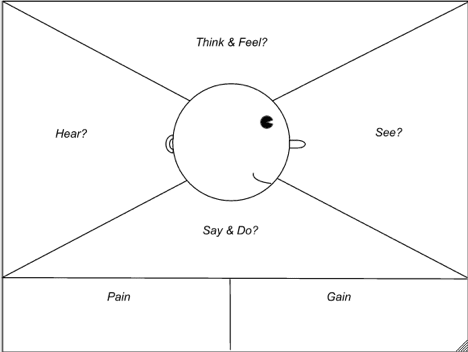
The big idea is to go over the different areas in the map and come up with the elements that create your listeners’ mental world in relation to the topic.
Suppose you are to deliver a speech on the use of sugar in processed foods. Some questions the empathy map would trigger are:
- What do they think about the use of sugar and how does it make them feel ?
- What do they hear about sugar from their environment or in the news?
- What do they see when it comes to sugar, e.g. in terms of advertising or packaging?
- What do they say about sugar to their peers? What do they do – what actions do they take (or not take)?
- What pain, or significant disadvantages, do they associate with sugar?
- What gain, or significant advantages, do they associate with sugar?
Note that the answers to some of these questions will overlap. Don’t worry about that — this is just a brainstorming tool to trigger relevant information stored in your memory. The point is not to organise information in any neat way.
Try it, even if it’s for 5 minutes! You’ll be surprised how helpful the answers are for:
- finding an angle
- finding the right words
- creating goodwill
- overcoming resistance
- and much more.
3. Add significance
Why significance is key when you prepare a speech.
Crafting any good story starts with the why . What’s the point exactly?
There’s a saying in public speaking: you win the heart before you win the mind. Knowing the why of your speech is essential in accomplishing that.
Speakers engage an audience by being significant; by creating meaning. Audiences feel engaged when they have the feeling the talk is also about them. A great example is Martin Luther King’s famous ‘I have a dream’ speech. The audience did not come to see Martin Luther King, they came because they identified with his ideas. They felt his speech was about them, their lives, and their dreams.
That explains the importance of step 2: Know your audience. You can only add significance if you have a clear image of the receiving end of your speech.
How to find your speech’s significance
To find the significance of your speech, ask yourself the following questions when you prepare a speech:
- Why am I giving this speech?
- What do I believe, that I want to share? What do I stand for?
- So what?! Why should my audience care?
4. Define your clear message
Today, people are flooded with information. There is an image circulating on the web which goes so far to say that a person today receives more information in a day than a person in the middle ages in his entire life!
True or not, we can all agree that in a device-rich world, the information intake has never been more intense.
How does that translate to speeching? Well: to make your speech memorable, I suggest you focus on extracting one key message .
Your key message should be as simple as possible, regardless of the complexity of the issues and topics at hand. It will consist of one or two phrases that express your main point.
If that sounds daunting, let’s look at a model that can help.
The Message House model is a time-tested PR tool to condense complex stories into a thematic ‘house’. This house is made of a set of three messages that together form the overarching key message (called the Umbrella Statement in the model).
The Core Messages on the second level represent your Umbrella Statement, but in greater detail. They can be supporting arguments, sequential steps to take, conditional statements, descriptive (think: who, what, where, when, why and how), or of another kind.
Finally, the lower part of the house provides evidence, proof points and support. This is the foundation of your story.
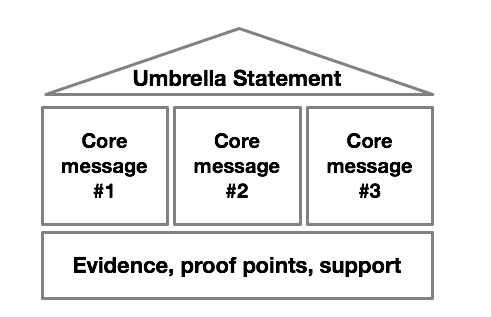
How to use the Message House
In some cases, your Umbrella Statement (that’s your key message) will be very clear to you. If that’s so, it’s useful to come up with the 3 Core Messages that make up the Umbrella Statement.
At other times, you’ll have 2 or 3 messages in mind as you prepare a speech. In that case, consider those your Core messages and start to look for the single Umbrella Statement.
Examples of Umbrella Statements and their Core Messages
- Employees lose time and energy in traffic.
- Some employees report they feel less productive in larger office spaces.
- Candidates for jobs that are hard to fill, are not attracted to our current policy.
- First, I will introduce the idea at the annual shop owner’ meeting.
- Then, I will have the team communicate the exact steps to each shop owner.
- Finally, our sales representatives will check each shop they visit.
- The Polish and Swedish teams did exceptionally well.
- May and June were top periods for sales.
- Orange bicycles are super popular and account for a large part of the profits.
5. Establish your structure
The way you organise information is essential if you want your audience to follow and understand your speech. Ideas must be put together in an orderly manner.
I therefore recommend every speaker to use an outline as the backbone for their speech.
An outline is simply 10,000 feet view of your speech. It’s as if you would zoom out completely and see the major turns your speech takes.

Why use an outline?
That’s easy: our brains are simply not capable of creating quality content from beginning to end.
Compare it to cooking a meal. Imagine yourself standing in front of different foods. Without thinking ahead, you grab a couple of ingredients and start cutting, cleaning and preparing them.
Unless you’re an experienced chef, that won’t result in a remarkable meal, will it? Without a gameplan to prepare a speech, the end result of your creation will be underwhelming.
Here are a few general directions your outlines can take. These are based on effective storytelling principles:
- Problem – pathway – solution
- Problem – solution – reasoning
- Situation – complication – solution
- Past – present – future
After you’ve decided on the general direction, flesh out your outline. See if you can describe your speech in ten to fifteen bullets. Refer to your Message House (see previous point) to make sure your outline includes your Core messages.
What structure works best for your purpose? Do you have a preference? Try a few structures for your speeches and choose the one that is most persuading.
Related article: How to structure a victory speech in three steps
Next, integrate even more storytelling. Your bigger picture might be represented by a story, but can you integrate ‘mini-stories’ to illustrate specific points?
6. Prepare a strong opening and strong ending
Scientific research shows it again and again. If you ask people to rate a certain experience they had recently, they will base a lot of their opinion on how it began and how it ends. Looking back at an experience, whatever happens in the middle seems to carry less weight for us.
A classic example is a visit to a restaurant. Smart restaurant owners focus extra on doing two things impeccably: the welcoming and the dessert. Although they pay great attention to the overall experience, of course, they know that a sloppy greeting of their guests, or a below-standard dessert, can easily spoil their guests’ memory of the whole evening.
For you, it means it’s smart to think twice about how you open and how you close.
Ideas for a strong opening
Here are a few angles to inspire you in crafting your opening:
- ‘Start with a bang’: use a quote, bold claim or striking fact, or ask a question.
- ‘So what?’: Go straight to the point and open with why your audience should care.
- ‘Introduce yourself’: But do it in a compelling way. Tell a juicy story. What would the tabloids write about you?
- Make the purpose clear – What impact do you want to achieve?
Ideas for a memorable ending
- Repeat your Key Message. Think ‘key takeaway’. This is a natural-feeling and effective way to make a firm point.
- Refer to the beginning. Most good stories develop in a circular way. A problem introduced in the beginning gets solved in the end. Balance gets restored; etcetera.
- Present a call-to-action . If you want your audience to take a certain action, always end with that.
7. Rehearse
1. write out, practice and tweak (optional).
At this point, you could write out your speech in full text – if you have the time.
Read your text out loud for a few times until you’re comfortable with the content. You will probably still tweak a few parts.
If you don’t have the time, or you feel comfortable working with just bullet points, feel free to skip to step 2!
I do highly recommend you write out your opening and ending.
2. Bring back to bullet points and practice again
Once on stage, you don’t want to hold the full text of your speech in your hand. You will be tempted to look at it often, which will break your connection with the audience.
So now, reduce your text to a list of main points, keywords, facts and anecdotes. And practice your speech again. Refer back your outline from step 5 for the general structure.
This will also help you memorise the speech completely by heart faster.
Do I have to know my whole speech by heart, you ask?
My answer is: not necessarily. But as just mentioned, do know your opening and ending from the inside out.
3. Take your practice to the next level
Here are my rehearsing tips for the best results:
- Record yourself . Most beginning speakers find this tough, but it’s an essential way of spotting weaknesses in your speaking and improving them.
- Practice for real people. The gap between practising in front of a mirror and practising in front of a crowd is just too large. Practice for a small group of colleagues or family members to get used to the stress that comes with having an audience.
- Ask for specific feedback. If you practice in front of people, help them evaluate you by asking them specific questions. It could be the content, your body language, or your opening. Anything you feel you need feedback on.
- Rehearse often. Once you’re happy with your speech’s content and your performance, practice your speech ten times – if you have that luxury of time. If you need more practice, go for it. There’s no better confidence booster as knowing you’ve rehearsed your speech until it hurt 🙂
That’s it!
Although I could elaborate on each on the above points, this provides you with a larger plan to optimally prepare a speech.
Are you a busy professional looking for a speaker coach to get you from good to great in the most efficient way. Look no further. I am here to help all my clients achieve exactly that.
“I knew that Elizabeth really understands what I want to achieve and whom I want to reach, and that she is a bad-ass coach with mad skills. When I was asked to give a keynote at an event, I was determined to really take my talk to the next level. So it was a no-brainer to work with her. Could I have done it on my own? Perhaps, but it would have taken me more time, stress and effort and I would not have achieved the same results. Working with a coach who you can trust, like Elizabeth, creates an extremely comfortable starting position, which made me step onto the stage on the Big Day without any nerves.” – Anouck Meier, CEO of Ampersand
Book your free call via this link.
- Features for Creative Writers
- Features for Work
- Features for Higher Education
- Features for Teachers
- Features for Non-Native Speakers
- Learn Blog Grammar Guide Community Events FAQ
- Grammar Guide
How to Write a Speech: Top Tips

Ashleigh Ferguson

Table of Contents
9 engaging speech writing tips, what are the different speech types , how to find help writing a speech.
A great speech is impactful and engaging. It should eloquently and clearly express your ideas.
Whatever the topic, a good speech should showcase your authority on a topic and demonstrate excellent communication and leadership skills.
Many people don't know how to write a speech, so the process seems daunting. But there are a few best practices and tips that can make the writing process easier.
In this article, we’ll discuss some best practices to help you write an effective speech that engages and captures your audience.
Public speaking can be nerve-racking. However, having a well-written speech can decrease some of that anxiety.
Even if you’ve never written a speech before, there are still best practices you can follow.
An engaging speech should be clear, to the point, and follow a logical order. But how do you ensure your speech follows these criteria? Follow these nine engaging speech writing tips.

