

The Ultimate Guide to Qualitative Research - Part 1: The Basics

- Introduction and overview
- What is qualitative research?
- What is qualitative data?
- Examples of qualitative data
- Qualitative vs. quantitative research
- Mixed methods
- Qualitative research preparation
- Theoretical perspective
- Theoretical framework
- Literature reviews
Research question
- Conceptual framework
- Conceptual vs. theoretical framework
Data collection
- Qualitative research methods
- Focus groups
- Observational research
What is a case study?
Applications for case study research, what is a good case study, process of case study design, benefits and limitations of case studies.
- Ethnographical research
- Ethical considerations
- Confidentiality and privacy
- Power dynamics
- Reflexivity
Case studies
Case studies are essential to qualitative research , offering a lens through which researchers can investigate complex phenomena within their real-life contexts. This chapter explores the concept, purpose, applications, examples, and types of case studies and provides guidance on how to conduct case study research effectively.

Whereas quantitative methods look at phenomena at scale, case study research looks at a concept or phenomenon in considerable detail. While analyzing a single case can help understand one perspective regarding the object of research inquiry, analyzing multiple cases can help obtain a more holistic sense of the topic or issue. Let's provide a basic definition of a case study, then explore its characteristics and role in the qualitative research process.
Definition of a case study
A case study in qualitative research is a strategy of inquiry that involves an in-depth investigation of a phenomenon within its real-world context. It provides researchers with the opportunity to acquire an in-depth understanding of intricate details that might not be as apparent or accessible through other methods of research. The specific case or cases being studied can be a single person, group, or organization – demarcating what constitutes a relevant case worth studying depends on the researcher and their research question .
Among qualitative research methods , a case study relies on multiple sources of evidence, such as documents, artifacts, interviews , or observations , to present a complete and nuanced understanding of the phenomenon under investigation. The objective is to illuminate the readers' understanding of the phenomenon beyond its abstract statistical or theoretical explanations.
Characteristics of case studies
Case studies typically possess a number of distinct characteristics that set them apart from other research methods. These characteristics include a focus on holistic description and explanation, flexibility in the design and data collection methods, reliance on multiple sources of evidence, and emphasis on the context in which the phenomenon occurs.
Furthermore, case studies can often involve a longitudinal examination of the case, meaning they study the case over a period of time. These characteristics allow case studies to yield comprehensive, in-depth, and richly contextualized insights about the phenomenon of interest.
The role of case studies in research
Case studies hold a unique position in the broader landscape of research methods aimed at theory development. They are instrumental when the primary research interest is to gain an intensive, detailed understanding of a phenomenon in its real-life context.
In addition, case studies can serve different purposes within research - they can be used for exploratory, descriptive, or explanatory purposes, depending on the research question and objectives. This flexibility and depth make case studies a valuable tool in the toolkit of qualitative researchers.
Remember, a well-conducted case study can offer a rich, insightful contribution to both academic and practical knowledge through theory development or theory verification, thus enhancing our understanding of complex phenomena in their real-world contexts.
What is the purpose of a case study?
Case study research aims for a more comprehensive understanding of phenomena, requiring various research methods to gather information for qualitative analysis . Ultimately, a case study can allow the researcher to gain insight into a particular object of inquiry and develop a theoretical framework relevant to the research inquiry.
Why use case studies in qualitative research?
Using case studies as a research strategy depends mainly on the nature of the research question and the researcher's access to the data.
Conducting case study research provides a level of detail and contextual richness that other research methods might not offer. They are beneficial when there's a need to understand complex social phenomena within their natural contexts.
The explanatory, exploratory, and descriptive roles of case studies
Case studies can take on various roles depending on the research objectives. They can be exploratory when the research aims to discover new phenomena or define new research questions; they are descriptive when the objective is to depict a phenomenon within its context in a detailed manner; and they can be explanatory if the goal is to understand specific relationships within the studied context. Thus, the versatility of case studies allows researchers to approach their topic from different angles, offering multiple ways to uncover and interpret the data .
The impact of case studies on knowledge development
Case studies play a significant role in knowledge development across various disciplines. Analysis of cases provides an avenue for researchers to explore phenomena within their context based on the collected data.

This can result in the production of rich, practical insights that can be instrumental in both theory-building and practice. Case studies allow researchers to delve into the intricacies and complexities of real-life situations, uncovering insights that might otherwise remain hidden.
Types of case studies
In qualitative research , a case study is not a one-size-fits-all approach. Depending on the nature of the research question and the specific objectives of the study, researchers might choose to use different types of case studies. These types differ in their focus, methodology, and the level of detail they provide about the phenomenon under investigation.
Understanding these types is crucial for selecting the most appropriate approach for your research project and effectively achieving your research goals. Let's briefly look at the main types of case studies.
Exploratory case studies
Exploratory case studies are typically conducted to develop a theory or framework around an understudied phenomenon. They can also serve as a precursor to a larger-scale research project. Exploratory case studies are useful when a researcher wants to identify the key issues or questions which can spur more extensive study or be used to develop propositions for further research. These case studies are characterized by flexibility, allowing researchers to explore various aspects of a phenomenon as they emerge, which can also form the foundation for subsequent studies.
Descriptive case studies
Descriptive case studies aim to provide a complete and accurate representation of a phenomenon or event within its context. These case studies are often based on an established theoretical framework, which guides how data is collected and analyzed. The researcher is concerned with describing the phenomenon in detail, as it occurs naturally, without trying to influence or manipulate it.
Explanatory case studies
Explanatory case studies are focused on explanation - they seek to clarify how or why certain phenomena occur. Often used in complex, real-life situations, they can be particularly valuable in clarifying causal relationships among concepts and understanding the interplay between different factors within a specific context.

Intrinsic, instrumental, and collective case studies
These three categories of case studies focus on the nature and purpose of the study. An intrinsic case study is conducted when a researcher has an inherent interest in the case itself. Instrumental case studies are employed when the case is used to provide insight into a particular issue or phenomenon. A collective case study, on the other hand, involves studying multiple cases simultaneously to investigate some general phenomena.
Each type of case study serves a different purpose and has its own strengths and challenges. The selection of the type should be guided by the research question and objectives, as well as the context and constraints of the research.
The flexibility, depth, and contextual richness offered by case studies make this approach an excellent research method for various fields of study. They enable researchers to investigate real-world phenomena within their specific contexts, capturing nuances that other research methods might miss. Across numerous fields, case studies provide valuable insights into complex issues.
Critical information systems research
Case studies provide a detailed understanding of the role and impact of information systems in different contexts. They offer a platform to explore how information systems are designed, implemented, and used and how they interact with various social, economic, and political factors. Case studies in this field often focus on examining the intricate relationship between technology, organizational processes, and user behavior, helping to uncover insights that can inform better system design and implementation.
Health research
Health research is another field where case studies are highly valuable. They offer a way to explore patient experiences, healthcare delivery processes, and the impact of various interventions in a real-world context.

Case studies can provide a deep understanding of a patient's journey, giving insights into the intricacies of disease progression, treatment effects, and the psychosocial aspects of health and illness.
Asthma research studies
Specifically within medical research, studies on asthma often employ case studies to explore the individual and environmental factors that influence asthma development, management, and outcomes. A case study can provide rich, detailed data about individual patients' experiences, from the triggers and symptoms they experience to the effectiveness of various management strategies. This can be crucial for developing patient-centered asthma care approaches.
Other fields
Apart from the fields mentioned, case studies are also extensively used in business and management research, education research, and political sciences, among many others. They provide an opportunity to delve into the intricacies of real-world situations, allowing for a comprehensive understanding of various phenomena.
Case studies, with their depth and contextual focus, offer unique insights across these varied fields. They allow researchers to illuminate the complexities of real-life situations, contributing to both theory and practice.
Whatever field you're in, ATLAS.ti puts your data to work for you
Download a free trial of ATLAS.ti to turn your data into insights.
Understanding the key elements of case study design is crucial for conducting rigorous and impactful case study research. A well-structured design guides the researcher through the process, ensuring that the study is methodologically sound and its findings are reliable and valid. The main elements of case study design include the research question , propositions, units of analysis, and the logic linking the data to the propositions.
The research question is the foundation of any research study. A good research question guides the direction of the study and informs the selection of the case, the methods of collecting data, and the analysis techniques. A well-formulated research question in case study research is typically clear, focused, and complex enough to merit further detailed examination of the relevant case(s).
Propositions
Propositions, though not necessary in every case study, provide a direction by stating what we might expect to find in the data collected. They guide how data is collected and analyzed by helping researchers focus on specific aspects of the case. They are particularly important in explanatory case studies, which seek to understand the relationships among concepts within the studied phenomenon.
Units of analysis
The unit of analysis refers to the case, or the main entity or entities that are being analyzed in the study. In case study research, the unit of analysis can be an individual, a group, an organization, a decision, an event, or even a time period. It's crucial to clearly define the unit of analysis, as it shapes the qualitative data analysis process by allowing the researcher to analyze a particular case and synthesize analysis across multiple case studies to draw conclusions.
Argumentation
This refers to the inferential model that allows researchers to draw conclusions from the data. The researcher needs to ensure that there is a clear link between the data, the propositions (if any), and the conclusions drawn. This argumentation is what enables the researcher to make valid and credible inferences about the phenomenon under study.
Understanding and carefully considering these elements in the design phase of a case study can significantly enhance the quality of the research. It can help ensure that the study is methodologically sound and its findings contribute meaningful insights about the case.
Ready to jumpstart your research with ATLAS.ti?
Conceptualize your research project with our intuitive data analysis interface. Download a free trial today.
Conducting a case study involves several steps, from defining the research question and selecting the case to collecting and analyzing data . This section outlines these key stages, providing a practical guide on how to conduct case study research.
Defining the research question
The first step in case study research is defining a clear, focused research question. This question should guide the entire research process, from case selection to analysis. It's crucial to ensure that the research question is suitable for a case study approach. Typically, such questions are exploratory or descriptive in nature and focus on understanding a phenomenon within its real-life context.
Selecting and defining the case
The selection of the case should be based on the research question and the objectives of the study. It involves choosing a unique example or a set of examples that provide rich, in-depth data about the phenomenon under investigation. After selecting the case, it's crucial to define it clearly, setting the boundaries of the case, including the time period and the specific context.
Previous research can help guide the case study design. When considering a case study, an example of a case could be taken from previous case study research and used to define cases in a new research inquiry. Considering recently published examples can help understand how to select and define cases effectively.
Developing a detailed case study protocol
A case study protocol outlines the procedures and general rules to be followed during the case study. This includes the data collection methods to be used, the sources of data, and the procedures for analysis. Having a detailed case study protocol ensures consistency and reliability in the study.
The protocol should also consider how to work with the people involved in the research context to grant the research team access to collecting data. As mentioned in previous sections of this guide, establishing rapport is an essential component of qualitative research as it shapes the overall potential for collecting and analyzing data.
Collecting data
Gathering data in case study research often involves multiple sources of evidence, including documents, archival records, interviews, observations, and physical artifacts. This allows for a comprehensive understanding of the case. The process for gathering data should be systematic and carefully documented to ensure the reliability and validity of the study.
Analyzing and interpreting data
The next step is analyzing the data. This involves organizing the data , categorizing it into themes or patterns , and interpreting these patterns to answer the research question. The analysis might also involve comparing the findings with prior research or theoretical propositions.
Writing the case study report
The final step is writing the case study report . This should provide a detailed description of the case, the data, the analysis process, and the findings. The report should be clear, organized, and carefully written to ensure that the reader can understand the case and the conclusions drawn from it.
Each of these steps is crucial in ensuring that the case study research is rigorous, reliable, and provides valuable insights about the case.
The type, depth, and quality of data in your study can significantly influence the validity and utility of the study. In case study research, data is usually collected from multiple sources to provide a comprehensive and nuanced understanding of the case. This section will outline the various methods of collecting data used in case study research and discuss considerations for ensuring the quality of the data.
Interviews are a common method of gathering data in case study research. They can provide rich, in-depth data about the perspectives, experiences, and interpretations of the individuals involved in the case. Interviews can be structured , semi-structured , or unstructured , depending on the research question and the degree of flexibility needed.
Observations
Observations involve the researcher observing the case in its natural setting, providing first-hand information about the case and its context. Observations can provide data that might not be revealed in interviews or documents, such as non-verbal cues or contextual information.
Documents and artifacts
Documents and archival records provide a valuable source of data in case study research. They can include reports, letters, memos, meeting minutes, email correspondence, and various public and private documents related to the case.

These records can provide historical context, corroborate evidence from other sources, and offer insights into the case that might not be apparent from interviews or observations.
Physical artifacts refer to any physical evidence related to the case, such as tools, products, or physical environments. These artifacts can provide tangible insights into the case, complementing the data gathered from other sources.
Ensuring the quality of data collection
Determining the quality of data in case study research requires careful planning and execution. It's crucial to ensure that the data is reliable, accurate, and relevant to the research question. This involves selecting appropriate methods of collecting data, properly training interviewers or observers, and systematically recording and storing the data. It also includes considering ethical issues related to collecting and handling data, such as obtaining informed consent and ensuring the privacy and confidentiality of the participants.
Data analysis
Analyzing case study research involves making sense of the rich, detailed data to answer the research question. This process can be challenging due to the volume and complexity of case study data. However, a systematic and rigorous approach to analysis can ensure that the findings are credible and meaningful. This section outlines the main steps and considerations in analyzing data in case study research.
Organizing the data
The first step in the analysis is organizing the data. This involves sorting the data into manageable sections, often according to the data source or the theme. This step can also involve transcribing interviews, digitizing physical artifacts, or organizing observational data.
Categorizing and coding the data
Once the data is organized, the next step is to categorize or code the data. This involves identifying common themes, patterns, or concepts in the data and assigning codes to relevant data segments. Coding can be done manually or with the help of software tools, and in either case, qualitative analysis software can greatly facilitate the entire coding process. Coding helps to reduce the data to a set of themes or categories that can be more easily analyzed.
Identifying patterns and themes
After coding the data, the researcher looks for patterns or themes in the coded data. This involves comparing and contrasting the codes and looking for relationships or patterns among them. The identified patterns and themes should help answer the research question.
Interpreting the data
Once patterns and themes have been identified, the next step is to interpret these findings. This involves explaining what the patterns or themes mean in the context of the research question and the case. This interpretation should be grounded in the data, but it can also involve drawing on theoretical concepts or prior research.
Verification of the data
The last step in the analysis is verification. This involves checking the accuracy and consistency of the analysis process and confirming that the findings are supported by the data. This can involve re-checking the original data, checking the consistency of codes, or seeking feedback from research participants or peers.
Like any research method , case study research has its strengths and limitations. Researchers must be aware of these, as they can influence the design, conduct, and interpretation of the study.
Understanding the strengths and limitations of case study research can also guide researchers in deciding whether this approach is suitable for their research question . This section outlines some of the key strengths and limitations of case study research.
Benefits include the following:
- Rich, detailed data: One of the main strengths of case study research is that it can generate rich, detailed data about the case. This can provide a deep understanding of the case and its context, which can be valuable in exploring complex phenomena.
- Flexibility: Case study research is flexible in terms of design , data collection , and analysis . A sufficient degree of flexibility allows the researcher to adapt the study according to the case and the emerging findings.
- Real-world context: Case study research involves studying the case in its real-world context, which can provide valuable insights into the interplay between the case and its context.
- Multiple sources of evidence: Case study research often involves collecting data from multiple sources , which can enhance the robustness and validity of the findings.
On the other hand, researchers should consider the following limitations:
- Generalizability: A common criticism of case study research is that its findings might not be generalizable to other cases due to the specificity and uniqueness of each case.
- Time and resource intensive: Case study research can be time and resource intensive due to the depth of the investigation and the amount of collected data.
- Complexity of analysis: The rich, detailed data generated in case study research can make analyzing the data challenging.
- Subjectivity: Given the nature of case study research, there may be a higher degree of subjectivity in interpreting the data , so researchers need to reflect on this and transparently convey to audiences how the research was conducted.
Being aware of these strengths and limitations can help researchers design and conduct case study research effectively and interpret and report the findings appropriately.

Ready to analyze your data with ATLAS.ti?
See how our intuitive software can draw key insights from your data with a free trial today.
- Privacy Policy

Home » Case Study – Methods, Examples and Guide
Case Study – Methods, Examples and Guide
Table of Contents

A case study is a research method that involves an in-depth examination and analysis of a particular phenomenon or case, such as an individual, organization, community, event, or situation.
It is a qualitative research approach that aims to provide a detailed and comprehensive understanding of the case being studied. Case studies typically involve multiple sources of data, including interviews, observations, documents, and artifacts, which are analyzed using various techniques, such as content analysis, thematic analysis, and grounded theory. The findings of a case study are often used to develop theories, inform policy or practice, or generate new research questions.
Types of Case Study
Types and Methods of Case Study are as follows:
Single-Case Study
A single-case study is an in-depth analysis of a single case. This type of case study is useful when the researcher wants to understand a specific phenomenon in detail.
For Example , A researcher might conduct a single-case study on a particular individual to understand their experiences with a particular health condition or a specific organization to explore their management practices. The researcher collects data from multiple sources, such as interviews, observations, and documents, and uses various techniques to analyze the data, such as content analysis or thematic analysis. The findings of a single-case study are often used to generate new research questions, develop theories, or inform policy or practice.
Multiple-Case Study
A multiple-case study involves the analysis of several cases that are similar in nature. This type of case study is useful when the researcher wants to identify similarities and differences between the cases.
For Example, a researcher might conduct a multiple-case study on several companies to explore the factors that contribute to their success or failure. The researcher collects data from each case, compares and contrasts the findings, and uses various techniques to analyze the data, such as comparative analysis or pattern-matching. The findings of a multiple-case study can be used to develop theories, inform policy or practice, or generate new research questions.
Exploratory Case Study
An exploratory case study is used to explore a new or understudied phenomenon. This type of case study is useful when the researcher wants to generate hypotheses or theories about the phenomenon.
For Example, a researcher might conduct an exploratory case study on a new technology to understand its potential impact on society. The researcher collects data from multiple sources, such as interviews, observations, and documents, and uses various techniques to analyze the data, such as grounded theory or content analysis. The findings of an exploratory case study can be used to generate new research questions, develop theories, or inform policy or practice.
Descriptive Case Study
A descriptive case study is used to describe a particular phenomenon in detail. This type of case study is useful when the researcher wants to provide a comprehensive account of the phenomenon.
For Example, a researcher might conduct a descriptive case study on a particular community to understand its social and economic characteristics. The researcher collects data from multiple sources, such as interviews, observations, and documents, and uses various techniques to analyze the data, such as content analysis or thematic analysis. The findings of a descriptive case study can be used to inform policy or practice or generate new research questions.
Instrumental Case Study
An instrumental case study is used to understand a particular phenomenon that is instrumental in achieving a particular goal. This type of case study is useful when the researcher wants to understand the role of the phenomenon in achieving the goal.
For Example, a researcher might conduct an instrumental case study on a particular policy to understand its impact on achieving a particular goal, such as reducing poverty. The researcher collects data from multiple sources, such as interviews, observations, and documents, and uses various techniques to analyze the data, such as content analysis or thematic analysis. The findings of an instrumental case study can be used to inform policy or practice or generate new research questions.
Case Study Data Collection Methods
Here are some common data collection methods for case studies:
Interviews involve asking questions to individuals who have knowledge or experience relevant to the case study. Interviews can be structured (where the same questions are asked to all participants) or unstructured (where the interviewer follows up on the responses with further questions). Interviews can be conducted in person, over the phone, or through video conferencing.
Observations
Observations involve watching and recording the behavior and activities of individuals or groups relevant to the case study. Observations can be participant (where the researcher actively participates in the activities) or non-participant (where the researcher observes from a distance). Observations can be recorded using notes, audio or video recordings, or photographs.
Documents can be used as a source of information for case studies. Documents can include reports, memos, emails, letters, and other written materials related to the case study. Documents can be collected from the case study participants or from public sources.
Surveys involve asking a set of questions to a sample of individuals relevant to the case study. Surveys can be administered in person, over the phone, through mail or email, or online. Surveys can be used to gather information on attitudes, opinions, or behaviors related to the case study.
Artifacts are physical objects relevant to the case study. Artifacts can include tools, equipment, products, or other objects that provide insights into the case study phenomenon.
How to conduct Case Study Research
Conducting a case study research involves several steps that need to be followed to ensure the quality and rigor of the study. Here are the steps to conduct case study research:
- Define the research questions: The first step in conducting a case study research is to define the research questions. The research questions should be specific, measurable, and relevant to the case study phenomenon under investigation.
- Select the case: The next step is to select the case or cases to be studied. The case should be relevant to the research questions and should provide rich and diverse data that can be used to answer the research questions.
- Collect data: Data can be collected using various methods, such as interviews, observations, documents, surveys, and artifacts. The data collection method should be selected based on the research questions and the nature of the case study phenomenon.
- Analyze the data: The data collected from the case study should be analyzed using various techniques, such as content analysis, thematic analysis, or grounded theory. The analysis should be guided by the research questions and should aim to provide insights and conclusions relevant to the research questions.
- Draw conclusions: The conclusions drawn from the case study should be based on the data analysis and should be relevant to the research questions. The conclusions should be supported by evidence and should be clearly stated.
- Validate the findings: The findings of the case study should be validated by reviewing the data and the analysis with participants or other experts in the field. This helps to ensure the validity and reliability of the findings.
- Write the report: The final step is to write the report of the case study research. The report should provide a clear description of the case study phenomenon, the research questions, the data collection methods, the data analysis, the findings, and the conclusions. The report should be written in a clear and concise manner and should follow the guidelines for academic writing.
Examples of Case Study
Here are some examples of case study research:
- The Hawthorne Studies : Conducted between 1924 and 1932, the Hawthorne Studies were a series of case studies conducted by Elton Mayo and his colleagues to examine the impact of work environment on employee productivity. The studies were conducted at the Hawthorne Works plant of the Western Electric Company in Chicago and included interviews, observations, and experiments.
- The Stanford Prison Experiment: Conducted in 1971, the Stanford Prison Experiment was a case study conducted by Philip Zimbardo to examine the psychological effects of power and authority. The study involved simulating a prison environment and assigning participants to the role of guards or prisoners. The study was controversial due to the ethical issues it raised.
- The Challenger Disaster: The Challenger Disaster was a case study conducted to examine the causes of the Space Shuttle Challenger explosion in 1986. The study included interviews, observations, and analysis of data to identify the technical, organizational, and cultural factors that contributed to the disaster.
- The Enron Scandal: The Enron Scandal was a case study conducted to examine the causes of the Enron Corporation’s bankruptcy in 2001. The study included interviews, analysis of financial data, and review of documents to identify the accounting practices, corporate culture, and ethical issues that led to the company’s downfall.
- The Fukushima Nuclear Disaster : The Fukushima Nuclear Disaster was a case study conducted to examine the causes of the nuclear accident that occurred at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant in Japan in 2011. The study included interviews, analysis of data, and review of documents to identify the technical, organizational, and cultural factors that contributed to the disaster.
Application of Case Study
Case studies have a wide range of applications across various fields and industries. Here are some examples:
Business and Management
Case studies are widely used in business and management to examine real-life situations and develop problem-solving skills. Case studies can help students and professionals to develop a deep understanding of business concepts, theories, and best practices.
Case studies are used in healthcare to examine patient care, treatment options, and outcomes. Case studies can help healthcare professionals to develop critical thinking skills, diagnose complex medical conditions, and develop effective treatment plans.
Case studies are used in education to examine teaching and learning practices. Case studies can help educators to develop effective teaching strategies, evaluate student progress, and identify areas for improvement.
Social Sciences
Case studies are widely used in social sciences to examine human behavior, social phenomena, and cultural practices. Case studies can help researchers to develop theories, test hypotheses, and gain insights into complex social issues.
Law and Ethics
Case studies are used in law and ethics to examine legal and ethical dilemmas. Case studies can help lawyers, policymakers, and ethical professionals to develop critical thinking skills, analyze complex cases, and make informed decisions.
Purpose of Case Study
The purpose of a case study is to provide a detailed analysis of a specific phenomenon, issue, or problem in its real-life context. A case study is a qualitative research method that involves the in-depth exploration and analysis of a particular case, which can be an individual, group, organization, event, or community.
The primary purpose of a case study is to generate a comprehensive and nuanced understanding of the case, including its history, context, and dynamics. Case studies can help researchers to identify and examine the underlying factors, processes, and mechanisms that contribute to the case and its outcomes. This can help to develop a more accurate and detailed understanding of the case, which can inform future research, practice, or policy.
Case studies can also serve other purposes, including:
- Illustrating a theory or concept: Case studies can be used to illustrate and explain theoretical concepts and frameworks, providing concrete examples of how they can be applied in real-life situations.
- Developing hypotheses: Case studies can help to generate hypotheses about the causal relationships between different factors and outcomes, which can be tested through further research.
- Providing insight into complex issues: Case studies can provide insights into complex and multifaceted issues, which may be difficult to understand through other research methods.
- Informing practice or policy: Case studies can be used to inform practice or policy by identifying best practices, lessons learned, or areas for improvement.
Advantages of Case Study Research
There are several advantages of case study research, including:
- In-depth exploration: Case study research allows for a detailed exploration and analysis of a specific phenomenon, issue, or problem in its real-life context. This can provide a comprehensive understanding of the case and its dynamics, which may not be possible through other research methods.
- Rich data: Case study research can generate rich and detailed data, including qualitative data such as interviews, observations, and documents. This can provide a nuanced understanding of the case and its complexity.
- Holistic perspective: Case study research allows for a holistic perspective of the case, taking into account the various factors, processes, and mechanisms that contribute to the case and its outcomes. This can help to develop a more accurate and comprehensive understanding of the case.
- Theory development: Case study research can help to develop and refine theories and concepts by providing empirical evidence and concrete examples of how they can be applied in real-life situations.
- Practical application: Case study research can inform practice or policy by identifying best practices, lessons learned, or areas for improvement.
- Contextualization: Case study research takes into account the specific context in which the case is situated, which can help to understand how the case is influenced by the social, cultural, and historical factors of its environment.
Limitations of Case Study Research
There are several limitations of case study research, including:
- Limited generalizability : Case studies are typically focused on a single case or a small number of cases, which limits the generalizability of the findings. The unique characteristics of the case may not be applicable to other contexts or populations, which may limit the external validity of the research.
- Biased sampling: Case studies may rely on purposive or convenience sampling, which can introduce bias into the sample selection process. This may limit the representativeness of the sample and the generalizability of the findings.
- Subjectivity: Case studies rely on the interpretation of the researcher, which can introduce subjectivity into the analysis. The researcher’s own biases, assumptions, and perspectives may influence the findings, which may limit the objectivity of the research.
- Limited control: Case studies are typically conducted in naturalistic settings, which limits the control that the researcher has over the environment and the variables being studied. This may limit the ability to establish causal relationships between variables.
- Time-consuming: Case studies can be time-consuming to conduct, as they typically involve a detailed exploration and analysis of a specific case. This may limit the feasibility of conducting multiple case studies or conducting case studies in a timely manner.
- Resource-intensive: Case studies may require significant resources, including time, funding, and expertise. This may limit the ability of researchers to conduct case studies in resource-constrained settings.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Questionnaire – Definition, Types, and Examples

Observational Research – Methods and Guide

Quantitative Research – Methods, Types and...

