
- About NuWrite
- Writing Advice
- Engineering & Design
- First-Year Seminars
- Global Health
- 2010 Senior Thesis Prep Guide (B. Zakarin 2010)
- Local Library Collections (for Humanities research) (B. Zakarin 2010)
- solving-problems-in-history-proposal-research
- writing-history-proposals
- Science Writing
- Social Science Writing
- Writing for Graduate or Professional School
- Writing Advice for International Students
- Faculty-Only Resources

Effective Proposal-Writing Style (for History students)
Contributed by B. Zakarin, Office of Fellowships, [email protected] Posted: 2010 Originally written for History students writing proposals for a senior honors thesis, but applicable to all proposal writing
printable file (Word)
Personal pronouns
Writers use first person (“I,” “my”) when discussing their own interests and plans. This is appropriate in a research proposal because you will be admitted to the Senior Thesis Program and/or awarded a summer grant.
Well-organized paragraphs and headings
For the most part, writers use topic sentences to signal a paragraph’s key point. That point often corresponds to a required element, such as “what I want to learn,” “what scholars have previously studied,” or “where I plan to find sources.” Writers then add details that explain the topic sentence or argue the point it makes. Also, paragraphs should not be overly long.
In addition to well-organized paragraphs, writers sometimes use headings to identify key sections. Such organization is helpful because readers often skim the beginnings of sections and paragraphs to find a proposal’s main argument before they go back for details. Headings and topic sentences highlight a proposal’s structure.
Action-Oriented sentences
A preponderance of sentences should use active voice. In other words, sentences emphasize who (or what) performs the action:
- My project will use…
- The current literature does not show…
- I contend…
- I have prepared for this work by…
- To answer these questions, I will analyze…
- This project will allow me to…
- This study focuses on…
- Bibliographies mention…
- I need to visit…
Active voice makes sentences shorter and clearer and makes writers sound confident. Use passive voice when you have a legitimate reason for doing so, such as when the actor is not important or when passive voice promotes coherence. Consider these examples from the model proposals:
- “Several Connecticut newspapers circulated in Windham were known for their extreme zealotry.” It is not necessary for Alex Jarrell to say that the public knew these newspapers for their zealotry.
- “In the 18 th century, prostitutes were increasingly considered to be outside the sphere of womanhood. In the late 1760s, 2069 women were arrested.” Who “considered” or “arrested” the women is obvious and unimportant for Arianne Urus’s purposes.
- “Elisabeth Julie Lacroix, for example, was a 49-year-old woman arrested in 1778, who had been abandoned by her husband, out of work four to five days, and without food for one day. Her story is replicated countless times…” Arianne’s use of the passive voice allows her to keep the focus on Elisabeth’s story.
Active or passive voice is only an issue with action (transitive) verbs, which have objects. Some sentences simply use state-of-being (intransitive) verbs, such as “is” or “was”:
- “The New London Gazette is available at the Northwestern Library on microfilm.” ( Alex )
- “Martin Luther King’s status in the community was under fire.” ( Casey Kuklick )
These intransitive verbs are often necessary, but in a well-written proposal, active verbs in the active voice will dominate.
Conciseness
Good proposal writers explain their ideas as succinctly as possible. Most writers start with a proposal that is a little too long. Then they solicit help from advisors and peer reviewers to trim the fat. Along with unnecessary background information, you should be vigilant about clunky phrases and excessive qualifying words. The following strategies for revision will help.
- Change passive to active voice (see above)
- Wordy: “It is these three facts that call Jones’s theory into question.” Concise: “These three facts call Jones’s theory into question.”
- Wordy: “There were numerous laws in the 1890s that led to the arrests.” Concise: “Numerous laws in the 1890s led to the arrests.”
- Wordy: “It is my contention in this proposal that…” Concise: “In this proposal, I contend that…”
- Wordy: “It is the belief of most scholars that…” Concise: “Most scholars believe that…”
- Wordy: “This project focuses on the analysis of…” Concise: “This project will analyze…”
- Wordy: “Identification and evaluation of the first problem are necessary for resolution of the second.” Concise: “We must identify and evaluate the first problem before we can resolve the second.”
- Wordy: “Most critics are in agreement with this assessment.” Concise: “Most critics agree with this assessment.”
- Wordy: “at this point in time” Concise: “now”
- Wordy: “due to the fact that” Concise: “because”
- Wordy: “at a later time” Concise: “later” or “next” or “then”
- Wordy: “for the purpose of” (as in “for the purpose of determining”) Concise: “for” or “to” (as in “for determining” or “to determine”)
- Wordy: “a majority of” Concise: “most”
Effective use of transitions
Transitional words and phrases show how sentences and ideas are related to each other. Used correctly, they make it easier for readers to follow your argument. The following transitions at or near the beginnings of sentences will make your logic come through clearly and coherently to readers.
- To show results —“therefore,” “as a result,” “consequently,” “thus,” “hence.”
- To show addition —“moreover,” “furthermore,” “also,” “too,” “besides,” “in addition.”
- To show similarity —“likewise,” “also,” “similarly.”
- To show contrast —“however,” “but,” “yet,” “still,” “conversely,” “nevertheless,” “on the other hand” (if you have used “on the one hand” previously).
- To show examples —“for example,” “for instance,” “specifically,” “as an illustration.”
- To show sequence or tim e—“first,” “second,” “third”; “previously,” “now,” “finally,” “later”; “next,” “then.”
- To show spatial relations —“on the east,” “on the west”; “left,” “right”; “close up,” “far away.”
Repetition and parallelism
As the model proposals show, it is often effective to repeat key terms and phrases: “I will pursue research in three areas…; I will travel to X in July in order to…; I will then go to Y so that I can…“ The repetition in these sentences helps readers focus on the student’s proposed actions.

