Common Core Algebra 2 Math (Worksheets, Homework, Lesson Plans)
Related Topics: Common Core Math Resources, Lesson Plans & Worksheets for all grades
Looking for video lessons that will help you in your Common Core Algebra 2 math classwork or homework? Looking for Common Core Math Worksheets and Lesson Plans that will help you prepare lessons for Algebra 2 students?
The following lesson plans and worksheets are from the New York State Education Department Common Core-aligned educational resources. Eureka/EngageNY Math Algebra 2 Worksheets.
These Lesson Plans and Worksheets are divided into five modules.

Algebra 2 Homework, Lesson Plans and Worksheets
| Topics and Objectives (Module 1) |
|---|
| Polynomial, Rational, and Radical Relationships : Successive Differences in Polynomials ( ) : The Multiplication of Polynomials ( ) : The Division of Polynomials ( ) : Comparing Methods—Long Division, Again? ( ) : Putting It All Together ( ) : Dividing by 𝒙 − 𝒂 and by 𝒙 + 𝒂 ( ) : Mental Math ( ) : The Power of Algebra—Finding Primes ( ) : Radicals and Conjugates ( ) : The Power of Algebra—Finding Pythagorean Triples ( ) : The Special Role of Zero in Factoring ( ) |
| Factoring—Its Use and Its Obstacles : Overcoming Obstacles in Factoring ( ) : Mastering Factoring ( ) : Graphing Factored Polynomials ( ) : Structure in Graphs of Polynomial Functions ( ) : Modeling with Polynomials—An Introduction ( ) : Modeling with Polynomials—An Introduction ( ) : Overcoming a Second Obstacle in Factoring—What If There Is a Remainder? ( ) : The Remainder Theorem ( ) : Modeling Riverbeds with Polynomials ( ) : Modeling Riverbeds with Polynomials ( ) |
| Solving and Applying Equations—Polynomial, Rational, and Radical : Equivalent Rational Expressions ( ) : Comparing Rational Expressions ( ) : Multiplying and Dividing Rational Expressions ( ) : Adding and Subtracting Rational Expression ( ) : Solving Rational Equations: Solving Rational Equations ( ) : Word Problems Leading to Rational Equations ( ) : A Focus on Square Roots ( ) : Solving Radical Equations ( ) : Linear Systems in Three Variables ( ) : Systems of Equations ( ) : Graphing Systems of Equations ( ) : The Definition of a Parabola ( ) : Are All Parabolas Congruent? ( ) : Are All Parabolas Similar? ( ) |
| A Surprise from Geometry—Complex Numbers Overcome All Obstacles : Overcoming a Third Obstacle to Factoring—What If There Are No Real Number Solutions? ( ) : A Surprising Boost from Geometry ( ) : Complex Numbers as Solutions to Equations ( ) : Factoring Extended to the Complex Realm ( ) : Obstacles Resolved—A Surprising Result ( ) |
| Topics and Objectives (Module 2) |
|---|
| The Story of Trigonometry and Its Contexts : Ferris Wheels—Tracking the Height of a Passenger Car ( ) : The Height and Co-Height Functions of a Ferris Wheel ( ) : The Motion of the Moon, Sun, and Stars—Motivating Mathematics ( ) : From Circle-ometry to Trigonometry ( ) : Extending the Domain of Sine and Cosine to All Real Numbers : Why Call It Tangent? : Secant and the Co-Functions : Graphing the Sine and Cosine Functions : Awkward! Who Chose the Number 360, Anyway? : Basic Trigonometric Identities from Graphs |
| Understanding Trigonometric Functions and Putting Them to Use : Transforming the Graph of the Sine Function : Ferris Wheels—Using Trigonometric Functions to Model Cyclical Behavior : Tides, Sound Waves, and Stock Markets : Graphing the Tangent Function : What Is a Trigonometric Identity? : Proving Trigonometric Identities : Trigonometric Identity Proofs |
| Module 3 |
|---|
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| Module 4 |
|---|
| |
| |
| |
| |

