Graphical Representation of Data
Graphical representation of data is an attractive method of showcasing numerical data that help in analyzing and representing quantitative data visually. A graph is a kind of a chart where data are plotted as variables across the coordinate. It became easy to analyze the extent of change of one variable based on the change of other variables. Graphical representation of data is done through different mediums such as lines, plots, diagrams, etc. Let us learn more about this interesting concept of graphical representation of data, the different types, and solve a few examples.

Definition of Graphical Representation of Data
A graphical representation is a visual representation of data statistics-based results using graphs, plots, and charts. This kind of representation is more effective in understanding and comparing data than seen in a tabular form. Graphical representation helps to qualify, sort, and present data in a method that is simple to understand for a larger audience. Graphs enable in studying the cause and effect relationship between two variables through both time series and frequency distribution. The data that is obtained from different surveying is infused into a graphical representation by the use of some symbols, such as lines on a line graph, bars on a bar chart, or slices of a pie chart. This visual representation helps in clarity, comparison, and understanding of numerical data.
Representation of Data
The word data is from the Latin word Datum, which means something given. The numerical figures collected through a survey are called data and can be represented in two forms - tabular form and visual form through graphs. Once the data is collected through constant observations, it is arranged, summarized, and classified to finally represented in the form of a graph. There are two kinds of data - quantitative and qualitative. Quantitative data is more structured, continuous, and discrete with statistical data whereas qualitative is unstructured where the data cannot be analyzed.
Principles of Graphical Representation of Data
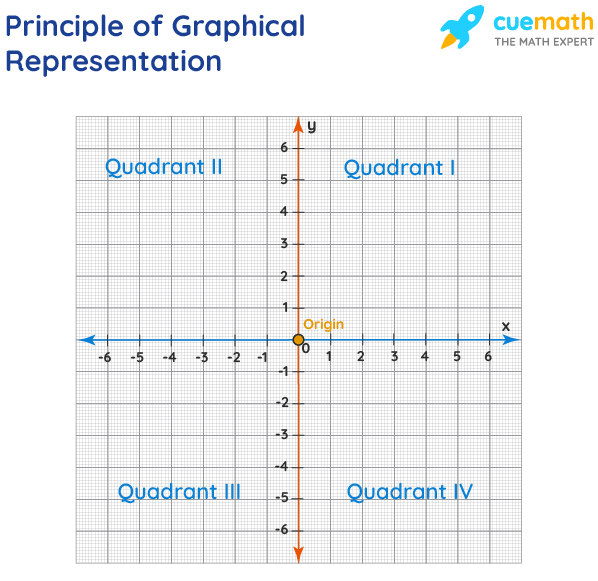
The principles of graphical representation are algebraic. In a graph, there are two lines known as Axis or Coordinate axis. These are the X-axis and Y-axis. The horizontal axis is the X-axis and the vertical axis is the Y-axis. They are perpendicular to each other and intersect at O or point of Origin. On the right side of the Origin, the Xaxis has a positive value and on the left side, it has a negative value. In the same way, the upper side of the Origin Y-axis has a positive value where the down one is with a negative value. When -axis and y-axis intersect each other at the origin it divides the plane into four parts which are called Quadrant I, Quadrant II, Quadrant III, Quadrant IV. This form of representation is seen in a frequency distribution that is represented in four methods, namely Histogram, Smoothed frequency graph, Pie diagram or Pie chart, Cumulative or ogive frequency graph, and Frequency Polygon.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Graphical Representation of Data
Listed below are some advantages and disadvantages of using a graphical representation of data:
- It improves the way of analyzing and learning as the graphical representation makes the data easy to understand.
- It can be used in almost all fields from mathematics to physics to psychology and so on.
- It is easy to understand for its visual impacts.
- It shows the whole and huge data in an instance.
- It is mainly used in statistics to determine the mean, median, and mode for different data
The main disadvantage of graphical representation of data is that it takes a lot of effort as well as resources to find the most appropriate data and then represent it graphically.
Rules of Graphical Representation of Data
While presenting data graphically, there are certain rules that need to be followed. They are listed below:
- Suitable Title: The title of the graph should be appropriate that indicate the subject of the presentation.
- Measurement Unit: The measurement unit in the graph should be mentioned.
- Proper Scale: A proper scale needs to be chosen to represent the data accurately.
- Index: For better understanding, index the appropriate colors, shades, lines, designs in the graphs.
- Data Sources: Data should be included wherever it is necessary at the bottom of the graph.
- Simple: The construction of a graph should be easily understood.
- Neat: The graph should be visually neat in terms of size and font to read the data accurately.
Uses of Graphical Representation of Data
The main use of a graphical representation of data is understanding and identifying the trends and patterns of the data. It helps in analyzing large quantities, comparing two or more data, making predictions, and building a firm decision. The visual display of data also helps in avoiding confusion and overlapping of any information. Graphs like line graphs and bar graphs, display two or more data clearly for easy comparison. This is important in communicating our findings to others and our understanding and analysis of the data.
Types of Graphical Representation of Data
Data is represented in different types of graphs such as plots, pies, diagrams, etc. They are as follows,
Related Topics
Listed below are a few interesting topics that are related to the graphical representation of data, take a look.
- x and y graph
- Frequency Polygon
- Cumulative Frequency
Examples on Graphical Representation of Data
Example 1 : A pie chart is divided into 3 parts with the angles measuring as 2x, 8x, and 10x respectively. Find the value of x in degrees.
We know, the sum of all angles in a pie chart would give 360º as result. ⇒ 2x + 8x + 10x = 360º ⇒ 20 x = 360º ⇒ x = 360º/20 ⇒ x = 18º Therefore, the value of x is 18º.
Example 2: Ben is trying to read the plot given below. His teacher has given him stem and leaf plot worksheets. Can you help him answer the questions? i) What is the mode of the plot? ii) What is the mean of the plot? iii) Find the range.
Solution: i) Mode is the number that appears often in the data. Leaf 4 occurs twice on the plot against stem 5.
Hence, mode = 54
ii) The sum of all data values is 12 + 14 + 21 + 25 + 28 + 32 + 34 + 36 + 50 + 53 + 54 + 54 + 62 + 65 + 67 + 83 + 88 + 89 + 91 = 958
To find the mean, we have to divide the sum by the total number of values.
Mean = Sum of all data values ÷ 19 = 958 ÷ 19 = 50.42
iii) Range = the highest value - the lowest value = 91 - 12 = 79
go to slide go to slide

Book a Free Trial Class
Practice Questions on Graphical Representation of Data
Faqs on graphical representation of data, what is graphical representation.
Graphical representation is a form of visually displaying data through various methods like graphs, diagrams, charts, and plots. It helps in sorting, visualizing, and presenting data in a clear manner through different types of graphs. Statistics mainly use graphical representation to show data.
What are the Different Types of Graphical Representation?
The different types of graphical representation of data are:
- Stem and leaf plot
- Scatter diagrams
- Frequency Distribution
Is the Graphical Representation of Numerical Data?
Yes, these graphical representations are numerical data that has been accumulated through various surveys and observations. The method of presenting these numerical data is called a chart. There are different kinds of charts such as a pie chart, bar graph, line graph, etc, that help in clearly showcasing the data.
What is the Use of Graphical Representation of Data?
Graphical representation of data is useful in clarifying, interpreting, and analyzing data plotting points and drawing line segments , surfaces, and other geometric forms or symbols.
What are the Ways to Represent Data?
Tables, charts, and graphs are all ways of representing data, and they can be used for two broad purposes. The first is to support the collection, organization, and analysis of data as part of the process of a scientific study.
What is the Objective of Graphical Representation of Data?
The main objective of representing data graphically is to display information visually that helps in understanding the information efficiently, clearly, and accurately. This is important to communicate the findings as well as analyze the data.
Home Blog Design Understanding Data Presentations (Guide + Examples)
Understanding Data Presentations (Guide + Examples)
In this age of overwhelming information, the skill to effectively convey data has become extremely valuable. Initiating a discussion on data presentation types involves thoughtful consideration of the nature of your data and the message you aim to convey. Different types of visualizations serve distinct purposes. Whether you’re dealing with how to develop a report or simply trying to communicate complex information, how you present data influences how well your audience understands and engages with it. This extensive guide leads you through the different ways of data presentation.
Table of Contents
What is a Data Presentation?
What should a data presentation include, line graphs, treemap chart, scatter plot, how to choose a data presentation type, recommended data presentation templates, common mistakes done in data presentation.
A data presentation is a slide deck that aims to disclose quantitative information to an audience through the use of visual formats and narrative techniques derived from data analysis, making complex data understandable and actionable. This process requires a series of tools, such as charts, graphs, tables, infographics, dashboards, and so on, supported by concise textual explanations to improve understanding and boost retention rate.
Data presentations require us to cull data in a format that allows the presenter to highlight trends, patterns, and insights so that the audience can act upon the shared information. In a few words, the goal of data presentations is to enable viewers to grasp complicated concepts or trends quickly, facilitating informed decision-making or deeper analysis.
Data presentations go beyond the mere usage of graphical elements. Seasoned presenters encompass visuals with the art of storytelling with data, so the speech skillfully connects the points through a narrative that resonates with the audience. Depending on the purpose – inspire, persuade, inform, support decision-making processes, etc. – is the data presentation format that is better suited to help us in this journey.
To nail your upcoming data presentation, ensure to count with the following elements:
- Clear Objectives: Understand the intent of your presentation before selecting the graphical layout and metaphors to make content easier to grasp.
- Engaging introduction: Use a powerful hook from the get-go. For instance, you can ask a big question or present a problem that your data will answer. Take a look at our guide on how to start a presentation for tips & insights.
- Structured Narrative: Your data presentation must tell a coherent story. This means a beginning where you present the context, a middle section in which you present the data, and an ending that uses a call-to-action. Check our guide on presentation structure for further information.
- Visual Elements: These are the charts, graphs, and other elements of visual communication we ought to use to present data. This article will cover one by one the different types of data representation methods we can use, and provide further guidance on choosing between them.
- Insights and Analysis: This is not just showcasing a graph and letting people get an idea about it. A proper data presentation includes the interpretation of that data, the reason why it’s included, and why it matters to your research.
- Conclusion & CTA: Ending your presentation with a call to action is necessary. Whether you intend to wow your audience into acquiring your services, inspire them to change the world, or whatever the purpose of your presentation, there must be a stage in which you convey all that you shared and show the path to staying in touch. Plan ahead whether you want to use a thank-you slide, a video presentation, or which method is apt and tailored to the kind of presentation you deliver.
- Q&A Session: After your speech is concluded, allocate 3-5 minutes for the audience to raise any questions about the information you disclosed. This is an extra chance to establish your authority on the topic. Check our guide on questions and answer sessions in presentations here.
Bar charts are a graphical representation of data using rectangular bars to show quantities or frequencies in an established category. They make it easy for readers to spot patterns or trends. Bar charts can be horizontal or vertical, although the vertical format is commonly known as a column chart. They display categorical, discrete, or continuous variables grouped in class intervals [1] . They include an axis and a set of labeled bars horizontally or vertically. These bars represent the frequencies of variable values or the values themselves. Numbers on the y-axis of a vertical bar chart or the x-axis of a horizontal bar chart are called the scale.
Real-Life Application of Bar Charts
Let’s say a sales manager is presenting sales to their audience. Using a bar chart, he follows these steps.
Step 1: Selecting Data
The first step is to identify the specific data you will present to your audience.
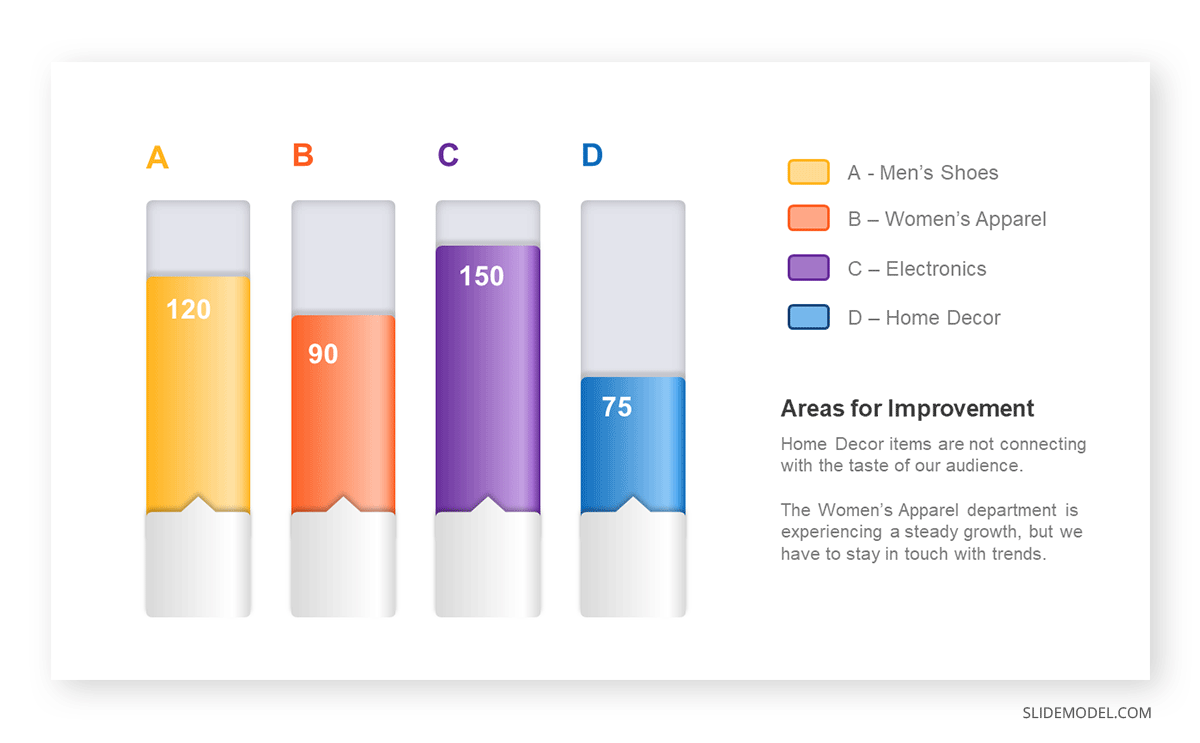
The sales manager has highlighted these products for the presentation.
- Product A: Men’s Shoes
- Product B: Women’s Apparel
- Product C: Electronics
- Product D: Home Decor
Step 2: Choosing Orientation
Opt for a vertical layout for simplicity. Vertical bar charts help compare different categories in case there are not too many categories [1] . They can also help show different trends. A vertical bar chart is used where each bar represents one of the four chosen products. After plotting the data, it is seen that the height of each bar directly represents the sales performance of the respective product.
It is visible that the tallest bar (Electronics – Product C) is showing the highest sales. However, the shorter bars (Women’s Apparel – Product B and Home Decor – Product D) need attention. It indicates areas that require further analysis or strategies for improvement.
Step 3: Colorful Insights
Different colors are used to differentiate each product. It is essential to show a color-coded chart where the audience can distinguish between products.
- Men’s Shoes (Product A): Yellow
- Women’s Apparel (Product B): Orange
- Electronics (Product C): Violet
- Home Decor (Product D): Blue
Bar charts are straightforward and easily understandable for presenting data. They are versatile when comparing products or any categorical data [2] . Bar charts adapt seamlessly to retail scenarios. Despite that, bar charts have a few shortcomings. They cannot illustrate data trends over time. Besides, overloading the chart with numerous products can lead to visual clutter, diminishing its effectiveness.
For more information, check our collection of bar chart templates for PowerPoint .
Line graphs help illustrate data trends, progressions, or fluctuations by connecting a series of data points called ‘markers’ with straight line segments. This provides a straightforward representation of how values change [5] . Their versatility makes them invaluable for scenarios requiring a visual understanding of continuous data. In addition, line graphs are also useful for comparing multiple datasets over the same timeline. Using multiple line graphs allows us to compare more than one data set. They simplify complex information so the audience can quickly grasp the ups and downs of values. From tracking stock prices to analyzing experimental results, you can use line graphs to show how data changes over a continuous timeline. They show trends with simplicity and clarity.
Real-life Application of Line Graphs
To understand line graphs thoroughly, we will use a real case. Imagine you’re a financial analyst presenting a tech company’s monthly sales for a licensed product over the past year. Investors want insights into sales behavior by month, how market trends may have influenced sales performance and reception to the new pricing strategy. To present data via a line graph, you will complete these steps.
First, you need to gather the data. In this case, your data will be the sales numbers. For example:
- January: $45,000
- February: $55,000
- March: $45,000
- April: $60,000
- May: $ 70,000
- June: $65,000
- July: $62,000
- August: $68,000
- September: $81,000
- October: $76,000
- November: $87,000
- December: $91,000
After choosing the data, the next step is to select the orientation. Like bar charts, you can use vertical or horizontal line graphs. However, we want to keep this simple, so we will keep the timeline (x-axis) horizontal while the sales numbers (y-axis) vertical.
Step 3: Connecting Trends
After adding the data to your preferred software, you will plot a line graph. In the graph, each month’s sales are represented by data points connected by a line.
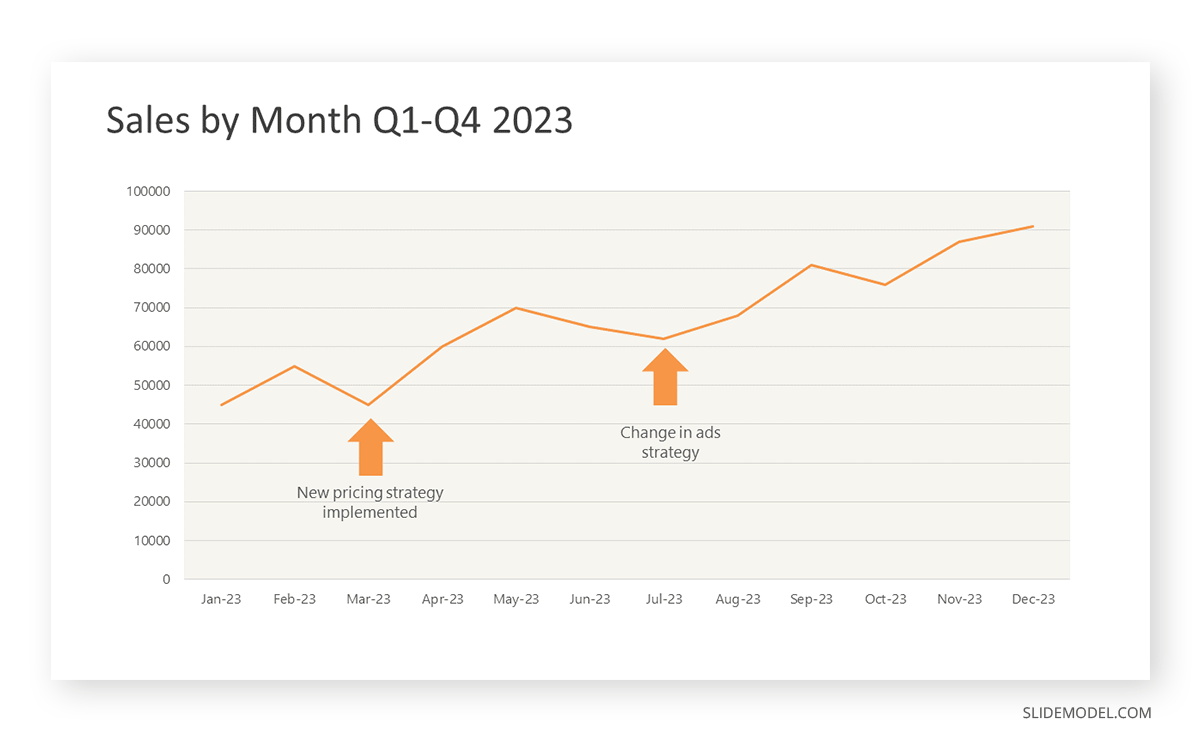
Step 4: Adding Clarity with Color
If there are multiple lines, you can also add colors to highlight each one, making it easier to follow.
Line graphs excel at visually presenting trends over time. These presentation aids identify patterns, like upward or downward trends. However, too many data points can clutter the graph, making it harder to interpret. Line graphs work best with continuous data but are not suitable for categories.
For more information, check our collection of line chart templates for PowerPoint and our article about how to make a presentation graph .
A data dashboard is a visual tool for analyzing information. Different graphs, charts, and tables are consolidated in a layout to showcase the information required to achieve one or more objectives. Dashboards help quickly see Key Performance Indicators (KPIs). You don’t make new visuals in the dashboard; instead, you use it to display visuals you’ve already made in worksheets [3] .
Keeping the number of visuals on a dashboard to three or four is recommended. Adding too many can make it hard to see the main points [4]. Dashboards can be used for business analytics to analyze sales, revenue, and marketing metrics at a time. They are also used in the manufacturing industry, as they allow users to grasp the entire production scenario at the moment while tracking the core KPIs for each line.
Real-Life Application of a Dashboard
Consider a project manager presenting a software development project’s progress to a tech company’s leadership team. He follows the following steps.
Step 1: Defining Key Metrics
To effectively communicate the project’s status, identify key metrics such as completion status, budget, and bug resolution rates. Then, choose measurable metrics aligned with project objectives.
Step 2: Choosing Visualization Widgets
After finalizing the data, presentation aids that align with each metric are selected. For this project, the project manager chooses a progress bar for the completion status and uses bar charts for budget allocation. Likewise, he implements line charts for bug resolution rates.
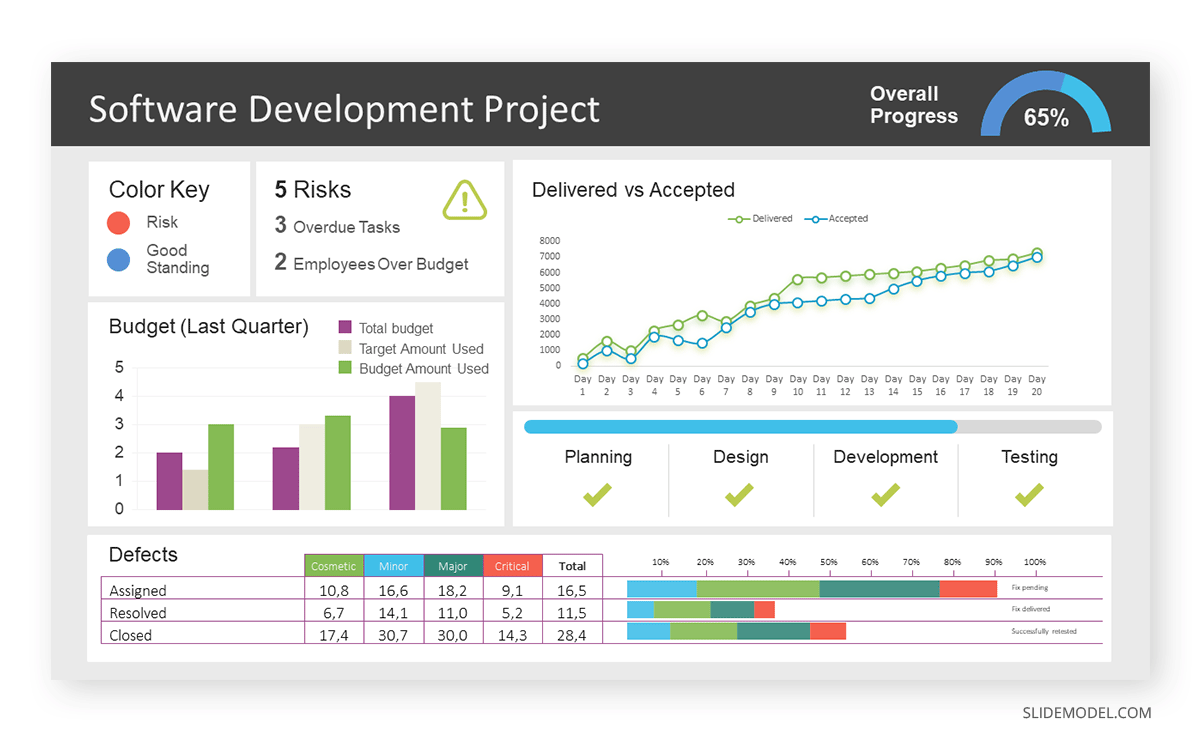
Step 3: Dashboard Layout
Key metrics are prominently placed in the dashboard for easy visibility, and the manager ensures that it appears clean and organized.
Dashboards provide a comprehensive view of key project metrics. Users can interact with data, customize views, and drill down for detailed analysis. However, creating an effective dashboard requires careful planning to avoid clutter. Besides, dashboards rely on the availability and accuracy of underlying data sources.
For more information, check our article on how to design a dashboard presentation , and discover our collection of dashboard PowerPoint templates .
Treemap charts represent hierarchical data structured in a series of nested rectangles [6] . As each branch of the ‘tree’ is given a rectangle, smaller tiles can be seen representing sub-branches, meaning elements on a lower hierarchical level than the parent rectangle. Each one of those rectangular nodes is built by representing an area proportional to the specified data dimension.
Treemaps are useful for visualizing large datasets in compact space. It is easy to identify patterns, such as which categories are dominant. Common applications of the treemap chart are seen in the IT industry, such as resource allocation, disk space management, website analytics, etc. Also, they can be used in multiple industries like healthcare data analysis, market share across different product categories, or even in finance to visualize portfolios.
Real-Life Application of a Treemap Chart
Let’s consider a financial scenario where a financial team wants to represent the budget allocation of a company. There is a hierarchy in the process, so it is helpful to use a treemap chart. In the chart, the top-level rectangle could represent the total budget, and it would be subdivided into smaller rectangles, each denoting a specific department. Further subdivisions within these smaller rectangles might represent individual projects or cost categories.
Step 1: Define Your Data Hierarchy
While presenting data on the budget allocation, start by outlining the hierarchical structure. The sequence will be like the overall budget at the top, followed by departments, projects within each department, and finally, individual cost categories for each project.
- Top-level rectangle: Total Budget
- Second-level rectangles: Departments (Engineering, Marketing, Sales)
- Third-level rectangles: Projects within each department
- Fourth-level rectangles: Cost categories for each project (Personnel, Marketing Expenses, Equipment)
Step 2: Choose a Suitable Tool
It’s time to select a data visualization tool supporting Treemaps. Popular choices include Tableau, Microsoft Power BI, PowerPoint, or even coding with libraries like D3.js. It is vital to ensure that the chosen tool provides customization options for colors, labels, and hierarchical structures.
Here, the team uses PowerPoint for this guide because of its user-friendly interface and robust Treemap capabilities.
Step 3: Make a Treemap Chart with PowerPoint
After opening the PowerPoint presentation, they chose “SmartArt” to form the chart. The SmartArt Graphic window has a “Hierarchy” category on the left. Here, you will see multiple options. You can choose any layout that resembles a Treemap. The “Table Hierarchy” or “Organization Chart” options can be adapted. The team selects the Table Hierarchy as it looks close to a Treemap.
Step 5: Input Your Data
After that, a new window will open with a basic structure. They add the data one by one by clicking on the text boxes. They start with the top-level rectangle, representing the total budget.
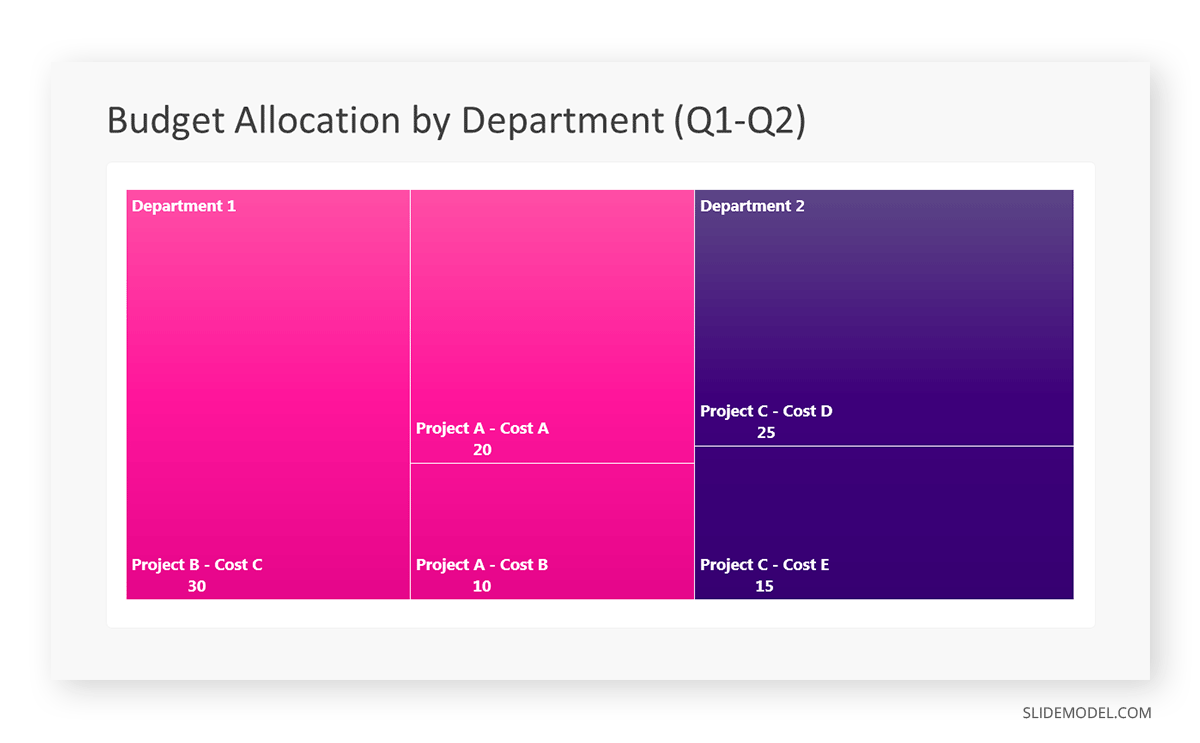
Step 6: Customize the Treemap
By clicking on each shape, they customize its color, size, and label. At the same time, they can adjust the font size, style, and color of labels by using the options in the “Format” tab in PowerPoint. Using different colors for each level enhances the visual difference.
Treemaps excel at illustrating hierarchical structures. These charts make it easy to understand relationships and dependencies. They efficiently use space, compactly displaying a large amount of data, reducing the need for excessive scrolling or navigation. Additionally, using colors enhances the understanding of data by representing different variables or categories.
In some cases, treemaps might become complex, especially with deep hierarchies. It becomes challenging for some users to interpret the chart. At the same time, displaying detailed information within each rectangle might be constrained by space. It potentially limits the amount of data that can be shown clearly. Without proper labeling and color coding, there’s a risk of misinterpretation.
A heatmap is a data visualization tool that uses color coding to represent values across a two-dimensional surface. In these, colors replace numbers to indicate the magnitude of each cell. This color-shaded matrix display is valuable for summarizing and understanding data sets with a glance [7] . The intensity of the color corresponds to the value it represents, making it easy to identify patterns, trends, and variations in the data.
As a tool, heatmaps help businesses analyze website interactions, revealing user behavior patterns and preferences to enhance overall user experience. In addition, companies use heatmaps to assess content engagement, identifying popular sections and areas of improvement for more effective communication. They excel at highlighting patterns and trends in large datasets, making it easy to identify areas of interest.
We can implement heatmaps to express multiple data types, such as numerical values, percentages, or even categorical data. Heatmaps help us easily spot areas with lots of activity, making them helpful in figuring out clusters [8] . When making these maps, it is important to pick colors carefully. The colors need to show the differences between groups or levels of something. And it is good to use colors that people with colorblindness can easily see.
Check our detailed guide on how to create a heatmap here. Also discover our collection of heatmap PowerPoint templates .
Pie charts are circular statistical graphics divided into slices to illustrate numerical proportions. Each slice represents a proportionate part of the whole, making it easy to visualize the contribution of each component to the total.
The size of the pie charts is influenced by the value of data points within each pie. The total of all data points in a pie determines its size. The pie with the highest data points appears as the largest, whereas the others are proportionally smaller. However, you can present all pies of the same size if proportional representation is not required [9] . Sometimes, pie charts are difficult to read, or additional information is required. A variation of this tool can be used instead, known as the donut chart , which has the same structure but a blank center, creating a ring shape. Presenters can add extra information, and the ring shape helps to declutter the graph.
Pie charts are used in business to show percentage distribution, compare relative sizes of categories, or present straightforward data sets where visualizing ratios is essential.
Real-Life Application of Pie Charts
Consider a scenario where you want to represent the distribution of the data. Each slice of the pie chart would represent a different category, and the size of each slice would indicate the percentage of the total portion allocated to that category.
Step 1: Define Your Data Structure
Imagine you are presenting the distribution of a project budget among different expense categories.
- Column A: Expense Categories (Personnel, Equipment, Marketing, Miscellaneous)
- Column B: Budget Amounts ($40,000, $30,000, $20,000, $10,000) Column B represents the values of your categories in Column A.
Step 2: Insert a Pie Chart
Using any of the accessible tools, you can create a pie chart. The most convenient tools for forming a pie chart in a presentation are presentation tools such as PowerPoint or Google Slides. You will notice that the pie chart assigns each expense category a percentage of the total budget by dividing it by the total budget.
For instance:
- Personnel: $40,000 / ($40,000 + $30,000 + $20,000 + $10,000) = 40%
- Equipment: $30,000 / ($40,000 + $30,000 + $20,000 + $10,000) = 30%
- Marketing: $20,000 / ($40,000 + $30,000 + $20,000 + $10,000) = 20%
- Miscellaneous: $10,000 / ($40,000 + $30,000 + $20,000 + $10,000) = 10%
You can make a chart out of this or just pull out the pie chart from the data.
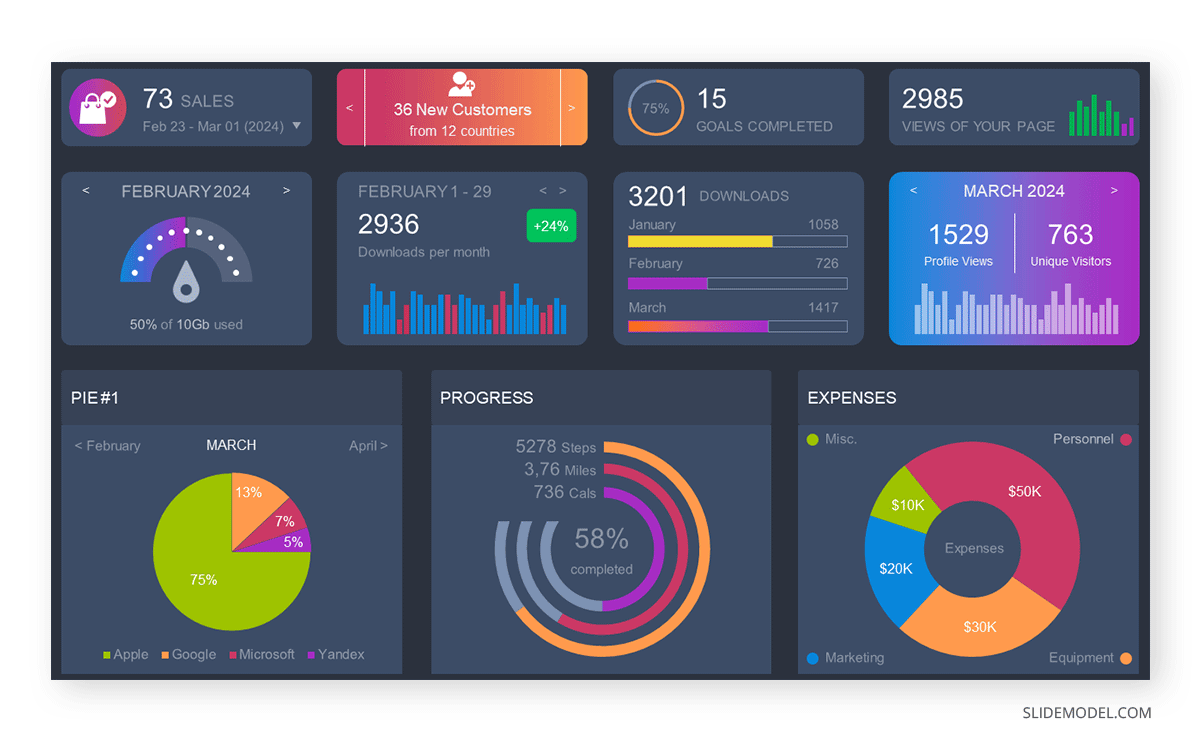
3D pie charts and 3D donut charts are quite popular among the audience. They stand out as visual elements in any presentation slide, so let’s take a look at how our pie chart example would look in 3D pie chart format.
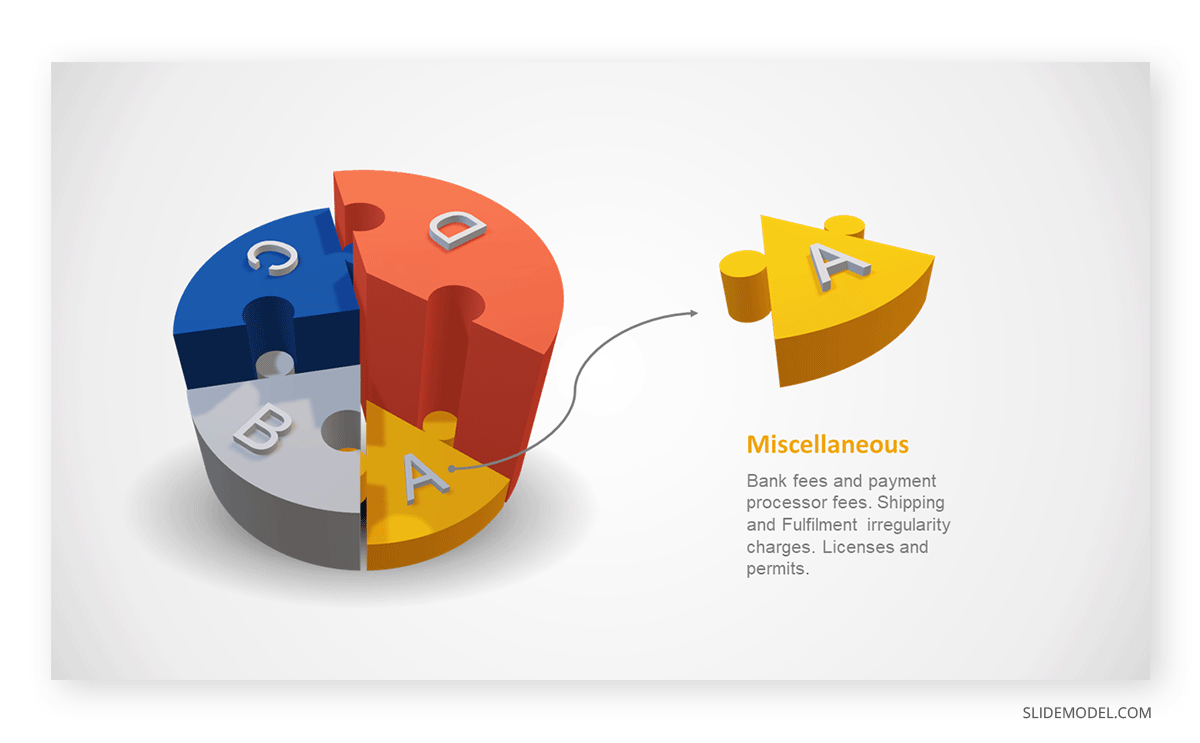
Step 03: Results Interpretation
The pie chart visually illustrates the distribution of the project budget among different expense categories. Personnel constitutes the largest portion at 40%, followed by equipment at 30%, marketing at 20%, and miscellaneous at 10%. This breakdown provides a clear overview of where the project funds are allocated, which helps in informed decision-making and resource management. It is evident that personnel are a significant investment, emphasizing their importance in the overall project budget.
Pie charts provide a straightforward way to represent proportions and percentages. They are easy to understand, even for individuals with limited data analysis experience. These charts work well for small datasets with a limited number of categories.
However, a pie chart can become cluttered and less effective in situations with many categories. Accurate interpretation may be challenging, especially when dealing with slight differences in slice sizes. In addition, these charts are static and do not effectively convey trends over time.
For more information, check our collection of pie chart templates for PowerPoint .
Histograms present the distribution of numerical variables. Unlike a bar chart that records each unique response separately, histograms organize numeric responses into bins and show the frequency of reactions within each bin [10] . The x-axis of a histogram shows the range of values for a numeric variable. At the same time, the y-axis indicates the relative frequencies (percentage of the total counts) for that range of values.
Whenever you want to understand the distribution of your data, check which values are more common, or identify outliers, histograms are your go-to. Think of them as a spotlight on the story your data is telling. A histogram can provide a quick and insightful overview if you’re curious about exam scores, sales figures, or any numerical data distribution.
Real-Life Application of a Histogram
In the histogram data analysis presentation example, imagine an instructor analyzing a class’s grades to identify the most common score range. A histogram could effectively display the distribution. It will show whether most students scored in the average range or if there are significant outliers.
Step 1: Gather Data
He begins by gathering the data. The scores of each student in class are gathered to analyze exam scores.
After arranging the scores in ascending order, bin ranges are set.
Step 2: Define Bins
Bins are like categories that group similar values. Think of them as buckets that organize your data. The presenter decides how wide each bin should be based on the range of the values. For instance, the instructor sets the bin ranges based on score intervals: 60-69, 70-79, 80-89, and 90-100.
Step 3: Count Frequency
Now, he counts how many data points fall into each bin. This step is crucial because it tells you how often specific ranges of values occur. The result is the frequency distribution, showing the occurrences of each group.
Here, the instructor counts the number of students in each category.
- 60-69: 1 student (Kate)
- 70-79: 4 students (David, Emma, Grace, Jack)
- 80-89: 7 students (Alice, Bob, Frank, Isabel, Liam, Mia, Noah)
- 90-100: 3 students (Clara, Henry, Olivia)
Step 4: Create the Histogram
It’s time to turn the data into a visual representation. Draw a bar for each bin on a graph. The width of the bar should correspond to the range of the bin, and the height should correspond to the frequency. To make your histogram understandable, label the X and Y axes.
In this case, the X-axis should represent the bins (e.g., test score ranges), and the Y-axis represents the frequency.
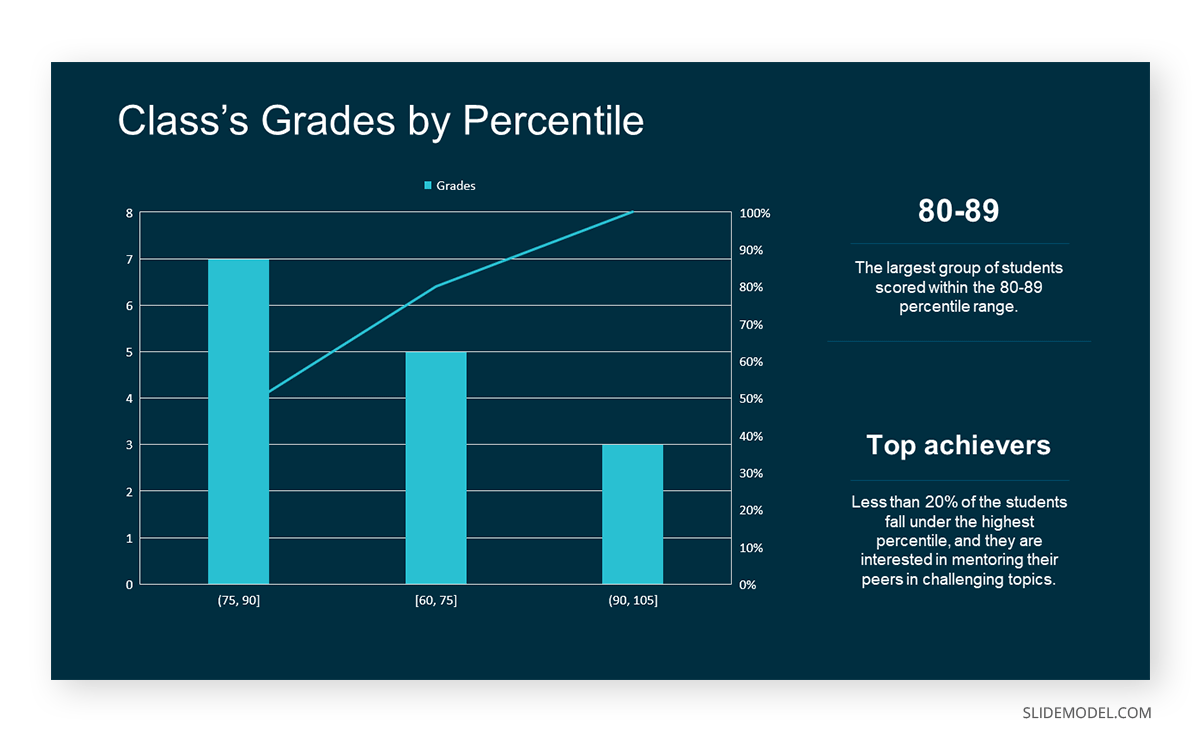
The histogram of the class grades reveals insightful patterns in the distribution. Most students, with seven students, fall within the 80-89 score range. The histogram provides a clear visualization of the class’s performance. It showcases a concentration of grades in the upper-middle range with few outliers at both ends. This analysis helps in understanding the overall academic standing of the class. It also identifies the areas for potential improvement or recognition.
Thus, histograms provide a clear visual representation of data distribution. They are easy to interpret, even for those without a statistical background. They apply to various types of data, including continuous and discrete variables. One weak point is that histograms do not capture detailed patterns in students’ data, with seven compared to other visualization methods.
A scatter plot is a graphical representation of the relationship between two variables. It consists of individual data points on a two-dimensional plane. This plane plots one variable on the x-axis and the other on the y-axis. Each point represents a unique observation. It visualizes patterns, trends, or correlations between the two variables.
Scatter plots are also effective in revealing the strength and direction of relationships. They identify outliers and assess the overall distribution of data points. The points’ dispersion and clustering reflect the relationship’s nature, whether it is positive, negative, or lacks a discernible pattern. In business, scatter plots assess relationships between variables such as marketing cost and sales revenue. They help present data correlations and decision-making.
Real-Life Application of Scatter Plot
A group of scientists is conducting a study on the relationship between daily hours of screen time and sleep quality. After reviewing the data, they managed to create this table to help them build a scatter plot graph:
In the provided example, the x-axis represents Daily Hours of Screen Time, and the y-axis represents the Sleep Quality Rating.
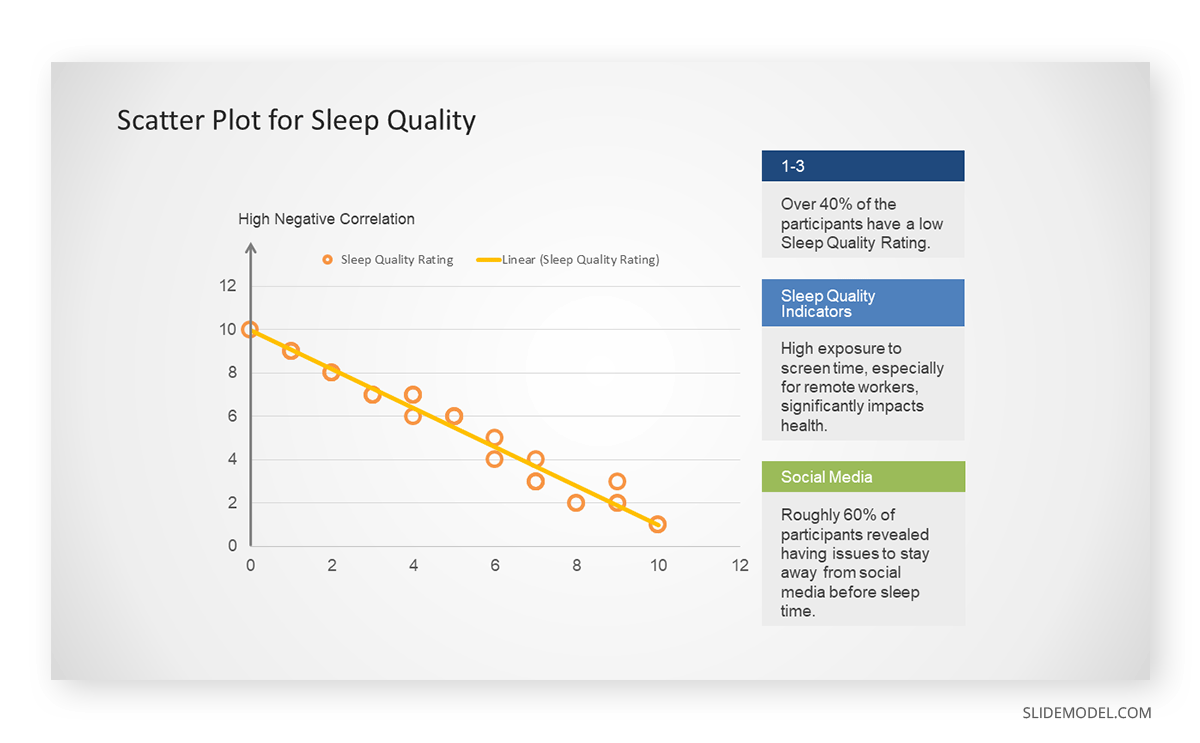
The scientists observe a negative correlation between the amount of screen time and the quality of sleep. This is consistent with their hypothesis that blue light, especially before bedtime, has a significant impact on sleep quality and metabolic processes.
There are a few things to remember when using a scatter plot. Even when a scatter diagram indicates a relationship, it doesn’t mean one variable affects the other. A third factor can influence both variables. The more the plot resembles a straight line, the stronger the relationship is perceived [11] . If it suggests no ties, the observed pattern might be due to random fluctuations in data. When the scatter diagram depicts no correlation, whether the data might be stratified is worth considering.
Choosing the appropriate data presentation type is crucial when making a presentation . Understanding the nature of your data and the message you intend to convey will guide this selection process. For instance, when showcasing quantitative relationships, scatter plots become instrumental in revealing correlations between variables. If the focus is on emphasizing parts of a whole, pie charts offer a concise display of proportions. Histograms, on the other hand, prove valuable for illustrating distributions and frequency patterns.
Bar charts provide a clear visual comparison of different categories. Likewise, line charts excel in showcasing trends over time, while tables are ideal for detailed data examination. Starting a presentation on data presentation types involves evaluating the specific information you want to communicate and selecting the format that aligns with your message. This ensures clarity and resonance with your audience from the beginning of your presentation.
1. Fact Sheet Dashboard for Data Presentation