Know Your Audience
Analyze your target audience to improve the effectiveness of your speech because different audiences will have different expectations.
Consider your audience’s age, level of understanding, attitudes, and what they expect to take away from your speech, then tailor your message accordingly.
For example, if your audience members are teenagers, it’s unlikely that references to the ’70s will be effective.
Start With a Clear Purpose
Decide on the main point of your speech, and make sure all your content supports that point. Choose a topic that fits the following criteria:
A topic that is relevant to your audience
A topic you’re excited about
A topic you have reasonable knowledge about
Organize Your Ideas
Use a speech outline to organize your thoughts and ideas logically.
Identify the introduction, body, and conclusion of your speech to help you stay focused and make your speech easier to follow.
Use Strong, Clear Language
Choose your words carefully, and use simple language that is easy to understand. Avoid jargon or technical terms that your audience may not be familiar with.
Again, your word choice will depend on your audience. For example, you’ll want to steer clear of slang when speaking to an older, conservative crowd.
Use Transitions
Speech transitions are words and phrases that allow you to move smoothly from one point to another. Use transitional words and phrases like “besides” to help your audience follow your thought process and understand how your points are connected.
Add Variety to Speech
A speech that is monotonous or lacks variety may cause your audience to lose interest.
Including a variety of elements in your speech, such as anecdotes, examples, and visual aids, can help keep your audience engaged and interested.
Practice, Practice, Practice
Practice your speech out loud to ensure it flows well and you’re comfortable with the material. Read your speech in front of the mirror or before someone you trust to give you critical feedback. Note the points for improvement, and incorporate them into how you deliver your speech.
End With a Strong Conclusion
How would you like to leave your audience members: inspired, informed, or mesmerized? Aim to end your speech on a high note. Summarize your main points, and leave your audience with a memorable takeaway.
Edit and Revise
Proofread and revise your speech to ensure it’s well written and error free. Use a grammar checker, such as ProWritingAid, to correct any grammar issues. You’ll also get suggestions on how to improve your sentence structures and transitions.
How to Write a Good Speech Introduction

The introduction can make or break your speech. It’s where you grab your audience’s attention to keep them engaged and state the purpose of your speech.
An introduction also gives you the opportunity to establish your credibility. You should aim to give your audience a reason to listen to the rest of the speech rather than tuning out.
Here are some tips on how to create a positive first impression.
Start With a Hook
Begin your introduction with a hook that will grab your audience’s attention and make them want to listen. There are several options for a hook:
A statistic
A personal anecdote
Reference to a current or historical event
When thinking of an attention grabber, consider how appropriate and relevant it is to your audience and the purpose of the speech. For example, if you’re giving a speech to an older audience, you can make a historical reference that they can easily relate to.

Provide Context
Provide context by giving your audience some background information about the topic of your speech. This will help them understand the importance of what you are talking about and why they should care.
State Your Thesis
Clearly and concisely state the main point or purpose of your speech. Your thesis should be easy to follow and clearly outline the main argument and your stance. This will give your audience a clear understanding of what they can expect to learn from your presentation.
Preview Your Main Points
Give your audience a sense of the structure of your speech by briefly outlining the key points or arguments you will be making. They’ll know what to expect, and your speech will be easier to follow.
Keep It Short
Your introduction should be concise and to the point, so don’t spend too much time on it. It’s important to keep your speech brief, and avoid including unnecessary or unrelated information.
The goal is to engage and interest your audience, not bore them, so aim for a few well-chosen words rather than a lengthy introduction. Aim for your introduction to be about 10-15% of the total length of your speech.

A speech is just like any other piece of writing. You’ll need to identify your purpose, audience, and intention and then write accordingly. There are many types of speeches, and each type has its own expectations.
Let’s look at some of the most popular speeches and how to write them.
How to Write a Short Speech
Short speeches may be the most tedious to write because of how condensed and concise the information has to be. However, if you ever have to give a farewell, birthday tribute, or just a quick welcome, there are still some tips available to make your speech great.
Start by identifying your topic, title, and the purpose of your speech, which will set the foundation of your outline. Then, determine the main points of your speech; keep it short with two to three points. Remember, a short speech is typically less than ten minutes long, so keep your points concise and to the point.
Since you have limited time to make the most impact, incorporate powerful words or other engaging elements. For example, you could throw out a thought-provoking question or anecdote, which will grab your audience’s attention and keep them engaged.
Finally, once you’ve written your speech, review it for brevity and clarity.
Be confident about grammar
Check every email, essay, or story for grammar mistakes. Fix them before you press send.
How to Write a Presentation Speech
A presentation speech is used to inform, persuade, explain, or demonstrate a particular topic.
Presentation speeches are well structured and follow a logical flow. They have an introduction, body, and conclusion. Use transition words and phrases to help your speech flow smoothly and prevent it from appearing disjointed.
You can use ProWritingAid to organize your speech and make it even clearer. ProWritingAid’s transition report will show you whether you’re using transitions effectively in your speech.
How to Write a Debate Speech
A debate is a formal argument on a particular topic. Debate speeches are persuasive since the aim is to convince the audience to agree with a stance.
Like most other speeches, a debate speech also follows the introduction, body, conclusion outline. This format helps the audience follow the speaker’s point in a linear and logical way.
When writing your introduction, clarify your stance so it’s clear to the audience. Anyone reading or listening to your speech shouldn’t have any doubt about your position on the topic. Take some time to prepare a solid opener, which can be an interesting fact, a personal story, or even a powerful quote.
The introduction also gives you the opportunity to explain terms your audience will need to understand throughout the speech. You should also provide an overview of your main points, but don’t spend long divulging too much.
Each body paragraph should cover a main point, whether that’s a key idea or a main claim, and each paragraph should begin with a topic sentence. The topic sentence is an initial sentence that summarizes the idea being presented.
Your conclusion should be a simple and clear reiteration of the points you made in the thesis statement and body paragraphs. Add an attention-grabbing element to leave a lasting impression on your audience.
Remember to use strong and emotive language throughout your speech, which makes it more likely for your audience to feel emotionally connected to your stance.
Always use transition words and phrases to maintain a logical flow between your arguments. Finally, edit and proofread your work for any potential grammar, punctuation, or spelling mistakes.
How to Write an Elevator Speech
An elevator speech is a brief speech that’s used to pitch a product, service, expertise, or credentials.
You have 30–60 seconds to persuade someone to act how you’d like: the same time as a quick elevator ride.
An effective elevator speech should contain an introduction, a clear value proposition, and a strong conclusion.

Your introduction should be polite and clear. Briefly explain who you are, what you do, and what you are offering. For example, if you’re pitching your expertise, condense your background into two sentences. Include things that will make your audience remember you.
End your speech with what you want to achieve. What are you trying to accomplish with this speech? Perhaps it’s a job opportunity, a follow-up meeting, or an internship.
Once you’ve written your speech, be sure to revise it for brevity. Then practice and record yourself to ensure you don’t go over the time limit.
Writing a good speech takes time, but these tips are a good start to improving your speech-writing process. If you encounter writer’s block, look up popular speeches for inspiration. Ask someone you trust to give you feedback once you’ve written your speech.
Finally, while ProWritingAid can’t write your speech for you, it can help you write in a cohesive and logical manner. It highlights any grammar, spelling, and punctuation issues. It also shows you suggestions on how to improve your sentence structure, transition, pacing, and readability, so your next speech can be impactful and memorable.
Ashleigh Ferguson is a Copywriter on the ProWritingAid Team. With an affinity for learning new things, you can always count on her to know some random fact. She’s a self-proclaimed ‘Fix-it Felix’ and a newly minted ‘candle lady’.
Get started with ProWritingAid
Drop us a line or let's stay in touch via :
- Games, topic printables & more
- The 4 main speech types
- Example speeches
- Commemorative
- Declamation
- Demonstration
- Informative
- Introduction
- Student Council
- Speech topics
- Poems to read aloud
- How to write a speech
- Using props/visual aids
- Acute anxiety help
- Breathing exercises
- Letting go - free e-course
- Using self-hypnosis
- Delivery overview
- 4 modes of delivery
- How to make cue cards
- How to read a speech
- 9 vocal aspects
- Vocal variety
- Diction/articulation
- Pronunciation
- Speaking rate
- How to use pauses
- Eye contact
- Body language
- Voice image
- Voice health
- Public speaking activities and games
- About me/contact
How to write a speech introduction
12 of the best attention getters to start a speech
By: Susan Dugdale | Last modified: 01-12-2023
The audience settles in their seats. The lights dim. You walk out to the center of the stage. You pause, take a deep breath, open your mouth and begin.
What you say over the next 30 seconds to introduce your speech or presentation is crucial.
That's how much time you have to make a positive impression on your audience. In it they will decide whether or not you have anything relevant or useful to say. Those first impressions count!
So how do you write an effective speech introduction to grab and hold their attention?
Begin by finding out how to choose the right opener.
What's on this page:
- how to choose the right opener for your speech
12 of the very best ways to start a speech
3. What if?
5. Key fact
7. Rhetorical
9. Headlines
10. History
11. Challenge

How to choose the right opener for your speech
The better way to make your choice of opener is after you have carefully considered who you are talking to and why you're talking to them.
One size does not fit all. Different audiences will respond differently. If you are giving the same speech multiple times think about what you may need to change to fit.
To work well your opening needs to be aligned with:
- the type of speech you're giving
- your main purpose for giving it
- your target audience and,
- their interests or needs
Both the hook * to catch their attention and your topic must be relevant to them. Unless they're a captive audience, they've come freely to listen to you and they're expecting something of value from you.
How are you going to let them know they're in the right place? Why should they listen? What are they going to get or gain through listening?
Out of all the different ways to open, what attention getter is absolutely the best way?
The only way I know to work out what is best is to go through each of them, and as you do, consider your audience. Make a short list of those you think might work then try them out before making your final choice.
* hook – an opening statement that immediately captures the audience's attention just like a well baited hook on a fishing line catches a fish.
Return to Top
1. Use imagination to create mind pictures
Ask the audience to use their imagination. Get them to build evocative compelling images in their minds. Make them large. Add vibrant color, sound and movement.
For example:
“Let's take a break. Make yourself comfortable. Now close your eyes for a moment. Take a deep breath, and you're there, in the place where you feel the most at ease, the place where all the tensions, all the demands of your normal everyday life disappear. Look around you. See it. Feel it. It's so good, it's perfect."
“Close your eyes. Take a deep breath and a moment to picture in your mind the people dearest to you, the people you feel you could not live without. Now when did you talk to them, or spend real time with them last?"
2. Use an item to build a connection
Choose an image or an object related to your speech, for instance a pair of shoes, to trigger interest and build a connection.
For example, if I were giving a speech on the lives of upper-middle class 19th century women I could open by holding up a pair of ornately decorated kid leather pumps.
“What's the name of the young woman who wore these? Listen. Can you hear the rustle of her silk skirts? And hear her heart beat bom-biddy-bom as the beau of the ball stepped her way? Would he, or wouldn't he ask her to dance?”
3. Ask a 'What if...?' rhetorical question
'What if...?' invites an audience to consider the possibilities of something becoming real. They can be positive somethings or negative, trivial or something that would have a significant impact if it came to pass.
The power of a 'what if...?' rhetorical question as an opener lies in the potency of the images and feelings it triggers. A well-chosen 'what if...?' will immediately have an audience wanting to hear the rest of your speech.
- "What if we don't find a way to successfully manage climate change?"
- "What if we really did solve the affordable housing crisis?"
- "What if questions of race and color ceased to matter?"
- "What if medicines were freely available to everybody who needed them?"
- "What if the person sitting next to you turned, looked into your eyes and said they loved you? Truly. Madly. Deeply."
4. Try a quotation from someone who's impacted your life in some way
To be effective a quotation doesn't have to be the clever quip or snippet of enduring wisdom: a famous quote from a well known person. It's origin could be personal, something someone important in your life said that's remained with you.
For example, my Mother answered all initial wails of outrage, pain or hurt from any of her five children with a command. "Breathe!" That was repeated, interwoven with encouraging asides, until whoever it was, was able to talk clearly and be understood. "It's OK.", she'd say. "Breathe. Come on. You can do it. Breathe. That's it. Keep going. Good."
Or I could use this line from one of my high school reports which read, "...with further maturity she should do well." (Thank you Mr Phillips. Your prediction was right on target.)
Or this from our son aged four as he watched me getting ready for another day of teaching: "When I grow up I'm going to wear pretty dresses and go to school just like you."
5. Use an interesting key fact
Choose an interesting key fact as an attention getting device: one of the most rarely known, or a shocking statistic from the body of your speech to open with.
For example: "Take a guess at what the most powerful and frequently used word is in the English language?
It's not one of those usually thought of candidates. Love? No. Money? Nope. Neither is it any member of your family... Mum, Dad, brother, sister, son, or daughter.
It's a three letter word, so common it's overlooked and taken for granted. 'The'. It's the humble 'the'."
(For more see this BBC article: Is this the most powerful word in the English language?
Or: "Between 2020/21 and 2021/2022, Americans consumed about 11 million metric tons of sugar, up from about 10 million metric tons in 2009/2010. Can you even begin to imagine the size of that sweet white mountain?"
(For more see: US sugar consumption statistics )
6. Share personal stories
Share a personal story related to your specific topic as the beginning of a speech. Done well, it lets the audience know you understand their situation and helps establish your credibility: your right to talk on the subject.
As an example here's the opening of a speech I gave about the impact of suicide on families and friends:
“One fine Spring day I biked home from school and found a policemen guarding our backdoor. Through it came sounds I'll never forget: my quiet Mother screaming. He said, "You can't go in."
I kicked him in the shins and did. It was the 15th of September, three days before my thirteenth birthday and my father was dead. Killed by his own hand. Suicide.”
(If you want to find out more about the speech and read it, it's here: After they're gone . It's an example persuasive speech using the five steps of Monroe's Motivated Sequence.)
7. Rhetorical questions
These are questions that although they are asked, they're never really intended to be answered by anyone other than the person asking them. * Their principal function is to act as a segue, or lead in, to what the person intends to say next. For instance, the first main point of your introduction.
Examples: "What if I were to say to you that there was no such thing as public speaking fear?"
"What do you think the main benefits of being able to speak up in public are?"
* Although there's bound to be someone in your audience who will. Be ready for them, and move on.
8. An empathetic question, aligning yourself with the audience and eliciting a response
These questions bring speaker and audience together, establishing a common ground, a mutual understanding, which is an effective way to ease into a speech. If your question 'works' you'll see heads nodding in agreement.
- "Have you ever experienced the butterflies in your stomach turning into a herd of rampaging elephants, just before you step up to give your presentation?"
- "Have you ever wanted a good day to never end?"
- "How often have you 'lost' your car in the supermarket car park?"
- "How often have you ever wanted to shout, NO? You want me to prepare a new presentation by tomorrow? NO. You want me to stay late, again? NO."
9. It's in the news
Take headlines from what's trending in media you know the audience will be familiar with and see.
Using those that relate to your speech topic as the opening of your speech is a good way to grab the attention of the audience. It shows how relevant and up-to-the-minute the topic is.
For example: "'Death toll soars to 76 in Florida after Hurricane Ian demolished entire communities.' 'Noru became a super typhoon in 6 hours. Scientists say powerful storms are becoming harder to forecast.' 'Hurricane Orlene strengthens into Category 4 storm as it heads toward western Mexico.'
Three front page headlines from CNN just today. Climate change. Let's do what we can."
10. This day in history
If you're giving a speech to celebrate a special birthday or an anniversary, consider using several carefully selected events that occurred on the same day as a speech opening. They could be either funny or serious, depending on the specific purpose of your speech. They're a great way to place the person in a much wider context and often with exalted company.
For example: "What do the 1863 National Thanksgiving Day proclamation by President Abraham Lincoln, National Boyfriend Day, and Gwen Stefani have in common with Joe? Yes, the 3rd of October! It's a great date made better by being Joe's birthday. And we say Gwen is truly privileged to have the same one as him."
11. Issue a challenge
Let the audience know first thing, at the beginning of the speech, what action you expect they'll be able to take by the time your presentation is complete. Then when you come to the final points, repeat the call to action, or challenge, as part of your closing statement.
For example: "I've a challenge for you. That's to sign up for our public speaking course. Right now you may not see yourself doing that. Public speaking? Me? I'd rather have a root canal done, without painkillers. However, by the end of the presentation...well, let's see. There's a first time for everything!"
Use a startling statement, a fact, or a series of facts, to jolt the audience into paying attention.
"Covid. We've had 1.06 million of us die in the US, so far. Today there are nearly 60,00 new cases. More mothers, fathers, friends, colleagues, children – people. People ill. People who might die. So why have we stopped wearing masks?"
For more: Google: Covid stats US
Other speech writing resources
- how to end a speech effectively : explanations with examples showing how to close a speech with impact
- how to write a speech : a detailed guide with examples covering audience analysis, planning, writing oral language, transitions, how to use an outline...
speaking out loud
Subscribe for FREE weekly alerts about what's new For more see speaking out loud