We welcome your feedback, comments and questions about this site or page. Please submit your feedback or enquiries via our Feedback page.
HIGH SCHOOL
- ACT Tutoring
- SAT Tutoring
- PSAT Tutoring
- ASPIRE Tutoring
- SHSAT Tutoring
- STAAR Tutoring
GRADUATE SCHOOL
- MCAT Tutoring
- GRE Tutoring
- LSAT Tutoring
- GMAT Tutoring
- AIMS Tutoring
- HSPT Tutoring
- ISAT Tutoring
- SSAT Tutoring
Search 50+ Tests
Loading Page
math tutoring
- Elementary Math
- Pre-Calculus
- Trigonometry
science tutoring
Foreign languages.
- Mandarin Chinese
elementary tutoring
- Computer Science
Search 350+ Subjects
- Video Overview
- Tutor Selection Process
- Online Tutoring
- Mobile Tutoring
- Instant Tutoring
- How We Operate
- Our Guarantee
- Impact of Tutoring
- Reviews & Testimonials
- About Varsity Tutors
Common Core: High School - Functions : Unit Circle in the Coordinate Plane: CCSS.Math.Content.HSF-TF.A.2
Study concepts, example questions & explanations for common core: high school - functions, all common core: high school - functions resources, example questions, example question #1 : unit circle in the coordinate plane: ccss.math.content.hsf tf.a.2.

This question is testing one's ability to understand the trigonometric relationships and how the relate to the unit circle for solving problems.
For the purpose of Common Core Standards, "Explain how the unit circle in the coordinate plane enables the extension of trigonometric functions to all real numbers, interpreted as radian measures of angles traversed counterclockwise around the unit circle." falls within the Cluster A of "Extend the domain of trigonometric functions using the unit circle" concept (CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.HSF-TF.A.2).
Knowing the standard and the concept for which it relates to, we can now do the step-by-step process to solve the problem in question.

Step 2: Use right triangles and the unit circle to identify the trigonometric characteristics of the describe situation.
The unit circle is an extremely helpful tool in solving trigonometric problems. For the purpose of trigonometry, the unit circle is located at the origin and has a radius of one unit. This is because right triangles can be formed using the x axis as one leg of the triangle and the line from the origin to a point on the circle as the hypotenuse with a measurement of one.

For this particular question,

Step 3: Answer the question.

Example Question #2 : Unit Circle In The Coordinate Plane: Ccss.Math.Content.Hsf Tf.A.2

Example Question #11 : Trigonometric Functions

Recall that using trigonometric identities tangent is,

Example Question #4 : Unit Circle In The Coordinate Plane: Ccss.Math.Content.Hsf Tf.A.2

Example Question #5 : Unit Circle In The Coordinate Plane: Ccss.Math.Content.Hsf Tf.A.2

Example Question #6 : Unit Circle In The Coordinate Plane: Ccss.Math.Content.Hsf Tf.A.2

Example Question #7 : Unit Circle In The Coordinate Plane: Ccss.Math.Content.Hsf Tf.A.2

Example Question #8 : Unit Circle In The Coordinate Plane: Ccss.Math.Content.Hsf Tf.A.2

Example Question #9 : Unit Circle In The Coordinate Plane: Ccss.Math.Content.Hsf Tf.A.2

Example Question #10 : Unit Circle In The Coordinate Plane: Ccss.Math.Content.Hsf Tf.A.2