Convey all the data you need to present in this one-pager format, an ideal solution tailored for users looking for presentation aids. Global maps, donut chats, column graphs, and text neatly arranged in a clean layout presented in light and dark themes.
Use This Template
2. 3D Column Chart Infographic PPT Template
Represent column charts in a highly visual 3D format with this PPT template. A creative way to present data, this template is entirely editable, and we can craft either a one-page infographic or a series of slides explaining what we intend to disclose point by point.
3. Data Circles Infographic PowerPoint Template
An alternative to the pie chart and donut chart diagrams, this template features a series of curved shapes with bubble callouts as ways of presenting data. Expand the information for each arch in the text placeholder areas.
4. Colorful Metrics Dashboard for Data Presentation
This versatile dashboard template helps us in the presentation of the data by offering several graphs and methods to convert numbers into graphics. Implement it for e-commerce projects, financial projections, project development, and more.
5. Animated Data Presentation Tools for PowerPoint & Google Slides
A slide deck filled with most of the tools mentioned in this article, from bar charts, column charts, treemap graphs, pie charts, histogram, etc. Animated effects make each slide look dynamic when sharing data with stakeholders.
6. Statistics Waffle Charts PPT Template for Data Presentations
This PPT template helps us how to present data beyond the typical pie chart representation. It is widely used for demographics, so it’s a great fit for marketing teams, data science professionals, HR personnel, and more.
7. Data Presentation Dashboard Template for Google Slides
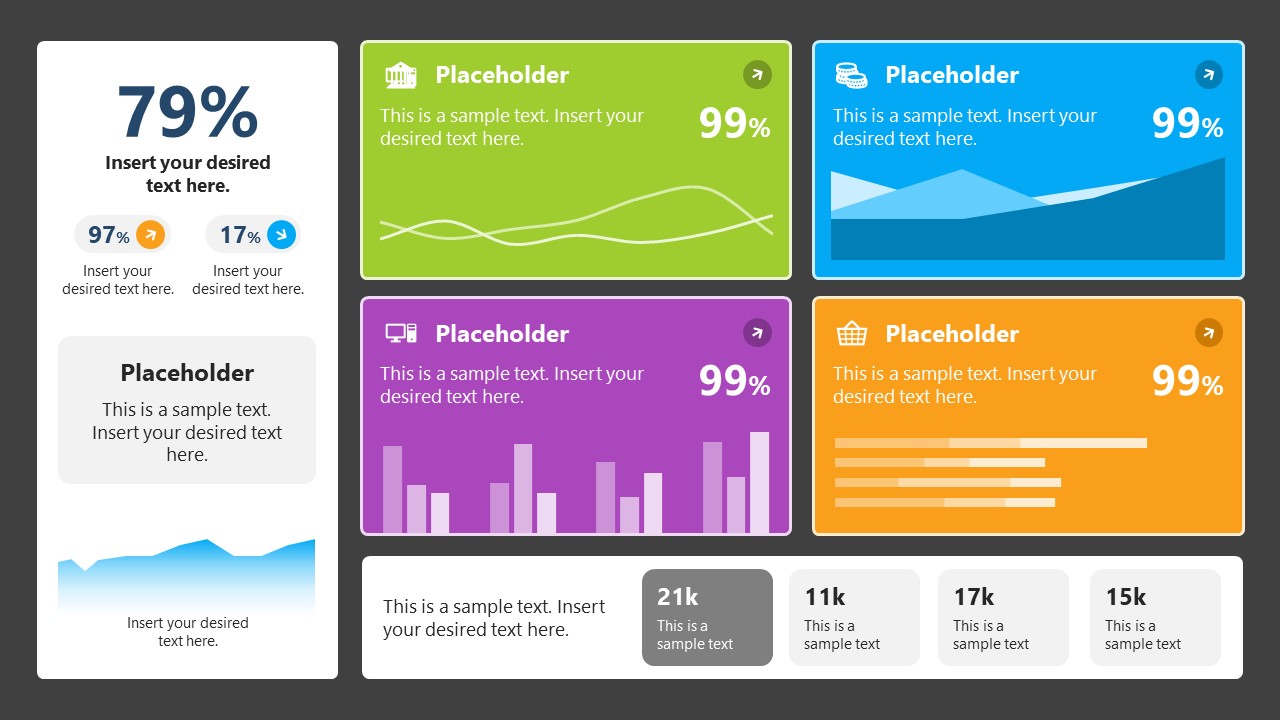
A compendium of tools in dashboard format featuring line graphs, bar charts, column charts, and neatly arranged placeholder text areas.
8. Weather Dashboard for Data Presentation
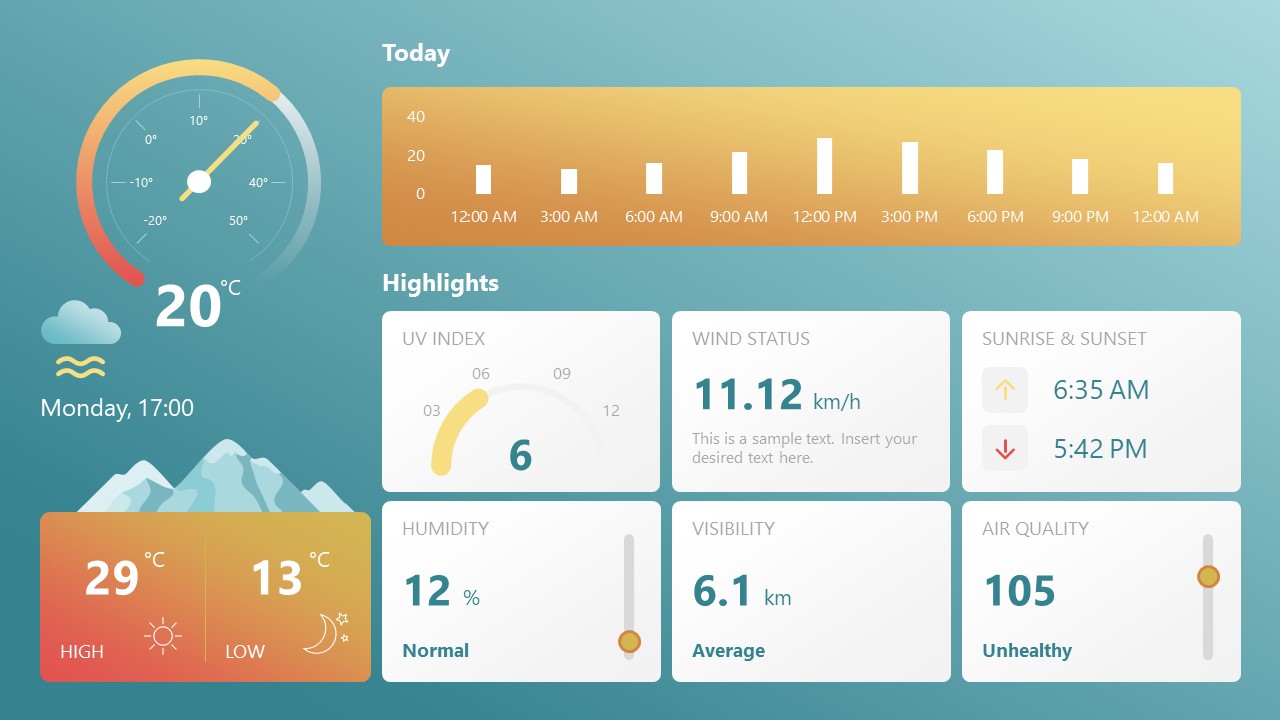
Share weather data for agricultural presentation topics, environmental studies, or any kind of presentation that requires a highly visual layout for weather forecasting on a single day. Two color themes are available.
9. Social Media Marketing Dashboard Data Presentation Template
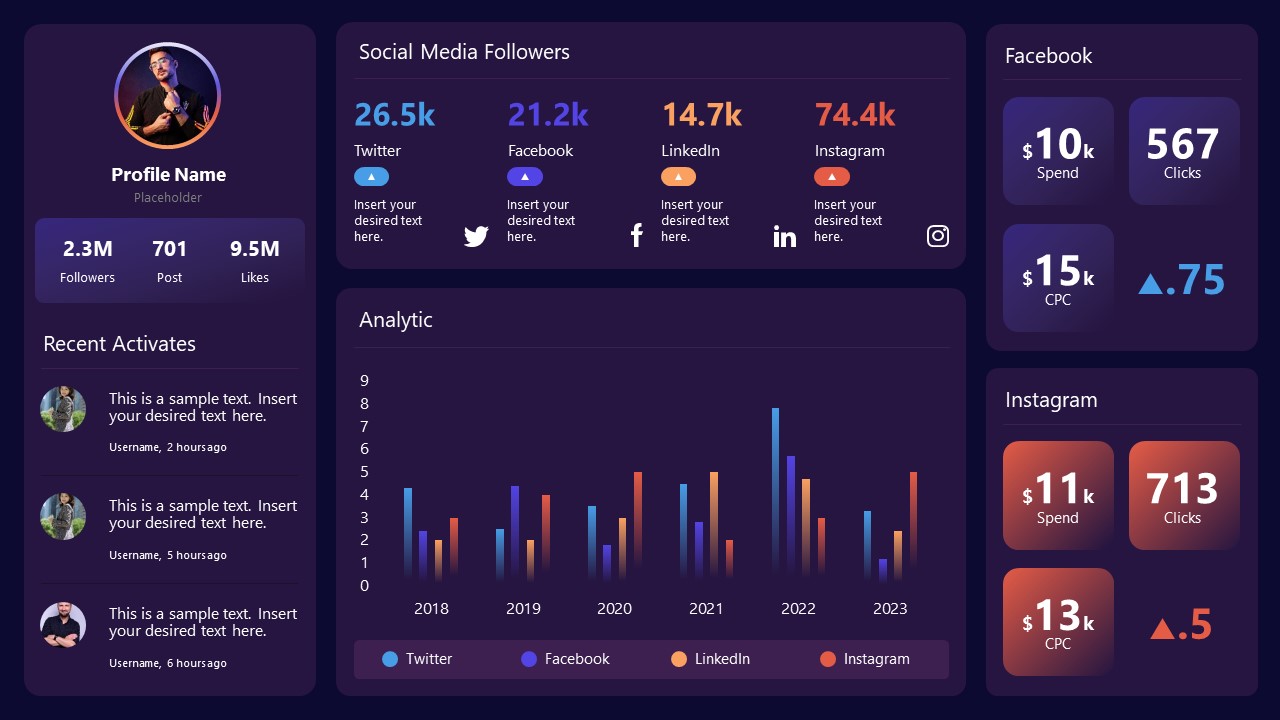
Intended for marketing professionals, this dashboard template for data presentation is a tool for presenting data analytics from social media channels. Two slide layouts featuring line graphs and column charts.
10. Project Management Summary Dashboard Template
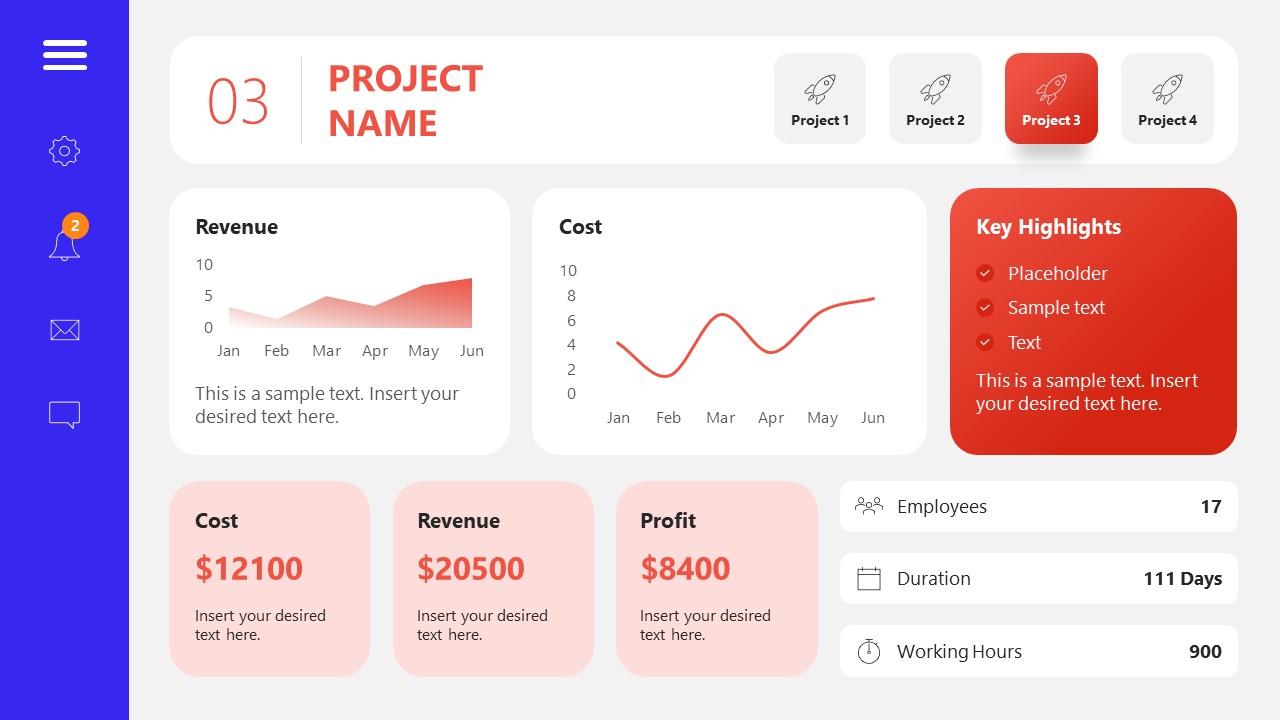
A tool crafted for project managers to deliver highly visual reports on a project’s completion, the profits it delivered for the company, and expenses/time required to execute it. 4 different color layouts are available.
11. Profit & Loss Dashboard for PowerPoint and Google Slides
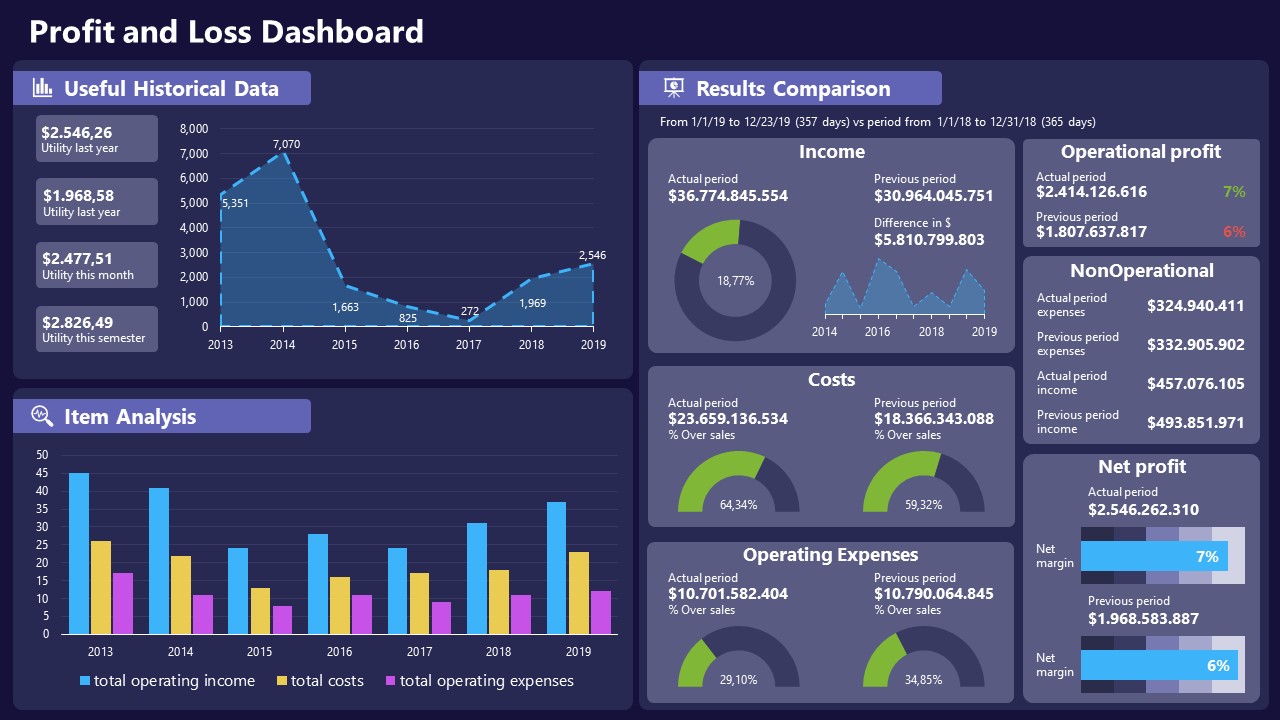
A must-have for finance professionals. This typical profit & loss dashboard includes progress bars, donut charts, column charts, line graphs, and everything that’s required to deliver a comprehensive report about a company’s financial situation.
Overwhelming visuals
One of the mistakes related to using data-presenting methods is including too much data or using overly complex visualizations. They can confuse the audience and dilute the key message.
Inappropriate chart types
Choosing the wrong type of chart for the data at hand can lead to misinterpretation. For example, using a pie chart for data that doesn’t represent parts of a whole is not right.
Lack of context
Failing to provide context or sufficient labeling can make it challenging for the audience to understand the significance of the presented data.
Inconsistency in design
Using inconsistent design elements and color schemes across different visualizations can create confusion and visual disarray.
Failure to provide details
Simply presenting raw data without offering clear insights or takeaways can leave the audience without a meaningful conclusion.
Lack of focus
Not having a clear focus on the key message or main takeaway can result in a presentation that lacks a central theme.
Visual accessibility issues
Overlooking the visual accessibility of charts and graphs can exclude certain audience members who may have difficulty interpreting visual information.
In order to avoid these mistakes in data presentation, presenters can benefit from using presentation templates . These templates provide a structured framework. They ensure consistency, clarity, and an aesthetically pleasing design, enhancing data communication’s overall impact.
Understanding and choosing data presentation types are pivotal in effective communication. Each method serves a unique purpose, so selecting the appropriate one depends on the nature of the data and the message to be conveyed. The diverse array of presentation types offers versatility in visually representing information, from bar charts showing values to pie charts illustrating proportions.
Using the proper method enhances clarity, engages the audience, and ensures that data sets are not just presented but comprehensively understood. By appreciating the strengths and limitations of different presentation types, communicators can tailor their approach to convey information accurately, developing a deeper connection between data and audience understanding.
[1] Government of Canada, S.C. (2021) 5 Data Visualization 5.2 Bar Chart , 5.2 Bar chart . https://www150.statcan.gc.ca/n1/edu/power-pouvoir/ch9/bargraph-diagrammeabarres/5214818-eng.htm
[2] Kosslyn, S.M., 1989. Understanding charts and graphs. Applied cognitive psychology, 3(3), pp.185-225. https://apps.dtic.mil/sti/pdfs/ADA183409.pdf
[3] Creating a Dashboard . https://it.tufts.edu/book/export/html/1870
[4] https://www.goldenwestcollege.edu/research/data-and-more/data-dashboards/index.html
[5] https://www.mit.edu/course/21/21.guide/grf-line.htm
[6] Jadeja, M. and Shah, K., 2015, January. Tree-Map: A Visualization Tool for Large Data. In GSB@ SIGIR (pp. 9-13). https://ceur-ws.org/Vol-1393/gsb15proceedings.pdf#page=15
[7] Heat Maps and Quilt Plots. https://www.publichealth.columbia.edu/research/population-health-methods/heat-maps-and-quilt-plots
[8] EIU QGIS WORKSHOP. https://www.eiu.edu/qgisworkshop/heatmaps.php
[9] About Pie Charts. https://www.mit.edu/~mbarker/formula1/f1help/11-ch-c8.htm
[10] Histograms. https://sites.utexas.edu/sos/guided/descriptive/numericaldd/descriptiven2/histogram/ [11] https://asq.org/quality-resources/scatter-diagram

Like this article? Please share
Data Analysis, Data Science, Data Visualization Filed under Design
Related Articles

Filed under Design • March 27th, 2024
How to Make a Presentation Graph
Detailed step-by-step instructions to master the art of how to make a presentation graph in PowerPoint and Google Slides. Check it out!
Filed under Presentation Ideas • January 6th, 2024
All About Using Harvey Balls
Among the many tools in the arsenal of the modern presenter, Harvey Balls have a special place. In this article we will tell you all about using Harvey Balls.

