

Business Plans: A Step-by-Step Guide for Kid Entrepreneurs

- March 21, 2024
Embarking on an entrepreneurial journey is exciting for kids, offering them a unique opportunity to learn valuable life skills such as problem-solving, financial literacy, and creativity. Creating a business plan is a foundational step in this journey, helping young entrepreneurs transform their ideas into actionable plans. This guide is designed to make the process engaging and accessible for kids and their parents, laying the groundwork for successful kidpreneur ventures.
Why Creating a Business Plan Matters for Kidpreneurs
A business plan is more than just a document; it’s a roadmap that guides Kidpreneurs through the stages of developing and growing their business. It encourages them to think critically, set realistic goals, and plan for the future. Crafting a business plan helps Kidpreneurs understand the basics of entrepreneurship and financial management, fostering a mindset geared towards growth and innovation.
Step 1: Discover Your Passion and Identify a Business Idea
The first step is for Kidpreneurs to explore their interests and talents, leading them to a business idea that excites them. Encourage them to think about problems they’d like to solve or hobbies they enjoy that could be turned into a business. This ideation process is crucial for finding a venture they’re passionate about and committed to developing.
Step 2: Research Your Market
Once a business idea is in place, the next step is understanding the market. Kidpreneurs should research who their potential customers are, what needs or wants their business could fulfill, and who their competitors might be. This step is about validating the idea and ensuring there’s a demand for what they plan to offer.
Step 3: Set Clear Goals and Objectives
Goals and objectives give direction and purpose to the business plan. Help your kid set specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) goals. These could range from learning new skills to achieving a certain number of sales within a specified time frame.
Step 4: Plan Your Product or Service
This stage involves detailing the product or service the business will offer. Kidpreneurs should think about what makes their offering unique and how it benefits their target customers. Encouraging creativity at this stage can lead to innovative ideas that set their business apart.
Step 5: Outline Your Marketing and Sales Strategy
Marketing and sales are how businesses attract and retain customers. Kids can brainstorm fun and engaging ways to promote their business, such as through social media, flyers, or word of mouth. They should also think about how they will sell their product or service, whether it’s online, at a local market, or through another channel.
Step 6: Create a Financial Plan
A basic financial plan is essential, even for small-scale kidpreneur ventures. This includes estimating startup costs, setting prices for products or services, and planning for future expenses. It’s a great opportunity for kids to learn about budgeting, profit, and financial management.
Step 7: Draft an Action Plan
The action plan breaks down the steps needed to launch and grow the business. It should include a timeline of activities, responsibilities, and milestones. This helps kids stay organized and focused on their goals.
Step 8: Review and Adjust
A business plan is a living document that should evolve as the business grows. Encourage kidpreneurs to review their plan regularly, celebrate achievements, and adjust their strategies as needed.
Creating a business plan is an exciting step for kidpreneurs, full of learning and growth opportunities. By following these steps, kids can turn their entrepreneurial dreams into reality, building a solid foundation for their business ventures.
To further explore entrepreneurship and financial literacy, Kidpreneurs can dive into the Kidpreneurs Academy. It’s a gamified online program designed to teach kids aged 6-12 the basics of entrepreneurship through engaging courses, games, and activities. Join today!
Related Posts

How to Start an Eco-Friendly Fashion Brand: A Guide for Kid Entrepreneurs

Why it’s so important for kids to learn about cryptocurrency

Why Digital Marketing Is Essential for Kidpreneurs

E-commerce for Kidpreneurs

7 Essential Tools For Kidpreneurs

How Kidpreneurs Can Create a Business Teaching Other
Subscribe to raising empowered kids® for free tips and kid-friendly resources.
Our weekly newsletter bringing you the latest and greatest in entrepreneurial parenting.
By clicking "Subscribe" below, you Agree to our Terms of Use and Privacy Policy .
You will also be subscribed to Kidpreneurs news and updates.
3120 W Carefree Hwy Suite 1-128 Phoenix, AZ 85086
- +1 (689) 244-4332
- [email protected]
- Cookie Policy (EU)
- Certification
The future of our children begins with us! Most people say, “It’s never too late.”
The Torens say, “It’s never too early to start learning the principles of entrepreneurship and money management.”
- 1-689-244-4332

7 Business Plan Templates for Kids (Free Printables!)
By: Author Amanda L. Grossman
Posted on Last updated: May 7, 2024
Download one of these (mostly) free business plan templates for kids to help your child focus on a business idea.
What do supersoakers, Apple computers, and Nike shoes all have in common?

They all started as a business plan.
A business plan template for kids is great for two reasons:
- Your child can play around with it and get familiar with what's required (even if they never start the business)
- It helps kids focus on just one business idea at a time, and to see if they should move forward with it
No matter which category your own child falls into – just playing with business plans, or they have an actual business idea – I’ve got just the free business plan template for you.
Honestly? I wish my own parents would’ve given me one of these when, as a kid, my childhood friend and I had come up with our first kid business idea: selling bean bags. So, good on you for getting your kids involved with business plans so early in life!
Best Business Plan Templates for Kids
Use one of the business plan templates for kids below with one of these 16 kid business ideas .
OR, help them to use one of their original ideas sending sparks in their brain. You can use these 3 kid business plan examples for help with filling it out.
1. Solid Gold Biz Plan
I’ve been in business for 7 years and I’ve made about every mistake in the book.
Probably one of the biggest? Was that I didn't sit down to write a proper business plan (or, ANY business plan) until I was several years into blogging.
Because of this, I created a free business plan template for kids and teens (on Page 6 of this free printable), so that they practice how to do it right, from the beginning!
What makes my free Solid Gold Biz Plan different is that it starts your child thinking about the problem that they want to solve – because ultimately, that is the purpose of creating a product or a service. To solve a specific problem for people.
It then goes on to ask them simple questions that will focus them in on what it takes to plan out a business idea.
For example, I raise the question of how much it will cost to not only create the product/service but to also deliver it and maintain it. These are sometimes costs forgotten costs when creating a business plan.
2. BizKids’ Guide to Writing a Business Plan
This free business plan guide for kids includes sections for your idea, your marketing (and what makes your product unique), your startup costs, and an area for pricing so that you can make sure you’ll make a profit.

At the end is a one-page summary where your child can write up their answers from the previous pages all in the same place. Great for tacking up on the wall!
3. Teen Entrepreneur Toolbox
Anthony ONeal partnered up with Dave Ramsey to create the Teen Entrepreneur Toolbox , a kid’s entrepreneur kit and small business guide for teens.
In other words, it’s so much more than just a business template for kids!
The entrepreneur kit includes the following:
- Access to the Free Entrepreneur Toolbox app
- Teen Portfolio Book
- DVD of Anthony’s Training Video
- Parent’s Guide Book
- Pack of Thank You Cards
- Deck of Conversation Starter Cards about Starting a Business
- Goal Tracker Poster
Here's my full review of the Teen Entrepreneur Toolbox .
4. Proverbial Home Maker’s Family Business Plan Guide
This is such a fun guide that you can fill out with your child, teen, tween, or even the whole family. It includes family business ideas, a sales ledger, an inventory worksheet, and much more.

Business Plan Examples
You may be wondering where you can find business plan examples to show your kids or teens.
For starters, you should look right at home. Are you a small business owner?
Then you’ll definitely want my free Take Your Child to Work Day printables – it’s got a section for you to fill in about your own business, which is a perfect business plan example to discuss with your child.
You can also find two business plan examples on the Small Business Administration’s site (scroll down until you see red buttons for Rebecca’s example business plan, and Andrew’s plan).
They’re not entirely kid-friendly but can give lots of ideas for the kind of information and research to put into a business plan.
Business Plan Activity Worksheets
Check out these free PDF Shark Tank worksheets for students . Students or kids can work through coming up with their own business ideas, create an advertisement for it, and a scoring card to judge the business ideas.
You’ll find a free 30-minute Small Business Administration course for young entrepreneurs meant for teens that you can use with your students (or have your child go through).
Hint: In Objective 3, it goes over how to create a business plan.
Are you an educator? Great – you can get a free entrepreneur curriculum for Grades 1 – 12, with lots of worksheets, from the Venture Lab .
Further resources include:
- Teen Business Video Lessons
- EverFI’s Entrepreneurial Expedition
- FEE’s Course on the Entrepreneur’s Role in Creating Value
- Business Plan Note Taker (lots of great prompts to create a business plan with)
Grab 23 more entrepreneur lesson plans here.
I hope you've found some business templates for kid resources that interest you. Below, you'll find other related kid entrepreneurship articles that will help your kids, teens, and students learn about the entrepreneur's career path.
Related Kid Entrepreneurship Resources
- 27 Youth Entrepreneur Awards and Scholarships
- 5 Kid Entrepreneur Kits
- 14 Kid Entrepreneur Books
- 11 Best Business Simulation Games for Kids
- Latest Posts
Amanda L. Grossman
Latest posts by amanda l. grossman ( see all ).
- The Factory Tour Entrepreneur Project (Free Printable) - May 30, 2024
- 9 Easy DIY Dollar Tree Gift Boxes for Tweens (Super Affordable!) - May 22, 2024
- 17 Indoor Summer Activities for Tweens (No Screens!) - May 18, 2024
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Money Management for Young People
- Youth Businesses
How to Make a Business Plan (for Kids)
Last Updated: April 17, 2024 Approved
This article was co-authored by Michael R. Lewis and by wikiHow staff writer, Amber Crain . Michael R. Lewis is a retired corporate executive, entrepreneur, and investment advisor in Texas. He has over 40 years of experience in business and finance, including as a Vice President for Blue Cross Blue Shield of Texas. He has a BBA in Industrial Management from the University of Texas at Austin. wikiHow marks an article as reader-approved once it receives enough positive feedback. This article received 21 testimonials and 82% of readers who voted found it helpful, earning it our reader-approved status. This article has been viewed 154,824 times.
There are plenty of kids out there running their own successful businesses.To get started, you’ll need a great idea for a business and a solid business plan. Business plans can get pretty complicated, but they don’t have to be. As long as your business plan includes a few crucial things, you’ll have all that you need to get started!
Developing Your Business Idea

- Are you currently busy with school or is it summertime? Think about when the work for your business will be done. [1] X Research source
- Consider business ideas that are seasonal. For example, if it’s near Christmas, consider ideas that cater to that, like a gift wrapping service or making gift baskets.
- Are you in the middle of a very hot summer? This might be a perfect time to launch a neighborhood lemonade stand.

- Examples of product-driven businesses: baking cookies, building birdhouses, making gift baskets, creating greeting cards, selling candy, making doggie treats.
- Examples of service-driven businesses: lawn care, car washing, computer repair, pet sitting, babysitting, cleaning houses, dog walking, and teaching computer skills to older people. [3] X Research source

- Are you an animal lover? Consider offering pet sitting services.
- Maybe you’re crafty and enjoy making handmade jewelry or gift baskets. These are great products to sell. [4] X Research source

- Make sure your business name is easy to pronounce, as well.
- Clever and unique business names work well, just remember that the name needs to relate to what your business entails.

- List any specific objectives and goals for your business, as well.
- Write out what you think makes your product/service unique. [6] X Research source
Planning Your Business

- If you have a sibling that wants to help out, that would be a good place to start.
- You will be splitting your profits, so you will need to decide how much and when your employees will be paid.

- You could also ask your parents if they’d consider donating some of your future allowance as seed money for your business.
- If you bring them a solid business plan, they will be more likely to help you.

- By adding up your ongoing expenses, you will have a pretty good idea of what it will cost to keep your business running. [8] X Research source
- Another example – if you’re making cookies to sell, you will need to total up how much the ingredients cost and how often you’ll need to buy them.

- Let’s say that when you add up the cost of the ingredients, it costs you $3.50 to make a dozen chocolate chip cookies. You will want to charge more than that for each dozen in order to make a profit.
- You should also factor in how much time it takes you to make your product/perform your service. [9] X Research source You can then work out prices based upon how much you want to make. You should also factor in time that you aren't being paid (such as advertising your business or walking to a customer's home).
- For example, if it takes you a half hour to make the chocolate chip cookies mentioned above and another half hour to sell them, you will need to charge an amount that represents the amount of time you spent preparing them. This additional time is your "wage" for preparing them.
- You can work out your hourly wage by dividing your pay for a project or product (minus your expenses) by the amount of time spent working.
- In this case, if you charged $9.50 for the dozen cookies, you would be making $6 for the hour that you spent making and selling them.
- Subtract your expenses from your revenue to get your profit amount. [10] X Research source
Marketing Your Business

- You should also consider your market area. Unless you have a car (or your parents' help), market area is relatively small. This may include only areas that you can safely walk or bike to.
- These customer types are called customer profiles. Once you have your customer profiles, you will have a better idea of how to market your business to them.
- Different customer profiles sometimes require entirely different marketing strategies.

- You can market most effectively once you know these specific details about your competitors.
- Offering lower prices or providing higher quality products/services are two ways you can compete with them.
- For example, if you start a lawn care business, you will be competing with established lawn care businesses. You can build a customer base by offering better service and encouraging customer recommendations.