Top 10 popular pages
- Welcome speech
- Demonstration speech topics
- Impromptu speech topic cards
- Thank you quotes
- Impromptu public speaking topics
- Farewell speeches
- Phrases for welcome speeches
- Student council speeches
- Free sample eulogies
From fear to fun in 28 ways
A complete one stop resource to scuttle fear in the best of all possible ways - with laughter.

Useful pages
- Search this site
- About me & Contact
- Blogging Aloud
- Free e-course
- Privacy policy
©Copyright 2006-24 www.write-out-loud.com
Designed and built by Clickstream Designs
English Basics
Tips on How to Prepare a Short Speech
If you are looking for tips on how to prepare a short speech, you are on the right track. The process is quite straightforward – you will need to do some brainstorming, get credible information, create a visual aid, edit and revise your speech, and practice giving it to different audiences. The following tips should help you prepare a short speech in a flash. By following these suggestions, you will be able to give a polished presentation that will impress your audience.
Brainstorming
The best way to come up with a good topic for your speech is to conduct a brainstorming session. Brainstorming involves gathering several ideas from different people and grouping them into categories. This way, you will have more variety in the ideas. Next, rank the ideas by using a set of criteria. As you work to create a shortlist of three to five ideas, make sure to acknowledge the contribution of each participant.
Once you have an initial list of ideas, refine each one to make it a focused topic. As you go through each category, look for commonalities, themes, and patterns that can help you narrow your topic and come up with a coherent message. It will also help to conduct research before you start writing your speech, in which you look up information on the topic that you are going to address. By doing this, you will be able to generate ideas for further topic refinement and adaptation. Also, know your audience and their interests.
It is also important to make sure that you have enough time to think about ideas before preparing a short speech. Brainstorming meetings can be productive because members can discuss and write down their ideas. In addition to brainstorming, group meetings help you organize who will speak next. However, brainstorming sessions that involve multiple members do not produce as many ideas as those done by an individual using a nominal group technique.
The main purpose of brainstorming before preparing a short speech is to weed out the ideas that you haven’t yet thought of. Brainstorming sessions can be helpful when you have a feeling that you don’t have any ideas. They can also be helpful if you’re feeling stressed, anxious, or tired. This will get your mind moving and help you come up with ideas that aren’t rooted in your personal beliefs or ideology.
Getting information from credible sources
The Internet is a wealth of information, but getting information from reliable sources is essential to ensure accuracy. Use scholarly and peer-reviewed sources to verify information’s accuracy. In this guide, we look at the types of sources that meet the criteria of a credible source, including journal articles, scholarly journals, and books. In addition, we explore the difference between primary and secondary sources.
Newspapers and books are excellent sources, particularly when your topic is new and developing quickly. Newspapers, like the New York Times, are updated daily and may include editorials and commentary that are relevant to your topic. Electronic databases, such as LexisNexis, are another excellent source of news, including local and national newspapers. Newspaper articles can be cited with attribution, so look for them in addition to scholarly journals.
Another excellent source of information is the official website of a famous organization. Most well-known organizations have official websites and publish relevant information on these sites. Getting information from such a site is always better than using other sources, especially if the information is original and not filtered by a political agenda. By citing the official website, you will create a sense of credibility. The National Geographic website has a mobile application and is known for its accurate sourcing.
It is also helpful to do CRAAP tests to judge the credibility of your sources. The CRAAP test measures the accuracy, authority, relevance, and currency of information. While this may take more time, it can help you avoid unreliable sources and save time. For example, you may find an interesting article online, but it is not credible. If you’re preparing a short speech about new technology, look for the CRAAP test and make sure it’s a reputable source.
Using a visual aid
Using a visual aid when preparing a short speech is a smart idea, but there are a few things you should know before you start. Visual aids can distract the audience and make it difficult to understand what you are saying. It is better to use them as a backdrop or a reminder of what you are saying rather than as the main focus of your speech. If you are using a visual aid to support your speech, make sure you choose one that follows the same principles.
A visual aid can be anything from a handout to a flip chart, or even an interesting object. While using a visual aid, make sure it follows the main theme of your speech and is not distracting to the audience. It should also be clear and of high quality. To keep the visual aids from distracting the audience, use them at the end after you have finished delivering your speech.
While using a visual aid will make a presentation more interesting, it should never be a substitute for good preparation. If you want to engage your audience, use a visual aid if possible. Research shows that 83% of human learning happens visually. According to psychologist Bruner, 80% of what we learn is remembered while only 20% of it is retained in our minds. Using a visual aid will help you explain your ideas more clearly and add variety to your speech. And a more engaged audience is more likely to be persuaded.
Using a visual aid when preparing a short speech is not recommended for everyone. However, if you do use one, it can make your presentation more engaging and make your presentation more effective. Remember that when using a visual aid, make sure that the item is relevant to the topic. It is also important to ensure that the item does not break or become distracting. It is best to check the aid before using it on stage.
Editing and revising
The process of revising involves looking at your work again and making changes. This can help you make your ideas clearer, more accurate, and more interesting. The editing process focuses on the small details, such as punctuation, grammar, and style. Revising is a vital part of writing a speech, so be sure to take your time and make sure that everything is perfect before submitting it. Here are some tips for revising your speech:
Revision is an essential part of writing. The most experienced writers regularly revise their work. Ernest Hemingway, for example, rewrote the last page of A Farewell to Arms 39 times. Re-reading your old papers can also help you discover some revision strategies. The next step in revising your speech is copyediting or proofreading. You should do it as many times as necessary to get it as perfect as possible.
Revision is the process of giving your writing a new life. Revise your essay or speech by adding a thesis (answer to a research question or a position on a controversial topic). First, organize your draft by grouping similar ideas and ensuring that they flow into a logical order. This step puts forward stronger points, background information, and earlier information. Make sure that your reader can understand what you’re trying to say and that they don’t misunderstand you.
Revision is the process of looking at your entire work. In it, you examine the content of your writing in terms of the ideas, the organization, the structure, and the voice. Revisions are meant to address any awkward areas and enhance the flow of your paper. In addition to improving cohesion, they also aim to clarify ideas and improve the writing style. The revision process also includes discussing your writing with your audience.
Keeping eye contact with members of your audience
If you are preparing a short speech for a business meeting, try to make eye contact with members of your audience, at least for a few seconds. You may notice people nodding or smiling in response to your gaze, and this makes you feel more confident. You should try to make eye contact with each member of your audience, even if the group is small. If you do not do this, you risk alienating some of your audience or distracting others.
It is important to make eye contact with members of your audience, even if you are delivering your speech in an audience room. Eye contact signals a meeting of minds and takes the focus off of the speaker. This technique can be particularly helpful when you are nervous about giving a speech because it allows you to react to cues from your audience. For instance, if someone looks away from you for a long time, you can clarify what they’re asking or expand on an issue. You can also become animated when necessary to persuade skeptical individuals.
Making eye contact with audience members is essential if you want your speech to be successful. During your presentation, it’s not practical to stare at people while they’re listening to your speech, but if you want to create a lasting bond with your audience, you should do so during key points. You should maintain eye contact with your audience for at least 3 seconds, and at certain points during your speech where it’s natural to shift your gaze.
When preparing a short speech, it is important to make eye contact with your audience. The best speakers maintain eye contact with their audience and persuade them in a short time. By doing so, you’re creating a personal connection with your audience and helping them understand what you’re trying to say. It’s also a great way to build energy in an audience, so don’t neglect it.
Related posts:
- How to Prepare for a Speech?
- Importance of Preparation in Public Speaking
- Importance of Practice in Public Speaking
- How to Prepare for a Speech in Class?
- How to Prepare for Public Speaking?
- Public Speaking Tips For Students
- How to Talk in Front in a Class Without Getting Nervous?
- Factors to Consider When Preparing a Speech
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Speech Topics For Kids
- How To Write A Speech
How to Write a Speech: A Guide to Enhance Your Writing Skills
Speech is a medium to convey a message to the world. It is a way of expressing your views on a topic or a way to showcase your strong opposition to a particular idea. To deliver an effective speech, you need a strong and commanding voice, but more important than that is what you say. Spending time in preparing a speech is as vital as presenting it well to your audience.
Read the article to learn what all you need to include in a speech and how to structure it.
Table of Contents
- Self-Introduction
The Opening Statement
Structuring the speech, choice of words, authenticity, writing in 1st person, tips to write a speech, frequently asked questions on speech, how to write a speech.
Writing a speech on any particular topic requires a lot of research. It also has to be structured well in order to properly get the message across to the target audience. If you have ever listened to famous orators, you would have noticed the kind of details they include when speaking about a particular topic, how they present it and how their speeches motivate and instill courage in people to work towards an individual or shared goal. Learning how to write such effective speeches can be done with a little guidance. So, here are a few points you can keep in mind when writing a speech on your own. Go through each of them carefully and follow them meticulously.
Self Introduction
When you are writing or delivering a speech, the very first thing you need to do is introduce yourself. When you are delivering a speech for a particular occasion, there might be a master of ceremony who might introduce you and invite you to share your thoughts. Whatever be the case, always remember to say one or two sentences about who you are and what you intend to do.
Introductions can change according to the nature of your target audience. It can be either formal or informal based on the audience you are addressing. Here are a few examples.
Addressing Friends/Classmates/Peers
- Hello everyone! I am ________. I am here to share my views on _________.
- Good morning friends. I, _________, am here to talk to you about _________.
Addressing Teachers/Higher Authorities
- Good morning/afternoon/evening. Before I start, I would like to thank _______ for giving me an opportunity to share my thoughts about ________ here today.
- A good day to all. I, __________, on behalf of _________, am standing here today to voice out my thoughts on _________.
It is said that the first seven seconds is all that a human brain requires to decide whether or not to focus on something. So, it is evident that a catchy opening statement is the factor that will impact your audience. Writing a speech does require a lot of research, and structuring it in an interesting, informative and coherent manner is something that should be done with utmost care.
When given a topic to speak on, the first thing you can do is brainstorm ideas and pen down all that comes to your mind. This will help you understand what aspect of the topic you want to focus on. With that in mind, you can start drafting your speech.
An opening statement can be anything that is relevant to the topic. Use words smartly to create an impression and grab the attention of your audience. A few ideas on framing opening statements are given below. Take a look.
- Asking an Engaging Question
Starting your speech by asking the audience a question can get their attention. It creates an interest and curiosity in the audience and makes them think about the question. This way, you would have already got their minds ready to listen and think.
- Fact or a Surprising Statement
Surprising the audience with an interesting fact or a statement can draw the attention of the audience. It can even be a joke; just make sure it is relevant. A good laugh would wake up their minds and they would want to listen to what you are going to say next.