Qualitative Research Methods

Explanatory Research – Types, Methods, Guide

Survey Research – Types, Methods, Examples
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Methodology
- Case Study | Definition, Examples & Methods
Case Study | Definition, Examples & Methods
Published on 5 May 2022 by Shona McCombes . Revised on 30 January 2023.
A case study is a detailed study of a specific subject, such as a person, group, place, event, organisation, or phenomenon. Case studies are commonly used in social, educational, clinical, and business research.
A case study research design usually involves qualitative methods , but quantitative methods are sometimes also used. Case studies are good for describing , comparing, evaluating, and understanding different aspects of a research problem .
Table of contents
When to do a case study, step 1: select a case, step 2: build a theoretical framework, step 3: collect your data, step 4: describe and analyse the case.
A case study is an appropriate research design when you want to gain concrete, contextual, in-depth knowledge about a specific real-world subject. It allows you to explore the key characteristics, meanings, and implications of the case.
Case studies are often a good choice in a thesis or dissertation . They keep your project focused and manageable when you don’t have the time or resources to do large-scale research.
You might use just one complex case study where you explore a single subject in depth, or conduct multiple case studies to compare and illuminate different aspects of your research problem.
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
Once you have developed your problem statement and research questions , you should be ready to choose the specific case that you want to focus on. A good case study should have the potential to:
- Provide new or unexpected insights into the subject
- Challenge or complicate existing assumptions and theories
- Propose practical courses of action to resolve a problem
- Open up new directions for future research
Unlike quantitative or experimental research, a strong case study does not require a random or representative sample. In fact, case studies often deliberately focus on unusual, neglected, or outlying cases which may shed new light on the research problem.
If you find yourself aiming to simultaneously investigate and solve an issue, consider conducting action research . As its name suggests, action research conducts research and takes action at the same time, and is highly iterative and flexible.
However, you can also choose a more common or representative case to exemplify a particular category, experience, or phenomenon.
While case studies focus more on concrete details than general theories, they should usually have some connection with theory in the field. This way the case study is not just an isolated description, but is integrated into existing knowledge about the topic. It might aim to:
- Exemplify a theory by showing how it explains the case under investigation
- Expand on a theory by uncovering new concepts and ideas that need to be incorporated
- Challenge a theory by exploring an outlier case that doesn’t fit with established assumptions
To ensure that your analysis of the case has a solid academic grounding, you should conduct a literature review of sources related to the topic and develop a theoretical framework . This means identifying key concepts and theories to guide your analysis and interpretation.
There are many different research methods you can use to collect data on your subject. Case studies tend to focus on qualitative data using methods such as interviews, observations, and analysis of primary and secondary sources (e.g., newspaper articles, photographs, official records). Sometimes a case study will also collect quantitative data .
The aim is to gain as thorough an understanding as possible of the case and its context.
In writing up the case study, you need to bring together all the relevant aspects to give as complete a picture as possible of the subject.
How you report your findings depends on the type of research you are doing. Some case studies are structured like a standard scientific paper or thesis, with separate sections or chapters for the methods , results , and discussion .
Others are written in a more narrative style, aiming to explore the case from various angles and analyse its meanings and implications (for example, by using textual analysis or discourse analysis ).
In all cases, though, make sure to give contextual details about the case, connect it back to the literature and theory, and discuss how it fits into wider patterns or debates.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, January 30). Case Study | Definition, Examples & Methods. Scribbr. Retrieved 21 May 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/research-methods/case-studies/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, correlational research | guide, design & examples, a quick guide to experimental design | 5 steps & examples, descriptive research design | definition, methods & examples.
- Open access
- Published: 27 June 2011
The case study approach
- Sarah Crowe 1 ,
- Kathrin Cresswell 2 ,
- Ann Robertson 2 ,
- Guro Huby 3 ,
- Anthony Avery 1 &
- Aziz Sheikh 2
BMC Medical Research Methodology volume 11 , Article number: 100 ( 2011 ) Cite this article
781k Accesses
1039 Citations
37 Altmetric
Metrics details
The case study approach allows in-depth, multi-faceted explorations of complex issues in their real-life settings. The value of the case study approach is well recognised in the fields of business, law and policy, but somewhat less so in health services research. Based on our experiences of conducting several health-related case studies, we reflect on the different types of case study design, the specific research questions this approach can help answer, the data sources that tend to be used, and the particular advantages and disadvantages of employing this methodological approach. The paper concludes with key pointers to aid those designing and appraising proposals for conducting case study research, and a checklist to help readers assess the quality of case study reports.
Peer Review reports
Introduction
The case study approach is particularly useful to employ when there is a need to obtain an in-depth appreciation of an issue, event or phenomenon of interest, in its natural real-life context. Our aim in writing this piece is to provide insights into when to consider employing this approach and an overview of key methodological considerations in relation to the design, planning, analysis, interpretation and reporting of case studies.
The illustrative 'grand round', 'case report' and 'case series' have a long tradition in clinical practice and research. Presenting detailed critiques, typically of one or more patients, aims to provide insights into aspects of the clinical case and, in doing so, illustrate broader lessons that may be learnt. In research, the conceptually-related case study approach can be used, for example, to describe in detail a patient's episode of care, explore professional attitudes to and experiences of a new policy initiative or service development or more generally to 'investigate contemporary phenomena within its real-life context' [ 1 ]. Based on our experiences of conducting a range of case studies, we reflect on when to consider using this approach, discuss the key steps involved and illustrate, with examples, some of the practical challenges of attaining an in-depth understanding of a 'case' as an integrated whole. In keeping with previously published work, we acknowledge the importance of theory to underpin the design, selection, conduct and interpretation of case studies[ 2 ]. In so doing, we make passing reference to the different epistemological approaches used in case study research by key theoreticians and methodologists in this field of enquiry.
This paper is structured around the following main questions: What is a case study? What are case studies used for? How are case studies conducted? What are the potential pitfalls and how can these be avoided? We draw in particular on four of our own recently published examples of case studies (see Tables 1 , 2 , 3 and 4 ) and those of others to illustrate our discussion[ 3 – 7 ].
What is a case study?
A case study is a research approach that is used to generate an in-depth, multi-faceted understanding of a complex issue in its real-life context. It is an established research design that is used extensively in a wide variety of disciplines, particularly in the social sciences. A case study can be defined in a variety of ways (Table 5 ), the central tenet being the need to explore an event or phenomenon in depth and in its natural context. It is for this reason sometimes referred to as a "naturalistic" design; this is in contrast to an "experimental" design (such as a randomised controlled trial) in which the investigator seeks to exert control over and manipulate the variable(s) of interest.
Stake's work has been particularly influential in defining the case study approach to scientific enquiry. He has helpfully characterised three main types of case study: intrinsic , instrumental and collective [ 8 ]. An intrinsic case study is typically undertaken to learn about a unique phenomenon. The researcher should define the uniqueness of the phenomenon, which distinguishes it from all others. In contrast, the instrumental case study uses a particular case (some of which may be better than others) to gain a broader appreciation of an issue or phenomenon. The collective case study involves studying multiple cases simultaneously or sequentially in an attempt to generate a still broader appreciation of a particular issue.
These are however not necessarily mutually exclusive categories. In the first of our examples (Table 1 ), we undertook an intrinsic case study to investigate the issue of recruitment of minority ethnic people into the specific context of asthma research studies, but it developed into a instrumental case study through seeking to understand the issue of recruitment of these marginalised populations more generally, generating a number of the findings that are potentially transferable to other disease contexts[ 3 ]. In contrast, the other three examples (see Tables 2 , 3 and 4 ) employed collective case study designs to study the introduction of workforce reconfiguration in primary care, the implementation of electronic health records into hospitals, and to understand the ways in which healthcare students learn about patient safety considerations[ 4 – 6 ]. Although our study focusing on the introduction of General Practitioners with Specialist Interests (Table 2 ) was explicitly collective in design (four contrasting primary care organisations were studied), is was also instrumental in that this particular professional group was studied as an exemplar of the more general phenomenon of workforce redesign[ 4 ].
What are case studies used for?
According to Yin, case studies can be used to explain, describe or explore events or phenomena in the everyday contexts in which they occur[ 1 ]. These can, for example, help to understand and explain causal links and pathways resulting from a new policy initiative or service development (see Tables 2 and 3 , for example)[ 1 ]. In contrast to experimental designs, which seek to test a specific hypothesis through deliberately manipulating the environment (like, for example, in a randomised controlled trial giving a new drug to randomly selected individuals and then comparing outcomes with controls),[ 9 ] the case study approach lends itself well to capturing information on more explanatory ' how ', 'what' and ' why ' questions, such as ' how is the intervention being implemented and received on the ground?'. The case study approach can offer additional insights into what gaps exist in its delivery or why one implementation strategy might be chosen over another. This in turn can help develop or refine theory, as shown in our study of the teaching of patient safety in undergraduate curricula (Table 4 )[ 6 , 10 ]. Key questions to consider when selecting the most appropriate study design are whether it is desirable or indeed possible to undertake a formal experimental investigation in which individuals and/or organisations are allocated to an intervention or control arm? Or whether the wish is to obtain a more naturalistic understanding of an issue? The former is ideally studied using a controlled experimental design, whereas the latter is more appropriately studied using a case study design.
Case studies may be approached in different ways depending on the epistemological standpoint of the researcher, that is, whether they take a critical (questioning one's own and others' assumptions), interpretivist (trying to understand individual and shared social meanings) or positivist approach (orientating towards the criteria of natural sciences, such as focusing on generalisability considerations) (Table 6 ). Whilst such a schema can be conceptually helpful, it may be appropriate to draw on more than one approach in any case study, particularly in the context of conducting health services research. Doolin has, for example, noted that in the context of undertaking interpretative case studies, researchers can usefully draw on a critical, reflective perspective which seeks to take into account the wider social and political environment that has shaped the case[ 11 ].
How are case studies conducted?
Here, we focus on the main stages of research activity when planning and undertaking a case study; the crucial stages are: defining the case; selecting the case(s); collecting and analysing the data; interpreting data; and reporting the findings.
Defining the case
Carefully formulated research question(s), informed by the existing literature and a prior appreciation of the theoretical issues and setting(s), are all important in appropriately and succinctly defining the case[ 8 , 12 ]. Crucially, each case should have a pre-defined boundary which clarifies the nature and time period covered by the case study (i.e. its scope, beginning and end), the relevant social group, organisation or geographical area of interest to the investigator, the types of evidence to be collected, and the priorities for data collection and analysis (see Table 7 )[ 1 ]. A theory driven approach to defining the case may help generate knowledge that is potentially transferable to a range of clinical contexts and behaviours; using theory is also likely to result in a more informed appreciation of, for example, how and why interventions have succeeded or failed[ 13 ].
For example, in our evaluation of the introduction of electronic health records in English hospitals (Table 3 ), we defined our cases as the NHS Trusts that were receiving the new technology[ 5 ]. Our focus was on how the technology was being implemented. However, if the primary research interest had been on the social and organisational dimensions of implementation, we might have defined our case differently as a grouping of healthcare professionals (e.g. doctors and/or nurses). The precise beginning and end of the case may however prove difficult to define. Pursuing this same example, when does the process of implementation and adoption of an electronic health record system really begin or end? Such judgements will inevitably be influenced by a range of factors, including the research question, theory of interest, the scope and richness of the gathered data and the resources available to the research team.
Selecting the case(s)
The decision on how to select the case(s) to study is a very important one that merits some reflection. In an intrinsic case study, the case is selected on its own merits[ 8 ]. The case is selected not because it is representative of other cases, but because of its uniqueness, which is of genuine interest to the researchers. This was, for example, the case in our study of the recruitment of minority ethnic participants into asthma research (Table 1 ) as our earlier work had demonstrated the marginalisation of minority ethnic people with asthma, despite evidence of disproportionate asthma morbidity[ 14 , 15 ]. In another example of an intrinsic case study, Hellstrom et al.[ 16 ] studied an elderly married couple living with dementia to explore how dementia had impacted on their understanding of home, their everyday life and their relationships.
For an instrumental case study, selecting a "typical" case can work well[ 8 ]. In contrast to the intrinsic case study, the particular case which is chosen is of less importance than selecting a case that allows the researcher to investigate an issue or phenomenon. For example, in order to gain an understanding of doctors' responses to health policy initiatives, Som undertook an instrumental case study interviewing clinicians who had a range of responsibilities for clinical governance in one NHS acute hospital trust[ 17 ]. Sampling a "deviant" or "atypical" case may however prove even more informative, potentially enabling the researcher to identify causal processes, generate hypotheses and develop theory.
In collective or multiple case studies, a number of cases are carefully selected. This offers the advantage of allowing comparisons to be made across several cases and/or replication. Choosing a "typical" case may enable the findings to be generalised to theory (i.e. analytical generalisation) or to test theory by replicating the findings in a second or even a third case (i.e. replication logic)[ 1 ]. Yin suggests two or three literal replications (i.e. predicting similar results) if the theory is straightforward and five or more if the theory is more subtle. However, critics might argue that selecting 'cases' in this way is insufficiently reflexive and ill-suited to the complexities of contemporary healthcare organisations.
The selected case study site(s) should allow the research team access to the group of individuals, the organisation, the processes or whatever else constitutes the chosen unit of analysis for the study. Access is therefore a central consideration; the researcher needs to come to know the case study site(s) well and to work cooperatively with them. Selected cases need to be not only interesting but also hospitable to the inquiry [ 8 ] if they are to be informative and answer the research question(s). Case study sites may also be pre-selected for the researcher, with decisions being influenced by key stakeholders. For example, our selection of case study sites in the evaluation of the implementation and adoption of electronic health record systems (see Table 3 ) was heavily influenced by NHS Connecting for Health, the government agency that was responsible for overseeing the National Programme for Information Technology (NPfIT)[ 5 ]. This prominent stakeholder had already selected the NHS sites (through a competitive bidding process) to be early adopters of the electronic health record systems and had negotiated contracts that detailed the deployment timelines.
It is also important to consider in advance the likely burden and risks associated with participation for those who (or the site(s) which) comprise the case study. Of particular importance is the obligation for the researcher to think through the ethical implications of the study (e.g. the risk of inadvertently breaching anonymity or confidentiality) and to ensure that potential participants/participating sites are provided with sufficient information to make an informed choice about joining the study. The outcome of providing this information might be that the emotive burden associated with participation, or the organisational disruption associated with supporting the fieldwork, is considered so high that the individuals or sites decide against participation.
In our example of evaluating implementations of electronic health record systems, given the restricted number of early adopter sites available to us, we sought purposively to select a diverse range of implementation cases among those that were available[ 5 ]. We chose a mixture of teaching, non-teaching and Foundation Trust hospitals, and examples of each of the three electronic health record systems procured centrally by the NPfIT. At one recruited site, it quickly became apparent that access was problematic because of competing demands on that organisation. Recognising the importance of full access and co-operative working for generating rich data, the research team decided not to pursue work at that site and instead to focus on other recruited sites.
Collecting the data
In order to develop a thorough understanding of the case, the case study approach usually involves the collection of multiple sources of evidence, using a range of quantitative (e.g. questionnaires, audits and analysis of routinely collected healthcare data) and more commonly qualitative techniques (e.g. interviews, focus groups and observations). The use of multiple sources of data (data triangulation) has been advocated as a way of increasing the internal validity of a study (i.e. the extent to which the method is appropriate to answer the research question)[ 8 , 18 – 21 ]. An underlying assumption is that data collected in different ways should lead to similar conclusions, and approaching the same issue from different angles can help develop a holistic picture of the phenomenon (Table 2 )[ 4 ].
Brazier and colleagues used a mixed-methods case study approach to investigate the impact of a cancer care programme[ 22 ]. Here, quantitative measures were collected with questionnaires before, and five months after, the start of the intervention which did not yield any statistically significant results. Qualitative interviews with patients however helped provide an insight into potentially beneficial process-related aspects of the programme, such as greater, perceived patient involvement in care. The authors reported how this case study approach provided a number of contextual factors likely to influence the effectiveness of the intervention and which were not likely to have been obtained from quantitative methods alone.
In collective or multiple case studies, data collection needs to be flexible enough to allow a detailed description of each individual case to be developed (e.g. the nature of different cancer care programmes), before considering the emerging similarities and differences in cross-case comparisons (e.g. to explore why one programme is more effective than another). It is important that data sources from different cases are, where possible, broadly comparable for this purpose even though they may vary in nature and depth.
Analysing, interpreting and reporting case studies
Making sense and offering a coherent interpretation of the typically disparate sources of data (whether qualitative alone or together with quantitative) is far from straightforward. Repeated reviewing and sorting of the voluminous and detail-rich data are integral to the process of analysis. In collective case studies, it is helpful to analyse data relating to the individual component cases first, before making comparisons across cases. Attention needs to be paid to variations within each case and, where relevant, the relationship between different causes, effects and outcomes[ 23 ]. Data will need to be organised and coded to allow the key issues, both derived from the literature and emerging from the dataset, to be easily retrieved at a later stage. An initial coding frame can help capture these issues and can be applied systematically to the whole dataset with the aid of a qualitative data analysis software package.
The Framework approach is a practical approach, comprising of five stages (familiarisation; identifying a thematic framework; indexing; charting; mapping and interpretation) , to managing and analysing large datasets particularly if time is limited, as was the case in our study of recruitment of South Asians into asthma research (Table 1 )[ 3 , 24 ]. Theoretical frameworks may also play an important role in integrating different sources of data and examining emerging themes. For example, we drew on a socio-technical framework to help explain the connections between different elements - technology; people; and the organisational settings within which they worked - in our study of the introduction of electronic health record systems (Table 3 )[ 5 ]. Our study of patient safety in undergraduate curricula drew on an evaluation-based approach to design and analysis, which emphasised the importance of the academic, organisational and practice contexts through which students learn (Table 4 )[ 6 ].
Case study findings can have implications both for theory development and theory testing. They may establish, strengthen or weaken historical explanations of a case and, in certain circumstances, allow theoretical (as opposed to statistical) generalisation beyond the particular cases studied[ 12 ]. These theoretical lenses should not, however, constitute a strait-jacket and the cases should not be "forced to fit" the particular theoretical framework that is being employed.
When reporting findings, it is important to provide the reader with enough contextual information to understand the processes that were followed and how the conclusions were reached. In a collective case study, researchers may choose to present the findings from individual cases separately before amalgamating across cases. Care must be taken to ensure the anonymity of both case sites and individual participants (if agreed in advance) by allocating appropriate codes or withholding descriptors. In the example given in Table 3 , we decided against providing detailed information on the NHS sites and individual participants in order to avoid the risk of inadvertent disclosure of identities[ 5 , 25 ].
What are the potential pitfalls and how can these be avoided?
The case study approach is, as with all research, not without its limitations. When investigating the formal and informal ways undergraduate students learn about patient safety (Table 4 ), for example, we rapidly accumulated a large quantity of data. The volume of data, together with the time restrictions in place, impacted on the depth of analysis that was possible within the available resources. This highlights a more general point of the importance of avoiding the temptation to collect as much data as possible; adequate time also needs to be set aside for data analysis and interpretation of what are often highly complex datasets.
Case study research has sometimes been criticised for lacking scientific rigour and providing little basis for generalisation (i.e. producing findings that may be transferable to other settings)[ 1 ]. There are several ways to address these concerns, including: the use of theoretical sampling (i.e. drawing on a particular conceptual framework); respondent validation (i.e. participants checking emerging findings and the researcher's interpretation, and providing an opinion as to whether they feel these are accurate); and transparency throughout the research process (see Table 8 )[ 8 , 18 – 21 , 23 , 26 ]. Transparency can be achieved by describing in detail the steps involved in case selection, data collection, the reasons for the particular methods chosen, and the researcher's background and level of involvement (i.e. being explicit about how the researcher has influenced data collection and interpretation). Seeking potential, alternative explanations, and being explicit about how interpretations and conclusions were reached, help readers to judge the trustworthiness of the case study report. Stake provides a critique checklist for a case study report (Table 9 )[ 8 ].
Conclusions
The case study approach allows, amongst other things, critical events, interventions, policy developments and programme-based service reforms to be studied in detail in a real-life context. It should therefore be considered when an experimental design is either inappropriate to answer the research questions posed or impossible to undertake. Considering the frequency with which implementations of innovations are now taking place in healthcare settings and how well the case study approach lends itself to in-depth, complex health service research, we believe this approach should be more widely considered by researchers. Though inherently challenging, the research case study can, if carefully conceptualised and thoughtfully undertaken and reported, yield powerful insights into many important aspects of health and healthcare delivery.
Yin RK: Case study research, design and method. 2009, London: Sage Publications Ltd., 4
Google Scholar
Keen J, Packwood T: Qualitative research; case study evaluation. BMJ. 1995, 311: 444-446.
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Sheikh A, Halani L, Bhopal R, Netuveli G, Partridge M, Car J, et al: Facilitating the Recruitment of Minority Ethnic People into Research: Qualitative Case Study of South Asians and Asthma. PLoS Med. 2009, 6 (10): 1-11.
Article Google Scholar
Pinnock H, Huby G, Powell A, Kielmann T, Price D, Williams S, et al: The process of planning, development and implementation of a General Practitioner with a Special Interest service in Primary Care Organisations in England and Wales: a comparative prospective case study. Report for the National Co-ordinating Centre for NHS Service Delivery and Organisation R&D (NCCSDO). 2008, [ http://www.sdo.nihr.ac.uk/files/project/99-final-report.pdf ]
Robertson A, Cresswell K, Takian A, Petrakaki D, Crowe S, Cornford T, et al: Prospective evaluation of the implementation and adoption of NHS Connecting for Health's national electronic health record in secondary care in England: interim findings. BMJ. 2010, 41: c4564-
Pearson P, Steven A, Howe A, Sheikh A, Ashcroft D, Smith P, the Patient Safety Education Study Group: Learning about patient safety: organisational context and culture in the education of healthcare professionals. J Health Serv Res Policy. 2010, 15: 4-10. 10.1258/jhsrp.2009.009052.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
van Harten WH, Casparie TF, Fisscher OA: The evaluation of the introduction of a quality management system: a process-oriented case study in a large rehabilitation hospital. Health Policy. 2002, 60 (1): 17-37. 10.1016/S0168-8510(01)00187-7.
Stake RE: The art of case study research. 1995, London: Sage Publications Ltd.
Sheikh A, Smeeth L, Ashcroft R: Randomised controlled trials in primary care: scope and application. Br J Gen Pract. 2002, 52 (482): 746-51.
PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
King G, Keohane R, Verba S: Designing Social Inquiry. 1996, Princeton: Princeton University Press
Doolin B: Information technology as disciplinary technology: being critical in interpretative research on information systems. Journal of Information Technology. 1998, 13: 301-311. 10.1057/jit.1998.8.
George AL, Bennett A: Case studies and theory development in the social sciences. 2005, Cambridge, MA: MIT Press
Eccles M, the Improved Clinical Effectiveness through Behavioural Research Group (ICEBeRG): Designing theoretically-informed implementation interventions. Implementation Science. 2006, 1: 1-8. 10.1186/1748-5908-1-1.
Article PubMed Central Google Scholar
Netuveli G, Hurwitz B, Levy M, Fletcher M, Barnes G, Durham SR, Sheikh A: Ethnic variations in UK asthma frequency, morbidity, and health-service use: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet. 2005, 365 (9456): 312-7.
Sheikh A, Panesar SS, Lasserson T, Netuveli G: Recruitment of ethnic minorities to asthma studies. Thorax. 2004, 59 (7): 634-
CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Hellström I, Nolan M, Lundh U: 'We do things together': A case study of 'couplehood' in dementia. Dementia. 2005, 4: 7-22. 10.1177/1471301205049188.
Som CV: Nothing seems to have changed, nothing seems to be changing and perhaps nothing will change in the NHS: doctors' response to clinical governance. International Journal of Public Sector Management. 2005, 18: 463-477. 10.1108/09513550510608903.
Lincoln Y, Guba E: Naturalistic inquiry. 1985, Newbury Park: Sage Publications
Barbour RS: Checklists for improving rigour in qualitative research: a case of the tail wagging the dog?. BMJ. 2001, 322: 1115-1117. 10.1136/bmj.322.7294.1115.
Mays N, Pope C: Qualitative research in health care: Assessing quality in qualitative research. BMJ. 2000, 320: 50-52. 10.1136/bmj.320.7226.50.
Mason J: Qualitative researching. 2002, London: Sage
Brazier A, Cooke K, Moravan V: Using Mixed Methods for Evaluating an Integrative Approach to Cancer Care: A Case Study. Integr Cancer Ther. 2008, 7: 5-17. 10.1177/1534735407313395.
Miles MB, Huberman M: Qualitative data analysis: an expanded sourcebook. 1994, CA: Sage Publications Inc., 2
Pope C, Ziebland S, Mays N: Analysing qualitative data. Qualitative research in health care. BMJ. 2000, 320: 114-116. 10.1136/bmj.320.7227.114.
Cresswell KM, Worth A, Sheikh A: Actor-Network Theory and its role in understanding the implementation of information technology developments in healthcare. BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. 2010, 10 (1): 67-10.1186/1472-6947-10-67.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Malterud K: Qualitative research: standards, challenges, and guidelines. Lancet. 2001, 358: 483-488. 10.1016/S0140-6736(01)05627-6.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Yin R: Case study research: design and methods. 1994, Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publishing, 2
Yin R: Enhancing the quality of case studies in health services research. Health Serv Res. 1999, 34: 1209-1224.
Green J, Thorogood N: Qualitative methods for health research. 2009, Los Angeles: Sage, 2
Howcroft D, Trauth E: Handbook of Critical Information Systems Research, Theory and Application. 2005, Cheltenham, UK: Northampton, MA, USA: Edward Elgar
Book Google Scholar
Blakie N: Approaches to Social Enquiry. 1993, Cambridge: Polity Press
Doolin B: Power and resistance in the implementation of a medical management information system. Info Systems J. 2004, 14: 343-362. 10.1111/j.1365-2575.2004.00176.x.
Bloomfield BP, Best A: Management consultants: systems development, power and the translation of problems. Sociological Review. 1992, 40: 533-560.
Shanks G, Parr A: Positivist, single case study research in information systems: A critical analysis. Proceedings of the European Conference on Information Systems. 2003, Naples
Pre-publication history
The pre-publication history for this paper can be accessed here: http://www.biomedcentral.com/1471-2288/11/100/prepub
Download references
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to the participants and colleagues who contributed to the individual case studies that we have drawn on. This work received no direct funding, but it has been informed by projects funded by Asthma UK, the NHS Service Delivery Organisation, NHS Connecting for Health Evaluation Programme, and Patient Safety Research Portfolio. We would also like to thank the expert reviewers for their insightful and constructive feedback. Our thanks are also due to Dr. Allison Worth who commented on an earlier draft of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Division of Primary Care, The University of Nottingham, Nottingham, UK
Sarah Crowe & Anthony Avery
Centre for Population Health Sciences, The University of Edinburgh, Edinburgh, UK
Kathrin Cresswell, Ann Robertson & Aziz Sheikh
School of Health in Social Science, The University of Edinburgh, Edinburgh, UK
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Sarah Crowe .
Additional information
Competing interests.
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Authors' contributions
AS conceived this article. SC, KC and AR wrote this paper with GH, AA and AS all commenting on various drafts. SC and AS are guarantors.
Rights and permissions
This article is published under license to BioMed Central Ltd. This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0 ), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Crowe, S., Cresswell, K., Robertson, A. et al. The case study approach. BMC Med Res Methodol 11 , 100 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2288-11-100
Download citation
Received : 29 November 2010
Accepted : 27 June 2011
Published : 27 June 2011
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2288-11-100
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Case Study Approach
- Electronic Health Record System
- Case Study Design
- Case Study Site
- Case Study Report
BMC Medical Research Methodology
ISSN: 1471-2288
- General enquiries: [email protected]
- Search Menu
- Sign in through your institution
- Browse content in Arts and Humanities
- Browse content in Archaeology
- Anglo-Saxon and Medieval Archaeology
- Archaeological Methodology and Techniques
- Archaeology by Region
- Archaeology of Religion
- Archaeology of Trade and Exchange
- Biblical Archaeology
- Contemporary and Public Archaeology
- Environmental Archaeology
- Historical Archaeology
- History and Theory of Archaeology
- Industrial Archaeology
- Landscape Archaeology
- Mortuary Archaeology
- Prehistoric Archaeology
- Underwater Archaeology
- Urban Archaeology
- Zooarchaeology
- Browse content in Architecture
- Architectural Structure and Design
- History of Architecture
- Residential and Domestic Buildings
- Theory of Architecture
- Browse content in Art
- Art Subjects and Themes
- History of Art
- Industrial and Commercial Art
- Theory of Art
- Biographical Studies
- Byzantine Studies
- Browse content in Classical Studies
- Classical History
- Classical Philosophy
- Classical Mythology
- Classical Literature
- Classical Reception
- Classical Art and Architecture
- Classical Oratory and Rhetoric
- Greek and Roman Papyrology
- Greek and Roman Epigraphy
- Greek and Roman Law
- Greek and Roman Archaeology
- Late Antiquity
- Religion in the Ancient World
- Digital Humanities
- Browse content in History
- Colonialism and Imperialism
- Diplomatic History
- Environmental History
- Genealogy, Heraldry, Names, and Honours
- Genocide and Ethnic Cleansing
- Historical Geography
- History by Period
- History of Emotions
- History of Agriculture
- History of Education
- History of Gender and Sexuality
- Industrial History
- Intellectual History
- International History
- Labour History
- Legal and Constitutional History
- Local and Family History
- Maritime History
- Military History
- National Liberation and Post-Colonialism
- Oral History
- Political History
- Public History
- Regional and National History
- Revolutions and Rebellions
- Slavery and Abolition of Slavery
- Social and Cultural History
- Theory, Methods, and Historiography
- Urban History
- World History
- Browse content in Language Teaching and Learning
- Language Learning (Specific Skills)
- Language Teaching Theory and Methods
- Browse content in Linguistics
- Applied Linguistics
- Cognitive Linguistics
- Computational Linguistics
- Forensic Linguistics
- Grammar, Syntax and Morphology
- Historical and Diachronic Linguistics
- History of English
- Language Evolution
- Language Reference
- Language Acquisition
- Language Variation
- Language Families
- Lexicography
- Linguistic Anthropology
- Linguistic Theories
- Linguistic Typology
- Phonetics and Phonology
- Psycholinguistics
- Sociolinguistics
- Translation and Interpretation
- Writing Systems
- Browse content in Literature
- Bibliography
- Children's Literature Studies
- Literary Studies (Romanticism)
- Literary Studies (American)
- Literary Studies (Asian)
- Literary Studies (European)
- Literary Studies (Eco-criticism)
- Literary Studies (Modernism)
- Literary Studies - World
- Literary Studies (1500 to 1800)
- Literary Studies (19th Century)
- Literary Studies (20th Century onwards)
- Literary Studies (African American Literature)
- Literary Studies (British and Irish)
- Literary Studies (Early and Medieval)
- Literary Studies (Fiction, Novelists, and Prose Writers)
- Literary Studies (Gender Studies)
- Literary Studies (Graphic Novels)
- Literary Studies (History of the Book)
- Literary Studies (Plays and Playwrights)
- Literary Studies (Poetry and Poets)
- Literary Studies (Postcolonial Literature)
- Literary Studies (Queer Studies)
- Literary Studies (Science Fiction)
- Literary Studies (Travel Literature)
- Literary Studies (War Literature)
- Literary Studies (Women's Writing)
- Literary Theory and Cultural Studies
- Mythology and Folklore
- Shakespeare Studies and Criticism
- Browse content in Media Studies
- Browse content in Music
- Applied Music
- Dance and Music
- Ethics in Music
- Ethnomusicology
- Gender and Sexuality in Music
- Medicine and Music
- Music Cultures
- Music and Media
- Music and Religion
- Music and Culture
- Music Education and Pedagogy
- Music Theory and Analysis
- Musical Scores, Lyrics, and Libretti
- Musical Structures, Styles, and Techniques
- Musicology and Music History
- Performance Practice and Studies
- Race and Ethnicity in Music
- Sound Studies
- Browse content in Performing Arts
- Browse content in Philosophy
- Aesthetics and Philosophy of Art
- Epistemology
- Feminist Philosophy
- History of Western Philosophy
- Metaphysics
- Moral Philosophy
- Non-Western Philosophy
- Philosophy of Language
- Philosophy of Mind
- Philosophy of Perception
- Philosophy of Science
- Philosophy of Action
- Philosophy of Law
- Philosophy of Religion
- Philosophy of Mathematics and Logic
- Practical Ethics
- Social and Political Philosophy
- Browse content in Religion
- Biblical Studies
- Christianity
- East Asian Religions
- History of Religion
- Judaism and Jewish Studies
- Qumran Studies
- Religion and Education
- Religion and Health
- Religion and Politics
- Religion and Science
- Religion and Law
- Religion and Art, Literature, and Music
- Religious Studies
- Browse content in Society and Culture
- Cookery, Food, and Drink
- Cultural Studies
- Customs and Traditions
- Ethical Issues and Debates
- Hobbies, Games, Arts and Crafts
- Lifestyle, Home, and Garden
- Natural world, Country Life, and Pets
- Popular Beliefs and Controversial Knowledge
- Sports and Outdoor Recreation
- Technology and Society
- Travel and Holiday
- Visual Culture
- Browse content in Law
- Arbitration
- Browse content in Company and Commercial Law
- Commercial Law
- Company Law
- Browse content in Comparative Law
- Systems of Law
- Competition Law
- Browse content in Constitutional and Administrative Law
- Government Powers
- Judicial Review
- Local Government Law
- Military and Defence Law
- Parliamentary and Legislative Practice
- Construction Law
- Contract Law
- Browse content in Criminal Law
- Criminal Procedure
- Criminal Evidence Law
- Sentencing and Punishment
- Employment and Labour Law
- Environment and Energy Law
- Browse content in Financial Law
- Banking Law
- Insolvency Law
- History of Law
- Human Rights and Immigration
- Intellectual Property Law
- Browse content in International Law
- Private International Law and Conflict of Laws
- Public International Law
- IT and Communications Law
- Jurisprudence and Philosophy of Law
- Law and Politics
- Law and Society
- Browse content in Legal System and Practice
- Courts and Procedure
- Legal Skills and Practice
- Primary Sources of Law
- Regulation of Legal Profession
- Medical and Healthcare Law
- Browse content in Policing
- Criminal Investigation and Detection
- Police and Security Services
- Police Procedure and Law
- Police Regional Planning
- Browse content in Property Law
- Personal Property Law
- Study and Revision
- Terrorism and National Security Law
- Browse content in Trusts Law
- Wills and Probate or Succession
- Browse content in Medicine and Health
- Browse content in Allied Health Professions
- Arts Therapies
- Clinical Science
- Dietetics and Nutrition
- Occupational Therapy
- Operating Department Practice
- Physiotherapy
- Radiography
- Speech and Language Therapy
- Browse content in Anaesthetics
- General Anaesthesia
- Neuroanaesthesia
- Clinical Neuroscience
- Browse content in Clinical Medicine
- Acute Medicine
- Cardiovascular Medicine
- Clinical Genetics
- Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics
- Dermatology
- Endocrinology and Diabetes
- Gastroenterology
- Genito-urinary Medicine
- Geriatric Medicine
- Infectious Diseases
- Medical Toxicology
- Medical Oncology
- Pain Medicine
- Palliative Medicine
- Rehabilitation Medicine
- Respiratory Medicine and Pulmonology
- Rheumatology
- Sleep Medicine
- Sports and Exercise Medicine
- Community Medical Services
- Critical Care
- Emergency Medicine
- Forensic Medicine
- Haematology
- History of Medicine
- Browse content in Medical Skills
- Clinical Skills
- Communication Skills
- Nursing Skills
- Surgical Skills
- Browse content in Medical Dentistry
- Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery
- Paediatric Dentistry
- Restorative Dentistry and Orthodontics
- Surgical Dentistry
- Medical Ethics
- Medical Statistics and Methodology
- Browse content in Neurology
- Clinical Neurophysiology
- Neuropathology
- Nursing Studies
- Browse content in Obstetrics and Gynaecology
- Gynaecology
- Occupational Medicine
- Ophthalmology
- Otolaryngology (ENT)
- Browse content in Paediatrics
- Neonatology
- Browse content in Pathology
- Chemical Pathology
- Clinical Cytogenetics and Molecular Genetics
- Histopathology
- Medical Microbiology and Virology
- Patient Education and Information
- Browse content in Pharmacology
- Psychopharmacology
- Browse content in Popular Health
- Caring for Others
- Complementary and Alternative Medicine
- Self-help and Personal Development
- Browse content in Preclinical Medicine
- Cell Biology
- Molecular Biology and Genetics
- Reproduction, Growth and Development
- Primary Care
- Professional Development in Medicine
- Browse content in Psychiatry
- Addiction Medicine
- Child and Adolescent Psychiatry
- Forensic Psychiatry
- Learning Disabilities
- Old Age Psychiatry
- Psychotherapy
- Browse content in Public Health and Epidemiology
- Epidemiology
- Public Health
- Browse content in Radiology
- Clinical Radiology
- Interventional Radiology
- Nuclear Medicine
- Radiation Oncology
- Reproductive Medicine
- Browse content in Surgery
- Cardiothoracic Surgery
- Gastro-intestinal and Colorectal Surgery
- General Surgery
- Neurosurgery
- Paediatric Surgery
- Peri-operative Care
- Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery
- Surgical Oncology
- Transplant Surgery
- Trauma and Orthopaedic Surgery
- Vascular Surgery
- Browse content in Science and Mathematics
- Browse content in Biological Sciences
- Aquatic Biology
- Biochemistry
- Bioinformatics and Computational Biology
- Developmental Biology
- Ecology and Conservation
- Evolutionary Biology
- Genetics and Genomics
- Microbiology
- Molecular and Cell Biology
- Natural History
- Plant Sciences and Forestry
- Research Methods in Life Sciences
- Structural Biology
- Systems Biology
- Zoology and Animal Sciences
- Browse content in Chemistry
- Analytical Chemistry
- Computational Chemistry
- Crystallography
- Environmental Chemistry
- Industrial Chemistry
- Inorganic Chemistry
- Materials Chemistry
- Medicinal Chemistry
- Mineralogy and Gems
- Organic Chemistry
- Physical Chemistry
- Polymer Chemistry
- Study and Communication Skills in Chemistry
- Theoretical Chemistry
- Browse content in Computer Science
- Artificial Intelligence
- Computer Architecture and Logic Design
- Game Studies
- Human-Computer Interaction
- Mathematical Theory of Computation
- Programming Languages
- Software Engineering
- Systems Analysis and Design
- Virtual Reality
- Browse content in Computing
- Business Applications
- Computer Security
- Computer Games
- Computer Networking and Communications
- Digital Lifestyle
- Graphical and Digital Media Applications
- Operating Systems
- Browse content in Earth Sciences and Geography
- Atmospheric Sciences
- Environmental Geography
- Geology and the Lithosphere
- Maps and Map-making
- Meteorology and Climatology
- Oceanography and Hydrology
- Palaeontology
- Physical Geography and Topography
- Regional Geography
- Soil Science
- Urban Geography
- Browse content in Engineering and Technology
- Agriculture and Farming
- Biological Engineering
- Civil Engineering, Surveying, and Building
- Electronics and Communications Engineering
- Energy Technology
- Engineering (General)
- Environmental Science, Engineering, and Technology
- History of Engineering and Technology
- Mechanical Engineering and Materials
- Technology of Industrial Chemistry
- Transport Technology and Trades
- Browse content in Environmental Science
- Applied Ecology (Environmental Science)
- Conservation of the Environment (Environmental Science)
- Environmental Sustainability
- Environmentalist Thought and Ideology (Environmental Science)
- Management of Land and Natural Resources (Environmental Science)
- Natural Disasters (Environmental Science)
- Nuclear Issues (Environmental Science)
- Pollution and Threats to the Environment (Environmental Science)
- Social Impact of Environmental Issues (Environmental Science)
- History of Science and Technology
- Browse content in Materials Science
- Ceramics and Glasses
- Composite Materials
- Metals, Alloying, and Corrosion
- Nanotechnology
- Browse content in Mathematics
- Applied Mathematics
- Biomathematics and Statistics
- History of Mathematics
- Mathematical Education
- Mathematical Finance
- Mathematical Analysis
- Numerical and Computational Mathematics
- Probability and Statistics
- Pure Mathematics
- Browse content in Neuroscience
- Cognition and Behavioural Neuroscience
- Development of the Nervous System
- Disorders of the Nervous System
- History of Neuroscience
- Invertebrate Neurobiology
- Molecular and Cellular Systems
- Neuroendocrinology and Autonomic Nervous System
- Neuroscientific Techniques
- Sensory and Motor Systems
- Browse content in Physics
- Astronomy and Astrophysics
- Atomic, Molecular, and Optical Physics
- Biological and Medical Physics
- Classical Mechanics
- Computational Physics
- Condensed Matter Physics
- Electromagnetism, Optics, and Acoustics
- History of Physics
- Mathematical and Statistical Physics
- Measurement Science
- Nuclear Physics
- Particles and Fields
- Plasma Physics
- Quantum Physics
- Relativity and Gravitation
- Semiconductor and Mesoscopic Physics
- Browse content in Psychology
- Affective Sciences
- Clinical Psychology
- Cognitive Psychology
- Cognitive Neuroscience
- Criminal and Forensic Psychology
- Developmental Psychology
- Educational Psychology
- Evolutionary Psychology
- Health Psychology
- History and Systems in Psychology
- Music Psychology
- Neuropsychology
- Organizational Psychology
- Psychological Assessment and Testing
- Psychology of Human-Technology Interaction
- Psychology Professional Development and Training
- Research Methods in Psychology
- Social Psychology
- Browse content in Social Sciences
- Browse content in Anthropology
- Anthropology of Religion
- Human Evolution
- Medical Anthropology
- Physical Anthropology
- Regional Anthropology
- Social and Cultural Anthropology
- Theory and Practice of Anthropology
- Browse content in Business and Management
- Business Ethics
- Business Strategy
- Business History
- Business and Technology
- Business and Government
- Business and the Environment
- Comparative Management
- Corporate Governance
- Corporate Social Responsibility
- Entrepreneurship
- Health Management
- Human Resource Management
- Industrial and Employment Relations
- Industry Studies
- Information and Communication Technologies
- International Business
- Knowledge Management
- Management and Management Techniques
- Operations Management
- Organizational Theory and Behaviour
- Pensions and Pension Management
- Public and Nonprofit Management
- Strategic Management
- Supply Chain Management
- Browse content in Criminology and Criminal Justice
- Criminal Justice
- Criminology
- Forms of Crime
- International and Comparative Criminology
- Youth Violence and Juvenile Justice
- Development Studies
- Browse content in Economics
- Agricultural, Environmental, and Natural Resource Economics
- Asian Economics
- Behavioural Finance
- Behavioural Economics and Neuroeconomics
- Econometrics and Mathematical Economics
- Economic History
- Economic Systems
- Economic Methodology
- Economic Development and Growth
- Financial Markets
- Financial Institutions and Services
- General Economics and Teaching
- Health, Education, and Welfare
- History of Economic Thought
- International Economics
- Labour and Demographic Economics
- Law and Economics
- Macroeconomics and Monetary Economics
- Microeconomics
- Public Economics
- Urban, Rural, and Regional Economics
- Welfare Economics
- Browse content in Education
- Adult Education and Continuous Learning
- Care and Counselling of Students
- Early Childhood and Elementary Education
- Educational Equipment and Technology
- Educational Strategies and Policy
- Higher and Further Education
- Organization and Management of Education
- Philosophy and Theory of Education
- Schools Studies
- Secondary Education
- Teaching of a Specific Subject
- Teaching of Specific Groups and Special Educational Needs
- Teaching Skills and Techniques
- Browse content in Environment
- Applied Ecology (Social Science)
- Climate Change
- Conservation of the Environment (Social Science)
- Environmentalist Thought and Ideology (Social Science)
- Natural Disasters (Environment)
- Social Impact of Environmental Issues (Social Science)
- Browse content in Human Geography
- Cultural Geography
- Economic Geography
- Political Geography
- Browse content in Interdisciplinary Studies
- Communication Studies
- Museums, Libraries, and Information Sciences
- Browse content in Politics
- African Politics
- Asian Politics
- Chinese Politics
- Comparative Politics
- Conflict Politics
- Elections and Electoral Studies
- Environmental Politics
- European Union
- Foreign Policy
- Gender and Politics
- Human Rights and Politics
- Indian Politics
- International Relations
- International Organization (Politics)
- International Political Economy
- Irish Politics
- Latin American Politics
- Middle Eastern Politics
- Political Behaviour
- Political Economy
- Political Institutions
- Political Methodology
- Political Communication
- Political Philosophy
- Political Sociology
- Political Theory
- Politics and Law
- Politics of Development
- Public Policy
- Public Administration
- Quantitative Political Methodology
- Regional Political Studies
- Russian Politics
- Security Studies
- State and Local Government
- UK Politics
- US Politics
- Browse content in Regional and Area Studies
- African Studies
- Asian Studies
- East Asian Studies
- Japanese Studies
- Latin American Studies
- Middle Eastern Studies
- Native American Studies
- Scottish Studies
- Browse content in Research and Information
- Research Methods
- Browse content in Social Work
- Addictions and Substance Misuse
- Adoption and Fostering
- Care of the Elderly
- Child and Adolescent Social Work
- Couple and Family Social Work
- Direct Practice and Clinical Social Work
- Emergency Services
- Human Behaviour and the Social Environment
- International and Global Issues in Social Work
- Mental and Behavioural Health
- Social Justice and Human Rights
- Social Policy and Advocacy
- Social Work and Crime and Justice
- Social Work Macro Practice
- Social Work Practice Settings
- Social Work Research and Evidence-based Practice
- Welfare and Benefit Systems
- Browse content in Sociology
- Childhood Studies
- Community Development
- Comparative and Historical Sociology
- Economic Sociology
- Gender and Sexuality
- Gerontology and Ageing
- Health, Illness, and Medicine
- Marriage and the Family
- Migration Studies
- Occupations, Professions, and Work
- Organizations
- Population and Demography
- Race and Ethnicity
- Social Theory
- Social Movements and Social Change
- Social Research and Statistics
- Social Stratification, Inequality, and Mobility
- Sociology of Religion
- Sociology of Education
- Sport and Leisure
- Urban and Rural Studies
- Browse content in Warfare and Defence
- Defence Strategy, Planning, and Research
- Land Forces and Warfare
- Military Administration
- Military Life and Institutions
- Naval Forces and Warfare
- Other Warfare and Defence Issues
- Peace Studies and Conflict Resolution
- Weapons and Equipment

