Supporting HSE improvement
News, insights and thought leadership.
Home / HSE News / Articles / How to deliver a safety presentation that stands out

How to deliver a safety presentation that stands out
Safety presentations are essential to ensure a business is up to date on health and safety regulations, as well as employers learning the skills to identify potential hazards in the workplace.
However, it’s vital this information is retained so it can be used when a situation arises during the working day. This shows how important it is to stand out in your presentation, so the critical information can be retained by the audience.
If you are struggling to make your presentation stand out, it may be beneficial to consider some presentation coaching .
What can be included in a safety presentation?
Although many presentations can include different attributes, as an overview a safety presentation should include how to prevent hazards in the workplace, legislation and enforcement, risk assessments, and emergency plans.
The Health and Safety Executive has put together some useful resources that can be beneficial when putting together a presentation, as a starting point.
Tailor your presentation to your audience
If you have access, learning about the audience before delivering the presentation may be beneficial during the preparation, as well as the execution of the safety presentation.
For example, if the team you are presenting to newer employees in a business, you could decide to invite experienced workers who can give an insight into past health and safety hazards experienced during their careers.
This personal touch to your safety presentation will be personalised and relatable, increasing the likelihood that it will stand out.
Use visual aids for communication
One of the main ways your presentation can stand out is by utilizing visual aids. Visual aids can help retain comprehension and retention, which will lead to a higher quality safety presentation. This can be achieved through high-quality graphics, images, videos, and graphics that make the presentation more appealing. This is particularly important when specific slides may come across as less engaging.
Practice what you are going to say
In order to help your presentation stand out and appear confident to your audience, practicing beforehand will help put you at ease, as well as reduce the need to look at notes or the presentation slides. This will allow you to engage more with the audience directly, even asking them to get involved. Not to mention that speaking with confidence will bring more authority and clarity.
Be current with industry trends
Being aware of current trends in the health and safety industry will help the audience resonate with what you are saying. If the safety presentation is about safety regulations that don’t relate to your industry, then it’s likely the information will not be retained by the audience.
For example, if you are discussing office set-ups, relating to home working and the pandemic will help the audience relate to the pandemic in 2020, and will reduce the chance of people switching off.
We hope this article has helped you understand how you can tailor a safety presentation to help it stand out.
News categories
Popular videos, connecting safety, health and wellbeing | jane le count and dr maggie samuel, do health and safety management systems make a difference | kate field: bsi group, andrew barratclough | the true cost of overlooking driver safety | edriving, how to transform your company’s health and safety performance | matt taylor, british steel, the importance of good safety and medical testing in the oil and gas industry | dr eva reichardt, popular articles, news: recent hse prosecutions highlight workplace safety failures, how to stay on top of road safety compliance for commercial vehicles, breaking down stigmas around mental health in construction, digital training for construction workers: connecting the skills gap safely, the best health and safety conferences in the uk, brands who we work with, keep up to date with all hse news and thought leadership interviews.

25 Safety Topics For Meetings To Discuss For a Better Workplace
Creating a safe and healthy work environment is a legal obligation and critical to maintaining productivity and employee satisfaction. Regular safety meetings play a crucial role in this effort. They provide an opportunity to reinforce safety policies, address concerns, and learn about potential hazards. However, organizing these meetings can often seem daunting, especially when selecting relevant topics that resonate with your team.
To help you facilitate effective discussions about safety, we’ve curated a list of 25 safety topics for meetings. Covering a wide range of issues from ergonomic practices to chemical safety , these topics can help ensure that safety is always at the forefront in your workplace, ultimately leading to a better and safer work environment for everyone.
Safety Meetings
Safety meetings, also known as safety briefings or safety talks, are formal gatherings in a professional setting where employees, management, and sometimes even third-party stakeholders come together to discuss health and safety concerns within the workplace. They typically last between 20 to 45 minutes and can involve a variety of formats, such as presentations, group discussions, or hands-on demonstrations.
The purpose of these meetings is to provide information about existing or potential hazards in the workplace , explain safety protocols and procedures, address any safety concerns or incidents that have occurred, and provide training as part of the organization’s safety program. They also reinforce the importance of safety guidelines and cultivate a safety culture within the organization.
Safety meetings are not usually daily or weekly occurrences. Instead, they tend to occur under specific circumstances, such as onboarding new employees, following a workplace incident, changing industry safety standards or regulations, or introducing new equipment or procedures that may carry additional risks. By maintaining open lines of communication about safety issues, these meetings help ensure the welfare of all employees and contribute to creating a safer, healthier work environment.

Safety Topics For Meetings
Safety topics for meetings are essential to promote a safety culture and ensure everyone’s well-being in the workplace. Here are some safety topics you can consider for your meetings:
1. Slipping, Tripping, and Falling
Slips, trips, and falls constitute some of the most frequent workplace accidents and can result in serious injuries. To mitigate these risks, it is essential to maintain clear, unobstructed walkways and workspaces. Regular cleaning and immediate attention to spills or wet surfaces can prevent slippery conditions.
Additionally, promoting suitable footwear with a good grip can reduce the risk of slips and trips. Adequate lighting is also critical, as it illuminates potential hazards and allows employees to navigate their environment safely. Implementing these practices can significantly reduce the incidence of these common accidents.
2. Ladder Safety
Ladder safety is essential in many workplaces, such as construction sites, warehouses, and offices. Incorrect use of ladders can lead to falls and serious injuries. Employees should be trained on the right way to use ladders, which includes choosing the correct ladder for the task, checking it for any defects before use, setting it up on a firm and level surface, and maintaining three points of contact (two hands and a foot, or two feet and a hand) at all times while climbing or descending.
The proper methods of ascent, descent, and dismounting should also be covered. Reinforcing these safety measures regularly can prevent ladder-related accidents and ensure a safer work environment.
3. Confined Space Safety
Confined space safety is a critical concern in construction, mining, or manufacturing industries, where employees may need to work in tight, enclosed areas. These spaces can present a range of hazards, including a lack of oxygen, toxic gases, or the risk of fire or explosion. It’s crucial to discuss the specific risks associated with each confined space, the necessary precautions to take before entering (like checking oxygen levels or removing flammable substances), and the appropriate use of personal protective equipment.
Workers should also be trained in emergency procedures in case of an incident. By addressing these topics, companies can help ensure their employees are prepared and protected when working in these challenging environments.
4. Hazard Communication
Hazard communication is a key safety concern in many workplaces, particularly those involving hazardous substances. Employees should receive training on identifying hazardous materials based on their labels and Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS). They should also understand the proper handling procedures to avoid exposure and disposal methods to prevent environmental harm.
The correct use of personal protective equipment when dealing with these substances should also be highlighted if necessary. By improving employees’ understanding of these hazards, businesses can reduce the risk of accidents and ensure safer handling and disposal of dangerous substances.
5. Lockout/Tagout Procedures
Lockout/Tagout procedures are critical in ensuring worker safety while servicing or maintaining machinery and equipment. These procedures involve de-energizing and disabling machinery to prevent unexpected startup or energy release, which could cause harm. Regular discussions about these procedures are essential and should include the step-by-step process of shutting down, isolating, blocking, and securing machines before performing maintenance tasks.
Additionally, they should cover the proper way of applying lockout/tagout devices and the importance of only allowing the individuals who applied them to remove them. By maintaining rigorous lockout/tagout practices, companies can significantly reduce the risk of injuries related to the maintenance of machinery and equipment.

6. Working at Heights
Working at heights is common in several industries and presents unique fall-related risks. It’s essential to discuss the safety measures needed to mitigate these risks. Employees should be trained on correctly using fall protection equipment, such as harnesses, guardrails, and safety nets, and understand the importance of regular equipment inspections. They should also know how to assess their environment for hazards like unstable surfaces or windy conditions.
Moreover, procedures for safely ascending, descending, and working at height should be covered. By emphasizing these precautions, you can significantly reduce the risk of fall-related injuries in the workplace.
7. Drug or Alcohol Abuse on the Job
Drug or alcohol abuse on the job is a serious issue that can severely impact an individual’s health, productivity, and workplace safety . It’s crucial to articulate the company’s policy regarding substance use clearly and strictly, highlighting that impairment at work is unacceptable. Employees should be educated about the detrimental effects of substance abuse on their work performance, personal lives, and health.
Organizations should also provide information on resources such as counseling or rehabilitation programs, offering support to those struggling with addiction and fostering an environment of understanding and assistance rather than judgment or punishment.
8. Workplace Violence
Workplace violence, ranging from threats and verbal abuse to physical assaults, poses significant safety and health risks. Educating employees about recognizing potential signs of workplace violence, including aggressive behavior, verbal threats, or sudden changes in behavior, is critical. Establishing clear protocols for responding to such situations, including immediate reporting mechanisms, can help prevent escalation.
By cultivating an environment of trust and support, employees will feel encouraged to express concerns about potential violence without fear of retribution, contributing to a safer and healthier workplace.
9. Manual Handling
Manual handling, involving lifting, carrying, moving, or otherwise manipulating objects by hand, is a common cause of workplace injuries . Proper training on safe manual handling techniques is essential to prevent these injuries. This includes understanding the principles of safe lifting (such as lifting with the legs, not the back), knowing when to ask for help or use equipment, and how to safely move or carry loads.
Regular refresher courses can help keep this knowledge up-to-date and reinforce the importance of safe manual handling. Companies can significantly reduce the risk of strains, sprains, and other related injuries by equipping employees with these skills.
10. Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) is a vital safety aspect in many work environments, particularly in healthcare, construction, and manufacturing industries. Proper use of PPE can significantly reduce the risk of injury or exposure to harmful substances.
Employees should be trained on how to use, maintain, and dispose of various types of PPE correctly. This includes understanding which type of PPE is appropriate for different tasks, how to wear it correctly for maximum protection, how to clean and maintain reusable PPE, and how to safely dispose of single-use PPE. Reinforcing these guidelines helps ensure the effectiveness of PPE and promotes a safer working environment.

