- Research Reviews
- Masterclass

A Guide to Study Designs in Physiotherapy Research
Physiotherapists rely on research to inform their own practice in evidence-based medicine (1). Evidence-based medicine is defined as the combination of research, clinical expertise, and patient values to guide decision-making in the care of patients.
In order to practice the research component of evidence-based medicine, physiotherapists must stay up-to-date on the vast body of scientific literature. They must also understand the hierarchy of study designs and how they are represented in physiotherapy research.
Here we will break down the different study designs you will find in physiotherapy research. For each study design, we will discuss scenarios in which they are used, as well as provide examples in physiotherapy research.
Randomized Controlled Trials
Randomized controlled trials are the highest level of research design, often considered the “gold standard” for determining effectiveness of a new treatment (2). They are prospective, meaning they are planned before any data collection occurs. They involve the random assignment of participants into an experimental or a control group.
Specific to physiotherapy research, the control group will often receive some kind of therapy, instead of no therapy like a true control group. For example, here is a randomized controlled trial that compared supervised resistance training to home-based resistance training (rather than no training) for patients with subacromial shoulder pain.
Randomization creates an equal opportunity for participants to be in either group. This reduces bias by balancing participant characteristics between the groups. Oftentimes, participants don’t know to which group they are assigned (also known as “blinding”).
Randomized controlled trials are the best way to determine causation (i.e. outcomes due to the intervention rather than other factors).
Cohort Studies
Cohort studies follow participants who share a common characteristic. They are longitudinal, meaning researchers observe participants for a certain period of time. They can be prospective (following participants forward in time) or retrospective (following participants back in time).
Cohort studies are best for determining the external factors that influence health. They also help determine risk factors for injuries or conditions.
In physiotherapy, researchers could use a cohort study to follow patients who have undergone physiotherapy treatment for a specific condition. All participants received the treatment and were not randomly assigned like in a randomized controlled trial. Researchers determine if factors (such as age, injury severity, compliance to therapy, etc.) affect outcomes of the treatment. This research review by Dr Mariana Wingwood provides an example of a retrospective cohort study that evaluated early rehab on function in patients with vertebral compression fractures.
Prospective cohort studies are a strong study design and quite common in physiotherapy research. Another review by Stacey Harden is an example of a prospective cohort study that followed professional football (soccer) players to evaluate risk factors for hip and groin pain which you can find here .
Case-Control Studies
Case-control studies are studies that look back in time to compare patients who have an injury/condition (cases) to patients who do not have injury/condition (controls). The controls are usually matched to the cases on several demographic variables, such as age, sex, and physical activity status.
Case-control studies are helpful in determining risk factors for injuries or conditions. Many researchers will conduct them as an initial study to learn more about an injury/condition prior to conducting a prospective trial.
Case-control studies are common in physiotherapy, such as this research review by Dr Melinda Smith on the investigation of risk factors in runners with medial tibial stress syndrome compared to matched asymptomatic runners.
Cross-Sectional Studies
Cross-sectional studies are observational studies that evaluate data from participants at a single time point. They are used to determine associations between two variables. For example, this research review by Steve Kamper used a cross-sectional design to determine if posture and smartphone use were related to neck pain in young adults.
Physiotherapy researchers use cross-sectional studies for survey-based research, as well as clinical-based studies. Cross-sectional studies are usually more time and cost effective, and are therefore more appealing and tangible in physiotherapy clinical settings.
Case Series and Case Studies
The last and weakest study designs are case series (~<10 people in a study) and case studies (1 person in a study). They are considered the weakest of study designs because due to the small sample size, they are less likely to be generalizable to the population of interest.
However, case series/studies can be extremely informative to physiotherapy practice, as they usually describe rare or unusual injuries or conditions. They provide a glimpse into the clinical practice of another therapist and healthcare team, which can help inform your own practice. An example you can find here was reviewed by Robin Kerr in a case series of 5 patients who underwent an alternative treatment approach for frozen shoulder.
Wrapping Up
In practicing evidence-based medicine, it is important to be familiar with the different study designs that can be found in physiotherapy research. Understanding the indications for each study design will aid physiotherapists in determining if the study should affect or change their clinical practice.
Keep in mind that each type of study has its advantages and disadvantages. Although they are ordered in a hierarchy of strongest (i.e., randomized controlled trials) to weakest (i.e., case studies) design, we have covered some considerations specific to physiotherapy research that make certain designs more common and efficient than others.
📚 Stay on the cutting edge of physio research!
📆 Every month our team of experts break down clinically relevant research into five-minute summaries that you can immediately apply in the clinic.
🙏🏻 Try our Research Reviews for free now for 7 days!
- Manchikanti L, Boswell MV, Giordano J. Evidence-based interventional pain management: principles, problems, potential and applications. Pain Physician. 2007 Mar;10(2):329-56. PMID: 17387356.
- Hariton E, Locascio JJ. Randomised controlled trials – the gold standard for effectiveness research: Study design: randomised controlled trials. BJOG. 2018;125(13):1716. doi:10.1111/1471-0528.15199.
Don’t forget to share this blog!
Leave a comment.
If you have a question, suggestion or a link to some related research, share below!
You must be logged in to post or like a comment.
Related blogs
Elevate your physio knowledge every month.
Get free blogs, infographics, research reviews, podcasts & more.
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- BMC Med Educ
- PMC10559614

Undergraduate research implementation in physiotherapy: a hands-on and real experience of a randomised controlled trial
Igor sancho.
Deusto Physical TherapIker, Physical Therapy Department, Faculty of Health Sciences, University of Deusto, Donostia-San Sebastián, Spain
Maialen Araolaza-Arrieta
Iker villanueva-ruiz, ane arbillaga-etxarri, associated data.
The datasets used and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Evidence-based practice (EBP) is the gold standard approach in physiotherapy, and it is essential that students are aware that it is the appropriate way to provide the patient with the best possible treatment. Undergraduate research (UR) can positively influence learning outcomes and research competencies related to EBP compared to traditional methods of higher education. The aim of this study was to evaluate the effect of implementing a research-based activity (i.e., active participation in a randomised controlled trial [RCT]) in the UR programme on the learning and acquisition of research methodology-related competencies by first-year physiotherapy students.
Students in the first academic year of the Bachelor´s Degree in Physiotherapy of University of Deusto (Donostia-San Sebastian, Spain) who were enrolled in the subject ‘Introduction to Research Methodology’ were invited to take part in a real RCT which consisted of three groups: intervention, placebo, and control group. While the RCT was carried out, researchers and/or participants roles were combined among students during the semester. At the end, a questionnaire that included open and closed questions was used to evaluate the effectiveness of the UR strategies used in students´ acquisition of theoretical knowledge, research competencies, self-efficacy of RCT skills and procedures. Lecturers also completed the questionnaire to evaluate their experience.
From the 114 students enrolled in the subject, 102 participated in the RCT and 110 answered the final questionnaire. Regarding the development of research competencies, UR had a positive or very positive impact on critical thinking (67% and 18%, respectively) and in the assessment of methodological quality (66% and 23%, respectively). Furthermore, most students reported that the implementation of the RCT facilitated their knowledge of placebo, detection of bias, development of critical thinking and a better understanding of methodological issues in research. Lecturers reported an additional burden that was difficult to reconcile with daily duties.
The novel UR program provided students with a new opportunity to improve their knowledge of RCT procedures, thus making the learning process more meaningful. Therefore, ways of teaching and learning focused on improving research and inquiry attitudes should be considered and integrated into the health care curriculum, especially in physiotherapy programs, to ensure the transfer of EBP for the provision of the best care.
Trial registration
Australian New Zealand Clinical Registry: ACTRN12622000263796p (14/02/2022).
Supplementary Information
The online version contains supplementary material available at 10.1186/s12909-023-04716-0.
The development of research skills at higher education is considered a challenge where the institutions and lecturers try to combine educational and research attitudes, while inexperienced and novice students need to develop scientific skills [ 1 ]. In this way, research and teaching should be connected as it provides the opportunity for lecturers and researchers, who usually are already involved in the natural process of academic or clinical research, to disseminate, promote and provide scientific knowledge to those students who are just about to develop the basic research skills for their incipient professional future. In this framework, the integration of hands-on research experiences is considered an effective solution to link both profiles [ 2 , 3 ]. However, in the field of physiotherapy, only a few studies had specifically investigated this relationship [ 4 ]. Indeed, rather than analysing which strategies are pedagogically effective for this purpose, most methodologies tend to focus on evidence-based practice (EBP) teaching, due to its relevance in clinical practice [ 4 ].
EBP consists in the application of the best scientific evidence in clinical decision-making by integrating clinical experience, incorporating patient values and preferences into the practice of professional patient care [ 5 ]. In health science disciplines like physiotherapy, the translation of EBP into practice is vital to adopt a critical stance to provide the best care. Therefore, knowledge of research methodology and critical thinking skills are essential. For example, it is essential to be aware of the issues related to randomized control trials (RCT), namely in terms of methodological biases and trial design features, and how these impact the interpretation of their results and treatment effect estimates. Physiotherapy students should naturally develop and integrate analytical and critical thinking about research to ensure the implementation of the best EBP [ 6 ].
However, the term EBP should be clarified since it is considered a general, universal, and gold standard learning outcome for clinical practice rather than a specific education strategy per se ( 4 ). In this sense, Bala et al. found that different teaching and learning focused on EBP improved knowledge and changed behaviour across a diverse range of teaching modalities and health students. Nevertheless, most of the studies were considered as critically low quality. Therefore, the most effective teaching strategies to promote the use of EBP in clinical practice are uncertain ( 7 – 9 ). In this context, one study showed that the meaning of EBP processes or principles are not well understood by undergraduate health students ( 10 ). Hence, the approach of linking research and teaching in higher education seems to require a holistic educational environment rather than a learning outcome.Undergraduate research (UR) can positively influence learning outcomes and facilitate the acquisition of research competencies related to EBP when compared to traditional methods in higher education ( 11 – 14 ). Undergraduate research consists of the application of a battery of teaching and learning strategies that aim to aid the student in gaining research-related knowledge and skills. This is accomplished by providing students with opportunities to acquire research skills and apply theoretical contents in real practice, for example, by involving students in a partial or full research project under the lecturer’s supervision [ 2 ]. This activity facilitates the appropriation and construction of knowledge through practice, collaborative learning, experimentation, and critical thinking. Active participation through first-hand experience helps students learn about and foster interest in the disciplines developed [ 15 ]. Consequently, UR provides a unique and special environment that merges scientific and educational procedures at the same time.
Evidence supports that UR implementation increases motivation and develops an investigative attitude and vital general skills in students [ 16 ]. Recent scoping reviews have been carried out among students involved in rehabilitation issues including physiotherapy and/or occupational therapy programmes [ 17 – 19 ]. However, the implementation of UR across healthcare programs (i.e., physiotherapy) is still limited [ 20 ]. The aim of this study was to evaluate the effect of the implementation of a research-based activity (i.e., active participation in an RCT) in the UR program on the learning and acquisition of competences related to research methodology by first-year physiotherapy students.
A real RCT where students could take part as researchers and/or participants as the main UR strategy was undertaken. The aim of the RCT was to evaluate the effectiveness of a superficial neuromodulation device developed by an external private company (© 2020 Irmoki). However, the true aim of the study reported here, to which students taking part were blind, was to evaluate the effect of the implementation of UR (through a teaching and learning strategy that included the design and active participation of students in an RCT) as described earlier.
First-year students of the Bachelor’s Degree in Physiotherapy and the Bachelor’s double Degree in Physiotherapy and Physical Activity and Sport Sciences, who were enrolled in the subject ‘Introduction to Research Methodology’ at University of Deusto during the course 2021-22 were invited to participate in the study. The lectures are taught by two lecturers in three different languages (Basque, Spanish, and English). One lecturer was in charge of one group (the Basque group), whereas the other lecturer led the Spanish and English groups. The number of students for both lecturers was very similar, and they were strictly coordinated to teach in parallel, sharing content, teaching methods, schedule, and evaluation system. Indeed, the subject of “Biostatistics” was also shared between both of them. Finally, they can be considered as active researchers (publishing articles, leading projects and attending congresses) in their background of musculoskeletal and respiratory physiotherapy area, respectively.
It is worth mentioning that the University of Deusto implemented the Degree in Physiotherapy in the academic year 2020–2021. The emerging academic frame allowed the early integration of UR thanks to a curriculum designed according to guidelines set by experts [ 3 ], that also included other innovative educational methodologies such as simulation or problem-based learning. ‘Introduction to Research Methodology’ is taught in the second semester of the first year with the aim of seeking across-effect and connecting subsequent courses of the Degree. In this sense, the subject is complemented by other syllabus oriented at EBP in the 2nd, 3rd, and 4th years, which includes research-related activities such as literature reviews, debates, attendance to scientific conferences, or clinical practices in the emerging research group, and the final year dissertation.
For the sake of clarity, two types of procedures have been distinguished: first, those related to RCT procedures, and then those related to UR programme implementation.
Procedures related to RCT
Study design and registration.
This RCT was designed following the Consolidated Standard of Reporting Trials for Controlled Studies (CONSORT) statement, registered with the Australian New Zealand Clinical Registry (ACTRN12622000263796p, 14/02/2022) and approved by the Research Ethics Committee of the University of Deusto (ETK-21/21–22). Details about the RCT are presented in Supplementary material A section.
Participants
All students (n = 114) enrolled in the subject were invited to participate and informed about the RCT including potential effects and demands of the intervention. Four students refused to participate in the study and eight students dropped out during the 14 weeks due to failure to complete the weekly questionnaire, general discomfort associated with the device, and an ankle sprain. In the end, 102 students finally completed the RCT.
Participants were randomly allocated to three groups (intervention, placebo, and control). Students allocated into the intervention group wore a superficial neuromodulation device (© 2020 Irmoki) while students remained seated at rest following lectures at University. The device consists of 4 wireless receptors to be placed on the distal third of the limbs by means of gloves and anklets and controlled through Bluetooth technology by a smartphone app (Fig. 1 ). The app remotely activates the device which emits rectangular biphasic and monophasic galvanic electrical impulses of very low frequency (0.5–14 Hz) coordinated through 28 electrodes that aim to modulate the autonomic nervous system. Students in the placebo group were blinded by wearing the device in the same way as the intervention group, but without being active (light was switched on but the device did not emit the electrical current). The control group did not receive any intervention.

Example of neuromodulation device placement of the intervention and placebo groups. Note: image provided by Irmoki company
Data collection and analysis
Sociodemographical data were collected at baseline. Outcomes were gathered by means of an online questionnaire at baseline and after weeks 2, 4, 6, and 8 which retrieved data about fatigue, sleep quality, muscular soreness, stress level, and mood. In addition, participants in the intervention and placebo groups were asked about the expectation towards the intervention and the perceived potential alterations.
Procedures related to the implementation of the UR programme
From 114 students enrolled in the subject, ergo involved in the implementation of the UR teaching strategies for 14 weeks, the same four students who refused to participate on the RCT also refused to answer the UR outcome evaluation questionnaires at the end of the semester. Thus, 110 responses were collected. In addition, the two lecturers completed the questionnaire.
UR strategies were executed according to the subject´s syllabus. These were based, combined, and integrated on the theoretical topics described in Fig. 2 . The key research-based strategy was to engage students (as participants and/or researchers) in the execution of a real RCT. In detail, the students allocated to the RCT control group were assigned, under the supervision of the lecturers, the role of managing the delivery and collection of the devices, as well as the adherence to the intervention and the sending and completion of the questionnaires. The students were involved and progressively integrated to work through practical hands-on experiences, in parallel with the theoretical content of the subject. The practical hands-on experiences were: (1) The assessment of the ethical aspects and consent-informed writing was carried out as an experiential activity with the aim of improving the analysis and understanding in depth of the meaning of signing a consent form; (2) In order to contextualise the EBP approach, different papers were used by the lecturers during the presentation to introduce the theoretical framework and the mechanism of action of the device. Likewise, the RCT was used as the thread of the scientific method; (3) The theoretical content of the structure and typology of the papers was introduced through the analysis of the evidence used in the RCT presentation; (4) In order to promote the trend of filtering and ranking the evidence, the quality analysis of the journals was carried out in relation to Journal Citation Reports ranking system; (5) The established RCT design aimed to foster the contrast in depth of the different trials modalities and their limitations in terms of randomisation, blinding, and the presence of a control group; (6) The limited sample size of the RCT prompted reflection about the importance on the previous sample size calculation. Indeed, the lecturers distributed the RCT database with the aim of promoting an experiential preliminary statistical analysis in small groups under the supervision of the lecturers, using the knowledge and skills acquired in the previous subject of “Biostatistics”. In addition, the students were able to carry out a self-assessment by comparing their analysis with the results of the lecturers in a collaborative way; (7) With the aim of fostering the capacity for critical methodological analysis validity, reliability, and especially the bias (such as, selection bias, performance bias, attrition bias, etc.) were thoroughly analysed; (8) As a final activity, the placebo group was revealed to promote critical thinking on the impact of suggestion, expectation, sample contamination, etc.

The strategies used during UR methodology implementation
The RCT, the implementation of UR strategies, and the evaluation were led by the two main lecturers of the subject. In addition, other lecturers from other subjects collaborated exclusively with the task of delivering and collecting the devices. In this sense, they also remained blinded to randomization and study information.
Data collection and outcome measures
At the end of the semester, an ad hoc questionnaire completed by participants in the study collected several outcomes focused on four dimensions: (a) the integration of research knowledge related to the theoretical contents; (b) the development of research competencies; (c) the level of self-efficacy about the skills trained; and (d) the RCT procedures. The questions related to the first two dimensions were based on the validated version of the “Cuestionario de Efectividad del Uso de Metodologías de Participación Activa (CEMPA)” ( 21 ) which measures the perception on the effectiveness of using active participation methodologies. The self-efficacy questions were adapted from the “Cuestionario de estrategias profundas de aprendizaje” validated by Panadero et al. [ 22 ]. The questionnaire is presented in the Supplementary material B section. Finally, participants and the two lecturers answered an open question to highlight specific elements during the learning process.
Statistical analysis
Statistical analysis was conducted using Jamovi (v. 1.6.23, The Jamovi Project, Sydney, Australia). Descriptive statistics were calculated with proportions and frequencies and the distribution of the investigated variables was presented with bar diagrams.
110 participants (sex: 48 M/54F; and age: 19.5 (1.63) years) completed the questionnaire about the impact of the UR teaching strategies. Figures 3 , ,4, 4 , ,5 5 and and6 6 report on the quantitative data provided by the questionnaire. The effect of UR on the acquisition of research knowledge related to theoretical content was very positive (Fig. 3 ) and especially topics related to the placebo effect, methodological bias, trial design and types of trials, and the concepts of reliability and validity were better adjusted. The smallest effect was found on scientific publications, journal rankings, and PICO strategy.