- Contact Northwestern University
- Campus Emergency Information
- University Policies
Northwestern University Library | 1970 Campus Drive, Evanston, IL 60208-2300 | Phone: 847.491.7658 | Fax: 847.491.8306 | Email: [email protected]

The Princeton Guide to Historical Research
- Zachary Schrag
50% off with code FIFTY
Before you purchase audiobooks and ebooks
Please note that audiobooks and ebooks purchased from this site must be accessed on the Princeton University Press app. After you make your purchase, you will receive an email with instructions on how to download the app. Learn more about audio and ebooks .
Support your local independent bookstore.
- United States
- United Kingdom
The essential handbook for doing historical research in the twenty-first century
- Skills for Scholars

- Look Inside
- Request Exam Copy
- Download Cover
The Princeton Guide to Historical Research provides students, scholars, and professionals with the skills they need to practice the historian’s craft in the digital age, while never losing sight of the fundamental values and techniques that have defined historical scholarship for centuries. Zachary Schrag begins by explaining how to ask good questions and then guides readers step-by-step through all phases of historical research, from narrowing a topic and locating sources to taking notes, crafting a narrative, and connecting one’s work to existing scholarship. He shows how researchers extract knowledge from the widest range of sources, such as government documents, newspapers, unpublished manuscripts, images, interviews, and datasets. He demonstrates how to use archives and libraries, read sources critically, present claims supported by evidence, tell compelling stories, and much more. Featuring a wealth of examples that illustrate the methods used by seasoned experts, The Princeton Guide to Historical Research reveals that, however varied the subject matter and sources, historians share basic tools in the quest to understand people and the choices they made.
- Offers practical step-by-step guidance on how to do historical research, taking readers from initial questions to final publication
- Connects new digital technologies to the traditional skills of the historian
- Draws on hundreds of examples from a broad range of historical topics and approaches
- Shares tips for researchers at every skill level
Skills for Scholars: The new tools of the trade
Awards and recognition.
- Winner of the James Harvey Robinson Prize, American Historical Association
- A Choice Outstanding Academic Title of the Year