11. Electrical and Fire Safety
Electrical and fire safety are paramount in virtually all work environments. Employers should discuss necessary precautions to prevent electrical shocks, such as not overloading outlets, keeping liquids away from electrical equipment, and not using equipment with damaged cords. Regular electrical equipment inspection and maintenance are essential to ensure they’re in safe working condition.
Regarding fire safety, employees should be educated on preventative measures like proper waste disposal and avoiding the blockage of fire exits. Additionally, fire safety training should be conducted periodically, ensuring that employees know how to use fire extinguishers, understand evacuation procedures, and know emergency exit locations. This comprehensive approach helps minimize the risk of electrical and fire-related incidents.
12. Ergonomic and Workplace Stress
Ergonomics and workplace stress are critical factors in employee productivity and overall well-being. In discussions about ergonomics, employees should learn how to design their workspace for comfort and efficiency, thus reducing strain and the risk of injury. This could include correct seating posture, optimal placement of computer screens, and usage of ergonomic office equipment.
Alongside this, it’s crucial to manage work-related stress by promoting regular breaks, time management, balanced workloads, and fostering a supportive work environment. A holistic approach addressing physical and mental stressors can significantly improve health outcomes and productivity.
13. Reporting Hazards and Incidents
Promptly reporting hazards and incidents is crucial in maintaining a safe workplace environment. Employees should feel encouraged and empowered to report any safety concerns or incidents without fear of reprisal. This reporting allows for quick corrective action, reducing the likelihood of accidents or injuries.
Companies should have clear, straightforward procedures for such reports, including dedicated reporting lines, online forms, or direct communication with safety officers or supervisors. Regular discussions on this topic ensure that all employees know the reporting process and its significance in workplace safety.
14. Chemical Safety
Chemical safety is vital to many workplaces, including labs, factories, and cleaning services. Employees handling chemicals should be trained to use, store, and dispose of these substances safely to prevent accidents , spills, and potential health hazards. They should understand how to interpret Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS), which provide detailed information about each chemical’s properties, hazards, protective measures, and safety precautions.
Training should also cover using personal protective equipment when handling chemicals and emergency procedures in case of accidental exposure or spillage. Regularly discussing these procedures helps ensure a safer workplace environment and reduces the risk of chemical-related incidents.

15. First Aid Training
First aid training is essential to workplace safety, equipping employees with the skills to respond quickly and effectively during medical emergencies. Such training can range from basic skills like wound dressing, CPR, and handling of minor injuries to more advanced practices for specific industries. By understanding these first aid techniques, employees can not only help stabilize a situation until professional medical help arrives but could potentially save lives.
It is recommended that these training sessions be conducted regularly to keep the information fresh and up-to-date. Creating a workplace where employees are confident in responding during emergencies promotes safety and readiness.
16. Equipment Safety
Equipment safety is crucial in many industries, from manufacturing and construction to hospitality and healthcare. All machinery or equipment employees should receive comprehensive training on correct usage, safety protocols, and the risks associated with improper use. This training should include preventative measures like regular equipment inspections, maintenance, and reporting faulty machinery immediately.
Ensuring that each employee is competent in handling their equipment, the risk of injuries due to mishandling or malfunctions can be significantly reduced, leading to a safer and more efficient workplace.
17. Mental Health Awareness
Mental health is a vital aspect of overall employee wellness and productivity. Creating an environment where mental health is acknowledged and supported is important. Regular discussions about the significance of mental well-being, signs of common mental health issues, and stress management techniques can help to destigmatize these topics and encourage employees to seek help when needed.
Additionally, companies should provide resources such as counseling services, mental health days, and wellness programs. Ensuring that employees are aware of these resources and feel comfortable using them is critical in supporting mental health in the workplace.
18. Noise Exposure
Noise exposure in the workplace can lead to permanent hearing loss or other hearing complications over time. Discussing ways to mitigate these risks is crucial in environments with high noise levels. This might include operating noisy machinery during specific hours, maintaining equipment to reduce noise, and creating quiet zones for employees. Alongside these measures, personal protective equipment such as earplugs or earmuffs is often necessary.
Employees should understand the correct usage of such protection and its importance in preventing hearing damage. Regular hearing checks can also help monitor employees’ hearing health and detect any issues early.
19. Office Safety
Office safety, though seemingly straightforward, is important in maintaining employee health and productivity. This includes setting up workstations correctly to minimize strain and discomfort—employees should be aware of the appropriate height for desks and screens, the correct positioning of keyboards and mice, and how to adjust chairs for optimal support. Discussing correct posture can help prevent long-term issues like back pain and repetitive strain injuries.
Additionally, the importance of taking regular short breaks should be emphasized, as this can help reduce fatigue and stress on the body. Companies can help ensure their employees remain healthy and productive by maintaining a safe and comfortable office environment.
20. Emergency Evacuation Plans
Emergency evacuation plans are vital to workplace safety designed to ensure quick and orderly evacuation during emergencies such as fires, earthquakes, or chemical spills. Regularly reviewing these procedures informs employees about the quickest and safest exit routes, meeting points, and roles during an evacuation.
Drills should be conducted periodically to practice these procedures and to identify any areas of confusion or inefficiency that need to be addressed. Ensuring all employees are familiar with these plans and can execute them calmly and efficiently in emergencies can significantly enhance safety and reduce potential harm.

21. Radiation Safety
Radiation safety is a significant concern in workplaces where employees might be exposed to radiation, such as in healthcare facilities, research laboratories, or nuclear power plants. Employees should be trained on the principles of radiation safety, often summarized as time, distance, and shielding – limiting exposure time, maintaining a safe distance from radiation sources, and using appropriate shielding materials.
They should understand the different types of radiation, the potential health effects, and the safety equipment and procedures designed to protect them, such as using dosimeters to monitor exposure and wearing lead aprons when necessary. Regularly revisiting these principles can help ensure employees remain vigilant and well-protected.
22. Fatigue Management
Fatigue management is critical to workplace safety, as tiredness can significantly impair work performance and lead to serious accidents. It’s important to discuss the signs of fatigue, such as persistent tiredness, decreased alertness, slow reaction times, and poor decision-making. Employees should understand the importance of adequate rest and sleep, balanced nutrition, and regular exercise in maintaining energy levels.
Additionally, discuss strategies for managing fatigue, including taking regular breaks, managing workload effectively, and seeking medical advice if persistent fatigue is experienced. By promoting a culture that values rest and recognizes the risks of fatigue, employers can contribute significantly to the overall safety and productivity of the workplace.
23. Safe Use of Power Tools
Safely using power tools is crucial in industries like construction, manufacturing, or woodworking, where these tools are frequently used. Employees should be educated about the proper use, maintenance, and safety precautions associated with each type of power tool they use. This includes understanding the functions and limitations of each tool, wearing appropriate personal protective equipment, checking tools for damage before use, and maintaining them correctly to ensure their safe operation.
Emphasizing that tools should only be used for their intended purposes can help prevent misuse-related accidents. Regular discussions and training on these topics help ensure employees operate power tools safely and competently, reducing the risk of injuries.
24. Biological Hazards
Biological hazards can pose a significant risk to health in certain workplaces, such as healthcare facilities, laboratories, or waste management sites. Employees in these settings should be trained to understand the potential risks of exposure to biological agents like bacteria, viruses, or other biohazardous materials. This includes proper use of personal protective equipment, good hygiene practices, safe handling procedures, and disposal methods for biohazardous waste.
Procedures for exposure incidents, including reporting, first aid, and medical follow-up, should also be explained. Regular discussion can help prevent exposure incidents and maintain a safer working environment.
25. Personal Hygiene
Personal hygiene is crucial in maintaining a healthy and safe working environment, particularly in preventing the spread of infectious diseases. Regular discussions should be held on best practices, such as regular handwashing with soap and water, using hand sanitizers when soap isn’t available, keeping workstations clean, and practicing good respiratory etiquette, like covering mouth and nose when coughing or sneezing.
It’s also important to encourage employees to stay home when feeling unwell to prevent the potential spread of illness. Additional measures like wearing masks or social distancing might be needed in public health crises. Maintaining good personal hygiene benefits everyone and contributes to a healthier working environment.
Prioritizing workplace safety ensures employees’ well-being and fosters a positive work culture and productivity. By discussing the 25 safety topics outlined in this article in your safety meetings, you can create an environment where everyone feels empowered to uphold safety standards.
Remember, creating a safer workplace is a continuous journey that requires regular discussions, ongoing training, and constant vigilance. By investing in these safety talks, you invest in the well-being of your most valuable resource – your employees.
- Our websites:
- Healthy Workplaces Campaign
- OSH Barometer

PowerPoint presentation
- Musculoskeletal disorders
Need to explain the campaign to your colleagues, clients or contacts quickly and clearly? Our PowerPoint presentation is just what you’re looking for. The slides summarise the key points, presenting facts and figures, legislation and prevention principles, and the importance of early intervention and supporting return to work, as well as providing information on how to get involved.
Additional publications on this topic

Safety and health in agri-food sector supply chains: the power of combining contractual and relational governance

Strategies for safety and health in an automated world

Advanced robotics and AI-based systems for the automation of tasks

- My presentations
Auth with social network:
Download presentation
We think you have liked this presentation. If you wish to download it, please recommend it to your friends in any social system. Share buttons are a little bit lower. Thank you!
Presentation is loading. Please wait.
Safety and Health at Work
Published by Marcia Leonard Modified over 8 years ago
Similar presentations
Presentation on theme: "Safety and Health at Work"— Presentation transcript:

Elements of an Effective Safety and Health Program

Health and Safety Chapter 10.