Results of the questionnaire: effect on integration of research knowledge related to the theoretical contents

Results of the questionnaire: effect on the development of research competences

Results of the questionnaire: effect on self-efficacy about the skills trained

Results of the questionnaire: Issues related to RCT implementation the aim of seeking across effect
Regarding the development of research competencies, most students reported that UR had a positive or very positive impact on critical thinking (67% and 18%, respectively) and assessment of methodological quality (66% and 23%, respectively) (Fig. 4 ).
Self-efficacy about the skills trained was highly rated, and skills that benefited the most were the ability to understand and explain the placebo effect, the capacity to read and integrate the results of an RCT, and the ability to identify bias and methodological gaps related to the design and execution of a clinical trial (Fig. 5 ).
Students evaluated very positively the inclusion of an RCT as an active learning strategy. Aspects that received the best evaluation were the adequacy of the UR strategy with the implementation of the RCT in the subject, the active participation of students during the learning process, and the involvement and structured organisation shown by the teaching staff responsible for the project (Fig. 6 ).
Answers from the open question are presented in Table 1 . Most students reported that their knowledge about the placebo effect had improved through the trial. In addition, the UR strategies were reported to contribute to the development of critical thinking and a better understanding of the strengths and limitations of the research. Finally, UR was perceived as a tool that facilitated the learning process, added dynamism, complemented the subject content to deepen it, and pointed to the need for EBP.
Answers to the open question
On the other hand, negative aspects identified by both lecturers include the excessive duration of the intervention, the extra daily burden of getting students to wear the devices to ensure adherence to the intervention and data collection, and the difficulty of combining it with other daily obligations. However, lecturers reported that confidence in the premise of fostering research awareness, seeing it as the first step on a progressive path within a built UR programme, the support among the academic staff involved and their research experience helped to overcome the obstacle. Lecturers considered that this educational approach helped students to get closer to the reality of research, feel the placebo effect first-hand, identify mistakes and limitations, and propose solutions based on self-criticism. Lecturers also concluded that the activity provided a valuable opportunity for active learning through real experimentation.
The research-based activity framed in a UR programme consisting of the implementation of a real RCT in which students were involved as participants and researchers, supervised by qualified lecturers, showed positive effects on the acquisition of theoretical content, the development of research competences, the level of self-efficacy in research skills and knowledge about RCT procedures. Furthermore, it provided a novel experience for students, making the learning process more meaningful.
Strategies such as journal clubs or conducting a systematic review or meta-analysis are common in UR programs [ 18 ]. In fact, in some universities, physiotherapy students conduct primary research projects, or lecturers assigned to a research group assist students conceptualise a project, recruit subjects, and collect data in the last academic year [ 23 – 25 ]. To our knowledge, this is the first study to apply a real RCT as a research-based strategy integrated in an UR programme in physiotherapy higher education.
In our study, most students reported that UR had a positive or very positive impact on critical thinking and assessment of methodological quality. Likewise, student showed that the RCT implementation improved the ability to understand and explain the placebo effect, the capacity to read and integrate the results of an RCT. This means that the students integrated better key knowledge of RCTs, such us how design features, risk of bias or placebo effect may distort results and lead to incorrect conclusions and substantially modulate clinical decision-making in physiotherapy [ 26 ]. In this sense, it is well known that an accurate assessment of the methodological quality of trials is essential in the synthesis of study findings in order to appropriately interpret results and effectively guide the clinical decision process [ 27 ]. In addition, the development of critical thinking about research methods and the long-term maintenance of the scientific attitude required by the EBP philosophy are fundamental to ensure its implementation [ 28 , 29 ]. In fact, the practice of EBP remains low among physiotherapists due to several barriers such as lack of resources, training, knowledge, time, and low availability of sources. Therefore, the use of a RCT as a UR strategy at a very early stage in higher education can reinforce academic responsibility and ethical awareness of students and help to overcome those barriers [ 28 , 29 ]. Also, according to the competencies proposed by the Europe Region World Physiotherapy, the commitment and honesty that comes implicit with the responsibility to keep up to date with the evidence should be ensured and continuously reinforced [ 30 ]. Consequently, students as future clinicians, researchers or stakeholders need to master these skills early in order to apply this ability in a natural and integrated way in their daily health care. Therefore, the implementation of first-hand RCT experience in early stages of higher education may be useful for future clinical practice [ 31 ], but more research is needed in this area.
According to the EBP approach of the physiotherapy degree curriculum developed at the University of Deusto, the emerging framework enabled the early integration of UR and other innovative educational methods. Moreover, the inclusion of EBP education in early stages is an accreditation requirement for many health professional disciplines [ 32 , 33 ]. In this sense, these results can confirm that implementation in an early educational setting can ensure the aim of seeking a progressive and cross-cutting effect that helps connect future concepts of the remaining degree courses [ 34 ]. Similarly, there should be a progressive development of research attitudes and skills [ 34 ], because this early experience is likely to evolve into progressively improved inquiry capabilities with different levels of independence and complexity. In addition, the research skills should be reinforced by other future research activities, adding more sophisticated searches about complex topics and from group to individual or more independent work. In turn, this is likely to allow for more selectivity in other initiatives as well (i.e., selected students invited to participate in lecturer-led research). However, these long-term effects of the early implementation of the RCT experience were not measured and should be investigated through longitudinal studies in the future [ 34 ].
The students evaluated very positively the adequacy of UR strategy, the active participation, and the involvement and structured organisation shown by the teaching staff. In this sense, the early and first-hand RCT experience within a subject related to research methodology, where students are actively involved in carrying out real research practical activities, fieldwork and/or act as participants is unique. This experience gave the students the opportunity to practise and become proficient at it, which has been described as an effective method to develop more sophisticated levels of intellectual development [ 35 ]. According to Debowski et al. 2006, students with limited active participation in research (i.e., where the lecturer-led activity is focused on teaching research findings or methods) may have a limited theoretical understanding and lack the ability to apply such knowledge to the real-world. To the contrary, by engaging in practical research strategies, students better understand the relevance of research to their professional practice as well as the complications, limitations, gaps, drawbacks, and value of the process [ 36 , 37 ].
The positive effect related to the integration of the placebo effect was most often mentioned by the students. To the best of our knowledge, this is the only UR strategy that has led to a real experience of the placebo effect among physiotherapy students. When the placebo group was revealed, the students could integrate how different design features of a trial, co-interventions, sample contamination, ambiguity of symptom detection, patient’s or researcher’s biases can have a substantial impact on estimates of treatment effects. Therewith, we consider the impact on the students’ critical appraisal skill was truly outstanding through unusual, exciting, and surprising pedagogical learning.The acquisition of research theoretical knowledge related to scientific articles, journals, systematic review and PICO did not improve as much as other items. We conclude that the design of the RCT encouraged students to focus on the theoretical content that engaged them most actively. Otherwise, the RCT itself is not very related to this type of theoretical content. If the design used was a systematic review instead of an RCT, the opposite would probably be the case with regard to the topics of theoretical content which scored lower.
Finally, the role of lecturers seems to be very important as an active knowledge transfer agent and the person who motivates, supervises, promotes, executes, and develops research linking students as technicians or voluntary participants during research procedures [ 38 ]. In this study, lecturers reported a daily extra burden related with RCT procedures which may impact on other academic and management tasks. This should be taken into account by departmental managers to ensure effective, appropriate, and sustainable teaching-research links and experiences [ 31 ].
Limitations
This study has some limitations. A systematic pre-post semester analysis and the lack of a control group of students without UR implementation are the most important. In this sense, a control group was very difficult to achieve because it was practically unfeasible to blind the students to the implementation of the RCT. However, this should be taken into account when interpreting the results obtained. In addition, a long-term view in line with other research and inquiry strategies are required to evaluate the effect on the students’ learning process. Further, increasing the sample size of students should also provide more insights into the teaching and learning capabilities of research. Finally, the lack of validated tools and the use of different points and not well-balanced scales when dimensions were assessed also could have had a negative impact.
This study presents a novel approach of the framework of UR in the unexplored healthcare discipline. Conducting an RCT is a challenging but valuable, useful, and effective way to integrate research and an inquiring attitude in physiotherapy students. Forms of teaching and learning focused on enhancing research and inquiring attitudes should be considered and integrated in the healthcare curriculum, especially in physiotherapy programmes, where students’ knowledge of RCT characteristics should be integrated early to ensure the transfer of EBP to provide the best care. In the future, this initiative should potentially be considered by lecturers, educational research promoters and stakeholders involved in UR programmes.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank all the students who participated as volunteers and the teachers who were involved for their contribution to the study. Likewise, we also want to thank the company Irmoki for the loan of the devices.
List of Abbreviations
Authors‘ contributions.
A.A., I.S. and M.A. conducted the RCT. I.S. and I.V. analyzed and interpreted the data. A.A. was a major contributor in writing the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
This research received no specific grant from any funding agency in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Data Availability
Declarations.
This study was approved by the Research Ethics Committee of the University of Deusto (ETK-21/21–22) and was undertaken according to the Helsinki declaration. Informed consent was obtained from all subjects.
Not Applicable.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.

Physical Therapy
- Useful Websites
- Primary vs. Secondary Sources
- Citing Sources
- Professional Organizations
- Institutional Review Board (IRB)
- Authorship Policy
- Abstract Format and Guidelines for Dissertation/Final Paper
- Thesis/Dissertation Binding Instructions
- Department of Physical Therapy Handbook All information found in this guide was taken from the University of Mary's Department of Physical Therapy Research Handbook.
In this section, you will find details of different parts of your proposal/final project. All of the information here is found in the Department of Physical Therapy Research Handbook.
- Institutional Review Board (IRB)
- Authorship Policy
- Forms
Delineation of Section Heading for the Proposal
Introduction
Justification
Purpose Statement
Reseach Hypothesis
Delimitations
Limitations
Assumptions
Methods
Research Participants
Research Procedures
Research Design
Data Analysis
Bibliogrpahy
- << Previous: Professional Organizations
- Next: Institutional Review Board (IRB) >>
- Last Updated: Jan 31, 2024 12:01 PM
- URL: https://libguide.umary.edu/PT
Brunel University Research Archive(BURA) preserves and enables easy and open access to all types of digital content. It showcases Brunel's research outputs. Research contained within BURA is open access, although some publications may be subject to publisher imposed embargoes. All awarded PhD theses are also archived on BURA.
- Brunel University Research Archive
- Research Areas
Physiotherapy Collection home page
- 11 De Souza, LH
- 9 Kilbride, C
- 6 Marston, L
- 6 O'Connell, NE
- 4 Norris, M
- 3 De Souza, L
- 3 Frank, AO
- 3 Naylor, S
- 2 Allison, R
- 6 Physiotherapy
- 5 Rehabilitation
- 3 Chronic pain
- 2 Action research
- 2 Assistive technology
- 2 Brain stimulation
- 2 Guidelines
- 2 2020 - 2023
- 29 2010 - 2019
- 10 2000 - 2009
- 1 1996 - 1999
Academic Misconduct
Edith Cowan University has firm rules governing academic misconduct and there are substantial penalties that can be applied to students who are found in breach of these rules. Academic misconduct includes, but is not limited to:
- plagiarism;
- unauthorised collaboration;
- cheating in examinations;
- theft of other students� work.
Additionally, any material submitted for assessment purposes must be work that has not been submitted previously, by any person, for any other unit at ECU or elsewhere.
The ECU rules and policies governing all academic activities, including misconduct, can be accessed through the ECU website.
This website uses cookies
We use essential cookies to make this website work. Additional cookies help us to make improvements (analytics) or are set when we incorporate functionality from other websites, such as video, social media feeds and ReachDeck (text-to-speech and translations). More on how we use cookies
Enable ReachDeck
This website uses text-to-speech software called ReachDeck to read and / or translate its content. To use ReachDeck, you must allow ReachDeck cookies; the ReachDeck icon will then appear at the bottom of your screen.
You can find out more about how ReachDeck uses cookies or change your cookie preferences at any time by going to our cookies page.
Allow ReachDeck cookies Do not use ReachDeck