- Adding a Quote
After you have found your topic to work on, look for a quote that best suits your topic. The quote can be one said by some famous personality or even from stories, movies or series. As long as it suits your topic and is appropriate to the target audience, use them confidently. Again, finding a quote that is well-known or has scope for deep thought will be your success factor.
To structure your speech easily, it is advisable to break it into three parts or three sections – an introduction, body and conclusion.
- Introduction: Introduce the topic and your views on the topic briefly.
- Body: Give a detailed explanation of your topic. Your focus should be to inform and educate your audience on the said topic.
- Conclusion: Voice out your thoughts/suggestions. Your intention here should be to make them think/act.
While delivering or writing a speech, it is essential to keep an eye on the language you are using. Choose the right kind of words. The person has the liberty to express their views in support or against the topic; just be sure to provide enough evidence to prove the discussed points. See to it that you use short and precise sentences. Your choice of words and what you emphasise on will decide the effect of the speech on the audience.
When writing a speech, make sure to,
- Avoid long, confusing sentences.
- Check the spelling, sentence structure and grammar.
- Not use contradictory words or statements that might cause any sort of issues.
Anything authentic will appeal to the audience, so including anecdotes, personal experiences and thoughts will help you build a good rapport with your audience. The only thing you need to take care is to not let yourself be carried away in the moment. Speak only what is necessary.
Using the 1st person point of view in a speech is believed to be more effective than a third person point of view. Just be careful not to make it too subjective and sway away from the topic.
- Understand the purpose of your speech: Before writing the speech, you must understand the topic and the purpose behind it. Reason out and evaluate if the speech has to be inspiring, entertaining or purely informative.
- Identify your audience: When writing or delivering a speech, your audience play the major role. Unless you know who your target audience is, you will not be able to draft a good and appropriate speech.
- Decide the length of the speech: Whatever be the topic, make sure you keep it short and to the point. Making a speech longer than it needs to be will only make it monotonous and boring.
- Revising and practicing the speech: After writing, it is essential to revise and recheck as there might be minor errors which you might have missed. Edit and revise until you are sure you have it right. Practise as much as required so you do not stammer in front of your audience.
- Mention your takeaways at the end of the speech: Takeaways are the points which have been majorly emphasised on and can bring a change. Be sure to always have a thought or idea that your audience can reflect upon at the end of your speech.
How to write a speech?
Writing a speech is basically about collecting, summarising and structuring your points on a given topic. Do a proper research, prepare multiple drafts, edit and revise until you are sure of the content.
Why is it important to introduce ourselves?
It is essential to introduce yourself while writing a speech, so that your audience or the readers know who the speaker is and understand where you come from. This will, in turn, help them connect with you and your thoughts.
| ENGLISH Related Links | |
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.
More From Forbes
How to create a short speech fast.
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter
- Share to Linkedin
I tweeted recently that every speaker needs a 3-minute and a 20-minute version of her speech. To that I would add that every speaker needs to know how to give a minute-long response, in answer to a question, for example, or for responding to the media.
So how do you all of these well? What are the pitfalls to avoid? It can be surprisingly hard to say something interesting in a very short time, and to avoid running on at the mouth and saying too much. What's the happy medium, and how do you think about it?
The minute speech is best handled as follows. Decide what you're going to say, take a deep breath, and then give the headline. "I don't think that mice should be allowed in the Vatican." Then go on to give up to 3 supporting reasons, depending on your thinking and the time allowed. Hygiene, worry about the destruction of precious manuscripts, and the eek factor during prayers. Finally, finish off with a repetition of the headline: "So that's why I think that mice should be banned from the Vatican."
When you've got more than 3 but less than 7 minutes, think in terms of problem-solution. If you have a great story to begin the problem section, then do so, but don't allow it to take over the problem section entirely. You need to spend half of your allotted time discussing the problem in as much detail as you can (which is not much). Heretical mice are running amok throughout the Vatican. This deplorable plague has led to illness, destruction of some of the Vatican's most precious artifacts, and the discomfort of many visitors and residents. ...About half way through your total time, switch to the solution and buttress that with as much logic and passion as you can muster. I recommend beginning with an excommunication, followed by mice traps, poison, and the playing of Barry Manilow recordings in the basement....
That's really all there is to it. Keep it simple. If you want to conclude by describing the benefits of your solution, then go ahead, in a sentence or two.
Repetition and simplicity will help you keep your remarks organized and under control, and will help your listeners follow you.
The same advice holds for the 20-minute version. You basically have to remove half of the detail that makes for a solid hour-long speech. And watch your stories, because they will loom much larger in a 20-minute précis of your speech than in the full version. You’ll need to shorten those too, without cutting the essential detail that enables your audience to make sense of the story.
A good way to prepare a 20-minute speech is to create the logical ‘spine’ of your full speech – the step-by-step logic of the speech that explains the thought structure, shorn of the detail. It should take the form of a series of declarative sentences. Then, once you’ve worked out the logic, add back in just enough detail to fill the allotted time.
You'll want to have these versions of your presentation on hand, ready to go, for times when your full speech is too long. If you're a professional speaker, it's part of the pro's arsenal to be ready to give the shorter versions in order to be prepped for any occasion.
- Editorial Standards
- Reprints & Permissions
- Newsletters
- Best Industries
- Business Plans
- Home-Based Business
- The UPS Store
- Customer Service
- Black in Business
- Your Next Move
- Female Founders
- Best Workplaces
- Company Culture
- Public Speaking
- HR/Benefits
- Productivity
- All the Hats
- Digital Transformation
- Artificial Intelligence
- Bringing Innovation to Market
- Cloud Computing
- Social Media
- Data Detectives
- Exit Interview
- Bootstrapping
- Crowdfunding
- Venture Capital
- Business Models
- Personal Finance
- Founder-Friendly Investors
- Upcoming Events
- Inc. 5000 Vision Conference
- Become a Sponsor
- Cox Business
- Verizon Business
- Branded Content
- Apply Inc. 5000 US
Inc. Premium

7 Things to Do When You Have to Give a Short Speech
You can find a lot of advice on how to give a big speech in front of a big audience. but more often, you're probably asked to take just a few minutes to address a smaller group. here's how to give a short speech that will leave your audience wanting more..

I once went to a small fundraising event for a nonprofit. They did so much good in my neighborhood that I truly thought they could do no wrong.
Then one of the organizers asked someone to stand up "to say a few words," and her presentation turned into the longest, least organized, most lifeless talk I've ever heard. Those who were standing near the back of the room slipped out. For the rest of us, the goodwill slipped away.
You can find a lot of advice out there on how to give a speech in front of a big audience, but how often do most of us do that? More often, you're likely asked to take a few minutes to address a smaller group--sometimes with little or no warning.
The next time that happens to you, here are seven things to keep in mind.
(Want to read more, make a suggestion, or be featured in a future column? Contact me or sign up for my weekly email .)
1. Strip it down.
There's an unfortunate temptation in a short speech to try to cram everything you have to say into a short time. Instead of trying to make the time fit the speech, however, recognize that you have to make your remarks fit the time allotted. If you've got five minutes to talk, you shouldn't have more than three main points.
Key: If your short speech is longer than this article, it's too long.
2. Plan and rehearse.
This applies whether you have five days notice before your speech or 30 seconds. If you're surprised to be called on to speak, your planning might consist only of conjuring up your three main points while someone else is trying to get everyone's attention and introduce you, but that's better than nothing. Ideally, you want to plan everything you're going to say, rehearse in front of other people, and rewrite over and over.
Key: Don't fall into the trap of thinking that short remarks require less preparation. In fact, giving a good short speech can be harder than giving a long one.
3. Cut yourself off.
In the history of the entire world, I don't think anyone has ever said, "I wish that speech had been longer." So keep track of time, and by all means don't ramble. If you've run out of time to make a major point, either work it into the questions people have for you afterward, or send a follow-up note to the members of the audience.
Key: Take the length of time you've been asked to speak for, and cut it down by 20 percent.
4. Use milestones
For a five minute speech, you want to organize in roughly one-minute intervals, and you want to offer milestones to the audience at the top of each minute. You get one minute for your introduction, during which you explain what you plan to say. Then you get 60 seconds each for your three main points. That last 60 seconds can be used either for a short conclusion, or as a buffer in case you run long.
Key: Use verbal cues to keep the audience on track. Phrases that seem obvious on the written page can be much more helpful in oral remarks: "That was the first point. Now we'll talk about the second of my three points."
5. Show. Don't tell.
For a short speech, I generally like to have something physical to show the audience--a couple of photos, a prop, anything that gives the audience's eyes something to focus on. Think of the difference between announcing, "Yesterday, we signed an important deal," versus holding up a ballpoint pen and saying, "With this pen, we made history yesterday when we signed Spacely Sprockets to a five-year contract." (Or else, raise your coffee cup and proposing a toast, rather than just making an announcement.) It can be a little bit corny, granted, but it's much more memorable.
Key: If you use props, you almost always want to use them early in your remarks. Don't distract the audience and have them wondering what the projector is for, or why you are holding a teddy bear or a vacuum cleaner (or whatever your prop may be).
6. Make it personal
You do not need to bare your soul, but in almost every short speech there is an opportunity to connect on a personal level with your audience. Don't be afraid to allow emotion to enter into your voice if appropriate. If the news is good, say you're happy and proud; if you have to share something sad or infuriating, make your tone and your expressions match the news.
Key: A few short words can be enough to make a connection. Simply saying with sincerity something like, "On a personal note, I'm so incredibly proud of this group" or "I can't tell you yet how we will overcome this challenge, but I can tell you for damn sure we will find a way"--depending on the circumstance--can be enough.
7. Speak up.
All of your preparation, cutting, organizing, and emotion goes for naught if people can't hear you. If you have good audio equipment, use it. If not, at least start out by asking whether people can hear your voice. One trick: Ask the audience to raise their hands if they can hear you well. If you see a patch of people somewhere without their hands up, you know there's an issue you need to address.
Key: Remember that ensuring everyone can hear is your responsibility. Project your voice, and if you find that people in the back can't hear what you have to say consider moving to the center. If you run into trouble and can't find a solution, cut your remarks short, and find a way to follow up later.
The Daily Digest for Entrepreneurs and Business Leaders
Privacy Policy
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- Communication Skills
- Public Speaking
How to Give a Great Impromptu Speech
Last Updated: March 19, 2024 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by Lynn Kirkham . Lynn Kirkham is a Professional Public Speaker and Founder of Yes You Can Speak, a San Francisco Bay Area-based public speaking educational business empowering thousands of professionals to take command of whatever stage they've been given - from job interviews, boardroom talks to TEDx and large conference platforms. Lynn was chosen as the official TEDx Berkeley speaker coach for the last four years and has worked with executives at Google, Facebook, Intuit, Genentech, Intel, VMware, and others. There are 7 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 408,677 times.
Most speeches are the result of careful planning, revision and practice. There may be times, however, when a situation demands that you give an impromptu speech with little or no time to prepare. When you find yourself in an unexpected public speaking scenario, you’ll be improvising what you say, which means you’ll have to be able to think on your feet. Following a basic structure, pacing yourself and staying composed will help you deliver an oration you can be proud of, or at least survive with minimal embarrassment.
Setting Up an Unexpected Speech