SAFETY AND HEALTH AT WORK CHAPTER 7. Safety- protecting employees from injuries caused by work- related accidents Safety- protecting employees from injuries.

Accident Investigation for Supervisors

February, 2010 Workplace Violence Module 2 – Follow-up, Rules and Resources.

Safety and Health Management Program

Accident Investigation State of Florida Loss Prevention Program.

Accident Investigations

Learning Objectives Recognize the need for an investigation Investigate the scene of the accident Interview victims & witnesses Distinguish.

ACCIDENT IN WORKPLACE Department of Public Health Faculty of Medicine, UNPAD.

Understanding the management of risks to health and safety on the premises of a retail business Unit 352.

© 2002 McGraw-Hill Ryerson Ltd.1 Ch15 Ensuring Safety and Health at the Workplace 2000 Uniform Restaurant Server.

School Safety Training

Workplace Safety and Health Program

Chapter 10 Health, Safety, and Preparedness

Workplace Violence Research has identified factors that may increase the risk of violence at worksites. Such factors include working with the public or.

Occupational Road Risk Health and safety issues for vehicles and drivers Mike Lewis MIOSH, RSP.

Occupational health and safety

Why HSE in an Organization

OCCUPATIONAL HEALTH AND SAFETY (1). 1 Explain the application of the Occupational safety and Health Act 1994 (C2) 2 Discuss the provisions and protection.
About project
© 2024 SlidePlayer.com Inc. All rights reserved.
Health and Safety at Work Act presentation
The Working together on health and safety presentation provides you with the basic facts you need to know about the Health and Safety at Work Act (HSWA).
Watch the video
The Working together on health and safety presentation provides you with the basic facts you need to know about the Health and Safety at Work Act (HSWA). The video below, presented by former WorkSafe Chief Executive Gordon MacDonald, is a great resource for getting the message across to your business.
Download the presentation
This presentation covers the main concepts of the Health and Safety at Work Act 2015 (HSWA), at a high level.
The presentation was last updated on 26 July 2016. It may be updated in future, so please check back here for the most up to date version.
Last updated 11 October 2017 at 09:53
Newly Launched - World's Most Advanced AI Powered Platform to Generate Stunning Presentations that are Editable in PowerPoint

Powerpoint Templates
Icon Bundle
Kpi Dashboard
Professional
Business Plans
Swot Analysis
Gantt Chart
Business Proposal
Marketing Plan
Project Management
Business Case
Business Model
Cyber Security
Business PPT
Digital Marketing
Digital Transformation
Human Resources
Product Management
Artificial Intelligence
Company Profile
Acknowledgement PPT
PPT Presentation
Reports Brochures
One Page Pitch
Interview PPT
All Categories

Health And Safety Of Employees In Organization Powerpoint Presentation Slides
Workplace safety refers to the provision of a safe working environment, with the limitation of elements that can cause damage, injury, and other negative outcomes in the workplace. Check out our professionally designed Health and Safety of Employees in Organization PowerPoint presentation. First, this deck covers the problems related to workplace incidents which include occupational diseases, occupation of fatal and injured employees, and safety violations by employees. Additionally, it covers the causes of accidents, and the impact of accidents on employees and organizations. It also highlights why there is a need for workplace safety with detailed objectives. Moreover, this deck covers how to examine risks and hazards, It also lays emphasis on hazard identification and their control measures which includes air compressor hazards and safety guidelines, fire hazards and safety guidelines, Injuries from power tools with safety guidelines, chemical hazards with safety guidelines, and drug and alcohol abuse with safety guidelines. At last, it includes the recommended practices for safety management, penalties for non compliance, and the positive impact of workplace safety in an organization. Download this deck now.

- Add a user to your subscription for free
You must be logged in to download this presentation.
PowerPoint presentation slides
Deliver this complete deck to your team members and other collaborators. Encompassed with stylized slides presenting various concepts, this Health And Safety Of Employees In Organization Powerpoint Presentation Slides is the best tool you can utilize. Personalize its content and graphics to make it unique and thought-provoking. All the Fifty Six slides are editable and modifiable, so feel free to adjust them to your business setting. The font, color, and other components also come in an editable format making this PPT design the best choice for your next presentation. So, download now.
People who downloaded this PowerPoint presentation also viewed the following :
- Complete Decks , All Decks , General , HR , Operations , Strategy
- Workplace Safety Violation ,
- Causes Of Accidents At Work ,
- Need Of Workplace Safety ,
- Organization Risks And Hazards ,
- Hazard Identification And Evaluation ,
- Hazard Prevention And Control
Content of this Powerpoint Presentation
Slide 1 : This slide displays the title Health and Safety of Employees in Organization. Slide 2 : This slide displays the title Agenda for health and safety of employees in organization. Slide 3 : This slide exhibit table of content. Slide 4 : This slide exhibit table of content- Current Problems related to Workplace Incidents. Slide 5 : This slide highlights the workplace injuries and occupational diseases. Slide 6 : This slide highlights the occupation of fatal and injured employees on the organization. Slide 7 : This slide showcases the common safety violation by employees at worksite which includes the scaffolds accidents, electrical wiring, lockout/tagout and chemicals. Slide 8 : This slide exhibit table of content- Causes of Accidents and Its Impacts. Slide 9 : This slides highlights the key reason of accidents at work. Slide 10 : The following slide highlights the effect of workplace accidents on the organization. Slide 11 : This slide highlights the consequences of accidents on workers and employers which includes loss of job, loss of income, and damage to organization equipment's etc. Slide 12 : This slide exhibit table of content- Why Workplace Safety is Important. Slide 13 : This slide highlights the need or importance of workplace safety at organization. Slide 14 : The following slide highlights the major objectives for workplace safety in accordance with organization. Slide 15 : This slide exhibit table of content- Examining Organization Risks and Hazards. Slide 16 : This slide highlights the four steps to identify the organization risks. Slide 17 : This slide highlights the poor work practices at worksites. Slide 18 : Hazard Identification and Control Measures. Slide 19 : The following slide showcases the hazard identification and evaluation and workplace. Slide 20 : This slide highlights the hard prevention and control measures. Slide 21 : This slide highlights the common air compressor hazards. Slide 22 : This slides highlights the operational safety guidelines to minimize air compressor hazards. Slide 23 : This slide highlights the different fire hazards including flammable materials, dust and debris, overusing power socket. Slide 24 : This slide highlights the measures to control fire at workplace. Slide 25 : This slide showcases the common injuries caused by power tools. Slide 26 : This slide highlights the safety guidelines which showcases the general precautions while handling power tools to prevent accidents. Slide 27 : This slide highlights the different hazards from chemical at workplace. Slide 28 : The following slide showcases the steps or measures for chemical hazards at organization. Slide 29 : The following slide highlights the problems with excessive drug and alcohol at workplace. Slide 30 : This slide highlights the preventive and detective measures for alcohol abuse which showcase multiple ways to deal the situation. Slide 31 : This slide exhibit table of content- Recommended Practices for Safety Management. Slide 32 : This slide highlights the importance of management leadership for workplace safety. Slide 33 : This slide highlights the worker participation to remove safety risks. Slide 34 : This slide highlights the safety training program for workers. Slide 35 : This slide showcases the assessment and improvement of safety program. Slide 36 : This slide highlights the coordination with contractors and staffing center by host employer. Slide 37 : This slide exhibit table of content- Penalties for Non Compliance of Safety Guidelines. Slide 38 : The following slide highlights the disciplinary action against employees for not complying the rules and safety guidelines. Slide 39 : This slide exhibit table of content- Dashboard for workplace safety. Slide 40 : This slide highlights the positive impacts of workplace safety training program. Slide 41 : This slide highlights the positive impacts from the workplace safety. Slide 42 : This slide exhibit table of content- Dashboard for workplace safety. Slide 43 : This slide highlights the dashboard which showcase the critical incidents, incident cost, injury consequence, type of incident and severity level of the injury. Slide 44 : This slide highlights the workplace safety dashboard which showcase incidents per employee, worksite incident total. Slide 45 : This is the icons slide. Slide 46 : This slide presents title for additional slides. Slide 47 : This slide highlights the recommended practices for safety management at organization level. Slide 48 : This slide highlights the pictograms of chemical hazards which showcase health hazard, flame, exclamation mark, gas cylinder, exploding bomb. Slide 49 : This slide depicts 30-60-90 days plan for projects. Slide 50 : This slide showcase Comparison. Slide 51 : This slide showcase Roadmap for process flow. Slide 52 : This slide depicts posts for past experiences of clients. Slide 53 : This slide shows puzzle for displaying elements of company. Slide 54 : This slide showcases financials of company. Slide 55 : This slide display Venn. Slide 56 : This is thank you slide & contains contact details of company like office address, phone no., etc.
Health And Safety Of Employees In Organization Powerpoint Presentation Slides with all 61 slides:
Use our Health And Safety Of Employees In Organization Powerpoint Presentation Slides to effectively help you save your valuable time. They are readymade to fit into any presentation structure.