- Physiotherapy
- Outpatients
- Paediatrics
- Information zone
This site is best viewed with a modern browser. You appear to be using an old version of Internet Explorer.
Current research projects
Physiotherapy rehabilitation for osteoporotic vertebral fracture (prove).
Karen Barker, Muhammad K Javaid, Meredith Newman, Catherine Minns Lowe, Tamsin Hughes, Nigel Stallard, Jose Leal, Varsha Gandhi, Sallie Lamb.
Objective : to evaluate the effects of exercise and manual therapy physiotherapy treatments upon quality of life, function and pain, for people who have had one or more spinal fractures due to Osteoporosis.
research.ndorms.ox.ac.uk/prove
Community based Rehabilitation after Knee Arthroplasty (CORKA)
Karen Barker, David Beard, Gary Collins, Avril Drummond, Sally Lamb, Andrew Price, Helen Campbell, Fran Toye, Martin Underwood, Susan Dutton.
Objective : to compare the patient reported functional outcome and quality of life of the CORKA rehabilitation protocol versus usual care in those at risk of a poor outcome post knee arthroplasty.
www.ndorms.ox.ac.uk/clinical-trials/current-trials-and-studies/corka
'WALK30X5': The development and feasibility evaluation of a physiotherapy walking programme for people with mild to moderate musculoskeletal conditions
Catherine Minns Lowe, Paul Kelly, Charlie Foster, Karen Barker.
Objective : to develop and refine an evidence-based, web-based physiotherapy walking programme intervention including podcasts, blog and links. To test the feasibility and acceptability of the intervention.
Cementless versus cemented unicompartmental knee replacement: 1-5 year post-operative outcome study
Cathy Jenkins , Hemant Pandit,Karen Barker , David Murray.
Objective : to determine the incidence of problems following cementless medial UKR and compare this with cemented medial UKR.
jbjs.org/content/95/15/1365
Oxford unicompartmental knee replacement: second decade outcome study
Objective : to identify, from postoperative X-rays, which patients are more at risk of developing Lateral Compartment Osteoarthritis (LCOA) in the second decade after UKR surgery.
What interventions are used to improve excercise adherence in community dwelling older people: a systematic review
Jonathan Room, Mary Boulton, Helen Dawes , Karen Barker Faculty of Health and Life Sciences, Oxford Brookes University
Objectives : to establish what interventions are used to improve adherence to prescribed exercise for older people and determine the effectiveness of these interventions.
MAPS: Measuring Alignment and Posture of the Spine
Erin Hannink, Helen Dawes, Karen Barker
Objective: to measure concurrent validity and test-retest reliability of measuring sagittal spine alignment with a postural topography method compared to the Cobb angle from a lateral X-ray of the spine.
AERO - Adherence to Exercise Rehabilitation in Older people: Can a brief behavioural assessment improve exercise adherence in older people with musculoskeletal conditions
Jonathan Room, Helen Dawes, Mary Boulton, Karen Barker
Objective : to test the feasibility of a behavioural assessment based on the COM-B behaviour change model, and tailored exercise adherence strategies based on that assessment.
PRU is supporting the following studies
A randomised, multi-centre, non-blinded, prospective, parallel group trial of total ankle replacement (TAR) versus ankle arthrodesis in the treatment of patients with end stage ankle osteoarthritis, comparing clinical outcomes and cost-effectiveness.
Goldberg A, Rogers M, Tetlow M, Skene S.
www.anklearthritis.co.uk
The BOOST study is a randomised controlled trial (RCT) studying two different physiotherapy treatment approaches for back and leg pain or symptoms due to lumbar spinal stenosis (also called neurogenic claudication). This is a condition that affects older people and limits their ability to walk and stand which impacts on their ability to remain independent. The study will recruit over 400 adults over 10 NHS hospitals across England. Participants will be 65 years and over who experience symptoms due to lumbar spinal stenosis. Participants will be randomised into one of two groups:
- TREATMENT 1: One-to-one physiotherapy treatment (1 to 3 appointments)
- TREATMENT 2: A group physiotherapy programme (12 classes)
www.ndorms.ox.ac.uk/clinical-trials/current-trials-and-studies/boost
FAIT: Femoroacetabular Impingement Trial
FAIT is a multicentre randomised controlled clinical trial determining whether arthroscopic surgery or physiotherapy and activity modification are superior at improving symptoms and preventing the development of osteoarthritis in patients with femoroacetabular impingement.
www.ndorms.ox.ac.uk/clinical-trials/current-trials-and-studies/fait
HOAST: Hip Osteoarthritis Treatment using Autologous Stem cell Therapy
HOAST is a study looking into whether stem cells can replace damaged tissue in the hip joint, delaying the need for a hip replacement in younger people.
www.ndorms.ox.ac.uk/clinical-trials/current-trials-and-studies/hoast
This is a long term audit of the outcomes of the Oxford Uni-compartmental Knee Replacement. The study is entering its 20th year of audit.
UK FROST: United Kingdom Frozen Shoulder Trial
The UK FROST trial aims to evaluate the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of the treatments for frozen shoulder. In addition, patient experiences of both the surgical interventions and physiotherapy will be examined, providing important patient-centred insight to further guide clinical decision making
www.ndorms.ox.ac.uk/rrio/uk-frost
PANDA-S: Prognostic AND Diagnostic Assessment of Shoulder pain
This study aims to develop and evaluate a better approach ('stratified care') to assessing the likely cause (diagnosis) and future outcome (prognosis) of shoulder problems, so that GPs and physiotherapists can ensure that patients are matched to the treatment most likely to improve their shoulder pain.
PEP-TALK: A behaviour change physiotherapy intervention to increase physical activity following hip and knee replacement
PEP-TALK is a pragmatic multi-centre, randomised controlled trial which will test a group exercise and behaviour change treatment which targets barriers people have which can stop them being physically active, to maximise their 'whole-body' health and the effect of this on their NHS needs.
www.ndorms.ox.ac.uk/clinical-trials/current-trials-and-studies/peptalk
S-PROM: Development of a sarcoma-specific patient-reported outcome measure
The aim of this project is to develop a sarcoma-specific PROM (SAM) and a strategy to incorporate this into clinical practice.
sarcoma.org.uk/research/funded-projects
WORKWELL: Testing work advice for people with arthritis
WORKWELL is a randomised controlled trial for the development and evaluation of a work retention programme for employed people with inflammatory arthritis.
In this section
TheScholarsRepository@LLU: Digital Archive of Research, Scholarship & Creative Works
Home > SAHP > PT > ETD-PT
Theses, Dissertations and Projects - Physical Therapy
Theses/dissertations from 2022 2022.
High-Intensity Interval Training and Biological Age , Trevor Lohman
Theses/Dissertations from 2021 2021
The Impact of Intraneural Facilitation Therapy on Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy , Kyan Zhra-Sahba Alnajafi
The Influence of Strength and Mobility on Lumbar Biomechanics During Lifting , Christopher S. Patterson
Theses/Dissertations from 2019 2019
Spine Kinematics and Muscle Activities in Non-specific Chronic Low Back Pain Subgroups in Sitting , Mansoor Ahmed Alameri
Relationship between Balance and Physical Activity in Subjects with Non-Specific Chronic Low Back Pain , Muhsen B. Alsufiany
Does self-evaluation and education in students change attitudes and beliefs towards Weight Stigma? , Henry A. Garcia
Effects of Head Motion on Balance in Middle-Aged and Young Adults with Chronic Motion Sensitivity , Ammar E. Hafiz
Effect of Pediatric Ear Infections on Postural Stability , Ohud A. Sabir
Biomechanics and Postural Control Characteristics in Low Back Pain Subgroups During Dynamic Task , Amjad Shallan
Theses/Dissertations from 2018 2018
Effect of Adding Stretching Techniques to Standardized Intervention on Nonspecific Mechanical Neck Pain , Saad S. Alfawaz
Theses/Dissertations from 2017 2017
Effects of Head Motion on Postural Stability in Participants with Chronic Motion Sensitivity , Abdulaziz A. Albalwi
Relationship between Vestibular System, Vision, Anxiety, and Chronic Motion Sensitivity , Ahmad A. Alharbi
The Effects of Frequent Smartphone Use on Children’s Upper Posture and Pulmonary Function , Asma Alonazi
The Effects of Wearing Headscarves on Cervical Spine Proprioception and Range of Motion , Samiah Alqabbani
A Comparison of Neuromuscular Control between Subjects with and without Chronic Ankle Instability , Hatem Jaber
Theses/Dissertations from 2016 2016
Effects of Adjustments to Wheelchair Seat to Back Support Angle on Head, Neck, and Shoulder Postures , Afnan M. Alkhateeb
Effect of Jet Lag on Postural Stability , Faisal M. Al Mubarak
Effect of Heavy Lifting with a Head Strap on the Pelvic Floor across the Menstrual Cycle , Yvonne Biswokarma
Theses/Dissertations from 2015 2015
Physical Therapy after Triangular Fibrocartilage Injuries and Ulnar Wrist Pain , Mohamed A. Abdelmegeed
The Effect of Cervical Muscle Fatigue on Postural Stability during Immersion Virtual Reality , Mazen M. Alqahtani
The Effects of a Novel Therapeutic Intervention in Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy Patients , Adel M. Alshahrani
Cross-cultural Adaption and Psychometric Properties Testing of The Arabic Anterior Knee Pain Scale , Abdullah S. Alshehri
Effect of Tai Chi Exercise Combined with Mental Imagery in Improving Balance , Abdulrahman Alsubiheen
Effect of Vestibular Adaptation Exercises on Chronic Motion Sensitivity , Danah Alyahya
Muscle Dynamics as the Result of Whole Body Vibration and Plyometrics , Richard Jeremy Hubbard
Theses/Dissertations from 2014 2014
Effect of Monophasic Pulsed Current on the Treatment of Plantar Fasciitis , Abdullah Alotaibi
Screening for Torticollis and Plagiocephaly: The Role of the Pediatrician , Lisa Ann Change-Yee Hwang
Effect of 17β Estradiol & Foot Strike Patterns on Physiological & Biomechanical Changes in Runners , Iman Akef Khowailed
Theses/Dissertations from 2013 2013
Inter-rater Reliability of Lumbar Segmental Instability Tests and the Subclassification , Faisal Mohammad Alyazedi
Sleep-wake Cycle Assessment in Type 2 Diabetes and Salivary Melatonin Correlates , Paula Regina Aguiar Cavalcanti
Anterior Cruciate Ligament Elasticity and Force for Knee Flexion during the Menstrual Cycle in Women , Haneul Lee
Effect of Passive Vibration on Skin Blood Flow in Good Glycemic Control and Poor Glycemic Control Type 2 Diabetics , Kanikkai Steni Balan Sackiriyas
Theses/Dissertations from 2012 2012
Co-diagnosis Frequency of Peripheral Vestibular Disorders and Physical Therapy , Summer M. San Lucas
Postural Sway, EEG and EMG Analysis of Hip and Ankle Muscles during Eight Balance Training Tasks , Yuen Yi Florence Tse
Effect of a Single High-Fat Meal and Vitamins on the Circulatory Response to Local Heat in Koreans and Caucasians , JongEun Yim
Theses/Dissertations from 2011 2011
Virtual Reality Gaming as a Tool for Rehabilitation in Physical Therapy , Abel A. Rendon
Theses/Dissertations from 2010 2010
Aerobic Exercise and Bone Turnover in Trained and Untrained Premenopausal Women , Michelle Prowse
Theses/Dissertations from 2008 2008
Effect of 3-Electrode Electrical Stimulation on Current Delivery and Healing in Chronic Wounds , HyeJin Suh
Theses/Dissertations from 2007 2007
Is Electrical Stimulation a Predictive Tool for Autonomic Dysfunction in Males with Diabetes? , Susan Dorothy Rand
Theses/Dissertations from 2005 2005
The Effect of Posterior Versus Anterior Glide Joint Mobilization on External Rotation Range of Motion of Patients with Shoulder Adhesive Capsulitis , Andrea J. Johnson
The Effect of Electrical Stimulation on Blood Flow in Chronic Wounds in Patients with and without Diabetes , Daryl J. Lawson
Isokinetic Knee Strength in Females with Fibromyalgia , Flora F. Shafiee
Difference in Transverse Plane Scapular Position of Professional Baseball Players Relative to Baseball Field Position , James M. Syms
The Effect of Positioning on Pelvic Floor Muscle Activity as Evaluated with Surface Electromyography in Normals , Karen R. Whitter-Brandon
Theses/Dissertations from 2004 2004
Orthopedic Treatment Outcomes and Physical Therapists' Orthopedic Clinical Specialist Status , Karin Granberg
The Effectiveness of a Physical Therapy Intervention for Children with Hypotonia and Flatfeet , Charmayne G. Ross
Theses/Dissertations from 2003 2003
The Role of Health Promotion in Physical Therapy , Brenda L. Rea
Predicting Sacroiliac Syndrome: The Association Between Noninvasive Sacroiliac Joint Tests and Sacroiliac Joint Injections , Lorraine D. Webb
Theses/Dissertations from 2002 2002
Prevalence of various Upper Extremity Disorders in Patients with Carpal Tunnel Syndrome versus Patients without Carpal Tunnel Syndrome , Daniel C. Buda
Effect of Electrode Size, Shape, and Placement on Electrical Current and Subject Comfort During Electrical Stimulation , Bonnie J. Forrester
Patterns of Scholarly Productivity in Physical Therapy Faculty , Ardith L. Williams-Meyer
Theses/Dissertations from 2001 2001
The Effects of Education on Fear-Avoidance Behavior of Subjects with Work-Related Low Back Pain , Marie A. Anger
Toward the Optimal Waveform for Electrical Stimulation , Scott Douglas Bennie
Factors in Predicting the Number of Home Care Physical Visits , Bruce D. Bradley
A Practice Analysis Survey: Defining the Clinical Practice of Primary Care Physical Therapy , Edsen Bermudez Donato
Disability Self-Assessment and Upper Quarter Muscle Balance in Females , Eric Glenn Johnson
Theses/Dissertations from 2000 2000
Comparison of Elderly Non-Fallers and Fallers on Performance Measures of Functional Reach, Sensory Organizations, and Limits of Stability , Harvey W. Wallmann
Theses/Dissertations from 1999 1999
Patient participation in physical therapy goal-setting , Susan M. Baker
Theses/Dissertations from 1998 1998
Prediction of Discharge Destination from Initial Physical Therapy Assessment using the Physical Assessment Key (PAK) , Wendy L. Chung and Kimberly A. Vieten
Does the Oswestry or SF-36 Help a Therapist to Predict Treatment Classification , Amy Crawford and Denese D. Kaufeldt-Soliz
Reliability and Validity of Assessing Student Performance of Psychomotor Skills in Entry Level Physical Therapy Curricula , Nancy Sue Darr
Theses/Dissertations from 1997 1997
Reference Serum Chemistry and Hematological Values for Spinal Cord Injured Patients , Michael S. Laymon and Antone L. Davis II
Discharge Outcomes : An Evaluation of a Functional Index of Physical Assistance , Jan R. Snell
Theses/Dissertations from 1985 1985
A Comparison of Strength Improvement on Free Weights and the Universal Centurion , David J. Davies
Theses/Dissertations from 1984 1984
The effect of dextrose ingestion on cardiovascular endurance , Judith M. Axford
Theses/Dissertations from 1980 1980
The Ingestion of Garlic and its Effect on Cardiovascular Endurance , Thomas G. Blackwelder
- Collections
- Disciplines
Advanced Search
- Notify me via email or RSS
Author Corner
- Faculty Research (Pure)
Home | About | FAQ | My Account | Accessibility Statement
Privacy Copyright
- Open access
- Published: 21 May 2024
Efficacy of interventions and techniques on adherence to physiotherapy in adults: an overview of systematic reviews and panoramic meta-analysis
- Clemens Ley ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-1700-3905 1 &
- Peter Putz ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-2314-3293 2
Systematic Reviews volume 13 , Article number: 137 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
344 Accesses
3 Altmetric
Metrics details
Adherence to physiotherapeutic treatment and recommendations is crucial to achieving planned goals and desired health outcomes. This overview of systematic reviews synthesises the wide range of additional interventions and behaviour change techniques used in physiotherapy, exercise therapy and physical therapy to promote adherence and summarises the evidence of their efficacy.
Seven databases (PEDro, PubMed, Cochrane Library, Web of Science, Scopus, PsycINFO and CINAHL) were systematically searched with terms related to physiotherapy, motivation, behaviour change, adherence and efficacy (last searched on January 31, 2023). Only systematic reviews of randomised control trials with adults were included. The screening process and quality assessment with AMSTAR-2 were conducted independently by the two authors. The extracted data was synthesised narratively. In addition, four meta-analyses were pooled in a panoramic meta-analysis.
Of 187 reviews identified in the search, 19 were included, comprising 205 unique trials. Four meta-analyses on the effects of booster sessions, behaviour change techniques, goal setting and motivational interventions showed a significantly small overall effect (SMD 0.24, 95% CI 0.13, 0.34) and no statistical heterogeneity ( I 2 = 0%) in the panoramic meta-analysis. Narrative synthesis revealed substantial clinical and methodological diversity. In total, the certainty of evidence is low regarding the efficacy of the investigated interventions and techniques on adherence, due to various methodological flaws. Most of the RCTs that were included in the reviews analysed cognitive and behavioural interventions in patients with musculoskeletal diseases, indicating moderate evidence for the efficacy of some techniques, particularly, booster sessions, supervision and graded exercise. The reviews provided less evidence for the efficacy of educational and psychosocial interventions and partly inconsistent findings. Most of the available evidence refers to short to medium-term efficacy. The combination of a higher number of behaviour change techniques was more efficacious.
Conclusions
The overview of reviews synthesised various potentially efficacious techniques that may be combined for a holistic and patient-centred approach and may support tailoring complex interventions to the patient’s needs and dispositions. It also identifies various research gaps and calls for a more holistic approach to define and measure adherence in physiotherapy.
Systematic review registration
PROSPERO CRD42021267355.
Peer Review reports
Adherence to physiotherapeutic1 treatment and recommendations is crucial to achieving the planned goals and desired effects [ 1 , 2 ]. This is because the desired effects are usually only achieved in the long term if the recommended treatment and home-based exercises are carried out regularly. However, non-adherence in physiotherapy can be as high as 70%, particularly in unsupervised home exercise programmes [ 1 , 3 ] and may differ among medical conditions [ 4 ]. The World Health Organization defines adherence to therapy as ‘the extent to which a person’s behaviour—taking medication, following a diet and/or executing lifestyle changes, corresponds with agreed recommendations from a health care provider’ [ 5 ]. Long-term adherence often requires lifestyle changes, which can be supported by behaviour change techniques (BCTs). BCTs are considered the ‘active, replicable and measurable component of any intervention designed to modify behaviour’ ([ 6 ],cf. [ 7 ]). BCTs are defined and operationalised in the behaviour change taxonomy [ 8 ], based on theoretical underpinnings and a Delphi study. Theoretical models to explain (non-)adherence and (a) motivation as well as techniques to promote behaviour change have been extensively studied in health and exercise psychology [ 9 , 10 , 11 ]. Rhodes and Fiala [ 12 ] argue that despite several strong psychological theories that have been developed to explain behaviour, few provide guidance for the design and development of interventions. Furthermore, theories may not be equally applicable to all behavioural domains, therapeutic regimes and settings. For example, the factors determining adherence to (passive) medication use differ from those influencing adherence to (active) physical therapies and exercise behaviour (cf. [ 5 ]). This review specifically addresses the domain of physiotherapy and therapeutic exercise.
Existing reviews of predictive studies identified factors influencing adherence positively or negatively, showing the predominately conflicting and low evidence of a wide range of predictive factors for adherence [ 1 , 2 , 13 ]. Moderate to strong evidence was shown for some factors, referring to previous (adherence) behaviour and treatment experiences, physical activity level, social support and psychosocial conditions, number of exercises and motivational dispositions. Such predictive studies have identified the possible targets for intervention but do not provide evidence on the efficacy of interventions. In contrast, randomised control trials (RCTs) are recognized as the preferred study design for investigating the efficacy of interventions. Thus, this overview of reviews Footnote 1 aimed at providing a synthesis of reviews that examined RCTs, allowing for the discussion of the efficacy of different interventions and BCTs on adherence-related outcomes.
There are numerous reviews on adherence to physiotherapy and (home-based) exercise, and on BCTs to increase physical activity levels, therapeutic exercise or self-organised exercise [ 1 , 2 , 3 , 14 , 15 , 16 , 17 , 18 ]. Yet, no systematic overview of reviews has been identified that specifically synthesised the efficacy of interventions and techniques to enhance adherence to physiotherapy.