- Most of the time when you’re giving an impromptu speech, you’ll be singled out to say a few words on the spot. Since you’ll only have a few moments, preparing yourself is more about getting yourself in the right state of mind than it is knowing exactly what you’re going to say.
- If you really need to milk it, you can buy yourself some extra time by shaking hands, exchanging pleasantries or adjusting the microphone stand before speaking.

- Assume that everyone around you wants to see you succeed. This will help put you at ease. Expecting yourself to fail will only destroy your composure and make you more fearful of your audience.
- Confront the reality of your situation to avoid being blindsided by panic. Accept that you have to give a speech and then focus all your resources on giving a good one.

- Oftentimes, the more confident you make yourself appear, the more confident you’ll feel.
- Relax! Speaking in front of a crowd is not that big a deal. Even if you make a mistake, it’s not the end of the world.

- Don’t just jump right into the main idea of your speech. Test the waters by getting used to speaking and sharing a little about yourself first.
Delivering an Effective Speech

- Use simple sentences that follow a logical progression and enunciate your words carefully to keep yourself from getting tongue-tied.
- Slowing yourself down a little will give your mind time to catch up and formulate new ideas.

- Two minutes will fly by once you start speaking. Despite your reservations about being put on the spot, you may actually find it harder to give a short speech than a long one.

- A good way to give your speech a solid beginning, middle and end is to present details chronologically. For example start with “when I first became friends with John, he…”, follow that up with “now that we’re coworkers, we have more fun than ever…” and conclude with “I have no doubt that the future of our friendship will be just as entertaining.”
- When describing personal experiences, avoid sharing opinions on irrelevant controversial subjects.

- Humor is a great icebreaker and also makes it easier to hold your audience’s attention.
- Be sure any jokes you make are suitable for the age and demographic of your audience, as well as the occasion itself.
Ending on a High Note

- As with the rest of your speech, keep your conclusion brief. It’s alright to sign off with a simple “thank you for your time” or “let’s hear it for the newlyweds.”

- If you’re planning on making a specific request or appeal, as for a business conference, the end of your speech is the proper time to do it.
- The conclusion is the perfect occasion to come out with something especially heartfelt. Emotions will run high and the crowd will be moved by your sentiments.

- You don’t have to thank every important figure at the event individually. A general expression of gratitude is all that’s needed.
- Be clear who you’re supposed to hand the microphone or floor off to so that you don’t end your speech by looking around in confusion. [11] X Research source

- Impromptu speeches are mostly appraised by the willingness of the speaker to rise to the occasion. There’s no sense in being too critical of your performance since you’ll have had no time to work on it beforehand.
Expert Q&A

- Practice for unexpected speaking scenarios by volunteering to give impromptu speeches at casual events. Thanks Helpful 17 Not Helpful 2
- If you're using a microphone, stay within optimal range for your voice to be amplified. Don't move the microphone too close or too far away from your mouth. Thanks Helpful 14 Not Helpful 2
- While brainstorming, quickly come up with three or four main points to cover. Thanks Helpful 18 Not Helpful 4
Tips from our Readers
- Speak clearly and be confident. This will make you seem more credible even if some parts of your speech aren't as strong as others.
- Don't waste your time by writing full sentences, write bullet points and then expand on them when you give the speech.
- Make sure not to be too cocky or sound sarcastic, or you might not win over the audience.
- Use your own stories. Relate the topic to some of the moments in your life.

- Steer clear of subjects you don't know much about. Thanks Helpful 13 Not Helpful 2
- Be careful not to offend your audience. Not only is it bad form and will make your speech be perceived as a failure, it could actually harm your standing among your acquaintances. Thanks Helpful 12 Not Helpful 3
- Take a moment to get your appearance in order before presenting yourself. Steal a quick glance in the mirror or have a trusted friend tell you if your hair is a mess, your shirt is untucked, you have food stuck in your teeth, etc. Thanks Helpful 10 Not Helpful 3
- Don't use generic, pre-written speeches pulled from the internet or oration guidebooks. These can easily come off as stilted and inorganic. Your audience will be able to tell if you're simply going through the motions. Thanks Helpful 9 Not Helpful 4
You Might Also Like

- ↑ Lynn Kirkham. Public Speaking Coach. Expert Interview. 20 November 2019.
- ↑ http://wittcom.com/how-to-develop-confidence-speaking/
- ↑ http://sixminutes.dlugan.com/how-to-impromptu-speech/
- ↑ http://www.askmen.com/money/body_and_mind_150/192b_better_living.html
- ↑ http://www.write-out-loud.com/how-to-use-humor-effectively.html
- ↑ https://speakingwithoutnet.wordpress.com/2012/02/08/ending-on-a-high-note-the-last-sentence/
- ↑ https://www.workingvoices.com/insights/presenting-how-to-react-when-you-make-a-mistake/
About This Article

- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Bridget Harris
Mar 1, 2023
Did this article help you?
Veeraraghavan. Santhanam
Jul 21, 2017
Dharyl Bizu
Mar 27, 2017
Apr 30, 2017
Sameed Ahsan
Jan 28, 2019

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Get all the best how-tos!
Sign up for wikiHow's weekly email newsletter
- Internet , Productivity
15 Short Memorized Speech Examples
Giving a speech feels hard and that feeling is so common that a majority of people would rather die than speak publicly. But when it is inevitable, maybe as the best man, mother of the bride, or a speech assignment for class, we turn to memorization.
Why? Because we assume that if we know and remember what to say, we won’t embarrass ourselves. Slightly effective, but it comes with its own limitations.
Here, I will show you how to memorize a speech with 15 examples worth referencing.
But first, let’s go over how to write a speech, because it doesn’t matter how well you memorize one if the content is bad.
How to Write a Speech
The anxiety that fuels the need to memorize a speech comes from either not knowing what to say or how to say it. A sure fire way to overcome that is by writing the speech.
And contrary to what you might think, it is not hard to write a good speech. If you know how to have a meaningful conversation, moving from point A to point B, you can write a speech. You just need to follow these tips.
Set the stage with an introduction
How exactly you start depends on the context of your speech. For instance, you may need to introduce yourself if your audience isn’t familiar with you. This is unnecessary if you’ve been introduced or you’re speaking among your peers.
But the main point here is about how you start your speech. The goal is to explain the what and why in a way that captures the audience’s attention.
It could be a famous quote, a shocking statement, or a rhetorical question. As long as it gets ears to perk up and eyes to focus on you.
Create and follow a structure
Now that you have their attention, it is time to hold it. As the speaker, the audience expects a path and destination from you. They want to know where the gist leads and why the point matters.
Ergo, structure.
Each paragraph in your speech must have a central point and connect with the next. Don’t try and stuff everything you know about the subject in the paragraphs. Focus on the key issues and maintain clear, logical transitions from idea to idea.
That is why it is crucial to understand the purpose of the speech. Are you trying to entertain, argue a point, inspire, or educate? The answer will inform the structure and overall tone of the speech.
Use Anecdotes to illustrate key points
When you write a speech, tailor your language and ideas to your audience. The way you speak in a school seminar is different from how you will talk at your best friend’s wedding, and there is no place where this matters more than in your anecdotes.
Countless studies have shown that our brains remember stories pretty well. That means if you want your speech to be memorable, you have to sprinkle some of them in there to illustrate your points.
That way, even if the facts and figures fly over their heads, the story will stick. And the good thing about anecdotes is, you don’t have to memorize them.
Use Transitions
No matter how great every line in your speech is, there will be moments when the audience drifts off. Use transitions to recall their attention. It signals to them that the oncoming part is worth paying attention to.
There are different ways to deploy this. It could be a rhetorical question like “Why does this matter?” followed by a pause, just long enough to create anticipation.
Other examples include “So here’s the lesson” or “In a similar fashion.”
Summarize with a call to action
Your audience won’t remember everything you say, but they are more likely to remember the last thing you said to them. That means, alongside the introduction, this is an integral part of your speech.
Summarize the speech using sentences that drive home the main point. You can do this by repeating a few key takeaways or sharing an anecdote that illustrates the point.
How to Memorize a Speech

Image by Rodnae Productions ( Pexels )
Hopefully, after reading that section, you are starting to get the idea. Once you know what to say and how to say it, you’ve cracked the first step to memorizing a speech.
The next thing is to observe a few steps, and you are well on your way to delivering a captivating speech from memory.
Rehearse the Speech
After writing the speech, try reading it out loud. The goal here is to figure out how it sounds to fix what doesn’t work.
You can add, delete, or reorder parts of the speech until it sounds compelling and natural during this phase. Like something you wouldn’t mind sitting through yourself.
This process could take a few times, so feel free to pause and come back with fresh eyes and ears. You could also try reading it to someone for a different perspective.
Memorize the main ideas
The best way to memorize a speech is to learn the main points. This is where you benefit from writing the speech. Once you understand the subject matter and the goal of the speech, your mind has a framework to follow.
Instead of trying to capture the entire speech word-for-word, you have memorized the main ideas. Enough to talk about it to an audience as if you are having a regular conversation.
There are two main benefits to this. One, it gives a natural feel to your speech. Regurgitating a speech word-for-word makes you seem like a robot. There is no warmth, and it makes your content less engaging.
Two, it makes you immune to a slip-up. When you forget a word or sentence, it has little to zero impact because you know what you are trying to say and how to say it. You have maximum flexibility.
A practical way to memorize each idea is by quizzing yourself over each paragraph. “What is it about?” “What problem is it describing?” “Why does this matter?”
Practice your delivery
Finally, a speech is only as good as its delivery. Think about the most remarkable speeches you’ve heard or seen. What made them stand out?
One thing that is for sure is it isn’t because they remembered every single word. Not that you would know. But instead how the speaker spoke, entertainingly and informatively.
It is possible to memorize this by rehearsing over and over again.
Since you are more concerned about the meaning than the syntax of your sentence, you start to get a feel of when it’s okay to make a joke, change the timing or intonation.
That is how to memorize a speech, and it all starts with focusing on the content. Now, let’s see some good examples of these tips being put to use in different scenarios.
Short Memorized Speech Examples
Short memorized speech for a college paper.