Ratings and Reviews
by Earl Contreras
March 14, 2023
by Connor Lopez


Health and Safety At Work Act (1974)
Nov 12, 2014
270 likes | 1.08k Views
Health and Safety At Work Act (1974). The Health and Safety at Work etc. Act 1974 is the primary piece of legislation covering occupational health and safety in the United Kingdom. The main principles are below : Securing the health, safety and welfare of people at work
Share Presentation
- work activates
- safety risks
- main aims principles
- legislation covering occupational health

Presentation Transcript
The Health and Safety at Work etc. Act 1974 is the primary piece of legislation covering occupational health and safety in the United Kingdom. • The main principles are below: • Securing the health, safety and welfare of people at work • Protecting others against health or safety risks in connection with the activities of people at work • Controlling the keeping and use of dangerous substances • Preventing the unlawful possession and use of dangerous substances • Controlling certain emissions into the atmosphere • To amend the law relating to building regulations, and the Building (Scotland) Act 1959 The main aims / principles of the law and Reasons
Who / What does it protect or prevent • It protects employees, employers, contractors, suppliers, maintainers and managers from risks to health, safety and welfare. • Protects from accidents concerning equipment, work areas, machines, substances, emissions, dirt and work activates.
This piece of legalisation needs to be complied by all organisations that could potentially pose a risk to people, • Organisations must comply with these regulations or they can be at risk of termination. • The negative affects include increased monetary cost, large amounts of time spent on introducing or improving current measures and systems to comply with the legalisation • As a result profits could decrease and the company may not be able to afford to add these changes, however the legalisation does emphasise the phrase ‘so far as is reasonably practicable’ which means if the cost or effort/sacrifice outweighs the benefits in averting risk then it is not reasonably practicable and so alternatives should be though of. • The positive benefits include increase safety, and therefore decreased risk of accidents concerning health, safety and welfare. How it affects organisations
What must they do to comply with the Act • It is the duty of every employer to ensure, the health, safety and welfare at work of all his employees. • Must ensure that the provision and maintenance of plant and systems of work are safe and without risks to health • Arrangements for ensuring safety and absence of risks to health in connection with the use, handling, storage and transport of articles and substances • Provision of information, instruction, training and supervision to ensure, the health and safety at work of his employees • The maintenance of any workplace under the employers control must be in a condition that is safe and without risks to health • The provision and maintenance of means of access to and must be safe and without such risks
- More by User

HEALTH AND SAFETY AT WORK ACT 1974
HEALTH AND SAFETY AT WORK ACT 1974. Produced as part of the Partnership Development Schools (PDS) Strategy Phase 3 2008-09 (Lead PDS: The Park Community School. Contact Chris Ley ([email protected]). DUTIES OF SCHOOLS. Produce a health and safety policy
1.69k views • 66 slides

Health & Safety at Work Act 1974
Health & Safety at Work Act 1974. Health & Safety at Work Act 1974. TEMPERATURE Minimum temperature of 60oF Windows must be opened or suitable ventilation eg fans etc TOILET FACILITIES There must be toilets available They must be kept clean Well-maintained
1.55k views • 9 slides

Health and Safety at Work - your legal obligations
Health and Safety at Work - your legal obligations. Dr Ann Maconnachie Departmental Safety Officer. Health and Safety at Work Act, 1974 Management of Health and Safety at Work Regulations 1992. Health and Safety at Work Act, 1974.
754 views • 18 slides

The Health and Safety at Work Act 1974
1.25k views • 52 slides

NSW Work Health and Safety Act
NSW Work Health and Safety Act . Module: Incident Notification. WHS Act . About this Module. Purpose: To outline the requirements for incident notification under the WHS Act. WHS Act . Learning Outcomes. The key learning outcomes of this module are:
308 views • 12 slides


SAFETY HEALTH AND WELFARE AT WORK ACT 1989
SAFETY HEALTH AND WELFARE AT WORK ACT 1989. HISTORY. First comprehensive reform of safety and health legislation since the formation of the state.
521 views • 19 slides

Work Health and Safety Act Senior Managers
Work Health and Safety Act Senior Managers . Senior Managers . 01 What is new for NSW under the WHS Act?. Summary. Summary. Summary. Summary. New Terminology. New Terminology. New Terminology. Definitions. ‘Person conducting a business or undertaking’ . Definitions. ‘Worker’ .
704 views • 55 slides

Health and Safety
Health and Safety. The Health and Safety at Work Act 1974.
368 views • 14 slides

Health and Safety. By Callum van Aswegen. Health and Safety at Work Act 1974. Preliminary HSWA , the HSW Act, the 1974 Act or HASAWA Who does it apply to General Duties Good Management and Common Sense Risk Assessment, straight forward Facts Do not Who enforces this Law.
223 views • 7 slides

NSW Work Health & Safety Act
NSW Work Health & Safety Act. Module: H&S Committees – Roles and Functions. About this Module. Purpose: To outline the requirement for establishing H&S Committees, their roles and functions and how this differs from existing requirements. Learning Outcomes.
287 views • 18 slides

HEALTH AND SAFETY AT WORK
HEALTH AND SAFETY AT WORK. MMag. Christian Mandl Austrian Federal Economic Chamber. Headlines. Introduction and Overview Horizontal Actions and Framework Directive Sectoral Issues Austrian Situation and Legislation. Why health and safety at work ?.
922 views • 64 slides

Leading Health and Safety at Work
Leading Health and Safety at Work. Health and Safety Management Responsibilities of Principal Investigators and Managers. Why Health and Safety Is Important. Reputation University of Nottingham aims for excellence in teaching and research
423 views • 16 slides

HEALTH and SAFETY AT WORK
HEALTH and SAFETY AT WORK. "Lost Youth - Four stories of injured young workers (17 min). http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=DMT5OFw5OCQ. Just got your first or second job? That's great! But if you want to make it to payday, there are... 7 Things You'd Better Know. What you don't know can hurt you.
357 views • 18 slides

Health & Safety
Health & Safety. Why Do It?. The Employer must provide Safety Training. upon recruitment change of job or responsibility new equipment or technology changes in systems of work. s2. HASAW Act 1974. Health & Safety at Work Act 1974. Employers’ Duties.
230 views • 5 slides

Health and Safety at Work
Health and Safety at Work. The Darwin Awards.
260 views • 17 slides

Health and Safety at Work Act (1974)
Health and Safety at Work Act (1974). By Tara and Sabrina. What is the Health and Safety at Work Act?. The Health and Safety at Work Act 1974 which is also referred to as HSWA, is the primary piece of legislation covering work-related health and safety in the UK.
685 views • 5 slides

Health and Safety At Work Etc. Act 1974 J Health and Safety Policy Statement
J. C. Pomfret Construction. Health and Safety At Work Etc. Act 1974 J Health and Safety Policy Statement. ACCIDENT STATISTISTICS 2011 -2013. CONTENTS. Part 1 – Introduction Part 2 – General Statement of Intent Part 3 - General Policy Part 4 – Organisation Part 5 – Arrangements
375 views • 11 slides

HEALTH AND SAFETY AT WORK. Regulatory change, roles and responsibilities. GENOVA, January 17 th 2013. Cultural evolutions and social expectations. DEGREE OF ATTENTION. 2010. 1955. 1898. Attention directed to the health and safety of workers and to primary prevention.
426 views • 26 slides

Health and Safety at Work Act 2015 NZ Aid Programme
Health and Safety at Work Act 2015 NZ Aid Programme. January 2017. Introduction. Brief refresher of MFAT’s key duties under Health & Safety at Work Act 2015 (HSWA) How the key duties relate to the NZ Aid Programme Understand MFAT’s approach to H&S in Aid Programme Activities
190 views • 14 slides

SAFETY AND HEALTH AT WORK
7. Chapter. SAFETY AND HEALTH AT WORK. PREVIEW. The provisions of the Occupational Safety and Health Act which affect employers. The importance of encouraging safe work practices and healthy lifestyles among employees. Reducing incidences of sexual harassment at work.
293 views • 25 slides

HEALTH & SAFETY AT WORK etc ACT 1974
HEALTH & SAFETY AT WORK etc ACT 1974. LEVELS OF DUTY/LEGAL TERMS. “It is the duty”:- Absolute - it must/shall/will be done Summers Vs Frost (1955) “Practicable”:- If it can be done, in light of current technological, scientific knowledge, then it MUST BE
333 views • 17 slides

Health & Safety at Work Etc. Act 1974
Health & Safety at Work Etc. Act 1974. Section 2 (1)-Employers Duty. “to ensure, so far as is reasonably practicable, the health, safety and welfare at work of all his employees”. Section 2(2). Provide and maintain plant & systems of work that are, sfairp, safe and without risks to health.
815 views • 27 slides
Got any suggestions?
We want to hear from you! Send us a message and help improve Slidesgo
Top searches
Trending searches

6 templates

indigenous canada
9 templates

121 templates

education technology
232 templates
39 templates

29 templates
Health and Safety in the Workplace Project Proposal
It seems that you like this template, health and safety in the workplace project proposal presentation, free google slides theme, powerpoint template, and canva presentation template.
To have safety in the workplace is a must in every company and it should be properly taken care of. At Slidesgo we’re very serious about this, so this is why we want to help you with your project proposal regarding that matter. Speak about the best tips for health and safety in the workplace, such as defining better policies, building a communication plan and taking legal responsibilities into account, among other things. Use this template, specifically conceived for this topic, and edit the brutalist slides into what you prefer for your presentation!
Features of this template
- 100% editable and easy to modify
- 31 different slides to impress your audience
- Contains easy-to-edit graphics such as graphs, maps, tables, timelines and mockups
- Includes 500+ icons and Flaticon’s extension for customizing your slides
- Designed to be used in Google Slides, Canva, and Microsoft PowerPoint
- 16:9 widescreen format suitable for all types of screens
- Includes information about fonts, colors, and credits of the resources used
How can I use the template?
Am I free to use the templates?
How to attribute?
Combines with:
This template can be combined with this other one to create the perfect presentation:

Attribution required If you are a free user, you must attribute Slidesgo by keeping the slide where the credits appear. How to attribute?
Related posts on our blog.

How to Add, Duplicate, Move, Delete or Hide Slides in Google Slides

How to Change Layouts in PowerPoint

How to Change the Slide Size in Google Slides
Related presentations.