Filed under Business • December 8th, 2023
How to Design a Dashboard Presentation: A Step-by-Step Guide
Take a step further in your professional presentation skills by learning what a dashboard presentation is and how to properly design one in PowerPoint. A detailed step-by-step guide is here!
Leave a Reply
- Artificial Intelligence
- Generative AI
- Business Operations
- Cloud Computing
- Data Center
- Data Management
- Emerging Technology
- Enterprise Applications
- IT Leadership
- Digital Transformation
- IT Strategy
- IT Management
- Diversity and Inclusion
- IT Operations
- Project Management
- Software Development
- Vendors and Providers
- Enterprise Buyer’s Guides
- United States
- Middle East
- Italia (Italy)
- Netherlands
- United Kingdom
- New Zealand
- Data Analytics & AI
- Newsletters
- Foundry Careers
- Terms of Service
- Privacy Policy
- Cookie Policy
- Copyright Notice
- Member Preferences
- About AdChoices
- Your California Privacy Rights
Our Network
- Computerworld
- Network World
What is data visualization? Presenting data for decision-making
Data visualization is the presentation of data in a graphical format to make it easier for decision makers to see and understand trends, outliers, and patterns in data..

Data visualization definition
Data visualization is the presentation of data in a graphical format such as a plot, graph, or map to make it easier for decision makers to see and understand trends, outliers, and patterns in data.
Maps and charts were among the earliest forms of data visualization. One of the most well-known early examples of data visualization was a flow map created by French civil engineer Charles Joseph Minard in 1869 to help understand what Napoleon’s troops suffered in the disastrous Russian campaign of 1812. The map used two dimensions to depict the number of troops, distance, temperature, latitude and longitude, direction of travel, and location relative to specific dates.
Today, data visualization encompasses all manners of presenting data visually, from dashboards to reports, statistical graphs, heat maps, plots, infographics, and more.
What is the business value of data visualization?
Data visualization helps people analyze data, especially large volumes of data, quickly and efficiently.
By providing easy-to-understand visual representations of data, it helps employees make more informed decisions based on that data. Presenting data in visual form can make it easier to comprehend, enable people to obtain insights more quickly. Visualizations can also make it easier to communicate those insights and to see how independent variables relate to one another. This can help you see trends, understand the frequency of events, and track connections between operations and performance, for example.
Key data visualization benefits include:
- Unlocking the value big data by enabling people to absorb vast amounts of data at a glance
- Increasing the speed of decision-making by providing access to real-time and on-demand information
- Identifying errors and inaccuracies in data quickly
What are the types of data visualization?
There are myriad ways of visualizing data, but data design agency The Datalabs Agency breaks data visualization into two basic categories:
- Exploration: Exploration visualizations help you understand what the data is telling you.
- Explanation: Explanation visualizations tell a story to an audience using data .
It is essential to understand which of those two ends a given visualization is intended to achieve. The Data Visualisation Catalogue , a project developed by freelance designer Severino Ribecca, is a library of different information visualization types.
Some of the most common specific types of visualizations include:
2D area: These are typically geospatial visualizations. For example, cartograms use distortions of maps to convey information such as population or travel time. Choropleths use shades or patterns on a map to represent a statistical variable, such as population density by state.
Temporal: These are one-dimensional linear visualizations that have a start and finish time. Examples include a time series, which presents data like website visits by day or month, and Gantt charts, which illustrate project schedules.
Multidimensional: These common visualizations present data with two or more dimensions. Examples include pie charts, histograms, and scatter plots.
Hierarchical: These visualizations show how groups relate to one another. Tree diagrams are an example of a hierarchical visualization that shows how larger groups encompass sets of smaller groups.
Network: Network visualizations show how data sets are related to one another in a network. An example is a node-link diagram, also known as a network graph , which uses nodes and link lines to show how things are interconnected.
What are some data visualization examples?
Tableau has collected what it considers to be 10 of the best data visualization examples . Number one on Tableau’s list is Minard’s map of Napoleon’s march to Moscow, mentioned above. Other prominent examples include:
- A dot map created by English physician John Snow in 1854 to understand the cholera outbreak in London that year. The map used bar graphs on city blocks to indicate cholera deaths at each household in a London neighborhood. The map showed that the worst-affected households were all drawing water from the same well, which eventually led to the insight that wells contaminated by sewage had caused the outbreak.
- An animated age and gender demographic breakdown pyramid created by Pew Research Center as part of its The Next America project , published in 2014. The project is filled with innovative data visualizations. This one shows how population demographics have shifted since the 1950s, with a pyramid of many young people at the bottom and very few older people at the top in the 1950s to a rectangular shape in 2060.
- A collection of four visualizations by Hanah Anderson and Matt Daniels of The Pudding that illustrate gender disparity in pop culture by breaking down the scripts of 2,000 movies and tallying spoken lines of dialogue for male and female characters. The visualizations include a breakdown of Disney movies, the overview of 2,000 scripts, a gradient bar with which users can search for specific movies, and a representation of age biases shown toward male and female roles.
Data visualization tools
Data visualization software encompasses many applications, tools, and scripts. They provide designers with the tools they need to create visual representations of large data sets. Some of the most popular include the following:
Domo: Domo is a cloud software company that specializes in business intelligence tools and data visualization. It focuses on business-user deployed dashboards and ease of use, making it a good choice for small businesses seeking to create custom apps.
Dundas BI: Dundas BI is a BI platform for visualizing data, building and sharing dashboards and reports, and embedding analytics.
Infogram: Infogram is a drag-and-drop visualization tool for creating visualizations for marketing reports, infographics, social media posts, dashboards, and more. Its ease-of-use makes it a good option for non-designers as well.
Klipfolio: Klipfolio is designed to enable users to access and combine data from hundreds of services without writing any code. It leverages pre-built, curated instant metrics and a powerful data modeler, making it a good tool for building custom dashboards.
Looker: Now part of Google Cloud, Looker has a plug-in marketplace with a directory of different types of visualizations and pre-made analytical blocks. It also features a drag-and-drop interface.
Microsoft Power BI: Microsoft Power BI is a business intelligence platform integrated with Microsoft Office. It has an easy-to-use interface for making dashboards and reports. It’s very similar to Excel so Excel skills transfer well. It also has a mobile app.
Qlik: Qlik’s Qlik Sense features an “associative” data engine for investigating data and AI-powered recommendations for visualizations. It is continuing to build out its open architecture and multicloud capabilities.
Sisense: Sisense is an end-to-end analytics platform best known for embedded analytics. Many customers use it in an OEM form.
Tableau: One of the most popular data visualization platforms on the market, Tableau is a platform that supports accessing, preparing, analyzing, and presenting data. It’s available in a variety of options, including a desktop app, server, and hosted online versions, and a free, public version. Tableau has a steep learning curve but is excellent for creating interactive charts.
Data visualization certifications
Data visualization skills are in high demand. Individuals with the right mix of experience and skills can demand high salaries. Certifications can help.
Some of the popular certifications include the following:
- Data Visualization Nanodegree (Udacity)
- Professional Certificate in IBM Data Science (IBM)
- Data Visualization with Python (DataCamp)
- Data Analysis and Visualization with Power BI (Udacity)
- Data Visualization with R (Dataquest)
- Visualize Data with Python (Codecademy)
- Professional Certificate in Data Analytics and Visualization with Excel and R (IBM)
- Data Visualization with Tableau Specialization (UCDavis)
- Data Visualization with R (DataCamp)
- Excel Skills for Data Analytics and Visualization Specialization (Macquarie University)
Data visualization jobs and salaries
Here are some of the most popular job titles related to data visualization and the average salary for each position, according to data from PayScale .
- Data analyst: $64K
- Data scientist: $98K
- Data visualization specialist: $76K
- Senior data analyst: $88K
- Senior data scientist: $112K
- BI analyst: $65K
- Analytics specialist: $71K
- Marketing data analyst: $61K
Related content
Canteen australia’s pursuit of a greater good through tech, new us cio appointments, april 2024, seekr finds the ai computing power it needs in intel’s cloud, is the power of people skills enough to keep gen ai in check, from our editors straight to your inbox, show me more, atos staves off bankruptcy, casts wider net for refinancing.

Inferencing holds the clues to AI puzzles

6 trends defining the enterprise IT market today

CIO Leadership Live Australia with Scott Andrews, Chief Operating Officer, Idea Science

Eaton CIO Katrina Redmond on optimizing AI and digital services

Tech layoffs continue, while AI prevents them from getting new jobs quickly

3 Leadership Tips: Adam Ennamli, Chief Risk Officer, General Bank of Canada

Sponsored Links
- Digital infrastructure plays a big role in business outcomes. Read this IDC report to learn more.
- IDC report: Life-cycle services can help align technology, operational, and business outcomes.
Data presentation: A comprehensive guide
Learn how to create data presentation effectively and communicate your insights in a way that is clear, concise, and engaging.
Raja Bothra
Building presentations

Hey there, fellow data enthusiast!
Welcome to our comprehensive guide on data presentation.
Whether you're an experienced presenter or just starting, this guide will help you present your data like a pro.
We'll dive deep into what data presentation is, why it's crucial, and how to master it. So, let's embark on this data-driven journey together.
What is data presentation?
Data presentation is the art of transforming raw data into a visual format that's easy to understand and interpret. It's like turning numbers and statistics into a captivating story that your audience can quickly grasp. When done right, data presentation can be a game-changer, enabling you to convey complex information effectively.
Why are data presentations important?
Imagine drowning in a sea of numbers and figures. That's how your audience might feel without proper data presentation. Here's why it's essential:
- Clarity : Data presentations make complex information clear and concise.
- Engagement : Visuals, such as charts and graphs, grab your audience's attention.
- Comprehension : Visual data is easier to understand than long, numerical reports.
- Decision-making : Well-presented data aids informed decision-making.
- Impact : It leaves a lasting impression on your audience.
Types of data presentation
Now, let's delve into the diverse array of data presentation methods, each with its own unique strengths and applications. We have three primary types of data presentation, and within these categories, numerous specific visualization techniques can be employed to effectively convey your data.
1. Textual presentation
Textual presentation harnesses the power of words and sentences to elucidate and contextualize your data. This method is commonly used to provide a narrative framework for the data, offering explanations, insights, and the broader implications of your findings. It serves as a foundation for a deeper understanding of the data's significance.
2. Tabular presentation
Tabular presentation employs tables to arrange and structure your data systematically. These tables are invaluable for comparing various data groups or illustrating how data evolves over time. They present information in a neat and organized format, facilitating straightforward comparisons and reference points.
3. Graphical presentation
Graphical presentation harnesses the visual impact of charts and graphs to breathe life into your data. Charts and graphs are powerful tools for spotlighting trends, patterns, and relationships hidden within the data. Let's explore some common graphical presentation methods:
- Bar charts: They are ideal for comparing different categories of data. In this method, each category is represented by a distinct bar, and the height of the bar corresponds to the value it represents. Bar charts provide a clear and intuitive way to discern differences between categories.
- Pie charts: It excel at illustrating the relative proportions of different data categories. Each category is depicted as a slice of the pie, with the size of each slice corresponding to the percentage of the total value it represents. Pie charts are particularly effective for showcasing the distribution of data.
- Line graphs: They are the go-to choice when showcasing how data evolves over time. Each point on the line represents a specific value at a particular time period. This method enables viewers to track trends and fluctuations effortlessly, making it perfect for visualizing data with temporal dimensions.
- Scatter plots: They are the tool of choice when exploring the relationship between two variables. In this method, each point on the plot represents a pair of values for the two variables in question. Scatter plots help identify correlations, outliers, and patterns within data pairs.
The selection of the most suitable data presentation method hinges on the specific dataset and the presentation's objectives. For instance, when comparing sales figures of different products, a bar chart shines in its simplicity and clarity. On the other hand, if your aim is to display how a product's sales have changed over time, a line graph provides the ideal visual narrative.
Additionally, it's crucial to factor in your audience's level of familiarity with data presentations. For a technical audience, more intricate visualization methods may be appropriate. However, when presenting to a general audience, opting for straightforward and easily understandable visuals is often the wisest choice.
In the world of data presentation, choosing the right method is akin to selecting the perfect brush for a masterpiece. Each tool has its place, and understanding when and how to use them is key to crafting compelling and insightful presentations. So, consider your data carefully, align your purpose, and paint a vivid picture that resonates with your audience.
What to include in data presentation
When creating your data presentation, remember these key components:
- Data points : Clearly state the data points you're presenting.
- Comparison : Highlight comparisons and trends in your data.
- Graphical methods : Choose the right chart or graph for your data.
- Infographics : Use visuals like infographics to make information more digestible.
- Numerical values : Include numerical values to support your visuals.
- Qualitative information : Explain the significance of the data.
- Source citation : Always cite your data sources.
How to structure an effective data presentation
Creating a well-structured data presentation is not just important; it's the backbone of a successful presentation. Here's a step-by-step guide to help you craft a compelling and organized presentation that captivates your audience:
1. Know your audience
Understanding your audience is paramount. Consider their needs, interests, and existing knowledge about your topic. Tailor your presentation to their level of understanding, ensuring that it resonates with them on a personal level. Relevance is the key.
2. Have a clear message
Every effective data presentation should convey a clear and concise message. Determine what you want your audience to learn or take away from your presentation, and make sure your message is the guiding light throughout your presentation. Ensure that all your data points align with and support this central message.
3. Tell a compelling story
Human beings are naturally wired to remember stories. Incorporate storytelling techniques into your presentation to make your data more relatable and memorable. Your data can be the backbone of a captivating narrative, whether it's about a trend, a problem, or a solution. Take your audience on a journey through your data.
4. Leverage visuals
Visuals are a powerful tool in data presentation. They make complex information accessible and engaging. Utilize charts, graphs, and images to illustrate your points and enhance the visual appeal of your presentation. Visuals should not just be an accessory; they should be an integral part of your storytelling.
5. Be clear and concise
Avoid jargon or technical language that your audience may not comprehend. Use plain language and explain your data points clearly. Remember, clarity is king. Each piece of information should be easy for your audience to digest.
6. Practice your delivery
Practice makes perfect. Rehearse your presentation multiple times before the actual delivery. This will help you deliver it smoothly and confidently, reducing the chances of stumbling over your words or losing track of your message.
A basic structure for an effective data presentation
Armed with a comprehensive comprehension of how to construct a compelling data presentation, you can now utilize this fundamental template for guidance:
In the introduction, initiate your presentation by introducing both yourself and the topic at hand. Clearly articulate your main message or the fundamental concept you intend to communicate.
Moving on to the body of your presentation, organize your data in a coherent and easily understandable sequence. Employ visuals generously to elucidate your points and weave a narrative that enhances the overall story. Ensure that the arrangement of your data aligns with and reinforces your central message.
As you approach the conclusion, succinctly recapitulate your key points and emphasize your core message once more. Conclude by leaving your audience with a distinct and memorable takeaway, ensuring that your presentation has a lasting impact.
Additional tips for enhancing your data presentation
To take your data presentation to the next level, consider these additional tips:
- Consistent design : Maintain a uniform design throughout your presentation. This not only enhances visual appeal but also aids in seamless comprehension.
- High-quality visuals : Ensure that your visuals are of high quality, easy to read, and directly relevant to your topic.
- Concise text : Avoid overwhelming your slides with excessive text. Focus on the most critical points, using visuals to support and elaborate.
- Anticipate questions : Think ahead about the questions your audience might pose. Be prepared with well-thought-out answers to foster productive discussions.
By following these guidelines, you can structure an effective data presentation that not only informs but also engages and inspires your audience. Remember, a well-structured presentation is the bridge that connects your data to your audience's understanding and appreciation.
Do’s and don'ts on a data presentation
- Use visuals : Incorporate charts and graphs to enhance understanding.
- Keep it simple : Avoid clutter and complexity.
- Highlight key points : Emphasize crucial data.
- Engage the audience : Encourage questions and discussions.
- Practice : Rehearse your presentation.
Don'ts:
- Overload with data : Less is often more; don't overwhelm your audience.
- Fit Unrelated data : Stay on topic; don't include irrelevant information.
- Neglect the audience : Ensure your presentation suits your audience's level of expertise.
- Read word-for-word : Avoid reading directly from slides.
- Lose focus : Stick to your presentation's purpose.
Summarizing key takeaways
- Definition : Data presentation is the art of visualizing complex data for better understanding.
- Importance : Data presentations enhance clarity, engage the audience, aid decision-making, and leave a lasting impact.
- Types : Textual, Tabular, and Graphical presentations offer various ways to present data.
- Choosing methods : Select the right method based on data, audience, and purpose.
- Components : Include data points, comparisons, visuals, infographics, numerical values, and source citations.
- Structure : Know your audience, have a clear message, tell a compelling story, use visuals, be concise, and practice.
- Do's and don'ts : Do use visuals, keep it simple, highlight key points, engage the audience, and practice. Don't overload with data, include unrelated information, neglect the audience's expertise, read word-for-word, or lose focus.
1. What is data presentation, and why is it important in 2023?
Data presentation is the process of visually representing data sets to convey information effectively to an audience. In an era where the amount of data generated is vast, visually presenting data using methods such as diagrams, graphs, and charts has become crucial. By simplifying complex data sets, presentation of the data may helps your audience quickly grasp much information without drowning in a sea of chart's, analytics, facts and figures.
2. What are some common methods of data presentation?
There are various methods of data presentation, including graphs and charts, histograms, and cumulative frequency polygons. Each method has its strengths and is often used depending on the type of data you're using and the message you want to convey. For instance, if you want to show data over time, try using a line graph. If you're presenting geographical data, consider to use a heat map.
3. How can I ensure that my data presentation is clear and readable?
To ensure that your data presentation is clear and readable, pay attention to the design and labeling of your charts. Don't forget to label the axes appropriately, as they are critical for understanding the values they represent. Don't fit all the information in one slide or in a single paragraph. Presentation software like Prezent and PowerPoint can help you simplify your vertical axis, charts and tables, making them much easier to understand.
4. What are some common mistakes presenters make when presenting data?
One common mistake is trying to fit too much data into a single chart, which can distort the information and confuse the audience. Another mistake is not considering the needs of the audience. Remember that your audience won't have the same level of familiarity with the data as you do, so it's essential to present the data effectively and respond to questions during a Q&A session.
5. How can I use data visualization to present important data effectively on platforms like LinkedIn?
When presenting data on platforms like LinkedIn, consider using eye-catching visuals like bar graphs or charts. Use concise captions and e.g., examples to highlight the single most important information in your data report. Visuals, such as graphs and tables, can help you stand out in the sea of textual content, making your data presentation more engaging and shareable among your LinkedIn connections.
Create your data presentation with prezent
Prezent can be a valuable tool for creating data presentations. Here's how Prezent can help you in this regard:
- Time savings : Prezent saves up to 70% of presentation creation time, allowing you to focus on data analysis and insights.
- On-brand consistency : Ensure 100% brand alignment with Prezent's brand-approved designs for professional-looking data presentations.
- Effortless collaboration : Real-time sharing and collaboration features make it easy for teams to work together on data presentations.
- Data storytelling : Choose from 50+ storylines to effectively communicate data insights and engage your audience.
- Personalization : Create tailored data presentations that resonate with your audience's preferences, enhancing the impact of your data.
In summary, Prezent streamlines the process of creating data presentations by offering time-saving features, ensuring brand consistency, promoting collaboration, and providing tools for effective data storytelling. Whether you need to present data to clients, stakeholders, or within your organization, Prezent can significantly enhance your presentation-making process.
So, go ahead, present your data with confidence, and watch your audience be wowed by your expertise.
Thank you for joining us on this data-driven journey. Stay tuned for more insights, and remember, data presentation is your ticket to making numbers come alive!
Sign up for our free trial or book a demo !
Get the latest from Prezent community
Join thousands of subscribers who receive our best practices on communication, storytelling, presentation design, and more. New tips weekly. (No spam, we promise!)

Guide On Graphical Representation of Data – Types, Importance, Rules, Principles And Advantages
What are Graphs and Graphical Representation?
Graphs, in the context of data visualization, are visual representations of data using various graphical elements such as charts, graphs, and diagrams. Graphical representation of data , often referred to as graphical presentation or simply graphs which plays a crucial role in conveying information effectively.
Principles of Graphical Representation
Effective graphical representation follows certain fundamental principles that ensure clarity, accuracy, and usability:Clarity : The primary goal of any graph is to convey information clearly and concisely. Graphs should be designed in a way that allows the audience to quickly grasp the key points without confusion.
- Simplicity: Simplicity is key to effective data visualization. Extraneous details and unnecessary complexity should be avoided to prevent confusion and distraction.
- Relevance: Include only relevant information that contributes to the understanding of the data. Irrelevant or redundant elements can clutter the graph.
- Visualization: Select a graph type that is appropriate for the supplied data. Different graph formats, like bar charts, line graphs, and scatter plots, are appropriate for various sorts of data and relationships.
Rules for Graphical Representation of Data
Creating effective graphical representations of data requires adherence to certain rules:
- Select the Right Graph: Choosing the appropriate type of graph is essential. For example, bar charts are suitable for comparing categories, while line charts are better for showing trends over time.
- Label Axes Clearly: Axis labels should be descriptive and include units of measurement where applicable. Clear labeling ensures the audience understands the data’s context.
- Use Appropriate Colors: Colors can enhance understanding but should be used judiciously. Avoid overly complex color schemes and ensure that color choices are accessible to all viewers.
- Avoid Misleading Scaling: Scale axes appropriately to prevent exaggeration or distortion of data. Misleading scaling can lead to incorrect interpretations.
- Include Data Sources: Always provide the source of your data. This enhances transparency and credibility.
Importance of Graphical Representation of Data
Graphical representation of data in statistics is of paramount importance for several reasons:
- Enhances Understanding: Graphs simplify complex data, making it more accessible and understandable to a broad audience, regardless of their statistical expertise.
- Helps Decision-Making: Visual representations of data enable informed decision-making. Decision-makers can easily grasp trends and insights, leading to better choices.
- Engages the Audience: Graphs capture the audience’s attention more effectively than raw data. This engagement is particularly valuable when presenting findings or reports.
- Universal Language: Graphs serve as a universal language that transcends linguistic barriers. They can convey information to a global audience without the need for translation.
Advantages of Graphical Representation
The advantages of graphical representation of data extend to various aspects of communication and analysis:
- Clarity: Data is presented visually, improving clarity and reducing the likelihood of misinterpretation.
- Efficiency: Graphs enable the quick absorption of information. Key insights can be found in seconds, saving time and effort.
- Memorability: Visuals are more memorable than raw data. Audiences are more likely to retain information presented graphically.
- Problem-Solving: Graphs help in identifying and solving problems by revealing trends, correlations, and outliers that may require further investigation.
Use of Graphical Representations
Graphical representations find applications in a multitude of fields:
- Business: In the business world, graphs are used to illustrate financial data, track performance metrics, and present market trends. They are invaluable tools for strategic decision-making.
- Science: Scientists employ graphs to visualize experimental results, depict scientific phenomena, and communicate research findings to both colleagues and the general public.
- Education: Educators utilize graphs to teach students about data analysis, statistics, and scientific concepts. Graphs make learning more engaging and memorable.
- Journalism: Journalists rely on graphs to support their stories with data-driven evidence. Graphs make news articles more informative and impactful.
Types of Graphical Representation
There exists a diverse array of graphical representations, each suited to different data types and purposes. Common types include:
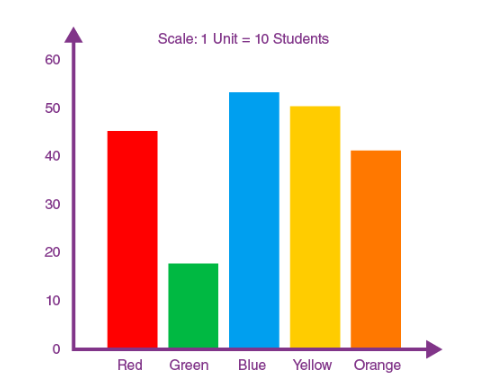
1.Bar Charts:
Used to compare categories or discrete data points, often side by side.
2. Line Charts:
Ideal for showing trends and changes over time, such as stock market performance or temperature fluctuations.
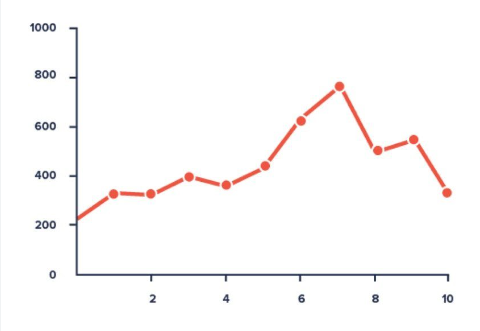
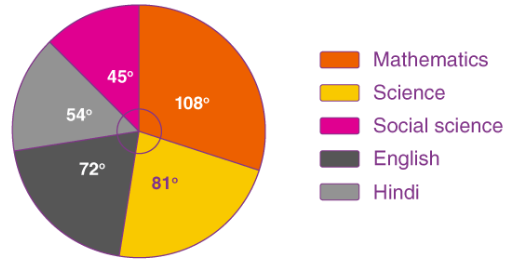
3. Pie Charts:
Display parts of a whole, useful for illustrating proportions or percentages.
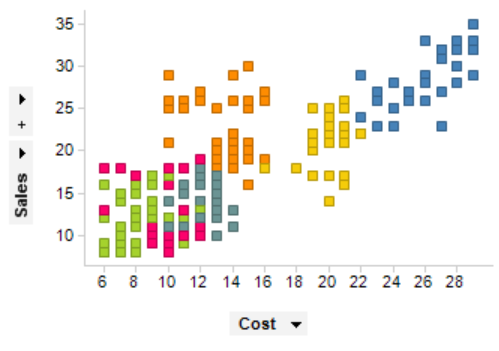
4. Scatter Plots:
Reveal relationships between two variables and help identify correlations.
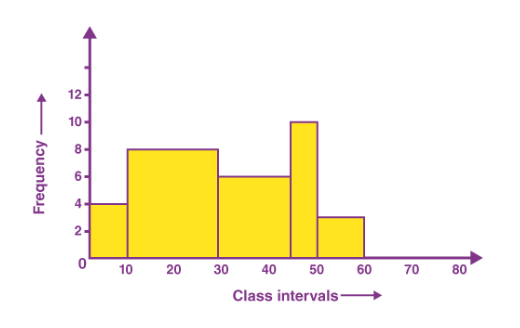
5. Histograms:
Depict the distribution of data, especially in the context of continuous variables.
In conclusion, the graphical representation of data is an indispensable tool for simplifying complex information, aiding in decision-making, and enhancing communication across diverse fields. By following the principles and rules of effective data visualization, individuals and organizations can harness the power of graphs to convey their messages, support their arguments, and drive informed actions.
Download PPT of Graphical Representation
Video On Graphical Representation
FAQs on Graphical Representation of Data
What is the purpose of graphical representation.
Graphical representation serves the purpose of simplifying complex data, making it more accessible and understandable through visual means.
Why are graphs and diagrams important?
Graphs and diagrams are crucial because they provide visual clarity, aiding in the comprehension and retention of information.
How do graphs help learning?
Graphs engage learners by presenting information visually, which enhances understanding and retention, particularly in educational settings.
Who uses graphs?
Professionals in various fields, including scientists, analysts, educators, and business leaders, use graphs to convey data effectively and support decision-making.
Where are graphs used in real life?
Graphs are used in real-life scenarios such as business reports, scientific research, news articles, and educational materials to make data more accessible and meaningful.
Why are graphs important in business?
In business, graphs are vital for analyzing financial data, tracking performance metrics, and making informed decisions, contributing to success.
Leave a comment
Cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Related Posts

Best Google AdWords Consultants in India...
What is a Google Ads Consultant? A Google Ads Consultant is an expert who specializes in delivering expertise and advice on Google Ads, which is Google’s online advertising medium. Google Ads permits companies to develop and run ads that are visible on Google’s search engine and other Google platforms. The function of a Google Ads […]

Best PPC Consultants in India –...
What Is a PPC Consultant? A PPC consultant or a pay per click consultant is an expert who specializes in handling and optimizing PPC advertisement drives for companies. PPC is a digital marketing model where advertisers pay a price each time their ad is clicked. Standard PPC mediums include Bing Ads, Google Ads, and social media advertisement platforms like […]

Top 20 Generic Digital Marketing Interview...
1. What is Digital Marketing? Digital marketing is also known as online marketing which means promoting and selling products or services to potential customers using the internet and online platforms. It includes email, social media, and web-based advertising, but also text and multimedia messages as a marketing channel. 2. What are the types of Digital […]

Best Social Media Consultants in India...
What Is a Social Media Consultant? A social media advisor is a specialist who delivers direction, recommendation, and assistance linked to the usage of social media for people, companies, or associations. Their prime objective is to support customers effectively by employing social media platforms to gain specific objectives, such as improving brand awareness, entertaining target […]

Gaurav Mittal
Had a great time spent with some awesome learning at The Digital Education Institute. It really helped me to build my career and i am thankful to the institute for making me what i am today.
Company where our students are working

Enroll Now for 2 Hour Free Digital Marketing Class
Lorem Ipsum is simply dummy text of the printing and typesetting industry
Lorem Ipsum is simply dummy text of the printing and typesetting industry . Lorem Ipsum is simply dummy text of the printing and typesetting industry
We use essential cookies to make Venngage work. By clicking “Accept All Cookies”, you agree to the storing of cookies on your device to enhance site navigation, analyze site usage, and assist in our marketing efforts.
Manage Cookies
Cookies and similar technologies collect certain information about how you’re using our website. Some of them are essential, and without them you wouldn’t be able to use Venngage. But others are optional, and you get to choose whether we use them or not.
Strictly Necessary Cookies
These cookies are always on, as they’re essential for making Venngage work, and making it safe. Without these cookies, services you’ve asked for can’t be provided.
Show cookie providers
- Google Login
Functionality Cookies
These cookies help us provide enhanced functionality and personalisation, and remember your settings. They may be set by us or by third party providers.
Performance Cookies
These cookies help us analyze how many people are using Venngage, where they come from and how they're using it. If you opt out of these cookies, we can’t get feedback to make Venngage better for you and all our users.
- Google Analytics
Targeting Cookies
These cookies are set by our advertising partners to track your activity and show you relevant Venngage ads on other sites as you browse the internet.
- Google Tag Manager
Infographics
- Daily Infographics
- Graphic Design
- Graphs and Charts
- Data Visualization
- Human Resources
- Training and Development
- Beginner Guides
Blog Graphic Design
What is Data Visualization? (Definition, Examples, Best Practices)
By Midori Nediger , Jun 05, 2020
Words don’t always paint the clearest picture. Raw data doesn’t always tell the most compelling story.
The human mind is very receptive to visual information. That’s why data visualization is a powerful tool for communication.
But if “data visualization” sounds tricky and technical don’t worry—it doesn’t have to be.
This guide will explain the fundamentals of data visualization in a way that anyone can understand. Included are a ton of examples of different types of data visualizations and when to use them for your reports, presentations, marketing, and more.
Table of Contents
- What is data visualization?
What is data visualization used for?
Types of data visualizations.
- How to present data visually (for businesses, marketers, nonprofits, and education)
- Data visualization examples
Data visualization is used everywhere.
Businesses use data visualization for reporting, forecasting, and marketing.
CREATE THIS REPORT TEMPLATE
Nonprofits use data visualizations to put stories and faces to numbers.