Report an issue with this question
If you've found an issue with this question, please let us know. With the help of the community we can continue to improve our educational resources.
DMCA Complaint
If you believe that content available by means of the Website (as defined in our Terms of Service) infringes one or more of your copyrights, please notify us by providing a written notice (“Infringement Notice”) containing the information described below to the designated agent listed below. If Varsity Tutors takes action in response to an Infringement Notice, it will make a good faith attempt to contact the party that made such content available by means of the most recent email address, if any, provided by such party to Varsity Tutors.
Your Infringement Notice may be forwarded to the party that made the content available or to third parties such as ChillingEffects.org.
Please be advised that you will be liable for damages (including costs and attorneys’ fees) if you materially misrepresent that a product or activity is infringing your copyrights. Thus, if you are not sure content located on or linked-to by the Website infringes your copyright, you should consider first contacting an attorney.
Please follow these steps to file a notice:
You must include the following:
A physical or electronic signature of the copyright owner or a person authorized to act on their behalf; An identification of the copyright claimed to have been infringed; A description of the nature and exact location of the content that you claim to infringe your copyright, in \ sufficient detail to permit Varsity Tutors to find and positively identify that content; for example we require a link to the specific question (not just the name of the question) that contains the content and a description of which specific portion of the question – an image, a link, the text, etc – your complaint refers to; Your name, address, telephone number and email address; and A statement by you: (a) that you believe in good faith that the use of the content that you claim to infringe your copyright is not authorized by law, or by the copyright owner or such owner’s agent; (b) that all of the information contained in your Infringement Notice is accurate, and (c) under penalty of perjury, that you are either the copyright owner or a person authorized to act on their behalf.
Send your complaint to our designated agent at:
Charles Cohn Varsity Tutors LLC 101 S. Hanley Rd, Suite 300 St. Louis, MO 63105
Or fill out the form below:
Contact Information
Complaint details.

| Email address: | |
| Your name: | |
| Feedback: |
Using the Unit Circle
By upgrading a subject, you'll have access to the rest of the Prompt, a Sample Response, and an Explanation.
algebra 2 unit circle
All Formats
Resource types, all resource types.
- Rating Count
- Price (Ascending)
- Price (Descending)
- Most Recent
Algebra 2 unit circle

Angles and the Unit Circle ( Algebra 2 - Unit 11)


Algebra 2 Trig Bundle | Trig Activities | Unit Circle | Graphing Trig Functions

Trig Functions and The Unit Circle ( Algebra 2 )

Radians and the Unit Circle - Unit and Activities - Algebra 2 Curriculum

Trigonometric Functions and Unit Circle | Algebra 2 | Video | Notes | Homework

Trigonometry Unit Circle MINI UNIT - Algebra 2 and Pre-Calculus

ALGEBRA 2 Trig Graph Practice | Activities | Discovery Lesson | Unit Circle
Algebra 2 UNIT 14: UNIT CIRCLE PART 2

Radians and the Unit Circle - Algebra 2 Curriculum Unit
Algebra 2 UNIT 13: UNIT CIRCLE PART 1
The Unit Circle Guided Notes for Algebra 2 Trigonometry No Prep

Algebra 2 | Unit Circle Lesson PowerPoint

Trigonometry on the Unit Circle Note Guide | Algebra 2 , PreCalculus

Algebra 2 Curriculum Florida - Unit 11 - Trigonometry - Unit Circle Angles

Notes Packet - Unit Circle Trig Functions ( Algebra 2 )

Unit Circle ( Algebra 2 )

Trigonometric Functions & Unit Circle Unit Plan ( Algebra 2 /PreCalculus)

- Word Document File
Trigonometry ( Algebra 2 Curriculum - Unit 12) | All Things Algebra ®

- Google Apps™

Unit Circle | Mazes

Unit Circle Activity Pack

- Easel Activity

Unit Circle Paper Plate Activity

Unit Circle Math Classroom Word Wall

Unit Circle | Triples Activity
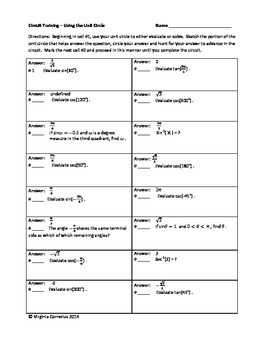
Circuit Training - Using the Unit Circle (Trigonometry)