Premium template
Unlock this template and gain unlimited access

NDWorks Campus news for faculty and staff
- Home ›
- Latest ›
Safety Talk: Identify and Address Safety Hazards
by Risk Management and Safety
June 10, 2024

Hazards surround us in both our work and home environments, manifesting in various forms. This could range from a cord across a pathway to a repetitive task, a chilly worksite, or a burnt-out light outside. A hazard is any current or potential condition that, alone or in conjunction with other factors, can lead to harm, damage, or loss. Vigilance is crucial for all of us. Identifying hazards promptly allows employers to address and rectify them, thus preventing accidents and illnesses.
Reporting hazards is a key aspect of our safety strategy. Whether informing your supervisor, maintenance team, safety committee, or using a designated reporting system, reporting hazards promptly is essential. It's better to report a hazard multiple times than not at all. You are the expert in your role, workspace, tasks, and tools. Don't hesitate to speak up if something seems amiss. Avoid falling into the trap of complacency - even routine tasks can conceal hidden dangers after being performed countless times.
TYPES OF HAZARDS
As per the Nine Elements of a Successful Safety & Health System, hazards are classified into four main categories:
Chemical : Such as inhaling, ingesting, or skin contact with various chemical substances.
Physical : Includes risks like slipping, falling, being hit by objects, exposure to fire, or electrical hazards.
Biological : Involves exposure to molds, bloodborne pathogens, wastewater, plant toxins, or insect poisons.
Ergonomic : Involves tasks like working in awkward postures, repetitive movements, forceful actions, or poor workstation design.
The Nine Elements also highlight common hazards to be mindful of:
Environment : lighting, noise, temperature, and humidity
Workstation Design : control and display setup, positioning and alignment of work areas, chair ergonomics, task/job structure
Movement and Repetition : exertion, vibration, posture requirements, physical strain, work pace, tool ergonomics, size and shape of work tools, weight of equipment and objects
Machinery and Equipment Design : motion needed for operation, force required, vibration, posture demands, and necessary pace to operate equipment.
Remember to consider your own physical well-being for potential hazards. Lack of proper rest or experiencing new discomfort can be initial signs of issues. Even medications you take might present risks, especially if they induce drowsiness.
In the event of an incident or near miss at your workplace, make sure to the incident investigation process. This enables the investigator to pinpoint the root causes and uncover all potential hazards that could have played a role. Delving into this level of detail also assists the safety team in determining the most effective methods to prevent the hazards from reoccurring, thus averting future injuries and illnesses.
HOW TO CONTROL HAZARDS
To mitigate hazards, either engineer them out or modify the process or environment to remove the hazard. Alternatively, substitute with a safer option.
Implement administrative controls, which involve using policies or procedures to minimize exposure to hazards. This could include establishing protocols for chemical handling or rotating workers on repetitive tasks.
Utilize suitable personal protective equipment like gloves or eye protection to act as a barrier between you and the hazard.
Remember to adhere to established safety protocols and don't hesitate to suggest alternative solutions for a safer work environment. Let us know if you see an unsafe situation or have a safety concern by completing a Good Catch !
For a fresh perspective on hazard identification, explore the visual literacy research available from the Campbell Institute at thecampbellinstitute.org/research .
Stay vigilant for hazards at home as similar risks present themselves in domestic settings. Empower your family to recognize hazards by taking on the role of safety manager at home. Encourage your loved ones to report safety concerns to you promptly to prevent accidents. While hazards are ever-present, acknowledging and addressing them can help maintain safety for everyone.
References: According to NSC Publication, Nine Elements of a Successful Safety & Health
Test your Hazard Recognition with this fun Spot the Hazard Activity .
Contact Risk Management & Safety for Questions about this or other Safety Related topics @ 574.631.5037 or [email protected]
Workplace bullying
If you are being bullied at work and need support, you can read this fact sheet, see the Get Help section of the website for details on further support. If you know or see someone being bullied, see our Supportive Bystander Fact Sheet to find out how to help them.
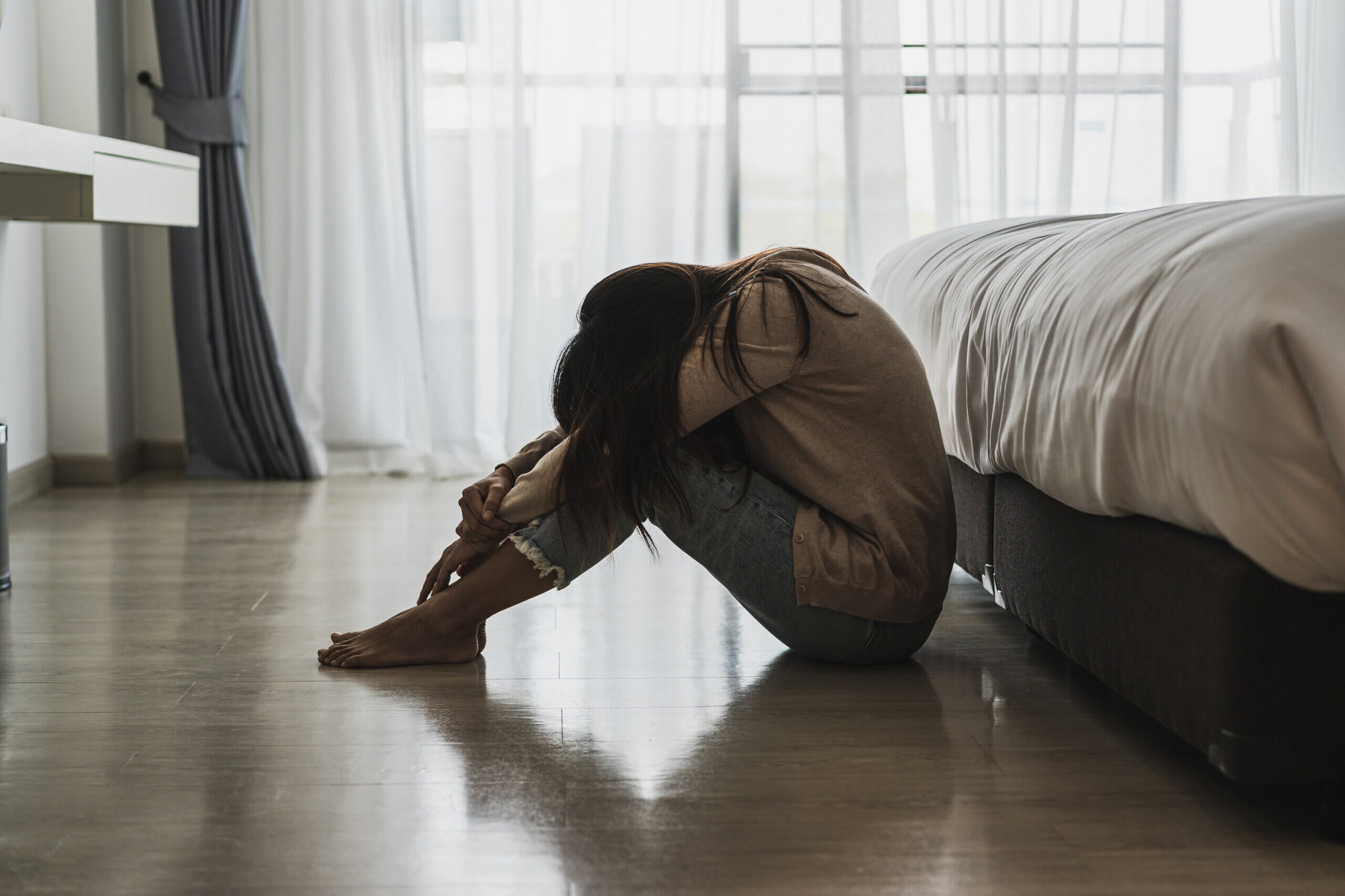