Source: Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation
Scholars and scientists use data visualization to illustrate concepts and reinforce their arguments.
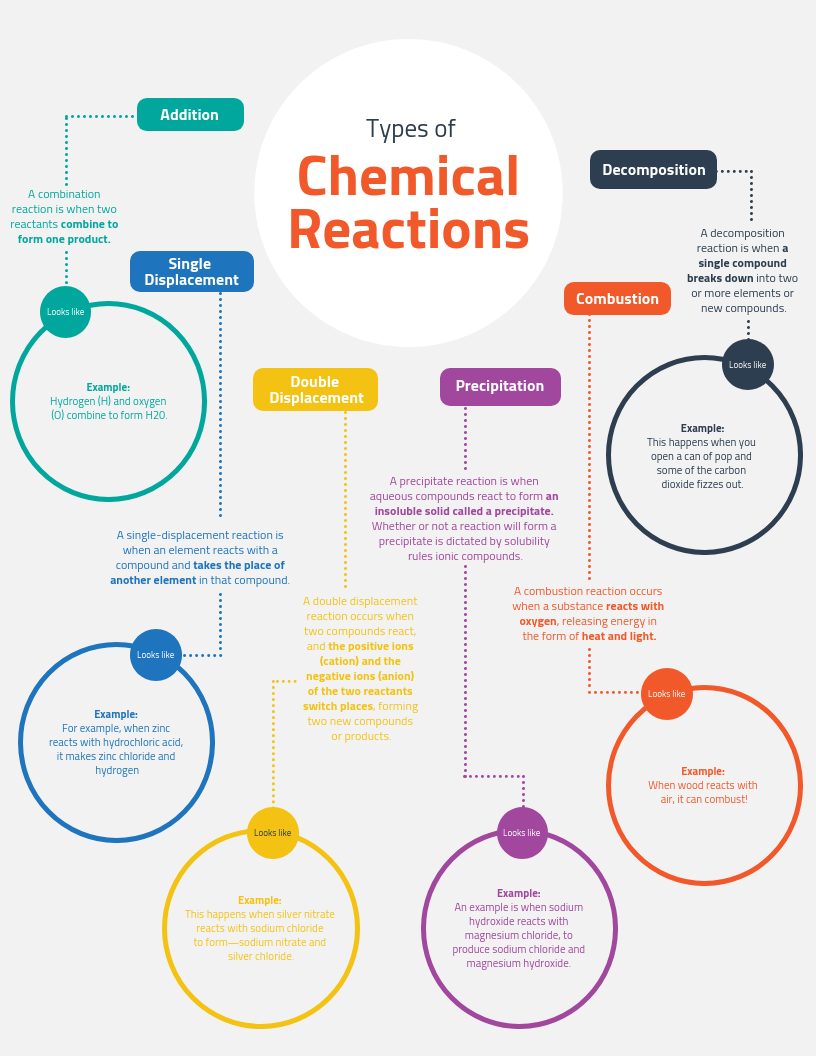
CREATE THIS MIND MAP TEMPLATE
Reporters use data visualization to show trends and contextualize stories.
While data visualizations can make your work more professional, they can also be a lot of fun.
What is data visualization? A simple definition of data visualization:
Data visualization is the visual presentation of data or information. The goal of data visualization is to communicate data or information clearly and effectively to readers. Typically, data is visualized in the form of a chart , infographic , diagram or map.
The field of data visualization combines both art and data science. While a data visualization can be creative and pleasing to look at, it should also be functional in its visual communication of the data.
Data, especially a lot of data, can be difficult to wrap your head around. Data visualization can help both you and your audience interpret and understand data.
Data visualizations often use elements of visual storytelling to communicate a message supported by the data.
There are many situations where you would want to present data visually.
Data visualization can be used for:
- Making data engaging and easily digestible
- Identifying trends and outliers within a set of data
- Telling a story found within the data
- Reinforcing an argument or opinion
- Highlighting the important parts of a set of data
Let’s look at some examples for each use case.
1. Make data digestible and easy to understand
Often, a large set of numbers can make us go cross-eyed. It can be difficult to find the significance behind rows of data.
Data visualization allows us to frame the data differently by using illustrations, charts, descriptive text, and engaging design. Visualization also allows us to group and organize data based on categories and themes, which can make it easier to break down into understandable chunks.
Related : How to Use Data Visualization in Your Infographics
For example, this infographic breaks down the concept of neuroplasticity in an approachable way:
Source: NICABM
The same goes for complex, specialized concepts. It can often be difficult to break down the information in a way that non-specialists will understand. But an infographic that organizes the information, with visuals, can demystify concepts for novice readers.

CREATE THIS INFOGRAPHIC TEMPLATE
NEW! Introducing: Marketing Statistics Report 2022
It’s 2022 already. Marketers, are you still using data from pre-COVID times?
Don’t make decisions based on outdated data that no longer applies. It’s time you keep yourself informed of the latest marketing statistics and trends during the past two years, and learn how COVID-19 has affected marketing efforts in different industries — with this FREE marketing statistics report put together by Venngage and HubSpot .
The report uses data gathered from over 100,000 customers of HubSpot CRM. In addition to that, you’ll also know about the trends in using visuals in content marketing and the impacts of the pandemic on visual content, from 200+ marketers all over the world interviewed by Venngage.

GET YOUR FREE COPY
2. Identify trends and outliers
If you were to sift through raw data manually, it could take ages to notice patterns, trends or outlying data. But by using data visualization tools like charts, you can sort through a lot of data quickly.
Even better, charts enable you to pick up on trends a lot quicker than you would sifting through numbers.
For example, here’s a simple chart generated by Google Search Console that shows the change in Google searches for “toilet paper”. As you can see, in March 2020 there was a huge increase in searches for toilet paper:
Source: How to Use SEO Data to Fuel Your Content Marketing Strategy in 2020
This chart shows an outlier in the general trend for toilet paper-related Google searches. The reason for the outlier? The outbreak of COVID-19 in North America. With a simple data visualization, we’ve been able to highlight an outlier and hint at a story behind the data.
Uploading your data into charts, to create these kinds of visuals is easy. While working on your design in the editor, select a chart from the left panel. Open the chart and find the green IMPORT button under the DATA tab. Then upload the CSV file and your chart automatically visualizes the information.
3. Tell a story within the data
Numbers on their own don’t tend to evoke an emotional response. But data visualization can tell a story that gives significance to the data.
Designers use techniques like color theory , illustrations, design style and visual cues to appeal to the emotions of readers, put faces to numbers, and introduce a narrative to the data.
Related : How to Tell a Story With Data (A Guide for Beginners)
For example, here’s an infographic created by World Vision. In the infographics, numbers are visualized using illustrations of cups. While comparing numbers might impress readers, reinforcing those numbers with illustrations helps to make an even greater impact.

Source: World Vision
Meanwhile, this infographic uses data to draw attention to an often overlooked issue:
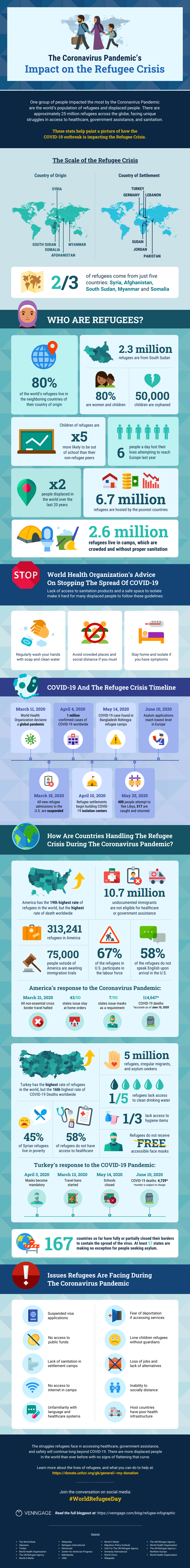
Read More: The Coronavirus Pandemic and the Refugee Crisis
4. Reinforce an argument or opinion
When it comes to convincing people your opinion is right, they often have to see it to believe it. An effective infographic or chart can make your argument more robust and reinforce your creativity.
For example, you can use a comparison infographic to compare sides of an argument, different theories, product/service options, pros and cons, and more. Especially if you’re blending data types.

5. Highlight an important point in a set of data
Sometimes we use data visualizations to make it easier for readers to explore the data and come to their own conclusions. But often, we use data visualizations to tell a story, make a particular argument, or encourage readers to come to a specific conclusion.
Designers use visual cues to direct the eye to different places on a page. Visual cues are shapes, symbols, and colors that point to a specific part of the data visualization, or that make a specific part stand out.
For example, in this data visualization, contrasting colors are used to emphasize the difference in the amount of waste sent to landfills versus recycled waste:
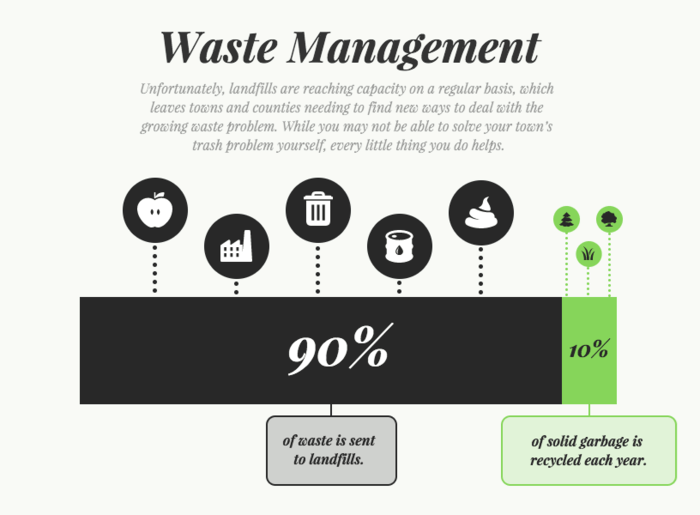
Here’s another example. This time, a red circle and an arrow are used to highlight points on the chart where the numbers show a drop:
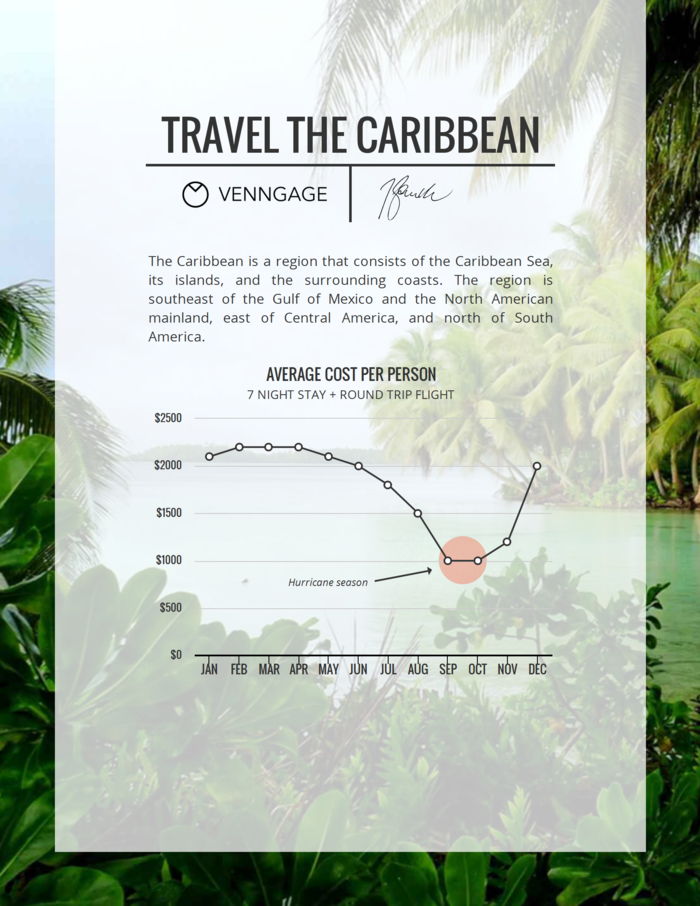
Highlighting specific data points helps your data visualization tell a compelling story.
6. Make books, blog posts, reports and videos more engaging
At Venngage, we use data visualization to make our blog posts more engaging for readers. When we write a blog post or share a post on social media, we like to summarize key points from our content using infographics.
The added benefit of creating engaging visuals like infographics is that it has enabled our site to be featured in publications like The Wall Street Journal , Mashable , Business Insider , The Huffington Post and more.
That’s because data visualizations are different from a lot of other types of content people consume on a daily basis. They make your brain work. They combine concrete facts and numbers with impactful visual elements. They make complex concepts easier to grasp.
Here’s an example of an infographic we made that got a lot of media buzz:
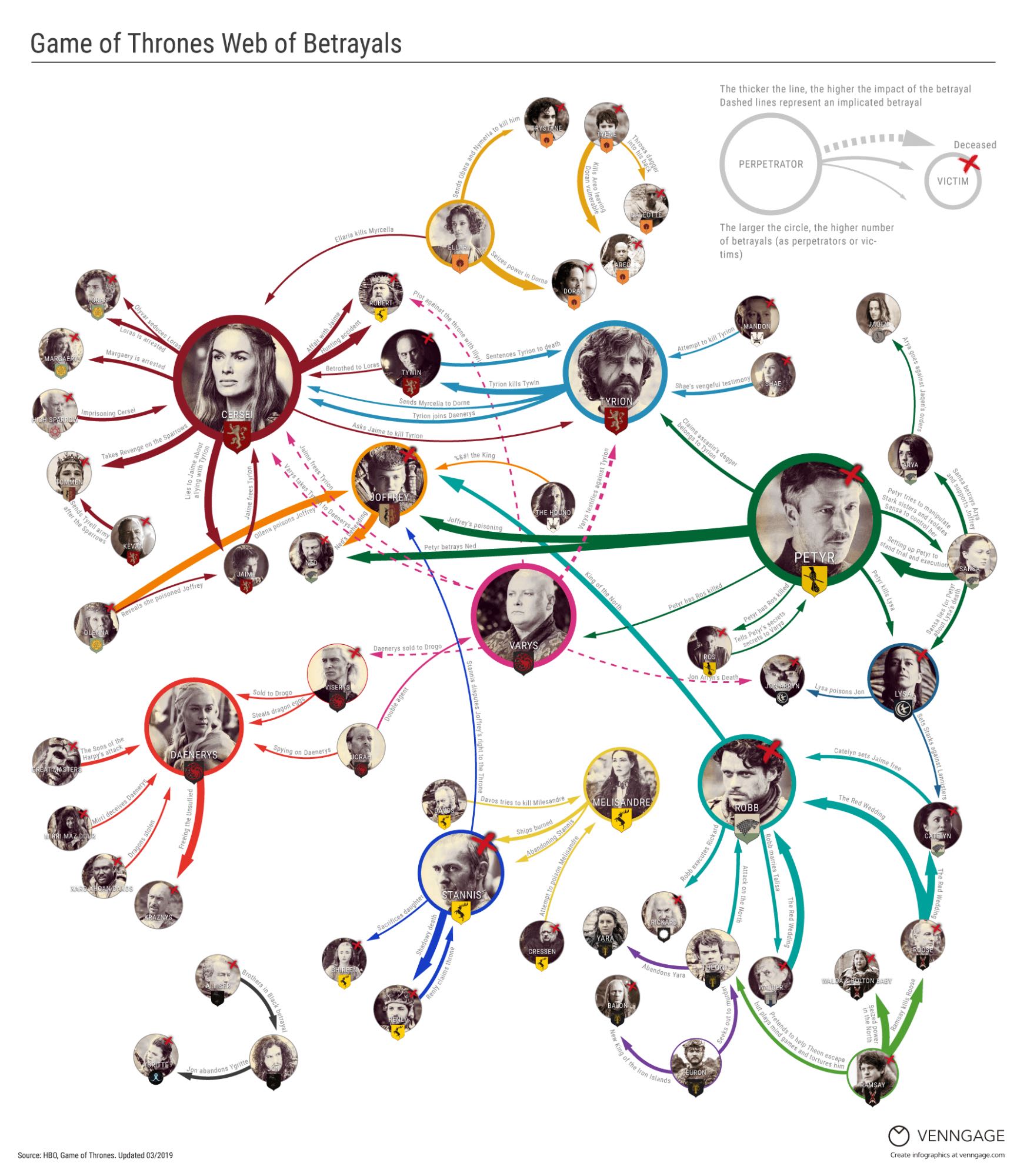
Read the Blog Post: Every Betrayal Ever in Game of Thrones
We created this infographic because a bunch of people on our team are big Game of Thrones fans and we wanted to create a visual that would help other fans follow the show. Because we approached a topic that a lot of people cared about in an original way, the infographic got picked up by a bunch of media sites.
Whether you’re a website looking to promote your content, a journalist looking for an original angle, or a creative building your portfolio, data visualizations can be an effective way to get people’s attention.
Data visualizations can come in many different forms. People are always coming up with new and creative ways to present data visually.
Generally speaking, data visualizations usually fall under these main categories:
An infographic is a collection of imagery, charts, and minimal text that gives an easy-to-understand overview of a topic.
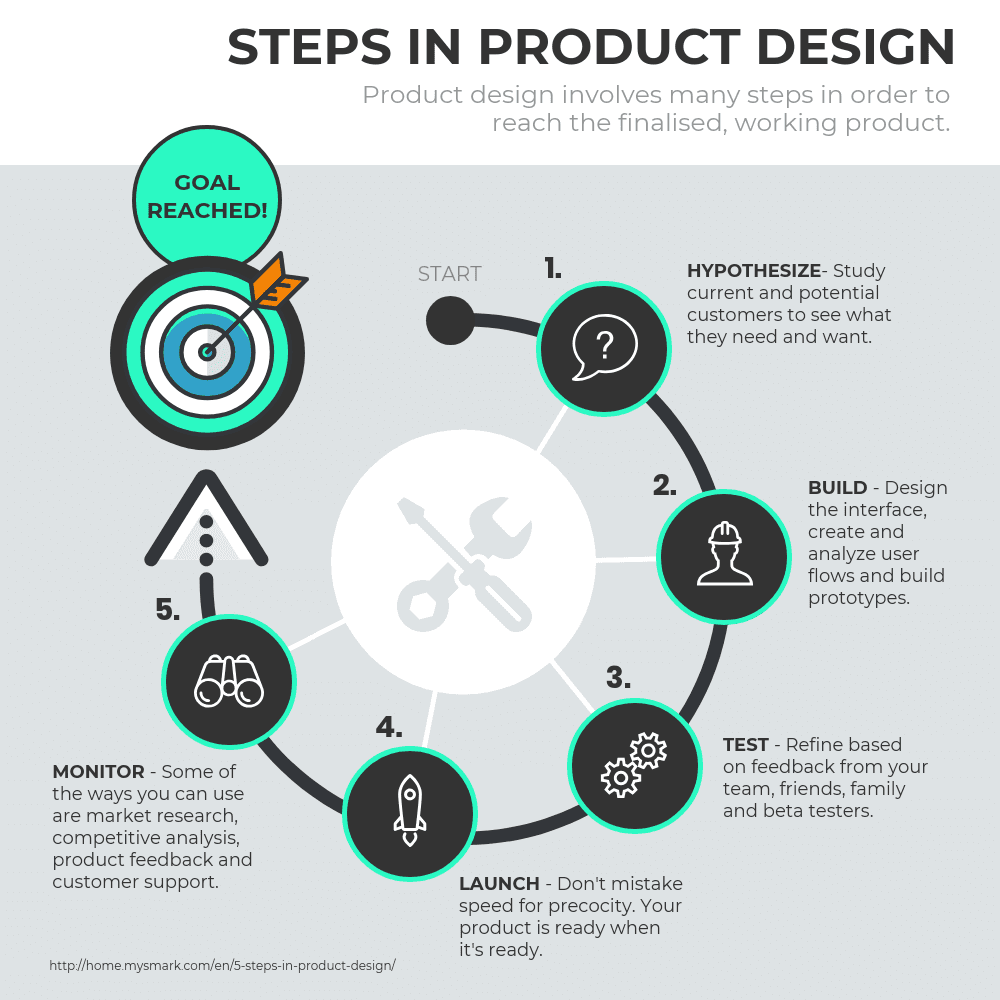
While infographics can take many forms, they can typically be categorized by these infographic types:
- Statistical infographics
- Informational infographics
- Timeline infographics
- Process infographics
- Geographic infographics
- Comparison infographics
- Hierarchical infographics
- List infographics
- Resume infographics
Read More: What is an Infographic? Examples, Templates & Design Tips
Charts
In the simplest terms, a chart is a graphical representation of data. Charts use visual symbols like line, bars, dots, slices, and icons to represent data points.
Some of the most common types of charts are:
- Bar graphs /charts
- Line charts
- Bubble charts
- Stacked bar charts
- Word clouds
- Pictographs
- Area charts
- Scatter plot charts
- Multi-series charts
The question that inevitably follows is: what type of chart should I use to visualize my data? Does it matter?
Short answer: yes, it matters. Choosing a type of chart that doesn’t work with your data can end up misrepresenting and skewing your data.
For example: if you’ve been in the data viz biz for a while, then you may have heard some of the controversy surrounding pie charts. A rookie mistake that people often make is using a pie chart when a bar chart would work better.
Pie charts display portions of a whole. A pie chart works when you want to compare proportions that are substantially different. Like this:
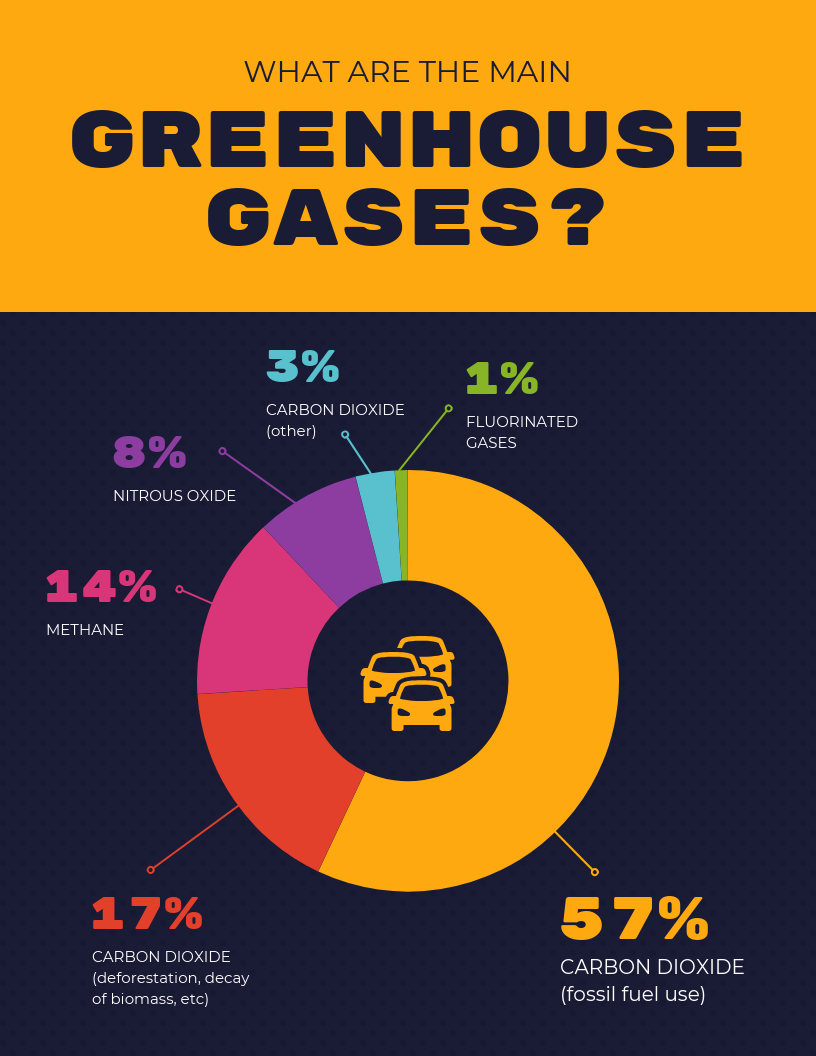
CREATE THIS CHART TEMPLATE
But when your proportions are similar, a pie chart can make it difficult to tell which slice is bigger than the other. That’s why, in most other cases, a bar chart is a safer bet.
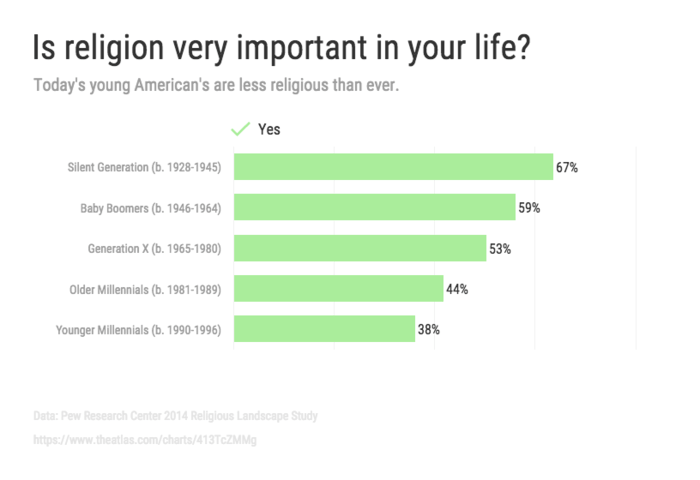
Here is a cheat sheet to help you pick the right type of chart for your data:

Want to make better charts? Make engaging charts with Venngage’s Chart Maker .
Related : How to Choose the Best Types of Charts For Your Data
Similar to a chart, a diagram is a visual representation of information. Diagrams can be both two-dimensional and three-dimensional.
Some of the most common types of diagrams are:
- Venn diagrams
- Tree diagrams
- SWOT analysis
- Fishbone diagrams
- Use case diagrams
Diagrams are used for mapping out processes, helping with decision making, identifying root causes, connecting ideas, and planning out projects.
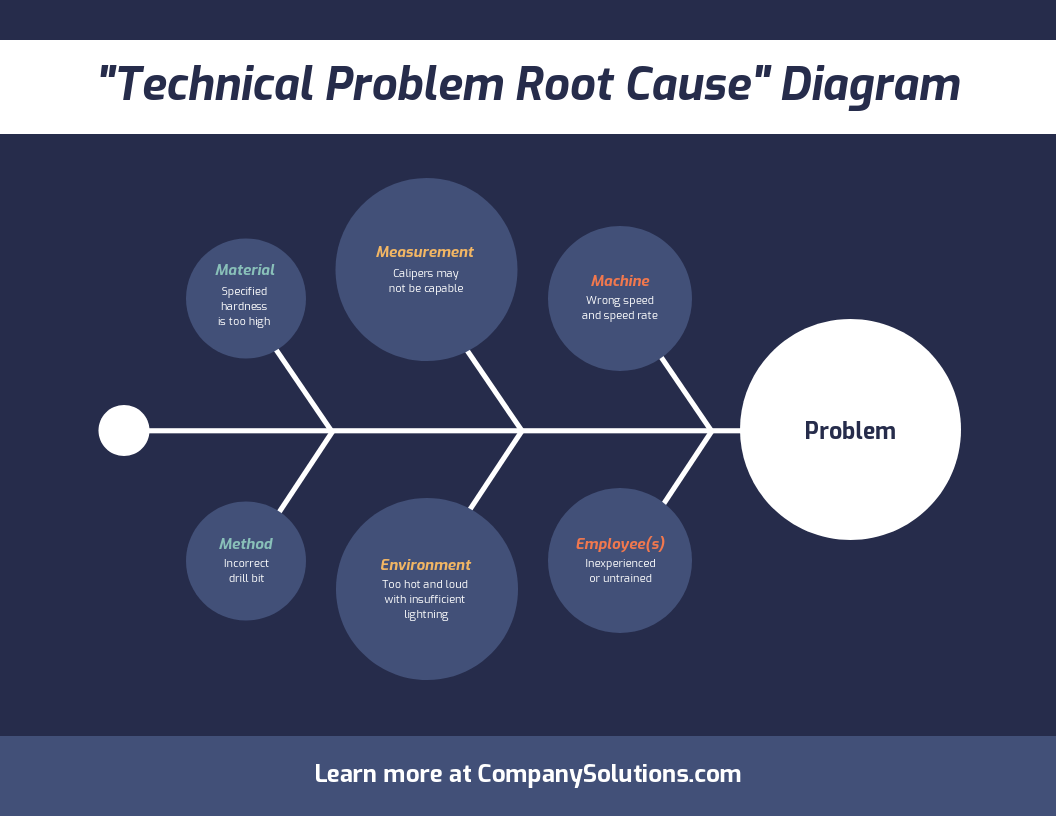
CREATE THIS DIAGRAM TEMPLATE
Want to make a diagram ? Create a Venn diagram and other visuals using our free Venn Diagram Maker .
A map is a visual representation of an area of land. Maps show physical features of land like regions, landscapes, cities, roads, and bodies of water.
Source: National Geographic
A common type of map you have probably come across in your travels is a choropleth map . Choropleth maps use different shades and colors to indicate average quantities.
For example, a population density map uses varying shades to show the difference in population numbers from region to region:
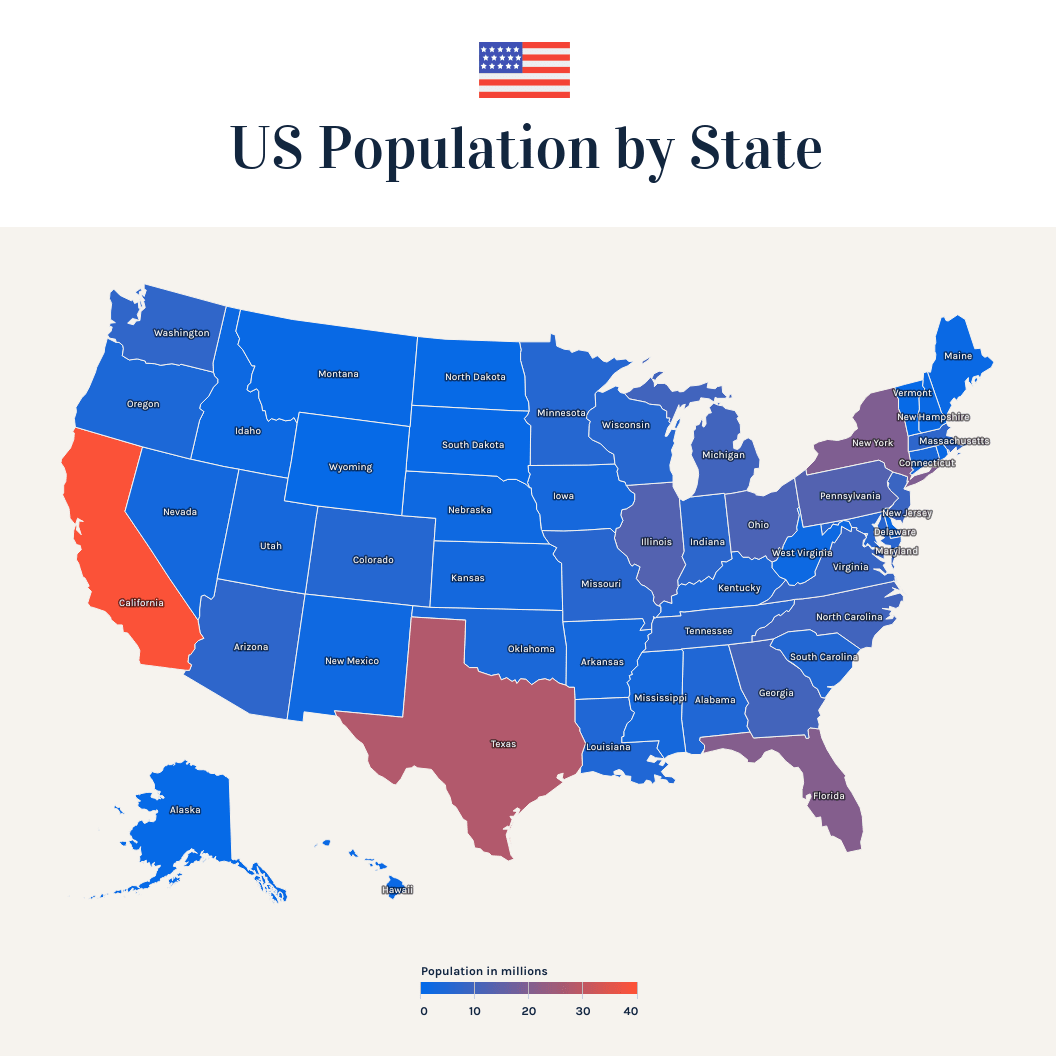
Create your own map for free with Venngage’s Map Maker .
How to present data visually (data visualization best practices)
While good data visualization will communicate data or information clearly and effectively, bad data visualization will do the opposite. Here are some practical tips for how businesses and organizations can use data visualization to communicate information more effectively.
Not a designer? No problem. Venngage’s Graph Maker will help you create better graphs in minutes.
1. Avoid distorting the data
This may be the most important point in this whole blog post. While data visualizations are an opportunity to show off your creative design chops, function should never be sacrificed for fashion.
The chart styles, colors, shapes, and sizing you use all play a role in how the data is interpreted. If you want to present your data accurately and ethically, then you need to take care to ensure that your data visualization does not present the data falsely.
There are a number of different ways data can be distorted in a chart. Some common ways data can be distorted are:
- Making the baselines something other than 0 to make numbers seem bigger or smaller than they are – this is called “truncating” a graph
- Compressing or expanding the scale of the Y-axis to make a line or bar seem bigger or smaller than it should be
- Cherry picking data so that only the data points you want to include are on a graph (i.e. only telling part of the story)
- Using the wrong type of chart, graph or diagram for your data
- Going against standard, expected data visualization conventions
Because people use data visualizations to reinforce their opinions, you should always read data visualizations with a critical eye. Often enough, writers may be using data visualization to skew the data in a way that supports their opinions, but that may not be entirely truthful.
Read More: 5 Ways Writers Use Graphs To Mislead You
Want to create an engaging line graph? Use Venngage’s Line Graph Maker to create your own in minutes.
2. Avoid cluttering up your design with “chartjunk”
When it comes to best practices for data visualization, we should turn to one of the grandfather’s of data visualization: Edward Tufte. He coined the term “ chartjunk ”, which refers to the use of unnecessary or confusing design elements that skews or obscures the data in a chart.
Here’s an example of a data visualization that suffers from chartjunk:
Source: ExcelUser
In this example, the image of the coin is distracting for readers trying to interpret the data. Note how the fonts are tiny – almost unreadable. Mistakes like this are common when a designers tries to put style before function.
Read More : The Worst Infographics of 2020 (With Lessons for 2021)
3. Tell a story with your data
Data visualizations like infographics give you the space to combine data and narrative structure in one page. Visuals like icons and bold fonts let you highlight important statistics and facts.
For example, you could customize this data visualization infographic template to show the benefit of using your product or service (and post it on social media):
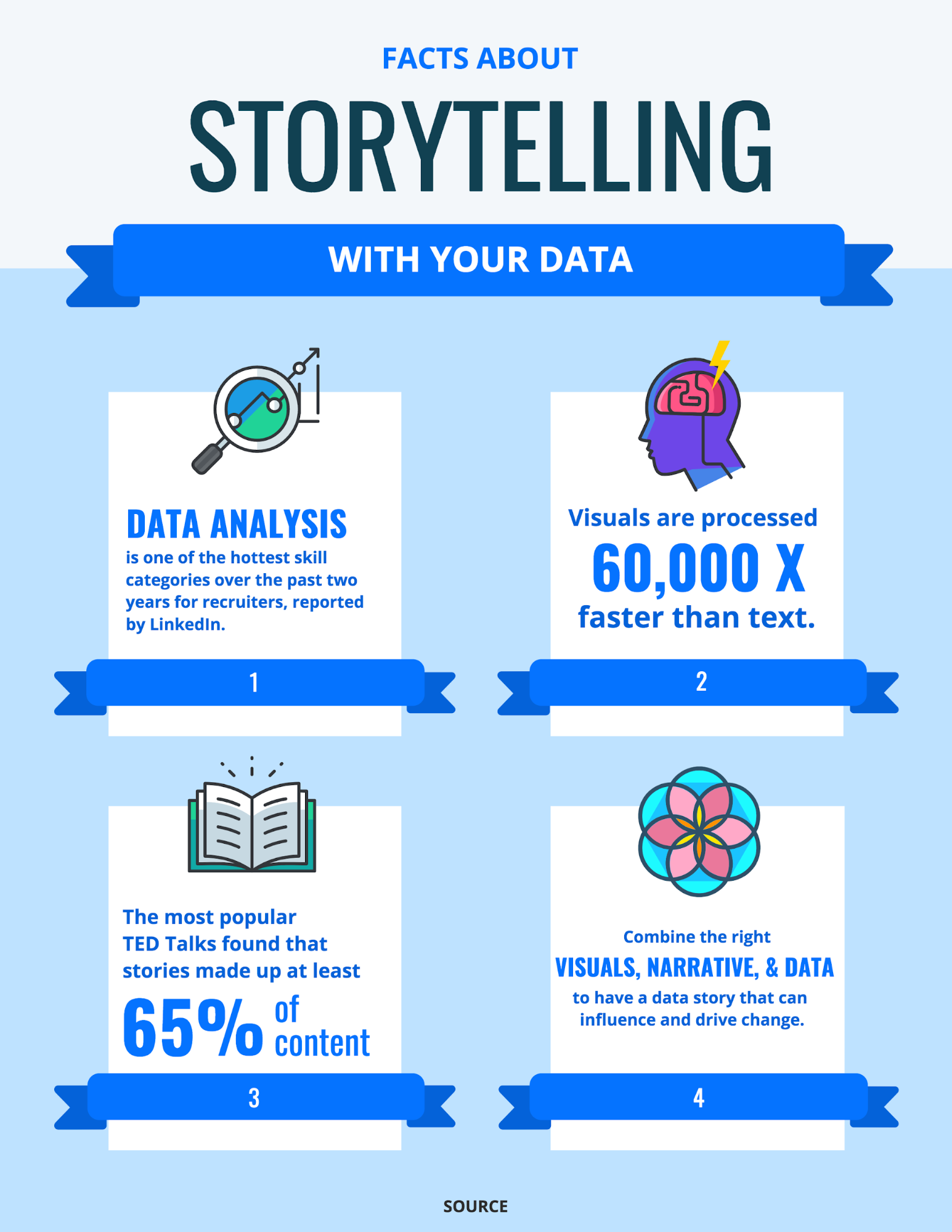
USE THIS TEMPLATE
This data visualization relies heavily on text and icons to tell the story of its data:
This type of infographic is perfect for those who aren’t as comfortable with charts and graphs. It’s also a great way to showcase original research, get social shares and build brand awareness.
4. Combine different types of data visualizations
While you may choose to keep your data visualization simple, combining multiple types of charts and diagrams can help tell a more rounded story.
Don’t be afraid to combine charts, pictograms and diagrams into one infographic. The result will be a data visualization infographic that is engaging and rich in visual data.

Design Tip: This data visualization infographic would be perfect for nonprofits to customize and include in an email newsletter to increase awareness (and donations).
Or take this data visualization that also combines multiple types of charts, pictograms, and images to engage readers. It could work well in a presentation or report on customer research, customer service scores, quarterly performance and much more:
Design Tip: This infographic could work well in a presentation or report on customer research, customer service scores, quarterly performance and much more.
Make your own bar graph in minutes with our free Bar Graph Maker .
5. Use icons to emphasize important points
Icons are perfect for attracting the eye when scanning a page. (Remember: use visual cues!)
If there are specific data points that you want readers to pay attention to, placing an icon beside it will make it more noticeable:
Design Tip: This infographic template would work well on social media to encourage shares and brand awareness.
You can also pair icons with headers to indicate the beginning of a new section.
Meanwhile, this infographic uses icons like bullet points to emphasize and illustrate important points.
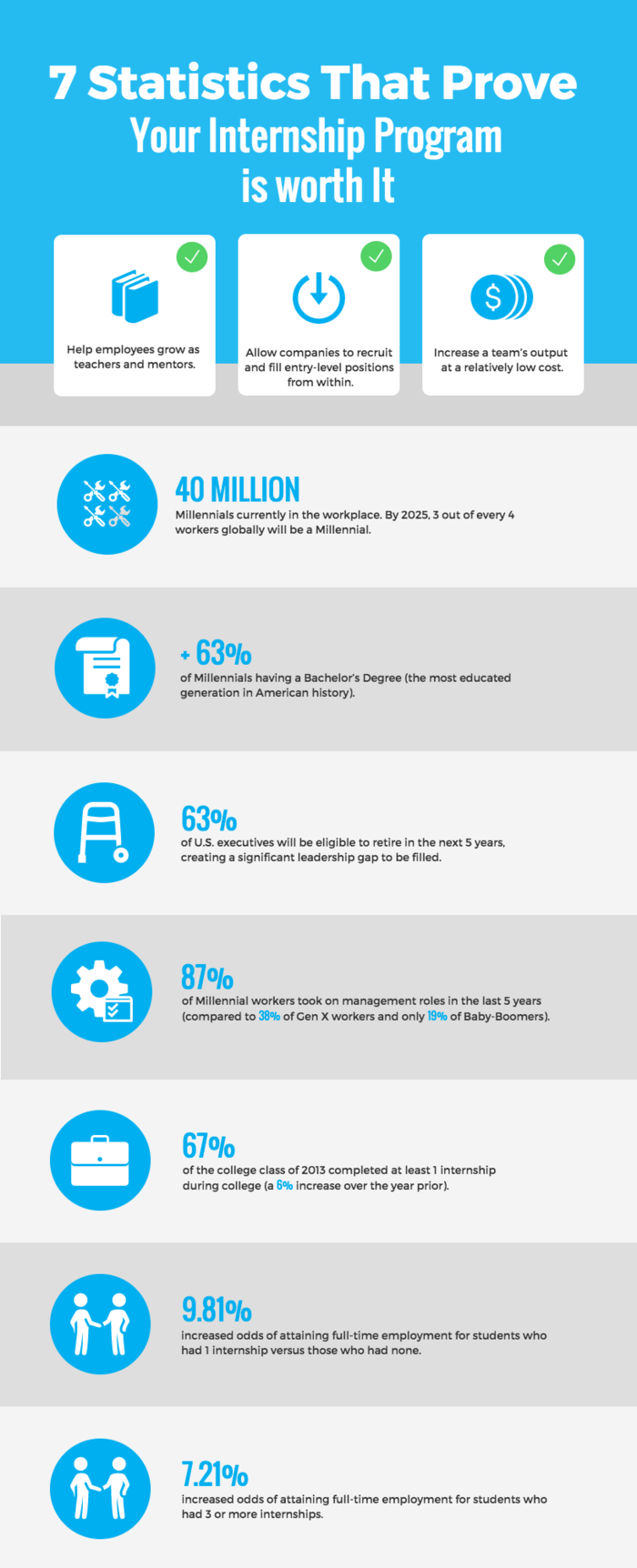
Design Tip: This infographic would make a great sales piece to promote your course or other service.
6. Use bold fonts to make text information engaging
A challenge people often face when setting out to visualize information is knowing how much text to include. After all, the point of data visualization is that it presents information visually, rather than a page of text.
Even if you have a lot of text information, you can still create present data visually. Use bold, interesting fonts to make your data exciting. Just make sure that, above all else, your text is still easy to read.
This data visualization uses different fonts for the headers and body text that are bold but clear. This helps integrate the text into the design and emphasizes particular points:

Design Tip: Nonprofits could use this data visualization infographic in a newsletter or on social media to build awareness, but any business could use it to explain the need for their product or service.
As a general rule of thumb, stick to no more than three different font types in one infographic.
This infographic uses one font for headers, another font for body text, and a third font for accent text.
Read More: How to Choose Fonts For Your Designs (With Examples)
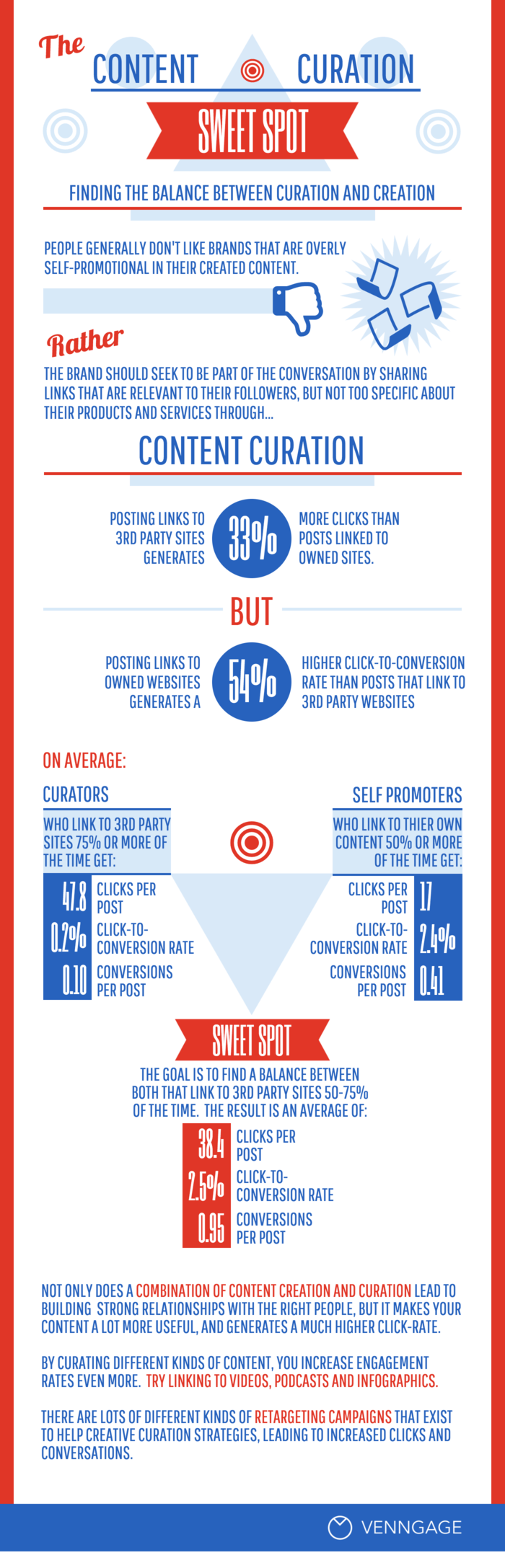
Design Tip: Venngage has a library of fonts to choose from. If you can’t find the icon you’re looking for , you can always request they be added. Our online editor has a chat box with 24/7 customer support.
7. Use colors strategically in your design
In design, colors are as functional as they are fashionable. You can use colors to emphasize points, categorize information, show movement or progression, and more.
For example, this chart uses color to categorize data:
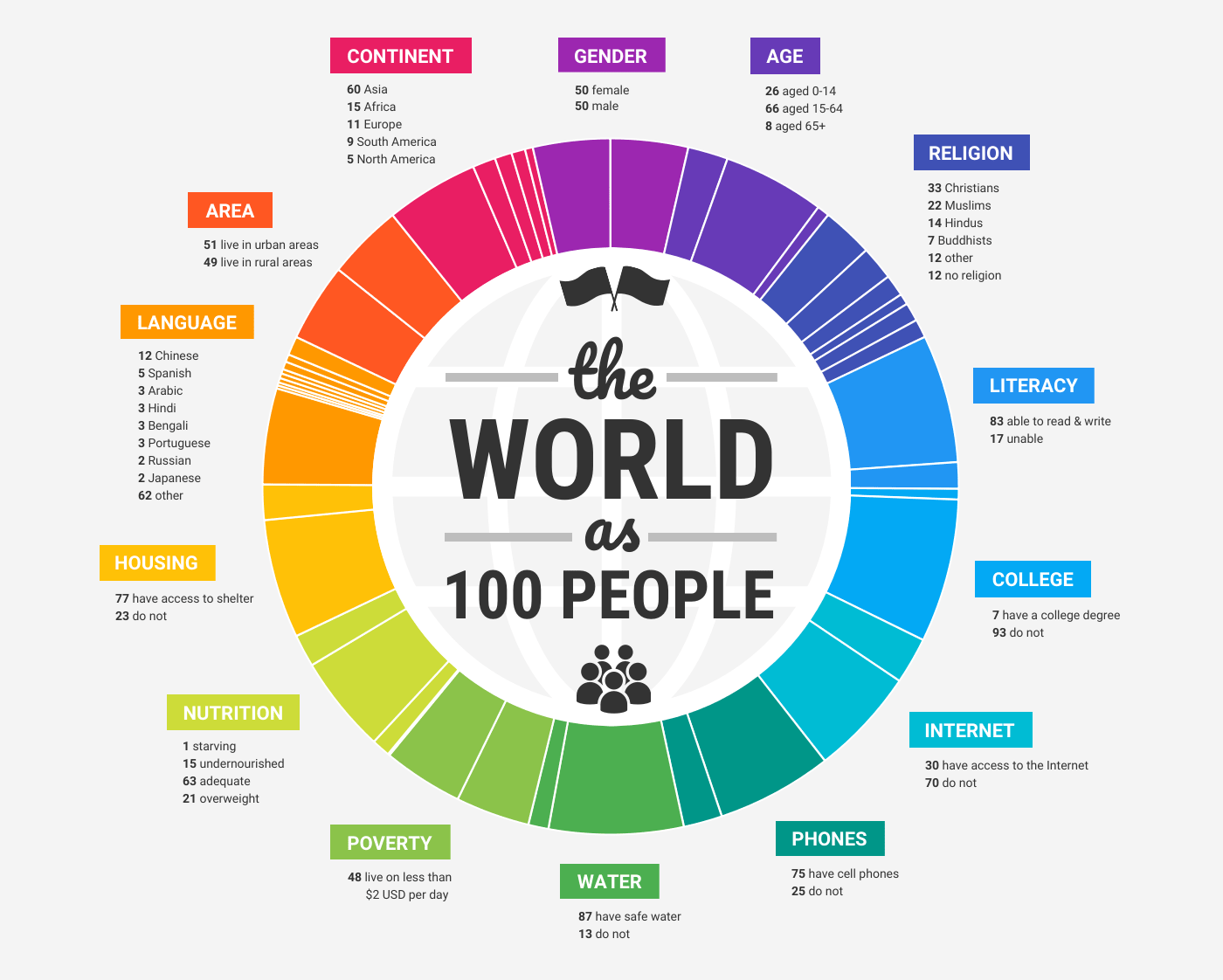
Design Tip : This pie chart can actually be customized in many ways. Human resources could provide a monthly update of people hired by department, nonprofits could show a breakdown of how they spent donations and real estate agents could show the average price of homes sold by neighbourhood.
You can also use light colored text and icons on dark backgrounds to make them stand out. Consider the mood that you want to convey with your infographic and pick colors that will reflect that mood. You can also use contrasting colors from your brand color palette.
This infographic template uses a bold combination of pinks and purples to give the data impact:
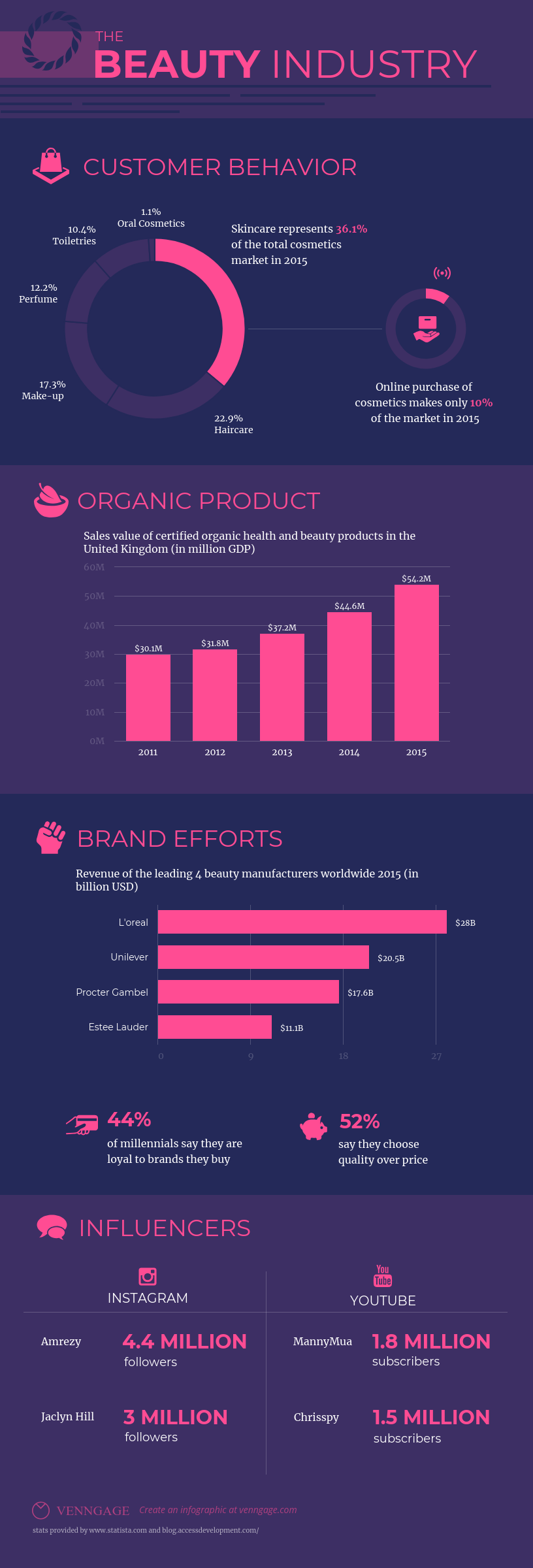
Read More: How to Pick Colors to Captivate Readers and Communicate Effectively
8. Show how parts make up a whole
It can be difficult to break a big topic down into smaller parts. Data visualization can make it a lot easier for people to conceptualize how parts make up a whole.
Using one focus visual, diagram or chart can convey parts of a whole more effectively than a text list can. Look at how this infographic neatly visualizes how marketers use blogging as part of their strategy:
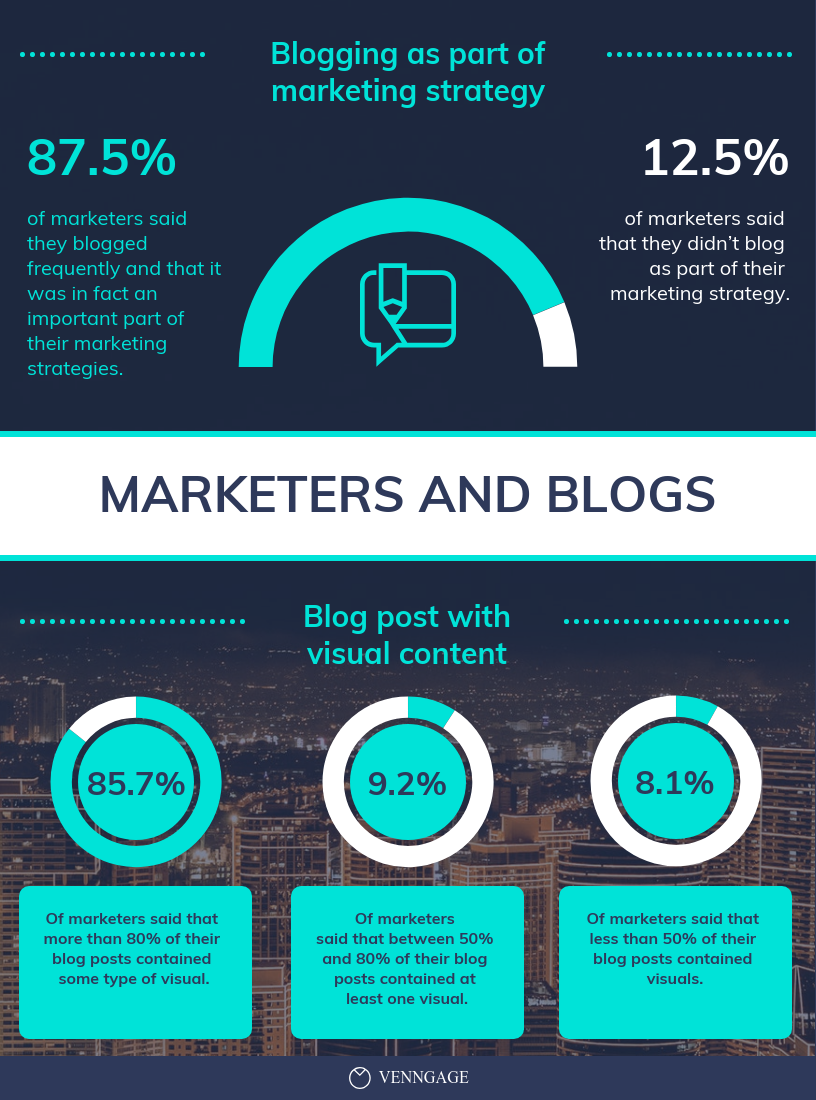
Design Tip: Human resources could use this graphic to show the results of a company survey. Or consultants could promote their services by showing their success rates.
Or look at how this infographic template uses one focus visual to illustrate the nutritional makeup of a banana:
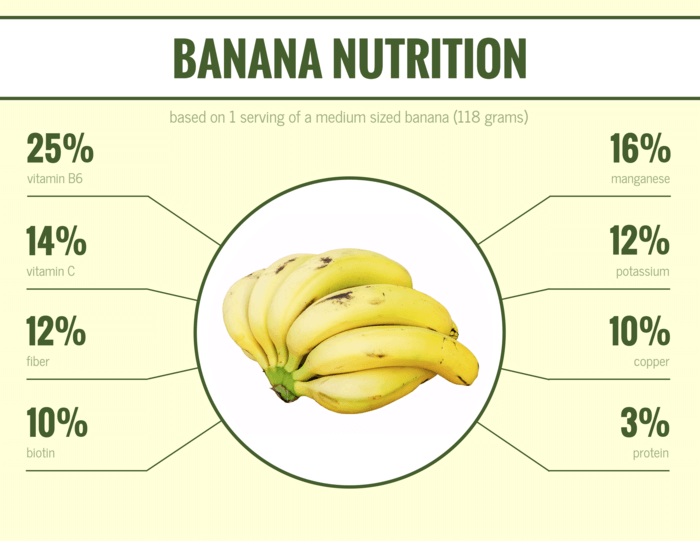
CREATE THIS FLYER TEMPLATE
9. Focus on one amazing statistic
If you are preparing a presentation, it’s best not to try and cram too many visuals into one slide. Instead, focus on one awe-inspiring statistic and make that the focus of your slide.
Use one focus visual to give the statistic even more impact. Smaller visuals like this are ideal for sharing on social media, like in this example:

Design Tip: You can easily swap out the icon above (of Ontario, Canada) using Venngage’s drag-and-drop online editor and its in-editor library of icons. Click on the template above to get started.
This template also focuses on one key statistic and offers some supporting information in the bar on the side:

10. Optimize your data visualization for mobile
Complex, information-packed infographics are great for spicing up reports, blog posts, handouts, and more. But they’re not always the best for mobile viewing.
To optimize your data visualization for mobile viewing, use one focus chart or icon and big, legible font. You can create a series of mobile-optimized infographics to share multiple data points in a super original and attention-grabbing way.
For example, this infographic uses concise text and one chart to cut to the core message behind the data:
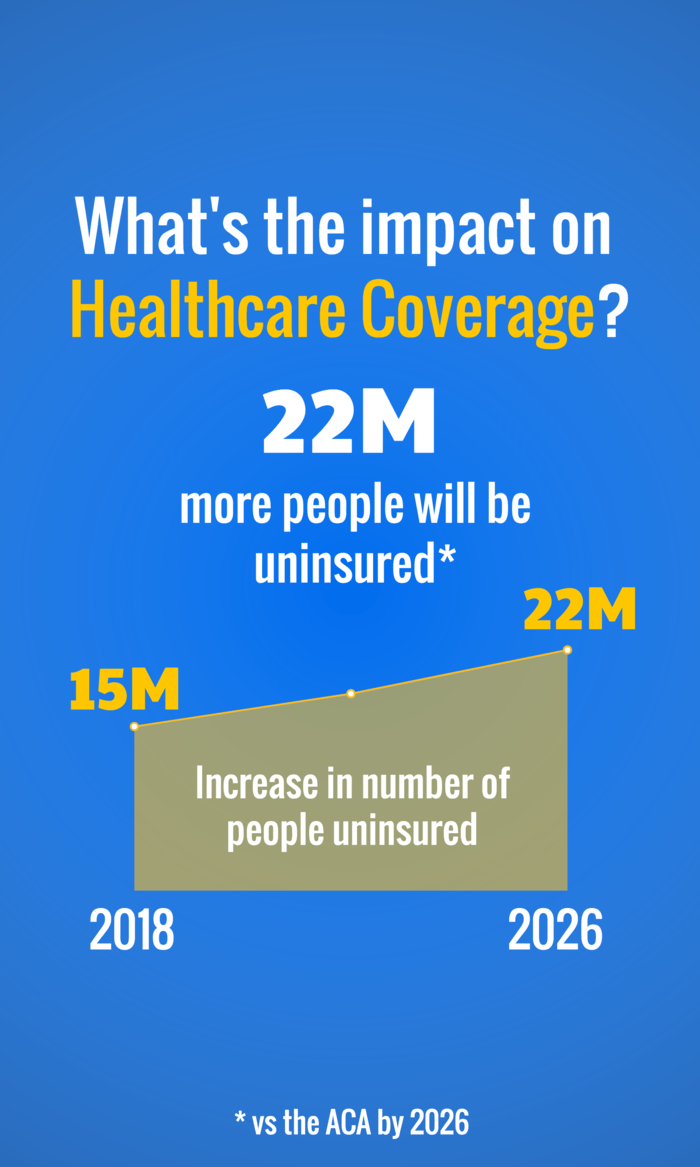
CREATE THIS SOCIAL MEDIA TEMPLATE
Some amazing data visualization examples
Here are some of the best data visualization examples I’ve come across in my years writing about data viz.
Evolution of Marketing Infographic
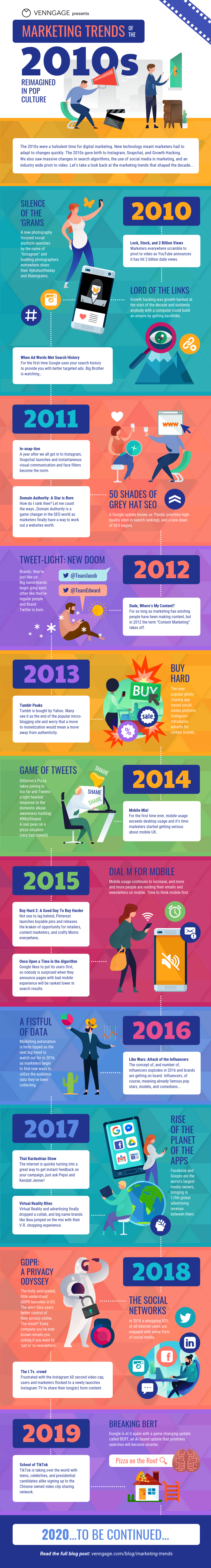
Graphic Design Trends Infographic