Objectives and research questions
Therefore, the aim of this overview of reviews was to synthesise the evidence on the efficacy of interventions and techniques on adherence in physiotherapy, to explore heterogeneity regarding the theoretical underpinnings, types of interventions used, and the adherence-related measures and outcomes reported, and finally to identify research gaps. Thus, the primary research question is the following: How efficacious are interventions and techniques in increasing adherence to physiotherapy? Secondary research questions are as follows: What types of intervention and behaviour change techniques were investigated? Which theoretical underpinning was reported? How was adherence defined and related outcomes measured?
This overview of reviews is guided by the research questions and aligns with the common purposes of overviews [ 19 , 20 ] and the three functions for overviews proposed by Ballard and Montgomery [ 21 ], i.e. to explore heterogeneity, to summarize the evidence and to identify gaps. This overview approach is appropriate for addressing the research questions specified above by exploring different types of interventions and behaviour change techniques and by synthesising the evidence from systematic reviews of RCTs on their efficacy. The review protocol was registered ahead of the screening process in PROSPERO (reg.nr. CRD42021267355). The only deviations from the registration were that we excluded reviews of only cohort studies, due to the already broad heterogeneity of intervention and outcome measures, and that we additionally performed a panoramic meta-analysis.
Information sources, search strategy and eligibility criteria
The search in seven databases, PEDro, PubMed, Cochrane Library, Web of Science, Scopus, PsycInfo and CINAHL (Cumulative Index to Nursing and Allied Health Literature), was last updated on January 31, 2023. The search strategy was structured according to the PICOS (Population, Intervention, Comparison, Outcome and Study Type) scheme. The search terms related to physiotherapy and motivation or behaviour change and adherence and effectiveness/efficacy (details on the searches are listed in Additional file 1 ). A filter was applied limiting the search to (systematic) reviews. No publication date restrictions were applied.
Table 1 outlines the study inclusion and exclusion criteria. Only studies published in peer-reviewed journals were included. The review addressed adult patients, with any illness, disease or injury, and thus excluded studies on healthy populations. Reviews in the field of physiotherapy, physical therapy or the therapeutic use of exercise or physical activity were included if they investigated adherence as a primary outcome. Studies measuring adherence as a secondary outcome were excluded as they do analyse interventions that were not primarily designed to promote adherence and thus are outside the scope of this overview. Reviews that analysed only studies on digital apps or tools (e.g. virtual reality, gamification, exergames or tele-rehabilitation) were excluded from this overview, as they were outside of the scope of this overview. Only systematic reviews that appraised RCTs were included. Reviews appraising RCTs and other study designs were included if RCT results could be extracted separately. Systematic reviews are in our understanding literature reviews of primary studies with a comprehensive description of objectives, materials and methods; considering the risk of bias and confidence in the findings; and reporting according to the PRISMA statement [ 22 , 23 , 24 ]. Adherence is defined as the extent to which a person’s behaviour corresponds with treatment goals, plans or recommendations [ 5 ]. Related terms used in the literature are compliance, maintenance, attendance, participation and behaviour change or lifestyle modification and were thus included in the search strategy.
Screening and selection process
Author CL conducted the search in the seven different databases and removed duplicates, using the Zotero bibliography management tool. Following this, authors CL and PP both independently screened the titles and abstracts of the resulting sources (see Fig. 1 Flow diagram). After removing the excluded studies, PP and CL independently screened the remaining full texts in an unblinded standardised manner. Reasons for exclusion were noted in a screening spreadsheet. Any discrepancy was discussed, verified and resolved by consensus.
Data collection process and data items
Data extraction was done by CL after agreeing with PP on the criteria. A spreadsheet was created with the following data extraction components: (i) objectives and main topic of the review; (ii) study design(s) and number of studies included and excluded; (iii) search strategies (incl. PICO); (iv) population including diagnosis, sample sizes and age; (v) intervention and comparison, theoretical foundations and models used for designing the intervention; (vi) time frames, including follow-up; (vii) adherence-related outcome and outcome measures; (viii) key findings; (ix) analysis of primary studies (meta-analytical, other statistical or narrative analysis); and (x) tools used for the quality assessment, risk of bias and evidence grading. Primary outcomes on adherence included, adherence rates or categories, engagement, attendance and participation, and accomplished physical activity levels. PP verified the data extraction results. The data was extracted as reported in the systematic reviews, then reformatted and displayed in the tables and used for the narrative synthesis.
Assessment of risk of bias across reviews
Systematic reviews of RCTs are ranked highest in the evidence level [ 25 ], but are subjected to risk of bias (RoB). In an overview of reviews of systematic reviews, there are further risks of bias, in addition to those deriving from the primary studies and those deriving from the review of those studies. Particularly, the overlap of reviews regarding the included individual studies may bias the findings. According to the purpose of this overview, i.e. to synthesise the wide range of interventions and behaviour change techniques used to promote adherence and to summarise the evidence of their efficacy, the overlap of reviews regarding intervention or population was not an exclusion criterion. For considering the overlap of primary studies among the reviews, CL extracted the primary RCTs from the included reviews, identified the unique trials and compared the frequency of their use across the reviews (see results overlap of review and Additional file 2 ). Furthermore, where two or more reviews provided findings on the same technique (e.g. on the efficacy of behavioural graded activities), the overlap of primary studies was assessed specifically for that finding. If the evidence came from the same study, this was taken into account and marked accordingly in Table 5 to avoid double counting and overestimation of evidence.
Assessment of risk of bias within the reviews
CL and PP independently assessed the quality and risk of bias of the systematic reviews included, using the AMSTAR-2 tool [ 26 ]. Any discrepancy was discussed and resolved by consensus. AMSTAR (A MeaSurement Tool to Assess systematic Reviews) was developed to evaluate systematic reviews of randomised trials. The AMSTAR-2 revision enables a more detailed assessment of systematic reviews which may also include non-randomised studies of healthcare interventions. The applied AMSTAR-2 checklist consists of 16 items, whereof seven are classified as critical, and the appraisal results in an overall confidence rating distinguishing between critically low, low, moderate or high [ 26 ]. In addition, the overall confidence in the review was stipulated by the number of positive assessments in relation to the applicable domains (depending if meta-analysis was performed or not) and considering whether an item represents a critical domain or not [ 26 ].
Synthesis methods
Panoramic meta-analysis.
Among the included reviews, there were four meta-analyses [ 7 , 16 , 27 , 28 ], which were pooled as a panoramic meta-analysis based on the reported effect sizes and standard errors using IBM SPSS Version 29 (IBM Corp., Armonk, NY, USA). All four meta-analyses used the standardized mean difference as effect size. Standard errors were calculated from the reported 95% CI as \(\frac{\mathrm{upper bound }-\mathrm{ lower bound}}{3.92}\) . Inverse variance was used to weight the meta-analyses, statistical heterogeneity was assessed by I -squared and a fixed-effects model was selected based on the absence of statistical heterogeneity of true effects. Eisele et al. [ 7 ] included 15 primary trials that examined the effect of BCTs on physical activity adherence. They pooled results for medium-term (3–6 months) and long-term (7–12 months) interventions, from which we selected the medium-term model that best matched the eligibility criteria of the other included meta-analyses. Levack et al. [ 27 ] included nine primary trials that examined the effect of goal-setting strategies on engagement in rehabilitation. Among models with other outcomes, we selected this model because it best matched the aim of this overview, and it was most consistent with the outcomes of the other included meta-analyses. McGrane et al. [ 28 ] included six primary trials, representing 378 subjects that examined the effects of motivational interventions on physiotherapy session attendance. They reported another model with perceived self-efficacy as an outcome, but we selected the attendance model because it best matched the aim of this overview, and it was most consistent with the outcomes of the other included meta-analyses. Nicolson et al. [ 16 ] included two primary trials that examined the effect of booster sessions on self-rated adherence. Results were summarized by a forest plot and publication bias was assessed graphically by a funnel plot, although the small number of individual meta-analyses included limits its interpretability. Alpha was set at 0.05.
Narrative synthesis
The narrative synthesis was performed by CL in constant dialogue with and verification of PP. Guided by the research questions, the narrative synthesis of the extracted data was manifold. First, we explored the heterogeneity of interventions, measures and adherence-related outcomes across and within the reviews using the data extraction table. Definitions and measures of adherence were compared among the reviews and discussed. Second, analysis of the descriptions of the interventions and their respective components/techniques, their theoretical underpinning and their objectives was used to classify the interventions according to different types of intervention, namely the informational/educational, the cognitive/behavioural/motivational and the relational/psychosocial intervention. Consequently, for each type of intervention, the results on the efficacy were narratively synthesised. In addition, reported differences in efficacy among medical conditions, theoretical underpinnings and physiotherapeutic settings were summarised based on the data extraction table. Third, the results on the efficacy of the interventions and BCTs were further summarised in a table and then restructured according to the evidence level as reported in the systematic reviews and the confidence in the reviews as analysed by the AMSTAR-2. Therefore, the levels of evidence were extracted as reported in the reviews, which are based on different evidence appraisal schemes: GRADE (high, moderate, low, very low certainty of evidence), Cochrane Collaboration Back Review Group Evidence Levels (strong, moderate, conflicting, limited, no evidence) and self-developed tools. Afterwards, they were compared for the respective intervention/technique across the relevant reviews, considering the confidence in the review and the comprehensiveness of the review as well. The levels of evidence are presented in the table with the categories high, moderate, low and very low. The efficacy supported by the evidence is also based on the results reported in the reviews. In case of overlapping reviews or discrepancies between the reviews, the primary studies were consulted. The category yes refers to results of merely positive effects, and inconsistent refers to findings of positive and no effects of the intervention (techniques) analysed. The category no indicates that the intervention was not efficacious. No negative effects (i.e. favouring the control condition) were reported for the intervention (techniques) shown.
The reporting of findings followed the PRIOR reporting guideline for overviews of reviews of healthcare interventions [ 29 ].
Study selection results
Of the 187 records screened, 19 were included (see Fig. 1 ). Main reasons for exclusion were not a systematic review of RCTs ( n = 79), adherence not the primary outcome ( n = 60), and lack of physiotherapy relevance ( n = 39) (see Fig. 1 ).
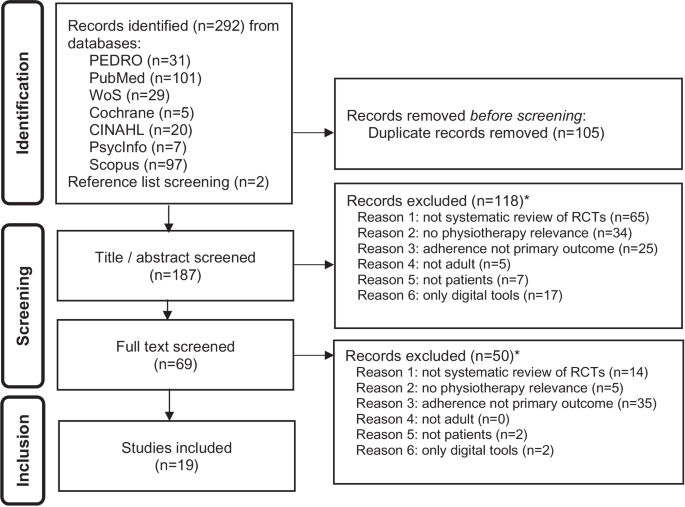
Flow diagram, based on PRISMA [ 24 ] and PRIOR [ 29 ] guidelines. Legend: *Multiple reasons for exclusion were possible
Characteristics and diversity of included reviews
The selection strategy resulted in a broad heterogeneity of included reviews. The 19 included reviews differed in their eligibility criteria of the primary studies as well, resulting in substantial clinical diversity, i.e. the inclusion of heterogenous conditions, intervention types and settings (see Table 2 ) and methodological diversity, i.e. the variability in study design, outcome measurements and risk of bias (see Tables 3 , 4 and 5 ). Musculoskeletal diseases [ 6 , 7 , 17 , 30 , 31 , 32 ] and pain [ 13 , 16 , 33 , 34 , 35 ] were the most investigated medical conditions. Those reviews that did not limit their search to a specific disease [ 12 , 27 , 28 , 36 , 37 , 38 , 39 , 40 ] yielded predominantly studies on musculoskeletal diseases. All reviews included adults only (18 and older). One focused on elderly (65 and older) people [ 40 ] and one on older (45 and older) adults [ 16 ]. Fourteen of the 19 reviews analysed RCTs only [ 6 , 7 , 16 , 17 , 27 , 28 , 30 , 31 , 32 , 33 , 34 , 35 , 36 , 39 , 40 ]; one also included besides RCT cohort studies [ 13 ] and three [ 12 , 37 , 38 ] also included any other quantitative study design (see Table 3 ). Four reviews performed a meta-analysis [ 7 , 16 , 27 , 28 ], and two studies were Cochrane Reviews [ 27 , 35 ]. Four reviews [ 6 , 7 , 17 , 40 ] analysed the use of BCTs and rated the interventions according to a BCT taxonomy [ 8 ].
Results of the individual reviews
The 19 reviews contained a total of 205 unique RCTs. Table 3 shows the main results of each review.
Results of quality assessment and confidence in the reviews
The critical appraisal with the AMSTAR-2 tool (see Table 4 ) showed that four reviews were rated with moderate to high quality [ 7 , 16 , 27 , 35 ], whereas all others resulted in a critically low to low overall confidence in the review. Frequent shortcomings were not explaining the reasons for the inclusion of primary study designs, and an insufficient discussion of the heterogeneity observed. Furthermore, as many reviews did not explicitly mention a pre-established, published or registered protocol or study plan, it is uncertain whether the research followed a pre-specified protocol and whether there were changes and/or deviations from it, and, if so, whether decisions during the review process may have biased the results [ 26 ].
Risk of bias and evidence assessment within reviews
The reviews used various approaches to appraise the evidence, particularly the GRADE (Grades of Recommendation, Assessment, Development and Evaluation) system [ 13 , 16 , 26 , 27 ], the evidence levels by the Oxford Centre for Evidence-Based Medicine [ 28 ] or the system by Cochrane Collaboration Back Review Group [published by 25,30] [ 31 , 32 , 33 , 34 ]. Three reviews modified existing or developed their own tool or checklist [ 12 , 35 , 36 ]. For the assessment of the risk of bias and/or quality of the individual studies, the reviews used the following tools: PEDro Scale [ 7 , 13 , 26 , 32 , 37 ], Cochrane Collaboration Back Review Group Quality Assessment Tool [ 31 , 34 ], Cochrane Risk of Bias criteria [ 6 , 16 , 17 , 27 , 33 , 37 , 38 , 39 ], the Delphi List [ 40 ] or modified or developed own tools [ 12 , 35 , 36 ].
A recurring concern regarding potential performance bias was the lack of therapist blinding, which is almost impossible to implement in this research field [ 7 ]. Attrition bias, due to low sample size or drop-outs, and measurement bias, due to the mere use of subjective measures, were also highlighted in the reviews. Another concern was the availability and selection of adequate control groups. Control groups, such as usual practice, unspecific exercise group or alternative intervention commonly include varying numbers of BCTs which must be considered when assessing and comparing contents of interventions [ 7 ]. The comparability of the intervention and control group regarding adherence-related outcomes is further hindered by poor descriptions of the intervention, uncertainty about treatment fidelity and implementation processes, varying competences and proficiency of the therapist, and the diverse translation of theoretical models and use of intervention techniques [ 7 , 34 , 39 ]. Rhodes and Fiala [ 12 ] pointed out that procedures of RCTs, such as several pre-screenings and measurement batteries, may lead to a potential self-selecting of only the most motivated individuals. This may limit the ability to compare intervention to the control group, as both groups are (already) highly motivated, and to detect changes, due to the already high motivation and disposition to adhere. This may explain in part, that the reviews reported many studies that failed to provide evidence for intervention efficacy on adherence. In addition, the restricted timeline (limited duration for observation and follow-up) of the studies may confound/skew the results, as drop-out may occur shortly after the end of the study and long-term adherence is not measured [ 12 ].
Overlap of reviews
The 19 reviews included from 3 to 42 individual RCTs. In sum, the reviews included 261 RCTs (multiple publications on the same trial were counted as one; thus, the number of trials was counted), whereby 34 trials were included in various reviews (see Additional file 2 , Overlap of reviews), resulting in 205 unique RCTs. Of these 34 trials included in multiple reviews, 25 were included in two different reviews. The following trials were included more than twice: Basler et al. 2007 (8x), Friedrich et al. 1998 (7x), Schoo et al. 2005 (4x), Vong et al. 2011 (4x), Asenlof et al. 2005 (3x), Bassett and Petrie 1999 (3x), Brosseau et al. 2012 (3x), Bennell et al. 2017 (3x), Gohner and Schlicht 2006 (3x) and Duncan and Pozehl 2002, 2003 (3x).
In total, the overlap of primary trials in the reviews is considered low; except among reviews [ 27 , 39 ] and among reviews [ 12 , 16 , 28 , 30 ]. Two reviews [ 27 ] and [ 39 ] were conducted by the same authors, within the same field, i.e. goal planning and setting, however with a different approach and research question. Reviews [ 12 , 16 , 28 , 30 ] have a considerable amount of overlap. Still, each of these reviews included unique RCTs, not analysed in any of the other reviews, and they do focus on different research questions, foci and analyses. Therefore, we did not exclude an entire review due to an overlap of studies.
Synthesis of results
The synthesis focused on answering the research questions. We began by presenting the narrative synthesis findings on how adherence was measured, what types of intervention and BCTs were investigated, and which theoretical underpinnings were reported. Afterwards, we synthesised the evidence on the efficacy of the interventions and BCTs, both meta-analytically and narratively.
Measures of adherence and related outcomes
The reviews included studies with a heterogeneous use, breadth and measures of adherence. Mostly, they refer to adherence as the extent to which a person’s behaviour corresponds with treatment goals, plans or recommendations ([ 30 ],cf. [ 5 ]). McLean and colleagues [ 30 ] expressed that within physiotherapy, the concept of adherence is multi-dimensional and could refer to attending appointments, following advice or undertaking prescribed exercises. The terms adherence and compliance were sometimes used interchangeably, referring to the degree of treatment attendance or accomplishment of physical activity levels, participation and recommendations, irrespective of how the treatment goals and plans were established. Yet, for definition purposes, the distinction between agreed and prescribed goals and plans was occasionally used in the reviews to distinguish adherence from compliance .
For analytical purposes, adherence was frequently dichotomised, establishing a cutoff point or percentage used to distinguish adherence from non-adherence. One was considered adherent, for example, if he/she achieved more than 70% or 80% of the targeted, recommended or prescribed sessions. Few studies graded the degree of adherence according to multi-categorical cut-off points (e.g. very low, low, moderate and high adherence). Only in one review [ 13 ], one study was named that distinguished a certain fluctuation in the adherence pattern, i.e. Dalager et al. [ 41 ] included besides the minutes exercised in a week the regularity of participation, distinguishing regular from irregular participation. Self-reported diaries, exercise logs and attendance lists were the most commonly used data recording instruments [ 33 , 35 , 37 ]. Adherence to home-based programmes was mainly measured with self-reported diaries, which are problematic as the only source, due to poor completion rates, and the possibility of inaccurate recall and self-presentation bias [ 18 , 33 ]. Digital devices (e.g. accelerometers or pedometers) may be used additionally to measure adherence; however, their use may also be problematic, as they require certain adherence to a systematic use of the device and the mere use of the device also may increase adherence [ 18 , 33 ]. One study reported the use of the Sport Injury Rehabilitation Adherence Scale (SIRAS) [ 42 ], which measures the patients’ degree and manner of participation in a session and compliance with the therapist’s instructions and plan. Thus, it does not measure adherence over a certain period of time nor adherence to recommendations or home-based exercise, but it can be used to assess the intensity of rehabilitation exercises, the frequency with which they follow the practitioner’s instructions and advice, and their receptivity to changes in the rehabilitation programme during that day’s appointment [ 42 ].
Interventions used to promote adherence
The reviews included a wide range of different interventions, which we grouped into three different intervention types:
Information provision and patient education were investigated in seven reviews [ 12 , 13 , 30 , 31 , 33 , 34 , 36 ], including (i) video- and audio-assisted patient education, (ii) phone calls, (iii) use of supporting materials and spoken or graphically presented information or (iv) other didactical interventions. Patient education has been defined as ‘any combination of learning experiences designed to facilitate voluntary adoption of behaviour conducive to health’ [ 43 ]. Niedermann et al. [ 31 ] distinguished between ‘purely’ educational programs based on knowledge transfer and psychoeducational programs. In the latter, motivational techniques and shared knowledge-building processes are added to the educational programme, which is done similarly in health coaching [ 34 ], and thus also relate to the cognitive, behavioural and relational/psychosocial interventions.
Cognitive and behavioural motivational interventions were relating frequently to cognitive-behavioural and social-cognitive theories, and applied (i) behavioural graded exercise; (ii) booster sessions, refresher or follow-up in situ by the therapist or via phone call; (iii) behavioural counselling (focusing on readiness to change); (iv) psychoeducational counselling; (v) supervision; (vi) (unspecified) motivational intervention; (vii) positive reinforcement; (viii) action and coping planning; and (ix) goal setting [ 7 , 12 , 13 , 16 , 27 , 28 , 30 , 32 , 33 , 34 , 39 ].
Relational and psychosocial interventions were less investigated overall. Related aspects included (i) social support; (ii) patient-centeredness, in particular patient-led goal setting, motivational interviewing and the therapeutic or working alliance; and (iii) emotional components [ 6 , 13 , 17 , 33 ].
The included reviews focused either on one particular or several types of intervention. Particularly, four reviews [ 6 , 7 , 17 , 40 ], which used a BCT taxonomy to analyse the interventions of the primary studies, described BCTs relating to all three intervention types. While this distinction of different types of interventions is useful to showcase the range of diverse interventions and techniques, they do have a great overlap and include a mix of different BCTs. For example, the way of facilitation of information, supervision or goal setting was approached differently according to the relational approach, i.e. being more instructive, directive or more collaborative, participatory, patient-led ([ 31 ],cf. [ 34 ]).
Theoretical underpinning of interventions
No review focused on only one theoretical foundation or excluded studies based on any theoretical model or not underpinning the intervention. In total, the reviews included studies with diverse theoretical models and varying degrees of theoretical underpinning. References to the cognitive behavioural theory (CBT) and to the social-cognitive theory were frequent in the individual studies. Furthermore, the self-determination theory, the transtheoretical model, the health belief model, the social learning theory and the socioemotional selectivity theory were used in some individual studies (cf. [ 11 ]). The heterogeneity in the theoretical underpinning of the interventions is reinforced by the given overlap of the theories and models (cf. [ 11 ],[ 28 ]) and various BCTs are key components of several theories [ 17 ]. Furthermore, theories were not used enough to explicitly inform and underpin interventions and they were translated into practise in different ways; thus, interventions based on the same theory may differ substantially [ 17 ].
The BCT Taxonomy v1 [ 8 ], which relates to various theoretical models, was used in four reviews [ 6 , 7 , 17 , 40 ] to identify BCTs in interventions in a standardized manner. The Behaviour Change Wheel [ 44 ], which is linked to the BCT Taxonomy v1, was referred to in one review [ 40 ] pointing to its usefulness for designing a behaviour change intervention. The number of BCTs used appears to be relevant, as interventions using a higher number (≥ 8) of BCTs achieved a significant effect (pooled SMD = 0.29, 95% CI 0.19–0.40, p < 0.001), whereas interventions using a lower number (< 8) of BCTs did not (pooled SMD = 0.08, 95% CI -0.11 to 0.27, p = 0.41).
Overall efficacy and heterogeneity according to the panoramic meta-analysis
Although there was statistical heterogeneity ( I 2 from 41 to 63%) between the primary studies included in each meta-analysis [ 7 , 16 , 27 , 28 ], there was no heterogeneity between the pooled effects of these four meta-analyses ( I 2 0%). This means that all variability in the effect size estimates (SMD from 0.20 to 0.39) was attributable to sampling error, but there was no variability in the true effects. Although the interventions were selected based on different eligibility criteria (BCTs, goal-setting strategies, motivational interventions and booster sessions), they appear to be very similar in terms of the effects they trigger. There was no overlap between the primary trials included in the meta-analyses. The pooled SMD was 0.24 (95% CI 0.13, 0.34) (Fig. 2 ). Effect size estimates were somewhat larger in those meta-analyses with less weight in the model (i.e. due to a larger standard error). However, no obvious publication bias could be detected in the funnel plot (Fig. 3 ). Sensitivity analyses in the meta-analysis in Eisele et al. [ 7 ], considering only studies with PEDro scores of 6 or more, revealed slightly lower effect sizes but still statistically significant effect sizes regarding medium-term effects (SMD PEDro>=6 0.16, 95% CI 0.04–0.28, p < 0.01 versus SMD all 0.20, 95% CI 0.08–0.33, p < 0.01) and higher numbers of BCTs (SMD PEDro>=6 = 0.26, 95% CI 0.16–0.37, p < 0.001 versus SMD all = 0.29, 95% CI 0.19–0.40, p < 0.001), indicating that low-quality studies may tend to overestimate the efficacy ([ 7 ],cf. [ 31 ]).