- Introduction: History Is for Everyone
- History Is the Study of People and the Choices They Made
- History Is a Means to Understand Today’s World
- History Combines Storytelling and Analysis
- History Is an Ongoing Debate
- Autobiography
- Everything Has a History
- Narrative Expansion
- From the Source
- Public History
- Research Agenda
- Factual Questions
- Interpretive Questions
- Opposing Forces
- Internal Contradictions
- Competing Priorities
- Determining Factors
- Hidden or Contested Meanings
- Before and After
- Dialectics Create Questions, Not Answers
- Copy Other Works
- History Big and Small
- Pick Your People
- Add and Subtract
- Narrative versus Thematic Schemes
- The Balky Time Machine
- Local and Regional
- Transnational and Global
- Comparative
- What Is New about Your Approach?
- Are You Working in a Specific Theoretical Tradition?
- What Have Others Written?
- Are Others Working on It?
- What Might Your Critics Say?
- Primary versus Secondary Sources
- Balancing Your Use of Secondary Sources
- Sets of Sources
- Sources as Records of the Powerful
- No Source Speaks for Itself
- Languages and Specialized Reading
- Choose Sources That You Love
- Workaday Documents
- Specialized Periodicals
- Criminal Investigations and Trials
- Official Reports
- Letters and Petitions
- Institutional Records
- Scholarship
- Motion Pictures and Recordings
- Buildings and Plans
- The Working Bibliography
- The Open Web
- Limits of the Open Web
- Bibliographic Databases
- Full-Text Databases
- Oral History
- What Is an Archive?
- Archives and Access
- Read the Finding Aid
- Follow the Rules
- Work with Archivists
- Types of Cameras
- How Much to Shoot?
- Managing Expectations
- Duck, Duck, Goose
- Credibility
- Avoid Catastrophe
- Complete Tasks—Ideally Just Once, and in the Right Order
- Maintain Momentum
- Kinds of Software
- Word Processors
- Means of Entry
- A Good Day’s Work
- Word Count Is Your Friend
- Managing Research Assistants
- Research Diary
- When to Stop
- Note-Taking as Mining
- Note-Taking as Assembly
- Identify the Source, So You Can Go Back and Consult if Needed
- Distinguish Others’ Words and Ideas from Your Own
- Allow Sorting and Retrieval of Related Pieces of Information
- Provide the Right Level of Detail
- Notebooks and Index Cards
- Word Processors for Note-Taking
- Plain Text and Markdown
- Reference Managers
- Note-Taking Apps
- Relational Databases
- Spreadsheets
- Glossaries and Alphabetical Lists
- Image Catalogs
- Other Specialized Formats
- The Working Draft
- Variants: The Ten- and Thirty-Page Papers
- Thesis Statement
- Historiography
- Sections as Independent Essays
- Topic Sentences
- Answering Questions
- Invisible Bullet Points
- The Perils of Policy Prescriptions
- A Model (T) Outline
- Flexibility
- Protagonists
- Antagonists
- Bit Players
- The Shape of the Story
- The Controlling Idea
- Alchemy: Turning Sources to Stories
- Turning Points
- Counterfactuals
- Point of View
- Symbolic Details
- Combinations
- Speculation
- Is Your Jargon Really Necessary?
- Defining Terms
- Word Choice as Analysis
- Period Vocabulary or Anachronism?
- Integrate Images into Your Story
- Put Numbers in Context
- Summarize Data in Tables and Graphs
- Why We Cite
- Citation Styles
- Active Verbs
- People as Subjects
- Signposting
- First Person
- Putting It Aside
- Reverse Outlining
- Auditing Your Word Budget
- Writing for the Ear
- Conferences
- Social Media
- Coauthorship
- Tough, Fair, and Encouraging
- Manuscript and Book Reviews
- Journal Articles
- Book chapters
- Websites and Social Media
- Museums and Historic Sites
- Press Appearances and Op-Eds
- Law and Policy
- Graphic History, Movies, and Broadway Musicals
- Acknowledgments
"This volume is a complete and sophisticated addition to any scholar’s library and a boon to the curious layperson. . . . [A] major achievement."— Choice Reviews
"This book is quite simply a gem. . . . Schrag’s accessible style and comprehensive treatment of the field make this book a valuable resource."—Alan Sears, Canadian Journal of History
"A tour de force that will help all of us be more capable historians. This wholly readable, delightful book is packed with good advice that will benefit seasoned scholars and novice researchers alike."—Nancy Weiss Malkiel, author of "Keep the Damned Women Out": The Struggle for Coeducation
"An essential and overdue contribution. Schrag's guide offers a lucid breakdown of what historians do and provides plenty of examples."—Jessica Mack, Roy Rosenzweig Center for History and New Media, George Mason University
"Extraordinarily useful. If there is another book that takes apart as many elements of the historian's craft the way that Schrag does and provides so many examples, I am not aware of it."—James Goodman, author of But Where Is the Lamb?
"This is an engaging guide to being a good historian and all that entails."—Diana Seave Greenwald, Assistant Curator of the Collection, Isabella Stewart Gardner Museum
"Impressive and engaging. Schrag gracefully incorporates the voices of dozens, if not hundreds, of fellow historians. This gives the book a welcome conversational feeling, as if the reader were overhearing a lively discussion among friendly historians."—Sarah Dry, author of Waters of the World: The Story of the Scientists Who Unraveled the Mysteries of Our Oceans, Atmosphere, and Ice Sheets and Made the Planet Whole
"This is a breathtaking book—wide-ranging, wonderfully written, and extremely useful. Every page brims with fascinating, well-chosen illustrations of creative research, writing, and reasoning that teach and inspire."—Amy C. Offner, author of Sorting Out the Mixed Economy
historyprofessor.org website, maintained by Zachary M. Schrag, Professor of History at George Mason University
Stay connected for new books and special offers. Subscribe to receive a welcome discount for your next order.
50% off sitewide with code FIFTY | May 7 – 31 | Some exclusions apply. See our FAQ .
- ebook & Audiobook Cart
- My Account |
- StudentHome |
- TutorHome |
- IntranetHome |
- Contact the OU Contact the OU Contact the OU |
- Accessibility Accessibility
Postgraduate
- International
- News & media
- Business & apprenticeships
Faculty of Arts and Social Sciences
You are here
- School of Arts & Humanities
- Postgraduate Research
Preparing a History PhD proposal
The carefully thought-out and detailed research proposal to be submitted with the formal application is the product of a sometimes prolonged negotiation with your potential supervisor. The supervisor may be enthusiastic about your project or might advise you to consider a different subject or change your angle on it; they may query aspects of your plan such as its breadth, the availability of primary sources or the extent to which you are familiar with the secondary literature. You may be asked to demonstrate the originality of your research question or be advised to consider applying to another institution which may have more appropriate expertise. During this process you will likely be asked to submit a specimen of written-up historical research, such as your Masters or BA dissertation. The sooner you start developing the structure that is expected in a research proposal, the more productive your exchanges with your potential supervisor will be.
You may find different advice for writing a research proposal across different OU webpages. Given that a research proposal can vary significantly across different disciplines, when applying to the History Department you should follow the guidance provided here.
The research proposal you submit in January should be approximately 1000 words, plus a bibliography, and should contain the following:
A title, possibly with a subtitle
The title should not take the form of a question and it may run to a dozen words or more. Like the title of a book, it should clearly convey the topic you propose to work on. A subtitle may explain the chronological or geographical focus of your work, or the methodological approach you will take. Choosing a title is a good way for focusing on the topic you want to investigate and the approach you want to take.
These are examples of poor titles and topics to research:
- Captain Cook’s Third Voyage
- Women in eighteenth-century England
These would be poor topics to research because they lack a strong question and it is not clear which approach they take to their already well-researched subjects. They are generic or merely descriptive.
Examples of good research topics
- Constructing the Eternal City: visual representations of Rome, 1500-1700
- Rearing citizens for the state: manuals for parents in France, 1900-1950
These projects combine a sharp chronological and geographical focus with a clear indication of how the sources will be analysed to respond to a precise question. In the first case, for example, the premise is that visual representations are critical in the making of a city’s eminence. This indicates the type of sources that will be analysed (paintings, engravings and other visual sources). The chronology is particularly well chosen because in these two centuries Rome turned from being the capital of the Catholic world to becoming the much sought-after destination of the Grand Tour; interesting questions of change and continuity come into focus.
Brief summary of your argument
An acceptable PhD thesis must have a central argument, a 'thesis'. You need to have something to argue for or against, a point to prove or disprove, a question to answer. What goes into this section of the proposal is a statement of your question and the answer you plan to give, even if, for now, it remains a hypothesis.
Why this subject is important
We expect originality in a thesis and so under this rubric we expect you to explain why the knowledge you seek on the subject you propose to work on is important for its period and place, or for historians’ views on its period and place. Finding some early-modern English laundry lists would not suffice on its own to justify writing a PhD thesis about them. But those laundry lists could be important evidence for a thesis about the spread of the Great Plague in London, for example.
Framing your research
Your proposal has to show awareness of other scholarly writing on the subject. This section positions your approach to the subject in relation to approaches in some of those works, summarising how far you think it differs. For instance, you could challenge existing interpretations of the end the Cold War, or you might want to support one historian or another; you could open up a neglected aspect of the debate - say by considering the role of an overlooked group or national government - and perhaps kick-start a debate of your own. All this is to show that you have read into your subject and familiarised yourself with its contours. We don’t expect you to have done all your research at the start, but it is essential for you to show familiarity with the key texts and main authors in your chosen field.
What sources might you need to consult in libraries and archives?
Here you should describe or at least list the primary materials you are likely to use in researching your thesis. This demonstrates your confidence that enough relevant sources exist to support a sustained scholarly argument. Many archival catalogues are available online and can be searched remotely, including The National Archives, the National Archives of Scotland, the National Archives (Ireland), the Public Record Office of Northern Ireland and Archives Wales. You can search the London-based Historical Manuscripts Commission and the National Register of Archives, both of which provide access to local county record offices. Databases such as ‘Eighteenth Century Collections Online’ and the British Library’s ‘British Newspapers Online 1600-1900’ will help you identify and locate relevant sources.
What skills are required to work on the sources you plan to use?
You need to show that you have the linguistic competence to pursue your research. With few exceptions, original sources must be read in the original languages; if the principal historical literature is not in English, you must be able to read it too. Palaeographic problems aren’t confined to ancient writing. You might have to tackle early modern or other scripts that are hard to decipher. Even with fluent German, an applicant baffled by the Gothic script and typeface would flounder without undertaking ancillary study. Training is available at The Open University, or in some circumstances you can be funded to undertake training elsewhere, and you should demonstrate awareness of the skills that you need to acquire.
Do you have the technical competence to handle any data-analysis your thesis may require?
Databases, statistical evidence and spreadsheets are used increasingly by historians in certain fields. If your research involves, say, demographic or economic data, you will need to consider whether you have the necessary IT and statistical skills and, if not, how you will acquire them.
How will you arrange access to the libraries and archives where you need to work?
Although primary sources are increasingly available in digitised form, you should consider that important sources may be closed or in private hands. To consult them may require some travelling and so you should be realistic as to what you will be able to do, particularly if you are applying to study part-time as not all archives are open out of regular office hours.
A bibliography
This should come at the end and include a list of the primary sources you plan to use and the relevant secondary literature on the subject. While you should show that you are on top of recent work (and of important older studies) on the topic, there is no point in having a long list of works only marginally related to your subject. As always, specificity is the best policy.
Please follow this link to see an example of a successful research proposal [PDF].
All this may seem daunting, as if the department is asking you to write a thesis before you apply. But that is not our intention; the advice is to help you perform the necessary spadework before entering the formal application process. Working up a proposal under the headings suggested above will, if your application is successful, save you and your supervisor(s) much time if and when the real work begins.
- Study with Us
- News (OU History Blog)