Stop Shark Finning Nonprofit Infographic

Source: Ripetungi
Coronavirus Impact on Environment Data Visualization

What Disney Characters Tell Us About Color Theory
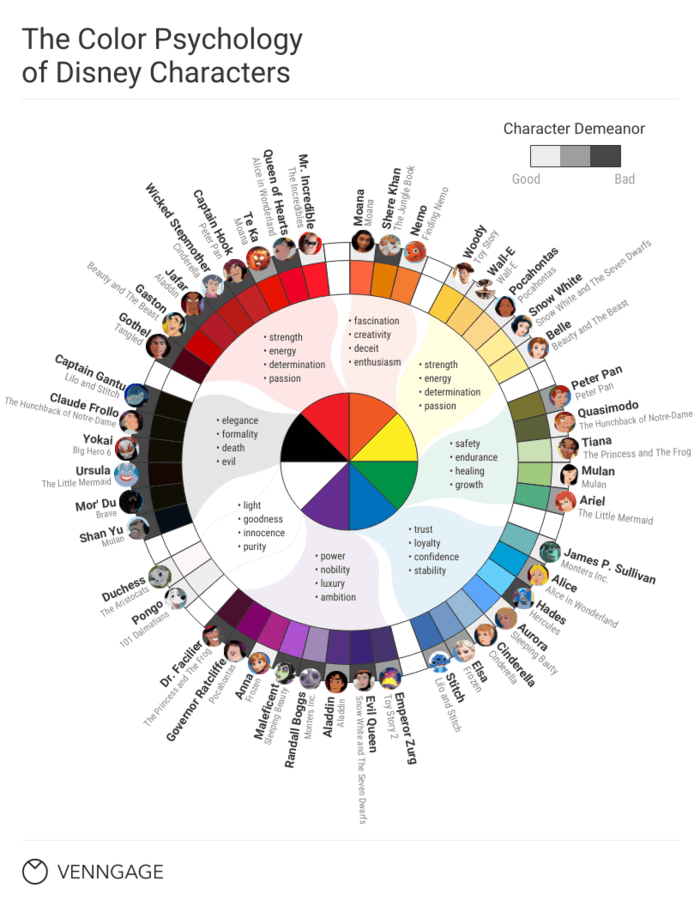
World’s Deadliest Animal Infographic
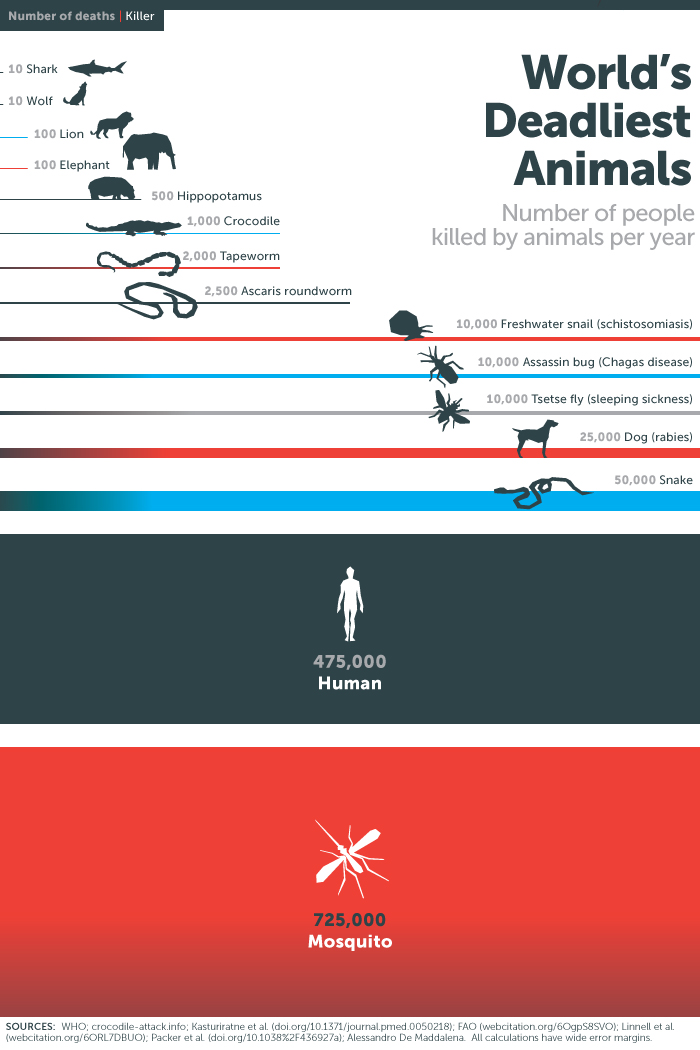
Source: Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation
The Secret Recipe For a Viral Creepypasta
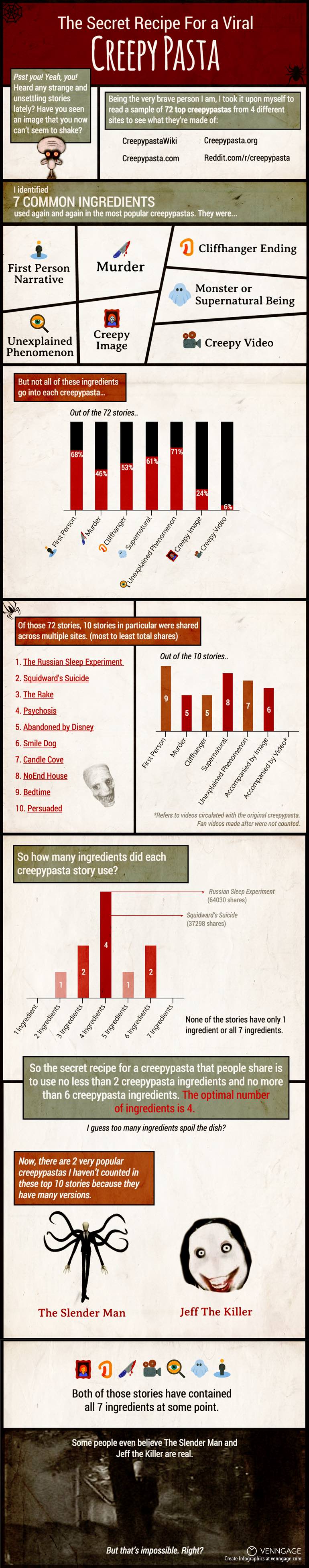
Read More: Creepypasta Study: The Secret Recipe For a Viral Horror Story
The Hero’s Journey Infographic
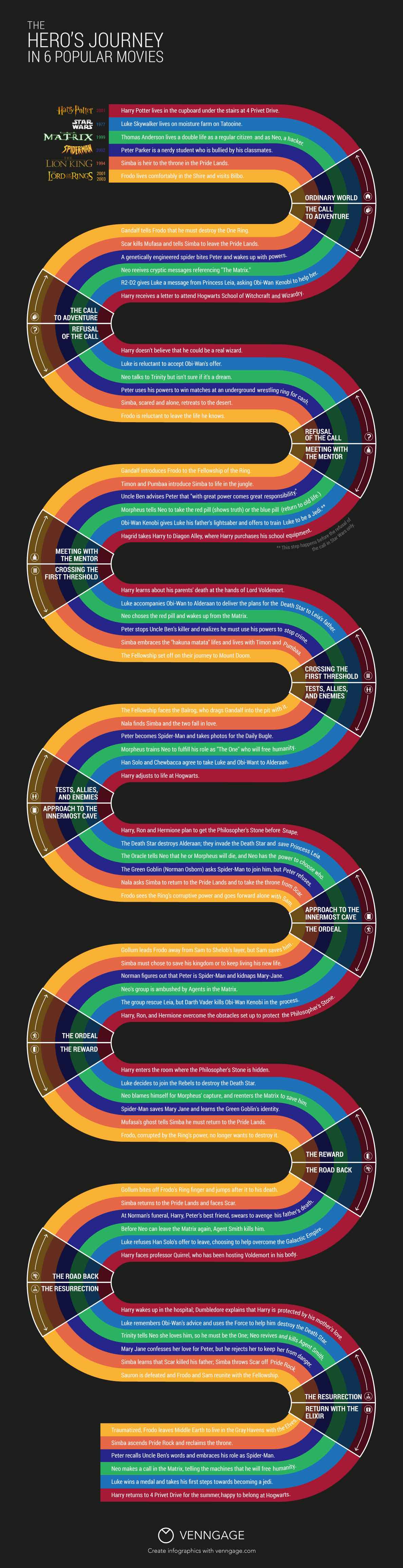
Read More: What Your 6 Favorite Movies Have in Common
Emotional Self Care Guide Infographic

Source: Carley Schweet
Want to look at more amazing data visualization? Read More: 50+ Infographic Ideas, Examples & Templates for 2020 (For Marketers, Nonprofits, Schools, Healthcare Workers, and more)
tableau.com is not available in your region.

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

1.3: Presentation of Data
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 577

Learning Objectives
- To learn two ways that data will be presented in the text.
In this book we will use two formats for presenting data sets. The first is a data list, which is an explicit listing of all the individual measurements, either as a display with space between the individual measurements, or in set notation with individual measurements separated by commas.
Example \(\PageIndex{1}\)
The data obtained by measuring the age of \(21\) randomly selected students enrolled in freshman courses at a university could be presented as the data list:
\[\begin{array}{cccccccccc}18 & 18 & 19 & 19 & 19 & 18 & 22 & 20 & 18 & 18 & 17 \\ 19 & 18 & 24 & 18 & 20 & 18 & 21 & 20 & 17 & 19 &\end{array} \nonumber \]
or in set notation as:
\[ \{18,18,19,19,19,18,22,20,18,18,17,19,18,24,18,20,18,21,20,17,19\} \nonumber \]
A data set can also be presented by means of a data frequency table, a table in which each distinct value \(x\) is listed in the first row and its frequency \(f\), which is the number of times the value \(x\) appears in the data set, is listed below it in the second row.
Example \(\PageIndex{2}\)
The data set of the previous example is represented by the data frequency table
\[\begin{array}{c|cccccc}x & 17 & 18 & 19 & 20 & 21 & 22 & 24 \\ \hline f & 2 & 8 & 5 & 3 & 1 & 1 & 1\end{array} \nonumber \]
The data frequency table is especially convenient when data sets are large and the number of distinct values is not too large.
Key Takeaway
- Data sets can be presented either by listing all the elements or by giving a table of values and frequencies.

Statistics and Research Methods in Psychology with Excel pp 135–160 Cite as
Graphical Presentation of Data
- J. P. Verma 2
- First Online: 28 August 2019
2253 Accesses
Graphs are used to showcase relationships between different variables in a pictorial form. Different types of graphs including bar diagram, histogram, line diagram, cumulative frequency curve, pie diagram and ogive have been discussed with illustrations in the chapters. The procedure of identifying linear and curvilinear relationships on the basis of equation has been discussed. The objective-type and multiple-choice questions provide readers enough practice to understand the basic concepts of developing a graph.
Download chapter PDF
Introduction
A graph is a pictorial representation of data. In fact, it is a mathematical picture which presents the data in a visual mode. It is a much better way of communicating information in comparison with numerical data. One sees them in newspapers, magazines, journals and television due to their power of communicating information more effectively. Graphics are used to represent relationships between different variables, groups or classes. It is basically used to explain how the value of one variable or group changes with the change in the related variable or group. Taking the perspective of a student learning psychology, graphs are useful because they can summarize plenty of information into one picture. While doing research, one does not know anything about the relationships among the variables under study. A researcher uses graph to get an idea about how these variables change relative to one another. Graphic presentation can be used in interpolation and extrapolation of data and helps in drawing inferences. Due to this reason, one will see many graphs, of course, in different forms in books, journals and theses. For example, to illustrate how the eye–hand coordination varies as one gets older, a line diagram drawn based on a large set of data will give instant findings which are otherwise not possible by simply observing the data set until some statistical treatments are done. The best part of the graphs is that people understand the data quickly.
In day-to-day life, you must have encountered different types of graphical pictures. Some of them are shown in terms of line diagram, vertical or horizontal bars, area diagram, Venn diagram or pie diagram. These are different forms of the graph. These visual methods can express the point of view in a much better way than simply describing the data. While the graphics may be powerful tools, they may spoil one’s presentation as well if they convey wrong message. It is, therefore, important to choose an appropriate graphic option to show the data in a pictorial form. Appropriate use of graph enhances the message delivery.
Basics of Graph
In drawing most of the graphs or charts except pie chart, the data is plotted in two dimensions. The relationship between the variables can either be linear or curvilinear. In an equation showing linear relationship, power of any variable cannot be more than one, whereas in curvilinear relation, at least one variable should have power more than one. Most of the graphs that are drawn in two dimensions are discussed in this chapter. The graph can be drawn in more than two dimensions as well, but that becomes too complicated to be drawn manually. Such graphs may be drawn by using some suitable computer software package. Before discussing different types of graphs and their applications in different situations, it is important to know some of its basic features.
Deciding the Axes
The graph is usually plotted in two dimensions. The horizontal axis is normally known as x -axis and vertical axis as y -axis. These two axes meet each other at right angle as shown in Fig. 4.1 . The horizontal and vertical axes are also known as abscissa and ordinate, respectively. The arrow sign is put at the tip of the x -axis as well as y -axis. This is done to indicate that the lines can be extended further. In plotting the graph, the intention is to show the relationship between the two variables. It is sometimes confusing as to which variable should be marked along x -axis and which one along y -axis. Follow the simple rule in deciding the axes; “Take the variable whose value is known, along x -axis and the variable whose value is to be estimated, along y -axis”.
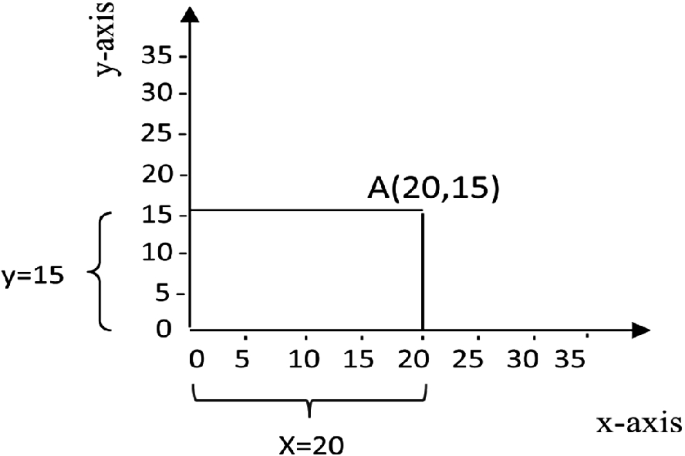
Measuring the coordinates of a point
Detailing the Graph
In order to make the graph readable and easily understood, the following details must be incorporated in the graph:
The title of the graph must be short and convey the exact contents.
The variables marked along both the axes must be clearly defined along with their units.
The patterns or colours differentiating different components of the graph must be visibly distinct.
Locating a Point and its Coordinates on the Graph
A graph is obtained by plotting different points on a two-dimensional ( X − Y ) scale. The point where the two axes x and y meet is known as origin and is represented by (0, 0). A point on the graph represents a relationship. Each point on the graph is denoted by a pair of numbers containing two coordinates ( x and y ). These coordinates are used to identify the location of the point on a graph.
The x -coordinate of a point A refers to the distance of this point from the origin on the x -axis. The x -coordinate of the point A is obtained by drawing a perpendicular line from the point on the x -axis so that it cuts the x -axis at right angle as shown in Fig. 4.1 . The number where this vertical line intersects the x -axis is the value of the x -coordinate.
Similarly, y -coordinate of the point A is its distance from the origin on the y -axis. The y -coordinate of the point A is obtained by drawing a horizontal line parallel to x -axis so that it intersects the y -axis at right angle as shown in Fig. 4.1 . The number at which this horizontal line intersects with the y -axis is the value of the y -coordinate.
Deciding the Scale Unit
The scale of x - and y -axis should be decided on the basis of nature of the data and their fluctuations. Normally, complete range of data should have equal or nearly equal range of distances on x -axis as well as on y -axis. In case the x -axis is stretched more than the y -axis, then the graph will de-emphasize the fluctuations, whereas stretching the y -axis will tend to overemphasize the fluctuations.
If the variable on the x -axis ranges from 18 to 28, the scale starts with 0 but a cut mark is made to accommodate the score in between 0 and 18. Similarly, if the variable on the y -axis ranges from 45 to 70, a similar cut mark is made on the y -axis to accommodate the scores in between 0 and 45. Figure 4.2 shows the procedure graphically.
Marking of axes where data does not start from zero
Points on the Axes
If any point falls on an axis, then one of its coordinates will be zero. For example, in Fig. 4.3 , the point A lies on y -axis and therefore its x -coordinate will be zero because its distance from the origin on the x -axis is zero. Similarly, the point B lies on the x -axis and therefore its distance from the origin on the y -axis is zero and hence its y -coordinate is zero.
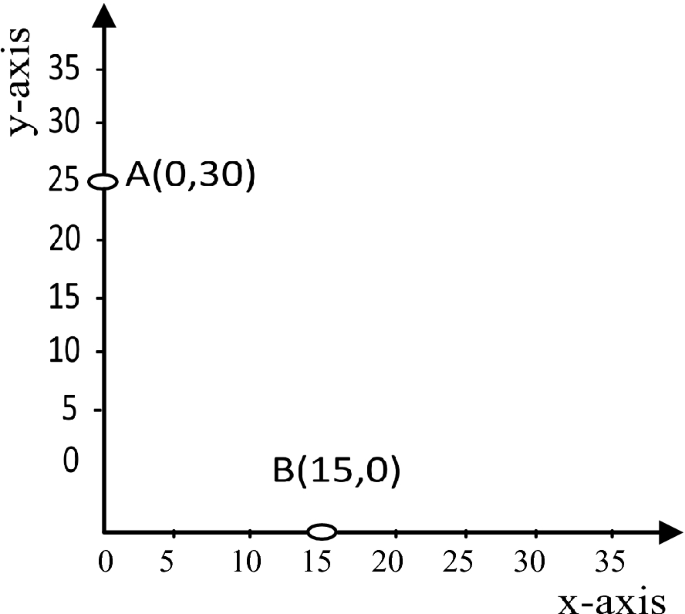
Points lying on the axes
Features of a Good Graph
In order to show the data graphically, one must follow certain guidelines mentioned below for effective presentation.
The graph must be simple and easy to understand by a common man.
It must convey important features of the graph effectively.
It must have an appropriate title and labels.
The graph must be visually accurate. For instance, if there are two graphic values 20 and 40, then 40 must appear to be twice the size of 20.
Check Your Graphical Concepts-I
Note: Following statements are either true or false. Write T for true and F for false.
In plotting the graph, the independent variable is marked along y -axis.
If x = 0, then the line lies on the y -axis.
The dependent variable is marked along x -axis.
If the coordinate of a point A is (25, 0), then it lies on the x -axis.
If a point lies on the x -axis, its y -coordinate is zero.
The equation of the line lying on the y -axis is y = 0.
Types of Graph
There are many types of graphs available, but six types of graph, namely, bar diagram, histogram, frequency polygon, frequency curve, ogive and pie diagram are more frequently used by the researchers. These are explained in detail in this chapter.
Bar Diagram
A bar diagram is a graph in which rectangular bars are created with lengths equal to their values that they represent. These bars can be created vertically or horizontally. The bar diagram is used for comparing the magnitudes of some discrete groups having measured either in discrete or continuous manner. Let us discuss the procedure of constructing the bar diagram by using the data obtained on a number of students in different age categories in a school as shown in Table 4.1 .
Steps in Constructing the Bar Diagram
Since the number of students in different age groups needs to be compared, mark the age on the x -axis and the number of students along the y -axis by taking appropriate scale.
Erect five bars of equal width having height equal to the number of students in each age group. These bars can be erected vertically or horizontally.
Give the title of the graph.
The bar diagram obtained by using the above-mentioned data is shown in Fig. 4.4 .
Bar diagram showing number of students in different age categories
Histogram is used for showing the data, organized in class interval form where the class interval is continuous. It is obtained by plotting the class interval along the x -axis and frequencies along the y -axis. The difference between a bar diagram and a histogram is that, in bar diagram, there is a fixed space in between any two consecutive bars, whereas in histogram, all the rectangular bars are erected consecutively so that their boundaries touch each other. The histogram can also be constructed for discrete class intervals as well. In that case, it assumed that the upper limit of a class interval coincides with the lower limit of the next higher class interval. The procedure of creating a histogram shall be discussed by using the data on anxiety obtained on the college students as shown in Table 4.2 .
Steps for Constructing Histogram
Mark the class intervals along the x -axis.
Mark the frequencies along the y -axis.
Erect the rectangular bar for each class interval with the vertical height equal to the frequency of that class interval.
Write suitable labels for the x - and y -axis and an appropriate title for the graph.
The histogram so obtained by using the above-mentioned steps for the data shown in Table 4.2 is shown in Fig. 4.5 .
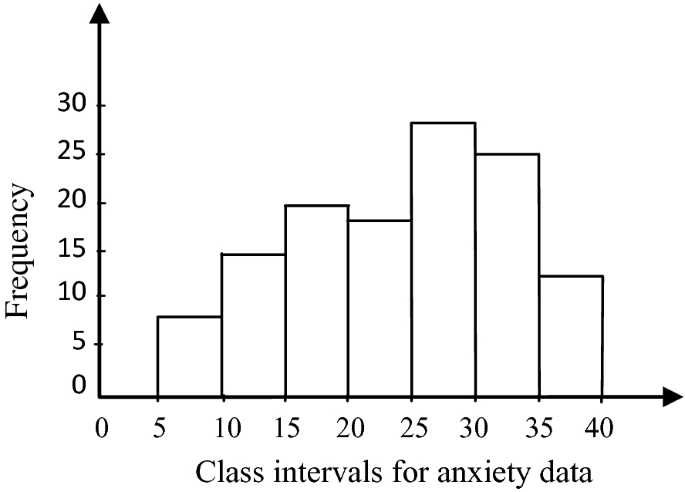
Histogram for the data on anxiety
Check Your Graphic Skill-I
Which of the following equation is linear and why?
y = 3 x 2 + 2 x + 4
y = 42 x + 3 x + 7
63 y = 5 x + 32
8 y 2 = 3 x − 2
8 y = 3 x + 7 x + 4 y.
Following are the mode of advertisements through which the students have taken admission in a stress management programme. Prepare the bar diagram to show the data.
Frequency Polygon
Frequency polygon is a graphic method used to show the trend of the data arranged in different class intervals or groups. In plotting frequency polygon for the data arranged in class interval form, it is assumed that the frequencies are concentrated at the mid-point of the class interval. In constructing the frequency polygon, the mid-points of the class intervals are plotted against their frequencies and the points so obtained are joined by straight lines. Frequency polygon can be used to interpolate the value of the frequency ( y ) based on the value of x . The procedure of constructing the frequency polygon has been explained in the following steps by using the data in Table 4.2 .
Steps in Constructing the Frequency Polygon
Mark the mid-points of the class intervals along the x -axis.
Identify the points by marking points so obtained by taking the mid-points of class intervals corresponding to their respective frequencies.
Join the points by straight lines. The graph so obtained is shown in Fig. 4.6 and is known as frequency polygon.
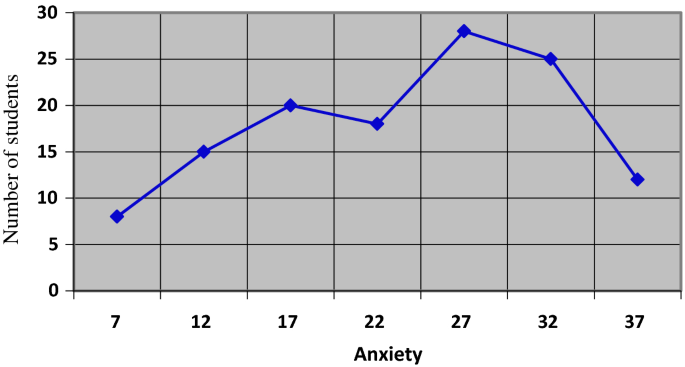
Frequency polygon showing distribution of anxiety scores
Frequency Curve
A frequency curve is a pictorial representation used to show the smooth trend of data arranged in different class intervals or groups. The only difference between frequency curve and frequency polygon is that in frequency curve all the points are joined by free hand instead of straight line. Like in frequency polygon, here also the points are identified for each mid-point of the class intervals against their respective frequencies. These points are then joined by free hand to obtain the frequency curve. The steps involved in constructing the frequency curve are shown below.
Steps in Constructing the Frequency Curve
Mark the mid-point of the class intervals along the x -axis.
Join the points by smooth curve. The graph so obtained is shown in Fig. 4.7 and is known as frequency curve.
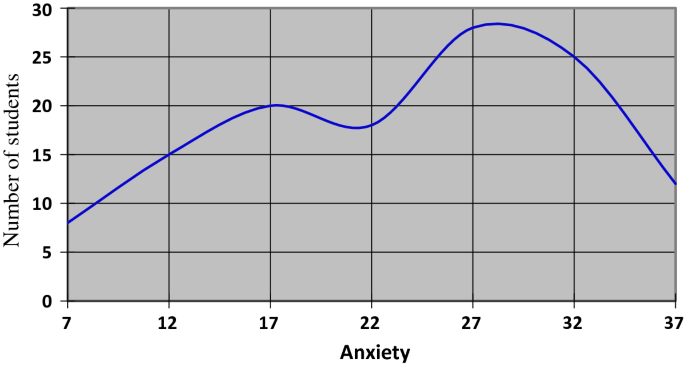
Frequency curve showing distribution of anxiety scores
Cumulative Frequency Polygon
In cumulative frequency polygon, instead of frequency, cumulative frequency is plotted against the mid-points of the class intervals. This type of graph is used to find the percentiles of scores. One may find the percentage of scores lying below a particular point by using the cumulative frequency polygon. In cumulative frequency polygon, the points are joined by straight lines. If these points are joined by the smooth curve, then the graph will be known as cumulative frequency curve . Further, if instead of cumulative frequency, the percentage of frequency is plotted against the mid-points of the class intervals, then the graph so obtained is known as cumulative percentage polygon . Let us now discuss the procedure in developing the cumulative frequency polygon by using the data in Table 4.2 . The steps involved are as follows.
Steps in Constructing the Cumulative Frequency Polygon
Mark the cumulative frequency as shown in Table 4.2 along the y -axis.
Identify the points by marking square/circle so obtained by plotting the mid-points of the class intervals along the x -axis and cumulative frequencies along the y -axis.
Join these points by straight lines for getting cumulative frequency polygon as shown in Fig. 4.8 .
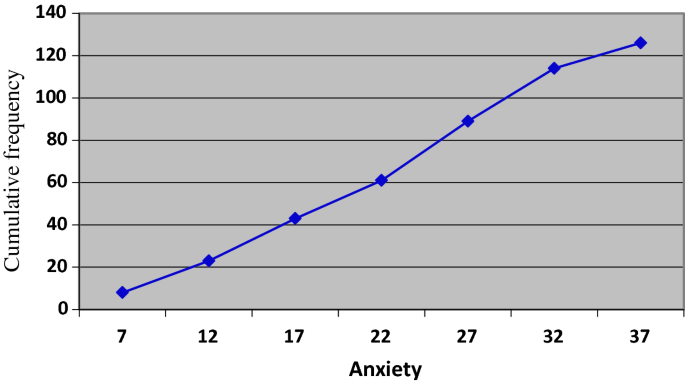
Cumulative frequency polygon for the data on anxiety
Ogive is a combination of two curves: less than and more than types. The first curve is obtained by plotting the mid-points of the class intervals against the cumulative frequencies obtained by adding the frequencies in a cumulative fashion from lower to higher class intervals. This curve is known as less-than-type curve. The second curve in the ogive is obtained by plotting the mid-points of the class intervals against the cumulative frequencies obtained by adding the frequencies in a cumulative fashion from higher to lower class intervals. This second curve is known as more-than-type curve. The two curves together are known as ogive . The point at which these two curves cut each other determines the median of the data set. Draw a perpendicular line on the x -axis from the point at which these two curves intersect each other. The point so obtained on the x -axis is the median. Let us consider the same data set as shown in Table 4.2 for the purpose of discussing the procedure of constructing the ogive. The cumulative frequencies have been calculated from the lowest to higher as well as higher to lower class intervals. This data along with the less-than- and more-than-type cumulative frequencies is shown in Table 4.3 .
Steps in Constructing the Ogive
Find the mid-points of each class interval and mark it along the x -axis.
Find the cumulative frequency (less than type) starting from the lower to higher class intervals. Mark the cumulative frequencies along the y -axis.
Find the cumulative frequency (more than type) starting from the higher to the lower class intervals.
Obtain the points by plotting the mid-points of the class intervals along with the cumulative frequency f 1 (less than type) and join them by free hands. The curve so obtained is known as less than type.
Obtain the points by plotting the mid-points of the class intervals along with the cumulative frequency f 2 (more than type) and join them by free hands. The curve so obtained is known as more than type.
The two curves obtained in steps 4 and 5 together are known as ogive and are shown in Fig. 4.9 .
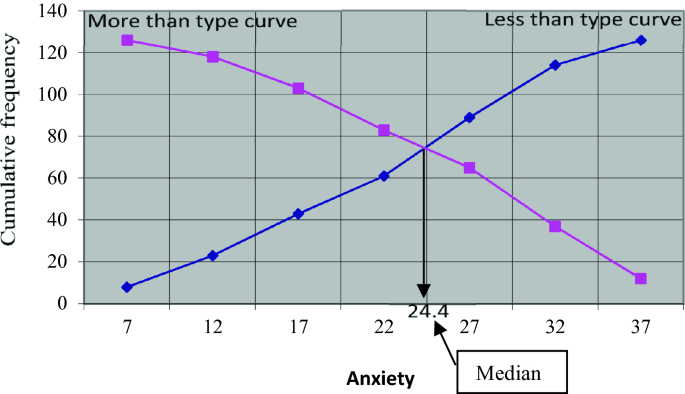
Ogive graph for the data on anxiety
Drop a perpendicular form the point, at which these two curves intersect, on the x -axis. The point on the x -axis is known as median of the data set. In this example, median is 24.4.
Pie Diagram
Pie diagram is a circle diagram that is used to compare different parts of the same whole. It is represented by the different parts of a circle. It is different than other types of graphs discussed before. Here, there are no axes and the points are not plotted in the x – y plane. Rather, the whole circle is used to represent 100% cases and each portion of the circle represents the percentages of cases in the whole domain. For instance, in comparing the number of students securing grades A , B , C , D and E using pie diagram, the total number of students securing all the grades will show the 100% cases and is represented by the whole circle, whereas different parts of the circle represent different grades.
The pie diagram is suitable if the whole domain is divided into not more than six subgroups. In case of more than six groups, the pie diagram looks clumsy, and in that case, one should use the bar diagram. If any of the subgroup needs to be highlighted, then that portion of the circle may be detached a bit from the main circle. This visual separation makes it distinct and more visible.
The pie diagram is developed by deciding the magnitude of each portion of the circle. This is done on the basis of the angle subtended by each portion at the centre. The whole angle of the circle subtended at the centre is 360°, which is equal to 100% cases, and therefore, angle for each section of the circle is computed in proportion to its frequency. Let us now discuss the procedure of constructing a pie diagram by using the data obtained on the students offering different courses in a college as shown in Table 4.4 .
Steps in Constructing the Pie Diagram
Since there are five categories, one shall first compute the angles attached to each category shall be computed first:
Here, total number of students is 120, which is equal to 360° angle.
Since 120 is equal to 360°, 25 shall be equal to \(\frac{360}{120} \times 25 = 75\) .
On the same analogy, compute the angles equivalent to each frequency of the subgroups which is shown in Table 4.5 .
Divide the circle into five subgroups according to their angles.
If desired, any slice of the circle may be cut to highlight it.
Label each portion of the circle by its corresponding course name.
If so desired, mention the frequencies of each group along with the name of the subject.
Write an appropriate title of the graph. The graph so obtained is known as pie diagram and is shown in Fig. 4.10 .
Pie diagram showing distribution of students in different courses
Check Your Graphical Skill-II
In an examination, the grades obtained by the students are as follows:
Prepare pie diagram by computing the angles corresponding to each grade.
Following are the weights of the persons in kg arranged in the class intervals along with their frequency. Construct cumulative frequency polygon, and find out how many persons are having weight less than 60 kg. based on the curve so obtained.
In a psychology test, students’ performance was recorded which is listed below in the form of class interval along with their frequencies. Prepare ogive, and find the median performance of the students based on ogive.
Check Your Graphical Concepts-II
In the bar diagram, the width of the bars may be unequal.
If frequencies that are marked along the y -axis are 30, 42, 38, 40, 45, 41, then, to accommodate the frequency from 0 to 30, a cut is marked along the y -axis near zero.
In drawing the frequency curve, if the x -axis is stretched more than the y -axis, then the graph will overemphasize the fluctuations.
Cumulative frequency curve can be used to find the number of data points around a score.
If total of all the frequencies is 200, then the angle corresponding to the frequency 36 is obtained by multiplying it by 9/5.
The value of x obtained by dropping the perpendicular from the intersection point of the two curves in ogive is known as mean.
In histogram, all the bars are adjacent to each other.
In frequency polygon, all the points are joined by smooth curve.
In pie diagram, the frequency of each group is converted to its equivalent angle.
Frequency curve is obtained by plotting the mid-points of the class intervals along x -axis and frequencies along y -axis and joining the points so obtained by free hand.
In ogive, the less-than-type frequencies are obtained by adding frequencies in a cumulative fashion from highest to lowest class intervals.
Computing with Excel
Constructing histogram.
Histogram can be constructed by using the functionality of Excel. It provides the knowledge about the distribution of data. Histogram is created by using the Analysis ToolPak. The procedure in creating histogram shall be discussed by means of an example.
The histogram discussed below can only be constructed in Excel if the Add-ins ‘Analysis ToolPak’ is already installed. The readers can install this Add-ins ‘Analysis ToolPak’ in their Excel by following the procedure discussed in Chap. 2 .
Example 4.1
Following are the IQ scores obtained in 20 subjects. Construct the histogram to investigate the distribution of scores.
The histogram can be constructed by following the below-mentioned steps:
Enter the data of IQ in the first column and class interval in the second column. User can select the interval as per the range of the data. Since in this example minimum and maximum performance of the IQ scores is in the range of 64 and 105, class interval of width 5 has been chosen. Click on the following commands in the header of the Excel to get Fig. 4.11 .
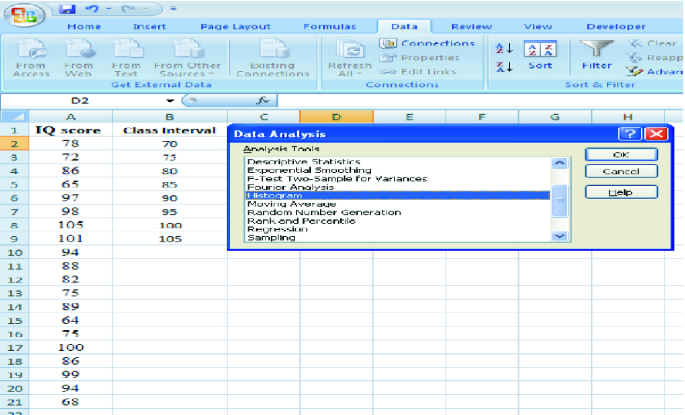
Command for histogram
Data → Data Analysis
Bring the cursor on the option Histogram and then click OK . This will take you to Fig. 4.12 . You can now define the range of data which you would like to use for constructing histogram.
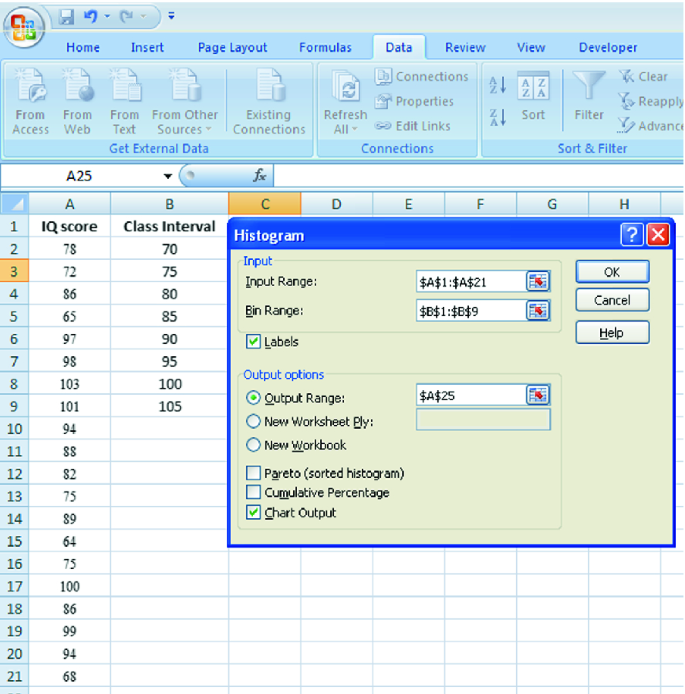
Options in computing histogram in Excel
In this example, the scores on IQ are in the column A of the Excel sheet. The data range therefore would be A1:A21 for the IQ and B1:B9 for the class interval. Do the following steps to fill the entries in the screen shown in Fig. 4.12 .
Input range : A1:A21
Bin range : B1:B9
(Bin denotes the class interval. User may select the interval as per their requirements. In this example, width of the class interval has been chosen as 5.)
If the first row of your data contains the variable name, then check the option Labels .
Fill the entry in the output range. The output can be obtained on the same Excel sheet, new worksheet or new workbook. Here, the output is obtained on the same sheet starting from A25 location onward and therefore the following entry should be filled.
Output range : A25.
Check Chart Output option. Other entries are optional, and you can check them if so required.
Click OK to get the output as shown in Table 4.6 and Fig. 4.13 .
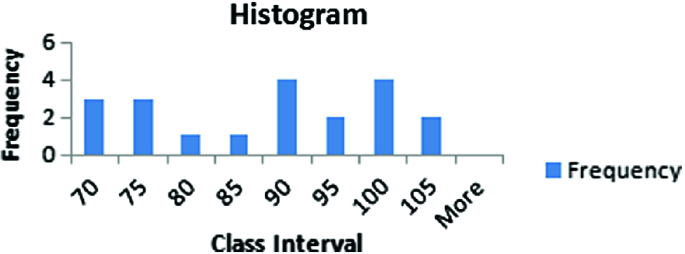
Output showing histogram along with the anxiety data in class interval form
The output obtained in Fig. 4.13 can be customized by changing the labels. To change the label, double click ‘CI’ and retype the required label. Similarly, heading ‘Histogram’ can also be changed. To done away with the ‘Frequency’ on the right of the figure, double click it and delete.
Important Definitions
Bar diagram is a graphical representation of data in the form of rectangular bars shown vertically or horizontally proportional to their group frequencies.
Histogram is a graphical presentation of group scores in the form of adjacent bars with the height proportional to their group frequencies.
Frequency polygon can be defined as the line diagram obtained by plotting the two sets of data along the x - and y -axis and joining the points by straight line.
Frequency curve is a smooth curve diagram obtained by plotting the two sets of data along the x - and y -axis and joining the points by free hand.
Cumulative frequency polygon is a line diagram obtained by plotting the group variable along the x -axis and cumulative frequency along the y -axis and joining the points so obtained by straight lines.
Ogive can be defined as the combination of two curves, less than type and more than type, obtained by plotting the class intervals data along the x -axis and cumulative frequencies along the y -axis.
Pie diagram can be defined as a circle diagram which is used to compare different parts of the same whole and is obtained by dividing the circle in different sectors proportional to the magnitudes of groups to be shown.
Graphs are used to represent relationships between different variables in a pictorial form. In drawing most of the graphs except pie chart, the data is plotted in two dimensions. The horizontal axis is normally known as x -axis and vertical axis as y -axis. The horizontal and vertical axes are also known as abscissa and ordinate, respectively. By convention independent variable is marked along x -axis and dependent variable along y -axis. Equation of x -axis is y = 0, and that of y -axis is x = 0. Although many types of graph exist, six types of graphs that are used generally by the researchers are bar diagram, histogram, frequency polygon, frequency curve, ogive and pie diagram.
Types of Graphs
Bar diagram is constructed by using rectangular bars with lengths equal to their values that they represent. These bars can be created vertically or horizontally. Histogram is constructed when the data is organized in continuous class intervals. It is obtained by plotting the class intervals along x -axis and frequencies along y -axis. In this graph, bars are created adjacent to each other. Frequency polygon is a line diagram used to show the trend of the data arranged in different class intervals or groups. In constructing the frequency polygon, the mid-points of the class intervals are plotted against their frequencies and the points so obtained are joined by straight lines. On the other hand, a frequency curve is a pictorial representation used to show the smooth trend of data arranged in different class intervals or groups. The only difference between frequency curve and frequency polygon is that in frequency curve all the points are joined by free hand instead of straight line. Cumulative frequency polygon is used to find the percentiles of scores. In plotting this graph instead of frequency, cumulative frequency is plotted against the mid-points of the class intervals. Ogive is a combination of two curves: less than type and more than type. Less-than-type curve is obtained by plotting the mid-points of the class intervals against the cumulative frequencies obtained from lower to higher class intervals, whereas more-than-type curve is obtained by plotting the mid-points of the class intervals against the cumulative frequencies obtained from higher to lower class intervals. The point at which these two curves intersect each other determines median of the data set. Pie diagram is a circle diagram that is used to compare different parts of the same whole. It is represented by the different parts of a circle. Whole circle is used to represent 100% cases, and each portion of the circle represents the percentage of cases in the whole domain.
Objective-Type Questions
Select the most appropriate answer.
Which of the following statements is not true?
Graphs are mathematical pictures which present the data in the form of a visual model
Graphs can be used to get an idea about how the variables under study change relative to one another
Graphs are used to find the significance of mean
Graphics are used to represent relationships between different variables, groups or classes
In plotting the graph, the variable whose value is known is taken along
(a) Abscissa (b) Ordinate
(c) y -axis (d) x -axis
While plotting the graph, the variable whose value is to be estimated is taken along
(a) x -axis (b) y -axis
(c) b -axis (d) a -axis
If the coordinates of a point A is (15, 0), then it lies on the
(a) Ordinate (b) Abscissa
(c) In between x and y axes (d) None of the above
In a bar diagram,
The width of all bars is equal
The height of all bars is equal
Width and height of bars vary according to the variable being plotted
The width of bars varies according to the variable being plotted
In histogram
Frequencies are plotted along the x -axis
Class intervals are plotted along the y -axis
Frequencies can be plotted on both the x -axis and y -axis
Frequencies are plotted on the y -axis
Which of the following statements is true?
Histogram is constructed for continuous data
Histogram is constructed for discrete data
Histogram is constructed for both continuous and discrete data
In histogram, consecutive bars may or may not be at equidistance
In frequency polygon, the frequency of each interval is plotted against
the upper limit −0.5 of the class intervals
the mid-point of the class intervals
the upper limit of the class intervals
the lower limit of the class intervals
The difference between frequency polygon and frequency curve is that
In frequency polygon, curve is plotted against the upper limits of the class intervals
In frequency curve, cumulative frequency is plotted against the mid-points of the class intervals
In frequency curve, all the points are joined by straight line
In frequency curve, all the points are joined by free hand
Which of the following types of graphs is used to find the percentiles of scores?
Frequency polygon
Cumulative frequency polygon
Bar diagram
The two curves of ogive may not intersect each other
In ogive, the less-than-type frequencies are obtained by adding frequencies in a cumulative fashion from lowest to highest class intervals
In ogive, the more-than-type frequencies are obtained by adding frequencies in a cumulative fashion from highest to lowest class intervals
The value of x obtained by dropping the perpendicular from the intersection point of the two curves in ogive is known as median
In a total of 60 students, the angle corresponding to the 12 students in a pie diagram will be
(a) 50 (b) 55 (c) 60 (d) 72
Long-Answer-Type Questions
The marks obtained by the students in education and psychology are shown below:
Plot this data along with the trend line, and answer the following questions:
Is there any correlation between the marks obtained in education and psychology?
On the basis trend line what would be the estimate of psychology marks of a student if his marks in the education is 60
The following table shows the daily maximum temperature for New Delhi, recorded for six days, in degrees centigrade. Prepare frequency polygon.
Following is the distribution of marks in English test obtained by the students. Construct histogram and frequency polygon, and explain the findings about the trend.
Following is the line diagram indicating the number of customers at different time of a day in a bank.
By reading the graph, answer the following questions:
What does the graph tell you?
Which is the busiest time of day in the bank?
At what time does the customers start coming in less numbers?
When the bank opens how many customers are there?
How many people are in the bank at 3:30 p.m.?
The line graph shows the minimum temperature of the day in a city during a week. Read the graph carefully, and answer the following questions.
On which day there was the lowest temperature and what it was?
On which day the temperature was 14 °C?
This pie chart shows a survey results which were carried out to find the student’s preferences about different sports in a school.
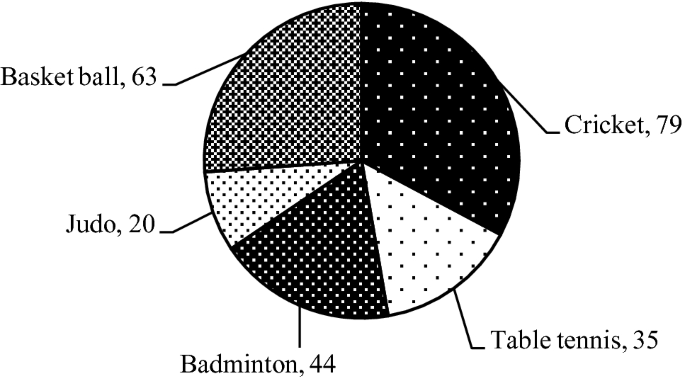
Which is the most popular sport in the school?
What percentage of the students prefers to play table tennis?
Based on the same pattern, if 40 students play cricket, how many total students would play these five sports?
In a college, the distribution of students belonging to different regions of India are as follows. Construct a pie diagram.
In an industry, the break-up of the employees in different categories is as follows:
Construct a suitable graph to show these data. Also explain as to why you have chosen a particular graph for this data.
The following table shows the data on IQ obtained on the college students, arranged in the class interval form. Construct ogive, and find the median IQ of the students.
In a management institute, the students come from different states to complete their MBA programme. Following are the distribution of students during the last five years. Construct pie diagram.
The following are the marks of the students in English. Prepare ogive, and find its median. Check whether median obtained by the ogive is equal to the median obtained by computing its value.
In a college, following number of male and female students formed different sports teams. The director of sports wants to make a presentation for the annual report. Suggest the kind of graph he should make and draw the graph accordingly.
In a survey, it was found that the people use different modes of media to know the current news. The details are as follows:
Construct bar diagram horizontally as well as vertically.
Following is the number of patients reported in the health centre during last one year. How will you find the trend of the patient’s arrival? Construct a suitable graph to know the trend of patient’s arrival. (Hint: prepare frequency polygon).
Discuss the situations under which different types of graphs should be constructed. Explain their merits and demerits.
Check Your Graphical Skill
b , c and e . In all these equations, power of none of the variables is more than 1.
The angles for the grades are as follows:
47 approximately
Median = 60.
Check Your Graphical Concepts
1. (c) 2. (a) 3. (b) 4. (b) 5. (a) 6. (d)
7. (a) 8. (b) 9. (d) 10. (c) 11. (a) 12. (d)
(a) There is a high degree of correlation.
(b) The estimated marks in psychology would be 60.
As the number of marks in English increases, the number of students decreases. In other words, fewer students secure higher marks in English.
(a) The graph tells the arrival pattern of the customers in the bank.
(b) The busiest time in the bank is 1 p.m.
(c) The customers start coming in less numbers from 3 p.m. onward.
(d) At the time of opening the bank, 3 customers are there.
(e) Four people are there at 3.30 pm in the bank.
(a) On Thursday, there was the lowest temperature and it was 4 °C.
(b) On Sunday the temperature was 14 °C.
(a) Cricket is the most popular sport in the school.
(b) 14.52% of the students prefer to play table tennis.
Median = 59
Distribution of angle would be as follows:
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Sport Psychology, Lakshmibai National Institute of Physical Education, Gwalior, India
Prof. J. P. Verma
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to J. P. Verma .
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2019 Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this chapter
Cite this chapter.
Verma, J.P. (2019). Graphical Presentation of Data. In: Statistics and Research Methods in Psychology with Excel. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-13-3429-0_4
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-13-3429-0_4
Published : 28 August 2019
Publisher Name : Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN : 978-981-13-3428-3
Online ISBN : 978-981-13-3429-0
eBook Packages : Mathematics and Statistics Mathematics and Statistics (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
- Graphic Presentation of Data
Apart from diagrams, Graphic presentation is another way of the presentation of data and information. Usually, graphs are used to present time series and frequency distributions. In this article, we will look at the graphic presentation of data and information along with its merits, limitations , and types.
Suggested Videos
Construction of a graph.
The graphic presentation of data and information offers a quick and simple way of understanding the features and drawing comparisons. Further, it is an effective analytical tool and a graph can help us in finding the mode, median, etc.
We can locate a point in a plane using two mutually perpendicular lines – the X-axis (the horizontal line) and the Y-axis (the vertical line). Their point of intersection is the Origin .
We can locate the position of a point in terms of its distance from both these axes. For example, if a point P is 3 units away from the Y-axis and 5 units away from the X-axis, then its location is as follows:

Browse more Topics under Descriptive Statistics
- Definition and Characteristics of Statistics
- Stages of Statistical Enquiry
- Importance and Functions of Statistics
- Nature of Statistics – Science or Art?
- Application of Statistics
- Law of Statistics and Distrust of Statistics
- Meaning and Types of Data
- Methods of Collecting Data
- Sample Investigation
- Classification of Data
- Tabulation of Data
- Frequency Distribution of Data
- Diagrammatic Presentation of Data
- Measures of Central Tendency
- Mean Median Mode
- Measures of Dispersion
- Standard Deviation
- Variance Analysis
Some points to remember:
- We measure the distance of the point from the Y-axis along the X-axis. Similarly, we measure the distance of the point from the X-axis along the Y-axis. Therefore, to measure 3 units from the Y-axis, we move 3 units along the X-axis and likewise for the other coordinate .
- We then draw perpendicular lines from these two points.
- The point where the perpendiculars intersect is the position of the point P.
- We denote it as follows (3,5) or (abscissa, ordinate). Together, they are the coordinates of the point P.
- The four parts of the plane are Quadrants.
- Also, we can plot different points for a different pair of values.
General Rules for Graphic Presentation of Data and Information
There are certain guidelines for an attractive and effective graphic presentation of data and information. These are as follows:
- Suitable Title – Ensure that you give a suitable title to the graph which clearly indicates the subject for which you are presenting it.
- Unit of Measurement – Clearly state the unit of measurement below the title.
- Suitable Scale – Choose a suitable scale so that you can represent the entire data in an accurate manner.
- Index – Include a brief index which explains the different colors and shades, lines and designs that you have used in the graph. Also, include a scale of interpretation for better understanding.
- Data Sources – Wherever possible, include the sources of information at the bottom of the graph.
- Keep it Simple – You should construct a graph which even a layman (without any exposure in the areas of statistics or mathematics) can understand.
- Neat – A graph is a visual aid for the presentation of data and information. Therefore, you must keep it neat and attractive. Choose the right size, right lettering, and appropriate lines, colors, dashes, etc.
Merits of a Graph
- The graph presents data in a manner which is easier to understand.
- It allows us to present statistical data in an attractive manner as compared to tables. Users can understand the main features, trends, and fluctuations of the data at a glance.
- A graph saves time.
- It allows the viewer to compare data relating to two different time-periods or regions.
- The viewer does not require prior knowledge of mathematics or statistics to understand a graph.
- We can use a graph to locate the mode, median, and mean values of the data.
- It is useful in forecasting, interpolation, and extrapolation of data.
Limitations of a Graph
- A graph lacks complete accuracy of facts.
- It depicts only a few selected characteristics of the data.
- We cannot use a graph in support of a statement.
- A graph is not a substitute for tables.
- Usually, laymen find it difficult to understand and interpret a graph.
- Typically, a graph shows the unreasonable tendency of the data and the actual values are not clear.
Types of Graphs
Graphs are of two types:
- Time Series graphs
- Frequency Distribution graphs
Time Series Graphs
A time series graph or a “ histogram ” is a graph which depicts the value of a variable over a different point of time. In a time series graph, time is the most important factor and the variable is related to time. It helps in the understanding and analysis of the changes in the variable at a different point of time. Many statisticians and businessmen use these graphs because they are easy to understand and also because they offer complex information in a simple manner.
Further, constructing a time series graph does not require a user with technical skills. Here are some major steps in the construction of a time series graph:
- Represent time on the X-axis and the value of the variable on the Y-axis.
- Start the Y-value with zero and devise a suitable scale which helps you present the whole data in the given space.
- Plot the values of the variable and join different point with a straight line.
- You can plot multiple variables through different lines.
You can use a line graph to summarize how two pieces of information are related and how they vary with each other.
- You can compare multiple continuous data-sets easily
- You can infer the interim data from the graph line
Disadvantages
- It is only used with continuous data.
Use of a false Base Line
Usually, in a graph, the vertical line starts from the Origin. However, in some cases, a false Base Line is used for a better representation of the data. There are two scenarios where you should use a false Base Line:
- To magnify the minor fluctuation in the time series data
- To economize the space
Net Balance Graph
If you have to show the net balance of income and expenditure or revenue and costs or imports and exports, etc., then you must use a net balance graph. You can use different colors or shades for positive and negative differences.
Frequency Distribution Graphs
Let’s look at the different types of frequency distribution graphs.
A histogram is a graph of a grouped frequency distribution. In a histogram, we plot the class intervals on the X-axis and their respective frequencies on the Y-axis. Further, we create a rectangle on each class interval with its height proportional to the frequency density of the class.

Frequency Polygon or Histograph
A frequency polygon or a Histograph is another way of representing a frequency distribution on a graph. You draw a frequency polygon by joining the midpoints of the upper widths of the adjacent rectangles of the histogram with straight lines.

Frequency Curve
When you join the verticals of a polygon using a smooth curve, then the resulting figure is a Frequency Curve. As the number of observations increase, we need to accommodate more classes. Therefore, the width of each class reduces. In such a scenario, the variable tends to become continuous and the frequency polygon starts taking the shape of a frequency curve.
Cumulative Frequency Curve or Ogive
A cumulative frequency curve or Ogive is the graphical representation of a cumulative frequency distribution. Since a cumulative frequency is either of a ‘less than’ or a ‘more than’ type, Ogives are of two types too – ‘less than ogive’ and ‘more than ogive’.

Scatter Diagram
A scatter diagram or a dot chart enables us to find the nature of the relationship between the variables. If the plotted points are scattered a lot, then the relationship between the two variables is lesser.

Solved Question
Q1. What are the general rules for the graphic presentation of data and information?
Answer: The general rules for the graphic presentation of data are:
- Use a suitable title
- Clearly specify the unit of measurement
- Ensure that you choose a suitable scale
- Provide an index specifying the colors, lines, and designs used in the graph
- If possible, provide the sources of information at the bottom of the graph
- Keep the graph simple and neat.
Customize your course in 30 seconds
Which class are you in.

Descriptive Statistics
- Nature of Statistics – Science or Art?
2 responses to “Stages of Statistical Enquiry”
Im trying to find out if my mother ALICE Desjarlais is registered with the Red Pheasant Reserve, I applied with Metie Urban Housing and I need my Metie card. Is there anyway you can help me.
Quite useful details about statistics. I’d also like to add one point. If you need professional help with a statistics project? Find a professional in minutes!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Download the App

- Business Essentials
- Leadership & Management
- Credential of Leadership, Impact, and Management in Business (CLIMB)
- Entrepreneurship & Innovation
- *New* Digital Transformation
- Finance & Accounting
- Business in Society
- For Organizations
- Support Portal
- Media Coverage
- Founding Donors
- Leadership Team

- Harvard Business School →
- HBS Online →
- Business Insights →
Business Insights
Harvard Business School Online's Business Insights Blog provides the career insights you need to achieve your goals and gain confidence in your business skills.
- Career Development
- Communication
- Decision-Making
- Earning Your MBA
- Negotiation
- News & Events
- Productivity
- Staff Spotlight
- Student Profiles
- Work-Life Balance
- Alternative Investments
- Business Analytics
- Business Strategy
- Business and Climate Change
- Design Thinking and Innovation
- Digital Marketing Strategy
- Disruptive Strategy
- Economics for Managers
- Entrepreneurship Essentials
- Financial Accounting
- Global Business
- Launching Tech Ventures
- Leadership Principles
- Leadership, Ethics, and Corporate Accountability
- Leading with Finance
- Management Essentials
- Negotiation Mastery
- Organizational Leadership
- Power and Influence for Positive Impact
- Strategy Execution
- Sustainable Business Strategy
- Sustainable Investing
- Winning with Digital Platforms
17 Data Visualization Techniques All Professionals Should Know

- 17 Sep 2019
There’s a growing demand for business analytics and data expertise in the workforce. But you don’t need to be a professional analyst to benefit from data-related skills.
Becoming skilled at common data visualization techniques can help you reap the rewards of data-driven decision-making , including increased confidence and potential cost savings. Learning how to effectively visualize data could be the first step toward using data analytics and data science to your advantage to add value to your organization.
Several data visualization techniques can help you become more effective in your role. Here are 17 essential data visualization techniques all professionals should know, as well as tips to help you effectively present your data.
Access your free e-book today.
What Is Data Visualization?
Data visualization is the process of creating graphical representations of information. This process helps the presenter communicate data in a way that’s easy for the viewer to interpret and draw conclusions.
There are many different techniques and tools you can leverage to visualize data, so you want to know which ones to use and when. Here are some of the most important data visualization techniques all professionals should know.
Data Visualization Techniques
The type of data visualization technique you leverage will vary based on the type of data you’re working with, in addition to the story you’re telling with your data .
Here are some important data visualization techniques to know:
- Gantt Chart
- Box and Whisker Plot
- Waterfall Chart
- Scatter Plot
- Pictogram Chart
- Highlight Table
- Bullet Graph
- Choropleth Map
- Network Diagram
- Correlation Matrices
1. Pie Chart

Pie charts are one of the most common and basic data visualization techniques, used across a wide range of applications. Pie charts are ideal for illustrating proportions, or part-to-whole comparisons.
Because pie charts are relatively simple and easy to read, they’re best suited for audiences who might be unfamiliar with the information or are only interested in the key takeaways. For viewers who require a more thorough explanation of the data, pie charts fall short in their ability to display complex information.
2. Bar Chart
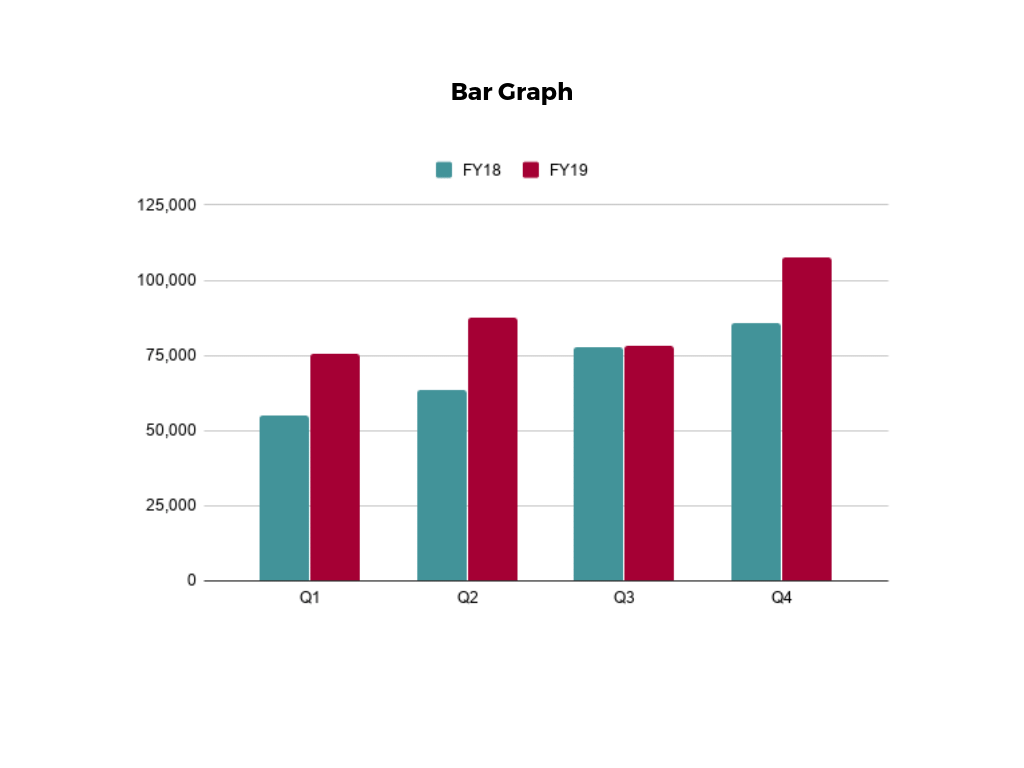
The classic bar chart , or bar graph, is another common and easy-to-use method of data visualization. In this type of visualization, one axis of the chart shows the categories being compared, and the other, a measured value. The length of the bar indicates how each group measures according to the value.
One drawback is that labeling and clarity can become problematic when there are too many categories included. Like pie charts, they can also be too simple for more complex data sets.
3. Histogram

Unlike bar charts, histograms illustrate the distribution of data over a continuous interval or defined period. These visualizations are helpful in identifying where values are concentrated, as well as where there are gaps or unusual values.
Histograms are especially useful for showing the frequency of a particular occurrence. For instance, if you’d like to show how many clicks your website received each day over the last week, you can use a histogram. From this visualization, you can quickly determine which days your website saw the greatest and fewest number of clicks.
4. Gantt Chart

Gantt charts are particularly common in project management, as they’re useful in illustrating a project timeline or progression of tasks. In this type of chart, tasks to be performed are listed on the vertical axis and time intervals on the horizontal axis. Horizontal bars in the body of the chart represent the duration of each activity.
Utilizing Gantt charts to display timelines can be incredibly helpful, and enable team members to keep track of every aspect of a project. Even if you’re not a project management professional, familiarizing yourself with Gantt charts can help you stay organized.
5. Heat Map
A heat map is a type of visualization used to show differences in data through variations in color. These charts use color to communicate values in a way that makes it easy for the viewer to quickly identify trends. Having a clear legend is necessary in order for a user to successfully read and interpret a heatmap.
There are many possible applications of heat maps. For example, if you want to analyze which time of day a retail store makes the most sales, you can use a heat map that shows the day of the week on the vertical axis and time of day on the horizontal axis. Then, by shading in the matrix with colors that correspond to the number of sales at each time of day, you can identify trends in the data that allow you to determine the exact times your store experiences the most sales.
6. A Box and Whisker Plot
A box and whisker plot , or box plot, provides a visual summary of data through its quartiles. First, a box is drawn from the first quartile to the third of the data set. A line within the box represents the median. “Whiskers,” or lines, are then drawn extending from the box to the minimum (lower extreme) and maximum (upper extreme). Outliers are represented by individual points that are in-line with the whiskers.
This type of chart is helpful in quickly identifying whether or not the data is symmetrical or skewed, as well as providing a visual summary of the data set that can be easily interpreted.
7. Waterfall Chart
A waterfall chart is a visual representation that illustrates how a value changes as it’s influenced by different factors, such as time. The main goal of this chart is to show the viewer how a value has grown or declined over a defined period. For example, waterfall charts are popular for showing spending or earnings over time.
8. Area Chart

An area chart , or area graph, is a variation on a basic line graph in which the area underneath the line is shaded to represent the total value of each data point. When several data series must be compared on the same graph, stacked area charts are used.
This method of data visualization is useful for showing changes in one or more quantities over time, as well as showing how each quantity combines to make up the whole. Stacked area charts are effective in showing part-to-whole comparisons.
9. Scatter Plot

Another technique commonly used to display data is a scatter plot . A scatter plot displays data for two variables as represented by points plotted against the horizontal and vertical axis. This type of data visualization is useful in illustrating the relationships that exist between variables and can be used to identify trends or correlations in data.
Scatter plots are most effective for fairly large data sets, since it’s often easier to identify trends when there are more data points present. Additionally, the closer the data points are grouped together, the stronger the correlation or trend tends to be.
10. Pictogram Chart
Pictogram charts , or pictograph charts, are particularly useful for presenting simple data in a more visual and engaging way. These charts use icons to visualize data, with each icon representing a different value or category. For example, data about time might be represented by icons of clocks or watches. Each icon can correspond to either a single unit or a set number of units (for example, each icon represents 100 units).
In addition to making the data more engaging, pictogram charts are helpful in situations where language or cultural differences might be a barrier to the audience’s understanding of the data.
11. Timeline

Timelines are the most effective way to visualize a sequence of events in chronological order. They’re typically linear, with key events outlined along the axis. Timelines are used to communicate time-related information and display historical data.
Timelines allow you to highlight the most important events that occurred, or need to occur in the future, and make it easy for the viewer to identify any patterns appearing within the selected time period. While timelines are often relatively simple linear visualizations, they can be made more visually appealing by adding images, colors, fonts, and decorative shapes.
12. Highlight Table

A highlight table is a more engaging alternative to traditional tables. By highlighting cells in the table with color, you can make it easier for viewers to quickly spot trends and patterns in the data. These visualizations are useful for comparing categorical data.
Depending on the data visualization tool you’re using, you may be able to add conditional formatting rules to the table that automatically color cells that meet specified conditions. For instance, when using a highlight table to visualize a company’s sales data, you may color cells red if the sales data is below the goal, or green if sales were above the goal. Unlike a heat map, the colors in a highlight table are discrete and represent a single meaning or value.
13. Bullet Graph

A bullet graph is a variation of a bar graph that can act as an alternative to dashboard gauges to represent performance data. The main use for a bullet graph is to inform the viewer of how a business is performing in comparison to benchmarks that are in place for key business metrics.
In a bullet graph, the darker horizontal bar in the middle of the chart represents the actual value, while the vertical line represents a comparative value, or target. If the horizontal bar passes the vertical line, the target for that metric has been surpassed. Additionally, the segmented colored sections behind the horizontal bar represent range scores, such as “poor,” “fair,” or “good.”
14. Choropleth Maps

A choropleth map uses color, shading, and other patterns to visualize numerical values across geographic regions. These visualizations use a progression of color (or shading) on a spectrum to distinguish high values from low.
Choropleth maps allow viewers to see how a variable changes from one region to the next. A potential downside to this type of visualization is that the exact numerical values aren’t easily accessible because the colors represent a range of values. Some data visualization tools, however, allow you to add interactivity to your map so the exact values are accessible.
15. Word Cloud

A word cloud , or tag cloud, is a visual representation of text data in which the size of the word is proportional to its frequency. The more often a specific word appears in a dataset, the larger it appears in the visualization. In addition to size, words often appear bolder or follow a specific color scheme depending on their frequency.
Word clouds are often used on websites and blogs to identify significant keywords and compare differences in textual data between two sources. They are also useful when analyzing qualitative datasets, such as the specific words consumers used to describe a product.
16. Network Diagram

Network diagrams are a type of data visualization that represent relationships between qualitative data points. These visualizations are composed of nodes and links, also called edges. Nodes are singular data points that are connected to other nodes through edges, which show the relationship between multiple nodes.
There are many use cases for network diagrams, including depicting social networks, highlighting the relationships between employees at an organization, or visualizing product sales across geographic regions.
17. Correlation Matrix

A correlation matrix is a table that shows correlation coefficients between variables. Each cell represents the relationship between two variables, and a color scale is used to communicate whether the variables are correlated and to what extent.
Correlation matrices are useful to summarize and find patterns in large data sets. In business, a correlation matrix might be used to analyze how different data points about a specific product might be related, such as price, advertising spend, launch date, etc.
Other Data Visualization Options
While the examples listed above are some of the most commonly used techniques, there are many other ways you can visualize data to become a more effective communicator. Some other data visualization options include:
- Bubble clouds
- Circle views
- Dendrograms
- Dot distribution maps
- Open-high-low-close charts
- Polar areas
- Radial trees
- Ring Charts
- Sankey diagram
- Span charts
- Streamgraphs
- Wedge stack graphs
- Violin plots

Tips For Creating Effective Visualizations
Creating effective data visualizations requires more than just knowing how to choose the best technique for your needs. There are several considerations you should take into account to maximize your effectiveness when it comes to presenting data.
Related : What to Keep in Mind When Creating Data Visualizations in Excel
One of the most important steps is to evaluate your audience. For example, if you’re presenting financial data to a team that works in an unrelated department, you’ll want to choose a fairly simple illustration. On the other hand, if you’re presenting financial data to a team of finance experts, it’s likely you can safely include more complex information.
Another helpful tip is to avoid unnecessary distractions. Although visual elements like animation can be a great way to add interest, they can also distract from the key points the illustration is trying to convey and hinder the viewer’s ability to quickly understand the information.
Finally, be mindful of the colors you utilize, as well as your overall design. While it’s important that your graphs or charts are visually appealing, there are more practical reasons you might choose one color palette over another. For instance, using low contrast colors can make it difficult for your audience to discern differences between data points. Using colors that are too bold, however, can make the illustration overwhelming or distracting for the viewer.
Related : Bad Data Visualization: 5 Examples of Misleading Data
Visuals to Interpret and Share Information
No matter your role or title within an organization, data visualization is a skill that’s important for all professionals. Being able to effectively present complex data through easy-to-understand visual representations is invaluable when it comes to communicating information with members both inside and outside your business.
There’s no shortage in how data visualization can be applied in the real world. Data is playing an increasingly important role in the marketplace today, and data literacy is the first step in understanding how analytics can be used in business.
Are you interested in improving your analytical skills? Learn more about Business Analytics , our eight-week online course that can help you use data to generate insights and tackle business decisions.
This post was updated on January 20, 2022. It was originally published on September 17, 2019.