- Remember to keep your customer profiles in mind when choosing your marketing strategies.
- For instance, if you’re starting a pet sitting business, you could post flyers at veterinary offices and pet stores, and also hand deliver flyers to people in your neighborhood with pets.

Putting Your Business Plan on Paper

- Write the business name in large letters, or use a large font, and make it bold. It’s the most important thing on the page.
- The description paragraph can be in a normal size or standard 12 point font.

- Owner/Management example: “Kelly’s Doggy Daycare is owned by Kelly Klein. She has several years of experience pet-sitting and truly loves working with and caring for dogs of all kinds.”
- Business History example: "Kelly noticed that most of her neighbors were dog owners who worked long hours every day. Occasionally, they took vacations and/or experienced family emergencies, which could take them away from their pets for days at a time."
- "With her love for dogs, Kelly knew she could provide a pet care service that her neighbors would benefit from, and that’s how Kelly’s Doggy Daycare was born."

- You don’t need to get incredibly detailed – summarize and highlight the most important information for each.
- Example for product/service: "Kelly’s Doggy Daycare will provide hands-on pet care for today’s busy pet owner. The business will offer day rates along with in-house extended stay pet sitting. Walking services are included at no charge with every appointment."

- "It’s her mission to put your mind at ease when you have to be away from your pets. Kelly will make sure your pets are loved and cared for in your absence."
- "An email summary of every pet sitting appointment will always be sent to you via email during your absence or upon your return."

- Example: “Kelly’s Doggy Daycare caters to today’s busy adults. These are business people who work long hours every day and/or travel regularly for work, family vacationers, and anyone who finds themselves in need of last minute pet care."
- "The business has one competitor, Sam’s Sitting Service, but Kelly offers lower pricing and in-house extended stay care."
- "She plans to post flyers about the new business in her neighborhood to promote it. She will also be going door-to-door to introduce herself and inform neighbors of her services.”

- Example: "Kelly will need very few supplies to launch the business – a bag of doggie treats, 1 dog leash for a small dog and 1 dog leash for a large dog."
- "Ongoing expenses will be the replenishment of doggie treats and occasionally dog toys and/or dog blankets. The rate is $5.00 for each hour of pet care provided. The rate for in-house extended care is $25 per day."
- "Customers will need to provide their own pet food or reimburse Kelly for any food she has to purchase during pet care. Profit for each hour is approximately $3.50 after expenses."
- "Profit for each day of extended care is approximately $18.50 after expenses."
Expert Q&A
You Might Also Like

- ↑ http://www.wisebread.com/create-a-business-plan-by-answering-4-simple-questions
- ↑ http://www.mikemichalowicz.com/the-37-greatest-business-ideas-for-young-entrepreneurs/
- ↑ http://www.teachingkidsbusiness.com/business-plan-example.htm
- ↑ http://content.moneyinstructor.com/664/kids-starting-business.html
About This Article

To make a business plan for kids, create a cover sheet with the business name in large, bold font and a 5-6 sentence description of the business. Have a logo? Include that, too! Start writing up the company’s management and history on the second page, talking about yourself in 1-2 sentences and how and why you came up with your business in another 2-3 sentences. Then craft 3-4 sentences, each, to describe your product or service, business goals, marketing strategy, and funding needs. To learn more from our Entrepreneur co-author, like how much to charge for your product or service, keep reading the article! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Feb 24, 2023
Did this article help you?

Molly-Claire Keely
Jan 14, 2021
Feb 11, 2018
Margret James
Feb 11, 2017
Valentina Tocasuche
Nov 24, 2018

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Get all the best how-tos!
Sign up for wikiHow's weekly email newsletter
Business Plan Templates for Teens
What to include in a business plan, best business plan templates for teenagers, bizkids’ guide to writing a business plan, teen entrepreneur toolbox: the small-business guide for teens, home sweet road’s my business plan, proverbial homemaker’s family business plan guide, boss club kid entrepreneur kit.
This kit is literally a business in a box, so kids and teens can get started right away as soon as they have it in their hands! Choose your kit and create the following businesses:
Small Business Administration
Solid gold biz plan, shark tank lessons in business and entrepreneurship from scholastic.
A free lesson plan with a teacher’s guide that can be used in a group setting or as a family! Topics covered include entrepreneurship basics, writing an effective business plan, crafting persuasive pitches for investment presentations, and how to find a great business mentor. The target age group is grades 6 to 12.
Shark Tank Marketing Plan
Shark tank analysis worksheet.
Use this worksheet when evaluating businesses to learn what investors are looking for when assessing whether or not to invest in a business. Understanding what investors are looking for in a management team, mission, vision, product/service, research and development, and strategic implementation will help you create that within your own business to make your foundation strong.
Related Reading
About the author, jessica anglin.

Free Printable Kits – Business Plan Template for Kids

Business Plan Template for Kids
To Setup A Business, A lot Of Planning Is Required. Fill This Business Plan Template And Put Your Best Foot Forward.
Components of a
Business plan.

Product Strategy
Business Strategy
Sales & Marketing
Financial Strategy
Operations Strategy
Answer all the questions asked below and you will have a business plan ready!
Register NOW to get a copy of business plan template for kids worth $7
Share a filled up business plan template with us and win FREE worksheets worth $21
| Business Idea-Product & Business Strategy | |
|---|---|
| Problem/need Identification: What Problem Are You Solving? | - |
A business plan is a formal document written by a business owner describing their business goals, how to achieve the goals, the timeframe within which the goals will be achieved, the capital and much more. A full business plan includes an executive overview, budget, competitor analysis, and marketing plan.
A template is a guide that is followed to create a roadmap for a business. Therefore, in writing a business plan, it is important you follow a good business plan template. For experiencing entrepreneurship at an early age, kids are often advised to download free business plan samples to use as a guide in writing their own business plan because kid entrepreneurs should also know how to write business plans after deciding on the business ideas they want to work on.
Why Business Plan Template for Kids
- As a kid entrepreneur planning to start a business, you are new to the concept of business and the best way to understand it and write your business plan is to download a free business plan template, go through it and understand the right way to write a business plan.
- A business plan template will help organize your thoughts and direct you in the right way to put your thoughts and passion for the business into writing.
- A business plan template is a complete guide on how to write a plan for your own business. A template gives complete instructions on how to go about it, you do not have to be so unsure of your business plan when there is a template to follow.
You may also like

Holiday Camps & Workshops

Regular Program

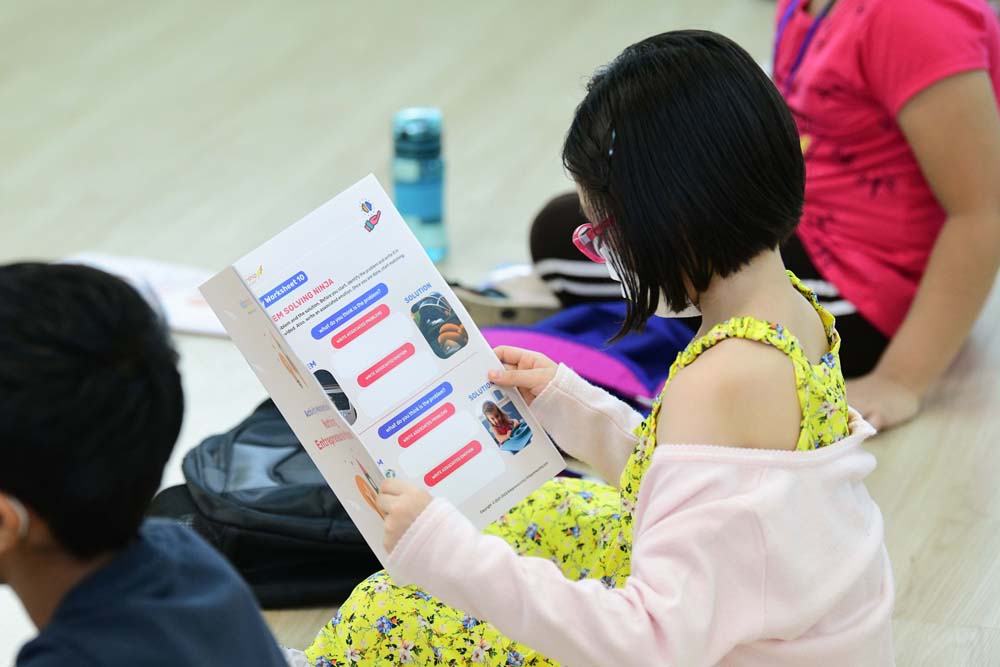
Worksheets for Kids
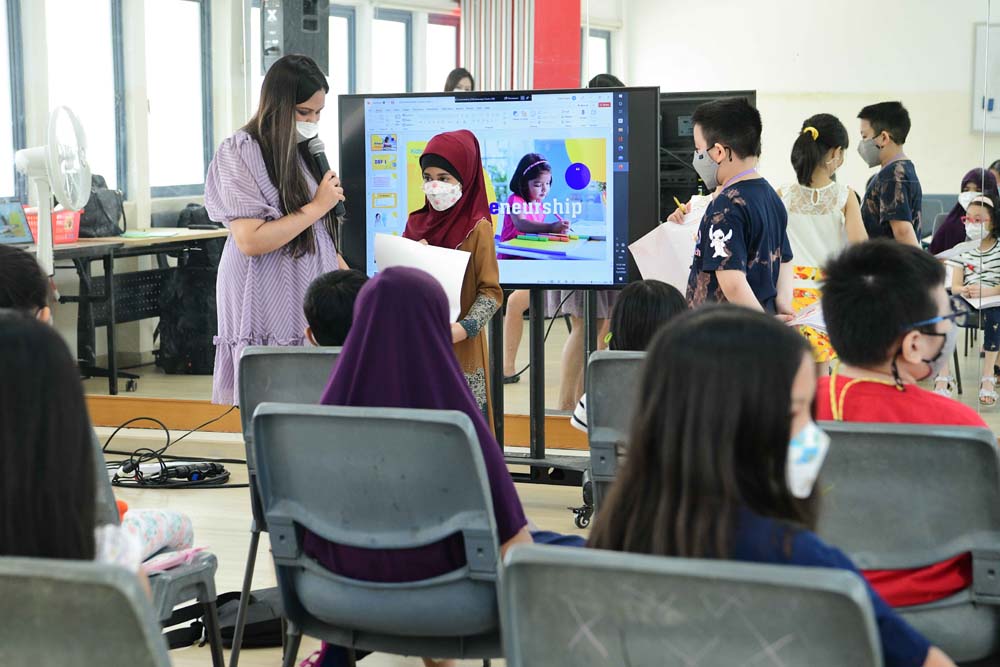
- Kidspreneurship has been awarded "Leaders in Early Entrepreneurship Education" at the fifth annual Singapore Awards by APAC Insider.
You can see how this popup was set up in our step-by-step guide: https://wppopupmaker.com/guides/auto-opening-announcement-popups/

Michelle Hon
CEO and founder of Momboss Academy
Michelle Hon is the CEO and founder of Momboss Academy, a platform to help moms start and scale their own businesses. She is also an author, investor and leader for 4 businesses, from F&B, publishing, digital marketing to education. Her story has been featured on Channel News Asia, Lifetime Asia, Money Asia, Parenting World and more. In 2019, Zine named her one of the Top 10 Mom Influencers in the world.

Swati Gauba Kochar
Lead Coach, Founder & CEO – Kidspreneurship
Swati holds a bachelor’s degree in Information Technology and a Masters in Communication Management and Entrepreneurship. She has over 10 years of experience and has spent the better part of her career helping corporates, startups, small and medium enterprises with digital marketing strategies. She is an entrepreneur at heart and has raised investments to scale her business. In 2018, while consulting an edtech startup she realized the gap between industry and school curriculum and created a new age curriculum & blueprint that focuses onn entrepreneurial mind-set for pre-teens. Swati is a regular trainer with many enrichment centers and schools in Singapore. GIIS recognized her valuable support as a mentor and judge for Star Young Achievers Program. Swati has trained thousands of students till date. She is now seeing an increased number of training request for Early Entrepreneurship Education from schools across Asia (including International Schools in India). Most parents observed increased emotional intelligence and an enhanced problem solving ability in their kids after few sessions with Kidspreneurship. Some students came up with extraordinary ideas during the class and are now pursuing those ideas. Kidspreneurship program developed by Swati has also been awarded “Leaders in Early Entrepreneurship Education” at the fifth annual Singapore Awards by APAC Insider. Swati has trained several professional trainers in Singapore including some veteran trainers from Adam Khoo Learning Centre , a leading education brands in South East Asia. All of them unanimously found the program to be extremely beneficial for their students. Enrichment centers have incorporated the trainings for their students. She is on a mission to create an edu-system that promotes entrepreneurial mindset through workshops & regular programs for kids and teacher training programs for educators.