- We're hiring
- Help & FAQ
- Privacy policy
- Student privacy
- Terms of service
- Tell us what you think
Common Core Algebra II.Unit 2.Lesson 1.Introduction to Functions
emathinstruction
Sep 22, 2016
Hello and welcome to another common core algebra two lesson by E math instruction. My name is Kirk weiler and today we're going to be doing unit two lesson number one on introduction to functions. There is hardly any concept in math that is more important or more fundamental than that of a function. So we're going to begin our discussion today by reviewing just what a function is. Let's go ahead and do that. All right. A function is any rule. Notice how I put rule in quotes because rule is taken by a lot of different things by a lot of different people. But a function is any rule that it signs exactly one output value for each input value. Then we typically think of the outputs as being Y and the inputs as being X so think of it that way. When I put an X value in, what happens is only one Y value comes out. Now functions come in a lot of different forms, but the three most common are equations. You know, like Y equals 5 X plus two. Graphs like this beautiful one. And tables. Something like that. Now, because functions are all about converting inputs to outputs. We have special names for them. The input variable is often called the independent variable. In other words, X is just X, it can not exactly be anything at once to be, but it's sort of independent. Then again, we call the output, the Y variable, the D dependent variable, because it really doesn't get to choose what it wants to be. When I put X in, then the rule converts that X into a Y and I don't really have any choice about it. The Y variable depends on the value of the X variable. Typically not the other way around. So let's jump right into a real world scenario where we have a function. Exercise one, an Internet music service offers a plan whereby users pay a flat monthly fee of $5. And then can download songs for ten cents each. Sounds like a good deal. I like it. Especially if I'm downloading a lot of songs in a month. What are the independent and dependent variables in this scenario? Well, the independent variable is simply the number of downloads, right? That's independent. All it depends on is how much music you want to download. But the dependent is how much we pay or how much we are charged, right? Obviously, the more songs we download, the more we're going to pay. The less songs we download, the less we're going to pay. Letter B, fill in the table below for a variety of independent values. In other words, how much are we going to have to pay if we don't download anything? How much are we going to have to pay if we download 5 songs or ten songs or 20 songs? Now, you should be able to do this with the information that the problem gave you. So why don't you go ahead and do that? And if you want to use your calculator that's fine, but why don't you fill out that table, okay? All right, let's go through it. Well, there's not much we have to do for zero downloads, but it is important to note that we are charged something. In other words, we're charged that flat monthly fee $5. So if we have a bad month, we don't get on to the music service. We don't order anything. Well, we're still being charged $5. On the other hand, if we do 5 downloads, think about this at ten cents apiece, well, that's going to be 50 cents. We're going to have to pay. But then we're going to have to take that 50 cents. And add it to the $5 because we are always charged that $5. And we're going to get 5 50. We could do the same thing for ten songs, right? We would have ten songs times ten cents. Oh, that just gives us $1. But then we'd have to have that $1 and add $5 to it. To get $6. We would find the same for 20, that would be $7. Okay. Now, the reason I like doing something like letter B, even though it's relatively easy, is it's going to lead us to the formula for this function and keep in mind it really is a function. The definition of a function is that any given input gives us exactly one output. It wasn't like you said, hey, if you downloaded ten songs, you would be charged $6 or 6 25. It was no. You download ten songs. Your charge $6. One input gives you exactly one output. Okay, pause the video now, and then we'll clear out the text. Okay, here we go. All right, we're going to continue to work on this. Let her see says let the number of downloads be represented by the variable X and the amount charged be represented by the variable Y write an equation that models Y as a function of X so we can do mathematical modeling in many different ways, but here we like that formula, right? So think about that for a little bit and look back at B if you need help. All right, well, what did we do? In B, we kept taking ten cents, and multiplying it by the number of songs that we downloaded. But