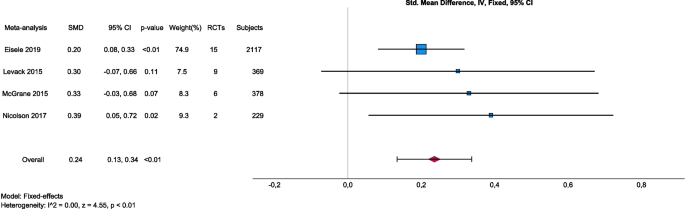
Forest plot of panoramic meta-analysis: interventions aiming at improving adherence, adherence-related outcomes
Legend: Eisele 2019. Intervention: Interventions aiming at improving physical activity levels or adherence, containing at least one BCT. Comparison: Usual care, minimal intervention, placebo or no intervention. Outcome: Any measure of physical activity level or adherence to any kind of physical activity. Levack 2015. Intervention: Goal setting (with or without strategies to enhance goal pursuit). Comparison: No goal setting. Outcome: Engagement in rehabilitation. McGrane 2015. Intervention: Motivational interventions as part of a package, psychological strategies, theory-based instructional manuals, Internet-based behavioural programmes and relapse prevention, and re-inforcement strategies. Comparison: Any comparison (not specified). Outcome: Attendance at physiotherapy sessions/exercise classes. Nicolson 2017. Intervention: Booster sessions to increase adherence to therapeutic exercise. Comparison: Contextually equivalent control treatments. Outcome: Self-rated adherence
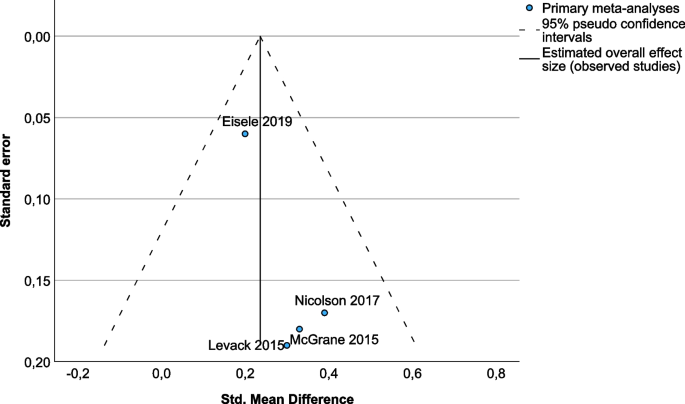
Funnel plot of publication bias
Efficacy of informational and educational interventions
The results of five—partly overlapping—reviews [ 12 , 30 , 31 , 34 , 36 ] showed, with a very low evidence base, that interventions that primarily aimed at information provision and knowledge transfer to the patient had limited efficacy on adherence-related outcomes. There was conflicting evidence and inconsistent efficacy of video-assisted patient education [ 36 ] and individualised exercise videos [ 12 , 30 ] in modifying behaviour or adherence. However, the authors identified the format in which the educational information is presented and the complexity of the addressed behaviour as crucial factors [ 36 ]. Videos that provide only spoken or graphically presented health information are inappropriate tools for changing patient behaviour. However, videos with a narrative format appear to be a powerful education tool [ 36 ]. Low evidence based on one study [ 12 , 30 ] indicates that additional written information seems superior to verbal instructions alone (mean difference between groups 39.3%, p < 0.001). With a high overlap of studies, two reviews [ 30 , 31 ] showed that there is limited evidence for long-term effects of patient education targeting knowledge acquisition. While the informative and instructive educational approach is an essential part of patient education, patient education often involves more than the transfer of knowledge [ 30 , 31 , 34 ]. Niedermann et al. [ 31 ] compared educational and psychoeducational interventions and provided arguments in favour of psychoeducational approaches that enrich patient education with motivational strategies and techniques (cf. [ 34 ]).
Efficacy of cognitive and behavioural motivational interventions
Several (though partly overlapping) reviews [ 12 , 16 , 28 , 30 , 33 , 37 ] examined studies on additional motivational interventions that were based on social-cognitive or cognitive-behavioural theories. McGrane et al. [ 28 ] concluded heterogeneity of motivational interventions, outcomes and measurements as potential causes for conflicting evidence regarding effects on exercise attendance and PT adherence, as they found no significant difference ( p = 0.07) in exercise attendance between additional motivational intervention groups and their controls (pooled SMD 0.33, 95% CI -0.03 to 0.68, I 2 62%), but a significant ( p < 0.01) medium-sized effect of additional motivational interventions on self-efficacy beliefs (pooled SMD 0.71, 95% CI 0.55 to 0.87, I 2 41%). The heterogeneity hindered in this meta-analysis the statistical analysis of subgroups to determine and compare the efficacy of different components and approaches to motivational interventions [ 28 ]. Another meta-analysis [ 16 ] found moderate-quality evidence that booster sessions with a physiotherapist helped people with hip/knee osteoarthritis to better adhere to therapeutic exercise (pooled SMD 0.39, 95% CI 0.05 to 0.72, p = 0.02, I 2 35%). Moderate evidence for the efficacy of supervision (2 studies, n = 193) favouring adherence was shown [ 13 , 33 , 35 ].
In four reviews [ 16 , 32 , 33 , 35 ], four unique high-quality trials supported the use of motivational strategies and behavioural graded exercise to improve adherence to exercise (effect sizes 0.26–1.23)[ 16 ]. Behavioural graded exercise includes a preset gradual increase of the physical activity through facility-based interventions followed by booster sessions [ 45 ] and uses principles of operant conditioning and self-regulation [ 16 ].
While cognitive behavioural programmes seem superior to exercise alone for short-term adherence and clinical attendance [ 30 ], behavioural counselling focusing on readiness to change, action and coping plans and/or audio/video exercise cues seem not to improve adherence significantly [ 16 ]. Holden [ 34 ] concludes inconsistent evidence for health coaching based on the transtheoretical model of change, with one RCT showing some efficacy on exercise compliance (SMD = 1.3). However, the frequently referred to study of Göhner and Schlicht [ 46 ], who analysed a cognitive-behavioural intervention with a strong emphasis on action and coping planning [ 12 ], showed no difference between experimental and control groups in the first 11 weeks, but a significant difference 5 months later on behaviour (SMD = 0.83) as well as differences over all time-points on self-efficacy (interaction effect of time by group, F (3, 43) 10.36, p < 0.001, n = 47) favouring the intervention [ 46 ]. Motivational interventions, including positive reinforcement, increased (i) adherence to home exercise in one RCT [ 33 ], (ii) reported frequency of exercise in two RCTs [ 35 ] and (iii) self-efficacy beliefs in two RCTs, in the short-term (SMD = 1.23) and in the long-term (SMD = 0.44) ([ 16 ],cf. [ 30 ]). Self-efficacy beliefs relate to the trust in one’s capacities/competencies to cope with daily demands [ 47 ] and are associated (moderate evidence) with adherence [ 13 , 48 ].
Levack et al. [ 27 ] conclude some evidence that goal planning/setting improves engagement in rehabilitation (motivation, involvement and adherence) over the duration of the programme (9 studies, 369 participants, SMD 0.30, 95% CI -0.07 to 0.66). Furthermore, they show a low-quality evidence for effects on patient self-efficacy from more structured goal setting compared to usual care with or without goal setting (2 studies, 134 participants; SMD 0.37, 95% CI 0.02 to 0.71) and from goal setting compared to no goal setting (3 studies; 108 participants; SMD 1.07, 95% CI 0.64 to 1.49). The review did not detect differences in efficacy between the approach taken to goal planning. However and similar to patient education [ 34 ], the review authors argue that the lack of clarity about the effects and the low evidence is due to the heterogeneity of the implementation of goal planning, lack of detailed descriptions of the goal-setting process in the intervention groups but also in the control groups, and methodological flaws ([ 27 , 39 ],cf. [ 13 ]).
The BCTs from the cluster goals and planning showed various positive effects, although not fully consistently [ 6 , 7 , 40 ]. Eisele et al. [ 7 ] identified goal setting (behaviour) , problem-solving , goal setting (outcome) , action planning and reviewing behaviour goal(s) as often used in non-effective interventions but also in effective ones. A trial that showed negative effects included problem-solving and goal setting (outcome) as well. Room et al. [ 40 ] found one study on older people and Thacker et al. [ 6 ] two home-exercise-related studies that used BCTs from the goals and planning cluster (i.e. problem-solving and action planning), but none of the studies found differences in favour of the intervention. Willett et al. [ 17 ] adjusted the BCTv1 taxonomy to differentiate patient-led and therapist-led goal setting and showed that patient-led goal setting (behaviour) achieved among the highest efficacy ratios across time points.
Efficacy of relational and psychosocial interventions
The BCT Social Support (unspecified) refers to ‘advise on, arrange or provide social support (e.g. from friends, relatives, colleagues, ’buddies’ or staff) or non-contingent praise or reward for the performance of the behaviour . It includes encouragement and counselling, but only when it is directed at the behaviour’ [8, Supplementary Material]. Eisele et al. [ 7 ] identified this BCT in 19 interventions and 10 control conditions. They found this BCT in three trials supporting efficacy and in seven trials supporting inefficacy. In contrast, Thacker et al. [ 6 ] found this BCT in all effective interventions but not in the non-effective ones. Willet et al. [ 17 ] concluded from their review that this BCT has among the highest efficacy ratios across time points to promote adherence to physical activity.
Social support may come along with monitoring and feedback, which can be graphically or narratively presented by the therapist. Willett et al. [ 17 ] recommend that self-monitoring (e.g. activity diaries), feedback on behaviour as well as social support should be used—beyond monitoring purposes—for explicit intervention purposes (e.g. to foster self-efficacy beliefs). Feedback on behaviour alone does not seem to be efficacious [ 6 ], but feedback can be efficacious for instance in combination with social support or goal setting and planning [ 17 , 40 ].
Patient-centred approaches were also included in the relational/psychosocial intervention type. Motivational interviewing, which is a collaborative, patient-centred communication style to promote behaviour change [ 49 ], was used in three studies, indicating positive effects on exercise compliance, physical activity and exercise at home in two trials, whereas no effect in a pilot study [ 28 ]. There is low evidence from three RCTs for positive effects of the therapist-patient alliance on global assessments; however, the efficacy on adherence-related outcomes is unclear [ 36 ]. The terms working or therapeutic alliance refer to the social connection or bond between therapist and patient/client, including reciprocal positive feelings, (assertive) communication, empathy, and mutual respect as well as collaboration, shared decision-making, agreement on the treatment goals and tasks [ 36 , 50 ]. The therapeutic alliance is a patient-centred approach as well. Patient-led goal setting was more often a component within efficacious interventions than therapist-led goal setting [ 17 ].
None of the included reviews focused specifically on affective interventions. However, some interventions relate to affective components, for example patient-led goal setting or motivational interviewing may cover emotional needs [ 27 ]; health coaching, therapeutic alliance or social support may include emotional support [ 13 , 34 , 35 , 38 ]; monitoring may consider emotional consequences [ 6 ]; or messaging and information provision may include emotional components [ 36 ]. Room et al. [ 40 ] included one RCT [ 51 ], comparing emotionally meaningful messages against factual informational messages, but with no significant differences between the groups.
Efficacy according to the theoretical underpinning
McGrane et al. [ 28 ] provide a narrative analysis of the efficacy of interventions according to the different theoretical underpinnings. In their review, the cognitive-behavioural theory (CBT) was the most popular theory (4 primary studies) and showed to be efficacious in improving self-efficacy and activity limitations, but not consistently regarding attendance and attrition [ 28 ]. The social-cognitive theory was used in three studies, showing improvements in self-efficacy, action and coping planning, and attendance, but conflicting results for exercising in the short and long term. One intervention [ 52 ] based on self-determination theory showed to be efficacious to improve adherence to physical activity. In contrast to McGrane et al. [ 28 ], the reviews [ 12 , 30 , 35 ] point to moderate to conflicting evidence for no or inconsistent efficacy of CBT-based approaches to physiotherapy programmes (see Efficacy of cognitive and behavioural motivational interventions ). Jordan [ 35 ] concluded that the addition of transtheoretical model-based counselling to physiotherapy is no more effective than physiotherapy and a sham intervention (GRADE: High (high quality); Silver). Notably, the interventions may not be representative of the theory described due to diverse translations of the theory into practice and the overlap of the same BCTs among the theories.
Various theories (e.g. the transtheoretical model or the Health Action Process Approach [ 53 ]) and studies [ 54 ] distinguish the action or adoption phase from the maintenance phase at 6 months. Interestingly, Willet et al. [ 17 ] found in total higher short (< 3 months) and long-term (12 months and more) than medium-term (around 6 months) efficacy ratios, pointing to the risk of drop-out when changing from the (short-term) adoption phase to the (long-term) maintenance phase [ 17 ]. Eisele et al. [ 7 ] divided in their meta-analysis the short-term (< 3 months), medium-term (3–6 months) and long-term (7–12 months post-intervention) differently, showing a small medium-term overall effect (pooled SMD 0.20, 95% CI 0.08–0.33, p < 0.01), but no significant long-term effect of interventions comprising BCTs in enhancing physical activity adherence (pooled SMD 0.13, 95% CI 0.02–0.28, p = 0.09).
Efficacy according to the different types of exercise, physiotherapeutic settings and medical condition
In their Cochrane review, Jordan et al. [ 35 ] compared the evidence for the efficacy of different types of exercises and physiotherapy settings. Graded exercise is beneficial for adherence (moderate evidence). The exercise type does not appear to play an important role (moderate evidence). Whether water-based exercise favours adherence is unclear (low evidence and inconsistent results). Furthermore, the supervision of exercising (moderate evidence) is beneficial for adherence, but also self-management programmes improve exercise frequency compared to waiting list or no-intervention control groups (moderate evidence). Exercising individually seems to improve attendance at exercise classes more than exercising in a group (moderate evidence), as individual sessions could be scheduled at more convenient times and missed sessions could be rescheduled, whereas group sessions were scheduled at relatively inflexible times, and missed sessions could not be rescheduled [ 35 ]. However, adding group exercise to a home exercise programme can increase overall physical activity levels (moderate evidence) [ 35 ]. While the results of home- versus clinic-based interventions were conflicting and confounded by the intervention approaches, a combination of home- and clinic-based approaches may be promising [ 12 ] and aligns with the moderate-quality evidence that self-management programmes, refresher or booster sessions with a physiotherapist assist people to better adhere to therapeutic exercise [ 16 ].
No study was identified in the reviews that compared other settings, such as private- and public-funded physiotherapy or primary care and rehabilitation settings regarding adherence outcomes. No review and no study comparing the same educational, motivational, or BCT-based intervention across different conditions were identified.
This overview of systematic reviews addresses adherence in the physiotherapy and therapeutic exercise domain, aiming to summarise the evidence on the efficacy of interventions, to explore heterogeneity and to identify research gaps. The overview of reviews provided an adequate approach to generate answers to the research questions. Nineteen reviews, covering 205 unique trials, were included and narratively synthesised. In addition, four meta-analyses were pooled in a panoramic meta-analysis. The findings provide an overview of the diverse interventions and techniques aiming to enhance adherence, ranging from informational/educational to cognitive/behavioural/motivational and to relational/psychosocial intervention types. Furthermore, it synthesised their efficacy in physiotherapy for adults.
Confidence in the reviews was rated moderate or high in four reviews [ 7 , 16 , 27 , 35 ], but low or very low in the others (Table 3 ). The individual reviews considered the evidence levels as mostly low or very low (Table 4 ; see Risk of bias and evidence assessment ). Table 5 summarizes the evidence on the efficacy of each intervention and technique according to (a) whether the evidence supports efficacy, (b) the evidence level based on the report in the systematic reviews and (c) the confidence in the reviews as assessed with AMSTAR-2. It must be noted that the components of the intervention which caused the efficacy were not always clear. Some interventions lacked detailed definitions and descriptions of the specific BCTs included [ 33 ]. A single technique or mechanism of action was not always identifiable; moreover, various techniques seem to influence each other in such a way that they achieved efficacy only jointly [ 17 , 40 ].
No clear conclusion can be drawn on the efficacy of informational/educational interventions. Five reviews [ 12 , 30 , 31 , 34 , 36 ] showed low evidence for the efficacy of interventions on knowledge acquisition and low evidence for limited short-term efficacy on adherence. Providing knowledge alone seems not enough and should be complemented with supportive material (very low evidence) and combined with other interventions (low evidence). Patient education should also include social-cognitive or cognitive-behavioural approaches, psychoeducational interventions and collaborative processes as it is included in the therapeutic alliance approach [ 31 , 34 , 36 ]. Patient education with a more constructive educational approach builds upon the knowledge of the patient, supporting him/her in exploring and co-constructing knowledge which is very relevant in physiotherapy as research has shown [ 55 , 56 ].
The reviews on additional motivational, cognitive and behavioural interventions showed findings ranging from non-efficacy of behavioural counselling based on readiness to change (with low to moderate evidence) to moderate efficacy for booster sessions and behavioural graded physical activity (with moderate evidence) (see Table 5 ). Overall, a small overall effect size (SMD 0.24) for motivational interventions is indicative of the findings of the panoramic meta-analysis. The four pooled meta-analyses [ 7 , 16 , 27 , 28 ] included studies analysing interventions with a considerable amount of content overlap (e.g. goal-setting and booster sessions are BCTs and often part of motivational interventions), and no statistical heterogeneity of the true effect was found. Nevertheless, the diversity of interventions and techniques included constrain the explanatory power for potential components responsible for the efficacy of adherence. The sensitivity analyses in the meta-analysis of Eisele et al. [ 7 ] indicate that low-quality studies tend to overestimate the efficacy (cf. [ 31 ]). While some evidence exists on short- and medium-term effects of motivational programmes on adherence, no clear evidence for long-term effects can be concluded [ 7 , 30 ]. Furthermore, there is moderate and low evidence that additional motivational interventions and goal planning/setting improve adherence to self-efficacy beliefs [ 27 , 28 , 39 ]. Since self-efficacy beliefs play an important role in motivation and adherence [ 13 , 48 ], the results are relevant for physiotherapists to promote motivation and adherence. Experiencing that one can reach the set goals and manage daily challenges, complemented with feedback and reinforcement from the therapist (or important others), may increase self-efficacy beliefs and human agency [ 48 , 57 , 58 , 59 ].
A closer look at how and in which manner goals and actions are planned and reviewed seems crucial. The patient-led approach was only reported in 5 of the 26 interventions that incorporated the BCT goal setting (behaviour) , although it is associated with greater engagement and achievement than goals which are set by the therapist [ 17 ]. Goal setting and action planning should be informed by the patient’s motives, interests and values in order to promote intrinsic motivation, self-determination and subsequently better adherence ([ 17 ],cf. [ 27 , 28 , 60 , 61 ]). The reviews on the BCTs displayed various positive effects relating to the BCT cluster goals and planning ; however, they point out that the BCT goal setting is not used alone but in connection with several other BCTs. Feedback on outcomes of behaviour , behavioural contract and non-specific reward as well as patient led-goal setting , self-monitoring of behaviour and social support (unspecified) was included in efficacious interventions [ 17 ]. Social support seems to have an important influence on adherence [ 6 , 7 , 17 , 40 ], for example through regular phone-calls or home visits, encouraging messaging, supervision or community-based group programs (cf. [ 1 , 2 , 3 ],[ 37 , 62 ]). Social support also relates to the promotion of self-efficacy beliefs, if it endorses confidence in own abilities and competences [ 6 ].
Some BCTs seem inherent to standard practices of physiotherapy [ 6 ] even though physiotherapists seem to use rather a small number of BCTs [ 15 ]. Control groups also contained BCTs [ 6 , 7 ]; in particular instruction on how to perform a behaviour , generalisation of the target behaviour and social support (unspecified) were frequently coded [ 6 ]. Thus, it seems difficult to identify those BCTs that are (most) efficacious in promoting adherence ([ 7 ],cf. [ 50 ]). Unsurprisingly, the reviews revealed conflicting results and a high risk of bias in the individual studies. However, combining a greater number of BCTs (≥ 8) can be highly recommended, as this achieved a larger effect than interventions using fewer BCTs [ 7 ]. It is fairly unlikely that any single BCT changes adherence [ 6 , 7 , 17 , 40 ]. In that regard, Ariie et al. [ 63 ] argue that not only the amount of BCTs but also the quality, appropriateness and feasibility of the use of the BCTs is crucial.
Meaningful combinations of several BCTs are required. However, the combinations of BCTs may also differ among conditions, personal factors and therapeutic interventions ([ 7 ],cf. [ 63 , 64 ], [ 64 , 65 , 66 ]), and over the time. Two reviews consistently point to the same crucial time point (i.e. after 6 months) when BCT efficacy seems to drop, and more attention is required to maintain adherence [ 7 , 17 ]. Action planning , feedback on behaviour and behavioural practice/rehearsal seem efficacious particularly on short-term. Patient led-goal setting , self-monitoring of behaviour and social support (unspecified) are among those BCTs that seem more efficacious at long-term [ 17 ]. These findings are also in line with findings in non-clinical adults [ 54 ] and with motivational theories (e.g. the Health Action Process Approach [ 53 ]).
Limitations
Conducting an overview of reviews is per se associated with methodological limitations. A limitation is that reviews were analysed and not the original RCTs, which adds further risks of bias domains such as selection, analysis and reporting bias. A specific potential source of bias in overviews of reviews is the overlap of primary studies among the included reviews. The small overlap, caused by a few reviews with similar thematic scope, was controlled for in the data analysis. The substantial non-overlap of primary studies across the reviews reflects the clinical and methodological diversity of the included reviews and showcases the efforts to address (a) motivation and (non-)adherence as complex phenomena and from various perspectives.
Another methodological limitation originates from the search strategies. Considering different health-care systems and delimitations of the physiotherapy profession among countries, divergences among the definitions of terms and the use of diverse approaches to physical therapy, physiotherapy or the therapeutic use of exercise and physical activity, made a clear delimitation in the search strategy and inclusion/exclusion criteria difficult. Therefore, we may have missed out some relevant reviews by reducing our search to the two terms physiotherapy and physical therapy. Equally, we may also have included some aspects that were not primarily investigated for physiotherapists or physical therapists. Including only studies with adults, the findings may not be applicable to promote adherence among children.
While we did not exclude reviews from another language, the search was conducted only in English, which may omit important reviews in other languages. All included reviews (and as far as reported, also the original RCTs) were conducted in economically developed countries; however, social-cultural and context-specific factors influence participation and adherence [ 67 , 68 , 69 , 70 , 71 ]. Furthermore, we are aware that our own cultural background and experiences may have influenced the analysis and synthesis of the results and that conclusions drawn in this overview of reviews may not be suitable for every setting around the world. Therefore, we encourage the readers to critically assess the applicability of the findings to their specific context.
Another gap in coverage of this overview is that interventions that were analysed in RCTs but not included in any systematic review are not considered in this overview. Thus, there may be new or alternative intervention approaches that resulted efficacious but were not covered by this overview. Furthermore, reviews that focused only on the use of digital apps or tools, e.g. virtual reality, gamification, exergames or tele-rehabilitation, were excluded from this overview. Several reviews in this field include adherence-related outcomes, showing potential efficacy as well as limitations of the use of digital tools [ 72 , 73 , 74 , 75 , 76 , 77 , 78 , 79 , 80 , 81 , 82 , 83 ].
Research gaps, recommendations and measuring adherence
This overview of reviews highlighted some gaps in the existing knowledge. First, there is a lack of clear evidence on the efficacy of the interventions. The use of BCTs in the intervention as well as in the control groups may be a reason for inconsistent findings and conflicting evidence. Furthermore, the clinical and methodological heterogeneity constrains drawing clear conclusions on the efficacy. Second (and related to the previous), interventions are insufficiently described regarding their theoretical underpinning and active ingredients/techniques and thus limit the comparison of interventions. Theoretical underpinnings were used partly and translated into practise differently. Difficulties concerning the derivation or deduction of concrete, practical techniques or strategies from the theories were reported. A broader use of the BCT taxonomies would make interventions more comparable. Recently, the BCT Ontology was published, which claims to provide a standard terminology and a comprehensive classification system for the content of behaviour change interventions, suitable for describing interventions [ 84 ]. Third, there is a need for studies on holistic approaches, complex interventions based on integrative theories and the combination of multiple BCTs. While many theories are based on cognitive and behavioural approaches, affective and psychosocial factors are hardly investigated, overlooked and probably underestimated. Rhodes and Fiala [ 12 ] call for studying the influences of affective attitudes on adherence (e.g. enjoyment and pleasing behaviour) which may oppose the more cognitive, instrumental attitudes (e.g. the utility of behaviour). Jordan et al. [ 35 ] refer to a meta-analysis in another therapeutic regime [ 85 ] to explicit the potential efficacy of affective interventions (e.g. appealing to feelings, emotions or social relationships and social supports) in combination with educational and behavioural interventions on patient adherence [ 35 ]. Fourth, more research in patient-led approaches to goal setting and action planning and the relationship of patient-centeredness to adherence is promising [ 60 , 61 , 86 , 87 ].