Prantik Mazumdar
Entrepreneur & Venture Investor
Prantik is an entrepreneur & venture investor and acts as a Digital Transformation Catalyst in organizations to drive change, growth & impact. After graduating from NUS, he kick-started his career with the Singapore government to drive international trade promotion for the country. He started his entrepreneurial journey with Happy Marketer in 2011 where he spent a decade scaling up one of the most awarded independent digital marketing services firm, before a successful exit to dentsu International. He is a regular columnist and in 2015, he was recognized as one of the Top 50 Most Influential Marketers in the World.

Rahul Narvekar
Serial Entrepreneur
Rahul Narvekar, CEO & Founder, India Network and India Angel Fund, the man behind several successful entrepreneurial ventures, is on a mission to create a million entrepreneurs in the next three years. Everyone calls Rahul the North Star of Entrepreneurship. One would imagine why? Well, the North Star is the anchor of the northern sky and helps those who follow it to determine direction while navigating them towards a purposeful destination.

Saurabh Kale
An HR thought leader in my professional life and an Explorer in my personal life. I love to understand the ‘WHY’ behind almost everything. I am seasoned talent management, learning, leadership and organization development leader with 15+ years of experience working with the CXOs, setting up the L&OD function and scaling learning programs globally. I have worked with some of the world’s best-known companies; across the US, Middle East, India and the Asia Pacific. I have a reputation as an outcome-focused enabler, who challenges and reframes thinking.

Dr. Elaine Kim
Co-founder and CEO, CRIB
Dr Elaine Kim is a medical doctor and entrepreneur. She is the co-founder and CEO of Trehaus, an integrated co-lifestyle space for families with a preschool, office space/ business club with creche, and family club. Trehaus School is a Silicon Valley-inspired preschool and childcare that is changing early education, focuses on building character and future skills, and lets parents be present for their children’s learning journey. Prior to taking the helm at Trehaus, she was the CEO of CRIB, a social enterprise she co-founded to empower women to become successful entrepreneurs through networking, co-founder and investor/start-up matching and training and equipping of female founders. Her experiences inspired her to start Trehaus and provide a solution for other working parents to find work-life integration, pursuing successful careers and businesses while prioritizing family and not missing out on their children’s’ precious, formative first years. After a decade as a doctor caring for terminally ill patients, she continues her involvement in palliative care through her work with the Singapore Ministry of Health Ageing Planning Office and remains involved in various charitable causes, especially through the philanthropic arm CRIB Gives Back that she launched at the helm of CRIB. She is married to venture capitalist John Kim of Amasia VC and they have 3 young children.

Kshama Alur
Founder and Chief Of All Things, indigrow
Kshama Alur is the Founder + Chief of All Things at indigrow, an early culture learning platform to raise confident and empathetic kids of tomorrow. She is also founder of The Better Alternative a sustainable consulting agency. Formerly in senior positions with Unilever and ABInbev, she has more than 17 years of brand marketing strategy, innovation and sustainability planning experience. She left the standard corporate life to be an entrepreneur and diligently juggles between her two companies. On one hand, she specialises in designing and facilitating customised learning workshops on branding, digital marketing and sustainability through her company The Better Alternative. On the other hand, she heads up indigrow, which makes delightful books and games that create cultural connections for little kids growing up to be global citizens of the world. While not wearing her entrepreneur hat, you can find her sipping on her favourite craft brew or spending time in her garden with two lovely dogs and her two-year-old son.

Ujjwal Sarao
Ujjwal Sarao has been successfully working in the upper echelons of talent management across Asia Pacific and has been on the forefront of innovation in the HR industry for over two decades. During her career she has managed talent at all levels at international organization’s and has helped future proof organizations using her unique talent management & learning approaches. In her years working at the highest level she has become a strategic business partner for the CEO and the executive leadership team. Not only did she become a strategic business partner for C-level executives at organizations like Dentsu, Aegis Media, ESPN, CNBC and ESPN Star Sports, but she also has been pivotal in developing young, promising processionals in these organizations and help them reach their full potential.

VS Hariharan
Hariharan has been leading Singapore start-up Third Wave Power for the past several years. Third Wave Power develops affordable and innovative portable renewable power solutions that serve portable energy needs for consumers living in off grid rural areas. The solutions range from solar lighting, solar education, entertainment, and livelihood solutions. Hari brings more than 25 years’ experience from the information technology industry. In Hewlett-Packard Company and Wipro Infotech, he was in general management roles as well as senior positions in sales and marketing. Among the various roles at HP, he held the position of Vice President/General Manager for the worldwide Monochrome LaserJet Division and also served as Vice President of Sales & Field Operations for the Imaging/Printing Business for Asia-Pacific. Hari is also on the Board of several companies. Hari has extensive experience in Product Marketing as well as building go-to-market for consumer and business products. Throughout his career, he has been involved in scaling many New and Emerging businesses. Hari holds a Bachelor degree in Mechanical Engineering from IIT Chennai and a Master degree in Business Administration from IIM Bangalore.

Ajit Kaikini
He is the Director of Corporate Training at Buoyancee. He has a knack of making people to perform better, by helping them to discover themselves, enable and monitor to develop the right tools, enhance skills & productive habits, and mentor them to reach their goals. He trains all over India in 6 languages and has been a part of large change initiatives of Adidas, Ajax Fiori, Bisleri, Brigade group, Canara Bank, ITC group, Lupin Pharma, SBI, and many more blue-chip companies. With his 15 yrs experience in the industry spanning sales/ marketing, production/ planning & admin/ training at top positions in blue chip companies, he is able to connect employees who work in cross-functions, and make them gel as performing teams. He has conducted schooling for the Rotary & the Lions executives in 4 states, and through their projects, empowered over 200,000 teens and youth, all over India. Apart from training over 50,000 parents and another 25,000 teachers all over India, he had the privilege to conduct training for over 2500 engineering college lecturers, through the world bank aided TEQIP – Technical Education Quality Improvement Project in Karnataka and Goa.

MOE Certified Instructor Location – Singapore
Swati is a certified happiness coach specializing in kids’ well-being (Certified by Happiitude & Berkeley Institute of Well-being, California). In 2018, while consulting an ed-tech start-up she realized the gap between industry and school curriculum and created a new age curriculum & blueprint that focuses on an entrepreneurial mindset for young students. She started Kidspreneurship , an edtech venture focused on inculcating an entrepreneurial mindset in kids. Swati is a regular trainer with many enrichment centres and schools in Singapore. GIIS recognized her valuable support as a mentor and judge for Star Young Achievers Program. Kidspreneurship program developed by Swati has also been awarded “Leaders in Early Entrepreneurship Education” for two consecutive years at Singapore Awards by APAC Insider. Swati has trained several professional trainers in Singapore including some veteran trainers from Adam Khoo Learning Centre, a leading education brand in Southeast Asia.

Location – India
Sidra is a dynamic trainer with experience in conducting offline and online training sessions for pre-schoolers, and primary and secondary schools. At a young age, Sidra has already trained for 300+ hours and helped students develop problem-solving abilities. She is immensely passionate about teaching students about skills, mindset, and knowledge required to think like an entrepreneur. Sidra believes e ducation should prepare students for their lives and it needs to evolve . Sidra loves reading books and writing. She has around 2 years of experience in teaching.

Somya Rajat
Location – Hong Kong
With 7 years experience in digital space, Somya started her own entrepreneurial journey by establishing a digital agency in Singapore. She has been associated with Kidspreneurship since 2019. She has conducted sessions on building self-esteem & confidence, problem-solving, growth mindset, design thinking and entrepreneurship for primary school students. She has experience in conducting offline and online training sessions.

Silas Koh is a dynamic trainer with experience in developing training materials and conducting training for Junior College students in public speaking for Model United Nations (MUN) conferences. Silas also conducted workshops on leadership skills. This was done in his capacity as president of the MUN club in Victoria Junior College; he also won several personal accolades at various MUNs during his time at the club. Silas believes in igniting passion in students towards learning.

Min Htaw Yama
Yama Min is a visionary entrepreneur with extensive experience focused on technical training and innovative education. He is a founder and managing director of in3labs learning, a technological and engineering education company that aims to empower the young generation to be creators of technology, inspiring individuals, and the next generation of entrepreneurs. He was also featured in all the leading media publishing outlets for robotics and coding education. He has been actively involved in business development, collaborative partnership, and management of the business operation, and plays an important role in organizing the annual Asia Pacific Youth Robotics Competition (APYRC), an annual event that attracts 800+ students from more than 5 countries. Yama believes that an entrepreneurial mindset can help students develop a positive attitude towards life and learning. It changes students’ outlook. Hence, the associated himself with Kidspreneurship and created a program “Technopreneurship”.

Ong Kok Siang Ivan
Ivan has more than 6 years of experience in conducting training sessions for corporate organisations, MOE schools, private enrichment centres and even pre-schools. Ivan doesn’t transfer subject knowledge. More importantly, he seeks to develop the participants’ thinking skills, character strengths and moral values through the subjects that he teaches. Learning is most effective when the learners are actively engaged and having fun – so that is something Ivan tries to do for every lesson. Ivan has a knack to engage his learners. He is also a certified financial planner. He has worked with close to 60 MOE schools in Singapore and trained on subjects related to Entrepreneurship, Design Thinking, Financial Literacy, Public Speaking and more.

Sharon Wan is a dynamic trainer with experience in conducting offline and online training sessions for primary and secondary schools in Singapore. Sharon Wan believes mindset training is very critical for young students as it sets them up for success. Sharon Wan has over 10 years of experience. She has served as a French Teacher at Global Indian International School from 2009 to 2014. She has also been serving as an Adjunct Lecturer at Temasek Polytechnic from 2012 to the present.

Chua Suan Eng Maggie Theresa
Maggie Theresa Chua Suan Eng is a dynamic trainer with experience in conducting offline and online training sessions for pre-schoolers and primary & secondary schools in Singapore. Maggie Theresa Chua Suan Eng has trained on topics like developing problem-solving ability. Maggie Theresa Chua Suan Eng believes in nurturing children to be self-directed and independent lifelong learners Maggie Theresa Chua Suan Eng loves reading, exercising, cooking, and taking up courses to upgrade herself. Maggie Theresa Chua Suan Eng has over 23 years of experience in teaching. She has trained primary school students on various topics including design thinking and environmental sustainability.

Chua Boon Seng Ronald
For more than 27 years, Ronald is highly experienced and dedicated in his interest and passion to engage and enrich every learning moment for learners, both online and face-to-face, for pre-schoolers, and primary and secondary schools in Singapore. Ronald exercises great care and, coupled with his vast experience, infuses strong values whilst developing the mental, social and emotional competencies of learners to effectively problem-solve. Over the last 2 years, he has served 30+ public schools (primary & secondary) on social skills.

Yeo Eng Pheow, Johnny
Yeo Eng Pheow, Johnny has 12 years of experience as an adjunct Lecturer in Supply Chain Management diploma modules at Republic Polytechnic including 8 years of lecturing on Cognitive Processes (including design thinking) and Problem-Solving modules for all first-year students. He has also served 4 years as Adjunct Lecturer and Tutor at the Business School in Temasek Polytechnic. Yeo Eng Pheow, Johnny has 2 years of life skill training for Business School undergraduates at SIM which included subjects like Personal Mastery, Leadership, Emotional Intelligence and Strategic Thinking. He also has 8 years of experience in conducting Tony Buzan Mind Mapping and Habits of the Mind to Secondary Schools assigned by the Nurture Craft and Brain Capital Group. He has taught learners in all age groups.

When students are exposed to entrepreneurial thinking, a profound change takes place. They become aware of the opportunities around them. They think more critically and creatively. The result: they become more confident and experimental in their ability to problem-solve and tackle challenges.