then we kept having to add that to $5 to get our total cost. So there's our equation. Y equals 0.10 times X plus 5. So we took what we did in letter B and we just turned it into an equation. Letter D, based on the equation you found in part C, produce a graph of this function. For all values of X on the interval zero to 40, use a calculator table to generate additional coordinate pairs to the ones you found in part B all right, well, why don't we do it? Let's bring open the TI 84 plus. There it is. There's not a lot of room on the screen. I apologize for that. I'll try to make the calculator screen as big as I can when I need to. But let's generate a table of values. Let's hit Y equals. All right, if there's any equations in Y one, Y two, et cetera, clear them out. So I'm going to get rid of anything I've got in there now. All right. And then Y one, I'm going to put that equation. So I'm going to type in zero point one zero X don't want to have ten X plus 5.0 zero. All right. Now, sometimes we'll use the graphing calculator to actually graph. To produce a graph on the screen. But here we're going to use it to create a table. And I think I noticed something. I think there's really nice numbers. Every ten songs that we download because songs cost ten cents apiece. So let's go into our table setup. Remember, we do that by hitting second window. Let's start our table at zero. And let's go make it go by tens. Now tens, that's kind of cool. Because that means every ten downloads, I'm going to see something else. All right, let's go into my table. And look at that. Now you don't have to have your table set up exactly like me or like mine. But it is kind of nice, right? When there were zero downloads, we saw that RY output was 5. Ten downloads or output was 6. 20 downloads or output was 7. 30 downloads or output was 8. And 40 downloads are outputs 9. So we can now graph this, you can probably graph it a little bit better than me, but I'll have zero 5. Ten. Oh, what are these going by? 50 6. They're going by 50 cents each. So at ten, we're at 6, which is right there. At 20, we're at 7, which is right there. 30. We're going to be at $8. A little bit tricky to see. We're right there. And 40 will be at $9. All right? I think I'm going to actually try to use my line command. And there it is. And there's my functions graph. All right. Now, technically, this is actually, if you remember something from algebra one, this is the case of a discrete variable. So really, I shouldn't be connecting these with a nice solid line because obviously the number of downloads would have to be an integer. It would have to be an integer. But sometimes we'll draw a graph is continuous, even when it's not, because it's too difficult to show just the dots instead of connected with a nice solid curve. Okay, I'm going to be clearing this out in a moment, getting rid of the TI calculator. So write down what you need to. All right, I'm going to clear it out. Let's get rid of our calculator. It'll be back later. One more time. All right, let's take a look at exercise two. That took us a while to get through exercise one. Exercise two involves something very important in terms of the graphs of relationships. Not functions, relationships. One of the following graphs shows a relationship where Y is a function of X and one does not. Let array says draw the vertical line whose equation is X equals three on both graphs. Again, I think that we're going to use our nice line utility on that. Here's X equals three on that graph. And here's X equals three on that graph. So X equals three. X equals three. Letter B says give all output values for each graph at an input of three. Well, a, we have an output there, right? So that's at the .3 comma four. And we also have an output here, and that's at three negative four. So the outputs are negative four. And four. Relationship B well, there, we had three common negative two. So only negative two. The letter C asks us to explain which of these relationships is a function. And why? Well, only B and the reason is because it has only one output. For a given input. This leads to what's called the vertical line test, the vertical line test. All students who study functions have heard of this guy, the vertical line test. And the vertical line test is relatively easy. It just says, look. If I draw a vertical line like I did in relationship a and it hits more than once, then it's not a function. But if it hits only once, then it is a function. All right, the vertical line test. It's helpful. It's helpful to quickly tell whether a graph is the graph of a function or not. All right, pause the video now, write down whatever you need to. Okay, I'm going to clear this out, and then we'll move on. Exercise three. The graph of the function Y equals X squared minus four X plus one is shown below. State this function's Y intercept. I bet