- @history_ou
Request your prospectus
Explore our qualifications and courses by requesting one of our prospectuses today.
Request prospectus
Are you already an OU student?
Go to StudentHome
The Open University
- Study with us
- Supported distance learning
- Funding your studies
- International students
- Global reputation
- Apprenticeships
- Develop your workforce
- Contact the OU
Undergraduate
- Arts and Humanities
- Art History
- Business and Management
- Combined Studies
- Computing and IT
- Counselling
- Creative Writing
- Criminology
- Early Years
- Electronic Engineering
- Engineering
- Environment
- Film and Media
- Health and Social Care
- Health and Wellbeing
- Health Sciences
- International Studies
- Mathematics
- Mental Health
- Nursing and Healthcare
- Religious Studies
- Social Sciences
- Social Work
- Software Engineering
- Sport and Fitness
- Postgraduate study
- Research degrees
- Masters in Art History (MA)
- Masters in Computing (MSc)
- Masters in Creative Writing (MA)
- Masters degree in Education
- Masters in Engineering (MSc)
- Masters in English Literature (MA)
- Masters in History (MA)
- Master of Laws (LLM)
- Masters in Mathematics (MSc)
- Masters in Psychology (MSc)
- A to Z of Masters degrees
- Accessibility statement
- Conditions of use
- Privacy policy
- Cookie policy
- Manage cookie preferences
- Modern slavery act (pdf 149kb)
Follow us on Social media
- Student Policies and Regulations
- Student Charter
- System Status
- Contact the OU Contact the OU
- Modern Slavery Act (pdf 149kb)
© . . .
College of Arts and Sciences
History and American Studies
- What courses will I take as an History major?
- What can I do with my History degree?
- History 485
- History Resources
- What will I learn from my American Studies major?
- What courses will I take as an American Studies major?
- What can I do with my American Studies degree?
- American Studies 485
- For Prospective Students
- Student Research Grants
- Honors and Award Recipients
- Phi Alpha Theta
Alumni Intros
- Internships
A proposal is a chance to explain your topic, discuss the resources critical to your research, and justify the need for your proposed paper.
Proposal Guidelines
Goals of a proposal.
1) Precisely defines your topic and the need for studying it (i.e., it briefly takes apart the topic and tells what one will learn from reading your proposed paper).
2) Explains the sources critical to your proposed research, demonstrating that they are adequate for your project.
1) Narrow and break down your topic and your approach to it as much as possible. (ONE SENTENCE ON THE PROPOSED TOPIC IS NOT ENOUGH.)
2) Discuss the issues and questions which you foresee your paper addressing.
3) To demonstrate your competence, you must exhibit a level of research and thinking suitable for this stage of your work. Remember, you are expected to have done a fair amount of research already. It should indicate that you have done extensive research in library catalogs, databases and the internet.
4) Explain why you are using your secondary and primary sources, to explain which will be especially valuable, and, perhaps, to explain what important sources are not available and are likely to be missing from your paper–and why your topic is manageable nonetheless.
Do not try to cover every source. Provide a useful view of the critical sources that anyone doing your topic must look at. Whether or not you have yet finished your study of them, or you have yet to acquire them, you should have determined which are the critical ones.
In referring to sources, always provide author (full name on first reference) and date of work; generally the full title is also necessary or useful.
5) Exclude irrelevant information. Since the proposal is a discussion of sources and not a research trail, do not include comments about where, in what order, or how you found sources (e.g., in the UMW library or through ILL) or that you are “still waiting” for ILL to provide you with a book.
6) Include a bibliography of relevant sources cited using the Turabian/Chicago Manual of Style citation guidelines . That list of sources should not include finding aids, bibliographies, encyclopedias, or children’s books.
7) Although footnotes/endnotes are not usefully employed in a proposal, you must make clear where your information came from.
8) Use of first-person perspective can be appropriate, but do so only in consultation with your professor.
For general writing guidelines, see here .