Attend FREE Trial class to train your child to have a growth and entrepreneurial mindset

[anr_nocaptcha g-recaptcha-response]
I agree to get updates via whatsapp
Error: Contact form not found.
- Skip to primary navigation
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
KidsKonnect
Reading Comprehension Cause and Effect Context Clues Compare and Contrast
Noun Worksheets Writing Prompts Compound Words Figurative Language
The Wizard of Oz Hans Christian Andersen Types of Writing Text Structure
Literary Devices
Alliteration Hyperbole Metaphor Irony
Subject Verb Agreement Poetry Climax Rhyme
View all reading worksheets
Action Verbs Tragedy Transition Words Phonics
View all writing worksheets
Dramatic Irony Cacophony Anaphora Setting
View all literature worksheets
Abbreviations Transition Words Conclusion Situational Irony
View all literary device worksheets
Women’s History
Inspirational Women Women's History Month First Lady of the US Women's Equality Day International Women's Day
View all Women's History worksheets
American Revolution
American Revolution Patriots & Loyalists Patrick Henry Sons of Liberty
View all American Revolution worksheets
US Constitution US Independence Trail of Tears The Pilgrims
View all US History worksheets
Ancient History
Ancient China Ancient Mayan Ancient Rome Ancient Aztec
View all Ancient History worksheets
World History
Roaring Twenties Industrial Revolution Middle Ages The Renaissance
View all World History worksheets
Famous Wars
World War 1 World War 2 Vietnam War American Civil War
View all Famous War worksheets
Anne Frank Sally Ride Neil Armstrong Christopher Columbus
View all famous figure worksheets
Joe Biden Donald Trump Abraham Lincoln George Washington
View all President worksheets
Roald Dahl Dr Seuss JK Rowling Michael Morpurgo
View all author worksheets
Civil Rights
Rosa Parks Sojourner Truth Medger Evers Martin Luther King
Elvis Presley Johann Sebastian Bach Ella Fitzgerald Wolfgang Mozart
View all musician worksheets
Thomas Edison Albert Einstein Henry Ford Wright Brothers
View all inventor worksheets
Muhammad Ali Michael Jordan Jackie Robinson Jesse Owens
View all athlete worksheets
Nat Turner Ruby Bridges Harriet Tubman Booker T Washington Malcolm X
View all civil rights worksheets
Natural Wonders
River Nile Mount Everest Sahara Desert Mount Etna Ancient Pyramids Amazon River
Landmarks/Sights
Mount Rushmore Statue Of Liberty White House Stonehenge Great Wall of China Santa Fe Trail
New York Texas South Carolina Alaska Nevada Ohio
Australia United Kingdom China Canada Argentina Brazil
Mount Fuji Mississippi River Rocky Mountains Volcano Glacier The Great Barrier Reef
View all natural wonders worksheets
Hoover Dam Bermuda Triangle Leaning Tower Of Pisa Arc De Triomphe Golden Gate Bridge Colosseum
View all landmark worksheets
California Colorado Indiana Florida Washington Georgia
View all US state worksheets
Poland Greece Philippines Japan France India
View all country worksheets
June Topics
Juneteenth D Day Flag Day Father’s Day Shavuot Summer Solstice Eid al-Adha Marshall Plan Summer Northern Hemisphere
View all Seasonal worksheets
Social Emotional Learning
Morals and Values Self Management Ethics Depression Relationship Skills Self-Awareneess Self-Esteem Emotions and Feelings Goal-Setting Interpersonal Skills
View all Social-Emotional Learning worksheets
Celebrations
Easter Saint Patrick’s Day Valentines Day Chinese New Year Rosh Hashanah Thanksgiving Flag Day Cinco de Mayo Beginning Of Lent Yom Kippur View all Celebrations worksheets
Remembrance
Pearl Harbor Day Veterans’ Day Memorial Day Battle Of The Somme D-Day 9/11 Anzac Day Martin Luther King Jr. Day International Women’s Day Victoria Day View all Remembrance worksheets
Camels Fox Bears Penguin Wolf Beavers Mountain Lion Red Panda Snow Leopard White Tigers Silverback Gorilla Okapi
View all mammal worksheets
Marine Life
Crabs Starfish Fish Octopus Great White Shark Dolphin Walrus Narwhal Megalodon Shark Killer Whale Beluga Whale Lionfish
View all marine life worksheets
Insects/Invertebrates/Reptiles
Millipede Praying Mantis Ladybug Ants Spider Iguana Chameleon Komodo Dragon Lizard Bearded Dragon Gila Monster Snakes
View all insect worksheets
Eagle Peregrine Falcon Snowy Owl Emu Woodpecker Albatross Swan Quail Bald Eagle Hummingbird Peacock
View all Bird worksheets
Natural World
Avalanche Flood Tsunami Natural Disasters Fossils Ice Age
View all natural world worksheets
Earth Sciences
Water Cycle Global Warming Deciduous Forests Hurricane Sandy Hurricane Katrina Global Warming
View all earth science worksheets
Food Chain Fossils Photosynthesis Cells Ecosystem Plants
View all biology worksheets
Solar System Black Holes Eclipse Stars and Constellations The Moon Comets
View all space worksheets
Chemistry/Physics
Magnetism Graduated Cylinders Solid, Liquid, Gas Gravity Light Sound
View all science worksheets
Kangaroo Horse Bear Lion Lizard Octopus
View all animal worksheets
Addition Sentences Single Digital Addition Two-Digit Addition Three Digit Addition Repeated Addition
View all Addition Worksheets
Ordinal Numbers Cardinal Numbers Rounding Numbers Odd & Even Numbers Comparing Numbers
View all Numbers Worksheets
Counting Money Subtracting Money Change Money Coin Name & Value Calculate Change (Money)
View all Money Worksheets
Number Line Single Digit Subtraction Place Value Subtraction Sentences Input & Output Tables
View all Math Worksheets
Business Plan Template for Kids
Use this business plan template for kids as a guide to planning a business., search for worksheets, download the business plan template for kids.
Click the button below to get instant access to these worksheets for use in the classroom or at a home.
Download This Worksheet
This download is exclusively for KidsKonnect Premium members! To download this worksheet, click the button below to signup (it only takes a minute) and you'll be brought right back to this page to start the download! Sign Me Up
Edit This Worksheet
Editing resources is available exclusively for KidsKonnect Premium members. To edit this worksheet, click the button below to signup (it only takes a minute) and you'll be brought right back to this page to start editing! Sign Up
This worksheet can be edited by Premium members using the free Google Slides online software. Click the Edit button above to get started.
Download This Sample
This sample is exclusively for KidsKonnect members! To download this worksheet, click the button below to signup for free (it only takes a minute) and you'll be brought right back to this page to start the download! Sign Me Up
Table of Contents
A business plan is important to people who want to start their own businesses. This business plan template for kids will serve as a guide to understand how entrepreneurs use business plans to keep them from making mistakes.
See the fact file below for more information on Business Plan Template or alternatively, you can download our 19-page Business Plan Template for Kids worksheet pack to utilise within the classroom or home environment.
Key Facts & Information
Making a business plan.
- A business plan is an overall outline of your business: how you will be working on it, and how will it bring you profit in the long run.
Determine what business you would like to establish
- Choose a business that interests you, shows your skills, or a business that is needed in your area.
- Determine if your business will offer either a service or a product or even both.
- Think of a business that will make you stand out among your competitors.
Make your business name
- Decide on a business name that is unique but easy to pronounce and remember.
- People should be able to easily determine what your business offers.
- Provide a brief discussion of what your business is all about.
- Include your goals, objectives, your product, and what makes your business different among others.
Plan your team
- You can do your business by yourself, hire employees, or seek help from your family members.
- Identify all your materials and determine the cost for each.
- If you are going to hire employees, compute how much you will pay them.
- If commercial spaces are to be rented, include the renting and utility costs in your expenses.
- After considering all expenses, you can now make a price for your product and estimate how much will be your profit.
Know your market
- Determine who will be your customers.
- Consider the place of your business and research the demographics of the area.
- Are there more professional people, young, old, mothers, fathers, or students?
Competitors
- Know who will be your competitors.
- Do research on businesses in the same location that have the same product or service as you.
- Identify how long they have been established, how much they charge for their product, and how does their product differs from yours.
- With all the information you have gathered, determine how you can make an edge with your business.
- You can either offer lower prices without sacrificing the quality of your product or you can also offer additional services that your competitors don’t have.
Marketing Strategy
- Think of how you will market your business.
- How will you advertise your business?
- You can promote using social media platforms, send out flyers, make posters, make door-to-door advertising, or whichever strategy you think will work best for your business.
- With an effective marketing strategy, people will get curious about what you sell and this will push the consumers to try your product or service.
Business Plan Template Worksheets
This is a fantastic bundle that includes everything you need to know about Business Plan Template across 19 in-depth pages. These are ready-to-use worksheets that are perfect for teaching students about Business Plan Template for Kids which will serve as a guide to understand how entrepreneurs use business plans to keep them from making mistakes.

Complete List Of Included Worksheets
- Business Plan for Kids Facts
- My Own Product
- Do You Like My Service?
- The Clothing Line
- Free for All
- What Went Wrong?
- In 5 Years…
- Click and Sell
- Special Delivery
- Show Me Your Strategy

Link/cite this page
If you reference any of the content on this page on your own website, please use the code below to cite this page as the original source.
Link will appear as Business Plan Template for Kids: https://kidskonnect.com - KidsKonnect, November 10, 2021
Use With Any Curriculum
These worksheets have been specifically designed for use with any international curriculum. You can use these worksheets as-is, or edit them using Google Slides to make them more specific to your own student ability levels and curriculum standards.
KidsKonnect is a growing library of high-quality, printable worksheets for teachers and homeschoolers.
Home Facts Privacy About Blog Contact Terms
Safe & Secure
We pride ourselves on being a safe website for both teachers and students. KidsKonnect uses a secure SSL connection to encrypt your data and we only work with trusted payment processors Stripe and PayPal.
- https://www.instagram.com/thestartupsquad/
- https://www.facebook.com/thestartupsquad/
- https://twitter.com/thestartupsquad
- https://www.tiktok.com/@thestartupsquad
- Raising Entrepreneurial Girls
- -
THE ULTIMATE BUSINESS PLAN FOR KIDS TO HELP THEM START OR GROW A BIZ

- The Startup Squad May 6, 2021 February 23, 2022
With some advance planning, your kids can set their business goals and achieve their entrepreneurial dreams.
Starting a business has to start somewhere. And that ‘somewhere’ can be found in a plan. To be specific, a business plan; a road map that describes how a startup operates, what the goals are, and how to achieve these goals. So, if your future girl boss has a passion or an idea that she believes has real business potential, encourage her to put her thoughts into words.
Putting pen to paper is key to turning an idea into a reality and starting a business off on the right foot. And we can help! The Startup Squad has created the ultimate kid-friendly business plan template. We call it the Startup Roadmap.

It has everything she’ll need to plan out her business including:
- Motivation: What’s Your Why? Encourage your girl to self-reflect with this question, “Why do you want to start a business?” She can list as many answers as possible and refer to them when she feels like she’s lost her way and needs a motivation boost.
- The Big Idea: What Problem Will You Solve? Ask your girl what she enjoys doing or what she’s passionate about. Lots of hobbies and interests have business potential. Or, your girl can improve an existing product or service and base her business on the improvements.
- “It” Factor: What Makes You or Your Product Different? Your girl can either develop a compelling startup story or think of specific benefits that set her product or service apart from other businesses.
- Customer Research: How Will You Make Sure People Will Buy Your Product? Customer research is an essential section of a business plan. It allows your girl to collect candid feedback from product testers and tweak what’s needed before launching her business.
- Money Matters: How Will You Make a Profit? Empower your girl to do the math. Remind her to factor in all costs, from one-time upfront charges to operating expenses. And if her startup is a service-based one, she should include how much her time is worth in the calculation.
- Sales Pitch: What Will You Say to People to Convince Them to Buy Your Product or Service? Similar to advertising, a sales pitch is your girl’s go-to spiel for convincing a prospect and closing a sale. It’s the first few words a customer hears, so it’s best if the pitch is creative, clear, and concise. And that your girl rehearses it often.
- And so much more!
You can download your Startup Roadmap here . It’s the perfect companion to The Startup Squad Book #3: Party Problems . In our latest book, Didi gets a job creating place cards for a wedding but then is thrown into having to plan the entire wedding! Meanwhile, Amelia creates a business plan to help her think through all aspect of her video business.
Party Problems also includes tips about finding a business to match your passions and market research as well as a profile of an inspiring entrepreneur. Order your copy today!