you can figure this one out. What's Y intercept? Y intercept is the Y coordinate where we cross the Y axis. And that's at Y equals one. Between what two consecutive integers, consecutive means right in a row integers whole numbers. Does the larger X intercept lie? Well, here's an X intercept and here's an X intercept. This is the larger one, so that must lie between three and four. Letter C, draw the horizontal line Y equals negative two on this graph. Let me do that in a different color. There it is. That's Y equals negative two. Great. Using these two graphs find all values of X that solve the equation below. Remember, when I'm graph solving an equation graphically, and I have this equation graphed and I have this equation graphed, then all I have to do is come up with the X values in this case X equals one and X equals three, one, and three, where they intersect. Letter E says verify that these values of X's XR solutions by using the store on your graphing calculator. Well, we could use store. We could use a table. We could use a variety of things, but let me use store since that's what the direction said. Let me open up the TI 84 plus again. Great. Now let me use store. Now how am I going to do this? Well, what I'm going to do is I'm going to store X equals I'm going to store one into X so let's do that one. Store X and then what I'm going to do is I'm going to type out the left hand side of that expression. So watch X squared minus four X plus one. Now I'm going to hit enter. And it tells me negative two. Which tells me it's a solution. I could do the same thing for three, but I'm not for X equals three, but I don't think I'm going to. I just wanted to show you how easy it is to use stored check to see if something is the solution to an equation very, very simple. All right? Anyhow, I'm going to clear out the text and get rid of the calculator, so pause the video if you need to. All right, let's go on. Let's get rid of the calculator. It's gone as well. And let's move on. So in today's lesson, we laid the groundwork for maybe the most important idea in all of mathematics. The idea of a function. Its definition is simple. If I put an input in, there can only be one output out. This has a lot of different ramifications, and one of the things it gives rise to is that vertical line test, right? So use that on the homework to test whether or not graphs are, in fact, graphs of functions. We're going to see functions a lot this year. So take the homework seriously, really try to understand them upfront. All right, because you'll need them a lot later. For now, let me thank you for joining me for another common core algebra two lesson by E math instruction. My name is Kirk weiler, and until next time, keep thinking, and keep solving problems.
Embeddable Player
Related categories.
If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website.
If you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked.
To log in and use all the features of Khan Academy, please enable JavaScript in your browser.
Unit 1: Algebra foundations
Unit 2: solving equations & inequalities, unit 3: working with units, unit 4: linear equations & graphs, unit 5: forms of linear equations, unit 6: systems of equations, unit 7: inequalities (systems & graphs), unit 8: functions, unit 9: sequences, unit 10: absolute value & piecewise functions, unit 11: exponents & radicals, unit 12: exponential growth & decay, unit 13: quadratics: multiplying & factoring, unit 14: quadratic functions & equations, unit 15: irrational numbers, unit 16: creativity in algebra.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Assessment. Unit 11 Mid-Unit Quiz (through Lesson 5) - Form B. ASSESSMENT. ANSWER KEY. EDITABLE ASSESSMENT. EDITABLE KEY.
About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How YouTube works Test new features NFL Sunday Ticket Press Copyright ...
Share your videos with friends, family, and the world
Module 2 Overview. Topic A Overview. Lesson 1: Ferris Wheels—Tracking the Height of a Passenger Car ( Video Lesson) Lesson 2: The Height and Co-Height Functions of a Ferris Wheel ( Video Lesson) Lesson 3: The Motion of the Moon, Sun, and Stars—Motivating Mathematics ( Video Lesson) Lesson 4: From Circle-ometry to Trigonometry ( Video Lesson ...
Free practice questions for Common Core: High School - Functions - Unit Circle in the Coordinate Plane: CCSS.Math.Content.HSF-TF.A.2. Includes full solutions an ... For the purpose of Common Core Standards, "Explain how the unit circle in the coordinate plane enables the extension of trigonometric functions to all real numbers, interpreted as ...
• Lesson #2 - Radian Angle Measurement • Lesson #3 - The Unit Circle • Lesson #4 - The Definition of the Sine and Cosine Functions • Lesson #5 - More Work with the Sine and Cosine Functions • Lesson #6 - Basic Graphs of Sine and Cosine • Lesson #7 - Vertical Shifting of Sinusoidal Graphs