How have History & American Studies majors built careers after earning their degrees? Learn more by clicking the image above.
Recent Posts
- History and American Studies Symposium–April 26, 2024
- Fall 2024 Courses
- Fall 2023 Symposium – 12/8 – All Welcome!
- Spring ’24 Course Flyers
- Internship Opportunity – Chesapeake Gateways Ambassador
- Congratulations to our Graduates!
- History and American Studies Symposium–April 21, 2023
- View umwhistory’s profile on Facebook
- View umwhistory’s profile on Twitter
Research Proposal Example/Sample
Detailed Walkthrough + Free Proposal Template
If you’re getting started crafting your research proposal and are looking for a few examples of research proposals , you’ve come to the right place.
In this video, we walk you through two successful (approved) research proposals , one for a Master’s-level project, and one for a PhD-level dissertation. We also start off by unpacking our free research proposal template and discussing the four core sections of a research proposal, so that you have a clear understanding of the basics before diving into the actual proposals.
- Research proposal example/sample – Master’s-level (PDF/Word)
- Research proposal example/sample – PhD-level (PDF/Word)
- Proposal template (Fully editable)
If you’re working on a research proposal for a dissertation or thesis, you may also find the following useful:
- Research Proposal Bootcamp : Learn how to write a research proposal as efficiently and effectively as possible
- 1:1 Proposal Coaching : Get hands-on help with your research proposal

PS – If you’re working on a dissertation, be sure to also check out our collection of dissertation and thesis examples here .
FAQ: Research Proposal Example
Research proposal example: frequently asked questions, are the sample proposals real.
Yes. The proposals are real and were approved by the respective universities.
Can I copy one of these proposals for my own research?
As we discuss in the video, every research proposal will be slightly different, depending on the university’s unique requirements, as well as the nature of the research itself. Therefore, you’ll need to tailor your research proposal to suit your specific context.
You can learn more about the basics of writing a research proposal here .
How do I get the research proposal template?
You can access our free proposal template here .
Is the proposal template really free?
Yes. There is no cost for the proposal template and you are free to use it as a foundation for your research proposal.
Where can I learn more about proposal writing?
For self-directed learners, our Research Proposal Bootcamp is a great starting point.
For students that want hands-on guidance, our private coaching service is recommended.

Psst… there’s more!
This post is an extract from our bestselling short course, Research Proposal Bootcamp . If you want to work smart, you don't want to miss this .
You Might Also Like:
10 Comments
I am at the stage of writing my thesis proposal for a PhD in Management at Altantic International University. I checked on the coaching services, but it indicates that it’s not available in my area. I am in South Sudan. My proposed topic is: “Leadership Behavior in Local Government Governance Ecosystem and Service Delivery Effectiveness in Post Conflict Districts of Northern Uganda”. I will appreciate your guidance and support
GRADCOCH is very grateful motivated and helpful for all students etc. it is very accorporated and provide easy access way strongly agree from GRADCOCH.
Proposal research departemet management
I am at the stage of writing my thesis proposal for a masters in Analysis of w heat commercialisation by small holders householdrs at Hawassa International University. I will appreciate your guidance and support
please provide a attractive proposal about foreign universities .It would be your highness.
comparative constitutional law
Kindly guide me through writing a good proposal on the thesis topic; Impact of Artificial Intelligence on Financial Inclusion in Nigeria. Thank you
Kindly help me write a research proposal on the topic of impacts of artisanal gold panning on the environment
I am in the process of research proposal for my Master of Art with a topic : “factors influence on first-year students’s academic adjustment”. I am absorbing in GRADCOACH and interested in such proposal sample. However, it is great for me to learn and seeking for more new updated proposal framework from GRADCAOCH.
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