What is workplace bullying?
Workplace bullying is verbal, physical, social or psychological abuse by your employer (or manager), another person or group of people at work.
Workplace bullying can happen in any type of workplace , from offices to shops, cafes, restaurants, workshops, community groups and government organisations.
Workplace bullying can happen to volunteers, work experience students, interns, apprentices, casual and permanent employees.
Some types of workplace bullying are criminal offences. If you have experienced violence, assault and stalking you can report it directly to the police.
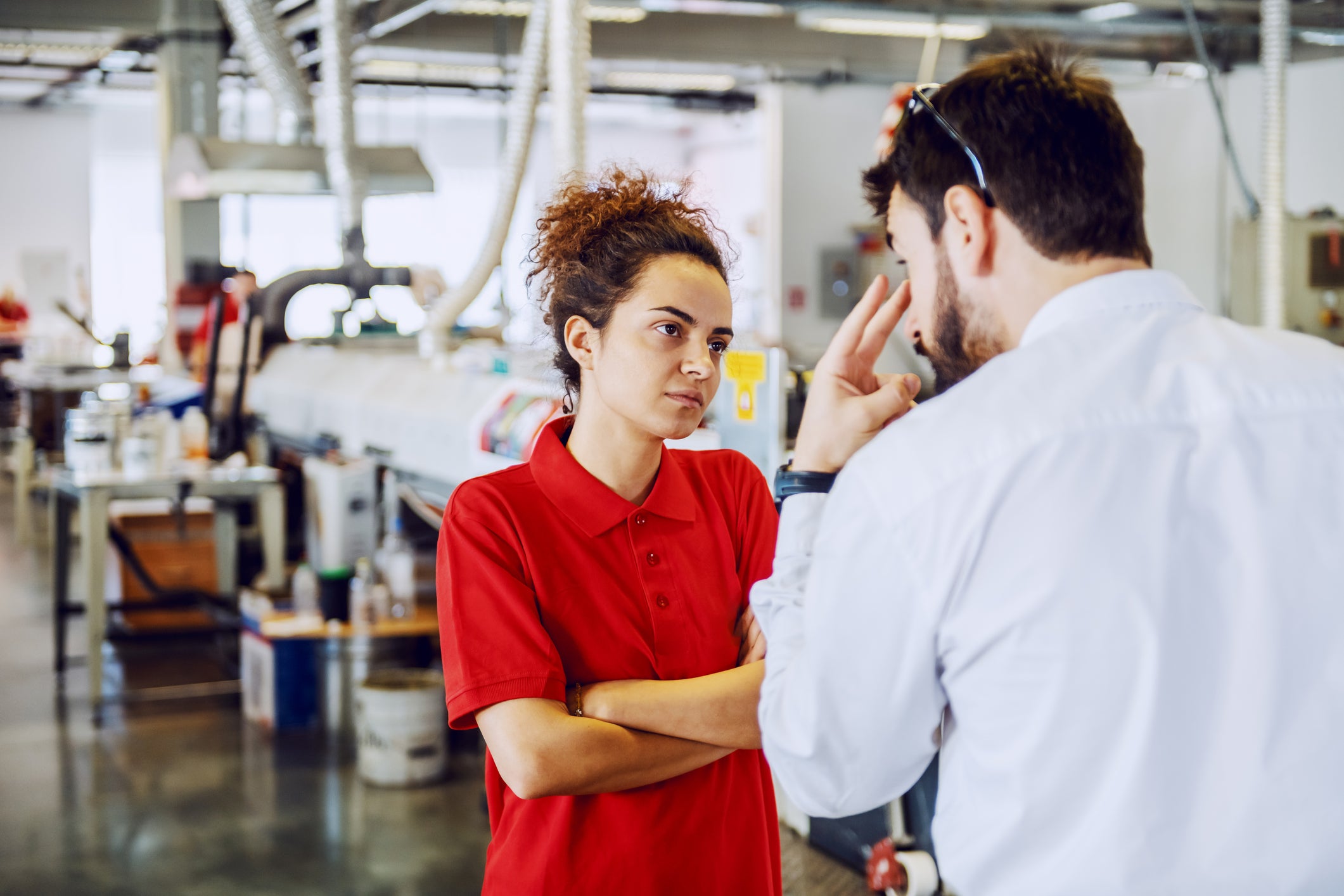
What does bullying in the workplace look like?
- repeated hurtful remarks or attacks, or making fun of your work or you as a person (including your family, sex, sexuality, gender identity, race or culture, education or economic background)
- sexual harassment, particularly stuff like unwelcome touching and sexually explicit comments and requests that make you uncomfortable
- excluding you or stopping you from working with people or taking part in activities that relates to your work
- playing mind games, ganging up on you, or other types of psychological harassment
- intimidation (making you feel less important and undervalued)
- giving you pointless tasks that have nothing to do with your job
- giving you impossible jobs that can't be done in the given time or with the resources provided
- deliberately changing your work hours or schedule to make it difficult for you
- deliberately holding back information you need for getting your work done properly
- pushing, shoving, tripping, grabbing you in the workplace
- attacking or threatening with equipment, knives, guns, clubs or any other type of object that can be turned into a weapon
- initiation or hazing - where you are made to do humiliating or inappropriate things in order to be accepted as part of the team.