Fifth, the reviews reported many studies that failed to provide evidence for intervention efficacy on adherence, particularly on long-term adherence. There is a need for prolonged observation to investigate long-term effects on adherence. Probably, intervention or follow-up interventions (e.g. booster sessions) must also be prolonged or repeated to avoid drop out to medium-term follow-ups (around 6 months) and to maintain participation. Sixth, studies should pay more attention to the actual efficacy of adherent behaviour on the desired therapeutic outcomes.
Seventh, another research gap lies in the analysis of the potential variation of the intervention efficacy across medical conditions, physiotherapeutic settings, personal characteristics (e.g. age, gender, sociocultural background) and dispositions (e.g. motives, affective attitudes, previous behaviour) and diverse context-related factors. Huynh et al. [ 79 ] showed for the case of multiple sclerosis that the efficacy of BCTs is not investigated in all disease stages or throughout the disease course; participants with mild-to-moderate level disability were more frequently included in the studies (cf. [ 18 ]). Ariie et al. [ 73 ] stated that the response to BCTs may be different according to the condition (cf. [ 76 ]). On the one hand, studies analysing the use of the same intervention or same combination of BCTs in different intervention groups (according to the categories mentioned above) could be beneficial for comparison purposes. On the other hand, studies should analyse how to find the ‘right’ (ideally, the ‘most efficacious’) adherence promotion intervention for the patient or target group. Qualitative studies may explore adequate combinations of BCTs and contribute to the understanding of complex intervention processes. The findings showcased that different interventions and BCTs may contribute to adherence and that the BCT Taxonomy defines a wide range of techniques, providing the physiotherapists with an overview of which techniques are useable and thus may inspire and support them to develop additional interventions and to enrich their current physiotherapeutic practise. The physiotherapist may use this knowledge to tailor interventions in a patient-centred manner to promote adherence, and to adapt to the condition, characteristics, dispositions and context-related factors of the patient. Hence, experimental studies could compare the efficacy of tailored to not-tailored interventions.
Finally, the outcome adherence should be better defined and holistically assessed. The definition of adherence (as the extent to which a person’s behaviour corresponds with treatment goals or plans) and calculation of adherence rates (by reported exercise or attended sessions divided by the recommended or prescribed exercise or sessions) are simplifying a complex phenomenon. The average or the percentages of attended or completed sessions do not picture interruptions, regularity or periods of more and less adherence. Attendance regularity can change over the time and different participation and fluctuation patterns can be identified [ 88 , 89 ]. For example, an adherence rate of 50% can imply (a) that a person attended regularly every second session throughout the period of observation or (b) that a person attended all sessions of the first half of the observation period and then stopped attending. The underlying reasons and motivational factors may be quite different in these two cases. Besides assessing participation and fluctuation patterns, the three dimensions of the SIRAS scale [ 42 ], i.e. frequency, intensity and reciprocity, could be considered for a holistic account of adherence. The findings of this overview emphasized the importance of a patient-led goal setting and planning, which includes a shared decision-making process and the mutual agreement to adhere to the jointly established plan (cf. WHO definition of adherence, [ 5 ]). The measurement of adherence should be able to distinguish a patient-led approach from a therapist-led approach (cf. [ 17 ]) and to appraise the extent of a shared decision-making process. In conclusion, a holistic approach to measure adherence in physiotherapy may include measures of the frequency of attendance/exercising (e.g. attended sessions out of the prescribed/recommended sessions), the regularity of participation and fluctuation (e.g. timeline with pauses and interruptions, visualizing more and less adherent periods), the intensity of attendance/exercising (e.g. the number or the increment of exercises and repetitions performed in comparison to the plan), reciprocity and fidelity to the agreed goals and plan (e.g. therapist’s and patient’s subjective appraisal of the degree of accomplishment of the agreed plan) and persistence/perseverance over the time (e.g. measuring volition via questionnaires or rating persistence in participation in spite of the experienced challenges and barriers).
We conclude that moderate certainty of evidence supports that (i) additional motivational interventions and behaviour change programmes can increase adherence and patients’ self-efficacy beliefs and (ii) interventions applying BCTs increase adherence, particularly when using a greater number of BCTs and combining various BCTs, and particularly on short to medium term. The BCTs’ patient-led goal setting , self-monitoring of behaviour and social support seem promising to promote maintenance; (iii) graded activities, booster sessions with a physiotherapist and supervision foster adherence.
There is low certainty of evidence that (i) goal setting and planning improves adherence to treatment regimens, particularly if a patient-centred approach is taken; (ii) motivational interventions including various techniques, such as positive reinforcement, social support, monitoring or feedback, can foster adherence; (iii) social support seems to play an important role in promoting adherence; however, evidence is low as this BCT is frequently found in the control group; and (iv) information provision and transfer of knowledge to the patient may improve adherence-related outcomes when combined with motivational techniques, as in psychoeducational programmes. Additional written information is superior to verbal instructions alone; (v) a combination of home-based exercise programmes with clinical supervision, refresher or booster sessions, or/and self-management programmes seems promising to increase adherence.
Regarding the implications for future research, a holistic approach to measure adherence in physiotherapy and the investigation of clearly defined interventions combining multiple BCTs is recommended.
Availability of data and materials
All data generated or analysed during this study are included in this published article and its supplementary information files.
Overview of reviews, umbrella review and reviews of reviews are considered as synonyms in this article (cf. [ 19 ]).
Abbreviations
Behaviour change technique
Cognitive behavioural/cognitive behavioural theory
Control/comparator group
Grades of Recommendation, Assessment, Development and Evaluation
Intervention/experimental group
Physical activity
Preferred Reporting Items for Overviews of Reviews
Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analysis
Physiotherapy
Randomised controlled trial
Standardised mean difference
Systematic review
Essery R, Geraghty AW, Kirby S, Yardley L. Predictors of adherence to home-based physical therapies: a systematic review. Disabil Rehabil. 2017;39:519–34.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Jack K, McLean SM, Moffett JK, Gardiner E. Barriers to treatment adherence in physiotherapy outpatient clinics: a systematic review. Man Ther. 2010;15:220–8.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Peek K, Sanson-Fisher R, Mackenzie L, Carey M. Interventions to aid patient adherence to physiotherapist prescribed self-management strategies: a systematic review. Physiotherapy. 2016;102:127–35.
Bullard T, Ji M, An R, Trinh L, Mackenzie M, Mullen SP. A systematic review and meta-analysis of adherence to physical activity interventions among three chronic conditions: cancer, cardiovascular disease, and diabetes. BMC Public Health. 2019;19:636.
World Health Organization. Adherence to long-term therapies: evidence for action. World Health Organization; 2003. Available from: https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/42682
Thacker J, Bosello F, Ridehalgh C. Do behaviour change techniques increase adherence to home exercises in those with upper extremity musculoskeletal disorders? A systematic review. Musculoskeletal care. 2020;19(3):340-62.
Eisele A, Schagg D, Kramer L, Bengel J, Gohner W. Behaviour change techniques applied in interventions to enhance physical activity adherence in patients with chronic musculoskeletal conditions: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Patient Educ Couns. 2019;102:25–36.
Michie S, Richardson M, Johnston M, Abraham C, Francis J, Hardeman W, et al. The behavior change technique taxonomy (v1) of 93 hierarchically clustered techniques: building an international consensus for the reporting of behavior change interventions. Ann Behav Med. 2013;46:81–95.
Davis R, Campbell R, Hildon Z, Hobbs L, Michie S. Theories of behaviour and behaviour change across the social and behavioural sciences: a scoping review. Health Psychol Rev. 2015;9:323–44.
Michie S, Johnston M. Theories and techniques of behaviour change: developing a cumulative science of behaviour change. Health Psychol Rev. 2012;6:1–6.
Article Google Scholar
Rhodes RE, McEwan D, Rebar AL. Theories of physical activity behaviour change: a history and synthesis of approaches. Psychol Sport Exerc. 2019;42:100–9.
Rhodes RE, Fiala B. Building motivation and sustainability into the prescription and recommendations for physical activity and exercise therapy: the evidence. Physiother Theory Pract. 2009;25:424–41.
Areerak K, Waongenngarm P, Janwantanakul P. Factors associated with exercise adherence to prevent or treat neck and low back pain: a systematic review. Musculoskeletal Science and Practice. 2021;52.
Husebø AML, Dyrstad SM, Søreide JA, Bru E. Predicting exercise adherence in cancer patients and survivors: a systematic review and meta-analysis of motivational and behavioural factors. J Clin Nurs. 2013;22:4–21.
Kunstler BE, Cook JL, Freene N, Finch CF, Kemp JL, O’Halloran PD, et al. Physiotherapists use a small number of behaviour change techniques when promoting physical activity: a systematic review comparing experimental and observational studies. J Sci Med Sport. 2018;21:609–15.
Nicolson PJA, Bennell KL, Dobson FL, Van Ginckel A, Holden MA, Hinman RS. Interventions to increase adherence to therapeutic exercise in older adults with low back pain and/or hip/knee osteoarthritis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Br J Sports Med. 2017;51:791–9.
Willett M, Duda J, Fenton S, Gautrey C, Greig C, Rushton A. Effectiveness of behaviour change techniques in physiotherapy interventions to promote physical activity adherence in lower limb osteoarthritis patients: a systematic review. Regnaux J-P, editor. PLoS ONE. 2019;14:e0219482.
Kim Y, Mehta T, Lai B, Motl RW. Immediate and sustained effects of interventions for changing physical activity in people with multiple sclerosis: meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2020;101:1414–36.
Pollock M, Fernandes R, Becker L, Pieper D, Hartling L. Chapter V: overviews of reviews. In: Higgins J, Thomas J, Chandler J, Cumpston M, Li T, Page M, et al., editors. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions version 63 (updated February 2022). Cochrane; 2022 [cited 2022 May 19]. Available from: https://training.cochrane.org/handbook/current/chapter-v
Aromataris E, Fernandez R, Godfrey C, Holly C, Khalil H, Tungpunkom P. Chapter 10: umbrella reviews. In: Aromataris E, Munn Z, editors. JBI Manual for Evidence Synthesis. JBI; 2020 [cited 2021 Apr 19]. Available from: https://jbi-global-wiki.refined.site/space/MANUAL/4687363/Chapter+10%3A+Umbrella+reviews
Ballard M, Montgomery P. Risk of bias in overviews of reviews: a scoping review of methodological guidance and four-item checklist. Res Synth Methods. 2017;8:92–108.
Centre for Reviews and Dissemination. Undertaking systematic reviews of research on effectiveness: CRD’s guidance for carrying out or commissioning reviews. York, UK: NHSCentre for Reviews and Dissemination, University of York; 2001 [cited 2023 Feb 20]. Available from: http://www.york.ac.uk/inst/crd/crdreports.htm
Higgins J, Thomas J, Chandler J, Cumpston M, Li T, Page M, et al., editors. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions version 6.3 (updated February 2022). Cochrane; 2022 [cited 2022 May 19]. Available from: www.training.cochrane.org/handbook
Page MJ, McKenzie JE, Bossuyt PM, Boutron I, Hoffmann TC, Mulrow CD, et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ. 2021;372: n71.
Furlan AD, Malmivaara A, Chou R, Maher CG, Deyo RA, Schoene M, et al. 2015 Updated Method Guideline for Systematic Reviews in the Cochrane Back and Neck Group. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2015;40:1660–73.
Shea BJ, Reeves BC, Wells G, Thuku M, Hamel C, Moran J, et al. AMSTAR 2: a critical appraisal tool for systematic reviews that include randomised or non-randomised studies of healthcare interventions, or both. BMJ. 2017;358:j4008.
Levack WMM, Weatherall M, Hay-Smith EJC, Dean SG, Mcpherson K, Siegert RJ. Goal setting and strategies to enhance goal pursuit for adults with acquired disability participating in rehabilitation. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2015;2015.
McGrane N, Galvin R, Cusack T, Stokes E. Addition of motivational interventions to exercise and traditional Physiotherapy: a review and meta-analysis. Physiotherapy. 2015;101:1–12.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Gates M, Gates A, Pieper D, Fernandes RM, Tricco AC, Moher D, et al. Reporting guideline for overviews of reviews of healthcare interventions: development of the PRIOR statement. BMJ. 2022;378: e070849.
McLean SM, Burton M, Bradley L, Littlewood C. Interventions for enhancing adherence with physiotherapy: a systematic review. Man Ther. 2010;15:514–21.
Niedermann K, Fransen J, Knols R, Uebelhart D. Gap between short- and long-term effects of patient education in rheumatoid arthritis patients: a systematic review. Arthritis Care Res. 2004;51:388–98.
Cinthuja P, Krishnamoorthy N, Shivapatham G. Effective interventions to improve long-term physiotherapy exercise adherence among patients with lower limb osteoarthritis. A systematic review BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2022;23:147.
Beinart NA, Goodchild CE, Weinman JA, Ayis S, Godfrey EL. Individual and intervention-related factors associated with adherence to home exercise in chronic low back pain: a systematic review. The Spine Journal. 2013;13:1940–50.
Holden J, Davidson M, O’Halloran PD. Health coaching for low back pain: a systematic review of the literature. Int J Clin Pract. 2014;68:950–62.
Jordan JL, Holden MA, Mason EE, Foster NE. Interventions to improve adherence to exercise for chronic musculoskeletal pain in adults. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2010;CD005956.
Abu Abed M, Himmel W, Vormfelde S, Koschack J. Video-assisted patient education to modify behavior: a systematic review. Patient Educ Couns. 2014;97:16–22.
Bachmann C, Oesch P, Bachmann S. Recommendations for improving adherence to home-based exercise: a systematic review. Phys Med Rehab Kuror. 2018;28:20–31.
Hall AM, Ferreira PH, Maher CG, Latimer J, Ferreira ML. The influence of the therapist-patient relationship on treatment outcome in physical rehabilitation: a systematic review. Phys Ther. 2010;90:1099–110.
Levack WMM, Taylor K, Siegert RJ, Dean SG, McPherson KM, Weatherall M. Is goal planning in rehabilitation effective? A systematic review Clin Rehabil. 2006;20:739–55.
Room J, Hannink E, Dawes H, Barker K. What interventions are used to improve exercise adherence in older people and what behavioural techniques are they based on? A systematic review BMJ Open. 2017;7: e019221.
Dalager T, Bredahl TGV, Pedersen MT, Boyle E, Andersen LL, Sjøgaard G. Does training frequency and supervision affect compliance, performance and muscular health? A cluster randomized controlled trial. Man Ther. 2015;20:657–65.
Kolt GS, Brewer BW, Pizzari T, Schoo AMM, Garrett N. The Sport Injury Rehabilitation Adherence Scale: a reliable scale for use in clinical physiotherapy. Physiotherapy. 2007;93:17–22.
Green LW. Determining the impact and effectiveness of health education as it relates to federal policy. Health Educ Monogr. 1978;6:28–66.
Google Scholar
Michie S, van Stralen MM, West R. The behaviour change wheel: a new method for characterising and designing behaviour change interventions. Implement Sci. 2011;6:42.
Pisters MF, Veenhof C, de Bakker DH, Schellevis FG, Dekker J. Behavioural graded activity results in better exercise adherence and more physical activity than usual care in people with osteoarthritis: a cluster-randomised trial. J Physiother. 2010;56:41–7.
Göhner W, Schlicht W. Preventing chronic back pain: evaluation of a theory-based cognitive-behavioural training programme for patients with subacute back pain. Patient Educ Couns. 2006;64:87–95.
Bandura A. Toward a psychology of human agency: pathways and reflections. Perspect Psychol Sci. 2018;13:130–6.
Ashford S, Edmunds J, French DP. What is the best way to change self-efficacy to promote lifestyle and recreational physical activity? A systematic review with meta-analysis. Br J Health Psychol. 2010;15:265–88.
Frost H, Campbell P, Maxwell M, O’Carroll RE, Dombrowski SU, Williams B, et al. Effectiveness of motivational interviewing on adult behaviour change in health and social care settings: a systematic review of reviews. PLoS ONE. 2018;13: e0204890.
Michie S, West R, Sheals K, Godinho CA. Evaluating the effectiveness of behavior change techniques in health-related behavior: a scoping review of methods used. Translational Behavioral Medicine. 2018;8:212–24.
Gallagher KM. Helping older adults sustain their physical therapy gains: a theory-based intervention to promote adherence to home exercise following rehabilitation. Journal of Geriatric Physical Therapy. 2016;39:20–9.
Silva MN, Vieira PN, Coutinho SR, Minderico CS, Matos MG, Sardinha LB, et al. Using self-determination theory to promote physical activity and weight control: a randomized controlled trial in women. J Behav Med. 2010;33:110–22.
Schwarzer R, Lippke S, Luszczynska A. Mechanisms of health behavior change in persons with chronic illness or disability: the Health Action Process Approach (HAPA). Rehabil Psychol. 2011;56:161–70.
Murray JM, Brennan SF, French DP, Patterson CC, Kee F, Hunter RF. Effectiveness of physical activity interventions in achieving behaviour change maintenance in young and middle aged adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Soc Sci Med. 2017;192:125–33.
Areskoug Josefsson K, Andersson A-C. The co-constructive processes in physiotherapy. Lee A, editor. Cogent Medicine. 2017;4:1290308.
Qasem M. Constructivist learning theory in physiotherapy education: a critical evaluation of research. Journal of Novel Physiotherapies. 2015;5.
Brinkman C, Baez SE, Genoese F, Hoch JM. Use of goal setting to enhance self-efficacy after sports-related injury: a critically appraised topic. J Sport Rehabil. 2019;29:498–502.
Fillipas S, Oldmeadow LB, Bailey MJ, Cherry CL. A six-month, supervised, aerobic and resistance exercise program improves self-efficacy in people with human immunodeficiency virus: a randomised controlled trial. Australian Journal of Physiotherapy. 2006;52:185–90.
Ley C, Karus F, Wiesbauer L, Rato Barrio M, Spaaij R. Health, integration and agency: sport participation experiences of asylum seekers. J Refug Stud. 2021;34:4140–60.
Melin J, Nordin Å, Feldthusen C, Danielsson L. Goal-setting in physiotherapy: exploring a person-centered perspective. Physiother Theory Pract. 2021;37:863–80.
Wijma AJ, Bletterman AN, Clark JR, Vervoort SC, Beetsma A, Keizer D, et al. Patient-centeredness in physiotherapy: what does it entail? A systematic review of qualitative studies. Physiother Theory Pract. 2017;33:825–40.
Meade LB, Bearne LM, Sweeney LH, Alageel SH, Godfrey EL. Behaviour change techniques associated with adherence to prescribed exercise in patients with persistent musculoskeletal pain: systematic review. Br J Health Psychol. 2019;24:10–30.
Ariie T, Takasaki H, Okoba R, Chiba H, Handa Y, Miki T, et al. The effectiveness of exercise with behavior change techniques in people with knee osteoarthritis: a systematic review with meta-analysis. PM R. 2022;
Demmelmaier I, Iversen MD. How are behavioral theories used in interventions to promote physical activity in rheumatoid arthritis? A systematic review. Arthritis Care Res. 2018;70:185–96.
Larkin L, Gallagher S, Cramp F, Brand C, Fraser A, Kennedy N. Behaviour change interventions to promote physical activity in rheumatoid arthritis: a systematic review. Rheumatol Int. 2015;35:1631–40.
Rausch Osthoff A-K, Juhl CB, Knittle K, Dagfinrud H, Hurkmans E, Braun J, et al. Effects of exercise and physical activity promotion: meta-analysis informing the 2018 EULAR recommendations for physical activity in people with rheumatoid arthritis, spondyloarthritis and hip/knee osteoarthritis. RMD Open. 2018;4: e000713.
Armstrong TL, Swartzman LC. 3 - cross-cultural differences in illness models and expectations for the health care provider-client/patient interaction. In: Shané S. Kazarian, David R. Evans, editors. Handbook of Cultural Health Psychology. San Diego: Academic Press; 2001 [cited 2013 Aug 20]. p. 63–84. Available from: http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B9780124027718500052
Brady B, Veljanova I, Chipchase L. Culturally informed practice and physiotherapy. J Physiother. 2016;62:121–3.
Jimenez DE, Burrows K, Aschbrenner K, Barre LK, Pratt SI, Alegria M, et al. Health behavior change benefits: perspectives of Latinos with serious mental illness. Transcult Psychiatry. 2016;53:313–29.
Jorgensen P. Concepts of body and health in physiotherapy: the meaning of the social/cultural aspects of life. Physiother Theory Pract. 2000;16:105–15.
Teng B, Rosbergen ICM, Gomersall S, Hatton A, Brauer SG. Physiotherapists’ experiences and views of older peoples’ exercise adherence with respect to falls prevention in Singapore: a qualitative study. Disabil Rehabil. 2022;44:5530–8.
Alfieri FM, da Silva DC, de Oliveira NC, Battistella LR. Gamification in musculoskeletal rehabilitation. Curr Rev Musculoskelet Med. 2022;15:629–36.
Cox NS, Dal Corso S, Hansen H, McDonald CF, Hill CJ, Zanaboni P, et al. Telerehabilitation for chronic respiratory disease. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021;1:CD013040.
Cruz-Cobo C, Bernal-Jiménez MÁ, Vázquez-García R, Santi-Cano MJ. Effectiveness of mHealth interventions in the control of lifestyle and cardiovascular risk factors in patients after a coronary event: systematic review and meta-analysis. JMIR Mhealth Uhealth. 2022;10: e39593.
Darabseh MZ, Aburub A, Davies S. The effects of virtual reality physiotherapy interventions on cardiopulmonary function and breathing control in cystic fibrosis: a systematic review. Games Health J. 2023;12:13–24.
Fernandes CS, Magalhães B, Gomes JA, Santos C. Exergames to improve rehabilitation for shoulder injury: Systematic Review and GRADE Evidence Synthesis. REHABIL NURS. 2022;47:147–59.
García-Bravo S, Cuesta-Gómez A, Campuzano-Ruiz R, López-Navas MJ, Domínguez-Paniagua J, Araújo-Narváez A, et al. Virtual reality and video games in cardiac rehabilitation programs. A systematic review Disabil Rehabil. 2021;43:448–57.
Hawley-Hague H, Lasrado R, Martinez E, Stanmore E, Tyson S. A scoping review of the feasibility, acceptability, and effects of physiotherapy delivered remotely. Disability and Rehabilitation. 2022;
Melillo A, Chirico A, De Pietro G, Gallo L, Caggianese G, Barone D, et al. Virtual reality rehabilitation systems for cancer survivors: a narrative review of the literature. Cancers. 2022;14.
Moulaei K, Sheikhtaheri A, Nezhad MS, Haghdoost A, Gheysari M, Bahaadinbeigy K. Telerehabilitation for upper limb disabilities: a scoping review on functions, outcomes, and evaluation methods. Arch Public Health. 2022;80:196.
Patsaki I, Dimitriadi N, Despoti A, Tzoumi D, Leventakis N, Roussou G, et al. The effectiveness of immersive virtual reality in physical recovery of stroke patients: a systematic review. Frontiers in Systems Neuroscience. 2022;16.
Skov Schacksen C, Henneberg NC, Muthulingam JA, Morimoto Y, Sawa R, Saitoh M, et al. Effects of telerehabilitation interventions on heart failure management (2015–2020): scoping review. JMIR Rehabil Assist Technol. 2021;8: e29714.
Thompson D, Rattu S, Tower J, Egerton T, Francis J, Merolli M. Mobile app use to support therapeutic exercise for musculoskeletal pain conditions may help improve pain intensity and self-reported physical function: a systematic review. J Physiother. 2023;69:23–34.
Marques MM, Wright AJ, Corker E, Johnston M, West R, Hastings J, et al. The behaviour change technique ontology: transforming the behaviour change technique taxonomy v1. Wellcome Open Res. 2023;8:308.
Roter DL, Hall JA, Merisca R, Nordstrom B, Cretin D, Svarstad B. Effectiveness of interventions to improve patient compliance: a meta-analysis. Med Care. 1998;36:1138–61.
Hansen LS, Præstegaard J, Lehn-Christiansen S. Patient-centeredness in physiotherapy–a literature mapping review. Physiotherapy theory and practice. 2022;38(12):1843-56.
Robinson JH, Callister LC, Berry JA, Dearing KA. Patient-centered care and adherence: definitions and applications to improve outcomes. J Am Acad Nurse Pract. 2008;20:600–7.
Seelig H, Fuchs R. Physical exercise participation: a continuous or categorical phenomenon? Psychol Sport Exerc. 2011;12:115–23.
Shang B, Duan Y, Huang WY, Brehm W. Fluctuation – a common but neglected pattern of physical activity behaviour: an exploratory review of studies in recent 20 years. European Journal of Sport Science. 2018;18(2):266-78.
Download references
Acknowledgements
Not applicable
No funding was received.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department Health Sciences, Physiotherapy, FH Campus Wien University of Applied Sciences, Favoritenstrasse 226, 1100, Vienna, Austria
Clemens Ley
Department Health Sciences, Competence Center INDICATION, FH Campus Wien, University of Applied Sciences, Favoritenstrasse 226, 1100, Vienna, Austria
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
CL and PP conceived and designed the review. CL did the database search and data extraction. CL and PP did screening and quality assessment. CL did the narrative synthesis and drafted the manuscript. PP conducted the panoramic meta-analysis and critically revised and substantially contributed throughout the writing of the manuscript. The authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Clemens Ley .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate, consent for publication, competing interests.
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Additional file 1:.
Search details
Additional file 2:
Rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Ley, C., Putz, P. Efficacy of interventions and techniques on adherence to physiotherapy in adults: an overview of systematic reviews and panoramic meta-analysis. Syst Rev 13 , 137 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13643-024-02538-9
Download citation
Received : 29 November 2023
Accepted : 17 April 2024
Published : 21 May 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s13643-024-02538-9
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Umbrella review
- Physical therapy
- Rehabilitation
- Behaviour change techniques
- Effectiveness
Systematic Reviews
ISSN: 2046-4053
- Submission enquiries: Access here and click Contact Us
- General enquiries: [email protected]
- How it works