HISTORICAL RESEARCH: A QUALITATIVE RESEARCH METHOD

This paper is a write-up about one of many qualitative research method, namely historical research method.
Related Papers
International Journal for Research in Applied Science & Engineering Technology (IJRASET)
IJRASET Publication
Historical research describes the past things what was happened. This is related with investigating, recording as well as interpreting the past events with respect to the in present perspectives. Historical research is a procedure for the observation with which researcher. It is a systematic collection and objective evaluation of the collected data with respect to the first occurrence to verify causes and effects related to the events with the help of these two explain the present events as well as anticipate for the future work purpose
Dr Yashpal D Netragaonkar
To find out how and why theories and practices have been developed which are now prevail in schools , a study on the purpose of historical research is very helpful. It deals with the significance of education and its interrel ationship with school and curriculum. In the said research, a study of Historical Research was conducted. Keywords - Historical, Perspective, Predictions, Facts, Past, Hypothesis
ICERI2009 Proceedings
Costas Vassilakis
The paper presents the results of a study on how historians conduct research in a historical archive, and the methodologies they use while searching. Historic research involves finding, using and correlating information within primary and secondary sources, in order to understand past events. Historians conduct research systematically, by examining past events to renew the past; historic research may involve interpretation to recapture the nuances, personalities, and ideas that have influenced these events, and the expected ...
Methods of Analysis
Stephen Petrina
It would seem that historical method has always implied case study if interpreted as the history of single events, episodic history as different from universal history, courtes durées as different from longues durées. From the early twentieth century, historical case study was basically biography, particularities of individuals used to counter the “vast amount of generalization” marking most histories and textbooks (Nichols, 1927, p. 270). Yet historical case study, in the way historians think of it, is primarily a post-WWII methodology.
Miguel S. Valles
El uso de materiales de archivo como punto de partida al disenar y acometer la investigacion social da por supuesto que en nuestras sociedades complejas ha echado raices hace tiempo una cultura de archivo (para compartir y reusar). Esta mentalidad y practica de investigacion se ha desarrollado primero y esta bien asentada en el caso de las estadisticas, encuestas y otros documentos primarios o secundarios. En cambio, es menos frecuente y ciertamente no una actividad rutinaria por lo que respecta a los datos cualitativos. Unicamente algunos de los materiales primarios y elaborados que se reunen durante la investigacion cualitativa pasan a formar parte de un archivo para su ulterior re-analisis. Pueden ser practicas y experiencias de trastienda de un proyecto, materiales en bruto tales como notas de campo, grabaciones de audio y visuales, y otros documentos producidos a lo largo del proceso de investigacion. Este volumen presenta una variopinta gama de articulos que abordan experienci...
Joseph Bryant
The Research on History I
ISTES Publication
The Research on History I Editors Özlem Muraz Budak Through its wide field of study, the science of history has succeeded in addressing all kinds of issues that have happened in the past. Many events that have happened in the past and affect the future have found a place in the science of history. It is important for every nation to know its history in order to learn lessons from the past. Every nation has a unique culture and these cultures extend to the present day. The science of history is used to learn about the past. This book aims to contribute to the development of scientific publications and publishing in social sciences in general and history in particular. In this sense, qualified studies covering every subject related to both national and regional history and world history are included. We will be pleased to contribute to the literature with these original works written in every field of history and to the qualified scientific studies related to the auxiliary branches of history. Citation Budak, Ö. M. (Ed.). (2023). The Research on History I. ISTES Organization.
Albert Mills
Forum Qualitative Sozialforschung/Forum: Qualitative Social Research
Maria Tamboukou
The use of archival materials as a point of departure when designing and launching social research takes for granted that a culture of archiving (for sharing and re-use) has rooted time ago in our complex societies. This mentality and research practice first flourished and is fairly well installed in the case of statistics, surveys and certain other primary or secondary documents. On the contrary, it is less frequent and certainly not a routine activity for qualitative data. Only some of the raw and elaborated materials gathered during ...
RELATED PAPERS
William Gallois
Russian Chemical Bulletin
Erhard Kemnitz
bob pritchard
Dina Septi Nugraheni
Pharmacoepidemiology and Drug Safety
Mohamed Magdy
Francisco José Lopes de Lima
Frontiers in Education
Ika Suswanti
Kamna Gupta
trudie gerrits
Saude E Sociedade
José Palacios Ramírez
Informática na educação: teoria & prática
Paula Cristina Marques
Rosalyn Acuna
Nature Medicine
Davide Serrano
IEEE Access
Wajid Hussain
Annales Universitatis Apulensis Series Oeconomica
Vasile Cocris
Chenning Tong
hjhjgf frgtg
Information and Communication Technologies in Tourism 2004
Francesco Ricci
Cancer Letters
Stuart Spechler
Synthesis Lectures on Signal Processing
Sameeksha katoch
Luseko Chilagane
RELATED TOPICS
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024

Historical Research
Ai generator.

One of the most significant historical events that changed the world is the invention of written language around 3500-3000 BCE in Sumer. Originally, Sumerians started to use writing to communicate with people from other cities and regions to trade resources. From then on, they did multiple enhancements on the invention to maximize its use. Today, needless to say, this invention has been serving us its purpose in many ways, such as in developing procedure documentation and writing a research paper for historical research.
What Is Historical Research?
Historical research is a research methodology that allows people to study past events that have molded the present. This investigation involves systematically retaking the pieces of information from one or more data sources which can let you, as a researcher or a detective, create a theory of how a phenomenon happened to be in its present situation. Although this type of research usually uses primary sources, such as journals and testimonies in many forms, the data it gets may also come from secondary sources, such as textbooks in the public library, newspapers, etc. Due to the nature of historical research, comparing and preserving historical records can also be good reasons to conduct this kind of research.
Strong Historical Research Design
For effective execution of the data collection and analysis for historical research in education and other fields, you will need a strong research design that includes the following stages.
1. Data Collection
We have mentioned earlier that in gathering the necessary data for historical research, you can use either or both primary and secondary data sources. Additionally, although this research is under the vast category of qualitative research , you can use quantitative data to interpret the facts you use.
2. Data Criticism
One of the advantages of conducting historical research is, aside from the present, you may gather evidence to explain the event that is yet to happen, which can be a delicate piece of information. In coming up with an explanation about a future phenomenon, you must evaluate the reliability of your sources. You can do it through internal and external validity . Through an external validity, you can determine the authenticity of a reference. Meanwhile, with internal validity, you can ensure that the data you gather is reliable by interpreting the content correctly.
3. Data Presentation
Once you have assured that the data you have collected is competent enough, you will analyze it and test the hypothesis of your research. We recommend you to do this step carefully since you will use logical methods instead of statistical tools. Avoid over-simplifying details and incorporating personal observations.
10+ Historical Research Examples
Now, you know the elements to include in your research. Let’s take a look at how researchers write their history research paper.
1. Biography of Historical Research Example