Leave a Reply Cancel reply
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.
How it all began…
Want to know how The Startup Squad, well, started? Check out this note from founder, Brian Weisfeld.
All Categories
- Books We Love 10
- Fun Business Ideas 24
- Let’s Get Down to Business with Girl CEOs 27
- Raising Entrepreneurial Girls 58
- The Startup Squad News 11
- Where it All Began With Female Leaders 7
Check out our books

Latest Blog Posts

Kids Business Plan Template & Guidebook
How to write a kids business plan in 7 steps:, 1. describe the purpose of your kids business..
It also helps to include a vision statement so that readers can understand what type of company you want to build.
Our mission is to inspire and educate children to reach their full potential through creative, interactive learning experiences. We strive to create an environment that encourages collaboration, creativity, and exploration while helping kids develop valuable life skills.
2. Products & Services Offered by Your Kids Business.
You may want to do a comparison of your business plan against those of other competitors in the area, or even with online reviews. This way, you can find out what people like about them and what they don’t like, so that you can either improve upon their offerings or avoid doing so altogether.
3. Build a Creative Marketing Stratgey.
Target market, customer base , product or service description, competitive analysis, marketing channels, form an llc in your state, 4. write your operational plan..
Next, you'll need to build your operational plan. This section describes the type of business you'll be running, and includes the steps involved in your operations.
What equipment, supplies, or permits are needed to run a kids business?
5. management & organization of your kids business., 6. kids business startup expenses & captial needed..
Running costs refer to ongoing expenses related directly with operating your business over time like electricity bills or salaries paid out each month. These types of expenses will vary greatly depending on multiple variables such as location, team size, utility costs, etc.
7. Financial Plan & Projections
Here are some steps you can follow to devise a financial plan for your kids business plan:
Frequently Asked Questions About Kids Business Plans:
Why do you need a business plan for a kids business, who should you ask for help with your kids business plan, can you write a kids business plan yourself.
Writing a business plan can be a complex task, so it is generally recommended that you seek the help of an experienced professional. If you do decide to write the business plan yourself, it is important to have a clear understanding of what elements should be included and be aware of the resources available to help ensure your plan is successful.
Related Business Plans
Home inventory business plan template & guidebook, home inspection business plan template & guidebook, home decor business plan template & guidebook, health and wellness business plan template & guidebook, hauling business plan template & guidebook, hardware business plan template & guidebook, handyman business plan template & guidebook, hair extension business plan template & guidebook, handbag business plan template & guidebook.
I'm Nick, co-founder of newfoundr.com, dedicated to helping aspiring entrepreneurs succeed. As a small business owner with over five years of experience, I have garnered valuable knowledge and insights across a diverse range of industries. My passion for entrepreneurship drives me to share my expertise with aspiring entrepreneurs, empowering them to turn their business dreams into reality.
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
What Is a Business Plan?
Understanding business plans, how to write a business plan, common elements of a business plan, how often should a business plan be updated, the bottom line, business plan: what it is, what's included, and how to write one.
Adam Hayes, Ph.D., CFA, is a financial writer with 15+ years Wall Street experience as a derivatives trader. Besides his extensive derivative trading expertise, Adam is an expert in economics and behavioral finance. Adam received his master's in economics from The New School for Social Research and his Ph.D. from the University of Wisconsin-Madison in sociology. He is a CFA charterholder as well as holding FINRA Series 7, 55 & 63 licenses. He currently researches and teaches economic sociology and the social studies of finance at the Hebrew University in Jerusalem.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/adam_hayes-5bfc262a46e0fb005118b414.jpg)
- How to Start a Business: A Comprehensive Guide and Essential Steps
- How to Do Market Research, Types, and Example
- Marketing Strategy: What It Is, How It Works, How To Create One
- Marketing in Business: Strategies and Types Explained
- What Is a Marketing Plan? Types and How to Write One
- Business Development: Definition, Strategies, Steps & Skills
- Business Plan: What It Is, What's Included, and How to Write One CURRENT ARTICLE
- Small Business Development Center (SBDC): Meaning, Types, Impact
- How to Write a Business Plan for a Loan
- Business Startup Costs: It’s in the Details
- Startup Capital Definition, Types, and Risks
- Bootstrapping Definition, Strategies, and Pros/Cons
- Crowdfunding: What It Is, How It Works, and Popular Websites
- Starting a Business with No Money: How to Begin
- A Comprehensive Guide to Establishing Business Credit
- Equity Financing: What It Is, How It Works, Pros and Cons
- Best Startup Business Loans
- Sole Proprietorship: What It Is, Pros & Cons, and Differences From an LLC
- Partnership: Definition, How It Works, Taxation, and Types
- What is an LLC? Limited Liability Company Structure and Benefits Defined
- Corporation: What It Is and How to Form One
- Starting a Small Business: Your Complete How-to Guide
- Starting an Online Business: A Step-by-Step Guide
- How to Start Your Own Bookkeeping Business: Essential Tips
- How to Start a Successful Dropshipping Business: A Comprehensive Guide
A business plan is a document that details a company's goals and how it intends to achieve them. Business plans can be of benefit to both startups and well-established companies. For startups, a business plan can be essential for winning over potential lenders and investors. Established businesses can find one useful for staying on track and not losing sight of their goals. This article explains what an effective business plan needs to include and how to write one.
Key Takeaways
- A business plan is a document describing a company's business activities and how it plans to achieve its goals.
- Startup companies use business plans to get off the ground and attract outside investors.
- For established companies, a business plan can help keep the executive team focused on and working toward the company's short- and long-term objectives.
- There is no single format that a business plan must follow, but there are certain key elements that most companies will want to include.
Investopedia / Ryan Oakley
Any new business should have a business plan in place prior to beginning operations. In fact, banks and venture capital firms often want to see a business plan before they'll consider making a loan or providing capital to new businesses.
Even if a business isn't looking to raise additional money, a business plan can help it focus on its goals. A 2017 Harvard Business Review article reported that, "Entrepreneurs who write formal plans are 16% more likely to achieve viability than the otherwise identical nonplanning entrepreneurs."
Ideally, a business plan should be reviewed and updated periodically to reflect any goals that have been achieved or that may have changed. An established business that has decided to move in a new direction might create an entirely new business plan for itself.
There are numerous benefits to creating (and sticking to) a well-conceived business plan. These include being able to think through ideas before investing too much money in them and highlighting any potential obstacles to success. A company might also share its business plan with trusted outsiders to get their objective feedback. In addition, a business plan can help keep a company's executive team on the same page about strategic action items and priorities.
Business plans, even among competitors in the same industry, are rarely identical. However, they often have some of the same basic elements, as we describe below.
While it's a good idea to provide as much detail as necessary, it's also important that a business plan be concise enough to hold a reader's attention to the end.
While there are any number of templates that you can use to write a business plan, it's best to try to avoid producing a generic-looking one. Let your plan reflect the unique personality of your business.
Many business plans use some combination of the sections below, with varying levels of detail, depending on the company.
The length of a business plan can vary greatly from business to business. Regardless, it's best to fit the basic information into a 15- to 25-page document. Other crucial elements that take up a lot of space—such as applications for patents—can be referenced in the main document and attached as appendices.
These are some of the most common elements in many business plans:
- Executive summary: This section introduces the company and includes its mission statement along with relevant information about the company's leadership, employees, operations, and locations.
- Products and services: Here, the company should describe the products and services it offers or plans to introduce. That might include details on pricing, product lifespan, and unique benefits to the consumer. Other factors that could go into this section include production and manufacturing processes, any relevant patents the company may have, as well as proprietary technology . Information about research and development (R&D) can also be included here.
- Market analysis: A company needs to have a good handle on the current state of its industry and the existing competition. This section should explain where the company fits in, what types of customers it plans to target, and how easy or difficult it may be to take market share from incumbents.
- Marketing strategy: This section can describe how the company plans to attract and keep customers, including any anticipated advertising and marketing campaigns. It should also describe the distribution channel or channels it will use to get its products or services to consumers.
- Financial plans and projections: Established businesses can include financial statements, balance sheets, and other relevant financial information. New businesses can provide financial targets and estimates for the first few years. Your plan might also include any funding requests you're making.
The best business plans aren't generic ones created from easily accessed templates. A company should aim to entice readers with a plan that demonstrates its uniqueness and potential for success.
2 Types of Business Plans
Business plans can take many forms, but they are sometimes divided into two basic categories: traditional and lean startup. According to the U.S. Small Business Administration (SBA) , the traditional business plan is the more common of the two.
- Traditional business plans : These plans tend to be much longer than lean startup plans and contain considerably more detail. As a result they require more work on the part of the business, but they can also be more persuasive (and reassuring) to potential investors.
- Lean startup business plans : These use an abbreviated structure that highlights key elements. These business plans are short—as short as one page—and provide only the most basic detail. If a company wants to use this kind of plan, it should be prepared to provide more detail if an investor or a lender requests it.
Why Do Business Plans Fail?
A business plan is not a surefire recipe for success. The plan may have been unrealistic in its assumptions and projections to begin with. Markets and the overall economy might change in ways that couldn't have been foreseen. A competitor might introduce a revolutionary new product or service. All of this calls for building some flexibility into your plan, so you can pivot to a new course if needed.
How frequently a business plan needs to be revised will depend on the nature of the business. A well-established business might want to review its plan once a year and make changes if necessary. A new or fast-growing business in a fiercely competitive market might want to revise it more often, such as quarterly.
What Does a Lean Startup Business Plan Include?
The lean startup business plan is an option when a company prefers to give a quick explanation of its business. For example, a brand-new company may feel that it doesn't have a lot of information to provide yet.
Sections can include: a value proposition ; the company's major activities and advantages; resources such as staff, intellectual property, and capital; a list of partnerships; customer segments; and revenue sources.
A business plan can be useful to companies of all kinds. But as a company grows and the world around it changes, so too should its business plan. So don't think of your business plan as carved in granite but as a living document designed to evolve with your business.
Harvard Business Review. " Research: Writing a Business Plan Makes Your Startup More Likely to Succeed ."
U.S. Small Business Administration. " Write Your Business Plan ."
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/GettyImages-1456193345-2cc8ef3d583f42d8a80c8e631c0b0556.jpg)
- Terms of Service
- Editorial Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
- Building Your Business
What Is a Business Plan?
Business Plan Explained in Less Than 5 Minutes
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/KhadijaKhartit-4f144e2b63ee4dd4af60ac8a02233c50.jpg)
Definition and Examples of a Business Plan
How a business plan works, types of business plans, business plan vs. business model.
Geber86 / Getty Images
A business plan is a detailed written document that describes your business’s activities, goals, and strategy. A strong plan outlines everything from the products a company sells to the executive summary to the overall management. In essence, a business plan should guide a founder’s actions through each stage of growth
Think of your business plan as a road map. It documents the various stages of starting and running your business, including business activities and objectives. Business plans create the structure you need to make decisions by outlining the financial and operational goals you’re striving toward.
One of the most common reasons for crafting a business plan is to attract investors—and, in return, receive funding. As an early stage company, for example, you may leverage your business plan to convince investors or banks that your entity is credible and worthy of funding. The business plan should prove that their money will be returned .
A business plan can also be useful for when a well-developed company goes through a merger or acquisition . As outlined by the U.S. Small Business Administration (SBA), a merger creates a new entity via the combination of two businesses. An acquisition, on the other hand, is when a company is purchased and absorbed into an existing business. In either case, a business plan helps establish relationships between business entities, making a merger or acquisition more likely.
- Alternate name : Strategic plan
A business plan is a formalized outline of the business operations, finances, and goals you aim to achieve to be a successful company. When designing a business plan, companies have leeway for how long, short, or detailed it can be. So long as it outlines the foundational aspects of the business, in most cases, it will be effective.
The most common type of business plan is a traditional business plan. This style tends to have the following common elements, generally in this order.
- Executive summary : Tells your reader why your company will be successful. Includes the company’s mission statement , product information, and basics regarding the business structure.
- Company description : Where you brag about your entity’s strengths. Answer the question, what problem is your team solving?
- Market analysis : A deep dive into your industry and the competition. Consider why competitors are successful. How can your offering do it better? If applicable, how can you enhance the experience for the consumer?
- Management plan : Outlines leadership structure of the company and may be best detailed as a chart. This way, readers can see exactly who is planning to run the company and how they will impact growth.
- Marketing and sales plan : Details how you’ll attract consumers with your product or service, and how you will retain those customers. All strategies outlined in this section, such as the use of digital marketing , will be referenced in your financial plan.
- Funding request : For those companies asking for funding, this is where you’ll detail the amount of funding you’ll need to achieve your goals. Clearly explain how much you need and what it will be used for.
- Financial plan : Convinces the reader that your company is financially stable and can turn a profit . You will need to include a balance sheet , an income statement, and the cash flow statement (or cash flow projection, in the case of a new venture).
- Appendix : Where any supporting documents, such as legal documents, licenses of employees, and pictures of the product will be included.
Your company’s business plan should fit your needs, which will often depend on what stage of growth you are in. If you are considering starting a new venture, for example, writing a detailed business plan can help prove if your concept is viable or not.
If your business is seeking financial capital, though, you will want your business plan to be investor-ready. This will require you to have a funding request section, which would be placed right above your financial plan.
You should avoid using lofty terms or technical jargon that those outside your team won’t understand. A business plan is meant to be shared with those inside and outside your organization. Simple and effective language is best.
Your business’s stage impacts the length and detail of a business plan. As discussed, a traditional plan follows a detailed structure, from the executive summary to the appendix. It is a lengthier document, often amounting to dozens of pages, and is often used when seeking funding to prove business viability. In most cases, crafting a traditional plan will take lots of due diligence work.
The other main type of business plan is a lean startup plan. A lean startup plan is much more high-level and shorter than the traditional version. Companies just starting development will often create a lean startup plan to help them navigate where they should start. These can be as short as one or two pages.
A lean plan will include the following elements.
- Key partnerships : Notes other services or businesses you will work with, such as manufacturers and suppliers.
- Key activities and resources : Outlines how your company will gain a competitive advantage and create value for your consumers. Resources you may leverage include capital, staff, or intellectual property.
- Value proposition : Clearly defines the unique value your company offers.
- Customer relationships : Details the customer experience from start to finish.
- Channels : How will you stay connected with your customers? Detail those methods here.
- Cost structure and revenue streams : Details the most significant costs you will face as well as how your business will actually make money.
Remember that business plans are meant to change as your company grows or pivots. You should actively review and edit your business plan to keep it up to date with business activities. For example, you may start with a lean plan and move to a traditional plan when you hit the fundraising stage.
| Describes a business’s operations and objectives, including financial goals | Describes the method by which a company generates profits |
| Is the structure of the business | Is the foundation of the business |
| Sections include mission statement, market analysis, and financial plan | Examples include retailer, franchise, and distributor |
| Needs review and revisions over time | Needs review and revisions over time |
A business plan may often be confused with a business model, and it is easy to understand why. Simply put, a business plan is the holistic overview of the business, while a business model is a skeleton for how money will be made.
Key Takeaways
- A business plan is a comprehensive document that outlines a business’s operations, finances, and goals. It guides the business’s day-to-day decisions.
- A business plan is necessary for your company’s success, as it creates a path to scalability.
- There are two main types of business plans: a traditional business plan and a lean startup plan.
- A traditional business plan will be essential when you begin to seek debt or equity capital for your company.
U.S. Small Business Administration. “ Merge and Acquire Businesses .” Accessed June 8, 2021.
U.S. Small Business Administration. " Write Your Business Plan ." Accessed June 8, 2021.