Useful Links
How much will your dissertation cost?
Have an expert academic write your dissertation paper!
Dissertation Services

Get unlimited topic ideas and a dissertation plan for just £45.00
Order topics and plan

Get 1 free topic in your area of study with aim and justification
Yes I want the free topic

Physiotherapy Dissertation Topics – Industry-Oriented Suggestions
Published by Grace Graffin at January 4th, 2023 , Revised On May 3, 2024
Physiotherapy is a healthcare profession that deals with movement disorders of the body arising from different conditions. Physiotherapy focuses on performing practices that reduce physical ailments without going through surgery or traditional medication. There are many other practices related to physiotherapy, such as chiropractic treatment, but they do not fall under the umbrella of physiotherapy. A person who performs physiotherapy is known as a physiotherapist.
To become a physiotherapist, you must complete a physiotherapy degree course. But, of course, you cannot become a professional physiotherapist unless you do not complete it. In order to complete your degree, it is mandatory to complete the most important and considerably hard dissertation.
If you are finding it ambiguous and uncertain about starting your dissertation, you can look at some of the current, striking, and potential topics suggested by our PhD scholars at ResearchProspect.
You may also want to start your dissertation by requesting a brief research proposal from our writers on any of these topics, which includes an introduction to the topic, research question, aim and objectives, literature review, and the proposed methodology of research to be conducted. Let us know if you need any help in getting started.
Check our dissertation examples to get an idea of how to structure your dissertation .
Review the full list of dissertation topics here.
Want to know what essay structure and style will work best for your assignment?
Problem fixed! We can write any type of essay in any referencing style. We ensure every essay written is beyond your expectations.

Physiotherapy Dissertation Topics
Topic 1: an evaluation of the impact of hyperbaric oxygen therapy in repairing cutaneous injury.
Research Aim: The research aims to evaluate the impact of Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy in Repairing Cutaneous Injury.
Objectives:
- To analyse the concept of Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy used in physiotherapy.
- To evaluate the impact of Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy on the duration of healing and postinjury complications.
- To investigate the impact of hyperbaric oxygen therapy in repairing cutaneous injury.
Topic 2: A comparison of the effectiveness of underwater aerobic exercises and manual knee exercises in the rehabilitation of knee osteoarthritis.
Research Aim: The research aims to compare the effectiveness of underwater aerobic exercises and manual knee exercises in the rehabilitation of knee osteoarthritis.
- To analyse the mechanisms of administering underwater aerobic exercises and manual knee exercises.
- To evaluate the methods of rehabilitating knee osteoarthritis.
- To establish a comparison between underwater aerobic exercises and manual knee exercises in terms of their effectiveness for rehabilitation of knee osteoarthritis.
Topic 3: An investigation into the effectiveness of therapeutic ultrasound and resistance training for rheumatoid arthritis.
Research Aim: The research aims to investigate the effectiveness of therapeutic ultrasound and resistance training for rheumatoid arthritis.
- To analyse the areas of application of therapeutic ultrasound and resistance training in physiotherapy.
- To analyse the physiotherapy approaches for treating rheumatoid arthritis pain.
- To investigate the impact of therapeutic ultrasound and resistance training on treating rheumatoid arthritis pain to determine their effectiveness.
Topic 4: Evaluating the impact of strengthening exercises on diabetic patients with shoulder pain.
Research Aim: The aim of the research will be to evaluate the impact of strengthening exercises on diabetic patients with shoulder pain.
- To determine the benefits of strengthening exercises on patients with pain.
- To analyse if any additional precatory measures are required while rehabilitating diabetic patients.
- To evaluate the impact of strengthening exercises on diabetic patients with shoulder pain.
Topic 5: An analysis of the implications of strengthening exercises on alleviation of lower back pain and cervical pain.
Research Aim: An analysis of the implications of strengthening exercises on the alleviation of lower back pain and cervical pain.
- To determine the types of strengthening exercises in physiotherapy for pain relief.
- To analyse the causes of lower back pain and cervical pain in patients and the common methods of treatment.
- To investigate the impact of strengthening exercises on the alleviation of lower back pain and cervical pain.
Topic. 6: Physiotherapy vs. chiropractic
Research Aim: There are many similar practices to physiotherapy; one of them is chiropractic. It deals with the diagnosis and treatment of the musculoskeletal system, especially the spine. The chiropractic health care system was founded on the basis that the human body’s health is determined by its nervous system.
The aim of the research would be to find out the difference between physiography and chiropractic. The researcher will identify the differences and similarities between both professions, types, and methodologies and identify the ways they resemble or differentiate.
Topic. 7: Why Physiotherapy is beneficial
Research Aim: There are ongoing discussions regarding physiotherapy and its benefits. The research will identify how physiotherapy is beneficial for the body and aim to make new revelations by experimenting with certain bodily impairments.
Topic. 8: Future of physiotherapy
Research Aim: Physiotherapy is the best way to get treatment for injuries as the results are permanent and provide complete relief. It is the best alternative for people who do not want to take heavy doses of medicines. However, whether it will remain as significant in the future as it is today is a big question to address. The researcher will focus on the current trends and forecasts in the field of physiotherapy and find out how far this discipline will go and how long it can remain useful for humans.
Topic. 9: Physiotherapy vs. Orthopedic surgery
Research Aim: Physiotherapy and orthopaedic surgery are two different ways to treat acute injuries in bones, joints, and their associated soft tissues. The research will focus on differentiating the practices of physiotherapy and orthopaedic surgery.
Topic. 10: Effectiveness of mirror therapy for stroke patients
Research Aim: Mirror therapy is a kind of therapy in which a mirror is placed between the arms or legs to make an image of the moving limb and give an impression of normal movement of the affected limb. It is said that rehabilitation therapy is effective for stroke patients. The research paper will aim to find out the level of effectiveness of mirror therapy for stroke patients.
Topic. 11: Physiotherapy for athletes
Research Aim: Physiotherapy has a wide range of uses; it is vitally important on and off the field for athletes and sportsmen. The research will aim to find out the significance of physiotherapy for athletes, how it is used, why it is used, and what are the preferable techniques by worldwide athletes.
Topic. 12: Effective methods of physiotherapy
Research Aim: The aim of the research is to probe all methods and techniques of physiotherapy and identify the most effective methods of all. The researcher will do qualitative research and present the best types of physiotherapy for specific conditions and situations.
Topic. 13: Physiotherapy vs. other medical treatments
Research Aim: There are still many people who find physiotherapy more effective than other medical treatments, and to some, it is inverse. The aim of the research is to juxtapose physiotherapy with other types of related medical treatment and determine which one of them, in a true sense, is effective.
Also Read: Medicine and Nursing Dissertation Topics
Topic. 14: Physiotherapy and lower back pain
Research Aim: Lower back pain is one of the most common types of pain that people suffer from during their middle and young age. Lower back pain ranges from mild to chronic pain that can last forever. Lower back pain is usually treated with physical therapy. The main aim of the research is to find the extent to which physiotherapy is effective in treating lower back pain and in which conditions it is the most effective.
Topic. 15: Ankylosing spondylitis and physiotherapy
Research Aim: Ankylosing spondylitis is a common inflammatory disease that can fuse some of the bones in the spine. As a result, the spine becomes less flexible and causes pain when sitting, standing, and moving, leading to a hunched posture. The aim of the research is to find out if physiotherapy can help relieve ankylosing spondylitis.
Topic. 16: Physiotherapy for knee replacement
Research Aim: Knee replacement is a surgical procedure carried out on patients with severe pain and immobilisation in their knee joint. The procedure is only recommended for severe cases, and the mild cases can be treated in other ways; the research will aim to find if physiotherapy can be an alternative to knee replacement.
Topic. 17: Physiotherapy equipment and their uses
Research Aim: The way there are many strategies and types of physiotherapy, and so are the equipment and tools. The research will study different kinds of physiotherapy and their uses. The main aim of the research is to find if the same or different tools are used for the same method around the world.
Topic. 18: Physiotherapy and stress control
Research Aim: While physiotherapy has a lot to do with the physical body, it can also relieve the mind and help unwind mental stress. The research will carry out thorough research to find out how physiotherapy helps stress control and how often one can see a physiotherapist to unwind mental strain.
How Can ResearchProspect Help?
ResearchProspect writers can send several custom topic ideas to your email address. Once you have chosen a topic that suits your needs and interests, you can order for our dissertation outline service which will include a brief introduction to the topic, research questions , literature review , methodology , expected results , and conclusion . The dissertation outline will enable you to review the quality of our work before placing the order for our full dissertation writing service !
Topic. 19: Technology and physiotherapy
Research Aim: Since technology has taken over and substituted human practices with technology-led machines, it is necessary to understand technological advancements in the field of physiotherapy. The advancements can range from tools to practices. The research will focus on learning about the current technological advancements in the field and the future prospects.
Topic. 20: Post-accident physiotherapy
Research Aim: Post-traumatic disorder is one of the common results of experiencing a highly traumatic accident. Therefore, it is highly essential to recover and stabilise oneself physically, mentally, and emotionally. Physiotherapy is said to be one of the most effective techniques for helping people get over trauma. The research will study the level of effectiveness of post-accident physiotherapy. The research can do a case study to drive accurate results.
Topic. 21: Equine physiotherapy
Research Aim: A type of physiotherapy, equine physiotherapy, is not widely understood. The aim of the research is to explore and understand equine physiotherapy, its practice, and its significance for humans.
Topic. 22: Physiotherapy and fibromyalgia
Research Aim: Fibromyalgia is a chronic condition that affects people severely. Patients experience pain and stiffness in the muscles. While fibromyalgia does not damage the joints or organs, constant aches and fatigue become part of normal life. The aim of the research is to study fibromyalgia and the role of physiotherapy in its treatment.
Topic. 23: Physiotherapy and massage therapy
Research Aim: Physiotherapy and massage are not interchangeable terms that very few people know about. The research will throw light on the specialities and specific details of each of the practices and differentiate them from each other.
Topic. 24: Yoga for physiotherapy patients
Research Aim: Yoga has gained immense attention lately. Yoga is recommended for teens, youngsters, elders, and pregnant women, but this research will discover if it is beneficial for physiotherapy patients.
Topic. 25: Physiotherapy, its history, and specialities
In order to understand the roots of physiotherapy, it is important to delve into its conventional practices. The research will study and investigate the history of physiotherapy and its specialities; it will evaluate if it is still practised the same or different in the 21st century.
You may also be interested in medicine dissertation topics, mental health dissertation topics , physical health & education dissertation topics , and healthcare dissertation topics.
List of Trending Dissertation Topics on Physiotherapy
- The Role of Physiotherapy in the Management of Chronic Pain Conditions
- An Analysis of Exercise Therapy in Cardiac Rehabilitation Programs
- Physiotherapy Interventions for Improving Balance and Preventing Falls in Older Adults
- Investigating the Role of Manual Therapy in the Treatment of Musculoskeletal Disorders
- The Impact of Prehabilitation on Postoperative Outcomes in Orthopedic Surgery Patients
- The Role of Physiotherapy in Enhancing Respiratory Function in Patients with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)
- Investigating the Effects of Exercise Therapy on Mental Health and Well-being
- The Role of Physiotherapy in the Management of Sports Injuries
- Exploring the Use of Biomechanical Analysis in Optimising Gait Rehabilitation
- Manual Therapy Techniques for the Treatment of Myofascial Pain Syndrome
- Physiotherapy Interventions for Improving Functional Mobility in Stroke Survivors
- The Role of Acupuncture in Physiotherapy Practice for Pain Management
- Investigating the Effects of Exercise Therapy on Quality of Life in Cancer Patients
- Role of Physiotherapy in the Management of Postural Dysfunction and Ergonomics Awareness
- Investigating the Effectiveness of Hydrotherapy in Rehabilitation Programs
- Physiotherapy Interventions for Improving Functional Independence in Parkinson’s Disease Patients
- Assessing the Role of Psychological Interventions in Physiotherapy Practice for Chronic Pain Management
- Investigating the Role of Exercise Therapy in the Prevention and Management of Osteoporosis
- The Impact of Mindfulness-Based Interventions on Pain Perception and Functional Outcomes
- Physiotherapy Approaches for Managing Work-Related Musculoskeletal Disorders
- Investigating the Effects of Aquatic Therapy on Physical Function and Pain Relief
- The Role of Physiotherapy in the Management of Post-Concussion Syndrome
- Exploring the Role of Exercise Therapy in Improving Cognitive Function in Older Adults
- Investigating the Role of Physiotherapy in Preparing Patients for Joint Replacement Surgery: Prehabilitation Strategies
Free Dissertation Topic
Phone Number
Academic Level Select Academic Level Undergraduate Graduate PHD
Academic Subject
Area of Research
Frequently Asked Questions
How to find physiotherapy dissertation topics.
To discover physiotherapy dissertation topics:
- Research recent advancements.
- Address healthcare challenges.
- Explore niche areas (e.g., sports, geriatrics).
- Review patient outcomes and therapies.
- Consult experts and mentors.
- Pick a topic aligning with your passion and research potential.
You May Also Like
Counselling psychology is one of the various subfields of psychology. It addresses a variety of situational issues that affect people from different social groups. In order to receive a psychology degree, students must present a dissertation.
Portfolio management examines the projects and programs of an organization. There are three aspects involved here: selection, prioritization, and control. This is done by taking into account the strategic goals of the organization.
Pick from our top 50 taxation dissertation topic ideas varying from laws in taxation to the effects of tax evasion to help you in your taxation dissertation
USEFUL LINKS
LEARNING RESOURCES