Size: 410 KB
2. Historical Research in Library Example

Size: 335 KB
3. Historical Reserch Agenda Example

4. Sample Historical Research Example

Size: 130 KB
5. Historical Research Information Systems Research Example

Size: 424 KB
6. Historical Research in Social Work Example

Size: 406 KB
7. Stndard Historical Research Example

Size: 18 KB

8. Legal History and Historical Research Example

Size: 58 KB
9. Methods and Principles of Historical Research Example

Size: 34 KB
10. Historical Research in Communication Example

Size: 129 KB
11. Historical Research in Education Example

Size: 54 KB
Best Practices in Conducting Historical Research
Now that you know almost everything that you need to cover about historical research, strengthen your project by keeping the following guidelines in mind.
1. Narrow Down the Direction of Your Project
Before you start writing your research paper , think of the topic that you choose to research. List down the research questions that you will focus on throughout the research process. Gather useful information and take note of the source information such as the author, etc. Then, decide on the specific type of information that you want to focus on. These steps will ensure that your research will not go astray.
2. Be Mindful of Your Sources
There are many sources available to gather information for your inquiry, especially on the internet. However, the question is, are these contents reliable enough? For historical research, we recommend you to ask assistance to the public librarians or historical consultants before you incorporate the information that you have gathered from the internet and the library.
3. Balance your Searches
Nowadays, you can always find the information that you need through the internet. However, when conducting research, you must do well-balanced data gathering. Meaning, aside from one source like the internet, you can gather data that you can only find in a particular root. A good example is local news.
4. Dig Deeper
It is essential to narrow down the scope of your research. It will be more interesting if you use the information that you have gathered to know more about a particular event or topic. It can also be an excellent way to find new leads that can support your research.
Countless historical events changed the way we perceive things. Among these phenomena, is the invention of written language. It also allows us to know how to deal with the obstacles that we are yet to encounter. Enlighten the people of a significant phenomenon by applying what you learned today to the research project that you are going to conduct.
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
38+ SAMPLE History Proposal in PDF | MS Word
History proposal | ms word, 38+ sample history proposal, what is a history proposal, ideas for a history proposal, tips to read history better, how to create a history proposal, how do you write a history proposal, what should a history research proposal include, what are the main sources of historical research.

History Thesis Proposal

Public History Collaborative Proposal

Department of History Proposal

History Day Topic Proposal Sheet

History and Government Course Proposal Form
History Annual Meeting Session Proposal

Depatrtment of History Senior Thesis Proposal

Comparative History Research Proposal

History and Digital Media Project Proposal Assignment

History Course Proposal

History Day Thesis Proposal

History Program Proposal

Financial Transaction Tax History Proposal

History Proposal in PDF

Administrative History Proposal

History Fund Proposal
History Month Program Proposal Form

History Press Publication Proposal

Natural History Proposal

History Thesis Proposal Form

Public History Proposal For a Certificate

History Senior Proposal

Minor in History Proposal

Basic History Proposal

History Honors Thesis Proposal
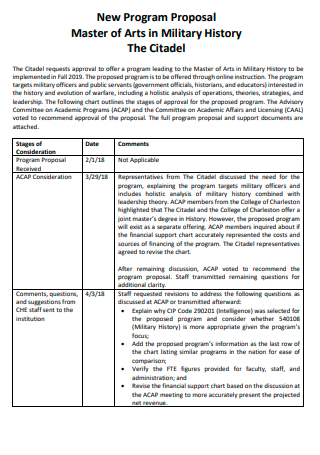
Master of Arts in Military History Program Proposal

Graduate Program History Proposal Form For Master Research

World History Research Proposal

Criminal History Records Scope Proposal

Family Water Alliance History Project Proposal

History Disseration Proposal Form

Program in History Proposal For Minor Field

History Center Proposal

History Proposal Grading Policy

Board of Nursing History Proposal

High School History Proposal

History and Visual Culture Dissertation Proposal

History Design Proposal

Oral History Proposal
Step 1: introduction, step 2: research problem , step 3: review of related literature , step 4: research design and methods, share this post on your network, file formats, word templates, google docs templates, excel templates, powerpoint templates, google sheets templates, google slides templates, pdf templates, publisher templates, psd templates, indesign templates, illustrator templates, pages templates, keynote templates, numbers templates, outlook templates, you may also like these articles, 25+ sample construction company proposal in ms word.
Navigating the intricate world of construction demands a seasoned company with a proven track record. Our comprehensive guide on the Construction Company Proposal is your blueprint to understanding the…
8+ SAMPLE Drama Proposal in PDF

Julia Child said: “Drama is very important in life: You have to come on with a bang. You never want to go out with a whimper. Everything can have…
browse by categories
- Questionnaire
- Description
- Reconciliation
- Certificate
- Spreadsheet
Information
- privacy policy
- Terms & Conditions