Business Plan Example
Writing the plan, what goes in a business plan, sample plans.
One of the best ways to learn about writing a business plan is to study the plans of established businesses in your industry.
http://www.bplans.com/sp/businessplans.cfm
Develop a Business Plan Worksheet
This worksheet describes the basic components of any business plan. Please note that every plan will be unique to its particular company.
The Executive Summary
Include crisp, clear descriptions of the following elements:
- Company history
- Company objectives
- Product/service offerings
- Competitive advantage (A persuasive statement of why and how the business will succeed)
- Projected growth for the company and the market
- Key management team members
- Funding requirements, including a timeline and details on how the funds will be used
The Products and Services
Answer the following questions in this section:
- Why is there a need for your offering?
- Is your product or service already on the market, or is it still in the research and development stage? If you are still in the development stage, what is the rollout strategy or timeline to bring the product to market?
- What makes your product or service unique? What competitive advantage does the product or service have over its competition?
- Can you price the product or service competitively and still maintain a healthy profit margin?
- What patents, copyrights and trademarks does your company currently own or plan to obtain?
- What confidential and non-disclosure protection have you secured?
- What barriers do you face in bringing the product to market, such as government regulations, competing products, high product-development costs, the need for manufacturing materials, etc.?
Include the following elements:
- A detailed description of your market
- A detailed description of your niche and why you chose it
- An explanation of the market demand for your product or service offering (Requires supporting documentation)
- What percentage of market share do you project you can capture?
- What is the growth potential of the market? (Requires supporting documentation)
- Will your share of the market increase or decrease as the market grows?
- How will you satisfy market growth?
- How will you price your goods or services to remain competitive in a growing market?
Note: If you are launching a new product, include your market research data. Likewise, if you have existing customers, provide a customer profile, detailing their purchasing habits and their buying cycle.
The Marketing Strategy
The following are some promotional options to consider:
- Social Media
- Direct mail
- Trade shows
- Public relations
- Promotional materials
- Telephone sales
- One-on-one sales
- Strategic alliances
If you have current samples of marketing materials or strategies that have proven successful for you, include them with your plan.
Discuss your distribution strategy:
- Will you mail order, personally deliver, hire sales reps, contract with distributors or resellers, or use some other method?
- What are the costs associated with your proposed delivery methods?
- How will you track the effectiveness of the methods you choose?
The Competition
Specific areas to address in this section are:
- Who are your closest competitors and what are their product/service offerings?
- Where are they located?
- What are their revenues?
- How long have they been in business?
- Who is their target market?
- What percentage of market share do they currently hold?
- Do they service a local, geographic market or a national customer base? Is that the same or different from your approach?
- In what other ways do your operations differ from each of them? How are they similar?
- What do your rivals do well? Where is there room for improvement?
- In what ways is your business superior to the competition?
- How is their business doing? Is it growing, declining or stable?
- Are there certain areas of the business where the competition surpasses you (management team, economies of scale, better distribution, volume discounts, etc.)? If so, what are those areas, and how do you plan on compensating for them?
This section of the plan should describe the following requirements of your business:
- Manufacturing
Note: Provide a rollout strategy as to when these requirements need to be purchased and implemented. In addition, describe the vendors you will need to build the business. Do you have current relationships, or do you need to establish new ones? Who will you choose and why?
The Management Team
When preparing this section of the business plan, you should address the following five areas:
- Business background of the principals
- Past experience — tracking successes, responsibilities and capabilities
- Educational background (formal and informal)
- Personal data: age, current address, past addresses, interests, education, special abilities, reasons for entering into business
- Personal financial statements with supporting documentation
- Direct operational and managerial experience in related businesses
- Indirect managerial experiences
- Who will do what and why? Who is responsible for final decisions?
- Organizational chart with chain of command and listing of duties
- A simple statement of what management members will be paid, by position
- Listing of bonuses in realistic terms
- Benefits (medical, life insurance, disability, etc.)
- Insurance brokers
- Accountants
- Consulting groups
- Small Business Association
- Local business information centers
- Chambers of Commerce
- Local colleges and universities
- Federal, state and local agencies
- Board of Directors
- World Wide Web (various search engines)
Consider the following questions in completing this section of the business plan:
- What are your current personnel needs (full- and/or part-time)? How many employees do you envision in the near future, and then in the next three to five years?
- What skills must your employees have?
- What will their job descriptions be?
- Are the people you need readily available? If not, how will you attract them?
- Will you pay salaries or hourly wages?
- Will you provide benefits? If so, what will they be, and at what cost?
- Will you pay overtime?
Financial Data
Have a certified public accountant establish your accounting system before the start of business to provide you with data in the following four areas:
- Balance Sheet – indicates what the cash position of the business is and what the owner’s equity is at any given point (the balance sheet will show assets, liabilities and retained earnings).
- Break-Even Analysis – Shows the volume of revenue from sales that are needed to balance the fixed and variable expenses. Without exception, all businesses should perform this analysis, which is based on the income statement and cash flow.
- Income Statement (also called the profit and loss statement) – Indicates how well the company is managing its cash, by subtracting disbursements from receipts.
- Cash Flow – Projects all cash receipts and disbursements. Healthy cash flow is critical to the survival of any business.
Supporting Documentation
You will need to include all documents that lend support to statements made in the body of your company’s business plan. Please be aware that this list is not complete and may vary depending on the stage of development of your business.
- Credit information (include in appendix)
- Quotes or estimates
- Letters of intent from prospective customers
- Letters of support from credible personal references
- Leases or buy/sell agreements
- Legal documents relevant to the business
- Census/demographic data

— Lesson
Biz kid$ did you know videos, business plans, clips for this lesson.

Piggy Bank Hunt

Teacher’s Forum

Life on the Edge

Family Activities

Debt: The Good, The Bad & The Ugly
What students learn, it’s easy to spend more than you make. learn how to avoid the pitfalls of overspending and meet a few entrepreneurs who didn’t..

Your first big Purchase
Make sure your first big purchase is b.r.o.w.n. - whether it’s the latest computer, a new smart phone, or a car. learn about budgeting, researching, negotiating, and more..

Whats Up with the Stock Market?
Learn the weird, abbreviated language of the stock market, and the difference between a bull and bear market..
Crash Course on Starting a Business
So you’ve got an idea – now what the ultimate crash course – find an idea, get funded, market your business, make a profit, and write a business plan..

How to Make a Million Bucks
If you start early and save often, the power of compound interest can make you millions.

The Value of Money
Considering all the global currencies, what determines the value of money what are the factors that impact the american dollar.

Have a Plan, Stan!
Explore the different elements of a business plan and see why it’s crucial to develop a plan before starting a business..

Money Math – Who Needs It?
Whether you need to calculate the tip, make change, or grow your savings, it’s all about the math in money..

How Credit Affects Your Life
Your credit score could impact getting into college, landing a job, or renting an apartment. learn how to build good credit and what happens when you don’t..

Money Moves
Follow a dollar bill as it moves from a depositor’s hand, to the bank vault, over to the federal reserve, and finally out to a project the bank is financing..

How to Succeed in Biz-ness
Discover the three key steps to succeeding in business: identify a need, make a plan, and take action..

Cash and Credit
What's the difference between cash and credit learn the pros and cons to using your own money versus someone else's..

How to Achieve Your Financial Goals
Learn how to track expenses, control spending, and invest what’s left over to reach your financial goal..

Don’t Blow Your Dough
Biz kid$ beware put your money in a safe place and beware of scams, schemers, and identity theft..

Using Your Credit
Don’t live on borrowed time. learn how employers, insurers, colleges, etc. use credit scores to make major decisions that affect your future..

Budgeting Basics
The first rule of money management: you can’t manage what you don’t know. learn how to track expenses to build a better budget..

Saving and Investing for Your Future
Start a savings plan early in life, and discover how to evaluate different investment options..

A Closer Look at Careers
Learn ways to start exploring careers, and find your true calling..

The Global Economy
Go around the world and follow the flow of imports and exports that make up the interconnected world economy..

Sell, Sell, Sell (The Science of Sales)
All sales final join the biz kid$ in sales training as they explore effective sales techniques..

Understanding Income and Expenses
Learn proven methods for getting expenses under control while growing income with new ideas, smart work habits, and innovation..

Understanding Your Paycheck
What’s on your stub, bub check out the modern american pay stub to learn about the deductions on your paycheck from social security to workman’s compensation to a 401(k) plan..

The World Is A Risky Place
Be smart about taking risks in life. learn about liability, contracts, and insurance, and how to protect your business, your assets, and yourself..

Economic Cycles
Economic cycles go up and down. learn how to protect yourself against negative effects and plan for the positive trends..

Are You Financially Literate
Get financially empowered by learning how to set goals, create a budget, save, and manage money..

Wheel of Misfortune
Find out how to avoid common money mistakes such as overspending, too much debt, lack of planning, or no emergency fund..

More Bang for Your buck
Whether you’re facing good times or tough times, know how to get the best value for your money. discover tips for stretching your dollars..

Secrets To Success
It’s simple – explore education options and build the best toolbox for your future..

Where’s My Allowance?
What can you do with your allowance spend, save, share.

The Marketing Mix
You can market anything once you understand the four p’s of marketing: product, price, place and promotion..

Escape the Box
Opportunity knocks learn how to act on new opportunities and to be creative in solving problems..

Hidden Careers
You don’t have to be perfect at your passion to build a career in it. if you love something, there are many roles you can play behind the scenes..

Movin’ On Out
What’s the true cost of cutting the cord we take you through it all — budgeting, roommates, finding a place, and learning about all the hidden costs mom and dad used to pay..

You Are the Target!
….of advertisers, that is. recognize how to resist manipulation, and how to apply good consumer skills to cut through the commercial fog..

The Economics of Economics
See how businesses use economic principles to make financial decisions, from micro to macro economics, supply and demand, and economic indicators..

Take it to the Bank
Learn the difference between banks, credit unions and other financial institutions, and which one is right for you..

It’s a Job Getting a Job!
Learn tips and tricks for writing a great resume, dressing for success, and nailing the interview..

What to do with a Windfall?
A financial windfall now what evaluate investment alternatives based on time, risk, and rate of return..

How to turn $100 into $1,000,000
Develop your mdm (million dollar mindset), maximize saving strategies, and get the best return on your investments..

College Bound
The average college student graduates with $35,000 in debt. consider the return-on-investment of college and how to get educated without taking on debt..

My First Credit Card
Biz kid$ demystifies the process of getting a credit card, how to use it correctly, and explains terms like credit score and apr..

Money Really Does Grow On Trees
From products to services, offline to online, and the basics to the bizarre -- this episode explores ways to bring in the bucks..