A newer edition of this book is available.
- < Previous chapter
- Next chapter >

22 Case Study Research: In-Depth Understanding in Context
Helen Simons, School of Education, University of Southampton
- Published: 01 July 2014
- Cite Icon Cite
- Permissions Icon Permissions
This chapter explores case study as a major approach to research and evaluation. After first noting various contexts in which case studies are commonly used, the chapter focuses on case study research directly Strengths and potential problematic issues are outlined and then key phases of the process. The chapter emphasizes how important it is to design the case, to collect and interpret data in ways that highlight the qualitative, to have an ethical practice that values multiple perspectives and political interests, and to report creatively to facilitate use in policy making and practice. Finally, it explores how to generalize from the single case. Concluding questions center on the need to think more imaginatively about design and the range of methods and forms of reporting requiredto persuade audiences to value qualitative ways of knowing in case study research.
Introduction
This chapter explores case study as a major approach to research and evaluation using primarily qualitative methods, as well as documentary sources, contemporaneous or historical. However, this is not the only way in which case study can be conceived. No one has a monopoly on the term. While sharing a focus on the singular in a particular context, case study has a wide variety of uses, not all associated with research. A case study, in common parlance, documents a particular situation or event in detail in a specific sociopolitical context. The particular can be a person, a classroom, an institution, a program, or a policy. Below I identify different ways in which case study is used before focusing on qualitative case study research in particular. However, first I wish to indicate how I came to advocate and practice this form of research. Origins, context, and opportunity often shape the research processes we endorse. It is helpful for the reader, I think, to know how I came to the perspective I hold.
The Beginnings
I first came to appreciate and enjoy the virtues of case study research when I entered the field of curriculum evaluation and research in the 1970s. The dominant research paradigm for educational research at that time was experimental or quasi- experimental, cost-benefit, or systems analysis, and the dominant curriculum model was aims and objectives ( House, 1993 ). The field was dominated, in effect, by a psychometric view of research in which quantitative methods were preeminent. But the innovative projects we were asked to evaluate (predominantly, but not exclusively, in the humanities) were not amenable to such methodologies. The projects were challenging to the status quo of institutions, involved people interpreting the policy and programs, were implemented differently in different contexts and regions, and had many unexpected effects.
We had no choice but to seek other ways to evaluate these complex programs, and case study was the methodology we found ourselves exploring, in order to understand how the projects were being implemented, why they had positive effects in some regions of the country and not others, and what the outcomes meant in different sociopolitical and cultural contexts. What better way to do this than to talk with people to see how they interpreted the “new” curriculum; to watch how teachers and students put it into practice; to document transactions, outcomes, and unexpected consequences; and to interpret all in the specific context of the case ( Simons, 1971 , 1987 , pp. 55–89). From this point on and in further studies, case study in educational research and evaluation came to be a major methodology for understanding complex educational and social programs. It also extended to other practice professions, such as nursing, health, and social care ( Zucker, 2001 ; Greenhalgh & Worrall, 1997 ; Shaw & Gould, 2001 ). For further details of the evolution of the case study approach and qualitative methodologies in evaluation, see House, 1993 , pp. 2–3; Greene, 2000 ; Simons, 2009 , pp. 14–18; Simons & McCormack, 2007 , pp. 292–311).
This was not exactly the beginning of case study, of course. It has a long history in many disciplines ( Simons, 1980; Ragin, 1992; Gomm, Hammersley, & Foster, 2004 ; Platt, 2007 ), many aspects of which form part of case study practice to this day. But its evolution in the context just described was a major move in the contemporary evolution of the logic of evaluative inquiry ( House, 1980 ). It also coincided with movement toward the qualitative in other disciplines, such as sociology and psychology. This was all part of what Denzin & Lincoln (1994) termed “a quiet methodological revolution” (p. ix) in qualitative inquiry that had been evolving over the course of forty years.
There is a further reason why I continue to advocate and practice case study research and evaluation to this day and that is my personal predilection for trying to understand and represent complexity, for puzzling through the ambiguities that exist in many contexts and programs and for presenting and negotiating different values and interests in fair and just ways.
Put more simply, I like interacting with people, listening to their stories, trials and tribulations—giving them a voice in understanding the contexts and projects with which they are involved, and finding ways to share these with a range of audiences. In other words, the move toward case study methodology described here suited my preference for how I learn.
Concepts and Purposes of Case Study
Before exploring case study as it has come to be established in educational research and evaluation over the past forty years, I wish to acknowledge other uses of case study. More often than not, these relate to purpose, and appropriately so in their different contexts, but many do not have a research intention. For a study to count as research, it would need to be a systematic investigation generating evidence that leads to “new” knowledge that is made public and open to scrutiny. There are many ways to conduct research stemming from different traditions and disciplines, but they all, in different ways, involve these characteristics.
Everyday Usage: Stories We Tell
The most common of these uses of case study is the everyday reference to a person, an anecdote or story illustrative of a particular incident, event, or experience of that person. It is often a short, reported account commonly seen in journalism but also in books exploring a phenomenon, such as recovery from serious accidents or tragedies, where the author chooses to illustrate the story or argument with a “lived” example. This is sometimes written by the author and sometimes by the person whose tale it is. “Let me share with you a story,” is a phrase frequently heard
The spirit behind this common usage and its power to connect can be seen in a report by Tim Adams of the London Olympics opening ceremony’s dramatization by Danny Boyle.
It was the point when we suddenly collectively wised up to the idea that what we are about to receive over the next two weeks was not only about “legacy collateral” and “targeted deliverables,” not about G4S failings and traffic lanes and branding opportunities, but about the second-by-second possibilities of human endeavour and spirit and communality, enacted in multiple places and all at the same time. Stories in other words. ( Adams, 2012 )
This was a collective story, of course, not an individual one, but it does convey some of the major characteristics of case study—that richness of detail, time, place, multiple happenings and experiences—that are also manifest in case study research, although carefully evidenced in the latter instance. We can see from this common usage how people have come to associate case study with story. I return to this thread in the reporting section.
Professions Individual Cases
In professional settings, in health and social care, case studies, often called case histories , are used to accurately record a person’s health or social care history and his or her current symptoms, experience, and treatment. These case histories include facts but also judgments and observations about the person’s reaction to situations or medication. Usually these are confidential. Not dissimilar is the detailed documentation of a case in law, often termed a case precedent when referred to in a court case to support an argument being made. However in law there is a difference in that such case precedents are publicly documented.
Case Studies in Teaching
Exemplars of practice.
In education, but also in health and social care training contexts, case studies have long been used as exemplars of practice. These are brief descriptions with some detail of a person or project’s experience in an area of practice. Though frequently reported accounts, they are based on a person’s experience and sometimes on previous research.
Case scenarios
Management studies are a further context in which case studies are often used. Here, the case is more like a scenario outlining a particular problem situation for the management student to resolve. These scenarios may be based on research but frequently are hypothetical situations used to raise issues for discussion and resolution. What distinguishes these case scenarios and the case exemplars in education from case study research is the intention to use them for teaching purposes.
Country Case Studies
Then there are case studies of programs, projects, and even countries, as in international development, where a whole-country study might be termed a case study or, in the context of the Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD), where an exploration is conducted of the state of the art of a subject, such as education or environmental science in one or several countries. This may be a contemporaneous study and/or what transpired in a program over a period of time. Such studies often do have a research base but frequently are reported accounts that do not detail the design, methodology, and analysis of the case, as a research case study would do, or report in ways that give readers a vicarious experience of what it was like to be there. Such case studies tend to be more knowledge and information-focused than experiential.
Case Study as History
Closer to a research context is case study as history—what transpired at a certain time in a certain place. This is likely to be supported by documentary evidence but not primary data gathering unless it is an oral history. In education, in the late 1970s, Stenhouse (1978) experimented with a case study archive. Using contemporaneous data gathering, primarily through interviewing, he envisaged this database, which he termed a “case record,” forming an archive from which different individuals,, at some later date, could write a “case study.” This approach uses case study as a documentary source to begin to generate a history of education, as the subtitle of Stenhouse’s 1978 paper indicates “Towards a contemporary history of education.”
Case Study Research
From here on, my focus is on case study research per se, adopting for this purpose the following definition:
Case study is an in-depth exploration from multiple perspectives of the complexity and uniqueness of a particular project, policy, institution or system in a “real-life” context. It is research based, inclusive of different methods and is evidence-led. ( Simons, 2009 , p. 21).
For further related definitions of case study, see Stake (1995) , Merriam (1998), and Chadderton & Torrance (2011) . And for definitions from a slightly different perspective, see Yin (2004) and Thomas (2011a) .
Not Defined by Method or Perspective
The inclusion of different methods in the definition quoted above definition signals that case study research is not defined by methodology or method. What defines case study is its singularity and the concept and boundary of the case. It is theoretically possible to conduct a case study using primarily quantitative data if this is the best way of providing evidence to inform the issues the case is exploring. It is equally possible to conduct case study that is mainly qualitative, to engage people with the experience of the case or to provide a rich portrayal of an event, project, or program.
Or one can design the case using mixed methods. This increases the options for learning from different ways of knowing and is sometimes preferred by stakeholders who believe it provides a firmer basis for informing policy. This is not necessarily the case but is beyond the scope of this chapter to explore. For further discussion of the complexities of mixing methods and the virtue of using qualitative methods and case study in a mixed method design, see Greene (2007) .
Case study research may also be conducted from different standpoints—realist, interpretivist, or constructivist, for example. My perspective falls within a constructivist, interpretivist framework. What interests me is how I and those in the case perceive and interpret what we find and how we construct or co-construct understandings of the case. This not only suits my predilection for how I see the world, but also my preferred phenomenological approach to interviewing and curiosity about people and how they act in social and professional life.
Qualitative Case Study Research
Qualitative case study research shares many characteristics with other forms of qualitative research, such as narrative, oral history, life history, ethnography, in-depth interview, and observational studies that utilize qualitative methods. However, its focus, purpose, and origins, in educational research at least, are a little different.
The focus is clearly the study of the singular. The purpose is to portray an in-depth view of the quality and complexity of social/educational programs or policies as they are implemented in specific sociopolitical contexts. What makes it qualitative is its emphasis on subjective ways of knowing, particularly the experiential, practical, and presentational rather than the propositional ( Heron, 1992 , 1999 ) to comprehend and communicate what transpired in the case.
Characteristic Features and Advantages
Case study research is not method dependent, as noted earlier, nor is it constrained by resources or time. Although it can be conducted over several years, which provides an opportunity to explore the process of change and explain how and why things happened, it can equally be carried out contemporaneously in a few days, weeks, or months. This flexibility is extremely useful in many contexts, particularly when a change in policy or unforeseen issues in the field require modifying the design.
Flexibility extends to reporting. The case can be written up in different lengths and forms to meet different audience needs and to maximize use (see the section on Reporting). Using the natural language of participants and familiar methods (like interview, observation, oral history) also enables participants to engage in the research process, thereby contributing significantly to the generation of knowledge of the case. As I have indicated elsewhere ( Simons, 2009 ), “This is both a political and epistemological point. It signals a potential shift in the power base of who controls knowledge and recognizes the importance of co-constructing perceived reality through the relationships and joint understandings we create in the field” (p. 23).
Possible Disadvantages
If one is an advocate, identifying advantages of a research approach is easier than pointing out its disadvantages, something detractors are quite keen to do anyway! But no approach is perfect, and here are some of the issues that often trouble people about case study research. The “sample of one” is an obvious issue that worries those convinced that only large samples can constitute valid research and especially if this is to inform policy. Understanding complexity in depth may not be a sufficient counterargument, and I suspect there is little point in trying to persuade otherwise For frequently, this perception is one of epistemological and methodological, if not ideological, preference.
However, there are some genuine concerns that many case researchers face: the difficulty of processing a mass of data; of “telling the truth” in contexts where people may be identifiable; personal involvement, when the researcher is the main instrument of data gathering; and writing reports that are data-based, yet readable in style and length. But one issue that concerns advocates and nonadvocates alike is how inferences are drawn from the single case.
Answers to some of these issues are covered in the sections that follow. Whether they convince may again be a question of preference. However, it is worth noting here that I do not think we should seek to justify these concerns in terms identified by other methodologies. Many of them are intrinsic to the nature and strength of qualitative case study research.
Subjectivity, for instance, both of participants and researcher is inevitable, as it is in many other qualitative methodologies. This is often the basis on which we act. Rather than see this as bias or something to counter, it is an intelligence that is essential to understanding and interpreting the experience of participants and stakeholders. Such subjectivity needs to be disciplined, of course, through procedures that examine both the validity of individuals’ representations of “their truth”, and demonstrate how the researcher took a reflexive approach to monitoring how his or her own values and predilections may have unduly influenced the data.
Types of Case Study
There are numerous types of case study, too many to categorize, I think, as there are overlaps between them. However, attempts have been made to do this and, for those who value typologies, I refer them to Bassey (1999) and, for a more extended typology, to Thomas (2011b) . A slightly different approach is taken by Gomm, Hammersley, and Foster (2004) in annotating the different emphases in major texts on case study. What I prefer to do here is to highlight a few familiar types to focus the discussion that follows on the practice of case study research.
Stake (1995) offers a threefold distinction that is helpful when it comes to practice, he says, because it influences the methods we choose to gather data (p. 4). He distinguishes between an intrinsic case study , one that is studied to learn about the particular case itself and an instrumental case study , in which we choose a case to gain insight into a particular issue (i.e., the case is instrumental to understanding something else; p. 3). The collective case study is what its name suggests: an extension of the instrumental to several cases.
Theory-led or theory-generated case study is similarly self-explanatory, the first starting from a specific theory that is tested through the case; the second constructing a theory through interpretation of data generated in the case. In other words, one ends rather than begins with a theory. In qualitative case study research, this is the more familiar route. The theory of the case becomes the argument or story you will tell.
Evaluation case study requires a slightly longer description as this is my context of practice, one which has influenced the way I conduct case study and what I choose to emphasize in this chapter. An evaluation case study has three essential features: to determine the value of the case, to include and balance different interests and values, and to report findings to a range of stakeholders in ways that they can use. The reasons for this may be found in the interlude that follows, which offers a brief characterization of the social and ethical practice of evaluation and why qualitative methods are so important in this practice.
Interlude: Social and Ethical Practice of Evaluation
Evaluation is a social practice that documents, portrays, and seeks to understand the value of a particular project, program, or policy. This can be determined by different evaluation methodologies, of course. But the value of qualitative case study is that it is possible to discern this value without decontextualizing the data. While the focus of the case is usually a project, program, policy, or some unit within, studies of key individuals, what I term case profiles , may be embedded within the overall case. In some instances, these profiles, or even shorter cameos of individuals, may be quite prominent. For it is through the perceptions, interpretations, and interactions of people that we learn how policies and programs are enacted ( Kushner, 2000 , p. 12). The program is still the main focus of analysis, but, in exploring how individuals play out their different roles in the program, we get closer to the actual experience and meaning of the program in practice.
Case study evaluation is often commissioned from an external source (government department or other agency) keen to know the worth of publicly funded programs and policies to inform future decision making. It needs to be responsive to issues or questions identified by stakeholders, who often have different values and interests in the expected outcomes and appreciate different perspectives of the program in action. The context also is often highly politicized, and interests can conflict. The task of the evaluator in such situations becomes one of including and balancing all interests and values in the program fairly and justly.
This is an inherently political process and requires an ethical practice that offers participants some protection over the personal data they give as part of the research and agreed audiences access to the findings, presented in ways they can understand. Negotiating what information becomes public can be quite difficult in singular settings where people are identifiable and intricate or problematic transactions have been documented. The consequences that ensue from making knowledge public that hitherto was private may be considerable for those in the case. It may also be difficult to portray some of the contextual detail that would enhance understanding for readers.
The ethical stance that underpins the case study research and evaluation I conduct stems from a theory of ethics that emphasizes the centrality of relationships in the specific context and the consequences for individuals, while remaining aware of the research imperative to publicly report. It is essentially an independent democratic process based on the concepts of fairness and justice, in which confidentiality, negotiation, and accessibility are key principles ( MacDonald, 1976 ; Simons, 2009 , pp. 96–111; and Simons 2010 ). The principles are translated into specific procedures to guide the collection, validation, and dissemination of data in the field. These include:
engaging participants and stakeholders in identifying issues to explore and sometimes also in interpreting the data;
documenting how different people interpret and value the program;
negotiating what data becomes public respecting both the individual’s “right to privacy” and the public’s “right to know”;
offering participants opportunities to check how their data are used in the context of reporting;
reporting in language and forms accessible to a wide range of audiences;
disseminating to audiences within and beyond the case.
For further discussion of the ethics of democratic case study evaluation and examples of their use in practice, see Simons (2000 , 2006 , 2009 , chapter 6, 2010 ).
Designing Case Study Research
Design issues in case study sometimes take second place to those of data gathering, the more exciting task perhaps in starting research. However, it is critical to consider the design at the outset, even if changes are required in practice due to the reality of what is encountered in the field. In this sense, the design of case study is emergent, rather than preordinate, shaped and reshaped as understanding of the significance of foreshadowed issues emerges and more are discovered.
Before entering the field, there are a myriad of planning issues to think about related to stakeholders, participants, and audiences. These include whose values matter, whether to engage them in data gathering and interpretation, the style of reporting appropriate for each, and the ethical guidelines that will underpin data collection and reporting. However, here I emphasize only three: the broad focus of the study, what the case is a case of, and framing questions/issues. These are steps often ignored in an enthusiasm to gather data, resulting in a case study that claims to be research but lacks the basic principles required for generation of valid, public knowledge.
Conceptualize the Topic
First, it is important that the topic of the research is conceptualized in a way that it can be researched (i.e., it is not too wide). This seems an obvious point to make, but failure to think through precisely what it is about your research topic you wish to investigate will have a knock-on effect on the framing of the case, data gathering, and interpretation and may lead, in some instances, to not gathering or analyzing data that actually informs the topic. Further conceptualization or reconceptualization may be necessary as the study proceeds, but it is critical to have a clear focus at the outset.
What Constitutes the Case
Second, I think it is important to decide what would constitute the case (i.e., what it is a case of) and where the boundaries of this lie. This often proves more difficult than first appears. And sometimes, partly because of the semifluid nature of the way the case evolves, it is only possible to finally establish what the case is a case of at the end. Nevertheless, it is useful to identify what the case and its boundaries are at the outset to help focus data collection while maintaining an awareness that these may shift. This is emergent design in action.
In deciding the boundary of the case, there are several factors to bear in mind. Is it bounded by an institution or a unit within an institution, by people within an institution, by region, or by project, program or policy,? If we take a school as an example, the case could be comprised of the principal, teachers, and students, or the boundary could be extended to the cleaners, the caretaker, the receptionist, people who often know a great deal about the subnorms and culture of the institution.
If the case is a policy or particular parameter of a policy, the considerations may be slightly different. People will still be paramount—those who generated the policy and those who implemented it—but there is likely also to be a political culture surrounding the policy that had an influence on the way the policy evolved. Would this be part of the case?
Whatever boundary is chosen, this may change in the course of conducting the study when issues arise that can only be understood by going to another level. What transpires in a classroom, for example, if this is the case, is often partly dependent on the support of the school leadership and culture of the institution and this, in turn, to some extent is dependent on what resources are allocated from the local education administration. Much like a series of Russian dolls, one context inside the other.
Unit of analysis
Thinking about what would constitute the unit of analysis— a classroom, an institution, a program, a region—may help in setting the boundaries of the case, and it will certainly help when it comes to analysis. But this is a slightly different issue from deciding what the case is a case of. Taking a health example, the case may be palliative care support, but the unit of analysis the palliative care ward or wards. If you took the palliative care ward as the unit of analysis this would be as much about how palliative care was exercised in this or that ward than issues about palliative care support in general. In other words, you would need to have specific information and context about how this ward was structured and managed to understand how palliative care was conducted in this particular ward. Here, as in the school example above, you would need to consider which of the many people who populate the ward form part of the case—nurses, interns, or doctors only, or does it extend to patients, cleaners, nurse aides, and medical students?
Framing Questions and Issues
The third most important consideration is how to frame the study, and you are likely to do this once you have selected the site or sites for study. There are at least four approaches. You could start with precise questions, foreshadowed issues ( Smith & Pohland, 1974 ), theories, or a program logic. To some extent, your choice will be dictated by the type of case you have chosen, but also by your personal preference for how to conduct it—in either a structured or open way.
Initial questions give structure; foreshadowed issues more freedom to explore. In qualitative case study, foreshadowed issues are more common, allowing scope for issues to change as the study evolves, guided by participants’ perspectives and events in the field. With this perspective, it is more likely that you will generate a theory of the case toward the end, through your interpretation and analysis.
If you are conducting an instrumental case study, staying close to the questions or foreshadowed issues is necessary to be sure you gain data that will illuminate the central focus of the study. This is critical if you are exploring issues across several cases, although it is possible to do a cross-case analysis from cases that have each followed a different route to discovering significant issues.
Opting to start with a theoretical framework provides a basis for formulating questions and issues, but it can also constrain the study to only those questions/issues that fit the framework. The same is true with using program logic to frame the case. This is an approach frequently adopted in evaluation case study where the evaluator, individually or with stakeholders, examines how the aims and objectives of the program relate to the activities designed to promote it and the outcomes and impacts expected. It provides direction, although it can lead to simply confirming what was anticipated, rather than documenting what transpired in the case.
Whichever approach you choose to frame the case, it is useful to think about the rationale or theory for each question and what methods would best enable you to gain an understanding of them. This will not only start a reflexive process of examining your choices—an important aspect of the process of data gathering and interpretation—it will also aid analysis and interpretation further down the track.
Methodology and Methods
Qualitative case study research, as already noted, appeals to subjective ways of knowing and to a primarily qualitative methodology, that captures experiential understanding ( Stake, 2010 , pp. 56–70). It follows that the main methods of data gathering to access this way of knowing will be qualitative. Interviewing, observation, and document analysis are the primary three, often supported by critical incidents, focus groups, cameos, vignettes, diaries/journals, and photographs. Before gathering any primary data, however, it is useful to search relevant existing sources (written or visual) to learn about the antecedents and context of a project, program, or policy as a backdrop to the case. This can sharpen framing questions, avoid unnecessary data gathering, and shorten the time needed in the field.
Given that there are excellent texts on qualitative methods (see, for example, Denzin & Lincoln, 1994 ; Seale, 1999 ; Silverman, 2000 , 2004 ), I will not discuss all potential relevant methods here, but simply focus on the qualities of the primary methods that are particularly appropriate for case study research.
Primary Qualitative Data Gathering Methods
Interviewing.
The most effective style of interviewing in qualitative case study research to gain in-depth data, document multiple perspectives and experiences and explore contested issues is the unstructured interview, active listening and open questioning are paramount, whatever prequestions or foreshadowed issues have been identified. This can include photographs—a useful starting point with certain cultural groups and the less articulate, to encourage them to tell their story through connecting or identifying with something in the image.
The flexibility of unstructured interviewing has three further advantages for understanding participants’ experiences. First, through questioning, probing, listening, and, above all, paying attention to the silences and what they mean, you can get closer to the meaning of participants’ experiences. It is not always what they say.
Second, unstructured interviewing is useful for engaging participants in the process of research. Instead of starting with questions and issues, invite participants to tell their stories or reflect on specific issues, to conduct their own self-evaluative interview, in fact. Not only will they contribute their particular perspective to the case, they will also learn about themselves, thereby making the process of research educative for them as well as for the audiences of the research.
Third, the open-endedness of this style of interviewing has the potential for creating a dialogue between participants and the researcher and between the researcher and the public, if enough of the dialogue is retained in the publication ( Bellah, Madsen, Sullivan, Swidler, & Tipton, 1985 ).
Observations
Observations in case study research are likely to be close-up descriptions of events, activities, and incidents that detail what happens in a particular context. They will record time, place, specific incidents, transactions, and dialogue, and note characteristics of the setting and of people in it without preconceived categories or judgment. No description is devoid of some judgment in selection, of course, but, on the whole, the intent is to describe the scene or event “as it is,” providing a rich, textured description to give readers a sense of what it was like to be there or provide a basis for later interpretation.
Take the following excerpt from a study of the West Bromwich Operatic Society. It is the first night of a new production, The Producers , by this amateur operatic society. This brief excerpt is from a much longer observation of the overture to the first evening’s performance, detailing exactly what the production is, where it is, and why there is such a tremendous sense of atmosphere and expectation surrounding the event. Space prevents including the whole observation, but I hope you can get a glimmer of the passion and excitement that precedes the performance:
Birmingham, late November, 2011, early evening.... Bars and restaurants spruce up for the evening’s trade. There is a chill in the air but the party season is just starting....
A few hundred yards away, past streaming traffic on Suffolk Street, Queensway, an audience is gathering at the New Alexandra Theatre. The foyer windows shine in the orange sodium night. Above each one is the rubric: WORLD CLASS THEATRE.
Inside the preparatory rituals are being observed; sweets chosen, interval drinks ordered and programmes bought. People swap news and titbits about the production.... The bubble of anticipation grows as the 5-minute warning sounds. People make their way to the auditorium. There have been so many nights like this in the past 110 years since a man named William Coutts invested £10,000 to build this palace of dreams.... So many fantasies have been played under this arch: melodramas and pantomimes, musicals and variety.... So many audiences, settling down in their tip-up seats, wanting to be transported away from work, from ordinariness and private troubles.... The dimming lights act like a mother’s hush. You could touch the silence. Boinnng! A spongy thump on a bass drum, and the horns pipe up that catchy, irrepressible, tasteless tune and already you’re singing under your breath, ‘Springtime for Hitler and Germany....’ The orchestra is out of sight in the pit. There’s just the velvet curtain to watch as your fingers tap along. What’s waiting behind? Then it starts it to move. Opening night.... It’s opening night! ( Matarasso, 2012 , pp. 1–2)
For another and different example—a narrative observation of an everyday but unique incident that details date, time, place, and experience—see Simons (2009 , p. 60).
Such naturalistic observations are also useful in contexts where we cannot understand what is going on through interviewing alone—in cultures with which we are less familiar or where key actors may not share our language or have difficulty expressing it. Careful description in these situations can help identify key issues, discover the norms and values that exist in the culture, and, if sufficiently detailed, allow others to cross corroborate what significance we draw from these observations. This last point is very important to avoid the danger in observation of ascribing motivations to people and meanings to transactions.
Finally, naturalistic observations are very important in highly politicized environments, often the case in commissioned evaluation case study, where individuals in interview may try to elude the “truth” or press on you that their view is the “right” view of the situation. In these contexts, naturalistic observations not only enable you to document interactions as you perceive them, but they also provide a cross-check on the veracity of information obtained in interviews.
Document analysis
Analysis of documents, as already intimated, is useful for establishing what historical antecedents might exist to provide a springboard for contemporaneous data gathering. In most cases, existing documents are also extremely pertinent for understanding the policy context.
In a national policy case study I conducted on a major curriculum change, the importance of preexisting documentation was brought home to me sharply when certain documentation initially proved elusive to obtain. It was difficult to believe that it did not exist, as the evolution of the innovation involved several parties who had not worked together before. There was bound, I thought, to be minuted meetings sharing progress and documentation of the “new” curriculum. In the absence of some crucial documents, I began to piece together the story through interviewing. Only there were gaps, and certain issues did not make sense.
It was only when I presented two versions of what I discerned had transpired in the development of this initiative in an interim report eighteen months into the study that things started to change. Subsequent to the meeting at which the report was presented, the “missing” documents started to appear. Suddenly found. What lay behind the “missing documents,” something I suspected from what certain individuals did and did not say in interview, was a major difference of view about how the innovation evolved, who was key in the process, and whose voice was more important in the context. Political differences, in other words, that some stakeholders were trying to keep from me. The emergence of the documents enabled me to finally produce an accurate and fair account.
This is an example of the importance of having access to all relevant documents relating to a program or policy in order to study it fairly. The other major way in which document analysis is useful in case study is for understanding the values, explicit and hidden, in policy and program documents and in the organization where the program or policy is implemented. Not to be ignored as documents are photographs, and these, too, can form the basis of a cultural and value analysis of an organization ( Prosser, 2000 ).
Creative artistic approaches
Increasingly, some case study researchers are employing creative approaches associated with the arts as a means of data gathering and analysis. Artistic approaches have often been used in representing findings, but less frequently in data gathering and interpretation ( Simons & McCormack, 2007 ). A major exception is the work of Richardson (1994) , who sees the very process of writing as an interpretative act, and of Cancienne and Snowber (2003) , who argue for movement as method.
The most familiar of these creative and artistic forms are written—narratives and short stories ( Clandinin & Connelly, 2000 ; Richardson, 1994 ; Sparkes, 2002 ), poems or poetic form ( Butler-Kisber, 2010 ; Duke, 2007 ; Richardson, 1997 ; Sparkes & Douglas, 2007 ), cameos of people, or vignettes of situations. These can be written by participants or by the researcher or developed in partnership. They can also be shared with participants to further interpret the data. But photographs also have a long history in qualitative research for presenting and constructing understanding ( Butler-Kisber, 2010 ; Collier, 1967 ; Prosser, 2000 ; Rugang, 2006 ; Walker, 1993 ).
Less common are other visual forms of gathering data, such as “draw and write” ( Sewell, 2011 ), artefacts, drawings, sketches, paintings, and collages, although all forms are now on the increase. For examples of the use of collage in data gathering, see Duke (2007) and Butler-Kisber (2010) , and for charcoal drawing, Elliott (2008) .
In qualitative inquiry broadly, these creative approaches are now quite common. And in the context of arts and health in particular (see, for example, Frank, 1997 ; Liamputtong & Rumbold, 2008 ; Spouse, 2000 ), we can see how artistic approaches illuminate in-depth understanding. However, in case study research to date, I think narrative forms have tended to be most prominent.
Finally, for capturing the quality and essence of peoples’ experience, nothing could be more revealing than a recording of their voices. Video diaries—self-evaluative portrayals by individuals of their perspectives, feelings, or experience of an event or situation—are a most potent way both of gaining understanding and communicating that to others. It is rather more difficult to gain access for observational videos, but they are useful for documentation and have the potential to engage participants and stakeholders in the interpretation.
Getting It All Together
Case study is so often associated with story or with a report of some event or program that it is easy to forget that much analysis and interpretation has gone on before we reach this point. In many case study reports, this process is hidden, leaving the reader with little evidence on which to assess the validity of the findings and having to trust the one who wrote the tale.
This section briefly outlines possibilities, first, for analyzing and interpreting data, and second, for how to communicate the findings to others. However it is useful to think of these together and indeed, at the start, because decisions about how you report may influence how you choose to make sense of the data. Your choice may also vary according to the context of the study—what is expected or acceptable—and your personal predilections, whether you prefer a more rational than intuitive mode of analysis, for example, or a formal or informal style of writing up that includes images, metaphor, narratives, or poetic forms.
Analyzing and Interpreting Data
When it comes to making sense of data, I make a distinction between analysis—a formal inductive process that seeks to explain—and interpretation, a more intuitive process that gains understanding and insight from a holistic grasp of data, although these may interact and overlap at different stages.
The process, whichever emphasis you choose, is one of reducing or transforming a large amount of data to themes that can encapsulate the overarching meaning in the data. This involves sorting, refining, and refocusing data until they make sense. It starts at the beginning with preliminary hunches, sometimes called “interpretative asides” or “working hypotheses,” later moving to themes, analytic propositions, or a theory of the case.
There are many ways to conduct this process. Two strategies often employed are concept mapping —a means of representing data visually to explore links between related concepts—and progressive focusing ( Parlett & Hamilton, 1976 ), the gradual reframing of initially identified issues into themes that are then further interpreted to generate findings. Each of these strategies tends to have three stages: initial sense making, identification of themes, and examination of patterns and relationships between them.
If taking a formal analytic approach to the task, the data would likely be broken down into segments or datasets (coded and categorized) and then reordered and explored for themes, patterns, and possible propositions. If adopting a more intuitive process, you might focus on identifying insights through metaphors and images, lateral thinking, or puzzling over paradoxes and ambiguities in the data, after first immersing yourself in the total dataset, reading and re-reading interview scripts, observations and field notes to get a sense of the whole. Trying out different forms of making sense through poetry, vignettes, cameos, narratives, collages, and drawing are further creative ways to interpret data, as are photographs taken in the case arranged to explain or tell the story of the case.
Reporting Case Study Research
Narrative structure and story.
As indicated in the introduction, telling a story is often associated with case study and some think this is what a case study is. In one sense, it is and, given that story is the natural way in which we learn ( Okri, 1997 ), it is a useful framework both for gathering data and for communicating case study findings. Not any story will do however. To count as research, it must be authentic, grounded in data, interpreted and analyzed to convey the meaning of the case.
There are several senses in which story is appropriate in qualitative case study: in capturing stories participants tell, in generating a narrative structure that makes sense of the case (i.e., the story you will tell), and in deciding how you communicate this narrative (i.e., in story form). If you choose a written story form (and advice here can be sought from Harrington (2003) and Caulley (2008) ), it needs to be clearly structured, well written, and contain only the detail that is necessary to give readers the vicarious experience of what it was like in the case. If the story is to be communicated in other ways, through, for example, audio or videotape, or computer or personal interaction, the same applies, substituting visual and interpersonal skill for written.
Matching forms of reporting to audience
The art of reporting is strongly connected to usability, so forms of reporting need to connect to the audiences we hope to inform: how they learn, what kind of evidence they value, and what kind of reporting maximizes the chances they will use the findings to promote policies and programs in the interests of beneficiaries. As Okri (1997) further reminds us, the writer only does half the work; the reader does the other (p. 41).
There may be other considerations as well: how open are commissioners to receiving stories of difficulties, as well as success stories? What might they need to hear beyond what is sought in the technical brief? And through what style of reporting would you try and persuade them? If conducting noncommissioned case study research, the scope for different forms of reporting is wider. In academia, for instance, many institutions these days accept creative and artistic forms of reporting when supported by supervisors and appreciated by examiners.
Styles of Reporting
The most obvious form of reporting is linear, often starting with a short executive summary and a brief description of focus and context, followed by methodology, the case study or thematic analysis, findings, and conclusions or implications. Conclusion-led reporting is similar in terms of its formality, but simply starts the other way around. From the conclusions drawn from the analyzed data, it works backward to tell the story through narrative, verbatim, and observational data of how these conclusions were reached. Both have a strong story line. The intent is analytic and explanatory.
Quite a different approach is to engage the reader in the experience and veracity of the case. Rather like constructing a portrait or editing a documentary film, this involves the sifting, constructing, re-ordering of frames, events and episodes to tell a coherent story primarily through interview excerpts, observations, vignettes, and critical incidents that depict what transpired in the case. Interpretation is indirect through the weaving of the data. The story can start at any point provided the underlying narrative structure is maintained to establish coherence ( House, 1980 , p. 116).
Different again, and from the other end of a continuum, is a highly interpretative account that may use similar ways of presenting data but weaves a story from the outset that is highly interpretative. Engaging metaphor, images, short stories, contradictions, paradoxes, and puzzles, it is invariably interesting to read and can be most persuasive. However, the evidence is less visible and therefore less open to alternative interpretations.
Even more persuasive is a case study that uses artistic forms to communicate the story of the case. Paintings, poetic form, drawings, photography, collage, and movement can all be adopted to report findings, whether the data was acquired using these forms or by other means. The arts-based inquiry movement ( Mullen & Finley, 2003 ) has contributed hugely to the validation and legitimation of artistic and creative ways of representing qualitative research findings. The journal Qualitative Inquiry contains many good examples, but see also Liamputtong & Rumbold (2008) . Such artistic forms of representation may not be for everyone or appropriate in some contexts, but they do have the power to engage an audience and the potential to facilitate use.
Generalization in Case Study Research
One of the potential limitations of case study often proposed is that it is impossible to generalize. This is not so. However, the way in which one generalizes from a case is different from that adopted in traditional forms of social science research that utilize large samples (randomly selected) and statistical procedures and which assume regularities in the social world that allow cause and effect to be determined. In this form of research inferences from data are stated as formal propositions that apply to all in the target population. See Donmoyer (1990) for an argument on the restricted nature of this form of generalization when considering single-case studies.
Making inferences from cases with a qualitative data set arises more from a process of interpretation in context, appealing to tacit and situated understanding for acceptance of their validity. Such inferences are possible where the context and experience of the case is richly described so the reader can recognize and connect with the events and experiences portrayed. There are two ways to examine how to reach these generalized understandings. One is to generalize from the case to other cases of a similar or dissimilar nature. The other is to see what we learn in-depth from the uniqueness of the single case itself.
Generalizing from the Single Case
A common approach to generalization and one most akin to a propositional form is cross-case generalization. In a collective or multi-site case study, each case is explored to see if issues that arise in one case also exist in other cases and what interconnecting themes there are between them. This kind of generalization has a degree of abstraction and potential for theorizing and is often welcomed by commissioners of research concerned that findings from the single case do not provide an adequate or “safe” basis for policy determination.
However, there are four additional ways to generalize from the single case, all of which draw more on tacit knowledge and recognition of context, although in different ways. In naturalistic generalization , first proposed by Stake (1978) , generalization is reached on the basis of recognition of similarities and differences to cases with which we are familiar. To enable such recognition, the case needs to feature rich description; people’s voices; and enough detail of time, place, and context to provide a vicarious experience to help readers discern what is similar and dissimilar to their own context ( Stake, 1978 ).
Situated generalization ( Simons, Kushner, Jones, & James, 2003 ) is close to the concept of naturalistic generalization in relying for its generality on retaining a connectedness with the context in which it first evolved. However, it has an extra dimension in a practice context. This notion of generalization was identified in an evaluation of a research project that engaged teachers in and with research. Here, in addition to the usual validity criteria to establish the warrant for the findings, the generalization was seen as dependable if trust existed between those who conducted the research (teachers, in this example) and those thinking about using it (other teachers). In other words, beyond the technical validity of the research, teachers considered using the findings in their own practice because they had confidence in those who generated them. This is a useful way to think about generalization if we wish research findings to improve professional practice.
The next two concepts of generalization— concept and process generalization —relate more to what you discover in making sense of the case. As you interpret and analyze, you begin to generate a theory of the case that makes sense of the whole. Concepts may be identified that make sense in the one case but have equal significance in other cases of a similar kind, even if the contexts are different.
It is the concept that generalizes, not the specific content or context. This may be similar to the process Donmoyer (2008) identifies of “intellectual generalization” (quoted by Butler-Kisber, 2010 , p. 15) to indicate the cognitive understanding one can gain from qualitative accounts even if settings are quite different.
The same is true for generalization of a process. It is possible to identify a significant process in one case (or several cases) that is transferable to other contexts, irrespective of the precise content and contexts of those other cases. An example here is the collaborative model for sustainable school self-evaluation I identified in researching school self-evaluation in a number of schools and countries ( Simons, 2002 ). Schools that successfully sustained school self-evaluation had an infrastructure that was collaborative at all stages of the evaluation process from design to conduct of the study, to analyzing the results and to reporting the findings. This ensured that the whole school was involved and that results were discussed and built into the ongoing development of school policies and practice. In other cases, different processes may be discovered that have applicability in a range of contexts. As with concept generalization, it is the process that generalizes not the substantive content or specific context.
Particularization
The forms of generalization discussed above are useful when we have to justify case study in a research or policy context. But the overarching justification for how we learn from case study is particularization —a rich portrayal of insights and understandings interpreted in the particular context. Several authors have made this point ( Stake, 1995 ; Flyvberg, 2006 ; Simons 2009 ). Stake puts it most sharply when he observes that “The real business of case study is particularization, not generalization” (p. 8), referring here to the main reason for studying the singular, which is to understand the uniqueness of the case itself.
My perspective (explored further in Simons, 1996 ; Simons, 2009 , p. 239; Simons & McCormack, 2007 ) is similar in that I believe the “real” strength of case study lies in the insights we gain from in-depth study of the particular. But I also argue for the universality of such insights—if we get it “right.” By which I mean that if we are able to capture and report the uniqueness, the essence, of the case in all its particularity and present this in a way we can all recognize, we will discover something of universal significance. This is something of a paradox. The more you learn in depth about the particularity of one person, situation, or context, the more likely you are to discover something universal. This process of reaching understanding has support both from the way in which many discoveries are made in science and in how we learn from artists, poets, and novelists, who reach us by communicating a recognizable truth about individuals, human relationships, and/or social contexts.
This concept of particularization is far from new, as the quotation from a preface to a book written in 1908 attests. Stephen Reynolds, the author of A Poor Man’s House , notes that the substance of the book was first recorded in a journal, kept for purposes of fiction, and in letters to one of his friends, but fiction proved an inappropriate medium. He felt that the life and the people were so much better than anything he could invent. The book therefore consists of the journal and letters drawn together to present a picture of a typical poor man’s house and life, much as we might draw together a range of data to present a case study. It is not the substance of the book that concerns us here but the methodological relevance to case study research. Reynolds notes that the conclusions expressed are tentative and possibly go beyond this man’s life, so he thought some explanation of the way he arrived at them was needed:
Educated people usually deal with the poor man’s life deductively; they reason from the general to the particular; and, starting with a theory, religious, philanthropic, political, or what not, they seek, and too easily find, among the millions of poor, specimens—very frequently abnormal—to illustrate their theories. With anything but human beings, that is an excellent method. Human beings, unfortunately, have individualities. They do what, theoretically, they ought not to do, and leave undone those things they ought to do. They are even said to possess souls—untrustworthy things beyond the reach of sociologists. The inductive method—reasoning from the particular to the general... should at least help to counterbalance the psychological superficiality of the deductive method. ( Reynolds, 1908 : preface) 1
Slightly overstated perhaps, but the point is well made. In our search for general laws, we not only lose sight of the uniqueness and humanity of individuals, but reduce them in the process, failing to present their experience in any “real” sense. What is astonishing about the quotation is that it was written over a century ago and yet many still argue today that you cannot generalize from the particular.
Going even further back, in 1798, Blake proclaimed that “To Generalize is to be an Idiot. To Particularize is the Alone Distinction of Merit.” In research, we may not wish to make such a strong distinction: these processes both have their uses in different kinds of research. But there is a major point here for the study of the particular that Wilson (2008) notes in commenting on Blake’s perception when he says: “Favouring the abstract over the concrete, one ‘sees all things only thro’ the narrow chinks of his cavern”’ (referring here to Blake’s The Marriage of Heaven and Hell [1793]; in Wilson, 2008 , p. 62). The danger Wilson is pointing to here is that abstraction relies heavily on what we know from our past understanding of things, and this may prevent us experiencing a concrete event directly or “apprehend[ing] a particular moment” ( Wilson, 2008 , p. 63).
Blake had a different mission, of course, than case researchers, and he was not himself free from abstractions, as Wilson points out, although he fought hard “to break through mental barriers to something unique and living” ( Wilson, 2008 , p. 65). It is this search for the “unique and living” and experiencing the “isness” of the particular that we should take from the Blake example to remind ourselves of the possibility of discovering something “new,” beyond our current understanding of the way things are.
Focusing on particularization does not diminish the usefulness of case study research for policy makers or practitioners. Grounded in recognizable experience, the potential is there to reach a range of audiences and to facilitate use of the findings. It may be more difficult for those who seek formal generalizations that seem to offer a safe basis for policy making to accept case study reports. However, particular stories often hold the key to why policies have or have not worked well in the past. It is not necessary to present long cases—a criticism frequently levelled—to demonstrate the story of the case. Such case stories can be most insightful for policy makers who, like many of us in everyday life, often draw inferences from a single instance or case, whatever the formal evidence presented. “I am reminded of the story of....”
The case for studying the particular to inform practice in professional contexts needs less persuasion because practitioners can recognize the content and context quite readily and make the inference to their own particular context ( Simons et al., 2003 ). In both sets of circumstances—policy and practice—it is more a question of whether the readers of our case research accept the validity of findings determined in this way, how they choose to learn, and our skill in telling the case study story.
Conclusion and Future Directions
In this chapter, I have presented an argument for case study research, making the case, in particular, for using qualitative methods to highlight what it is that qualitative case study research can bring to the study of social and educational programs. I outlined the various ways in which case study is commonly used before focusing directly on case study as a major mode of research inquiry, noting characteristics it shares with other qualitative methodologies, as well as itsdifference and the difficulties it is sometimes perceived to have. The chapter emphasizes the importance of thinking through what the case is, to be sure that the issues explored and the data generated do illuminate this case and not any other.
But there is still more to be done. In particular, I think we need to be more adventurous in how we craft and report the case. I suspect we may have been too cautious in the past in how we justified case study research, borrowing concepts from other disciplines and forms of educational research. More than 40 years on, it is time to take a greater risk—in demonstrating the intrinsic nature of case study and what it can offer to our understanding of human and social situations.
I have already drawn attention to the need to design the case, although this could be developed further to accentuate the uniqueness of the particular case. One way to do this is to feature individuals more in the design itself, not only to explore programs and policies through perspectives of key actors or groups and transactions between them, which to some extent happens already, but also to get them to characterize what makes the context unique. This is the reversal of many a design framework that starts with the logic of a program and takes forward the argument for personal evaluation ( Kushner, 2000 ), noted in the interlude on evaluation. Apart from this attention to design, there are three other issues I think we need to explore further: the warrant for creative methods in case study, more imaginative reporting; and how we learn from a study of the singular.
Warrant for More Creative Methods in Case Study Research
The promise that creative methods have for eliciting in-depth understanding and capturing the unusual, the idiosyncratic, the uniqueness of the case, was mentioned in the methods section. Yet, in case study research, particularly in program and policy contexts, we have few good examples of the use of artistic approaches for eliciting and interpreting data, although more, as acknowledged later, for presenting it. This may be because case study research is often conducted in academic or policy environments, where propositional ways of knowing are more valued.
Using creative and artistic forms in generating and interpreting case study data offers a form of evidence that acknowledges experiential understanding in illuminating the uniqueness of the case. The question is how to establish the warrant for this way of knowing and persuade others of its virtue. The answer is simple. By demonstrating the use of these methods in action, by arguing for a different form of validity that matches the intrinsic nature of the method, and, above all, by good examples.
Representing Findings to Engage Audiences in Learning
In evaluative and research policy contexts, where case study is often the main mode of inquiry or part of a broader study, case study reports often take a formal structure or sometimes, where the context is receptive, a portrayal or interpretative form. But, too often, the qualitative is an add-on to a story told by other means or reduced to issues in which the people who gave rise to the data are no longer seen. However, there are many ways to put them center stage.
Tell good stories and tell them well. Or, let key actors tell their own stories. Explore the different ways technology can help. Make video clips that demonstrate events in context, illustrate interactions between people, give voice to participants—show the reality of the program, in other words. Use graphics to summarize key issues and interactive, cartoon technology, as seen on some TED presentations, to summarize and visually show the complexity of the case. Video diaries were mentioned in the methods section: seeing individuals tell their tales directly is a powerful way of communicating, unhindered by “our” sense making. Tell photo stories. Let the photos convey the narrative, but make sure the structure of the narrative is evident to ensure coherence. These are just the beginnings. Those skilled in information technology could no doubt stretch our imagination further.
One problem and a further question concerns our audiences. Will they accept these modes of communication? Maybe not, in some contexts. However, there are three points I wish to leave you with. First, do not presume that they won’t. If people are fully present in the story and the complexity is not diminished, those reading, watching, or hearing about the case will get the message. If you are worried about how commissioners might respond, remember that they are no different from any other stakeholder or participant when it comes to how they learn from human experience. Witness the reference to Okri (1997) earlier about how we learn.
Second, when you detect that the context requires a more formal presentation of findings, respond according to expectation but also include elements of other forms of presentation. Nudge a little in the direction of creativity. Third, simply take a chance, that risk I spoke about earlier. Challenge the status quo. Find situations and contexts where you can fully represent the qualitative nature of the experience in the cases you study with creative forms of interpretation and representation. And let the audience decide.
Learning from a Study of the Singular
Finally, to return to the issue of “generalization” in case study that worries some audiences. I pointed out in the generalization section several ways in which it is possible to generalize from case study research, not in a formal propositional sense or from a case to a population, but by retaining a connection with the context in which the generalization first arose—that is, to realize in-depth understanding in context in different circumstances and situations. However, I also emphasized that, in many instances, it is particularization from which we learn. That is the point of the singular case study, and it is an art to perceive and craft the case in ways that we can.
Acknowledgments
Parts of this chapter build on ideas first explored in Simons, 2009 .
I am grateful to Bob Williams for pointing out the relevance of this quotation from Reynolds to remind us that “there is nothing new under the sun” and that we sometimes continue to engage endlessly in debates that have been well rehearsed before.
Adams, T. ( 2012 ) ‘ Olympics 2012: Team GB falters but London shines bright on opening day ’, Observer, 29.07.12.
Google Scholar
Google Preview
Bassey, M. ( 1999 ). Case study research in educational settings . Buckingham: Open University Press.
Bellah, R. N. , Madsen, R. , Sullivan, W. M. , Swidler, A. , & Tipton, S. M. ( 1985 ). Habits of the heart . London: Harper and Row.
Blake, W. (1798– 1809 ). Annotations to Sir Joshua Reynolds’s Discourses , pp. xvii–xcviii (c. 1798–1809) repr. In Complete Writings , ed. Geoffrey Keynes (1957). ‘Discourse II,’ annotations to Sir Joshua Reynolds, Discourses (c. 1808) .
Butler-Kisber, L. ( 2010 ). Qualitative inquiry: Thematic, narrative and arts-informed perspectives . London: Sage.
Cancienne, M. B. , & Snowber, C. N. ( 2003 ). Writing rhythm: Movement as method. Qualitative Inquiry , 9 (2), 237–253.
Caulley, D. N. ( 2008 ). Making qualitative research reports less boring: The techniques of writing creative nonfiction. Qualitative Inquiry , 14 (3) pp. 424–449.
Chadderton, C. , & Torrance, H. ( 2011 ). Case study. In B. Somekh & C. Lewin (Eds.), Theory and methods in social research . (2nd ed. pp 53–60). London and Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.
Clandinin, D. J. & Connelly, F. M. ( 2000 ) Narrative inquiry: Experience and story in qualitative research. Ist edn. SanFrancisco: Jossey Bass Publishers.
Collier, J., Jr. ( 1967 ). Visual anthropology: Photography as a research method . New York: Holt, Reinhart, & Winston.
Denzin, N. K. & Lincoln, Y. S. (Eds.) ( 1994 ) Handbook of Qualitative Research , London and Thousand Oaks, CA:Sage
Donmoyer, R. ( 1990 ). Generalization and the single case study. In E. W. Eisner & A. Peshkin (Eds.), Qualitative inquiry in education (pp. 175–200). New York: Teachers College Press.
Donmoyer, R. ( 2008 ). Generalizability. In L. M. Givens (Ed.), The Sage encyclopedia of qualitative inquiry (vol. 2, pp. 371–372). Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.
Duke, S. (2007). A narrative case study evaluation of the role of the Nurse Consultant in palliative care. PhD thesis, University of Southampton, England.
Elliott, J. (2008). Dance mirrors: Embodying, actualizing and operationalizing a dance experience in a healthcare context. PhD thesis, University of Ulster, Belfast.
Frank. A. ( 1997 ). Enacting illness stories: When, what, why. In H. L. Nelson (Ed.), Stories and their limits (pp. 31–49). London: Routledge.
Flyvberg, B. ( 2006 ). Five misunderstandings about case-study research. Qualitative Inquiry , 12 (2), 219–245.
Gomm, R. , Hammersley, M. , & Foster, P. (Eds.). ( 2004 ). Case study method: Key issues, key texts . [First published in 2000]. London and Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.
Greene, J. C. ( 2000 ). Understanding social programs through evaluation. In N. K. Denzin and Y. S. Lincoln (Eds.), The handbook of qualitative research (2nd ed., pp. 981–999). Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.
Greene, J. C. ( 2007 ). Mixing methods in social inquiry . San Francisco: Jossey Bass.
Greenhalgh, T. , & Worrall, J. G. ( 1997 ). From EBM to CSM: The evolution of context-sensitive medicine. Journal of Evaluation in Clinical Practice , 3 (2), 105–108.
Harrington, W. ( 2003 ). What journalism can offer ethnography. Qualitative Inquiry . 9 (1), 90–114.
Heron, J. ( 1992 ). Feeling and personhood . Sage: London.
Heron, J. ( 1999 ). The complete facilitator’s handbook . London: Kogan Page.
House, E. R. ( 1980 ). Evaluating with validity . London, Beverly Hills, CA: Sage.
House, E. R. ( 1993 ). Professional evaluation: Social impact and political consequences . Newbury Park and London: Sage
Kushner, S. ( 2000 ). Personalizing evaluation . London and Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.
Liamputtong, P. , & Rumbold, J. (Eds.). ( 2008 ). Knowing differently: Arts-based and collaborative research methods . New York: Nova Science Publishers.
MacDonald, B. ( 1976 ). Evaluation and the control of education. In D. Tawney (Ed.), Curriculum evaluation today: Trends and implications . Schools Council Research Studies (pp. 125– 136). London: Macmillan.
Matarasso, F. ( 2012 ). West Bromwich Operatic Society: fine art of musical theatre . West Bromwich, UK: Multistory.
Merriam, S. B. ( 1988 ). Case study research in education: A qualitative Approach . San Francisco: Jossey Bass.
Mullen, C. A. , & Finley, S. (Eds.). ( 2003 ). Arts-based approaches to qualitative inquiry [Special Issue]. Qualitative Inquiry , 9 (2), 165–329.
Okri, B. ( 1997 ). A way of being free . London: Phoenix.
Parlett, M. , & Hamilton, D. ( 1976 ). Evaluation as illumination: A new approach to the study of innovatory programmes. In G. Glass (Ed.), Evaluation studies review annual, I (pp. 140–157). [First published in 1972 as Occasional Paper 9, Centre for Research in the Educational Sciences, University of Edinburgh.] Beverly Hills: CA: Sage.
Platt, J. ( 2007 ). Case study. In W. Outhwaite & S. P. Turner (Eds.), The Sage handbook of social science methodology (pp. 100–118). London: Sage.
Prosser, J. ( 2000 ). The moral maze of image ethics. In H. Simons & R. Usher (Eds.), Situated ethics in educational research (pp. 116–132). London and New York: Routledge/Falmer.
Ragin, C. C. ( 1992 ). Cases of “What is a case?” In C. C. Ragin & H. S. Becker (Eds.), What is a case?: Exploring the foundations of social inquiry (pp. 1–17). Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Reynolds, S. S. (1908). A Poor Man’s House . The Project Guttenberg eBook, July 25, 2008 [eBook#26126]. Accessed February 26, 2013, http.//www.gutenberg.org
Richardson, L. ( 1994 ). Writing as a form of inquiry. In N. K. Denzin & Y. S. Lincoln (Eds.), Handbook of Qualitative Research (pp. 516–529). London: Sage.
Richardson, L. ( 1997 ). Fields of play (Constructing an academic life) . New Brunswick, NJ: Rutgers University Press.
Rugang, L. (2006). Chinese culture in globalisation: A multi-modal case study on visual discourse. PhD thesis, University of Southampton, England.
Seale, C. ( 1999 ). The quality of qualitative research . London and Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.
Sewell, K. ( 2011 ). Researching sensitive issues: A critical appraisal of “draw and write” as a data collection technique in eliciting children’s perceptions. International Journal of Research Methods in Education 34(2), pp.175–191.
Shaw, I. , & Gould, N. ( 2001 ). Qualitative research in social work: Context and method . London: Sage.
Silverman, D. ( 2000 ). Doing qualitative research: A practical handbook . London and Thousand Oaks. CA: Sage.
Silverman, D. (Ed.). ( 2004 ). Qualitative research: Theory, methods and practice (2nd ed.). London and Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.
Simons, H. ( 1971 ). Innovation and the case study of schools. Cambridge Journal of Education , 3 , 118–123.
Simons, H. (Ed.). ( 1980 ). Towards a science of the singular: Essays about case study in educational research and evaluation . Occasional Papers No. 10. Norwich, UK: Centre for Applied Research, University of East Anglia.
Simons, H. ( 1987 ). Getting to know schools in a democracy: The politics and process of evaluation . Lewes, UK: Falmer Press.
Simons, H. ( 1996 ). The paradox of case study. Cambridge Journal of Education , 26 (2), 225–240.
Simons, H. ( 2000 ). Damned if you do, damned if you don’t: ethical and political dilemmas in evaluation. In H. Simons & R. Usher (Eds.) Situated ethics in educational research (pp.39– 55) London and New York: Routledge/Falmer.
Simons, H. ( 2002 ). School self-evaluation in a democracy. In D. Nevo (Ed.), School-based evaluation: An international perspective . Advances in Program Evaluation. London: Sage.
Simons, H. ( 2006 ). Ethics and evaluation. In I. F. Shaw , J. C. Greene , & M. M. Mark (Eds.), The international handbook of evaluation (pp. 243–265). London and Thousand Oaks, CA Sage.
Simons, H. ( 2009 ). Case study research in practice . London: Sage.
Simons, H. (2010). Democratic evaluation: Theory and practice. Paper prepared for Virtual Evaluation Conference, University of the Witwatersrand, Johannesburg, South Africa, May, 2010.
Simons, H. , Kushner, S. , Jones, K. , & James, D. ( 2003 ). From evidence-based practice to practice-based evidence: The idea of situated generalization. Research Papers in Education: Policy and Practice , 18 (4), 347–364.
Simons, H. , & McCormack, B. ( 2007 ). Integrating arts-based inquiry in evaluation methodology. Qualitative Inquiry , 13 (2) 292–311.
Simons, H. , & Usher, R. (Eds.). ( 2000 ). Situated ethics in educational research . London and New York: Routledge/Falmer.
Smith, L. M. , & Pohland, P. A. ( 1974 ). Education, technology, and the rural highlands. In R. H. P. Kraft ., L. M. Smith ., P. A. Pohland ., C. J. Brauner , & C. Gjerde (Eds.), Four evaluation examples: Anthropological, economic, narrative and portrayal (pp. 5–54), AERA Monograph Series on Curriculum Evaluation 7. Chicago: Rand McNally.
Sparkes, A. ( 2002 ). Telling tales in sport and physical activity: A qualitative journey . Champaign, IL: Human Kinetics Press.
Sparkes, A. C. , & Douglas, K. ( 2007 ). Making the case for poetic representations: An example in action. The Sport Psychologist , 21(2) , 170–190.
Spouse, J. ( 2000 ). Talking pictures: Investigating personal knowledge though illuminating artwork. Nursing Times Research Journal , 5 (4), 253–261.
Stake, R. E. ( 1978 ) The case study method in social inquiry. Educational Researcher , 7(2), 5–9.
Stake, R. E. ( 1995 ). The art of case study research . Thousand Oaks, CA and London: Sage.
Stake, R. E. ( 2010 ). Qualitative research: Studying how things work . New York & London: Guildford Press.
Stenhouse, L. ( 1978 ). Case study and case records: Towards a contemporary history of education. British Educational Research Journal , 4 (2), 21–39.
Thomas, G. ( 2011 b)). A typology for the case study in social science following a review of definition, discourse and structure. Qualitative Inquiry , 17 (6) , 511–521.
Thomas, G. ( 2011 a). How to do your case study: A guide for students and researchers . London: Sage.
Walker, R. ( 1993 ). Finding a silent voice for the researcher: Using photographs in evaluation and research. In M. Schratz (Ed.), Qualitative voices in educational research (pp. 72–92). Lewes, UK: Falmer Press.
Wilson, E. G. ( 2008 ). Against happiness . New York: Sarah Crichton Books.
Yin, R. K. ( 2004 ). Case study research: Design and methods . Thousand Oaks, CA and London: Sage.
Zucker, D. M. ( 2001 ). Using case study methodology in nursing research. Qualitative Report , 6 (2) June.
- About Oxford Academic
- Publish journals with us
- University press partners
- What we publish
- New features
- Open access
- Institutional account management
- Rights and permissions
- Get help with access
- Accessibility
- Advertising
- Media enquiries
- Oxford University Press
- Oxford Languages
- University of Oxford
Oxford University Press is a department of the University of Oxford. It furthers the University's objective of excellence in research, scholarship, and education by publishing worldwide
- Copyright © 2024 Oxford University Press
- Cookie settings
- Cookie policy
- Privacy policy
- Legal notice
This Feature Is Available To Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account
This PDF is available to Subscribers Only
For full access to this pdf, sign in to an existing account, or purchase an annual subscription.
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
What the Case Study Method Really Teaches
- Nitin Nohria