About the Author
Talk to our experts
1800-120-456-456
- Graphs and Graphical Representation

What are Graphs and Graphical Representation?
Graphical representation refers to the use of charts and graphs to visually analyze and display, interpret numerical value, clarify the qualitative structures. The data is represented by a variety of symbols such as line charts, bars, circles, ratios. Through this, greater insight is stuck in the mind while analyzing the information.
Graphs can easily illustrate the behavior, highlight changes, and can study data points that may sometimes be overlooked. The type of data presentation depends upon the type of data being used.
Graphical Representation of Data
The graphical representation is simply a way of analyzing numerical data. It comprises a relation between data, information, and ideas in a diagram. Anything portrayed in a graphical manner is easy to understand and is also termed as the most important learning technique. The graphical presentation is always dependent on the type of information conveyed. There are different types of graphical representation. These are as follows:
Line Graphs:
Also denoted as linear graphs are used to examine continuous data and are also useful in predicting future events in time.
Histograms:
This graph uses bars to represent the information. The bars represent the frequency of numerical data. All intervals are equal and hence, the width of each bar is also equal.
Bar Graphs:
These are used to display the categories and compare the data using solid bars. These bars represent the quantities.
Frequency Table:
This table shows the frequency of data that falls within that given time interval.
Line Plot:
It shows the frequency of data on a given line number.
Circle Graph:
It is also known as a pie chart and shows the relationship between the parts of the whole. The circle consists of 100% and other parts shown are in different proportions.
Scatter Plot:
The diagram shows the relationship between two sets of data. Each dot represents individual information of the data.
Venn Diagram:
It consists of overlapping circles, each depicting a set. The inner-circle made is a graphical representation.
Stem and Leaf Plot:
The data is organized from the least value to the highest value. The digits of the least place value form the leaf and that of the highest place value form the stem.
Box and Whisker Plot:
The data is summarised by dividing it into four parts. Box and whisker show the spread and median of the data.
Graphical Presentation of Data - Definition
It is a way of analyzing numerical data. It is a sort of chart which shows statistical data in the form of lines or curves which are plotted on the surface. It enables studying the cause and effect relationships between two variables . It helps to measure the extent of change in one variable when another variable changes.
Principles of Graphical Representation
The variables in the graph are represented using two lines called coordinate axes. The horizontal and vertical axes are denoted by x and y respectively. Their point of intersection is called an origin ‘O’. Considering x-axes, the distance from the origin to the right will take a positive value, and the distance from the origin to the left will take a negative value. Taking the same procedure on y-axes. The points above origin will take the positive values and the points below origin will take negative values. As discussed in the earlier section about the types of graphical representation. There are four most widely used graphs namely histogram, pie diagram, frequency polygon, and ogive frequency graph.
Rules for Graphical Representation of Data
There are certain rules to effectively represent the information in graphical form. Certain rules are discussed below:
Title: One has to make sure that a suitable title is given to the graph which indicates the presentation subject.
Scale: It should be used efficiently to represent data in an accurate manner.
Measurement unit: It is used to calculate the distance between the box
Index: Differentiate appropriate colors, shades, and design I graph for a better understanding of the information conveyed.
Data sources: Include the source of information at the bottom graph wherever necessary. It adds to the authenticity of the information.
Keep it simple: Construct the graph in an easy to understand manner and keep it simple for the reader to understand. Looking at the graph the information portrayed is easily understandable.
Importance of Graphical Representation of Data
Some of the importance and advantages of using graphs to interpret data are listed below:
The graph is easiest to understand as the information portrayed is in facts and figures. Any information depicted in facts, figures, comparison grabs our attention, due to which they are memorizable for the long term.
It allows us to relate and compare data for different time periods.
It is used in statistics to determine the mean , mode, and median of different data.
It saves a lot of time as it covers most of the information in facts and figures. This in turn compacts the information.

FAQs on Graphs and Graphical Representation
Q1. State the Advantages and Disadvantages of Graphical Representation of Data?
Ans: These graphical presentations of data are vital components in analyzing the information. Data visualization is one of the most fundamental approaches to data representation. Its advantages include the following points:
Facilitates and improves learning
Flexibility of use
Understands content
Increase structure thinking
Supports creative thinking
Portrays the whole picture
Improves communication
With advantages, certain disadvantages are also linked to the graphical representation. The disadvantages concern the high cost of human effort, the process of selecting the most appropriate graphical and tabular presentation, creative thinking, greater design to interpret information, visualizing data, and as human resource is used. The potential for human bias plays a huge role.
Q2. What is the Graphical Representation of Data in Statistics?
Graphs are powerful data evaluation tools. They provide a quick visual summary of the information. In statistics information depicted is of mean, mode, and median. Box plots, histograms are used to depict the information. These graphs provide information about ranges, shapes, concentration, extreme values, etc. It studies information between different sets and trends whether increasing or decreasing. Since graphical methods are qualitative, they are not only the basis of comparison and information.
- School Guide
- Class 9 Syllabus
- Maths Notes Class 9
- Science Notes Class 9
- History Notes Class 9
- Geography Notes Class 9
- Political Science Notes Class 9
- NCERT Soln. Class 9 Maths
- RD Sharma Soln. Class 9
- Math Formulas Class 9
- CBSE Class 9 Maths Revision Notes
Chapter 1: Number System
- Number System in Maths
- Natural Numbers | Definition, Examples, Properties
- Whole Numbers | Definition, Properties and Examples
- Rational Number: Definition, Examples, Worksheet
- Irrational Numbers- Definition, Identification, Examples, Symbol, Properties
- Real Numbers
- Decimal Expansion of Real Numbers
- Decimal Expansions of Rational Numbers
- Representation of Rational Numbers on the Number Line | Class 8 Maths
- Represent √3 on the number line
- Operations on Real Numbers
- Rationalization of Denominators
- Laws of Exponents for Real Numbers
Chapter 2: Polynomials
- Polynomials in One Variable - Polynomials | Class 9 Maths
- Polynomial Formula
- Types of Polynomials
- Zeros of Polynomial
- Factorization of Polynomial
- Remainder Theorem
- Factor Theorem
- Algebraic Identities
Chapter 3: Coordinate Geometry
- Coordinate Geometry
- Cartesian Coordinate System in Maths
- Cartesian Plane
Chapter 4: Linear equations in two variables
- Linear Equations in One Variable
- Linear Equation in Two Variables
- Graph of Linear Equations in Two Variables
- Graphical Methods of Solving Pair of Linear Equations in Two Variables
- Equations of Lines Parallel to the x-axis and y-axis
Chapter 5: Introduction to Euclid's Geometry
- Euclidean Geometry
- Equivalent Version of Euclid’s Fifth Postulate
Chapter 6: Lines and Angles
- Lines and Angles
- Types of Angles
- Pairs of Angles - Lines & Angles
- Transversal Lines
- Angle Sum Property of a Triangle
Chapter 7: Triangles
- Triangles in Geometry
- Congruence of Triangles |SSS, SAS, ASA, and RHS Rules
- Theorem - Angle opposite to equal sides of an isosceles triangle are equal | Class 9 Maths
- Triangle Inequality Theorem, Proof & Applications
Chapter 8: Quadrilateral
- Angle Sum Property of a Quadrilateral
- Quadrilateral - Definition, Properties, Types, Formulas, Examples
- Introduction to Parallelogram: Properties, Types, and Theorem
- Rhombus: Definition, Properties, Formula, Examples
- Kite - Quadrilaterals
- Properties of Parallelograms
- Mid Point Theorem
Chapter 9: Areas of Parallelograms and Triangles
- Area of Triangle | Formula and Examples
- Area of Parallelogram
- Figures on the Same Base and between the Same Parallels
Chapter 10: Circles
- Circles in Maths
- Radius of Circle
- Tangent to a Circle
- What is the longest chord of a Circle?
- Circumference of Circle - Definition, Perimeter Formula, and Examples
- Angle subtended by an arc at the centre of a circle
- What is Cyclic Quadrilateral
- Theorem - The sum of opposite angles of a cyclic quadrilateral is 180° | Class 9 Maths
Chapter 11: Construction
- Basic Constructions - Angle Bisector, Perpendicular Bisector, Angle of 60°
- Construction of Triangles
Chapter 12: Heron's Formula
- Area of Equilateral Triangle
- Area of Isosceles Triangle
- Heron's Formula
- Applications of Heron's Formula
- Area of Quadrilateral
- Area of Polygons
Chapter 13: Surface Areas and Volumes
- Surface Area of Cuboid
- Volume of Cuboid | Formula and Examples
- Surface Area of Cube
- Volume of a Cube
- Surface Area of Cylinder (CSA and TSA) |Formula, Derivation, Examples
- Volume of Cylinder
- Surface Area of Cone
- Volume of Cone | Formula, Derivation and Examples
- Surface Area of Sphere | CSA, TSA, Formula and Derivation
- Volume of a Sphere
- Surface Area of a Hemisphere
- Volume of Hemisphere
Chapter 14: Statistics
- Collection and Presentation of Data
Graphical Representation of Data
- Bar graphs and Histograms
- Central Tendency
- Mean, Median and Mode
Chapter 15: Probability
- Experimental Probability
- Empirical Probability
- CBSE Class 9 Maths Formulas
- NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths
- RD Sharma Class 9 Solutions
In today’s world of the internet and connectivity, there is a lot of data available and some or the other method is needed for looking at large data, the patterns, and trends in it. There is an entire branch in mathematics dedicated to dealing with collecting, analyzing, interpreting, and presenting the numerical data in visual form in such a way that it becomes easy to understand and the data becomes easy to compare as well, the branch is known as Statistics . The branch is widely spread and has a plethora of real-life applications such as Business Analytics, demography, astrostatistics, and so on. There are two ways of representing data,
- Pictorial Representation through graphs.
They say, “A picture is worth the thousand words”. It’s always better to represent data in graphical format. Even in Practical Evidence and Surveys, scientists have found that the restoration and understanding of any information is better when it is available in form of visuals as Human beings process data better in visual form than any other form. Does it increase the ability 2 times or 3 times? The answer is it increases the Power of understanding 60,000 times for a normal Human being, the fact is amusing and true at the same time. Let’s look at some of them in detail.
Types of Graphical Representations
Comparison between different items is best shown with graphs, it becomes easier to compare the crux out of the data pertaining to different items. Let’s look at all the different types of graphical representations briefly:
Line Graphs
A line graph is used to show how the value of particular variable changes with time. We plot this graph by connecting the points at different values of the variable. It can be useful for analyzing the trends in the data predicting further trends.
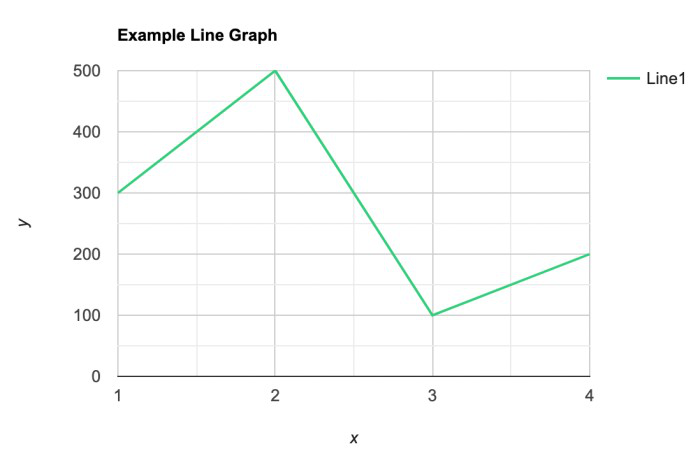
A bar graph is a type of graphical representation of the data in which bars of uniform width are drawn with equal spacing between them on one axis (x-axis usually), depicting the variable. The values of the variables are represented by the height of the bars.
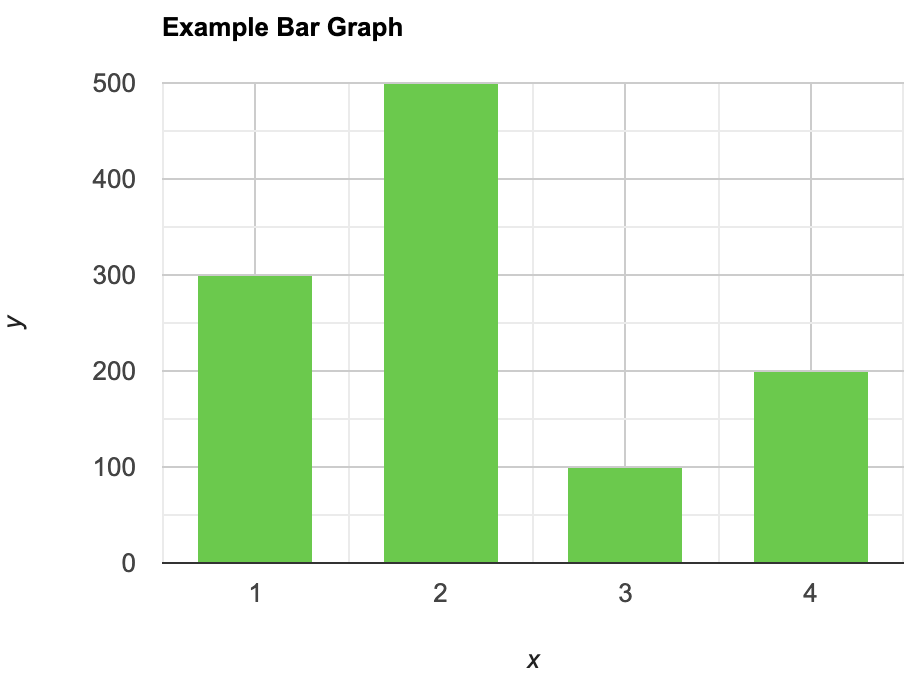
Histograms
This is similar to bar graphs, but it is based frequency of numerical values rather than their actual values. The data is organized into intervals and the bars represent the frequency of the values in that range. That is, it counts how many values of the data lie in a particular range.
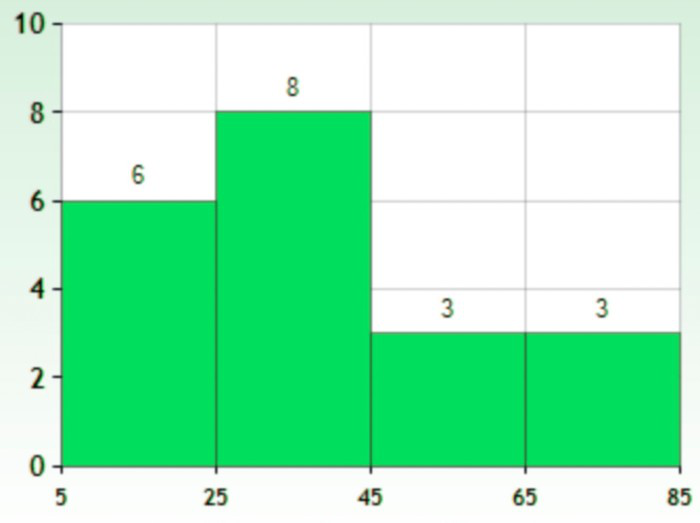
Line Plot
It is a plot that displays data as points and checkmarks above a number line, showing the frequency of the point.
Stem and Leaf Plot
This is a type of plot in which each value is split into a “leaf”(in most cases, it is the last digit) and “stem”(the other remaining digits). For example: the number 42 is split into leaf (2) and stem (4).
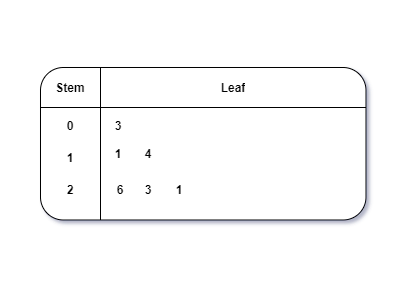
Box and Whisker Plot
These plots divide the data into four parts to show their summary. They are more concerned about the spread, average, and median of the data.
It is a type of graph which represents the data in form of a circular graph. The circle is divided such that each portion represents a proportion of the whole.

Graphical Representations used in Maths
Graphs in maths are used to study the relationships between two or more variables that are changing. Statistical data can be summarized in a better way using graphs. There are basically two lines of thoughts of making graphs in maths:
- Value-Based or Time Series Graphs
Frequency Based
Value-based or time series graphs .
These graphs allow us to study the change of a variable with respect to another variable within a given interval of time. The variables can be anything. Time Series graphs study the change of variable with time. They study the trends, periodic behavior, and patterns in the series. We are more concerned with the values of the variables here rather than the frequency of those values.
Example: Line Graph
These kinds of graphs are more concerned with the distribution of data. How many values lie between a particular range of the variables, and which range has the maximum frequency of the values. They are used to judge a spread and average and sometimes median of a variable under study.
Example: Frequency Polygon, Histograms.
Principles of Graphical Representations
All types of graphical representations require some rule/principles which are to be followed. These are some algebraic principles. When we plot a graph, there is an origin, and we have our two axes. These two axes divide the plane into four parts called quadrants. The horizontal one is usually called the x-axis and the other one is called the y-axis. The origin is the point where these two axes intersect. The thing we need to keep in mind about the values of the variable on the x-axis is that positive values need to be on the right side of the origin and negative values should be on the left side of the origin. Similarly, for the variable on the y-axis, we need to make sure that the positive values of this variable should be above the x-axis and negative values of this variable must be below the y-axis.
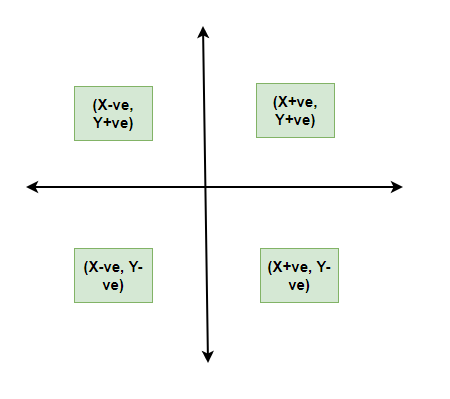
Advantages and Disadvantages of using Graphical System
Advantages:
- It gives us a summary of the data which is easier to look at and analyze.
- It saves time.
- We can compare and study more than one variable at a time.
Disadvantage:
It usually takes only one aspect of the data and ignores the other. For example, A bar graph does not represent the mean, median, and other statistics of the data.
General Rules for Graphical Representation of Data
We should keep in mind some things while plotting and designing these graphs. The goal should be a better and clear picture of the data. Following things should be kept in mind while plotting the above graphs:
- Whenever possible, the data source must be mentioned for the viewer.
- Always choose the proper colors and font sizes. They should be chosen to keep in mind that the graphs should look neat.
- The measurement Unit should be mentioned in the top right corner of the graph.
- The proper scale should be chosen while making the graph, it should be chosen such that the graph looks accurate.
- Last but not the least, a suitable title should be chosen.
Frequency Polygon
A frequency polygon is a graph that is constructed by joining the midpoint of the intervals. The height of the interval or the bin represents the frequency of the values that lie in that interval.
Sample Problems
Question 1: What are different types of frequency-based plots?
Answer:
Types of frequency based plots: Histogram Frequency Polygon Box Plots
Question 2: A company with an advertising budget of Rs 10,00,00,000 has planned the following expenditure in the different advertising channels such as TV Advertisement, Radio, Facebook, Instagram, and Printed media. The table represents the money spent on different channels.
Draw a bar graph for the following data.
Solution:
Steps: Put each of the channels on the x-axis The height of the bars is decided by the value of each channel.
Question 3: Draw a line plot for the following data
Steps: Put each of the x-axis row value on the x-axis joint the value corresponding to the each value of the x-axis.
Question 4: Make a frequency plot of the following data:
Steps: Draw the class intervals on the x-axis and frequencies on the y-axis. Calculate the mid point of each class interval. Class Interval Mid Point Frequency 0-3 1.5 3 3-6 4.5 4 6-9 7.5 2 9-12 10.5 6 Now join the mid points of the intervals and their corresponding frequencies on the graph. This graph shows both the histogram and frequency polygon for the given distribution.
Please Login to comment...
Similar reads.
- Mathematics
- School Learning
- 10 Ways to Use Slack for Effective Communication
- 10 Ways to Use Google Docs for Collaborative Writing
- NEET MDS 2024 Result: Toppers List, Category-wise Cutoff, and Important Dates
- NDA Admit Card 2024 Live Updates: Download Your Hall Ticket Soon on upsc.gov.in!
- 30 OOPs Interview Questions and Answers (2024)
Improve your Coding Skills with Practice
What kind of Experience do you want to share?
Presentation of Data
Statistics deals with the collection, presentation and analysis of the data, as well as drawing meaningful conclusions from the given data. Generally, the data can be classified into two different types, namely primary data and secondary data. If the information is collected by the investigator with a definite objective in their mind, then the data obtained is called the primary data. If the information is gathered from a source, which already had the information stored, then the data obtained is called secondary data. Once the data is collected, the presentation of data plays a major role in concluding the result. Here, we will discuss how to present the data with many solved examples.
What is Meant by Presentation of Data?
As soon as the data collection is over, the investigator needs to find a way of presenting the data in a meaningful, efficient and easily understood way to identify the main features of the data at a glance using a suitable presentation method. Generally, the data in the statistics can be presented in three different forms, such as textual method, tabular method and graphical method.
Presentation of Data Examples
Now, let us discuss how to present the data in a meaningful way with the help of examples.
Consider the marks given below, which are obtained by 10 students in Mathematics:
36, 55, 73, 95, 42, 60, 78, 25, 62, 75.
Find the range for the given data.
Given Data: 36, 55, 73, 95, 42, 60, 78, 25, 62, 75.
The data given is called the raw data.
First, arrange the data in the ascending order : 25, 36, 42, 55, 60, 62, 73, 75, 78, 95.
Therefore, the lowest mark is 25 and the highest mark is 95.
We know that the range of the data is the difference between the highest and the lowest value in the dataset.
Therefore, Range = 95-25 = 70.
Note: Presentation of data in ascending or descending order can be time-consuming if we have a larger number of observations in an experiment.
Now, let us discuss how to present the data if we have a comparatively more number of observations in an experiment.
Consider the marks obtained by 30 students in Mathematics subject (out of 100 marks)
10, 20, 36, 92, 95, 40, 50, 56, 60, 70, 92, 88, 80, 70, 72, 70, 36, 40, 36, 40, 92, 40, 50, 50, 56, 60, 70, 60, 60, 88.
In this example, the number of observations is larger compared to example 1. So, the presentation of data in ascending or descending order is a bit time-consuming. Hence, we can go for the method called ungrouped frequency distribution table or simply frequency distribution table . In this method, we can arrange the data in tabular form in terms of frequency.
For example, 3 students scored 50 marks. Hence, the frequency of 50 marks is 3. Now, let us construct the frequency distribution table for the given data.
Therefore, the presentation of data is given as below:
The following example shows the presentation of data for the larger number of observations in an experiment.
Consider the marks obtained by 100 students in a Mathematics subject (out of 100 marks)
95, 67, 28, 32, 65, 65, 69, 33, 98, 96,76, 42, 32, 38, 42, 40, 40, 69, 95, 92, 75, 83, 76, 83, 85, 62, 37, 65, 63, 42, 89, 65, 73, 81, 49, 52, 64, 76, 83, 92, 93, 68, 52, 79, 81, 83, 59, 82, 75, 82, 86, 90, 44, 62, 31, 36, 38, 42, 39, 83, 87, 56, 58, 23, 35, 76, 83, 85, 30, 68, 69, 83, 86, 43, 45, 39, 83, 75, 66, 83, 92, 75, 89, 66, 91, 27, 88, 89, 93, 42, 53, 69, 90, 55, 66, 49, 52, 83, 34, 36.
Now, we have 100 observations to present the data. In this case, we have more data when compared to example 1 and example 2. So, these data can be arranged in the tabular form called the grouped frequency table. Hence, we group the given data like 20-29, 30-39, 40-49, ….,90-99 (As our data is from 23 to 98). The grouping of data is called the “class interval” or “classes”, and the size of the class is called “class-size” or “class-width”.
In this case, the class size is 10. In each class, we have a lower-class limit and an upper-class limit. For example, if the class interval is 30-39, the lower-class limit is 30, and the upper-class limit is 39. Therefore, the least number in the class interval is called the lower-class limit and the greatest limit in the class interval is called upper-class limit.
Hence, the presentation of data in the grouped frequency table is given below:
Hence, the presentation of data in this form simplifies the data and it helps to enable the observer to understand the main feature of data at a glance.
Practice Problems
- The heights of 50 students (in cms) are given below. Present the data using the grouped frequency table by taking the class intervals as 160 -165, 165 -170, and so on. Data: 161, 150, 154, 165, 168, 161, 154, 162, 150, 151, 162, 164, 171, 165, 158, 154, 156, 172, 160, 170, 153, 159, 161, 170, 162, 165, 166, 168, 165, 164, 154, 152, 153, 156, 158, 162, 160, 161, 173, 166, 161, 159, 162, 167, 168, 159, 158, 153, 154, 159.
- Three coins are tossed simultaneously and each time the number of heads occurring is noted and it is given below. Present the data using the frequency distribution table. Data: 0, 1, 2, 2, 1, 2, 3, 1, 3, 0, 1, 3, 1, 1, 2, 2, 0, 1, 2, 1, 3, 0, 0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 2, 2, 0.
To learn more Maths-related concepts, stay tuned with BYJU’S – The Learning App and download the app today!
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
- Share Share
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.

METHODS article
Xputer: bridging data gaps with nmf, xgboost, and a streamlined gui experience provisionally accepted.

- 1 Division of Translational Cancer Research, Department of Laboratory Medicine, Faculty of Medicine, Lund University, Sweden
The final, formatted version of the article will be published soon.
The rapid proliferation of data across diverse fields has accentuated the importance of accurate imputation for missing values. This task is crucial for ensuring data integrity and deriving meaningful insights. In response to this challenge, we present Xputer, a novel imputation tool that adeptly integrates Non-negative Matrix Factorization (NMF) with the predictive strengths of XGBoost. One of Xputer's standout features is its versatility: it supports zero imputation, enables hyperparameter optimization through Optuna, and allows users to define the number of iterations. For enhanced user experience and accessibility, we have equipped Xputer with an intuitive Graphical User Interface (GUI) ensuring ease of handling, even for those less familiar with computational tools. In performance benchmarks, Xputer not only rivals the computational speed of established tools such as IterativeImputer but also often outperforms them in terms of imputation accuracy. Furthermore, Xputer autonomously handles a diverse spectrum of data types, including categorical, continuous, and Boolean, eliminating the need for prior preprocessing. Given its blend of performance, flexibility, and user-friendly design, Xputer emerges as a state-of-the-art solution in the realm of data imputation.
Keywords: Imputation, mix-type data, tabular data, ensemble learning, Matrix Factorization
Received: 27 Nov 2023; Accepted: 08 Apr 2024.
Copyright: © 2024 Younus, Rönnstrand and Kazi. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY) . The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) or licensor are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
* Correspondence: Mx. Julhash U. Kazi, Division of Translational Cancer Research, Department of Laboratory Medicine, Faculty of Medicine, Lund University, Lund, 404-406, Skane County, Sweden
People also looked at

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Graphical representation is a form of visually displaying data through various methods like graphs, diagrams, charts, and plots. It helps in sorting, visualizing, and presenting data in a clear manner through different types of graphs. Statistics mainly use graphical representation to show data.
Step 1: Define Your Data Hierarchy. While presenting data on the budget allocation, start by outlining the hierarchical structure. The sequence will be like the overall budget at the top, followed by departments, projects within each department, and finally, individual cost categories for each project. Example:
Data visualization definition. Data visualization is the presentation of data in a graphical format such as a plot, graph, or map to make it easier for decision makers to see and understand trends ...
Definition: Data presentation is the art of visualizing complex data for better understanding. Importance: Data presentations enhance clarity, engage the audience, aid decision-making, and leave a lasting impact. Types: Textual, Tabular, and Graphical presentations offer various ways to present data.
What are Graphs and Graphical Representation? Graphs, in the context of data visualization, are visual representations of data using various graphical elements such as charts, graphs, and diagrams.Graphical representation of data, often referred to as graphical presentation or simply graphs which plays a crucial role in conveying information effectively.
Data visualization is the graphical representation of information and data. By using v isual elements like charts, graphs, and maps, data visualization tools provide an accessible way to see and understand trends, outliers, and patterns in data. Additionally, it provides an excellent way for employees or business owners to present data to non ...
A histogram is a graphic version of a frequency distribution. The graph consists of bars of equal width drawn adjacent to each other. The horizontal scale represents classes of quantitative data values and the vertical scale represents frequencies. The heights of the bars correspond to frequency values. Histograms are typically used for large ...
A simple definition of data visualization: Data visualization is the visual presentation of data or information. The goal of data visualization is to communicate data or information clearly and effectively to readers. Typically, data is visualized in the form of a chart, infographic, diagram or map. The field of data visualization combines both ...
Data visualization is the representation of information and data using charts, graphs, maps, and other visual tools. These visualizations allow us to easily understand any patterns, trends, or outliers in a data set. Data visualization also presents data to the general public or specific audiences without technical knowledge in an accessible ...
Data visualisation beginner's guide: a definition, examples and learning resources. Data visualisation is the graphical representation of information and data. By using visual elements like charts, graphs and maps, data visualisation tools provide an accessible way to see and understand trends, outliers and patterns in data.
Graphs are a powerful and concise way to communicate information. Representing data from an experiment in the form of an x-y graph allows relationships to be examined, scatter in data to be assessed and allows for the rapid identification of special or unusual features. A well laid out graph containing all the components discussed in this chapter can act as a 'one stop' summary of a whole ...
Guidelines for Making Graphs. Remove stray lines, legends, points, and any other unintended additions by the computer that does not add to your graph. The scales should be chosen such that the data covers most of the area of the graph. The origin 0,0 is oftentimes included, but not always.
This page titled 1.3: Presentation of Data is shared under a CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by Anonymous via source content that was edited to the style and standards of the LibreTexts platform; a detailed edit history is available upon request. In this book we will use two formats for presenting data sets.
A researcher uses graph to get an idea about how these variables change relative to one another. Graphic presentation can be used in interpolation and extrapolation of data and helps in drawing inferences. Due to this reason, one will see many graphs, of course, in different forms in books, journals and theses.
Data Sources - Wherever possible, include the sources of information at the bottom of the graph. Keep it Simple - You should construct a graph which even a layman (without any exposure in the areas of statistics or mathematics) can understand. Neat - A graph is a visual aid for the presentation of data and information.
The fundamental benefits or merits of a diagrammatic and graphical representation of data are as follows: 1. To simplify the data: Outlines and charts present information in a simple manner that can be perceived by anyone without any problem. Huge volume of data can be easily presented using graphs and diagrams. 2.
Bullet Graph. Choropleth Map. Word Cloud. Network Diagram. Correlation Matrices. 1. Pie Chart. Pie charts are one of the most common and basic data visualization techniques, used across a wide range of applications. Pie charts are ideal for illustrating proportions, or part-to-whole comparisons.
Graph 2 Same data as in Graph 1, but in 2‐D. Better Representation of the data. •Values are not distorted by the skewed perspective. • Category labels are more space‐efficient. •The graph, not its title, occupies the most space. •Colors can be distin‐ guished, even by a color‐ blind reader Graph 3
Graphical Presentation of Data - Definition. It is a way of analyzing numerical data. It is a sort of chart which shows statistical data in the form of lines or curves which are plotted on the surface. It enables studying the cause and effect relationships between two variables. It helps to measure the extent of change in one variable when ...
What Is Data Presentation? Data presentation is a process of comparing two or more data sets with visual aids, such as graphs. Using a graph, you can represent how the information relates to other data. This process follows data analysis and helps organise information by visualising and putting it into a more readable format.
Data Sources: Include the source of information wherever it is necessary at the bottom of the graph. Keep it Simple: Construct a graph in an easy way that everyone can understand. Neat: Choose the correct size, fonts, colours etc in such a way that the graph should be a visual aid for the presentation of information. Graphical Representation in ...
A bar graph is a type of graphical representation of the data in which bars of uniform width are drawn with equal spacing between them on one axis (x-axis usually), depicting the variable. The values of the variables are represented by the height of the bars. Histograms.
So, these data can be arranged in the tabular form called the grouped frequency table. Hence, we group the given data like 20-29, 30-39, 40-49, ….,90-99 (As our data is from 23 to 98). The grouping of data is called the "class interval" or "classes", and the size of the class is called "class-size" or "class-width".
The rapid proliferation of data across diverse fields has accentuated the importance of accurate imputation for missing values. This task is crucial for ensuring data integrity and deriving meaningful insights. In response to this challenge, we present Xputer, a novel imputation tool that adeptly integrates Non-negative Matrix Factorization (NMF) with the predictive strengths of XGBoost. One ...