This example might not align with your definition of “short,” but it gets a whole lot right when it comes to speeches.
First, it starts with a question that piques attention, then immediately establishes what and why they are talking about it. The sentence structure is also conversational, and the author doesn’t have to memorize each word.
The rest of the speech maintains that tone, and the thought flows logically. From explaining what dreaming big is to its downsides and negative impact, all told through anecdotal lenses.
Not only is this speech easier to memorize because it is their story, but it makes it more engaging. More than what a rollout of psychological facts would have been.
Finally, the speaker ties it up in a compelling conclusion that summarizes the key point with a call to action.
Short speech for a company event

This is a much shorter speech than the previous example, but it still follows the same principles. In the introduction, the author uses the scale of time to capture the audience’s attention. With a few sentences, it transports their mind to the past and the future. Engaging!
That thought continues its logical progression in the body. The CEO (presumably) zeroes in on the implications and impact of that journey in time on members of the organization. Relatable!
Finally, they tie up the speech with a nice bow with a call back to the beginning.
Not only does this speech have the perfect length for the occasion, but it is also stirring enough to leave a lasting impression.
Short wedding speech

If you have ever attended a wedding, you are probably familiar with speeches like this. What makes them so common yet effective is how much it understands its audience.
A wedding reception is a relaxed atmosphere, which means the audience experts jokes and laughter. The author doesn’t waste time and delivers right from the beginning. Humor makes us attractive, and with that, the audience is interested in what the writer has to say.
Another thing that makes this speech good and easy to memorize is a total familiarity with the subject matter. In this case, that’s Josh. Because of that, the author can craft a structural narrative that establishes Josh’s personality and character and its relevance to the current event.
Short memorized speech for a presentation

Here is a nice example of a proper introduction if you ever have to give a speech to your peers at school, work, or any other setting. They already know who you are, which means your primary focus is to give them something to listen to.
Next, dive into the what and why it matters. Here, the writer offers both at the end of the first paragraph and in the next. In two paragraphs, the audience knows why she’s talking about her future and why it matters to the speaker and them.
The next logical question is how the speaker plans to achieve that, and they answer in the final paragraph.
Short introductory speech for a college seminar

What if you had to come up with an introductory speech for an event? Well, you still follow the same beats as other types of speeches. Establish the what and the why.
For What, this college seminar speech covers the relevance of the seminar by mentioning the dignitaries that have supported it. Without explicitly stating that it is an important event, the roster of those in attendance and the organizing team conveys that to the audience.
To answer Why, the principal plainly states the value of the seminar. The audience understands they are part of a long history, and the content is valuable enough for commercial publication.
Short Personal Introductory Speech

When you have to introduce yourself, you have a limited time to establish who you are and why you should be listened to.
Thankfully there is not much to learn in this scenario because you are the subject, and no one knows you better than you. Start with your name and your experience like this example to prove your credibility.
Since it is a personal introduction, the body of your content should be something that humanizes you. That way, you go from a name and title to a person, and in this example, a relatable one.
The good thing about this type of speech is it is fun to memorize, and you can rehearse and shape it by giving it to as many people as possible.
Short persuasive speech to students

In the game of attention that is speech writing and delivery, there are multiple paths to victory. This example deploys the rhetorical question method to command the attention of its audience.
By asking questions audience members have most likely asked themselves, the speaker has positioned himself as someone with answers. After all, if you know about these questions, then they have probably figured it out.
Furthermore, each point builds on the one before it, in the direction of a typical day. Because it follows the logical progression of their regular day, the audience has permission to insert themselves into the narrative, making them more receptive to the advice and suggestion.
Persuasive for a diverse audience

What if you are trying to write and memorize a speech for a diverse audience? First, you need to find something that unites you all. In this short excerpt from a speech, the speaker has chosen their identity as residents of Thailand.
It would be difficult for the speaker to memorize every single word in this speech. However, by crafting points around how the central purpose of the speech benefits everyone, they don’t have to.
All that needs memorizing are the broader supporting points. To provide jobs, improve the local economy. Each point is bolstered with verifiable facts, which makes it more convincing.
Short speech for an argumentative speech

If you ever find yourself having a debate, the trick to making a convincing argument is to display a complete understanding of the topic interspersed with your opinions and verifiable facts.
This example does two of those things excellently. It starts by recognizing the conflict. Phones are helpful, and they serve an essential role in modern society, but it has its downsides. Then there’s the referenced medical fact that adds credibility to the conflict.
These points are connected by transitional phrases and words like “On the other hand” and “Worryingly” that make it easy for the audience to follow the speaker’s train of thought.
Short Memorizable speech for a proposal

Found the perfect partner and want to propose? Besides the content, writing and delivering your proposal speech is no different from any other kind of speech. It is all about connecting with your audience.
That means, like this example, you need to speak in the first person a lot, i.e., lots of Is. Your key points, as shown here, should focus on how your partner makes you feel and what their presence in your life means to you.
Memorizing the main points of your proposal is especially important in this context because your speech should come from the heart. Or at least feel like it did.
Memorized acceptance speech

Suppose you’ve received an award or recorded an accomplishment that requires a speech. In that case, the majority of your content should focus on showing appreciation.
First, start by thanking the people giving you the award, then move on to thank everyone else, specifically those who contributed to the achievement.
Feel free to introduce humor into your speech, but it should be appropriate for the event and place.
As always, when you memorize this kind of speech, you should focus more on each section than on the exact words. For instance, you could thank the awarding body first, then move to your peers, then family last.
That way, even after rehearsing multiple times in front of a mirror, it still feels natural and spontaneous.
Short acceptance speech with commentary

There are occasions when you want to do more than simply thank you in your acceptance speech. In scenarios like that, find a way to connect your appreciation with your commentary, as seen in this example.
Start by appreciating the organization or people responsible for the award or accomplishment. Then use transitional phrases or a topic sentence to segue into your commentary.
The example above used “…all the effort of my entire team…” to segue into an inspiring comment. It also used an anecdote to illustrate the point further.
Finally, end with a note of thanks to close the circle.
When crafted this way, you only need to memorize the broad strokes of your speech and perhaps the connective phrase if you came up with the perfect line in your draft.
Short Goodwill speech

Above is an excerpt of the famous Ich bin ein Berliner speech by President John F. Kennedy in 1963. You can watch and read the whole thing here .
The popular name appears at the very end of the speech, but it would have made zero sense or had little impact if it wasn’t the conclusion of logically progressive thought.
Goodwill speeches should be informative and persuasive, and this example does that brilliantly from the first paragraph. It starts by showing great respect to the city and sticks to the theme by highlighting the shared values and beliefs.
If you ever have to deliver one, focus your memorization efforts on what you have in common with your hosts and build out from there.
Short memorized speech for a funeral

Many of us will have to deliver a speech at a funeral someday. When that time comes, it is better to memorize the order of your thoughts than the exact words.
A good order starts with introducing yourself and your relationship with the deceased. Then spend the following paragraphs talking about their life and personality. This includes speaking about their accomplishments, major life events. Each talking point should connect back to the impact on you.
Finally, summarize with a final takeaway from the theme, how you want others to remember the individual, and a thank you to attendees.
Short Farewell Speech after leaving a place or position

Your farewell speech is your last time to leave an impression on your audience. This could be your colleagues, boss, or students. Whoever they are, they will determine the exact tone and style you choose in your speech.
Depending on your experience and emotional attachment to the organization, your speech could be a simple thank you. It could also be exciting stories that highlight your history and journey there.
Whatever you decide, make sure it is personal. The second half of the first paragraph and the second paragraph above is an excellent example of this.
Wrapping it Up
That makes it 15, and depending on the scenario, each one is a useful reference when crafting your speech. Remember, the first step to memorizing a speech is to write one.
It gives you a chance to organize your thoughts, deepen your understanding of the topic, and familiarize yourself with the audience. In turn, you get the confidence to deliver in a way that is both engaging and convincing.
By following these tips and examples, you too will be able to deliver a speech that makes you proud.
Tom loves to write on technology, e-commerce & internet marketing. I started my first e-commerce company in college, designing and selling t-shirts for my campus bar crawl using print-on-demand. Having successfully established multiple 6 & 7-figure e-commerce businesses (in women’s fashion and hiking gear), I think I can share a tip or 2 to help you succeed.

Writing Short Speech
Short speech generator.

Speeches are normally given in a classroom setting when the teacher will give it as some sort of project for the students in the middle of the school year. But not everyone is a huge fan of public speaking. Research shows that people would rather die than speak in front of a crowd. But as crazy as it is, it is perfectly understandable. Why you may ask? There are many reasons for this unexplained behavior. However, it can be boiled down to just one factor: preparation. In death, there is absolutely nothing to prepare for. But in public speaking, preparation is everything. From the tone that you use to the emphasis on some of the words that you need to the timing the precision, the research and etc… You may also see examples of writing a short speech
- Speech Examples in PDF
- How to Start a Speech
The list just goes on and on from there. But what happens after you deliver that speech up front? Your hard work and effort will not go unrecognized, after all. Not only will you be praised with a roaring round of applause from the audience, but you will also feel a sense of pride and relief that the worst is over and that all the effort and dedication that you put into has finally paid off. And so your mission begins to improve all the aspects about your speech in order to become better at it. There are people who get jittery even after delivering their speeches more than once. But the key to all great speeches is to simply rise above it. You may also see student speech examples to give you a better idea.

Tips in Writing a Great Speech
Speeches are given when there is an occasion: graduation ceremonies, awarding ceremonies, welcome remarks, topics assigned for you to talk on stage, and many other various events. But it is important to learn a few tips on how they are typically written to give you an idea in order to make you speech more meaningful and impacting. You may also check out informative speech writing and analyze what its differences and similarities are from that of a short speech.
1. Be Memorable. Keep in mind that the audience loves a good opening. They say that the opening of your speech will determine as to whether you will be boring or interesting. Even if the topic is considered old and common knowledge, people would normally lend their undivided attention when the speaker would give an unexplored angle which the public does not know about or makes an opening that is interesting enough to get their attention piqued. Tell a story. Share a joke. Look back at one of your experiences that you had in relation to the topic. Quote a quote. Once you have managed to hook the attention of your audience, then you are ready to to continue your speech. You may also see appreciation speech examples & samples
2. Have a Structure. It is very common for speakers to get sidetracked all the time on what they are trying to convey to the audience. But how can one avoid this? Well, it starts by making an outline. An outline serves as your guide as to the order and sequence on how your speech is going to go. Your outline does not have to be too detailed or complicated, it is just your guide after all. What is important that there should be an introduction, a body and a conclusion– the basic structure of every good speech. If ever there are main points that are found in the body of your speech, then it is best to arrange them in order to avoid confusion. Here is a sample speech outline:

Introduction
It should contain the opening statements of the speech
Every speech introduction must also include the thesis of the speech
The introduction part would normally take up at least 20 percent of the speech
The best way to start your speech would be adding an “attention-getter” (often the best way to start)
Transition from the introduction should also be placed that serves as a marker to let the audience know that the body of the speech will be talked about next. You may also like special occasion speech examples & samples
The body of the speech can contain 3-4 main points about the central idea being presented.
Though main points are already encompassed in the speech, it is possible to add sub-points within the main points that allows a more organized and detailed speech. You may also check out introduction speech examples & samples
Make sure that when stating your speech, the content must be original and not copied from other speeches elsewhere. Should you decide to borrow some quotes or lines from other transcripts or speeches not your own, do not forget to give them the proper due credit it deserves. Otherwise, it would be an act of plagiarism. You may also see presentation speech examples & samples
It is important to know that the time allotted to deliver the said speech will be centered on your on the body.
Thus typically comprising 70% of the delivery time for the speech. So make sure when delivering your short speech, there will be enough time to state your conclusion. Otherwise, you just have to wing it. You may also see wedding speech examples & samples
If you are planning to make use of visual aids, try practicing the timing of your speech with your visual aids so that you are able to adjust the timing of it.
Ensure that you still have the audience’s undivided and full attention and cooperation.
Other than visual aids, you can also show some video presentations or other source material to keep the speech interesting. Keep your audience hooked to the very end, otherwise, they may just get bored of you. You may also like tribute speech examples & samples
***At this point there should be a transition from the Body to the Conclusion.
At this stage, it is important to reiterate the main points that you have told the audience so that they may be able to remember. You may also check out dedication speech examples
Only 10 percent of the speech delivery time must be used at the conclusion stage.
3. Strike the Right Tone. Learn your audience. Who are they and where do they come from? And what are they expecting out of the message that you will be delivering? Sometimes, saying the same speech twice with a different audience may not have the same impact as before. You may also see self-introduction speech examples & samples
4. Humanize Yourself. You and your message are one-and-the-same. If your audience doesn’t buy into you, they’ll resist your message too. It’s that simple. No doubt, your body language and delivery will leave the biggest impression. Still, there are ways you can use words to connect. It is crucial that the audience can relate to you. Not only that, it also determines on the kind of content that you place in your speech. Because there might be times that the audience cannot understand the point you are trying to give across if they do not really understand where it’s coming from. You may also like declamation speech examples
5. Repeat Yourself. In writing a speech, repetition is the key to leaving an impression. Hammer home key words, phrases, and themes. Always be looking for places to tie back and reinforce earlier points. And repeat critical points as if they were a musical refrain. The more you repeat your points to the audience, the better their retention towards these main points that will serve as their take-away pointers if they forget everything else. You may also check out leadership speech examples & samples
6. Use Transitions. Sometimes, audiences won’t recognize what’s important. That’s why you use transitional phrases to signal intent. For example, take a rhetorical question like “What does this mean” – and follow it with a pause. Silence gets attention – and this tactic creates anticipation (along with awakening those who’ve drifted off). Similarly, a phrase like “So here’s the lesson” also captures an audience’s interest. It alerts them that something important is about to be shared. Even if they weren’t paying attention before, they can tune in now and catch up. You may also see orientation speech examples & samples