Seven meta-skills that stick even if the cases fade from memory.
It’s been 100 years since Harvard Business School began using the case study method. Beyond teaching specific subject matter, the case study method excels in instilling meta-skills in students. This article explains the importance of seven such skills: preparation, discernment, bias recognition, judgement, collaboration, curiosity, and self-confidence.
During my decade as dean of Harvard Business School, I spent hundreds of hours talking with our alumni. To enliven these conversations, I relied on a favorite question: “What was the most important thing you learned from your time in our MBA program?”
- Nitin Nohria is the George F. Baker Professor of Business Administration, Distinguished University Service Professor, and former dean of Harvard Business School.
Partner Center
Case Study Research Method in Psychology
Saul Mcleod, PhD
Editor-in-Chief for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MRes, PhD, University of Manchester
Saul Mcleod, PhD., is a qualified psychology teacher with over 18 years of experience in further and higher education. He has been published in peer-reviewed journals, including the Journal of Clinical Psychology.
Learn about our Editorial Process
Olivia Guy-Evans, MSc
Associate Editor for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MSc Psychology of Education
Olivia Guy-Evans is a writer and associate editor for Simply Psychology. She has previously worked in healthcare and educational sectors.
On This Page:
Case studies are in-depth investigations of a person, group, event, or community. Typically, data is gathered from various sources using several methods (e.g., observations & interviews).
The case study research method originated in clinical medicine (the case history, i.e., the patient’s personal history). In psychology, case studies are often confined to the study of a particular individual.
The information is mainly biographical and relates to events in the individual’s past (i.e., retrospective), as well as to significant events that are currently occurring in his or her everyday life.
The case study is not a research method, but researchers select methods of data collection and analysis that will generate material suitable for case studies.
Freud (1909a, 1909b) conducted very detailed investigations into the private lives of his patients in an attempt to both understand and help them overcome their illnesses.
This makes it clear that the case study is a method that should only be used by a psychologist, therapist, or psychiatrist, i.e., someone with a professional qualification.
There is an ethical issue of competence. Only someone qualified to diagnose and treat a person can conduct a formal case study relating to atypical (i.e., abnormal) behavior or atypical development.
Famous Case Studies
- Anna O – One of the most famous case studies, documenting psychoanalyst Josef Breuer’s treatment of “Anna O” (real name Bertha Pappenheim) for hysteria in the late 1800s using early psychoanalytic theory.
- Little Hans – A child psychoanalysis case study published by Sigmund Freud in 1909 analyzing his five-year-old patient Herbert Graf’s house phobia as related to the Oedipus complex.
- Bruce/Brenda – Gender identity case of the boy (Bruce) whose botched circumcision led psychologist John Money to advise gender reassignment and raise him as a girl (Brenda) in the 1960s.
- Genie Wiley – Linguistics/psychological development case of the victim of extreme isolation abuse who was studied in 1970s California for effects of early language deprivation on acquiring speech later in life.
- Phineas Gage – One of the most famous neuropsychology case studies analyzes personality changes in railroad worker Phineas Gage after an 1848 brain injury involving a tamping iron piercing his skull.
Clinical Case Studies
- Studying the effectiveness of psychotherapy approaches with an individual patient
- Assessing and treating mental illnesses like depression, anxiety disorders, PTSD
- Neuropsychological cases investigating brain injuries or disorders
Child Psychology Case Studies
- Studying psychological development from birth through adolescence
- Cases of learning disabilities, autism spectrum disorders, ADHD
- Effects of trauma, abuse, deprivation on development
Types of Case Studies
- Explanatory case studies : Used to explore causation in order to find underlying principles. Helpful for doing qualitative analysis to explain presumed causal links.
- Exploratory case studies : Used to explore situations where an intervention being evaluated has no clear set of outcomes. It helps define questions and hypotheses for future research.
- Descriptive case studies : Describe an intervention or phenomenon and the real-life context in which it occurred. It is helpful for illustrating certain topics within an evaluation.
- Multiple-case studies : Used to explore differences between cases and replicate findings across cases. Helpful for comparing and contrasting specific cases.
- Intrinsic : Used to gain a better understanding of a particular case. Helpful for capturing the complexity of a single case.
- Collective : Used to explore a general phenomenon using multiple case studies. Helpful for jointly studying a group of cases in order to inquire into the phenomenon.
Where Do You Find Data for a Case Study?
There are several places to find data for a case study. The key is to gather data from multiple sources to get a complete picture of the case and corroborate facts or findings through triangulation of evidence. Most of this information is likely qualitative (i.e., verbal description rather than measurement), but the psychologist might also collect numerical data.
1. Primary sources
- Interviews – Interviewing key people related to the case to get their perspectives and insights. The interview is an extremely effective procedure for obtaining information about an individual, and it may be used to collect comments from the person’s friends, parents, employer, workmates, and others who have a good knowledge of the person, as well as to obtain facts from the person him or herself.
- Observations – Observing behaviors, interactions, processes, etc., related to the case as they unfold in real-time.
- Documents & Records – Reviewing private documents, diaries, public records, correspondence, meeting minutes, etc., relevant to the case.
2. Secondary sources
- News/Media – News coverage of events related to the case study.
- Academic articles – Journal articles, dissertations etc. that discuss the case.
- Government reports – Official data and records related to the case context.
- Books/films – Books, documentaries or films discussing the case.
3. Archival records
Searching historical archives, museum collections and databases to find relevant documents, visual/audio records related to the case history and context.
Public archives like newspapers, organizational records, photographic collections could all include potentially relevant pieces of information to shed light on attitudes, cultural perspectives, common practices and historical contexts related to psychology.
4. Organizational records
Organizational records offer the advantage of often having large datasets collected over time that can reveal or confirm psychological insights.
Of course, privacy and ethical concerns regarding confidential data must be navigated carefully.
However, with proper protocols, organizational records can provide invaluable context and empirical depth to qualitative case studies exploring the intersection of psychology and organizations.
- Organizational/industrial psychology research : Organizational records like employee surveys, turnover/retention data, policies, incident reports etc. may provide insight into topics like job satisfaction, workplace culture and dynamics, leadership issues, employee behaviors etc.
- Clinical psychology : Therapists/hospitals may grant access to anonymized medical records to study aspects like assessments, diagnoses, treatment plans etc. This could shed light on clinical practices.
- School psychology : Studies could utilize anonymized student records like test scores, grades, disciplinary issues, and counseling referrals to study child development, learning barriers, effectiveness of support programs, and more.
How do I Write a Case Study in Psychology?
Follow specified case study guidelines provided by a journal or your psychology tutor. General components of clinical case studies include: background, symptoms, assessments, diagnosis, treatment, and outcomes. Interpreting the information means the researcher decides what to include or leave out. A good case study should always clarify which information is the factual description and which is an inference or the researcher’s opinion.
1. Introduction
- Provide background on the case context and why it is of interest, presenting background information like demographics, relevant history, and presenting problem.
- Compare briefly to similar published cases if applicable. Clearly state the focus/importance of the case.
2. Case Presentation
- Describe the presenting problem in detail, including symptoms, duration,and impact on daily life.
- Include client demographics like age and gender, information about social relationships, and mental health history.
- Describe all physical, emotional, and/or sensory symptoms reported by the client.
- Use patient quotes to describe the initial complaint verbatim. Follow with full-sentence summaries of relevant history details gathered, including key components that led to a working diagnosis.
- Summarize clinical exam results, namely orthopedic/neurological tests, imaging, lab tests, etc. Note actual results rather than subjective conclusions. Provide images if clearly reproducible/anonymized.
- Clearly state the working diagnosis or clinical impression before transitioning to management.
3. Management and Outcome
- Indicate the total duration of care and number of treatments given over what timeframe. Use specific names/descriptions for any therapies/interventions applied.
- Present the results of the intervention,including any quantitative or qualitative data collected.
- For outcomes, utilize visual analog scales for pain, medication usage logs, etc., if possible. Include patient self-reports of improvement/worsening of symptoms. Note the reason for discharge/end of care.
4. Discussion
- Analyze the case, exploring contributing factors, limitations of the study, and connections to existing research.
- Analyze the effectiveness of the intervention,considering factors like participant adherence, limitations of the study, and potential alternative explanations for the results.
- Identify any questions raised in the case analysis and relate insights to established theories and current research if applicable. Avoid definitive claims about physiological explanations.
- Offer clinical implications, and suggest future research directions.
5. Additional Items
- Thank specific assistants for writing support only. No patient acknowledgments.
- References should directly support any key claims or quotes included.
- Use tables/figures/images only if substantially informative. Include permissions and legends/explanatory notes.
- Provides detailed (rich qualitative) information.
- Provides insight for further research.
- Permitting investigation of otherwise impractical (or unethical) situations.
Case studies allow a researcher to investigate a topic in far more detail than might be possible if they were trying to deal with a large number of research participants (nomothetic approach) with the aim of ‘averaging’.
Because of their in-depth, multi-sided approach, case studies often shed light on aspects of human thinking and behavior that would be unethical or impractical to study in other ways.
Research that only looks into the measurable aspects of human behavior is not likely to give us insights into the subjective dimension of experience, which is important to psychoanalytic and humanistic psychologists.
Case studies are often used in exploratory research. They can help us generate new ideas (that might be tested by other methods). They are an important way of illustrating theories and can help show how different aspects of a person’s life are related to each other.
The method is, therefore, important for psychologists who adopt a holistic point of view (i.e., humanistic psychologists ).
Limitations
- Lacking scientific rigor and providing little basis for generalization of results to the wider population.
- Researchers’ own subjective feelings may influence the case study (researcher bias).
- Difficult to replicate.
- Time-consuming and expensive.
- The volume of data, together with the time restrictions in place, impacted the depth of analysis that was possible within the available resources.
Because a case study deals with only one person/event/group, we can never be sure if the case study investigated is representative of the wider body of “similar” instances. This means the conclusions drawn from a particular case may not be transferable to other settings.
Because case studies are based on the analysis of qualitative (i.e., descriptive) data , a lot depends on the psychologist’s interpretation of the information she has acquired.
This means that there is a lot of scope for Anna O , and it could be that the subjective opinions of the psychologist intrude in the assessment of what the data means.
For example, Freud has been criticized for producing case studies in which the information was sometimes distorted to fit particular behavioral theories (e.g., Little Hans ).
This is also true of Money’s interpretation of the Bruce/Brenda case study (Diamond, 1997) when he ignored evidence that went against his theory.
Breuer, J., & Freud, S. (1895). Studies on hysteria . Standard Edition 2: London.
Curtiss, S. (1981). Genie: The case of a modern wild child .
Diamond, M., & Sigmundson, K. (1997). Sex Reassignment at Birth: Long-term Review and Clinical Implications. Archives of Pediatrics & Adolescent Medicine , 151(3), 298-304
Freud, S. (1909a). Analysis of a phobia of a five year old boy. In The Pelican Freud Library (1977), Vol 8, Case Histories 1, pages 169-306
Freud, S. (1909b). Bemerkungen über einen Fall von Zwangsneurose (Der “Rattenmann”). Jb. psychoanal. psychopathol. Forsch ., I, p. 357-421; GW, VII, p. 379-463; Notes upon a case of obsessional neurosis, SE , 10: 151-318.
Harlow J. M. (1848). Passage of an iron rod through the head. Boston Medical and Surgical Journal, 39 , 389–393.
Harlow, J. M. (1868). Recovery from the Passage of an Iron Bar through the Head . Publications of the Massachusetts Medical Society. 2 (3), 327-347.
Money, J., & Ehrhardt, A. A. (1972). Man & Woman, Boy & Girl : The Differentiation and Dimorphism of Gender Identity from Conception to Maturity. Baltimore, Maryland: Johns Hopkins University Press.
Money, J., & Tucker, P. (1975). Sexual signatures: On being a man or a woman.
Further Information
- Case Study Approach
- Case Study Method
- Enhancing the Quality of Case Studies in Health Services Research
- “We do things together” A case study of “couplehood” in dementia
- Using mixed methods for evaluating an integrative approach to cancer care: a case study
Related Articles

Research Methodology
Qualitative Data Coding

What Is a Focus Group?

Cross-Cultural Research Methodology In Psychology

What Is Internal Validity In Research?

Research Methodology , Statistics
What Is Face Validity In Research? Importance & How To Measure

Criterion Validity: Definition & Examples

What is the Case Study Method?

Overview Dropdown up
Overview dropdown down, celebrating 100 years of the case method at hbs.
The 2021-2022 academic year marks the 100-year anniversary of the introduction of the case method at Harvard Business School. Today, the HBS case method is employed in the HBS MBA program, in Executive Education programs, and in dozens of other business schools around the world. As Dean Srikant Datar's says, the case method has withstood the test of time.
Case Discussion Preparation Details Expand All Collapse All
In self-reflection in self-reflection dropdown down, in a small group setting in a small group setting dropdown down, in the classroom in the classroom dropdown down, beyond the classroom beyond the classroom dropdown down, how the case method creates value dropdown up, how the case method creates value dropdown down, in self-reflection, in a small group setting, in the classroom, beyond the classroom.

How Cases Unfold In the Classroom
How cases unfold in the classroom dropdown up, how cases unfold in the classroom dropdown down, preparation guidelines expand all collapse all, read the professor's assignment or discussion questions read the professor's assignment or discussion questions dropdown down, read the first few paragraphs and then skim the case read the first few paragraphs and then skim the case dropdown down, reread the case, underline text, and make margin notes reread the case, underline text, and make margin notes dropdown down, note the key problems on a pad of paper and go through the case again note the key problems on a pad of paper and go through the case again dropdown down, how to prepare for case discussions dropdown up, how to prepare for case discussions dropdown down, read the professor's assignment or discussion questions, read the first few paragraphs and then skim the case, reread the case, underline text, and make margin notes, note the key problems on a pad of paper and go through the case again, case study best practices expand all collapse all, prepare prepare dropdown down, discuss discuss dropdown down, participate participate dropdown down, relate relate dropdown down, apply apply dropdown down, note note dropdown down, understand understand dropdown down, case study best practices dropdown up, case study best practices dropdown down, participate, what can i expect on the first day dropdown down.
Most programs begin with registration, followed by an opening session and a dinner. If your travel plans necessitate late arrival, please be sure to notify us so that alternate registration arrangements can be made for you. Please note the following about registration:
HBS campus programs – Registration takes place in the Chao Center.
India programs – Registration takes place outside the classroom.
Other off-campus programs – Registration takes place in the designated facility.
What happens in class if nobody talks? Dropdown down
Professors are here to push everyone to learn, but not to embarrass anyone. If the class is quiet, they'll often ask a participant with experience in the industry in which the case is set to speak first. This is done well in advance so that person can come to class prepared to share. Trust the process. The more open you are, the more willing you’ll be to engage, and the more alive the classroom will become.
Does everyone take part in "role-playing"? Dropdown down
Professors often encourage participants to take opposing sides and then debate the issues, often taking the perspective of the case protagonists or key decision makers in the case.
View Frequently Asked Questions
Subscribe to Our Emails
Log in using your username and password
- Search More Search for this keyword Advanced search
- Latest content
- For authors
- Browse by collection
- BMJ Journals More You are viewing from: Google Indexer
You are here
- Volume 14, Issue 5
- Exploring the influence of health system factors on adaptive capacity in diverse hospital teams in Norway: a multiple case study approach
- Article Text
- Article info
- Citation Tools
- Rapid Responses
- Article metrics
- http://orcid.org/0000-0002-4689-8376 Birte Fagerdal 1 ,
- http://orcid.org/0000-0001-7107-4224 Hilda Bø Lyng 1 ,
- http://orcid.org/0000-0002-9124-1664 Veslemøy Guise 1 ,
- Janet E Anderson 2 ,
- http://orcid.org/0000-0003-0296-4957 Jeffrey Braithwaite 3 ,
- http://orcid.org/0000-0003-0186-038X Siri Wiig 1
- 1 SHARE, Faculty of Health Sciences , University of Stavanger , Stavanger , Norway
- 2 Anaesthesiology and Perioperative Medicine , Monash University Faculty of Medicine Nursing and Health Sciences , Melbourne , Victoria , Australia
- 3 Australian Institute of Health Innovation , Macquarie University , North Ryde , New South Wales , Australia
- Correspondence to Mrs Birte Fagerdal; birte.fagerdal{at}uis.no
Objectives Understanding flexibility and adaptive capacities in complex healthcare systems is a cornerstone of resilient healthcare. Health systems provide structures in the form of standards, rules and regulation to healthcare providers in defined settings such as hospitals. There is little knowledge of how hospital teams are affected by the rules and regulations imposed by multiple governmental bodies, and how health system factors influence adaptive capacity in hospital teams. The aim of this study is to explore the extent to which health system factors enable or constrain adaptive capacity in hospital teams.
Design A qualitative multiple case study using observation and semistructured interviews was conducted between November 2020 and June 2021. Data were analysed through qualitative content analysis with a combined inductive and deductive approach.
Setting Two hospitals situated in the same health region in Norway.
Participants Members from 8 different hospital teams were observed during their workday (115 hours) and were subsequently interviewed about their work (n=30). The teams were categorised as structural, hybrid, coordinating and responsive teams.
Results Two main health system factors were found to enable adaptive capacity in the teams: (1) organisation according to regulatory requirements to ensure adaptive capacity, and (2) negotiation of various resources provided by the governing authorities to ensure adaptive capacity. Our results show that aligning to local context of these health system factors affected the team’s adaptive capacity.
Conclusions Health system factors should create conditions for careful and safe care to emerge and provide conditions that allow for teams to develop both their professional expertise and systems and guidelines that are robust yet sufficiently flexible to fit their everyday work context.
- Health & safety
- Organisation of health services
- Quality in health care
- Protocols & guidelines
- QUALITATIVE RESEARCH
Data availability statement
Data are available upon reasonable request.
This is an open access article distributed in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution Non Commercial (CC BY-NC 4.0) license, which permits others to distribute, remix, adapt, build upon this work non-commercially, and license their derivative works on different terms, provided the original work is properly cited, appropriate credit is given, any changes made indicated, and the use is non-commercial. See: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/ .
https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2023-076945
Statistics from Altmetric.com
Request permissions.
If you wish to reuse any or all of this article please use the link below which will take you to the Copyright Clearance Center’s RightsLink service. You will be able to get a quick price and instant permission to reuse the content in many different ways.
STRENGTHS AND LIMITATIONS OF THIS STUDY
Data for this study were collected during the COVID-19 pandemic, which enabled the research team to observe how novel national policy measures affected the frontline.
The study contributes to resilient healthcare as there have been few multilevel studies looking at how macrolevel factors affect microlevel adaptive capacity.
The combination of observations and interviews provided a substantial amount of data which were then triangulated.
Data collected at the national level are limited as our study focused on the hospital team level.
Introduction
Healthcare systems provide the formal healthcare delivery structures for a defined population, whose funding, management, scope and content are defined by laws, policies and regulations. They provide services to people, aiming to contribute to their health and well-being. Services are usually delivered in defined settings, such as homes, nursing homes and hospitals. Healthcare systems are complex and adaptive and continuously responsive to multiple factors including patients’ needs, innovations, pressures, pandemics and funding structures. 1 Understanding flexibility and adaptive capacities in these complex healthcare systems is a key focus of investigators of resilient healthcare. 2 3 Resilience in healthcare can briefly be defined as ‘the capacity to adapt to challenges and changes at different system levels, to maintain high quality care’ p6. 4
To date, research on resilient healthcare has paid most attention to work as done at the sharp end of the system. Less is therefore known about how actions, strategies and practices enacted by regulatory bodies and policy-makers affect every day work at the microlevel, such as hospital teams. 5 While regulations in the form of standards, rules and protocols are known to be key drivers in the structuring of healthcare activities and in the design of healthcare organisations, the interfaces between policy-making, regulation and resilience are subtle and nuanced, and regulatory strategies to improve quality and safety are therefore complex and multifarious. 6 7 However, the relationship between governmental bodies and adaptive capacity at the sharp end of the system has received insufficient attention and is thus in need of closer examination. 2 8 9
In this study, we define macrolevel healthcare system actors as governmental bodies, regulators and national and regional bodies, who act or intend to shape, monitor, control and modify practices within organisations in order to achieve an identifiable, desirable state of affairs. 10 They aim to constrain action, optimise performance and attempt to prevent error.
In complex systems like hospitals, much work is performed in teams. 11–13 Understanding the nature of teams and team performance is important to promote team effectiveness. The few studies that have been undertaken are limited in scope as they have not considered how teams are defined and structured, what their functions are or differences across healthcare teams. 11 14 Most research on teams in healthcare has focused on the dynamic domains in healthcare, such as emergency medicine or operating rooms, and teams that are similar to the teams in other industries, for instance in aviation. 15 16 However, not all teams in hospitals operate in an emergency setting. Teams in hospitals differ depending on their goals, tasks, structure, membership and situation, affecting how they adapt to a multitude of contingencies that are encountered in everyday work. 17 Hence, their requirements for support could differ depending on these attributes but this question has not been addressed sufficiently in previous research. Knowledge of these differences may enable optimisation of support and better function for the different teams. This study will address these knowledge gaps.
Aim and research question
This study aims to explore whether and how health system factors enable adaptive capacity in different types of hospital teams in Norway. We asked: What kind of health system factors enable adaptive capacity in hospital teams, and how do these factors affect adaptive capacity?
Design and setting
A qualitative exploratory methodology was chosen, using a multiple-embedded case study design. 11 18 A case was defined as one hospital containing four different types of teams. Two case hospitals were recruited to the study, featuring a total of eight teams. The study’s design was in line with that of an international comparative study, involving six countries (The Netherlands, Japan, Australia, England, Switzerland and Norway), where this article reports partial findings from the Norwegian case (see protocol of Anderson et al ). 11 The two Norwegian hospitals and the four team types were recruited in line with the study protocol. Findings from each of the countries will be written up as country case reports following an agreed on template. Furthermore, an international cross-case comparative analysis will be performed using the Qualitative Comparative Analysis method 19 with the aim of exploring how multilevel system factors interact to support or hinder adaptive capacity in different types of hospital teams in different countries, and how this leads to performance variability. This international comparative analysis is currently in progress. This article stands alone and uses Norwegian data only.
Recruitment and study context
The Norwegian health system is a semidecentralised system with the Norwegian Parliament as its highest decision-making body. The municipalities are responsible for providing primary care for their citizens, mainly through nursing homes, homecare, general practitioners and rehabilitation services. The hospitals are mainly state owned and administered by four Regional Health Authorities. The Norwegian Board of Health Supervision is a national regulatory body, organised under the Ministry of Health and Care Services. County Governors at the regional level oversee services within primary and specialised healthcare. Norway has a comprehensive set of legislation governing the health services, including requirements for the quality of services, regulations for authorised healthcare personnel and service users’ rights. These legislated requirements are subject to supervision and investigation by the Norwegian Board of Health Supervision and the County Governors. 20 21
The two hospitals in this study were selected and recruited based on their size and role in teaching provision. 11 Both hospitals are situated in the same health region in Norway. Hospital 1 is a large teaching hospital and hospital 2 is a middle-sized local hospital which is also responsible for educating healthcare professionals. The four different team types were structural, hybrid, responsive and coordinating, and are displayed in table 1 . See Fagerdal et al 22 for further descriptions of the teams.
- View inline
Descriptions of the four different teams studied in each hospital
Data were collected through observation, interviews and document analysis, all undertaken between December 2020 and June 2021. Researcher BF and HBL conducted the observations, which entailed following one or more team members for two workdays using an observation guide. Both researchers wrote their own individual fields notes which were both included in the data material. Using the observation guide enabled a structuring of the text in line with the central concepts used in resilience literature. 23 During observations, we looked for various types of demands from the different levels of the organisations, the teams’ capacities to meet the demands and types of adaptations that were performed by the teams and team members. The observed teams differed in how they work together and consequently our undertaking of the observations had to align with those differences. The structural and hybrid teams were observed during two shifts, including evening and dayshifts. With the responsive teams, we followed one team member during their workday and their response to acute alarms. The coordinating teams meet for 10 min every weekday, and the researchers attended all their meetings during a 14-day period. Due to the COVID-19 pandemic, one of the coordinating teams held their meetings digitally, which we also attended. The observations totalled 115 hours (see table 2 ).
Overview of data collection methods and data material according to team types and case sites
All interviews were undertaken post observation by researcher BF using a semistructured interview guide based on content from the Concepts for Applying Resilience Engineering (CARE) model, that is, demand, capacity, misalignments and adaptations, 24 and the four potentials of resilience; monitoring, anticipating, responding and learning. 23 Team members and one leader from each team were interviewed, resulting in 30 interviews (see table 3 ). Participants comprised 27 females and 3 males and their ages ranged between 24 and 56. The interview length varied from 40 to 90 min with a median of 55 min. All participants signed a written consent form and were given the opportunity to withdraw without any negative implications; all invited participants accepted the invitation to interview.
Overview of the interviewed participants in the study
Patient and public involvement statement
A coresearcher employed in the overall Resilience in Healthcare project, of which this study is a part, 11 collaborated in the planning and design of the study, and access to teams at hospital 1. In hospital 2, we used a local coordinator to help identify and facilitate access to the different teams.
All interviews were audio recorded and transcribed verbatim by researcher BF. Observation notes were included in the analysis, and all notes and interview transcripts were grouped according to hospital and team types to streamline the analysis work. We conducted a within-case analysis of each hospital and a cross-case analysis to identify patterns and themes in our overall material. 18 The data material was first read through in full by all the researchers to get a sense of the whole. The analysis was then done using a combined deductive and inductive approach. 25 The CARE model 24 was used as a framework to assist the deductive part of the analysis as visualised in figure 1 .
- Download figure
- Open in new tab
- Download powerpoint
Concepts for Applying Resilience Engineering model after Anderson et al 24 visualising the study’s focus on team adaptation.
Data were organised using three of the four key concepts in the CARE model matrix: capacities, misalignments and adaptations. The capacities were defined as health system factors in this analysis and represent the factors that influence teams’ ability to adapt. All data were in addition coded for team type and hospital which allowed for a cross hospital and cross-team analysis. After the data material had been divided into three parts of text, to enable further analysis, we proceeded with an inductive content analysis approach. 25 The categories were inductively reviewed and recoded and further developed into latent themes across the four teams. This process resulted in overarching themes representing health system factors, that influence teams’ adaptive capacity (see table 4 ).
Inductive coding structure
The national and regional health authorities set the scene for how the hospitals prioritises and arrange their work. System-level decisions filter down through the organisation and influence the team’s everyday work. Our analysis shows that the effect of system factors on teams’ everyday work and adaptive capacity can be divided into two main themes, each with associated subthemes: (1) organisation according to regulatory requirements to ensure adaptive capacity and (2) negotiation of various resources provided by the governing authorities to ensure adaptive capacity. In table 4 , we present the themes along with their subthemes, codes and examples of quotes from the participants or description from the observation.
Organising according to regulatory requirements to ensure adaptive capacity
National and regional guidelines, financial governance and regulatory inspections by the health supervision authorities all shaped the organisation of the hospitals.
Context and organisational structure
The organisational context was important. It affected how the teams enacted and performed patient care. For instance, the smaller hospital 2 had restrictions and limitations regarding both the types of diagnoses and the number of patients they were able to treat due to regional regulations. These regulations had a large impact on the smaller hospital and their teams in how they organised their work, their competence requirements and what kind of learning opportunities were available to the team members. For instance, since hospital provided an acute function for surgical patients, it could continue to be an educational institution for healthcare personnel, which also meant that healthcare professionals in the structural and hybrid teams could maintain and develop their skills in acute care. In addition, it also impacted the hybrid and structural teams in how they arranged their work by always being prepared for the admission of acute surgical patients during their workday. Furthermore, the regional health authority maintained overall flexibility in acute care provision by having this function in both hospitals.
Both the coordinating teams in our study had been established by the hospitals in response to a government policy of preventing corridor beds in hospitals as a means of improving patients’ safety. The teams were set up to include all ward managers cooperating to manage patient flow, and with a goal of evening out the overall strain across the hospital. These teams’ main assignment was to allocate patients to free beds within the hospital. In addition, a positive consequence of having these teams was that the team members got a better mutual understanding of the overall situation within the hospitals and an improved understanding of each other’s challenges across the hospital. This provided them with a greater range of solutions to use when making adaptations to avoid patients in the corridors. The coordinating team in hospital 2 also functioned as an arena for the team members to exchange advice and suggest solutions to other challenges in their work. This was to a certain extent also valid for the team in hospital 1, but due to the comparatively larger size of the team there, it was more difficult for the team members to get well acquainted. In addition to better patient flow and avoiding corridor patients, the hospitals aimed for the teams to focus on building a culture of helping each other across their respective hospitals and to foster a feeling of joint responsibility for the betterment of the hospital overall (see table 4 ). Similar to the responsive teams, the coordinating teams had been enabled to make quick decisions spanning hospital units, allowing for a wider range of alternative solutions to the problems encountered than if they were to make decisions on their own. Also, team members felt more of a responsibility to help each other and found that it was more difficult to say no to requests for free beds when meeting face to face with colleagues. Both the individual team members and the hospital organisation as a whole were thus found to have widened their adaptive capacities after establishing these teams.
Aligning with national and regional guidelines
The use of clinical guidelines provided teams with direction in the different treatment courses offered to patients. National guidelines were translated and aligned to work practices within the organisation to fit the current work in the teams. This gave the team a standard to maintain, a structure for their work and also brought them a sense of safety in knowing their boundaries and priorities for adaptation. For instance, the national guideline for sepsis treatment recommends starting antibiotics treatment within 1 hour of the start of symptoms and also lists early important diagnostic signs to look for in patients who are deteriorating. Early intervention and treatment improve the overall survival of these patients and both hospitals needed to ensure proper alignment to these standards (see table 4 ). The hybrid and structural teams were well aware of this, due to guidelines and information campaigns. The teams thus adapted their work to meet the national demands imposed here, prioritising this work over what were considered other less important tasks, such as helping patients with personal hygiene.
Another example of how guidelines shaped the organisation of hospital teams and how teams acted was seen in the work of both the responsive teams in the study. The two hospitals had to comply with the national requirements of diagnostic and treatment guidelines for cerebral infarction, and both hospitals had created responsive stroke teams to allow for quick diagnostics and treatment. Tailoring the responsive teams to fit the requirements of the national guidelines, reduced the ‘door to needle time’ in both hospitals significantly. This was accomplished by providing and designing equipment, procedures, role descriptions and facilities along with the right competent personnel. The responsive teams frequently made adaptations to the clinical procedure to fit with the patient’s condition, the proximity of the competent team members and the tailored equipment and location enabled for quick decision-making within the team, instead of encountering communication via phones or waiting for each other to finish other tasks.
Negotiating various resources provided by the governing authorities to ensure adaptive capacity
Financial incentives.
Incentives like the national funding model which generates income for the hospitals impacted both what kind of and how the hospitals prioritised treatment. Governing authorities use financial incentives to orient the hospitals towards planned direction. Budget cuts and other financial restraints imposed on hospitals demanded that both hospitals adapt their priorities, which consequently affected the teams’ delivery of treatment and care in the sharp end of the system. The government requirements for increased efficiency in the healthcare system, such as financial incentives for reducing beds, increased the pace of work and often required development of new work practices to cope with these demands. For instance, in both hospitals, there had been a decrease in hospital beds, and a shift towards outpatient treatment due to governing authorities funding schemes. To cope with this, both the hybrid and structural teams in both hospitals treated patients for a shorter amount of time. For example, the structural teams no longer admitted patients overnight preoperatively and discharged patients earlier postoperatively to primary healthcare service or the home. The teams coped with this by planning the discharge of the patient already at admittance to facilitate a safe and good-quality discharge. However, they often adapted their plans by not discharging patients due to either lack of capacity in primary care services, or disagreement and concern with the level of care offered in the municipalities. This example shows that the teams in practice negotiated the consequences of government funding restrictions to suit the patients’ needs.
In addition, they could to some extent handle some demands by determining how they could change procedures to fit certain requirements. For instance, one of the changes the structural team in hospital 2 made to manage earlier discharge was to have the nightshift staff remove the postoperative urine catheter from patients. The clinical procedure stated that for the patient to be discharged, they had to be able to urinate spontaneously after catheter removal. Catheter removal later in the day regularly meant that the patient had to stay an extra night, so by changing the timing of its removal staff still managed to provide care within the frame of guidelines given.
Physical surroundings
Both the hybrid and responsive teams in both hospitals had been placed in new premises designed specifically to accommodate their way of working, with well-designed spaces to facilitate their workday with proximity to necessary equipment, and a nearness to each other that enabled team members to easily assist if needed. Similarly, the structural team in hospital 2 had new premises, with a uniform design across the new hospital building making it easy for personnel to change teams and wards since their premises were already familiar to them. This uniformity in building design improved the teams’ overall adaptive capacity in peak situations, or when there was an absence of key personnel across wards and teams. Staff could easily assist personnel from other wards as they knew where equipment was stored and how the different facilities in the ward functioned (patient rooms, nurses’ stations, etc). The structural team in hospital 1, however, worked in old premises with narrow hallways and few physical meeting arenas for the team members, which hampered their workflow in that they had to spend time looking for each other, and otherwise had few opportunities to engage in direct communication with each other during their workday. The physical surroundings of the two coordinating teams differed. Due to the size of the team in hospital 1, the team there used digital software to manage the overall patient flow in the hospital. The smaller team in hospital 2 managed the same using a paper form that each member completed. However, both of the teams used the meeting to elaborate on their numbers with additional information as the numbers alone did not provide a sufficient representation of the overall situation on the wards.
Training and development resources
Training and development resources were crucial for a team’s adaptive capacity. The national attention on patient safety in recent decades has led to improved treatment courses and changed the focus on how healthcare personnel can learn from adverse events to avoid similar incidents in the future. Consequently, this has led to innovative solutions in how hospital managers organise learning activities for their employees. In accordance with a growing focus on simulation-based training and learning from regulatory bodies and policy-makers, all the teams in the study apart from the coordinating teams increasingly used simulation training (see table 4 ). Often, the teams would make simulation scenario cases based on adverse events or incidents that had happened on their ward and used them in their training. For the responsive teams, this type of training was mandatory and part of regulatory requirements for the teams. Also, for these teams that only worked together for limited episodes and had changing membership and different professional cultures, these simulation trainings were their only chance to practice and improve their team communication. During the period of our observation, they developed new cases with COVID-19 themes and used them to train and learn before they received actual COVID-19 patients. This improved their performance, as they had found several shortcomings in their COVID-19 procedure and thus changed it accordingly. For instance, they made efforts to prevent unnecessary contamination of team members and had detected a lack in the procedure of personal protective equipment. This shows that these types of prescribed training exercises enable teams to adapt procedures to fit their everyday work conditions.
Quality improvement resources
Quality improvement resources outside the hospital organisation supported team’s adaptive capacity. The national and regional healthcare authorities arrange various conferences and campaigns for hospitals and other healthcare institutions. Here, policy-makers, leaders and healthcare professionals meet and create reflexive spaces. As part of such efforts, the best practices are displayed and workshops are provided to encourage and translate quality and safety improvement into practice in different ways, alongside guidelines, learning tools and other materials for the different organisations to use and implement in their quality improvement work. Having this competence base within the health regions and at the national level to support teams added knowledge and increased adaptive capacity as it required knowledge transfer and new ideas anchored in research and practice. Moreover, the patient safety focus within the wards and teams like the safe care screening programme and safety huddles, launched by the Norwegian Directorate of Health and implemented through the regional health authorities, increased the team’s awareness of patient safety culture. The increased amount of quality measures the clinicians had to undertake and report on in their daily work were generally seen as good quality measures from both the organisations and the team’s point of view. However, it sometimes felt counterproductive constantly having to cope with balancing patients’ needs with the requirements of screening procedures, especially if staff felt they had little room for autonomous clinical assessment. For instance, the safe care screening programme where every patient over the age of 18 had to be screened for their risk of falling, bedsores and possible malnutrition within 24 hours was questioned. Screening young patients for this felt unnecessary and if there were other more pressing tasks that were seen as more important, they adapted the way they prioritised.
This study investigated the relationship between health system factors and adaptive capacity in hospital teams. Our results have shown that health system-level factors influence adaptive capacity in the teams through the provision of guidelines and resources, and how the teams align these to their current demands and capacity situation. Their effects on different teams are not uniform; some are advantageous to one team but disadvantageous to another. 5 6 We argue that it is the team’s opportunity to align these factors to context that are key for enabling adaptive capacity, as illustrated in figure 2 .
Illustrating the teams aligning system-levels factors to context for adaptive capacity.
All levels of a health system can influence each other, especially in an integrated and tightly coupled system. Higher system levels can affect lower levels through, for example, explicit instructions, by the provision or limitation of resources, or by establishing incentive systems. 26–28 On the other hand, lower system levels may use discretion when they interpret and implement directives from higher levels, and they may control the information flow to higher levels. 26 Our results show that decisions made at one level of the system can support or hinder adaptive capacity at other lower hierarchical levels of the system. 29–31 Accordingly, the system-level governing factors affect adaptive capacity at the sharp end by setting the framework and boundaries within which activity can take place. Regulatory bodies have system-wide responsibilities and must respond to system-wide disturbances, without detailed knowledge of how work is done in practice at the sharp end. Consequently, the sharp end must adapt to respond appropriately to disturbances within its own field of responsibility. 32
This study has operationalised adaptation using the CARE model 24 to see how different teams at the sharp end work in practice to negotiate system-level factors, such as regulations and guidelines. The findings show that factors at the macrolevel required different forms of adaptations within different team types to managing everyday work. Enabling adaptation at the team level by taking action at the macrolevel to attempt to reconcile work as imagined with work as done ( figure 1 ). The system-level factors also represent long-term planning and transformation of practices rather than short-term adaptations or adjustments in the system. 33 They envisage setting up the processes that design, produce and circulate resources that underpin safety, and prevent errors through standardisation, regulation and training. 32 How the teams negotiate these long-term transformations to their everyday work determines their adaptive capacity as our results have shown. Adaptation and adjustments to local context are inevitable in healthcare. 9 11 34 35 However, the vast number of protocols, policies, checklists, standards, guidelines, pathways and other regulatory requirements may lead those working at the sharp end to feel overwhelmed. 6 If not aligned with goals, tasks and current challenges, these governing factors may end up being counterproductive. 5 The teams studied talked about their everyday work and their primary focus on patient care along with their willingness to act in the best interest of the patients. 36 They talked about feeling a compound pressure in order to align system-level demands with their context and patients’ wishes and needs. 37 38 Taking the perspective of the patient into account was important to the teams. 39 40 Consequently, different teams had to align system-level demands differentially to ensure quality care for patients.
Our study showed that teams must balance continuous efficiency with thoroughness assessments 32 41–43 in everyday work (eg, making the nightshift prepare discharge adding more work to reduce corridor patients). Ways that the teams in our study continuously adapted regulatory requirements to their work context illuminated how resilient systems must have robust yet flexible structures to assist the system to deal with both everyday work and unexpected events. 8 30 44 45 System-level factors must therefore provide flexibility to fit different situations and types of teams, as teams differ in how they cooperate and function in everyday work. To ensure alignment of perspectives between macrolevel and microlevel actors, common arenas and structures for mutual feedback and reflections between stakeholders are crucial. 7 Furthermore, system factors need to entail robustness in the directions they provide to practice and the implementation of improvement efforts. 33
The findings show that for the responsive and coordinating teams the size of the hospital played a significant role in their ability to adapt. These two team types operated in part at the mesolevel of the hospital organisation, spanning hospital departments. Their work was characteristically ad hoc, dynamically changing team memberships and members who work primarily in other teams. The large size of hospital 1 hampered development of relationships between the team members in both the responsive and the coordinating team, whereas in the smaller hospital 2 it was easier to develop close relationships between colleagues. This implies that ad hoc teams, and especially large ones, need to have structure and guidelines in place that direct their work, and support to adapt their work based on the team members understanding of the tasks and their roles. The structural and hybrid teams were colocated and this seemed to allow for the development of long-term collegial relationships, better cooperation between team members, more flexible adaptation of their work and also seemed to allow for working with greater levels of independence and a larger room for self-organisation. Their work is influenced by system-level demands, but the size of the organisation does not affect their day-to-day work to the same degree as for the coordination and responsive teams.
Strengths and limitations
A strength of the study is that by combining observation and interviews we have gathered in-depth data of the team’s everyday work.
Data collection during COVID-19 pandemic could hamper everyday work practice; however, we collaborated closely with the sites to avoid any problems for the involved teams and units. Only two hospitals contributed to the data collection and including additional hospitals could add more than we have from two hospitals. However, the inclusion of eight teams, the total amount of data gave rich information to analyse our research questions.
Interview data from the macrolevel could have added additional perspectives from the regulators and policy-makers. We suggest further studies to integrate this in their activities to uncover the role of system factors seen from the policy-makers’ and regulators’ perspectives.
Conclusions and implications
This study illuminated how teams negotiate the health system factors that shape their work to provide as much adaptive capacity as possible and attempt to align system-level regulation and guidelines with everyday work demands. The results show that the size of both the organisation and team had an effect on adaptive capacity. Our findings imply that healthcare systems need to facilitate conditions that allow for teams to develop their professional expertise and develop systems that are robust and flexible to fit the context. Teams should be enabled to adapt to the functions and structure of the health system to carry out their everyday work in a changing environment.
Ethics statements
Patient consent for publication.
Not applicable.
Ethics approval
This study involves human participants and was approved by Regional committe for Medical and Health Research Ethics, ref.nr. 166280. Participants gave informed consent to participate in the study before taking part.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank all participating teams and their leaders at the two hospitals who shared their valuable knowledge and reflections.
- Hollnagel E ,
- Braithwaite J
- Anderson JE ,
- Macrae C , et al
- Billett S , et al
- Smaggus A ,
- Ellis LA , et al
- Bal R , et al
- Christian JS ,
- Christian MS ,
- Pearsall MJ , et al
- Roberts APJ ,
- Webster LV ,
- Salmon PM , et al
- Lavelle M ,
- Cross S , et al
- Ballangrud R ,
- Husebø SE ,
- Aase K , et al
- Salas E , et al
- Saunes IS ,
- Karanikolos M ,
- Saunes, I.S., M. Karanikolos, and A. Sagan, Norway
- Fagerdal B ,
- Guise V , et al
- Hollnagel E
- Back J , et al
- Rasmussen J
- Bergström J ,
- Blanchet K ,
- Ramalingam B , et al
- Schubert CC
- Johannessen T ,
- Krystallidou D ,
- Deveugele M , et al
- Dillon EC ,
- Tai-Seale M ,
- Meehan A , et al
- Hofmeyer A ,
- Svensson I ,
- von Knorring M ,
- Hagerman H , et al
- Churruca K ,
- Clay-Williams R , et al
- Glette MK ,
X @fagerbirte
Contributors The study design was developed in collaboration with the whole research team. BF and HBL conducted the data collection. BF conducted and transcribed all the interviews. The analysis and interpretation of data were conducted in close collaboration between BF, HBL, VG, JEA and SW. SW is the guarantor of this study. All authors contributed with writing, critical revision and approval of the final version.
Funding This project is part of the Resilience in Healthcare Research program which has received funding from the Research Council of Norway from the FRIPRO TOPPFORSK program, grant agreement no. 275367. The University of Stavanger, Norway, NTNU Gjøvik, Norway supports the study with kind funding.
Competing interests None declared.
Patient and public involvement Patients and/or the public were not involved in the design, or conduct, or reporting, or dissemination plans of this research.
Provenance and peer review Not commissioned; externally peer reviewed.
Read the full text or download the PDF:
- Open access
- Published: 22 May 2024
Joint interprofessional education of pharmacy and dietetics undergraduates - a scoping review
- Anna Rudzińska ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-8369-2131 1 ,
- Piotr Guzy ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-4071-2080 2 ,
- Agnieszka Skowron ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-3768-4958 2 ,
- Jerzy Gąsowski ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-8025-5323 1 &
- Karolina Piotrowicz ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-4760-8588 1
BMC Medical Education volume 24 , Article number: 557 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
Metrics details
Introduction
Interprofessional education (IPE) is an integrative approach that enables collaboration of students of two or more different health professions in aim to acquire skills and competencies related not only to their field of study but also to ensure the standard of care based on collaborative practice. IPE has not yet been explored in relation to collaboration between dietetics-nutrition and pharmacy students, while there is evidence that in many cases nutrition is complementary to pharmacotherapy in the treatment process.
The aim of this scoping review was to gather, describe and discuss all relevant literature regarding joint interprofessional training of pharmacy and dietetics-nutrition undergraduates.
We performed a literature search for studies where IPE between dietetics-nutrition and pharmacy students was described. 2204 articles on this topic were identified. After eligibility assessment, 8 articles were included in the review.
Eight studies were included in the review. Two of these described IPE activities between dietetics and pharmacy students only. The included studies varied in setting, methodology and outcome measures and covered a wide range of topics relevant to clinical practice, such as management of inflammatory bowel diseases, care of the older adults or counselling skills. The most common teaching method was the use of case studies. Some of the included studies did not identify specific learning objectives. The most common way of gathering feedback from participants was through questionnaires and interviews.
Conclusions
IPE of pharmacy and dietetics-nutrition students is feasible and may be beneficial in many aspects related to learning. However, there is no well-established model or standard that would facilitate the implementation of such activities in individual educational institutions.
Peer Review reports
Collaborative, interprofessional healthcare should become the model for healthcare delivery. According to the World Health Organization (WHO) document published in 2010, the benefits of interprofessional education (IPE) and interprofessional collaborative practice include shorter hospital stays, lower rates of complications and reduced mortality [ 1 ]. IPE is a topic of interest for research on graduate-level education in various aspects of medical care. However, literature reports vary in the models of educational approach evaluated, including, but not limited to, the number of different professions or specialties included, the educational level of participants (graduate or undergraduate), the learning settings, and the educational topics [ 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 ]. There are also significant differences in the effects measured across studies. These may aim to measure students’ knowledge, skills, or opinions and experiences, as well as clinical skills or effects on the functioning of care systems [ 2 , 4 , 5 ]. Student-oriented outcomes include effects related to specific clinical or professional areas, as well as general collaborative skills, including teamwork or communication skills [ 4 , 6 , 7 ].
In recent years, there has been a growing emphasis on incorporating elements of interdisciplinary education into the curricula of medical schools. This has been highlighted by the accreditation committees of medical and nursing schools in the United States, such as the Liaison Committee on Medical Education (LCME) [ 8 ] and the Accreditation Commission for Education in Nursing (ACEN) [ 9 ], which include in their guidelines requirements for teaching aimed at effective collaboration between different professions. The Accreditation Council for Pharmacy Education (ACPE) publishes guidelines for accreditation that include a requirement to introduce interprofessional activities aimed at teaching skills such as conflict resolution and recognition of different professional roles [ 10 ]. In the UK, the General Medical Council requires medical schools to provide opportunities for students to work with other health and social care professionals during the course of their studies [ 11 ].
There are well-documented examples of good practice in providing such learning activities for the aforementioned majors, while care teams in both hospital and community settings are becoming increasingly multi-professional [ 12 ]. Nowadays, pharmacological and nutritional lifestyle interventions are considered important and complementary treatment modalities and pharmacists and dietitians are becoming more common members of these care teams. This creates an area for collaborative learning between dietitian-nutritionists and pharmacists, which may be considered beneficial in training on topics relevant to clinical practice where the required competencies are cross-disciplinary and part of the curriculum overlaps. This approach of combining pharmacological and dietary interventions is reflected in the clinical guidelines for diabetes [ 13 , 14 , 15 ], hypertension [ 16 ], dyslipidaemia [ 17 , 18 ], chronic kidney disease [ 19 , 20 ] or exocrine pancreatic insufficiency [ 21 , 22 ].
The two curricula have in common not only the learning outcomes related to knowledge of therapeutic interventions, but also the role of both professions in the health care system. Both dieticians and pharmacists are responsible for delivering elements of health education in many European countries. Tasks that used to be carried out mainly by doctors and nurses are now largely carried out by members of both professions. This creates favourable conditions for learning using interprofessional education methods. Dietetics and pharmacy students can transfer knowledge on chronic disease management to each other and support each other in acquiring skills for effective communication with other members of the healthcare team and, most importantly, with the patient. Such an approach at the undergraduate level can lay a solid basis for future professional collaboration.
The purpose of this scoping review is to gather, describe and discuss all relevant literature regarding joint interprofessional training of pharmacy and dietetics-nutrition undergraduates with particular focus on learning settings, methods, topics, and outcome measures of joint learning used in research.
We used the extended definition of IPE proposed by Centre for the Advancement of Interprofessional Education (CAIPE), according to which IPE can be defined as occasions when members or students of two or more professions learn with, from and about each other to improve collaboration and the quality of care and services [ 23 ].
We decided to conduct this review in accordance with scoping review methodology, following PRISMA Extension for Scoping Reviews [ 24 ].
Inclusion/exclusion criteria
We included each study that examined the interprofessional education initiatives involving pharmacy students and dietetics-nutrition students.
We excluded studies where:
students of either pharmacy or dietetics-nutrition were not included;
the majority (> 50%) of the group were postgraduates;
it was uncertain, whether dietetics-nutrition and pharmacy students had the opportunity to work together;
described learning outcomes of interprofessional learning activity were unrelated with future working environment and patient care (e.g. language courses, time management training).
During the screening stage, we considered only publications in English and Polish. We excluded narrative reviews, conference abstracts, letters, opinions, and editorials.
Search strategy
We conducted systematic search of 3 medical databases: Medline (via PubMed), Cochrane Library and Embase with following queries:
For PubMed and Cochrane: (((((((((((dietician) OR (nutritionist)) OR (dietitian)) OR (dieticians)) OR (nutritionists)) OR (dietitians)) OR (dietetics student)) OR (dietetics students)) OR (“Dietetics“[Mesh]))) AND ((((((pharmacist) OR (pharmacists)) OR (Pharmacy student)) OR (Pharmacy students)) OR (“Students, Pharmacy“[Mesh]))))
For Embase: ((‘pharmacist’/exp OR pharmacist) OR ‘pharmacy education’/exp OR ‘pharmacy student’/exp) AND ((‘dietitian’/exp OR ‘dietitian’) OR ‘dietetics’/exp OR ‘dietetics student’/exp).
Search results are current as of May 17, 2023.
The selection of relevant studies was carried out independently by two researchers with didactic experience (PG, MPharm and AR, Master of Dietetics) in three step eligibility assessment process compliant with PRISMA Statement Extension for Scoping Reviews [ 24 ]. After the removal of duplicates, we screened titles and abstracts of identified literature. In the next step full texts have been screened. After selection of studies, we additionally reviewed the reference lists of the included full texts and checked the manuscripts citing the retrieved papers. Any disagreements on the inclusion of the study were resolved by discussion with third researcher with high level of competence in university-level teaching, research, and clinical experience (KP; MD, PhD).
Of the initial 2204 records screened, we included 8 manuscripts. Details on the sources, reasons for exclusion, and selection process are presented in PRISMA diagram (Fig. 1 ).