Can Money Buy Happiness?
Hear heart-warming stories of how kids identified a need in their community and used an entrepreneurial mindset to solve it..
- Disaster recovery planning and management

Downtime can do serious damage to an organization's bottom line and reputation. Business continuity and disaster recovery -- two closely related practices -- help keep an organization running even in the wake of disaster. This guide explains how BCDR works, why you need it and how to build a BCDR plan for your organization to protect it today and into the future.
Disaster recovery (dr).
- Kinza Yasar, Technical Writer
- Erin Sullivan, Senior Site Editor
- Paul Crocetti, Executive Editor
What is disaster recovery (DR)?
Disaster recovery (DR) is an organization's ability to respond to and recover from an event that negatively affects business operations.
The goal of DR is to reduce downtime, data loss and operational disruptions while maintaining business continuity by restoring critical applications and infrastructure ideally within minutes after an outage. To prepare for this, organizations often perform an in-depth analysis of their systems and IT infrastructure and create a formal document to follow in times of crisis. This document is known as a disaster recovery plan .
What is a disaster?
The practice of DR revolves around serious events. These events are often thought of in terms of natural disasters, but they can also be caused by systems or technical failures, human errors or intentional attacks. These events are significant enough to disrupt or completely stop critical systems and business operations for a period of time. Types of disasters include the following:
- Cyberattacks, such as malware, distributed denial-of-service and ransomware .
- Power outages.
- Hardware failures.
- Equipment failures.
- Epidemics or pandemics, such as COVID-19.
- Terrorist attacks or biochemical threats.
- Industrial accidents.
- Hurricanes.
- Earthquakes.
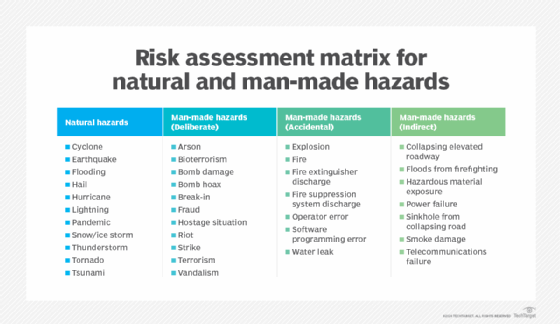
Why is disaster recovery important?
Disasters can inflict damage with varying levels of severity, depending on the scenario. A brief network outage could result in frustrated customers and some loss of business to an e-commerce system. A hurricane or tornado could destroy an entire manufacturing facility, data center or office.
Also, the shift to public, private, hybrid and multi-cloud systems and the rise of remote workforces are making IT infrastructures more complex and potentially risky. An effective disaster recovery plan lets organizations respond promptly to disruptive events, offering the following benefits in return:
This article is part of
What is BCDR? Business continuity and disaster recovery guide
- Which also includes:
- 7 top business continuity certifications to consider in 2024
- ITGC audit checklist: 6 controls you need to address
- 12 key points a disaster recovery plan checklist must include
- Business continuity. Disasters can significantly harm business operations, incurring costs and disrupting productivity. A DR plan enables automation and the swift restart of backup systems and data, ensuring a prompt resumption of scheduled operations.
- Data loss reduction. A well-designed disaster recovery plan aims to reduce the amount of data lost by using methods such as frequent backups, quick recovery and redundancy checks. The probability of data loss increases with the length of time an organization experiences a system outage, but effective DR planning reduces this risk.
- Cost reduction. The monetary costs of disasters and outages can be significant. According to results from Uptime Institute's "Annual outage analysis 2023" survey , 25% of respondents reported in 2022 that their latest outage incurred more than $1 million in direct and indirect costs, indicating a consistent upward trend in expenses. In addition, 45% reported that the cost of their most recent outage ranged between $100,000 and $1 million. With disaster recovery procedures in place, companies can get back on their feet quickly after outages, reducing recovery and operational costs.
- Help with compliance regulations. Many businesses are required to create and follow plans for disaster recovery, business continuity and data protection to meet compliance regulations. This is particularly important for organizations operating in the financial, healthcare, manufacturing and government sectors. Failure to have DR procedures in place can result in legal or regulatory penalties, so understanding how to comply with resilience standards is important.
- System security. A business can reduce the detrimental effects of ransomware, malware and other security threats by incorporating data protection, backup and restoration procedures into a disaster recovery plan. For instance, several built-in security mechanisms in cloud data backups can minimize questionable activity before it affects the company.
- Improved customer retention. When a disaster strikes, customer confidence in an organization's security and services can be questioned and easily lost. A solid disaster recovery plan, including employee training for handling inquiries, can boost customer assurance by demonstrating that the company is prepared for any disaster.
- Emergency preparedness. Thinking about disasters before they happen and creating a response plan can provide many benefits. It raises awareness about potential disruptions and helps an organization prioritize its mission-critical functions. It also provides a forum for discussing these topics and making careful decisions about how to best respond in a low-pressure setting. While preparing for every potential disaster might seem extreme, the COVID-19 pandemic illustrated that even scenarios that seem farfetched can happen. For example, businesses with emergency measures to support remote work had a clear advantage over unprepared companies when stay-at-home orders were enacted during the pandemic.
DR initiatives are more attainable by businesses of all sizes today due to widespread cloud adoption and the high availability of virtualization technologies that make backup and replication easier. However, much of the terminology and best practices developed for DR were based on enterprise efforts to re-create large-scale physical data centers. This involved plans to transfer, or failover , workloads from a primary data center to a secondary location or DR site to restore data and operations.
What is the difference between disaster recovery and business continuity?
On a practical level, DR and business continuity are often combined into a single corporate initiative and even abbreviated together as BCDR , but they aren't the same thing. While the two disciplines have similar goals relating to an organization's resilience, they differ greatly in scope.
Key points of DR and business continuity include the following:
- BC is a proactive discipline intended to minimize risk and help ensure the business can continue to deliver its products and services no matter the circumstances. It focuses especially on how employees continue to work and how the business continues operations while a disaster is occurring.
- DR is a subset of business continuity that focuses on the IT systems that enable business functions. It addresses the specific steps an organization must take to recover and resume technology operations following an event.
- BC is also closely related to business resilience , crisis management and risk management, but each of these disciplines has different goals and parameters.
- DR measures could typically include developing extra safety precautions for employees, such as buying emergency supplies or holding fire drills.
- A business continuity plan helps guarantee that communication channels, including phones and network servers, stay operational during a disaster.
- DR is also a reactive process by nature. While planning for it must be done in advance, DR activity isn't kicked off until a disaster actually occurs.
- Business continuity ensures the overall functioning and resilience of an organization throughout the entirety of an event, rather than solely focusing on the immediate aftermath.
- The disaster recovery process is complete once systems fail over to backup systems and are finally restored. With business continuity, plans stay in place for the entirety of the event and even after the systems are back up following the disaster.
- Top of Form
Elements of a disaster recovery strategy
Organizations should consider several factors while developing a disaster recovery strategy. Common elements of a DR strategy include the following:
Risk analysis
Risk analysis, or risk assessment , is an evaluation of all the potential risks the business could face, as well as their outcomes. Risks can vary greatly depending on the industry the organization is in and its geographic location. The assessment should identify potential hazards, determine whom or what these hazards would harm, and use the findings to create procedures that take these risks into account.
Business impact analysis
A business impact analysis ( BIA ) evaluates the effects of the identified risks on business operations. A BIA can help predict and quantify costs, both financial and nonfinancial. It also examines the effects of different disasters on an organization's safety, finances, marketing, business reputation, legal compliance and quality assurance.
Understanding the difference between risk analysis and BIA and conducting the assessments can also help an organization define its goals when it comes to data protection and the need for backup. Organizations generally quantify these using measurements called recovery point objective ( RPO ) and recovery time objective ( RTO ).
- RPO. RPO is the maximum age of files that an organization must recover from backup storage for normal operations to resume after a disaster. The RPO determines the minimum frequency of backups. For example, if an organization has an RPO of four hours, the system must back up at least every four hours.
- RTO. RTO refers to the amount of time an organization estimates its systems can be down without causing significant or irreparable damage to the business. In some cases, applications can be down for several days without severe consequences. In others, seconds can do substantial harm to the business.
RPO and RTO are both important elements in disaster recovery, but the metrics have different uses. RPO is acted on before a disruptive event takes place to ensure data is backed up, while RTO comes into play after an event occurs.
Incident response
This encompasses detecting, containing, analyzing and resolving a disruptive event. Incident response includes activating the disaster recovery plan, evaluating the incident's scope and effect, executing the recovery strategy, restoring normal operations and deactivating the plan. To maintain accountability and promote ongoing improvement, it's also essential to record and report incident response actions and results.
The components of a DR strategy can vary depending on the size, industry and particular demands of an organization. Therefore, these plans should be customized to meet the unique requirements of each business.
What's in a disaster recovery plan?
Once an organization has thoroughly reviewed its risk factors , recovery goals and technology environment, it can write a disaster recovery plan. The DR plan is the formal document that specifies these elements and outlines how the organization will respond when disruption or disaster occurs. The plan details recovery goals including RTO and RPO, as well as the steps the organization will take to minimize the effects of the disaster.
A DR plan should include the following components:
- A DR policy statement, plan overview and main goals of the plan.
- Key personnel and DR team contact information.
- A risk assessment and BIA to identify potential threats, vulnerabilities and negative effects on business.
- An updated IT inventory that includes details on hardware, software assets and essential cloud computing services, specifying their business-critical status and ownership, such as owned, leased or utilized as a service.
- A plan outlining how backups will be carried out along with an RPO that states the frequency of backups and an RTO that defines the maximum downtime that's acceptable after a disaster.
- A step-by-step description of disaster response actions immediately following an incident.
- A diagram of the entire network and recovery site.
- Directions for how to get to the recovery site.
- A list of software and systems that staff will use in the recovery.
- Sample templates for a variety of technology recoveries, including technical documentation from vendors.
- A communication that includes internal and external contacts, as well as a boilerplate for dealing with the media.
- A summary of insurance coverage.
- Proposed actions for dealing with financial and legal issues.
An organization should consider its DR plan a living document. It should schedule regular disaster recovery testing to ensure the plan is accurate and will work when a recovery is required. The plan should also be evaluated against consistent criteria whenever there are changes in the business or IT systems that could affect disaster recovery.
How to build a disaster recovery team
A DR team is entrusted with creating, documenting and carrying out processes and procedures for an organization's data recovery and business continuity in the event of a disaster or failure.
The key steps and considerations for building a disaster recovery team include the following:
- Identify the key stakeholders. Determine who within the organization should be involved in the disaster recovery planning process. A DR team typically includes cross-departmental employees and executives, such as the chief information officer , IT personnel, department heads, business continuity experts, impact assessment and recovery advisors and crisis management coordinators.
- Define roles and responsibilities. Once the members of the DR team are determined, the next step is to assign them specific roles and responsibilities to ensure effective management of the recovery process. Common roles include team leaders, IT experts, business continuity experts, disaster recovery coordinators and department liaisons.
- Assess expertise. If the organization lacks internal expertise, it can outsource or engage a service provider. These providers can offer external expertise to aid the team, deliver disaster recovery as a service ( DRaaS ), or provide consulting services to bolster the capabilities of the internal team.
- Develop a recovery plan. The team should outline a detailed disaster recovery plan that outlines procedures for responding to various types of disasters. This plan should include steps for data backup and recovery, system restoration, communication protocols and employee safety procedures.
- Train team members. It's important to teach and train team members on their responsibilities within the disaster recovery strategy. This could entail doing frequent drills and simulations to evaluate the plan's efficacy and pinpointing areas in need of development. For example, this could include testing all apps and finding ways to access the critical ones in the event of a disaster.
- Regularly revise the DR plan. The disaster recovery plan needs to be reviewed and updated regularly to reflect organizational changes and how they affect the recovery process.
- Document the procedures. All procedures and protocols within the DR plan should be documented in a clear and accessible format. This ensures that team members can easily reference and follow the necessary steps during a crisis.
Disaster recovery sites
An organization uses a DR site to recover and restore its data, technology infrastructure and operations when its primary data center is unavailable. DR sites can be internal, external or cloud-based.
An organization sets up and maintains an internal DR site. Organizations with large information requirements and aggressive RTOs are more likely to use an internal DR site, which is typically a second data center. When building an internal site, the business must consider hardware configuration, supporting equipment, power maintenance, heating and cooling of the site, layout design, location and staff.
An external disaster recovery site is owned and operated by a third-party provider. External sites can be hot, warm or cold.
- Hot site. A hot site is a fully functional data center with hardware and software, personnel and customer data, which is typically staffed 24/7 and operationally ready in the event of a disaster.
- Warm site. A warm site is an equipped data center that doesn't have customer data. An organization can install additional equipment and introduce customer data following a disaster.
- Cold site. This type of site has infrastructure to support IT systems and data, but no technology until an organization activates DR plans and installs equipment. These sites are sometimes used to supplement hot and warm sites during a long-term disaster.
A cloud-based disaster recovery site is another option, which is also scalable. An organization should consider site proximity, internal and external resources, operational risks, service-level agreements (SLAs) and cost when contracting with cloud providers to host their DR assets or outsourcing additional services .
Disaster recovery tiers
In addition to choosing the most appropriate DR site, it can be helpful for organizations to consult the tiers of disaster recovery identified by the Share Technical Steering Committee and IBM in the 1980s. The tiers feature a variety of recovery options organizations can use as a blueprint to help determine the best DR approach depending on their business needs.
The recognized disaster recovery tiers include the following:
- Tier 7. Tier 7 is a highly advanced level of disaster recovery capability. At this level, artificial intelligence and automation are likely to play a key part in the recovery process.
- Tier 6. Tier 6 disaster recovery capabilities are comparable to Tier 5's, but they often include even more sophisticated technology and techniques for rapid recovery and minimal data loss.
- Tier 5. Tier 5 often implies advanced disaster recovery capabilities beyond a hot site. This can include capabilities such as real-time data replication , automated failover and enhanced monitoring and administration tools.
- Tier 4. This tier includes a hot site, which is a DR site that's fully functioning and ready to use. Hot sites replicate the primary data center's systems and operations in real time, enabling quick failover and minimal downtime. They provide the maximum availability and recovery speed, but they're also the most expensive alternative.
- Tier 3. By electronically vaulting mission-critical data, Tier 3 options improve upon the capabilities of Tier 2. Electronic vaulting of data involves electronically transferring data to a backup site, in contrast to the traditional method of physically shipping backup tapes or disks. After a disaster, there's less chance of data loss or re-creation because the electronically vaulted data is usually more recent than data sent through conventional means.
- Tier 2. This tier improves upon Tier 1 with the addition of a hot site, which are disaster recovery locations that have hardware and network infrastructure already set up to facilitate faster recovery times. There might still be a need for additional setup and configuration.
- Tier 1. This level consists of cold sites that provide basic infrastructure but lack preinstalled systems. Businesses in this category have data backups, but recovery involves manual intervention and hardware configuration, which lengthens recovery times.
- Tier 0. This tier denotes the lowest preparedness level and is usually associated with organizations that don't have disaster recovery or off-site data backups . Because recovery in this tier is entirely dependent on on-site technologies, recovery times can be unpredictable.