7. Include Theatrics. It’s good to add a little bit of finesse in your speech, especially when you bring props to the scene. If your speech is about how technology is currently destroying the creativity of the youth, there are many ways to demonstrate this to the crowd: such as volunteering themselves to the speaker in order to prove his or her point towards the audience. Theatrics act as an icebreaker that give the audience a chance for themselves to be entertained while learning something all the while. You may also like farewell speech examples
8. End Strong. They say it is important to start strong and end strong. That is very much true. There are many ways to accomplish this. If ever the audience completely forgets about the main points in your speech, at least you can give them a strong takeaway if they forget everything else. It can be a story, and it can even be a quote. However you see fit, it is entirely up to your discretion. You may also check out speech templates and examples
9. Keep it Short. It is important to apply the keep it short and simple (KISS) rule whenever you are asked to make a speech. There’s not really a problem when you make the speech too short as long as you are able to get your points across. But make it too long and lengthy, you might just drag out the whole thing altogether, losing the audience interest instead if you beat around the bush too much. The shorter the speech, the better. Discern and ask yourself if this part is really needed to make your speech better. If you don’t think it’s needed, omit it. You may also see how to conclude a speech
Remember, that there is no right or wrong in drafting your short speech. Just as creativity and imagination is important in giving your speech more color, structure and organization is also critical in making sure you do not go sideways with the speech. Limit your speech to only 5 to 7 minutes and you should be fine. You may also like youth speech examples
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
Create a Short Speech on gratitude
Generate a Short Speech on the power of kindness
Quote Investigator®
Tracing Quotations
If I Am To Speak Ten Minutes, I Need a Week for Preparation; If an Hour, I Am Ready Now
Woodrow Wilson? Abraham Lincoln? Rufus Choate? Thomas B. Macaulay? William Howard Taft? Mark Twain? Anonymous?
Dear Quote Investigator: A biography of President Woodrow Wilson included an entertaining quotation about the preparation time needed for speeches of varying lengths. Here is an excerpt from the book: [1] 1946, The Wilson Era: Years of War and After 1917-1923 by Josephus Daniels, Quote Page 624,The University of North Carolina Press, Chapel Hill, North Carolina. (Verified with scans)
A member of the Cabinet congratulated Wilson on introducing the vogue of short speeches and asked him about the time it took him to prepare his speeches. He said: “It depends. If I am to speak ten minutes, I need a week for preparation; if fifteen minutes, three days; if half an hour, two days; if an hour, I am ready now.”
This biography was published in 1946, i.e., many years after the death of Wilson in 1924. Could you search for earlier support of this quotation?
Quote Investigator: QI has located a match for a close variant quotation in 1918 that was attributed to Woodrow Wilson. The details are given further below.
There is a family of statements expressing this central idea, and it has been evolving for more than one hundred years. Tracing this family is difficult because of the high variability of the wording.
The first relevant instance found by QI was spoken in 1893 by the Governor of California. He ascribed the words to Abraham Lincoln, but this linkage was weak because Lincoln died decades earlier in 1865.This rudimentary version mentioned two different speech lengths instead of four: [2] 1893, Appendix to the Journals of the Senate and Assembly of the Thirtieth Session of the Legislature of the State of California, Volume 1, First Biennial Message of Governor H. H. Markham to the … Continue reading
Lincoln once made a most apt suggestion applicable to such cases. When asked to appear upon some important occasion and deliver a five-minute speech, he said that he had no time to prepare five-minute speeches, but that he could go and speak an hour at any time.
In 1895 a minister named J. N. Hall gave a speech at a meeting of the Men’s Sunday Evening Club as reported in a Rockford, Illinois newspaper. Hall ascribed an instance of the saying to Rufus Choate who was an orator and Senator from Massachusetts who died decades earlier in 1859. This version was tripartite; however, the third part referred to talking all day instead of speaking for an hour: [3] 1895 December 3, Rockford Daily Register Gazette, It’s Second Birthday: Men’s Sunday Evening Club Properly Celebrates, Quote Page 5, Column 2, (GNB Page 3), Rockford, Illinois. … Continue reading
There is a great deal in condensation in these days of compressed yeast and potted ham, and I am reminded of an incident told of Rufus Choate, who being asked to make a speech on a certain occasion said, “If it is to be a minute speech I shall need four weeks in which to prepare, if a half hour speech, then two weeks, but if I am to talk all day I’m ready now.”
The QI website also has an entry for a popular related quotation: “If I had more time, I would have written a shorter letter”. Here is a link .
Here are additional selected citations in chronological order.
In 1900 a doctor employed an instance of the schema while speaking at a convention of the New Hampshire Medical Society. The crafter of the statement was unidentified: [4] 1900, Transactions of the New Hampshire Medical Society at the One Hundred and Ninth Anniversary, (Held at Concord, New Hampshire on May 31 and June 1, 1900), “Nutrition” by J. G. Quimby … Continue reading
Discussion opened by H. L. Stickney, M.D. of Newport. Mr. President and Fellows: Some one has said that “if you want me to speak two minutes you give me a notification of two weeks; if you want me to speak five minutes, I should have a notification of one week, but if you want me to talk all day, here I am.”
In 1915 a textbook chapter titled “The Art of Public Speaking” by Grenville Kleiser presented an instance of the expression with an anonymous ascription: [5] 1915, Kleiser’s Complete Guide to Public Speaking, Compiled and Edited by Grenville Kleiser, Section: The Art of Public Speaking by Grenville Kleiser, Start Page vii, Quote Page ix, Funk & … Continue reading
A man should take ample time in which properly to prepare his speech. “How long do you wish me to speak?” asked a man who was invited by a society to attend its annual dinner. “Why do you ask?” inquired the secretary. “Because,” said the orator, “if you want me to give a ten-minute address I must have at least two weeks in which to prepare myself, but if you want me to talk for an hour or more, I am ready.”
In 1918 the saying was attributed to President Woodrow Wilson in the pages of a trade publication for the flour milling industry. The third part of this version used the phrase “talk as long as I want” instead of “an hour”: [6] 1918 April, The Operative Miller, Volume 23, Number 4, (Short freestanding item), Quote Page 130, Column 1, Operative Miller Press, Chicago, Illinois. (Google Books Full View) link
“How long does it take you to prepare one of your speeches?” asked a friend of President Wilson not long ago. “That depends on the length of the speech,” answered the President. “If it is a ten-minute speech it takes me all of two weeks to prepare it; if it is a half-hour speech it takes me a week; if I can talk as long as I want to it requires no preparation at all. I am ready now.”
In 1922 a textbook titled “Public Speaking Today: A High School Manual” included a variant of the expression which was attributed to Thomas Babington Macaulay, a British statesman and historian who died in 1859: [7] 1922, Public Speaking Today: A High School Manual by Francis Cummins Lockwood and Clarence DeWitt Thorpe, Quote Page 155 and 156, Published by Benj. H. Sanborn & Company, New York. (Google Books … Continue reading
“It takes longer,” says Professor Alden in his Art of Debate, “to prepare a short speech than a long one on almost any subject.” It takes longer to round out a fifteen-minute speech than one an hour long on the same subject. “How long does it take you to work up your speeches?” Macaulay was asked. “That depends,” he replied, “on the length of the speech; if it is a two-hour speech I can prepare it in two days; if it is an hour speech, two weeks; but if it is a ten-minute speech it takes two months.” In the short speech every word must count.
Also in 1922 a college fraternity publication reported on an interfraternity dinner held in Chicago. A speaker stated that a professor he knew had employed a variant of the expression: [8] 1922 July, Banta’s Greek Exchange: A Journal Published in the Interest of the College Fraternity World, The Chicago Interfraternity Dinner, Remarks of Mr. Don R. Almy (Sigma Alpha Epsilon), … Continue reading
…that reminds me of a professor that I knew in college in that very much over praised institution that you have heard about here tonight; the boys used to go to him frequently and ask him to address the class of Umpty-ump, or the Wearers of the C, or some other distinguished gathering, and he used to say to them, “Well, now, if you want me to talk fifteen minutes, I must have two weeks to prepare; if you want me to talk half an hour, why I can get along with one week; but if I can talk about the Elmira Reformatory and talk as long as I want to, I am ready now.”
In 1931 “The Rotarian” magazine printed a variant with a reverse ordering. The longest speech length was mentioned first: [9] 1931 December, The Rotarian, Volume 39, Number 6, Talking for Action by L. B. Smelser, Start Page 17, Quote Page 56, Column 2 and 3, Published by Rotary International. (Google Books Full View) link
Some wise speaker once said that if he had fifteen minutes to prepare, he could speak two hours; if he had a day, he could speak an hour; but that if he had two weeks in which to prepare he could make his speech in fifteen minutes.
In 1938 a humor column called “In Lighter Vein” of the “Christian Science Monitor” newspaper printed an instance with an attribution to Woodrow Wilson that closely matched the text of the 1918 citation: [10] 1938 May 20, Christian Science Monitor, In Lighter Vein, Quote Page 21, Column 6, Boston, Massachusetts. (ProQuest)
The Longer the Quicker “How long does it take you to prepare one of your speeches?” asked a friend of President Wilson. “That depends on the length of the speech,” answered the President. “If it is a 10-minute speech, it takes me all of two weeks to prepare it; if it is a half hour speech, it takes me a week; if I can talk as long as I want to, it requires no preparation at all. I am ready now.”
In 1943 the “Boston Herald” of Massachusetts printed a version that was closer to the modern version ascribed to Wilson. The third part mentioned a two-hour speech instead of a speech of unlimited duration: [11] 1943 July 14, Boston Herald, Doolittle Tokio Raid Told in War Book by Alice Dixon Bond, Quote Page 12, Column 4, Boston, Massachusetts. (GenealogyBank)
Someone once asked Woodrow Wilson how long it took him to prepare for a ten-minute speech. He said, “Two weeks.” “How long for an hour speech?” “One week,” he answered. “And for a two-hour one?” his interrogator went on, “I am ready now,” replied the late president.
In 1948 a biography titled “The Wilson Era: Years of War and After 1917-1923” included an instance of the saying credited to Wilson as mentioned previously by the questioner: [12] 1946, The Wilson Era: Years of War and After 1917-1923 by Josephus Daniels, Quote Page 624,The University of North Carolina Press, Chapel Hill, North Carolina. (Verified with scans)
The above citation appears in three key reference works: “Respectfully Quoted” (1989), [13] 1989, Respectfully Quoted: A Dictionary of Quotations Requested from the Congressional Research Service, Edited by Suzy Platt, Section: Oratory, Quote Page 244, Library of Congress, Washington D.C. … Continue reading “Cassell’s Humorous Quotations” (2001), [14] 2001, Cassell’s Humorous Quotations, Compiled by Nigel Rees, Section: Woodrow Wilson, Page 408, Published by Cassell, London and Sterling Pub. Co., New York. (Verified on paper) and “The Yale Book of Quotations” (2006). [15] 2006, The Yale Book of Quotations by Fred R. Shapiro, Section: Woodrow Wilson, Quote Page 831, Yale University Press, New Haven. (Verified on paper)
In 1985 the “New York Times” published remarks by a diplomat named Andor C. Klay who presented an anecdote featuring President William Howard Taft: [16] 1985 December 10, New York Times, Required Reading; Presidential Speeches, (Excerpt from remarks by Andor C. Klay upon receiving the Abraham Lincoln Award of the American Hungarian Federation, … Continue reading
Kohanyi requested President William Howard Taft to attend the 20th anniversary banquet of Szabadsag and make a speech there: “Just a brief one, Mr. President, since we can imagine how busy you must be – perhaps five minutes.” The President smiled and declined: “Do you realize my friends, that to prepare even a five-minute speech would take several hours to plan, to draft, to rewrite, to pass through channels for clearances? I’m afraid that I just haven’t got the time.” Kohanyi pressed: “Well, as far as that goes, we would be delighted to have you speak for an hour.” The monumental body of the heaviest statesman of his time straightened up: “Gentlemen, I am ready, now!”
By 1998 a version of the saying had been connected to the popular humorist Mark Twain on the website of a company providing assistance to public speakers: [17] Website: LJL seminars, Article title: Gathering Information & Materials, Article Author: Lenny Laskowski, Date on website: Copyright Notice 1997, Date from Internet Archive Wayback Machine: … Continue reading
In fact, Mark Twain is one of the earliest known professional speakers and when asked one day if he could prepare a speech for an upcoming engagement, he responded ,”If you want me to speak for an hour, I am ready today.” “If you want me to speak for just a few minutes, it will take me a few weeks to prepare.”
In conclusion, QI believes that Woodrow Wilson probably did employ an instance of this expression. However, the family of sayings had already been established a couple decades before the first ascription to Wilson was published. Wilson was from an academic milieu and the 1922 citation in a fraternity periodical suggested that the saying was in circulation within academia. QI hypothesizes that Wilson was using a pre-existing template.
The attributions to Abraham Lincoln, Rufus Choate, and Mark Twain were all very weak because they occurred many years after the death of the named individuals.
The evolution of this family of sayings does not point to a single authorship, and QI would label the set anonymous.
(Special thanks to Christine Haynie whose inquiry led QI to construct this question and initiate this exploration.)
| ↑1, ↑12 | 1946, The Wilson Era: Years of War and After 1917-1923 by Josephus Daniels, Quote Page 624,The University of North Carolina Press, Chapel Hill, North Carolina. (Verified with scans) |
|---|---|
| ↑2 | 1893, Appendix to the Journals of the Senate and Assembly of the Thirtieth Session of the Legislature of the State of California, Volume 1, First Biennial Message of Governor H. H. Markham to the Legislature of the State of California, Thirtieth Session, (Delivered on January 3, 1893 in Sacramento, California), Start Page 3, Quote Page 5, Published by A. J. Johnston, Superintendent of State Printing, Sacramento, California. (Google Books Full View) |
| ↑3 | 1895 December 3, Rockford Daily Register Gazette, It’s Second Birthday: Men’s Sunday Evening Club Properly Celebrates, Quote Page 5, Column 2, (GNB Page 3), Rockford, Illinois. (GenealogyBank) |
| ↑4 | 1900, Transactions of the New Hampshire Medical Society at the One Hundred and Ninth Anniversary, (Held at Concord, New Hampshire on May 31 and June 1, 1900), “Nutrition” by J. G. Quimby and M. D. Lakeport, (Discussion section: Speaker: H. L. Stickney), Start Page 245, Quote Page 253, Printer Ira C. Evans, Concord, New Hampshire. (Google Books Full View) |
| ↑5 | 1915, Kleiser’s Complete Guide to Public Speaking, Compiled and Edited by Grenville Kleiser, Section: The Art of Public Speaking by Grenville Kleiser, Start Page vii, Quote Page ix, Funk & Wagnalls Company, New York. (Google Books Full View) |
| ↑6 | 1918 April, The Operative Miller, Volume 23, Number 4, (Short freestanding item), Quote Page 130, Column 1, Operative Miller Press, Chicago, Illinois. (Google Books Full View) |
| ↑7 | 1922, Public Speaking Today: A High School Manual by Francis Cummins Lockwood and Clarence DeWitt Thorpe, Quote Page 155 and 156, Published by Benj. H. Sanborn & Company, New York. (Google Books Full View) |
| ↑8 | 1922 July, Banta’s Greek Exchange: A Journal Published in the Interest of the College Fraternity World, The Chicago Interfraternity Dinner, Remarks of Mr. Don R. Almy (Sigma Alpha Epsilon), Start Page 144, Quote Page 146, Published by George Banta Publishing Company (The Collegiate Press), Menasha Wisconsin.(Google Books Full View) |
| ↑9 | 1931 December, The Rotarian, Volume 39, Number 6, Talking for Action by L. B. Smelser, Start Page 17, Quote Page 56, Column 2 and 3, Published by Rotary International. (Google Books Full View) |
| ↑10 | 1938 May 20, Christian Science Monitor, In Lighter Vein, Quote Page 21, Column 6, Boston, Massachusetts. (ProQuest) |
| ↑11 | 1943 July 14, Boston Herald, Doolittle Tokio Raid Told in War Book by Alice Dixon Bond, Quote Page 12, Column 4, Boston, Massachusetts. (GenealogyBank) |
| ↑13 | 1989, Respectfully Quoted: A Dictionary of Quotations Requested from the Congressional Research Service, Edited by Suzy Platt, Section: Oratory, Quote Page 244, Library of Congress, Washington D.C. (HathiTrust) |
| ↑14 | 2001, Cassell’s Humorous Quotations, Compiled by Nigel Rees, Section: Woodrow Wilson, Page 408, Published by Cassell, London and Sterling Pub. Co., New York. (Verified on paper) |
| ↑15 | 2006, The Yale Book of Quotations by Fred R. Shapiro, Section: Woodrow Wilson, Quote Page 831, Yale University Press, New Haven. (Verified on paper) |
| ↑16 | 1985 December 10, New York Times, Required Reading; Presidential Speeches, (Excerpt from remarks by Andor C. Klay upon receiving the Abraham Lincoln Award of the American Hungarian Federation, November 24, 1985), (Online New York Times Archive at nytimes.com; accessed Mar 1, 2014) |
| ↑17 | Website: LJL seminars, Article title: Gathering Information & Materials, Article Author: Lenny Laskowski, Date on website: Copyright Notice 1997, Date from Internet Archive Wayback Machine: Snapshot on February 12, 1998 showed that the excerpt was present on the website, Website description: “Public Speaking Seminars, Customer Service Programs, Serving business needs around the world” (Accessed ljlseminars.com on March 1, 2014) |