Angles and the Unit Circle Algebra 2 Lesson: ... All Common Core Standards listed pertaining ... each part includes guided notes, homework assignments, quizzes, and study guides to cover the following topics:Unit 12 Part I:• Pythagorean Theorem• Special Right Triangles• Trigonometric Functions (sin, cos, tan, csc, sec, cot)• Finding ...
Use the unit circle as a reference to answer the questions below. ### Part A Sketch a unit circle and mark an angle in standard position, ...
An introduction to the unit circle and angles on the unit circle. From the trig lessons in the Algebra 2 course by Derek Owens. More details on this course...
Prove the Pythagorean identity sin² (θ) + cos² (θ) = 1 and use it to find sin (θ), cos (θ), or tan (θ) given sin (θ), cos (θ), or tan (θ) and the quadrant of the angle. This product has not yet been rated. In this 11 lesson unit the sine and cosine functions are extended from right triangle trigonometry by the use of the unit circle.
ü Equation of a circle and completing the square ... "Algebra 2 (Common Core) Facts You Must Know Cold for the Regents Exam". Her input was invaluable. ... The imaginary unit, ", is the number whose square is negative one. −>=" ⇔ "3=−> To solve for a value of Ä, you can use your calculator or you can use ...
2. Angles and the Unit Circle - Pages 840-842 - 13. Periodic Functions and Trigonometry - Pearson Algebra 2 Common Core, 2011 (9780133186024) - Algebra 2 - Got It?, Lesson Check, Practice and Problem-Solving Exercises, Standardized Test Prep
Find step-by-step solutions and answers to Algebra 2 Common Core - 9780547647074, as well as thousands of textbooks so you can move forward with confidence. ... Section 2-3: Solving Quadratic Equations by Graphing and Factoring. Section 2-4: Completing the Square. Section 2-5: Complex Numbers and Roots. Section 2-6: The Quadratic Formula. Page ...
352 4 10 5 0 x fx x f f (b) 25 2 4 3 x x g g (c) x 30 1.2 3 0 hx h h 3. Based on the graph of the function y g x shown below, answer the following questions. (a) Evaluate g g g g 2 , 0 , 3 and 7 . (b) What values of x solve the equation gx 0 above and label. ? (c) Graph the horizontal line y 2 on the grid (d) How many values of x solve the ...
Your Algebra 2 Honors students will have foldables, guided notes, homework, and a content quiz in the Angles and the Unit Circle lesson of a six-lesson unit on Introduction to Trigonometry for students with a general knowledge of right triangle properties.Students will be able to :★ Analyze, graph and evaluate angles in standard position★ Find and use coterminal angles★ Understand ...
Pearson Algebra 2 Common Core, 2011 View details . arrow_back 2. Angles and the Unit Circle. Entry-Level Assessment 1 subchapters. 1. Expressions, Equations, and Inequalities p. 1-56 12 subchapters. 2. Functions, Equations, and Graphs p. 57-130 15 subchapters. 3. Linear Systems p. 131-190 13 subchapters. 4.
Algebra 2 Common Core: Home List of Lessons Semester 1 > > > > > > Semester 2 > > > > > > > Teacher Resources 9.3 Unit Circle and Radians. Common Core ... 9.3 Unit Circle and Radians. Common Core Standard: F-TF.C.8. Packet. To purchase this lesson packet, or lessons for the entire course, please click here.
Common Core Algebra II.Unit 2.Lesson 3.Function Composition Math. emathinstruction. Sep 22, 2016. 6432 views. 9th Grade. Learning Common Core Algebra II.Unit 2.Lesson 3. Function Composition by eMathInstruction ... So if the radius is 15 feet, then the area of the circle is going to be pi times 15 squared. Because we want this to the nearest ...
from Common Core Geometry that in a right triangle the sine and cosine ratios were defined as: side length opposite of sin ... unit circle. (1) 7 13 (3) 3 2 (2) 5 3 (4) 11 4 7. For an angle drawn in standard position, it is known that its cosine is negative and its sine is positive. The
Watch Common Core Algebra II.Unit 11.Lesson 4.The Definition of the Sine and Cosine Functions, Math, Middle School, Math, Algebra Videos on TeacherTube. ... The sine and cosine functions are defined in terms of angles and coordinates on the Unit Circle. Remove Ads. ... Algebra 1 Unit 2 Lesson 1 . Algebra: Linear equations 1 | Linea...
Now functions come in a lot of different forms, but the three most common are equations. You know, like Y equals 5 X plus two. Graphs like this beautiful one. And tables. Something like that. Now, because functions are all about converting inputs to outputs. We have special names for them.
The Algebra 1 course, often taught in the 9th grade, covers Linear equations, inequalities, functions, and graphs; Systems of equations and inequalities; Extension of the concept of a function; Exponential models; and Quadratic equations, functions, and graphs. Khan Academy's Algebra 1 course is built to deliver a comprehensive, illuminating, engaging, and Common Core aligned experience!