Another type of DR tiering involves assigning levels of importance to different types of data and applications and treating each tier differently based on the tolerance for data loss. This approach recognizes that some mission-critical functions might not be able to tolerate any data loss or downtime, while others can be offline for longer or have smaller sets of data restored.
Types of disaster recovery
In addition to choosing a DR site and considering DR tiers, IT and business leaders must evaluate the best way to put their DR plan into action. This will depend on the IT environment and the technology the business chooses to support its DR strategy.
Types of disaster recovery can vary, based on the IT infrastructure and assets that need protection, as well as the method of backup and recovery the organization decides to use. Depending on the size and scope of the organization, it might have separate DR plans and response and resilience teams specific to different departments.
Major types of DR include the following:
- Data center disaster recovery. Organizations that house their own data centers must have a DR strategy that considers all the IT infrastructure within the data center as well as the physical facility. Backup to a failover site at a secondary data center or a colocation facility is often a large part of the plan. IT and business leaders should also document and make alternative arrangements for a wide range of facilities-related components, including power systems, heating and cooling, fire safety, and physical security.
- Network disaster recovery. Network connectivity is essential for internal and external communication, data sharing, and application access during a disaster. A network DR strategy must provide a plan for restoring network services, especially in terms of access to backup sites and data.
- Virtualized disaster recovery. Virtualization provides disaster recovery by letting organizations replicate workloads in an alternate location or the cloud. The benefits of virtual DR include flexibility, ease of deployment, efficiency and speed. Since virtualized workloads have a small IT footprint, replication can be done frequently, and failover can be initiated quickly.
- Cloud disaster recovery. The widespread acceptance of cloud services lets organizations, typically reliant on alternate or on-premises DR locations, host their disaster recovery in the cloud. Cloud DR goes beyond simple backup to the cloud. It requires an IT team to set up automatic failover of workloads to a public cloud platform in the event of a disruption.
- DRaaS. DRaaS is the commercially available version of cloud DR. In DRaaS, a third party provides replication and hosting of an organization's physical and virtual machines. The provider assumes responsibility for deploying the DR plan when a crisis arises, based on an SLA. In the event of a disaster, the DRaaS provider shifts an organization's computer processing to its cloud infrastructure. This enables uninterrupted business operations to be carried out seamlessly from the provider's location, even if the organization's servers are offline.
- Point-in-time snapshots. Point-in-time snapshots or copies generate a precise replica of the database at a specific time. Data recovery from these backups is possible, provided they're stored offsite or on an external machine unaffected by the catastrophe.
Disaster recovery services and vendors
Disaster recovery providers can take many forms, as DR is more than just an IT issue, and business continuity affects the entire organization. DR vendors include those selling backup and recovery software, as well as those offering hosted or managed services. Because disaster recovery is also an element of organizational risk management, some vendors couple it with other aspects of security planning, such as incident response and emergency planning.
Examples of options for DR services and vendors include the following:
- Backup and data protection platforms.
- DRaaS providers.
- Add-on services from data center and colocation providers.
- Infrastructure-as-a-service providers.
Choosing the best option for an organization ultimately depends on top-level business continuity plans and data protection goals, as well as which option best meets those needs and budgetary goals.
Examples of DR software and DRaaS providers include the following:
- Acronis Cyber Protect Cloud.
- Carbonite Disaster Recovery.
- Dell EMC RecoverPoint.
- Druva Data Resiliency Cloud.
- IBM Storage Protect Plus.
- Microsoft Azure Site Recovery.
- Unitrends Backup and Recovery.
- Veeam Backup & Replication.
- VMware Live Cyber Recovery (formerly known as VMware Cloud DR).
Emergency communication vendors are also a key part of the disaster recovery process, as they help keep employees informed during a crisis by sending them notifications and communications. Examples of vendors and their systems include AlertMedia, BlackBerry AtHoc, Cisco Emergency Responder, Everbridge Crisis Management and Rave Alert.
Download a free SLA template for use with disaster recovery products and services .
While some organizations might find it challenging to invest in comprehensive disaster recovery planning, none can afford to ignore the concept when planning for long-term growth and sustainability. In addition, if the worst were to happen, organizations that have prioritized DR would experience less downtime and be able to resume normal operations faster.
Businesses often prepare for minor disruptions, but it's easy to overlook larger and more intricate disasters. Examine the top scenarios for IT disasters that disaster recovery teams should test vigorously.
Continue Reading About disaster recovery (DR)
- SME disaster recovery: Key points to consider
- Game-changing disaster recovery trends
- Maximize the benefits of virtual disaster recovery
- Real-life business continuity failures: Examples to study
- Disaster recovery plan best practices for any business
Related Terms
Dig deeper on disaster recovery planning and management.

Get the most out of Azure Site Recovery DRaaS

Define RPO and RTO tiers for storage and data protection strategy

IT resilience management, planning top of mind for DR pros

The tiers of disaster recovery, explained

The capacity of LTO tape breaks records yet again in annual shipments, but it might be the increase in density more than new ...
Veeam products and services in the spotlight at the VeeamON 2024 user conference included secure backups in the cloud, a ...
After going public in April, Rubrik is returning to its roots, saying additions to its Rubrik Security Cloud platform are all in ...
As the focus for enterprise AI spreads beyond compute, Western Digital introduces a new SSD and HDD. It also released an AI ...
This HPE Discover 2024 conference guide will cover event news from June 17 to 20. There will be three new programs: edge and ...
Explore this updating guide on Dell Technologies World 2024. The show will shine a major spotlight on AI, but also cover topics ...
APIs are essential, but hackers find them attractive targets. A comprehensive API risk assessment strategy helps you identify ...
Threat actors are targeting vulnerable Progress Telerik Report Server systems just days after a proof of concept was published ...
The public sector took the brunt of ransomware in May, while another damaging attack against a healthcare company disrupted ...
As U.S. states like Colorado pass their own AI laws, businesses will need to prepare compliance measures if they do business in ...
Digital transformation success requires cross-organizational alignment, actionable goals and top-notch project management. Here's...
President Joe Biden throws his support behind Microsoft to build an AI data center in Racine, Wis., as big tech companies invest ...

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Embarking on an entrepreneurial journey is exciting for kids, offering them a unique opportunity to learn valuable life skills such as problem-solving, financial literacy, and creativity. Creating a business plan is a foundational step in this journey, helping young entrepreneurs transform their ideas into actionable plans. This guide is designed to make the process engaging […]
Business Plan for Kids. Teach your students how to write their own business plan and create a successful business. Download the Sample Business Plan for Kids. More Business Planning Resources. The 4 p's of marketing. Learn how to market your business with product, pricing, promoting and placement.
Here's my full review of the Teen Entrepreneur Toolbox. 4. Proverbial Home Maker's Family Business Plan Guide. This is such a fun guide that you can fill out with your child, teen, tween, or even the whole family. It includes family business ideas, a sales ledger, an inventory worksheet, and much more.
Write the business name at the top of the paper, then write a business description a few spaces down. All you need for this is a short paragraph that describes your business idea, objectives and goals. If you've created a business logo, put it on the cover sheet, as well. Aim for 5-6 sentences.
When you plan a business, you must know what your competitors offer to gain a competitive edge. Some of the items you should include in your competitor analysis are: A product list for each competitor. A price list for each product, for each competitor. The needs that each competitor fulfils in the target market. A list of the gaps in the market.
If your child's thinking of starting a business, help them prepare by making a business plan. A business plan is not just a tool to attract investors. Or a roadmap to navigate the inevitable ups and downs — as well as the unexpected issues you might encounter along the way. Making a business plan will also help your child see if an idea's ...
Plan the Budget & Financial Projections. This stage talks about the financial plan or the money-phase. It teaches your kid about business revenue, profit, ongoing expenses, financial projections, and more.
Proverbial Homemaker's Family Business Plan Guide. Families can work together to build a business that kids and teens can run themselves and are passionate about running using this comprehensive business template and associated resources. Consider first why you want to start a business and why you are choosing THIS specific business.
As a kid entrepreneur planning to start a business, you are new to the concept of business and the best way to understand it and write your business plan is to download a free business plan template, go through it and understand the right way to write a business plan. A business plan template will help organize your thoughts and direct you in ...
What is a business plan? A business plan is a written document that describes an idea for a product or service and how it will make money. It includes your marketing plan as well as estimates for revenue, expenses, and how to make a pro˜t. Why do I need this? A business plan is like a roadmap. It allows you to plan out the various aspects of ...
Kids' Guide To Business Table Of Contents Introduction This book takes a unique approach to discussing business. The author talks to parents and kids and hopes both will participate in the activities and discussions throughout this book. A key to teaching kids business is to respect kids and include them in discussions about business.
A business plan is important to people who want to start their own businesses. This business plan template for kids will serve as a guide to understand how entrepreneurs use business plans to keep them from making mistakes.. See the fact file below for more information on Business Plan Template or alternatively, you can download our 19-page Business Plan Template for Kids worksheet pack to ...
A good template should show you the areas that you need to cover in the plan and provide you with questions that should be answered throughout the plan. We are exposing you to business planning to help you understand the many things that have to be considered when developing and managing a business. As you experience your own business start-up ...
Invest! Inspire your 10+ year old kids to become millionaires with our best-selling money book. Brought to you by the creators of Biz Kid$ and Bill Nye The Science Guy, this book gets 5 stars from thousands of Amazon readers. Bonus content for parents includes video clips, digital tools, and full episodes that bring the money lessons to life.
A business plan is to business what a map and a travel plan (packing, money, food, accommodation etc.) is to a long road trip in a car. If you want to obtain your goals (get there) you need to give some thought to figure out the best way or options to take. You will be surprised at how often you use components of business planning in regular ...
THE ULTIMATE BUSINESS PLAN FOR KIDS TO HELP THEM START OR GROW A BIZ. The Startup Squad May 6, 2021. With some advance planning, your kids can set their business goals and achieve their entrepreneurial dreams. Starting a business has to start somewhere. And that 'somewhere' can be found in a plan. To be specific, a business plan; a road map ...
How to Write a Kids Business Plan in 7 Steps: 1. Describe the Purpose of Your Kids Business. The first step to writing your business plan is to describe the purpose of your kids business. This includes describing why you are starting this type of business, and what problems it will solve for customers. This is a quick way to get your mind ...
Business Plan: A business plan is a written document that describes in detail how a business, usually a new one, is going to achieve its goals. A business plan lays out a written plan from a ...
If your child's thinking of starting a business, help them prepare by making a business plan. A business plan is not just a tool to attract investors. Or a roadmap to navigate the inevitable ups and downs - as well as the unexpected issues you might encounter along the way. Making a business plan will also help your child see if an idea's ...
Definition. A business plan is a detailed written document that describes your business's activities, goals, and strategy. A strong plan outlines everything from the products a company sells to the executive summary to the overall management. In essence, a business plan should guide a founder's actions through each stage of growth.
This section of the plan should describe the following requirements of your business: Manufacturing. R&D. Purchasing. Staffing. Equipment. Facilities. Note: Provide a rollout strategy as to when these requirements need to be purchased and implemented. In addition, describe the vendors you will need to build the business.
The Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries and its allies — a group of leading oil producers known as OPEC+ — agreed Sunday to extend production cuts announced last year into 2025.
Explore the different elements of a business plan and see why it's crucial to develop a plan before starting a business. Lesson . Money Math - Who Needs It? ... Biz Kid$ demystifies the process of getting a credit card, how to use it correctly, and explains terms like credit score and APR. Lesson .
Adam Dobrinich. A standard essay helper is an expert we assign at no extra cost when your order is placed. Within minutes, after payment has been made, this type of writer takes on the job. A standard writer is the best option when you're on a budget but the deadline isn't burning. Within a couple of days, a new custom essay will be done ...
Overview. Our mission is to assist Pennsylvanians in leading safe, healthy, and productive lives through equitable, trauma-informed, and outcome-focused services while being an accountable steward of commonwealth resources. Report Abuse or Neglect. Report Assistance Fraud. Program Resources & Information.
backup and recovery testing: A backup and recovery test is the process of assessing the effectiveness of an organization's software and methods of replicating data for security and its ability to reliably retrieve that data should the need arise.