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
A research proposal, also known as a research prospectus, describes a project's intended course and its intellectual merit. In the process, you are expected to explain its historiographical context and how you intend to complete it. A well-written proposal should demonstrate that your project is unique and necessary. The Parts of a Research ...
In A Short Guide to Writing About History Richard Marius outlines fourteen steps that every student should follow in writing a historical research paper. 1. Identify your audience. All writing assignments are intended to be read, and the intended audience should always determine what is written. History is no different. An entry on Napoleon in
travel costs, software, photocopying or other necessary research resources with your supervisors and include a brief statement of those needs in the full proposal. Preliminary Bibliography List: a) all the sources you used when preparing your proposal, and b) the sources that you know that you must use when researching your topic.
These intransitive verbs are often necessary, but in a well-written proposal, active verbs in the active voice will dominate. Conciseness. Good proposal writers explain their ideas as succinctly as possible. Most writers start with a proposal that is a little too long. Then they solicit help from advisors and peer reviewers to trim the fat.
History-as-record consists of the documents and memorials pertaining to history-as-actuality on which written-history is or should be based. (p. 5) All three lend themselves to cliché yet despite this familiarity, or perhaps because of this, non-historians struggle with historical understanding and analysis. History teachers consistently
research and drafting stage and far too little time on developing the project correctly and revising their work after its initial drafting. You will find, therefore, that in this handbook ... History & Literature senior thesis proposal. In this chapter we talk about what the proposal is. We talk about what it isn't. And we give you a few ...
M.A. HISTORY THESIS PROPOSAL GUIDELINES. Each student must complete and submit a thesis proposal -- and receive approval from both Thesis Advisor / Director and the Graduate Program Director -- prior to beginning work on a research project. The items that should be included in the Thesis Proposal are listed in the outline below.
A good PhD proposal should do the following things, probably in the following order: 1. W ha t. E xplain w ha t his to rical p roblem (s) you w ant to und e rstan d . i.e. W h a t a re your research objectives, and what else do we need to know to understand why you re framing the historical problem as you are?
Department of History Guidelines for Writing a Research Proposal No matter if you are an undergraduate or a graduate student, all students in the Department of History will have to write a research proposal. Undergraduate students need to write a Research Proposal before they start to write their Senior Thesis.
Offers practical step-by-step guidance on how to do historical research, taking readers from initial questions to final publication. Connects new digital technologies to the traditional skills of the historian. Draws on hundreds of examples from a broad range of historical topics and approaches. Shares tips for researchers at every skill level.
"The study of history requires investigation, imagination, empathy, and respect." ~ Jill Lepore This guidebook is designed to serve professionals in the field of public history in identifying and securing grant funding. It is based in part on my experience working as a Sponsored Research Officer at California State University, Sacramento.
The research proposal you submit in January should be approximately 1000 words, plus a bibliography, and should contain the following: A title, possibly with a subtitle. The title should not take the form of a question and it may run to a dozen words or more. Like the title of a book, it should clearly convey the topic you propose to work on.
A proposal is a chance to explain your topic, discuss the resources critical to your research, and justify the need for your proposed paper. 1) Precisely defines your topic and the need for studying it (i.e., it briefly takes apart the topic and tells what one will learn from reading your proposed paper). 2) Explains the sources critical to ...
Research proposal Religious Institutions, Secular Muslims: A Comparative Analysis of Turkey and Yugoslavia, 1953-1991 My research interests are in the comparative study of state-sponsored secularism in two post-Ottoman successor states that are generally not studied together: Turkey and Yugoslavia. While
Historical research methods and approaches can improve understanding of the most appropriate techniques to confront data and test theories in internationalisation research. A critical analysis of ...
Table 7-1 Breakdown of the research proposal per semester 136 Table 7-2 Main assessment criteria 141 Figures Figure 3-1 Link between topic, question and conceptual significance 40 Figure 3-2 Logical sequence of a research proposal based on a research question 53 Figure 3-3 Logical sequence of a research proposal based on a
Sample Thesis Proposals. 'My broken dreams of peace and socialism': Youth propaganda, personality, and selfhood in the GDR, 1979-1989. Lanfranc of Bec: Confrontation and Compromise. The ecclesiastical history of Europe in the 11th century revolves around the investiture conflict and the Gregorian reform effort.
Detailed Walkthrough + Free Proposal Template. If you're getting started crafting your research proposal and are looking for a few examples of research proposals, you've come to the right place. In this video, we walk you through two successful (approved) research proposals, one for a Master's-level project, and one for a PhD-level ...
Historical Method: A Critical Review. 2023 •. IJRASET Publication. Historical research describes the past things what was happened. This is related with investigating, recording as well as interpreting the past events with respect to the in present perspectives. Historical research is a procedure for the observation with which researcher.
10+ Historical Research Examples. Now, you know the elements to include in your research. Let's take a look at how researchers write their history research paper. 1. Biography of Historical Research Example. lrec-conf.org. Details. File Format. Size: 410 KB.
research, and reading / theories that you expect to draw upon (200 words) Aims: list 4‐5 key aims of your research project (100 words) Bibliography: include a short bibliography relevant to your research topic (1‐2 pages) Curriculum Vitae (CV)
Research Proposal on Historical - Free download as PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or read online for free. This proposal explores the writing of Ephraim Pagitt, a 17th century London parson, to understand religious belief, literature, and politics during this period. The researcher will study Pagitt's print and manuscript writings within the context of other London clergy to analyze how ...
Step 2: Research Problem. The next step is to state your research problem statement and provide some background on it. The objective of a history proposal, after all, is to explore and gain insight to your historical topic. The significance of the study and its relation to society can be further examined in this section.
PHASE II PROPOSAL CERTIFICATIONS. ... If yes, you are required to include a PDF or Word document of your NASA Research License as part of your proposal package submission. As described in section 3 of this solicitation, the offeror meets the following requirements completely: 7. All 10 parts of the proposal narrative are included in part order ...
Scholarship, and Creative Activities Program Proposal Review Committee. The committee will read and review project proposals from Montclair undergraduate and graduate students and make funding recommendations to the Vice Provost for Research. Applications to serve on the SL-RSCA Proposal Review Committee are due via the form linked . here
The HMSO anticipates awarding up to four research grants in 2024. The HMSO is especially interested in projects that graduate students and post-docs initiate that are not part of their mentors' funded research: i.e., independent projects driven by individuals' own interests and agendas. Proposal guidelines are below. Duration and Level of Support
award will advance the applicant's career. Letter(s) of support will be requested at the Full Proposal stage if your LOI is accepted, and you are invited to submit a Full Proposal. Organization Detail • This information is used to assess the capability of the organizational resources available to perform the effort proposed. Budget Detail