How bullying can affect your work
If you are being bullied at work you might:
- be less active or successful
- be less confident in your work
- feel scared, stressed, anxious or depressed
- have your life outside of work affected, e.g. study, relationships
- want to stay away from work
- feel like you can’t trust your employer or the people who you work with
- lack confidence and happiness about yourself and your work
- have physical signs of stress like headaches, backaches, sleep problems
What is not workplace bullying
Some practices in the workplace may not seem fair but are not bullying.
Your employer is allowed to transfer, demote, discipline, counsel, retrench or sack you (as long as they are acting reasonably).
What you need to know if you are being bullied at work
When you are being bullied it's important that you know there are things you can do and people who can help.
You have the right to be in a safe workplace free from violence, harassment and bullying.
Bullying and abuse information for young Australians
If you are under 16 years old, bullying and violence may also be child abuse. See the Youth Law Australia website for further information.
Bullying and discrimination
Bullying may also be discrimination if it is because of your age, sex, pregnancy, race, disability, sexual orientation, religion or certain other reasons. Sexual harassment and racial hatred are also against the law.
Responsibility of employers
Your employer has a legal responsibility under Occupational Health and Safety and anti-discrimination law to provide a safe workplace. Employers have a duty of care for your health and wellbeing whilst at work. An employer that allows bullying to occur in the workplace is not meeting this responsibility.
Responsibility of bystanders
We all have a moral responsibility to help create a positive, safe workplace. If someone in your workplace is experiencing harassment or bullying, you can tell them about the steps they can take to solve it.
What you can do if you are being bullied at work
- Make sure you're informed. Check to see if your workplace has a bullying policy and complaints procedure.
- Keep a diary. Documenting everything that happens, including what you've done to try stopping it. This can help if you make a complaint.
- Get support from someone you trust or contact support services. Even if you don’t know anyone you can talk to, there are support services which are immediately available to help and support you in the Get Help section. Getting support can also include contacting your union.
- Approach the bully. If you feel safe and confident, you can approach the person who is bullying you and tell them that their behaviour is unwanted and not acceptable. If you are unsure how to approach them, you might be able to get advice from an appointed contact person, or from a colleague or manager.
- Tell someone at your work. Your workplace will usually have a process for making a complaint and resolving disputes, which might include a warning, requiring the bully to have counselling, a mediation process, or even firing the bully if the situation continues. The person to talk to might be your supervisor/manager, a harassment contact officer, or a health and safety representative (if your work has one).
- Get information and advice. If the bullying is serious, if the situation has not changed after complaining to your manager, or if there is not anyone you can safely talk to at work you can get outside information and advice.
- Make a formal complaint to the state and territory workplace health and safety authority or to the Australian Human Rights Commission, using the links below.
Getting Help
If you have made a complaint to your manager or others in your workplace and there have not been adequate steps taken to stop the bullying there are a number of options that you can take to get help.
When to contact the police
If bullying is violent or threatening it may be a criminal offence and you should contact the police immediately call 000
If the situation in not urgent you can call the Police Assistance Line on 131 444 for all states and territories except for Victoria, where you will need to visit your local police station.
Making a complaint about workplace bullying to the Australian Human Rights Commission
If you are been bullied, harassed or discriminated against because of your race, sex, age, sexual orientation, religion or because you have a disability or are pregnant you can contact the Australian Human Rights Commission. Call 1300 656 419 . See further information about making a complaint to the Commission for young people.
The Commonwealth FairWork Ombudsman
The Commonwealth FairWork Ombudsman can provide information and advice about Australia’s workplace rights and rules and the protection you have against harassment and discrimination. Call 13 13 94 . You can access FairWork's resources on their website.
Report bullying to a State or Territory work health and safety authority
Your boss has a duty to ensure the health, safety and welfare at work of all their employees. You can report bullying incidences to the following state and territory work health and safety authorities.
- Australian Capital Territory WorkSafe ACT can provide advice and help if you are experiencing workplace bullying. Call 02 6207 3000
- New South Wales SafeWork NSW can provide advice and help if you are experiencing workplace bullying. Call 13 10 50
- Northern Territory NT WorkSafe can provide advice and help if you are experiencing workplace bullying. Call 1800 019 115
- Queensland WorkSafe Queensland 1300 362 128 can provide advice if you are experiencing workplace bullying. For information for young workers, see WorkSafe Queensland's resource for young workers .
- South Australia SafeWork SA can provide advice and help if you are experiencing workplace bullying. Call 1300 365 255
- Tasmania WorkSafe Tas can provide advice and help if you are experiencing workplace bullying. Call 1300 366 322 (within Tasmania) or (03) 6166 4600 (outside Tasmania)
- Victoria WorkSafe Victoria can provide advice and help if you are experiencing workplace bullying. Call 1800 136 089
- Western Australia WorkSafe WA can provide advice and help if you are experiencing workplace bullying. Call 1300 307 877
Other Helpful Resources
- Contact Australian Unions or the union representing your industry who can give you advice on your options and your rights. You can get advice on workplace bullying from the Workers helpline 1300 486 466
- Youth Law Australia for legal information especially for young people
- To learn more about your rights at work see the Australian Council of Trade Unions website for students.
Further Reading about Bullying
- Understand what Cyberbullying looks like, what to do and how to get help
- Explore advice and resources on being a Supportive Bystander
- Recognise Workplace Bullying , its impact and what you can do
- Be informed about Human Rights , their origins and the international human rights system
This Violence, Harassment and Bullying fact sheet was developed in partnership with the ReachOut.com , 2011
The state of AI in early 2024: Gen AI adoption spikes and starts to generate value
If 2023 was the year the world discovered generative AI (gen AI) , 2024 is the year organizations truly began using—and deriving business value from—this new technology. In the latest McKinsey Global Survey on AI, 65 percent of respondents report that their organizations are regularly using gen AI, nearly double the percentage from our previous survey just ten months ago. Respondents’ expectations for gen AI’s impact remain as high as they were last year , with three-quarters predicting that gen AI will lead to significant or disruptive change in their industries in the years ahead.
About the authors
This article is a collaborative effort by Alex Singla , Alexander Sukharevsky , Lareina Yee , and Michael Chui , with Bryce Hall , representing views from QuantumBlack, AI by McKinsey, and McKinsey Digital.
Organizations are already seeing material benefits from gen AI use, reporting both cost decreases and revenue jumps in the business units deploying the technology. The survey also provides insights into the kinds of risks presented by gen AI—most notably, inaccuracy—as well as the emerging practices of top performers to mitigate those challenges and capture value.
AI adoption surges
Interest in generative AI has also brightened the spotlight on a broader set of AI capabilities. For the past six years, AI adoption by respondents’ organizations has hovered at about 50 percent. This year, the survey finds that adoption has jumped to 72 percent (Exhibit 1). And the interest is truly global in scope. Our 2023 survey found that AI adoption did not reach 66 percent in any region; however, this year more than two-thirds of respondents in nearly every region say their organizations are using AI. 1 Organizations based in Central and South America are the exception, with 58 percent of respondents working for organizations based in Central and South America reporting AI adoption. Looking by industry, the biggest increase in adoption can be found in professional services. 2 Includes respondents working for organizations focused on human resources, legal services, management consulting, market research, R&D, tax preparation, and training.
Also, responses suggest that companies are now using AI in more parts of the business. Half of respondents say their organizations have adopted AI in two or more business functions, up from less than a third of respondents in 2023 (Exhibit 2).
Gen AI adoption is most common in the functions where it can create the most value
Most respondents now report that their organizations—and they as individuals—are using gen AI. Sixty-five percent of respondents say their organizations are regularly using gen AI in at least one business function, up from one-third last year. The average organization using gen AI is doing so in two functions, most often in marketing and sales and in product and service development—two functions in which previous research determined that gen AI adoption could generate the most value 3 “ The economic potential of generative AI: The next productivity frontier ,” McKinsey, June 14, 2023. —as well as in IT (Exhibit 3). The biggest increase from 2023 is found in marketing and sales, where reported adoption has more than doubled. Yet across functions, only two use cases, both within marketing and sales, are reported by 15 percent or more of respondents.
Gen AI also is weaving its way into respondents’ personal lives. Compared with 2023, respondents are much more likely to be using gen AI at work and even more likely to be using gen AI both at work and in their personal lives (Exhibit 4). The survey finds upticks in gen AI use across all regions, with the largest increases in Asia–Pacific and Greater China. Respondents at the highest seniority levels, meanwhile, show larger jumps in the use of gen Al tools for work and outside of work compared with their midlevel-management peers. Looking at specific industries, respondents working in energy and materials and in professional services report the largest increase in gen AI use.
Investments in gen AI and analytical AI are beginning to create value
The latest survey also shows how different industries are budgeting for gen AI. Responses suggest that, in many industries, organizations are about equally as likely to be investing more than 5 percent of their digital budgets in gen AI as they are in nongenerative, analytical-AI solutions (Exhibit 5). Yet in most industries, larger shares of respondents report that their organizations spend more than 20 percent on analytical AI than on gen AI. Looking ahead, most respondents—67 percent—expect their organizations to invest more in AI over the next three years.
Where are those investments paying off? For the first time, our latest survey explored the value created by gen AI use by business function. The function in which the largest share of respondents report seeing cost decreases is human resources. Respondents most commonly report meaningful revenue increases (of more than 5 percent) in supply chain and inventory management (Exhibit 6). For analytical AI, respondents most often report seeing cost benefits in service operations—in line with what we found last year —as well as meaningful revenue increases from AI use in marketing and sales.
Inaccuracy: The most recognized and experienced risk of gen AI use
As businesses begin to see the benefits of gen AI, they’re also recognizing the diverse risks associated with the technology. These can range from data management risks such as data privacy, bias, or intellectual property (IP) infringement to model management risks, which tend to focus on inaccurate output or lack of explainability. A third big risk category is security and incorrect use.
Respondents to the latest survey are more likely than they were last year to say their organizations consider inaccuracy and IP infringement to be relevant to their use of gen AI, and about half continue to view cybersecurity as a risk (Exhibit 7).
Conversely, respondents are less likely than they were last year to say their organizations consider workforce and labor displacement to be relevant risks and are not increasing efforts to mitigate them.
In fact, inaccuracy— which can affect use cases across the gen AI value chain , ranging from customer journeys and summarization to coding and creative content—is the only risk that respondents are significantly more likely than last year to say their organizations are actively working to mitigate.
Some organizations have already experienced negative consequences from the use of gen AI, with 44 percent of respondents saying their organizations have experienced at least one consequence (Exhibit 8). Respondents most often report inaccuracy as a risk that has affected their organizations, followed by cybersecurity and explainability.
Our previous research has found that there are several elements of governance that can help in scaling gen AI use responsibly, yet few respondents report having these risk-related practices in place. 4 “ Implementing generative AI with speed and safety ,” McKinsey Quarterly , March 13, 2024. For example, just 18 percent say their organizations have an enterprise-wide council or board with the authority to make decisions involving responsible AI governance, and only one-third say gen AI risk awareness and risk mitigation controls are required skill sets for technical talent.
Bringing gen AI capabilities to bear
The latest survey also sought to understand how, and how quickly, organizations are deploying these new gen AI tools. We have found three archetypes for implementing gen AI solutions : takers use off-the-shelf, publicly available solutions; shapers customize those tools with proprietary data and systems; and makers develop their own foundation models from scratch. 5 “ Technology’s generational moment with generative AI: A CIO and CTO guide ,” McKinsey, July 11, 2023. Across most industries, the survey results suggest that organizations are finding off-the-shelf offerings applicable to their business needs—though many are pursuing opportunities to customize models or even develop their own (Exhibit 9). About half of reported gen AI uses within respondents’ business functions are utilizing off-the-shelf, publicly available models or tools, with little or no customization. Respondents in energy and materials, technology, and media and telecommunications are more likely to report significant customization or tuning of publicly available models or developing their own proprietary models to address specific business needs.
Respondents most often report that their organizations required one to four months from the start of a project to put gen AI into production, though the time it takes varies by business function (Exhibit 10). It also depends upon the approach for acquiring those capabilities. Not surprisingly, reported uses of highly customized or proprietary models are 1.5 times more likely than off-the-shelf, publicly available models to take five months or more to implement.
Gen AI high performers are excelling despite facing challenges
Gen AI is a new technology, and organizations are still early in the journey of pursuing its opportunities and scaling it across functions. So it’s little surprise that only a small subset of respondents (46 out of 876) report that a meaningful share of their organizations’ EBIT can be attributed to their deployment of gen AI. Still, these gen AI leaders are worth examining closely. These, after all, are the early movers, who already attribute more than 10 percent of their organizations’ EBIT to their use of gen AI. Forty-two percent of these high performers say more than 20 percent of their EBIT is attributable to their use of nongenerative, analytical AI, and they span industries and regions—though most are at organizations with less than $1 billion in annual revenue. The AI-related practices at these organizations can offer guidance to those looking to create value from gen AI adoption at their own organizations.
To start, gen AI high performers are using gen AI in more business functions—an average of three functions, while others average two. They, like other organizations, are most likely to use gen AI in marketing and sales and product or service development, but they’re much more likely than others to use gen AI solutions in risk, legal, and compliance; in strategy and corporate finance; and in supply chain and inventory management. They’re more than three times as likely as others to be using gen AI in activities ranging from processing of accounting documents and risk assessment to R&D testing and pricing and promotions. While, overall, about half of reported gen AI applications within business functions are utilizing publicly available models or tools, gen AI high performers are less likely to use those off-the-shelf options than to either implement significantly customized versions of those tools or to develop their own proprietary foundation models.
What else are these high performers doing differently? For one thing, they are paying more attention to gen-AI-related risks. Perhaps because they are further along on their journeys, they are more likely than others to say their organizations have experienced every negative consequence from gen AI we asked about, from cybersecurity and personal privacy to explainability and IP infringement. Given that, they are more likely than others to report that their organizations consider those risks, as well as regulatory compliance, environmental impacts, and political stability, to be relevant to their gen AI use, and they say they take steps to mitigate more risks than others do.
Gen AI high performers are also much more likely to say their organizations follow a set of risk-related best practices (Exhibit 11). For example, they are nearly twice as likely as others to involve the legal function and embed risk reviews early on in the development of gen AI solutions—that is, to “ shift left .” They’re also much more likely than others to employ a wide range of other best practices, from strategy-related practices to those related to scaling.
In addition to experiencing the risks of gen AI adoption, high performers have encountered other challenges that can serve as warnings to others (Exhibit 12). Seventy percent say they have experienced difficulties with data, including defining processes for data governance, developing the ability to quickly integrate data into AI models, and an insufficient amount of training data, highlighting the essential role that data play in capturing value. High performers are also more likely than others to report experiencing challenges with their operating models, such as implementing agile ways of working and effective sprint performance management.
About the research
The online survey was in the field from February 22 to March 5, 2024, and garnered responses from 1,363 participants representing the full range of regions, industries, company sizes, functional specialties, and tenures. Of those respondents, 981 said their organizations had adopted AI in at least one business function, and 878 said their organizations were regularly using gen AI in at least one function. To adjust for differences in response rates, the data are weighted by the contribution of each respondent’s nation to global GDP.
Alex Singla and Alexander Sukharevsky are global coleaders of QuantumBlack, AI by McKinsey, and senior partners in McKinsey’s Chicago and London offices, respectively; Lareina Yee is a senior partner in the Bay Area office, where Michael Chui , a McKinsey Global Institute partner, is a partner; and Bryce Hall is an associate partner in the Washington, DC, office.
They wish to thank Kaitlin Noe, Larry Kanter, Mallika Jhamb, and Shinjini Srivastava for their contributions to this work.
This article was edited by Heather Hanselman, a senior editor in McKinsey’s Atlanta office.
Explore a career with us
Related articles.