The PRISMA flowchart for the scoping review of joint interprofessional education of pharmacy and dietetics undergraduates
In total, 234 students of dietetics and 721 students of pharmacy participated in the included studies. The characteristics of individual studies are compared in Table 1 .
Students (majors) involved in the interdisciplinary training
Only in the studies by Wilby et al. and Khalafalla et al. did pharmacy and dietetics students have the opportunity to work together without the participation of students from other disciplines [ 26 , 29 ]. Wilby et al. described a one-day course-based voluntary IPE session in which students were given a case of a patient with Crohn’s disease and aimed to develop a care plan taking into account nutritional and pharmacological issues. Attitudes towards team-based care were assessed using an adapted survey (Heinemann, Schmitt, Farrell and Brallier; 1999). The survey consisted of 11 items measuring attitudes towards interprofessional care [ 26 , 33 ]. 95.1% of students agreed that the team approach improves the quality of patient care and 87.8% agreed that team meetings promote communication between team members from different disciplines. In general, the vast majority of participants agreed that interprofessional care was an applicable and beneficial concept, but there were few items in the questionnaire where opinions were divided. Controversies tended to relate to the leading role of doctors in interprofessional care and whether they had the right to interfere with patient care plans developed by other members of the healthcare team. 56.1% of respondents disagreed with the statement ‘Physicians are natural team leaders’. The other controversial items in the survey were ‘When developing interdisciplinary patient care plans, much time is wasted translating jargon from other disciplines’ (only 56.1% disagreed) and ‘Patients are less satisfied with their care when it is provided by a team’ (only 61.0% disagreed) [ 26 ]. In a study by Khalafalla et al., pharmacy and dietetics students participated in a voluntary university course aimed at improving communication between future health professionals, clarifying roles and developing teamwork skills. The authors did not specify why they chose to include these two professions in the interprofessional course. The teaching method used in this course was team-based learning (TBL) [ 29 ]. Although only pharmacy and dietetics students attended the course, the curriculum was facilitated by a team consisting of a registered dietitian, a clinical pharmacist, a paediatrician and a cardiovascular researcher. The course consisted of four sessions. Three were dedicated to theoretical knowledge on healthy eating, lifestyle and obesity, and the development of soft skills such as motivational interviewing, coaching and cultural competence. In the fourth session, students conducted mock interviews and had the opportunity to receive feedback from the registered dietitian. Student outcomes were assessed using the Interprofessional Collaborative Competencies Attainment Survey (ICCAS). In general, students’ self-perceived competencies increased in all areas assessed. In presenting the results of this study, the authors did not make a comparison between nutrition and pharmacy students [ 29 ].
In other studies, the number of majors varied from five (Watts et al.) [ 32 ] to eleven (Van Digelle et al.) [ 31 ]. The most common major to participate in an interprofessional learning environment was nursing, which was included in every study except the two that included only students of pharmacy and dietetics. Other common majors included were physiotherapy (in three studies) [ 25 , 27 , 31 ], social work and occupational therapy (each in four studies) [ 25 , 27 , 28 , 30 , 31 , 32 ] and psychology (in three studies) [ 25 , 28 , 30 ]. Based on the data we obtained from the included manuscripts, none of the authors provided a rationale for the selection of specific majors.
Learning setting and subject
The majority of the described interprofessional initiatives were implemented as university courses (voluntary or compulsory). In two studies an interprofessional clinic, where students could perform their professional roles was set (Kent et al., Watts et al.) [ 25 , 32 ].One study was based in a clinical setting, as the described intervention was interprofessional clinical rotations as part of the curriculum of the participating programmes (Pelham et al.) [ 27 ].
Four studies (Kent et al., Khalafalla et al., Bhattacharya et al., Van Diggele et al.) mentioned specific learning outcomes achieved by students upon completion of the course [ 25 , 29 , 30 , 31 ]. Six of the included studies defined subject areas (e.g., childhood obesity) or skills that students were expected to develop through participation in a course (e.g., cultural competency). In the study by Kent et al. students worked in an outpatient clinic for older adults, and the study aimed to report learning outcomes related to interprofessional collaboration in this specific setting [ 25 ]. In the study by Wilby et al., nutrition and pharmacy students worked on a case study of a patient with Crohn’s disease, but no learning objectives or specific topics were mentioned. In the study by Reitsma et al. no specific learning outcomes were mentioned, but the authors mentioned that the case studies used during the course reflected patients referred to their local clinics, e.g. patients with cancer, human immunodeficiency virus, Alzheimer’s disease, a teenager with an eating disorder and older adults. The project was planned with the involvement of a multidisciplinary team of teachers from six different health professions [ 26 ]. In the study by Khalafalla et al. the learning outcomes were defined but only related to the different aspects of nutrition education and motivational interviewing and not to the interdisciplinary practice of pharmacists and dietitians. Topics covered in the course included obesity, healthy nutrition, and lifestyle, coaching and motivational interviewing skills, and cultural competency [ 29 ]. The study by Bhattacharya et al. was part of the Geriatrics Champions Programme (GCP), a multidisciplinary project designed to train health professionals in different aspects of geriatric care. Thirty learning objectives were divided into eight domains: special considerations in geriatric care; medication management; cognitive, affective and behavioural health; complex or chronic illness in older adults; palliative and end-of-life care; hospital patient safety; transitions of care; ambulatory care. The domains were based on the American Geriatrics Society Internal Medicine-Family Medicine (IM-FM) Residency Competencies. Learning objectives within each domain were adapted for each specialty involved in interprofessional learning [ 30 ]. In study by van Diggele et al. three learning outcomes related to interprofessional collaboration were defined. The manuscript lacked in information on specific topics covered during the course [ 31 ]. Studies by Watts et al. and Pelham et al. lacked in information on learning outcomes provided by described courses [ 27 , 32 ].
Learning approach
Two of the included studies (Kent et al., Watts et al.) used the service-learning (SL) method [ 25 , 32 ]. Service-learning is a learning approach that combines theoretical knowledge gained in an academic setting with practical outcomes that benefit community members in some way. The important parts of service-learning are established learning objectives that meet the needs of the beneficiaries, reflection on the learning experience, reciprocity between beneficiaries and learners so that both parties have the opportunity to learn and teach, and structuring of the learning experience [ 34 ]. In Kent et al. and Watts et al. studies SL was used to create student-led clinics. In a study by Kent et al., the student-led clinic aimed to address the needs of senior citizens being discharged from hospital. Students from different disciplines formed interdisciplinary teams and provided advice and, if an unmet health need was identified, wrote a recommendation to the patient’s GP. After each day students presented each case study to other participants [ 25 , 32 ]. The study by Watts et al. aimed to compare face-to-face mobile community clinics run by students from different professions with the experience of a virtual student-run clinic. While the online clinic sessions were conducted using case studies and real patients were not present during the course, the face-to-face mobile clinics involved community members, particularly underserved older adults, and were offered in assisted living and senior centres. During the patient’s visit to the clinic, students collected health and dietary information, carried out supervised medication reconciliation and assessed the need for social support services. Debriefing sessions were held after the clinics to allow students to discuss the impact of interdisciplinary medical practice [ 32 ].
Case-based learning was the main intervention described in three of the included manuscripts (Wilby et al., Reitsma et al., van Diggele et al.) [ 26 , 28 , 31 ]. Case-based learning is a structured teaching approach that aims to prepare students for the future practice using clinical cases [ 35 ]. In the study by Reitsma et al., students participated in weekly meetings to discuss treatment approaches from the perspective of different health professions. The authors aimed to assess team dynamics and identify students who took on leadership roles during the intervention, as the course lasted 4–6 weeks. The number of nutrition and pharmacy students who took a leadership role during the meeting increased between the first and last meeting of the course [ 28 ]. In the van Diggele et al. study, students were asked to solve a case study and produce a video of their case management and treatment plan for this particular patient. The results of an intervention were evaluated using thematic analysis of the qualitative data. The following themes were identified in students’ responses to an open-ended question “What was most beneficial to your learning?“: opportunity to practice working in an interprofessional team, peer learning and collaboration (for both dietetics and pharmacy students), role clarification (for pharmacy students), perspectives of other disciplines in patient management (for dietetics students) [ 31 ].
The study by Khalafalla et al. used the team-based learning method, previously defined in this article [ 29 ]. The main components of this teaching approach are individual student preparation, individual and team Readiness Assessment Tests (tRATs), and in-class assignments requiring team-based decision making [ 36 ]. The second manuscript that described an intervention based on a team-based learning approach was the study by Bhattacharya et al. The intervention studied was a 24-month course in geriatrics led by facilitators from different faculties. The sessions were structured and consisted of individual and team readiness assessment tests, case studies, discussions and feedback. Before each session, students had access to online materials such as articles and patient cases. Participation in discussions and other activities was rewarded with points, and the team with the highest score received a prize at the end of the academic year [ 30 ].
Measure of outcomes
Two studies used qualitative methods to assess the outcomes of the educational intervention delivered. (Kent et al., Pelham et al.) [ 25 , 27 ]. The majority of included studies used both qualitative and quantitative approaches to the effectiveness and/or usefulness of the intervention for learners. (Reitsma et al., Khalafalla et al., Bhattacharya et al., Van Diggele et al.) [ 28 , 29 , 30 , 31 ]. In the Watts et al. and Wilby et al. studies, the only tool used to measure outcomes was a validated questionnaire [ 26 , 32 ]. One study analysed clinical workplace providers’ experiences with IPE (Pelham et al.) [ 27 ], one (Kent et al.) mentioned both students’ and educators’ perspective, while other focused on students’ experiences [ 25 ]. A comparison of the included studies in terms of used measures of outcomes is presented in Table 2 .
We identified eight manuscripts relating to the described interprofessional learning for dietetics and pharmacy students. Of the included studies, two focused exclusively on dietetics and pharmacy students. Clinical teaching (particularly including geriatrics, gastroenterology, obesity, infectious diseases, oncology), cultural competence and interprofessional collaboration were identified as areas where interprofessional learning for dietetics and pharmacy students could be considered useful. However, some of the included studies did not identify specific learning objectives that would be useful in optimising future collaborations between pharmacy and nutrition or dietetics students. The included studies varied in setting, methodology and outcome measures and covered a wide range of topics relevant to clinical practice. In the included studies, case-based learning was the most commonly used teaching method. The use of this approach allows students from different disciplines to be involved in the care of the patient within their area of expertise, while encouraging interdisciplinary discussion of case management.
In the study by Wilby et al. [ 26 ], which included only dietetics and pharmacy students, authors draw attention to the important issue of involving all potential members of the interprofessional care team in interprofessional learning activities. On the one hand, such an approach would create an environment for more complex collaboration, and on the other hand, joint work between two health professions allows students to become better acquainted with the specifics of a particular health profession. What is more, in this study, only 44% of the students surveyed felt that doctors were natural leaders of the care team. It is also possible that working in teams made up exclusively of two professions allowed them to take on a significant amount of responsibility that would otherwise have been shared between team members.
This finding is in line with what was found in another study on IPE. Mei-Chi Ho et al. [ 37 ] conducted a study involving nursing and physiotherapy students. At the end of the study, the participants described a better recognition of the roles of the different health professions and how they complement each other. The students emphasised that doctors may not have sufficient knowledge of subjects that are directly related to other professions, and therefore achieved better role clarification. Similar observations about collaboration between pairs of different medical professions suggest that it may be worth exploring the potential benefits of collaboration in interprofessional, yet less diverse groups, with the aim of achieving better role awareness and encouraging communication between groups of professionals who traditionally do not share the decision-making process in patient care.
None of the papers justified why particular groups of students were included in the study. To our knowledge, there are no guidelines on this aspect of setting up interprofessional learning groups. An important observation from our review is the suggestion that when setting up classes for students of different professions, it is important to ensure that the learners are provided with educational material that allows to demonstrate the skills of each of the professions included in the study. It is also important to identify thematic areas that can be used as a basis for interdisciplinary activities. The included studies show that a variety of topics can be explored by dietetics-nutrition and pharmacy students in collaborative educational environment. The themes identified in our review where dietetics and pharmacy students collaborated were geriatrics, gastroenterology, infectious diseases and oncology, and obesity. Students also achieved learning outcomes related to cultural competence, motivational interviewing and health coaching. In the study involving only dietetics and pharmacy students, topics included managing the treatment process of a patient with Crohn’s disease and developing soft skills useful in counselling. The case of a patient with Crohn’s disease may be used to illustrate the areas in which students from these disciplines can work together. Crohn’s disease is often associated with the need for enteral or parenteral nutrition. It is essential that at least four professionals are involved in the process of managing the patient’s nutritional needs: a medical doctor, a nurse, a dietitian and a pharmacist [ 38 ]. For this reason, the management of inflammatory bowel diseases seems to be a good field for joint competence development for dietitians and pharmacists. Another area of clinical practice where interprofessional training of dietitians and pharmacists seems relevant is geriatric care, including the management of nutrition-related adverse effects of medications. It is known that anorexia [ 39 ] of ageing can be caused by some groups of prescribed and over-the-counter medications as well as polypharmacy, which causes drug-drug interactions. By working together, dietitians and pharmacists can identify the problem of loss of appetite and resolve it by suggesting deprescribing or changing the schedule of medications and meals. An education that includes the above fields allows for the systematic development of skills from the higher levels of Bloom’s Taxonomy [ 40 ] as students are not only aware of the presence of other health professions (remember), but also have the opportunity to familiarise themselves with their competencies and identify challenges that require collaboration (understand), implement protocols of practice (apply), draw conclusions on the relevance of cooperation (analyze), discuss the advantages and disadvantages of implemented solutions (evaluate), and propose innovative solutions to patient care based on the skills and knowledge of all team members (create). One of the examples of the collaboration between postgraduate dietitians and pharmacists regarding remember and understand levels of Bloom’s taxonomy is the study by Kizaki et al. [ 41 ]., in which pharmacists and dietitians were asked to rate their feelings about the availability of dietary advice in pharmacies in Japan. When surveyed, 70% of pharmacists found this type of service useful. Pharmacists also agreed that the availability of dietary advice reduces the number of medicines a patient has to take. More than 80% of pharmacists thought that the number of pharmacies offering dietary advice would increase in the future. The successful implementation of such services in Japan, followed by a satisfactory level of mutual recognition of the competences of each profession, leads to the conclusion that there is an area for collaboration between practitioners of these two professions in relation to the higher levels of Bloom’s Taxonomy model. This is also in line with the implementation of the patient-centred model of care, as integrated education at undergraduate level seems a reasonable way to build skills and awareness that are crucial for future successful collaboration between health professions to achieve high standards of patient-centred care. In such patient-centered care model, patients’ preferences, goals and beliefs take precedence over medical paternalism. This often requires a shift from a disease-centred approach, which promotes the central role of the physician, to a perspective in which other needs of the patient are considered equally important, allowing other health-related professions to take the lead. As patient treatment is often influenced by nutritional status and polypharmacy, the added value of IPE between dietitians and pharmacists would be to teach such approaches from the outset, rather than putting health professionals from different disciplines in a situation where they have to start working together as a team without proper training on how to do so. Another important component of IPE approach is promoting an inclusive attitude where uncertainties are resolved with respect for each profession and attempts are made to establish common communication practices. In such an approach, IPE is not only a teaching format aimed at the acquisition of knowledge related to the future profession, but also an opportunity for students of different disciplines to learn communication beyond the boundaries of the profession. In this way, IPE is more about giving students a space to share their thoughts, discuss and collaborate, rather than teaching them the principles of effective communication in the artificial conditions of a classroom.
The results presented by the authors of the included studies tended to focus on the overall student experience. Most projects did not use standardised assessment tools. In addition, only one study considered teachers’ perceptions of the interprofessional education experience (Kent et al.) [ 25 ] and one study considered employers’ perceptions (Pelham et al.) [ 27 ]. An important direction for further research in the area of interprofessional education of dietetics and pharmacy students seems to be not only the student experience, but also the evaluation of the educational process by experienced educators and, in later stages, by potential employers. Involving employers in the evaluation of the usefulness of interprofessional educational activities may help to identify further areas where this collaboration could have long-term benefits. Another area where further research could be undertaken is the element of evaluating the uptake of leadership by students on different courses, introduced in one of the included articles. The effectiveness of the educational interventions described could then be assessed through a shift in the perception of the relevance of one’s role in the patient care process and the willingness to take initiative and responsibility for the outcomes achieved.
The included studies represented a wide range of educational and research approaches. In view of the conclusions drawn by the authors, we have decided to summarise the implications for the further planning of joint educational and research activities for students of nutrition and dietetics and pharmacy (Table 3 .).
Our scoping review needs to be considered in the context of its limitations. All included papers provided information on the type of learning project evaluated. However, only 4 of them (Kent et al., Khalafalla et al., Bhattacharya et al., Van Diggele et al.) reported specific learning outcomes. These outcomes differed significantly between studies [ 25 , 29 , 30 , 31 ]. In other studies authors included only a description of the skills (Wilby et al.) [ 26 ] or competencies (Reitsma et al.) [ 28 ] that the students should acquire during the training, but these were not specified or comparable between studies.
Several published studies addressed the issue of IPE jointly in pharmacy and dietetics-nutrition. The studies ranged in setting, methodology and outcome measures. Although the topics of educational courses varied, most of the included studies used case studies as the main teaching method during the courses described, two of the studies used student-led clinics and other types of problem-based learning. All of the teaching strategies used focused on students taking action and being encouraged to work together. The IPE, as delivered in the included studies, was feasible and was providing measurable benefit. The students who took part experienced improved skills both in individual soft competences and teamwork.
Changing paradigms of patient care lead to changes in educational approaches. Despite methodological differences, the reviewed papers suggest that IPE is a viable educational option. Its implementation can facilitate teamwork that is better adapted to the changing needs of the patient and thus lead to improvements in patient care. The main challenge to the wider use of IPE among students of dietetics-nutrition and pharmacy appears to be the lack of scientific evidence to support the decisions needed to carefully plan and implement IPE activities. However, the available data suggest that IPE in these programmes is feasible in a variety of settings and can be beneficial for learners.
Data availability
All data generated or analysed during this study are included in this published article and its supplementary information files.
Abbreviations
World Health Organization
Interprofessional education
Centre for the Advancement of Interprofessional Education
Team-based learning
Interprofessional Collaborative Competencies Attainment Survey
Geriatrics Champions Program
American Geriatrics Society Internal Medicine-Family Medicine
Service-learning
Team readiness assurance tests
World Health Organization. Framework for action on interprofessional education & collaborative practice. 2010. https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/framework-for-action-on-interprofessional-education-collaborative-practice Accessed 12 May 2023.
Reeves S, Perrier L, Goldman J, Freeth D, Zwarenstein M. Interprofessional education: effects on professional practice and healthcare outcomes. Cochrane Database Syst Reviews. 2013;3(3). https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD002213.pub3 .
Guraya SY, Barr H. The effectiveness of interprofessional education in healthcare: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 2018;34(3):160–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.kjms.2017.12.009 .
Article Google Scholar
Spaulding EM, Marvel FA, Jacob E, Rahman A, Hansen BR, Hanyok LA, et al. Interprofessional education and collaboration among healthcare students and professionals: a systematic review and call for action. J Interprof Care. 2019;35(4):1–10. https://doi.org/10.1080/13561820.2019.1697214 .
Berger-Estilita J, Fuchs A, Hahn M, Chiang H, Greif R. Attitudes towards interprofessional education in the medical curriculum: a systematic review of the literature. BMC Med Educ. 2020;20(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12909-020-02176-4 .
van Diggele C, Roberts C, Burgess A, Mellis C. Interprofessional education: Tips for design and implementation. BMC Med Educ. 2020;20(2). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12909-020-02286-z .
Miselis HH, Zawacki S, White S, Yinusa-Nyahkoon L, Mostow C, Furlong J, et al. Interprofessional education in the clinical learning environment: a mixed-methods evaluation of a longitudinal experience in the primary care setting. J Interprof Care. 2022;1–11. https://doi.org/10.1080/13561820.2022.2025768 .
Standards P. & Notification Forms. LCME. [accessed 2024 Mar 9]. https://lcme.org/publications/#Standards .
2023 Accreditation Manual [accessed 2024 Mar 9]. https://resources.acenursing.org/space/AM/1842642947/2023+Accreditation+Manual .
Accreditation Standards And Key Elements For The Professional Program. in Pharmacy Leading to The Doctor of Pharmacy Degree. Accreditation Council for Pharmacy Education. [accessed 2024 Mar 9]. https://www.acpe-accredit.org/pdf/Standards2016FINAL.pdf .
General Medical Council. Promoting Excellence: standards for medical education and training. 2015. https://www.gmc-uk.org/-/media/documents/promoting-excellence-standards-for-medical-education-and-training-2109_pdf-61939165.pdf .
Schot E, Tummers L, Noordegraaf M. Working on working together: A systematic review on how healthcare professionals contribute to interprofessional collaboration. Journal of Interprofessional Care. 2020;34(3):1–11. [Accessed online 2024 Mar 9]. https://www.tandonline.com/doi/full/ https://doi.org/10.1080/13561820.2019.1636007 .
NICE. Type 2 Diabetes in Adults: Management Type 2 Diabetes in Adults: Management NICE Guideline. 2022. https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ng28/resources/type-2-diabetes-in-adults-management-pdf-1837338615493 Accessed 12 May 2023.
NICE. Type 1 diabetes in adults: diagnosis and management NICE guideline. 2015. https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ng17/resources/type-1-diabetes-in-adults-diagnosis-and-management-pdf-1837276469701 Accessed 12 May 2023.
Davies MJ, Aroda VR, Collins BS, Gabbay RA, Green J, Maruthur NM, et al. Management of hyperglycemia in type 2 diabetes, 2022. A consensus report by the American Diabetes Association (ADA) and the European association for the study of diabetes (EASD). Diabetes Care. 2022;45(11). https://doi.org/10.2337/dci22-0034 .
Unger T, Borghi C, Charchar F, Khan NA, Poulter NR, Prabhakaran D, et al. 2020 International Society of Hypertension Global Hypertension Practice Guidelines. Hypertension. 2020;75(6):1334–57. https://doi.org/10.1161/hypertensionaha.120.15026 .
Grundy SM, Stone NJ, Bailey AL, Beam C, Birtcher KK, Blumenthal RS, AHA/ACC/AACVPR/AAPA/ABC/ACPM/ADA/AGS/APhA, /ASPC/NLA/PCNA Guideline on the Management of Blood Cholesterol. Circulation. 2018;139(25). https://professional.heart.org/idc/groups/ahamah-public/@wcm/@sop/@smd/documents/downloadable/ucm_502856.pdf Accessed 12 May 2023.
NICE. Cardiovascular disease: risk assessment vascular disease: risk assessment and reduction, including lipid and reduction, including lipid modification modification Clinical guideline. 2014. https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/cg181/resources/cardiovascular-disease-risk-assessment-and-reduction-including-lipid-modification-pdf-35109807660997 Accessed 12 May 2023.
NICE. Chronic kidney disease: assessment and management NICE guideline. 2021. https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ng203/resources/chronic-kidney-disease-assessment-and-management-pdf-66143713055173 Accessed 12 May 2023.
Fiaccadori E, Sabatino A, Barazzoni R, Carrero JJ, Cupisti A, De Waele E et al. ESPEN guideline on clinical nutrition in hospitalized patients with acute or chronic kidney disease. Clinical Nutrition. 2021 Feb. https://www.espen.org/files/ESPEN-Guidelines/ESPEN-guideline-on-clinical-nutrition-in-hospitalized-patients-with-acute-or-chronic-kidney-disease.pdf Accessed 12 May 2023.
Dominguez-Munoz JE, Drewes AM, Lindkvist B, Ewald N, Czakó L, Rosendahl J, et al. Recommendations from the United European Gastroenterology evidence-based guidelines for the diagnosis and therapy of chronic pancreatitis. Pancreatology. 2018;18(8):847–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pan.2018.09.016 .
Durie P, Baillargeon J, Bouchard S, Donnellan F, Zepeda-Gomez S, Teshima C. Diagnosis and management of pancreatic exocrine insufficiency (PEI) in primary care: consensus guidance of a Canadian expert panel. Curr Med Res Opin. 2018;34(1):25–33. https://doi.org/10.1080/03007995.2017.1389704 .
Collaborative practice through learning together to work together. Caipe.org. 2019. https://www.caipe.org/resource/CAIPE-Statement-of-Purpose-2016.pdf Accessed 12 May 2023.
Tricco AC, Lillie E, Zarin W, O’Brien KK, Colquhoun H, Levac D, et al. PRISMA Extension for scoping reviews (PRISMA-ScR): Checklist and Explanation. Ann Intern Med. 2018;169(7):467–73. https://doi.org/10.7326/M18-0850 .
Kent F, Drysdale P, Martin N, Keating JL. The mixed-discipline aged-care student clinic: an authentic interprofessional learning initiative. J Allied Health. 2014;43(1):51–6. PMID: 24598900.
Google Scholar
Wilby KJ, Al-Abdi T, Hassan A, Brown MA, Paravattil B, Khalifa SI. Attitudes of pharmacy and nutrition students towards team-based care after first exposure to interprofessional education in Qatar. J Interprof Care. 2015;29(1):82–4. https://doi.org/10.3109/13561820.2014.933949 .
Pelham K, Skinner MA, McHugh P, Pullon S. Interprofessional education in a rural community: the perspectives of the clinical workplace providers. J Prim Health Care. 2016;8(3):210–9. https://doi.org/10.1071/HC16010 .
Reitsma G, Scrooby B, Rabie T, Viljoen M, Smit K, Du Preez A, Pretorius R, Van Oort A, Swanepoel M, Naudé A, Dolman R. Health students’ experiences of the process of interprofessional education: a pilot project. J Interprof Care. 2019;33(3):298–307. https://doi.org/10.1080/13561820.2019.1572600 .
Khalafalla FG, Covarrubias K, Fesperman M, Eichmann K, VanGarsse A, Ofstad W. Enhancing nutrition and lifestyle education for healthcare professional students through an interprofessional, team-based training program. Currents Pharm Teach Learn. 2020;12(12):1484–90. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cptl.2020.07.017 .
Bhattacharya SB, Jernigan S, Hyatt M, Sabata D, Johnston S, Burkhardt C. Preparing a healthcare workforce for geriatrics care: an interprofessional team based learning program. BMC Geriatr. 2021;21(1):644. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12877-021-02456-8 .
van Diggele C, Roberts C, Haq I. Optimising student-led interprofessional learning across eleven health disciplines. BMC Med Educ. 2021;21(1):157. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12909-021-02527-9 .
Watts SO, Tuggle FJ, Sewell J, Slay JL, Ellison KJ, Frugé AD. Achievement of interprofessional competencies in live and virtual community clinics: a comparative study. Nurse Educ Today. 2022;119:105578. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nedt.2022.105578 .
Heinemann GD, Schmitt MH, Farrell MP, Brallier SA. Development of an attitudes toward Health Care teams Scale. Eval Health Prof. 1999;22(1):123–42. https://doi.org/10.1177/01632789922034202 .
Yoong SQ, Liao AWX, Goh SH, Zhang H. Educational effects of community service-learning involving older adults in nursing education: an integrative review. Nurse Educ Today. 2022;113:105376. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nedt.2022.105376 .
McLean SF. Case-based learning and its application in Medical and Health-Care fields: a review of Worldwide Literature. J Med Educ Curric Dev. 2016;3. https://doi.org/10.4137/JMECD.S20377 . JMECD.S20377.
Parmelee D, Michaelsen LK, Cook S, Hudes PD. Team-based learning: a practical guide: AMEE Guide 65. Med Teach. 2012;34(5):e275–87. https://doi.org/10.3109/0142159x.2012.651179 .
Ho JM, Wong AY, Schoeb V, Chan AS, Tang PM, Wong FK. Interprofessional team-based learning: a qualitative study on the experiences of nursing and physiotherapy students. Front Public Health. 2022;9:706346. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpubh.2021.706346 .
Landi F, Calvani R, Tosato M, Martone AM, Ortolani E, Savera G, Sisto A, Marzetti E. Anorexia of aging: risk factors, consequences, and potential treatments. Nutrients. 2016;8(2):69. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu8020069 .
Barrocas A, Schwartz DB, Bistrian BR, Guenter P, Mueller C, Chernoff R, Hasse JM. Nutrition support teams: Institution, evolution, and innovation. Nutr Clin Practice: Official Publication Am Soc Parenter Enter Nutr. 2023;38(1):10–26. https://doi.org/10.1002/ncp.10931 .
Bloom BS, Engelhart MD, Furst EJ, Hill WH, Krathwohl DR. Taxonomy of educational objectives: the classification of educational goals. Vol. Handbook I: cognitive domain. New York: David McKay Company; 1956.
Kizaki H, Ota T, Mashima S, Nakamura Y, Kiyokawa S, Kominato H, Satoh H, Sawada Y, Hori S. Questionnaire survey investigation of the present status of dietetic consultation at community pharmacies from the perspectives of registered dietitians and pharmacists. BMC Health Serv Res. 2021;21(1):935. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12913-021-06959-3 .
Download references
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Internal Medicine and Gerontology, Faculty of Medicine, Jagiellonian University Medical College, 2 Jakubowskiego St., building I, 5th floor, 30- 688, Kraków, Poland
Anna Rudzińska, Jerzy Gąsowski & Karolina Piotrowicz
Faculty of Pharmacy, Jagiellonian University Medical College, 30-688, Krakow, Poland
Piotr Guzy & Agnieszka Skowron
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
AR and PG contributed equally to this paper. They established inclusion/exclusion criteria, developed search strategy, conducted screening and articles review. They also extracted data from included papers. KP consulted AR and PG throughout the entire process, resolved disagreements on the inclusion of the study. AR, PG, KP, AS, JG analyzed and interpreted data. All authors reviewed manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Karolina Piotrowicz .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate, consent for publication, competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Rudzińska, A., Guzy, P., Skowron, A. et al. Joint interprofessional education of pharmacy and dietetics undergraduates - a scoping review. BMC Med Educ 24 , 557 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12909-024-05411-4
Download citation
Received : 15 December 2023
Accepted : 10 April 2024
Published : 22 May 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12909-024-05411-4
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Medical education
- Interprofessional
- Undergraduates
BMC Medical Education
ISSN: 1472-6920
- Submission enquiries: [email protected]
- General enquiries: [email protected]
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- BMC Med Res Methodol

The case study approach
Sarah crowe.
1 Division of Primary Care, The University of Nottingham, Nottingham, UK
Kathrin Cresswell
2 Centre for Population Health Sciences, The University of Edinburgh, Edinburgh, UK
Ann Robertson
3 School of Health in Social Science, The University of Edinburgh, Edinburgh, UK
Anthony Avery
Aziz sheikh.
The case study approach allows in-depth, multi-faceted explorations of complex issues in their real-life settings. The value of the case study approach is well recognised in the fields of business, law and policy, but somewhat less so in health services research. Based on our experiences of conducting several health-related case studies, we reflect on the different types of case study design, the specific research questions this approach can help answer, the data sources that tend to be used, and the particular advantages and disadvantages of employing this methodological approach. The paper concludes with key pointers to aid those designing and appraising proposals for conducting case study research, and a checklist to help readers assess the quality of case study reports.
Introduction
The case study approach is particularly useful to employ when there is a need to obtain an in-depth appreciation of an issue, event or phenomenon of interest, in its natural real-life context. Our aim in writing this piece is to provide insights into when to consider employing this approach and an overview of key methodological considerations in relation to the design, planning, analysis, interpretation and reporting of case studies.
The illustrative 'grand round', 'case report' and 'case series' have a long tradition in clinical practice and research. Presenting detailed critiques, typically of one or more patients, aims to provide insights into aspects of the clinical case and, in doing so, illustrate broader lessons that may be learnt. In research, the conceptually-related case study approach can be used, for example, to describe in detail a patient's episode of care, explore professional attitudes to and experiences of a new policy initiative or service development or more generally to 'investigate contemporary phenomena within its real-life context' [ 1 ]. Based on our experiences of conducting a range of case studies, we reflect on when to consider using this approach, discuss the key steps involved and illustrate, with examples, some of the practical challenges of attaining an in-depth understanding of a 'case' as an integrated whole. In keeping with previously published work, we acknowledge the importance of theory to underpin the design, selection, conduct and interpretation of case studies[ 2 ]. In so doing, we make passing reference to the different epistemological approaches used in case study research by key theoreticians and methodologists in this field of enquiry.
This paper is structured around the following main questions: What is a case study? What are case studies used for? How are case studies conducted? What are the potential pitfalls and how can these be avoided? We draw in particular on four of our own recently published examples of case studies (see Tables Tables1, 1 , ,2, 2 , ,3 3 and and4) 4 ) and those of others to illustrate our discussion[ 3 - 7 ].
Example of a case study investigating the reasons for differences in recruitment rates of minority ethnic people in asthma research[ 3 ]
Example of a case study investigating the process of planning and implementing a service in Primary Care Organisations[ 4 ]
Example of a case study investigating the introduction of the electronic health records[ 5 ]
Example of a case study investigating the formal and informal ways students learn about patient safety[ 6 ]
What is a case study?
A case study is a research approach that is used to generate an in-depth, multi-faceted understanding of a complex issue in its real-life context. It is an established research design that is used extensively in a wide variety of disciplines, particularly in the social sciences. A case study can be defined in a variety of ways (Table (Table5), 5 ), the central tenet being the need to explore an event or phenomenon in depth and in its natural context. It is for this reason sometimes referred to as a "naturalistic" design; this is in contrast to an "experimental" design (such as a randomised controlled trial) in which the investigator seeks to exert control over and manipulate the variable(s) of interest.
Definitions of a case study
Stake's work has been particularly influential in defining the case study approach to scientific enquiry. He has helpfully characterised three main types of case study: intrinsic , instrumental and collective [ 8 ]. An intrinsic case study is typically undertaken to learn about a unique phenomenon. The researcher should define the uniqueness of the phenomenon, which distinguishes it from all others. In contrast, the instrumental case study uses a particular case (some of which may be better than others) to gain a broader appreciation of an issue or phenomenon. The collective case study involves studying multiple cases simultaneously or sequentially in an attempt to generate a still broader appreciation of a particular issue.
These are however not necessarily mutually exclusive categories. In the first of our examples (Table (Table1), 1 ), we undertook an intrinsic case study to investigate the issue of recruitment of minority ethnic people into the specific context of asthma research studies, but it developed into a instrumental case study through seeking to understand the issue of recruitment of these marginalised populations more generally, generating a number of the findings that are potentially transferable to other disease contexts[ 3 ]. In contrast, the other three examples (see Tables Tables2, 2 , ,3 3 and and4) 4 ) employed collective case study designs to study the introduction of workforce reconfiguration in primary care, the implementation of electronic health records into hospitals, and to understand the ways in which healthcare students learn about patient safety considerations[ 4 - 6 ]. Although our study focusing on the introduction of General Practitioners with Specialist Interests (Table (Table2) 2 ) was explicitly collective in design (four contrasting primary care organisations were studied), is was also instrumental in that this particular professional group was studied as an exemplar of the more general phenomenon of workforce redesign[ 4 ].
What are case studies used for?
According to Yin, case studies can be used to explain, describe or explore events or phenomena in the everyday contexts in which they occur[ 1 ]. These can, for example, help to understand and explain causal links and pathways resulting from a new policy initiative or service development (see Tables Tables2 2 and and3, 3 , for example)[ 1 ]. In contrast to experimental designs, which seek to test a specific hypothesis through deliberately manipulating the environment (like, for example, in a randomised controlled trial giving a new drug to randomly selected individuals and then comparing outcomes with controls),[ 9 ] the case study approach lends itself well to capturing information on more explanatory ' how ', 'what' and ' why ' questions, such as ' how is the intervention being implemented and received on the ground?'. The case study approach can offer additional insights into what gaps exist in its delivery or why one implementation strategy might be chosen over another. This in turn can help develop or refine theory, as shown in our study of the teaching of patient safety in undergraduate curricula (Table (Table4 4 )[ 6 , 10 ]. Key questions to consider when selecting the most appropriate study design are whether it is desirable or indeed possible to undertake a formal experimental investigation in which individuals and/or organisations are allocated to an intervention or control arm? Or whether the wish is to obtain a more naturalistic understanding of an issue? The former is ideally studied using a controlled experimental design, whereas the latter is more appropriately studied using a case study design.
Case studies may be approached in different ways depending on the epistemological standpoint of the researcher, that is, whether they take a critical (questioning one's own and others' assumptions), interpretivist (trying to understand individual and shared social meanings) or positivist approach (orientating towards the criteria of natural sciences, such as focusing on generalisability considerations) (Table (Table6). 6 ). Whilst such a schema can be conceptually helpful, it may be appropriate to draw on more than one approach in any case study, particularly in the context of conducting health services research. Doolin has, for example, noted that in the context of undertaking interpretative case studies, researchers can usefully draw on a critical, reflective perspective which seeks to take into account the wider social and political environment that has shaped the case[ 11 ].
Example of epistemological approaches that may be used in case study research
How are case studies conducted?
Here, we focus on the main stages of research activity when planning and undertaking a case study; the crucial stages are: defining the case; selecting the case(s); collecting and analysing the data; interpreting data; and reporting the findings.
Defining the case
Carefully formulated research question(s), informed by the existing literature and a prior appreciation of the theoretical issues and setting(s), are all important in appropriately and succinctly defining the case[ 8 , 12 ]. Crucially, each case should have a pre-defined boundary which clarifies the nature and time period covered by the case study (i.e. its scope, beginning and end), the relevant social group, organisation or geographical area of interest to the investigator, the types of evidence to be collected, and the priorities for data collection and analysis (see Table Table7 7 )[ 1 ]. A theory driven approach to defining the case may help generate knowledge that is potentially transferable to a range of clinical contexts and behaviours; using theory is also likely to result in a more informed appreciation of, for example, how and why interventions have succeeded or failed[ 13 ].
Example of a checklist for rating a case study proposal[ 8 ]
For example, in our evaluation of the introduction of electronic health records in English hospitals (Table (Table3), 3 ), we defined our cases as the NHS Trusts that were receiving the new technology[ 5 ]. Our focus was on how the technology was being implemented. However, if the primary research interest had been on the social and organisational dimensions of implementation, we might have defined our case differently as a grouping of healthcare professionals (e.g. doctors and/or nurses). The precise beginning and end of the case may however prove difficult to define. Pursuing this same example, when does the process of implementation and adoption of an electronic health record system really begin or end? Such judgements will inevitably be influenced by a range of factors, including the research question, theory of interest, the scope and richness of the gathered data and the resources available to the research team.
Selecting the case(s)
The decision on how to select the case(s) to study is a very important one that merits some reflection. In an intrinsic case study, the case is selected on its own merits[ 8 ]. The case is selected not because it is representative of other cases, but because of its uniqueness, which is of genuine interest to the researchers. This was, for example, the case in our study of the recruitment of minority ethnic participants into asthma research (Table (Table1) 1 ) as our earlier work had demonstrated the marginalisation of minority ethnic people with asthma, despite evidence of disproportionate asthma morbidity[ 14 , 15 ]. In another example of an intrinsic case study, Hellstrom et al.[ 16 ] studied an elderly married couple living with dementia to explore how dementia had impacted on their understanding of home, their everyday life and their relationships.
For an instrumental case study, selecting a "typical" case can work well[ 8 ]. In contrast to the intrinsic case study, the particular case which is chosen is of less importance than selecting a case that allows the researcher to investigate an issue or phenomenon. For example, in order to gain an understanding of doctors' responses to health policy initiatives, Som undertook an instrumental case study interviewing clinicians who had a range of responsibilities for clinical governance in one NHS acute hospital trust[ 17 ]. Sampling a "deviant" or "atypical" case may however prove even more informative, potentially enabling the researcher to identify causal processes, generate hypotheses and develop theory.
In collective or multiple case studies, a number of cases are carefully selected. This offers the advantage of allowing comparisons to be made across several cases and/or replication. Choosing a "typical" case may enable the findings to be generalised to theory (i.e. analytical generalisation) or to test theory by replicating the findings in a second or even a third case (i.e. replication logic)[ 1 ]. Yin suggests two or three literal replications (i.e. predicting similar results) if the theory is straightforward and five or more if the theory is more subtle. However, critics might argue that selecting 'cases' in this way is insufficiently reflexive and ill-suited to the complexities of contemporary healthcare organisations.
The selected case study site(s) should allow the research team access to the group of individuals, the organisation, the processes or whatever else constitutes the chosen unit of analysis for the study. Access is therefore a central consideration; the researcher needs to come to know the case study site(s) well and to work cooperatively with them. Selected cases need to be not only interesting but also hospitable to the inquiry [ 8 ] if they are to be informative and answer the research question(s). Case study sites may also be pre-selected for the researcher, with decisions being influenced by key stakeholders. For example, our selection of case study sites in the evaluation of the implementation and adoption of electronic health record systems (see Table Table3) 3 ) was heavily influenced by NHS Connecting for Health, the government agency that was responsible for overseeing the National Programme for Information Technology (NPfIT)[ 5 ]. This prominent stakeholder had already selected the NHS sites (through a competitive bidding process) to be early adopters of the electronic health record systems and had negotiated contracts that detailed the deployment timelines.
It is also important to consider in advance the likely burden and risks associated with participation for those who (or the site(s) which) comprise the case study. Of particular importance is the obligation for the researcher to think through the ethical implications of the study (e.g. the risk of inadvertently breaching anonymity or confidentiality) and to ensure that potential participants/participating sites are provided with sufficient information to make an informed choice about joining the study. The outcome of providing this information might be that the emotive burden associated with participation, or the organisational disruption associated with supporting the fieldwork, is considered so high that the individuals or sites decide against participation.
In our example of evaluating implementations of electronic health record systems, given the restricted number of early adopter sites available to us, we sought purposively to select a diverse range of implementation cases among those that were available[ 5 ]. We chose a mixture of teaching, non-teaching and Foundation Trust hospitals, and examples of each of the three electronic health record systems procured centrally by the NPfIT. At one recruited site, it quickly became apparent that access was problematic because of competing demands on that organisation. Recognising the importance of full access and co-operative working for generating rich data, the research team decided not to pursue work at that site and instead to focus on other recruited sites.
Collecting the data
In order to develop a thorough understanding of the case, the case study approach usually involves the collection of multiple sources of evidence, using a range of quantitative (e.g. questionnaires, audits and analysis of routinely collected healthcare data) and more commonly qualitative techniques (e.g. interviews, focus groups and observations). The use of multiple sources of data (data triangulation) has been advocated as a way of increasing the internal validity of a study (i.e. the extent to which the method is appropriate to answer the research question)[ 8 , 18 - 21 ]. An underlying assumption is that data collected in different ways should lead to similar conclusions, and approaching the same issue from different angles can help develop a holistic picture of the phenomenon (Table (Table2 2 )[ 4 ].
Brazier and colleagues used a mixed-methods case study approach to investigate the impact of a cancer care programme[ 22 ]. Here, quantitative measures were collected with questionnaires before, and five months after, the start of the intervention which did not yield any statistically significant results. Qualitative interviews with patients however helped provide an insight into potentially beneficial process-related aspects of the programme, such as greater, perceived patient involvement in care. The authors reported how this case study approach provided a number of contextual factors likely to influence the effectiveness of the intervention and which were not likely to have been obtained from quantitative methods alone.
In collective or multiple case studies, data collection needs to be flexible enough to allow a detailed description of each individual case to be developed (e.g. the nature of different cancer care programmes), before considering the emerging similarities and differences in cross-case comparisons (e.g. to explore why one programme is more effective than another). It is important that data sources from different cases are, where possible, broadly comparable for this purpose even though they may vary in nature and depth.
Analysing, interpreting and reporting case studies
Making sense and offering a coherent interpretation of the typically disparate sources of data (whether qualitative alone or together with quantitative) is far from straightforward. Repeated reviewing and sorting of the voluminous and detail-rich data are integral to the process of analysis. In collective case studies, it is helpful to analyse data relating to the individual component cases first, before making comparisons across cases. Attention needs to be paid to variations within each case and, where relevant, the relationship between different causes, effects and outcomes[ 23 ]. Data will need to be organised and coded to allow the key issues, both derived from the literature and emerging from the dataset, to be easily retrieved at a later stage. An initial coding frame can help capture these issues and can be applied systematically to the whole dataset with the aid of a qualitative data analysis software package.
The Framework approach is a practical approach, comprising of five stages (familiarisation; identifying a thematic framework; indexing; charting; mapping and interpretation) , to managing and analysing large datasets particularly if time is limited, as was the case in our study of recruitment of South Asians into asthma research (Table (Table1 1 )[ 3 , 24 ]. Theoretical frameworks may also play an important role in integrating different sources of data and examining emerging themes. For example, we drew on a socio-technical framework to help explain the connections between different elements - technology; people; and the organisational settings within which they worked - in our study of the introduction of electronic health record systems (Table (Table3 3 )[ 5 ]. Our study of patient safety in undergraduate curricula drew on an evaluation-based approach to design and analysis, which emphasised the importance of the academic, organisational and practice contexts through which students learn (Table (Table4 4 )[ 6 ].
Case study findings can have implications both for theory development and theory testing. They may establish, strengthen or weaken historical explanations of a case and, in certain circumstances, allow theoretical (as opposed to statistical) generalisation beyond the particular cases studied[ 12 ]. These theoretical lenses should not, however, constitute a strait-jacket and the cases should not be "forced to fit" the particular theoretical framework that is being employed.
When reporting findings, it is important to provide the reader with enough contextual information to understand the processes that were followed and how the conclusions were reached. In a collective case study, researchers may choose to present the findings from individual cases separately before amalgamating across cases. Care must be taken to ensure the anonymity of both case sites and individual participants (if agreed in advance) by allocating appropriate codes or withholding descriptors. In the example given in Table Table3, 3 , we decided against providing detailed information on the NHS sites and individual participants in order to avoid the risk of inadvertent disclosure of identities[ 5 , 25 ].
What are the potential pitfalls and how can these be avoided?
The case study approach is, as with all research, not without its limitations. When investigating the formal and informal ways undergraduate students learn about patient safety (Table (Table4), 4 ), for example, we rapidly accumulated a large quantity of data. The volume of data, together with the time restrictions in place, impacted on the depth of analysis that was possible within the available resources. This highlights a more general point of the importance of avoiding the temptation to collect as much data as possible; adequate time also needs to be set aside for data analysis and interpretation of what are often highly complex datasets.
Case study research has sometimes been criticised for lacking scientific rigour and providing little basis for generalisation (i.e. producing findings that may be transferable to other settings)[ 1 ]. There are several ways to address these concerns, including: the use of theoretical sampling (i.e. drawing on a particular conceptual framework); respondent validation (i.e. participants checking emerging findings and the researcher's interpretation, and providing an opinion as to whether they feel these are accurate); and transparency throughout the research process (see Table Table8 8 )[ 8 , 18 - 21 , 23 , 26 ]. Transparency can be achieved by describing in detail the steps involved in case selection, data collection, the reasons for the particular methods chosen, and the researcher's background and level of involvement (i.e. being explicit about how the researcher has influenced data collection and interpretation). Seeking potential, alternative explanations, and being explicit about how interpretations and conclusions were reached, help readers to judge the trustworthiness of the case study report. Stake provides a critique checklist for a case study report (Table (Table9 9 )[ 8 ].
Potential pitfalls and mitigating actions when undertaking case study research
Stake's checklist for assessing the quality of a case study report[ 8 ]
Conclusions
The case study approach allows, amongst other things, critical events, interventions, policy developments and programme-based service reforms to be studied in detail in a real-life context. It should therefore be considered when an experimental design is either inappropriate to answer the research questions posed or impossible to undertake. Considering the frequency with which implementations of innovations are now taking place in healthcare settings and how well the case study approach lends itself to in-depth, complex health service research, we believe this approach should be more widely considered by researchers. Though inherently challenging, the research case study can, if carefully conceptualised and thoughtfully undertaken and reported, yield powerful insights into many important aspects of health and healthcare delivery.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Authors' contributions
AS conceived this article. SC, KC and AR wrote this paper with GH, AA and AS all commenting on various drafts. SC and AS are guarantors.
Pre-publication history
The pre-publication history for this paper can be accessed here:
http://www.biomedcentral.com/1471-2288/11/100/prepub
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to the participants and colleagues who contributed to the individual case studies that we have drawn on. This work received no direct funding, but it has been informed by projects funded by Asthma UK, the NHS Service Delivery Organisation, NHS Connecting for Health Evaluation Programme, and Patient Safety Research Portfolio. We would also like to thank the expert reviewers for their insightful and constructive feedback. Our thanks are also due to Dr. Allison Worth who commented on an earlier draft of this manuscript.
- Yin RK. Case study research, design and method. 4. London: Sage Publications Ltd.; 2009. [ Google Scholar ]
- Keen J, Packwood T. Qualitative research; case study evaluation. BMJ. 1995; 311 :444–446. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Sheikh A, Halani L, Bhopal R, Netuveli G, Partridge M, Car J. et al. Facilitating the Recruitment of Minority Ethnic People into Research: Qualitative Case Study of South Asians and Asthma. PLoS Med. 2009; 6 (10):1–11. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Pinnock H, Huby G, Powell A, Kielmann T, Price D, Williams S, The process of planning, development and implementation of a General Practitioner with a Special Interest service in Primary Care Organisations in England and Wales: a comparative prospective case study. Report for the National Co-ordinating Centre for NHS Service Delivery and Organisation R&D (NCCSDO) 2008. http://www.sdo.nihr.ac.uk/files/project/99-final-report.pdf
- Robertson A, Cresswell K, Takian A, Petrakaki D, Crowe S, Cornford T. et al. Prospective evaluation of the implementation and adoption of NHS Connecting for Health's national electronic health record in secondary care in England: interim findings. BMJ. 2010; 41 :c4564. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Pearson P, Steven A, Howe A, Sheikh A, Ashcroft D, Smith P. the Patient Safety Education Study Group. Learning about patient safety: organisational context and culture in the education of healthcare professionals. J Health Serv Res Policy. 2010; 15 :4–10. doi: 10.1258/jhsrp.2009.009052. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- van Harten WH, Casparie TF, Fisscher OA. The evaluation of the introduction of a quality management system: a process-oriented case study in a large rehabilitation hospital. Health Policy. 2002; 60 (1):17–37. doi: 10.1016/S0168-8510(01)00187-7. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Stake RE. The art of case study research. London: Sage Publications Ltd.; 1995. [ Google Scholar ]
- Sheikh A, Smeeth L, Ashcroft R. Randomised controlled trials in primary care: scope and application. Br J Gen Pract. 2002; 52 (482):746–51. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- King G, Keohane R, Verba S. Designing Social Inquiry. Princeton: Princeton University Press; 1996. [ Google Scholar ]
- Doolin B. Information technology as disciplinary technology: being critical in interpretative research on information systems. Journal of Information Technology. 1998; 13 :301–311. doi: 10.1057/jit.1998.8. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- George AL, Bennett A. Case studies and theory development in the social sciences. Cambridge, MA: MIT Press; 2005. [ Google Scholar ]
- Eccles M. the Improved Clinical Effectiveness through Behavioural Research Group (ICEBeRG) Designing theoretically-informed implementation interventions. Implementation Science. 2006; 1 :1–8. doi: 10.1186/1748-5908-1-1. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Netuveli G, Hurwitz B, Levy M, Fletcher M, Barnes G, Durham SR, Sheikh A. Ethnic variations in UK asthma frequency, morbidity, and health-service use: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet. 2005; 365 (9456):312–7. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Sheikh A, Panesar SS, Lasserson T, Netuveli G. Recruitment of ethnic minorities to asthma studies. Thorax. 2004; 59 (7):634. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hellström I, Nolan M, Lundh U. 'We do things together': A case study of 'couplehood' in dementia. Dementia. 2005; 4 :7–22. doi: 10.1177/1471301205049188. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Som CV. Nothing seems to have changed, nothing seems to be changing and perhaps nothing will change in the NHS: doctors' response to clinical governance. International Journal of Public Sector Management. 2005; 18 :463–477. doi: 10.1108/09513550510608903. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Lincoln Y, Guba E. Naturalistic inquiry. Newbury Park: Sage Publications; 1985. [ Google Scholar ]
- Barbour RS. Checklists for improving rigour in qualitative research: a case of the tail wagging the dog? BMJ. 2001; 322 :1115–1117. doi: 10.1136/bmj.322.7294.1115. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Mays N, Pope C. Qualitative research in health care: Assessing quality in qualitative research. BMJ. 2000; 320 :50–52. doi: 10.1136/bmj.320.7226.50. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Mason J. Qualitative researching. London: Sage; 2002. [ Google Scholar ]
- Brazier A, Cooke K, Moravan V. Using Mixed Methods for Evaluating an Integrative Approach to Cancer Care: A Case Study. Integr Cancer Ther. 2008; 7 :5–17. doi: 10.1177/1534735407313395. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Miles MB, Huberman M. Qualitative data analysis: an expanded sourcebook. 2. CA: Sage Publications Inc.; 1994. [ Google Scholar ]
- Pope C, Ziebland S, Mays N. Analysing qualitative data. Qualitative research in health care. BMJ. 2000; 320 :114–116. doi: 10.1136/bmj.320.7227.114. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Cresswell KM, Worth A, Sheikh A. Actor-Network Theory and its role in understanding the implementation of information technology developments in healthcare. BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. 2010; 10 (1):67. doi: 10.1186/1472-6947-10-67. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Malterud K. Qualitative research: standards, challenges, and guidelines. Lancet. 2001; 358 :483–488. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(01)05627-6. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Yin R. Case study research: design and methods. 2. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publishing; 1994. [ Google Scholar ]
- Yin R. Enhancing the quality of case studies in health services research. Health Serv Res. 1999; 34 :1209–1224. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Green J, Thorogood N. Qualitative methods for health research. 2. Los Angeles: Sage; 2009. [ Google Scholar ]
- Howcroft D, Trauth E. Handbook of Critical Information Systems Research, Theory and Application. Cheltenham, UK: Northampton, MA, USA: Edward Elgar; 2005. [ Google Scholar ]
- Blakie N. Approaches to Social Enquiry. Cambridge: Polity Press; 1993. [ Google Scholar ]
- Doolin B. Power and resistance in the implementation of a medical management information system. Info Systems J. 2004; 14 :343–362. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2575.2004.00176.x. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Bloomfield BP, Best A. Management consultants: systems development, power and the translation of problems. Sociological Review. 1992; 40 :533–560. [ Google Scholar ]
- Shanks G, Parr A. Proceedings of the European Conference on Information Systems. Naples; 2003. Positivist, single case study research in information systems: A critical analysis. [ Google Scholar ]
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- My Account Login
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- Open access
- Published: 15 May 2024
Arresting failure propagation in buildings through collapse isolation
- Nirvan Makoond ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-5203-6318 1 ,
- Andri Setiawan ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-2791-6118 1 ,
- Manuel Buitrago ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-5561-5104 1 &
- Jose M. Adam ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-9205-8458 1
Nature volume 629 , pages 592–596 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
10k Accesses
226 Altmetric
Metrics details
- Civil engineering
- Mechanical engineering
Several catastrophic building collapses 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 occur because of the propagation of local-initial failures 6 , 7 . Current design methods attempt to completely prevent collapse after initial failures by improving connectivity between building components. These measures ensure that the loads supported by the failed components are redistributed to the rest of the structural system 8 , 9 . However, increased connectivity can contribute to collapsing elements pulling down parts of a building that would otherwise be unaffected 10 . This risk is particularly important when large initial failures occur, as tends to be the case in the most disastrous collapses 6 . Here we present an original design approach to arrest collapse propagation after major initial failures. When a collapse initiates, the approach ensures that specific elements fail before the failure of the most critical components for global stability. The structural system thus separates into different parts and isolates collapse when its propagation would otherwise be inevitable. The effectiveness of the approach is proved through unique experimental tests on a purposely built full-scale building. We also demonstrate that large initial failures would lead to total collapse of the test building if increased connectivity was implemented as recommended by present guidelines. Our proposed approach enables incorporating a last line of defence for more resilient buildings.
Similar content being viewed by others
Design principles for strong and tough hydrogels