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
How to write a five-minute speech. Here are the steps you can follow to prepare and deliver a short speech: 1. Prepare. Short speeches require preparation because you have to condense your information into only the most useful points. The first step in preparing a brief speech is to determine the purpose of your talk.
Create an outline: Develop a clear outline that includes the introduction, main points, supporting evidence, and a conclusion. Share this outline with the speaker for their input and approval. Write in the speaker's voice: While crafting the speech, maintain the speaker's voice and style.
To "top and tail" simply means starting with a story/quote that hints at your message. At the end, you recall that story and link it to your message. This short speech from a 3 minute speech competition makes excellent use of this approach. Start your speech ("the top") with a compelling metaphor to make a memorable point, and end the ...
Tell them (Body of your speech - the main ideas plus examples) Tell them what you told them (The ending) TEST before presenting. Read aloud several times to check the flow of material, the suitability of language and the timing. Return to top. A step by step guide for writing a great speech.
So for 2-minute speeches, 260-300 words should be sufficient. When it comes to the number of pages for a 2-minute speech, then your speech can be half to one page long. It all depends on the font size that you use! Similarly, the number of sentences that would make up a 2-minute speech can vary depending on the font size that you use or your ...
1. Give yourself plenty of time. The more time you have to practice your speech, the more prepared you'll feel, and as a result, the less nervous you'll feel. One guideline for the amount of time to spend on preparing a speech is one to two hours for every minute you'll be speaking.
For example, people use one writing tool to put the speech's theme in a 15-20 word short poem or memorable paragraph, then build your speech around it. 3. Have a Clear Structure. When your speech has a clear structure to it your speech becomes more memorable. When writing your speech, have a clear path and a destination.
Establish your structure. Develop a middle part with one or two points supported by an anecdote, story, and preferably backed up by facts and data. Prepare a strong opening and a strong ending. Rehearse. 1. Define your purpose. For a speech to be effective, it must have a clear goal. A goal also helps you focus while creating the speech.
Start by identifying your topic, title, and the purpose of your speech, which will set the foundation of your outline. Then, determine the main points of your speech; keep it short with two to three points. Remember, a short speech is typically less than ten minutes long, so keep your points concise and to the point.
9. It's in the news. Take headlines from what's trending in media you know the audience will be familiar with and see. Using those that relate to your speech topic as the opening of your speech is a good way to grab the attention of the audience. It shows how relevant and up-to-the-minute the topic is. For example:
To prepare and give a speech, start by thinking about the topic, audience, and location of the speech. Write a detailed outline that includes your main topics, supporting points, and facts. Then, transfer the speech to note cards or handouts if necessary. Remember to practice your speech a few times in front of a mirror or a friend, and set a ...
The act of one human speaking to a group has evolved over hundreds of thousands of years. Chris Anderson, owner of TED and TED Talks, gives his Brief but Spe...
Brainstorming. The best way to come up with a good topic for your speech is to conduct a brainstorming session. Brainstorming involves gathering several ideas from different people and grouping them into categories. This way, you will have more variety in the ideas. Next, rank the ideas by using a set of criteria.
When given a topic to speak on, the first thing you can do is brainstorm ideas and pen down all that comes to your mind. This will help you understand what aspect of the topic you want to focus on. With that in mind, you can start drafting your speech. An opening statement can be anything that is relevant to the topic.
6. Make it personal. But while doing so, make sure it does not sound so pretentious. You are not expected to be such a drama queen when delivering your speech, but allow your speech to form a personal connection with the audience. Emotions click with the crowd.
A good way to prepare a 20-minute speech is to create the logical 'spine' of your full speech - the step-by-step logic of the speech that explains the thought structure, shorn of the detail ...
1. Strip it down. There's an unfortunate temptation in a short speech to try to cram everything you have to say into a short time. Instead of trying to make the time fit the speech, however ...
Confront the reality of your situation to avoid being blindsided by panic. Accept that you have to give a speech and then focus all your resources on giving a good one. 3. Project a confident aura. Face your audience boldly and smile. Make eye contact with those closest to you.
The basic outline for a speech is the introduction, the body, and the conclusion. And depending on the length of the speech, we need to take different approa...
Short speech for a company event. This is a much shorter speech than the previous example, but it still follows the same principles. In the introduction, the author uses the scale of time to capture the audience's attention. With a few sentences, it transports their mind to the past and the future. Engaging!
Tell a story. Share a joke. Look back at one of your experiences that you had in relation to the topic. Quote a quote. Once you have managed to hook the attention of your audience, then you are ready to to continue your speech. You may also see appreciation speech examples & samples. 2.
A member of the Cabinet congratulated Wilson on introducing the vogue of short speeches and asked him about the time it took him to prepare his speeches. He said: "It depends. If I am to speak ten minutes, I need a week for preparation; if fifteen minutes, three days; if half an hour, two days; if an hour, I am ready now." ...
Biden gave a previously scheduled speech and made the point that his administration is making strides to make America's schools and streets safer from guns, on the same day his son was convicted ...