COMPANY DETAILS

- How It Works

20 Sports Physiotherapy Research Topic Ideas
Sports physiotherapy is an area of physical therapy that focuses on the prevention and treatment of injuries related to sports and exercise. It is a specialized field of physiotherapy that requires a comprehensive understanding of the physical demands of sport and exercise.
Research in the field of sports physiotherapy is important to identify the most effective ways to prevent and treat sports injuries as well as injury mechanism.
This article provides some research topics related to sports physiotherapy that can be used as a starting point for exploring this area of research further.
We can divide sports research into 4 areas:
- Injury prevention
Rehabilitation after Injury
- Return to play.
- Injury mechanism
Injury Prevention
Preventing sports injuries from occurring in the first place is one of the most important goals of sports physiotherapy. By proactively addressing risk factors and addressing underlying problems before they lead to injury, physiotherapists can help their patients stay healthy, active, and performing at their best.
There are a number of strategies that can be used to prevent sports injuries, including:
- Strength and conditioning programs to improve overall fitness, reduce the risk of injury, and enhance performance.
- Biomechanical assessments to identify and address any underlying mechanical problems that may be contributing to injury.
- Correction of training errors, such as overtraining or inadequate recovery, to reduce the risk of overuse injuries.
- Proper warm-up and cool-down techniques to prepare the body for physical activity and reduce the risk of injury.
- Use of appropriate equipment, such as well-fitting shoes and properly sized athletic gear, to reduce the risk of injury.
By incorporating these and other injury prevention strategies into their treatment plans, physiotherapists can help their patients stay healthy and active, and reduce the risk of injury. Additionally, by conducting research in the area of injury prevention, physiotherapists can contribute to the advancement of the field and help to identify new and innovative strategies for injury prevention.
Examples of injury prevention research topics include:
- The impact of strength and conditioning programs on injury risk in athletes.
- The effectiveness of warm-up and cool-down routines in reducing the risk of injury in athletes.
- The impact of proper equipment use on injury risk in athletes.
- The role of biomechanical assessments in reducing the risk of injury in athletes.
* DO NOT sign up if you don’t plan to read the newsletter: Signing up for our newsletter gives you access to the latest physiotherapy research and insights. However, all website features are freely accessible without a subscription. We don’t offer additional incentives for signing up, and managing subscriptions costs us money and we don’t make any money from it. If you don’t plan to read the newsletter, we kindly ask that you DO NOT sign up. This helps us focus on providing valuable content to those who are truly interested.
One of the most important aspects of sports physiotherapy is the rehabilitation of athletes after injury. The goal of rehabilitation is to help athletes recover from their injuries, regain their physical function, and return to their sport as safely and quickly as possible.
To achieve these goals, physiotherapists use a range of techniques and interventions, including exercise therapy, manual therapy, and the use of assistive devices such as braces and crutches. The specific rehabilitation plan will depend on the nature and severity of the injury, as well as the individual needs and goals of the athlete.
In addition to helping athletes recover from injury, rehabilitation also plays a critical role in reducing the risk of reinjury. By addressing any underlying problems and improving physical function, physiotherapists can help to reduce the risk of future injury and improve the long-term health and performance of their patients.
Examples of rehabilitation research topics include:
- The effectiveness of different exercise interventions for the rehabilitation of specific types of sports injuries.
- The role of manual therapy in the rehabilitation of sports injuries.
- The impact of rehabilitation programs on the risk of reinjury in athletes.
- The use of assistive devices in the rehabilitation of sports injuries.
Return to Play
Returning to play after an injury is a key goal for many athletes, and a critical aspect of sports physiotherapy. The process of returning to play involves a gradual progression from rest and rehabilitation to a return to full competition, and is guided by a number of principles and considerations, including:
- The nature and severity of the injury.
- The athlete’s physical function and readiness to return to play.
- The athlete’s goals and expectations for their return to play.
- The potential risks and benefits of returning to play.
The return to play process is typically managed by a multidisciplinary team, including physiotherapists, physicians, and other healthcare professionals. The team works together to develop a safe and effective plan for the athlete’s return to play, and to monitor their progress and adjust the plan as needed.
Examples of return to play research topics include:
- The impact of different rehabilitation interventions on the return to play process.
- The role of medical clearance in the return to play process.
- The impact of injury on the psychological readiness of athletes to return to play.
- The impact of previous injury on the risk of future injury in athletes.
Injury Mechanism
In addition to exploring the various topics related to sports injury prevention, rehabilitation, and return to play, it is also important to have a thorough understanding of injury mechanisms. This refers to the underlying causes of sports injuries, such as biomechanical factors, training errors, and external factors such as playing surface and equipment.
By understanding the mechanisms of injury, physiotherapists can better identify and address the root cause of an injury, leading to more effective treatment and injury prevention strategies. For example, if a specific type of injury is found to be caused by poor biomechanics during running, a physiotherapist could focus on correcting these mechanics through targeted exercises and training.
In order to fully understand injury mechanisms, it is important to consider multiple factors, including an athlete’s age, level of play, and sport-specific demands. By conducting research in this area, physiotherapists can contribute to a growing body of knowledge that can be used to improve injury prevention and treatment practices in sports.
Some examples of injury mechanism research topics include:
- The impact of foot mechanics on the risk of lower limb injury in athletes.
- The role of fatigue in the development of musculoskeletal injuries in athletes.
- The impact of playing surface and equipment on the risk of injury in athletes.
- The impact of training volume and intensity on the risk of overuse injuries in athletes.
Sports Physiotherapy Research Topics
Update: january 31 2024.
- The impact of high-intensity functional training on athletes’ speed, balance, and technical and tactical performance parameters. Suggested by this article: Effects of high-intensity functional training on physical fitness and sport-specific performance among the athletes: A systematic review with meta-analysis
- Effects of Blood Flow Restriction on Explosive Power in Athletes Suggested by this article: Effects of Resistance Training with Blood Flow Restriction on Explosive Power of Lower Limbs: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- Resistance training with elastic bands vs proprioceptive training in patients with chronic ankle instability Suggested by this article: Efficacy of resistance training with elastic bands compared to proprioceptive training on balance and self-report measures in patients with chronic ankle instability: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- Optimal dosage and load of exercise in eccentric training for Achilles tendinopathy.
- Efficacy of Combined Eccentric–Concentric Training and Heavy Slow Resistance Exercise in the Treatment of Achilles Tendinopathy Suggested by this article: Comparability of the Effectiveness of Different Types of Exercise in the Treatment of Achilles Tendinopathy: A Systematic Review
- The Effectiveness of ESWT for rotator cuff injuries, tibialis posterior tendinopathy, bone stress injuries or muscle injuries in Athletes
- Exploring the role of ESWT in postoperative recovery in common athletic injuries such as anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction
- The role of ESWT to hasten recovery and prevent recurrent overuse injuries in active populations. Suggested by this article: Use of extracorporeal shockwave therapies for athletes and physically active individuals: a systematic review
- The effectiveness of manual therapy techniques in treating sports injuries.
- The impact of strength training on injury prevention in athletes.
- The role of physiotherapy in rehabilitation after ACL surgery.
- The use of wearable technology in monitoring and managing sports injuries.
- The effectiveness of stretching programs in reducing muscle soreness and improving athletic performance.
- The role of physiotherapy in reducing the risk of overuse injuries in endurance athletes.
- The impact of nutrition on injury recovery and rehabilitation in athletes.
- The benefits of physiotherapy-led injury prevention programs in youth sports.
- The impact of mental health on injury rehabilitation and return to play in athletes.
- The effectiveness of physiotherapy interventions in reducing concussions in contact sports.
- The effectiveness of dry needling in treating sports-related musculoskeletal pain.
- The impact of aquatic therapy on rehabilitation outcomes in athletes.
- The role of physiotherapy in improving joint mobility and flexibility in athletes.
- The impact of high-intensity interval training on injury prevention in athletes.
- The effectiveness of physiotherapy in reducing the risk of reinjury in athletes who have returned to play after an injury.
- The impact of sleep quality on injury rehabilitation and recovery in athletes.
- The role of physiotherapy in the prevention and management of running-related injuries.
- The impact of environmental factors, such as temperature and altitude, on injury risk in outdoor sports.
- The effectiveness of physiotherapy-led rehabilitation programs in older athletes.
- The impact of posture and body mechanics on injury risk in athletes.
See All Journals
(Click here to see journals by field)
Discover Research Articles by Journal Discipline
Similar posts, #019-kinesiotaping for rotator cuff–related shoulder pain, #044 – 7 articles on knee osteoarthritis (oa) in 2021, neuro physiotherapy research topics, #042 – 6 articles on lateral elbow tendinopathy in 2021, #011- total hip arthroplasty and dynamic knee valgus, featured articles #002: hyperkyphosis, stroke, lateral epicondylitis and ui.
- Necessary These cookies are not optional. They are needed for the website to function.
- Statistics In order for us to improve the website's functionality and structure, based on how the website is used.
- Experience In order for our website to perform as well as possible during your visit. If you refuse these cookies, some functionality will disappear from the website.
- Marketing By sharing your interests and behavior as you visit our site, you increase the chance of seeing personalized content and offers.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
(Rushton et al., 2011), with simple advice being found to be as effective as physiotherapy interventions (Michaeleff et al., (2014). CWAD research has focused on the primary complaint of neck pain (Bortsov et al. 2014) although symptoms may also include stiffness (Sterling et al., 2004; Woodhouse & Vasseljen, 2008) and pain
delivered a blended approach to physiotherapy, as although in-person physiotherapy became an option, it was still restricted (based on risk assessment and social distancing) and delivery needed to be considered in the context of the ongoing pandemic. In all three studies, we found that either the fully remote or blended physiotherapy was safe,
They are used to determine associations between two variables. For example, this research review by Steve Kamper used a cross-sectional design to determine if posture and smartphone use were related to neck pain in young adults. Physiotherapy researchers use cross-sectional studies for survey-based research, as well as clinical-based studies.
Therefore, knowledge of research methodology and critical thinking skills are essential. For example, it is essential to be aware of the issues related to randomized control trials (RCT), namely in terms of methodological biases and trial design features, and how these impact the interpretation of their results and treatment effect estimates.
Qualitative Research Proposal. View metadata, citation and similar papers at core.ac.uk. brought to you by CORE. provided by Plymouth Electronic Archive and Research Library. THE EXPERIENCES OF PHYSIOTHERAPISTS TREATING PEOPLE WITH DEMENTIA WHO FRACTURE. THEIR HIP. AN EXPLORATORY QUALITATIVE STUDY.
Students often are uncertain about choosing a research topic for assignments, and or how to come up with a topic for their a research proposal. Your backgrounds at this stage often differ from the typical experienced researcher. On this page, find specific strategies to help you get started:
The 32-item consolidated criteria for reporting qualitative research checklist is used to design and report the study (Tong, Sainsbury, & Craig, 2007). 2.2 Participants and setting. Seventeen participants were recruited from three primary care physiotherapy practices in Rotterdam, The Netherlands.
In this section, you will find details of different parts of your proposal/final project. All of the information here is found in the Department of Physical Therapy Research Handbook. Institutional Review Board (IRB) Authorship Policy ; Forms ; Examples
A good example of presenting information in the introduction section was described in the "chain of reasoning for research", originally described by ... A Proposed Model for Writing Experimental Research Proposals for Physical Therapy Graduate Students. EJPT. 2022; 12:20-28. here to show the need to perform the work on a larger sample.
Study Proposal Version 1.5 vom 03.12.18 population. For example, Grindstaff et al. (2012) examined the effect of lumbopelvic manipu-lation on quadriceps activation capacity in patients with AKP (but without present lumbopelvic impairments) and found that there was no immediate effect. However, one rationale behind
1. A systematic review evaluated the effectiveness of post discharge physiotherapy exercise on function, walking, range of motion, quality of life and muscle strength, for patients following elective primary TKA. Functional physiotherapy exercise interventions following discharge resulted in short term, but not long term, benefit.
2016. Exercise and physical activity in people with multiple sclerosis: an exploration of priorities, meanings and implications for clinical practice. Stennett, Andrea M. 2011. The first ever episode of non-specific low back pain: advancing knowledge of lay definitions, causal theories and attributions. King, Jenny C.
The research thesis is completed during four trimesters of full-time study. The student is under the supervision of a member of the physiotherapy academic staff. In this unit the student develops their research skills by designing a project which is achievable in the time available, to answer a research question, and which extends existing ...
Proposal for Clinical Doctorate in Physical Therapy (DPT) premier comprehensive, regional research university in the United States. The UCCS Academic Center for Sports Medicine and Performance integrates sports medicine and sports science in the teaching, training and treatment of high performance, able bodied and specially challenged athletes ...
Physiotherapy Rehabilitation for Osteoporotic Vertebral Fracture (PROVE) Karen Barker, Muhammad K Javaid, Meredith Newman, Catherine Minns Lowe, Tamsin Hughes, Nigel Stallard, Jose Leal, Varsha Gandhi, Sallie Lamb. Objective: to evaluate the effects of exercise and manual therapy physiotherapy treatments upon quality of life, function and pain ...
Theses/Dissertations from 2015. Physical Therapy after Triangular Fibrocartilage Injuries and Ulnar Wrist Pain, Mohamed A. Abdelmegeed. The Effect of Cervical Muscle Fatigue on Postural Stability during Immersion Virtual Reality, Mazen M. Alqahtani. The Effects of a Novel Therapeutic Intervention in Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy Patients, Adel ...
Physical Therapy Research 21(1) DOI:10.1298 ... Effectiveness of classic physical therapy proposals for chronic ... Patient sample Forty-seven AS patients who were diagnosed with thoracolumbar ...
Background Adherence to physiotherapeutic treatment and recommendations is crucial to achieving planned goals and desired health outcomes. This overview of systematic reviews synthesises the wide range of additional interventions and behaviour change techniques used in physiotherapy, exercise therapy and physical therapy to promote adherence and summarises the evidence of their efficacy ...
Topic 4: Evaluating the impact of strengthening exercises on diabetic patients with shoulder pain. Topic 5: An analysis of the implications of strengthening exercises on alleviation of lower back pain and cervical pain. Topic. 6: Physiotherapy vs. chiropractic. Topic. 7: Why Physiotherapy is beneficial.
The impact of posture and body mechanics on injury risk in athletes. See All Journals. (Click here to see journals by field) Neuro Physiotherapy Research Topics. Blood Flow Restriction (BFR) Research. 20 Sports physiotherapy research topics ideas: injury prevention, rehabilitation, return to play, injury mechanism.
Dissertations on Physiotherapy. Physiotherapy is the practice of targeted exercise and movement to provide rehabilitation and restore or improve function and correct movement following injury, illness, or disability. Physiotherapy can also help to maintain health and prevent future debilitation. View All Dissertation Examples.
This research proposal aims to study how physiotherapists in Bangladesh use the Bobath approach for stroke rehabilitation. The study will use a cross-sectional design to survey physiotherapists in Dhaka and Savar areas through questionnaires. The objectives are to identify if physiotherapists in Bangladesh use the Bobath approach, the extent to which they use it, and if they maintain ...
Research Proposal | Download Free PDF | Physical Therapy | Health Sciences. Research Proposal - Free download as Powerpoint Presentation (.ppt / .pptx), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or view presentation slides online.