Frequent disturbances enhanced the resilience of past human populations
Clarifying the four core effects of high-entropy materials
Disasters recorded from 2000 to 2019 are estimated to have caused economic losses of US$2.97 trillion and claimed approximately 1.23 million lives 11 . Most of these losses can be attributed to building collapses 12 , which are often characterized by the propagation of local-initial failures 13 that can arise because of extreme or abnormal events such as earthquakes 13 , 14 , 15 , 16 , floods 17 , 18 , 19 , 20 , storms 21 , 22 , landslides 23 , 24 , explosions 25 , vehicle impacts 26 and even construction or design errors 6 , 26 . As the world faces increasing trends in the frequency and intensity of extreme events 27 , 28 , it is arguably now more important than ever to design robust structures that are insensitive to initial damage 13 , 29 , irrespective of the underlying threat causing it.
Most robustness design approaches used at present 8 , 9 , 30 , 31 aim to completely prevent collapse initiation after a local failure by providing extensive connectivity within a structural system. Although these measures can ensure that the load supported by a failed component is redistributed to the rest of the structure, they are neither viable nor sustainable when considering larger initial failures 13 , 25 , 32 . In these situations, the implementation of these approaches can even result in collapsing parts of the building pulling down the rest of the structure 10 . The fact that several major collapses have occurred because of large initial failures 6 raises serious concerns about the inadequacy of the current robustness measures.
Traditionally, research in this area has focused on preventing collapse initiation after initial failures rather than on preventing collapse propagation. This trend dates back to the first impactful studies in the field of structural robustness, which were performed after a lack of connectivity enabled the progressive collapse of part of the Ronan Point tower in 1968 (ref. 33 ). Although completely preventing any collapse is certainly preferable to limiting the extent of a collapse, the occurrence of unforeseeable incidents is inevitable 34 and major building collapses keep occurring 1 , 2 , 3 .
Here we present an original approach for designing buildings to isolate the collapse triggered by a large initial failure. The approach, which is based on controlling the hierarchy of failures in a structural system, is inspired by how lizards shed their tails to escape predators 35 . The proposed hierarchy-based collapse isolation design ensures sufficient connectivity for operational conditions and after local-initial failures for which collapse initiation can be completely prevented through load redistribution. These local-initial failures can even be greater than those considered by building codes. Simultaneously, the structural system is also designed to separate into different parts and isolate a collapse when its propagation would otherwise be inevitable. As in the case of lizard tail autotomy 35 , this is achieved by promoting controlled fracture along predefined segment borders to limit failure propagation. In this work, hierarchy-based collapse isolation is applied to framed building structures. Developing this approach required a precise characterization of the collapse propagation mechanisms that need to be controlled. This was achieved using computational simulations that were validated through a specifically designed partial collapse test of a full-scale building. The obtained results demonstrate the viability of incorporating hierarchy-based collapse isolation in building design.
Hierarchy-based collapse isolation
Hierarchy-based collapse isolation design makes an important distinction between two types of initial failures. The first, referred to as small initial failures, includes all failures for which it is feasible to completely prevent the initiation of collapse by redistributing loads to the remaining structural system. The second type of initial failure, referred to as large initial failures, includes more severe failures that inevitably trigger at least a partial collapse.
The proposed design approach aims to (1) arrest unimpeded collapse propagation caused by large initial failures and (2) ensure the ability of a building to develop alternative load paths (ALPs) to prevent collapse initiation after small initial failures. This is achieved by prioritizing a specific hierarchy of failures among the components on the boundary of a moving collapse front.
Buildings are complex three-dimensional structural systems consisting of different components with very specific functions for transferring loads to the ground. Among these, vertical load-bearing components such as columns are the most important for ensuring global structural stability and integrity. Therefore, hierarchy-based collapse isolation design prevents the successive failure of columns, which would otherwise lead to catastrophic collapse. Although the exact magnitude of dynamic forces transmitted to columns during a collapse process is difficult to predict, these forces are eventually limited by the connections between columns and floor systems. In the proposed approach, partial-strength connections are designed to limit the magnitude of transmitted forces to values that are lower than the capacity of columns to resist unbalanced forces (see section ‘ Building design ’). This requirement guarantees a specific hierarchy of failures during collapse, whereby connection failures always occur before column failures. As a result, the collapse following a large initial failure is always restricted to components immediately adjacent to those directly involved in the initial failure. However, it is still necessary to ensure a lower bound on connection strengths to activate ALPs after small initial failures. Therefore, cost-effective implementation of hierarchy-based collapse isolation design requires finding an optimal balance between reducing the strength of connections and increasing the capacity of columns.
To test and verify the application of our proposed approach, we designed a real 15 m × 12 m precast reinforced concrete building with two 2.6-m-high floors. This basic geometry represents a building size that can be built and tested at full-scale while still being representative of current practices in the construction sector. The structural type was selected because of the increasing use of prefabricated construction for erecting high-occupancy buildings such as hospitals and malls because of several advantages in terms of quality, efficiency and sustainability 36 .
The collapse behaviour of possible design options (Extended Data Fig. 1 ) subjected to both small and large initial failures was investigated using high-fidelity collapse simulations (Fig. 1 ) based on the applied element method (AEM; see section ‘ Modelling strategy ’). The ability of these simulations to accurately represent collapse phenomena for the type of building being studied was later validated by comparing its predictions to the structural response observed during a purposely designed collapse test of a full-scale building (Extended Data Fig. 2 and Supplementary Video 7 ).
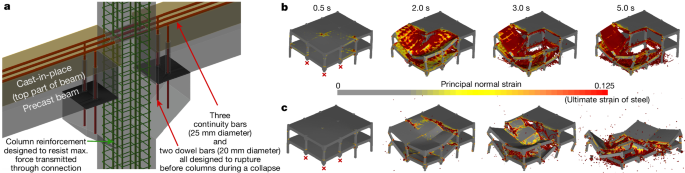
a , Partial-strength beam–column connection optimized for hierarchy-based collapse isolation. b , Partial collapse of a building designed for hierarchy-based collapse isolation (design H) after the loss of a corner column and two penultimate-edge columns. c , Total collapse of conventional building design (design C) after the same large initial failure scenario.
Following the preliminary design of a structure to resist loads suitable for office buildings, two building design options considering different robustness criteria were further investigated (see section ‘ Building design ’). The first option, design H (hierarchy-based), uses optimized partial-strength connections and enhanced columns (Fig. 1a ) to fulfil the requirements of hierarchy-based collapse isolation design. The second option, design C (conventional), is strictly based on code requirements and provides a benchmark comparison for evaluating the effectiveness of the proposed approach. It uses full-strength connections to improve robustness as recommended in current guidelines 37 and building codes 8 , 9 .
Simulations predicted that both design H and design C could develop stable ALPs that are able to completely prevent the initiation of collapse after small initial failure scenarios that are more severe than those considered in building codes 8 , 9 (Extended Data Fig. 3 ).
When subjected to a larger initial failure, simulations predict that design H can isolate the collapse to only the region directly affected by the initial failure (Fig. 1b ). By contrast, design C, with increased connectivity, causes collapsing elements to pull down the rest of the structure, leading to total collapse (Fig. 1c ). These two distinct outcomes demonstrate that the prevention of unimpeded collapse propagation can only be ensured when hierarchy-based collapse isolation is implemented (Extended Data Fig. 4 and Supplementary Video 1 ).
Testing a full-scale precast building
To confirm the expected performance improvement that can be achieved with the hierarchy-based collapse isolation design, a full-scale building specimen corresponding to design H was purposely built and subjected to two phases of testing as part of this work (Fig. 2a and Supplementary Information Sections 1 and 2 ). The precast structure was constructed with continuous columns cast together with corbels (Supplementary Video 4 ). The columns were cast with prepared dowel bars and sleeves for placing continuous top beam reinforcement bars through columns (Fig. 2b,c ). The bars used for these two types of reinforcing element (Fig. 1a ) were specifically selected to produce partial-strength connections. These connections are strong enough for the development of ALPs after small initial failures but weak enough to enable hierarchy-based collapse isolation after large initial failures.
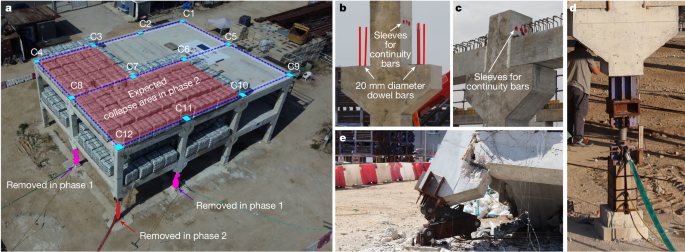
a , Full-scale precast concrete structure and columns removed in different testing phases. The label used for each column is shown. The location of beams connecting the different columns is indicated by the dotted lines above the second-floor level. The expected collapse area in the second phase of testing is indicated. b , Typical first-floor connection before placement of beams during construction. c , Typical second-floor connection after placement of precast beams during construction. Both b and c show columns with two straight precast beams on either side (C2, C3, C6, C7, C10 and C11). d , Device used for quasi-static removal of two columns in the first phase of testing. e , Three-hinged mechanism used for dynamic removal of corner column in the second phase of testing.
After investigating different column-removal scenarios from different regions of the test building (see section ‘ Experiment and monitoring design ’, Extended Data Fig. 5 and Supplementary Video 2 ), two phases of testing were defined to capture relevant collapse-related phenomena and validate the effectiveness of hierarchy-based collapse isolation. Separating the test into two phases allowed two different aspects to be analysed: (1) the prevention of collapse initiation after small initial failures and (2) the isolation of collapse after large initial failures.
Phase 1 involved the quasi-static removal of two penultimate-edge columns using specifically designed removable supports (Fig. 2d and Extended Data Fig. 6 ). This testing phase corresponds to a small initial failure scenario for which design H was able to develop ALPs to prevent collapse initiation. Phase 2 reproduced a large initial failure through the dynamic removal of the corner column found between the two previously removed columns using a three-hinged collapsible column (Fig. 2e ).
During both testing phases, a distributed load (11.8 kN m −2 ) corresponding to almost twice the magnitude specified in Eurocodes 38 for accidental design situations (6 kN m −2 ) was imposed on bays expected to collapse in phase 2 (Fig. 2a and Supplementary Video 5 ). Predictive simulations indicated that the failure mode and overall collapse would be almost identical when comparing this partial loading configuration with that in which the entire building is loaded (Supplementary Video 3 ). However, the partial loading configuration turns out to be more demanding for the part of the structure expected to remain upright as evidenced by the greater drifts it produces during collapse (see section ‘ Experiment and monitoring design ’ and Extended Data Fig. 7 ). The structural response during all phases of testing was extensively monitored with an array of different sensors (see section ‘ Experiment and monitoring design ’ and Supplementary Information Section 3 ) that provided the information used as a basis for the analyses presented in the following sections.
Preventing collapse initiation
Collapse initiation was completely prevented after the removal of two penultimate-edge columns in phase 1 of testing (Fig. 3a ), demonstrating that design H complies with the robustness requirements included in current building standards 8 , 9 , 39 . As this initial failure scenario is more severe than those considered by standardized design methods 8 , 9 , 30 , it represents an extreme case for which ALPs are still effective. As such, the outcome of phase 1 demonstrates that implementing hierarchy-based collapse isolation design does not impair the ability of this structure to prevent collapse initiation.
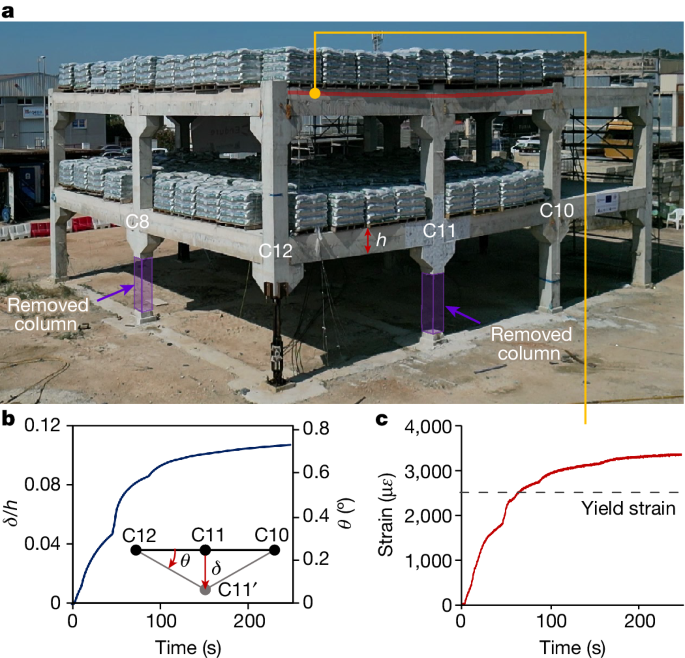
a , Test building during phase 1 of testing after removal of columns C8 and C11. The beam depth ( h ) used to compute the ratio plotted in b is shown and the location of the strain measurement plotted in c is indicated. b , Evolution of beam deflection expressed as a ratio of beam depth at the location of removed column C11. The chord rotation of the beams bridging over this removed column is also indicated using a secondary vertical axis. c , Strain increase in continuity reinforcement in the second-floor beam between C12 and C11.
Source Data
Analysis of the structural response during phase 1 (Supplementary Information Section 4 ) shows that collapse was prevented because of the redistribution of loads through the beams (Fig. 3b,c ), columns (Extended Data Fig. 8 ) and slabs (Supplementary Report 4 ) adjacent to the removed columns. The beams bridging over the removed columns sustained loads through flexural action, as evidenced by the magnitude of the vertical displacement recorded at the removal locations (Fig. 3b ). These values were far too small to allow the development of catenary forces, which only begin to appear when displacements exceed the depth of the beam 40 .
The flexural response of the structure after the loss of two penultimate-edge columns was only able to develop because of the specific reinforcement detailing introduced in the design. This was verified by the increase in tensile strains recorded in the continuous beam reinforcement close to the removed column (Fig. 3c ) and in ties placed between the precast hollow-core planks in the floor system close to column C7 (Supplementary Information Section 4 ). The latter also proves that the slabs contributed notably to load redistribution after column removal.
In general, the structure experienced only small movements and suffered very little permanent damage during phase 1 (Supplementary Information Section 4 ), despite the high imposed loads used for testing. The only reinforcement bars showing some signs of yielding were the continuous reinforcement bars of beams close to the removed columns (Fig. 3c ).
Arresting collapse propagation
Following the removal of two penultimate-edge columns in phase 1, the sudden removal of the C12 corner column in phase 2 triggered a collapse that was arrested along the border delineated by columns C3, C7, C6 and C10 (Fig. 4a–d and Supplementary Video 6 ). Thus, the viability of hierarchy-based collapse isolation design is confirmed.
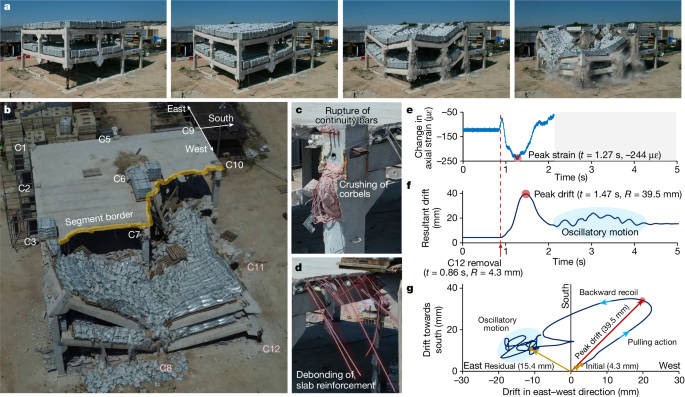
a , Collapse sequence during phase 2 of testing. b , Partial collapse of full-scale test building (design H) after the removal of three columns. The segment border in which collapse propagation was arrested is indicated. The axes shown at column C9 correspond to those used in f to indicate the changing direction of the resultant drift measured at this location. c , Failure of beam–column connections at collapse border. d , Debonding of reinforcement in the floor at collapse border. e , Change in average axial strains measured in column C7. A negative change represents an increase in compressive strains. f , Magnitude of resultant drift measured at C9. g , Change in direction of resultant drift measured at C9. The initial drift after phase 1 of testing and the residual drift after the upright part of the building stabilized are also shown in the plot.
During the initial stages following the removal of C12, the collapsing bays next to this column pulled up the columns on the opposite corner of the building (columns C1, C3 and C6). During this process, column C7 behaves like a pivot point, experiencing a significant increase in compressive forces (Fig. 4e and Supplementary Information Section 5 ). This phenomenon was enabled by the connectivity between collapsing parts and the rest of the structure. If allowed to continue, this could have led to successive column failures and unimpeded collapse propagation. However, during the test, the rupture of continuous reinforcement bars (Fig. 4c ) occurred as the connections failed and halted the transmission of forces to columns. These connection failures occurred before any column failures, as intended by the hierarchy-based collapse isolation design of the structural system. Specifically, this type of connection failure occurred at the junctions with the two columns (C7 and C10) immediately adjacent to the failure origin (around C8, C11 and C12), effectively segmenting the structure along the border shown in Fig. 4b . Segmentation along this border was completed by the total separation of the floor system, which was enabled by the debonding of slab reinforcements at the segment border (Fig. 4d and Supplementary Video 8 ).
Observing the building drift measured at the top of column C9 (Fig. 4f ) enabled us to better understand the nature of forces acting on the building further away from the collapsing region. The initial motion shows the direction of pulling forces generated by the collapsing elements (Fig. 4g ). This drift peaks very shortly after the point in time when separation of the collapsing parts occurs (Fig. 4f ). After this peak, the upright part of the structure recoiled backwards and experienced an attenuated oscillatory motion before finding a new stable equilibrium (Fig. 4g ). The magnitude of the measured peak drift is comparable to the drift limits considered in seismic regions when designing against earthquakes with a 2,500-year return period 41 (Supplementary Information Section 5 ). This indicates that the upright part of the structure was subjected to strong dynamic horizontal forces as it was effectively tugged by the collapsing elements falling to the ground. The building would have failed because of these unbalanced forces had hierarchy-based collapse isolation design not been implemented.
The upright building segment suffered permanent damages as evidenced by the residual drift recorded at the top of column C9 (Fig. 4g ). This is further corroborated by the fact that several reinforcement bars in this part of the structure yielded, particularly in areas close to the segment border (Supplementary Report 5 ). Despite the observed level of damage, safe evacuation and rescue of people from this building segment would still be possible after an extreme event, saving lives that would have been lost had a more conventional robustness design (design C) been used instead.
Discussion and future outlook
Our results demonstrate that the extensive connectivity adopted in conventional robustness design can lead to catastrophic collapse after large initial failures. To address this risk, we have developed and tested a collapse isolation design approach based on controlling the hierarchy of failures occurring during the collapse. Specifically, it is ensured that connection failures occur before column failures, mitigating the risk of collapse propagation throughout the rest of the structural system. The proposed approach has been validated through the partial collapse test of a full-scale precast building, showing that propagating collapses can be arrested at low cost without impairing the ability of the structure to completely prevent collapse initiation after small initial failures.
The reported findings show a last line of defence against major building collapses due to extreme events. This paves the way for the proposed solution to be developed, tested and implemented in different building types with different building elements. This discovery opens opportunities for robustness design that will lead to a new generation of solutions for avoiding catastrophic building collapses.
Building design
Our hierarchy-based collapse isolation approach ensures buildings have sufficient connectivity for operational conditions and small initial failures, yet separate into different parts and isolate a collapse after large initial failures. We chose a precast construction as our main structural system for our case study. A notable particularity of precast systems compared with cast-in-place buildings is that the required construction details can be implemented more precisely. We designed and systematically investigated two precast building designs: designs H and C.
Design H is our building design in which the hierarchy-based collapse isolation approach is applied. Design H was achieved after several preliminary iterations by evaluating various connections and construction details commonly adopted in precast structures. The final design comprises precast columns with corbels connected to a floor system (partially precast beams and hollow-core slabs) through partial-strength beam–column connections (Extended Data Fig. 1 and Supplementary Information Section 1 ). This partial-strength connection was achieved by (1) connecting the bottom part of the beam (precast) to optimally designed dowel bars anchored to the column corbels and (2) passing continuous top beam bars through the columns. With this partial-strength connection, we have more direct control over the magnitude of forces being transferred from the floor system to the columns, which is a key aspect for achieving hierarchy-based collapse isolation. The hierarchy of failures was initially implemented through the beam–column connections (local level) and later verified at the system (global) level.
At the local level, three main components are designed according to the hierarchy-based concept: (1) top continuity bars of the beams; (2) dowel bars connecting beams to corbels; and (3) columns.
Top continuity bars of beams: To allow the structural system to redistribute the loads after small initial failures, top reinforcement bars in all beams were specifically designed to fulfil structural robustness requirements (Extended Data Fig. 3 ). Particularly, we adopted the prescriptive tying rules (referred to as Tie Forces) of UFC 4-023-03 (ref. 9 ) to perform the design of the ties. The required tie strength F i in both the longitudinal and transverse directions for the internal beams is expressed as
For the peripheral beams, the required tie strength F P is expressed as
where w F = floor load (in kN m −2 ); D = dead load (in kN m −2 ); L = live load (in kN m −2 ); L 1 = greater of the distances between the centres of the columns, frames or walls supporting any two adjacent floor spaces in the direction under consideration (in m); L P = 1.0 m; and W C = 1.2 times dead load of cladding (neglected in this design).
These required tie strengths are fulfilled with three bars (20 mm diameter) for the peripheral beams and three bars (25 mm diameter) for the internal beams. These required reinforcement dimensions were implemented through the top bars of the beam and installed continuously (lap-spliced, internally, and anchored with couplers at the ends) throughout the building (Extended Data Fig. 1 ).
Dowel bars connecting the beam and corbel of the column: The design of the dowel bars is one of the key aspects in achieving partial-strength connections that fail at a specific threshold to enable segmentation. These dowel bars would control the magnitude of the internal forces between the floor system and column while allowing for some degree of rotational movement. The dowels were designed to resist possible failure modes using expressions proposed in the fib guidelines 37 . Several possible failure modes were checked: splitting of concrete around the dowel bars, shear failure of the dowel bars and forming a plastic hinge in the dowel. The shear capacity of a dowel bar loaded in pure shear can be determined according to the Von Mises yield criterion:
where f yd is the design yield strength of the dowel bar and A s is the cross-sectional area of the dowel bar. In case of concrete splitting failure, the highly concentrated reaction transferred from the dowel bar shall be designed to be safely spread to the surrounding concrete. The strut and tie method is recommended to perform such a design 42 . If shear failure and splitting of concrete do not occur prematurely, the dowel bar will normally yield in bending, indicated by the formation of a plastic hinge. This failure mode is associated with a significant tensile strain at the plastic hinge location of the dowel bar and the crushing of concrete around the compression part of the dowel. The shear resistance achieved at this state for dowel (ribbed) bars across a joint of a certain width (that is, the neoprene bearing) can be expressed as
where α 0 is a coefficient that considers the bearing strength of concrete and can be taken as 1.0 for design purposes, α e is a coefficient that considers the eccentricity, e is the load eccentricity and shall be computed as the half of the joint width (half of the neoprene bearing thickness), Φ and A s are the diameter and the cross-sectional area of the dowel bar, respectively, f cd,max is the design concrete compressive strength at the stronger side, σ sn is the local axial stress of the dowel bar at the interface location, \({f}_{{\rm{yd}},{\rm{red}}}={f}_{{\rm{yd}}}-{\sigma }_{{\rm{sn}}}\) is the design yield strength available for dowel action, f yd is the yield strength of the dowel bar and μ is the coefficient of friction between the concrete and neoprene bearing. By performing the checks on these three possible failure modes, we selected the final (optimum) design with a two dowel bars (20 mm diameter) configuration.
Columns: The proposed hierarchy-based approach requires columns to have adequate capacity to resist the internal forces transmitted by the floor system during a collapse. By fulfilling this strength hierarchy, we can ensure and control that failure happens at the connections first before the columns fail, thus preventing collapse propagation. The columns were initially designed according to the general procedure prescribed by building standards. Then, the resulting capacity was verified using the modified compression field theory (MCFT) 43 to ensure that it was higher than the maximum expected forces transmitted by the connection to the floor system. MCFT was derived to consistently fulfil three main aspects: equilibrium of forces, compatibility and rational stress–strain relationships of cracked concrete expressed as average stresses and strains. The principal compressive stress in the concrete f c 2 is expressed not only as a function of the principal compressive strain ε 2 but also of the co-existing principal tensile strain ε 1 , known as the compression softening effect:
where f c 2max is the peak concrete compressive strength considering the perpendicular tensile strain, \({f}_{c}^{{\prime} }\) is the uniaxial compressive strength, and \({\varepsilon }_{{c}^{{\prime} }}\) is the peak uniaxial concrete compressive strain and can be taken as −0.002. In tension, concrete is assumed to behave linearly until the tensile strength is achieved, followed by a specific decaying function 43 . Regarding aggregate interlock, the shear stress that can be transmitted across cracks v ci is expressed as a function of the crack width w , and the required compressive stress on the crack f ci (ref. 44 ):
where a refers to the maximum aggregate size in mm and the stresses are expressed in MPa. The MCFT analytical model was implemented to solve the sectional and full-member response of beams and columns subjected to axial, bending and shear in Response 2000 software (open access) 45 , 46 . In Response 2000, we input key information, including the geometries of the columns, reinforcement configuration and the material definition for the concrete and the reinforcing bars. Based on this information, we computed the M – V (moment and shear interaction envelope) and M – N (moment and axial interaction envelope) diagrams that represent the capacity of the columns. The results shown in Extended Data Fig. 4 about the verification of the demand and capacity envelopes were obtained using the analytical procedure described here.
At the global level, the initially collapsing regions of the building generate a significant magnitude of dynamic unbalanced forces. The rest of the building system must collectively resist these unbalanced forces to achieve a new equilibrium state. Depending on the design of the structure, this phenomenon can lead to two possible scenarios: (1) major collapse due to failure propagation or (2) partial collapse only of the initially affected regions. The complex interaction between the three-dimensional structural system and its components must be accounted for to evaluate the structural response during collapse accurately. Advanced computational simulations, described in the ‘ Modelling strategy ’ section, were adopted to analyse the global building to verify that major collapse can be prevented. The final design obtained from the local-level analysis (top continuity bars, dowel bars and columns) was used as an input for performing the global computational simulations. Certain large initial failures deemed suitable for evaluating the performance of this building were simulated. In case failure propagation occurs, the original hierarchy-based design must be further adapted. An iterative process is typically required involving several simulations with various building designs to achieve an optimum result that balances the cost and desired collapse performance. The final iteration of design H, which fulfils both the local and global hierarchy checks, is provided in Extended Data Fig. 1 .
Design C is a conventional building design that complies with current robustness standards but does not explicitly fulfil our hierarchy-based approach. The same continuity bars used in design H were used in design C. We adopted a full-strength connection as recommended by the fib guideline 37 . The guideline promotes full connectivity to enhance the development of alternative load paths for preventing collapse initiation. In design C, we used a two dowel bars (32 mm diameter) configuration to ensure full connectivity when the beams are working at their maximum flexural capacity. Another main difference was that the columns in design C were designed according to codes and current practice (optimal solution) without explicitly checking that hierarchy-based collapse isolation criteria are fulfilled. The final design of the columns and connections adopted in design C is provided in Extended Data Fig. 1 .
Modelling strategy
We used the AEM implemented in the Extreme Loading for Structures software to perform all the computational simulations presented in this study 47 (Extended Data Figs. 2 – 5 and 7 and Supplementary Videos 1 , 2 , 3 and 7 ). We chose the AEM for its ability to represent all phases of a structural collapse efficiently and accurately, including element separation (fracture), contact and collision 47 . The method discretizes a continuum into small, finite-size elements (rigid bodies) connected using multiple normal and shear springs distributed across each element face. Each element has six degrees of freedom, three translational and three rotational, at its centre, whereas the behaviour of the springs represents all material constitutive models, contact and collision response. Despite the simplifying assumptions in its formulation 48 , its ability to accurately account for large displacements 49 , cyclic loading 50 , as well as the effects of element separation, contact and collision 51 has been demonstrated through many comparisons with experimental and theoretical results 47 .
Geometric and physical representations
We modelled each of the main structural components of the building separately, including the columns, beams, corbels and hollow-core slabs. We adopted a consistent mesh size with an average (representative) size of 150 mm. Adopting this mesh configuration resulted in a total number of 98,611 elements. We defined a specialized interface with no tensile or shear strength between the precast and cast-in-situ parts to allow for localized deformations that occur at these locations. The behaviour of the interface was mainly governed by a friction coefficient of 0.6, which was defined according to concrete design guidelines 52 , 53 , 54 . The normal stiffness of these interfaces corresponded to the stiffness of the concrete cast-in-situ topping. The elastomeric bearing pads supporting the precast beams on top of the corbels were also modelled with a similar interface having a coefficient of friction of 0.5 (ref. 55 ).
Element type and constitutive models
We adopted an eight-node hexahedron (cube) element with the so-called matrix-springs connecting adjacent cubes to model the concrete parts. We adopted the compression model in refs. 56 , 57 to simulate the behaviour of concrete under compression. Three specific parameters are required to define the response envelope: the initial elastic modulus, the fracture parameter and the compressive plastic strain. For the behaviour in tension, the spring stiffness is assumed to be linear (with the initial elastic modulus) until reaching the cracking point. The shear behaviour is considered to remain linear up to the cracking of the concrete. The interaction between normal compressive and shear stress follows the Mohr–Coulomb failure criterion. After reaching the peak, the shear stress is assumed to drop to a certain residual value affected by the aggregate interlock and friction at the cracked surface. By contrast, under tension, both normal and shear stresses drop to zero after the cracking point. The steel reinforcement bars were simulated as a discrete spring element with three force components: the normal spring takes the principal/normal forces parallel to the rebar, and two other springs represent the reinforcement bar in shear (dowelling). Three distinct stages are considered: elastic, yield plateau and strain hardening. A perfect bond behaviour between the concrete and the reinforcement bars was adopted. We assigned the material properties based on the results of the laboratory tests performed on reinforcement bars and concrete cylinders (Supplementary Information Section 2 ).
Boundary conditions and loading protocol
We assumed that all the ground floor columns are fully restrained in all six degrees of freedom at the base location. This assumption is reasonable, as we expected that the footing would provide sufficient rigidity to constrain any significant deformations. We assigned the reflecting domain boundaries to allow a realistic representation of the collapsing elements (debris) that might fall and rebound after hitting the ground. The ground level was assumed to be at the same elevation at which the column bases are restrained. We applied the additional imposed uniform distributed load as an extra volume of mass assigned to the slabs. To perform the column removal, we used the element removal feature that allows some specific designated elements to be immediately removed at the beginning of the loading stage. This represents a dynamic (sudden) removal, as we expected from the actual test.
Extended Data Tables 1 and 2 summarize all key parameters and assumptions adopted in the modelling process. To validate these assumptions for simulating the precast building designs described previously, it was ensured that the full-scale test performed as part of this work captured all relevant phenomena influencing collapse (large displacements, fracture, contact and collision).
Experiment and monitoring design
We used computational simulations of design H subjected to different initial failure scenarios to define a suitable testing sequence and protocol. The geometry, reinforcement configurations, connection system and construction details of the purpose-built specimen representing design H are provided in Supplementary Information Section 1 and Supplementary Video 4 .
Initial failure scenarios
Initial failure scenarios occurring in edge and corner regions of the building were prioritized for this study because they are usually exposed to a wider range of external threats 58 , 59 , 60 , 61 . After performing a systematic sensitivity study, we identified three critical scenarios (Extended Data Fig. 5 and Supplementary Video 2 ):
Scenario 1: a scenario involving a two-column failure—a corner column and the adjacent edge column. We determined that the required gravity loads to induce collapse equal 11.5 kN m −2 and that partial collapse would occur locally.
Scenario 2: a scenario involving a three-column failure—two corner columns and the edge column in between the two corner columns. We determined that the required gravity loads to induce collapse equal 8.5 kN m −2 and that segmentation (partially collapsing two bays) would take place only across one principal axis of the building.
Scenario 3: a scenario involving a three-column failure: one corner column and two edge columns on both sides of the corner column. We determined that the required gravity loads to induce collapse equal 7.0 kN m −2 and that segmentation (partially collapsing three bays) would take place across both principal axes of the building.
Scenario 3 was ultimately chosen after considering three main aspects: (1) it requires the lowest gravity loads to trigger partial collapse; (2) the failure mode involves activating segmentation mechanisms in two principal axes of the building (more realistic collapse pattern); and (3) the ratio of the area of the intact part and the collapsed part was predicted to be 50:50, leading to the largest collapse area among the three scenarios.
Testing phases
To allow us to investigate the behaviour of the building specimen under small and large initial failures in only one building specimen, we decided to perform two separate testing phases. Phase 1 involved the quasi-static (gradual) removal of two edge columns (C8 and C11), whereas phase 2 involved the sudden removal of the corner column (C12) found between the columns removed in phase 1. A uniformly distributed load of 11.8 kN m −2 was applied only on the bays directly adjacent to these three columns without loading the remaining bays (Supplementary Video 5 ). This was achieved by placing more than 8,000 sandbags in the designated bays on the two floors (the first- and second-floor slabs). We performed additional computational simulations to compare this partial loading configuration and loading of the entire building. The simulations indicated that both would have resulted in almost identical final collapse states (Extended Data Fig. 7 and Supplementary Video 3 ). However, the partial loading configuration introduced a higher magnitude of unbalanced moment to surrounding columns, which induces more demanding bending and shear in columns. Simulations confirmed that the lateral drift of the remaining part of the building would be higher when only three bays are loaded, indicating that its stability would be tested to a greater extent with this loading configuration (Extended Data Fig. 7 ).
Specially designed elements to trigger initial failures
We designed special devices to perform the column removal (Extended Data Fig. 6 ). For phase 1, we constructed two hanging concrete columns (C8 and C11) supported only on a vertical hydraulic jack. The pressure in the jack could be gradually released from a safe distance to remove the vertical reaction supporting the column. In phase 2, a three-steel-hinged column was used as the corner column. The middle part of the column represents a central hinge that was able to rotate if unlocked. During the second testing phase, we unlocked the hinge by pulling the column from outside the building using a forklift to induce a slight destabilization. This resulted in a sudden removal of the corner column C12 and the initiation of the collapse.
Monitoring plan
To monitor the structural behaviour, we heavily instrumented the building specimen with multiple sensors. A total of 57 embedded strain gauges, 17 displacement transducers and 5 accelerometers were placed at key locations in different parts of the structure (Extended Data Fig. 8 and Supplementary Information Section 3 ) during all phases of testing. The data from these sensors (Supplementary Information Sections 4 and 5 ) were complemented by the pictures and videos of the structural response captured by five high-resolution cameras and two drones (Supplementary Videos 6 and 8 ).
Data availability
All experimental data recorded during testing of the full-scale building are available from Zenodo ( https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.10698030 ) 62 . Source data are provided with this paper.
National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST). Champlain Towers South collapse. NIST https://www.nist.gov/disaster-failure-studies/champlain-towers-south-collapse-ncst-investigation (2022).
Jones, M. Nigeria’s Ikoyi building collapse: anger and frustration grows. BBC News (4 November 2021).
Berg, R. Iran building collapse death toll jumps to 26. BBC News (27 May 2022).
Corres Peiretti, H. & Romero Rey, E. Reconstrucción “Módulo D” aparcamiento Madrid Barajas T-4. In IV Congreso de Asociación científico-técnica del hormigón estructural (ACHE) (2008).
Manik, J. A. & Yardley, J. Building collapse in Bangladesh leaves scores dead. The New York Times (24 April 2013).
Caredda, G. et al. Learning from the progressive collapse of buildings. Dev. Built Environ. 15 , 100194 (2023).
Article Google Scholar
Adam, J. M., Parisi, F., Sagaseta, J. & Lu, X. Research and practice on progressive collapse and robustness of building structures in the 21st century. Eng. Struct. 173 , 122–149 (2018).
European Committee for Standardization (CEN). EN 1991-1-7:2006: Eurocode 1 - Actions on Structures - Part 1-7: General Actions - Accidental Actions (CEN, 2006).
Department of Defense (DoD). UFC 4-023-03. Design of Buildings to Resist Progressive Collapse , 34–37 (2016).
Loizeaux, M. & Osborn, A. E. Progressive collapse—an implosion contractor’s stock in trade. J. Perform. Constr. Facil. 20 , 391–402 (2006).
United Nations Office for Disaster Risk Reduction (UNDRR). The Human Cost of Disasters: An Overview of the Last 20 Years (2000–2019) . (UNDRR, 2020).
Wake, B. Buildings at risk. Nat. Clim. Change 11 , 642 (2021).
Article ADS Google Scholar
Starossek, U. Progressive Collapse of Structures (ICE, 2017).
Moehle, J. P., Elwood, K. J. & Sezen, H. Gravity load collapse of building frames during earthquakes. in SP-197: S.M. Uzumeri Symposium - Behavior and Design of Concrete Structures for Seismic Performance (American Concrete Institute, 2002).
Gurley, C. Progressive collapse and earthquake resistance. Pract. Period. Struct. Des. Constr. 13 , 19–23 (2008).
Lu, X., Lu, X., Guan, H. & Ye, L. Collapse simulation of reinforced concrete high-rise building induced by extreme earthquakes. Earthq. Eng. Struct. Dyn. 42 , 705–723 (2013).
Tellman, B. et al. Satellite imaging reveals increased proportion of population exposed to floods. Nature 596 , 80–86 (2021).
Article ADS CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Rentschler, J. et al. Global evidence of rapid urban growth in flood zones since 1985. Nature 622 , 87–92 (2023).
Cantelmo, C. & Cuomo, G. Hydrodynamic loads on buildings in floods. J. Hydraul. Res. 59 , 61–74 (2021).
Lonetti, P. & Maletta, R. Dynamic impact analysis of masonry buildings subjected to flood actions. Eng. Struct. 167 , 445–458 (2018).
Li, Y. & Ellingwood, B. R. Hurricane damage to residential construction in the US: Importance of uncertainty modeling in risk assessment. Eng. Struct. 28 , 1009–1018 (2006).
Khanduri, A. & Morrow, G. Vulnerability of buildings to windstorms and insurance loss estimation. J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 91 , 455–467 (2003).
Ozturk, U. et al. How climate change and unplanned urban sprawl bring more landslides. Nature 608 , 262–265 (2022).
Luo, H. Y., Zhang, L. L. & Zhang, L. M. Progressive failure of buildings under landslide impact. Landslides 16 , 1327–1340 (2019).
Thöns, S. & Stewart, M. G. On the cost-efficiency, significance and effectiveness of terrorism risk reduction strategies for buildings. Struct. Saf. 85 , 101957 (2020).
Ellingwood, B. et al. NISTIR 7396: Best Practices for Reducing the Potential for Progressive Collapse in Buildings (National Institute of Standards and Technology, 2007).
Rockström, J. et al. A safe operating space for humanity. Nature 461 , 472–475 (2009).
Article ADS PubMed Google Scholar
Steffen, W. et al. Planetary boundaries: guiding human development on a changing planet. Science 347 , 1259855 (2015).
Article PubMed Google Scholar
United Nations Office for Disaster Risk Reduction (UNDRR). Principles for Resilient Infrastructure (UNDRR, 2022).
General Services Administration (GSA). Alternate Path Analysis & Design Guidelines for Progressive Collapse Resistance (GSA, 2016).
Izzuddin, B. A. & Sio, J. Rational horizontal tying force method for practical robustness design of building structures. Eng. Struct. 252 , 113676 (2022).
Starossek, U. & Wolff, M. Design of collapse-resistant structures. In JCSS and IABSE Workshop on Robustness of Structures (2005).
Russell, J. M., Sagaseta, J., Cormie, D. & Jones, A. E. K. Historical review of prescriptive design rules for robustness after the collapse of Ronan Point. Structures 20 , 365–373 (2019).
Cormie, D. Manual for the Systematic Risk Assessment of High-Risk Structures Against Disproportionate Collapse (The Institution of Structural Engineers, 2013).
Baban, N. S., Orozaliev, A., Kirchhof, S., Stubbs, C. J. & Song, Y.-A. Biomimetic fracture model of lizard tail autotomy. Science 375 , 770–774 (2022).
Article ADS MathSciNet CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Chen, Y., Okudan, G. E. & Riley, D. R. Sustainable performance criteria for construction method selection in concrete buildings. Autom. Constr. 19 , 235–244 (2010).
fib Commission 6. Guide to Good Practice: Structural Connections for Precast Concrete Buildings, Bulletin 43 (fib, 2008).
European Committee for Standardization (CEN). EN 1990:2002: Eurocode 0 - Basis of Structural Design (CEN, 2002).
American Society of Civil Engineers (ASCE). Standard for Mitigation of Disproportionate Collapse Potential in Buildings and Other Structures (American Society of Civil Engineers, 2023).
Lew, H. S. et al . NIST Technical Note 1720: An Experimental and Computational Study of Reinforcd Concrete Assemblies Under a Column Removal Scenario (NIST, 2011).
American Society of Civil Engineers. ASCE 7-2002: Minimum Design Loads for Buildings and Other Structures (American Society of Civil Engineers, 2002).
fib Commission 2. Design and Assessment With Strut-and-Tie Models and Stress Fields: From Simple Calculations to Detailed Numerical Analysis, Bulletin 100 (fib, 2021).
Vecchio, F. J. & Collins, M. P. The modified compression-field theory for reinforced concrete elements subjected to shear. ACI Struct. J. 83 , 219–231 (1986).
Google Scholar
Walraven, J. C. Fundamental analysis of aggregate interlock. J. Struct. Div. 107 , 2245–2270 (1981).
Bentz, E. C. Response Manual https://www.hadrianworks.com/about-programs.html (2019).
Bentz, E. C. Sectional Analysis of Reinforced Concrete Members . Doctoral dissertation, Univ. Toronto (2000).
Extreme Loading for Structures. Extreme Loading ® for Structures Theoretical Manual v.9 www.extremeloading.com/wp-content/uploads/els-v9-theoretical-manual.pdf (ASI, 2004).
Meguro, K. & Tagel-Din, H. Applied element method for structural analysis. Doboku Gakkai Ronbunshu 2000 , 31–45 (2000).
Tagel-Din, H. & Meguro, K. Applied element method for dynamic large deformation analysis of structures. Doboku Gakkai Ronbunshu 2000 , 1–10 (2000).
Tagel-Din, H. & Meguro, K. Analysis of a small scale RC building subjected to shaking table tests using applied element method. In 12th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering, Auckland, New Zealand (2000).
Tagel-Din, H. & Meguro, K. Applied element simulation for collapse analysis of structures. Bull. Earthq. Resist. Struct. 32 , 113–123 (1999).
European Committee for Standardization (CEN). EN 1992-1-1: Eurocode 2: Design of Concrete Structures - Part 1-1: General Rules and Rules for Buildings (CEN, 2004).
Precast/Prestressed Concrete Institute. PCI Design Handbook: Precast and Prestressed Concrete 7th edn (2010).
ACI Committee 318. Building Code Requirements for Structural Concrete (ACI 318-08) and Commentary (ACI, 2008).
Jun, X., Zhang, Y. & Shan, C. Compressive behavior of laminated neoprene bridge bearing pads under thermal aging condition. AIP Conf. Proc. 1890 , 040018 (2017).
Maekawa, K. The Deformational Behavior and Constitutive Equation of Concrete Based on the Elasto-Plastic and Fracture Model . Doctoral dissertation, Univ. Tokyo (1985).
Okamura, H. & Maekawa, K. Non-linear analysis and constitutive models of reinforced concrete. In Conf. Computer-Aided Analysis and Design of Concrete Structures, Austria (1990).
Makoond, N., Shahnazi, G., Buitrago, M. & Adam, J. M. Corner-column failure scenarios in building structures: current knowledge and future prospects. Structures 49 , 958–982 (2023).
Adam, J. M., Buitrago, M., Bertolesi, E., Sagaseta, J. & Moragues, J. J. Dynamic performance of a real-scale reinforced concrete building test under a corner-column failure scenario. Eng. Struct. 210 , 110414 (2020).
Starossek, U. Progressive Collapse of Structures 2nd edn (ICE, 2017).
Zhao, Z., Guan, H., Li, Y., Xue, H. & Gilbert, B. P. Collapse-resistant mechanisms induced by various perimeter column damage scenarios in RC flat plate structures. Structures 59 , 105716 (2024).
Makoond, N., Setiawan, A., Buitrago, M. & Adam, J. M. Arresting failure propagation in buildings through collapse isolation—experimental dataset. Zenodo https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.10698030 (2024).
Download references
Acknowledgements
This article is part of a project (Endure) that has received funding from the European Research Council (ERC) under the Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme of the European Union (grant agreement no. 101000396). We acknowledge the assistance of the following colleagues from the ICITECH-UPV institute in preparing and executing the full-scale building tests: J. J. Moragues, P. Calderón, D. Tasquer, G. Caredda, D. Cetina, M. L. Gerbaudo, L. Marín, M. Oliver and G. Sempértegui. We are also grateful to the Levantina, Ingeniería y Construcción S.L. (LIC) company for providing human resources and access to their facilities for testing. Finally, we thank A. Elfouly and Applied Science International for their support in performing simulations.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
ICITECH, Universitat Politècnica de València, Valencia, Spain
Nirvan Makoond, Andri Setiawan, Manuel Buitrago & Jose M. Adam
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
N.M. prepared the main text, performed the computational simulations and validated the test results. A.S. analysed the experimental data, performed data curation and prepared the Methods section. M.B. contributed to the design of the building specimen, the design of the test and data curation. J.M.A. contributed to the design of the research methodology, supervised the research and was responsible for funding acquisition. N.M., A.S. and M.B. contributed to the execution of the experimental test and to preparing figures, extended data and supplementary information. All authors interpreted the test and simulation results and edited the paper.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Jose M. Adam .
Ethics declarations
Competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Peer review
Peer review information.
Nature thanks Valerio De Biagi and the other, anonymous, reviewer(s) for their contribution to the peer review of this work. Peer reviewer reports are available.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Extended data figures and tables
Extended data fig. 1 summary of building designs..
General building layout, connection details, and reinforcement configurations of Design H (“Hierarchy-based”) and Design C (“Conventional”).
Extended Data Fig. 2 Comparison of measured experimental data and simulation predictions.
a, Location of shown comparisons. All data shown in panels b to d refer to the change in structural response following the sudden removal of column C12 (after having removed columns C8 and C11 in a previous phase). b, Change in axial load in lower part of column C7. c, Change in axial load in lower part of column C9. d , Change in drift measured in both directions parallel to each building side.
Extended Data Fig. 3 Computational simulations of Design H and Design C subjected to small initial failures.
Principal strains and relative vertical displacement at the location of column C11 after removal of columns C8 and C11 from Design H ( a ) and Design C ( b ).
Extended Data Fig. 4 Demand and capacity envelopes of internal forces in Designs H and C subjected to large initial failures.
Evolution of axial loads, bending moments, and shear forces in column C7 compared to lower and upper bounds of its capacity after the removal of columns C8, C11, and C12 from Design H ( a ) and Design C ( b ).
Extended Data Fig. 5 Initial failure scenarios considered for testing.
Simulation of three different initial failure scenarios that were considered for testing. Scenario 3 was selected for the experimental test.
Extended Data Fig. 6 Specially designed removable supports to perform column removals.
Removable supports designed for quasi-static column removals in phase 1 and sudden column removal in phase 2.
Extended Data Fig. 7 Comparison of simulations of fully loaded and partially loaded building specimen.
a, Loaded bays, deformed shape, and principal normal strains following the sudden removal of column C12 (after having removed columns C8 and C11 in a previous phase). b, Horizontal displacement in the east-west and north-south directions at the top of columns C1 and C9 (2nd floor).
Extended Data Fig. 8 Measured redistribution of column axial forces during phase 1.
Maximum change in axial load of columns during phase 1 of testing based on recorded strain measurements.
Supplementary information
Supplementary information.
This file contains a supplementary test report that covers as-built building design, material properties, monitoring plan, structural response in phase 1 of testing and structural response in phase 2 of testing.
Peer Review File
Supplementary video 1.
Structural response of designs H and C.
Supplementary Video 2
Initial failure scenarios.
Supplementary Video 3
Comparison of partial and full loading.
Supplementary Video 4
Construction of the building.
Supplementary Video 5
An aerial view of the building before the test.
Supplementary Video 6
Multiple perspectives of the partial collapse of the building specimen in testing phase 2.
Supplementary Video 7
Experimental and simulation comparison of the partial collapse in testing phase 2.
Supplementary Video 8
Post-collapse inspection drone video.
Source data
Source data fig. 3, source data fig. 4, source data extended data fig. 2, source data extended data fig. 3, source data extended data fig. 4, rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Makoond, N., Setiawan, A., Buitrago, M. et al. Arresting failure propagation in buildings through collapse isolation. Nature 629 , 592–596 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-024-07268-5
Download citation
Received : 07 December 2023
Accepted : 05 March 2024
Published : 15 May 2024
Issue Date : 16 May 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-024-07268-5
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines . If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
Sign up for the Nature Briefing newsletter — what matters in science, free to your inbox daily.
An alternative soil erodibility estimation approach for data-scarce regions: a case study in Ethiopian Rift Valley Lake Basin
- Published: 19 May 2024
Cite this article