Moving past gen AI’s honeymoon phase: Seven hard truths for CIOs to get from pilot to scale

A generative AI reset: Rewiring to turn potential into value in 2024

Implementing generative AI with speed and safety
Recommitting to blood donation
Mbabane – Marcia Motsa, a human-resources professional and mother of two, from Manzini, Eswatini, started her journey with blood donation during high school, when the local blood bank visited and provided detailed information about the process. Although she stopped donating after school as work and family shifted her focus, in 2023 her commitment was reignited by a presentation given by the Ministry of Health at her workplace.
“The realization that donating blood is a crucial, sacrificial, act anyone can perform made me decide to start donating again,” she says. “Blood is not a resource that can be purchased anywhere. So, the lack of that ‘product’, makes it even more important for people to realize that blood donation is something that they should consider doing.”
Reflecting on her early experience, Motsa acknowledges that donating blood as a young person influenced her renewed commitment as an adult. "I knew the process and wasn't afraid. Now, as a mother, I'm more aware of the need for blood in health care facilities and I am more committed to donating," she says.
Reflecting on a recent blood donation drive in which she participated, Motsa says the process was quick and relaxed due to the professionalism of health care workers. Despite her fear of needles, the supportive environment and awareness of the vital need for blood help her overcome any anxieties. “I didn't feel dizzy, I didn't feel anything,” she says. “I felt like they could take more blood, but they say they have a threshold. So, I felt good afterwards and I was okay for the rest of the day.”
Motsa believes that workplaces can contribute to making blood donation more accessible to professionals and the working class by having clinics on site. “I appreciate the work that is being done, through various partnerships, by the Ministry of Health,” she says “As a professional the challenge is balancing work and other commitments. If there was a clinic here that I can just go and pop by any time, it would make things even easier.”
She urges young people to start the habit of donating blood early in life, as she did. “There are certain decisions that you need to start cultivating yourself into doing, which feed into the person that you become at a later stage,” she says. “It’s good to start such a noble behaviour young.”
WHO Communications Officer Email: mavusow [at] who.int Tel: +26878020180 WhatsApp: +26876509256
Communications and marketing officer Tel: + 242 06 520 65 65 (WhatsApp) Email: boakyeagyemangc [at] who.int

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Safety and Health Programs can help reduce these fatalities through a proactive approach to finding and fixing hazards before they cause injury, illness, or death. Introduction. Lesson objectives: Recognize the costs of workplace accidents. Recognize benefits of implementing an effective safety and health program.
Here are 12 great safety presentation ideas for your workplace: 1. How to prevent slips, trips, and falls. 2. How to stay safe when working on an elevated work platform...
Organization Risks And Hazards, Hazard Identification And Evaluation, Hazard Prevention And Control. Slide 1: This slide displays the title Maintaining Health and Safety at Workplace. Slide 2: This slide displays the title Agenda for Maintaining health and safety at workplace. Slide 3: This slide exhibit table of content.
Template 1- Focus on Employee Safety to Avoid Critical Incident. This PPT Template is a torchbearer for the activities that an organization can implement to employ the best employee safety practices in the construction business. It highlights the agenda for a safety program, major issues, goals, impact of safety training, and performance sheet.
Download Safety And Health At Work Hazards PPT PowerPoint Templates. Template 3. Create an invigorating workplace safety plan that provides a two-fold system of ensuring employee safety. Besides, you can also take advantage of the smart art given in the template and design a framework for policies and procedures to make safety a top priority ...
7. Safety And Health Hazards In The Workplace 1-Organizational qualities 1. The working conditions and time 2. The tools and technology available to do the job 3. The availability of guns brought to work The size of the organization has also been shown to be related to incidence rates. Small organizations (those with fewer than 50 employees ...
Use visual aids for communication. One of the main ways your presentation can stand out is by utilizing visual aids. Visual aids can help retain comprehension and retention, which will lead to a higher quality safety presentation. This can be achieved through high-quality graphics, images, videos, and graphics that make the presentation more ...
The document discusses various topics related to workplace health and safety. It covers the importance of occupational health and safety (OHS), OHS management programs, sample company OHS policies, responsibilities of supervisors and workers, safety signs and symbols, identifying hazards, personal protective equipment (PPE), types of workplace hazards, hazard prevention and control, risk ...
Free Google Slides theme, PowerPoint template, and Canva presentation template. Feeling overwhelmed about organizing a health and safety workshop? Don't worry, we've got you covered! With our creative template, you'll have all the tools you need to make your next workshop a huge success. Not only does it come fully loaded with interesting ...
Safety Meetings. Safety meetings, also known as safety briefings or safety talks, are formal gatherings in a professional setting where employees, management, and sometimes even third-party stakeholders come together to discuss health and safety concerns within the workplace. They typically last between 20 to 45 minutes and can involve a variety of formats, such as presentations, group ...
Worker management through AI - From technology development to the impacts on workers and their safety and health. Need to explain the campaign to your colleagues, clients or contacts quickly and clearly? Our PowerPoint presentation is just what you're looking for. The slides summarise the key points, presenting facts and figures, legislation ...
Occupational Health & Safety Presentation. Oct 1, 2009 • Download as PPT, PDF •. 194 likes • 137,041 views. M. Mark Zeeman. Presentation to (New & Old) employees on OH & S issues. An informed package to refresh & introduce others to issues involved within the workplace. It is focused on everyday issues occuring in work.
For this reason, on April 28 is celebrated the world day of safety and health at work. At Slidesgo we are very aware of this issue, and that is why we bring you today this template that you can edit to inform your employees about the importance of prevention measures, especially now in times of coronavirus. It has a blue color, which is ...
Unit 7 Safety and Health at Work. 2 Introduction Most employees spend at least eight hours at their workplace, the work environment should be safe and healthy for them to perform their best. Organizations take steps to prevent accidents and to improve the health of their employees. 3 Law Books The Occupational Safety and Health Act 1994.
Watch the video. The Working together on health and safety presentation provides you with the basic facts you need to know about the Health and Safety at Work Act (HSWA). The video below, presented by former WorkSafe Chief Executive Gordon MacDonald, is a great resource for getting the message across to your business.
Slide 1: This slide displays the title Health and Safety of Employees in Organization. Slide 2: This slide displays the title Agenda for health and safety of employees in organization. Slide 3: This slide exhibit table of content. Slide 4: This slide exhibit table of content- Current Problems related to Workplace Incidents.
Health and Safety at Workplace Presentation - Free download as Powerpoint Presentation (.ppt), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or view presentation slides online. heath
Workplace Safety Powerpoint Presentation - Free download as Powerpoint Presentation (.ppt), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or view presentation slides online. The document discusses workplace safety and outlines several topics related to creating a safe workplace for both typical employees and supported employees, including: providing safety training and information; maintaining safe ...
R. RaviPrashant5. - Good health and safety procedures have many benefits for workplaces like reduced costs and risks, increased productivity, and more motivated workers. - The main causes of workplace illness are stress, musculoskeletal injuries, and respiratory diseases. The most serious accidents are falls from heights and being struck by ...
Presentation Transcript. The Health and Safety at Work etc. Act 1974 is the primary piece of legislation covering occupational health and safety in the United Kingdom. • The main principles are below: • Securing the health, safety and welfare of people at work • Protecting others against health or safety risks in connection with the ...
A well-written and implemented workplace violence prevention program can reduce the incidence of workplace violence. Previous Next OSHA's Safety and Health Topics pages provide regulatory and enforcement information, hazard identification and controls as well as best practices and other resources to assist employers, workers and safety and ...
To have safety in the workplace is a must in every company and it should be properly taken care of. At Slidesgo we're very serious about this, so this is why we want to help you with your project proposal regarding that matter. Speak about the best tips for health and safety in the workplace, such as defining better policies, building a ...
Encourage your loved ones to report safety concerns to you promptly to prevent accidents. While hazards are ever-present, acknowledging and addressing them can help maintain safety for everyone. References: According to NSC Publication, Nine Elements of a Successful Safety & Health. Test your Hazard Recognition with this fun Spot the Hazard ...
Workplace Safety and Health: 833-579-0927: Labor Commissioner's Office: Wages, breaks, retaliation and labor laws: 833-526-4636: Division of Workers' Compensation: Benefits for work-related injuries and illnesses: 1-800-736-7401: Office of the Director: Any other topic related to the Department of Industrial Relations:
The document summarizes the key aspects and history of health and safety legislation in the UK, including the Health and Safety at Work Act of 1974. It established general duties for employers and employees, and created the Health and Safety Executive body to regulate workplace health, safety, and welfare. The legislation set a basic principle ...
a serious violation of the workplace violence prevention program exists . an imminent danger exists . The employee or authorized employee representative may submit a written request for an inspection by filing a complaint with the Public Employee Safety and Health (PESH) bureau at the Department of Labor's Division of Safety and Health
Your employer has a legal responsibility under Occupational Health and Safety and anti-discrimination law to provide a safe workplace. Employers have a duty of care for your health and wellbeing whilst at work. An employer that allows bullying to occur in the workplace is not meeting this responsibility. Responsibility of bystanders
If 2023 was the year the world discovered generative AI (gen AI), 2024 is the year organizations truly began using—and deriving business value from—this new technology.In the latest McKinsey Global Survey on AI, 65 percent of respondents report that their organizations are regularly using gen AI, nearly double the percentage from our previous survey just ten months ago.
The Workplace Health and Safety Act aims to protect workers through promoting safety awareness. It outlines mandatory requirements for employers and employees. Regular inspections identify hazards, which must be addressed. Managers must ensure inspections occur and issues are resolved. Workplace hazards can arise from substances, equipment ...
The World Health Organization (WHO) is building a better future for people everywhere. Health lays the foundation for vibrant and productive communities, stronger economies, safer nations and a better world. Our work touches lives around the world every day - often in invisible ways. As the lead health authority within the United Nations (UN) system, we help ensure the safety of the air we ...