- Alemu Osore Aga 1 &
- Assefa M. Melesse 2
Explore all metrics
Soil erodibility (K) is an essential factor for erosion prediction, conservation planning and assessment of sediment-related environmental problems. K estimation methods have been developed in many soil erosion and water quality models, which are developed for soil data-rich areas and pose a challenge for areas with limited data. Unlike others, using the erosion productivity impact calculator (EPIC) model, the required soil parameters for calculating K can be extracted from the Food and Agricultural Organization (FAO) world database. To verify the FAO soil database and develop an alternative K method (KET) by mimicking the equation of K used in the EPIC model, we collected 203 soil samples from different soil units in the Ethiopian Rift Valley Lake Basin (ERVLB). Unlike the K of EPIC model, KET is developed based on the physical properties of soils that can be easily measured in a laboratory. The results from KET were compared with those from the EPIC-K. Statistically, the performance of KET is excellent and the soil analysis result of ERVLB deviates from the FAO soil database on lower altitude areas of the basin. When KET is projected for the overall soil units of the country, it predicts 35.7% of the country’s soil with less than ± 5% relative error. On average, the KET can be applied to overall country soils with a relative error of − 9.88% with a standard deviation of 6.4. By applying KET, the ERVLB and the country K map were produced. The developed K map of ERVLB and the country can be used for sediment-related studies since it is validated using field measured soil data’s.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this article
Price includes VAT (Russian Federation)
Instant access to the full article PDF.
Rent this article via DeepDyve
Institutional subscriptions
Similar content being viewed by others
Reliability of soil erodibility estimation in areas outside the us: a comparison of erodibility for main agricultural soils in the us and china.
Depth of the pedological profile as a conditioning factor of soil erodibility (RUSLE K-Factor) in Ecuadorian basins
Using soil erosion as an indicator for integrated water resources management: a case study of Ruiru drinking water reservoir, Kenya
Data availability.
You can request access to the study’s data from the corresponding author.
Addis, H. K., & Klik, A. (2015). Predicting the spatial distribution of soil erodibility factor using USLE nomograph in an agricultural watershed, Ethiopia. International Soil and Water Conservation Research, 3 , 282–290. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.iswcr.2015.11.002
Article Google Scholar
Aga, A.O. (2019). Modeling sediment yield, transport and deposition in the data scarce region of Ethiopian Rift Valley Lake Basin (PhD Dissertation). Addis Ababa Institute of Technology, Addis Ababa.
Aga, A. O. (2023). Examining sediment accumulation pattern and storage capacity loss of Lake Ziway, Ethiopia. International Journal of Water, 15 , 232–247. https://doi.org/10.1504/IJW.2023.133993
Aga, A. O., Chane, B., & Melesse, A. M. (2018). Soil erosion modelling and risk assessment in data scarce Rift Valley Lake Regions, Ethiopia. Water, 10 , 1–17. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10111684
Aga, A. O., Melesse, A. M., & Chane, B. (2019). Estimating the sediment flux and budget for a data limited Rift Valley Lake in Ethiopia. Hydrology, 6 , 1–23. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology6010001
Aga, A. O., Melesse, A. M., & Chane, B. (2020). An alternative empirical model to estimate watershed sediment yield based on hydrology and geomorphology of the basin in data-scarce Rift Valley Lake Regions, Ethiopia. Geosciences, 10 , 31. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences10010031
Aliye, M. A., Aga, A. O., Tadesse, T., & Yohannes, P. (2020). Evaluating the performance of HEC-HMS and SWAT hydrological models in simulating the rainfall-runoff process for data scarce region of Ethiopian Rift Valley Lake Basin. Open Journal of Modern Hydrology, 10 , 105–122. https://doi.org/10.4236/ojmh.2020.104007
Anache, J. A. A., Bacchi, C. G. V., Panachuki, E., & Sobrinho, T. A. (2016). Assessment of methods for predicting soil erodibility in soil loss modeling. Geociências (são Paulo), 34 , 32–40.
Google Scholar
Assouline, S. (2006). Modeling the relationship between soil bulk density and the hydraulic conductivity function. Vadose Zone Journal, 5 , 697–705. https://doi.org/10.2136/vzj2005.0084
Auerswald, K., Fiener, P., Martin, W., & Elhaus, D. (2014). Use and misuse of the K factor equation in soil erosion modeling: An alternative equation for determining USLE nomograph soil erodibility values. CATENA, 118 , 220–225. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2014.01.008
Ayele, H. A., Aga, A. O., Belayneh, L., & Wanjala, T. W. (2023). Hydrological responses to land use/land cover changes in Koga Watershed, Upper Blue Nile, Ethiopia. Geographies, 3 , 1–22.
Carter, M. R. (1990). Relationship of strength properties to bulk density and macroporosity in cultivated loamy sand to loam soils. Soil and Tillage Research, 15 , 257–268. https://doi.org/10.1016/0167-1987(90)90082-O
Römkens, M.J., Young, R.A., Poesen, J.W.A., McCool, D.K., El-Swaify, S.A., Bradford, J.M. (1997). Chapter 3. Soil erodibility factor In: K. G. Renard, G. R. Foster, G. A. Weesies, D. K. McCool, and D. C. Yoder (Eds.), Predicting soil erosion by water: a guide to conservation planning with the Revised Universal Soil Equation (RUSLE). Agriculture Handbook No. 703. Washington, D.C.: US Department of Agriculture.
Dananto, M., Aga, A. O., Yohannes, P., & Shura, L. (2022). Assessing the water-resources potential and soil erosion hotspot areas for sustainable land management in the Gidabo Watershed, Rift Valley Lake Basin of Ethiopia. Sustainability, 14 , 1–19.
Dec, D., Dörner, J., Becker-Fazekas, O., & Horn, R. (2008). Effect of bulk density on hydraulic properties of homogenized and structured soils. The Journal of Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 8 , 1–13.
Dechasa, A., Aga, A. O., & Dufera, T. (2022). Erosion risk assessment for prioritization of conservation measures in the watershed of Genale dawa-3 hydropower dam, Ethiopia. Quaternary, 5 , 39. https://doi.org/10.3390/quat5040039
Defersha, M. B., & Melesse, A. M. (2012). Field-scale investigation of the effect of land use on sediment yield and runoff using runoff plot data and models in the Mara River basin, Kenya. CATENA, 89 , 54–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2011.07.010
Defersha, M. B., Quraishi, S., & Melesse, A. (2010). Interrill erosion, runoff and sediment size distribution as affected by slope steepness and antecedent moisture content. Hydrology and Earth System Sciences Discussions, 7 , 6447–6489. https://doi.org/10.5194/hessd-7-6447-2010
García, A. J. H., Jaime, Y. N. M., Maryelis, Á., Contreras, Z., Bastardo, L. D. S., & Subero, F. A. (2012). Savanna soil water content effect on its shear strength-compaction relationship. Revista Científica UDO Agrícola, 12 , 324–337.
Gashaw, T., Tulu, T., & Argaw, M. (2017). Erosion risk assessment for prioritization of conservation measures in Geleda watershed, Blue Nile basin, Ethiopia. Environmental Systems Research . https://doi.org/10.1186/s40068-016-0078-x
Geleta, H.I. (2011). Watershed Sediment Yield Modeling for Data Scarce Areas. PhD Dissertation, Institut fur Wasserbau der Universität Stuttgart Von, Germany.
Grey, O., St, F., Webber, D., Setegn, S., & Melesse, A. M. (2014). Application of the soil and water assessment tool (SWAT model) on a small tropical island (Great River watershed, Jamaica) as a tool in integrated watershed and coastal zone management. The Journal of Tropical Biology and Conservation, 62 , 293–305.
Helldén, U. (1987). An assessment of woody biomass, community forests, land use and soil erosion in Ethiopia. A feasibility study on the use of remote sensing and GIS [geographical information system]-analysis for planning purposes in developing countries . Lund University Press.
Hurni, H. (1985). Erosion-productivity-conservation systems in Ethiopia, in: Proceedings of Paper Presented at the 4th International Conference, Soil Conservation. Maracay, Venezuela.
Jepsen, R., Roberts, J., & Lick, W. (1997). Effects of bulk density on sediment erosion rates. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 99 , 21–31. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1018355626070
Article CAS Google Scholar
Juliana, J.M., Melesse, A.M. (2015). Sediment Yield modeling and dentification of Erosion hotspots in ropical watersheds: The case of Upper Ruvu catchment in Tanzania. Addis Ababa Ethiopia.
Mathewos, M., & Aga, A. O. (2023). Evaluation of the linkages between ecosystem services and land use/land cover changes in Matenchose watershed, Rift Valley Basin. Ethiopia. Quaternary, 6 , 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/quat6010013
Mekonnen, M., Melesse, A.M. (2011). Soil Erosion Mapping and Hotspot Area Identification Using GIS and Remote Sensing in Northwest Ethiopian Highlands, Near Lake Tana, in: Nile River Basin. Springer, Dordrecht, pp. 207–224. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-007-0689-7_10
Melesse, A., & Abtew, W. (Eds.). (2016). Landscape dynamics, soils and hydrological processes in varied climates . Springer International Publishing.
Miheretu, B. A., & Yimer, A. A. (2018). Estimating soil loss for sustainable land management planning at the Gelana sub-watershed, northern highlands of Ethiopia. International Journal of River Basin Management, 16 , 41–50. https://doi.org/10.1080/15715124.2017.1351978
Moriasi, D. N., Arnold, J. G., Liew, M. W. V., Bingner, R. L., Harmel, R. D., & Veith, T. L. (2007). Model evaluation guidelines for systematic quantification of accuracy in watershed simulations. Transactions of the ASABE, 50 , 885–900. https://doi.org/10.13031/2013.23153
MOWR (2010). The federal democratic republic of Ethiopia-Ministry of Water Resources: Rift Valley Lakes basin integrated resources development master plan study project.
Renard, K., Foster, G.R., Weesies, G.A., McCool, D.K., Yoder, D.C. (1997). Predicting soil erosion by water, a guild to conservation planning with the Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation (RUSLE). USDA Agricultural Handbook No. 703.Washington D.C., USA: U.S. Government Printing Office.
Römkens, M.J.M., Poesen, J., Wang, J.Y. (1988). Relationship between the USLE Soil Erodibility Factor and soil properties. pp. 371–385.
Römkens, M. J. M., Roth, C. B., & Nelson, D. W. (1977). Erodibility of selected clay subsoils in relation to physical and chemical properties 1. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 41 , 954–960. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj1977.03615995004100050030x
Sharply, A.N., Williams, J.R. (1990). EPIC-Erosion/Productivity Impact Calculator I, model documentation.
Torri, D., Poesen, J., & Borselli, L. (1997). Predictability and uncertainty of the soil erodibility factor using a global dataset. CATENA, 31 , 1–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0341-8162(97)00036-2
Walker, S.J. (2017). An alternative method for deriving a USLE nomograph K factor equation.
Wang, B., Zheng, F., & Guan, Y. (2016). Improved USLE-K factor prediction: A case study on water erosion areas in China. International Soil and Water Conservation Research, 4 , 168–176. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.iswcr.2016.08.003
Wang, B., Zheng, F., & Römkens, M. J. M. (2013). Comparison of soil erodibility factors in USLE, RUSLE2, EPIC and Dg models based on a Chinese soil erodibility database. Acta Agriculturae Scandinavica, Section B— Soil & Plant Science, 63 , 69–79. https://doi.org/10.1080/09064710.2012.718358
Wang, B., Zheng, F., & Wang, Y. (2012). Adaptability analysis on soil erodibility models in typical thin layer black soil area of Northeast China. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (TCSAE), 28 , 126–131.
Wawer, R., Nowocien, E., & Podolski, B. (2005). Real and calculated KUSLE erodibility factor for selected polish soils. Polish Journal of Environmental Studies, 14 , 655–658.
Wischmeier, W., Smith, D. (1978). Predicting Rainfall Erosion Losses:A Guide to Conservation Planning, Agriculture Handbook, No. 537. USDA, Washington, DC.
Wischmeier, W. H., Johnson, C. B., & Cross, B. V. (1971). soil erodibility nomograph for farmland and construction sites. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 26 , 189–193.
Yesuf, H. M., Assen, M., Alamirew, T., & Melesse, A. M. (2015). Modeling of sediment yield in Maybar gauged watershed using SWAT; northeast Ethiopia. CATENA, 127 , 191–205. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2014.12.032
Zhang, B., Zhaoa, Q. G., Horn, R., & Baumgart, T. (2001). Shear strength of surface soil as affected by soil bulk density and soil water content. Soil and Tillage Research, 59 , 97–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0167-1987(01)00163-5
Zhang, K., Shu, A., Xu, X., Yang, Q., & Yu, B. (2008). Soil erodibility and its estimation for agricultural soils in China. Journal of Arid Environments, 72 , 1002–1011. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaridenv.2007.11.018
Download references
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank the Ethiopia Ministry of Water and Electricity for providing the soil laboratory analyzed data free of charge.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Water Works Construction Technology, Faculty of Civil Technology, Ethiopia Technical University, Addis Ababa, Ethiopia
Alemu Osore Aga
Department of Earth and Environment, Florida International University, Miami, FL, 33199, USA
Assefa M. Melesse
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
A.O.A. conceived the study. He has also participated in the design of the study, carried out the data collection, analysis of data, and performed the statistical analysis. A.M.M. participated in the sequence alignment of the draft manuscript. He also participated in its design and coordination, and helped to draft and edit the manuscript. Both authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Alemu Osore Aga .
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Aga, A.O., Melesse, A.M. An alternative soil erodibility estimation approach for data-scarce regions: a case study in Ethiopian Rift Valley Lake Basin. J. Sediment. Environ. (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s43217-024-00179-5
Download citation
Received : 11 December 2023
Revised : 15 April 2024
Accepted : 20 April 2024
Published : 19 May 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s43217-024-00179-5
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Soil erodibility (K)
- EPIC (erosion productivity impact calculator) model
- FAO soil database
- Rift valley
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
- Open access
- Published: 16 May 2024
Accommodating detection limits of multiple exposures in environmental mixture analyses: an overview of statistical approaches
- Myeonggyun Lee 1 ,
- Abhisek Saha 2 ,
- Rajeshwari Sundaram 2 ,
- Paul S. Albert 3 &
- Shanshan Zhao 1
Environmental Health volume 23 , Article number: 48 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
227 Accesses
Metrics details
Identifying the impact of environmental mixtures on human health is an important topic. However, such studies face challenges when exposure measurements lie below limit of detection (LOD). While various approaches for accommodating a single exposure subject to LOD have been used, their impact on mixture analysis has not been thoroughly investigated. Our study aims to understand the impact of five popular LOD accommodation approaches on mixture analysis results with multiple exposures subject to LOD, including omitting subjects with any exposures below LOD (complete case analysis); single imputations by LOD/ \(\sqrt{2}\) , and by estimates from a censored accelerated failure time (AFT) model; and multiple imputation (MI) with or without truncation based on LOD.
In extensive simulation studies with high-dimensional and highly correlated exposures and a continuous health outcome, we examined the performance of each LOD approach on three mixture analysis methods: elastic net regression, weighted quantile sum regression (WQS) and Bayesian kernel machine regression (BKMR). We further analyzed data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) on how persistent organic pollutants (POPs) influenced leukocyte telomere length (LTL).
Complete case analysis was inefficient and could result in severe bias for some mixture methods. Imputation by LOD/ \(\sqrt{2}\) showed unstable performance across mixture methods. Conventional MI was associated with consistent mild biases, which can be reduced by using a truncated distribution for imputation. Estimating censored values by AFT models had a minimal impact on the results. In the NHANES analysis, imputation by LOD/ \(\sqrt{2}\) , truncated MI and censored AFT models performed similarly, with a positive overall effect of POPs on LTL while PCB126, PCB169 and furan 2,3,4,7,8-pncdf being the most important exposures.
Conclusions
Our study favored using truncated MI and censored AFT models to accommodate values below LOD for the stability of downstream mixture analysis.
Peer Review reports
Environmental exposures to chemical, biological, or physical substances found in air, water, food, or soil are common during the human life course [ 1 , 2 , 3 ]. These high-dimensional and highly correlated exposures can act synergistically or antagonistically on human health [ 4 , 5 ]. Studying individual exposures only addresses their marginal effects, without accounting for others, which can result in misleading conclusions about effects of the whole mixture [ 6 , 7 ].
Several popular modeling approaches exist to analyze complex environmental mixtures, including but not limited to regularized regressions, weighted quantile sum regression (WQS) [ 8 , 9 ], and Bayesian kernel machine regression (BKMR) [ 10 , 11 ]. Briefly, regularized regressions such as elastic net regression [ 12 ] and lasso (least absolute shrinkage and selection operator) [ 13 ] can be used to identify the relative importance of driver(s) in the mixture through variable selection [ 14 , 15 , 16 ]. WQS derives a one-dimensional weighted sum score of the exposures with a linear relationship to a continuous health outcome under the assumption that all exposure effects are in the same direction. WQS has been generalized to several types of outcomes [ 17 ] and is widely used in practice [ 16 , 18 , 19 , 20 ]. BKMR is a Bayesian nonparametric method to handle complex nonlinear relationships between exposure mixtures and continuous, binary, and time-to-event outcomes [ 10 , 21 ]. It has been widely used in mixtures studies, due to its flexibility and abundant visualization tools [ 16 , 22 ]. Details of these methods are illustrated in Appendix A .
Environmental health studies often face challenges of exposure values below limit of detection (LOD) (i.e., left-censored). All the above-mentioned mixture methods assume accurate measurements of exposures, thus some procedure for accommodating LOD is needed before applying these mixture methods. For example, with data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) 2001–2002 cycle, Gibson et al. [ 23 ] investigated the relationship between persistent organic pollutants (POPs) and leukocyte telomere length (LTL), a biomarker associated with chronic diseases [ 24 , 25 , 26 , 27 ] and dioxin-associated cancers [ 28 , 29 , 30 , 31 ]. Among the 34 POPs with 1.4% to 99.9% of values below LOD [ 32 ], Gibson et al. [ 23 ] restricted their analysis to the 18 POPs with less than 40% of values below LOD and imputed all values below LOD by LOD/ \(\sqrt{2}\) . However, it is unclear how this imputation influenced the analysis results.
Recovering the true effects of environmental mixtures, where multiple exposures are subject to different proportions of values below LOD, is thus an important problem to address. Several approaches for accommodating values below LOD for a single exposure have been used in practice, including complete case analysis by omitting subjects with any measured values below LOD, single imputation by LOD/ \(\sqrt{2}\) , and multiple imputation. Ortega-Villa et al. [ 33 ] empirically compared these approaches in an environmental study setting with a binary outcome and a single exposure. However, the impact of these LOD approaches on downstream mixture analysis results has not been thoroughly investigated in settings where multiple exposures within the high-dimensional and highly correlated exposure mixtures are subject to LOD.
In this manuscript, we aim to understand the impact of five popular approaches for accommodating LOD: complete case analysis; single imputation of values below LOD by LOD/ \(\sqrt{2}\) and by estimates from censored accelerated failure time (AFT) models; and multiple imputation (MI) with and without LOD-based truncation. We conducted extensive simulation studies to examine their influences on three popular mixture methods, including elastic net regression, WQS and BKMR, after applying the above-mentioned LOD approaches. We also re-analyzed the 2001–2002 NHANES dataset as described in Gibson et al. [ 23 ], to illustrate how different ways of handling LOD can impact the identification of associations between the POPs and LTL. Through these simulated and real data examples, we would like to draw readers’ attention to carefully choose LOD accommodation approaches for mixture analysis, rather than recommending one approach as the gold standard.
LOD accommodation approaches
Here we give a brief review of the five LOD accommodation approaches. Complete case analysis only includes subjects whose exposure values are all above LOD. In theory, this approach provides unbiased results for linear regressions when the missingness only depends on the exposures [ 34 , 35 ]. However, its performance may be unstable in practice with reduced sample sizes [ 36 , 37 ]. An alternative approach is to replace values below LOD with a pre-specified constant value such as LOD, LOD/2, or LOD/ \(\sqrt{2}\) based on the observed exposure distribution [ 37 , 38 , 39 ]. In this study we chose LOD/ \(\sqrt{2}\) , which is widely used for log-normally distributed (or right skewed) chemical exposures. This approach is popular due to its simplicity, but results may be biased when the distribution of values below LOD is not centered on the substitution value [ 37 , 38 , 40 ].
Chen et al. [ 41 ] recently proposed a new approach using multivariate accelerated failure time (AFT) regressions to model multiple left-censored chemicals through baseline covariates, which is a flexible approach specialized to handle censored outcomes with mild assumptions about the joint distribution. Note that this is an extension of the approach proposed in Kong and Nan [ 42 ] from a single exposure subject to LOD to multiple exposures. Due to simultaneously fitting multiple AFT models, it allows one to specifically account for the correlations between chemicals through shared baseline covariates and correlation between error terms. The originally proposed approach in Chen et al. [ 41 ] allows one to simultanueous model the exposures and health outcomes with efficiency gain. However, due to practical considerations, we only adopted the first part of this approach with the multivariate AFT model to conduct a single imputation for simplicity. The details of this approach are described in Appendix B .
Lastely, instead of single imputation approaches described above, multiple imputation (MI) also has been widely used by treating values below LOD as missing, and then imputing with models such as Bayesian linear regression or linear regression with bootstrap samples [ 35 , 43 ]. MI generates multiple datasets (e.g., 5 or 10) for downstream analysis and combine analysis results using the Rubin’s rule [ 44 ]. In this study we chose to use the bootstrap linear regression implemented in the R ‘mice’ package [ 45 ] due to its superior performance in the settings we investigated. However, conventional MI does not guarantee that imputed values are below LOD. Thus, we improved it by truncating the estimated normal distribution at LOD to ensure all imputed values are in the correct range, and named this approach as truncated MI. The details of conventional and truncated MI are described in Appendix C .
Simulation settings
We conducted extensive simulations to empirically evaluate the impact of LOD accommodation approaches on three popular downstream mixture analysis methods, including elastic net regression, WQS and BKMR, under various settings. First, covariates \(X={\left(1, {X}_{1},{X}_{2}\right)}^{T}\) were independently generated from \({X}_{1} \sim Bern\left(p=0.5\right)\) and \({X}_{2} \sim N\left(1, 1\right)\) . Given that environmental exposures are commonly highly correlated, right-skewed and associated through covariates, a mixture of \(p=10\) exposures \(Z={\left({Z}_{1},\dots , {Z}_{10}\right)}^{T}\) was generated from a multivariate linear regression model with covariates \(X\) and log link, that is, \({Z}_{log}={\text{log}}\left(Z\right)={\eta }^{T}X+\xi\) , with \(\eta =\left[{\eta }_{1},\dots , {\eta }_{10}\right]=\left[\begin{array}{ccc}0.20& 0.35& \begin{array}{ccc}0.30& 0.25& \begin{array}{ccc}0.35& 0.25& \begin{array}{ccc}0.25& 0.40& \begin{array}{cc}0.25& 0.30\end{array}\end{array}\end{array}\end{array}\\ 0.50& 0.50& \begin{array}{ccc}0.25& 0.05& \begin{array}{ccc}0.03& 0.10& \begin{array}{ccc}0.25& 0.25& \begin{array}{cc}0.50& 0.25\end{array}\end{array}\end{array}\end{array}\\ 0.05& 0.02& \begin{array}{ccc}0.00& 0.50& \begin{array}{ccc}0.25& 0.25& \begin{array}{ccc}0.25& 0.50& \begin{array}{cc}0.25& 0.25\end{array}\end{array}\end{array}\end{array}\end{array}\right],\) and \(\xi \sim MVN\left(0,\Sigma \right)\) with \(\Sigma ={\upsigma }^{2}\left(\begin{array}{ccc}{R}_{1}& 0& 0\\ 0& {R}_{2}& 0\\ 0& 0& {R}_{3}\end{array}\right)\) , where \({R}_{1}\) and \({R}_{2}\) are 3 × 3 correlation matrices with all off-diagonal entries as 0.25 and 0.75, respectively, and \({R}_{3}\) is a 4 × 4 correlation matrix with all off-diagonal entries as 0.5. Through this formulation, we imposed correlations between exposures through two sources: shared covariate effects \(X\) , where the correlations are governed by \(\eta\) , and correlation between error terms through off-diagonal entries in \(\Sigma\) . By the group structure in \(\Sigma\) (i.e., \(\left\{{Z}_{1},{Z}_{2}, {Z}_{3}\right\}\) for group 1, \(\left\{{Z}_{4},{Z}_{5}, {Z}_{6}\right\}\) for group 2, and \(\left\{{Z}_{7},{Z}_{8}, {Z}_{9}, {Z}_{10}\right\}\) for group 3), we allowed a higher within-group correlation than between-group correlations. We varied \(\sigma =1/2\) and \(1/8\) for moderate and high correlations within the groups, respectively (see Figure S1 for Spearman correlation coefficients between simulated variables). Because \(Z\) were right-skewed, we generated outcome \(Y\) under a linear regression with the log-transformed \({Z}_{log}\) , as in many environmental health studies, that is, \(Y={\beta }^{T}{Z}_{log}+{\alpha }^{T}X+\epsilon ,\) where \(\epsilon \sim N\left(0, 2\right)\) . With a sample size of 500, we fixed \(\alpha =\left(1, 1, 1\right)\) , and varied \(\beta\) and percent of value below LOD in various scenarios as follows.
Scenario 1. We set \(\beta ={\left(1.0, 0.8, 0.0, 0.6, 0.4, 0.0, 0.2, 0.1, 0.0, 0.0\right)}^{T}\) to reflect the relative importance of these exposures, and assumed that \({Z}_{2},{Z}_{3},{Z}_{5},{Z}_{7}\) , and \({Z}_{9}\) have approximately 30% of values below LOD.
Scenario 2. \({Z}_{2}\) is assumed to have approximately 70% of values below LOD, while all the other settings are the same as in Scenario 1. In this scenario, we handled \({Z}_{2}\) in two ways that are widely used in practice: (i) \({Z}_{2}\) was completely excluded from the analysis (Scenario 2A), and (ii) an indicator variable of whether \({Z}_{2}\) is above the LOD was used (Scenario 2B), while the other exposures subject to LOD were handled with the above-mentioned approaches. This scenario allows us to understand how to handle an exposure with a high percent of values below LOD.
Scenario 3 . We generated all the exposures as in Scenario 1, but we re-generated a new \({Z}_{2}\) from \(Unif\left(0, LOD\right)\) if the original \({Z}_{2}\) was below LOD. This essentially resulted in the marginal distribution of \({Z}_{2}\) being a mixture distribution of uniform below LOD and normal above LOD, and the new \({Z}_{2}\) was used to simulate the outcome \(Y\) . In this scenario, we aim to investigate whether the LOD accommodation approaches hold when the distributions of exposures are different below and above LOD. In this example, we arbitarily assumed that the change point of distribution was exactly at LOD as a case study. In practice we may not know the change point unless there are external information. All the other settings are the same as in Scenario 1.
Scenario 4. We assumed a null effect (i.e., \({\beta }_{2}=0\) ) of \({Z}_{2}\) for values below LOD and \({\beta }_{2}=0.8\) for values above LOD. The other settings are the same as those in Scenario 1. This allows us to investigate whether the LOD accommodation approaches hold when the relationships between exposures and outcome are different below and above the LOD. Again, as a case study we arbitrarily picked the LOD as the changing point for simplicity, which may not happen in practice
For each exposure and a given percent of values below LOD, we pre-determined the LOD values as the corresponding percentile from an independently simulated exposure dataset with sample size 20,000. With each simulated dataset, we first employed each of the five LOD accommodation approaches, then analyzed the resulting datasets with elastic net regression, WQS and BKMR under a unified formulation, that is, \(Y=h\left({Z}_{log}\right)+{\alpha }^{T}X+\epsilon ,\) where \(h\left({Z}_{log}\right)\) is the exposure–response function. Specifically, \(h\left({Z}_{log}\right)\) is \({\beta }^{T}{Z}_{log}\) for elastic net, \(\psi ({w}^{T}{\overline{Z} }_{log})\) for WQS with \(\psi\) being the total effect of a mixture, \(w\) as the vector of weights (or relative importance) and \({\overline{Z} }_{log}\) as the pre-specified quantized \({Z}_{log}\) , and a general form \(h\left({Z}_{log}\right)\) for BKMR that allows non-linear relationship and interactions (see Appendix A ). The R packages ‘glmnet’ [ 46 ], ‘gWQS’ [ 17 ] and ‘bkmr’ [ 47 ] with R version 4.2.1 (The R Foundation for Statistical Computing: http://www.r-project.org/ ) were used to implement these mixture methods.
In our implementations, all packages in R were applied as a default setting. Tuning parameters for elastic net were obtained from tenfold cross-validation. In WQS, we used quartiles of exposures after applying each approach for handling LOD with 200 bootstrap samples and 60% validation dataset. Five imputed datasets were generated for conventional and truncated MI approaches, and the final estimates of the MI and truncated MI were obtained using Rubin’s rules [ 44 ]. The R package ‘bkmrhat’ was used to combine the estimates of the MI and truncated MI in BKMR ( https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/bkmrhat/index.html ). We conducted 1000 simulation runs for each scenario. R code is available on GitHub at https://github.com/ml5977/LOD_accommodation .
The goal of our simulation study is to evaluate how different LOD accommodations influence the results of downstream mixture analysis. Note that since we simulated the data, all comparisons are made to estimates from the using the full datasets (i.e., not subject to LOD). We made this choice instead of comparing to the truth because some models are expected to exhibit biases even when all data are observed due to departure from the true underlying model, and certain model coefficients may have different interpretations. For example, elastic net regression explores a bias-variance trade-off, so we expect to see biases due to shrinkage [ 48 ]. WQS is based on exposure quantiles, so all the parameters can be interpreted as the average effect when exposures increase by one quantile, whereas the parameter in the true underlying model represents the effect corresponding to a one-unit change. We also do not compare across the three mixture analysis methods, which is beyond the scope of the current study.
For elastic net regression and WQS, we reported the average bias and empirical standard error (SE) of the parameter estimations. For BKMR, using model assessment measures similar to those in Bobb et al. [ 11 ], we regressed the estimated exposure–response function \(\widehat{h}\) with each LOD accommodation approach on \(\widehat{h}\) from the full dataset and reported the average intercept, slope, \({R}^{2}\) , and standard error (SE) of \(\widehat{h}\) to assess the goodness of fit of the overall effects [ 11 ]. An intercept close to 0 and slope close to 1 indicate no influence of the LOD accommodation approach on the downstream mixture analysis. We further reported posterior inclusion probabilities (PIPs) for each exposure. To be consistent with BKMR results in assessing overall effect, \({R}^{2}\) of regressing \(\widehat{h}\) from each LOD accommodation on \(\widehat{h}\) with the full dataset were also reported for elastic net regression and WQS.
NHANES data to explore the relationship between POPs and LTL
In addition to the simulation studies, we applied the above LOD accommodation approaches to the NHANES data collected between 2001 and 2002 as described in Gibson et al. [ 23 ] and Mitro et al. [ 32 ]. We considered a subset of 1,003 participants who were over twenty years old, and provided blood samples and consented to DNA analysis, with sufficient stored samples to estimate telomere length, and without any missing values for individual exposures and covariates not related to LOD, as described in Gibson et al. [ 23 ]. The Institutional Review Board of the National Center for Health Statistics approved the survey [ 49 ].
To be consistent with Gibson et al. [ 23 ], we restricted our analysis to 18 POPs with less than 40% of values below LOD, which include 11 polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs), 3 dioxins, and 4 furans (Gibson et al. [ 23 ]). All samples were measured using high-resolution gas chromatography/isotope-dilution high-resolution mass spectrometry [ 50 , 51 ]. LODs were typically \(\sim 2 ng/g\) , although they could be as high as \(10.5 ng/g\) [ 32 ], and 68.4% of subjects had at least one exposure below LOD. Using the data, Gibson et al. [ 23 ] and Mitro et al. [ 32 ] hypothesized that exposures to dioxins, furans, and PCBs were associated with longer LTL, which is the outcome of interest in this analysis.
Demographics and exposure levels were described in Gibson et al. [ 23 ]. POPs are moderately to highly correlated with Spearman correlation from 0.20 to 0.95 approximately (Gibson et al. [ 23 ]). These exposures can be categorized into three groups as described in Gibson et al. [ 23 ]: (i) non-dioxin-like PCBs (including PCBs 74, 99, 138, 153, 170, 180, 187 and 194), (ii) non-ortho PCBs (including PCBs 126 and 169), and (iii) all other exposures including mono-ortho-substituted PCB 118, four dibenzo-furans, and three chlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins, here refered to as mPFDs.
We employed the above-mentioned approaches for accommodating exposures subject to LOD. All exposures were log-transformed due to their right-skewness. We adjusted for all the covariates as in Mitro et al. [ 32 ] and Gibson et al. [ 23 ], including age, age 2 , sex, race/ethnicity, educational attainment, BMI, serum cotinine, and blood cell count and distribution (white blood cell count, percent lymphocytes, percent monocytes, percent neutrophils, percent eosinophils and percent basophils).
Using the same data, Gibson et al. [ 23 ] handled exposure values below LOD through substituting them by LOD/ \(\sqrt{2}\) . They found three potential drivers (PCB 126, PCB 118, and furan 2,3,4,7,8-pncdf) selected by penalized regression methods, a positive overall effect of the POPs by WQS, a positive linear association with furan 2,3,4,7,8-pncdf, suggestive evidence of linear associations with PCBs 126 and 169, and a positive overall effect of the mixture but no interactions among exposures by BKMR. We re-analyzed the data with the same mixture methods after processing the values below LOD with five LOD accommodation approaches.
We recognized the need for sampling weights to account for the complex NHANES sampling scheme, in order to obtain results generalizable to the US population [ 49 ]. However, our goal was to empirically compare the impact of different LOD accommodation approaches, rather than to provide estimates generalizable to the population. Thus, we simplified our analysis here by not including sampling weights for the NHANES cohort, so our results were consistent with those in Gibson et al. [ 23 ]. We do recommend incorporating sampling weights into the analysis if an generalizable estimate is needed. We note some of the mixture analysis methods explored here, such as BKMR and WQS, require additional efforts to appropriately incorporate sampling weights, which is beyond the scope of this paper.
Simulation results: elastic net regression
Depending on the scenarios, the overall percent of subjects without any value below LOD in the simulated data was approximately 30% to 40%. Table 1 showed the bias of exposures \({Z}_{1}\) to \({Z}_{3}\) (group 1) and \({R}^{2}\) for each LOD accommodation approach with elastic net regression, while all other results for elastic net is in Table S1 .
In Scenario 1 as a general case, when the exposures were moderately correlated, most approaches were unbiased except for the complete case analysis which also had higher SE, indicating inefficiency. In the high correlation setting, the biases in complete case analysis persisted, while imputing values below LOD by LOD/ \(\sqrt{2}\) and conventional MI also showed biases for \({\beta }_{2}\) . The bias in MI decreased when truncated MI was used. Imputation by estimates from the AFT model (F-AFT) and truncated MI were empirically unbiased and efficient in both moderate and high correlation settings under Scenario 1.
When \({Z}_{2}\) was subject to 70% values below LOD and was completely ignored in the elastic net regression (Scenario 2A), all LOD accommodations performed poorly with low \({R}^{2}\) and large biases for exposures in the same group ( \({\beta }_{1} {\text{and}} {\beta }_{3}\) ) and covariate \({X}_{1}\) ( \({\alpha }_{1}\) ). Note that exposures in other groups were relatively less impacted since the effect of \({Z}_{2}\) was potentially accounted for by those in the same group (i.e., \({Z}_{1}\) and \({Z}_{3}\) ). These biases decreased when correlations were higher, again presumably because the information in \({Z}_{2}\) was better captured by other exposures in the same group. These biases in \({\beta }_{1}\) and \({\beta }_{3}\) were further alleviated when an indicator variable of \({Z}_{2}\) (Scenario 2B), i.e., \(I({Z}_{2}>{\text{LOD}}\) ), was used. However, \({\beta }_{2}\) now has a different interpretation (i.e., the difference between values above LOD versus below the LOD), so we expected to see its large bias. Although Group 1 exposures were still biased in Scenario 2B for most of the LOD accommodation approaches, F-AFT and truncated MI generally performed well, especially in high correlation setting, followed by imputation by LOD/ \(\sqrt{2}\) and conventional MI.
When different distributions below and above LOD were assumed for \({Z}_{2}\) (Scenario 3) or \({Z}_{2}\) had different effects below and above LOD (Scenario 4), all approaches for handling LOD, including model-based approaches such as truncated MI and F-AFT, performed poorly for \({\beta }_{2}\) because we lack any information to make inference about the values and relationship below LOD. Surprisingly, we observed a smaller bias of \({\beta }_{2}\) with conventional MI. However, the bias increased dramatically when the percent of values below LOD increased (results not shown). Furthermore, conventional MI was substantially biased in the intercept \({\alpha }_{0}\) and was inefficient in \({\beta }_{2}\) compared to other LOD approaches with a lower \({R}^{2}.\) Therefore, truncated MI and F-AFT still performed relatively better than other approaches and using LOD/ \(\sqrt{2}\) yielded slightly worse results but comparable.
Simulation results: WQS regression
We summarized the \({\beta }_{1}\) to \({\beta }_{3}\) and \({R}^{2}\) results in Table 2 and all remaining results for WQS in Table S2. We expected WQS to be less sensitive to values below LOD due to using quantized exposures. However, some LOD accommodations could disrupt the quantiles and result in large biases. For example, in Scenario 1, we found that F-AFT and truncated MI mostly maintained the exposures’ quantiles and were empirically unbiased and efficient (Table 2 ). Complete case analysis showed relatively large biases, especially for overall effect estimate ( \(\psi\) ) in the setting of moderate correlation, due to the loss of all values below LOD and complete change of quantiles. Conventional MI also showed slightly larger biases compared to truncated MI because the imputed values could occasionally exceed the detection limit that can change quantile estimates. When LOD/ \(\sqrt{2}\) was used, performance was unstable because the exposure’s quantiles may not be maintained in the analysis of WQS if the percent of value below LOD is high (e.g., potential mis-assignment of quantiles). In evaluating the overall effects of the mixture with \({R}^{2}\) , complete case analysis underperformed across all LOD approaches while the others were similar.
When the percent of values below the LOD for \({Z}_{2}\) was increased to 70% and \({Z}_{2}\) was ignored in the WQS analysis (Scenario 2A), in the moderate correlation setting, the biases increased, especially for effects of exposures in the same group ( \({Z}_{1}\) and \({Z}_{3}\) ), total effect \(\psi\) , intercept and covariate \({X}_{1}\) . When an indicator variable \(I({Z}_{2}>LOD)\) was used as in Scenario 2B, the bias of total effects was slightly alleviated, but biases in weights of group 1 exposures, intercept and covariate \({X}_{1}\) persisted. All LOD accommodations performed similarly well in the high correlation setting, except complete case analysis was substantially biased in intercept and with lower \({R}^{2}\) . In the scenarios with different distributions (Scenario 3) or different effects (Scenario 4) below and above LOD for \({Z}_{2}\) , truncated MI and F-AFT maintained better performance in both parameter estimates and \({R}^{2}\) compared to the other LOD accommodation approaches. Imputation by LOD/ \(\sqrt{2}\) showed similar \({R}^{2}\) , but there was a large bias in estimating the total effect \(\psi\) .
Simulation results: BKMR
Table 3 showed the simulation results of BKMR under different scenarios. In Scenario 1, F-AFT performed the best among all the approaches, with intercept close to 0 and slope close to 1, indicating empirically unbiased results of \(h\left({Z}_{log}\right)\) . The F-AFT also led to high \({R}^{2}\) and lower SE. Truncated MI performed similarly to F-AFT but was slightly less efficient. Complete case analysis and imputation by LOD/ \(\sqrt{2}\) underperformed, especially in the high correlation setting. In Scenario 2, none of the LOD accommodation approaches performed satisfactorily, despite the indicator variable (Scenario 2B) resulting in slightly better estimation than Scenario 2A. In Scenarios 3 and 4, F-AFT and truncated MI were the most unbiased and efficient in both correlation settings. In identifying important mixture components by PIPs, F-AFT and truncated MI performed similarly to using the full dataset, while complete case analysis showed discrepancies (Figure S2). The performance of imputation by LOD/ \(\sqrt{2}\) in PIPs was comparable to those of F-AFT and truncated MI, despite this approach showing unstable results in some cases (e.g., high correlation settings).
NHANES data analysis results
When applying the elastic net regression to the mixture, F-AFT, truncated MI, and imputation by LOD/ \(\sqrt{2}\) generally resulted in similar findings (Fig. 1 ). Specifically, they all identified six important POPs: PCB99, PCB118, PCB126, PCB169, furan 2,3,4,7,8-pncdf, and furan 1,2,3,4,6,7-hxcdf with similar effects. Complete case analysis only identified PCB126 and PCB169 to be important, while conventional MI resulted in selecting many more exposures. We additionally conducted group lasso with the 18 POPs categorized into three groups: non-dioxin-like PCBs, non-ortho-PCBs, and mPFD, as described above. None of exposures in non-dioxin-like PCBs were selected except when using conventional MI, while non-ortho PCBs (i.e., PCB126 and PCB169) were associated with non-zero coefficients in all LOD approaches (Figure S3). The magnitudes of the non-ortho PCB effects were larger with complete case analysis and conventional MI while the other three approaches yielded similar effects. For the mPFD exposures, again, F-AFT, truncated MI and imputaiton by LOD/ \(\sqrt{2}\) estimated similar coefficients and they all selected furan 2,3,4,7,8-pncdf as the most important exposures, followed by PCB118. Complete case analysis resulted in null effects for all mPFDs, and conventional MI showed mild effects for some non-dioxin-like PCBs and opposite direction for some of the mPFDs.

Coefficients for 18 POPs with elastic net regression and each LOD approach using NHANES data 2001–2002. Abbreviations: Imputation by LOD/ \(\sqrt{2}\) (LOD/sqrt(2)); conventional multiple imputation (MI); truncated multiple imputation (Truncated MI); imputation by estimates using the AFT model (F-AFT)
Deciles in exposures were used in the analysis of WQS regression to be consistent with Gibson et al. [ 23 ]. The total effect of 18 POPs ranged between 0.014 and 0.018 under various LOD-handling approaches, and they were statistically significant except for with complete case analysis, which is expected due to loss of efficiency with only 317 subjects included in the analysis (Table 4 ). Applying a priori cut-off weight of 1/18, we found 3 to 4 important POPs across these LOD accommodation approaches. Imputation by LOD/ \(\sqrt{2}\) and truncated MI found 2,3,4,7,8-pncdf as the most important exposure, followed by PCB126 and 1,2,3,4,6,7,8-hxcdf. In addition to these three, the F-AFT approach also identified PCB194.
Using BKMR, we employed hierarchical variable selection with the three pre-defined groups, which provided importance scores for both the groups (i.e., group PIPs) and each exposure within a group (i.e., conditional PIPs). Truncated MI and imputation by LOD/ \(\sqrt{2}\) both resulted in the non-ortho PCB group with the highest PIP among three groups, while mPFD group has the highest PIP with F-AFT, conventional MI and complete case analysis (Table S3). Within the mPFD exposures, furan 2,3,4,7,8-pncdf contributed most to the model, followed by PCB 118 when imputation by LOD/ \(\sqrt{2}\) , truncated MI and F-AFT approaches were used. PCB 169 and PCB 126 in the non-ortho PCB group had similar importance weights when we applied imputation by LOD/ \(\sqrt{2}\) , truncated MI and F-AFT approaches. The individual effects of the POP exposures showed linear trends across LOD accommodation approaches (Fig. 2 A), while the magnitudes of associations varied, especially for PCB169 and furan 2,3,4,7,8-pncdf which were selected as important exposures among the 18 POPs. The overall mixture effect was also close to a positive linear trend on the LTL outcome across LOD approaches, while the strength and efficiency varied (Fig. 2 B).

Individual and overall relationships of 18 POPs with log-LTL from BKMR using NHANES 2001–2002 data. A Exposure-specific effect estimates of mixture members. B Overall effect of the mixture. Abbreviations: Imputation by LOD/ \(\sqrt{2}\) (LOD/sqrt(2)); conventional multiple imputation (MI); truncated multiple imputation (Truncated MI); imputation by estimates using the AFT model (F-AFT)
In this study we have compared how five popular approaches for handling exposures subject to LOD influence the results of mixture analysis. We did not mean to provide a guideline on how to handle values below LOD, rather to draw attention about how results can be misled by the various LOD accommodation approaches, and would like to advocate for careful examination of LOD accommodation prior to applying downstream mixtures analysis.
Through our extensive simulations, we generally favored using truncated MI and censored AFT models to impute values below LOD for the stability of downstream mixture analysis when the percent of the LOD was low to moderate (e.g., 30–50%). Compared to other approaches, truncated MI and censored AFT models generate imputed values based on the information from other exposures and covariates and guarantee that the imputed values are below LOD. Satisfactory results were also found with these two approaches when evaluating statistical uncertainties, such as mean squared error and coverage probability of the 95% confidence interval, in additional linear regression simulations (Table S4), as well as when incorporating grouping information in the analysis of group lasso and BKMR with hierarchical variable selection (Tables S5 and S6). Of course, these model-based approaches rely on modeling assumptions and borrowing information from other exposures and baseline demographics. However, we argue since we do not get to observe any information below LOD, we need some assumptions, and the modeling assumptions made in these two approaches are relatively mild and reasonable in practice.
Complete case analysis and imputations by LOD/ \(\sqrt{2}\) are frequently used in environmental health studies due to their easy implementation. However, we found that their performance can be quite unstable, especially in scenarios with high correlations or high percent of values below the LOD as commonly observed in environmental mixture studies. Richardson and Ciampi [ 38 ] also reported the bias in risk estimates when an arbitrary constant value such as LOD or LOD/2 was used to replace values below the LOD, and pointed out the magnitude of bias depends on the differences between the substitution value and true exposure distribution below LOD.
When the percent of values below LOD increased to 70% in our simulations, using an indicator variable of whether the values are above LOD performed better than excluding the exposure variable in the analysis. When other exposures were highly correlated with the exposure that had a high percent of values below LOD, its influence on the overall effect was limited because its information was well captured by other exposures. Based on our simulation studies with various percent of values below the LOD (results not shown), we recommend using the indicator variable approach when the percent of exposures below LOD is above 50%. For the NHANES data analysis, we restricted to exposures with less than 40% of values below LOD, in order to replicate the analysis in Gibson et al. [ 23 ]. If we were to perform our own analysis, we will likely use 50% as a cutoff to include three additional POPs in the analysis.
We acknowledge that it is difficult to verify an assumed relationship or distribution between exposure subject to LOD and disease outcome for values below the LOD. To address this, we examined various LOD accommodation approaches assuming that the relationship has no impact below the LOD (Scenario 3) and the distribution is different for values below LOD (Scenario 4) as a case study. In our simulation study, none of the approaches for handling LOD in this study performed satisfactorily, which is similar to the results given by Ortega-Villa et al. [ 33 ] for a single exposure. In such cases, we recommend considering the binary indicator approach for exposures with suspected differential distribution or relationship with outcome [ 52 ], while truncated MI or F-AFT can still be used for all other exposures subject to LOD. Even though BKMR with imputation by LOD/ \(\sqrt{2}\) , truncated MI and F-AFT performed satisfactorily in such scenarios due to its flexibility in allowing non-linear relationship, the implementation of the missing indicator approach could lead to further performance enhancement in BKMR. Yet, interpreting the estimated coefficient for the missing indicator within the exposure–response function of BKMR might prove challenging, especially when indicators are needed for multiple exposures.
We applied the LOD approaches to NHANES 2001–2002 where 18 selected POPs were subject to different proportions of values below the LOD. In our analysis, we did not include sampling weights because our goal was to understand the impact of different LOD accommodation approaches on downstream mixture analysis as a comparison with Gibson et al. [ 23 ], which did not incorporate sampling weights. To incorporate sampling weights, Zhang et al. [ 53 ] sampled one bootstrap sample with replacement from the NHANES data, with probabilities proportional to the sampling weights to test the results. We also implemented the same procedure. Although the mixture analysis results were different, we observed similar patterns across LOD accommodation approaches (results not shown).
In this study, we considered a two-stage approach as a practical implementation where we first performed the LOD accommodation to get a “complete” dataset, then conducted mixture analyses using this dataset. In the multiple imputation (MI) with or without truncation, we generated five imputed datasets, and combined the results of mixture analysis using the Rubin’s rule [ 44 ], which takes imputation variability into account in the final results. However, single imputations by LOD/ \(\sqrt{2}\) , and by estimates from the censored AFT model did not account for the uncertainty resulting from the imputation, which could lead to an overestimation of the precision. This can also be seen in the linear regression simulation results in Table S4, with somewhat worse coverage probabilities by F-AFT and LOD/ \(\sqrt{2}\) . Nevertheless, in our experience working with epidemiologists, this two-stage approach is highly preferred in practice due to its convenience. It requires handling the LOD only once and allows the resulting dataset to be used as the “true” dataset for multiple studies in the future. As mentioned above, Chen et al. [ 41 ] proposed a semiparametric multivariate AFT approach with multiple exposures to simultaneously model the exposures subject to LOD and the outcome, which accounts for uncertainty in the exposure assessment. This approach was applied to study the relationship between a panel of urinary trace metals and oxidative stress in pregnant women. The use of this powerful approach is limited by its computational complexity. Thus, it is of great interest to extend this approach to allow simultaneous modeling of the exposures subject to LOD with various mixture outcome models, and provide user-friendly software.
Some analytical laboratories often provide the machine readings for specimens whose observed values is declared to be below the LOD, with the understanding that the specimen’s level of analyte cannot reliably distinguished from zero; these readings may involve substantial measurements errors. Machine-read values have been often used in environmental mixture studies [ 54 , 55 , 56 ]. However, we did not consider the machine-read approach in our case study because it is difficult to justify the actual mechanism of the machine-raed approach given that each machine in each lab has its unique way of generating the reads, and the accuracy could vary dramatically. In our data analysis, NHANES 2001–2002 also did not provide machine-read values.
Here, we limited to three mixture analysis methods including elastic net regression, WQS, and BKMR which have been widely used in environmental mixture studies. We are aware of many other mixtures anslysis methods and performed simulations to understand the impact of LOD accommodations on these methods too. However, they were not included due to the length of the current manuscript. For example, Keil et al. [ 57 ] recently proposed a quantile-based g-computation method (q-gcomp) that builds up on WQS regression integrating its estimation procedure with a g-computation technique, which is widely used for causal inference [ 58 ]. The q-gcomp method relaxes the unidirectionality and linearity assumptions of the WQS regression. Results were similar to those for WQS, which is likely due to their similar model structures and our simulated exposures were all in one direction (e.g., see Table S7 for q-gcomp results under Scenario 1).
Several methodological extensions are of interest for further exploration. First, in this study we assumed a linear combination of variables in MI and F-AFT for imputation. However, these approaches could allow non-linearity and/or non-additivity for better recovering the true effects in the mixture setting. We also assumed all the effects were in the same direction with no interactions, which limits generalizability, and assumed a multivariate normal distribution for the exposures. Second, our study employed popular approaches for accommodating LOD before applying the mixture analysis methods to the revised data (i.e., a two-stage approach). Lastly, environmental mixture exposures are often repeatedly measured (i.e., longitudinal mixture exposures), which could allow more accurate modeling of the exposure trajectories. We leave a consideration of LOD adjustments that can appropriately incorporate longitudinal mixture exposures as a project for further development.
Quantifying the impact of mixtures of environmental exposures is becoming increasingly important for identifying disease risk factors and developing targeted public health interventions. Our case study delved into the issue of LOD in detail to understand how common approaches for handling LOD impact downstream mixture analysis. Our exploration provides insight into various LOD accommodation approaches in downstream mixture analyses, enhancing the quality and reliability of environmental health studies.
Availability of data and materials
The data that support the findings in this paper are available on GitHub at https://github.com/lizzyagibson/SHARP.Mixtures.Workshop , published along side Gibson et al. (2019) [ 23 ]. R code for LOD accommodation approaches is available at https://github.com/ml5977/LOD_accommodation .
Aylward LL, et al. Evaluation of biomonitoring data from the CDC National Exposure Report in a risk assessment context: perspectives across chemicals. Environ Health Perspect. 2013;121(3):287–94.
Article Google Scholar
Exley K, et al. Pilot study testing a European human biomonitoring framework for biomarkers of chemical exposure in children and their mothers: experiences in the UK. Environ Sci Pollut Res. 2015;22:15821–34.
Article CAS Google Scholar
Frederiksen H, et al. Human urinary excretion of non-persistent environmental chemicals: an overview of Danish data collected between 2006 and 2012. Reproduction. 2014;147(4):555–65.
Hamra GB, Buckley JP. Environmental exposure mixtures: questions and methods to address them. Current epidemiology reports. 2018;5:160–5.
Kortenkamp A, Ten,. years of mixing cocktails: a review of combination effects of endocrine-disrupting chemicals. Environ Health Perspect. 2007;115(Suppl 1):98–105.
Braun JM, et al. What can epidemiological studies tell us about the impact of chemical mixtures on human health? Environ Health Perspect. 2016;124(1):A6–9.
Kelley AS, et al. Early pregnancy exposure to endocrine disrupting chemical mixtures are associated with inflammatory changes in maternal and neonatal circulation. Sci Rep. 2019;9(1):5422.
Carrico C, et al. Characterization of weighted quantile sum regression for highly correlated data in a risk analysis setting. J Agric Biol Environ Stat. 2015;20:100–20.
Gennings C, et al. A cohort study evaluation of maternal PCB exposure related to time to pregnancy in daughters. Environ Health. 2013;12:1–12.
Bobb JF, et al. Statistical software for analyzing the health effects of multiple concurrent exposures via Bayesian kernel machine regression. Environ Health. 2018;17:1–10.
Bobb JF, et al. Bayesian kernel machine regression for estimating the health effects of multi-pollutant mixtures. Biostatistics. 2015;16(3):493–508.
Zou H, Hastie T. Regularization and variable selection via the elastic net. J R Stat Soc Ser B Stat Methodol. 2005;67(2):301–20.
Tibshirani R. Regression shrinkage and selection via the lasso. J R Stat Soc Ser B Stat Methodol. 1996;58(1):267–88.
Aung MT, et al. Cross-sectional estimation of endogenous biomarker associations with prenatal phenols, phthalates, metals, and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in single-pollutant and mixtures analysis approaches. Environ Health Perspect. 2021;129(3): 037007.
Lenters V, et al. Prenatal phthalate, perfluoroalkyl acid, and organochlorine exposures and term birth weight in three birth cohorts: multi-pollutant models based on elastic net regression. Environ Health Perspect. 2016;124(3):365–72.
Vuong AM, et al. Prenatal exposure to a mixture of persistent organic pollutants (POPs) and child reading skills at school age. Int J Hyg Environ Health. 2020;228: 113527.
Renzetti, S., Curtin, P., Just, A. C., Bello, G. and Gennings, C. (2020) gWQS: Generalized Weighted Quantile Sum Regression. R package version 3.0.0. https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=gWQS . Accessed 8 Oct 2021.
Christensen KLY, et al. Multiple classes of environmental chemicals are associated with liver disease: NHANES 2003–2004. Int J Hyg Environ Health. 2013;216(6):703–9.
Colicino E, et al. Per-and poly-fluoroalkyl substances and bone mineral density: results from the Bayesian weighted quantile sum regression. Environmental Epidemiology. 2020;4(3): e092.
Czarnota J, Gennings C, Wheeler DC. Assessment of weighted quantile sum regression for modeling chemical mixtures and cancer risk. Cancer Inform. 2015;14:S17295.
Domingo-Relloso A, et al. The association of urine metals and metal mixtures with cardiovascular incidence in an adult population from Spain: the Hortega Follow-Up Study. Int J Epidemiol. 2019;48(6):1839–49.
Tanner E, Lee A, Colicino E. Environmental mixtures and children’s health: identifying appropriate statistical approaches. Curr Opin Pediatr. 2020;32(2):315–20.
Gibson EA, et al. An overview of methods to address distinct research questions on environmental mixtures: an application to persistent organic pollutants and leukocyte telomere length. Environ Health. 2019;18:1–16.
Aubert G, Lansdorp PM. Telomeres and aging. Physiol Rev. 2008;88(2):557–79.
Haycock, P.C., et al., Leucocyte telomere length and risk of cardiovascular disease: systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ. 2014;349:g4227.
Révész D, et al. Telomere length as a marker of cellular aging is associated with prevalence and progression of metabolic syndrome. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2014;99(12):4607–15.
Willeit P, et al. Leucocyte telomere length and risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus: new prospective cohort study and literature-based meta-analysis. PLoS ONE. 2014;9(11): e112483.
Lan Q, et al. A prospective study of telomere length measured by monochrome multiplex quantitative PCR and risk of non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2009;15(23):7429–33.
Sanchez-Espiridion B, et al. Telomere length in peripheral blood leukocytes and lung cancer risk: a large case–control study in Caucasians. Can Res. 2014;74(9):2476–86.
Seow WJ, et al. Telomere length in white blood cell DNA and lung cancer: a pooled analysis of three prospective cohorts. Can Res. 2014;74(15):4090–8.
Xie H, et al. Long telomeres in peripheral blood leukocytes are associated with an increased risk of soft tissue sarcoma. Cancer. 2013;119(10):1885–91.
Mitro SD, et al. Cross-sectional associations between exposure to persistent organic pollutants and leukocyte telomere length among US adults in NHANES, 2001–2002. Environ Health Perspect. 2016;124(5):651–8.
Ortega-Villa AM, et al. New insights into modeling exposure measurements below the limit of detection. Environmental Epidemiology. 2021;5(1): e116.
Little RJ. Regression with missing X’s: a review. J Am Stat Assoc. 1992;87(420):1227–37.
Google Scholar
Little, R.J. and D.B. Rubin, Statistical analysis with missing data. Vol. 793. Hoboken: Wiley; 2019.
D’Angelo G, Weissfeld L, Investigators G. An index approach for the Cox model with left censored covariates. Stat Med. 2008;27(22):4502–14.
Nie L, et al. Linear regression with an independent variable subject to a detection limit. Epidemiology. 2010;21(4):S17–24.
Richardson DB, Ciampi A. Effects of exposure measurement error when an exposure variable is constrained by a lower limit. Am J Epidemiol. 2003;157(4):355–63.
Schisterman EF, et al. The limitations due to exposure detection limits for regression models. Am J Epidemiol. 2006;163(4):374–83.
Helsel D: Nondetects and data analysis: statistics for censored environmental data. Hoboken: Wiley-Interscience; 2005.
Chen LW, et al. Semiparametric analysis of a generalized linear model with multiple covariates subject to detection limits. Stat Med. 2022;41(24):4791–808.
Kong S, Nan B. Semiparametric approach to regression with a covariate subject to a detection limit. Biometrika. 2016;103(1):161–74.
Van Buuren, S. van. Flexible Imputation of Missing Data, Second Edition. (Chapman and Hall/CRC, New York, 2018). https://doi.org/10.1201/9780429492259 .
Little RJA, Rubin DB: Statistical Analysis with Missing Data. New York: Wiley; 1987.
Van Buuren S, Groothuis-Oudshoorn K. mice: Multivariate imputation by chained equations in R. J Stat Softw. 2011;45:1–67.
Friedman J, Hastie T, Tibshirani R, Narasimhan B, Tay K, Simon N, Qian J. Package ‘glmnet’. J Stat Softw. 2022;33(1):2010a.
Bobb JF. bkmr: Bayesian Kernel Machine Regression. R package version 0.2.0; Published online 2017.
Blei, D.M. (2015) Regularized regression. Columbia University, New York, 1–11. http://www.cs.columbia.edu/~blei/fogm/2015F/notes/regularized-regression.pdf .
Zipf G, Chiappa M, Porter KS, Ostchega Y, Lewis BG, Dostal J. Health and nutrition examination survey planand operations, 1999-2010. Vital Health Stat. 2013;1(56).
U.S. CDC (U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention). 2002. Laboratory Procedure Manual: PCBs and Persistent Pesticides in Serum. 2001–2002. Atlanta, GA: U.S. CDC. https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/data/nhanes/nhanes_01_02/l28poc_b_met_pcb_pesticides.pdf . Accessed 7 Sept 2021.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 2006. Laboratory Procedure Manual: PCBs and PersistentPesticides. Available: http://www.cdc.gov/nchs/data/nhanes/nhanes_03_04/l28_c_met_%20PCBs_and_Persistent_Pesticides.pdf .Accessed 23 Apr 2009.
Chiou SH, Betensky RA, Balasubramanian R. The missing indicator approach for censored covariates subject to limit of detection in logistic regression models. Ann Epidemiol. 2019;38:57–64.
Zhang W, et al. Nonparametric estimation of distributions and diagnostic accuracy based on group-tested results with differential misclassification. Biometrics. 2020;76(4):1147–56.
Bloom MS, et al. Association between gestational phthalate exposure and newborn head circumference; impacts by race and sex. Environ Res. 2021;195: 110763.
Kim SS, et al. Urinary trace metals individually and in mixtures in association with preterm birth. Environ Int. 2018;121:582–90.
Trowbridge J, et al. Extending nontargeted discovery of environmental chemical exposures during pregnancy and their association with pregnancy complications—a cross-sectional study. Environ Health Perspect. 2023;131(7): 077003.
Keil AP, et al. A quantile-based g-computation approach to addressing the effects of exposure mixtures. Environ Health Perspect. 2020;128(4): 047004.
Robins J. A new approach to causal inference in mortality studies with a sustained exposure period—application to control of the healthy worker survivor effect. Mathematical modelling. 1986;7(9–12):1393–512.
Lee L-F. On the first and second moments of the truncated multi-normal distribution and a simple estimator. Econ Lett. 1979;3(2):165–9.
Leppard P, Tallis G. Algorithm AS 249: Evaluation of the mean and covariance of the truncated multinormal distribution. J R Stat Soc Society Series C (Applied Statistics). 1989;38(3):543–53.
Tallis GM. The moment generating function of the truncated multi-normal distribution. J R Stat Soc Ser B Stat Methodol. 1961;23(1):223–9.
Wilhelm S, Manjunath BG, 2015. Package ’tmvtnorm’: Truncated Multivariate Normal and Student t Distribution, TMVTNORM: Truncated Multivariate Normal and Student t Distribution. Available from CRAN.Rproject.org/package=tmvtnorm . last accessed May 2024.
Download references
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Drs. Danping Liu and Alexander P. Keil at the National Cancer Institute, NIH and Drs. Clarice R. Weinberg and David M. Umbach at the National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences, NIH for their helpful suggestions.
Open access funding provided by the National Institutes of Health This study was supported by the Intramural Research Program of the NIH, National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences (ZIA ES103307 and ES103308).
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Biostatistics and Computational Biology Branch, National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences, National Institutes of Health, Durham, NC, USA
Myeonggyun Lee & Shanshan Zhao
Biostatistics and Bioinformatics Branch, Division of Population Health Research, Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development, National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, MD, USA
Abhisek Saha & Rajeshwari Sundaram
Biostatistics Branch, Division Cancer Epidemiology and GeneticsBiostatistics Branch, Division of Cancer Epidemiology and Genetics, National Cancer Institute, National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, MD, USA
Paul S. Albert
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
SZhao and MLee: designed study and algorithm, performed the statistical analyses and simulations, prepared original manuscript draft, acquired funding to support this analysis. PAlbert, RSundaram, and ASaha: provided conceptual insight and feedback on revisions, assisted in interpretation of results. All authors critically reviewed and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Shanshan Zhao .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Supplementary material 1., appendix a. detailed descriptions of mixture analysis methods.
For each subject \(i \left(i=1,\dots ,n\right)\) , let \({Y}_{i}\) be a continuous outcome of interest. Let \({Z}_{i}\) and \({X}_{i}\) denote \(p\) - and \(q\) -vector of exposures and covariates, respectively. Note that \({X}_{i}\) includes 1 for the intercept term. Thus, we observe data \(\left\{{Y}_{i}, {Z}_{i}, {X}_{i}, i=1,\dots ,n\right\}\) with sample size \(n\) . Using these notations, ordinary linear regression can be specified as \({Y}_{i}={\beta }^{T}{Z}_{i}+{\alpha }^{T}{X}_{i}+{\epsilon }_{i}\) , with \({\epsilon }_{i} \sim N\left(0, {\sigma }^{2}\right)\) .
Elastic net is a regularized regression method that incorporates the linear combination of \({L}_{1}\) and \({L}_{2}\) penalties of the lasso and ridge methods [ 12 ]. The estimates can be obtained from \({\underset{\beta , \alpha }{{\text{argmin}}}\Vert y-\left({\beta }^{T}Z+{\alpha }^{T}X\right)\Vert }^{2}+{\lambda }_{1}\left(\frac{\left(1-{\lambda }_{2}\right)}{2}{\Vert \beta \Vert }_{2}^{2}+{\lambda }_{2}{\Vert \beta \Vert }_{1}\right),\) where tuning parameters \({\lambda }_{1}\) and \({\lambda }_{2}\) can be determined by cross validation (CV). Note that \({\lambda }_{2}=0\) and 1 yield ridge and lasso regressions, respectively. We used the R package ‘glmnet’ [ 46 ].
WQS regression can be specified as \({Y}_{i}=\psi \left({w}^{T}{\overline{Z} }_{i}\right)+{\alpha }^{T}{X}_{i}+{\epsilon }_{i}\) , where \(\overline{Z }\) is a pre-specified quantized variable of exposure \(Z\) . \(\psi\) represents the coefficient for the overall linear effect of the mixture, and \(w\) is the weight of each exposure. This method assumes that sum of all weights is 1 and each weight is between 0 and 1. Furthermore, this method assumes the same direction in all exposures (i.e., unidirectionality assumption). To conduct the WQS regression, we used ‘gWQS’ R package [ 17 ].
BKMR includes a completely nonparametric function of exposures as \({Y}_{i}=h\left({Z}_{1i}, \dots , {Z}_{pi}\right)+{\alpha }^{T}{X}_{i}+{\epsilon }_{i}\) , where \(h\left(\cdot\right)\) characterizes a high-dimensional exposure–response function that may incorporate non-linearity and/or interaction among the mixture components. BKMR provides the posterior inclusion probabilities for each exposure, plotting the exposure–response function, and the cumulative (or overall) effects of the mixture. The R package ‘bkmr’ was used for the analysis [ 47 ].
Appendix B. Algorithm for LOD accommodation using the AFT model (F-AFT)
Using the same notations from Appendix A , the following steps are performed to produce imputation values from the multivariate AFT model:
Step 1 . Apply a monotone decreasing transformation \({h}^{-1}\left(\cdot \right)\) to rewrite left-censored \(Z\) as right-censored \(T\) (e.g., \(T={h}^{-1}\left(Z\right)=-{\text{log}}\left(Z\right)\) ).
Step 2 . Fit the AFT model with a normal distribution for each exposure, \({Z}_{j} \left(j=1,\dots ,p\right)\) , subject to LOD, where \({T}_{j}={h}^{-1}\left({Z}_{j}\right)={\eta }_{j}^{T}{X}_{j}+{\epsilon }_{j}\) . Note that we use the estimate residuals \({\widehat{\epsilon }}_{j}\) to estimate the parameter \(\Sigma\) where \(\epsilon ={\left({\epsilon }_{1},\dots , {\epsilon }_{p}\right)}^{T} \sim MVN\left(0,\Sigma \right)\)
Step 3 . Using the estimates from Step 2, obtain the conditional truncated multivariate normal distribution [ 59 , 60 , 61 ] for the \(i\) th subject, \({\epsilon }_{i}^{\left(c\right)} \sim {f}_{\left(c\right)|\left(o\right), {\epsilon }_{i}^{\left(c\right)}>{\widehat{\epsilon }}_{i}^{(c)}}\) where \(\left(c\right)\) and \(\left(o\right)\) indicate the vector for the index of the censored variables and observed variables in \(Z\) , respectively, and \({f}_{\left(c\right), \left(o\right)}\) is the multivariate normal distribution with mean zero and covariance \(\widehat{\Sigma }\) . For implementation, we used mtmvnorm function in ‘tmvtnorm’ R package [ 62 ].
Step 4 . Impute \({Z}_{i}^{imp}=h\left({T}_{i}^{imp}\right)=h\left({\widehat{\eta }}^{T}{X}_{i}+{\widehat{\epsilon }}_{i}^{imp}\right)\) , where \({\widehat{\epsilon }}_{i}^{imp}\) is the conditional expectation of \({f}_{\left(c\right)|\left(o\right), {\epsilon }_{i}^{\left(c\right)}>{\widehat{\epsilon }}_{i}^{(c)}}\) for each subject.
Appendix C. Algorithm for multiple imputation using bootstrap linear regression
Using the notations from Appendix A , the following procedures are performed to produce imputation values from conventional MI:
Step 1 . Draw a bootstrap sample from observed samples.
Step 2 . Obtain estimates from linear regression for each exposure \(Z\) subject to LOD, \(Z={\gamma }^{T}W+{\epsilon }_{MI}\) with \({\epsilon }_{MI} \sim N(0, {\sigma }_{MI}^{2})\) . Note that \(W\) includes all available variables including the outcome.
Step 3 . Draw imputed values \({Z}_{imp} \sim N\left({\widehat{\gamma }}^{T}W, {\widehat{\sigma }}_{MI}^{2}\right)\) .
Note that this approach can be easily generalized to multiple exposures using multivariate imputation by chained equations (see Sect. 4.5.2 of Van Buuran [ 43 ]). In the truncated MI, we draw the imputed values \({Z}_{imp}\) from a truncated normal distribution, \(N\left({\widehat{\gamma }}^{T}W, {\widehat{\sigma }}_{MI}^{2}\right)\) within the range based on LOD (e.g., \([0, LOD]\) ) in Step 3 .
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Lee, M., Saha, A., Sundaram, R. et al. Accommodating detection limits of multiple exposures in environmental mixture analyses: an overview of statistical approaches. Environ Health 23 , 48 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12940-024-01088-w
Download citation
Received : 18 March 2024
Accepted : 06 May 2024
Published : 16 May 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12940-024-01088-w
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Left-censored exposures
- Detection limits
- Environmental mixtures
Environmental Health
ISSN: 1476-069X
- General enquiries: [email protected]
A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
A lock ( ) or https:// means you've safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
- Test for Fentanyl
- if You Think Someone is Overdosing
- Stop Overdose
- Naloxone FAQs
- Stigma Reduction
About Stop Overdose
- Through preliminary research and strategic workshops, CDC identified four areas of focus to address the evolving drug overdose crisis.
- Stop Overdose resources speak to the reality of drug use, provide practical ways to prevent overdoses, educate about the risks of illegal drug use, and show ways to get help.

Drugs take nearly 300 lives every day. 1 To address the increasing number of overdose deaths related to both prescription opioids and illegal drugs, we created a website to educate people who use drugs about the dangers of illegally manufactured fentanyl, the risks and consequences of mixing drugs, the lifesaving power of naloxone, and the importance of reducing stigma around recovery and treatment options. Together, we can stop drug overdoses and save lives.
What you can do
- Get the facts on fentanyl
- Learn about lifesaving naloxone
- Understand the risks of polysubstance use
- Reduce stigma around recovery and treatment
Explore and download Stop Overdose and other educational materials on CDC's Overdose Resource Exchange .
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National Center for Health Statistics. National Vital Statistics System, Mortality 2018-2021 on CDC WONDER Online Database, released in 2023. Data are from the Multiple Cause of Death Files, 2018-2021, as compiled from data provided by the 57 vital statistics jurisdictions through the Vital Statistics Cooperative Program. Accessed at http://wonder.cdc.gov/mcd-icd10-expanded.html on Mar 5, 2024
Every day, drugs claim hundreds of lives. The Stop Overdose website educates drug users on fentanyl, naloxone, polysubstance use, and dealing with stigma.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
A case study is one of the most commonly used methodologies of social research. This article attempts to look into the various dimensions of a case study research strategy, the different epistemological strands which determine the particular case study type and approach adopted in the field, discusses the factors which can enhance the effectiveness of a case study research, and the debate ...
Case study can be combined with other methodologies, such as ethnography, grounded theory, or phenomenology. In such studies the research on the case uses another framework to further define the study and refine the approach. Case study is also described as a method, given particular approaches used to collect and analyze data.
A case study is a detailed study of a specific subject, such as a person, group, place, event, organization, or phenomenon. Case studies are commonly used in social, educational, clinical, and business research. A case study research design usually involves qualitative methods, but quantitative methods are sometimes also used.
A case study protocol outlines the procedures and general rules to be followed during the case study. This includes the data collection methods to be used, the sources of data, and the procedures for analysis. Having a detailed case study protocol ensures consistency and reliability in the study.
McMaster University, West Hamilton, Ontario, Canada. Qualitative case study methodology prov ides tools for researchers to study. complex phenomena within their contexts. When the approach is ...
Qualitative case study methodology enables researchers to conduct an in-depth exploration of intricate phenomena within some specific context. ... (ICT) industry of New Zealand. A multiple case studies approach was adopted that spanned over 2 years, as it is difficult to investigate all the aspects of a phenomenon in a single case study (Cruzes ...
Experienced qualitative researchers have identified case study research as a stand-alone qualitative approach. Case study research has a level of flexibility that is not readily offered by other qualitative approaches such as grounded theory or phenomenology. ... Yazan B. (2015). Three approaches to case study methods in education: Yin, Merriam ...
Defnition: A case study is a research method that involves an in-depth examination and analysis of a particular phenomenon or case, such as an individual, organization, community, event, or situation. It is a qualitative research approach that aims to provide a detailed and comprehensive understanding of the case being studied.
A case study is a detailed study of a specific subject, such as a person, group, place, event, organisation, or phenomenon. Case studies are commonly used in social, educational, clinical, and business research. A case study research design usually involves qualitative methods, but quantitative methods are sometimes also used.
A case study is a research approach that is used to generate an in-depth, multi-faceted understanding of a complex issue in its real-life context. It is an established research design that is used extensively in a wide variety of disciplines, particularly in the social sciences. A case study can be defined in a variety of ways (Table 5 ), the ...
Qualitative case study methodology provides tools for researchers to study complex phenomena within their contexts. When the approach is applied correctly, it becomes a valuable method for health science ... approaches that guide case study methodology; one proposed by Robert Stake (1995) and . 545 . The Qualitative Report. December 2008. the ...
From this point on and in further studies, case study in educational research and evaluation came to be a major methodology for understanding complex educational and social programs. It also extended to other practice professions, such as nursing, health, and social care ( Zucker, 2001 ; Greenhalgh & Worrall, 1997 ; Shaw & Gould, 2001 ).
Purpose of case study methodology. Case study methodology is often used to develop an in-depth, holistic understanding of a specific phenomenon within a specified context. 11 It focuses on studying one or multiple cases over time and uses an in-depth analysis of multiple information sources. 16,17 It is ideal for situations including, but not limited to, exploring under-researched and real ...
Case studies are designed to suit the case and research question and published case studies demonstrate wide diversity in study design. There are two popular case study approaches in qualitative research. The first, proposed by Stake ( 1995) and Merriam ( 2009 ), is situated in a social constructivist paradigm, whereas the second, by Yin ( 2012 ...
What the Case Study Method Really Teaches. Summary. It's been 100 years since Harvard Business School began using the case study method. Beyond teaching specific subject matter, the case study ...
Researchers consider case study as a methodology, method, approach, and design of research. Methodology guides research view-point towards a phenomenon under study. "Qualitative paradigms broadly emphasize and include exploratory, explanatory, interpretive, or descriptive purposes.
the three case study perspectives on the same ground in all aspects of case study method. For instance, in Stake's (1995) The Art of Case Study Research,the main addressee is students who are planning to employ case study as a methodology in their research projects. The chief
The following key attributes of the case study methodology can be underlined. 1. Case study is a research strategy, and not just a method/technique/process of data collection. 2. A case study involves a detailed study of the concerned unit of analysis within its natural setting. A de-contextualised study has no relevance in a case study ...
Case studies are in-depth investigations of a person, group, event, or community. Typically, data is gathered from various sources using several methods (e.g., observations & interviews). The case study research method originated in clinical medicine (the case history, i.e., the patient's personal history). In psychology, case studies are ...
Overview. Simply put, the case method is a discussion of real-life situations that business executives have faced. On average, you'll attend three to four different classes a day, for a total of about six hours of class time (schedules vary). To prepare, you'll work through problems with your peers. Read More.
Design and setting. A qualitative exploratory methodology was chosen, using a multiple-embedded case study design.11 18 A case was defined as one hospital containing four different types of teams. Two case hospitals were recruited to the study, featuring a total of eight teams.
In the included studies, case-based learning was the most commonly used teaching method. The use of this approach allows students from different disciplines to be involved in the care of the patient within their area of expertise, while encouraging interdisciplinary discussion of case management.
A case study is a research approach that is used to generate an in-depth, multi-faceted understanding of a complex issue in its real-life context. It is an established research design that is used extensively in a wide variety of disciplines, particularly in the social sciences. A case study can be defined in a variety of ways (Table.
A design approach arrests collapse propagation in buildings after major initial failures by ensuring that specific elements fail before the failure of the most important components for global ...
3.1 K estimation methods. One of the oldest K estimation methods was originally developed by Wischmeier et al. ().Wischmeier and Smith (), Sharply and Williams (), and Renard et al. then proposed formulas for K estimation with specific soil properties, which are widely used today.For specific study areas, the selection of K estimation methods depends on the availability of the required soil ...
Background Identifying the impact of environmental mixtures on human health is an important topic. However, such studies face challenges when exposure measurements lie below limit of detection (LOD). While various approaches for accommodating a single exposure subject to LOD have been used, their impact on mixture analysis has not been thoroughly investigated. Our study aims to understand the ...
New Zealand. A multiple case studies approach was adopted that spanned over 2 years, as it is difficult to investigate all the aspects of a phenomenon in a single case study (Cruzes, Dyba˚, ... Case study method is the most widely used method in aca-demia for researchers interested in qualitative research (Bas-karada, 2014). Research students ...
Key points. Through preliminary research and strategic workshops, CDC identified four areas of focus to address the evolving drug overdose crisis. Stop Overdose resources speak to the reality of drug use, provide practical ways to prevent overdoses, educate about the risks of illegal drug use, and show ways to get help.
The urban texture is the physical manifestation of the urban form's evolution. In the rapid process of urbanization, protecting and reshaping the urban texture has become an essential means to sustain the overall form and vitality of cities. Previous studies in this field have primarily relied on image analysis or typological methods, lacking a quantitative approach to identify and analyze ...
The main aim of this study is to introduce an implicit personality assessment method (e.g., implicit association test) to Kuwait. We adapted an existing personality-related implicit association test (IAT; Big Five IAT), while also constructed the first trait EI IAT based on Petrides' four-factor model. We investigated the psychometric properties of the implicit association test through ...